- DL manuals
- Farymann Diesel
- Engine
- 15W
- Repair Manual
Farymann Diesel 15W Repair Manual
Summary of 15W
Page 1
- 1 - diesel engines : 15 / 18 / 32w.
Page 2: Table of Contents
Table of contents - 2 - 1. General information, handling 5 1.3 o rganisation and u se of this r epair m anual .............................................................................5 1.4 s ervice .....................................................................................................
Page 3: Table of Contents
Table of contents - 3 - 8.2 e ngine starts but fires intermittently or dies ........................................................................76 8.3 p oor engine performance and / or black smoke .......................................................................76 8.4 p oor engine performa...
Page 4: Preface
Preface - 4 - we congratulate you on your choice of a farymann engine and wish you much pleasure with this german quality product. These operating instructions are based on the latest state of technical development. In preparing them, every effort has been made to avoid errors. However, we accept no...
Page 5: General Information
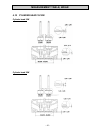
General information - 5 - 1. General information, handling farymann diesel engines type 15/18/32w are 4 stroke, direct injection diesel engines. They are built as single cylinder engines vertical cylinder configuration. The direct injection guarantees an outstanding level of efficiency, with low fue...
Page 6: General Information
General information - 6 - 1.6 engine, model and type designation every engine can be unmistakably identified using the manufacturer’s nameplate. As well as the clearly defined 12-digit code number, this refers to the order number (sn) and the date of construction. This information must always be pro...
Page 7: General Information
General information - 7 - 1.7 safety instructions only use transport devices specified by the manufacturer, and only follow hoisting instructions specified by the manufacturer. When handling fuels, lubricants and other chemical substances, follow the safety regulations which apply to the product. Do...
Page 8: General Information
General information - 8 - 1.5 safety instructions only operate ic engines in enclosed areas if there is adequate ventilation. Before you start the engine in an enclosed environment, make sure that there is sufficient ventilation. Ensure that the engine only slows down to full stop after 10 - 20 seco...
Page 9: Technical Data
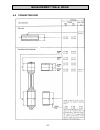
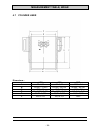
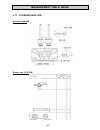
Technical data - 9 - 2. Technical data engine type 15w 18w 32w design verticall number of cylinders 1 bore 75 mm 82 mm 95 mm stroke 55 mm 55 mm 74 mm cubic capacity (piston displacement) 242 cm3 290 cm3 524 cm3 direction of rotation (looking at power take- off side) anti clockwise max. Power / 3000 ...
Page 10: Technical Data
Technical data - 10 - 2.1 construction data, consumptions and pressures technical data table 1 engine type 15w 18w 32w construction data dimen- sion system * four stroke combustion proce- dure * direct injection cooling system * water-cooled design / configuration * 1-cylinder / vertical bore (mm) 7...
Page 11: Technical Data
Technical data - 11 - 2.1 construction data, consumptions and pressures technical data table 2 engine type 15w 18w 32w adjustment data valves, inlet / outlet (mm) 0,2 all inlet opens btdc * 5,3°- 7,5° = 12 - 17 mm 5,3°- 7,5° = 12 - 17 mm 5,2°- 7,5° = 14 - 20 mm exhaust closes atdc * 4,4°- 6,7° = 10 ...
Page 12: Technical Data
Technical data - 12 - 2.2 output, torque, consumption 15w leistung / output / puissance / potencia 18w leistung / output / puissance / potencia drehmoment / torque / couple / par drehmoment / torque / couple / par verbrauch / consumption / consommation / consumo verbrauch / consumption / consommatio...
Page 13: Technical Data
Technical data - 13 - 2.2 output, torque, consumption 32w leistung / output / puissance / potencia the values shown are related to the optimal load setting at the correspond- ing nominal engine speed. Drehmoment / torque / couple / par.
Page 14: Technical Data
Technical data - 14 - verbrauch / consumption / consommation / consumo.
Page 15: Technical Data
Technical data - 15 - 2.3 screws - tightening torques, sealing and adhesive materials technical data table 1 engine type 15w 18w 32w tightening torques cylinder head torque / wrench width (nm) (mm) 30- 33 / 13 30 - 33 / 13 52 - 56 / 17 rocker bracket torque / wrench width (nm) (mm) * * * bearing cov...
