- DL manuals
- H3C
- Switch
- S10500 Series
- Mpls Configuration Manual
H3C S10500 Series Mpls Configuration Manual
Summary of S10500 Series
Page 1
H3c s5500-hi switch series mpls configuration guide hangzhou h3c technologies co., ltd. Http://www.H3c.Com software version: release 5501 document version: 6w100-20140103.
Page 2
Copyright © 2014, hangzhou h3c technologies co., ltd. And its licensors all rights reserved no part of this manual may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means without prior written consent of hangzhou h3c technologies co., ltd. Trademarks h3c, , h3cs, h3cie, h3cne, aolynk, , h 3 car...
Page 3
Preface the h3c s5500-hi documentation set includes 12 configuration guides, which describe the software features for the h3c s5500-hi switch series and guide you through the software configuration procedures. These configuration guides also provide configuration examples to help you apply software ...
Page 5
Port numbering in examples the port numbers in this document are for illustration only and might be unavailable on your device. About the h3c s5500-hi documentation set the h3c s5500-hi documentation set includes: category documents purposes product description and specifications marketing brochure ...
Page 6
Obtaining documentation you can access the most up-to-date h3c product documentation on the world wide web at http://www.H3c.Com . Click the links on the top navigation bar to obtain different categories of product documentation: [technical support & documents > technical documents] – provides hardw...
Page 7
I contents configuring mce ························································································································································· 1 mce overview ········································································································...
Page 8
Ii configuring remote ldp session parameters ······································································································ 65 configuring php ·····································································································································...
Page 9
Iii configuring rsvp-te resource reservation confirmation ················································································· 110 configuring rsvp authentication ······················································································································· 111 ...
Page 10
Iv configuring an ldp vpls instance····················································································································· 170 configuring bgp vpls ··························································································································...
Page 11
V inter-as vpn ························································································································································ 235 carrier's carrier ··············································································································...
Page 12
Vi configuration prerequisites ································································································································ 357 configuring inter-as ipv6 vpn option a ·································································································...
Page 13
1 configuring mce the term "router" in this document refers to both routers and layer 3 switches. The term "interface" in this document refers to layer 3 interfaces that include vlan interfaces, layer 3 ethernet interfaces, and layer 3 aggregate interfaces. You can set an ethernet port as a layer 3 ...
Page 14
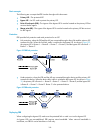
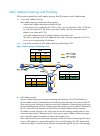
2 figure 1 network diagram for mpls l3vpn model ces and pes mark the boundary between the service providers and the customers. After a ce establishes adjacency with a directly connected pe, it advertises its vpn routes to the pe and learns remote vpn routes from the pe. A ce and a pe use bgp/igp to ...
Page 15
3 address space overlapping each vpn independently manages the addresses it uses. The assembly of such addresses for a vpn is called an address space. The address spaces of vpns may overlap. For example, if both vpn 1 and vpn 2 use the addresses on network segment 10.110.10.0/24, address space overl...
Page 16
4 an rd can be in one of the following formats distinguished by the type field: • when the value of the type field is 0, the administrator subfield occupies two bytes, the assigned number subfield occupies four bytes, and the rd format is 16-bit as number:32-bit user-defined number. For example, 100...
Page 17
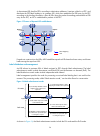
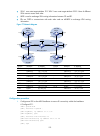
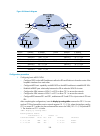
5 how mce works figure 3 shows how an mce maintains the routing entries of multiple vpns and how an mce exchanges vpn routes with pes. Figure 3 network diagram for the mce function on the left-side network, there are two vpn sites, both of which are connected to the mpls backbone through the mce dev...
Page 18
6 by establishing multiple tunnels between two mce devices and binding the tunnel interfaces with vpn instances, you can make the routing information and data of the vpn instances delivered to the peer devices through the bound tunnel interfaces. According to the tunnel interfaces receiving the rout...
Page 19
7 • ebgp this section briefly introduces the cooperation of routing protocols and mce. For information about the routing protocols, see layer 3—ip routing configuration guide. Static routes an mce can communicate with a site through static routes. As static routes configured for traditional ces take...
Page 20
8 route exchange between an mce and a pe routing information entries are bound to specific vpn instances on an mce device, and packets of each vpn instance are forwarded between mce and pe according to interface. As a result, vpn routing information can be transmitted by performing relatively simple...
Page 21
9 step command remarks 4. Configure a description for the vpn instance. Description text optional associating a vpn instance with an interface after vpn instances are configured, you must associate the vpn instances with the interfaces connecting the vpn sites, and: • in an mpls l3vpn application, y...
Page 23
11 • configure the link layer and network layer protocols on related interfaces to ensure ip connectivity. Configuring routing between mce and vpn site configuring static routing between mce and vpn site an mce can reach a vpn site through a static route. Static routing on a traditional ce is global...
Page 25
13 step command remarks 5. Configure the external route tag for imported vpn routes. Route-tag tag-value optional. By default, no route tag is configured. In some networks, a vpn might be connected to multiple mces. When one mce advertise the routes learned from bgp to the vpn, the other mces might ...
Page 30
18 step command remarks 3. Disable routing loop detection. Vpn-instance-capability simple disabled by default. You must disable routing loop detection for a vpn ospf process on the mce. Otherwise, the mce cannot receive ospf routes from the pe. 4. Configure the ospf domain id. Domain-id domain-id [ ...
Page 35
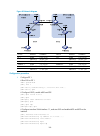
23 figure 6 network diagram configuration procedure assume that the system name of the mce device is mce, the system names of the edge devices of vpn 1 and vpn 2 are vr1 and vr2, respectively, and the system name of pe 1 is pe1. 1. Configure the vpn instances on the mce and pe 1: # on the mce, confi...
Page 36
24 [mce-vlan-interface10] ip address 10.214.10.3 24 # configure vlan 20, add port gigabitethernet 1/0/2 to vlan 20, bind vlan-interface 20 with vpn instance vpn2, and specify an ip address for vlan-interface 20. [mce-vlan-interface10] quit [mce] vlan 20 [mce-vlan20] port gigabitethernet 1/0/2 [mce-v...
Page 37
25 # run rip in vpn 2. Create rip process 20 and bind it with vpn instance vpn2 on the mce, so that the mce can learn the routes of vpn 2 and add them to the routing table of the vpn instance vpn2. [mce] rip 20 vpn-instance vpn2 # advertise subnet 10.214.20.0. [mce-rip-20] network 10.214.20.0 [mce-r...
Page 38
26 [mce-vlan-interface30] ip binding vpn-instance vpn1 [mce-vlan-interface30] ip address 30.1.1.1 24 [mce-vlan-interface30] quit # on the mce, create vlan 40 and vlan-interface 40, bind the vlan interface with vpn instance vpn2, and configure an ip address for the vlan interface. [mce] vlan 40 [mce-...
Page 39
27 [pe1-ospf-10] quit # on pe 1, display the routing table of vpn1. [pe1] display ip routing-table vpn-instance vpn1 routing tables: vpn1 destinations : 5 routes : 5 destination/mask proto pre cost nexthop interface 30.1.1.0/24 direct 0 0 30.1.1.2 vlan30 30.1.1.2/32 direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 inloop0 127....
Page 40
28 figure 7 network diagram configuration procedure 1. Configure vpn instances: # create vpn instances on the mce and pe 1, and bind the vpn instances with vlan interfaces. For the configuration procedure, see " using ospf to advertise vpn routes to the pe ." 2. Configure routing between the mce and...
Page 41
29 127.0.0.1/32 direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 inloop0 192.168.0.0/24 ospf 10 1 10.214.10.2 vlan10 the output shows that the mce has learned the private route of vpn 1 through ospf process 10. # on mce, bind ospf process 20 with vpn instance vpn2 to learn the routes of vpn 2. The configuration procedure is si...
Page 42
30 127.0.0.1/32 direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 inloop0 192.168.0.0/24 bgp 255 2 30.1.1.1 vlan30 # perform similar configuration on the mce and pe 1 for vpn 2. Redistribute the ospf routes of vpn instance vpn2 into the ebgp routing table. (details not shown.) the following output shows that pe 1 has learned th...
Page 43
31 network is simplified into two separate topologies, as shown in figure 9 and figure 10 . Thus, mces advertise routes of different vpns through different paths. For vpn 1, advertise interface addresses on the two mces in area 0, making the entire vpn a single ospf domain. For vpn 2, advertise inte...
Page 44
32 # specify the tunnel protocol as gre. [mce1-tunnel0] tunnel-protocol gre # specify the source address of the tunnel. [mce1-tunnel0] source vlan-interface 100 # specify the destination address of the tunnel. [mce1-tunnel0] destination 172.16.1.1 [mce1-tunnel0] quit # create loopback group 1 and sp...
Page 45
33 [mce2-vlan-interface101] ip address 172.16.2.1 255.255.255.0 [mce2-vlan-interface101] quit # create the interface tunnel0. [mce2] interface tunnel 0 # configure an ip address for the tunnel0 interface. [mce2-tunnel0] ip address 10.1.1.2 255.255.255.0 # specify the tunnel protocol as gre. [mce2-tu...
Page 46
34 [mce1-vpn-instance-vpn2] route-distinguisher 1:3 [mce1-vpn-instance-vpn2] vpn-target 1:3 [mce1-vpn-instance-vpn2] quit # bind vlan-interface 10 and tunnel 0 with vpn instance vpn1, and configure ip addresses for the vlan interface and tunnel interface. [mce1] vlan 10 [mce1-vlan10] port gigabiteth...
Page 47
35 [mce2] interface vlan-interface 20 [mce2-vlan-interface20] ip binding vpn-instance vpn1 [mce2-vlan-interface20] ip address 10.214.30.1 24 [mce2-vlan-interface20] quit [mce2] interface tunnel 0 [mce2-tunnel0] ip binding vpn-instance vpn1 [mce2-tunnel0] ip address 10.1.1.2 24 # bind vlan-interface ...
Page 48
36 [mce1-ospf-2-area-0.0.0.0] # advertise the address of tunnel interface tunnel 1. [mce1-ospf-2-area-0.0.0.0] network 10.1.2.1 0.0.0.255 # configure rip process 1 for vpn instance vpn2. [mce1] rip 1 vpn-instance vpn2 [mce1-rip-1] # advertise the ip address of vlan-interface 11. [mce1-rip-1] network...
Page 49
37 configuring ipv6 mce overview in an ipv6 mpls l3 vpn, an ipv6 mce advertises ipv6 routing information between the vpn and the connected pe and forwards ipv6 packets. An ipv6 mce operates in the same way as an ipv4 mce. For more information, see " configuring mce ." configuring an ipv6 mce configu...
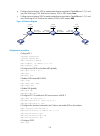
Page 50
38 step command remarks 1. Enter system view. System-view n/a 2. Enter interface view. Interface interface-type interface-number n/a 3. Associate a vpn instance with the interface. Ip binding vpn-instance vpn-instance-name by default, no vpn instance is associated with the interface. Configuring rou...
Page 51
39 note: • route related attributes configured in vpn instance view are applicable to both ipv4 vpns and ipv6 vpns. • you can configure route related attributes for ipv6 vpns in both vpn instance view and ipv6 vpn view. Those configured in ipv6 vpn view take precedence. Configuring routing on an ipv...
Page 53
41 for more information about ospfv3, see layer 3—ip routing configuration guide. To configure ospfv3 between ipv6 mce and vpn site: step command remarks 1. Enter system view. System-view n/a 2. Create an ospfv3 process for a vpn instance and enter ospfv3 view. Ospfv3 [ process-id ] vpn-instance vpn...
Page 55
43 2. Configure a vpn site: step command remarks 1. Enter system view. System-view n/a 2. Enter bgp view. Bgp as-number n/a 3. Enter ipv6 address family view. Ipv6-family n/a 4. Configure the ipv6 mce as the ebgp peer. Peer ipv6-address as-number as-number n/a 5. Redistribute the igp routes of the v...
Page 58
46 resetting bgp connections when bgp configuration changes, you can use the soft reset function or reset bgp connections to make new configurations take effect. Soft reset requires that bgp peers have route refreshment capability (supporting route-refresh messages). Use the following commands to ha...
Page 59
47 ipv6 mce configuration examples using ipv6 isis to advertise vpn routes to the pe network requirements as shown in figure 11 , the ipv6 mce device is connected to vpn 1 through vlan-interface 10 and to vpn 2 through vlan-interface 20. Ripng is used in vpn 2. Configure the ipv6 mce to separate rou...
Page 60
48 [mce-vpn-instance-vpn1] vpn-target 10:1 [mce-vpn-instance-vpn1] quit [mce] ip vpn-instance vpn2 [mce-vpn-instance-vpn2] route-distinguisher 20:1 [mce-vpn-instance-vpn2] vpn-target 20:1 [mce-vpn-instance-vpn2] quit # create vlan 10, add port gigabitethernet 1/0/1 to vlan 10, and create vlan-interf...
Page 61
49 # run ripng in vpn 2. Configure ripng process 20 for vpn instance vpn2 on the mce, so that the mce can learn the routes of vpn 2 and add them to the routing table of vpn instance vpn2. # configure ripng process 20, binding it with vpn instance vpn2. [mce] ripng 20 vpn-instance vpn2 # advertise su...
Page 62
50 destinations : 5 routes : 5 destination: ::1/128 protocol : direct nexthop : ::1 preference: 0 interface : inloop0 cost : 0 destination: 2002:1::/64 protocol : direct nexthop : 2002:1::1 preference: 0 interface : vlan20 cost : 0 destination: 2002:1::1/128 protocol : direct nexthop : ::1 preferenc...
Page 63
51 [mce-vlan40] quit [mce] interface vlan-interface 40 [mce-vlan-interface40] ip binding vpn-instance vpn2 [mce-vlan-interface40] ipv6 address 40::1 64 [mce-vlan-interface40] quit # on pe 1, create vlan 30 and vlan-interface 30, bind vlan-interface 30 with vpn instance vpn1 and configure an ipv6 add...
Page 64
52 destination: ::1/128 protocol : direct nexthop : ::1 preference: 0 interface : inloop0 cost : 0 destination: 30::/64 protocol : direct nexthop : 30::2 preference: 0 interface : vlan30 cost : 0 destination: 30::2/128 protocol : direct nexthop : ::1 preference: 0 interface : inloop0 cost : 0 destin...
Page 65
53 configuring basic mpls the s5500-28sc-hi and s5500-52sc-hi switches do not support mpls. Mpls overview multiprotocol label switching (mpls) enables connection-oriented label switching on connectionless ip networks. It integrates both the flexibility of ip routing and the simplicity of layer 2 swi...
Page 66
54 • s—one bit in length. Mpls supports multiple levels of labels. This field indicates whether a label is at the bottom of the label stack. A value of 1 indicates that the label is at the bottom of the label stack. • ttl—eight bits in length. Like the homonymous ip header field, it is used to preve...
