- DL manuals
- Cabletron Systems
- Network Hardware
- TRBMIM-T
- User Manual
Cabletron Systems TRBMIM-T User Manual
Summary of TRBMIM-T
Page 1
Trbmim-t token ring bridge/management module user’s guide booktitle2 optional trbmim-t book page 1 tuesday, july 2, 1996 10:35 am.
Page 2
Trbmim-t book page 2 tuesday, july 2, 1996 10:35 am.
Page 3: Notice
I notice cabletron systems reserves the right to make changes in specifications and other information contained in this document without prior notice. The reader should in all cases consult cabletron systems to determine whether any such changes have been made. The hardware, firmware, or software de...
Page 4
Notice ii fcc notice this device complies with part 15 of the fcc rules. Operation is subject to the following two conditions: (1) this device may not cause harmful interference, and (2) this device must accept any interference received, including interference that may cause undesired operation. Not...
Page 5
Notice iii cabletron systems, inc. Program license agreement important: before utilizing this product, carefully read this license agreement. This document is an agreement between you, the end user, and cabletron systems, inc. (“cabletron”) that sets forth your rights and obligations with respect to...
Page 6
Notice iv united states government restricted rights the enclosed product (a) was developed solely at private expense; (b) contains “restricted computer software” submitted with restricted rights in accordance with section 52227-19 (a) through (d) of the commercial computer software - restricted rig...
Page 7
Notice v declaration of conformity application of council directive(s): 89/336/eec 73/23/eec manufacturer’s name: cabletron systems, inc. Manufacturer’s address: 35 industrial way po box 5005 rochester, nh 03867 european representative name: mr. J. Solari european representative address: cabletron s...
Page 8
Notice vi trbmim-t book page vi tuesday, july 2, 1996 10:35 am.
Page 9: Contents
Vii contents chapter 1 introduction 1.1 document conventions ............................................................... 1-2 1.2 getting help................................................................................. 1-2 1.3 using this manual...................................................
Page 10
Contents viii chapter 4 establishing the bridge connection 4.1 setting up the station port .........................................................4-1 4.1.1 configuring tpims...........................................................4-1 4.1.2 installing a tpim .........................................
Page 11: Chapter 1
1-1 chapter 1 introduction welcome to the trbmim-t token ring bridge/management module user’s guide . This manual describes trbmim-t (see figure 1-1) capabilities and features, operating specifications, and configuration, installation, and troubleshooting procedures. Users of the trbmim-t should hav...
Page 12: 1.1 Document Conventions
Introduction 1-2 1.1 document conventions the following conventions are used throughout this document: bold italics for references to cabletron systems documents and other publications 1.2 getting help if you need assistance installing or using the trbmim-t, or if you have any questions, comments, o...
Page 13: 1.3 Using This Manual
Introduction 1-3 1.3 using this manual the manual is organized as follows: chapter 1, introduction , describes this manual’s conventions and organizational structure, how to get technical help, trbmim-t features and capabilities, source-route bridging concepts, and related reading and reference sour...
Page 14: 1.4 Trbmim-T Overview
Introduction 1-4 1.4 trbmim-t overview the trbmim-t is two-port source-route bridge with management capabilities. The two trbmim-t bridge ports are described as follows: • the fnb backplane connector on the trbmim-t component board interfaces with the fnb ring in the mmac. • the media-configurable s...
Page 15
Introduction 1-5 • local management (lm) applications, accessible via: - out-of-band connection to the front-panel rs-232 console port to a vt-series terminal or a pc running a vt-series emulation program - in-band telnet connection from any tcp/ip - based node linked to the trbmim-t • selectable op...
Page 16
Introduction 1-6 1.4.1 describing bridge-only mode capabilities the bridge-only mode is the default operational mode for the trbmim-t. When in the bridge-only mode, the trbmim-t serves exclusively as a source-route bridge in the mmac for linking separate token rings. It neither automatically segment...
