- DL manuals
- CAC / BDP
- Portable Generator
- FOR BYPASS AND FAN POWERED HUMIDIFIERS
- Diagnostic Repair Manual
CAC / BDP FOR BYPASS AND FAN POWERED HUMIDIFIERS Diagnostic Repair Manual
Summary of FOR BYPASS AND FAN POWERED HUMIDIFIERS
Page 1
Diagnostic repair manual a u t o m a t i c s t a n d b y g e n e r a t o r s air-cooled product 0g9266reva.Indd 1 10/15/2008 11:25:38 am models: 7 kw ng, 8 kw lp 9 kw ng, 10 kw lp 13 kw ng, 14 kw lp 16 kw ng, 17 kw lp 18 kw ng, 20 kw lp.
Page 2
Electrical formulas to find known values 1-phase 3-phase kilowatts (kw) volts, current, power factor e x i 1000 e x i x 1.73 x pf 1000 kva volts, current e x i 1000 e x i x 1.73 1000 amperes kw, volts, power factor kw x 1000 e kw x 1000 e x 1.73 x pf watts volts, amps, power factor volts x amps e x ...
Page 3
Page 1 contents specifications .......................................................... 4 generator ................................................................ 4 engine ..................................................................... 5 fuel consumption ......................................
Page 4
Test 7 – testing the stator with a vom (12-20 kw)...........................................44 test 8 – test brushless stator..........................45 test 9 – check capacitor .................................46 test 10 – test dpe winding on brushless units ....................................47 ...
Page 5
Page 3 part 4 - dc control ......................................... 95 4.1 description and components .......................... 96 general ............................................................96 terminal strip / interconnection terminal .........96 circuit board ...............................
Page 6
Page 4 generator unit 8 kw 10 kw 12 kw 14 kw 16 kw 17 kw 20 kw rated max. Continuous power capacity (watts*) 7,000 ng 8,000 lp 9,000 ng 10,000 lp 12,000 ng 12,000 lp 13,000 ng 14,000 lp 16,000 ng 16,000 lp 16,000 ng 17,000 lp 18,000 ng 20,000 lp rated voltage 120/240 rated voltage at no-load (ng) 22...
Page 7
Specifications page 5 fuel consumption model # natural gas* lp vapor** 1/2 load full load 1/2 load full load 7/8 kw 77 140 0.94/34 1.68/62 9/10 kw 102 156 1.25/46 1.93/70 12/12 kw 152 215 1.53/56 2.08/76 13/14 kw 156 220 1.56/58 2.30/84 16/16 kw 183 261 1.59/58 2.51/91 16/17 kw 183 261 1.61/59 2.57/...
Page 8
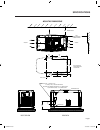
Page 6 specifications mounting dimensions air intake air outlet front of unit hole locations for optional mounting to a concrete pad minimum distance air intake front view left side view right side view rear view "do not lift by roof" grounding lug Ø30.2 [Ø1.2] lifting holes 4 corners cable access h...
Page 9
Page 7 specifications mounting dimensions air intake air outlet front of unit hole locations for optional mounting to a concrete pad minimum distance air intake front view left side view right side view rear view "do not lift by roof" grounding lug Ø30.2 [Ø1.2] lifting holes 4 corners cable access h...
Page 10
Specifications page 8 major features data label (see sample) oil dipstick exhaust enclosure composite base oil filter battery compartment fuel regulator fuel inlet (back) air filter circuit breaker control panel data label (see sample) oil dipstick exhaust enclosure composite base oil filter battery...
Page 11: Part 1
Part 1 general information air-cooled, automatic standby generators page 9 table of contents part title page 1.1 generator identification 10 1.2 installation basics 11 1.3 non-prepackaged interconnections 14 1.3 preparation before use 16 1.4 testing, cleaning and drying 18 1.5 engine-generator prote...
Page 12
Introduction this diagnostic repair manual has been prepared especially for the purpose of familiarizing service per- sonnel with the testing, troubleshooting and repair of air-cooled, automatic standby generators. Every effort has been expended to ensure that information and instructions in the man...
Page 13
Page 11 general information section 1.2 installation basics introduction information in this section is provided so that the service technician will have a basic knowledge of installation requirements for home standby systems. Problems that arise are often related to poor or unau- thorized installat...
Page 14
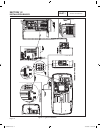
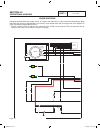
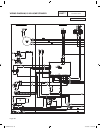
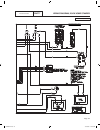
Part 1 page 12 general information section 1.2 installation basics figure 1. Typical installation 0g9266reva.Indd 12 10/15/2008 11:26:40 am.
Page 15
General information section 1.2 installation basics power source and load lines the utility power supply lines, the standby (genera- tor) supply lines, and electrical load lines must all be connected to the proper terminal lugs in the transfer switch. The following rules apply: in 1-phase systems wi...
Page 16
Page 14 part 1 general information section 1.3 non-prepackaged interconnections discussion: on the current model air-cooled generators wire 194 was changed to 15b. Wire 15b is still utilized for posi- tive voltage for the transfer relay and wire 23 is still the control ground for transferring the ge...
Page 17
General information section 1.3 non-prepackaged interconnections part 1 connect a 2008 and later load center switch to a pre-2008 air-cooled generator. Procedure: 1. Follow all instructions located in the installation manual that was supplied with the unit regarding mounting of the switch, junction ...
Page 18
General the installer must ensure that the home standby gen- erator has been properly installed. The system must be inspected carefully following installation. All appli- cable codes, standards and regulations pertaining to such installations must be strictly complied with. In addition, regulations ...
Page 19
General information section 1.4 preparation before use in the selector knob and pull out to overcome spring pressure and then twist clockwise 90 degrees and allow the selector to return in once aligned with the lp (liquid propane) position. 6. Save this tool with the owner's manual. 7. Install the b...
Page 20
Fuel selection lever - “out” position for liquid propane (vapor) fuel figure 5. 12/14/16/17/20 kw, gt-990/gt-999 (airbox cover removed) engine oil recommendations all oil should meet minimum american petroleum institute (api) service class sj, sl or better. Use no special additives. Select the oil's...
Page 21
Page 19 general information section 1.5 testing, cleaning and drying meters devices used to measure electrical properties are called meters. Meters are available that allow one to measure (a) ac voltage, (b) dc voltage, (c) ac frequency, and (d) resistance in ohms. The following apply: • tomeasureac...
Page 22
Part 1 measuring current clamp-on: to read the current flow, in amperes, a clamp-on ammeter may be used. This type of meter indicates current flow through a conductor by measuring the strength of the magnetic field around that conductor. The meter consists essentially of a current trans- former with...
Page 23
General information section 1.5 testing, cleaning and drying component testing may require a specific resis- tance value or a test for infinity or continuity. Infinity is an open condition between two electrical points, which would read as no resistance on a vom. Continuity is a closed condition bet...
Page 24
Part 1 visual inspection when it becomes necessary to test or troubleshoot a generator, it is a good practice to complete a thorough visual inspection. Remove the access covers and look closely for any obvious problems. Look for the following: • burned or broken wires, broken wire connectors, damage...
Page 25
General information section 1.5 testing, cleaning and drying part 1 hi-pot tester: a “hi-pot” tester is shown in figure 7. The model shown is only one of many that are commercially available. The tester shown is equipped with a voltage selector switch that permits the power supply voltage to be sele...
Page 26
Part 1 general information section 1.5 testing, cleaning and drying testing all stator windings to ground: 1. Disconnect stator output leads 11 and 44 from the generator main line circuit breaker. 2. Disconnect stator output leads 2 and 6 from the capacitor located on the end of the stator assembly....
