- DL manuals
- IAI
- Controller
- PCON-C
- Operation Manual
IAI PCON-C Operation Manual
Summary of PCON-C
Page 1
Operation manual sixth edition pcon-c/cg/cf controller positioner type.
Page 2: Caution
Caution changes to zone function applicable application versions: v0016 and later among the zone signal settings, those that result in “zone setting+ v0015 and earlier: “zone setting+ zone setting-” a zone signal is not output. V0016 and later: “zone setting+ = zone setting-” this is the onl...
Page 3: Caution
Caution 1. 24-v power supplies required for ul certification pcon controllers (pcon-c/cg, cy, se, pl/po) are ul-certified, where one condition for the certification is to use class 2 24-v power supplies. Accordingly, you must use class 2 power supplies for both the input power supply and i/o power s...
Page 4: Caution
Caution 5. Initial parameter settings at startup after applying power, at least the three parameters specified below must be set in accordance with the specific application. Inappropriate settings of these parameters will prevent the controller from operating properly, so exercise due caution. For d...
Page 5: Caution
Caution [2] enabling/disabling the servo on input signal (son) the servo on input signal has been added to allow for servo on/off control on the plc side. Depending on the needs, therefore, the user must enable/disable this signal. To select a desired setting, set “0” or “1” in parameter no. 21 (ser...
Page 6
Ce marking 1 european union ec directive the european union ec directive was issued for the products to be distributed in eu (european union) region to protect the health and secure the safety of the users and consumers of the products. It aims at the respect and satisfaction of the new approach dir...
Page 7
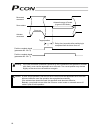
3 peripheral unit configuration circuit breaker earth leakage breaker dc24v power supply power terminal surge protector* *r • a • v-781bw7-4 (maker : okaya electric industies) control board ac power bus fg fixing using the main body set bolt.
Page 8
(1) environments use the acon or pcon under the environment with the contamination level 2 or 1 specified in iec60664-1. For example, it is installed on the control board with the structure (ip54) where water, oil, carbon or dust is not entered. (2) power unit a) use it under the environment with th...
Page 9
(5) surge protector install the surge protector on the primary side of the dc24v power unit. Maker : okaya electric industries co. , ltd. Model name: r x a x v-781bw7-4 surge protector external view (6) cable for all the cables, such as the motor cable, encoder cable and various network cables to be...
Page 10
Safety precautions (please read before using the product.) before installing, operating, maintaining or inspecting this product, please peruse this operating manual as well as the operating manuals and other related documentations for all equipment and peripheral devices connected to this product in...
Page 11
[installation] do not use this product in a place exposed to ignitable, inflammable or explosive substances. The product may ignite, burn or explode. Avoid using the product in a place where the main unit or controller may come in contact with water or oil droplets. Never cut and/or reconnect the ca...
Page 12
If the product is generating heat, smoke or a strange smell, turn off the power immediately. Continuing to use the product may result in product damage or fire. If any of the internal protective devices (alarms) of the product has actuated, turn off the power immediately. Continuing to use the produ...
Page 13
Before installing or adjusting the product or performing other operations on the product, display a sign that reads, “work in progress. Do not turn on power.” if the power is turned on inadvertently, injury may result due to electric shock or sudden activation of an actuator. [operation] turn on the...
Page 14: Table of Contents
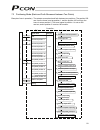
Table of contents 1. Overview ................................................................................................................... 1 1.1 introduction.................................................................................................................................. 1 1.2...
Page 15
5.1.2 external output specifications.............................................................................. 39 5.2 pio patterns and signal assignments ...................................................................................... 40 5.2.1 explanation of signal names......................
Page 16
(3) ss8c type........................................................................................................ 62 rod type ....................................................................................................................... 63 (1) ra2c type.....................................
Page 17
7.8 zone signal output.................................................................................................................. 104 7.9 incremental moves .................................................................................................................. 107 7.9.1 judgment met...