Page 17
Introduction 1-7 bridging token rings in separate mmacs figure 1-3 illustrates how the trbmim-t can be used to bridge ring 1 in one mmac and ring 2 in another mmac. In this configuration the trbmim-t’s fnb port is connected to ring 1. Its front-panel bridge station port is connected to ring 2 via ca...
Page 18
Introduction 1-8 collapsed backbone configuration figure 1-4 illustrates how multiple trbmim-ts can be used in the mmac to constitute a single collapsed backbone ring to provide network connectivity for multiple rings, running at either 4 mbps or 16 mbps ring speeds and linked to the backbone via ei...
Page 19
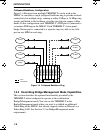
Introduction 1-9 management functionality in the mmac when configured for operation as a combination bridge/management module and installed in any mim slot in the mmac, the trbmim-t automatically bisects the fnb backplane. This creates a new fnb ring, supporting token ring stations connected to the ...
Page 20
Introduction 1-10 figure 1-5 ring management in the mmac bridging functionality in bridge/management mode the trbmim-t performs the same source-route bridging functions when in the bridge/management operational mode as it does when it is in the bridge-only operational mode. The trbmim-t must simulta...
Page 21: 1.4.4 System Safeguards
Introduction 1-11 the power up diagnostic screen displays information about the system-initialization process you can view from the management terminal during the power-up or reset cycle. You can use the power up diagnostic screen to assess the status of system elements during the power up cycle and...
Page 22
Introduction 1-12 you access local management from the front-panel rs232 com port via console-cable connection or remote modem connection to: • a “dumb” vt-series terminal • a pc running a vt-series terminal emulation program you can also access lm via in-band telnet connection from any tcp/ip - bas...
Page 23
Introduction 1-13 1.4.6 ip address auto-configuration if the trbmim-t does not have an ip address when it is powered up, it automatically transmits up to seven bootp requests for an ip address from any bootp server on the network that can provide it. Causative conditions include: • initial power up ...
Page 24: 1.6 Related Manuals
Introduction 1-14 by the time the explorer frames arrives at the destination station, the route it took to the destination, represented by the data in the ri field, can serve as the map for all subsequent data-exchange between the source and destination stations. The destination station reverses the...
Page 25: 1.7 Recommended Reading
Introduction 1-15 1.7 recommended reading the following publications are recommended if more information is required on designing and implementing a token ring network. Local area networks, ieee standard 802.5 token ring access method and physical layer specifications commercial building wiring stan...
Page 26
Introduction 1-16 trbmim-t book page 16 tuesday, july 2, 1996 10:35 am.
Page 27: Chapter 2
2-1 chapter 2 requirements and specifications review this chapter before installing the trbmim-t. It describes requirements and specifications for hardware and media in the installation. Failure to follow specified operational guidelines could result in poor network performance. 2.1 mmac requirement...
Page 28: 2.4 Front-Panel Components
Requirements and specifications 2-2 figure 2-1 mmac mim slots 2.3 bridge/management mode requirements to operate in the bridge/management mode, the trbmim-t must be used in conjunction with either of the following management modules installed in the management slot in the mmac: • trmm – token ring m...
Page 29: 2.4.1 Port Specifications
Requirements and specifications 2-3 figure 2-2 front panel components 2.4.1 port specifications this section describes functional specifications for the trbmim-t front-panel ports. Station port the station port serves as the external bridge port on the trbmim-t. You can install any of the token ring...
Page 30
Requirements and specifications 2-4 see appendix a for information about tpim operational specifications and appendix b for information about media specifications. Console port you can connect a management terminal to the rs-232c female db9 console port on the trbmim-t to access local management. Se...
Page 31: 2.4.2 Lanview Leds
Requirements and specifications 2-5 figure 2-4 shows pinouts diagrams for the console cable configured with the rj45-to-db25 vt-series adaptor and the rj45-to-db9 pc adaptor. Figure 2-4 console cable connector pinouts 2.4.2 lanview leds front-panel lanview leds together with the lnk led on the tpim ...
