- DL manuals
- Cabletron Systems
- Switch
- SEHI-22
- User Manual
Cabletron Systems SEHI-22 User Manual
Summary of SEHI-22
Page 1
Sehi-22 and sehi-24 10base-t intelligent stackable hubs user’s guide cabletron systems, p. O. Box 5005, rochester, nh 03866-5005.
Page 2
Sehi user’s guide i notice cabletron systems reserves the right to make changes in specifications and other information contained in this document without prior notice. The reader should in all cases consult cabletron systems to determine whether any such changes have been made. The hardware, firmwa...
Page 3
Notice ii sehi user’s guide fcc notice this device complies with part 15 of the fcc rules. Operation is subject to the following two conditions: (1) this device may not cause harmful interference, and (2) this device must accept any interference received, including interference that may cause undesi...
Page 4
Notice sehi user’s guide iii cabletron systems, inc. Program license agreement important: before utilizing this product, carefully read this license agreement. This document is an agreement between you, the end user, and cabletron systems, inc. (“cabletron”) that sets forth your rights and obligatio...
Page 5
Notice iv sehi user’s guide exclusion of warranty and disclaimer of liability 1. Exclusion of warranty. Except as may be specifically provided by cabletron in writing, cabletron makes no warranty, expressed or implied, concerning the program (including its documentation and media). Cabletron disclai...
Page 6: Table of Contents
Sehi user’s guide v table of contents chapter 1 introduction 1.1 using this manual ............................................................................ 1-1 1.2 getting help ...................................................................................... 1-2 1.3 sehi overview .............
Page 7
Contents vi sehi user’s guide chapter 5 troubleshooting 5.1 installation check-out .................................................................5-1 5.2 using lanview ....................................................................................5-2 5.3 using the reset button...................
Page 8: Chapter 1
Sehi user’s guide 1-1 chapter 1 introduction welcome to the cabletron systems sehi-22 and sehi-24 10base-t intelligent stackable hub user’s guide . This manual provides installation instructions and reference information for the sehi-22 and sehi-24. Figure 1-1. Front and rear views of the sehi-22 an...
Page 9: Introduction
Chapter 1: introduction 1-2 sehi user’s guide chapter 1, introduction , outlines the contents of this manual, briefly describes sehi features, and concludes with a list of related manuals. Chapter 2, installation requirements/specifications , describes installation requirements, network guidelines, ...
Page 10: 1.3
Sehi overview sehi user’s guide 1-3 1.3 sehi overview the 10base-t sehi-22 and sehi-24 are intelligent repeater hubs. The sehi-22 has 12 rj45 ports and one ethernet port interface module (epim) port on the front panel for network connections while the sehi-24 has 24 rj45 ports and two epim ports on ...
Page 11: Lanview Leds
Chapter 1: introduction 1-4 sehi user’s guide lanview leds cabletron systems lanview status monitoring and diagnostics system is a troubleshooting tool that helps in diagnosing power failures, collisions, cable faults, and link problems. The lanview leds are conveniently located on the sehi front pa...
Page 12: 1.6
Remote network management capabilities sehi user’s guide 1-5 1.6 remote network management capabilities manage the sehi remotely with any snmp network management system. Cabletron systems offers the following remote management packages: • cabletron systems spectrum • cabletron systems remote lanview...
Page 13
Chapter 1: introduction 1-6 sehi user’s guide table 1-2 lists the board revision requirements for epims used in the sehi-22/24. The board revision number is located on the epim’s printed circuit board directly after the part number as shown in figure 1-2. Figure 1-2. Epim board revision number table...
Page 14: Hubstack Interconnect Cables
Related manuals sehi user’s guide 1-7 hubstack interconnect cables stack hubs together with cabletron hubstack interconnect cables. Table 1-3 lists the part number and the application for each cable. Rack mount capabilities the sehi can be installed in a 19-inch rack. Cabletron offers an accessory p...
Page 15: Chapter 2
Sehi user’s guide 2-1 chapter 2 installation requirements/specifications this chapter describes cabling requirements, network guidelines, and operating specifications for the sehi. The network must meet the requirements and conditions specified in this chapter to obtain satisfactory performance from...