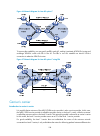
Page 67
55 mpls network structure figure 14 diagram of the mpls network structure lsrs in the same routing or administrative domain form an mpls domain. An mpls domain consists of the following types of lsrs: • ingress lsrs receive and label packets coming into the mpls domain. • transit lsrs forward packet...
Page 68
56 a downstream lsr classifies fecs according to destination addresses. It assigns a label to a fec, and distributes the fec-label binding to its upstream lsr, which then establishes an lfib entry for the fec according to the binding information. After all lsrs along the packet forwarding path estab...
Page 69
57 • in du mode, an lsr assigns a label to a fec and then distributes the fec-label binding to its upstream lsr without solicitation. The switch supports only the du mode. • in dod mode, an lsr assigns a label to a fec and distributes the fec-label binding to its upstream lsr only when it receives a...
Page 70
58 mpls forwarding lfib an lfib comprises the following table entries: • next hop label forwarding entry (nhlfe)—describes the label operation to be performed. It is used to forward mpls packets. • fec to nhlfe (ftn) map—ftn maps each fec to a set of nhlfes at the ingress lsr. The ftn map is used fo...
Page 71
59 2. Upon receiving the labeled packet, router c looks for the ilm entry that contains the label 40 to get the token value. Because the token value is not empty, router c looks for the corresponding nhlfe entry containing the token value. According to the nhlfe entry, router c swaps the original la...
Page 72
60 basic concepts of ldp • ldp session—ldp sessions are established between lsrs over tcp connections to exchange messages for label binding, label releasing, and error notification. • ldp peer—two lsrs using ldp to exchange fec-label bindings are ldp peers. Ldp message type ldp messages fall into t...
Page 73
61 3. Lsp establishment and maintenance ldp sends label requests and label binding messages between ldp peers to establish lsps. For the lsp establishment process, see " lsp establishment and label distribution ." 4. Session termination an lsr terminates its ldp session with an ldp peer in the follo...
Page 74
62 task remarks configuring ldp loop detection optional configuring ldp md5 authentication optional configuring ldp label filtering optional configuring dscp for outgoing ldp packets optional maintaining ldp sessions configuring bfd for mpls ldp optional resetting ldp sessions optional managing and ...
Page 75
63 step command remarks 2. Configure the mpls lsr id. Mpls lsr-id lsr-id by default, no mpls lsr id is configured. An mpls lsr id is in the format of an ip address and must be unique within an mpls domain. H3c recommends using the ip address of a loopback interface on an lsr as the mpls lsr id. 3. E...
Page 77
65 configuring local ldp session parameters ldp sessions established between local ldp peers are local ldp sessions. To establish a local ldp session: • determine the ldp transport addresses of the two peers and make sure that the ldp transport addresses are reachable to each other. This step is to ...
Page 78
66 step command remarks 1. Enter system view. System-view n/a 2. Create a remote peer entity and enter mpls ldp remote peer view. Mpls ldp remote-peer remote-peer-name n/a 3. Configure the remote peer ip address. Remote-ip ip-address the remote peer ip address must be different from all existing rem...
Page 81
69 • ldp loop detection can result in lsp update, which generates redundant information and consume many system resources. H3c recommends configuring the routing protocol's loop detection mechanism. Configuration procedure to configure ldp loop detection: step command remarks 1. Enter system view. S...
Page 82
70 does lsr a accept the label binding of the fec from lsr b. Lsr a does not filter label bindings received from downstream device lsr c. Figure 19 network diagram of label acceptance control label advertisement control label advertisement control is for filtering label bindings to be advertised. A ...
Page 83
71 to configure ldp label filtering policies: step command remarks 1. Enter system view. System-view n/a 2. Enter mpls ldp view. Mpls ldp n/a 3. Configure a label acceptance control policy. Accept-label peer peer-id ip-prefix ip-prefix-name optional. Not configured by default. 4. Configure a label a...
Page 84
72 resetting ldp sessions if you change ldp session parameters when some ldp sessions are up, the ldp sessions cannot function normally. In this case, reset ldp sessions so the ldp peers will renegotiate parameters and establish new sessions. Use the following command to reset ldp sessions: task com...
Page 85
73 figure 22 label ttl processing when ip ttl propagation is disabled configuration guidelines to enable ip ttl propagation for a vpn, you must enable it on all pe devices in the vpn, so you can get the same traceroute result (hop count) from those pes. For more information about pes, see " configur...
Page 86
74 carry only one level of labels but these devices have no ip routes to the packet senders, the first method is not applicable. In this case, you can configure the undo ttl expiration pop command on these devices so the devices use the second method. For more information about hovpn and nested vpn,...
Page 87
75 figure 23 ldp gr as shown in figure 23 , two ldp peers perform gr negotiation when establishing an ldp session. The ldp session established is gr capable only when both peers support ldp gr. The working procedure of ldp gr is as follows: 1. Whenever restarting, the gr restarter preserves all mpls...
Page 88
76 step command remarks 1. Enter system view. System-view n/a 2. Enter mpls ldp view. Mpls ldp n/a 3. Enable mpls ldp gr. Graceful-restart disabled by default. 4. Set the ft reconnect time. Graceful-restart timer reconnect timer optional. 300 seconds by default. 5. Set the ldp neighbor liveness time...
Page 89
77 • mpls lsp tracert • bfd for lsps • periodic lsp tracert configuring mpls lsp ping mpls lsp ping is for checking the connectivity of an lsp. At the ingress, it adds the label for the fec to be inspected into an mpls echo request, which then is forwarded along the lsp to the egress. The egress pro...
Page 91
79 configuration procedure to configure bfd for lsps: step command remarks 1. Enter system view. System-view n/a 2. Enable lsp verification and enter the mpls lspv view. Mpls lspv not enabled by default 3. Configure bfd to detect lsp connectivity. Bfd enable destination-address mask-length [ nexthop...
Page 92
80 enabling mpls trap with the mpls trap function enabled, trap packets of the notifications level are generated to report critical mpls events. Such trap packets are sent to the information center of the device. Whether and where the packets are output depend on the configurations of the informatio...
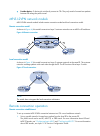
Page 95
83 figure 24 network diagram configuration considerations • on an lsp, the out label of an upstream lsr must be identical with the in label of its downstream lsr. • configure an lsp for each direction on the forwarding path. • configure a static route to the destination address of the lsp on each in...
Page 96
84 [switchb-vlan-interface3] quit # configure switch c. [switchc] mpls lsr-id 3.3.3.9 [switchc] mpls [switchc-mpls] quit [switchc] interface vlan-interface 3 [switchc-vlan-interface3] mpls [switchc-vlan-interface3] quit 4. Create a static lsp from switch a to switch c: # configure the lsp ingress, s...
Page 97
85 0.00% packet loss round-trip min/avg/max = 1/1/2 ms # on switch c, test the connectivity of the lsp from switch c to switch a. [switchc] ping lsp -a 21.1.1.1 ipv4 11.1.1.0 24 lsp ping fec: ipv4 prefix 11.1.1.0/24 : 100 data bytes, press ctrl_c to break reply from 10.1.1.1: bytes=100 sequence=1 ti...
Page 98
86 [sysname] sysname switcha [switcha] ospf [switcha-ospf-1] area 0 [switcha-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 1.1.1.9 0.0.0.0 [switcha-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 10.1.1.0 0.0.0.255 [switcha-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 11.1.1.0 0.0.0.255 [switcha-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] quit [switcha-ospf-1] quit # confi...
Page 99
87 # configure mpls and mpls ldp on switch a. [switcha] mpls lsr-id 1.1.1.9 [switcha] mpls [switcha-mpls] quit [switcha] mpls ldp [switcha-mpls-ldp] quit [switcha] interface vlan-interface 2 [switcha-vlan-interface2] mpls [switcha-vlan-interface2] mpls ldp [switcha-vlan-interface2] quit # configure ...
Page 100
88 ldp peer information in public network total number of peers: 1 ----------------------------------------------------------------- peer-id transport-address discovery-source ---------------------------------------------------------------- 2.2.2.9:0 2.2.2.9 vlan-interface2 -------------------------...
Page 101
89 5 packet(s) transmitted 5 packet(s) received 0.00% packet loss round-trip min/avg/max = 1/2/3 ms # on switch c, test the connectivity of the ldp lsp from switch c to switch a. [switchc] ping lsp ipv4 11.1.1.0 24 lsp ping fec: ipv4 prefix 11.1.1.0/24 : 100 data bytes, press ctrl_c to break reply f...
Page 102
90 tunnel id : --- nexthop : --- session state : up source ip : 3.3.3.9 session role : passive fec : 21.1.1.0/24 type : lsp local discr : 129 remote discr : 129 tunnel id : 0x6040000 nexthop : 10.1.1.2 session state : up source ip : 1.1.1.9 session role : active total session num: 2 the output indic...
Page 103
91 configuring mpls te the s5500-28sc-hi and s5500-52sc-hi switches do not support mpls te. Overview network congestion is one of the major problems that can degrade your network backbone performance. It may occur either when network resources are inadequate or when load distribution is unbalanced. ...
Page 104
92 with mpls te, a network administrator can eliminate network congestion by creating some lsps and congestion bypass nodes. Special offline tools are also available for the traffic analysis performed when the number of lsps is large. Basic concepts of mpls te lsp tunnel on an lsp, after packets are...
Page 105
93 they are different in that cr-ldp establishes lsps using tcp while rsvp-te uses raw ip. Rsvp is a well-established technology in terms of its architecture, protocol procedures and support to services. Cr-ldp is an emerging technology with better scalability. The switch supports only the rsvp-te s...
Page 106
94 explicit route (er-hop) with required resources is used. The established cr-lsp, however, may change when the route changes, for example, when a better next hop becomes available. If this is undesirable, the network administrator can set up the cr-lsp using route underpinning to make it a permane...
Page 107
95 { fixed-filter (ff) style—resources are reserved for individual senders and cannot be shared among senders on the same session. { shared-explicit (se) style—resources are reserved for senders on the same session and shared among them. Se is only used for make-before-break because multiple lsps ca...
Page 108
96 • resvconf messages—sent to receivers to confirm resv messages. • hello messages—sent between any two directly connected rsvp neighbors to set up and maintain the neighbor relationship that has local significance on the link. The te extension to rsvp adds new objects to the path message and the r...
Page 109
97 on an interface enabled with the message_id mechanism, you can configure rsvp message retransmission. If a node sends a message carrying the message_id object, and the ack_desired flag in the object is set, the node expects a response that carries the message_id_ack object during the initial retr...
Page 110
98 if a gr helper and the gr restarter reestablish a hello session before the restart timer expires, the recovery timer is started and signaling packet exchanging is triggered to restore the original soft state. Otherwise, all rsvp soft state information and forwarding entries relevant to the neighb...
Page 111
99 figure 28 igp shortcut and forwarding adjacency a te tunnel is present between router d and router c. With igp shortcut enabled, the ingress node router d can use this tunnel when calculating igp routes. This tunnel, however, is invisible to router a; therefore, router a cannot use this tunnel to...
Page 112
100 basic concepts the following are concepts that frr involves throughout this document: • primary lsp—the protected lsp. • bypass lsp—an lsp used to protect the primary lsp. • point of local repair (plr)—the ingress of the bypass lsp. It must be located on the primary lsp but must not be the egres...
Page 113
101 ps for an mpls te tunnel protection switching (ps) refers to establishing one or more protection tunnels (backup tunnels) for a primary tunnel. A primary tunnel and its protection tunnels form a protection group. When the primary tunnel fails, data is switched to a protection tunnel immediately,...
Page 114
102 • rfc 2961, rsvp refresh overhead reduction extensions • rfc 3564, requirements for support of differentiated service-aware mpls traffic engineering • itu-t recommendation y.1720, protection switching for mpls networks mpls te configuration task list task remarks configuring basic mpls te n/a co...
Page 115
103 step command remarks 6. Enable interface mpls te. Mpls te disabled by default. 7. Return to system view. Quit n/a 8. Create a tunnel interface and enter its view. Interface tunnel tunnel-number n/a 9. Assign an ip address to the tunnel interface. Ip address ip-address netmask optional. 10. Set t...
Page 116
104 step command remarks 3. Configure the tunnel to use static cr-lsp. Mpls te signal-protocol static n/a 4. Submit the current tunnel configuration. Mpls te commit n/a 5. Exit to system view. Quit n/a 6. Create a static cr-lsp on your device depending on its location in the network. • at the ingres...
Page 117
105 • configure basic mpls te. Configuration procedure complete the following tasks to configure an mpls te tunnel using a dynamic signaling protocol: task remarks configuring cspf optional. Configuring ospf te required when cspf is configured. Choose one depending on the igp protocol used. Configur...
Page 118
106 step command remarks 4. Enter ospf area view. Area area-id n/a 5. Enable mpls te in the ospf area. Mpls-te enable disabled by default. 6. Exit to ospf view. Quit n/a configuring is-is te configure is-is te if the routing protocol is is-is and a dynamic signaling protocol is used for mpls te tunn...
Page 119
107 when inserting nodes to an explicit path or modifying nodes on it, you can configure the include keyword to have the established lsp traverse the specified nodes or the exclude keyword to have the established lsp bypass the specified nodes. To configure an mpls te explicit path: step command rem...
Page 120
108 step command remarks 4. Submit current tunnel configuration. Mpls te commit n/a establishing an mpls te tunnel with rsvp-te to use rsvp-te as the signaling protocol for setting up the mpls te tunnel, you must enable both mpls te and rsvp-te on the interfaces for the tunnel to use on each node al...
Page 121
109 • ff—resources are reserved for individual senders and cannot be shared among senders on the same session. • se—resources are reserved for senders on the same session and shared among them. In current mpls te applications, the se style is mainly used for make-before-break. The ff style is rarely...
Page 122
110 step command remarks 1. Enter system view. System-view n/a 2. Enter interface view of mpls te link. Interface interface-type interface-number n/a 3. Enable the reliability mechanism of rsvp-te. Mpls rsvp-te reliability optional. Disabled by default. 4. Enable retransmission. Mpls rsvp-te timer r...
Page 123
111 to configure rsvp-te resource reservation confirmation: step command remarks 1. Enter system view. System-view n/a 2. Enter mpls view. Mpls n/a 3. Enable resource reservation confirmation. Mpls rsvp-te resvconfirm disabled by default. Configuring rsvp authentication rsvp adopts hop-by-hop authen...
Page 124
112 step command remarks 3. Enable global rsvp hello extension. Mpls rsvp-te hello disabled by default. 4. Enable mpls rsvp-te gr. Mpls rsvp-te graceful-restart disabled by default. 5. Set the rsvp-te gr restart timer. Mpls rsvp-te timer graceful-restart restart restart-time optional. 120 seconds by...
