- DL manuals
- 3Com
- Switch
- Switch 8807
- Configuration Manual
3Com Switch 8807 Configuration Manual
Summary of Switch 8807
Page 1
3com ® switch 8800 family configuration guide switch 8807 switch 8810 switch 8814 www.3com.Com part no. 10015594, rev. Aa published: january 2007.
Page 2
3com corporation 350 campus drive marlborough, ma usa 01752-3064 copyright © 2007, 3com corporation. All rights reserved. No part of this documentation may be reproduced in any form or by any means or used to make any derivative work (such as translation, transformation, or adaptation) without writt...
Page 3: Ontents
C ontents a bout t his g uide conventions 15 related documentation 16 1 p roduct o verview product overview 17 function features 18 2 c ommand l ine i nterface command line interface 21 command line view 21 features and functions of command line 29 3 l ogging in to s witch setting up configuration e...
Page 4
Configure the cpu port in an vlan 58 displaying and debugging a vlan 59 vlan configuration example 59 8 s uper vlan c onfiguration super vlan overview 61 configuring a super vlan 61 9 i solate - user -vlan c onfiguration isolate-user-vlan overview 65 isolate-use-vlan configuration task 65 displaying...
Page 5
15 p ort i solation c onfiguration port isolation overview 111 configuration tasks 111 port isolation configuration example 113 16 mac a ddress t able m anagement mac address table management overview 115 mac address table management configuration 116 maximum mac address number learned by ethernet p...
Page 6
Qos configuration example 202 23 l ogon u ser acl c ontrol c onfiguration overview 209 configuring acl for telnet/ssh users 209 configuring acl for snmp users 212 24 vlan-acl c onfiguration vlan-acl overview 215 vlan-acl configuration 215 25 802.1 x c onfiguration 802.1x overview 221 802.1x configur...
Page 7
30 rip c onfiguration introduction to rip 291 configuring rip 292 displaying and debugging rip 300 typical rip configuration example 300 troubleshooting rip faults 301 31 ospf c onfiguration ospf overview 303 ospf gr overview 307 configuring ospf 311 displaying and debugging ospf 330 typical ospf co...
Page 8
Implementation of ip multicast 411 rpf mechanism for ip multicast packets 414 38 s tatic m ulticast mac a ddress c onfiguration static multicast mac address overview 417 configuring a static multicast mac address 417 displaying and maintaining static multicast mac address configuration 418 39 igmp s...
Page 9
Pim-sm configuration example 469 45 msdp c onfiguration msdp overview 473 msdp configuration 476 displaying and debugging msdp 482 msdp configuration examples 483 46 mbgp m ulticast e xtension c onfiguration mbgp multicast extension overview 493 mbgp multicast extension configuration 494 displaying ...
Page 10
Kompella mpls l2vpn configuration 625 displaying and debugging mpls l2vpn 629 troubleshooting mpls l2vpn 630 52 vpls c onfiguration vpls overview 633 basic vpls network architectures 634 vpls operational principle 635 concepts related to vpls 637 vpls basic configuration 638 displaying and debugging...
Page 11
58 dns c onfiguration introduction to dns 709 configuring static domain name resolution 710 configuring dynamic domain name resolution 710 displaying and debugging domain name resolution 711 dns configuration example 711 troubleshooting domain name resolution configuration 712 59 n etstream c onfigu...
Page 12
65 rmon c onfiguration rmon overview 747 configuring rmon 747 displaying and debugging rmon 750 rmon configuration example 751 66 ntp c onfiguration brief introduction to ntp 753 ntp configuration 755 displaying and debugging ntp 760 ntp configuration example 761 67 ssh t erminal s ervice ssh termin...
Page 13
74 p acket s tatistics c onfiguration introduction to egress packet statistics 843 75 e thernet p ort l oopback d etection ethernet port loopback detection function 845 configuring the loopback detection function 845 displaying and maintaining the loopback detection function 845 76 q in q c onfigura...
Page 15: Bout
Conventions 15 a bout t his g uide this guide describes the 3com ® switch 8800 and how to install hardware, configure and boot software, and maintain software and hardware. This guide also provides troubleshooting and support information for your switch. This guide is intended for qualified service ...
Page 16
16 a bout t his g uide related documentation the following manuals offer additional information necessary for managing your switch 8800: ■ switch 8800 command reference guide — provides detailed descriptions of command line interface (cli) commands, that you require to manage your switch 8800. ■ swi...
Page 17: Roduct
1 p roduct o verview product overview the 3com switch 8800 family series routing switches (hereinafter referred to as switch 8800 family series) are a series of large capacity, modularized l2/l3 switches. They are mainly designed for broadband man, backbone, switching core and convergence center of ...
Page 18
18 c hapter 1: p roduct o verview function features table 1 function features features implementation vlan vlan compliant with ieee 802.1q standard port-based, protocol-based, and ip subnet-based vlan garp vlan registration protocol (gvrp) super vlan vlan isolation guest vlan dynamic vlan stp protoc...
Page 19
Function features 19 mpls l3 multiprotocol label switching (mpls) vpn (option1/2/3), embedded mpls vpn, hierarchical pe (hope), ce dual homing, mce, and multi-role host vll, including martini, kompella and ccc modes vpls quality of service (qos) supports different types of traffic classification, in...
Page 20
20 c hapter 1: p roduct o verview management and maintenance command line interface configuration local configuration through the console port and the aux port local and remote configuration through telnet on an ethernet port remote configuration through modem dialup through the aux port. Snmp manag...
Page 21: Ommand
2 c ommand l ine i nterface command line interface 3com series switches provide a series of configuration commands and command line interfaces for configuring and managing the switch. The command line interface has the following characteristics: ■ local configuration via the console port and aux por...
Page 22
22 c hapter 2: c ommand l ine i nterface ■ configuration level: service configuration commands, including routing command and commands on each network layer, are used to provide direct network service to the user. ■ management level: they are commands that influence basis operation of the system and...
Page 23
Command line view 23 ■ ospf area view ■ bgp view ■ is-is view ■ route policy view ■ basic acl view ■ advanced acl view ■ layer-2 acl view ■ conform-level view ■ wred index view ■ radius server group view ■ isp domain view ■ mpls view ■ vpnv4 sub-address family view ■ vpn-instance sub-address family ...
Page 24
24 c hapter 2: c ommand l ine i nterface port view ethernet port view: configure ethernet port parameters [3com-ethernet2/1/1 ] 100m ethernet port view key in interface ethernet 2/1/1 in system view use quit to return to system view use return to return to user view [3com-gigabitether net2/1/1] giga...
Page 25
Command line view 25 sftp client view configure sftp client parameters key in sftp ip-address in system view use quit to return to system view use return to return to user view mst region view configure mst region parameters [3com-mst-region] key in stp region-configur ation in system view use quit ...
Page 26
26 c hapter 2: c ommand l ine i nterface bgp view configure bgp parameters [3com-bgp] key in bgp 100 in system view use quit to return to system view use return to return to user view is-is view configure is-is parameters [3com-isis] key in isis in system view use quit to return to system view use r...
Page 27
Command line view 27 wred index view configure wred parameters [3com-wred-0] key in wred 0 in system view use quit to return to system view use return to return to user view radius server group view configure radius parameters [3com-radius-1] key in radius scheme 1 in system view use quit to return ...
Page 29
Features and functions of command line 29 features and functions of command line online help of command line the command line interface provides the following online help modes. ■ full help ■ partial help you can get the help information through these online help commands, which are described as fol...
Page 30
30 c hapter 2: c ommand l ine i nterface 7 to switch to the chinese display for the above information, perform the language-mode command. Displaying characteristics of command line command line interface provides the following display characteristics: ■ for users’ convenience, the instruction and he...
Page 31
Features and functions of command line 31 editing characteristics of command line command line interface provides the basic command editing function and supports to edit multiple lines. A command cannot longer than 256 characters. See the table below. Incomplete command the input command is incomple...
Page 32
32 c hapter 2: c ommand l ine i nterface.
Page 33: Ogging
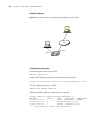
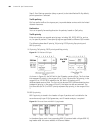
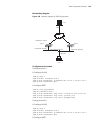
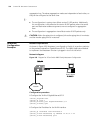
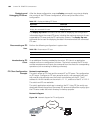
3 l ogging in to s witch setting up configuration environment through the console port step 1: as shown in the figure below, to set up the local configuration environment, connect the serial port of a pc (or a terminal) to the console port of the switch with the console cable. Figure 1 set up the lo...
Page 34
34 c hapter 3: l ogging in to s witch figure 3 configure the port for connection figure 4 set communication parameters step 3: the switch is powered on. Display self-test information of the switch and prompt you to press enter to show the command line prompt such as . Step 4: input a command to conf...
Page 35
Setting up configuration environment through telnet 35 step 1: before logging into the switch through telnet, you need to configure the telnet user name and password on the switch through the console port. N by default, the password is required for authenticating the telnet user to log in to the swi...
Page 36
36 c hapter 3: l ogging in to s witch n ■ when configuring the switch via telnet, do not modify the ip address of it unless necessary, for the modification might cut the telnet connection. ■ by default, when a telnet user passes the password authentication to log on to the switch, he can access the ...
Page 37
Setting up configuration environment through modem dial-up 37 setting up configuration environment through modem dial-up step 1: the modem user is authenticated via the console port of the switch before he or she logs in to the switch through a dial-up modem. N by default, the password is required f...
Page 38
38 c hapter 3: l ogging in to s witch figure 10 dial on the remote pc step 4: enter the preset login password on the remote terminal emulator and wait for the prompt such as . Then you can configure and manage the switch. Enter "?" to get the immediate help. For details of specific commands, refer t...
Page 39: Ser
4 u ser i nterface c onfiguration user interface overview to facilitate system management, the switches support user interface based configuration for the configuration and management of port attributes. Presently, the switch 8800 family series switches support the following user interface based con...
Page 40
40 c hapter 4: u ser i nterface c onfiguration ■ aux user interface is numbered as the second interface designated as user interface 1. ■ vty is numbered after aux user interface. The absolute number of the first vty is incremented by 1 than the aux user interface number. Relative number the relativ...
Page 41
User interface configuration 41 note that if you press after typing any of the three keywords shell, login and incoming in the command, then what you type after the word header is the contents of the login information, instead of identifying header type. Configuring asynchronous port attributes the ...
Page 42
42 c hapter 4: u ser i nterface c onfiguration by default, an asynchronous port supports 1 stop bit. Note that setting 1.5 stop bits is not available on switch 8800 family series at present. Configuring the data bit by default, an asynchronous port supports 8 data bits. Configuring terminal attribut...
Page 43
User interface configuration 43 by default, idle-timeout is enabled and set to 10 minutes on all the user interfaces. That is, the user interface will be disconnected automatically after 10 minutes without any operation. Idle-timeout 0 means disabling idle-timeout. Locking user interface this config...
Page 44
44 c hapter 4: u ser i nterface c onfiguration configuring the authentication method the following command is used for configuring the user login authentication method to deny the access of an unauthorized user. Perform the following configuration in user interface view. By default, terminal authent...
Page 45
User interface configuration 45 # perform username and password authentication when a user logs in through vty 0 user interface and set the username and password to zbr and 3com respectively. [3com-ui-vty0] authentication-mode scheme [3com-ui-vty0] quit [sw8800] local-user zbr [3com-luser-zbr] passw...
Page 46
46 c hapter 4: u ser i nterface c onfiguration n when a user logs in the switch, the command level that it can access depends on two points. One is the command level that the user itself can access, the other is the set command level of this user interface. If the two levels are different, the forme...
Page 47
User interface configuration 47 configuring redirection send command the following command can be used for sending messages between user interfaces. Perform the following configuration in user view. Auto-execute command the following command is used to automatically run a command after you log in. A...
Page 48
48 c hapter 4: u ser i nterface c onfiguration displaying and debugging user interface after the above configuration, execute display command in any view to display the running of the user interface configuration, and to verify the effect of the configuration. Execute free command in user view to re...
Page 49: Anagement
5 m anagement i nterface c onfiguration management interface overview switch 8800 family series provides a 10/100base-tx management interface on the fabric. The management interface can connect a background pc for software loading and system debugging, or a remote network management station for remo...
Page 50
50 c hapter 5: m anagement i nterface c onfiguration.
Page 51: Onfiguration
6 c onfiguration f ile m anagement configuration file management configuration file management overview the management module of configuration file provides a user-friendly operation interface. It saves the configuration of the switch in the text format of command line to record the whole configurat...
Page 52
52 c hapter 6: c onfiguration f ile m anagement n the configuration files are displayed in their corresponding saving formats. Modifying and saving the current-configuration you can modify the current configuration of the switch through the cli. Use the save command to save the current-configuration...
Page 53
Configuration file management 53 cfgfile is the name of the configuration file and its extension name can be ".Cfg". The file is stored in the root directory of the storage devices. After the above configuration, execute display command in any view to display the running of the configuration files, ...
Page 54
54 c hapter 6: c onfiguration f ile m anagement.
Page 55: Vlan C
7 vlan c onfiguration vlan overview virtual local area network (vlan) groups the devices in a lan logically, not physically, into segments to form virtual workgroups. Ieee issued the ieee 802.1q in 1999 to standardize the vlan implementations. The vlan technology allows network administrators to log...
Page 56
56 c hapter 7: vlan c onfiguration c caution: ■ vlan 1 is the system-default vlan and cannot be removed. ■ vlans with their ports being vlan vpn-enabled cannot be removed. ■ guest vlans cannot be deleted. ■ protocol-enabled vlans cannot be deleted. Specifying a description character string for a vla...
Page 57
Configuring protocol-based vlan 57 configuring port-based vlan you can use the following commands to specify ethernet ports for a vlan. Perform the following configuration in vlan view. By default, the system adds all the ports to a default vlan whose id is 1. Note that you can add/remove the trunk ...
Page 58
58 c hapter 7: vlan c onfiguration ■ you cannot delete a protocol-based vlan that has ports associated with. ■ you cannot delete a protocol-based vlan on a port while the port is associated with the vlan. Configuring ip subnet-based vlan the following sections describe the ip subnet-based vlan confi...
Page 59
Displaying and debugging a vlan 59 you can also move the cpu ports out of/into all the vlans at a time. Perform the following configuration in system view. Displaying and debugging a vlan after the above configuration, execute the display command in any view to display the running of the vlan config...
Page 60
60 c hapter 7: vlan c onfiguration configuration procedure # create vlan 2 and enter its view. [sw8800] vlan 2 # add ethernet3/1/1 and ethernet4/1/1 to vlan 2. [3com-vlan2] port ethernet3/1/1 ethernet4/1/1 # create vlan 3 and enters its view. [3com-vlan2] vlan 3 # add ethernet3/1/2 and ethernet4/1/2...
Page 61: Uper
8 s uper vlan c onfiguration super vlan overview super vlan is also called vlan aggregation. The following is the fundamental principle: a super vlan contains multiple sub vlans. A super vlan can be configured with an ip address of the virtual port, while a sub vlan cannot be configured with the ip ...
Page 62
62 c hapter 8: s uper vlan c onfiguration c caution: ■ a super vlan cannot contain ports. ■ after you set the vlan type to super vlan, the arp proxy is automatically enabled on the vlan port, and you do not need to configure the proxy. ■ when a super vlan exists, the arp proxy should be enabled on t...
Page 63
Configuring a super vlan 63 these sub vlans are isolated at layer 2. It is required that these sub vlans communicate with one another at layer 3. Network diagram omitted configuration procedure system-view system view: return to user view with ctrl+z. [sw8800] vlan 10 [3com-vlan10] supervlan [3com-v...
Page 64
64 c hapter 8: s uper vlan c onfiguration.
Page 65: Solate
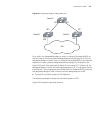
9 i solate - user -vlan c onfiguration isolate-user-vlan overview isolate-user-vlan can save the vlan resource in a network. It adopts the two-level vlan architecture. One level is isolate-user-vlan level, and the other is secondary vlan level, as shown in figure 12. ■ an isolate-user-vlan correspon...
Page 66
66 c hapter 9: i solate - user -vlan c onfiguration configuring an isolate-user-vlan configuring a secondary vlan n ■ an isolate-user-vlan can correspond to up to 64 secondary vlans. ■ you can configure up to 32 isolate-user-vlans for a system. ■ you can configure up to 1,024 secondary vlans for a s...
Page 67
Displaying and debugging an isolate-user-vlan 67 note the following when mapping an isolate-user-vlan to secondary vlans 1 if the isolate-user-vlan contains ports ■ for hybrid ports, if the default port vlan id is the same as the isolate-user-vlan id, and the port joins the isolate-user-vlan in the ...
Page 68
68 c hapter 9: i solate - user -vlan c onfiguration isolate-user-vlan configuration example network requirements switch a is connected to switch b and switch c in the downstream. 1 on switch b vlan 5 is an isolate-user-vlan, including an upstream port (ethernet2/1/1 port) and two secondary vlans, vl...
Page 69
Isolate-user-vlan configuration example 69 # configure the mapping relationship between the isolate-user-vlan and the secondary vlans. [3com-vlan2] quit [sw8800] isolate-user-vlan 5 secondary 2 to 3 2 configuration on switch c # configure an isolate-user-vlan. System-view [sw8800] vlan 6 [3com-vlan6...
Page 70
70 c hapter 9: i solate - user -vlan c onfiguration.
Page 71: Ip A
10 ip a ddress c onfiguration introduction to ip addresses ip address classification and representation an ip address is a 32-bit address allocated to a device that accesses the internet. It consists of two fields: net-id field and host-id field. Ip addresses are allocated by network information cen...
Page 72
72 c hapter 10: ip a ddress c onfiguration subnet and mask nowadays, with rapid development of the internet, ip (v4) addresses are depleting very in a few years. The traditional ip address allocation method wastes ip addresses greatly. In order to make full use of the available ip addresses, the con...
Page 73
Configuring ip address 73 a mask is a 32-bit number corresponding to an ip address. The number consists of 1s and 0s. Principally, these 1s and 0s can be combined randomly. However, the first consecutive bits are set to 1s when you design a mask. The mask divides the ip address into two parts: subne...
Page 74
74 c hapter 10: ip a ddress c onfiguration by default, there is no host name associated to any host ip address. Configuring the ip address of the vlan interface you can configure an ip address for every vlan interface of the switch. Generally, it is enough to configure one ip address for an interfac...
Page 75
Configuring ip address 75 configure static arp entries that have only ip addresses. The switch will automatically fill the mac address in the arp mapping entries so that only users configured with static arp entries can have access to the network. Ip address protection configuration the tasks of ip ...
Page 76
76 c hapter 10: ip a ddress c onfiguration displaying ip address after the above configuration, execute the display command in any view to display the ip addresses configured on interfaces of the network device, and to verify the effect of the configuration. Ip address configuration example network ...
Page 77
Troubleshooting ip address configuration 77 troubleshooting ip address configuration fault 1: the switch cannot ping through a certain host in the lan. Troubleshooting can be performed as follows: 1 check the configuration of the switch. Use the display arp command to view the arp entry table that t...
Page 78
78 c hapter 10: ip a ddress c onfiguration.
Page 79: Ip P
11 ip p erformance c onfiguration configuring ip performance ip performance configuration includes: ■ “configuring tcp attributes” configuring tcp attributes tcp attributes that can be configured include: ■ synwait timer: when sending the syn packets, tcp starts the synwait timer. If response packet...
Page 80
80 c hapter 11: ip p erformance c onfiguration execute the reset command in user view to clear ip, tcp and udp statistics information. Execute the debugging command to debug ip performance. Display tcp connection statistics data display tcp statistics display udp statistics information display udp s...
Page 81
Troubleshooting ip performance 81 troubleshooting ip performance fault: ip layer protocol works normally but tcp and udp cannot work normally. Troubleshoot: in the event of such a fault, you can enable the corresponding debugging information output to view the debugging information. ■ use the displa...
Page 82
82 c hapter 11: ip p erformance c onfiguration flag = ack window = 16079.
Page 83: Garp&gvrp C
12 garp&gvrp c onfiguration configuring garp garp overview generic attribute registration protocol (garp) offers a mechanism that is used by the members in the same switching network to distribute, propagate and register such information as vlan and multicast addresses. Garp dose not exist in a swit...
Page 84
84 c hapter 12: garp&gvrp c onfiguration n ■ the value of garp timer will be used in all the garp applications, including gvrp and gmrp, running in one switched network. ■ in one switched network, the garp timers on all the switching devices should be set to the same value. Otherwise, garp applicati...
Page 85
Configuring gvrp 85 ■ the lower limit of hold timer is 10 centiseconds. You can change its upper limit by changing the value of join timer. ■ you can change the lower limit and upper limit of join timer by changing the value of hold timer and leave timer respectively. ■ you can change the lower limi...
Page 86
86 c hapter 12: garp&gvrp c onfiguration in the above-mentioned configuration tasks, gvrp should be enabled globally before it is enabled on the port. Configuration of gvrp registration type can only take effect after the port gvrp is enabled. Besides, gvrp must be configured on the trunk port. N ■ ...
Page 87
Configuring gvrp 87 ■ when a trunk port is set as fixed, the port is not allowed to dynamically register/deregister a vlan, it only propagates information about static vlans that are manually configured instead of that of dynamic vlans. That is, a trunk port that is of fixed type only permits manual...
Page 88
88 c hapter 12: garp&gvrp c onfiguration [sw8800] gvrp # set ethernet3/1/1 as a trunk port and allows all the vlans to pass through. [sw8800] interface ethernet3/1/1 [3com-ethernet3/1/1] port link-type trunk [3com-ethernet3/1/1] port trunk permit vlan all # enable gvrp on the trunk port. [3com-ether...
Page 89: Thernet
13 e thernet p ort c onfiguration ethernet port overview switch 8800 family series can provide conventional ethernet ports, fast ethernet ports, 1000 mbps ethernet ports and 10 gbps ethernet ports. The configurations of these ethernet ports are basically the same, which will be described in the foll...
Page 90
90 c hapter 13: e thernet p ort c onfiguration enabling/disabling an ethernet port after configuring the related parameters and protocol of the port, you can use undo shutdown command to enable the port. If you do not want a port to forward data any more, use shutdown command to disable it. Perform ...
Page 91
Ethernet port configuration 91 setting speed on the ethernet port you can use the following command to set the speed on the ethernet port. If the speed is set to auto-negotiation mode, the local and peer ports will automatically negotiate about the port speed. Perform the following configuration in ...
Page 92
92 c hapter 13: e thernet p ort c onfiguration perform the following configuration in ethernet port view. By default, ethernet port flow control is disabled. Setting the interval of performing statistics on ports use the following configuration tasks to set the interval of performing statistics on p...
Page 93
Setting the interval of performing statistics on ports 93 effective jumbo frame value for the 1536-1552 section is 1552, that for the 1553-9022 section is 9022, that for the 9023-9192 section is 9192, and that for the 9193-10240 section is 10240. Setting broadcast/multicast suppression on ethernet p...
Page 94
94 c hapter 13: e thernet p ort c onfiguration by default, ethernet ports works in lan mode. 10ge ethernet ports support wan mode. Setting the link type for the ethernet port ethernet port can operate in three different link types, access, hybrid, and trunk types. The access port carries one vlan on...
Page 95
Setting the interval of performing statistics on ports 95 note that the access port shall be added to an existing vlan other than vlan 1. The vlan to which hybrid port is added must have been existed. After adding the ethernet port to specified vlans, the local port can forward packets of these vlan...
Page 96
96 c hapter 13: e thernet p ort c onfiguration already carries a vlan tag, the packet will get two tags; if the part receives an untagged packet, the packet will be given a default vlan tag of the port. Perform the following configuration in ethernet port view. Note that if any of gvrp, stp, and 802...
Page 97
Setting the interval of performing statistics on ports 97 n ■ using copy configuration command will clear protocol vlan attributes of the destination port, but it can not copy protocol vlan attributes of source port to the destination port. ■ using the copy configuration command, you can only copy t...
Page 98
98 c hapter 13: e thernet p ort c onfiguration displaying and debugging ethernet port after the above configuration, execute display command in any view to display the running of the ethernet port configuration, and to verify the effect of the configuration. Execute reset command in user view to cle...
Page 99
Ethernet port troubleshooting 99 [sw8800] interface gigabitethernet2/1/1 # set the gigabitethernet2/1/1 as a trunk port and allows vlans 2, 6 through 50, and 100 to pass. [3com-gigabitethernet2/1/1] port link-type trunk [3com-gigabitethernet2/1/1] port trunk permit vlan 2 6 to 50 100 # create the vl...
Page 100
100 c hapter 13: e thernet p ort c onfiguration.
Page 101: Ink
14 l ink a ggregation c onfiguration overview introduction to link aggregation link aggregation means aggregating several ports together to implement the outgoing/incoming payload balance among the member ports and enhance the connection reliability. Link aggregation may be manual aggregation, dynam...
Page 102
102 c hapter 14: l ink a ggregation c onfiguration aggregation port is the same as the aggregation group id. In a dynamic aggregation group, the member ports must have the same operation key. In manual and static aggregation groups, the active ports have the same operation key. Aggregation types por...
Page 103
Overview 103 ■ the system sets to inactive state the ports which cannot be aggregated with the port, due to hardware limit (for example, trans-module aggregation is forbidden). ■ the system sets to inactive state the ports with basic configurations different from the active port. Since only a define...
Page 104
104 c hapter 14: l ink a ggregation c onfiguration ■ aggregation groups of special ports with hardware aggregation resources included, such as non-limited-speed 10ge ports ■ aggregation groups that probably reach the maximum potential rate after the resources are allocated to them ■ aggregation grou...
Page 105
Link aggregation configuration 105 ■ “configuring/deleting aggregation group description” ■ “configuring system priority” ■ “configuring port priority” n ■ the active state and inactive state correspond to selected and standby respectively. ■ when configuring an aggregation group, the status of gvrp...
Page 106
106 c hapter 14: l ink a ggregation c onfiguration during creating an aggregation group, if it already exists in the system but contains no member port, it changes to the new type. When you change a static lacp aggregation group to a manual one, lacp shall be disabled at the member ports automatical...
Page 107
Link aggregation configuration 107 ■ when a port is added into an aggregation group, the original arp information of the port will be lost. Configuring/deleting aggregation group description you can use the following command to create/delete aggregation group description (for manual aggregation and ...
Page 108
108 c hapter 14: l ink a ggregation c onfiguration by default, port priority is 32,768. Displaying and debugging link aggregation after the above configuration, execute the display command in any view to display the running of the link aggregation configuration, and to verify the effect of the confi...
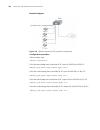
Page 109
Link aggregation configuration example 109 network diagram figure 19 network diagram for link aggregation configuration configuration procedure the following only lists the configuration for switch a, and that on switch b is similar. 1 manual aggregation # create aggregation group 1. [sw8800] link-a...
Page 110
110 c hapter 14: l ink a ggregation c onfiguration [3com-ethernet2/1/2] interface ethernet2/1/3 [3com-ethernet2/1/3] lacp enable you must set basic configuration, rate and duplex attribute consistent at both ends to aggregate successfully the lacp-enabled ports into a dynamic aggregation group and a...
Page 111: Ort
15 p ort i solation c onfiguration port isolation overview using the port isolation feature, you can place different user ports into the same vlan. As these users cannot communicate with each other, network security improved, a flexible networking scheme is provided, and vlan resources are conserved...
Page 112
112 c hapter 15: p ort i solation c onfiguration configuring isolated ports for an isolated group configure the upstream port in the isolated group port-isolate uplink-port group isolate-group-id required ■ you can configure the uplink port for the isolated group only after you create the isolated g...
Page 113
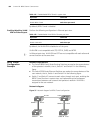
Port isolation configuration example 113 port isolation configuration example network requirements users in a community connect to a switch. The switch communicates with the external network through port ethernt2/1/1. These users are in vlan 1 and cannot communicate with each other. Network diagram ...
Page 114
114 c hapter 15: p ort i solation c onfiguration.
Page 115: Mac A
16 mac a ddress t able m anagement mac address table management overview a switch maintains a mac address table for fast forwarding packets. A table entry includes the mac address of a device and the port id of the switch connected to the device. The dynamic entries (not configured manually) are lea...
Page 116
116 c hapter 16: mac a ddress t able m anagement you can configure (add or modify) the mac address entries manually according to the actual networking environment. The entries can be static ones or dynamic ones. Mac address table management configuration the following sections describe the mac addre...
Page 117
Maximum mac address number learned by ethernet port and forwarding option configuration 117 in addition, this command takes effect on all the ports. However the address aging only functions on the dynamic addresses (the learned or configured as age entries by the user). By default, the aging-time is...