Page 16: Technical Data
Technical data - 16 - 2.4 tools part no. Description use 748.115.6 fuel line clamp to clamp fuel supply lines 748.130.2 hexagonal socket wrench, 36 mm for flywheel nuts 748.128.4 drive wrench for use with socket wrench, 748.154.2 748.108.5 special screw driver to adjust governor spring nuts 748.132....
Page 17: Technical Data
Technical data - 17 - 2.4 tools 748.120.4 bearing driver to press the crankshaft bearing bushes in and out 748.121.4 bearing driver to press the camshaft in and out 748.124.4 bearing driver to press out the crank- shaft roller bearing 748.173.2 oil filter wrench to remove the full flow oil filter 74...
Page 18: Technical Data
Technical data - 18 - 2.4 tools 748.126.2 oil pressure gauge to measure the oil pressure 748.131.5 valve spring lifter to remove and fit the valve springs.
Page 19: Technical Data
Technical data - 19 - 2.5 technical description diesel engine models 15w / 18w / 32w are water-cooled, single-cylinder, four-stroke die- sel engines with direct injection. The engines have oil pressure forced lubrication. The fuel injection pump and the valves are controlled by the camshaft which is...
Page 20: Re-Assembling Procedures
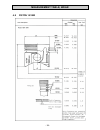
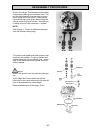
Re-assembling procedures - 20 - 3. Dismantling and assembly procedures on the basic engine 3.1 basic requirements − the aim of this repair manual is to pro- vide help with carrying out repairs to the engine. The requirements for this are as follows: − trained specialist staff (of at least the minimu...
Page 21: Re-Assembling Procedures
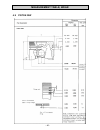
Re-assembling procedures - 21 - 3.2 dismantling procedures 1. Drain lubrication oil : place suitable container under the drain hole. Remove 2 screws and cupper washers, remove oilscreen . Caution clean oilscreen carefully. Replace if any deformations or other dam- ages. 2. Air cleaner engines instal...
Page 22: Re-Assembling Procedures
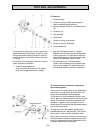
Re-assembling procedures - 22 - 4. Fuel lines, fuel filter remove banjo bolts, copper washers from injec- tion pump and injector. If existing – remove fuel filter bracket, setscrews and spring washers. Close ports of injection pump and injector with banjo bolts to prevent dirt. Caution use only orig...
Page 23: Re-Assembling Procedures
Re-assembling procedures - 23 - 5. High pressure fuel line : loosen the high pressure fuel line by holding a 14 mm wrench on the delivery valve while un- screwing the fuel line fitting . Loosen the high pressure line at the injector in the same way. Caution check taper ends of the high pressure line...
Page 24: Re-Assembling Procedures
Re-assembling procedures - 24 - 7. Cylinder head : remove the valve cover by removing the lock nuts and the plastic washers. If necessary tap the cover lightly with a soft faced hammer. Dis- card plastic washers and valve cover gasket. Remove the 2 locknuts and washers (1) holding the protection tub...
Page 25: Re-Assembling Procedures
Re-assembling procedures - 25 - 8. Decompression release remove 2 screws and pull the decompression release out of the gearhousing. Check gasket and o-seal. Replace if necessary. Caution take care not to loose the guide pin ! With missing guide pin shaft will move out when engine is in operation ! 9...
Page 26: Re-Assembling Procedures
Re-assembling procedures - 26 - 10. Piston rotate the flywheel until the piston is in tdc – position. Use a needle nose plier to remove the piston pin retainer. With a drift pin gently hammer piston pin out of the piston ( from flywheel-side ). Caution if the piston pin is sticking you’ve to remove ...
Page 27: Re-Assembling Procedures
Re-assembling procedures - 27 - 12. Crankhandle guide remove the 2 crankhandle guide screws. Pull of the guide in a twisting motion. 13. Gear end cover remove the 6 allen screws and pull off the gear end cover.If necessary tap with a soft faced hammer. Caution while removing the gear end cover the g...
Page 28: Re-Assembling Procedures
Re-assembling procedures - 28 - remove the 2 hex nuts and lock washers. Pull off the inj. Pump. If necessary turn the flywheel to decrease force from the camshaft-side. Caution leave gasket and shimson the gear end hous- ing. Re-install hex nuts and lock washers on their studs. To remove the injecti...