Page 27
General information section 1.6 engine-generator protective devices general standby electric power generators will often run unattended for long periods of time. Such operating parameters as (a) battery voltage, (b) engine oil pres- sure, (c) engine temperature, (d) engine operating speed, and (e) e...
Page 28
Part 1 overcrank shutdown this feature prevents the generator from damaging itself when it continually attempts to start and another problem, such as no fuel supply, prevents it from start- ing. The unit will crank and rest for a preset time limit. Then, it will stop cranking, and the lcd screen or ...
Page 29
General information section 1.7 operating instructions part 1 page 27 control panel set exercise system ready low battery low oil pressure high oil temperature overspeed rpm sensor loss overcrank enter ecs 8 kw units 10-20 kw units figure 1. Generator control panel auto-off-manual switch: use this s...
Page 30
Part 1 page 28 general information section 1.7 operating instructions 10-20 kw – installation assistant: upon first power up of the generator, the display inter- face will begin an installation assistant. The assistant will prompt the user to set the minimum settings to operate. These settings are s...
Page 31
General information section 1.8 automatic operating parameters part 1 page 29 introduction when the generator is installed in conjunction with a transfer switch, either manual or automatic opera- tion is possible. Manual transfer and engine startup, as well as manual shutdown and re-transfer are cov...
Page 32
Part 1 general information section 1.8 automatic operating parameters page 30 load transfer the transfer of load when the generator is running is dependent upon the operating mode as follows: 1. Manual • willnottransfertogeneratorifutilityispresent. • willtransfertogeneratorifutilityfails(below65%of...
Page 33: Air-Cooled, Automatic
Page 31 air-cooled, automatic standby generators part 2 ac generators table of contents part title page# 2.1. Description and components 32 2.2 operational analysis 35 2.3 troubleshooting flow charts 37 2.4 diagnostic tests 41 2.1 description and components .......................... 32 introduction...
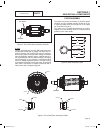
Page 34
"c" "b" "c" rotor "b" "c" 9 "d" "b" "c" "d" bearing carrier brush holder assembly engine adaptor "8kw" "8kw - 10kw" engine adaptor "10kw" 0.8 "d" "d" stator "12kw - 20kw" "12kw - 20kw" introduction the air-cooled, automatic standby system is an easy to install, fully enclosed and self-sufficient ele...
Page 35
Ac generators section 2.1 description & components part 2 page 33 slip rings bearing figure 2. The 2-pole rotor assembly 12-20 kw 8/10kw: like the 12-20 kw rotor, the 8/10 kw 2-pole rotor must be operated at 3600 rpm to supply a 60 hertz ac fre- quency. However, the 8/10kw rotor uses no slip rings. ...
Page 36
Brush holder and brushes (12-20 kw) the brush holder is retained to the rear bearing car- rier by means of two #10-32 x 9/16 taptite screws. A positive (+) and a negative (-) brush are retained in the brush holder, with the positive (+) brush riding on the slip ring nearest the rotor bearing. Wire 4...
Page 37
Page 35 ac generators section 2.2 operational analysis rotor residual magnetism the generator revolving field (rotor) may be consid- ered to be a permanent magnet. Some “residual” magnetism is always present in the rotor. This residual magnetism is sufficient to induce a voltage into the stator ac p...
Page 38
Part 2 operation (8/10 kw) startup: when the engine is started, residual magnetism from the rotor induces a voltage into (a) the stator ac power windings, and (b) the stator excitation or dpe windings. The capacitor on the dpe winding will be charged and then will discharge causing a voltage to be i...
Page 39
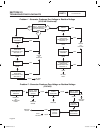
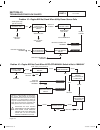
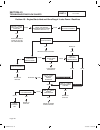
Ac generators section 2.3 troubleshooting flowcharts use the “flow charts” in conjunction with the detailed instructions in section 2.4. Test numbers used in the flow charts correspond to the numbered tests in section 2.4. The first step in using the flow charts is to correctly identify the problem....
Page 40
Page 38 stop testing good replace bad replace stator replace stator replace rotor test 1 - check main circuit breaker test 8 - test brushless stator test 9 - check capacitor replace capacitor test 10 - test dpe winding test 21 - field flash alternator test 2 - check ac output voltage bad bad good on...
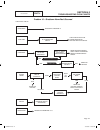
Page 41
Ac generators section 2.3 troubleshooting flowcharts part 2 page 39 stop tests frequency o.K., but voltage low test 14 - check ac output frequency test 15 - adjust engine governor test 16 - check stepper motor control test 2 - check ac output voltage test 17 - adjust voltage regulator test 9 - check...
Page 42
Part 2 page 40 ac generators section 2.3 troubleshooting flowcharts good good repair or replace if reconfigured to lp gas, verify that proper procedure was followed (refer to section 1.3) test 18 - check voltage and frequency under load test 19 - check for overload condition test 15 - check and adju...
Page 43
Ac generators section 2.4 diagnostic tests introduction this section is provided to familiarize the service technician with acceptable procedures for the test- ing and evaluation of various problems that could be encountered on standby generators with air-cooled engine. Use this section of the manua...
Page 44
* danger: use extreme caution during this test. The generator will be running. High and dangerous voltages will be present at the test terminals. Connect meter test clamps to the high voltage terminals while the generator is shut down. Stay clear of power terminals during the test. Make sure meter c...
Page 45
Ac generators section 2.4 diagnostic tests connect the other meter test lead to wire 4 (still dis- connected from previous tests). Measure and record static rotor amp draw. 13. Set the auto-off-manual switch to the manual position. Once the engine starts, repeat step 12. Measure and record running r...
Page 46
Test 6 – check field boost (12-20 kw) discussion: see “field boost circuit” in section 2.2. Field boost current (from the circuit board) is available to the rotor only while the engine is cranking. Loss of field boost output to the rotor may or may not affect power winding ac output voltage. The fol...
Page 47
Ac generators section 2.4 diagnostic tests 5. Turn the main breaker to the "on" or closed position. 6. Set a vom to measure resistance. 7. Connect one meter test lead to wire 11 on the load side of the main breaker. Connect the other meter test lead to wire 22 (power winding). Note the resistance re...
Page 48
• anopencircuitcondition • a“short-to-ground”condition • ashortcircuitbetweenwindings note: the resistance of stator windings is very low. Some meters will not read such a low resistance, and will simply indicate continuity. Recommended is a high quality, digital type meter capable of read- ing very...
Page 49
Ac generators section 2.4 diagnostic tests procedure: 1. Consult the owner’s manual of the meter being used for directions on measuring capacitance. Figure 7 shows a typical meter and how to check capacitance. 2. Connect the meter leads directly across the terminals of the capacitor. The rated µf (m...
Page 50
2. Testing for a “grounded” condition: any resistance reading indicated the winding is grounded. 3. Testing for a “shorted” condition: any resistance reading indicated the winding is shorted. 4. If stator tests good and wire continuity tests good, refer back to flow chart. Test 11 – resistance check...
Page 51
Ac generators section 2.4 diagnostic tests results: 1. Repair, replace or reconnect wires as necessary. 2. Replace any damaged slip rings or brush holder. 3. Clean and polish slip rings as required. Test 13 – test rotor assembly (12-20 kw) discussion: a rotor having completely open windings will cau...
Page 52
Part 2 governor shaft primary adjust screw governor clamp bolt secondary adjust screw figure 10. Engine governor adjustment single cylinder engines procedure (8 kw units with dual governor springs): 1. Loosen the governor clamp bolt (figure 10). 2. Hold the governor lever at its wide open throttle p...
Page 53
Stepper motor pull arm this direction to close throttle figure 11. Throttle positions 9/10 kw units stepper motor stepper motor arm pull arm this direction to close throttle figure 12. Throttle positions 9/10 kw units stepper motor stepper motor arm pull arm this direction to close throttle figure 1...