Page 118
118 c hapter 16: mac a ddress t able m anagement configuring maximum mac address number learned by ethernet port and forwarding option example network requirements ■ set the maximum number of mac addresses learned by ethernet port ethernet3/1/3 to 600 ■ set the switch to drop the packets whose sourc...
Page 119
Displaying and debugging mac address tables 119 displaying and debugging mac address tables after the above configuration, execute the display command in any view to display the running of the mac address table configuration, and to verify the effect of the configuration. Resetting mac addresses aft...
Page 120
120 c hapter 16: mac a ddress t able m anagement network diagram figure 22 network diagram for address table management configuration configuration procedure # enter the system view of the switch. System-view # add a mac address (specify the native vlan, port and state). [sw8800] mac-address static ...
Page 121: Mstp R
17 mstp r egion - configuration introduction to mstp mstp stands for multiple spanning tree protocol, which is compatible with spanning tree protocol (stp) and rapid spanning tree protocol (rstp). Stp is not fast in state transition. Even on a point-to-point link or an edge port, it has to take an i...
Page 122
122 c hapter 17: mstp r egion - configuration figure 23 basic mstp concepts mst region multiple spanning tree regions: a multiple spanning tree region contains several switches and the network segments between them. These mstp switches share the same region name, vlan-spanning tree mapping configura...
Page 123
Introduction to mstp 123 cst common spanning tree (cst): a lan has only one cst. Cst connects the spanning trees of all mst regions. Regard every mst region as a "switch", and the cst is generated by the computing of "switches" through stp/rstp. For example, the red line in figure 23 indicates the c...
Page 124
124 c hapter 17: mstp r egion - configuration a port can play different roles in different spanning tree instances. The following figure illustrates the earlier-mentioned concepts for your better understanding. In this figure, the switch a, b, c, and d make up a mst region. Port 1 and 2 on switch a ...
Page 125
Introduction to mstp 125 figure 25 bpdu packet format figure 26 msti information format of the last part in bpdu packets besides field root bridge priority, root path cost, local bridge priority and port priority, the field flags which takes one byte in an instance is also used for role selection. T...
Page 126
126 c hapter 17: mstp r egion - configuration figure 27 meaning of 1-byte flags in bpdu packets the second and third bits together indicate mstp port role. 2 tc packet a tc packet is also an mstp bpdu packet, but the lowest bit of its flags field is set to 1, which endows the tc packet with special ...
Page 127
Introduction to mstp 127 figure 28 designated bridge and designated port for a switch, the designated bridge is a switch in charge of forwarding bpdu to the local switch via a port called the designated port accordingly. For a lan, the designated bridge is a switch that is in charge of forwarding bp...
Page 128
128 c hapter 17: mstp r egion - configuration figure 29 ethernet switch networking to facilitate the descriptions, only the first four parts of the configuration bpdu are described in the example. They are root id (expressed as ethernet switch priority), path cost to the root, designated bridge id (...
Page 129
Introduction to mstp 129 the message and keep the local bpdu unchanged. When the port receives a higher-priority configuration bpdu, the switch uses the content in the received configuration bpdu to change the content of the local bpdu of this port. Then the switch compare the configuration bpdu of ...
Page 130
130 c hapter 17: mstp r egion - configuration switch b: bp1 receives the configuration bpdu from switch a and finds that the received bpdu has a higher priority than the local one, so it updates its configuration bpdu. Bp2 receives the configuration bpdu from switch c and finds that the local bpdu p...
Page 131
Introduction to mstp 131 for example, the link from switch b to switch c is down or the port receives any better configuration bpdu thus, the spanning tree is stabilized. The tree with the root bridge a is illustrated in the figure 30. Figure 30 the final stabilized spanning tree to facilitate the d...
Page 132
132 c hapter 17: mstp r egion - configuration designated port begin to send data again. That is, the root port and designated port should undergo a transitional state for a period of forward delay before they enter the forwarding state. And thus, the packets of a vlan will be forwarded along the fol...
Page 133
Configuring mstp 133 display commands. For detailed information, refer to the "display and debug mstp" section. N when gvrp and mstp start on the switch simultaneously, gvrp packets will propagate along cist which is a spanning tree instance. In this case, if you want to issue a certain vlan through...
Page 134
134 c hapter 17: mstp r egion - configuration by default, the mst region name is the switch mac address, all the vlans in the mst region are mapped to the sti 0, and the mstp region revision level is 0. You can restore the default settings of mst region, using the undo stp region-configuration comma...
Page 135
Configuring mstp 135 perform the following configuration in system view. After a switch is configured as the primary root bridge or the secondary root bridge, users cannot modify the bridge priority of the switch. You can configure the current switch as the primary or secondary root bridge of the st...
Page 136
136 c hapter 17: mstp r egion - configuration the switch ports send mstp or stp packets (when connected to the stp switch) and the switch provides multiple spanning tree function. You can use the following command to configure mstp running mode. Mstp can intercommunicate with stp. If there is a stp ...
Page 137
Configuring mstp 137 each time when it is forwarded by a switch, the max hops is reduced by 1. The switch discards the configuration bpdu with 0 hops left. This makes it impossible for the switch beyond the max hops to take part in the spanning tree calculation, thereby limiting the scale of the mst...
Page 138
138 c hapter 17: mstp r egion - configuration configuring the time parameters of a switch the switch has three time parameters, forward delay, hello time, and max age. Forward delay is the switch state transition mechanism. The spanning tree will be recalculated upon link faults and its structure wi...
Page 139
Configuring mstp 139 too short a max age may cause the network device frequently calculate the spanning tree and mistake the congestion as a link fault. However, if the max age is too long, the network device may not be able to discover the link fault and recalculate the spanning tree in time, which...
Page 140
140 c hapter 17: mstp r egion - configuration configuration in system view perform the following configuration in system view. Configuration in ethernet port view perform the following configuration in ethernet port view. You can configure the max transmission speed on a port with either of the earl...
Page 141
Configuring mstp 141 you can configure a port as an edge port or a non-edge port with either of the earlier-mentioned measures. After configured as an edge port, the port can fast transit from blocking state to forwarding state without any delay. You can only set the port connecting with the termina...
Page 142
142 c hapter 17: mstp r egion - configuration you can configure the path cost of a port with either of the earlier-mentioned measures. Upon the change of path cost of a port, mstp will recalculate the port role and transit the state. When instance-id takes 0, it indicates to set the path cost on the...
Page 143
Configuring mstp 143 the actual rate counts. 2 calculating the path cost table 121 details the correspondence between the rate range and the path cost values of the ports. 3com’s legacy calculation standard 1 calculating the rate ■ aggregation port the rate of the primary port in an aggregation grou...
Page 144
144 c hapter 17: mstp r egion - configuration by default, the switch calculates the default path cost of a port by the legacy standard. Configuring the priority of a port for spanning tree calculation, the port priority is an importance factor to determine if a port can be elected as the root port. ...
Page 145
Configuring mstp 145 configuration in system view perform the following configuration in system view. Configuration in ethernet port view perform the following configuration in ethernet port view. You can configure the port (not) to connect with the point-to-point link with either of the earlier-men...
Page 146
146 c hapter 17: mstp r egion - configuration configuring the mcheck variable of a port the port of an mstp switch operates in either stp-compatible or mstp mode. Suppose a port of an mstp switch on a switching network is connected to an stp switch, the port will automatically transit to operate in ...
Page 147
Configuring mstp 147 clearing dynamic arp entries in port view, the function takes effect only on the specified port. Configuring the switch protection function an mstp switch provides bpdu protection, root protection functions, loop protection and tc-protection. Bpdu protection for an access device...
Page 148
148 c hapter 17: mstp r egion - configuration operation till the specified interval is reached. This can avoid frequent delete operations on the mac address table and arp table. You can use the following command to configure the protection functions of the switch. Perform the following configuration...
Page 149
Configuring mstp 149 upstream port, some instances of the upstream port will be congested for a long time. By default, only the protection from tc-bpdu packet attack is enabled on the switch. Bpdu protection, root protection and loop protection are disabled. After configured with bpdu protection, th...
Page 150
150 c hapter 17: mstp r egion - configuration mstp can be enabled/disabled on a port through the following ways. Configuration in system view perform the following configuration in system view. Configuration in ethernet port view perform the following configuration in ethernet port view. You can ena...
Page 152
152 c hapter 17: mstp r egion - configuration typical mstp configuration example network requirements mstp provides different forwarding paths for packets of different vlans. The configurations are as follows: all the switches in the network belong to the same mst region, packets of vlan 10 travels ...
Page 153
Typical mstp configuration example 153 configuration procedure 1 configurations on switch a # mst region system-view [sw8800] stp region-configuration [3com-mst-region] region-name example [3com-mst-region] instance 1 vlan 10 [3com-mst-region] instance 3 vlan 30 [3com-mst-region] instance 4 vlan 40 ...
Page 154
154 c hapter 17: mstp r egion - configuration 4 configurations on switch d # mst region [sw8800] stp region-configuration [3com-mst-region] region-name example [3com-mst-region] instance 1 vlan 10 [3com-mst-region] instance 3 vlan 30 [3com-mst-region] instance 4 vlan 40 [3com-mst-region] revision-le...
Page 155: Igest
18 d igest s nooping c onfiguration introduction to digest snooping according to ieee 802.1s, two connected switches can communicate with each other through multiple spanning tree instances (mstis) in a multiple spanning tree protocol (mstp) region only when they are configured with the same region ...
Page 156
156 c hapter 18: d igest s nooping c onfiguration prerequisites switches of different manufacturers are interconnected in a network and have mstp employed. The network operates properly. Configuration procedure n ■ you must enable digest snooping on an port first before enabling it globally. ■ diges...
Page 157
Digest snooping configuration 157 network diagram figure 32 network diagram for digest snooping configuration configuration procedure # 3com b is directly connected to a through ge 1/1 and ge 1/2 ports. Enable digest snooping on these two ports by executing the following command: system-view system ...
Page 158
158 c hapter 18: d igest s nooping c onfiguration.
Page 159: Ast
19 f ast t ransition introduction the designated port fast transition mechanism of rstp and mstp uses two types of protocol packets: ■ proposal packet: requests for fast transition. ■ agreement packet: permits the opposite end to perform fast state transition. Rstp and mstp request that a designated...
Page 160
160 c hapter 19: f ast t ransition figure 34 designated port fast transition mechanism of mstp there is a certain limit on fast transition cooperation of rstp and mstp. For example, the upstream switch runs rstp and the downstream switch runs mstp, and the downstream mstp does not support the compat...
Page 161
Configuring fast transition 161 figure 35 network diagram configuration tasks configuring fast transition in system view configuring fast transition in ethernet port view n you can configure fast transition only on a root port or an alternate port. Port 1 port 2 switch from another vendor port 1 por...
Page 162
162 c hapter 19: f ast t ransition.
Page 163: Bpdu T
20 bpdu t unnel c onfiguration bpdu tunnel overview bpdu tunnel enables geographically segmented user networks to transmit bpdu packets transparently over the specified vlan vpn on the operator’s network. This allows the user network to participate in a uniform spanning tree calculation while mainta...
Page 164
164 c hapter 20: bpdu t unnel c onfiguration by default, bpdu tunnel is disabled. Enabling/disabling vlan vpn on ethernet port perform the following configuration in ethernet port view. By default, the vlan vpn is disabled on all the ports. Vlan vpn is not compatible with stp, dot1x, gvrp, and ntdp....
Page 165
Bpdu tunnel configuration example 165 configuration procedure 1 configure switch a # enable rapid spanning tree protocol (rstp) on the device. [switch_a] stp enable # set the port ethernet 0/1 as a trunk port and configure it to permit vlan 10 to pass through. [switch_a] vlan 10 [switch_a- ethernet ...
Page 166
166 c hapter 20: bpdu t unnel c onfiguration # enable mstp on the device. [switch_d] stp enable # enable bpdu tunnel on the device. [switch_d] vlan-vpn tunnel # add the port ethernet 3/1/2 into vlan 20. [switch_d] vlan 20 [switch_d- vlan 20 ]port ethernet 3/1/2 # first disable the stp protocol and t...
Page 167: Acl C
21 acl c onfiguration acl overview introduction to acl a series match rules must be configured to recognize the packets before they are filtered. Only when packets are identified, can the network take corresponding actions, allowing or prohibiting them to pass, according to the preset policies. Acce...
Page 168
168 c hapter 21: acl c onfiguration configured with any are put to the end and other rules follow config order; for advanced acl rules, first compare the wildcards of source addresses, then the wildcards of destination addresses if those of source addresses are equal, then the port ids if the wildca...
Page 169
Acl configuration tasks 169 a maximum of 12288 acl rules can be activated on the whole service processor card. Acl configuration tasks the following table describes the acl configuration tasks for interface cards. 3c17511 3c17512 3c17513 3c17514 3c17516 3c17526 3c17532 3c17532 mpls not supported 102...
Page 170
170 c hapter 21: acl c onfiguration the following table describes the configuration tasks for service processor cards. Configuring time range you may set such items in time range configuration: the defined time range includes absolute time range and periodic time range. The absolute time range is in...
Page 171
Acl configuration tasks 171 start-time and end-time days-of-the-week define periodic time range together. Start-time start-date and end-time end-date define absolute time range together. If a time range only defines the periodic time range, the time range is only active within the periodic time rang...
Page 172
172 c hapter 21: acl c onfiguration tcp ports, and then only those traffic rules including all these elements can be sent to target hardware and referenced for such qos functions as packet filtering, traffic policing, priority re-labeling. Otherwise, the rules cannot be activated on the hardware and...
Page 173
Acl configuration tasks 173 n ■ the numbers listed in the table are not the actual length of these elements in ip packets, but their length in flow template. Dscp field is one byte in flow template, but six bits in ip packets. You can determine whether the total length of template elements exceeds 1...
Page 174
174 c hapter 21: acl c onfiguration ■ if the time-range keyword is not selected, the acl will be effective at any time after being activated. ■ you can define multiple sub rules for the acl by using the rule command several times. ■ when the qos/acl action is configured under the port, if the qos/ac...
Page 175
Acl configuration tasks 175 c caution: ■ the port1 and port2 parameters in the command listed in table 152 should be tcp/udp ports for higher-layer applications. For some common ports, you can use mnemonic symbols to replace the corresponding port numbers. For example, you can use "bgp" to represent...
Page 176
176 c hapter 21: acl c onfiguration for service processor cards, perform the following configurations in vlan view. System-index index here is the system index for an acl rule. When delivering a rule, the system assigns a globally unique index to it, for convenience of later retrieval. You can also ...
Page 177
Acl configuration example 177 the display acl config command only displays the acl matching information processed by the cpu. See the corresponding command manual for description of parameters. Acl configuration example advanced acl configuration example network requirements the departments in the i...
Page 178
178 c hapter 21: acl c onfiguration 2 define inbound traffic to the wage server. # create a name-based advanced acl "traffic-of-payserver" and enter it. [sw8800] acl name traffic-of-payserver advanced # define acl rule for the wage server. [3com-acl-adv-traffic-of-payserver] rule 1 deny ip source an...
Page 179
Acl configuration example 179 [3com-ethernet2/1/1] packet-filter inbound ip-group traffic-of-host layer 2 acl configuration example network requirements with proper layer 2 acl configuration, during the time range from 8:00 to 18:00 everyday the switch filters the packets with source mac 00e0-fc01-0...
Page 180
180 c hapter 21: acl c onfiguration [3com-ethernet2/1/1] packet-filter inbound link-group traffic-of-link example of bt traffic control configuration network requirements bittorrent (bt) is a kind of shared software for file download. Its feature is as follows: the more people are using it to downlo...
Page 181: S C
22 q o s c onfiguration qos overview conventional packet network treats all packets equally. Each switch/router processes all packets in first-in-first-out (fifo) mode and then transfers them to the destination in the best effort, but it provides no commitment and guarantee to such transmission perf...
Page 182
182 c hapter 22: q o s c onfiguration step 2: run filtering operation (deny or permit) to the identified traffic. By default, permit operation is selected. Traffic policing qos can police traffic at the ingress port, to provide better services with the limited network resources. Redirection you can ...
Page 183
Qos overview 183 the 802.1q tag header contains a 2-byte tpid (tag protocol identifier, with the value 8100) and a 2-byte tci (tag control information). Tpid is newly defined by ieee to represent a packet with 802.1q tag added. The contents of 802.1q tag header are shown in figure 44. Figure 44 802....
Page 184
184 c hapter 22: q o s c onfiguration sent can those in lower priority queue be sent. This manner of putting key-service packets into high priority queue and non-key service packets into low priority queue does ensure that key-service packets are sent first, while non-key service packets are sent du...
Page 185
Introduction to qos configuration based on port groups 185 table 157 configure qos based on port groups configuration procedure command description enter system view system-view - enable descriptor share on the specified card share descriptors slotid this function is disabled by default. Enter port ...
Page 186
186 c hapter 22: q o s c onfiguration when you configure the port group of the common interface card except for the xp4 card, notice that: ■ do not add the ports of different cards to the same port group. Do not add the same port to multiple port groups. ■ after a port is added to the port group, th...
Page 187
Introduction to qos configuration based on port groups 187 ■ the xp4 card does not support inter-group port mirroring. A port group can have an inbound and an outbound monitoring port. There is only one monitoring port in other types of interface cards. ■ the xp4 card does not support queue scheduli...
Page 188
188 c hapter 22: q o s c onfiguration [3com-port-group1] port gigabitethernet 7/1/1 gigabitethernet 7/1/2 4 redirect the packet forwarded to the port group. # set the next hop of the packet forwarded to the port in port group 1 to 3.0.0.1. [3com-port-group1] traffic-redirect inbound ip-group 2000 ru...
Page 189
Qos configuration 189 configuring service parameter allocation rule qos is based on service parameters, a set of parameters for a packet, including 802.1p priority (cos priority), dscp priority, exp priority, local precedence and drop precedence. After receiving a packet, the switch allocates a set ...
Page 190
190 c hapter 22: q o s c onfiguration by default, the switch obtains local precedence and drop precedence according to the default mapping values. Configuring default local precedence perform the following configurations in ethernet port view. Perform the following configuration in port group view. ...
Page 191
Qos configuration 191 the system provides default mapping tables. Configuring traffic parameters (optional) use the following command to set the traffic parameters required before configuring traffic policing on service processor cards. C caution: this operation is not required for configuring traff...
Page 192
192 c hapter 22: q o s c onfiguration n it is required that cir is less than or equal to pir and cbs is less than or equal to ebs. You are recommended to configure cbs and ebs to numbers that are 100 to 150 times of cir. For service processor cards, perform the following configurations in vlan view....
Page 193
Qos configuration 193 retrieval. You can also assign a system index for it when delivering an acl rule with this command, but the index value may change while the system is running. However, you are not recommended to assign a system index if not urgently necessary. Tc-index index here is traffic po...
Page 194
194 c hapter 22: q o s c onfiguration for service processor cards, perform the following configurations in vlan view. C caution: ■ before executing the traffic-priority command on a service processor card, you must first configure traffic redirection in ethernet port view to redirect the packets of ...
Page 195
Qos configuration 195 however, you are not recommended to assign a system index if not urgently necessary. N ■ for mpls packets, other than that the dscp-value stands for their dscp priority value, the dscp-value is also mapped to the exp. You set the exp value when defining the dscp-value. Note tha...
Page 196
196 c hapter 22: q o s c onfiguration for service processor cards, perform the following configurations in vlan view. System-index index here is the system index for an acl rule. When delivering a rule, the system assigns a globally unique index to it, for convenience of later retrieval. You can als...
Page 197
Qos configuration 197 different outbound queues at the port may use different algorithms. The switch supports three scheduling modes: 1 all-sp scheduling mode 2 all-wrr mode: a queue is selected from each of the two wrr groups during scheduling, and then the two queues are compared for priority. The...
Page 198
198 c hapter 22: q o s c onfiguration configuring wred parameters the switch provides four sets of default wred parameters, respectively numbered as 0 to 3. Each set includes 80 parameters, 10 parameters for each of the eight queues. The ten parameters are green-min-threshold, yellow-min-threshold, ...
Page 199
Qos configuration 199 configuring traffic mirroring traffic mirroring duplicates the traffic that matches acl rules to the cpu or the designated destination port, for traffic analysis and monitoring. Perform the following configurations in ethernet port view. N the traffic-statistic command is used ...
Page 200
200 c hapter 22: q o s c onfiguration perform the following configurations in system view. You can implement port mirroring configuration by setting mirroring groups at the port. Up to 20 mirroring groups can be configured at a port, with each group including one monitoring port and multiple monitor...
Page 201
Qos configuration 201 perform the following configurations in ethernet port. System-index index here is the system index for an acl rule. When delivering a rule, the system assigns a globally unique index to it, for convenience of later retrieval. You can also assign a system index for it when deliv...
Page 202
202 c hapter 22: q o s c onfiguration see the corresponding command manual for description of display information and parameters. Qos configuration example traffic shaping configuration example network requirements set traffic shaping for the outbound queue 2 at the port ge7/1/8, with the maximum ra...
Page 203
Qos configuration example 203 network diagram figure 47 network diagram for qos configuration configuration procedure # enter ethernet port view. [sw8800] interface gigabitethernet 7/1/8 [3com-gigabitethernet7/1/8] # set traffic shaping for the outbound queue 2 at the port: maximum rate 650 kbps, bu...
Page 204
204 c hapter 22: q o s c onfiguration traffic priority configuration example network requirements re-allocate service parameters according to the mapping table for dscp 63 for the packets from pc1 (ip 1.0.0.1) during the time range 8:00 to 18:00 everyday. Network diagram figure 49 network diagram fo...
Page 205
Qos configuration example 205 4 define the dscp + conform-level -> service parameter mapping table. # define the dscp + conform-level -> service parameter mapping table. Allocate a set of service parameters for the packets from pc1 according the mapping table for dscp 63. [sw8800] qos conform-level ...
Page 206
206 c hapter 22: q o s c onfiguration [sw8800] time-range 3com 8:00 to 18:00 daily 2 define the traffic from pc1. # create a number-based basic acl 2000 and enter it. [sw8800] acl number 2000 # define acl rule for the traffic from pc1. [3com-acl-basic-2000] rule 0 permit source 1.0.0.1 0 time-range ...
Page 207
Qos configuration example 207 configuration procedure # re-specify the mapping between 802.1p priority and local precedence. [sw8800] qos cos-local-precedence-map 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 # use wrr algorithm for the queues 0 to 5. Set the queues 0, 1 and 2 into wrr queue 1, with weight respectively as 20, 20...
Page 208
208 c hapter 22: q o s c onfiguration 2 set drop algorithm and thresholds. # define the port ge7/1/1 in wred drop mode, set the parameters of wred 0. [3com-gigabitethernet7/1/1] drop-mode wred 0 traffic statistics configuration example network requirements suppose the ip address of pc1 is 1.0.0.1 an...
Page 209: Ogon
23 l ogon u ser acl c ontrol c onfiguration overview currently, an switch 8800 family series switch provides the following three measures for remote access: ■ telnet ■ security shell (ssh) ■ simple network management protocol (snmp) an switch 8800 family series switch provides security control for t...
Page 211
Configuring acl for telnet/ssh users 211 n ■ you can only use number-based acls to implement the acl control to telnet or ssh users. ■ when you use the basic or advanced acl to implement the acl control to telnet or ssh users, the incoming/outgoing requests are restricted based on the source or dest...
Page 212
212 c hapter 23: l ogon u ser acl c ontrol c onfiguration [sw8800] user-interface vty 0 4 # apply the layer 2 acl to restrict incoming requests. [3com-user-interface-vty0-4] acl 4000 inbound basic acl control configuration example network requirements only the telnet users with ip addresses of 10.11...
Page 213
Configuring acl for snmp users 213 configuration tasks n ■ you can apply different acls in the snmp-agent community, snmp-agent group and snmp-agent usm-use commands. ■ you can only apply number-based basic acls to implement acl control over snmp users. For the detailed description of these commands...
Page 214
214 c hapter 23: l ogon u ser acl c ontrol c onfiguration acl control over snmp users configuration example network requirements only snmp users from 10.110.100.52 and 10.110.100.46 can access the switch. Network diagram figure 56 network diagram for acl control over snmp users configuration procedu...
Page 215: Vlan-Acl C
24 vlan-acl c onfiguration vlan-acl overview vlan-acl is vlan-based acl. You can configure qacl for a vlan to control accesses made to all ports in the vlan. Vlan-acl enables you to manage a network in an easier way. After you configure qacl for a vlan, the system synchronizes the configuration to a...
Page 216
216 c hapter 24: vlan-acl c onfiguration the vlan-acl configuration is subject to the following limitations: 1 limitations on flow templates: ■ the system only applies vlan-acl to ports with the default flow template applied. The applied acl rule field must be specified by the default flow template....
Page 217
Vlan-acl configuration 217 newly added one. However, if the port delete the self-defined flow template, the system will apply qacl rules in the vlan to the new port automatically. ■ you will fail to change the flow template applied to a port with a vlan-acl already applied to a customized flow templ...
Page 218
218 c hapter 24: vlan-acl c onfiguration # define traffic classification rules for packets , and allow packets to pass during the specified time period. [3com-acl-basic-2000] rule 0 permit source any time-range 3com [3com-acl-basic-2000] quit 3 configure packet redirection in vlan 2. # set the next ...
Page 220
220 c hapter 24: vlan-acl c onfiguration.
Page 221: 802.1
25 802.1 x c onfiguration 802.1x overview 802.1x standard overview ieee 802.1x (hereinafter simplified as 802.1x) is a port-based network access control protocol that is used as the standard for lan user access authentication. In the lans complying with the ieee 802 standards, the user can access th...
Page 222
222 c hapter 25: 802.1 x c onfiguration there are two types of ports for the authenticator. One is the uncontrolled port, and the other is the controlled port. The uncontrolled port is always in bi-directional connection state. The user can access and share the network resources any time through the...
Page 223
802.1x configuration 223 implementing 802.1x on ethernet switches 3com series ethernet switches not only support the port access authentication method regulated by 802.1x, but also extend and optimize it in the following way: ■ support to connect several end stations in the downstream via a physical...
Page 224
224 c hapter 25: 802.1 x c onfiguration by default, 802.1x authentication has not been enabled globally and on any port. You cannot enable 802.1x on a port before you enable it globally. And you must disable 802.1x on each port before you disable 802,1x globally. Setting the port access control mode...
Page 225
802.1x configuration 225 the macbased keyword specifies to authenticate each user accessing through the port. And disconnection of a user does not affect other users. Whereas if you specify the portbased keyword, users can access a network without being authenticated if a user passes the authenticat...
Page 226
226 c hapter 25: 802.1 x c onfiguration by default, 802.1x allows up to 1024 supplicants on each port for 3com switch 8800 family series routing switches (hereinafter referred to as switch 8800 family series), and an switch 8800 family series routing switch can accommodate total of 2048 supplicants....
Page 227
802.1x configuration 227 vlan when the maximum number of re-authentications is reached. Users in a guest vlan can utilize resources in the guest vlan without undergoing the 802.1x authentication, but they can utilize the resources outside the guest vlan only when they have passed the 802.1x authenti...
Page 228
228 c hapter 25: 802.1 x c onfiguration handshake-period: this timer begins after the user has passed the authentication. After setting handshake-period, system will send the handshake packet by the period. Suppose the dot1x retry time is configured as n, the system will consider the user having log...
Page 229
Displaying and debugging 802.1x 229 ■ specifies the interval of multicasting 802.1x request packets periodically. In order to be compatible with clients who do not send eapol-start frames actively, switch 8800 family switches will multicast 802.1x request packets periodically. The clients will respo...
Page 230
230 c hapter 25: 802.1 x c onfiguration packet attack prevention configuration with the expansion of internet scale and the increase of internet users, the possibility that networking equipment gets attacked is increasing. Specific to some typical attack modes, the switch 8800 family series switches...
Page 231
802.1x configuration example 231 when the user is accessed, the domain name does not follow the user name. Normally, if the user’s traffic is less than 2000 byte/s consistently over 20 minutes, he will be disconnected. A server group, consisting of two radius servers at 10.11.1.1 and 10.11.1.2 respe...
Page 232
232 c hapter 25: 802.1 x c onfiguration # enable the 802.1x performance on the specified port ethernet 3/1/1. [sw8800] dot1x interface ethernet 3/1/1 # set the access control mode. (this command could not be configured, when it is configured as mac-based by default.) [sw8800] dot1x port-method macba...