Page 29: Re-Assembling Procedures
Re-assembling procedures - 29 - 16. Speed control assembly remove the retaining ring from the eccenter shaft using a pliers. Pull the exc. Shaft outwards till the ratchet plate is free from the compression pin. Unhook the outer torsion spring from the boss ( use a pliers and watch out for your fin- ...
Page 30: Re-Assembling Procedures
Re-assembling procedures - 30 - 18. Oil pump remove the oil pump and valve bracket by un- screwing the 3 mounting screws. Discard gasket. 19. Flywheel remove the oil pump and valve bracket by un- screwing the 3 mounting screws. Discard gasket. Leave the flywheel nut on the shaft. Install fly- wheel ...
Page 31: Re-Assembling Procedures
Re-assembling procedures - 31 - remove the key, belleville washers, angle ringe, o-ring and thrust washer. 21. Crankshaft remove the crankshaft from the crankcase, be- ing careful not to drag the crankshaft gear on the main bearing bushing. Use a puller to pull of the crankshaft gear. In case the ro...
Page 32: Measurement Table, Wear
Measurement table, wear - 32 - 4. Measurement table- wearing parts 4.1 crankcase.
Page 33: Measurement Table, Wear
Measurement table, wear - 33 - 4.2 crankshaft.
Page 34: Measurement Table, Wear
Measurement table, wear - 34 - 4.3 camshaft.
Page 35: Measurement Table, Wear
Measurement table, wear - 35 - 4.4 gear cover.
Page 36: Measurement Table, Wear
Measurement table, wear - 36 - 4.5 shafts, bearings.
Page 37: Measurement Table, Wear
Measurement table, wear - 37 - 4.6 connecting rod.
Page 38: Measurement Table, Wear
Measurement table, wear - 38 - 4.7 cylinder liner dimensions : 15w 18w 32w a 92 –0,05 92 –0,05 109,2 –0,1 b 75,050 – 75,030 82,050 – 82,030 95,040 – 95,020 c 78,8 –0,1 85,0 –0,2 100,5 –0,2 d 95 –0,036 /-0,071 95 –0,036 /-0,071 117 –0,1 / -0,15 e 86,75 –0,025 86,75 –0,025 111,2 –0,025 f 105,75 –0,1 1...
Page 39: Measurement Table, Wear
Measurement table, wear - 39 - 4.8 piston 15/18w.
Page 40: Measurement Table, Wear
Measurement table, wear - 40 - 4.9 piston 32w.
Page 41: Measurement Table, Wear
Measurement table, wear - 41 - 4.10 cylinder head 15/18w cylinder head 15w cylinder head 18w.
Page 42: Measurement Table, Wear
Measurement table, wear - 42 - 4.11 cylinder head 32w cylinder head 32w rocker arm 15/18/32w.
Page 43: Reassembly Procedures
Reassembly procedures - 43 - 5. Engine reassembly 1. Crankcase press the bearing bush with a suitable driver. Caution take care that the joining line of the bearing bush is located as shown and that the oil holes in the bushing and in the crankcase bore are properly linedup. 2. Crankshaft to install...
Page 44: Reassembly Procedures
Reassembly procedures - 44 - 3. Main bearing housing press the outer race of the driver into the bear- ing cover. Insert the retaining ring with pliers. Press the oil sealing ring into the housing using the correct driver. Don’t use grease for assem- bly. Insert o-ring in the bearing housing and put...
Page 45: Reassembly Procedures
Reassembly procedures - 45 - 5. Oilpump reassemble oilpump with thin pressure relief plate, spring retaining clip and gasket. Before tightening the screws to specified torque pull the pump downwards. The clearance in the screw holes allows a sufficient backslash between crankshaft gear and pump gear...
Page 46: Reassembly Procedures
Reassembly procedures - 46 - notice the stamped numbers on conrod and cap – side . These are matcjing marks i.E. Identical numbers must be on rod and cap. Oil the bearing shells and install conrod into the crankcase until it seats on the crank pin. Insert conrod cap through the bottom inspection cov...
Page 47: Reassembly Procedures
Reassembly procedures - 47 - now press the camshaft with a driver into the bearing. Use another driver as counter pressure piece for the bearing. Make sure that the bearing sears fully against the seat flange. Insert retaining ring. Install camfol- lower for the injection pump and tighten the fixing...
Page 48: Reassembly Procedures
Reassembly procedures - 48 - the notch of the eccentric shaft. Attention initiate performance test. The tension of the return spring must be acting against the pressure onto the seting screw. Speed control - stationary the outer torsion spring pulls the acceleration lever from the stop-position back...