Page 18
Minimum delay time for slave transmitter activation ................................................. 138 silent interval multiplier............................................................................................... 139 8.2.4 servo gain adjustment ...........................................
Page 19
1 1. Overview 1.1 introduction this product is a dedicated rcp2 / rcp3 actuator controller that provides the same functions of the rcp2 controller as well as a set of new functions designed to achieve greater convenience and safety. The product also provides a power-saving function in response to gr...
Page 20
2 1.2 how to read the model specification c: positioner type with internal drive- power cutoff relay cg: positioner type with external drive- power cutoff relay cf: high-output positioner type with internal drive-power cutoff relay [motor flange size] 20p: 20, square 28p: 28, square 28sp: 28, square...
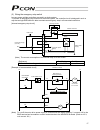
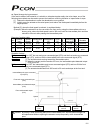
Page 21
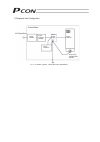
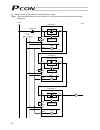
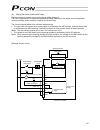
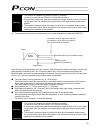
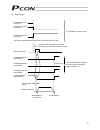
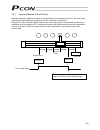
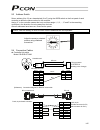
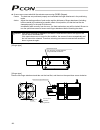
3 personal computer standard teaching pendant external emg switch 24 v 0 v host system supplied flat cable input power supply 24 vdc 24-vdc i/o power supply pc pc software (optional) rs232c type usb type rcp2 actuator 1.3 system configuration 1.3.1 internal drive-power cutoff relay type (pcon-c/cf) ...
Page 22
4 personal computer s1 s2 mpi mpo 24v 0v emg- standard teaching pendant host system supplied flat cable input power supply 24 vdc 24-vdc i/o power supply pc pc software (optional) rs232c type usb type rcp2 actuator motor drive- power cutoff circuit safety relay contactor 1.3.2 external drive-power c...
Page 23
5 1.4 procedure from unpacking to test operation and adjustment if you are using this product for the first time, carry out each step by referring to the procedure below to ensure that all necessary items are checked and all wires are connected correctly. 1 check the content in the package if you fo...
Page 24
6 6 turn on the servo confirm that the slider or rod is not contacting a mechanical end. If the slider/rod is contacting a mechanical end, move it away from the mechanical end. If the actuator is equipped with a brake, turn on the brake forced-release switch to forcibly release the brake before movi...
Page 25
7 1.5 warranty period and scope of warranty the controller you have purchased passed iai’s shipping inspection implemented under the strictest standards. The unit is covered by the following warranty: 1. Warranty period the warranty period shall be one of the following periods, whichever ends first:...
Page 26
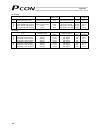
8 2. Specifications 2.1 basic specifications specification item pcon-c (internal drive-power cutoff relay type) pcon-cg (external drive-power cutoff relay type) pcon-cf (internal drive-power cutoff relay type) number of controlled axes 1 axis/unit supply voltage 24 vdc 10% actuator rated max. *2 ra...
Page 27
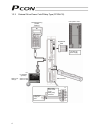
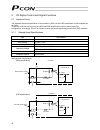
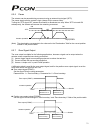
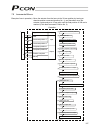
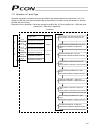
9 2.2 name and function of each part of the controller indication of pio pattern number if you have multiple systems and a different pio pattern is used for each system, it is recommended that you specify an applicable pio pattern number on each controller to prevent confusion. Explanation of input/...
Page 28
10 explanation of each switch [1] address switch if multiple axes are used, the pc/teaching pendant must be plugged into/out of different connectors to communicate with different axes. To save the hassle, you can use link cables to connect all axes via sio converters. Under this method, however, the...
Page 29
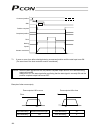
11 2.3 external dimensions an external view and dimensions of the product are shown below. (mounting dimen sion) 5.