Page 233
802.1x configuration example 233 [3com-isp-3com163.Net] radius-scheme radius1 # set a limit of 30 users to the domain 3com163.Net. [3com-isp-3com163.Net] access-limit enable 30 # enable idle cut function for the user and set the idle cut parameter in the domain 3com163.Net. [3com-isp-3com163.Net] id...
Page 234
234 c hapter 25: 802.1 x c onfiguration.
Page 235: Aaa
26 aaa and radius/hwtacacs p rotocol c onfiguration aaa and radius/hwtacacs protocol overview aaa overview authentication, authorization and accounting (aaa) provide a uniform framework used for configuring these three security functions to implement the network security management. The network secu...
Page 236
236 c hapter 26: aaa and radius/hwtacacs p rotocol c onfiguration request to the radius server. Radius server has a user database recording all the information of user authentication and network service access. When receiving user’s request from nas, radius server performs aaa through user database ...
Page 237
Aaa and radius/hwtacacs protocol overview 237 figure 60 network diagram for hwtacacs basic message exchange procedures in hwtacacs for example, use hwtacacs to implement authentication, authorization, and accounting for a telnet user. The basic message exchange procedures are as follows: ■ a user re...
Page 238
238 c hapter 26: aaa and radius/hwtacacs p rotocol c onfiguration figure 61 illustrates the basic message exchange procedures. Figure 61 basic message exchange procedures implementing aaa/radius on a switch by now, we understand that in the above-mentioned aaa/radius framework, 3com series switches,...
Page 239
Aaa configuration 239 figure 62 network diagram for using radius to authenticate aaa configuration the following sections describe aaa configuration tasks. ■ “creating/deleting an isp domain” ■ “configuring relevant attributes of an isp domain” ■ “configuring self-service server url” ■ “creating/del...
Page 240
240 c hapter 26: aaa and radius/hwtacacs p rotocol c onfiguration for 3com series switches, each supplicant belongs to an isp domain. Up to 16 domains can be configured in the system. If a user has not reported its isp domain name, the system will put it into the default domain. Perform the followin...
Page 241
Aaa configuration 241 both the radius-scheme and scheme radius-scheme commands can be used to specify the radius scheme for an isp domain with the same effect, and the system adopts the last configuration. By default, the local scheme is adopted, an isp domain is in active state once it is created, ...
Page 243
Aaa configuration 243 following table for reference), and cipher-force means that the password display mode of all the accessing users must be in cipher text. Setting/removing the attributes of a local user perform the following configuration in local user view. By default, users are not authorized ...
Page 244
244 c hapter 26: aaa and radius/hwtacacs p rotocol c onfiguration configuring dynamic vlan delivering dynamic vlan delivering aims to control the network resources available to a user. With this function enabled, a switch adds the ports connecting to authenticated users to specified vlans according ...
Page 245
Configuring radius protocol 245 by default, the integer mode is used. That is, the switch supports the radius server delivering vlan ids in integer form. Configuring name of a delivered vlan perform the following configuration in vlan view. By default, the delivered vlan does not have a name. Config...
Page 246
246 c hapter 26: aaa and radius/hwtacacs p rotocol c onfiguration ■ “setting the username format transmitted to radius server” ■ “setting the unit of data flow that transmitted to radius server” ■ “configuring the source address used by nas in radius packets” ■ “setting the port state of radius clie...
Page 247
Configuring radius protocol 247 by default, as for the "system" radius scheme created by the system: the ip address of the primary authentication server is 127.0.0.1, and the udp port number is 1645. The ip address of the secondary authentication server is 0.0.0.0, and the udp port number is 1812. T...
Page 248
248 c hapter 26: aaa and radius/hwtacacs p rotocol c onfiguration authentication/authorization and accounting packets, you shall set two different ports accordingly. Suggested by rfc2138/2139, authentication/authorization port number is 1812 and accounting port number is 1813. However, you may use v...
Page 249
Configuring radius protocol 249 the radius server does not belong to any vpn by default. Setting the port state of the local radius server the local radius server uses the switch itself as the radius server, with port 1645 as authentication port and port 1646 as accounting port. The two ports are en...
Page 250
250 c hapter 26: aaa and radius/hwtacacs p rotocol c onfiguration perform the following configuration in radius scheme view. The default value of the response timeout timer of a radius server is 3 seconds. Setting quiet time of radius server when the communication between the switch and the radius s...
Page 251
Configuring radius protocol 251 perform the following configuration in radius scheme view. By default, selection of radius accounting option is disabled. Setting a real-time accounting interval to implement real-time accounting, it is necessary to set a real-time accounting interval. After the attri...
Page 252
252 c hapter 26: aaa and radius/hwtacacs p rotocol c onfiguration you can use the following command to set the maximum times of real-time accounting request failing to be responded. Perform the following configuration in radius scheme view. How to calculate the value of retry-times? Suppose that rad...
Page 253
Configuring radius protocol 253 by default, the stopping accounting request can be retransmitted for up to 500 times. Setting the supported type of radius server 3com series switches support the standard radius protocol and the extended radius service platforms, such as ip hotel, 201+ and portal, in...
Page 254
254 c hapter 26: aaa and radius/hwtacacs p rotocol c onfiguration by default, the state of each server in radius scheme server group is active. Setting the username format transmitted to radius server as mentioned above, the supplicants are generally named in userid@isp-name format. The part followi...
Page 255
Configuring radius protocol 255 configuring the source address used by nas in radius packets perform the following configuration in the corresponding view. The effect of the two commands is the same. However, the configuration done in radius scheme view has a higher priority than the configuration d...
Page 256
256 c hapter 26: aaa and radius/hwtacacs p rotocol c onfiguration by default, the ip address of local radius authentication server group is 127.0.0.1 and the password is 3com. When using local radius server function, note that, 1 the number of udp port used for authentication/authorization is 1645 a...
Page 257
Configuring hwtacacs protocol 257 by default, no hwtacacs scheme exists. If the hwtacacs scheme you specify does not exist, the system creates it and enters hwtacacs view. In hwtacacs view, you can configure the hwtacacs scheme specifically. The system supports up to 16 hwtacacs schemes. You can onl...
Page 258
258 c hapter 26: aaa and radius/hwtacacs p rotocol c onfiguration n if only authentication and accounting servers are configured and no authorization server is configured, both authentication and accounting can be performed normally for the ftp, telnet, and ssh users, but the priority of these users...
Page 259
Configuring hwtacacs protocol 259 configuring the source address for hwtacacs packets sent by nas perform the following configuration in the corresponding view. The hwtacacs view takes precedence over the system view when configuring the source address for hwtacacs packets sent from the nas. By defa...
Page 260
260 c hapter 26: aaa and radius/hwtacacs p rotocol c onfiguration setting the unit of data flows destined for the tacacs server perform the following configuration in hwtacacs view. The default data flow unit is byte. Setting timers regarding tacacs server setting the response timeout timer since hw...
Page 261
Displaying and debugging aaa and radius protocol 261 the interval is in minutes and must be a multiple of 3. The setting of real-time accounting interval somewhat depends on the performance of the nas and the tacacs server: a shorter interval requires higher device performance. You are therefore rec...
Page 262
262 c hapter 26: aaa and radius/hwtacacs p rotocol c onfiguration aaa and radius/hwtacacs protocol configuration examples for the hybrid configuration example of aaa/radius/hwtacacs protocol and 802.1x protocol, refer to the part "802.1x". Perform the following configuration in system view. The anti...
Page 263
Aaa and radius/hwtacacs protocol configuration examples 263 configuring authentication at remote radius server n configuring telnet user authentication at the remote server is similar to configuring ftp users. The following description is based on telnet users. Network requirements in the environmen...
Page 264
264 c hapter 26: aaa and radius/hwtacacs p rotocol c onfiguration # associate the domain with radius. [3com-radius-cams] quit [sw8800] domain cams [3com-isp-cams] radius-scheme cams configuring authentication at local radius authentication server local radius authentication of telnet/ftp users is si...
Page 265
Troubleshooting aaa and radius/hwtacacs 265 n the configuration of the ftp and telnet users can refer to user interface configuration of getting started operation part in switch 8800 family series routing switches operation manual. # configure a hwtacacs scheme. [sw8800] hwtacacs scheme hwtac [3com-...
Page 266
266 c hapter 26: aaa and radius/hwtacacs p rotocol c onfiguration ■ ports of authentication/authorization and accounting services may not be set properly. So make sure they are consistent with the ports provided by radius/hwtacacs server. Symptom: after being authenticated and authorized, the user c...
Page 267: Ortal
27 p ortal c onfiguration portal overview introduction portal is also known as portal website, and portal authentication is also known as the web authentication. Its major advantages are: ■ users need not install any client software; ■ it is powerful in its ability to support new services. With the ...
Page 268
268 c hapter 27: p ortal c onfiguration ■ portal server is a web server. Users can access it by using standard www browsers. The portal server provides free portal service and web-authentication-based interface. The access device exchanges the authentication information of the authentication client ...
Page 269
Portal overview 269 accesses. That is to say, layer-3-protocol-enabled network devices cannot exist between the user and the access devices. ■ the layer 3 portal authentication method does not check mac addresses of the user, so the security performance is reduced. . You are not recommended to use t...
Page 270
270 c hapter 27: p ortal c onfiguration basic portal configuration configuration prerequisites ■ a valid ip address has been configured for this portal-enabled vlan interface. ■ 802.1x is not enabled on the switch. ■ the portal server has been installed and configured. Refer to cams portal service c...
Page 271
Basic portal configuration 271 c caution: ■ when a portal server is first configured, you must configure the ip address for it. ■ if a portal server has been enabled on a vlan interface, you must disable this portal server on the vlan interface before modifying its parameters. ■ when portal authenti...
Page 272
272 c hapter 27: p ortal c onfiguration network diagram figure 66 network diagram for portal direct authentication method configuration procedure n only the configurations on switches are listed below. Configurations on the portal servers and radius authentication/accounting servers are not describe...
Page 273
Basic portal configuration 273 3 configure portal authentication # configure the portal server. Its name is newp, ip address is 192.168.1.200, key is 3com, port is 50100, and url is http://192.168.1.200:81/portal/index_page.Jsp [sw8800] portal server newp ip 192.168.1.200 key 3com port 50100 url htt...
Page 274
274 c hapter 27: p ortal c onfiguration ■ when the portal redhcp authentication method is adopted, the switch must be configured as dhcp relay instead of dhcp server. Additionally, the master ip address ( public address ) and the slave ip address (private ip address) must be configured on the portal...
Page 275
Basic portal configuration 275 network diagram figure 67 network diagram for layer 3 portal authentication method configuration procedure n only the configurations related to the layer 3 portal authentication method are listed below. Refer to “portal direct authentication method configuration exampl...
Page 276
276 c hapter 27: p ortal c onfiguration portal authentication-free user and free ip address configuration configuration prerequisites the prerequisite of portal authentication-free user and free ip address configuration-the basic portal configuration has been finished. Portal authentication-free use...
Page 277
Portal authentication-free user and free ip address configuration 277 ■ server2 can access internet without passing the authentication. Network diagram figure 68 network diagram for authentication-free user and free ip address configuration configuration procedure n the following configurations are ...
Page 278
278 c hapter 27: p ortal c onfiguration portal rate limit function configuration portal rate limit function configuration procedure portal rate limit function configuration example network requirements ■ the upload interface for portal rate limit is specified. Network diagram refer to figure 66. Con...
Page 279: Ip R
28 ip r outing p rotocol o verview n a router that is referred to in the following or its icon represents a generalized router or an switch 8800 family series routing switch running routing protocols. To improve readability, this will not be described in the other parts of the manual. For the config...
Page 280
280 c hapter 28: ip r outing p rotocol o verview figure 69 the concept of route segment as the networks may have different sizes, the segment lengths connected between two different pairs of routers are also different. The number of route segments multiplies a weighted coefficient can serve as a wei...
Page 281
Introduction to ip route and routing table 281 ■ next hop address: it indicates the ip address of the next router that an ip packet will pass through. ■ priority added to the ip routing table for a route: there may be different next hops to the same destination. These routes may be discovered by dif...
Page 282
282 c hapter 28: ip r outing p rotocol o verview addition, the running switch will automatically obtain some direct routes according to the port state and user configuration. Routing management policy for switch 8800 family series, you can configure manually the static route to a specific destinatio...
Page 283
Routing management policy 283 precedence, the multiple routes will be adopted. Thus, the router will forward the packets to the destination through these paths according to a certain algorithm so as to implement load sharing. For the same destination, a specified routing protocol may find multiple d...
Page 284
284 c hapter 28: ip r outing p rotocol o verview.
Page 285: Tatic
29 s tatic r oute c onfiguration introduction to static route static route a static route is a special route configured manually by an administrator. You can set up an interconnecting network with the static route configuration. The problem for such configuration is when a fault occurs to the networ...
Page 286
286 c hapter 29: s tatic r oute c onfiguration this packet will be discarded, and an internet control message protocol (icmp) packet will be sent to the originating host to inform that the destination host or network is unreachable. Configuring static route static route configuration includes: ■ “co...
Page 287
Displaying and debugging static route 287 ■ other parameters the attributes reject and blackhole respectively indicate the unreachable route and the blackhole route. Configuring a default route perform the following configurations in system view. The meanings of parameters in the command are the sam...
Page 288
288 c hapter 29: s tatic r oute c onfiguration typical static route configuration example network requirements as shown in figure 71, the masks of all the ip addresses are 255.255.255.0. It is required that all the hosts or switch 8800 family series routing switches can be interconnected in pairs by...
Page 289
Troubleshooting static route faults 289 then, all the hosts or switches in the figure can be interconnected in pairs. Troubleshooting static route faults symptom: the switch is configured with the static routing protocol and both the physical status and the link layer protocol status of the interfac...
Page 290
290 c hapter 29: s tatic r oute c onfiguration.
Page 291: Rip C
30 rip c onfiguration introduction to rip routing information protocol (rip) is a relatively simple interior gateway protocol (igp), which is mainly applied to small scale networks. It is easy to implement rip. You can configure and maintain rip more easily than ospf and is-is, so rip still has a wi...
Page 292
292 c hapter 30: rip c onfiguration ■ if the rip route is not updated (a router receives the update packets from the neighbor) when the timeout timer expires, this route is regarded as unreachable. The cost is set to 16. ■ if the garbage-collection timer expires, and the unreachable route receives n...
Page 293
Configuring rip 293 you can make the following configurations for rip to advertise and receive routing information: ■ setting additional routing metric ■ configuring rip to import routers of other protocols ■ configuring rip route filtering ■ enabling/disabling host route receiving by the router ■ c...
Page 294
294 c hapter 30: rip c onfiguration when a command network is used for an address, you can enable the network address of the port, which also includes the subnet addresses. For example, for network 129.102.1.1, you can see network 129.102.0.0 either using display current-configuration or using displ...
Page 295
Configuring rip 295 by default, the additional routing metric added to the route when rip sends a packet is 1. The additional routing metric when rip receives the packet is 0 by default. N the metricout configuration takes effect only on the rip routes learnt by the router and rip routes generated b...
Page 296
296 c hapter 30: rip c onfiguration configuring rip to filter the routes advertised by rip by default, rip does not filter the received and advertised routing information. N ■ the filter-policy import command filters the rip routes received from its neighbors, and the routes that fail to pass the fi...
Page 297
Configuring rip 297 rip-1 only sends the route with natural mask, that is, it always sends routes in the route summary form. Rip-2 supports subnet mask and classless interdomain routing. To advertise all the subnet routes, the route summary function of rip-2 can be disabled. Perform the following co...
Page 298
298 c hapter 30: rip c onfiguration by default, the interface receives and sends the rip-1 packets. It will transmit packets in multicast mode when the interface rip version is set to rip-2. Configuring rip timers as mentioned previously, rip has three timers: period update, timeout and garbage-coll...
Page 299
Configuring rip 299 specifying the operating state of the interface in interface view, you can specify the operating state of rip on the interface. For example, whether rip operates on the interface, namely, whether rip update packets are sent and received on the interface. In addition, whether an i...
Page 300
300 c hapter 30: rip c onfiguration before configuring md5 authentication, you must configure md5 type. The usual packet format follows rfc1723 and the nonstandard follows rfc2082. Displaying and debugging rip after the above configuration, execute the display command in any view to display the runn...
Page 301
Troubleshooting rip faults 301 network diagram figure 72 network diagram for rip configuration configuration procedure n the following configuration only shows the operations related to rip. Before performing the following configuration, make sure the ethernet link layer can work normally. 1 configu...
Page 302
302 c hapter 30: rip c onfiguration solution: rip does not operate on the corresponding interface (for example, the undo rip work command is executed) or this interface is not enabled through the network command. The peer routing device is configured to be in the multicast mode (for example, the rip...
Page 303: Ospf C
31 ospf c onfiguration ospf overview introduction to ospf open shortest path first (ospf) is an interior gateway protocol based on the link state developed by ietf. At present, ospf version 2 (rfc2328) is used, which is available with the following features: ■ applicable scope: it can support networ...
Page 304
304 c hapter 31: ospf c onfiguration autonomous system. Obviously, the routing tables obtained by different routers are different. Furthermore, to enable individual routers to broadcast their local state information to the entire as, any two routers in the environment should establish adjacency betw...
Page 305
Ospf overview 305 ■ router-lsas: type-1. Each router generates router-lsas, which describe the link state and cost of the local router. Router-lsas are broadcast within the area where the router is located. ■ network-lsas: type-2. Drs on the broadcast network generate network-lsas, which describe th...
Page 306
306 c hapter 31: ospf c onfiguration ■ backup designated router (bdr) if the dr fails for some faults, a new dr must be elected and synchronized with other routers on the segment. This process will take a relatively long time, during which, the route calculation is incorrect. To shorten the process,...
Page 307
Ospf gr overview 307 figure 73 area and route summary ospf features supported by switch 8800 family series the switch 8800 family series support the following ospf features: ■ support stub areas: ospf defines stub areas to decrease the overhead when the routers within the area receive ase routes. ■ ...
Page 308
308 c hapter 31: ospf c onfiguration working mechanism of ospf gr 1. Implementation standard of ospf gr rfc3623:graceful ospf restart ietf drafts: draft-nguyen-ospf-lls-05; draft-nguyen-ospf-oob-resync-05; draft-nguyen-ospf-restart-05; work mechanism of rfc3623 rfc3623 defines two main principles fo...
Page 309
Ospf gr overview 309 the neighbor will keep the neighbor relationship and set the restartstat-flag after receiving hello packets of the rs_bit set. When both neighbors exit from the oob process, the standard ospf algorithm is performed. N the gr method on both ospf neighbors must be the same. Differ...
Page 310
310 c hapter 31: ospf c onfiguration figure 77 format of lls data tlv structure: eo_tlv and ca_tlv 1 format of eo_tlv figure 78 format of eo_tlv the meaning of each field in eo_tlv: the type field refers to the type of tlv, and the type of eo_tlv is 1; the length field refers to the length of tlv, a...
Page 311
Configuring ospf 311 the authlen field refers to the length of ca_tlv, and the length of ca_tlv is 20; the sequence number and authdata fields are determined by the ospf check information. N lls data can be included in only hello packets and dd packets. Only one lls data can be included in a packet....
Page 312
312 c hapter 31: ospf c onfiguration ospf configuration includes: 1 ospf basic configuration ■ “configuring router id” ■ “enabling ospf” ■ “entering ospf area view” ■ “specifying an interface to run ospf” 2 configuration related to ospf route ■ “configuring ospf to import routes of other protocols” ...
Page 313
Configuring ospf 313 perform the following configuration in system view. To ensure stability of ospf, the user should determine the division of router ids and manually configure them when planning the network. Enabling ospf perform the following configuration in system view. By default, ospf is disa...
Page 314
314 c hapter 31: ospf c onfiguration perform the following configuration in ospf area view. The ip-mask argument is ip address wildcard shielded text (similar to the complement of the ip address mask). Configuring ospf to import routes of other protocols the dynamic routing protocols on the router c...
Page 315
Configuring ospf 315 by default, ospf will not import the routing information of other protocols. For an imported route, type is 2, cost is 1, and tag is 1 by default. The routes that can be imported include direct, static, rip, is-is, and bgp. In addition, the routes of other ospf processes can als...
Page 316
316 c hapter 31: ospf c onfiguration by default, the type of imported route is type-2, the cost is 1 and the tag is 1 for a imported route. Configuring the default interval and number for ospf to import external routes ospf can import the external routing information and broadcast it to the entire a...
Page 317
Configuring ospf 317 ■ for an asbr, the system generates the corresponding type-5 lsa or type-7 lsa by default when a default route existed in the routing table. ■ for an abr, the system will generate a type-5 lsa or type-7 lsa no matter whether there is a default route in the routing table. ■ the b...
Page 318
318 c hapter 31: ospf c onfiguration by default, ospf does not receive the routes advertised by other routing protocols. N ■ the filter-policy import command only filters the ospf routes of this process received from the neighbors, and routes that cannot pass the filter will not be added to the rout...
Page 319
Configuring ospf 319 configuring the route summary of ospf configuring the route summary of ospf area route summary means that abr can aggregate information of the routes of the same prefix and advertise only one route to other areas. An area can be configured with multiple aggregate segments, there...
Page 320
320 c hapter 31: ospf c onfiguration if the local router works as an area border router (abr) and a router in the nssa, this command summarizes type-5 lsas transformed from type-7 lsas. If the router is not the router in the nssa, the summarization is disabled. Setting ospf route preference since ma...
Page 321
Configuring ospf 321 by default, the dead interval for the neighboring routers of p2p or broadcast interfaces is 40 seconds and that for the neighboring routers of p2mp interfaces is 120 seconds. Note that both hello and dead timer will restore to the default values after the user modify the network...
Page 322
322 c hapter 31: ospf c onfiguration note: 3com supports the broadcast domain only. By default, ospf determines the network type based on the link layer type. After the interface has been configured with a new network type, the original network type of the interface is removed automatically. Setting...
Page 323
Configuring ospf 323 use the ospf dr-priority and peer commands to set priorities with different usages: ■ use the ospf dr-priority command to set priority for dr selection. ■ the priority you use the peer command to set indicates whether the adjacent router is eligible for election. If you specify ...
Page 324
324 c hapter 31: ospf c onfiguration by default, the interface does not fill in the mtu field when transmitting dd packets. In other words, mtu in the dd packets is 0. Setting a shortest path first (spf) calculation interval for ospf whenever the lsdb of ospf takes changes, the shortest path require...
Page 325
Configuring ospf 325 configuring ospf authentication configuring the ospf area to support packet authentication all the routers in one area must use the same authentication mode (no authentication, simple text authentication or md5 cipher text authentication). If the mode of supporting authenticatio...
Page 326
326 c hapter 31: ospf c onfiguration two abrs. Both ends of the logic channel should be abrs and the connection can take effect only when both ends are configured. The virtual link is identified by the id of the remote router. The area, which provides the ends of the virtual link with a non-backbone...
Page 327
Configuring ospf 327 ■ no asbr can exist in a stub area. In other words, the external routes of the as cannot be propagated in the stub area. Perform the following configuration in ospf area view. By default, the stub area is not configured, and the cost of the default route to the stub area is 1. C...
Page 328
328 c hapter 31: ospf c onfiguration all the routers connected to the nssa should use the nssa command to configure the area with the nssa attribute. The keyword default-route-advertise is used to generate default type-7 lsas. When default-route-advertise is configured, a default type-7 lsa route wi...
Page 329
Configuring ospf 329 perform the following configuration in system view. By default, mib is bound to the first enabled ospf process. Configuring ospf trap the ospf trap function enables the switch to send multiple types of snmp trap packets in case of ospf process exceptions. In addition, you can sp...
Page 330
330 c hapter 31: ospf c onfiguration configuring gr method as ietf drafts resetting the ospf process if the undo ospf command is executed on a router and then the ospf command is used to restart the ospf process, the previous ospf configuration will lose. With the reset ospf command, you can restart...
Page 331
Typical ospf configuration example 331 typical ospf configuration example configuring dr election based on ospf priority network requirements four switch 8800 family series, switch a, switch b, switch c and switch d, which can perform the router functions and run ospf, are located on the same segmen...
Page 332
332 c hapter 31: ospf c onfiguration network diagram figure 83 network diagram for configuring dr election based on ospf priority configuration procedure # configure switch a [switch a] interface vlan-interface 1 [switch a-vlan-interface1] ip address 196.1.1.1 255.255.255.0 [switch a-vlan-interface1...
Page 333
Typical ospf configuration example 333 on switch a, execute the display ospf peer command to display the ospf peers. Note that switch a has three peers. The state of each peer is full, which means that adjacency is set up between switch a and each peer. (switch a and switch c should set up adjacenci...
Page 334
334 c hapter 31: ospf c onfiguration configuration procedure # configure switch a [switch a] interface vlan-interface 1 [switch a-vlan-interface1] ip address 196.1.1.1 255.255.255.0 [switch a] router id 1.1.1.1 [switch a] ospf [switch a-ospf-1] area 0 [switch a-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 196.1.1.0...
Page 335
Typical ospf configuration example 335 network diagram figure 85 network diagram configuration procedure # configure the switch switch 8800 familya system-view [switch 8800 familya] vlan 192 [switch 8800 familya-vlan192] port gigabitethernet 3/1/1 [switch 8800 familya-vlan192] interface vlan 192 [sw...
Page 336
336 c hapter 31: ospf c onfiguration troubleshooting ospf faults symptom 1: ospf has been configured in accordance with the earlier-mentioned steps, but ospf on the router cannot run normally. Solution: check according to the following procedure. Local troubleshooting: check whether the protocol bet...
Page 337
Troubleshooting ospf faults 337 figure 86 ospf areas ■ the backbone area (area 0) cannot be configured as the stub area and the virtual link cannot pass through the stub area. That is, if a virtual link has been set up between rtb and rtc, neither area1 nor area0 can be configured as a stub area. In...
Page 338
338 c hapter 31: ospf c onfiguration.
Page 339: Ntegrated
32 i ntegrated is-is c onfiguration introduction to integrated is-is intermediate system-to-intermediate system (is-is) intra-domain routing information exchange protocol is designed by the international organization for standardization (iso) for connection-less network protocol (clnp). This protoco...
Page 340
340 c hapter 32: i ntegrated is-is c onfiguration two-level structure of is-is routing protocol two-level structure of is-is routing protocol two-level structure of is-is routing protocol is adopted in a route area to support large scale route network. A large route area can be divided into one or m...
Page 341
Introduction to integrated is-is 341 figure 87 is-is topology nsap structure of is-is routing protocol address structure figure 88 nsap structure es routing domain boundary is-is area end system subnetwork path level 1 is-is routing level 2 is-is routing interdomain routing intermediate system es is...
Page 342
342 c hapter 32: i ntegrated is-is c onfiguration osi adopts the address structure as shown in figure 88. Nsap includes initial domain part (idp) and domain specific part (dsp). The idp is defined by iso; it consists of authority responsible for assigning the rest of the address and address format. ...
Page 343
Configuring integrated is-is 343 net network entity title (net) indicates the network layer information, which contains no transfer layer information (sel=0). You can regard it as a special nsap. In general, you can configure a net for a router. If you will redivide an area (combine multiple areas o...
Page 344
344 c hapter 32: i ntegrated is-is c onfiguration is-is configuration includes: 1 is-is basic configuration ■ enabling is-is and entering the is-is view ■ setting network entity title ■ enabling is-is on the specified interface ■ setting priority for dis election ■ setting router type ■ setting inte...
Page 345
Configuring integrated is-is 345 the tag argument identifies the is-is process. In the present version, just one is-is process is allowed. By default, the is-is routing process is disabled. Setting network entity title network entity titles (hereafter referred to as nets) defines the current is-is a...
Page 346
346 c hapter 32: i ntegrated is-is c onfiguration by default, the interface priority is 64. If the level-1 or level-2 is not specified, it defaults to setting the priority of level-1. Setting router type based upon the position of the router, the levels can be divided into level-1 (intra-domain rout...
Page 347
Configuring integrated is-is 347 perform the following configuration in is-is view. If the level is not specified in the command for importing the route, it defaults to importing the routes into level-2. Protocol specifies the routing protocol sources that can be imported, which can be direct, stati...
Page 348
348 c hapter 32: i ntegrated is-is c onfiguration ■ the filter-policy export command only takes effect to the routes imported by the import-route command. If you configure the switch with only the filter-policy export command, but without configuring the import-route command to import other external...
Page 349
Configuring integrated is-is 349 the default route generated by this command will only be imported to the router at the same level. Setting the preference of is-is protocol in a router on which several routing protocols are concurrently operating, there is an issue of sharing and selecting the routi...