Page 16: Length
Chapter 2: installation requirements/specifications 2-2 sehi user’s guide 2.1.2 utp and stp cable specifications the device at the other end of the twisted pair segment must meet ieee 802.3 10base-t specifications. When connecting a 10base-t twisted pair segment to the sehi 10base-t twisted pair net...
Page 17: Delay
Cable specifications sehi user’s guide 2-3 delay the maximum propagation delay of a 10base-t link segment must not exceed 1000 ns. This 1000 ns maximum delay limits the maximum link segment length to no greater than 200 meters. Crosstalk crosstalk is caused by signal coupling between the different c...
Page 18: 2.2
Chapter 2: installation requirements/specifications 2-4 sehi user’s guide 2.2 network port specifications the sehi-22 and sehi-24 network ports use shielded rj45 connectors that support stp and utp cabling. Figure 2-1 shows the rj45 pinouts. Figure 2-1. Rj45 network ports 2.3 com port requirements t...
Page 19: 2.4
Transceiver requirements sehi user’s guide 2-5 2.4 transceiver requirements when connecting an external network segment via a transceiver to the sehi with an epim-a, the following requirements must be met: • the transceiver or ethernet device to which the module will be connected must meet ieee 802....
Page 20
Chapter 2: installation requirements/specifications 2-6 sehi user’s guide delay times (start of packets): twisted pair to epim-a 1.10 µ s twisted pair to twisted pair 1.00 µ s epim-a to twisted pair 1.00 µ s delay times (jam): twisted pair to epim-a 960 ns preamble: input: minimum of 40 bits require...
Page 21: Output
Operating specifications sehi user’s guide 2-7 fault protection: each segment disconnects itself from the other segments if 32 consecutive collisions occur, or if the collision detector of a segment is on for longer than approximately 110 µ s. This fault protection resets automatically after one pac...
Page 22: Safety
Chapter 2: installation requirements/specifications 2-8 sehi user’s guide safety this unit meets the safety requirements of ul1950 (without d3 deviations), csa c22.2 no. 950, and en60950. Emi this unit meets the emi requirements of fcc part 15 class a, en55022 class a and vcci class i. Emc this unit...
Page 23: Chapter 3
Sehi user’s guide 3-1 chapter 3 installation this chapter outlines the procedure for attaching the sehi to the network as a stackable or standalone device. Ensure that the network meets the guidelines and requirements outlined in chapter 2, installation requirements/specifications, before installing...
Page 24: 3.2
Chapter 3: installation 3-2 sehi user’s guide 3.2 pre-installation checkout the sehi is equipped with an nvram reset switch (figure 3-1) located behind the grillwork on the side of the hub. Ensure that this switch is in the down position by looking in through the grillwork on the right side of the h...
Page 25
Installing the sehi sehi user’s guide 3-3 3.3.1 tabletop or shelf installation the following two subsections provide guidelines for installation on a tabletop or shelf. Guidelines for tabletop and shelf installations tabletop and shelf installations must be within reach of the network cabling and me...
Page 26: Tools Required
Chapter 3: installation 3-4 sehi user’s guide 3.3.2 rackmount installation requirements to install the sehi in a 19-inch rack, cabletron systems offers an accessory kit to install the sehi in a 19-inch rack that includes rack mount brackets, mounting screws, and a strain-relief bracket for cable man...
Page 27
Installing the sehi sehi user’s guide 3-5 figure 3-3. Sehi rack mount hardware 3.3.3 attaching the strain relief bracket attach the strain relief bracket to the front of the sehi as follows: 1. Locate the strain relief bracket and four 8-32 x 3/8 inch screws from the accessory kit included with the ...
Page 28: 3.3.4 Rackmounting The Sehi
Chapter 3: installation 3-6 sehi user’s guide 3.3.4 rackmounting the sehi refer to figure 3-5 and proceed as follows to install the sehi into a 19-inch rack. 1. Locate the four 8-32 x 1/4" screws and the two rackmount brackets in the sehi-accy-kit package. 2. Using the four 8-32 x 1/4" screws provid...
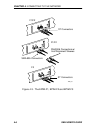
Page 29: 3.3.5 Stacking The Sehi
Installing the sehi sehi user’s guide 3-7 figure 3-6. Installing the sehi in the rack if the installation requires that the sehi is to be stacked, proceed to section 3.3.5. Otherwise, continue by connecting power as described in section 3.4. 3.3.5 stacking the sehi the rear panel of the sehi has an ...