Page 30
12 3. Installation and noise elimination pay due attention to the installation environment of the controller. 3.1 installation environment (1) when installing and wiring the controller, do not block the cooling ventilation holes. (insufficient ventilation will not only prevent the controller from de...
Page 31
13 [2] precautions regarding wiring method use a twisted cable for connection to the 24-vdc external power supply. Separate the controller cables from high-power lines such as a cable connecting to a power circuit. (do not bundle together the controller cables with high-power lines or place them in ...
Page 32
14 3.4 heat radiation and installation design the control panel size, controller layout and cooling method in such a way that the temperature around the controller will not exceed 40 c. Install the controller vertically on a wall, as shown below. Since cooling is provided by way of natural convecti...
Page 33
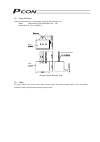
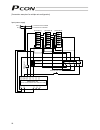
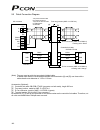
15 orange gray white yellow pink yellow (green) controller connected to teaching pendant or pc external emg switch input power supply 24 vdc i/o flat cable terminal block actuator motor encoder holding brake brake release switch tighten together with the mounting screw. 0 v (npn specification) 24 v ...
Page 34
16 4.1.2 wiring the power supply/emergency-stop switch (1) wiring the power supply to connect multiple controllers, provide a relay terminal block. Use a power cable satisfying the following specifications: item specification applicable wire length single wire: 1.0 / stranded: 0.8 mm 2 , awg size 1...
Page 35
17 (2) wiring the emergency-stop switch in many cases multiple controllers are used in a single system. To provide an emergency-stop function for the entire system, the controller circuit is designed in such a way that a single emg switch is able to actuate an emergency stop in all connected control...
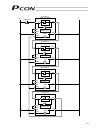
Page 36
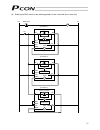
18 representative connection examples are explained below. Connecting the teaching pendant directly to the controller [1] connecting multiple controllers (8 units or less) using a single power supply short the mpi and mpo terminals using a jumper wire. (the controller is shipped with these termina...
Page 37
19 24v 0v s2 s1 0v mpi mpo 24v emg- s2 s1 0v mpi mpo 24v emg- s2 s1 0v mpi mpo 24v emg- s2 s1 0v mpi mpo 24v emg- [controller 1] [controller 2] [controller 3] [controller 4] emg signal teaching pendant relay teaching pendant relay teaching pendant relay teaching pendant relay connection detection ci...
Page 38
20 s2 s1 mpi mpo 24v 0v emg- control © 0v © 24v s2 s1 mpi mpo 24v 0v emg- s2 s1 mpi mpo 24v 0v emg- [controller 1] [controller 2] [controller 3] emg signal teaching pendant relay teaching pendant relay teaching pendant relay connection detection circuit connection detection circuit connection detect...
Page 39
21 cr [controller 1] [controller 2] [controller 3] emg signal teaching pendant 24v 0v mpo mpi 24v emg- relay s1 s2 0v mpo mpi 24v emg- relay s1 s2 0v teaching pendant mpo mpi 24v emg- relay s1 s2 0v teaching pendant cr connection detection circuit connection detection circuit connection detection ci...
Page 40
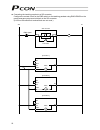
22 connecting the teaching pendant to a sio converter configure the contact circuit for the emg switch on the teaching pendant using emg1/emg2 on the power/emergency-stop terminal block on the sio converter. (s1/s2 on the controller’s terminal block are not used.) emg2 emg1 cr on off mpi mpo 24v emg...
Page 41
23 controller i/o flat cable 0 v (npn specification) 24 v (pnp specification) 24 v (npn specification) 0 v (pnp specification) 24-vdc power for input/output signals for details on i/o signal connection, refer to 4.3, “connecting the i/o cables.” connection detection circuit input output motor relay ...
Page 42
24 4.2.2 wiring the power supply/emergency-stop switch (1) wiring the power supply to connect multiple controllers, provide a relay terminal block. Use a power cable satisfying the following specifications: item specification applicable wire length single wire: 1.0 / stranded: 0.8 mm 2 , awg size 1...