Page 54
Test 18 – check voltage and frequency under load discussion: it is possible for the generator ac output frequency and voltage to be good at no-load, but they may drop excessively when electrical loads are applied. This condition, in which voltage and frequency drop exces- sively when loads are appli...
Page 55
Page 53 figure 18. Energizing cord connection figure 17. Construction of energizing cord generator capacitor wires 2 & 6 to dpe winding depress switch for one second plug energizing cord into ac outlet capicitor remains connected to generator danger: the capacitor may need to be dis- charged before ...
Page 56
Page 54 notes 0g9266reva.Indd 54 10/15/2008 11:27:21 am.
Page 57: Part 3
Part 3 transfer switch air-cooled, automatic standby generators page 55 3.1 description and components ...............................................56 general 5 6 enclosure ............................................................................ 56 transfer mechanism .............................
Page 58
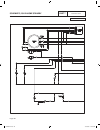
General the “w/v-type” transfer switch is rated 100 amps at 250 volts maximum. It is available in 2-pole configura- tion only and, for that reason, is usable with 1-phase systems only. Transfer switches do not have an intelligence sys- tem of their own. Instead, automatic operation of these transfer...
Page 59
Transfer switch section 3.1 description & components part 3 page 57 transfer mechanism the 2-pole transfer mechanism consists of a pair of moveable load contacts, a pair of stationary utility contacts, and a pair of stationary standby contacts. The load contacts can be connected to the utility conta...
Page 60
C. When de-energized, the relay’s normally open contacts are open and its normally-closed contacts are closed. D. The normally-closed relay contacts will deliver utility source power to the utility closing circuit of the transfer mechanism. E. The normally open relay contacts will deliver standby so...
Page 61
Transfer switch section 3.1 description & components part 3 page 59 terminals 0, 15b and 23: these terminals connect the transfer relay to the generator circuit board. See “transfer relay” in section 3.1. Fuse holder the fuse holder holds three (3) fuses, designated as fuses f1, f2 and f3. Each fuse...
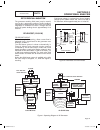
Page 62
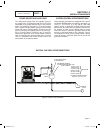
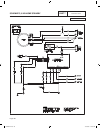
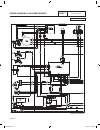
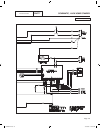
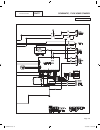
Operational analysis figure 1 is a schematic for a typical “w/v-type” transfer switch. Figure 1. Schematic page 60 neutral connection switch sw3 no c1 com sw2 vr1 nc nc com c2 vr2 no tr1 15b 23 1 7 4 7 9 3 6 9 f2 circuit 10 black (main 1) control transfer red (main 2) neutral (white) neutral (white)...
Page 63
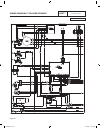
Transfer switch section 3.2 operational analysis part 3 page 61 figure 2 is a wiring diagram for a typical “w/v-type” transfer switch. Figure 2. Wiring diagram 205 n2a n1a red blk 10 circuit load center 12 circuit load center 14 circuit load center circuit 8 8 circuit load center circuit 1 circuit 3...
Page 64
Neutral connection switch sw3 no c1 com sw2 vr1 nc nc com c2 vr2 no tr1 15b 23 1 7 4 7 9 3 6 9 f2 circuit 10 black (main 1) control transfer red (main 2) neutral (white) neutral (white) 23 0 f1 n2 n1 15b 23 black red n2 n1 15b 240vac to to generator output panel main distribution t1 t2 t1 t2 e2 e2 e...
Page 65
Neutral connection switch sw3 no c1 com sw2 vr1 nc nc com c2 vr2 no tr1 15b 23 1 7 4 7 9 3 6 9 f2 circuit 10 black (main 1) control transfer red (main 2) neutral (white) neutral (white) 23 0 f1 n2 n1 15b 23 black red n2 n1 15b 240vac to to generator output panel main distribution t1 t2 t1 t2 e2 e2 e...
Page 66
Transfer to standby 12 vdc is delivered to the transfer relay via wire 15b and back to the circuit board via wire 23. However, circuit board action holds the wire 23 circuit open and the transfer relay remains de-energized. On generator startup, an “engine warm-up timer” on the generator circuit boa...
Page 67
Transfer to standby when the standby coil is energized it pulls the transfer switch mechanism to a overcenter position towards the standby power source side, the transfer switch mechanically snaps to the standby position. On closure of the main contacts to the standby power source side, limit switch...
Page 68
Utility restored utility voltage is restored and is available to terminals n1 and n2. The utility voltage is sensed by the generators circuit board. If it is above a preset value for a preset time interval a transfer back to utility power will occur. Page 66 neutral connection switch sw3 no c1 com s...
Page 69
Utility restored, transfer switch de-energized after the preset time interval expires the circuit board will open the wire 23 circuit to ground. The transfer relay de-energizes, it’s normally closed contacts close, and utility source voltage is delivered to the utility closing coil (c1), via wires n...
Page 70
Utility restored, retransfer back to utility as the utility coil pulls the transfer switch to an over center position, the switch mechanically snaps to utility. On closure of the main contacts to the utility power source side, limit switches sw2 and sw3 are mechanically actuated to “arm” the circuit...
Page 71
Transfer switch in utility when the transfer switch returns to the utility side, generator shutdown occurs after approximately one (1) minute. Page 69 transfer switch section 3.2 operational analysis part 3 neutral connection switch sw3 no c1 com sw2 vr1 nc nc com c2 vr2 no tr1 15b 23 1 7 4 7 9 3 6 ...
Page 72
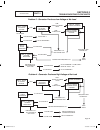
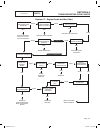
Introduction to troubleshooting the first step in troubleshooting is to correctly identify the problem. Once that is done, the cause of the an be found by performing the tests in the appropriate flow chart. Test numbers assigned in the flow charts are identical to test numbers in section 3.4, “diagn...
Page 73
Transfer switch section 3.3 troubleshooting flow charts part 3 page 71 problem 8 – in automatic mode, generator starts when loss of utility occurs, generator shuts down when utility returns but there is no retransfer to utility power or generator transfers to standby during excercise or in manual mo...
Page 74
Replace circuit board correct utility source voltage replace go to problem 7 repair or replace wiring repair or replace wire n1a/n2a between n1/n2 lugs and fuse holder repair n1/n2 open wiring between transfer switch and generator problem 10 – unit starts and transfer occurs when utility power is on...
Page 75
Replace printed circuit board repair or replace replace charger problem 11 – no battery charge “pre-wire load center” test 40 – check battery charger supply voltage test 41 – check battery charger output voltage test 42 – check wire 0/15b good good bad repair or replace bad bad no battery supply vol...
Page 76
General test numbers in this section correspond to the numbered tests in section 3.3, “troubleshooting flow charts”. When troubleshooting, first identify the problem. Then, perform the diagnostic tests in the sequence given in the flow charts. Test 26 – check voltage at terminal lugs e1, e2 discussi...
Page 77
Transfer switch section 3.4 diagnostic tests part 3 page 75 e. Set the generator auto-off-manual switch to auto. (1) the generator should crank and start. (2) when the generator starts, an “engine warm-up timer” should start timing. After about 15 seconds, the transfer relay should energize and tran...
Page 78
B. Actuate the operating lever down to move the load contacts against the standby contacts, i.E., load connected to the standby source. 6. Repeat step 5 several times. As the transfer switch operating lever is moved slight force should be needed until the lever reaches its center position. As the le...