Page 30
Chapter 3: installation 3-8 sehi user’s guide to stack seh non-intelligent hubs together: 1. Attach the seh hubstack interconnect cable to the “out” port on the rear panel of the seh as shown in figure 3-7. 2. Attach the other end of the seh hubstack interconnect cable to the “in” port on the rear p...
Page 31: 3.4
Connecting the sehi to the power source sehi user’s guide 3-9 figure 3-8. Disconnecting the hubstack interconnect cable proceed to section 3.4 to connect power. 3.4 connecting the sehi to the power source to connect the sehi to the power source: 1. Plug the power cord into the back panel of the sehi...
Page 32: 3.5
Chapter 3: installation 3-10 sehi user’s guide 3.5 adding/replacing epims this section contains procedures on how to add or replace an ethernet port interface module (epim) to upgrade or change the capabilities of your sehi. After installing a new epim, refer to the appropriate epim section in appen...
Page 33: Chapter 4
Sehi user’s guide 4-1 chapter 4 connecting to the network this chapter outlines the procedure for connecting the sehi to a network. Ensure that the network meets the guidelines and requirements outlined in chapter 2, installation requirements/specifications , before installing the sehi. 4.1 connecti...
Page 34
Chapter 4: connecting to the network 4-2 sehi user’s guide to connect the twisted pair segments to the sehi: 1. Insert the rj45 connector from each twisted pair segment into the desired network port on the sehi. See figure 4-1. Figure 4-1. Sehi network ports 2. Check that the applicable lnk led for ...
Page 35
Connecting the sehi to the network sehi user’s guide 4-3 4.1.2 connecting a utp segment to an epim-t before connecting a segment to the epim-t, check each end of the segment to determine if the wires have been crossed over for the proper connection. If the wires do not cross over, use the switch on ...
Page 36
Chapter 4: connecting to the network 4-4 sehi user’s guide d. Check that the twisted pair connection meets db loss and cable specifications outlined in chapter 2, section 2.1.2. E. Check that the crossover switch is in the correct position. If a link is not established, contact cabletron systems tec...
Page 37
Connecting the sehi to the network sehi user’s guide 4-5 to connect a fiber optic link segment to an epim-f1, epim-f2, or an epim-f3: 1. Remove the protective plastic covers from the fiber optic ports on the applicable port on the module and from the ends of the connectors on each fiber strand. 2. A...
Page 38
Chapter 4: connecting to the network 4-6 sehi user’s guide figure 4-3. The epim-f1, epim-f2 and epim-f3 sma 905 connectors sma 906 connectors w/ half alignment sleeves st connectors st connectors f1/f2 f1/f2 f3 1490_15.
Page 39: Labeled Term To:
Connecting the sehi to the network sehi user’s guide 4-7 4.1.4 connecting a thin-net segment to an epim-c to connect a thin-net segment to an epim-c: 1. Set the internal termination switch, located to the right of the port and labeled term to: • the on position ( • ) if the thin-net segment connecte...
Page 40
Chapter 4: connecting to the network 4-8 sehi user’s guide figure 4-4. The epim-c 4.1.5 connecting an aui cable to an epim-a to connect an epim-a to an external network segment: 1. Attach an external transceiver to the network segment that will be connected to the aui port. Refer to the applicable t...
Page 41
Connecting the sehi to the network sehi user’s guide 4-9 3. Connect the aui cable to the aui port located on the epim-a. See figure 4-5. 4. Lock the aui connector into place using the connector slide latch. Figure 4-5. The epim-a 5. Check that the pwr led on the epim-a is on. If the led is not on, c...
Page 42
Chapter 4: connecting to the network 4-10 sehi user’s guide 4.1.6 connecting an aui cable to an epim-x to connect an epim-x to a device not requiring sqe: 1. Check that the sqe led on the epim-x is off. If the sqe led is on, check the position of the sqe switch. 2. Attach one end of an aui cable of ...
Page 43: 4.2
Finishing the installation sehi user’s guide 4-11 4.2 finishing the installation the sehi is now ready for operation. Before placing the network into service, test the installation thoroughly, making sure that all stations can be addressed and that the sehi and all stations are indicating normal ope...