Page 43
25 24v 0v 0v emg- 24v mpo mpi s1 s2 (3a) emg switch (rush-in current: 8 a, rated current: 2 a) teaching pendant motor power supply external emg reset switch external emg circuit controller power supply coil current: 0.1 a or less (max. 2a) pcon-cg controller connection detection circuit mc mc mc (2)...
Page 44
26 [connection example of a multiple-axis configuration] input power supply [controller 1] [controller 2] [controller 3] connect to 24-v terminal connect to 0-v terminal emg signal contactor external reset switch safety relay unit phoenix contact (psr-scp-24uc-/esa2/4x1/1x2/b) s1 s2 mpi mpo 24v 0v e...
Page 45
27 4.3 connecting the i/o cables pio pattern 0 [standard type] 0 [v] 0 [v] +24 [v] +24 [v] pio controller end (signal abbreviation) brown 1 red 1 orange 1 yellow 1 green 1 blue 1 purple 1 gray 1 white 1 black 1 brown 2 red 2 orange 2 yellow 2 green 2 blue 2 purple 2 gray 2 white 2 black 2 brown 3 re...
Page 46
28 pio pattern 1 [teaching type] 0 [v] 0 [v] +24 [v] +24 [v] pio brown 1 red 1 orange 1 yellow 1 green 1 blue 1 purple 1 gray 1 white 1 black 1 brown 2 red 2 orange 2 yellow 2 green 2 blue 2 purple 2 gray 2 white 2 black 2 brown 3 red 3 orange 3 yellow 3 green 3 blue 3 purple 3 gray 3 white 3 black ...
Page 47
29 pio pattern 2 [256-piont mode] 0 [v] 0 [v] +24 [v] +24 [v] controller end pio (signal abbreviation) output s ide command position 1 command position 2 command position 4 command position 8 command position 16 command position 32 command position 64 command position 128 brake release operating mod...
Page 48
30 pio pattern 3 [512-piont mode] pio output s ide command position 1 command position 2 command position 4 command position 8 command position 16 command position 32 command position 64 command position 128 command position 256 brake release operating mode home return pause start alarm reset servo ...
Page 49
31 pio pattern 4 [solenoid valve mode 1] pio direct position command 0 direct position command 1 direct position command 2 direct position command 3 direct position command 4 direct position command 5 direct position command 6 brake release operating mode home return pause alarm reset servo on movem...
Page 50
32 pio pattern 5 [solenoid valve mode 2] pio output s ide rear end move front end move intermediate point move brake release operating mode alarm reset servo on rear end detected front end detected intermediate point detected zone output position zone output operating mode status home return complet...
Page 51
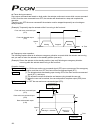
33 caution: when performing a continuity check of the flat cable, pay due attention not to expand the female pins in the connector. It may cause contact failure and disable normal operation of the controller. Lower stage upper stage black 4 brown 3 black 2 brown 1 20a 1a 1b 20b bulls-eye terminal bl...
Page 52
Bulls-eye terminal block kit - p,a,s-con (-cf) controller i/o wiring for tb with/without led's p i/o pattern setting definitions from parameter setting # 25 lower pin upper pin wire color 0=standard 1=teaching mode 2=256 point mode 3=512 point mode 4=7-point mode 5=3-point mode pnp wiring npn wiring...
Page 53
34 controller end actuator end pin layout pin layout (front view) cable model marking cable color signal name pin no. (front view) robot cable standard cable description pin no. Signal name blue (red 1) white red gray brown green purple pink yellow orange blue orange (black 2) orange (red 2) orange ...
Page 54
35 controller end actuator end (front view) cable model marking housing: d-2100d 1-1318119-3 (hirose) contact: d-2 1318105-1 cable name signal name pin no. Description signal name pin no. Cable name pin no. Black white red green yellow brown housing: phdr-16vs (j.S.T. Mfg.) contact: sphd-001t-p0.5 h...