Page 32
Requirements and specifications 2-6 an led conveys the information about the status of a network function with which it is associated either by lighting or not lighting the color it can produce. See chapter 5 for more information about leds, including information on led color codes and how to monito...
Page 33: 2.5.1 Dip Switch Settings
Requirements and specifications 2-7 • select bridge-only or bridge/management operational modes • assert the clear to send signal for the console port 2.5.1 dip switch settings refer to figure 2-5 and table 2-2 when configuring dip switch settings. Please note that switchblock 1 is labeled sw1 and s...
Page 34
Requirements and specifications 2-8 figure 2-5 default dip switch and jumper settings table 2-2 switch settings description switchblock sw 1 (firmware settings) switchblock sw 2 (hardware settings) switch 2 on = bridge-only mode off = bridge/management mode switch 7 on = 16 mbps fnb ring speed off =...
Page 35: 2.5.2 Jumper Settings
Requirements and specifications 2-9 2.5.2 jumper settings refer to figure 2-5 when setting jumpers. Please note that the backup battery jumper is labeled jp6 and the clear to send jumper is labeled jp5 on the component board. Enabling the nvram backup battery with the jp6 jumper use jp6 to enable or...
Page 36: 2.6 General Specifications
Requirements and specifications 2-10 asserting the clear to send signal with the jp5 jumper use the jp5 jumper to set the clear to send (cts) signal for the console port to either the internally asserted mode or the externally activated terminal-signal mode. • the jp5 jumper’s default position is ov...
Page 37
Requirements and specifications 2-11 2.6.5 environmental specifications operating temperature: 5 ° to 40 ° c storage temperature: -30 ° to 90 ° c relative humidity: 5% to 95% non-condensing trbmim-t book page 11 tuesday, july 2, 1996 10:35 am.
Page 38
Requirements and specifications 2-12 trbmim-t book page 12 tuesday, july 2, 1996 10:35 am.
Page 39: Chapter 3
3-1 chapter 3 installation this chapter describes the following procedures: • unpacking and handling the trbmim-t • installing the trbmim-t in an mmac check that all requirements listed in chapter 2 have been met before installing and operating the trbmim-t. 3.1 unpacking and handling the trbmim-t t...
Page 40
Installation 3-2 the trbmim-t can be installed into any mmac mim slot, as described in section 2.1. Perform the following tasks before you install the trbmim-t: • specify the ring speed for the fnb and bridge station port interfaces • specify the operational mode (bridge-only or bridge/management) •...
Page 41
Installation 3-3 2. Align the trbmim-t in the top and bottom module slots in the mmac and slide it in, as shown in figure 3-2, until you feel the backplane connectors on the trbmim-t firmly insert into the fnb backplane connector sockets. Figure 3-2 installing the trbmim-t 3. Tighten the fastening k...
Page 42
Installation 3-4 trbmim-t book page 4 tuesday, july 2, 1996 10:35 am.
Page 43: Chapter 4
4-1 chapter 4 establishing the bridge connection this section describes how to setup and establish the physical bridge connection between the trbmim-t station port and a lobe port on another ring. See the trbmim/trbmim-t local management user’s guide for information on configuring source-route bridg...
Page 44
Establishing the bridge connection 4-2 to configure tpims for use with the trbmim-t use a blunt, narrow-tipped instrument such as a screwdriver to move switches to the positions specified in figure 4-2. Figure 4-2 station-application switch settings for tpims note tpim-f2 hardware version-04 or high...
Page 45: 4.1.2 Installing A Tpim
Establishing the bridge connection 4-3 4.1.2 installing a tpim to install a tpim: 1. Remove the self-fastening faceplate covering the tpim/station receptacle. 2. Slide the tpim all the way into the tpim slot, as shown in figure 4-3, until you feel the tpim-slot connection pins insert securely into t...
Page 46
Establishing the bridge connection 4-4 4.2 connecting twisted pair cable this section describes how to connect shielded and unshielded twisted pair cable to the trbmim-t station port. It also describes how to check the status of the connection using the lnk led. Stp use the tpim-t1 to connect an stp...