Page 125
113 suppose the affinity of an mpls te tunnel is 0xffffffff and the mask is 0x0000ffff. For a link to be used by the tunnel, the leftmost 16 bits of its administrative group attribute can be 0s or 1s, but at least one of the rest bits must be 1. The affinity of an mpls te tunnel is configured at the...
Page 126
114 step command remarks 6. Perform reoptimization on all mpls te tunnels with reoptimization enabled. Mpls te reoptimization optional. Tuning mpls te tunnel setup this section only covers the configuration tasks for tuning mpls te tunnel setup. The configurations described in this section must be u...
Page 127
115 to configure tunnel setup retry: step command remarks 1. Enter system view. System-view n/a 2. Enter mpls te tunnel interface view. Interface tunnel tunnel-number n/a 3. Configure maximum number of tunnel setup retries. Mpls te retry times optional. The default is 10. 4. Configure the tunnel set...
Page 129
117 configuring forwarding adjacency to make forwarding adjacency take effect, create a bi-directional mpls te tunnel and enable forwarding adjacency at both ends of the tunnel. To configure forwarding adjacency: step command remarks 1. Enter system view. System-view n/a 2. Enter mpls te tunnel inte...
Page 130
118 specifying the link metric type for tunnel path calculation to specify the metric type for tunnel path calculation: step command remarks 1. Enter system view. System-view n/a 2. Enter mpls view. Mpls n/a 3. Specify the metric type to use when no metric type is explicitly configured for a tunnel....
Page 131
119 configuring cr-lsp backup cr-lsp backup provides end-to-end path protection to protect the entire lsp. Before you configure cr-lsp backup, complete the following tasks: • configure basic mpls • configure basic mpls te • configure mpls te tunnels configure cr-lsp backup mode at the ingress node o...
Page 132
120 • establish an mpls te tunnel with rsvp-te. • set up primary lsps. Enabling frr on the headend of a primary lsp step command remarks 1. Enter system view. System-view n/a 2. Enter tunnel interface view of the primary lsp. Interface tunnel tunnel-number n/a 3. Enable frr. Mpls te fast-reroute dis...
Page 133
121 step command remarks 6. Enter interface view of the outgoing interface of the protected lsp. Interface interface-type interface-number n/a 7. Bind the bypass tunnel with the protected interface. Mpls te fast-reroute bypass-tunnel tunnel tunnel-number n/a configuring node protection rsvp hello ex...
Page 134
122 inspecting an mpls te tunnel on an mpls te network, when an mpls te tunnel fails, the control plane cannot detect the failure or cannot do so in time. This brings difficulty to network maintenance. To detect mpls te tunnel failures in time and locate the failed node, the device provides the foll...
Page 135
123 bfd control packet received from the egress. Upon detecting an mpls te tunnel failure, bfd triggers protection switching to switch traffic to another tunnel. A bfd session for mpls te tunnel detection can be static or dynamic. • static—if you specify the local and remote discriminator values by ...
Page 136
124 step command remarks 2. Enable lsp verification and enter mpls lspv view. Mpls lspv by default, lsp verification is disabled. For more information about the mpls lspv command, see mpls command reference. 3. Return to system view. Quit n/a 4. Enter the tunnel interface view of an mpls te tunnel. ...
Page 137
125 step command remarks 6. Configure mpls te to tear down a failed rsvp te tunnel and reestablish it. Mpls te failure-action teardown optional. Not configured by default. Configuring protection switching before you configure protection switching, complete the following tasks: • configure basic mpls...
Page 141
129 2. Enable is-is to advertise host routes with lsr ids as destinations: # configure switch a. System-view [switcha] isis 1 [switcha-isis-1] network-entity 00.0005.0000.0000.0001.00 [switcha-isis-1] quit [switcha] interface vlan-interface 1 [switcha-vlan-interface1] isis enable 1 [switcha-vlan-int...
Page 142
130 3.2.1.0/24 isis 15 20 2.1.1.2 vlan1 3.3.3.3/32 isis 15 20 2.1.1.2 vlan1 127.0.0.0/8 direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 inloop0 127.0.0.1/32 direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 inloop0 3. Configure basic mpls te: # configure switch a. [switcha] mpls lsr-id 3.3.3.3 [switcha] mpls [switcha-mpls] mpls te [switcha-mpls] quit [sw...
Page 143
131 # configure switch a as the ingress node of the static cr-lsp. [switcha] static-cr-lsp ingress tunnel0 destination 3.3.3.3 nexthop 2.1.1.2 out-label 20 # configure switch b as the transit node of the static cr-lsp. [switchb] static-cr-lsp transit tunnel0 incoming-interface vlan-interface1 in-lab...
Page 144
132 3.3.3.3/32 null/20 -/vlan1 [switchb] display mpls lsp ------------------------------------------------------------------ lsp information: static crlsp ------------------------------------------------------------------ fec in/out label in/out if vrf name -/- 20/30 vlan1/vlan2 [switchc] display mp...
Page 145
133 figure 32 network diagram device interface ip address device interface ip address switch a loop0 1.1.1.9/32 switch d loop0 4.4.4.9/32 vlan-int1 10.1.1.1/24 vlan-int3 30.1.1.2/24 switch b loop0 2.2.2.9/32 switch c loop0 3.3.3.9/32 vlan-int1 10.1.1.2/24 vlan-int3 30.1.1.1/24 vlan-int2 20.1.1.1/24 ...
Page 146
134 [switchb-vlan-interface2] quit [switchb] interface loopback 0 [switchb-loopback0] isis enable 1 [switchb-loopback0] isis circuit-level level-2 [switchb-loopback0] quit # configure switch c. System-view [switchc] isis 1 [switchc-isis-1] network-entity 00.0005.0000.0000.0003.00 [switchc-isis-1] qu...
Page 147
135 20.1.1.0/24 isis 15 20 10.1.1.2 vlan1 30.1.1.0/24 isis 15 30 10.1.1.2 vlan1 127.0.0.0/8 direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 inloop0 127.0.0.1/32 direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 inloop0 3. Configure basic mpls te, and enable rsvp-te and cspf: # configure switch a. [switcha] mpls lsr-id 1.1.1.9 [switcha] mpls [switcha-mpls...
Page 148
136 [switchc-vlan-interface2] mpls te [switchc-vlan-interface2] mpls rsvp-te [switchc-vlan-interface2] quit # configure switch d. [switchd] mpls lsr-id 4.4.4.9 [switchd] mpls [switchd-mpls] mpls te [switchd-mpls] mpls rsvp-te [switchd-mpls] mpls te cspf [switchd-mpls] quit [switchd] interface vlan-i...
Page 149
137 6. Verify the configuration: # execute the display interface tunnel command on switch a. You can see that the tunnel interface is up. [switcha] display interface tunnel tunnel1 current state: up line protocol current state: up description: tunnel1 interface the maximum transmit unit is 64000 int...
Page 150
138 auto bw : disabled auto bw freq : - min bw : - max bw : - current collected bw: - interfaces protected: - vpn bind type : none vpn bind value : - car policy : disabled tunnel group : primary primary tunnel : - backup tunnel : - group status : - oam status : - # execute the display mpls te cspf t...
Page 151
139 3. Configure basic mpls te, and enable rsvp-te and rsvp hello extension: # configure switch a. System-view [switcha] mpls lsr-id 1.1.1.9 [switcha] mpls [switcha-mpls] mpls te [switcha-mpls] mpls rsvp-te [switcha-mpls] mpls rsvp-te hello [switcha-mpls] interface vlan-interface 1 [switcha-vlan-int...
Page 152
140 4. Configure is-is te. (details not shown.) 5. Configure the mpls te tunnel. (details not shown.) 6. Configure rsvp-te gr: # configure switch a. System-view [switcha] mpls [switcha-mpls] mpls rsvp-te graceful-restart # configure switch b. System-view [switchb] mpls [switchb-mpls] mpls rsvp-te gr...
Page 153
141 configuration procedure 1. Configure basic mpls rsvp-te: # configure switch a. System-view [switcha] mpls lsr-id 1.1.1.1 [switcha] mpls [switcha-mpls] mpls te [switcha-mpls] mpls rsvp-te [switcha-mpls] quit [switcha] interface vlan-interface 12 [switcha-vlan-interface12] mpls [switcha-vlan-inter...
Page 154
142 [switcha-vlan-interface12] ip address 12.12.12.1 24 [switcha-vlan-interface12] quit # configure switch b. [switchb] interface vlan-interface 12 [switchb-vlan-interface12] ip address 12.12.12.2 24 4. Configure the mpls te tunnel: # configure an rsvp-te tunnel between switch a and switch b. [switc...
Page 155
143 figure 35 network diagram device interface ip address device interface ip address switch a loop0 1.1.1.9/32 switch d loop0 4.4.4.9/32 vlan-int1 10.1.1.1/24 vlan-int4 30.1.1.2/24 vlan-int4 30.1.1.1/24 vlan-int3 40.1.1.1/24 switch b loop0 2.2.2.9/32 switch c loop0 3.3.3.9/32 vlan-int1 10.1.1.2/24 ...
Page 156
144 [switcha-vlan-interface4] mpls te [switcha-vlan-interface4] mpls rsvp-te [switcha-vlan-interface4] quit # follow the same steps to configure switch b, switch c, and switch d. (details not shown.) 4. Create an mpls te tunnel on switch a: # configure the mpls te tunnel carried on the primary lsp. ...
Page 157
145 hop information hop 0 10.1.1.1 hop 1 10.1.1.2 hop 2 2.2.2.9 hop 3 20.1.1.1 hop 4 20.1.1.2 hop 5 3.3.3.9 tunnel interface name : tunnel1 lsp id : 1.1.1.9 :2054 hop information hop 0 30.1.1.1 hop 1 30.1.1.2 hop 2 4.4.4.9 hop 3 40.1.1.1 hop 4 40.1.1.2 hop 5 3.3.3.9 # execute the tracert command to ...
Page 158
146 frr configuration example network requirements on a primary lsp switch a switch b switch c → → switch d, use frr to protect the link switch b → → switch c. • create a bypass lsp that traverses the path switch b switch → e switch c. Switch b is the plr and → switch c is the mp. • explicitly route...
Page 159
147 2.2.2.2/32 isis 15 10 2.1.1.2 vlan1 3.1.1.0/24 isis 15 20 2.1.1.2 vlan1 3.2.1.0/24 isis 15 20 2.1.1.2 vlan1 3.3.1.0/24 isis 15 30 2.1.1.2 vlan1 3.3.3.3/32 isis 15 20 2.1.1.2 vlan1 4.1.1.0/24 isis 15 30 2.1.1.2 vlan1 4.4.4.4/32 isis 15 30 2.1.1.2 vlan1 5.5.5.5/32 isis 15 20 2.1.1.2 vlan1 127.0.0....
Page 160
148 # create an explicit path for the primary lsp. [switcha] explicit-path pri-path [switcha-explicit-path-pri-path] next hop 2.1.1.2 [switcha-explicit-path-pri-path] next hop 3.1.1.2 [switcha-explicit-path-pri-path] next hop 4.1.1.2 [switcha-explicit-path-pri-path] next hop 4.4.4.4 [switcha-explici...
Page 161
149 signaling prot : rsvp resv style : se class type : ct0 tunnel bw : 0 kbps reserved bw : 0 kbps setup priority : 7 hold priority: 7 affinity prop/mask : 0/0 explicit path name : pri-path tie-breaking policy : none metric type : none record route : enabled record label : enabled frr flag : enabled...
Page 162
150 execute the display mpls lsp command on each switch. You can see that two lsps are traversing switch b and switch c. [switcha] display mpls lsp ------------------------------------------------------------------ lsp information: rsvp lsp -----------------------------------------------------------...
Page 163
151 lsp-id destination in/out-if name 1.1.1.1:1 4.4.4.4 vlan3/- tunnel4 [switche] display mpls te tunnel lsp-id destination in/out-if name 2.2.2.2:1 3.3.3.3 vlan4/vlan5 tunnel5 execute the display mpls lsp verbose command on switch b. You can see that the bypass tunnel is bound with the protected in...
Page 164
152 # execute the display interface tunnel 4 command on switch a to identify the state of the primary lsp. You can see that the tunnel interface is still up. # execute the display mpls te tunnel-interface command on switch a to verify the configuration of the tunnel interface. [switcha] display mpls...
Page 165
153 admin state : oper state : modified ingress lsr id : 1.1.1.1 egress lsr id: 4.4.4.4 signaling prot : rsvp resv style : se class type : ct0 tunnel bw : 0 kbps reserved bw : 0 kbps setup priority : 7 hold priority: 7 affinity prop/mask : 0x0/0x0 explicit path name : pri-path tie-breaking policy : ...
Page 166
154 in-interface : vlan-interface1 out-interface : vlan-interface2 lspindex : 4097 tunnel id : 0x22001 lsrtype : transit bypass in use : in use bypasstunnel : tunnel index[tunnel5], innerlabel[1024] no : 2 ingresslsrid : 2.2.2.2 locallspid : 1 tunnel-interface : tunnel5 fec : 3.3.3.3/32 nexthop : 3....
Page 167
155 • to allow the mpls l3vpn traffic to travel the te tunnel, configure a tunneling policy to use a cr-lsp as the vpn tunnel when creating the vpn. Figure 37 network diagram configuration procedure 1. Configure ospf, making sure that pe 1 and pe 2 can learn lsr-id routes from each other: # configur...
Page 168
156 after you complete the configuration, the pes establish an ospf neighborship. Execute the display ospf peer verbose command. You will see that the neighborship state is full. Execute the display ip routing-table command. You will see that the pes have learned the routes to the loopback interface...
Page 169
157 [pe2-vlan-interface2] mpls [pe2-vlan-interface2] mpls te [pe2-vlan-interface2] mpls rsvp-te [pe2-vlan-interface2] quit 3. Enable ospf te: # configure pe 1. [pe1] ospf [pe1-ospf-1] opaque-capability enable [pe1-ospf-1] area 0 [pe1-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] mpls-te enable [pe1-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] quit...
Page 170
158 [pe1] interface vlan-interface 1 [pe1-vlan-interface1] ip binding vpn-instance vpn1 [pe1-vlan-interface1] ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 [pe1-vlan-interface1] quit # configure on ce 2. System-view [ce2] interface vlan-interface 3 [ce2-vlan-interface3] ip address 192.168.2.2 255.255.255.0 [...
Page 171
159 # configure ce 1. [ce1] bgp 65001 [ce1-bgp] peer 192.168.1.1 as-number 100 [ce1-bgp] quit # configure pe 1 to establish the ebgp peer relationship with ce 1, and the ibgp peer relationship with pe 2. [pe1] bgp 100 [pe1-bgp] ipv4-family vpn-instance vpn1 [pe1-bgp-vpn1] peer 192.168.1.2 as-number ...