Page 350
350 c hapter 32: i ntegrated is-is c onfiguration configuring is-is timers setting the hello packet broadcast interval the is-is periodically sends the hello packets from the interface and the routers maintain the adjacency through the transmitting/receiving of the hello packets the hello packet int...
Page 351
Configuring integrated is-is 351 if the level is not specified, it defaults to setting csnp packet broadcast interval for level-1. By default, the csnp packet is transmitted via interface every 10 seconds. Setting lsp packet generation interval as specified in the is-is protocol, when an event takes...
Page 352
352 c hapter 32: i ntegrated is-is c onfiguration by default, the lsp packet is transmitted every five seconds over the p2p link. Configuring number of invalid hello packets for the interface the router maintains the adjacency by sending/receiving hello packets. When receiving no hello packets from ...
Page 353
Configuring integrated is-is 353 setting is-is area or is-is routing domain authentication password users can configure the is-is area or the is-is routing domain with authentication password. If area authentication is needed, the area authentication password will be encapsulated into the level-1 ls...
Page 354
354 c hapter 32: i ntegrated is-is c onfiguration setting overload flag bit sometimes, the router in the is-is domain may encounter some problems in operation thus errors may occur in the whole routing area. In order to avoid this problem, you can set the overload flag bit for this router. When the ...
Page 355
Configuring integrated is-is 355 by default, lsp is refreshed every 900 seconds (15 minutes). Setting lifetime of lsp when a router generates the lsp of the system, it will fill in the maximum lifetime of this lsp. When other routers receive this lsp, its life time will be reduced continuously as th...
Page 356
356 c hapter 32: i ntegrated is-is c onfiguration by default, spf calculation is not divided into slices but runs to the end once, which can also be implemented by setting the seconds argument to 0. After slice calculation is set, the routes that are not processed once will be calculated in one seco...
Page 357
Configuring integrated is-is 357 interfaces. On a switch, this command can disable/enable the specified vlan interface to send is-is packets. Configuring is-is gr the network is interrupted temporarily when an is-is router is restarted because the neighbor relationship of this router with other neig...
Page 358
358 c hapter 32: i ntegrated is-is c onfiguration by default, the is-is data structure is not cleared. Resetting the specified is-is peer when it is necessary to connect a specified peer again, perform the following configuration in user view. By default, the is-is peer is not cleared. Displaying an...
Page 359
Typical integrated is-is configuration example 359 typical integrated is-is configuration example network requirements as is shown in figure 89, switches a, b, c and d belong to the same autonomous system. The is-is routing protocol is running in these four switches so as to implement route intercon...
Page 360
360 c hapter 32: i ntegrated is-is c onfiguration # configure switch c [switch c] isis [switch c-isis] network-entity 86.0001.0000.0000.0007.00 [switch c] interface vlan-interface 101 [switch c-vlan-interface101] ip address 200.10.0.2 255.255.255.0 [switch c-vlan-interface101] isis enable [switch c]...
Page 361: Bgp C
33 bgp c onfiguration bgp/mbgp overview introduction to bgp border gateway protocol (bgp) is an inter-autonomous system (inter-as) dynamic route discovery protocol. Three early versions of bgp are bgp-1 (rfc1105), bgp-2 (rfc1163) and bgp-3 (rfc1267). The current version is bgp-4 (rfc1771) that is ap...
Page 362
362 c hapter 33: bgp c onfiguration the bgp is called ibgp when it runs in an as and ebgp when it runs among different ass. Bgp message types bgp is driven by messages, which include the following types: ■ type 1, open: the first message sent after the creation of a connection to create association ...
Page 363
Bgp/mbgp overview 363 route selection policy in the implementation of switch 8800 family series, these policies are adopted for bgp to select routes: ■ first discard the routes unreachable to the next hop. ■ first select the routes with the highest local preference. ■ first select the routes rooted ...
Page 364
364 c hapter 33: bgp c onfiguration switch 8800 family series provide various mbgp extended applications, including extension of multicast, vpn, and so on. Different extended applications should be configured in their own address family views. For more information about the commands executed in mbgp...
Page 365
Configuring bgp 365 ■ “configuring bgp timer” ■ “configuring the local preference” ■ “configuring med for as” 5 bgp application configuration ■ “comparing the med routing metrics from the peers in different ass” 6 bgp networking configuration ■ “configuring bgp route reflector” ■ “configuring bgp as...
Page 366
366 c hapter 33: bgp c onfiguration create an ebgp peer group and sub-as peer groups inside a confederation. Group-name is locally significant. The default type of bgp peer group is ibgp. Configuring as number of an ebgp peer group you can specify as number for an ebgp peer group, but ibgp needs no ...
Page 367
Configuring bgp 367 when exchanging routing information between bgp speakers, the peer group must be enabled first and then the peer should be added to the enabled peer group. Configuring the graceful-restart ability of a peer or peer group configuring graceful-restart restart-time of a peer or peer...
Page 368
368 c hapter 33: bgp c onfiguration by default, the keep-alive message is sent every 60 seconds and the value of the hold timer is 180 seconds. Configuring the interval at which route update messages are sent by a peer group by default, the intervals at which route update messages are sent by an ibg...
Page 369
Configuring bgp 369 this configuration can be applied to ibgp peer groups only. By default, all ibgp peers in the autonomous system must be fully connected. Moreover, neighbors do not notify the learned ibgp routes. Configuring to send default route to a peer group if you only need to notify a defau...
Page 370
370 c hapter 33: bgp c onfiguration is used to configure certain outbound routers to ignore the private as numbers while transmitting update messages. Perform the following configuration in bgp view. By default, the private as numbers are included during bgp update messages transmission. The configu...
Page 371
Configuring bgp 371 interior bgp session can be configured to specify the source interface. This command is usually used on the loopback interface. By default, bgp uses the interface to establish bgp links for the source interface of a route update packet. Configuring bgp md5 authentication password...
Page 372
372 c hapter 33: bgp c onfiguration configuring route filtering policy based on ip acl for a peer (group) configuring route filtering policy based on as path list for a peer (group) the acl-number argument indicates as path list number, which is configured by means of the ip as-path-acl command inst...
Page 373
Configuring bgp 373 configuring network routes for bgp distribution perform the following configuration in bgp view. By default, no network route is configured for bgp distribution. Configuring the interaction between bgp and igp (importing igp routes) bgp can transmit the internal network informati...
Page 374
374 c hapter 33: bgp c onfiguration ■ automatic aggregation (by means of the summary command): the aggregation of igp subnet routes imported by the bgp. With automatic aggregation enabled, the bgp will not receive subnet routes imported from the igp, and routes on natural network segments will be ag...
Page 375
Configuring bgp 375 by default, bgp does not receive the routing information advertised by other routing protocols. N ■ the filter-policy import command filters bgp route received from the neighbors. The routes that cannot pass the filter will not be added to the routing table, and will not be adver...
Page 376
376 c hapter 33: bgp c onfiguration after you use the reset bgp dampening command, the command will release the suppression of suppressed routes. Configuring bgp preference three types of routes may be involved in bgp: routes learned from external peers (ebgp), routes learned from internal peers (ib...
Page 377
Configuring bgp 377 the local preference is transmitted only when the ibgp peers exchange the update packets and it will not be transmitted beyond the local as. By default, the local preference is 100. Configuring med for as multi-exit discriminators (med) attribute is the external metric for a rout...
Page 378
378 c hapter 33: bgp c onfiguration configuring bgp route reflector to ensure the interconnection between ibgp peers, it is necessary to establish a fully connected network. If there are many ibgp peers, large overhead is needed to establish a fully connected network. Route reflecting can solve the ...
Page 379
Configuring bgp 379 configuring the route reflection between clients perform the following configuration in bgp view. By default, the route reflection between clients is allowed. If the clients are fully connected, for the purpose of overhead reduction, it is recommended to use the undo reflect betw...
Page 380
380 c hapter 33: bgp c onfiguration does not need to know the status of internal sub-ass, and the confederation id is the as number identifying the confederation as a whole. Perform the following configuration in bgp view. By default, the confederation_id is not configured. The configured confederat...
Page 381
Configuring bgp 381 configuring bgp load balancing as bgp is a routing protocol for route selection only, it does not provide a route calculation method. Therefore, it is not possible to determine whether to enable load balancing based on a definite metric value. However, the bgp owns a variety of r...
Page 382
382 c hapter 33: bgp c onfiguration n load balancing is not available for bgp default routes. Perform the following configuration in bgp view. By default, the bgp does not implement load balancing. Setting the switch for adjacency state output when the switch for adjacency state output is enabled, t...
Page 383
Displaying and debugging bgp 383 displaying and debugging bgp after the above configuration, execute the display command in any view to display the running of the bgp configuration, and to verify the effect of the configuration. Execute the reset command in user view to clear the statistics of the c...
Page 384
384 c hapter 33: bgp c onfiguration typical bgp configuration examples configuring bgp as confederation attribute network requirements divide the following as 100 into three sub-as: 1001, 1002, and 1003, and configure ebgp, confederation ebgp, and ibgp. Network diagram figure 92 network diagram for ...
Page 385
Typical bgp configuration examples 385 [switch a] bgp 1001 [switch a-bgp] confederation id 100 [switch a-bgp] confederation peer-as 1002 1003 [switch a-bgp] group confed1002 external [switch a-bgp] peer confed1002 as-number 1002 [switch a-bgp] group confed1003 external [switch a-bgp] peer confed1003...
Page 386
386 c hapter 33: bgp c onfiguration network diagram figure 93 network diagram for bgp route reflector configuration configuration procedure 1 configure switch a: [switch a] interface vlan-interface 2 [switch a-vlan-interface2] ip address 192.1.1.1 255.255.255.0 [switch a-vlan-interface2] interface v...
Page 387
Typical bgp configuration examples 387 [switch c] interface vlan-interface 4 [switch c-vlan-interface4] ip address 194.1.1.1 255.255.255.0 # configure bgp peers and route reflector. [switch c] bgp 200 [switch c-bgp] group rr internal [switch c-bgp] peer rr reflect-client [switch c-bgp] peer 193.1.1....
Page 388
388 c hapter 33: bgp c onfiguration configuration procedure 1 configure switch a: [switch a] interface vlan-interface 2 [switch a-vlan-interface2] ip address 192.1.1.1 255.255.255.0 [switch a] interface vlan-interface 3 [switch a-vlan-interface3] ip address 193.1.1.1 255.255.255.0 # enable bgp [swit...
Page 389
Typical bgp configuration examples 389 [switch b-vlan-interface4] ip address 194.1.1.2 255.255.255.0 [switch b] ospf [switch b-ospf-1] area 0 [switch b-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 194.1.1.0 0.0.0.255 [switch b-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 192.1.1.0 0.0.0.255 [switch b] bgp 200 [switch b-bgp] group ...
Page 390
390 c hapter 33: bgp c onfiguration [switch c] acl number 2000 [switch c-acl-basic-2000] rule permit source 1.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 [switch c-acl-basic-2000] rule deny source any define a route policy named localpref, and set the local preference of routes matching acl 2000 to 200, and that of routes ...
Page 391
Troubleshooting bgp 391 symptom 2: bgp route cannot be advertised correctly after route of igp is imported with the network command. Solution: route imported by the network command should be same as a route in the current routing table, which should include destination segment and mask. Route coveri...
Page 392
392 c hapter 33: bgp c onfiguration.
Page 393: Ip R
34 ip r outing p olicy c onfiguration introduction to ip routing policy when a router advertises or receives routing information, it possibly needs to implement some policies to filter the routing information, so as to receive or advertise the routing information which can meet the specified conditi...
Page 394
394 c hapter 34: ip r outing p olicy c onfiguration an ip-prefix is identified by the ip-prefix name. Each ip-prefix can include multiple list items, and each list item can independently specify the match range of the network prefix forms and is identified with an index-number. The index-number desi...
Page 395
Configuring ip routing policy 395 each node consists of a group of if-match clauses and apply clauses. The if-match clauses define the matching rules. The different if-match clauses for a node have the relationship of "and". That is, the route must satisfy all the if-match clauses for the node to ma...
Page 396
396 c hapter 34: ip r outing p olicy c onfiguration n for the details about the if-match mpls-label and if-match vpn-target commands, refer to the 08-mpls command module in the 3com switch 8800 family series routing switches command manual. By default, no matching will be performed. Note the followi...
Page 397
Configuring ip routing policy 397 defining apply clauses for a route-policy the apply clauses specify actions, which are the configuration commands executed after a route satisfies the filtering conditions specified by the if-match clauses. Thereby, some attributes of the route can be modified. Perf...
Page 398
398 c hapter 34: ip r outing p olicy c onfiguration by default, perform no settings. Note that if the routing information meets the match conditions specified in the route-policy and also notifies the med value configured with the apply cost-type internal when notifying the igp route to the ebgp pee...
Page 399
Configuring ip routing policy 399 configuring a community attribute list in bgp, community attribute is optional and transitive. Some community attributes known globally are called standard community attributes. Some community attributes are for special purpose. You can also define expanded communit...
Page 400
400 c hapter 34: ip r outing p olicy c onfiguration applying route policy on received or advertised routes configuring to filter the received routes perform the following configuration in routing protocol view. Define a policy to filter the routing information not satisfying the conditions while rec...
Page 401
Displaying and debugging the routing policy 401 bgp: route acquired by bgp by default, the filtering of the received and advertised routes will not be performed. Displaying and debugging the routing policy after the above configuration, execute the display command in any view to display the running ...
Page 402
402 c hapter 34: ip r outing p olicy c onfiguration # configure three static routes. [switch a] ip route-static 20.0.0.1 255.0.0.0 12.0.0.2 [switch a] ip route-static 30.0.0.1 255.0.0.0 12.0.0.2 [switch a] ip route-static 40.0.0.1 255.0.0.0 12.0.0.2 # enable the ospf protocol and specifies the numbe...
Page 403
Troubleshooting routing policy 403 the if-match mode of at least one list item of the ip-prefix should be the permit mode. The list items of the deny mode can be defined first to rapidly filter the routing information not satisfying the requirement, but if all the items are in the deny mode, any rou...
Page 404
404 c hapter 34: ip r outing p olicy c onfiguration.
Page 405: Oute
35 r oute c apacity c onfiguration route capacity configuration introduction to route capacity in an actual network application, a routing table may contain a large quantity of route entries (especially ospf routes and bgp routes). Generally, the routing information is stored in the memory of the sw...
Page 406
406 c hapter 35: r oute c apacity c onfiguration.
Page 407: Ecursive
36 r ecursive r outing c onfiguration recursive routing configuration recursive routing overview every route entry must have its next hop address. For a common route, its next hop address is within the network segment to which the router is directly connected; for a route requiring recursion, its ne...
Page 408
408 c hapter 36: r ecursive r outing c onfiguration.
Page 409: Ip M
37 ip m ulticast o verview n an ethernet switch functions as a router when it runs ip multicast protocol. A router that is referred to in the following represents a generalized router or a layer 3 ethernet switch running ip multicast protocol. Ip multicast overview problems with unicast/broadcast th...
Page 410
410 c hapter 37: ip m ulticast o verview figure 97 data transmission in broadcast mode suppose the users b, d, and e need the information, the information source server broadcasts the information through the router; user a and user c can also receive the information. In that case, information securi...
Page 411
Implementation of ip multicast 411 distribution of these users in the group. Finally, the information is transmitted to the intended receivers b,d and e properly and correctly. In multicast mode, the information sender is called the "multicast source", the receiver is called the "multicast group", a...
Page 412
412 c hapter 37: ip m ulticast o verview packet scales. Multicast packets use ip addresses of class d as their destination addresses, but class d ip addresses cannot be contained in the source ip field of ip packets. During unicast data transmission, a packet is transmitted "hop-by-hop" from the sou...
Page 413
Implementation of ip multicast 413 ethernet multicast mac addresses when a unicast ip packet is transmitted on the ethernet, the destination mac address is the mac address of the receiver. However, for a multicast packet, the destination is no longer a specific receiver but a group with unspecific m...
Page 414
414 c hapter 37: ip m ulticast o verview figure 100 application positions of multicast-related protocols multicast group management protocol multicast groups use internet group management protocol (igmp) as the management protocols. Igmp runs between the host and multicast router and defines the mem...
Page 415
Rpf mechanism for ip multicast packets 415 address is the rp address of the shared tree. A multicast packet arriving at the router will be forwarded according to the multicast forwarding entry if it passes the rpf check, or else, it will be discarded..
Page 416
416 c hapter 37: ip m ulticast o verview.
Page 417: Tatic
38 s tatic m ulticast mac a ddress c onfiguration static multicast mac address overview the concept of "static multicast mac address" is proposed to fulfill the feature of static layer 2 multicast. When some network users need some specific information, the multicast information sender (the multicas...
Page 418
418 c hapter 38: s tatic m ulticast mac a ddress c onfiguration static multicast mac address configuration example network requirements ■ data packets with the destination mac 0100-5e01-018d in vlan 2 are to be sent to three specified ports, ethernet 2/1/1, ethernet 2/1/2, and ethernet 2/1/3. Networ...
Page 419: Igmp S
39 igmp s nooping c onfiguration igmp snooping overview igmp snooping principle running on the link layer, igmp snooping is a multicast control mechanism on the layer 2 ethernet switch and it is used for multicast group management and control. When receiving the igmp messages transmitted between the...
Page 420
420 c hapter 39: igmp s nooping c onfiguration figure 103 multicast packet transmission when igmp snooping runs implementing igmp snooping related concepts of igmp snooping to facilitate the description, this section first introduces some related switch concepts of igmp snooping. ■ router port: the ...
Page 421
Igmp snooping overview 421 figure 104 implement igmp snooping ■ igmp general query message: transmitted by the multicast router to the multicast group members to query which multicast group contains member. When an igmp general query message arrives at a router port, the ethernet switch will reset t...
Page 422
422 c hapter 39: igmp s nooping c onfiguration ■ igmp leave message: transmitted from the multicast group member to the multicast router to notify that a host left the multicast group. When received a leave message of an ip multicast group, the ethernet switch transmits the specific query message co...
Page 423
Igmp snooping configuration 423 ■ isolate-user-vlan supports the igmp-snooping function. After igmp-snooping is enabled under isolate-user-vlan, all secondary vlans are igmp-snooping enabled. It makes no sense to enable igmp-snooping for a secondary vlan. ■ in a secondary vlan, igmp packets will be ...
Page 424
424 c hapter 39: igmp s nooping c onfiguration by default, the aging time of the multicast member is 260 seconds. Configuring unknown multicast packets not broadcasted within a vlan this configuration task is to enable/disable the function of not broadcasting unknown multicast packets within a vlan....
Page 425
Igmp snooping configuration 425 c caution: ■ if an inexistent acl-number is bound to the vlan, or if the bound acl-number is not configured with a rule, a host is still allowed to join any multicast group. ■ if no acl-number exists, you can also configure the filtering rule of multicast groups in vl...
Page 426
426 c hapter 39: igmp s nooping c onfiguration ■ when you configure igmp snooping fast leave on aggregation ports, the configuration takes effect only on primary aggregation ports. ■ if you add an igmp v1 host of the same multicast group to the port, the switch does not remove the port when the port...
Page 427
Displaying and maintaining igmp snooping 427 ■ you will fail to configure a port to be a static routing port if the vlan identified by the vlan-id argument does not exist or the port does not belong to the vlan. ■ you can configure multiple ports in a vlan to be static routing ports by performing th...
Page 428
428 c hapter 39: igmp s nooping c onfiguration network diagram figure 105 network diagram for igmp snooping configuration configuration procedure suppose you need to enable igmp snooping on vlan10. The procedures are as follows: # display the current state of igmp snooping. Display igmp-snooping con...
Page 429
Troubleshooting igmp snooping 429 ■ if igmp snooping is not enabled, carry out the igmp-snooping enable command in system view to enable igmp snooping. Then, use the same command in vlan view to enable igmp snooping in the corresponding vlan. 2 multicast forwarding table set up by igmp snooping is i...
Page 430
430 c hapter 39: igmp s nooping c onfiguration.
Page 431: Ulticast
40 m ulticast vlan c onfiguration multicast vlan overview based on the current multicast on demand, when users in different vlans request the service, multicast flow is duplicated in each vlan and thus a great deal of bandwidth is wasted. To solve this problem, we provide the multicast vlan feature....
Page 432
432 c hapter 40: m ulticast vlan c onfiguration multicast vlan configuration example network requirements configure a multicast vlan, so that users in vlan 2 and vlan 3 receive multicast flows through the multicast vlan10. Network diagram figure 106 network diagram for multicast vlan configuration c...
Page 433
Multicast vlan configuration example 433 [switch a-vlan-interface2] pim dm [switch a-vlan-interface2] quit # configure the ip address of the vlan 10 interface to 168.20.1.1. Enable the pim-dm and igmp protocols. [switch a] interface vlan-interface 10 [switch a-vlan-interface10] ip address 168.20.1.1...
Page 434
434 c hapter 40: m ulticast vlan c onfiguration # define ethernet 1/1/2 as hybrid port. Add the port to vlan 3 and vlan 10. Make the port carry no vlan label when it transmits packets of vlan 3 and vlan 10. Set the default vlan id of the port to vlan 3. [switch b] interface ethernet 1/1/2 [switch b-...
Page 435: Ommon
41 c ommon m ulticast c onfiguration introduction to common multicast configuration the multicast common configuration is for both the multicast group management protocol and the multicast routing protocol. The configuration includes enabling ip multicast routing, displaying multicast routing table ...
Page 436
436 c hapter 41: c ommon m ulticast c onfiguration n ■ when you insert a new interface module, if this interface module does not support the current multicast router table size configured in the system, this interface module will be disabled. ■ the new configuration replaces the earlier one when you...
Page 437
Managed multicast configuration 437 managed multicast configuration managed multicast overview the managed multicast feature controls user’s authority to join multicast groups. This feature is based on ports: users must first pass the 802.1x authentication set for their ports. Then they are allowed ...
Page 438
438 c hapter 41: c ommon m ulticast c onfiguration managed multicast configuration example network requirements as shown in figure 107, hosta and hostb join the multicast group. Layer 3 multicast is enabled on lsa, lsb, lsc and lsd. Managed multicast is enabled on lsa and lsc. Because managed multic...
Page 439
Configuring broadcast/multicast suppression 439 # create a local-user in system view. Then set the password and service type for the user. [sw8800] local-user liu [3com-luser-liu] password simple aaa [3com-luser-liu] service-type lan-access # in user view, configure the allowed multicast group for t...
Page 440
440 c hapter 41: c ommon m ulticast c onfiguration displaying and debugging common multicast configuration after the above configuration, execute display command in any view to display the running of the multicast configuration, and to verify the effect of the configuration. Execute debugging comman...
Page 441: Igmp C
42 igmp c onfiguration igmp overview introduction to igmp internet group management protocol (igmp) is a protocol in the tcp/ip suite responsible for management of ip multicast members. It is used to establish and maintain multicast membership among ip hosts and their directly connected neighboring ...
Page 442
442 c hapter 42: igmp c onfiguration leaving group mechanism in igmp version 1, hosts leave the multicast group quietly without informing the multicast router. In this case, the multicast router can only depend on the timeout of the response time of the multicast group to confirm that hosts leave th...
Page 443
Introduction to igmp proxy 443 description of igmp proxy configuration figure 108 a schematic diagram of igmp proxy figure 108 illustrates how igmp proxy works. In this figure: switch b is configured as follows: ■ multicast is enabled. ■ pim and igmp are configured on the interfaces of vlan 100 and ...
Page 444
444 c hapter 42: igmp c onfiguration ■ switch a processes the message after receiving the igmp message sent by switch b through the interface of vlan 100, just as the message is sent by a host directly connected to the interface of vlan 100. The procedures to process igmp normal group or specific gr...
Page 445
Igmp configuration 445 ■ configuring the igmp version ■ configuring the igmp query message interval ■ configuring the igmp querier present timer ■ configuring the maximum query response time ■ configuring the limit of igmp groups on an interface ■ adding a router to the specified multicast group. ■ ...
Page 446
446 c hapter 42: igmp c onfiguration by default, the compatibility control function of the switch is disabled. This command is often executed after igmp or igmp spooning protocol is enabled in the system. Configuring the igmp version perform the following configuration in vlan interface view. By def...
Page 447
Igmp configuration 447 ■ when other hosts receive the message from the igmp querier and are interested in this group, they return the igmp membership report message within the defined maximum response time. ■ if igmp querier receives the report messages from other hosts within the period equal to ro...
Page 448
448 c hapter 42: igmp c onfiguration by default, the value is twice the igmp query message interval, namely 120 seconds. Configuring maximum response time for igmp query message when a router receives a query message, the host will set a timer for each multicast group it belongs to. The value of the...
Page 449
Igmp configuration 449 configuring a router to join specified multicast group usually, the host operating igmp will respond to igmp query packet of the multicast router. In case of response failure, the multicast router will consider that there is no multicast member on this network segment and will...
Page 450
450 c hapter 42: igmp c onfiguration packets and the acl rule bound to the vlan, the switch determines whether to discard the packets or let them pass. By setting the filtering rule of multicast groups in the vlan, you can control access to ip multicast groups. You can only configure one acl rule fo...
Page 451
Igmp configuration 451 ■ fast leaves that are configured in system view and ethernet port view operate separately. ■ the configuration made in system view will be effective to ports within all the specified vlans, while the configuration in port view will be effective to the port within the specific...
Page 452
452 c hapter 42: igmp c onfiguration network diagram figure 109 network diagram for igmp proxy configuration configuration steps 1 configure switch b. # enable multicast. System-view system view: return to user view with ctrl+z. [switchb] multicast routing-enable # create vlan 200 and vlan 100. Add ...
Page 453
Displaying and debugging igmp 453 # enable multicast. System-view system view: return to user view with ctrl+z. [switcha] multicast routing-enable # enable igmp and pim-dm for the interface of vlan 100. [switcha] interface vlan-interface 100 [switcha-vlan-interface 100] igmp enable [switcha-vlan-int...
Page 454
454 c hapter 42: igmp c onfiguration.
Page 455: Pim-Dm C
43 pim-dm c onfiguration pim-dm overview introduction to pim-dm pim-dm (protocol independent multicast, dense mode) belongs to dense mode multicast routing protocols. Pim-dm is suitable for small networks. Members of multicast groups are relatively dense in such network environments. Pim-dm working ...
Page 456
456 c hapter 43: pim-dm c onfiguration forwarding. The unicast routing information as path judgment can come from any unicast routing protocol independent of any specified unicast routing protocol such as the routing information learned by rip and ospf assert mechanism as shown in the following figu...
Page 457
Pim-dm configuration 457 ■ configuring the maximum number of pim neighbor on an interface ■ clearing pim neighbors enabling multicast refer to “enabling multicast routing” “enabling multicast routing”. Enabling pim-dm pim-dm needs to be enabled in configuration of all interfaces. After pim-dm is ena...
Page 458
458 c hapter 43: pim-dm c onfiguration perform the following configuration in system view. Using undo pim command, you can, and back to system view. Configuring the filtering of multicast source/group you can set to filter the source (and group) address of multicast data packets via this command. Wh...
Page 459
Displaying and debugging pim-dm 459 by default, the pim neighbors on the interface are limited to 128. If the number of pim neighbors of an interface has exceeded the configured value by the time of configuration, the existing pim neighbors will not be deleted. Clearing pim routing table entries per...
Page 460
460 c hapter 43: pim-dm c onfiguration pim-dm configuration example network requirements lanswitch1 is connected to the multicast source through vlan-interface 10, connected to lanswitch2 through vlan-interface 11 and connected to lanswitch3 through vlan-interface 12. Through running pim-dm, you can...
Page 461
Pim-dm configuration example 461 [sw8800] interface vlan-interface 10 [3com-vlan-interface10] ip address 1.1.1.1 255.255.0.0 [3com-vlan-interface10] pim dm [3com-vlan-interface10] quit [sw8800] interface vlan-interface 11 [3com-vlan-interface11] ip address 2.2.2.2 255.255.0.0 [3com-vlan-interface11]...
Page 462
462 c hapter 43: pim-dm c onfiguration.
Page 463: Pim-Sm C
44 pim-sm c onfiguration pim-sm overview introduction to pim-sm pim-sm (protocol independent multicast, sparse mode) belongs to sparse mode multicast routing protocols. Pim-sm is mainly applicable to large-scale networks with broad scope in which group members are relatively sparse. Different from t...