Page 47
Establishing the bridge connection 4-5 utp use the tpim-t2 to connect a utp cable segment with an rj45 connector as shown in figure 4-6. Figure 4-6 connecting to the tpim-t2 checking the connection thelnk led on the tpim-t1/t2/t4 lights: • green if the station port detects phantom current asserted t...
Page 48
Establishing the bridge connection 4-6 4.3 connecting fiber optic cable use the tpim-f2/ f3 to connect fiber optic cable. When connecting a fiber optic link segment to the tpim-f2 or tpim-f3 consider the following: • fiber optic link segments with st connectors attach to st ports much like bnc conne...
Page 49
Establishing the bridge connection 4-7 figure 4-7 connecting to the tpim-f2/-f3 3. Attach the other end of the fiber strand connected to the tpim-f2/-f3’s rx port to the other device’s tx port. Attach the other end of the strand connected to the tpim-f2/-f3’s tx port to the other device’s rx port. T...
Page 50
Establishing the bridge connection 4-8 trbmim-t book page 8 tuesday, july 2, 1996 10:35 am.
Page 51: Chapter 5
5-1 chapter 5 monitoring and troubleshooting this chapter describes lanview led functions and color codes and how to use leds to monitor and troubleshoot the operational status of the trbmim-t. It also describes how to monitor the system start-up, or initialization, process using the power up diagno...
Page 52
Monitoring and troubleshooting 5-2 5.1.1 describing system leds system leds convey information about the status of system hardware and software elements. Bok (board okay) the bok led indicates the following operational conditions: solid green the trbmim-t is booting, is running system initialization...
Page 53: 5.1.2 Describing Fnb Leds
Monitoring and troubleshooting 5-3 5.1.2 describing fnb leds fnb leds convey information about the status of the fnb connection. 16 mb (ring speed) the 16 mb led indicates the fnb ring speed: solid yellow the fnb ring speed is set to 16 mbps, the default ring speed. Off the fnb ring speed is set to ...
Page 54
Monitoring and troubleshooting 5-4 nsrt (inserted) the nsrt led indicates the status of the trbmim-t’s insertion into the fnb ring: solid green the trbmim-t is inserted into the fnb ring, the normal condition. Off the trbmim-t is not inserted into the fnb ring. Rwrp (right wrapped) he rwrp led indic...
Page 55: 5.1.3 Describing Stn Leds
Monitoring and troubleshooting 5-5 5.1.3 describing stn leds stn leds convey information about the status of the bridge station port. 16 mb (ring speed) the 16 mb led indicates the ring speed for the bridge station port: solid yellow the bridge station-port ring speed is set to 16 mbps, the default ...
Page 56
Monitoring and troubleshooting 5-6 stby (standby) the stby led indicates the state of the bridge station port: solid yellow the bridge has placed the station port in an inactive state, not bridging data. Off the station port is bridging data, the normal condition. The stby condition is caused, typic...
Page 57
Monitoring and troubleshooting 5-7 to view the test, connect your management terminal, or pc, to the trbmim-t console port prior to power up or reset. See the trbmim/trbmim-t local management user’s guide for information about connecting the management terminal. Responding to a power up error messag...
Page 58: 5.2.2 Monitoring With Leds
Monitoring and troubleshooting 5-8 exiting the screen after the completion of power up tests, the local management password screen should automatically appear. If it does not appear, press the enter key. 5.2.2 monitoring with leds leds provide information about the working order of the trbmim-t duri...
Page 59
Monitoring and troubleshooting 5-9 • ensure that the err led, or equivalent led, on each mim in the mmac is not lit. Reset mims with lit err leds, which may be all that is necessary to resolve the problem. • verify that the lnk led on the tpim installed in the station receptacle is green. If it is n...
Page 60
Monitoring and troubleshooting 5-10 • check the stby led to ensure that the station port is not in the standby mode. - resetting the bridge may resolve this problem. - a standby condition may be caused by incorrectly configured ring numbers. See the trbmim/trbmim-t local management user’s guide for ...