Page 172
160 192.168.1.2 4 65001 4 5 0 00:02:13 established 0 ping ce 2 on ce 1 and vice versa to test connectivity. [ce1] ping 192.168.2.2 ping 192.168.2.2: 56 data bytes, press ctrl_c to break reply from 192.168.2.2: bytes=56 sequence=1 ttl=253 time=61 ms reply from 192.168.2.2: bytes=56 sequence=2 ttl=253...
Page 173
161 bypasstunnel : tunnel index[---] ------------------------------------------------------------------ lsp information: bgp lsp ------------------------------------------------------------------ no : 2 vrfindex : vpn1 fec : 192.168.1.0/24 nexthop : 192.168.1.1 in-label : 1024 out-label : null in-in...
Page 174
162 # execute the display interface tunnel command on pe 1. The output shows that traffic is being forwarded along the cr-lsp of the te tunnel. [pe1] display interface tunnel 1 tunnel1 current state: up line protocol current state: up description: tunnel1 interface the maximum transmit unit is 1500 ...
Page 175
163 configuring vpls this chapter describes how to configure vpls. The s5500-28sc-hi and s5500-52sc-hi switches do not support vpls. Vpls overview virtual private lan service (vpls), also called "transparent lan service (tls)" or "virtual private switched network service," can deliver a point-to-mul...
Page 176
164 • forwarders—a forwarder functions as the vpls forwarding table. Once a pe receives a packet from an ac, the forwarder selects a pw for forwarding the packet. • tunnel—a tunnel, usually an mpls tunnel, is a direct channel between a local pe and the peer pe for transparent data transmission in-be...
Page 177
165 mac address learning and flooding vpls provides reachability by mac address learning. Each pe maintains a mac address table. • source mac address learning mac address learning includes the following parts: { remote mac address learning associated with pws a pw consists of two unidirectional vc l...
Page 178
166 contains a null mac address tlv list, these pes remove all mac addresses from the specified vsi, except for those learned from the pw that sent the message. • mac address aging remote mac addresses learned by a pe that are related to vc labels but no longer in use must be aged out by an aging me...
Page 179
167 the pe adds the vlan tag expected by the peer pe or a null tag, and then a pw label and a tunnel label into the packet before sending the packet out. For a packet to be sent downstream, the pe rewrites, removes, or retains the service delimiter depending on your configuration. According to the p...
Page 180
168 h-vpls with qinq access figure 41 h-vpls with qinq access as shown in figure 41 , mtu is a standard bridging device and qinq is enabled on its interfaces connected to ces. Data forwarding in h-vpls with qinq access is as follows: 1. Upon receiving a packet from a ce, mtu labels the packet with a...
Page 181
169 the h-vpls with lsp access activates the backup link when: • the tunnel over which the primary pw is established is deleted, causing the pw to go down. • bfd detects a primary link failure. • the ldp session between the peers of the primary pw goes down, and the pw is deleted as a result. Vpls c...
Page 182
170 configuring an ldp vpls instance when creating an ldp vpls instance, perform the following configurations: 1. Specify a globally unique name for the vpls instance and set the peer discovery mechanism to manual configuration. 2. Configure ldp as the pw signaling protocol. 3. Specify the id of the...
Page 183
171 step command remarks 10. Return to vsi ldp view. Quit n/a 11. Enable the pw switchover function and set the switchover delay time. Dual-npe revertive [ wtr-time wtr-time ] optional. By default, pw switchover is disabled. Configuring bgp vpls before you configure bgp vpls, complete the following ...
Page 186
174 step command remarks 6. Specify a tunneling policy for the vpls instance. Tnl-policy tunnel-policy-name optional. By default, no tunneling policy is specified for a vpls instance and a vpls instance uses the default tunneling policy. The default tunneling policy selects only one tunnel in this o...
Page 188
176 • configure service instance 1000 to match packets that are received on gigabitethernet 1/0/1 and carry the vlan tag of 100. Bind service instance 1000 to vpls instance aaa. • configure service instance 2000 to match packets that are received on gigabitethernet 1/0/1 and carry vlan tag of 200. B...
Page 189
177 [pe1-ospf-1] area 0 [pe1-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 23.1.1.1 0.0.0.255 [pe1-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 1.1.1.9 0.0.0.0 [pe1-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] quit [pe1-ospf-1] quit # configure bgp extensions. [pe1] bgp 100 [pe1-bgp] peer 3.3.3.9 as-number 100 [pe1-bgp] peer 3.3.3.9 connect-interface loop...
Page 190
178 [p] mpls lsr-id 2.2.2.9 [p] mpls [p-mpls] quit # enable ldp globally. [p] mpls ldp [p-mpls-ldp] quit # configure the interface connected to pe 1 and enable ldp on the interface. [p] interface vlan-interface 2 [p-vlan-interface2] ip address 23.1.1.2 24 [p-vlan-interface2] mpls [p-vlan-interface2]...
Page 191
179 # configure the interface connected to the p device and enable ldp on the interface. [pe2] interface vlan-interface 3 [pe2-vlan-interface3] ip address 26.2.2.1 24 [pe2-vlan-interface3] mpls [pe2-vlan-interface3] mpls ldp [pe2-vlan-interface3] quit # configure ospf. [pe2] ospf [pe2-ospf-1] area 0...
Page 192
180 [pe2-gigabitethernet1/0/1] quit 4. Verify the configuration: issue the display vpls connection command on the pes. The output shows that a pw connection in up state has been established. Take pe 2 as an example: [pe2] display vpls connection vsi aaa verbose vsi name: aaa signaling: ldp **remote ...
Page 193
181 2. Configure upe: # configure basic mpls. System-view [sysname] sysname upe [upe] interface loopback 0 [upe-loopback0] ip address 1.1.1.1 32 [upe-loopback0] quit [upe] mpls lsr-id 1.1.1.1 [upe] mpls [upe-mpls] quit [upe] mpls ldp [upe-mpls-ldp] quit # configure an ip address for the interface co...
Page 194
182 [upe-gigabitethernet1/0/1-srv1000] encapsulation s-vid 10 [upe-gigabitethernet1/0/1-srv1000] xconnect vsi aaa [upe-gigabitethernet1/0/1-srv1000] quit # on the interface connected to ce 2, create a service instance and bind the vsi. [upe] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/2 [upe-gigabitethernet1/0/2]...
Page 195
183 [npe1] vsi aaa static [npe1-vsi-aaa] pwsignal ldp [npe1-vsi-aaa-ldp] vsi-id 500 [npe1-vsi-aaa-ldp] peer 1.1.1.1 upe [npe1-vsi-aaa-ldp] peer 4.4.4.4 [npe1-vsi-aaa-ldp] quit [npe1-vsi-aaa] quit the configuration procedure on npe 2 is similar to that on npe 1. (details not shown.) 4. Configure npe ...
Page 196
184 [npe3-vsi-aaa-ldp] peer 2.2.2.2 [npe3-vsi-aaa-ldp] peer 3.3.3.3 [npe3-vsi-aaa-ldp] quit [npe3-vsi-aaa] quit # create service instance on gigabitethernet 1/0/1, the interface connecting ce 3, and bind the vpls instance. [npe3] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1 [npe3-gigabitethernet1/0/1] service-in...
Page 197
185 [switcha-mpls-ldp] quit [switcha] mpls ldp remote-peer switchb [switcha-mpls-ldp-remote-switchb] remote-ip 2.2.2.9 [switcha-mpls-ldp-remote-switchb] remote-ip bfd [switcha-mpls-ldp-remote-switchb] quit [switcha] mpls ldp remote-peer switchc [switcha-mpls-ldp-remote-switchc] remote-ip 3.3.3.9 [sw...
Page 198
186 [switchc] mpls ldp remote-peer switcha [switchc-mpls-ldp-remote-switcha] remote-ip 1.1.1.9 [switchc-mpls-ldp-remote-switcha] remote-ip bfd [switchc-mpls-ldp-remote-switcha] quit [switchc] vlan 13 [switchc-vlan13] port gigabitethernet 1/0/1 [switchc-vlan13] quit [switchc] interface vlan-interface...
Page 199
187 [switchb-ospf-1] area 0 [switchb-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 12.1.1.2 0.0.0.255 [switchb-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 2.2.2.9 0.0.0.0 [switchb-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] quit [switchb-ospf-1] quit # configure switch c. [switchc] ospf [switchc-ospf-1] area 0 [switchc-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 13.1....
Page 200
188 [switchc-vsi-vpna-ldp] quit [switchc-vsi-vpna] quit 5. Verify the configuration: # use the display bfd session verbose command to display information about the bfd sessions from switch a to its neighbors. Display bfd session verbose total session num: 2 init mode: active session working under ct...
Page 201
189 connection(s): 1 up, 0 block, 0 down vsi name: vpna signaling: ldp vsiid vsitype peeraddr inlabel outlabel linkid vcstate 100 vlan 3.3.3.9 134216 140476 2 up the output shows that the link to 3.3.3.9 is up. Troubleshooting vpls symptom the vpls pw is not up. Analysis • the public network lsp tun...
Page 202
190 configuring mpls l2vpn this chapter describes how to configure mpls l2vpn. The s5500-28sc-hi and s5500-52sc-hi switches do not support mpls l2vpn. Mpls l2vpn overview mpls l2vpn is an mpls-based layer 2 vpn technology. It uses mpls to establish layer 2 connections between network nodes. Using mp...
Page 203
191 • provider device—p devices do not directly connect to ces. They only need to forward user packets between pes along the public tunnel. Mpls l2vpn network models mpls l2vpn network models include remote connection model and local connection model. Remote connection model as shown in figure 46 , ...
Page 204
192 if multiple public tunnels exist between two pes, you can configure a tunneling policy to control tunnel selection. For more information about tunneling policy, see " configuring mpls l3vpn ." 2. Set up a vc to identify customer networks. To set up a vc, the two pes assign vc labels to each othe...
Page 205
193 3. After pe 2 receives the packet from the public tunnel, it identifies the vc to which the packet belongs according to the vc label of the packet, deletes the tunnel tag and the vc label from the packet, and then forwards the resulting packet to ce 2 through the ac bound to the vc. This packet ...
Page 206
194 martini mpls l2vpn martini mpls l2vpn employs two levels of labels to transfer user packets, and uses ldp as the signaling protocol to distribute the inner vc label. To exchange vc labels between pes, martini extended ldp by adding the vc fec. The vc fec contains the following information: • vc ...
Page 207
195 in a word, route target attributes define which pes can receive l2vpn information, and from which pes that a pe can receive l2vpn information. Different from martini mode, the kompella mode does not distribute the vc label assigned by the local pe directly to the peer pe through the signaling pr...
Page 208
196 pe 1 compares the id (12) of the peer ce (ce 12) with the label blocks assigned by pe 1. If a label block satisfies lo block 2 (1055/5/10) satisfies lo from label block 2. The assigned label value = lb+ce id-lo, namely 1062 (1055+12-5). • pe 1 calculates the vc label that pe 2 assigns to the vc:...
Page 209
197 table 1 compares the implementation modes of mpls l2vpn. Table 1 comparing the mpls l2vpn implication modes mode vc label encapsulation and distribution advantages and disadvantages application scenario ccc vc label encapsulation: one level of label vc label distribution: static configuration ad...
Page 210
198 vc types before encapsulating layer 2 packets with vc labels, pes process the layer 2 packets of different link layer protocols in different manners. A vc type identifies the mode in which a pe processes the layer 2 packet on the vc. Vc types and ac (pe-ce link) types are closely related. An eth...
Page 211
199 task remarks configuring a pe-ce interface of a pe required. Perform this task to set up an ac between a pe and a ce. Configuring a remote ccc connection use one of the approaches according to the mpls l2vpn implementation method. Perform this task to set up a vc, and bind the vc to an ac. Confi...
Page 212
200 configuring vlan encapsulation when you configure martini mpls l2vpn for a service instance, you can specify the encapsulation type for the pe-ce interface. When you configure mpls l2vpn other than the martini mode, you can only use the default encapsulation type on the pe-ce interface. By defau...
Page 213
201 svc supports these tunnel types: ldp lsp and cr-lsp. By default, ldp lsp tunnels are used. After you configure svc on a layer 3 interface (layer 3 ethernet interface or vlan interface), packets arriving at this interface are forwarded over the vc. If the layer 3 interface is a vlan interface, al...
Page 214
202 users connected to the same vlan interface must use different vcs to forward packets. For more information about service instances, see " configuring vpls ." note: service instances can be created only on layer 2 ethernet interfaces or layer 2 aggregate interfaces. Configuring the remote peer st...
Page 216
204 inspecting vcs on a mpls l2vpn network, you can use the mpls lsp ping function to test the connectivity of vcs and get necessary information for troubleshooting vc failures on the local pe, the mpls lsp ping function adds the label of the vc to be tested into mpls echo request messages so the me...
Page 218
206 ce ce1 id 1 range 10 default-offset 0 ce ce1 id 1 range 22 ce ce1 id 1 range 36 • ce-offset ce-id: specifies the id of the peer ce that establishes a local or remote connection with the local ce. If you execute the connection command without specifying the ce-offset ce-id option: { when you firs...
Page 219
207 step command remarks 4. Create a kompella connection. Connection [ ce-offset ce-id ] interface interface-type interface-number [ tunnel-policy tunnel-policy-name ] the ce-offset ce-id option determines whether the connection is a local connection or a remote connection. If the specified ce is co...
Page 221
209 figure 53 network diagram device interface ip address device interface ip address ce 1 vlan-int10 100.1.1.1/24 ce 2 vlan-int10 100.1.1.2/24 pe 1 loop0 10.0.0.1/32 p loop0 10.0.0.2/32 vlan-int30 10.1.1.1/24 vlan-int20 10.2.2.2/24 pe 2 loop0 10.0.0.3/32 vlan-int30 10.1.1.2/24 vlan-int20 10.2.2.1/2...
Page 222
210 [pe1-vlan-interface30] ip address 10.1.1.1 24 [pe1-vlan-interface30] mpls [pe1-vlan-interface30] quit # create a remote connection from ce 1 to ce 2, using the interface connected to ce 1 as the incoming interface and that connecting the p device as the outgoing interface, setting the incoming l...
Page 223
211 [pe2-l2vpn] quit # configure interface vlan-interface 10. [pe2] interface vlan-interface 10 [pe2-vlan-interface10] quit # configure interface vlan-interface 20 and enable mpls. [pe2] interface vlan-interface 20 [pe2-vlan-interface20] ip address 10.2.2.1 24 [pe2-vlan-interface20] mpls [pe2-vlan-i...