Page 79
Transfer switch section 3.4 diagnostic tests part 3 page 77 13. Set vom to measure dc voltage. 14. Connect the (-) negative meter test lead to wire 0 at the terminal strip in the generator. Connect the (+) positive meter test lead to wire 23 at the terminal strip in the generator. 12 vdc should be m...
Page 80
4. Using jumper wires, connect the positive (+) post of a 12 volt battery to relay terminal “a” and the negative (-) battery post to relay terminal “b”. The relay should energize and the vom should read continuity. 5. Now, connect the vom test leads across relay terminals 1 and 7. A. Energize the re...
Page 81
Transfer switch section 3.4 diagnostic tests part 3 page 79 a b 7 9 4 6 1 3 tr1 sw1 205 c2 sw3 e1 sw2 c1 1 2 1 2 n1 n2 e1 e2 e2 t1 t2 b a g e f c d h figure 4. Standby control circuit test points 0g9266reva.Indd 79 10/15/2008 11:27:32 am.
Page 82
(2) press the right arrow key until “debug” is flashing. (3) press “enter”. (4) press the right arrow key until “outputs” is flashing. (5) press “enter”. (6) digital output 8 is wire 23 output from the board. Refer to figure 5. (7) if output 8 shows a “1” then the control board is grounding wire 23....
Page 83
Figure 7. Utility control circuit test points transfer switch section 3.4 diagnostic tests part 3 page 81 n1a n1a a b 7 9 4 6 1 3 tr1 sw1 b c2 sw3 sw2 c1 a n2a n2a f1 f2 f3 a a a b b b 1 2 1 2 n1 n2 e1 e2 t1 t2 126 a b i g c d e f h 0g9266reva.Indd 81 10/15/2008 11:27:33 am.
Page 84
5. Remove wire n2a from the utility coil c1. 6. Turn on utility power supply to the transfer switch. A. If transfer to utility occurs, wire 23 is grounded. Proceed to test 31. B. If transfer to utility does not occur, proceed to step 7. 7. Measure across points a and b. 240 vac should be measured. A...
Page 85
Procedure: 1. On the generator panel, set the auto-off-manual switch to off. 2. Turn off the utility power supply to the transfer switch, using whatever means provided. 3. Remove fuses f1 and f2 from the fuse holder (see figure 8). 4. Inspect and test fuses for blown condition. With a vom set to mea...
Page 86
240 vac n1 n2 test points figure 9. Terminal block test points test 37 – check utility sensing voltage at the circuit board discussion: if the generator starts and transfer to standby occurs in the automatic mode when acceptable utility source voltage is available at the terminal block, the next ste...
Page 87
Section x.X xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx page 85 transfer switch section 3.4 diagnostic tests part 3 23 tb1 a n lc b legend transfer switch generator lc-circuit breaker (loads) (16 circuit shown for reference only) sw1-automatic transfer switch c2-generator coil & rectifier c1-utility coil & rectifie...
Page 88
2. Test for utility source line-to-line voltage across terminal lugs n1 and n2 (see figure 1). Normal utility source voltage should be indicated. Results: 1. If low or no voltage is indicated, find the cause of the problem and correct. 2. If normal utility source voltage is indicated, refer to flow ...
Page 89
Page 87 transfer switch section 3.4 diagnostic tests part 3 a. If 115 ohms is measured, proceed to step 10. B. If zero resistance or continuity is measured, connect the meter test leads across terminals a and b on the transfer relay (tr1) c. If zero resistance is measured, a short exists. Replace tr...
Page 90
Page 88 e2 white green 23 15b 0 n1 det ail det ail n2 bc 00 bc line e1 n2 n1 15b 23 n1 n2 23 194 utility suppl y fr om ser vice disconnect e2 t o gr ounding electr ode neutral block (distrib ution p anel) gr ound bc line bc 00 5 amp fuse t1 t2 cust omer lo ad r ts transfer switch t1 t2 e1 (c2 & vr2)...
Page 91
Page 89 transfer switch section 3.4 diagnostic tests part 3 white green 0 n1 n2 15b 23 bc 00 bc line t o gr ounding electr ode ser vice disconnect a ts 23 e1 e2 bc line bc 00 fuse n2 n1 5 amp socket meter utility p anelbo ard 15b t1 t2 e1 e2 n2 n1 c d e a b h g f det ail det ail 23 15b 0 n1 n2 h g f...
Page 92
Page 90 6. Measure across points g and h on the terminal strip. 12 vdc should be measured. A. If 12 vdc is measured, proceed to step 8. B. If 12 vdc is not measured, proceed to step 7. 7. Measure across point h and ground lug. 12 vdc should be measured. A. If 12 vdc is measured, repair or replace wi...
Page 93
Page 91 transfer switch section 3.4 diagnostic tests part 3 connection p anel bc-line gen-read y lo ad center duplex breaker bc-00 utility socket meter engine genera t or n1 white green bc 00 n2 15b 23 0 e1 e2 bc line c d e a b f det ail det ail det ail det ail bc 00 bc line n1 n2 15b 23 0 e f c d f...
Page 94
3. Measure across points g and h on the terminal strip. 12vdc should be measured. A. If 12 vdc is measured, the charger should be functioning. B. If 12 vdc is not measured, proceed to step 4. 4. Remove wire 0 and wire 15b from generator terminal strip locations e and f. 5. Wait five (5) minutes afte...
Page 95
Page 93 transfer switch section 3.4 diagnostic tests part 3 fuse, 2a f3 gr ound lug limit switches , a ctu a t or rela y , transfer utility circuit breaker nb - neutral block lo ad shed contr oller rela y , lo ad shed lo ad shed transfer switch cont a ct or xa1,xb1 tr ucb gnd ls lsc lss nb solenoid ...
Page 96
Page 94 4. Reconnect battery charger black and red lead wires previously removed in step 2. 5. Measure across points g and h. 13.4 vdc should be measured. A. If 13.4 vdc is not measured, replace the battery charger. B. If 13.4 vdc is measured, the charger is working. *note: battery charger voltage w...
Page 97: Part 4
Part 4 dc control air-cooled, automatic standby generators page 95 4.1 description and components ....................................96 general ................................................................... 96 terminal strip / interconnection terminal ................. 96 circuit board ..........
Page 98
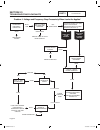
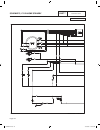
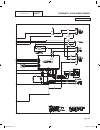
General this section will familiarize the reader with the various components that make up the dc control system. Major dc control system components that will be covered include the following: • aterminalstrip/interconnectionterminal • acircuitboard. • anauto-off-manualswitch. • a7.5ampfuse. Terminal...
Page 99
Divider panel divider panel to engine to engine 6 7 9 8 3 5 4 1 2 10 1. Control panel 2. 7.5 amp fuse 3. Starter contactor relay (10-20 kw) 4. 4 position terminal block 5. Terminal block 6. Circuit breaker (8kw) 7. 15 amp gfci duplex outlet (17 & 20 kw) 8. Circuit breaker (17 & 20 kw) 9. Circuit bre...
Page 100
Pin wire circuit function j1-1 85 high temperature shutdown: shutdown occurs when wire 85 is grounded by contact closure in hto j1-2 86 low oil pressure shutdown: shutdown occurs when wire 86 is grounded by loss of oil pressure to the lop j1-3 13 12 vdc source voltage for the circuit board j1-4 18 i...
Page 101
Dc control section 4.1 description and components part 4 pin wire circuit function j1-1 85 high temperature shutdown: shutdown occurs when wire 85 is grounded by contact closure in hto j1-2 86 low oil pressure shutdown: shutdown occurs when wire 86 is grounded by loss of oil pressure to the lop j1-3...
Page 102
Page 100 j2 j3 (stepper motor) remote wireless connection j1 j2 connector (harness end) 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 1 2 3 4 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 1 2 3 4 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 1 2 3 4 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 j1 connector (harness end) j2 connector (pcb end) j1 ...