Page 464
464 c hapter 44: pim-sm c onfiguration sent to leaf routers along the path built and then reach the hosts. In this way, an rp-rooted tree (rpt) is built as shown in figure 8-1. Figure 112 rpt schematic diagram multicast source registration when multicast source s sends a multicast packet to the mult...
Page 465
Pim-sm configuration 465 network robustness and enhances the operation and management capability of multicast network. Pim-sm configuration 1 pim-sm basic configuration includes: ■ enabling multicast ■ enabling pim-sm ■ entering the pim view ■ configuring candidate-bsrs ■ configuring candidate-rps ■...
Page 466
466 c hapter 44: pim-sm c onfiguration entering the pim view refer to “entering the pim view” “entering the pim view”. Configuring the time intervals for ports to send hello packets in general, pim-sm broadcasts hello packets on the pim-sm-enabled port periodically to detect pim neighbors and determ...
Page 467
Pim-sm configuration 467 when configuring rp, if the range of the served multicast group is not specified, the rp will serve all multicast groups. Otherwise, the range of the served multicast group is the multicast group in the specified range. It is suggested to configure candidate rp on the backbo...
Page 468
468 c hapter 44: pim-sm c onfiguration configuring the filtering of multicast source/group refer to “configuring the filtering of multicast source/group” “configuring the filtering of multicast source/group”. Configuring the filtering of pim neighbor refer to “configuring the filtering of pim neighb...
Page 469
Displaying and debugging pim-sm 469 for detailed information of crp-policy, refer to the 3com switch 8800 family series routing switches command manual clearing multicast route entries from pim routing table refer to “clearing pim routing table entries” “clearing pim routing table entries”. Clearing...
Page 470
470 c hapter 44: pim-sm c onfiguration network diagram figure 113 network diagram for pim-sm configuration configuration procedure configure lsa # enable pim-sm. System-view system view: return to user view with ctrl+z. [sw8800] multicast routing-enable [sw8800] vlan 10 [3com-vlan10] port ethernet 2...
Page 471
Pim-sm configuration example 471 [sw8800] multicast routing-enable [sw8800] vlan 10 [3com-vlan10] port ethernet 2/1/2 to ethernet 2/1/3 [3com-vlan10] quit [sw8800] interface vlan-interface 10 [3com-vlan-interface10] igmp enable [3com-vlan-interface10] pim sm [3com-vlan-interface10] quit [sw8800] vla...
Page 472
472 c hapter 44: pim-sm c onfiguration [3com-vlan11] quit [sw8800] interface vlan-interface 11 [3com-vlan-interface11] igmp enable [3com-vlan-interface11] pim sm [3com-vlan-interface11] quit [sw8800] vlan 12 [3com-vlan12] port ethernet 2/1/6 to ethernet 2/1/7 [3com-vlan12] quit [sw8800] interface vl...
Page 473: Msdp C
45 msdp c onfiguration msdp overview introduction no isp would like to forward multicast traffic depending on the rp of competitors, though it has to obtain information from the source and distribute it among its members, regardless of the location of the multicast source rp. Msdp is proposed to sol...
Page 474
474 c hapter 45: msdp c onfiguration working principle identifying multicast source and receiving multicast data as shown in figure 114, the rps of pim-sm domains 1, 2 and 3 establish peer relationship between them. Domain 3 contains a group member. Figure 114 msdp working principles (i) when the mu...
Page 475
Msdp overview 475 message forwarding and rpf check between msdp peers as shown in figure 115 “msdp working principles (ii)”, switch a, switch b, switch c, switch d, switch e and switch f belong to domain 1, domain 2 and domain 3 respectively. Msdp peer relationship is established between them, indic...
Page 476
476 c hapter 45: msdp c onfiguration if the sa message is sent from a msdp peer in a different domain which is the next autonomous domain along the optimal path to the rp in the domain of source, as from switch d to switch f, it is received and forwarded to other peers. For other sa messages, they a...
Page 477
Msdp configuration 477 the command to add description is optional. If the local router is also in bgp peer relation with a msdp peer, the msdp peer and the bgp peer should use the same ip address. Not any two routers between which msdp peer relationship has been established must run bgp or mbgp, so ...
Page 478
478 c hapter 45: msdp c onfiguration configuring originating rp during the creation of sa message, an msdp peer can be configured to use the ip address of a specified interface as the rp address in its sa message. Please perform the following configurations in msdp view. By default, the rp address i...
Page 479
Msdp configuration 479 please perform the following configurations in msdp view. The sa request message sent by a local rp will get the immediate response about all active sources. By default, the router does not send sa request message to its msdp peer when receiving the join message of a group. In...
Page 480
480 c hapter 45: msdp c onfiguration multicast group addresses are described in acl. If no acl is specified, all sa request messages sent by the corresponding msdp peer will be ignored. If an acl is specified, only sa request messages of the groups permitted by the acl will be processed. Controlling...
Page 481
Msdp configuration 481 controlling the received source information please perform the following configurations in msdp view. Similar to msdp outbound filter in function, msdp inbound filter controls the received sa messages. By default, the sa messages from all peers are accepted. Configuring msdp m...
Page 482
482 c hapter 45: msdp c onfiguration by default, msdp peer is enabled. Clearing msdp connections, statistics and sa caching configuration perform the following configurations in user view. Displaying and debugging msdp displaying and debugging msdp after the above configuration, execute display comm...
Page 483
Msdp configuration examples 483 locating information loss and reducing configuration faults can be realized by tracing the network path of the specified (s, g, rp) entries. After the transmission path of sa messages is determined, the overflow of sa messages can be avoided by the correct configurati...
Page 484
484 c hapter 45: msdp c onfiguration system-view system view: return to user view with ctrl+z. [switchd] ip ip-prefix list-a permit 10.10.0.0 16 [switchd] msdp [switchd-msdp] peer 10.10.1.1 connect-interface vlan-interface 10 [switchd-msdp] static-rpf-peer 10.10.1.1 rp-policy list-a [switchd-msdp] q...
Page 485
Msdp configuration examples 485 network diagram figure 117 network diagram for anycast rp configuration configuration procedure 1 configure switchb: # configure vlan system-view system view: return to user view with ctrl+z. [switchb] vlan 10 [switchb-vlan10] port ethernet1/1/2 [switchb-vlan10] quit ...
Page 486
486 c hapter 45: msdp c onfiguration [switchb-loopback10] pim sm [switchb-loopback10] quit # configure the ip address of vlan-interface10 and enable igmp and pim-sm. [switchb] interface vlan-interface10 [switchb-vlan-interface10] ip address 10.10.2.1 255.255.255.0 [switchb-vlan-interface10] igmp ena...
Page 487
Msdp configuration examples 487 [switcha-vlan20] port ethernet1/1/3 [switcha-vlan20] quit # enable multicast. [switcha] multicast routing-enable # configure the ip address of interface loopback0. [switcha] interface loopback0 [switcha-loopback0] ip address 10.21.1.1 255.255.255.255 [switcha-loopback...
Page 488
488 c hapter 45: msdp c onfiguration [switcha-msdp] originating-rp loopback0 [switcha-msdp] quit # configure c-rp and bsr. [switcha] pim [switcha-pim] c-rp loopback 10 [switcha-pim] c-bsr loopback 10 30 msdp integrated networking network requirement in the following network, enable msdp and configur...
Page 489
Msdp configuration examples 489 system-view system view: return to user view with ctrl+z. [switcha] vlan 10 [switcha-vlan10] port ethernet1/1/2 [switcha-vlan10] quit [switcha] vlan 30 [switcha-vlan30] port ethernet1/1/3 [switcha-vlan30] quit # enable multicast. [switcha] multicast routing-enable # c...
Page 490
490 c hapter 45: msdp c onfiguration [switcha] bgp 100 [switcha-bgp] undo synchronization [switcha-bgp] group in internal [switcha-bgp] peer 10.26.1.2 group in [switcha-bgp] peer 10.27.1.2 group in [switcha-bgp] peer in connect-interface loopback0 [switcha-bgp] ipv4-family multicast [switcha-bgp-af-...
Page 491
Msdp configuration examples 491 [switche] interface loopback0 [switche-loopback0] ip address 10.26.1.2 255.255.255.255 [switche-loopback0] pim sm [switche-loopback0] quit # configure the ip address of interface lookback10 and enable pim-sm. [switche] interface loopback10 [switche-loopback10] ip addr...
Page 492
492 c hapter 45: msdp c onfiguration [switche-bgp] ipv4-family multicast [switche-bgp-af-mul] peer ex enable [switche-bgp-af-mul] peer 10.29.1.1 group ex [switche-bgp-af-mul] peer ex next-hop-local [switche-bgp-af-mul] quit [switche-bgp] quit # configure msdp peer, mess group and originating rp. [sw...
Page 493: Mbgp M
46 mbgp m ulticast e xtension c onfiguration mbgp multicast extension overview introduction at present, the most widely used inter-domain unicast routing protocol is bgp-4. Because the multicast topology may be different from the unicast topology, bgp-4 must be modified in order to implement the tra...
Page 494
494 c hapter 46: mbgp m ulticast e xtension c onfiguration ■ send the routing information of a new reachable protocol. ■ send the next hop information about the new protocol with the same coding mode as that of nlri. ■ enable the router to report part or all of the snpas (sub-network points of attac...
Page 495
Mbgp multicast extension configuration 495 ■ configure mbgp timer ■ configure mbgp peer (group) ■ configure mbgp route aggregation ■ configure an mbgp route reflector ■ configure the mbgp community attributes ■ configure the interaction between mbgp and igp ■ define as path list and routing policy ■...
Page 496
496 c hapter 46: mbgp m ulticast e xtension c onfiguration configuring the med value for an as the med configured in bgp view is valid for both unicast and multicast. For the details of this configuration, refer to "bgp configuration" of the routing protocol part. Comparing med values from different...
Page 497
Mbgp multicast extension configuration 497 enabling a peer (group) please perform the following configurations in ipv4 multicast sub-address family view. Adding an mbgp peer to the group please perform the following configurations in ipv4 multicast sub-address family view. Advertising mbgp community...
Page 498
498 c hapter 46: mbgp m ulticast e xtension c onfiguration configuring the local address as the next hop when advertising routes this involves removing the next hop configuration in the routing information advertised to a peer (group) and configuring the local address as the next hop address. It is ...
Page 499
Mbgp multicast extension configuration 499 by default, a peer (group) does not perform route filtering based on the as path list. Configuring prefix-list-based route filtering policy for a peer (group) please perform the following configurations in ipv4 multicast sub-address family view. By default,...
Page 500
500 c hapter 46: mbgp m ulticast e xtension c onfiguration multicast networks are very large, and it costs a good sum to establish a fully-closed network. Route reflector solves this problem. The core is to specify a router as the focus of the internal sessions. Multiple mbgp multicast routers can b...
Page 501
Displaying and debugging mbgp configuration 501 for the detailed configuration of regular expression of as, refer to "bgp configuration" of the routing protocol part. For other configurations, refer to the "ip routing policy configuration" of the routing protocol part. Configuring mbgp route filteri...
Page 502
502 c hapter 46: mbgp m ulticast e xtension c onfiguration network diagram figure 119 network diagram for mbgp path selection configuration configuration procedure configure switch a: system-view system view: return to user view with ctrl+z. [switcha] vlan 20 [switcha-vlan20] port ethernet1/1/2 [swi...
Page 503
Mbgp multicast extension configuration example 503 [switcha-bgp-af-mul] peer a1 enable [switcha-bgp-af-mul] peer a2 enable # configure the med attribute of switch a. ■ add an acl on switch a to permit network 1.0.0.0/8. [switcha] acl number 2000 [switcha-acl-basic-2000] rule permit source 1.0.0.0 0....
Page 504
504 c hapter 46: mbgp m ulticast e xtension c onfiguration [switchb-bgp] ipv4-family multicast [switchb-bgp-af-mul] peer b1 enable [switchb-bgp-af-mul] peer b2 enable configure switch c: system-view system view: return to user view with ctrl+z. [switchc] vlan 30 [switchc-vlan30] port ethernet3/1/3 [...
Page 505
Mbgp multicast extension configuration example 505 [switchc] bgp 200 [switchc-bgp] ipv4-family multicast [switchc-bgp-af-mul] peer 193.1.1.1 route-policy localpref import configure switch d: system-view system view: return to user view with ctrl+z. [switchd] vlan 40 [switchd-vlan40] port ethernet4/1...
Page 506
506 c hapter 46: mbgp m ulticast e xtension c onfiguration.
Page 507: Mpls A
47 mpls a rchitecture n the 3com switch 8800 family series routing switches (hereinafter referred to as switch 8800 family series) running mpls can serve as routers. Routers mentioned in this manual can be either a router in common sense, or a layer 3 ethernet switch running mpls. Mpls (multiprotoco...
Page 508
508 c hapter 47: mpls a rchitecture different fecs, based on their fecs, different labels are encapsulated into the packets. Later forwarding is based on these labels. Label structure the structure of the label is shown in figure 120. Figure 120 label structure label is located between the link laye...
Page 509
Mpls basic concepts 509 figure 121 label position in packet in ethernet packets and ppp packets, label stack lies between layer 2 header and layer 3 data, acting like a shim. 3 label assignment and distribution label distribution refers to the process of creating a corresponding label switching path...
Page 510
510 c hapter 47: mpls a rchitecture n currently, the switch 8800 family series adopt the ordered label control mode. 5 label retention mode there are two label-retention modes: liberal label retention mode and conservative label retention mode. Suppose there are two lsrs: ru and rd. For a specific f...
Page 511
Mpls architecture 511 figure 122 mpls basic principle forwarding labeled packets at the ingress, the packets entering the network are classified into fecs according to their characteristics. Usually, packets are classified into fecs according to the ip address prefix or host address. Packets in the ...
Page 512
512 c hapter 47: mpls a rchitecture figure 123 label distribution process for the label distribution mentioned previously, there are two modes: dod and du. The main difference between these two modes is that the label mapping messages are distributed actively or passively. In dod mode, the label is ...
Page 513
Mpls architecture 513 the path vector method refers to that the path information is recorded in the message bound with the forwarding label, and, for every hop, the corresponding router checks if its id is contained in this record. If not, the router adds its id into the record; and if yes, it indic...
Page 514
514 c hapter 47: mpls a rchitecture mpls and other protocols (routing protocols) when ldp establishes lsp in hop-by-hop mode, the next hop is determined by using the information, which is usually collected by such routing protocols as igp, bgp in each lsr route forwarding table, on the way. However,...
Page 515: Mpls B
48 mpls b asic c apability c onfiguration mpls basic capability overview basic mpls forwarding functions includes ldp session establishment and lsp path maintenance. The typical configuration procedure for enabling basic mpls functions on a routing switch is as follows: 1 configure lsr id 2 enable m...
Page 516
516 c hapter 48: mpls b asic c apability c onfiguration by default, lsr id is not defined. Enabling mpls and entering mpls view in system view, you can first enable mpls globally and enter mpls view using the mpls command. Then you can directly enter mpls view after using the mpls command in system ...
Page 517
Ldp configuration 517 by default, the labels of all destination addresses are advertised to all ldp peers. Configuring static lsp you can manually set an lsr to be a node along an lsp, and place a limit on the traffic over the lsp. Depending on the position in an mpls domain, an lsr along an lsp can...
Page 518
518 c hapter 48: mpls b asic c apability c onfiguration by default, ldp is disabled. Enabling ldp on a vlan interface to make the vlan interface support ldp, you must enable ldp function on the interface in vlan interface mode. After enabling the ldp function, the interface then sets up session. It ...
Page 519
Ldp configuration 519 remoteip: the ip address of the remote-peer. It should be the id of the peer lsr. Configuring session parameters configuring session hold-time the ldp entity on the interface sends hello packets periodically to find out ldp peer, and the established sessions must also maintain ...
Page 520
520 c hapter 48: mpls b asic c apability c onfiguration transport-address defaults to the mpls lsr id of the current lsr. If there are multiple links connecting two neighboring lsrs, all the ldp-enabled interfaces on the links connecting lsr and its neighbor must have the same transport address. You...
Page 521
Displaying and debugging mpls basic capability 521 the maximum hop count of loop detection is 32 by default. Setting the maximum hop count in path vector mode when path vector mode is adopted for loop detection, it is also necessary to specify the maximum value of lsp path. In this way, when one of ...
Page 522
522 c hapter 48: mpls b asic c apability c onfiguration displaying mpls-enabled interfaces after accomplishing the configuration tasks mentioned previously, you can execute the display command in any view to view the information related to the mpls-enabled interfaces and thus to evaluate the effect ...
Page 523
Typical mpls configuration example 523 displaying and debugging ldp ldp display commands comware provides abundant mpls monitoring commands for monitoring states of lsrs, ldp sessions, interfaces and peers. These commands are the powerful debugging and diagnosing tools. After accomplishing the confi...
Page 524
524 c hapter 48: mpls b asic c apability c onfiguration the four switches all support mpls, and lsp can be established between any two switches with the routing protocol ospf.Ldp establishes lsp by using routing information of ospf. Network diagram figure 126 network diagram configuration procedure ...
Page 525
Typical mpls configuration example 525 [sw8800] mpls lsr-id 172.17.1.1 [sw8800] mpls [3com-mpls] quit [sw8800] mpls ldp # configure ip address and enable mpls and ldp for vlan interface 201. [sw8800] vlan 201 [3com-vlan201] port gigabitethernet 2/1/1 [3com-vlan201] quit [sw8800] interface vlan-inter...
Page 526
526 c hapter 48: mpls b asic c apability c onfiguration # configure ip address and enable ldp and mpls for vlan interface 202. [sw8800] vlan 202 [3com-vlan202] port gigabitethernet 2/1/1 [3com-vlan202] quit [sw8800] interface vlan-interface 202 [3com-vlan-interface202] ip address 100.10.1.1 255.255....
Page 527
Troubleshooting mpls configuration 527 solution: the default address for session transfer is mpls lsr id. The local machine should issue the lsr id route (often the loopback address) and lean the peer lsr id route..
Page 528
528 c hapter 48: mpls b asic c apability c onfiguration.
Page 529: Bgp/mpls Vpn C
49 bgp/mpls vpn c onfiguration bgp/mpls vpn overview traditional vpn, for which layer 2 tunneling protocols (l2tp, l2f and pptp, and so on.) or layer 3 tunnel technology (ipsec, gre and so on.) is adopted, is a great success and is therefore widely used. However, along with the increase of the size ...
Page 530
530 c hapter 49: bgp/mpls vpn c onfiguration bgp/mpls vpn model bgp/mpls vpn model figure 127 mpls vpn model as shown in figure 127, mpls vpn model contains three parts: ce, pe and p. ■ ce (customer edge) device: it is a composing part of the customer network, which is usually connected with the ser...
Page 531
Bgp/mpls vpn overview 531 manage their internal vpn division, and the service provider can be saved from participating into users’ internal vpn management. The following figure shows the network model for nested vpn: figure 128 network model for nested bgp/mpls vpn basic concepts in bgp/mpls vpn 1 v...
Page 532
532 c hapter 49: bgp/mpls vpn c onfiguration vpn is just a private network, so it can use the same ip address to indicate different sites. But the ip address is supposed as unique when mp-bgp advertises ce routes between pe routers, so routing errors may occur for the different meaning in two system...
Page 533
Bgp/mpls vpn overview 533 n the routes for other vpns will not appear in the vpn’s routing table by using vpn target attribute to filter routing information received at pe router, so the ce-transmitted data will only be forwarded within the vpn. Bgp/mpls vpn implementation bgp/mpls vpn works on this...
Page 534
534 c hapter 49: bgp/mpls vpn c onfiguration exterior-layer label, known as lsp initialization label, distributed by mpls ldp, is at the top of the label stack and indicates an lsp from the ingress pe to egress pe. By the switching of exterior-layer label, vpn packets can be forwarded along the lsp ...
Page 535
Bgp/mpls vpn overview 535 ■ configuring basic mpls capability on the mpls backbone network. ■ configuring mpls ldp and setting up ldp lsp on the mpls backbone network. ■ configuring bgp on the mpls backbone network (create ibgp peers between provider pes). ■ configuring basic mpls capability on user...
Page 536
536 c hapter 49: bgp/mpls vpn c onfiguration figure 131 hierarchical bgp/mpls vpn introduction to ospf multi-instance as one of the most popular igp routing protocols, ospf is used as an internal routing protocol in many vpns. Using ospf on pe-ce links brings convenience to you because in this case ...
Page 537
Bgp/mpls vpn configuration 537 figure 132 ospf multi-instance application in mpls/bgp vpn pe figure 133 multi-vpn-instance ce application in conventional lan introduction to multi-role host the vpn attribute of the packets from a ce to its pe lies on the vpn bound with the ingress interface. This, i...
Page 538
538 c hapter 49: bgp/mpls vpn c onfiguration physical link with ip capabilities from pe to pe; advertise and update vpn network information. Ce router the configuration on ce is relative simple. Only static route, rip, ospf or ebgp configuration is needed for vpn routing information exchange with th...
Page 539
Bgp/mpls vpn configuration 539 protocol in 3com switch 8800 family series routing switches operation manual volume i. Configuring ospf if you select ospf mode for ce-pe route switching, you should then configure ospf on ce. For configuring ospf, see the routing protocol part in 3com switch 8800 fami...
Page 540
540 c hapter 49: bgp/mpls vpn c onfiguration by default, no vpn-instance is defined. 1 configure rd for the vpn-instance after pe router is configured with rd, when a vpn route learned from ce is imported into bgp, bgp attaches the rd in front of the ipv4 address. Then the general ipv4 address which...
Page 541
Bgp/mpls vpn configuration 541 the second one is related to ip address, in the form of 32-bit ip address (can be 0.0.0.0 here):16-bit user-defined number, for example, 172.1.1.1:1. Perform the following configuration in the vpn-instance view. By default, the value is both. In general all sites in a ...
Page 542
542 c hapter 49: bgp/mpls vpn c onfiguration by default, the vlan-id range of mpls/vpn vlans is from 0 to 1023, and the default value of vlan-id is 0. The value range of vlan-id is from 1 to 3071. C caution: ■ this command can only be executed on trunk ports, and mpls/vpn-enabled vlans and vlans out...
Page 543
Bgp/mpls vpn configuration 543 c caution: ■ ports supporting this function stop supporting the application of acl rules. ■ associate interface with vpn-instance vpn instance is associated with the direct-connect site through interface binding. When the packets from the site reach the pe router thoug...
Page 544
544 c hapter 49: bgp/mpls vpn c onfiguration by default, the preference value for a static route is 60. You can also specify another preference for the static route you are configuring. 2 configure rip multi-instance if you select rip mode for ce-pe route switching, you should then specify running e...
Page 545
Bgp/mpls vpn configuration 545 perform the following configuration in the ospf view. By default, id-number is 0 and id-addr is 0.0.0.0. It is recommended that all ospf instances in a vpn are configured with either the same domain id or the default value. C caution: the configured value will not take...
Page 546
546 c hapter 49: bgp/mpls vpn c onfiguration by default, the cost value is 1, dead value is 40 seconds, hello value is 10 seconds, retransmit value is 5 seconds and trans-delay value is 1 second. 4 configure ebgp on pe if you select ebgp between pe and ce, you should configure a neighbor for each vp...
Page 547
Bgp/mpls vpn configuration 547 step 4: configure mbgp to import vpn route of direct-connect ce to advertise correct vpn route over public network to other pes with which bgp adjacency has been created, a pe must import the vpn routing information of the direct-connect ce into its mbgp routing table....
Page 548
548 c hapter 49: bgp/mpls vpn c onfiguration perform the following configuration in ipv4 instance sub-address family view. By default, the received route update information is not allowed to generate loop information. Step 7: configure bgp features. Configuring pe-pe route exchanging to exchange vpn...
Page 549
Bgp/mpls vpn configuration 549 2 configure mp-ibgp step 1: enter protocol address family view. Perform the following configuration in bgp view. Step 2: activate the peer (group). By default, bgp neighbor is active while mbgp neighbor is inactive. You must enable mbgp neighbor in vpnv4 sub-address fa...
Page 550
550 c hapter 49: bgp/mpls vpn c onfiguration this command adds a default route which uses local address as the next hop on the pe spe (system processing engine) perform the following configuration in vpnv4 sub-address family view. Step 6: configure bgp neighbor as the user-end pe (upe) of bgp/mpls v...
Page 551
Displaying and debugging bgp/mpls vpn 551 displaying ip routing table associated with vpn-instance after the above configuration, you can execute display command in any view to display the corresponding information in the ip routing tables related to vpn-instance, and to verify the effect of the con...
Page 552
552 c hapter 49: bgp/mpls vpn c onfiguration typical bgp/mpls vpn configuration example integrated bgp/mpls vpn configuration example network requirements ■ vpna includes ce1 and ce3; vpnb includes ce2 and ce4. ■ subscribers in different vpns cannot access each other. The vpn-target attribute for vp...
Page 553
Typical bgp/mpls vpn configuration example 553 [ce1-vlan201] quit [ce1] interface vlan-interface 201 [ce1-vlan-interface201] ip address 168.1.1.1 255.255.0.0 [ce1-vlan-interface201] quit [ce1] bgp 65410 [ce1-bgp] group 168 external [ce1-bgp] peer 168.1.1.2 group 168 as-number 100 [ce1-bgp] import-ro...
Page 554
554 c hapter 49: bgp/mpls vpn c onfiguration [pe1] mpls lsr-id 202.100.1.1 [pe1] mpls [pe1-mpls] quit [pe1] mpls ldp [pe1] vlan 201 [pe1-vlan201] port gigabitethernet 2/1/1 [pe1-vlan201] quit [pe1] interface vlan-interface 201 [pe1-vlan-interface201] ip address 172.1.1.1 255.255.0.0 [pe1-vlan-interf...
Page 555
Typical bgp/mpls vpn configuration example 555 [p-vlan302] port gigabitethernet 3/1/2 [p-vlan302] quit [p] interface vlan-interface 302 [p-vlan-interface302] ip address 172.2.1.2 255.255.0.0 [p-vlan-interface302] mpls [p-vlan-interface302] mpls ldp enable [p-vlan-interface302] quit [p] vlan 303 [p-v...
Page 556
556 c hapter 49: bgp/mpls vpn c onfiguration [pe3-bgp-af-vpn-instance] peer 168.3.1.1 group 168 as-number 65430 [pe3-bgp-af-vpn-instance] quit [pe3-bgp] quit # bind the interface connecting pe3 and ce3 to vpna. [pe3] vlan 202 [pe3-vlan202] port gigabitethernet 2/1/2 [pe3-vlan202] quit [pe3] interfac...
Page 557
Typical bgp/mpls vpn configuration example 557 [pe3-bgp-af-vpn] peer 202.100.1.1 group 202 [pe3-bgp-af-vpn] quit 5 configure pe2 and pe4 the configuration of pe2 and pe4 is similar to that of pe1 and pe3. The details are omitted here. Extranet configuration example network requirements company a and...
Page 558
558 c hapter 49: bgp/mpls vpn c onfiguration configuration procedure n this configuration procedure has omitted configurations between pe and p, and configurations on ces. For these details refer to the former example. 1 configure pe-a: # configure vpn-instance 1 for vpn1 on pe-a, so that it can sen...
Page 559
Typical bgp/mpls vpn configuration example 559 [pe-a-bgp-af-vpn] peer 20 enable [pe-a-bgp-af-vpn] peer 20.1.1.1 group 20 [pe-a-bgp-af-vpn] quit 2 configure pe-c. # create a vpn-instance 2 on pe-c, so that it can send and receive vpn routing information of vpn-target 111:1 and 222:2. [pe-c] ip vpn-in...
Page 560
560 c hapter 49: bgp/mpls vpn c onfiguration [pe-c-bgp] peer 30.1.1.1 group 30 [pe-c-bgp] peer 30.1.1.1 connect-interface loopback 0 [pe-c-bgp] ipv4-family vpnv4 [pe-c-bgp-af-vpn] peer 10 enable [pe-c-bgp-af-vpn] peer 10.1.1.1 group 10 [pe-c-bgp-af-vpn] peer 30 enable [pe-c-bgp-af-vpn] peer 30.1.1.1...
Page 561
Typical bgp/mpls vpn configuration example 561 [pe-b] bgp 100 [pe-b-bgp] group 20 [pe-b-bgp] peer 20.1.1.1 group 20 [pe-b-bgp] peer 20.1.1.1 connect-interface loopback 0 [pe-b-bgp] ipv4-family vpnv4 [pe-b-bgp-af-vpn] peer 20 enable [pe-b-bgp-af-vpn] peer 20.1.1.1 group 20 [pe-b-bgp-af-vpn] quit hub&...