Page 224
212 example for configuring svc mpls l2vpn network requirements ces are connected to pes through vlan interfaces. Establish an svc between ce 1 and ce 2, so ce 1 and ce 2 can exchange layer 2 packets across the backbone. Figure 54 network diagram device interface ip address device interface ip addre...
Page 225
213 [pe1-loopback0] ip address 192.2.2.2 32 [pe1-loopback0] quit [pe1] mpls lsr-id 192.2.2.2 [pe1] mpls [pe1-mpls] quit # enable l2vpn and mpls l2vpn. [pe1] l2vpn [pe1-l2vpn] mpls l2vpn [pe1-l2vpn] quit # enable ldp globally. [pe1] mpls ldp [pe1-mpls-ldp] quit # configure the interface connected wit...
Page 226
214 [p-vlan-interface20] mpls ldp [p-vlan-interface20] quit # configure the interface connected with pe 2, and enable ldp on the interface. [p] interface vlan-interface 30 [p-vlan-interface30] ip address 10.2.2.2 24 [p-vlan-interface30] mpls [p-vlan-interface30] mpls ldp [p-vlan-interface30] quit # ...
Page 227
215 # create a static vc on the interface connected to ce 2. The interface requires no ip address. [pe2] interface vlan-interface 10 [pe2-vlan-interface10] mpls static-l2vc destination 192.2.2.2 transmit-vpn-label 200 receive-vpn-label 100 [pe2-vlan-interface10] quit 5. Configure ce 2: # configure a...
Page 228
216 figure 55 network diagram device interface ip address device interface ip address ce 1 vlan-int10 100.1.1.1/24 ce 2 vlan-int10 100.1.1.2/24 pe 1 loop0 192.2.2.2/32 p loop0 192.4.4.4/32 vlan-int20 10.1.1.1/24 vlan-int20 10.1.1.2/24 pe 2 loop0 192.3.3.3/32 vlan-int30 10.2.2.2/24 vlan-int30 10.2.2....
Page 229
217 [pe1-mpls-ldp-remote-1] quit # configure the interface connected with the p device, and enable ldp on the interface. [pe1] interface vlan-interface 20 [pe1-vlan-interface20] ip address 10.1.1.1 24 [pe1-vlan-interface20] mpls [pe1-vlan-interface20] mpls ldp [pe1-vlan-interface20] quit # configure...
Page 230
218 [p-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 10.1.1.2 0.0.0.255 [p-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 10.2.2.2 0.0.0.255 [p-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 192.4.4.4 0.0.0.0 [p-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] quit [p-ospf-1] quit 4. Configure pe 2: # configure the lsr id and enable mpls globally. System-view [sysname] sysname p...
Page 231
219 system-view [sysname] sysname ce2 [ce2] interface vlan-interface 10 [ce2-vlan-interface10] ip address 100.1.1.2 24 6. Verify your configuration: # display vc information on pe 1. The output shows that a vc has been established. [pe1] display mpls l2vc total ldp vc : 1 1 up 0 down 0 blocked trans...
Page 232
220 figure 56 network diagram device interface ip address device interface ip address ce 1 vlan-int10 100.1.1.1/24 ce 2 vlan-int10 100.1.1.2/24 pe 1 loop0 2.2.2.2/32 p loop0 3.3.3.3/32 vlan-int20 10.1.1.1/24 vlan-int20 10.1.1.2/24 pe 2 loop0 4.4.4.4/32 vlan-int30 10.2.2.2/24 vlan-int30 10.2.2.1/24 c...
Page 233
221 [sysname] sysname pe2 [pe2] l2vpn [pe2-l2vpn] mpls l2vpn [pe2-l2vpn] quit [pe2] bgp 100 [pe2-bgp] peer 2.2.2.2 as-number 100 [pe2-bgp] peer 2.2.2.2 connect-interface loopback 0 [pe2-bgp] l2vpn-family [pe2-bgp-af-l2vpn] policy vpn-target [pe2-bgp-af-l2vpn] peer 2.2.2.2 enable [pe2-bgp-af-l2vpn] q...
Page 234
222 1 total connections, connections: 1 up, 0 down, 0 local, 1 remote, 0 unknown ce name: ce1, id: 1, rid type status peer-id route-distinguisher intf 2 rmt up 4.4.4.4 100:1 vlan10 # ping ce 2 from ce 1. The output shows that ce 1 and ce 2 can ping each other. [ce1] ping 100.1.1.2 ping 100.1.1.2: 56...
Page 235
223 # configure an ip address for the interface connected to pe 1. System-view [sysname] sysname ce1 [ce1] interface vlan-interface 10 [ce1-vlan-interface10] ip address 100.1.1.1 24 2. Configure pe 1: system-view [sysname] sysname pe1 [pe1] interface loopback 0 [pe1-loopback0] ip address 192.2.2.2 3...
Page 236
224 3. Configure the p device: system-view [sysname] sysname p [p] interface loopback 0 [p-loopback0] ip address 192.4.4.4 32 [p-loopback0] quit # configure the mpls lsr id and enable mpls globally. [p] mpls lsr-id 192.4.4.4 [p] mpls [p-mpls] quit # enable ldp globally. [p] mpls ldp [p-mpls-ldp] qui...
Page 237
225 # enable ldp globally. [pe2] mpls ldp [pe2-mpls-ldp] quit # configure pe 2 to establish a remote ldp connection with pe 1. [pe2] mpls ldp remote-peer 2 [pe2-mpls-ldp-remote-2] remote-ip 192.2.2.2 [pe2-mpls-ldp-remote-2] quit # configure the interface connected to the p device and enable ldp on t...
Page 238
226 transport client service vc local remote vc id intf id state vc label vc label 1000 ge1/0/1 1000 up 8192 8193 # ping ce 2 from ce 1. The output shows that ce 1 and ce 2 can ping each other. [ce1] ping 100.1.1.2 ping 100.1.1.2: 56 data bytes, press ctrl_c to break reply from 100.1.1.2: bytes=56 s...
Page 239
227 configuring mpls l3vpn the s5500-28sc-hi and s5500-52sc-hi switches do not support mpls l3vpn. This chapter describes only mpls l3vpn related information. For information about basic mpls configuration, see " configuring basic mpls ." for information about bgp, see layer 3—ip routing configurati...
Page 240
228 a ce is usually a router. After a ce establishes adjacency with a directly connected pe, it advertises its vpn routes to the pe and learns remote vpn routes from the pe. A ce and a pe use bgp/igp to exchange routing information. You can also configure static routes between them. After a pe learn...
Page 241
229 pes use mp-bgp to advertise vpn routes, and use vpn-ipv4 address family to solve the problem with traditional bgp. A vpn-ipv4 address consists of 12 bytes. The first eight bytes represent the rd, followed by a 4-byte ipv4 address prefix. Figure 59 vpn-ipv4 address structure when a pe receives an...
Page 242
230 in other words, route target attributes define which sites can receive vpn-ipv4 routes, and from which sites that a pe can receive routes. Like rds, route target attributes can be of the following formats: • 16-bit as number:32-bit user-defined number. For example, 100:1. • 32-bit ipv4 address:1...
Page 243
231 mpls l3vpn packet forwarding for basic mpls l3vpn applications in a single as, vpn packets are forwarded with the following layers of labels: • layer 1 labels—outer labels, used for label switching inside the backbone. They indicate lsps from the local pes to the remote pes. Based on layer 1 lab...
Page 244
232 for this networking scheme, the basic vpn networking scheme, you must assign a route target to each vpn for identifying the export target attribute and import target attribute of the vpn. Moreover, this route target cannot be used by any other vpns. Figure 61 network diagram for basic vpn networ...
Page 245
233 figure 62 network diagram for hub and spoke networking scheme in figure 62 , the spoke sites communicate with each other through the hub site. The arrows in the figure indicate the advertising path of routes from site 2 to site 1: • the hub pe can receive all the vpn-ipv4 routes advertised by sp...
Page 246
234 figure 63 network diagram for extranet networking scheme in figure 63 , vpn 1 and vpn 2 can access site 3 of vpn 1. • pe 3 can receive the vpn-ipv4 routes advertised by pe 1 and pe 2. • pe 1 and pe 2 can receive the vpn-ipv4 routes advertised by pe 3. • site 1 and site 3 of vpn 1 can communicate...
Page 247
235 the route between the ce and the pe can be a static route, rip route, ospf route, is-is route, ebgp route, or ibgp route. No matter which routing protocol is used, the ce always advertises standard ipv4 routes to the pe. Routing information exchange from the ingress pe to the egress pe after lea...
Page 248
236 figure 64 network diagram for inter-as option a inter-as option a is easy to carry out because no special configuration is required on the pes acting as the asbrs. However, it has limited scalability because the pes acting as the asbrs must manage all the vpn routes and create vpn instances on a...
Page 249
237 figure 65 network diagram for inter-as option b in terms of scalability, inter-as option b is better than option a. When adopting mp-ebgp method, note the following: • asbrs perform no route target filtering on vpn-ipv4 routes that they receive from each other. Therefore, the isps in different a...
Page 250
238 figure 66 network diagram for inter-as option c to improve the scalability, you can specify an rr in each as, making it maintain all vpn-ipv4 routes and exchange vpn-ipv4 routes with pes in the as. The rrs in two ass establish an inter-as vpnv4 connection to advertise vpn-ipv4 routes. Figure 67 ...
Page 251
239 of the level 2 carrier. Routes of the customer networks connected to a level 2 carrier are exchanged through the bgp session established between the routers of the level 2 carrier. This can greatly reduce the number of routes maintained by the level 1 carrier network. Implementation of carrier's...
Page 252
240 figure 69 scenario where the level 2 carrier is an mpls l3vpn service provider note: if equal cost routes exist between the level 1 carrier and the level 2 carrier, h3c recommends establishing equal cost lsps between them. Nested vpn background in an mpls l3vpn network, generally a service provi...
Page 253
241 figure 70 network diagram for nested vpn propagation of routing information in a nested vpn network, routing information is propagated in the following process: 1. A provider pe and its ces exchange vpnv4 routes, which carry information about users' internal vpns. 2. After receiving a vpnv4 rout...
Page 254
242 nested vpn is flexible and easy to implement and can reduce the cost because a customer only needs to pay for one mpls vpn to have multiple internal vpns connected. Nested vpn provides diversified vpn networking methods for a customer, and allows for multi-level hierarchical access control over ...
Page 255
243 as shown in figure 71 , devices directly connected to ces are called underlayer pes or user-end pes (upes), whereas devices that are connected with upes and are in the internal network are called superstratum pes or service provider-end pes (spe). The hierarchical pe consists of multiple upes an...
Page 256
244 figure 72 recursion of hopes figure 72 shows a three-level hope. The pe in the middle is called the middle-level pe (mpe). Mp-bgp runs between spe and mpe, and between mpe and upe. The term "mpe" does not really exist in a hovpn model. It is used here just for the convenience of description. Mp-...
Page 257
245 conventional ospf considers two sites to be in different ass even if they belong to the same vpn. Therefore, the routes that one site learns are advertised to the other as external routes. This results in more ospf traffic and network management problems. The extended ospf protocol supports mult...
Page 258
246 if the pe needs to advertise to a ce the routes from other ospf domains, it must indicate that it is the asbr, and advertise the routes using type 5 lsas. Sham link generally, bgp peers carry routing information on the mpls vpn backbone through the bgp extended community attributes. The ospf tha...
Page 259
247 the bgp as number substitution function allows physically dispersed ces to use the same as number. The function is a bgp outbound policy and functions on routes to be advertised. With the bgp as number substitution function, when a pe advertises a route to a ce of the specified peer, if an as nu...
Page 260
248 complete the following tasks to configure basic mpls l3vpn: task remarks configuring vpn instances creating a vpn instance required associating a vpn instance with an interface required configuring route related attributes for a vpn instance optional configuring a tunneling policy for a vpn inst...
Page 261
249 associating a vpn instance with an interface after creating and configuring a vpn instance, you need to associate the vpn instance with the interface for connecting the ce. Any ldp-capable interface can be associated with a vpn instance. For information about ldp-capable interfaces, see " config...
Page 263
251 to configure a tunneling policy for a vpn instance: step command remarks 1. Enter system view. System-view n/a 2. Create a tunneling policy and enter tunneling policy view. Tunnel-policy tunnel-policy-name n/a 3. Configure a preferred tunnel and specify a tunnel interface for it. Preferred-path ...
Page 264
252 configuring an ldp instance ldp instances are for carrier's carrier network applications. This task is to configure the ldp capability for an existing vpn instance, create an ldp instance for the vpn instance, and configure ldp parameters for the ldp instance. To configure an ldp instance: step ...
Page 267
255 step command remarks 5. Enter interface view. Interface interface-type interface-number n/a 6. Enable the is-is process on the interface. Isis enable [ process-id ] disabled by default. Configuring ebgp between pe and ce 1. Configure the pe: step command remarks 1. Enter system view. System-view...
Page 272
260 configuring specific routing features for bgp-vpnv4 subaddress family step command remarks 1. Enter system view. System-view n/a 2. Enter bgp view. Bgp as-number n/a 3. Configure the remote pe as the peer. Peer ip-address as-number as-number n/a 4. Specify the interface for tcp connection. Peer ...
Page 274
262 can be received by the asbr-pes (or pes). Route targets configured on the pes in different ass do not have such requirements. Configuring inter-as option b for inter-as option b, the following configuration methods are available: • do not change the next hop on an asbr. With this method, you sti...
Page 277
265 • do not give nested vpn peers addresses that public network peers use. • before specifying a nested vpn peer or peer group, configure the corresponding ce peer or peer group in bgp vpn instance view. • if a ce of a sub-vpn is directly connected to a service provider's pe, policy routing must be...
Page 280
268 instances on the same pe or pes with the same as number. Therefore, h3c recommends configuring different tags for different ospf vpn instances. Configuring bgp as number substitution and soo when ces at different sites have the same as number, configure the bgp as number substitution function to...
Page 281
269 soft reset of bgp connections refers to updating bgp routing information without breaking bgp neighbor relationships. Hard reset of bgp connections refers to updating bgp routing information by breaking and then reestablishing bgp neighbor relationships. To hard reset or soft reset bgp connectio...
Page 284
272 • vpn 1 uses route target attribute 111:1. Vpn 2 uses route target attribute 222:2. Users of different vpns cannot access each other. • ebgp is used to exchange vpn routing information between ce and pe. • pes use ospf to communicate with each other and use mp-ibgp to exchange vpn routing inform...
Page 285
273 [pe1-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] quit [pe1-ospf-1] quit # configure the p device. System-view [p] interface loopback 0 [p-loopback0] ip address 2.2.2.9 32 [p-loopback0] quit [p] interface vlan-interface 13 [p-vlan-interface13] ip address 172.1.1.2 24 [p-vlan-interface13] quit [p] interface vlan-interfa...