Page 103
Page 101 section 4.1 description and components pin wire circuit function j1-1 85 high temperature shutdown: shutdown occurs when wire 85 is grounded by contact closure in hto j1-2 86 low oil pressure shutdown: shutdown occurs when wire 86 is grounded by loss of oil pressure to the lop j1-3 13 12 vd...
Page 104
Part 4 page 102 dc control section 4.1 description and components female side male side 2 1 1 2 c3 figure 8. Choke solenoid connector pin number identification menu system navigation to get to the menu, use the "esc" key from any page. It may need to be pressed many times before getting to the menu ...
Page 105: Menu System
Section 4.1 description and components page 103 main menu run log alarm log hist or y st atus command st at e versions displa y genera tor freq uency engine hours engine rpm ba tter y vo lt ag e deb ug inputs outputs displa ys st ar tup dela y edit contrast langu age freq uency time/d ate exercise t...
Page 106
Controller display ready to run = 12 vdc always present = ac voltage = ground for control purposes = 12 vdc during cranking only = 12 vdc during engine run condition = dc field excitation = 5 vdc to led 0 4 4 0 ba 6 11 22 6 2 2 regulator 11 2 6 0 4 22 voltage 4 0 0 13 13 18 sp2 im2 16 13 scr 0 0 86 ...
Page 107
Controller display ready to run = 12 vdc always present = ac voltage = ground for control purposes = 12 vdc during cranking only = 12 vdc during engine run condition = dc field excitation = 5 vdc to led 0 4 4 0 ba 6 11 22 6 2 2 regulator 11 2 6 0 4 22 voltage 4 0 0 13 13 18 sp2 im2 16 13 scr 0 0 86 ...
Page 108
Controller display utility loss delay pausing 10 sec controller = 12 vdc always present = ac voltage = ground for control purposes = 12 vdc during cranking only = 12 vdc during engine run condition = dc field excitation = 5 vdc to led 0 4 4 0 ba 6 11 22 6 2 2 regulator 11 2 6 0 4 22 voltage 4 0 0 13...
Page 109
Controller display utility loss delay pausing 10 sec controller = 12 vdc always present = ac voltage = ground for control purposes = 12 vdc during cranking only = 12 vdc during engine run condition = dc field excitation = 5 vdc to led 0 4 4 0 ba 6 11 22 6 2 2 regulator 11 2 6 0 4 22 voltage 4 0 0 13...
Page 110
Controller display cranking attempt #1 = 12 vdc always present = ac voltage = ground for control purposes = 12 vdc during cranking only = 12 vdc during engine run condition = dc field excitation = 5 vdc to led 0 4 4 0 ba 6 11 22 6 2 2 regulator 11 2 6 0 4 22 voltage 4 0 0 13 13 18 sp2 im2 16 13 scr ...
Page 111
Controller display cranking attempt #1 = 12 vdc always present = ac voltage = ground for control purposes = 12 vdc during cranking only = 12 vdc during engine run condition = dc field excitation = 5 vdc to led 0 4 4 0 ba 6 11 22 6 2 2 regulator 11 2 6 0 4 22 voltage 4 0 0 13 13 18 sp2 im2 16 13 scr ...
Page 112
Controller display running - utility lost = 12 vdc always present = ac voltage = ground for control purposes = 12 vdc during cranking only = 12 vdc during engine run condition = dc field excitation = 5 vdc to led 0 4 4 0 ba 6 11 22 6 2 2 regulator 11 2 6 0 4 22 voltage 4 0 0 13 13 18 sp2 im2 16 13 s...
Page 113
Controller display running - utility lost = 12 vdc always present = ac voltage = ground for control purposes = 12 vdc during cranking only = 12 vdc during engine run condition = dc field excitation = 5 vdc to led 0 4 4 0 ba 6 11 22 6 2 2 regulator 11 2 6 0 4 22 voltage 4 0 0 13 13 18 sp2 im2 16 13 s...
Page 114
Controller display running - utility lost controller = 12 vdc always present = ac voltage = ground for control purposes = 12 vdc during cranking only = 12 vdc during engine run condition = dc field excitation = 5 vdc to led 0 4 4 0 ba 6 11 22 6 2 2 regulator 11 2 6 0 4 22 voltage 4 0 0 13 13 18 sp2 ...
Page 115
Controller display running - utility lost controller = 12 vdc always present = ac voltage = ground for control purposes = 12 vdc during cranking only = 12 vdc during engine run condition = dc field excitation = 5 vdc to led 0 4 4 0 ba 6 11 22 6 2 2 regulator 11 2 6 0 4 22 voltage 4 0 0 13 13 18 sp2 ...
Page 116
Controller display running / cooling down = 12 vdc always present = ac voltage = ground for control purposes = 12 vdc during cranking only = 12 vdc during engine run condition = dc field excitation = 5 vdc to led 0 4 4 0 ba 6 11 22 6 2 2 regulator 11 2 6 0 4 22 voltage 4 0 0 13 13 18 sp2 im2 16 13 s...
Page 117
• the utility closing coil (c1) energizes and moves the main current carrying contacts to their neutral position. The main contacts move to an over center position past neutral and spring force closes them to their utility side. Load terminals are now powered by the utility source. • movementofthema...
Page 118
Controller display ready to run = 12 vdc always present = ac voltage = ground for control purposes = 12 vdc during cranking only = 12 vdc during engine run condition = dc field excitation = 5 vdc to led 0 4 4 0 ba 6 11 22 6 2 2 regulator 11 2 6 0 4 22 voltage 4 0 0 13 13 18 sp2 im2 16 13 scr 0 0 86 ...
Page 119
Controller display ready to run = 12 vdc always present = ac voltage = ground for control purposes = 12 vdc during cranking only = 12 vdc during engine run condition = dc field excitation = 5 vdc to led 0 4 4 0 ba 6 11 22 6 2 2 regulator 11 2 6 0 4 22 voltage 4 0 0 13 13 18 sp2 im2 16 13 scr 0 0 86 ...
Page 120
Verify utility source is “off”* test 56 – check position of auto-off-manual switch test 58 – test auto-off-manual switch test 59 – check auto operation of controller test 57 – try a manual start on off switch is “off” switch is in “auto” engine does not crank engine cranks bad bad set to “auto” - re...
Page 121
Page 119 section 4.3 troubleshooting flow charts bad replace choke solenoid clean, regap or replace replace circuit board replace fuel solenoid test 66 – check fuel supply and pressure replace fuel regulator test 70 – check for ignition spark test 69 – check choke solenoid test 74 – check ignition m...
Page 122
Page 120 good bad good good good readjust refer to engine service manual repair or replace adjust or replace clean, regap or replace find and correct cause of no fuel or low pressure readjust test 78 – check fuel regulator good good good good bad bad bad bad bad bad bad problem 18 – engine starts ha...
Page 123
Section 4.3 troubleshooting flow charts page 121 bad no signal repair or replace bad proceed to problem 16 proceed to problems 10-13 check installation for proper airflow or replace defective switch repair linkage if binding. Check throttle operation. Refer to engine service manual test 15 – check a...
Page 124
Part 4 page 122 dc control section 4.3 troubleshooting flow charts fuse blows when placed in “auto” or “manual” problem 20 – 7.5 amp fuse (f1) blown test 80 – check cranking and running circuits problem 21 – generator will not exercise test 79 – test exercise function good bad problem 22 – no low sp...
Page 125
Page 123 section 4.4 diagnostic tests introduction perform these “diagnostic tests” in conjunction with the “troubleshooting flow charts” of section 4.3. The test procedures and methods presented in this section are not exhaustive. The manufacturer could not possibly know of, evaluate and advise the...