Page 49: Reassembly Procedures
Reassembly procedures - 49 - oil the ring and piston skirts. Check that piston ring gaps are 120 degrees offset. Compress rings with ring compressor. Lay the cylinder down on the bench with bottom facing up. Install piston from bottom side of the cylinder. Never tap on the piston crown. Attention ne...
Page 50: Reassembly Procedures
Reassembly procedures - 50 - grind in the valves. The rotocap and the conical shaped spring belong to the exhaust valve. The two thin steel washers must be under the cylin- drical spring of the inlet valve. Fit new sealing cap onto the inlet valve guide. Before fitting the rotocap check for proper f...
Page 51: Reassembly Procedures
Reassembly procedures - 51 - 12. Gear end cover to install the gear end cover, first bring the pis- ton to tdc ( top dead center ) position by aligning the flywheel timing mark with the tdc mark stamped on the crankcase. Insert the governor pin into the bore in the gov- ernor. Use grease to keep the...
Page 52: Reassembly Procedures
Reassembly procedures - 52 - move the timing mark on the camshaft gearex- actly 3 teeth to the left. Install the gear end cover. Align the flywheel mark and the crankcase timing mark. Check timing marks on camshaft gear and gear end cover. The timing is acceptable if these are within 0 – 2 mm to the...
Page 53: Reassembly Procedures
Reassembly procedures - 53 - when a new decompression device is installed the correct function must be checked. To do so install the decompression device with the 0,4 mm thick gasket. Continue with steps 14, 15 and 16. Turn the flywheel approx. 1/8 revolution be- fore tdc and measure with a depth ga...
Page 54: Reassembly Procedures
Reassembly procedures - 54 - 16. Valve setting check that the decompression device is in oper- ating position ( pin on 9 o’clock ). Set piston on tdc compression stroke. Use a 0,2 mm feeler gauge to control and reset the valve clearance of both valves. ( insert feeler gauge between valve stem and ro...
Page 55: Reassembly Procedures
Reassembly procedures - 55 - 19. Injection pump place acceleration lever in full load (max speed) position and pull excess fuel button. Place rod of the fuel injection pump to max position. When sliding in the pump, the pin of the rod must grip into the yoke of the control lever. Reinstall the injec...
Page 56: Test Run, Adjustments
Test run, adjustments - 56 - 6. Test run, adjustments, checks 1. Test run the engine is now completely reassembled. Install engine on test bench and carry out test run. The engine does not require a long time running-in program. After a ahort run according to low specifications the engine is ready f...
Page 57: Test Run, Adjustments
Test run, adjustments - 57 - 3. Oil pressure check the oil pressure depends mostly on the wearing conditions of the bearings. Before checking the oil pressure make sure that the oil level is topped and oil with correct viscosity is used. Remove the oil channel plug screw and connect oil pressure gau...
Page 58: Test Run, Adjustments
Test run, adjustments - 58 - 6. Fuel injector, injector nozzle the injector nozzle injects the fuel in a fine mist and under a high pressure into the combustion space. Due to the high mechanical and thermal stress, the nozzle requires regular maintenance. Carbon resuides on the nozzle tip are remove...
Page 59: Test Run, Adjustments
Test run, adjustments - 59 - 7. Excess starting fuel button for ease of starting all engines are fitted with an excess starting pull button. A cone limits the travel of the fuel rack. When the starting fuel button is pulled down prior to start, the cone allows the fuel rack to travel to a higher fue...
Page 60: Test Run, Adjustments
Test run, adjustments - 60 - 8. Adjustment of fuel injection timing the correct setting of the commencement of delivery is a basic requirement for a troublefree function of the engine. As the injection timing is fixed, a check and re-adjustment is only neces- sary when the engine speed is altered or...
Page 61: Test Run, Adjustments
Test run, adjustments - 61 - if shims have been added or removed the in- stallation deepth muist be checked. Measure distance from the mounting flange down to the edge inside the roller tapped. This value plus the thickness of the installed adjust- ment shims should be between 57,5 mm (2.263”) and 5...
Page 62: Test Run, Adjustments
Test run, adjustments - 62 - 9. Governor 1. Governor body 2. Governor spring, middle speed range in case of variable speed governor 3. Spacer, instead of item 2, end speed gover- nor 4. Governor pin 5. Spring bridge 6. Guide bush 7. Governor spring, max speed 8. Governor spring, idle speed 9. Cross ...