Page 44: Chapter 5
Sehi user’s guide 5-1 chapter 5 troubleshooting this chapter contains instructions for using lanview leds to troubleshoot physical layer network problems. It also describes how to reset the sehi and how to reset the nvram switch. 5.1 installation check-out after connecting the sehi to the network, v...
Page 45: 5.2
Chapter 5: troubleshooting 5-2 sehi user’s guide 2. If the remote station is ready and the lnk led is on, but no data passes through the port, one of two conditions may exist: • network management has disabled the port. • the port is segmented either because the collision detector was on for more th...
Page 46: Pwr
Using lanview sehi user’s guide 5-3 note: flashing indicates an irregular led pulse. Blinking indicates a steady led pulse. Figure 5-1. Lanview leds pwr when this green led is on, it indicates that the sehi is receiving power. If this led is off, it indicates a loss of input power. Check the input p...
Page 47: Cln
Chapter 5: troubleshooting 5-4 sehi user’s guide cln this red led indicates that a collision has occurred on one of the ports. Rcv when a yellow rcv led flashes, it indicates that the sehi is receiving data packets from the associated port segment. Each sehi port has a corresponding rcv led: • netwo...
Page 48: 5.4
Setting the nvram switch sehi user’s guide 5-5 5.4 setting the nvram switch the sehi uses nvram (non-volatile random access memory) to store user-entered parameters such as ip address and community names. To reset these parameters to the factory defaults, refer to figure 5-2 and perform the followin...
Page 49: Chapter 6
Sehi user’s guide 6-1 chapter 6 local management this chapter explains how to set up a management terminal to access the sehi local management. It also explains how to use the local management screens and commands. Local management supplies the tools to manage the sehi and all of its attached segmen...
Page 50: 6.1
Chapter 6: local management 6-2 sehi user’s guide 6.1 management terminal requirements use one of the following systems to access local management: • a digital equipment corporation vt series terminal • a vt type terminal running emulation programs for the digital equipment corporation vt series • a...
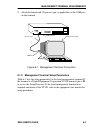
Page 51
Management terminal requirements sehi user’s guide 6-3 2. Attach the female end (25-pin or 9-pin, as applicable) to the com port on the terminal. Figure 6-1. Management terminal connection 6.1.2 management terminal setup parameters table 6-1 lists the setup parameters for the local management termin...
Page 52
Chapter 6: local management 6-4 sehi user’s guide table 6-1. Terminal setup parameters menu function selection display setup: columns 80 columns controls interpret controls auto wrap no auto wrap test cursor cursor general setup: mode 7 bit control cursor keys normal cursor keys communications setup...
Page 53: 6.2
Accessing local management sehi user’s guide 6-5 6.2 accessing local management after configuring the local management terminal and properly attaching the cables to the sehi, access the local management interface. To access local management: 1. Power up the terminal. The sehi password screen (figure...
Page 54: 3. Press The Return Key.
Chapter 6: local management 6-6 sehi user’s guide 3. Press the return key. • if the password entry is invalid, the cursor returns to the beginning of the password entry field. • if the password is valid, the associated access privilege appears briefly, then the sehi local management feature selectio...
Page 55: 6.3
Using the local management screens sehi user’s guide 6-7 6.3 using the local management screens the feature selection screen is the main menu screen for sehi local management. There are five screen options in the feature selection screen: community name table, ip address assignment, component trap t...
Page 56: Community Name
Chapter 6: local management 6-8 sehi user’s guide community names are set through the community name table option. Community names are passwords to local management and they are agents of security control to the sehi. Sehi access is controlled by establishing up to four different levels of security ...
Page 57: 3. Press The Return Key.
Using the local management screens sehi user’s guide 6-9 editing the community name field the password used to access local management at the password screen must have super-user privileges for the edits to take effect. If a password is entered with basic-read, read-only, or read-write privileges, l...
Page 58: I/f
Chapter 6: local management 6-10 sehi user’s guide 6.3.2 the configuration screen to access the configuration screen from the feature selection screen, use the arrow keys to highlight the ip address assignment option, then press the return key or f7. The configuration screen shown in figure 6-5 appe...