Page 126
Page 124 input 7 input 8 debug 1 2 3 inputs figure 2. The home page, debug and input screens 5. With the inputs screen displayed place the auto-off- manual switch to the manual position. If the control- ler reads an input from the switch input 8 will change from “0” to “1”. 6. With the auto-off-manu...
Page 127
Section 4.4 diagnostic tests page 125 b. Pe r fo r m a l o a d t e s t o n t h e b a t t e r y : (maintenance free battery) 1. Using a lead acid battery load tester test the load capability of the battery. 2. Follow the load tester’s manufacturer’s instructions carefully. Figure 3. A typical battery...
Page 128
Page 126 test 62 – check wire 56 voltage discussion: during an automatic start or when starting manually, a crank relay on the circuit board should energize. Each time the crank relay energizes, the circuit board should deliver 12 vdc to a starter contactor relay (scr), or starter contactor (sc), an...
Page 129
Section 4.4 diagnostic tests page 127 procedure: 1. Set a vom to measure dc voltage. 2. Remove wire 13 from the starter contactor relay located under the printed circuit board. 3. Connect the positive (+) meter test lead to the wire 13 connector. Connect the negative (-) meter test lead to a clean f...
Page 130
Page 128 test 65 – test starter motor conditions affecting starter motor performance: 1. A binding or seizing condition in the starter motor bearings. 2. A shorted, open or grounded armature. A. Shorted armature (wire insulation worn and wires touching one another). Will be indicated by low or no rp...
Page 131
Section 4.4 diagnostic tests page 129 pinion figure 13. Check pinion gear operation (single cylinder) tools for starter performance test: the following equipment may be used to complete a performance test of the starter motor: • aclamp-onammeter. • atachometercapableofreadingupto10,000rpm. • afullyc...
Page 132
Page 130 starter contactor starter motor tachometer 12 volt battery clamp on amp meter vise figure 17. Testing starter motor performance test 66 – check fuel supply and pressure discussion: the air-cooled generator was factory tested and adjusted using natural gas as a fuel. If desired, lp (propane)...
Page 133
Section 4.4 diagnostic tests page 131 port 3 port 1 port 2 figure 20 (12-20 kw) gas pressure test point note: where a primary regulator is used to estab- lish fuel inlet pressure, adjustment of that regula- tor is usually the responsibility of the fuel supplier or the fuel supply system installer. 1...
Page 134
Page 132 i. Set a vom to measure resistance. J. Connect one meter test lead to wire 14 that was disconnected in step 3. K. Connect the other meter test lead to wire 14 at j2-3. See figures on pages 92-95. L. C o n t i n u i t y s h o u l d b e m e a s u r e d . I f continuity is measured, repeat ste...
Page 135
Section 4.4 diagnostic tests page 133 choke solenoid choke plate figure 22. Solenoid de-energized, choke closed 12-20 kw units choke solenoid choke plate figure 23. Solenoid energized, choke open 12-20 kw units 3. Set a vom to measure dc voltage. 4. Connect the positive (+) test lead to wire 14 (pin...
Page 136
Page 134 2. Disconnect the c3 connector. 3. Set a vom to measure dc voltage. 4. Connect the positive (+) test lead to wire 56 (pin 1) of c3 connector going to the control panel (female side) connect the negative (-) test lead to wire 0 (pin 2). 5. Set the auto-off-manual switch to manual. While cran...
Page 137
Section 4.4 diagnostic tests page 135 figure 27. Spark tester figure 28. Checking ignition spark to determine if an engine miss is ignition related, connect the spark tester in series with the spark plug wire and the spark plug (figure 29). Then, crank and start the engine. A spark miss will be read...
Page 138
Page 136 figure 29. Checking engine miss results: 1. If no spark or very weak spark occurs, go to test 73. 2. If sparking occurs but engine still won’t start, go to test 71. 3. When checking for engine miss, if sparking occurs at regular intervals but engine miss continues, go to test 20. 4. When ch...
Page 139
Section 4.4 diagnostic tests page 137 discussion: the cylinder leak down tester checks the sealing (compression) ability of the engine by measuring air leakage from the combustion chamber. Compression loss can present many different symptoms. This test is designed to detect the section of the engine...
Page 140
Page 138 wire 18 connection figure 32. Wire 18 connection 10-20 kw units 2. Depending on engine type, do the following: a. On v-twin units, remove wire 56 from the starter contactor relay (scr). Using a jumper lead, jump 12 vdc from wire 15b at tb1 (customer connection) to the terminal on the scr fr...
Page 141
Section 4.4 diagnostic tests page 139 procedure, adjusting magneto flywheel gap: note: the air gap between the ignition magneto and the flywheel on single cylinder engines is not adjustable. Proceed directly to step 10 for single cylinder engines. For v-twin engines, proceed as follows. 1. See figur...
Page 142
Page 140 results: if sparking still does not occur after adjusting the armature air gap, testing the ground wires and performing the basic flywheel test, replace the ignition magneto(s). Procedure, replacing magnetos: 1. Follow all steps of the major disassembly procedures that are located in sectio...
Page 143
Section 4.4 diagnostic tests page 141 test 75 – check oil pressure switch and wire 86 discussion: if the oil pressure switch contacts have failed in their closed position, the engine will probably crank and start. However, shutdown will then occur within about 5 (five) seconds. If the engine cranks ...
Page 144
Page 142 a. Disconnect the j1 connector from the printed circuit board. B. Connect one test lead to wire 86 (disconnected from lop). Connect the other test lead to pin location 4 (wire 86) of the j1 connector at the circuit board (for all models). Continuity should be measured. If continuity is not ...
Page 145
Section 4.4 diagnostic tests page 143 procedure: (intake and exhaust) make sure that the piston is at top dead center (tdc) of it’s compression stroke (both valves closed). The valve clearance should be 0.05-0.1mm (0.002-0.004 in.) cold. Check and adjust the valve to rocker arm clearance as follows:...
Page 146
Page 144 10. Connect one meter test lead to wire 18 removed from the stud connector. Connect the other meter test lead to a clean frame ground. Infinity should be measured. If continuity is measured, repair or replace wire 18 between the stud connector and the j1 connector. Results: refer to flow ch...
Page 147
Procedure: 1. Set a vom to measure resistance. 2. Disconnect the j2 connector from the controller. 3. Connect one meter test lead to the ground terminal. Connect the other meter test lead to each of the follow- ing j2 connector pin locations. J2-11 wire 56 8kw if continuity was measured, go to step ...
Page 148
D. If coil resistance was measured in cs and fs, and fs2 wire 14 is shorted to ground between j2 connector and cs, fs, or fs2, repair or replace the shorted wire. 8. Disconnect wire 14 from the fuel solenoid (fs) and choke solenoid (cs). A. Connect one meter test lead to the fs terminal from which w...
Page 149: Part 5
Part 5 operational tests air-cooled, automatic standby generators page 147 table of contents part title 5.1. System functional tests 5.1 system functional tests ................................ 148 introduction ....................................................148 manual transfer switch operation ...
Page 150
Introduction following home standby electric system installation and periodically thereafter, the system should be tested functional tests of the system include the following: • manualtransferswitchoperation. • systemvoltagetests. • generatortestsunderload. • testingautomaticoperation. Before procee...
Page 151
Operational tests and adjustments section 5.1 system functional tests part 5 page 149 danger + the transfer switch is now electri- cally “hot”, contact with “hot” parts will result in extremely hazardous and possibly fatal electrical shock. Proceed with caution. 5. Use an accurate ac voltmeter to ch...
Page 152
11. Let the generator run at full rated load for 20-30 minutes. Listen for unusual noises, vibration or other indications of abnormal operation. Check for oil leaks, evidence of overheating, etc. 12. When testing under load is complete, turn off electrical loads. 13. Set the generator main circuit b...