Page 61
Monitoring and troubleshooting 5-11 • trace the ring path through the network to ensure that there are no cabling problems. While tracing the ring: - check the cable connections at mims, patch panels and wall plates, and token ring stations. Are all connectors inserted fully into or secured to ports...
Page 62
Monitoring and troubleshooting 5-12 trbmim-t book page 12 tuesday, july 2, 1996 10:35 am.
Page 63: Appendix A
A-1 appendix a tpim specifications this appendix describes performance specifications for cabletron systems tpims. A.1 tpim-t1/t2/t4 pinouts figure a-1 illustrates tpim-t1/t2/t4 pinouts for station application. Figure a-1 tpim pinouts tpim-t1 tpim-t2/t4 1. Receive + 2. Ground 3. +5v at 250ma 4. Grou...
Page 64
Tpim specifications a-2 a.2 tpim-f2/f3 specifications the tpim-f2 supports multimode fiber optic cabling, and the tpim-f3 supports single mode fiber optic cabling. Tpim-f2 the tpim-f2 is designed to operate with 50/125 µ m, 62.5/125 µ m, and 100/140 µ m fiber optic cable. Table a-1 lists receiver se...
Page 65
Tpim specifications a-3 transmitter power and receive sensitivity levels, shown in table a-1, table a-3, and table a-3 are peak power levels after optical overshoot. A peak power meter must be used to correctly compare the values given to those measured on any particular port. If power levels are be...
Page 66
Tpim specifications a-4 trbmim-t book page 4 tuesday, july 2, 1996 10:35 am.
Page 67: Appendix B
B-1 appendix b media specifications this appendix describes design and performance specifications for each of the media types used with the trbmim-t. B.1 unshielded twisted pair (utp) a utp segment consists of four pairs of 24 awg solid wire for data or voice communication and is typically used to w...
Page 68
Media specifications b-2 b.2 shielded twisted pair (stp) stp cable has a metallic shielded wrapped around the twisted pairs to protect the cable from intrusive and unwanted interference from outside sources. The tpim-t1 and tpim-t4 support ibm type 1, 2, 6, and 9 stp cabling, which is described belo...
Page 69: B.3 Fiber Optic
Media specifications b-3 . B.3 fiber optic a fiber optic cable is composed of a drawn fiber of pure glass, enveloped within a another layer of glass called cladding. Around the fiber (core and cladding) are wrapped multiple layers of reinforced matter that protect the fiber. Multimode fiber cable co...
Page 70
Media specifications b-4 attenuation testing fiber optic cable must be tested with an attenuation test set adjusted for an 850 nm wavelength for multimode and 1300 for single mode. This test ensures that a cable’s signal loss is within acceptable limits. Table b-4 single tolerance for single-mode fi...
Page 71: Index
Ix-1 index a anti-static wriststrap 3-1 automatic beacon recovery process (abrp) 1-11 b bootp server 1-13 bridge/management mode capabilities 1-8 to 1-10 management module compatibility 2-2 requirements 2-2 selecting 2-7 bridge-only mode capabilities 1-6 to 1-8 selecting 2-7 c cabling connecting fib...
Page 72
Index ix-2 i ibm lan net manager 1-4 installation tpim 4-3 trbmim-t in mmac 3-1 to 3-3 ip address, auto-configuration 1-13 j jp5 jumper 2-10 jp6 jumper 2-9 jumper settings battery backup 2-9 clear to send (cts) 2-10 l lanview leds describing 5-1 to 5-6 overview 2-5 see also fnb leds see also stn (st...
Page 73
Index ix-3 t telnet 1-12 tpim configuring 4-1 functional compatibility with trbmim-t 4-2 installation 4-3 led 5-6 models 2-4 specifications a-1 to a-3 tpim-f2/f3 connecting fiber segments to 4-6 to 4-7 tpim-t1/t2/t4 connecting twisted-pair segments to 4-4 to 4-5 pinouts for station application a-1 t...
Page 74
Index ix-4 trbmim-t book page 4 tuesday, july 2, 1996 10:35 am.