Page 286
274 172.1.1.1/32 direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 inloop0 172.2.1.0/24 ospf 10 1 172.1.1.2 vlan13 [pe1] display ospf peer verbose ospf process 1 with router id 1.1.1.9 neighbors area 0.0.0.0 interface 172.1.1.1(vlan-interface13)'s neighbors router id: 172.1.1.2 address: 172.1.1.2 gr state: normal state: full mo...
Page 287
275 after you complete the configurations, ldp sessions are established between pe 1, p, and pe 2. Issue the display mpls ldp session command. The output shows that the session status is operational. Issue the display mpls ldp lsp command. The output shows the lsps established by ldp. Take pe 1 as a...
Page 288
276 [pe2-vpn-instance-vpn2] route-distinguisher 200:2 [pe2-vpn-instance-vpn2] vpn-target 222:2 [pe2-vpn-instance-vpn2] quit [pe2] interface vlan-interface 11 [pe2-vlan-interface11] ip binding vpn-instance vpn1 [pe2-vlan-interface11] ip address 10.3.1.2 24 [pe2-vlan-interface11] quit [pe2] interface ...
Page 289
277 [pe1-bgp-vpn1] quit [pe1-bgp] ipv4-family vpn-instance vpn2 [pe1-bgp-vpn2] peer 10.2.1.1 as-number 65420 [pe1-bgp-vpn2] import-route direct [pe1-bgp-vpn2] quit [pe1-bgp] quit # configure pe 2 in a similar way as you configure pe 1. (details not shown.) after completing the configurations, issue ...
Page 290
278 routing tables: vpn1 destinations : 5 routes : 5 destination/mask proto pre cost nexthop interface 10.1.1.0/24 direct 0 0 10.1.1.2 vlan11 10.1.1.2/32 direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 inloop0 10.3.1.0/24 bgp 255 0 3.3.3.9 null0 127.0.0.0/8 direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 inloop0 127.0.0.1/32 direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 inloop...
Page 291
279 • vpn 1 uses route target attribute 111:1. Vpn 2 uses route target attribute 222:2. Users of different vpns cannot access each other. • ibgp is used to exchange vpn routing information between ce and pe. • pes use ospf to communicate with each other and use mp-ibgp to exchange vpn routing inform...
Page 292
280 [pe1-ospf-1] area 0 [pe1-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 172.1.1.0 0.0.0.255 [pe1-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 1.1.1.9 0.0.0.0 [pe1-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] quit [pe1-ospf-1] quit # configure the p switch. System-view [p] interface loopback 0 [p-loopback0] ip address 2.2.2.9 32 [p-loopback0] quit [p] i...
Page 293
281 127.0.0.0/8 direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 inloop0 127.0.0.1/32 direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 inloop0 172.1.1.0/24 direct 0 0 172.1.1.1 vlan13 172.1.1.1/32 direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 inloop0 172.2.1.0/24 ospf 10 1 172.1.1.2 vlan13 [pe1] display ospf peer verbose ospf process 1 with router id 1.1.1.9 neighbors area 0.0.0...
Page 294
282 [pe2-vlan-interface12] mpls [pe2-vlan-interface12] mpls ldp [pe2-vlan-interface12] quit after the configurations, p establishes an ldp session with pe 1 and pe 2 respectively. Issue the display mpls ldp session command. The output shows that the session status is operational. Issue the display m...
Page 295
283 [pe2-vpn-instance-vpn1] vpn-target 111:1 [pe2-vpn-instance-vpn1] quit [pe2] ip vpn-instance vpn2 [pe2-vpn-instance-vpn2] route-distinguisher 200:2 [pe2-vpn-instance-vpn2] vpn-target 222:2 [pe2-vpn-instance-vpn2] quit [pe2] interface vlan-interface 11 [pe2-vlan-interface11] ip binding vpn-instanc...
Page 296
284 [ce1-bgp] quit # configure the other three ces (ce 2 through ce 4) in a similar way as you configure ce 1. (details not shown.) # on pe 1, configure the ce 1 and ce 2 as the ibgp peers, and configure pe 1 as the route reflector. [pe1] bgp 100 [pe1-bgp] ipv4-family vpn-instance vpn1 [pe1-bgp-vpn1...
Page 297
285 # on pe 2, configure pe 1 as the mp-ibgp peer, and configure a routing policy for the routes received from pe 1, changing the next hop address of the routes as the loopback interface address of pe 1. [pe2] route-policy pe-ibgp permit node 0 [pe2-route-policy] apply ip-address next-hop 1.1.1.9 [p...
Page 298
286 10.4.1.0/24 bgp 255 0 3.3.3.9 null0 127.0.0.0/8 direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 inloop0 127.0.0.1/32 direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 inloop0 ces of the same vpn can ping each other, whereas those of different vpns cannot. For example, ce 1 can ping ce 3 (6.6.6.9), but cannot ping ce 4 (7.7.7.9): [ce1] ping 6.6.6.9 pi...
Page 299
287 figure 78 network diagram device interface ip address device interface ip address spoke-ce 1 vlan-int2 10.1.1.1/24 hub-ce vlan-int6 10.3.1.1/24 spoke-pe 1 loop0 1.1.1.9/32 vlan-int7 10.4.1.1/24 vlan-int2 10.1.1.2/24 hub-pe loop0 2.2.2.9/32 vlan-int4 172.1.1.1/24 vlan-int4 172.1.1.2/24 spoke-ce 2...
Page 300
288 [spoke-pe2-loopback0] quit [spoke-pe2] interface vlan-interface 5 [spoke-pe2-vlan-interface5] ip address 172.2.1.1 24 [spoke-pe2-vlan-interface5] quit [spoke-pe2] ospf [spoke-pe2-ospf-1] area 0 [spoke-pe2-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 172.2.1.0 0.0.0.255 [spoke-pe2-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 3....
Page 301
289 [spoke-pe1] display ospf peer verbose ospf process 1 with router id 1.1.1.9 neighbors area 0.0.0.0 interface 172.1.1.1(vlan-interface4)'s neighbors router id: 2.2.2.9 address: 172.1.1.2 gr state: normal state: full mode:nbr is master priority: 1 dr: 172.1.1.1 bdr: 172.1.1.2 mtu: 0 dead timer due...
Page 302
290 after the configuration, ldp sessions are established between spoke-pe 1 and hub-pe, and between spoke-pe 2 and hub-pe. Issue the display mpls ldp session command. The output shows that the session status is operational. Issue the display mpls ldp lsp command. The output shows the lsps establish...
Page 303
291 [hub-pe-vpn-instance-vpn1-in] vpn-target 222:2 import-extcommunity [hub-pe-vpn-instance-vpn1-in] quit [hub-pe] ip vpn-instance vpn1-out [hub-pe-vpn-instance-vpn1-out] route-distinguisher 100:4 [hub-pe-vpn-instance-vpn1-out] vpn-target 111:1 export-extcommunity [hub-pe-vpn-instance-vpn1-out] quit...
Page 304
292 [spoke-ce2-bgp] import-route direct [spoke-ce2-bgp] quit # configure the hub-ce. System-view [hub-ce] bgp 65430 [hub-ce-bgp] peer 10.3.1.2 as-number 100 [hub-ce-bgp] peer 10.4.1.2 as-number 100 [hub-ce-bgp] import-route direct [hub-ce-bgp] quit # configure spoke-pe 1. [spoke-pe1] bgp 100 [spoke-...
Page 305
293 10.1.1.1 65410 6 7 0 2 00:03:16 established 5. Configure an mp-ibgp peer relationship between a spoke-pe and the hub-pe: # configure spoke-pe 1. [spoke-pe1] bgp 100 [spoke-pe1-bgp] peer 2.2.2.9 as-number 100 [spoke-pe1-bgp] peer 2.2.2.9 connect-interface loopback 0 [spoke-pe1-bgp] ipv4-family vp...
Page 306
294 destinations : 8 routes : 8 destination/mask proto pre cost nexthop interface 10.0.0.0/24 bgp 255 0 2.2.2.9 null0 10.1.1.0/24 direct 0 0 10.1.1.2 vlan2 10.1.1.2/32 direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 inloop0 10.2.1.0/24 bgp 255 0 2.2.2.9 null0 10.3.1.0/24 bgp 255 0 2.2.2.9 null0 10.4.1.0/24 bgp 255 0 2.2.2.9 n...
Page 307
295 figure 79 network diagram device interface ip address device interface ip address ce 1 vlan-int12 10.1.1.1/24 ce 2 vlan-int12 10.2.1.1/24 pe 1 loop0 1.1.1.9/32 pe 2 loop0 4.4.4.9/32 vlan-int12 10.1.1.2/24 vlan-int12 10.2.1.2/24 vlan-int11 172.1.1.2/24 vlan-int11 162.1.1.2/24 asbr-pe 1 loop0 2.2....
Page 308
296 [pe1-vlan-interface11] mpls ldp [pe1-vlan-interface11] quit # configure mpls basic capability on asbr pe 1 and enable mpls ldp on the interface connected to pe 1. System-view [asbr-pe1] mpls lsr-id 2.2.2.9 [asbr-pe1] mpls [asbr-pe1-mpls] quit [asbr-pe1] mpls ldp [asbr-pe1-mpls-ldp] quit [asbr-pe...
Page 309
297 [ce1-vlan-interface12] ip address 10.1.1.1 24 [ce1-vlan-interface12] quit # configure pe 1. [pe1] ip vpn-instance vpn1 [pe1-vpn-instance-vpn1] route-distinguisher 100:1 [pe1-vpn-instance-vpn1] vpn-target 100:1 both [pe1-vpn-instance-vpn1] quit [pe1] interface vlan-interface 12 [pe1-vlan-interfac...
Page 310
298 the pes can ping the ces and the asbr pes can ping each other. 4. Establish ebgp peer relationships between pes and ces to allow vpn routes to be redistributed: # configure ce 1. [ce1] bgp 65001 [ce1-bgp] peer 10.1.1.2 as-number 100 [ce1-bgp] import-route direct [ce1-bgp] quit # configure pe 1. ...
Page 311
299 [asbr-pe1-bgp-af-vpnv4] quit [asbr-pe1-bgp] quit # configure asbr-pe 2. [asbr-pe2] bgp 200 [asbr-pe2-bgp] ipv4-family vpn-instance vpn1 [asbr-pe2-bgp-vpn1] peer 192.1.1.1 as-number 100 [asbr-pe2-bgp-vpn1] quit [asbr-pe2-bgp] peer 4.4.4.9 as-number 200 [asbr-pe2-bgp] peer 4.4.4.9 connect-interfac...
Page 312
300 figure 80 network diagram device interface ip address device interface ip address pe 1 loop0 2.2.2.9/32 pe 2 loop0 5.5.5.9/32 vlan-int12 30.0.0.1/8 vlan-int12 20.0.0.1/8 vlan-int11 1.1.1.2/8 vlan-int11 9.1.1.2/8 asbr-pe 1 loop0 3.3.3.9/32 asbr-pe 2 loop0 4.4.4.9/32 vlan-int11 1.1.1.1/8 vlan-int1...
Page 313
301 [pe1-vlan-interface11] quit # configure interface loopback 0 and start is-is on it. [pe1] interface loopback 0 [pe1-loopback0] ip address 2.2.2.9 32 [pe1-loopback0] isis enable 1 [pe1-loopback0] quit # create vpn instance vpn1 and configure the rd and route target attributes. [pe1] ip vpn-instan...
Page 314
302 [asbr-pe1-vlan-interface11] ip address 1.1.1.1 255.0.0.0 [asbr-pe1-vlan-interface11] isis enable 1 [asbr-pe1-vlan-interface11] mpls [asbr-pe1-vlan-interface11] mpls ldp [asbr-pe1-vlan-interface11] quit # configure interface vlan-interface 12 and enable mpls on it. [asbr-pe1] interface vlan-inter...
Page 315
303 [asbr-pe2-vlan-interface11] mpls ldp [asbr-pe2-vlan-interface1] quit # configure interface vlan-interface 12 and enable mpls on it. [asbr-pe2] interface vlan-interface 12 [asbr-pe2-vlan-interface12] ip address 11.0.0.1 255.0.0.0 [asbr-pe2-vlan-interface12] mpls [asbr-pe2-vlan-interface12] quit #...
Page 316
304 # configure interface loopback 0 and start is-is on it. [pe2] interface loopback 0 [pe2-loopback0] ip address 5.5.5.9 32 [pe2-loopback0] isis enable 1 [pe2-loopback0] quit # create vpn instance vpn1 and configure the rd and route target attributes. [pe2] ip vpn-instance vpn1 [pe2-vpn-instance-vp...
Page 317
305 • asbr-pe 1 and asbr-pe 2 use mp-ebgp to exchange labeled ipv4 routes. Figure 81 network diagram device interface ip address device interface ip address pe 1 loop0 2.2.2.9/32 pe 2 loop0 5.5.5.9/32 loop1 30.0.0.1/32 loop1 20.0.0.1/32 vlan-int11 1.1.1.2/8 vlan-int11 9.1.1.2/8 asbr-pe 1 loop0 3.3.3...
Page 318
306 [pe1-loopback0] ip address 2.2.2.9 32 [pe1-loopback0] isis enable 1 [pe1-loopback0] quit # create vpn instance vpn1 and configure the rd and route target attributes. [pe1] ip vpn-instance vpn1 [pe1-vpn-instance-vpn1] route-distinguisher 11:11 [pe1-vpn-instance-vpn1] vpn-target 3:3 import-extcomm...
Page 319
307 [asbr-pe1-mpls-ldp] quit # configure interface vlan-interface 11, and start is-is and enable mpls and ldp on the interface. [asbr-pe1] interface vlan-interface 11 [asbr-pe1-vlan-interface11] ip address 1.1.1.1 255.0.0.0 [asbr-pe1-vlan-interface11] isis enable 1 [asbr-pe1-vlan-interface11] mpls [...
Page 320
308 system-view [asbr-pe2] isis 1 [asbr-pe2-isis-1] network-entity 10.3333.3333.3333.3333.00 [asbr-pe2-isis-1] quit # configure lsr id, enable mpls and ldp. [asbr-pe2] mpls lsr-id 4.4.4.9 [asbr-pe2] mpls [asbr-pe2-mpls] label advertise non-null [asbr-pe2-mpls] quit [asbr-pe2] mpls ldp [asbr-pe2-mpls...
Page 321
309 [asbr-pe2-bgp] peer 5.5.5.9 route-policy policy2 export # use routing policy policy1 to filter routes advertised to ebgp peer 11.0.0.2. [asbr-pe2-bgp] peer 11.0.0.2 as-number 100 [asbr-pe2-bgp] peer 11.0.0.2 route-policy policy1 export # configure the capability to advertise labeled routes to eb...