Page 562
562 c hapter 49: bgp/mpls vpn c onfiguration network diagram figure 136 network diagram for hub&spoke configuration procedure n the following contents are omitted in this case: mpls basic capacity configuration between pes, configuration between pe and p, configuration between ces. For the details r...
Page 563
Typical bgp/mpls vpn configuration example 563 [pe1-bgp-af-vpn-instance] peer 172.17.1.1 allow-as-loop 1 [pe1-bgp-af-vpn] quit [pe1-bgp] quit # bind the vlan interface connecting pe1 and ce1 to different vpn-instances. Bind the interface of the vlan to which the ethernet port gigabitethernet 2/1/1 b...
Page 564
564 c hapter 49: bgp/mpls vpn c onfiguration # set up ebgp adjacency between pe2 and ce2, import intra-ce2 vpn routes learned into mbgp vpn-instance address family. [pe2] bgp 100 [pe2-bgp] ipv4-family vpn-instance vpn-instance1 [pe2-bgp-af-vpn-instance] import-route static [pe2-bgp-af-vpn-instance] ...
Page 565
Typical bgp/mpls vpn configuration example 565 [pe3-bgp-af-vpn-instance] import-route static [pe3-bgp-af-vpn-instance] import-route direct [pe3-bgp-af-vpn-instance] group 172 external [pe3-bgp-af-vpn-instance] peer 172.18.1.1 group 172 as-number 65001 [pe3-bgp-af-vpn-instance] quit [pe3-bgp] quit # ...
Page 566
566 c hapter 49: bgp/mpls vpn c onfiguration network diagram figure 137 network diagram for ce dual-home configuration procedure n the configuration of ce router is omitted in this case and you can refer to section “integrated bgp/mpls vpn configuration example” “integrated bgp/mpls vpn configuratio...
Page 567
Typical bgp/mpls vpn configuration example 567 [pe1-bgp-af-vpn-instance] group 17211 external [pe1-bgp-af-vpn-instance] peer 172.11.11.2 group 17211 as-number 65001 [pe1-bgp-af-vpn-instance] quit [pe1-bgp] quit # set up ebgp adjacency between pe1 and ce2 in vpn-instance 1.2, import intra-ce2 vpn rou...
Page 568
568 c hapter 49: bgp/mpls vpn c onfiguration [pe1-vlan214] quit [pe1] interface vlan-interface 214 [pe1-vlan-interface214] mpls [pe1-vlan-interface214] mpls ldp enable [pe1-vlan-interface214] mpls ldp transport-ip interface [pe1-vlan-interface214] ip address 30.1.1.2 255.255.255.0 [pe1-vlan-interfac...
Page 569
Typical bgp/mpls vpn configuration example 569 [pe2] bgp 100 [pe2-bgp] ipv4-family vpn-instance vpn-instance2.1 [pe2-bgp-af-vpn-instance] import-route direct [pe2-bgp-af-vpn-instance] import-route static [pe2-bgp-af-vpn-instance] group 17212 external [pe2-bgp-af-vpn-instance] peer 172.12.12.2 group ...
Page 570
570 c hapter 49: bgp/mpls vpn c onfiguration [pe3-bgp-af-vpn-instance] import-route direct [pe3-bgp-af-vpn-instance] import-route static [pe3-bgp-af-vpn-instance] group 192 external [pe3-bgp-af-vpn-instance] peer 192.168.13.2 group 192 as-number 65003 [pe3-bgp-af-vpn-instance] quit [pe3-bgp] quit # ...
Page 571
Typical bgp/mpls vpn configuration example 571 network diagram figure 138 network diagram for asbr configuration procedure 1 configure pe1 # enable mpls and ldp. [pe1] mpls lsr-id 1.1.1.1 [pe1] mpls [pe1-mpls] quit [pe1] mpls ldp # configure the vlan interface connecting ce. [pe1] vlan 201 [pe1-vlan...
Page 572
572 c hapter 49: bgp/mpls vpn c onfiguration [pe1] interface vlan-interface 205 [pe1-vlan-interface205] mpls [pe1-vlan-interface205] mpls ldp enable [pe1-vlan-interface205] ip address 10.1.1.2 255.255.255.0 # bind the vlan interface with the vpn-instance. [pe1] interface vlan-interface 201 [pe1-vlan...
Page 573
Typical bgp/mpls vpn configuration example 573 # configure loopback interface. [pe2] interface loopback 0 [pe2-loopback0] ip address 2.2.2.2 255.255.255.255 # configure vpn-instance. [pe2] ip vpn-instance vpna [pe2-vpn-vpna] route-distinguisher 200:1 [pe2-vpn-vpna] vpn-target 100:1 both [pe2] ip vpn...
Page 574
574 c hapter 49: bgp/mpls vpn c onfiguration # configure mpls basic capability. [p1] mpls lsr-id 3.3.3.3 [p1] mpls [p1-mpls] quit [p1] mpls ldp # configure the interface loopback 0. [p1] interface loopback 0 [p1-loopback0] ip address 3.3.3.3 255.255.255.255 # configure vlan interface connecting pe1....
Page 575
Typical bgp/mpls vpn configuration example 575 the example adopts option c to implement a cross-domain bgp/mpls vpn, that is, the vpn routing is managed by the multi-hop mp-ebgp which advertise label vpn-ipv4 routes between pes. Network diagram figure 139 network diagram for multihop ebgp cross-doma...
Page 576
576 c hapter 49: bgp/mpls vpn c onfiguration [asbr-pe1] vlan 110 [asbr-pe1-vlan110] interface vlan 110 [asbr-pe1-vlan-interface110] ip address 172.1.1.1 255.255.0.0 [asbr-pe1-vlan-interface110] quit [asbr-pe2] vlan 210 [asbr-pe1-vlan210] interface vlan 210 [asbr-pe1-vlan-interface210] ip address 192...
Page 577
Typical bgp/mpls vpn configuration example 577 [pe1] mpls lsr-id 172.1.1.2 [pe1-mpls] lsp-trigger all [pe1-mpls] quit [pe1] mpls ldp [pe1-mpls-ldp] quit [pe1] interface vlan 110 [pe1-vlan-interface110] mpls [pe1-vlan-interface110] mpls ldp [pe1-vlan-interface110] quit # configure basic mpls capabili...
Page 578
578 c hapter 49: bgp/mpls vpn c onfiguration # configure ce1 [ce1] vlan 410 [ce1-vlan410] interface vlan 410 [ce1-vlan-interface410] ip address 168.1.1.2 255.255.0.0 [ce1-vlan-interface410] quit # create a vpn instance on pe1 and bind it to the interface connected to ce1 [pe1] ip vpn-instance vpna [...
Page 579
Typical bgp/mpls vpn configuration example 579 [ce1-bgp] peer 168.1.1.1 group 20 as-number 100 [ce1-bgp] quit # configure pe1: set up ebgp peer relation with ce1, ibgp peer relation with asbr-pe1, and multihop mp-ebgp peer relation with pe2. [pe1] bgp 100 [pe1-bgp] ipv4-family vpn-instance vpna [pe1...
Page 580
580 c hapter 49: bgp/mpls vpn c onfiguration # configure ce2. [ce2] bgp 65002 [ce2-bgp] group 10 external [ce2-bgp] peer 168.2.2.1 group 10 as-number 200 [ce2-bgp] quit # configure pe2: set up ebgp peer relation with ce2, ibgp peer relation with asbr-pe2, and multihop mp-ebgp peer relation with pe1....
Page 581
Typical bgp/mpls vpn configuration example 581 [asbr-pe2-bgp] peer 20 route-policy rtp-ibgp export [asbr-pe2-bgp] peer 202.200.1.2 group 20 [asbr-pe2-bgp] peer 202.200.1.2 connect-interface loopback0 hierarchical bgp/mpls vpn configuration example network requirements for those vpns that have distin...
Page 582
582 c hapter 49: bgp/mpls vpn c onfiguration # configure vpn-instance [spe] ip vpn-instance vpn1 [spe-vpn-vpn1] route-distinguisher 100:1 [spe-vpn-vpn1] vpn-target 100:1 both # configure interfaces (so far as a pe router concerned, its loopback 0 interface must be assigned with a host address of 32-...
Page 583
Typical bgp/mpls vpn configuration example 583 [upe] ip vpn-instance vpn1 [upe-vpn-vpn1] route-distinguisher 100:1 [upe-vpn-vpn1] vpn-target 100:1 both # configure interfaces [upe] vlan 301 [upe-vlan301] port gigabitethernet 2/2/1 [upe-vlan301] quit [upe] interface vlan-interface 301 [upe-vlan-inter...
Page 584
584 c hapter 49: bgp/mpls vpn c onfiguration network diagram figure 141 network diagram for ospf multi-instance configuration procedure 1 configure pe1 # enable mpls and ldp. [pe1] mpls lsr-id 50.1.1.1 [pe1] mpls [pe1-mpls] quit [pe1] mpls ldp # configure vpn-instance. [pe1] ip vpn-instance vpn1 [pe...
Page 585
Typical bgp/mpls vpn configuration example 585 [pe1-vlan-interface201] ospf cost 1 [pe1-vlan-interface201] quit [pe1] vlan 202 [pe1-vlan202] port gigabitethernet 2/1/2 [pe1-vlan202] quit [pe1] interface vlan-interface 202 [pe1-vlan-interface202] ip address 168.1.13.1 255.255.255.0 [pe1-vlan-interfac...
Page 586
586 c hapter 49: bgp/mpls vpn c onfiguration [pe1] ospf 1000 [pe1-ospf-1000] area 0 [3com-ospf-1000-area-0.0.0.0] network 168.12.1.0 0.0.0.255 [3com-ospf-1000-area-0.0.0.0] network 50.1.1.1 0.0.0.0 2 configure pe2 # enable mpls and ldp. [pe2] mpls lsr-id 50.1.1.2 [pe2] mpls [pe2-mpls] quit [pe2] mpl...
Page 587
Typical bgp/mpls vpn configuration example 587 [pe2] bgp 100 [pe2-bgp] undo synchronization [pe2-bgp] group fc internal [pe2-bgp] peer 50.1.1.1 group fc [pe2-bgp] peer 50.1.1.1 connect-interface loopback1 [pe2-bgp] peer 50.1.1.3 group fc # configure vpn-instance and import ospf and direct-connect ro...
Page 588
588 c hapter 49: bgp/mpls vpn c onfiguration [ce1] vlan 201 [ce1-vlan201] port gigabitethernet 2/1/1 [ce1-vlan201] quit [ce1] interface vlan-interface 201 [ce1-vlan-interface201] ip address 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.0 [ce1-vlan-interface201] ospf cost 1 # configure ospf. [ce1] ospf 100 router-id 10.10.10...
Page 589
Typical bgp/mpls vpn configuration example 589 network diagram figure 142 network diagram for nested vpn configuration procedure n this procedure omits part of the configuration for ce router. 1 configure igp on the service provider’s backbone network. # configure prov_pe1. System-view [sw8800] sysn...
Page 590
590 c hapter 49: bgp/mpls vpn c onfiguration [prov_pe1-vlan-interface110] ip address 10.1.1.2 255.0.0.0 [prov_pe1-vlan-interface110] quit [prov_pe2] ospf [prov_pe2-ospf] area 0 [prov_pe2-ospf-area-0.0.0.0] network 4.4.4.4 0.0.0.0 [prov_pe2-ospf-area-0.0.0.0] network 10.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 configure ...
Page 591
Typical bgp/mpls vpn configuration example 591 # configure prov_pe1. [prov_pe1] ip vpn-instance customer_vpn [prov_pe1-vpn-instance] route-distinguisher 3:3 [prov_pe1-vpn-instance] vpn-target 3:3 export-community [prov_pe1-vpn-instance] quit [prov_pe1] ip vpn-instance vpn1 [prov_pe1-vpn-instance] ro...
Page 592
592 c hapter 49: bgp/mpls vpn c onfiguration [cust_pe2-vlan-interface410] mpls [cust_pe2-vlan-interface410] quit 3 configure ebgp between provider pe and customer pe. # configure prov_pe1 to access the corresponding customer pe. [prov_pe1] route-policy comm permit node 10 [prov_pe1-route-policy-comm...
Page 593
Typical bgp/mpls vpn configuration example 593 [cust_pe2-bgp] ipv4-family vpnv4 [cust_pe2-bgp-af-vpn] peer ebgp enable [cust_pe2-bgp-af-vpn] peer 2.1.1.2 group ebgp 4 on each customer pe, configure the sub-vpn that accesses the network through the customer pe. # configure cust_pe1. [cust_pe1] ip vpn...
Page 594
594 c hapter 49: bgp/mpls vpn c onfiguration configuration procedure 1 configuring ce router # configure instance vpn1 [ce] ip vpn-instance vpn1 [ce-vpn-vpn1] route-distinguisher 100:1 [ce-vpn-vpn1] vpn-target 100:1 export-extcommunity [ce-vpn-vpn1] vpn-target 100:1 import-extcommunity # configure i...
Page 595
Typical bgp/mpls vpn configuration example 595 [ce] ospf 100 vpn-instance vpn1 [ce-ospf-100] vpn-instance-capability simple [ce-ospf-100] area 0.0.0.0 [ce-ospf-100-area-0.0.0.0] network 10.1.1.0 0.0.0.255 [ce-ospf-100-area-0.0.0.0] network 10.2.1.0 0.0.0.255 # configure ospf 300. [ce] ospf 300 vpn-i...
Page 596
596 c hapter 49: bgp/mpls vpn c onfiguration [pe1] interface loopback 0 [pe1-loopback0] ip address 1.1.1.9 32 [pe1-loopback0] quit [pe1] vlan 110 [pe1-vlan110] interface vlan-interface 110 [pe1-vlan-interface110] ip address 192.168.1.1 24 [pe1-vlan-interface110] quit [pe1] ospf [pe1-ospf-1] area 0 [...
Page 597
Typical bgp/mpls vpn configuration example 597 [pe1-vlan-interface310] ip binding vpn-instance vpn1 [pe1-vlan-interface310] ip address 20.2.1.2 24 [pe1-vlan-interface310] quit [pe1] vlan 210 [pe1-vlan210] interface vlan-interface 210 [pe1-vlan-interface210] ip binding vpn-instance vpn2 [pe1-vlan-int...
Page 598
598 c hapter 49: bgp/mpls vpn c onfiguration [ce3] vlan 210 [ce3-vlan210] interface vlan-interface 210 [ce3-vlan-interface210] ip address 20.3.1.1 24 [ce3-vlan-interface210] quit [ce3] bgp 65430 [ce3-bgp] import-route direct [ce3-bgp] group 10 external [ce3-bgp] peer 20.3.1.2 group 10 as-number 100 ...
Page 599
Troubleshooting bgp/mpls vpn configuration 599 # configure a default route pointing to pe1 on ce2. [ce2] ip route-static 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 20.1.1.2 # configure a multiple-role host route on pe1. [pe1] ip route-static vpn-instance vpn1 172.16.0.0 16 vpn2 20.1.1.1 # import the route of vpn1 to vpn2 usin...
Page 600
600 c hapter 49: bgp/mpls vpn c onfiguration ■ check whether the bgp adjacent is established correctly. ■ check whether the routing import/export relation of the vpn-instance is correct. ■ check whether allow-as-loop is configured between spoke pe and hub pe. Symptom 4 fall to specify the loopback i...
Page 601: Ard
50 c ard i ntermixing for mpls s upport overview introduction to card intermixing the intermixing feature is used to enable deployment of mpls vpn services on cards that do not support mpls. Switch 8800 family routing switches support various modes of mpls vpn function and provide abundant and diffe...
Page 602
602 c hapter 50: c ard i ntermixing for mpls s upport n because the destination port in intermixing configuration is to be looped back and therefore is locked automatically, you cannot enter the port view. Therefore, you cannot perform other configurations on the destination port. Restrictions in in...
Page 603
Intermixing configuration task 603 ■ it is not allowed to make the redirected source port or destination port to leave redirected vlan in the normal way; ■ it is not allowed to configure protocol vlans on the redirected source port or destination port; ■ it is not allowed to delete the redirected vl...
Page 604
604 c hapter 50: c ard i ntermixing for mpls s upport configuring mpls vpn configure bgp/mpls vpn (l3vpn) or l2vpn. Refer to “bgp/mpls vpn configuration” and the "vpn operation" section in 3com switch 8800 family series routing switches operation manual. For detailed configuration information. Confi...
Page 605
Intermixing configuration task 605 you can define the flow template by means of the ip + vlan + dmac method to make sure that different kinds of packets are processed in different ways: ■ if arp packets do not match ip rules in redirection, they will be processed on the non-mpls card; ■ if layer 2 t...
Page 606
606 c hapter 50: c ard i ntermixing for mpls s upport n ■ the source port joins in the corresponding vlan automatically after the configuration of intermixing redirection, and the source port leaves the corresponding vlan automatically after the intermixing redirection is deleted. ■ when using the v...
Page 607
Intermixing configuration task 607 [ce1-bgp] import-route direct [ce1-bgp] import-route static n the configuration on ce2 is similar to that on ce1, so the configuration procedure is omitted. 2 configure pe1 # configure global mpls. [pe1] mpls lsr-id 1.1.1.1 [pe1] mpls [pe1] mpls ldp # configure pub...
Page 608
608 c hapter 50: c ard i ntermixing for mpls s upport c caution: if the vrrp protocol is enabled on the vlan port to which the source port of mpls vpn redirection belongs, you must configure another acl rule to redirect the packets whose destination address is the virtual mac address of vrrp, so tha...
Page 609
Intermixing configuration task 609 # configure an interface and enable mpls on the interface. [p] interface loopback0 [p-loopback0] ip address 3.3.3.3 32 [p-loopback0] quit [p] vlan 100 [p-vlan100] port gigabitethernet 2/1/1 [p-vlan100] interface vlan-interface 100 [p-vlan-interface100] ip address 1...
Page 610
610 c hapter 50: c ard i ntermixing for mpls s upport # configure vpn-instance. The configuration of vpn b is similar to that of vpn a, so followed is only the configuration of vpn a. [pe2] ip vpn-instance vpna [pe2-vpn-vpna] route-distinguisher 100:1 [pe2-vpn-vpna] vpn-target 100:1 both [pe2-vpn-vp...
Page 611
Restrictions in networking of various mpls cards 611 [pe2-bgp] peer 1.1.1.1 connect-interface loopback0 [pe2-bgp] ipv4-family vpnv4 [pe2-bgp-af-vpn] peer 100 enable [pe2-bgp-af-vpn] peer 1.1.1.1 group 100 n the configuration of l2 vpn vll intermixing is similar to that of l3vpn intermixing, so the d...
Page 612
612 c hapter 50: c ard i ntermixing for mpls s upport ■ in card intermixing networking, non-mpls cards can only be used for access at the private network side, and mpls card must be used for access at the public network side. ■ mpls card has influence on the forwarding performance of a switch. Combi...
Page 613: Mpls Vll
51 mpls vll mpls l2vpn overview introduction to mpls l2vpn mpls l2vpn provides mpls network-based layer 2 vpn services. For users, an mpls l2vpn is a layer 2 switched network, through which layer 2 connections can be established between network nodes. Figure 146 mpls l2vpn mpls l2vpn has the followi...
Page 614
614 c hapter 51: mpls vll figure 147 structure of an mpls l2vpn packet the fields in an mpls l2vpn packet are described as follows: tunnel label (the outer label) is an mpls label or a gre label. It is used to transmit a packet from one pe to anther. Vc label (the inner label) is a lower layer label...
Page 615
Mpls l2vpn overview 615 draft-martini-l2circuit-trans-mpls-09.Txt draft-kompella-ppvpn-l2vpn-02.Txt martini draft defines the way to implement mpls l2vpn by establishing point-to-point links. Here, ldp (label distribution protocol) is used as the signaling protocol to exchange vc labels. This kind o...
Page 616
616 c hapter 51: mpls vll n you also can configure lsps without p devices. Ccc mpls l2vpn configuration configuring ccc mpls l2vpn kompella similar to layer 3 bgp/mpls vpn defined in rfc2547. Pes discover layer 2 vpn nodes automatically through ibgp sessions established between them. They also propa...
Page 617
Ccc mpls l2vpn configuration 617 c caution: ■ in l2vpn, you can configure only one virtual circuit for each vlan interface. ■ l2vpn supports vlan interfaces only. When you configure an l2vpn on a vlan interface, data is encapsulated as ethernet packets by default. ■ you can configure only one vlan o...
Page 618
618 c hapter 51: mpls vll network diagram figure 149 network diagram for ccc mpls l2vpn configuration procedure 1 configure pe-a. # enable mpls globally. [pe_a] mpls lsr-id 1.1.1.1 [pe_a] mpls # enable mpls l2vpn globally. [pe_a] mpls l2vpn # configure vlan 211. [pe_a] vlan 211 [pe_a-vlan211] port g...
Page 619
Ccc mpls l2vpn configuration 619 # configure the local connection. [pe_a] ccc local-conn interface vlan-interface 211 out-interface vlan-interface 213 # configure a static lsp, with the out-label of 100 and the egress interface being the interface of vlan 214. [pe_a] mpls [3com-mpls] static-lsp ingr...
Page 620
620 c hapter 51: mpls vll [3com-mpls] static-lsp egress pea-peb l2vpn incoming-interface vlan- interface 212 in-label 101 # configure the remote connection. [sw8800] ccc remote-connection interface vlan-interface 211 transmit -lsp peb-pea receive-lsp pea-peb 3 configure p. [pe_p] mpls lsr-id 10.0.0....
Page 621
Martini mpls l2vpn configuration 621 martini mpls l2vpn configuration configuring martini mpls l2vpn c caution: ■ you can configure only one vlan on the access side of each vpn private network. Each vlan can have only one interface. And igmp must be disabled on the vlan. ■ l2vpn supports vlan interf...
Page 622
622 c hapter 51: mpls vll configuration procedure 1 configure pe-a. # configure the lsr id. Enable mpls, ldp, and mpls l2vpn. [pe-a] mpls lsr-id 192.1.1.1 [pe-a] mpls [pe-a-mpls] quit [pe-a] mpls ldp [pe-a] mpls l2vpn # configure vlan 212. [pe-a] vlan 212 [pe-a-vlan212] port gigabitethernet 2/1/2 [p...
Page 623
Martini mpls l2vpn configuration 623 2 configure pe-b. # configure the lsr id. Enable mpls, ldp, and mpls l2vpn. [pe-b] mpls lsr-id 192.1.1.2 [pe-b] mpls [pe-b-mpls] quit [pe-b] mpls ldp [pe-b] mpls l2vpn # configure vlan 22. [pe-b] vlan 22 [pe-b-vlan22] port gigabitethernet 2/1/1 [pe-b-vlan22] inte...
Page 624
624 c hapter 51: mpls vll [pe-p] mpls lsr-id 192.1.1.3 [pe-p] mpls [pe-p-mpls] quit [pe-p] mpls ldp [pe-p] mpls l2vpn # configure an ip address for the loopback interface, which is used as the lsr id. [pe-p] interface loopback 0 [pe-p-loopback0] ip address 192.1.1.3 255.255.255.255 [pe-p-loopback0] ...
Page 625
Kompella mpls l2vpn configuration 625 kompella mpls l2vpn configuration configuring kompella mpls l2vpn table 566 configure kompella mpls l2vpn operation command description enter system view system-view - configure the lsr id mpls lsr-id lsr-id required enable mpls mpls required enable mpls l2vpn g...
Page 626
626 c hapter 51: mpls vll c caution: ■ you can only change the ce range to a number larger than the existing one. For example, you can change a ce range from 10 to 20, rather than from 10 to 5. The only way to change a ce range to a smaller number is to remove the ce and create a new one. ■ you can ...
Page 627
Kompella mpls l2vpn configuration 627 vlan is trunk type. It is not recommended to use hybrid type as the port link type in a private network vlan. The user access modes of the instance in all peer pes must be consistent. Kompella mpls l2vpn configuration example network requirements ces shown in fi...
Page 628
628 c hapter 51: mpls vll [pe-a] bgp 100 [pe-a-bgp] group 100 internal [pe-a-bgp] peer 100 connect-interface loopback0 [pe-a-bgp] peer 3.3.3.3 group 100 [pe-a-bgp] l2vpn-family [pe-a-bgp-af-l2vpn] peer 100 enable # create and configure the vpn. [pe-a] mpls l2vpn vpn1 encapsulation ethernet [pe-a-mpl...
Page 629
Displaying and debugging mpls l2vpn 629 [pe-b-vlan-interface22] ip address 6.6.6.1 24 [pe-b-vlan-interface22] mpls [pe-b-vlan-interface22] mpls ldp enable [pe-b-vlan-interface22] mpls ldp transport-ip interface [pe-b-vlan-interface22] quit # configure bgp. [sw8800] bgp 100 [pe-b-bgp] group 100 inter...
Page 630
630 c hapter 51: mpls vll troubleshooting mpls l2vpn symptom 1: fail to configure layer 2 vpn on the vlan interface. Solution: ■ check to see if mpls/bgp vpn, multicast, or vll is enabled on the vlan interface. Because you cannot perform layer 2 vpn configuration on a vlan interface if mpls/bgp vpn,...
Page 631
Troubleshooting mpls l2vpn 631 ■ connection being down indicates configurations concerning encapsulation of the two ends are not the same. Make sure the encapsulation types and mtus configured for the local and remote pe devices are consistent. A connection fails if the encapsulation types configure...
Page 632
632 c hapter 51: mpls vll.
Page 633: Vpls C
52 vpls c onfiguration n the service processor card mentioned in this chapter refers to the 3c17548 vpls application module. Vpls overview introduction to vpls today, ip networks have spread throughout the world. And the operators are focusing on using their existing ip networks to provide enterpris...
Page 634
634 c hapter 52: vpls c onfiguration basic vpls network architectures there are two kinds of vpls network architectures: pw logical multipoint-to-multipoint connection architecture and hierarchical architecture. Figure 152 depicts a vpls network architecture with pw logical multipoint-to-multipoint ...
Page 635
Vpls operational principle 635 figure 153 hierarchical vpls network architecture as shown in figure 153, the network topology of the vpls network is hierarchical, and the access range of the network is expansible. The core devices (npes) in the core network require high performance because vpn traff...
Page 636
636 c hapter 52: vpls c onfiguration figure 154 l2vpn universal transmission components the transmission components and their functions in a vpls network are as follows: attachment circuit an attachment circuit (ac) is a virtual connection link between ce and pe. User’s layer 2 and layer 3 data are ...
Page 637
Concepts related to vpls 637 pw signaling pw signaling (pseudowire signaling) protocol on which vpls bases is used to establish and maintain pw. It can also be used to automatically discover peer pes of vsis. Currently, pw signaling protocol includes label distribution protocol (ldp) and border gate...
Page 638
638 c hapter 52: vpls c onfiguration npe it is a core pe device, located at the edge of the vpls core network. It provides vpls transparent transmission service in the core network. Vsi through virtual switching instance (vsi) you can map the actually connected links to each virtual links. Vpls basi...
Page 639
Vpls basic configuration 639 configuring routing protocols you must perform some basic routing configuration on your switch such that it can exchange routing information with other p and pe devices. Currently, you can choose the following routing protocols: static routing, routing information protoc...
Page 640
640 c hapter 52: vpls c onfiguration creating a vpls instance specifying a vpls instance name use the vsi command to create a vpls instance or enter vsi view. When creating a vpls instance, you must specify a locally unique vpls instance name, and must choose automatic discovery or manual configurat...
Page 641
Vpls basic configuration 641 by default, vc-id is as big as vsi-id. Specifying the vc encapsulation type of the vsi perform the following configuration in vsi view. By default, the vc encapsulation type in the vsi takes this value. Configuring vlan for user access and binding a vlps instance the por...
Page 642
642 c hapter 52: vpls c onfiguration ■ a vpls instance can be bound to multiple vlans. You can bind a vpls instance to up to eight vlans. ■ it is not allowed to bind vsi instances to vlan-interface1. Configuring static mac address use the mac-address command to configure a static mac address for the...
Page 643
Vpls basic configuration 643 when you define the flow template, the total size of all the elements in the template must be less than 16 bytes. Configuring acl rules use the following commands to define a layer 2 acl. Perform the following configuration in corresponding views. N delete related redire...
Page 644
644 c hapter 52: vpls c onfiguration configuring vpls load sharing when multiple moduloes exist within a single chassis, the load can be shared between them. For example, configure vsls through 7 with label ranges 0 through 7 respectively. Then associate the vpls module in slot 0 with label ranges 0...