Page 59: Ip Address
Using the local management screens sehi user’s guide 6-11 ip address displays the ip address of the sehi. Subnet mask displays the subnet mask for the sehi. A subnet mask is a 32-bit quantity which “masks out” the network bits of the ip address. This is done by setting the bits in the mask to 1 when...
Page 60: Setting The Ip Address
Chapter 6: local management 6-12 sehi user’s guide setting the ip address to set the ip address: 1. Use the arrow keys to highlight the ip address field. 2. Enter the ip address into this field. The format for this entry is xxx.Xxx.Xxx.Xxx, with values for xxx being from 0 to 255. The screen beeps i...
Page 61: 3. Press The Return Key.
Using the local management screens sehi user’s guide 6-13 to set the subnet mask: 1. Use the arrow keys to highlight the subnet mask field. 2. Enter the subnet mask into this field. The format for this entry is xxx.Xxx.Xxx.Xxx with values for xxx being from 0 to 255. 3. Press the return key. 4. Use ...
Page 62
Chapter 6: local management 6-14 sehi user’s guide using the port enable override to set the port enable override: 1. Use the arrow keys to highlight the port enable override field. 2. Press the return key to toggle from the default setting of “override disabled” to “override enabled”. 3. The adjace...
Page 63: Snmp Community Name
Using the local management screens sehi user’s guide 6-15 6.3.3 the trap table screen access the trap table screen from the features selection screen using the arrow keys to highlight the component trap table option, then press the return key or f8. The screen shown in figure 6-6 appears. Figure 6-6...
Page 64: Configuring The Trap Table
Chapter 6: local management 6-16 sehi user’s guide configuring the trap table to configure the trap table: 1. Use the arrow keys to highlight the snmp community name field, then enter the community name. 2. Press the return key. 3. Use the arrow keys to highlight the traps field and enter y (or y) t...
Page 65: 6.3.4 The Snmp Tools Screen
Using the local management screens sehi user’s guide 6-17 6.3.4 the snmp tools screen this section describes how to use the snmp tools screen to access management information bases (mibs). Access to screen options depends on the access status accorded to the user’s community name. This section descr...
Page 66: Community Name
Chapter 6: local management 6-18 sehi user’s guide the following sections describe snmp tools screen fields and instructions on how to change them. Community name identifies the community name used as a password to determine access level to the mib component. Oid prepend specifies the number prefix ...
Page 67: Step
Using the local management screens sehi user’s guide 6-19 step displays the mib walk, step by step, giving the user time to view specific leaves in detail. Cycles allows the user to specify the number of get next requests to cycle through and how much time will elapse between each request. Repeat re...
Page 69: Viewing Multiple Oids
Using the local management screens sehi user’s guide 6-21 viewing multiple oids viewing several object identifiers at one time allows the user to quickly scan a mib for the specific information that is needed. The walk scrolls through oids numerically sequential to the initial oid request. The step ...
Page 70: Cycling Through Oids
Chapter 6: local management 6-22 sehi user’s guide cycling through oids to cycle through an oid: 1. Use the arrow keys to highlight cycles, then press return. 2. Enter the number of cycles desired to occur after “enter cycle count:”, then press the return key. 3. Enter how many seconds delay desired...
Page 71: Bytes Received
Using the local management screens sehi user’s guide 6-23 figure 6-8. Device statistics screen the following sections describe device statistics screen fields and instructions on how to change them. Bytes received displays the number of bytes received. Frames received displays the number of frames r...
Page 72: Oow Collisions
Chapter 6: local management 6-24 sehi user’s guide oow collisions displays the number of out of window collisions. Oow collisions are usually caused by the network being too long where the round trip propagation delay is greater than 51.2 µ s (the collision domain is too large), a station somewhere ...
Page 73: Disable Port
Using the local management screens sehi user’s guide 6-25 disable port this command lets the user disable the selected port. Update-freq this command lets the user select the time interval between stack/module/port counter updates. Choose update intervals in increments of 3 seconds, with the maximum...
Page 74
Chapter 6: local management 6-26 sehi user’s guide selecting the appropriate module/port when the device statistics screen first appears, statistics are displayed for module 1 and port 1. To view statistics for another module and port, use the module x or port x commands at the bottom of the screen....
Page 75
Using the local management screens sehi user’s guide 6-27 using the disable port command the disable port command lets the user disable the port selected in the port command. The user must first use the port command to select the desired port. To set the port disable command: 1. Use the arrow keys t...