Page 322
310 [pe2] bgp 600 # configure the capability to advertise labeled routes to ibgp peer 4.4.4.9 and to receive labeled routes from the peer. [pe2-bgp] peer 4.4.4.9 as-number 600 [pe2-bgp] peer 4.4.4.9 connect-interface loopback 0 [pe2-bgp] peer 4.4.4.9 label-route-capability # configure the maximum ho...
Page 323
311 figure 82 network diagram device interface ip address device interface ip address ce 3 vlan-int11 100.1.1.1/24 ce 4 vlan-int11 120.1.1.1/24 pe 3 loop0 1.1.1.9/32 pe 4 loop0 6.6.6.9/32 vlan-int11 100.1.1.2/24 vlan-int11 120.1.1.2/24 vlan-int12 10.1.1.1/24 vlan-int12 20.1.1.2/24 ce 1 loop0 2.2.2.9...
Page 324
312 [pe1-loopback0] isis enable 1 [pe1-loopback0] quit [pe1] interface vlan-interface 12 [pe1-vlan-interface12] ip address 30.1.1.1 24 [pe1-vlan-interface12] isis enable 1 [pe1-vlan-interface12] mpls [pe1-vlan-interface12] mpls ldp [pe1-vlan-interface2] mpls ldp transport-address interface [pe1-vlan...
Page 325
313 [pe3-loopback0] quit [pe3] mpls lsr-id 1.1.1.9 [pe3] mpls [pe3-mpls] quit [pe3] mpls ldp [pe3-mpls-ldp] quit [pe3] isis 2 [pe3-isis-2] network-entity 10.0000.0000.0000.0001.00 [pe3-isis-2] quit [pe3] interface loopback 0 [pe3-loopback0] isis enable 2 [pe3-loopback0] quit [pe3] interface vlan-int...
Page 326
314 # configure pe 1 and inject is-is routes. [pe1] ip vpn-instance vpn1 [pe1-vpn-instance-vpn1] route-distinguisher 200:1 [pe1-vpn-instance-vpn1] vpn-target 1:1 [pe1-vpn-instance-vpn1] quit [pe1] mpls ldp vpn-instance vpn1 [pe1-mpls-ldp-vpn-instance-vpn1] quit [pe1] isis 2 vpn-instance vpn1 [pe1-is...
Page 327
315 [pe3-vpn-instance-vpn1] route-distinguisher 100:1 [pe3-vpn-instance-vpn1] vpn-target 1:1 [pe3-vpn-instance-vpn1] quit [pe3] interface vlan-interface 11 [pe3-vlan-interface11] ip binding vpn-instance vpn1 [pe3-vlan-interface11] ip address 100.1.1.2 24 [pe3-vlan-interface11] quit [pe3] bgp 100 [pe...
Page 328
316 1.1.1.9/32 isis 15 20 11.1.1.1 vlan11 2.2.2.9/32 isis 15 10 11.1.1.1 vlan11 5.5.5.9/32 bgp 255 0 4.4.4.9 null0 6.6.6.9/32 bgp 255 0 4.4.4.9 null0 10.1.1.0/24 isis 15 20 11.1.1.1 vlan11 11.1.1.0/24 direct 0 0 11.1.1.1 vlan11 11.1.1.1/32 direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 inloop0 11.1.1.2/32 direct 0 0 11.1.1.2...
Page 329
317 20.1.1.0/24 isis 15 84 10.1.1.2 vlan12 21.1.1.0/24 isis 15 84 10.1.1.2 vlan12 21.1.1.2/32 isis 15 84 10.1.1.2 vlan12 127.0.0.0/8 direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 inloop0 127.0.0.1/32 direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 inloop0 issue the display ip routing-table vpn-instance command on pe 3 and pe 4. The output shows that ...
Page 330
318 • pe 1 and pe 2 are pe devices on the service provider backbone. Both of them support the nested vpn function. • ce 1 and ce 2 are connected to the service provider backbone. Both of them support vpnv4 routes. • pe 3 and pe 4 are pe devices of the customer vpn. Both of them support mpls l3vpn. •...
Page 331
319 configuration procedure 1. Configure mpls l3vpn on the service provider backbone, using is-is as the igp protocol, and enabling ldp and establishing mp-ibgp peer relationship between pe 1 and pe 2: # configure pe 1. System-view [pe1] interface loopback 0 [pe1-loopback0] ip address 3.3.3.9 32 [pe...
Page 332
320 [pe1] display bgp peer bgp local router id : 3.3.3.9 local as number : 100 total number of peers : 1 peers in established state : 1 peer as msgrcvd msgsent outq prefrcv up/down state 4.4.4.9 100 162 145 0 0 02:12:47 established [pe1] display isis peer peer information for isis(1) ---------------...
Page 333
321 [ce1] interface loopback 0 [ce1-loopback0] isis enable 2 [ce1-loopback0] quit [ce1] interface vlan-interface 12 [ce1-vlan-interface12] ip address 10.1.1.2 24 [ce1-vlan-interface12] isis enable 2 [ce1-vlan-interface12] mpls [ce1-vlan-interface12] mpls ldp [ce1-vlan-interface12] quit after the con...
Page 334
322 [ce3-bgp] import-route direct [ce3-bgp] quit # configure ce 5. System-view [ce5] interface vlan-interface 13 [ce5-vlan-interface13] ip address 110.1.1.1 24 [ce5-vlan-interface13] quit [ce5] bgp 65411 [ce5-bgp] peer 110.1.1.2 as-number 200 [ce5-bgp] import-route direct [ce5-bgp] quit # configure ...
Page 335
323 [pe1-bgp-af-vpnv4] quit [pe1-bgp] quit # configure ce 1, enabling vpnv4 capability and establishing vpnv4 neighbor relationship between ce 1 and pe 1. [ce1] bgp 200 [ce1-bgp] ipv4-family vpnv4 [ce1-bgp-af-vpnv4] peer 11.1.1.2 enable # allow the local as number to appear in the as-path attribute ...
Page 336
324 4.4.4.9/32 isis 15 10 30.1.1.2 vlan12 30.1.1.0/24 direct 0 0 30.1.1.1 vlan12 30.1.1.1/32 direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 inloop0 30.1.1.2/32 direct 0 0 30.1.1.2 vlan12 127.0.0.0/8 direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 inloop0 127.0.0.1/32 direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 inloop0 execute the display ip routing-table vpn-instance comman...
Page 337
325 *^ 100.1.1.0/24 1.1.1.9 1024/1024 route distinguisher: 101:1 network nexthop in/out label med locprf * > 110.1.1.0/24 1.1.1.9 1025/1025 route distinguisher: 200:1 network nexthop in/out label med locprf * > 120.1.1.0/24 11.1.1.2 1026/1027 route distinguisher: 201:1 network nexthop in/out label m...
Page 338
326 execute the display ip routing-table command on ce5 and ce 6 to verify that the routing tables contain routes of remote sub-vpns. Take ce5 as an example. [ce5] display ip routing-table routing tables: public destinations : 5 routes : 5 destination/mask proto pre cost nexthop interface 110.1.1.0/...
Page 339
327 request time out request time out --- 130.1.1.1 ping statistics --- 5 packet(s) transmitted 0 packet(s) received 100.00% packet loss configuring hovpn network requirements there are two levels of networks, the backbone and the mpls vpn networks, as shown in figure 84 . • spes act as pes to allow...
Page 340
328 # configure mpls basic capability and mpls ldp to establish ldp lsps. System-view [upe1] interface loopback 0 [upe1-loopback0] ip address 1.1.1.9 32 [upe1-loopback0] quit [upe1] mpls lsr-id 1.1.1.9 [upe1] mpls [upe1-mpls] quit [upe1] mpls ldp [upe1-mpls-ldp] quit [upe1] interface vlan-interface ...
Page 341
329 [upe1-bgp-vpn1] import-route direct [upe1-bgp-vpn1] quit [upe1-bgp] ipv4-family vpn-instance vpn2 [upe1-bgp-vpn1] peer 10.4.1.1 as-number 65420 [upe1-bgp-vpn1] import-route direct [upe1-bgp-vpn1] quit [upe1-bgp] quit 2. Configure ce 1: system-view [ce1] interface vlan-interface 12 [ce1-vlan-inte...
Page 342
330 [upe2-ospf-1] quit # configure vpn instances vpn1 and vpn2, allowing ce 3 and ce 4 to access upe 2. [upe2] ip vpn-instance vpn1 [upe2-vpn-instance-vpn1] route-distinguisher 300:1 [upe2-vpn-instance-vpn1] vpn-target 100:1 both [upe2-vpn-instance-vpn1] quit [upe2] ip vpn-instance vpn2 [upe2-vpn-in...
Page 343
331 [ce4] bgp 65440 [ce4-bgp] peer 10.3.1.2 as-number 100 [ce4-bgp] import-route direct [ce4] quit 7. Configure spe 1: # configure mpls basic capability and mpls ldp to establish ldp lsps. System-view [spe1] interface loopback 0 [spe1-loopback0] ip address 2.2.2.9 32 [spe1-loopback0] quit [spe1] mpl...
Page 344
332 [spe1-bgp] peer 1.1.1.9 next-hop-local [spe1-bgp] peer 3.3.3.9 as-number 100 [spe1-bgp] peer 3.3.3.9 connect-interface loopback 0 [spe1-bgp] ipv4-family vpnv4 [spe1-bgp-af-vpnv4] peer 3.3.3.9 enable [spe1-bgp-af-vpnv4] peer 1.1.1.9 enable [spe1-bgp-af-vpnv4] peer 1.1.1.9 upe [spe1-bgp-af-vpnv4] ...
Page 345
333 [spe2-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 180.1.1.0 0.0.0.255 [spe2-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] quit [spe2-ospf-1] quit # configure vpn instances vpn1 and vpn2. [spe2] ip vpn-instance vpn1 [spe2-vpn-instance-vpn1] route-distinguisher 600:1 [spe2-vpn-instance-vpn1 ] vpn-target 100:1 both [spe2-vpn-instance-vpn...
Page 346
334 • vpn traffic between ce 1 and ce 2 is required to be forwarded through the mpls backbone, instead of any route in the ospf area. Figure 85 network diagram device interface ip address device interface ip address ce 1 vlan-int11 100.1.1.1/24 ce 2 vlan-int11 120.1.1.1/24 vlan-int13 20.1.1.1/24 vla...
Page 347
335 # configure mpls basic capability and mpls ldp on pe 1 to establish ldp lsps. System-view [pe1] interface loopback 0 [pe1-loopback0] ip address 1.1.1.9 32 [pe1-loopback0] quit [pe1] mpls lsr-id 1.1.1.9 [pe1] mpls [pe1-mpls] quit [pe1] mpls ldp [pe1-mpls-ldp] quit [pe1] interface vlan-interface 1...
Page 348
336 [pe2-bgp] peer 1.1.1.9 as-number 100 [pe2-bgp] peer 1.1.1.9 connect-interface loopback 0 [pe2-bgp] ipv4-family vpnv4 [pe2-bgp-af-vpnv4] peer 1.1.1.9 enable [pe2-bgp-af-vpnv4] quit [pe2-bgp] quit # configure ospf on pe 2. [pe2]ospf 1 [pe2-ospf-1]area 0 [pe2-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0]network 2.2.2.9 0.0...
Page 349
337 [pe2-ospf-100-area-0.0.0.1] quit [pe2-ospf-100] quit [pe2] bgp 100 [pe2-bgp] ipv4-family vpn-instance vpn1 [pe2-bgp-vpn1] import-route ospf 100 [pe2-bgp-vpn1] import-route direct [pe2-bgp-vpn1] quit [pe2-bgp] quit after completing the configurations, issue the display ip routing-table vpn-instan...
Page 350
338 destination/mask proto pre cost nexthop interface 3.3.3.3/32 direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 inloop0 5.5.5.5/32 bgp 255 0 2.2.2.9 null0 20.1.1.0/24 ospf 10 1563 100.1.1.1 vlan11 100.1.1.0/24 direct 0 0 100.1.1.2 vlan11 100.1.1.2/32 direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 inloop0 120.1.1.0/24 bgp 255 0 2.2.2.9 null0 issue the...
Page 351
339 figure 86 network diagram device interface ip address device interface ip address ce 1 vlan-int11 10.1.1.1/24 p loop0 2.2.2.9/32 vlan-int12 100.1.1.1/24 vlan-int11 30.1.1.1/24 pe 1 loop0 1.1.1.9/32 vlan-int12 20.1.1.2/24 vlan-int11 10.1.1.2/24 pe 2 loop0 3.3.3.9/32 vlan-int12 20.1.1.1/24 vlan-in...
Page 352
340 10.2.1.0/24 direct 0 0 10.2.1.1 vlan11 10.2.1.1/32 direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 inloop0 10.2.1.2/32 direct 0 0 10.2.1.2 vlan11 127.0.0.0/8 direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 inloop0 127.0.0.1/32 direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 inloop0 200.1.1.0/24 direct 0 0 200.1.1.1 inloop0 200.1.1.1/32 direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 inloop0 issue the ...
Page 353
341 [pe2] bgp 100 [pe2-bgp] ipv4-family vpn-instance vpn1 [pe2-bgp-vpn1] peer 10.2.1.1 substitute-as [pe2-bgp-vpn1] quit [pe2-bgp] quit the output shows that among the routes advertised by pe 2 to ce 2, the as_path of 100.1.1.1/32 has changed from 100 600 to 100 100: *0.13498737 pe2 rm/7/rmdebug: bg...
Page 354
342 --- 200.1.1.1 ping statistics --- 5 packet(s) transmitted 5 packet(s) received 0.00% packet loss round-trip min/avg/max = 66/79/109 ms configuring bgp as number substitution and soo network requirements ce 1, ce 2, and ce 3 belong to vpn 1 and connect to pe1, pe 2, and pe 3 respectively. Ce 1 an...
Page 355
343 { configure ospf on the mpls backbone to allow the pes and p device to learn the routes of the loopback interfaces from each other. { configure basic mpls and mpls ldp on the mpls backbone to establish ldp lsps. { establish mp-ibgp peer relationships between the pes to advertise vpn ipv4 routes....
Page 356
344 [pe1] route-policy soo permit node 10 [pe1-route-policy] apply extcommunity soo 1:100 additive [pe1-route-policy] quit # on pe 1, apply the routing policy soo to routes received from ce 1. [pe1] bgp 100 [pe1-bgp] ipv4-family vpn-instance vpn1 [pe1-bgp-vpn1] peer 10.1.1.1 route-policy soo import ...
Page 357
345 ipv6 mpls l3vpn configuration the s5500-28sc-hi and s5500-52sc-hi switches do not support ipv6 mpls l3vpn. Ipv6 mpls l3vpn overview mpls l3vpn applies to the ipv4 environment. It uses bgp to advertise ipv4 vpn routes and uses mpls to forward ipv4 vpn packets on the service provider backbone. Ipv...