Page 153: Part 6
Part 6 disassembly air-cooled, automatic standby generators page 151 table of contents part title 6.1. Major disassembly 6.1 major disassembly ........................................ 152 front engine access ......................................152 major disassembly ...................................
Page 154
Front engine access safety: 1. Set the auto-off-manual switch to off. 2. Remove the 7.5 amp main fuse. See figure 1. 3. Remove the n1 and n2 fuse from the transfer switch. Figure 1. Remove 7.5 amp fuse 4. Turn off fuel supply to the generator and remove the flex- line from the fuel regulator. 5. Rem...
Page 155
Disassembly section 6.1 major disassembly part 6 page 153 4. Remove stator wires: remove all wires from the voltage regulator, remove the neutral and ground wires from landing lugs, and remove n1 & n2 wires from main bea- kers. See figure 5. 5. Remove control wires: remove wires #n1,#n2, #0, #15b, #...
Page 156
8. Loosen side panel: using a 10mm socket remove the two bolts from the base of the enclosure side panel. See figure 10. 9. Unbolt enclosure side panel mounting bracket: using a 10mm socket remove the two bolts from the enclosure side panel mounting bracket. See figure 11. Figure 10. Figure 11. 10. ...
Page 157
Figure 14. 12. Remove air box: using a 6mm allen wrench remove the four intake manifold socket head cap screws. See figure 15. Using a 4mm allen wrench, remove the four airbox allen head shoulder bolts. While removing the airbox remove the four rubber washers. See figure 16. Figure 15. Figure 16. 13...
Page 158
Page 156 part 6 disassembly section 6.1 major disassembly 14. Remove blower housing: using a 4mm allen wrench remove one button head cap screw from top of blower housing. Using a 10mm socket remove one 10mm bolt from the top of the blower housing. See figure 19. Using a 10mm socket remove four 10mm ...
Page 159
Stator/rotor/engine removal: 1. Remove top exhaust enclosure covers: using a 10mm socket, remove the nine bolts from the exhaust top cov- ers. Remove covers. See figure 23. Figure 23. 2. Remove side exhaust enclosure cover: using a 10mm socket, remove the five bolts from the exhaust side cover. Remo...
Page 160
Figure 27. 6. Remove left-side enclosure: using a 10mm ratchet wrench remove the horizontal 10mm bolt that connects the side panel to the back panel. Using a 10mm socket, remove three bolts from the base of the enclosure. See figure 28. Using a 10mm socket and wrench remove the top hinge bolt and lo...
Page 161
Figure 31. 9. Remove fan: attach a steering wheel puller to the fan using two m8 x 1.25 bolts. Remove the fan from the rotor. Figure 32. Figure 32. 10. Remove brushes: using a 7mm socket remove brushes. See figure 33. Figure 33. 11. Remove alternator divider panel: using a 10mm socket remove two bot...
Page 162
12. Remove brush wires: using a side cutters remove the tie wraps securing the brush wires to the outside of sta- tor. See figure 35. Figure 35. 13. Remove controls cover: using a torx t-27 socket remove two bolts and ground washer from the controls cover. Remove the controls cover. See figure 36. F...
Page 163
Figure 39. Figure 40. Figure 41. 17. Rotor removal: cut 2.5 inches from the rotor bolt. Slot the end of the bolt to suit a flat blade screwdriver. Slide the rotor bolt back through the rotor and use a screw- driver to screw it into the crankshaft. Use a 3” m12x1.75 bolt to screw into rotor. Apply to...
Page 164
12. Remove engine: using proper lifting equipment remove the engine. See figure 44. Figure 44. Torque requirements (unless otherwise specified) stator bolts ................................................ 6 ft-lbs ( +1 / -0 ) rotor bolt .................................................................
Page 165: Part 7
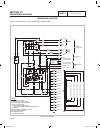
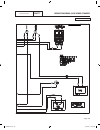
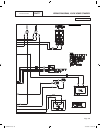
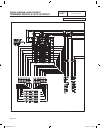
Part 7 electrical data air-cooled, automatic standby generators page 163 table of contents dwg# title 0g7945 wiring diagram, 8 kw hsb 0g8511 schematic, 8 kw hsb 0g7946 wiring diagram, 10 kw hsb 0g8512 schematic, 10 kw hsb 0g7947 wiring diagram, 14 kw hsb 0g8513 schematic, 14 kw hsb 0g7948 wiring dia...
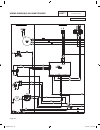
Page 166
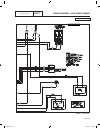
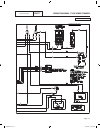
2 6 44 22 33 11 stator engine compartment control panel 1 5 2 3 4 7 6 8 11 9 10 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 j1 j2 main controller sp1 im1 hto 85 lop 86 0 0 1 2 3 4 85 86 13 18 choke solenoid red 1 2 blk frame gnd 0 engine gnd 0 18 10 10 10 10 n1 n2 1 2 n1 n2 6 6 panel gnd 0 0 0 0 0 0 gr ound + ba tter y tr...
Page 167
2 6 44 22 33 11 stator engine compartment control panel 1 5 2 3 4 7 6 8 11 9 10 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 j1 j2 main controller sp1 im1 hto 85 lop 86 0 0 1 2 3 4 85 86 13 18 choke solenoid red 1 2 blk frame gnd 0 engine gnd 0 18 10 10 10 10 n1 n2 1 2 n1 n2 6 6 panel gnd 0 0 0 0 0 0 gr ound + ba tter y tr...
Page 168
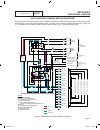
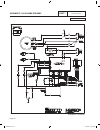
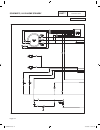
Part 7 electrical data schematic, 8 kw home standby page 166 output generator 240 vac neutral input utility 240 vac transfer + battery ground 56 0 15b 23 23 0 0 0 0 56 56 fs 16 13 sc 0 0 86 85 hto lop 18 battery warmer optional n1 00 22 33 11 44 cb 15b 14 0 13 0 12v battery sc 0 cs im sp excitation ...
Page 169
Electrical data schematic, 8 kw home standby part 7 page 167 output generator 240 vac neutral input utility 240 vac transfer + battery ground 56 0 15b 23 23 0 0 0 0 56 56 fs 16 13 sc 0 0 86 85 hto lop 18 battery warmer optional n1 00 22 33 11 44 cb 15b 14 0 13 0 12v battery sc 0 cs im sp excitation ...
Page 170
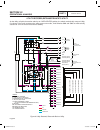
Page 168 2 6 44 22 33 11 stator engine compartment control panel 1 5 2 3 4 7 6 8 11 9 10 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 j3 j1 j2 main controller sp1 im1 sp2 im2 hto 85 lop 86 0 0 1 2 3 4 85 86 13 18 choke solenoid red 1 2 blk actuator governor sc sm frame gnd 0 engine gnd 0 18 13 14 90 0 0 56 a 0 b scr 16 13 ...
Page 171
Page 169 2 6 44 22 33 11 stator engine compartment control panel 1 5 2 3 4 7 6 8 11 9 10 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 j3 j1 j2 main controller sp1 im1 sp2 im2 hto 85 lop 86 0 0 1 2 3 4 85 86 13 18 choke solenoid red 1 2 blk actuator governor sc sm frame gnd 0 engine gnd 0 18 13 14 90 0 0 56 a 0 b scr 16 13 ...
Page 172
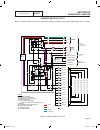
Page 170 part 7 electrical data schematic, 10 kw home standby 820 817 818 819 actuator j3 governor 14 0 14 fs 90 13 18 sp2 im2 output generator 240 vac neutral input utility 240 vac transfer + battery ground 56 0 15b 23 23 0 0 fs 16 13 scr 0 0 86 85 hto lop 18 battery warmer optional n1 00 22 33 11 ...