Page 645
Vpls basic configuration 645 by default, the vpn rate limitation is 102,400 kbps. Configuring vpn broadcast suppression percentage use the broadcast-restrain command to configure the vpn broadcast suppression percentage, which is in the range of 0 to 100. You cannot set the percentage to 0. In the v...
Page 646
646 c hapter 52: vpls c onfiguration displaying and debugging vpls vpls provides various displaying and debugging commands to monitor the ldp session status, tunnel configuration, all lsps and their status. Execute the following commands in any view. Execute the debugging command to debug various ld...
Page 647
Vpls basic configuration example 647 network diagram figure 155 network diagram for vpls configuration of back-to back pes configuration procedure n the vpls service processor card is on slot 5 on pe1 and pe2, and the common interface card is on slot 4. 1 configure pe1 # configure the router id used...
Page 648
648 c hapter 52: vpls c onfiguration # configure a ldp remote peer (pe2) to set up ldp session. [pe1] mpls ldp remote-peer 1 [pe1-mpls-remote1] remote-ip 1.2.3.4 # enable l2vpn globally. [pe1] mpls l2vpn # configure a vpls instance and vsi-id (vpn-id). Enter vsi-ldp view to configure the ip address ...
Page 649
Vpls basic configuration example 649 # enable the acl in port view. [pe1] interface gigabitethernet4/1/1 [pe1-gigabitethernet4/1/1] packet-filter inbound link-group 4001 rule 1 2 configure pe2 # configure the router id used to advertise ospf routing information. Generally, the interface address of b...
Page 650
650 c hapter 52: vpls c onfiguration [pe2-vsi-3com-ldp] vsi-id 500 [pe2-vsi-3com-ldp] peer 5.6.7.8 [pe2-vsi-3com-ldp] quit # configure a private vlan, add a port to it, and bind a vsi instance. [pe2] vlan 100 [pe2-vlan-100] port ethernet 6/1/48 [pe2-vlan-100] interface vlan 100 [pe2-vlan-interface10...
Page 651
Troubleshooting vpls 651 ■ expansion session is abnormal: verify that the commands used to configure the expansion session are executed on both ends, and the configurations are all right. ■ the interface of the private vlan is not bound with the corresponding vpls instance, or is down: make sure the...
Page 652
652 c hapter 52: vpls c onfiguration.
Page 653: Vrrp C
53 vrrp c onfiguration introduction to vrrp virtual router redundancy protocol (vrrp) is a fault-tolerant protocol. In general, a default route (for example, 10.100.10.1 as shown in the following internetworking diagram) will be configured for every host on a network, so that the packets destined to...
Page 654
654 c hapter 53: vrrp c onfiguration figure 157 network diagram for virtual router this virtual router has its own ip address: 10.100.10.1 (which can be the interface address of a switch within the virtual router). The switches within the virtual router have their own ip addresses (such as 10.100.10...
Page 655
Configuring vrrp 655 enabling/disabling the function to ping the virtual ip address this operation enables or disables the function to ping the virtual ip address of the virtual router. The standard protocol of vrrp does not support the ping function, then the user cannot judge with ping command whe...
Page 656
656 c hapter 53: vrrp c onfiguration the following commands can be used to set correspondence between the ip address and the mac address. Perform the following configuration in system view. By default, the virtual ip address of the virtual router corresponds to the virtual mac address. You should se...
Page 657
Configuring vrrp 657 the priority ranges from 0 to 255. The greater the number, the higher the priority. However the value can only be taken from 1 to 254. The priority 0 is reserved for special use and 255 is reserved for the ip address owner by the system. By default, the priority is 100. N the pr...
Page 658
658 c hapter 53: vrrp c onfiguration in a network under possible security threat, the authentication type can be set to simple. Then the switch will add the authentication key into the vrrp packets before transmitting it. The receiver will compare the authentication key of the packet with the locall...
Page 659
Displaying and debugging vrrp 659 by default, adver-interval is configured to be 1. Configuring switch to track a specified interface vrrp interface track function has expanded the backup function. Backup is provided not only to the interface where the virtual router resides, but also to some other ...
Page 660
660 c hapter 53: vrrp c onfiguration you can enable vrrp debugging to check its running. You may choose to enable vrrp packet debugging (option as packet), vrrp state debugging (option as state), and/or vrrp error debugging (option as error). By default, vrrp debugging is disabled. Vrrp configuratio...
Page 661
Vrrp configuration example 661 networking diagram figure 158 network diagram for vrrp configuration configuration procedure configure switch a # configure vlan 2. [lsw-a] vlan 2 [lsw-a-vlan2] interface vlan 2 [lsw-a-vlan-interface2] ip address 202.38.160.1 255.255.255.0 [lsw-a-vlan-interface2] quit ...
Page 662
662 c hapter 53: vrrp c onfiguration [lsw-b] vrrp ping-enable [lsw-b] interface vlan 2 [lsw-b-vlan-interface2] vrrp vrid 1 virtual-ip 202.38.160.111 [lsw-b-vlan-interface2] vrrp vrid 1 preempt-mode the virtual router can be used soon after configuration. Host a can configure the default gateway as 2...
Page 663
Vrrp configuration example 663 # track an interface. [lsw_a-vlan-interface2] vrrp vrid 1 track vlan-interface 3 reduced 30 configure switch b # configure vlan2. [lsw-b] vlan 2 [lsw-b-vlan2] interface vlan 2 [lsw-b-vlan-interface2] ip address 202.38.160.2 255.255.255.0 [lsw-b-vlan-interface2] quit # ...
Page 664
664 c hapter 53: vrrp c onfiguration [lsw-a] vlan 2 [lsw-a-vlan2] interface vlan 2 [lsw-a-vlan-interface2] ip address 202.38.160.1 255.255.255.0 # create virtual router 1. [lsw_a-vlan-interface2] vrrp vrid 1 virtual-ip 202.38.160.111 # set the priority for the virtual router. [lsw_a-vlan-interface2]...
Page 665
Troubleshooting vrrp 665 fault 2: more than one masters existing within the same virtual router there are also 2 reasons. One is short time coexistence of many master switches, which is normal and needs no manual intervention. Another is the long time coexistence of many master switches, which may b...
Page 666
666 c hapter 53: vrrp c onfiguration.
Page 667: Ha C
54 ha c onfiguration introduction to ha ha (high availability) is to achieve a high availability of the system and to recover the system as soon as possible in the event of fabric failures so as to shorten the mtbf (mean time between failure) of the system. The functions of ha are mainly implemented...
Page 668
668 c hapter 54: ha c onfiguration ■ “enabling/disabling automatic synchronization” ■ “synchronizing the configuration file manually” ■ “configuring the load mode of the master and slave modules” restarting the slave system manually in the environment in which the slave system is available, the user...
Page 669
Displaying and debugging ha configuration 669 himself, he can do it manually to backup the configuration file saved in the master module. Perform the following configuration in user view. This operation can backup the configuration file to the slave module only if a slave system is available. The co...
Page 670
670 c hapter 54: ha c onfiguration ha configuration example network requirements take the master module out and make the slave module take over the work of the master to ensure the normal operation. Configuration procedure # synchronize the configuration file manually. Slave update configuration # d...
Page 671: Arp C
55 arp c onfiguration introduction to arp address resolution protocol (arp) is used to resolve an ip address into a mac address. Necessity of arp an ip address cannot be directly used for communication between network devices because network devices can identify only mac addresses. An ip address is ...
Page 672
672 c hapter 55: arp c onfiguration normally, dynamic arp takes effect and automatically searches for the resolution from the ip address to the ethernet mac address without the help of an administrator. Arp concepts arp entries used in switch 8800 family series routing switches include dynamic arp e...
Page 673
Configuring arp 673 by default, the arp mapping table is empty and the address mapping is obtained through dynamic arp. Note that: ■ as long as a switch operates, its static arp mapping entries remain valid unless you perform operations that make arp invalid, such as change or remove vlan virtual in...
Page 674
674 c hapter 55: arp c onfiguration to cancel the configuration, use the corresponding undo command. After the configuration, you can use the display arp multi-port command in any view to check the detailed information about multicast arp configuration. C caution: ■ you cannot configure multicast ar...
Page 675
Displaying and debugging arp 675 ■ if a device finds that the ip addresses carried in a received gratuitous packet conflict with those of its own, it returns an arp response to the sending device to notify of the ip address conflict. By sending gratuitous arp packets, a network device can: ■ determi...
Page 677: Arp T
56 arp t able s ize c onfiguration introduction to arp table size configuration you can manually configure the maximum numbers of arp entries (that is, the sizes of arp tables) on an switch 8800 family routing switch to meet your actual needs. The following table lists the specifications and numbers...
Page 678
678 c hapter 56: arp t able s ize c onfiguration ■ as a short static arp entry is included into the number of normal arp entries like a normal long static arp entry, if a card is configured to support up to 8k aggregation arp entries, the card does not support the configuration of neither kinds. Con...
Page 679
Configuration example 679 configuration example network requirements a host is connected to a switch 8800 family series routing switch and appropriate modules are installed network diagram figure 159 diagram for arp table size configuration configuration procedure # configure the maximum number of a...
Page 680
680 c hapter 56: arp t able s ize c onfiguration.
Page 681: Dhcp C
57 dhcp c onfiguration some concepts about dhcp dhcp principles this is a world where networks are ever-growing in both size and complexity, and the network configuration is getting more and more complex. As is often the case, the number of hosts in a network exceeds that of the available ip address...
Page 682
682 c hapter 57: dhcp c onfiguration ■ automatic ip address assignment. The dhcp server automatically assigns fixed ip addresses to dhcp clients when they connect to the network for the first time. After that, the ip addresses are always occupied by the dhcp clients. ■ dynamic ip address assignment....
Page 683
Some concepts about dhcp 683 ip address carried in the packet, and broadcasts a dhcp_request packet to each dhcp server. The packet contains the ip address carried by the dhcp_offer packet. ■ acknowledgement. Upon receiving the dhcp_request packet, the dhcp server that owns the ip address the dhcp_r...
Page 684
684 c hapter 57: dhcp c onfiguration dhcp provide a framework about how to set a host on a tcp/ip network. Dhcp is derived from bootp, and possesses more function such as automatic allocation of reusable network addresses and additional configuration options. Dhcp can act as a bootp relay agent, so ...
Page 685
Configuring general dhcp 685 c caution: the dhcp select interface command cannot be used together with the ip relay address or dhcp relay security address-check enable command. Perform the following configuration in system view to configure the processing method of dhcp packets for multiple vlan int...
Page 686
686 c hapter 57: dhcp c onfiguration fake dhcp server detection is disabled by default. Configuring dhcp server the following sections describe the dhcp server configuration tasks: ■ “creating a global dhcp ip address pool” ■ “configuring ip address assignment mode” ■ “forbidding specified ip addres...
Page 687
Configuring dhcp server 687 common to all levels in the address pool structure or some subnets only for the network segment or for corresponding subnets. The display dhcp server tree command displays the tree-like structure of address pool, where address pools on the same level are sorted by the tim...
Page 688
688 c hapter 57: dhcp c onfiguration ip addresses in a global dhcp address pool are not statically bound by default. N the static-bind ip-address command and the static-bind mac-address command must be used together as a pair when you configure static binding entries. When you re-execute the command...
Page 689
Configuring dhcp server 689 each dhcp address pool can be configured with only one address range. If you execute the network command multiple times, then only the last configured address range works. C caution: when addresses are obtained through dhcp relay, the subnet mask of the normal address poo...
Page 690
690 c hapter 57: dhcp c onfiguration configuring a lease time for multiple vlan interfaces perform the following configuration in system view. The default lease times for global address pools and vlan interface address pools are all one day. Configuring dhcp client domain names you can configure a d...
Page 691
Configuring dhcp server 691 by default, global address pools and vlan interface address pools are not configured with any dhcp client domain name. If you execute the dhcp server domain-name command multiple times, the newly configured dhcp client domain name overwrites the existing one. Configuring ...
Page 692
692 c hapter 57: dhcp c onfiguration configuring netbios server address for dhcp clients for clients running a windows operating system and communicating through the netbios protocol, translations between host name and ip address are carried out by windows internet naming service (wins) servers. So ...
Page 693
Configuring dhcp server 693 ■ p-node: nodes of this type establish their mappings by communicating with netbios server. (p stands for peer-to-peer.) ■ m-node: nodes of this type are p nodes which take some broadcast features. (m stands for mixed.) ■ h-node: nodes of this type are b nodes which take ...
Page 694
694 c hapter 57: dhcp c onfiguration configuring custom dhcp options for current vlan interface perform the following configuration in vlan interface view. Configuring custom dhcp options for multiple vlan interfaces perform the following configuration in system view. If you execute the dhcp server ...
Page 695
Configuring dhcp server 695 if you execute the gateway-list command multiple times, the newly configured ip addresses overwrite the existing ones. Configuring parameters for dhcp server to send ping packets to avoid address conflict caused by reassigning an in-use ip address, before assigning an ip ...
Page 696
696 c hapter 57: dhcp c onfiguration perform the following configuration in user view. Clearing the configuration information of the dhcp server you can clear the configuration information of the dhcp server by executing the reset command in user view. Perform the following configuration in user vie...
Page 697
Configuring dhcp server 697 network diagram figure 161 network diagram for dhcp server configuration procedure # enter system view. System-view # create vlan2. [sw8800]vlan 2 # enter vlan interface view and create vlan-interface 2. [sw8800]interface vlan-interface 2 # assign an ip address to vlan-in...
Page 698
698 c hapter 57: dhcp c onfiguration configuring dhcp relay introduction to dhcp relay this is a world where networks are ever-growing in both size and complexity, and the network configuration is getting more and more complex. As is often the case, the number of hosts in a network exceeds that of t...
Page 699
Configuring dhcp relay 699 note that the entire configuration procedure may goes through multiples times of such interactions. Configuring dhcp relay dhcp relay configuration includes the following: the following text describes the dhcp relay configuration tasks: ■ “configuring a dhcp server for a v...
Page 700
700 c hapter 57: dhcp c onfiguration n ■ the dhcp client applies for an ip address through the dhcp relay. When the packet from dhcp client passes the dhcp relay, the dhcp relay adds its primary ip address in the packet and forwards the packet to the dhcp server. When receiving the packet, dhcp serv...
Page 701
Configuring dhcp relay 701 dhcp relay configuration example network requirements as shown in figure 163, two dhcp clients located at the same network segment (10.110.0.0) are connected to a switch through a port in vlan 2. The switch, acting as a dhcp relay, is supposed to forward dhcp packets betwe...
Page 702
702 c hapter 57: dhcp c onfiguration [3com-vlan-interface2]ip relay address 202.38.1.2 n besides the above configurations for dhcp relay, you need to configure address pool on the dhcp server and make sure the dhcp server and the switch interface connecting the two dhcp clients is routing reachable ...
Page 703
Dhcp option 82 configuration 703 sub-option 2 also belongs to option 82 and defines the remote id. Usually configured on the dhcp relay devices, it indicates that the forwarded packets will carry the mac address of the relay device. Generally, sub-option 1 and sub-option 2 are used together to ident...
Page 704
704 c hapter 57: dhcp c onfiguration figure 165 sub-option structure subopt: indicates the number of the sub-option. Sub-options contained in this packet are sub-option 1, sub-option 2 and sub-option 5. They have the following meanings: ■ sub-option 1 defines the circuit id. ■ sub-option 2 defines t...
Page 705
Dhcp option 82 configuration 705 configurations for maintenance convenience. You can select to use the bridge mac address of the relay, the device name (configured through sysname), or user-defined strings. The identifier format of sub-option1 in the 3com fixed network mode of option 82 is: accessno...
Page 706
706 c hapter 57: dhcp c onfiguration 5 after receiving the dhcp request packet forwarded by the dhcp relay, the dhcp server records the information carried by the option in the packet. Then, the dhcp server sends to the dhcp relay a response packet which carries the dhcp configuration information an...
Page 707
Dhcp option 82 configuration 707 perform the following configuration in system view to configure option 82 support on dhcp relay for multiple vlan interfaces at the same time. Option 82 support on dhcp relay configuration example network requirements two dhcp clients are on 10.110.0.0, and they acqu...
Page 708
708 c hapter 57: dhcp c onfiguration network diagram figure 166 network diagram for option 82 support on dhcp relay configuration configuration procedure suppose the dhcp relay and the dhcp server is reachable to each other. The following only introduces the configuration on the switch which serves ...
Page 709: Dns C
58 dns c onfiguration introduction to dns used in the tcp/ip application, domain name system (dns) is a distributed database which provides the translation between domain name and the ip address. In this way, the user can use domain names that are easy to memorize and meaningful, and never needs to ...
Page 710
710 c hapter 58: dns c onfiguration "3com", the system regards it as a host name and add a domain name suffix to search. After all the domain names are failed to be searched out in this way, the system finally searches with the primarily input domain name. If the input domain name does include ".", ...
Page 711
Displaying and debugging domain name resolution 711 configure the ip address of domain name server you are required to configure the domain name sever if you need to use the function of the dynamic domain name resolution. In this way, you can send the inquiry request packets to the appropriate sever...
Page 712
712 c hapter 58: dns c onfiguration network diagram figure 167 network diagram for dns client configuraiton procedure # enable dynamic domain name resolution [sw8800] dns resolve # configure the ip address of the domain name server to 172.16.1.1. [sw8800] dns server 172.16.1.1 # configure the domain...
Page 713: Etstream
59 n etstream c onfiguration n the application module described in this chapter refers to 3c17542 network monitoring module (nmm). Netstream overview introduction to netstream netstream provides the packet statistics function. It can classify the stream information according to the destination ip ad...
Page 714
714 c hapter 59: n etstream c onfiguration ■ if netstream aggregation is configured, the stream information will be classified and aggregated to generate aggregation information according to certain rules, and then sent in the format of version 8 udp packets. ■ the mpls stream statistics information...
Page 715
Netstream configuration 715 n for version 5 packets, the active aging time, inactive aging time, version template refresh rate, and version template aging time are the same as those of version 9 packets. The switch supports eleven aggregation modes currently: according to the selected aggregation mo...
Page 716
716 c hapter 59: n etstream c onfiguration aggregation log. The eleven aggregation modes are independent of each other, so they can be configured at the same time. N ■ the configuration in system view affects version 5 udp packets. Additionally, this configuration is also effective for version 8 udp...
Page 717
Netstream configuration examples 717 # map the packets received on gigabitethernet3/1/3 to slot 5. [switch_a] mirror-group 1 inbound gigabitethernet3/1/3 mirror-to slo t 5 # enable the netstream function on the module of slot 5. [switch_a] ip netstream enable slot 5 # configure the export source add...
Page 718
718 c hapter 59: n etstream c onfiguration.
Page 719: Ndp C
60 ndp c onfiguration introduction to ndp neighbor discovery protocol (ndp) is used to discover the information about a neighbor device directly connected, including the type, software/hardware version, port connected, id, port address, and hardware platform of the neighbor device. A device running ...
Page 720
720 c hapter 60: ndp c onfiguration n ■ on the management device, ndp must be enabled in the system and on the ports. ■ on member devices and candidate devices, the npd feature must also be enabled in the system and on the corresponding ports. The aging timer for the ndp information sent from the ma...
Page 721
Ndp configuration example 721 configuring the interval at which ndp packets are sent the ndp information of the adjacent device must be updated periodically to ensure that the switch can update the local ndp neighbor information table in time after the configuration of the adjacent device is changed...
Page 722
722 c hapter 60: ndp c onfiguration ■ the information of the neighbor switches switch b and switch c that are connected to switch a should be visible to switch a through ndp configuration. Network diagram figure 170 network diagram for ndp configuration configuration procedure 1 configure switch a. ...
Page 723: E C
61 p o e c onfiguration poe overview poe on the switch 3com switch 8800 family series routing switches (hereinafter referred to as switch 8800 family series) support power-over-ethernet (poe). Equipped with external power supply and poe-capable cards, switch 8800 family series can provide 48 vdc pow...
Page 724
724 c hapter 61: p o e c onfiguration external pse4500-a power system if pse4500-a power system is taken as the external power supply of the switch, the power distribution is as follows: 1 input voltage: 110 vac ■ one or two psus (power supply unit) of the pse4500-a power system can provide 1,200 w ...
Page 725
Poe configuration 725 to cancel the configurations, use the corresponding undo commands. For details about the parameters, refer to the command manual. N ■ before setting the maximum power supplied by a card, make sure the remaining power of the switch is no less than the full power of the card, and...
Page 726
726 c hapter 61: p o e c onfiguration ■ the reserved power for a blank slot will be recycled automatically by the system if you insert a poe-incapable card into the slot. ■ when a card is almost fully loaded and a new pd is added, the switch will respond to the pd according to the poe priority set o...
Page 727
Comprehensive configuration example 727 network diagram figure 171 poe remote power supplying configuration procedure # set the maximum power to 400 w on the card in slot 3. By default, the power of each card is full, so the power on the card in slot 5 need not be configured. [sw8800] poe max-power ...
Page 728
728 c hapter 61: p o e c onfiguration.
Page 729: E Psu S
62 p o e psu s upervision c onfiguration introduction to poe psu supervision the poe-capable switch 8800 family series can monitor the external poe psus through the power supervision module on the poe external power system. The poe psu supervision module enables you to: ■ set the alarm thresholds fo...
Page 730
730 c hapter 62: p o e psu s upervision c onfiguration configuration procedure # enter system view. System-view # set the overvoltage alarm threshold of ac input for poe psus to 264.0 v. [sw8800] poe-power input-thresh upper 264.0 # set the undervoltage alarm threshold of ac input for poe psus to 18...
Page 731
Displaying poe supervision information 731 [sw8800] poe-power output-thresh upper 57.0 # set the undervoltage alarm threshold of dc output for the poe psus to 45.0 v. [sw8800] poe-power output-thresh lower 45.0 # display the dc output state of the poe psus. [sw8800] display poe-power dc-output state...
Page 732
732 c hapter 62: p o e psu s upervision c onfiguration network diagram figure 172 network diagram for poe supervision configuration configuration procedure # enter system view. System-view # set the overvoltage alarm threshold of ac input for poe psus to 264.0 v. [sw8800] poe-power input-thresh uppe...
Page 733: Udp H
63 udp h elper c onfiguration overview udp helper functions as a relay that converts udp broadcast packets into unicast packets and forwards them to a specified server. With the udp helper function enabled, the device decides whether to forward a received udp broadcast packet according to the udp po...
Page 736
736 c hapter 63: udp h elper c onfiguration.
Page 737: Snmp C
64 snmp c onfiguration snmp overview by far, the simple network management protocol (snmp) has gained the most extensive application in the computer networks. Snmp has been put into use and widely accepted as an industry standard in practice. It is used for ensuring the transmission of the managemen...
Page 738
738 c hapter 64: snmp c onfiguration figure 173 architecture of the mib tree the mib (management information base) is used to describe the hierarchical architecture of the tree and it is the set defined by the standard variables of the monitored network device. In the above figure, the managed objec...
Page 739
Configuring snmp 739 ■ “setting the destination address of trap” ■ “setting lifetime of trap message” ■ “setting the engine id of a local device” ■ “setting/deleting an snmp group” ■ “setting the source address of trap” ■ “adding/deleting a user to/from an snmp group” ■ “creating/updating view infor...
Page 740
740 c hapter 64: snmp c onfiguration by default, the contact information for system maintenance is "r&d hangzhou, 3com 3com technology co., ltd.", the physical location information is "hangzhou china", and the version is snmpv1, snmpv2c, and snmpv3. Enabling/disabling snmp agent to send trap the man...
Page 741
Configuring snmp 741 setting lifetime of trap message you can use the following command to set lifetime of trap message. Trap message that exists longer than the set lifetime will be dropped. Perform the following configuration in system view. By default, the lifetime of trap message is 120 seconds....
Page 742
742 c hapter 64: snmp c onfiguration perform the following configuration in system view. N currently, this command takes effect only on the interfaces with vlan-interface type. Adding/deleting a user to/from an snmp group you can use the following commands to add or delete a user to/from an snmp gro...
Page 743
Displaying and debugging snmp 743 setting the size of the snmp packet sent/received by an agent you can use the following commands to set the size of snmp packet sent/received by an agent. Perform the following configuration in system view. The agent can receive/send the snmp packets of the sizes ra...
Page 744
744 c hapter 64: snmp c onfiguration that of the vlan interface on the switch is 129.102.0.1. Perform the following configurations on the switch: setting the community name and access authority, administrator id, contact and switch location, and enabling the switch to send trap packets. Network diag...
Page 745
Snmp configuration example 745 the switch supports 3com’s network management products. Users can query and configure the switch through the network management system. For details, see the manuals for the network management products..
Page 746
746 c hapter 64: snmp c onfiguration.
Page 747: Rmon C
65 rmon c onfiguration rmon overview remote network monitoring (rmon) is a type of ietf-defined mib. It is the most important enhancement to the mib ii standard. It mainly used for monitoring the data traffic on a segment and even on a whole network. It is one of the widely used network management s...
Page 748
748 c hapter 65: rmon c onfiguration the following sections describe the rmon configuration tasks. ■ “adding/deleting an entry to/from the event table” ■ “adding/deleting an entry to/from the alarm table” ■ “adding/deleting an entry to/from the extended rmon alarm table” ■ “adding/deleting an entry ...
Page 749
Configuring rmon 749 after you defined the alarm entry, the system then processes the entry in the following way: 1 sampling the defined alarm-variable according to the time interval sampling-time that you have set 2 comparing the sampled value with the configured threshold and handling them in the ...
Page 750
750 c hapter 65: rmon c onfiguration adding/deleting an entry to/from the history control table the history data management helps you set the history data collection, periodical data collection and storage of the specified ports. The sampling information includes the utilization ratio, error counts ...
Page 751
Rmon configuration example 751 rmon configuration example network requirements set an entry in rmon ethernet statistics table for the ethernet port performance, which is convenient for network administrators’ query. Network diagram figure 175 network diagram for rmon configuration configuration proc...
Page 752
752 c hapter 65: rmon c onfiguration 64 : 0 , 65-127 : 0 , 128-255 : 0 256-511: 0 , 512-1023: 0 , 1024-max : 0 # configure an event before configuring alarm and prialarm. [sw8800]rmon event 1 log owner 3com-rmon [sw8800]display rmon event 1 event table 1 owned by 3com-rmon is valid. Description: nul...
Page 753: Ntp C
66 ntp c onfiguration brief introduction to ntp ntp functions as the network topology gets more and more complex, it becomes important to synchronize the clocks of the equipment on the whole network. Network time protocol (ntp) is the tcp/ip that advertises the accurate time throughout the network. ...
Page 754
754 c hapter 66: ntp c onfiguration figure 176 basic operating principle of ntp in the figure above, switch a and switch b are connected through the ethernet port. They have independent system clocks. Before implement automatic clock synchronization on both switches, we assume that: ■ before synchro...
Page 755
Ntp configuration 755 ■ the delay for a round trip of an ntp packet traveling between switch a and b: delay= (t 4 -t 1 ) - (t 3 -t 2 ). ■ offset of switch a clock relative to switch b clock: offset= ( (t 2 -t 1 ) + (t 4 -t 3 ) ) /2. In this way, switch a uses the above-mentioned information to set t...
Page 756
756 c hapter 66: ntp c onfiguration configuring ntp server mode set a remote server whose ip address is ip-address as the local time server. Ip-address specifies a host address other than a broadcast, multicast or reference clock ip address. In this case, the local switch operates in client mode. In...
Page 757
Ntp configuration 757 by default, no broadcast service is configured and the version number number defaults to 3. This command can only be configured on the interface where the ntp broadcast packets will be transmitted. Configuring ntp broadcast client mode designate an interface on the local switch...
Page 758
758 c hapter 66: ntp c onfiguration configuring ntp multicast client mode designate an interface on the local switch to receive ntp multicast messages and operate in multicast client mode. The local switch listens to the multicast from the server. When it receives the first multicast packets, it sta...
Page 759
Ntp configuration 759 key number key-number ranges from 1 to 4294967295 designating an interface to transmit ntp messages if the local equipment is configured to transmit all the ntp messages, these packets will have the same source ip address, which is taken from the ip address of the designated in...
Page 760
760 c hapter 66: ntp c onfiguration ip address acl number is specified through the acl-number parameter and ranges from 2000 to 2999. The meanings of other authority levels are as follows: query: allow control query for the local ntp service only. Synchronization: allow request for local ntp time se...
Page 761
Ntp configuration example 761 ntp configuration example configuring a ntp server network requirements on 3com1, set local clock as the ntp master clock at stratum 2. On 3com2, configure 3com1 as the time server in server mode and set the local equipment as in client mode. (note: 3com1 supports to co...