Page 358
346 ipv6 mpls l3vpn packet forwarding figure 89 ipv6 mpls l3vpn packet forwarding diagram as shown in figure 89 , the ipv6 mpls l3vpn packet forwarding procedure is as follows: 1. The pc at site 1 sends an ipv6 packet destined for 2001:2::1, the pc at site 2. Ce 1 transmits the packet to pe 1. 2. Ba...
Page 359
347 then, the ingress pe advertises the vpn-ipv6 routes to the egress pe through mp-bgp. Finally, the egress pe compares the export target attributes of the vpn-ipv6 routes with the import target attributes that it maintains for the vpn instance and, if they are the same, adds the routes to the rout...
Page 360
348 task remarks configuring route related attributes for a vpn instance optional configuring a tunneling policy for a vpn instance optional configuring an ldp instance optional configuring routing between pe and ce required configuring routing between pes required configuring routing features for t...
Page 361
349 to associate a layer 3 aggregate interface with a vpn instance, you must associate all the member ports of the aggregate interface with the vpn instance. Executing the ip binding vpn-instance command on an interface deletes the ipv6 address of that interface. You must reconfigure the ipv6 addres...
Page 362
350 step command remarks 6. Apply an import routing policy. Import route-policy route-policy optional. By default, all routes matching the import target attribute are accepted. Make sure the routing policy to be applied already exists. Otherwise, the switch does not filter received routes. 7. Apply ...
Page 363
351 important: create a tunneling policy before applying it to a vpn instance. Otherwise, the default tunneling policy is used. The default tunneling policy selects only one tunnel in this order: lsp tunnel, cr-lsp tunnel. To configure a tunneling policy for a vpn instance: step command remarks 1. E...
Page 364
352 before configuring routing between pe and ce, complete the following tasks: • assign an ipv6 address to the ce-pe interface of the ce. • assign an ipv6 address to the pe-ce interface of the pe. Configuring ipv6 static routing between pe and ce step command remarks 1. Enter system view. System-vi...
Page 365
353 step command remarks 1. Enter system view. System-view n/a 2. Create an ospfv3 process for a vpn instance and enter the ospfv3 view. Ospfv3 [ process-id ] vpn-instance vpn-instance-name perform this configuration on pes. On ces, create a normal ospf process. 3. Set the router id. Router-id route...
Page 369
357 there are three inter-as vpn solutions (see " configuring mpls l3vpn " for more information). Currently, ipv6 mpls l3vpn supports only inter-as vpn option a and option c. Configuration prerequisites before configuring inter-as ipv6 vpn, complete these tasks: • configuring an igp for the mpls bac...
Page 372
360 ipv6 mpls l3vpn configuration examples configuring ipv6 mpls l3vpns network requirements • ce 1 and ce 3 belong to vpn 1. Ce 2 and ce 4 belong to vpn 2. • vpn 1 uses route target attributes 111:1. Vpn 2 uses route target attributes 222:2. Users of different vpns cannot access each other. • ebgp ...
Page 373
361 [pe1-loopback0] quit [pe1] interface vlan-interface 13 [pe1-vlan-interface13] ip address 172.1.1.1 24 [pe1- vlan-interface13] quit [pe1] ospf [pe1-ospf-1] area 0 [pe1-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 172.1.1.0 0.0.0.255 [pe1-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 1.1.1.9 0.0.0.0 [pe1-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] quit...
Page 374
362 destinations : 9 routes : 9 destination/mask proto pre cost nexthop interface 1.1.1.9/32 direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 inloop0 2.2.2.9/32 ospf 10 1 172.1.1.2 vlan13 3.3.3.9/32 ospf 10 2 172.1.1.2 vlan13 127.0.0.0/8 direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 inloop0 127.0.0.1/32 direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 inloop0 172.1.1.0/24 direct...
Page 375
363 # configure pe 2. [pe2] mpls lsr-id 3.3.3.9 [pe2] mpls [pe2-mpls] quit [pe2] mpls ldp [pe2-mpls-ldp] quit [pe2] interface vlan-interface 12 [pe2-vlan-interface12] mpls [pe2-vlan-interface12] mpls ldp [pe2-vlan-interface12] quit after you complete the configurations, ldp sessions are established ...
Page 376
364 [pe1] interface vlan-interface 12 [pe1-vlan-interface12] ip binding vpn-instance vpn2 [pe1-vlan-interface12] ipv6 address 2001:2::2 64 [pe1-vlan-interface12] quit # configure pe 2. [pe2] ip vpn-instance vpn1 [pe2-vpn-instance-vpn1] route-distinguisher 200:1 [pe2-vpn-instance-vpn1] vpn-target 111...
Page 377
365 4. Establish ebgp peer relationships between the pes and ces to allow them to exchange vpn routes: # configure ce 1. System-view [ce1] bgp 65410 [ce1-bgp] ipv6-family [ce1-bgp-af-ipv6] peer 2001:1::2 as-number 100 [ce1-bgp-af-ipv6] import-route direct [ce1-bgp-af-ipv6] quit # configure the other...
Page 378
366 [pe2-bgp] ipv6-family vpnv6 [pe2-bgp-af-vpnv6] peer 1.1.1.9 enable [pe2-bgp-af-vpnv6] quit [pe2-bgp] quit after completing the configurations, issue the display bgp peer command or the display bgp vpnv6 all peer command on the pes. The output shows a bgp peer relationship has been established be...
Page 379
367 # from each ce, ping other ces. Ces of the same vpn can ping each other, whereas those of different vpns are not. For example, ce 1 can ping ce 3 (2001:3::1), but cannot ping ce 4 (2001:4::1): [ce1] ping ipv6 2001:3::1 ping 2001:3::1 : 56 data bytes, press ctrl_c to break reply from 2001:3::1 by...
Page 380
368 figure 91 network diagram device interface ip address device interface ip address ce 1 vlan-int12 2001:1::1/64 ce 2 vlan-int12 2001:2::1/64 pe 1 loop0 1.1.1.9/32 pe 2 loop0 4.4.4.9/32 vlan-int12 2001:1::2/64 vlan-int12 2001:2::2/64 vlan-int11 172.1.1.2/24 vlan-int11 162.1.1.2/24 asbr-pe 1 loop0 ...
Page 381
369 [pe1-vlan-interface11] mpls [pe1-vlan-interface11] mpls ldp [pe1-vlan-interface11] quit # configure the mpls basic capability on asbr-pe 1 and enable mpls ldp for asbr-pe 1 and for the interface connected to pe 1. System-view [asbr-pe1] mpls lsr-id 2.2.2.9 [asbr-pe1] mpls [asbr-pe1-mpls] quit [a...
Page 382
370 [ce1] interface vlan-interface 12 [ce1-vlan-interface12] ipv6 address 2001:1::1 64 [ce1-vlan-interface12] quit # configure pe 1. [pe1] ip vpn-instance vpn1 [pe1-vpn-instance-vpn1] route-distinguisher 100:1 [pe1-vpn-instance-vpn1] vpn-target 100:1 both [pe1-vpn-instance-vpn1] quit [pe1] interface...
Page 383
371 after completing the configurations, you can view the vpn instance configurations by issuing the display ip vpn-instance command. Each pe can ping its attached ce, and asbr-pe 1 and asbr-pe 2 can ping each other. 4. Establish ebgp peer relationship between pe and ce switches to allow vpn routes ...
Page 384
372 [asbr-pe1-bgp] ipv6-family vpnv6 [asbr-pe1-bgp-af-vpnv6] peer 1.1.1.9 enable [asbr-pe1-bgp-af-vpnv6] quit [asbr-pe1-bgp] quit # configure asbr-pe 2. [asbr-pe2] bgp 200 [asbr-pe2-bgp] ipv6-family vpn-instance vpn1 [asbr-pe2-bgp-ipv6-vpn1] peer 2002:1::1 as-number 100 [asbr-pe2-bgp-ipv6-vpn1] quit...
Page 385
373 figure 92 network diagram device interface ip address device interface ip address pe 1 loop0 2.2.2.9/32 pe 2 loop0 5.5.5.9/32 loop1 2001:1::1/128 loop1 2001:1::2/128 vlan-int11 1.1.1.2/8 vlan-int11 9.1.1.2/8 asbr-pe 1 loop0 3.3.3.9/32 asbr-pe 2 loop0 4.4.4.9/32 vlan-int11 1.1.1.1/8 vlan-int11 9....
Page 386
374 [pe1-loopback0] quit # create vpn instance vpn1 and configure the rd and route target attributes for it. [pe1] ip vpn-instance vpn1 [pe1-vpn-instance-vpn1] route-distinguisher 11:11 [pe1-vpn-instance-vpn1] vpn-target 3:3 import-extcommunity [pe1-vpn-instance-vpn1] vpn-target 3:3 export-extcommun...
Page 387
375 # configure interface vlan-interface 11, and start is-is and enable mpls and ldp on the interface. [asbr-pe1] interface vlan-interface 11 [asbr-pe1-vlan-interface11] ip address 1.1.1.1 255.0.0.0 [asbr-pe1-vlan-interface11] isis enable 1 [asbr-pe1-vlan-interface11] mpls [asbr-pe1-vlan-interface11...
Page 388
376 [asbr-pe2] isis 1 [asbr-pe2-isis-1] network-entity 10.333.333.333.333.00 [asbr-pe2-isis-1] quit # configure an lsr id, enable mpls and ldp. [asbr-pe2] mpls lsr-id 4.4.4.9 [asbr-pe2] mpls [asbr-pe2-mpls] label advertise non-null [asbr-pe2-mpls] quit [asbr-pe2] mpls ldp [asbr-pe2-mpls-ldp] quit # ...
Page 389
377 [asbr-pe2-bgp] peer 11.0.0.2 as-number 100 [asbr-pe2-bgp] peer 11.0.0.2 route-policy policy1 export # configure the capability to advertise labeled routes to and receive labeled routes from ebgp peer 11.0.0.2. [asbr-pe2-bgp] peer 11.0.0.2 label-route-capability [asbr-pe2-bgp] quit 4. Configure p...
Page 390
378 # configure the capability to advertise labeled routes to ibgp peer 4.4.4.9 and to receive labeled routes from the peer. [pe2-bgp] peer 4.4.4.9 as-number 600 [pe2-bgp] peer 4.4.4.9 connect-interface loopback 0 [pe2-bgp] peer 4.4.4.9 label-route-capability # configure the maximum hop count from p...
Page 391
379 reply from 2001:1::2 bytes=56 sequence=5 hop limit=64 time = 1 ms --- 2001:1::2 ping statistics --- 5 packet(s) transmitted 5 packet(s) received 0.00% packet loss round-trip min/avg/max = 1/1/1 ms configuring carrier's carrier network requirements configure carrier's carrier for the scenario sho...
Page 392
380 figure 93 network diagram device interface ip address device interface ip address ce 3 vlan-int11 2001:1::1/64 ce 4 vlan-int11 2001:2::1/64 pe 3 loop0 1.1.1.9/32 pe 4 loop0 6.6.6.9/32 vlan-int11 2001:1::2/64 vlan-int11 2001:2::2/64 vlan-int12 10.1.1.1/24 vlan-int12 20.1.1.2/24 ce 1 loop0 2.2.2.9...
Page 393
381 [pe1-loopback0] isis enable 1 [pe1-loopback0] quit [pe1] interface vlan-interface 12 [pe1-vlan-interface12] ip address 30.1.1.1 24 [pe1-vlan-interface12] isis enable 1 [pe1-vlan-interface12] mpls [pe1-vlan-interface12] mpls ldp [pe1-vlan-interface2] mpls ldp transport-address interface [pe1-vlan...
Page 394
382 [pe3-loopback0] quit [pe3] mpls lsr-id 1.1.1.9 [pe3] mpls [pe3-mpls] quit [pe3] mpls ldp [pe3-mpls-ldp] quit [pe3] isis 2 [pe3-isis-2] network-entity 10.0000.0000.0000.0001.00 [pe3-isis-2] quit [pe3] interface loopback 0 [pe3-loopback0] isis enable 2 [pe3-loopback0] quit [pe3] interface vlan-int...
Page 395
383 [pe1] ip vpn-instance vpn1 [pe1-vpn-instance-vpn1] route-distinguisher 200:1 [pe1-vpn-instance-vpn1] vpn-target 1:1 [pe1-vpn-instance-vpn1] quit [pe1] mpls ldp vpn-instance vpn1 [pe1-mpls-ldp-vpn-instance-vpn1] quit [pe1] isis 2 vpn-instance vpn1 [pe1-isis-2] network-entity 10.0000.0000.0000.000...
Page 396
384 [pe3-vpn-instance-vpn1] route-distinguisher 100:1 [pe3-vpn-instance-vpn1] vpn-target 1:1 [pe3-vpn-instance-vpn1] quit [pe3] interface vlan-interface11 [pe3-vlan-interface11] ip binding vpn-instance vpn1 [pe3-vlan-interface11] ipv6 address 2001:1::2 64 [pe3-vlan-interface11] quit [pe3] bgp 100 [p...
Page 397
385 destinations : 11 routes : 11 destination/mask proto pre cost nexthop interface 1.1.1.9/32 isis 15 20 11.1.1.1 vlan11 2.2.2.9/32 isis 15 10 11.1.1.1 vlan11 5.5.5.9/32 bgp 255 0 4.4.4.9 null0 6.6.6.9/32 bgp 255 0 4.4.4.9 null0 10.1.1.0/24 isis 15 20 11.1.1.1 vlan11 11.1.1.0/24 direct 0 0 11.1.1.1...
Page 398
386 10.1.1.0/24 direct 0 0 10.1.1.1 vlan12 10.1.1.1/32 direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 inloop0 10.1.1.2/32 direct 0 0 10.1.1.2 vlan12 11.1.1.0/24 isis 15 20 10.1.1.2 vlan12 20.1.1.0/24 isis 15 84 10.1.1.2 vlan12 21.1.1.0/24 isis 15 84 10.1.1.2 vlan12 21.1.1.2/32 isis 15 84 10.1.1.2 vlan12 127.0.0.0/8 direct 0 ...
Page 399
387 index b c d e i m o r s t v b binding a service instance with a vpls instance, 172 c configuring a pe-ce interface of a pe, 199 configuring a remote ccc connection, 200 configuring a static lsp, 63 configuring an ipv6 mce, 37 configuring an mce, 8 configuring an ospf sham link, 266 configuring b...
Page 400
388 mpls overview, 53 mpls te configuration examples, 128 mpls te configuration task list, 102 o overview, 91 overview, 37 overview, 227 r resetting bgp connections, 46 resetting bgp connections, 20 resetting bgp connections, 358 resetting bgp connections, 268 s setting mpls statistics reading inter...