Page 63: Test Run, Adjustments
Test run, adjustments - 63 - a small tension spring assembled to the lever system ensures that there is always contact between the tapped bolt and the governor pin. The fuel pump rack is controlled whenever the engine is running. More fuel means higher speed, i.E. The governor pin is being pushed ou...
Page 64: Test Run, Adjustments
Test run, adjustments - 64 - 12. Speed setting to increase speed tighten the cross slotted nut on the governor shaft. ( turn clockwise )..... To reduce speed loosen the slotted nut ( turn anti- clockwise ). Procedure : for correct speed setting the use of the gover- nor adjustment tool is recommende...
Page 65: Test Run, Adjustments
Test run, adjustments - 65 - 13. Acceleration lever the acceleration lever is fixed in ist position on the eccentric shaft with a pin. The rachet plate behind the lever is not fixed and only kept in place by the m8 – thread lock nut. As the rachet plate is used as a buffer for the engine shut down, ...
Page 66: Electrical System
Electrical system - 66 - 7. Electrical system 7.1 flywheel – dynamo / regulator operation: the permanent magnets in the magnet holder (1) on the fly- wheel side induce an alternating voltage in the coils of the stator (2): this voltage is proportional to speed (rpms). The alternat- ing voltage is re...
Page 67: Electrical System
Electrical system - 67 - operating conditions: − permissible operating temperatures: -20 to 70°c (measured on the governor surface) − an intact earth connection must exist between the governor and the engine, and also between the governor and directly attached external construction (no painted or en...
Page 68: Electrical System
Electrical system - 68 - 7.4 12 v flywheel – dynamo / regulator, graphs idling voltage without governor graph a 10 15 20 25 30 35 u~ [v] 500 1000 1500 2000 2500 3000 3500 n [1/min] charging current graph b 0 4 8 12 16 20 i [a] 500 1000 1500 2000 2500 3000 3500 4000 n [1/min].
Page 69: Electrical System
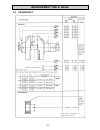
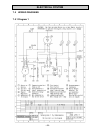
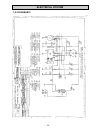
Electrical system - 69 - 7.5 wiring diagrams 7.5.1 diagram 1.
Page 70: Electrical System
Electrical system - 70 -.
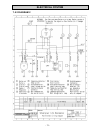
Page 71: Electrical System
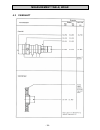
Electrical system - 71 - 7.5.2 diagram 2.
Page 72: Electrical System
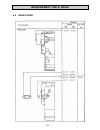
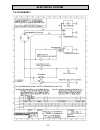
Electrical system - 72 - 7.5.3 diagram 3.
Page 73: Electrical System
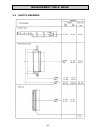
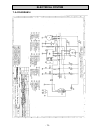
Electrical system - 73 - 7.5.4 diagram 4.
Page 74: Electrical System
Electrical system - 74 - 7.5.5 diagram 5.
Page 75: Troubleshooting
Troubleshooting - 75 - 8. Troubleshooting this section aims to suggest possible causes and remedies for faults. Please note that this list can never be complete. Whenever there is a fault, the guiding principle should be: “think before you act”. 8.1 engine will not start reason causes remedy if the ...
Page 76: Troubleshooting
Troubleshooting - 76 - 8.2 engine starts but fires intermittently or dies poor fuel supply fuel filter choked. Fuel line blocked. Leaking fuel lines. Water in fuel. Faulty injector nozzle. Faulty injector pump. Renew filter. Check lines. Check lines / tighten connections. Drain fuel, fill with clean...
Page 77: Troubleshooting
Troubleshooting - 77 - 8.4 poor engine performance and/or black smoke dirty engine dirty air filter. Excessive oil carbon deposits on piston and cylinder head. Clean / renew filter. Decoke components / change vent valve. General engine condition worn piston rings. Worn piston and cylinder. Worn bear...
Page 78: Troubleshooting
Troubleshooting - 78 - 8.5 imperfect operating behaviour engine stops suddenly fuel pipe broken. Seized piston. Seized crankshaft bearing. Renew pipe. Renew piston and cylinder. Repair / renew crankshaft and bearings. Blue smoke from engine oil level in oil bath air filter too high. Faulty vent valv...
Page 79: Notes
Notes - 79 -.
Page 80: Notes
Notes - 80 -.