Page 762
762 c hapter 66: ntp c onfiguration [3com2] display ntp-service status clock status: unsynchronized clock stratum: 16 reference clock id: none nominal frequency: 100.0000 hz actual frequency: 100.0000 hz clock precision: 2^17 clock offset: 0.0000 ms root delay: 0.00 ms root dispersion: 0.00 ms peer ...
Page 763
Ntp configuration example 763 # set the local clock as the ntp master clock at stratum 2. [3com3] ntp-service refclock-master 2 configure switch 3com4. # enter system view. System-view # set 3com1 as the ntp server at stratum 3 after synchronization. [3com4] ntp-service unicast-server 3.0.1.31 # set...
Page 764
764 c hapter 66: ntp c onfiguration [quidwa4] display ntp-service sessions source reference stra reach poll now offset delay disper ******************************************************************** [12345]3.0.1.33 local(0) 2 377 64 16 0.0 0.0 0.9 note: 1 source(master),2 source(peer),3 selected,4...
Page 765
Ntp configuration example 765 the above examples configured 3com4 and 3com1 to listen to the broadcast through vlan-interface2, 3com3 to broadcast packets from vlan-interface2. Since 3com1 and 3com3 are not located on the same segment, they cannot receive any broadcast packets from 3com3, while 3com...
Page 766
766 c hapter 66: ntp c onfiguration # enter system view. System-view # set the local clock as a master ntp clock at stratum 2. [3com3] ntp-service refclock-master 2 # enter vlan-interface2 view. [3com3] interface vlan-interface 2 # set it as a multicast server. [3com3-vlan-interface2] ntp-service mu...
Page 767
Ntp configuration example 767 network diagram figure 179 network diagram for ntp configuration example configuration procedure configure switch 3com1. # enter system view. System-view # set the local clock as the master ntp clock at stratum 2. [3com1] ntp-service refclcok-master 2 configure switch 3...
Page 768
768 c hapter 66: ntp c onfiguration # set the key. [3com1] ntp-service authentication-keyid 42 authentication-mode md5 anicekey # configure the key as reliable. [3com1] ntp-service reliable authentication-keyid 42.
Page 769: Ssh T
67 ssh t erminal s ervice ssh terminal service ssh overview this chapter introduces the secure shell (ssh) feature. When a user telnets to the switch from an insecure network, the ssh feature can provide secure information and powerful authentication functionality, thereby protecting the switch from...
Page 770
770 c hapter 67: ssh t erminal s ervice figure 181 establish an ssh channel through a wan to establish an ssh authentication secure connection, the server and the client must go through the following five phases: 1 version number negotiation: ■ the client sends a tcp connection request. ■ after the ...
Page 771
Ssh terminal service 771 ■ the server initiates a procedure to authenticate the user. If the server is configured not to authenticate the user, the process proceeds to session request phase directly. ■ the client employs an authentication mode to authenticate the server till the authentication succe...
Page 772
772 c hapter 67: ssh t erminal s ervice configuring the protocol the current user interface supports use this configuration task to specify the protocol the current user interface supports. Perform the following configuration in vty user interface view. By default, the system supports all protocols....
Page 773
Ssh terminal service 773 generating or destroying an rsa key pair use this configuration task to generate or destroy an rsa key pair (including the host key and server key) of the server. The naming conventions for the keys are switchname + host and switchname + server respectively. After this comma...
Page 774
774 c hapter 67: ssh t erminal s ervice authentication mode. In this case, whatever the default authentication mode, the user cannot log in because the user’s authentication mode is null. 2 standard radius does not support user-level attributes. Therefore, during remote authentication, you must spec...
Page 775
Ssh terminal service 775 by default, the system does not update the server key. Configuring the authentication timeout use this configuration task to set the authentication timeout of ssh connections. Perform the following configuration in system view. By default, the authentication timeout is 60 se...
Page 776
776 c hapter 67: ssh t erminal s ervice entering the public key edit view after entering the public key view by the rsa peer-public-key command, you can use the public-key-code begin command to enter the public key edit view and input the public key of the client. When inputting the public key, you ...
Page 777
Ssh terminal service 777 by default, the server is compatible with the ssh 1.X client. Ssh client configuration the following sections describe the ssh client configuration tasks. ■ set to perform the first-time authentication on the ssh server to be accessed ■ specifying the public key of the serve...
Page 778
778 c hapter 67: ssh t erminal s ervice perform the following configuration in system view. By default, the client does not perform the first-time authentication. Displaying and debugging ssh on completion of the above configurations, you can use the display command in any view to view the operation...
Page 779
Ssh terminal service 779 configuration procedure 1 generate the rsa key. [sw8800] rsa local-key-pair create n if the configuration for generating the local key has already been completed, skip this step. 2 set the user login authentication mode. The following shows the configuration methods for both...
Page 780
780 c hapter 67: ssh t erminal s ervice [sw8800] rsa peer-public-key sw8800002 [3com-rsa-public-key] public-key-code begin [8505a-rsa-public-key]public-key-code begin rsa key code view: return to last view with "public-key-code end". [8505a-rsa-key-code]30818602 8180507e db32853a 58d19a3e b216bdc9 a...
Page 781
Sftp service 781 connected to 10.165.87.136 ... Enter password: ********************************************************* * all rights reserved (1997-2004) * * without the owner’s prior written consent, * *no decompiling or reverse-engineering shall be allowed.* *************************************...
Page 782
782 c hapter 67: ssh t erminal s ervice configuring the default service type and the default directory for sftp users perform the following configuration in system view. The default service type is null and the default directory for sftp users is null. If a user is configured with a service type and...
Page 783
Sftp service 783 sftp client configuration the following table describes the sftp client configuration tasks. Starting the sftp client use this configuration task to start the sftp client program, establish a connection with the remote sftp server, and enter the sftp client view. Perform the followi...
Page 784
784 c hapter 67: ssh t erminal s ervice shutting down the sftp client use this configuration task to shut down the sftp client program. Perform the following configuration in sftp client view. N the three commands, bye, exit, and quit, have the same functionality. You can also use the quit command i...
Page 785
Sftp service 785 n ■ the dir command and the ls command have the same functionality. ■ the delete command and the remove command have the same functionality. Displaying help information use this command to display command-relevant help information such as the format of the command, parameter configu...
Page 786
786 c hapter 67: ssh t erminal s ervice configuration procedure 1 configure switch b. # start the sftp server. [sw8800] sftp server enable # specify the service type as sftp. [sw8800] ssh user 8040 service-type sftp # set the authentication mode to password. [sw8800] ssh user 8040 authentication-typ...
Page 787
Sftp service 787 -rwxrwxrwx 1 noone nogroup 225 aug 24 08:01 pubkey2 -rwxrwxrwx 1 noone nogroup 283 aug 24 07:39 pubkey1 drwxrwxrwx 1 noone nogroup 0 sep 01 06:22 new -rwxrwxrwx 1 noone nogroup 225 sep 01 06:55 pub -rwxrwxrwx 1 noone nogroup 0 sep 01 08:00 z sftp-client> delete z remove this file?(y...
Page 788
788 c hapter 67: ssh t erminal s ervice drwxrwxrwx 1 noone nogroup 0 sep 02 06:33 new2 -rwxrwxrwx 1 noone nogroup 283 sep 02 06:35 pu -rwxrwxrwx 1 noone nogroup 283 sep 02 06:36 puk sftp-client> # exit sftp. Sftp-client> quit bye [sw8800].
Page 789: Ile
68 f ile s ystem m anagement file system configuration file system overview the switch provides a file system module for user’s efficient management over the storage devices such as flash memory. The file system offers file access and directory management, mainly including creating the file system, ...
Page 790
790 c hapter 68: f ile s ystem m anagement file operation the file system can be used to delete or undelete a file and permanently delete a file. Also, it can be used to display file contents, rename, copy and move a file and display the information about a specified file. You can use the following ...
Page 791
File system configuration 791 considering that when dismounting the cf card you may be performing the write operation on it, the switch provides the umount command which can stop the cf card to ensure the safety and consistency of the file operations on it, that is, you must execute the umount comma...
Page 792
792 c hapter 68: f ile s ystem m anagement.
Page 793: Evice
69 d evice management device management overview with the device management function, the switch can display the current running state and event debugging information about the slots, thereby implementing the maintenance and management of the state and communication of the physical devices. In addit...
Page 794
794 c hapter 69: d evice management n the precision of switch timer is 1 minute. The switch will reboot in one minute when time comes to the specified rebooting point. Specifying the bootstrap programs for the switch you can specify two bootstrap programs for both active and standby srpcs of the swi...
Page 795
Device management configuration 795 n the 3com switch 8800 family series switches (hereinafter referred to as switch 8800 family series) support master/slave fabric switchover. The two modules both have a program system. The program user can operate the programs on both modules. When you specify the...
Page 796
796 c hapter 69: d evice management c caution: ■ when you use the update l3plus command to update service processing modules, you must use the switch host app file which includes the load program of l3plus service processing modules. ■ the maximum size of l3plus update file loaded by the update l3pl...
Page 797
Device management configuration example 797 network diagram figure 185 network diagram for ftp configuration configuration procedure 1 configure ftp server parameters on the pc: a user named as switch, password hello, read & write authority over the switch directory on the pc. No further details are...
Page 798
798 c hapter 69: d evice management boot bootrom boot.App slot 0 # use the boot boot-loader command to specify the downloaded program as the application at the next login and reboot the switch. Boot boot-loader primary flash:/switch.App slot 0 disp boot-loader the primary app to boot of slot 0 at th...
Page 799
Device management configuration example 799 c caution: if the flash memory on the switch is not sufficient, delete the original application program in the flash before uploading the new one into the flash of the switch. 1 after uploading, performs upgrading on the switch. # you can use the boot boot...
Page 800
800 c hapter 69: d evice management.
Page 801: Ftp&tftp C
70 ftp&tftp c onfiguration ftp configuration ftp overview ftp (file transfer protocol) is a universal method for transmitting files on the internet and ip networks. In this method, files are copied from one system to another. Ftp supports definite file types (such as ascii and binary) and file struc...
Page 802
802 c hapter 70: ftp&tftp c onfiguration the configuration of the switching as ftp server. C caution: the prerequisite for normal ftp function is that the switch and pc are reachable. Enabling/disabling ftp server you can use the following commands to enable/disable the ftp server on the switch. Per...
Page 803
Ftp configuration 803 only the clients who have passed the authentication and authorization can access the ftp server. C caution: when using the file manager or ie browser to perform the ftp operations, you are recommended to input the user name and password in the address column in the following fo...
Page 804
804 c hapter 70: ftp&tftp c onfiguration displaying and debugging ftp server after the above configuration, execute display command in any view to display the running of the ftp server configuration, and to verify the effect of the configuration. The display ftp-server command can be used for displa...
Page 805
Ftp configuration 805 configuration procedure 1 configure ftp server parameters on the pc: a user named as switch, password hello, read and write authority over the switch directory on the pc. 2 configure the switch # log into the switch through the console port locally or telnet remotely. Then type...
Page 806
806 c hapter 70: ftp&tftp c onfiguration the switch application switch.App is stored on the pc. Using ftp, the pc can upload the switch.App from the remote ftp server and download the vrpcfg.Cfg from the ftp server for backup purpose. Network diagram figure 189 network diagram for ftp configuration ...
Page 807
Tftp configuration 807 acknowledgement to it. To upload a file, the client sends a request to the tftp server and then transmits data to it and receives the acknowledgement from it. Tftp transmits files in two modes, binary mode for program files and ascii mode for text files. The administrator need...
Page 808
808 c hapter 70: ftp&tftp c onfiguration uploading files by means of tftp to upload a file, the client sends a request to the tftp server and then transmits data to it and receives the acknowledgement from it. You can use the following commands to upload files. Perform the following configuration in...
Page 809
Tftp configuration 809 [sw8800] interface vlan 1 [3com-vlan-interface1] ip address 1.1.1.1 255.255.255.0 [3com-vlan-interface1] quit # enter system view and download the switch.App from the tftp server to the flash memory of the switch. Tftp 1.1.1.2 get switch.App switch.App # upload the vrpcfg.Cfg ...
Page 810
810 c hapter 70: ftp&tftp c onfiguration.
Page 811: Nformation
71 i nformation c enter information center function introduction to information center the information center is an indispensable part of the switch. It serves as an information center of the system software modules. The logging system is responsible for most of the information outputs, and it also ...
Page 812
812 c hapter 71: i nformation c enter 3 timestamp if the logging information is send to the log host, the default format of timestamp is date the date format of timestamp is " mmm dd hh:mm:ss yyyy". Mmm " is month field, such as: jan, feb, mar, apr, may, jun, jul, aug, sep, oct, nov, dec. Dd" is day...
Page 813
Information center function 813 drvvpls virtual private lan service drive module eth ethernet module ftps ftp server module ha high availability module habp 3com authentication bypass protocol module hwcm 3com configuration management mib module ifnet interface management module igsp igmp snooping m...
Page 814
814 c hapter 71: i nformation c enter notice: there is a slash (’/’) between module name and severity. 6 severity switch information falls into three categories: log information, debugging information and trap information. The information center classifies every kind of information into 8 severity o...
Page 815
Information center function 815 the system assigns a channel in each output direction by default. See the table below. N the settings in the 7 directions are independent from each other. The settings will take effect only after enabling the information center. The information center of the switch ha...
Page 816
816 c hapter 71: i nformation c enter 2 sending the configuration information to the console terminal 3 sending the configuration information to the monitor terminal loghost refer to configuration cases for related log host configuration - - table 765 send the configuration information to the loghos...
Page 817
Information center function 817 4 sending the configuration information to the log buffer 5 sending the configuration information to the trap buffer table 767 send the configuration information to the monitor terminal device configuration default value configuration description switch enable informa...
Page 818
818 c hapter 71: i nformation c enter 6 sending the configuration information to snmp table 769 send the configuration information to the trap buffer device configuration default value configuration description switch enable information center by default, information center is enabled other configur...
Page 819
Information center function 819 sending the configuration information to the loghost to send configuration information to the loghost, follow the steps below: 1 enabling information center perform the following configuration in system view. N information center is enabled by default. After informati...
Page 820
820 c hapter 71: i nformation c enter modu-name specifies the module name; default represents all the modules; all represents all the information filter configuration in channel channel-number except default; level refers to the severity levels; severity specifies the severity level of information. ...
Page 821
Information center function 821 3 configuring information source on the switch by this configuration, you can define the information that sent to console terminal is generated by which modules, information type, information level, and so on. Perform the following configuration in system view: modu-n...
Page 822
822 c hapter 71: i nformation c enter 4 enable terminal display function to view the output information at the console terminal, you must first enable the corresponding log, debugging and trap information functions at the switch. For example, if you have set the log information as the information se...
Page 823
Information center function 823 n information center is enabled by default. After information center is enabled, system performances are affected when the system processes much information because of information classification and outputting. 2 configuring to output information to telnet terminal or...
Page 824
824 c hapter 71: i nformation c enter module-based filtering settings and severity threshold. When a user modifies these settings, it will be reflected on other clients. N if you want to view the debugging information of some modules on the switch, you must select debugging as the information type w...
Page 825
Information center function 825 sending the configuration information to the log buffer to send configuration information to the log buffer, follow the steps below: 1 enabling information center perform the following configuration in system view. N information center is enabled by default. After inf...
Page 826
826 c hapter 71: i nformation c enter modu-name specifies the module name; default represents all the modules; all represents all the information filter configuration in channel channel-number except default; level refers to the severity levels; severity specifies the severity level of information. ...
Page 827
Information center function 827 n information center is enabled by default. After information center is enabled, system performances are affected when the system processes much information because of information classification and outputting. 2 configuring to output information to the trap buffer pe...
Page 828
828 c hapter 71: i nformation c enter every channel has been set with a default record, whose module name is default and the module number is 0xffff0000. However, for different channels, the default record may have different default settings of log, trap and debugging. When there is no specific conf...
Page 829
Information center function 829 3 configuring information source on the switch by this configuration, you can define the information that sent to snmp nm is generated by which modules, information type, information level, and so on. Perform the following configuration in system view: modu-name speci...
Page 830
830 c hapter 71: i nformation c enter 4 configuring of snmp and network management workstation on the switch you have to configure snmp on the switch and the remote workstation to ensure that the information is correctly sent to snmp nm. Then you can get correct information from network management w...
Page 831
Information center function 831 ■ the modules that allowed to output information are arp and ip network diagram figure 192 network diagram configuration steps 1 configuration on the switch # enable information center [sw8800] info-center enable # set the host with the ip address of 202.38.1.10 as th...
Page 832
832 c hapter 71: i nformation c enter information center loghost a.B.C.D facility configured on the switch. Otherwise, the log information probably cannot be output to the loghost correctly. Step 3: after the establishment of information (log file) and the revision of /etc/syslog.Conf, you should se...
Page 833
Information center function 833 [sw8800] info-center loghost 202.38.1.10 facility local7 language english [sw8800] info-center source default channel loghost log level informational 2 configuration on the loghost this configuration is performed on the loghost. Step 1: perform the following command a...
Page 834
834 c hapter 71: i nformation c enter the modules that allowed to output information are arp and ip network diagram figure 194 network diagram configuration procedure 1 configuration on the switch # enable information center. [sw8800] info-center enable # configure console terminal log output; allow...
Page 835: Ystem
72 s ystem m aintenance and d ebugging basic system configuration the basic system configuration and management include: ■ switch name setting ■ system clock setting ■ time zone setting ■ summer time setting setting a name for a switch perform the following configuration in system view. Setting the ...
Page 836
836 c hapter 72: s ystem m aintenance and d ebugging by default, the summer time is not set. Displaying the status and information of the system the switch provides the display command for displaying the system status and statistics information. For the display commands related to each protocols and...
Page 837
System debugging 837 figure 195 debugging output you can use the following commands to control the above-mentioned debugging. Perform the following operations in user view. For more about the usage and format of the debugging commands, refer to the relevant chapters. N since the debugging output wil...
Page 838
838 c hapter 72: s ystem m aintenance and d ebugging n when using the display diagnostic-information command to keep track of the switch, you should execute the command at least twice so that you can compare the information for locating problems. Testing tools for network connection ping the ping co...
Page 839
Testing tools for network connection 839 tracert the tracert is used for testing the gateways passed by the packets from the source host to the destination one. It is mainly used for checking if the network is connected and analyzing where the fault occurs in the network. The execution process of th...
Page 840
840 c hapter 72: s ystem m aintenance and d ebugging.
Page 841: Rotocol
73 p rotocol p ort s ecurity c onfiguration introduction to protocol port security the protocol port security function is short for tcp, udp protocol port close check function. If a protocol is not enabled, this function can drop the packet whose destination ip is the virtual interface ip of the swi...
Page 842
842 c hapter 73: p rotocol p ort s ecurity c onfiguration by default, the port 80 of http protocol is enabled. Table 809 set the status of http protocol port operation command shutdown the port of http protocol ip http shutdown open the port of http protocol undo ip http shutdown.
Page 843: Acket
Introduction to egress packet statistics 843 74 p acket s tatistics c onfiguration introduction to egress packet statistics a card provides two sets of counters for monitoring egress packet statistics of the card. The monitored objects include ports, vlans, ports+vlans, and cards. In addition to the...
Page 844
844 c hapter 74: p acket s tatistics c onfiguration.
Page 845: Thernet
75 e thernet p ort l oopback d etection ethernet port loopback detection function use the following configuration tasks can enable the port loopback detection function, configure the vlan enabled with the loopback detection function (you can configure up to 800 such vlans) and set the interval for e...
Page 846
846 c hapter 75: e thernet p ort l oopback d etection.
Page 847: Q C
76 q in q c onfiguration qinq overview introduction to qinq qinq refers to the technology that enables packets to be transmitted across the operators’ backbone networks with vlan tags of private networks nested in those of public networks. In public networks, packets of this type are transmitted by ...
Page 848
848 c hapter 76: q in q c onfiguration implementation of qinq qinq can be implemented on switch 8800 family series switches in the following ways: 1 enabling vlan vpn on ports with vlan vpn enabled, a received packet is tagged with the default vlan tag of the port no matter whether or not the packet...
Page 849
Vlan vpn configuration 849 vlan vpn configuration configuration prerequisites ■ garp vlan registration protocol (gvrp), spanning tree protocol (stp), and 802.1x protocol are disabled on the ports. ■ igmp snooping is disabled in the vlan to which the ports belong. ■ igmp is disabled in the vlan to wh...
Page 850
850 c hapter 76: q in q c onfiguration traffic classification-based nested vlan configuration configuration prerequisites ■ acls and corresponding rules to be applied already exist. ■ the vlans to be specified by the nested-vlanid argument already exist. Configuration procedure enter pvc view pvc { ...
Page 852
852 c hapter 76: q in q c onfiguration network diagram figure 199 qinq network diagram configuration procedure # enable igmp-snooping in vlan 600. System-view [switch_a] vlan 600 [switch_a-vlan600] igmp-snooping enable [switch_a-vlan600] quit # configure the downlink port gigabitethernet 4/1/2 to a ...
Page 853
Adjusting tpid values for qinq packets 853 # configure the uplink port gigabitethernet 4/1/1 to a trunk port and allow the packets of vlan 1000 and vlan 600 to pass the uplink port. [switch_a] intface gigabitethernet4/1/1 [switch_a-gigabitethernet4/1/1] port link-type trunk [switch_a-gigabitethernet...
Page 854
854 c hapter 76: q in q c onfiguration ■ switch b only permits packets of vlan 10. ■ it is desired that packets of vlans other than vlan 10 can be exchanged between the networks connected to switch a and switch c. Network diagram figure 200 network diagram for adjusting tpid values configuration pro...
Page 855
Vlan-vpn tunnel configuration 855 because switch b is produced by other vendor, related commands may differ from those available to switch 8800 family switches. So only the operation is listed, as shown below: ■ configure gigabitethernet3/1/1 and gigabitethernet3/1/3 ports of switch b to be trunk po...
Page 856
856 c hapter 76: q in q c onfiguration figure 201 diagram of the vlan-vpn tunnel network hierarchy configuring vlan-vpn perform the following configuration to configure vlan-vpn tunnel. N vlan vpn is not compatible with stp, dot1x, gvrp, and ntdp. Vlan-vpn tunnel configuration example network requir...
Page 857
Vlan-vpn tunnel configuration 857 network diagram figure 202 configure vlan-vpn tunnel configuration procedure 1 configure switch a. # enable rstp. [switch_a] stp enable # set the port to a trunk port and allow the packets of vlan 10 to pass the port. [switch_a] vlan 10 [switch_a-ethernet0/1] port l...
Page 858
858 c hapter 76: q in q c onfiguration [switch_c] vlan 20 [switch_c-vlan20] port ethernet4/1/1 [switch_c-vlan20] quit # disable the stp protocol and enable vlan-vpn on ethernet4/1/1. [switch_c] interface ethernet4/1/1 [switch_c-ethernet4/1/1] stp disable [switch_c-ethernet4/1/1] vlan-vpn enable [swi...
Page 859
Vlan-vpn tunnel configuration 859 # disable the stp protocol and enable vlan-vpn on ethernet3/1/3. [switch_d] interface ethernet3/1/2 [switch_d-ethernet3/1/2] stp disable [switch_d-ethernet3/1/2] vlan-vpn enable [switch_d-ethernet3/1/2] quit # set ethernet3/1/3 to a trunk port and add this port to a...
Page 860
860 c hapter 76: q in q c onfiguration.
Page 861: Nqa C
77 nqa c onfiguration introduction to nqa nqa, which is an enhancement of the ping function, is used to test the performance of various protocols operating in the network.The ping function can only use the icmp protocol to test the round trip travel time of data packets between the local endpoint an...
Page 862
862 c hapter 77: nqa c onfiguration introduction to nqa configuration tasks table 818 introduction to the configuration tasks of the icmp test in nqa operation command remarks enter system view system-view - enable the client function of the nqa nqa-agent enable required; by default, nqa client is d...
Page 863
Nqa configuration 863 set the name of the vpn instance vpn-instance name optional; by default, no name of the vpn instance is set set the source ip address of this test source-ip ip-address optional; by default, no source ip address is configured. The system uses the ip address of the source interfa...
Page 864
864 c hapter 77: nqa c onfiguration c caution: ■ when the system is testing, parameters that are configured in the nqa test group view cannot be changed except the simple description of the operations and the condition of sending the trap information to the network management system. ■ you can use t...
Page 865
Displaying and maintaining nqa 865 system-view system view: return to user view with ctrl+z. [sw8800] nqa administrator icmp # configure the test type as icmp. [sw8800-nqa-administrator-icmp] test-type icmp # configure the destination ip to 192.168.80.80. [sw8800-nqa-administrator-icmp] destination-...
Page 866
866 c hapter 77: nqa c onfiguration.
Page 867: Assword
78 p assword c ontrol c onfiguration introduction to password control configuration switch 8800 family series switches provide the password control function. Before a user can log in to the switch, a system login password must be configured. After a password is configured, the user must enter the pa...
Page 868
868 c hapter 78: p assword c ontrol c onfiguration ■ when adding or deleting a history password record, the system requests the standby card to perform backup. ■ when purging all history records or the history records of a certain user, the system requests the standby card to perform backup. ■ when ...
Page 869
Introduction to password control configuration 869 ■ configuring system password parameters ■ configuring super password parameters ■ deleting history password records after the configuration, you can carry out display password-control in any view to view the password control information for all use...
Page 870
870 c hapter 78: p assword c ontrol c onfiguration to cancel an operation, use the undo form of the corresponding command. C caution: ■ if the history password recording function is not enabled, the password clearing command reset password-control history-record can also clear the history password r...
Page 871
Introduction to password control configuration 871 the password for super commands is processed in a similar way. However, no pre-expiration alert is given when the super password is to expire; the user is only notified whether the password has expired or not. For an ftp user, no pre-expiration aler...
Page 872
872 c hapter 78: p assword c ontrol c onfiguration the configuration of minimum password length involves two situations: the global configuration command can be used in the system view to configure the minimum length of all user passwords, and the minimum password length can be configure for a certa...
Page 873
Introduction to password control configuration 873 configuring the maximum number of history password records when a password used to log in to the system expires, the system will ask the user to enter a new password and will automatically save the password. You can configure the maximum number of h...
Page 874
874 c hapter 78: p assword c ontrol c onfiguration system logging function the system can automatically log related information in case of the following events: ■ when a user logs in successfully, the system will log the user name, ip address, and vty number ■ when a user is prohibited by the acl ru...
Page 875
Introduction to password control configuration 875 confirm :********** updating the password-file ,please wait... # enable password aging: [sw8800] password-control aging enable password aging enabled for all users. Default: 90 days. # enable limitation of the minimum password length: [sw8800] passw...
Page 876
876 c hapter 78: p assword c ontrol c onfiguration.
Page 877: Cronyms
79 a cronyms aaa authentication, authorization and accounting abr area border router ac access code ack acknowledgement acl access control list adsl asymmetric digital subscriber line afi authority and format identifier ah authentication header am accounting management ansi american national standar...
Page 878
878 c hapter 79: a cronyms cf call forwarding services cfm configuration file management chap challenge handshake authentication protocol cidr classless inter-domain routing cist common and internal spanning tree cl configuration librarian clnp connectionless network protocol con conference calling ...
Page 879
879 fifo first in first out fin finance management dept. Fr frame relay ftp file transfer protocol ftps ftp server garp generic attribute registration protocol ge gigabit ethernet gr graceful restart gre generic routing encapsulation ha high availability hdlc high-level data link control http hyper ...
Page 880
880 c hapter 79: a cronyms ldp label distribution protocol ler label edge router lib indicator light immobility board qos switch qos lr location registration ls latest start time lsa link state advertisement lsack low speed data lsd low speed data lsdb link state database lsp label switch path lspdu...
Page 881
881 nms network management station npdu network protocol data unit npe network facing pe nsap network service access point nsm neighbour state machine ntp network time protocol oam operation administration and maintenance oc-3 oc-3 osi open systems interconnection ospf open shortest path first pap p...
Page 882
882 c hapter 79: a cronyms rsoh regenerator section overhead rstp rapid spanning tree protocol rsvp resource reservation protocol rt rate rtd radio test device sa solution architecture safi subsequent address family identifier sbm sgsn basic module sdh synchronous digital hierarchy sel clock selecti...
Page 883
883 vdsl very high speed dsl; very high rate dsl vfs virtual file system vlan virtual lan vll virtual leased lines vos virtual operate system vpdn virtual private data network vpi virtual path identifier vpls virtual private local switch vpn virtual private network comware versatile routing platform...