Page 76: Appendix A
Sehi user’s guide a-1 appendix a epim information a.1 epim specifications epims enable the connection of the sehi to the main network using different media types. Cabletron systems offers a variety of epims. The following sections explain specifications for each epim. A.1.1 epim-t the epim-t is an r...
Page 77: A.1.2
Appendix a: epim information a-2 sehi user’s guide a.1.2 epim-f1 and epim-f2 the epim-f1 and epim-f2 shown in figure a-2 support multimode fiber optic cabling. Each epim has an internal cabletron systems fot-f fiber optic transceiver. The epim-f1 is equipped with sma connectors and the epim-f2 is eq...
Page 78: A.1.3
Epim specifications sehi user’s guide a-3 a.1.3 epim-f3 the epim-f3 shown in figure a-3 supports single mode fiber optic cabling. It has an internal cabletron systems fot-f fiber optic transceiver and is equipped with st connectors. Specifications for the epim-f3 are listed below. Figure a-3. Epim-f...
Page 79
Appendix a: epim information a-4 sehi user’s guide note : the transmitter power levels given above are peak power levels after optical overshoot. Use a peak power meter to correctly compare the values given above to those measured on any particular port. To measure power levels with an average power...
Page 80: A.1.4
Epim specifications sehi user’s guide a-5 a.1.4 epim-c the epim-c supports thin-net coaxial cabling and is equipped with an internal cabletron systems tms-3 transceiver. Use the term switch on the front of the epim-c to set the internal 50 ohm terminator. This eliminates the need to connect the port...
Page 81: A.1.5
Appendix a: epim information a-6 sehi user’s guide a.1.5 epim-a and epim-x (aui port) the epim-a is a db15 female connector used to attach segments to an external transceiver. The epim-x is equipped with dual internal transceivers. It has a db15 male connector used to attach segments to an aui cable...
Page 82: Appendix B
Sehi user’s guide b-1 appendix b image file download using oids this appendix provides instructions for setting up a tftp server and to download an image file to the sehi by setting specific mib oid strings. Set the oid strings with the snmp tools screen described in chapter 6. The sehi supports the...
Page 83
Appendix b: image file download using oids b-2 sehi user’s guide note:for convenience, cabletron includes the pkunzip utility for easy decompression of the “zipped” file. If you are using a unix workstation as a tftp server, and you do not have a decompression utility that recognizes the pkzip forma...
Page 84: B.2
Standard local download sehi user’s guide b-3 2. If you do not have a /tftpboot directory, then create one (e.G., unix% mkdir tftpboot). 3. Ensure that the /tftpboot directory is not owned (e.G., unix% chown nobody tftpboot). 4. Store the hex image file in the /tftpboot directory as sehi.Hex. 5. Edi...
Page 85
Appendix b: image file download using oids b-4 sehi user’s guide when performing the steps in table 1, keep the following in mind: • you must follow the steps in order. • enter the ip address of the tftp server in standard dotted decimal notation (e.G., 132.177.118.24). • enter the full path to the ...
Page 86: Numerics
Sehi user’s guide index-1 numerics 10base-t cable length 2-2 crosstalk 2-3 delay 2-3 impedance 2-2 insertion loss 2-2 jitter 2-2 noise 2-3 temperature 2-3 utp and stp specifications 2-2 a aui cable 4-8, 4-10 c cable specifications 2-1 utp and stp 2-2 cables hubstack interconnect 1-7 com port 2-4 d d...
Page 87
Index index-2 sehi user’s guide n network connection 4-1 aui 4-8, 4-10 epim-a 4-8 epim-c 4-7 epim-f1/f2/f3 4-4 epim-t 4-3 epim-x 4-10 fiber optic segment 4-4 sehi-22/24 4-1 thin-net 4-7 unshielded twisted pair 4-3 network port specifications sehi-22/24 2-4 nvram pre-installation checkout 3-2 setting...
Page 88: Power Supply Cord
Power supply cord the mains cord used with this equipment must be a 2 conductor plus ground type with minimum 0.75 mm square conductors and must incorporate a standard iec appliance coupler on one end and a mains plug on the other end which is suitable for the use and application of the product and ...