Page 173
Page 171 electrical data schematic, 10 kw home standby part 7 820 817 818 819 actuator j3 governor 14 0 14 fs 90 13 18 sp2 im2 output generator 240 vac neutral input utility 240 vac transfer + battery ground 56 0 15b 23 23 0 0 fs 16 13 scr 0 0 86 85 hto lop 18 battery warmer optional n1 00 22 33 11 ...
Page 174
Page 172 engine compartment control panel 1 5 2 3 4 7 6 8 11 9 10 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 j3 j1 j2 main controller sp1 im1 sp2 im2 hto 85 lop 86 0 0 1 2 3 4 85 86 13 18 choke solenoid red 1 2 blk actuator governor sc sm frame gnd 0 engine gnd 0 18 13 0 14 4 90 0 0 56 a 0 b scr 16 13 16 n1 n2 1 2 n1 n2 ...
Page 175
Page 173 engine compartment control panel 1 5 2 3 4 7 6 8 11 9 10 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 j3 j1 j2 main controller sp1 im1 sp2 im2 hto 85 lop 86 0 0 1 2 3 4 85 86 13 18 choke solenoid red 1 2 blk actuator governor sc sm frame gnd 0 engine gnd 0 18 13 0 14 4 90 0 0 56 a 0 b scr 16 13 16 n1 n2 1 2 n1 n2 ...
Page 176
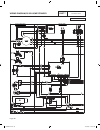
Page 174 part 7 electrical data schematic, 14 kw home standby 0 4 4 0 ba 6 11 22 6 2 2 regulator 11 2 6 0 4 22 voltage 4 0 0 13 13 18 sp2 im2 16 13 scr 0 0 86 85 hto lop 18 0 13 12v battery scr sm im1 sp1 44 11 power winding 33 22 winding power stator 4 0 56 0 sc 820 817 818 819 819 818 817 820 l2 l...
Page 177
Page 175 electrical data schematic, 14 kw home standby part 7 0 4 4 0 ba 6 11 22 6 2 2 regulator 11 2 6 0 4 22 voltage 4 0 0 13 13 18 sp2 im2 16 13 scr 0 0 86 85 hto lop 18 0 13 12v battery scr sm im1 sp1 44 11 power winding 33 22 winding power stator 4 0 56 0 sc 820 817 818 819 819 818 817 820 l2 l...
Page 178
Page 176 closest to bearing ba 0 4 6 22 11 44 22 33 11 stator 2 0 6 voltage regulator 4 11 22 2 2 6 22 11 engine compartment control panel 1 5 2 3 4 7 6 8 11 9 10 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 j3 j1 j2 main controller sp1 im1 sp2 im2 4 hto 85 lop 86 0 0 1 2 3 4 85 86 13 18 choke solenoid red 1 2 blk actuator...
Page 179
Page 177 closest to bearing ba 0 4 6 22 11 44 22 33 11 stator 2 0 6 voltage regulator 4 11 22 2 2 6 22 11 engine compartment control panel 1 5 2 3 4 7 6 8 11 9 10 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 j3 j1 j2 main controller sp1 im1 sp2 im2 4 hto 85 lop 86 0 0 1 2 3 4 85 86 13 18 choke solenoid red 1 2 blk actuator...
Page 180
Page 178 part 7 electrical data schematic, 17 kw home standby 0 4 4 0 ba 6 11 22 6 2 2 regulator 11 2 6 0 4 22 voltage 4 0 0 13 13 18 sp2 im2 16 13 scr 0 0 86 85 hto lop 18 0 13 0 12v battery scr sm im1 sp1 44 11 power winding 33 22 winding power stator 18 13 86 85 4 0 0 sc 13 0 0 00 00 11c l3 820 8...
Page 181
Page 179 electrical data schematic, 17 kw home standby part 7 0 4 4 0 ba 6 11 22 6 2 2 regulator 11 2 6 0 4 22 voltage 4 0 0 13 13 18 sp2 im2 16 13 scr 0 0 86 85 hto lop 18 0 13 0 12v battery scr sm im1 sp1 44 11 power winding 33 22 winding power stator 18 13 86 85 4 0 0 sc 13 0 0 00 00 11c l3 820 8...
Page 182
Page 180 closest to bearing ba 0 4 6 22 11 44 22 33 11 stator 2 0 6 voltage regulator 4 11 22 2 2 6 22 11 engine compartment control panel 1 5 2 3 4 7 6 8 11 9 10 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 j3 j1 j2 main controller sp1 im1 sp2 im2 4 hto 85 lop 86 0 0 1 2 3 4 85 86 13 18 choke solenoid red 1 2 blk actuator...
Page 183
Page 181 closest to bearing ba 0 4 6 22 11 44 22 33 11 stator 2 0 6 voltage regulator 4 11 22 2 2 6 22 11 engine compartment control panel 1 5 2 3 4 7 6 8 11 9 10 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 j3 j1 j2 main controller sp1 im1 sp2 im2 4 hto 85 lop 86 0 0 1 2 3 4 85 86 13 18 choke solenoid red 1 2 blk actuator...
Page 184
Page 182 part 7 electrical data schematic, 20 kw home standby 0 0 00 00 11c l3 0 4 4 0 ba 6 11 22 6 2 2 regulator 11 2 6 0 4 22 voltage 820 817 818 819 819 818 817 820 l2 l1 led board 4 3 2 1 4 4 0 0 actuator j3 governor 14 14 90 13 13 13 18 sp2 im2 output generator 240 vac neutral input utility 240...
Page 185
Page 183 electrical data schematic, 20 kw home standby part 7 0 0 00 00 11c l3 0 4 4 0 ba 6 11 22 6 2 2 regulator 11 2 6 0 4 22 voltage 820 817 818 819 819 818 817 820 l2 l1 led board 4 3 2 1 4 4 0 0 actuator j3 governor 14 14 90 13 13 13 18 sp2 im2 output generator 240 vac neutral input utility 240...
Page 186
Part 7 page 184 electrical data wiring diagram, home standby transfer switch, 9/10/12/16 circuit 205 n2a n1a red blk 10 circuit load center 12 circuit load center 14 circuit load center circuit 8 8 circuit load center circuit 1 circuit 3 circuit 10 circuit 12 circuit 14 circuit 16 circuit 5 circuit ...
Page 187
205 n2a n1a red blk 10 circuit load center 12 circuit load center 14 circuit load center circuit 8 8 circuit load center circuit 1 circuit 3 circuit 10 circuit 12 circuit 14 circuit 16 circuit 5 circuit 7 circuit 9 circuit 11 circuit 15 circuit 13 p anel output t o genera t or distrib ution 240v a c...
Page 188
Page 186 part 7 electrical data schematic, home standby transfer switch, 9/10/12/16 circuit neutral connection switch sw3 no c1 com sw2 vr1 nc nc com c2 vr2 no tr1 15b 23 1 7 4 7 9 3 6 9 f2 circuit 10 black (main 1) control transfer red (main 2) neutral (white) neutral (white) 23 0 f1 n2 n1 15b 23 b...
Page 189
Page 187 0g9266reva.Indd 187 10/15/2008 11:28:53 am.
Page 190
Page 188 0g9266reva.Indd 188 10/15/2008 11:28:53 am.
Page 191
0g9266reva.Indd 189 10/15/2008 11:28:53 am.
Page 192
Cac / bdp 7310 w. Morris street indianapolis, in 46231 specifications are subject to change without notice. Catalog no. Aspds-y-1dm printed in usa 01.09 0g9266reva.Indd 190 10/15/2008 11:28:53 am.