Page 55
36 controller end actuator end pin layout pin layout (front view) cable model marking cable color signal name pin no. Pin no. (front view) housing: 1-1318119-3 (amp) contact: 1318107-1 housing: slp-06v (j.S.T. Mfg.) socket contact: bsf-21t-p1.4 orange gray yellow yellow (green) 4.4.2 connecting the ...
Page 56
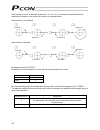
37 4.5 connecting the communication cable connect the communication cable to the sio connector. Brown yellow red orange blue green pin no. Brown/green centered orange black red/blue black - - pin assignments of the cable-end connector controller end signal name cable color shielded shielded, not con...
Page 57
38 +24v r=680 +24v r=5.6 k r =22 k r=68 r=5.6 k r=22 k c=0.1 f c=0.1 f 5. I/o signal control and signal functions 5.1 interface circuit the standard interface specification of the controller is npn, but the pnp specification is also available as an option. To prevent confusion during wiring, the n...
Page 58
39 p24v controller external power supply +24v internal circuit each output load load n p24v n controller external power supply +24v internal circuit each output load load 5.1.2 external output specifications item specification number of output points 16 points rated load voltage 24 vdc maximum curre...
Page 59
40 5.2 pio patterns and signal assignments this controller provides six pio pattern types to meet the needs of various applications. To select a desired type, set a corresponding value from 0 to 5 in parameter no. 25 (pio pattern selection). The features of each pio pattern are explained below: para...
Page 60
41 5.2.1 explanation of signal names the following explains the signal names, and gives a function overview of each signal. In the explanation of operation timings provided in a later section, each signal is referenced by its self- explanatory name for clarity. If necessary, however, such as when ma...
Page 61
42 pio pattern = 1: teaching mode [teaching type] category signal name signal abbreviation function overview pc1 pc2 pc4 pc8 pc16 command position number pc32 the target position number is input. A command position number must be specified by 6 ms before the start signal (cstr) turns on. Operation m...
Page 62
43 pio pattern = 2: 256-point mode [256-point type] category signal name signal abbreviation function overview pc1 pc2 pc4 pc8 pc16 pc32 pc64 command position number pc128 the target position number is input. A command position number must be specified by 6 ms before the start signal (cstr) turns on...
Page 63
44 pio pattern = 3: 512-point mode [512-point type] category signal name signal abbreviation function overview pc1 pc2 pc4 pc8 pc16 pc32 pc64 pc128 command position number pc256 the target position number is input. A command position number must be specified by 6 ms before the start signal (cstr) tu...
Page 64
45 pio pattern = 4: solenoid valve mode 1 [7- point type] category signal name signal abbreviation function overview direct position command 0 st0 the actuator will start moving to position no. 0 at a rise edge of this signal. Direct position command 1 st1 the actuator will start moving to position ...
Page 65
46 pio pattern = 5: solenoid valve mode 2 [3-point type] category signal name signal abbreviation function overview rear end move command st0 the actuator will move toward the rear end while this signal remains at on level. Front end move command st1 the actuator will move toward the front end while...
Page 66
47 5.2.2 signal assignment table for respective pio patterns when creating a plc sequence or wiring signals, assign each pin correctly by referring to the assignment table below. When “1 [teaching type]” is selected, the meaning of each pin number will vary depending on the mode. Accordingly, also p...
Page 67
48 5.3 details of i/o signal functions an input time constant is provided for the input signals of this controller, in order to prevent malfunction due to chattering, noise, etc. Except for certain signals, switching of each input signal will be effected when the signal has been received continuousl...
Page 68
49 pause (*stp) when this signal turns off while the actuator is moving, the actuator will decelerate to a stop. The remaining movement is retained and will be resumed when the signal is turned on again. To abort the movement command, turn on the alarm reset signal while this signal is off to cancel...
Page 69
50 brake release (bkrl) when the actuator is equipped with a brake, you may want to forcibly release the brake in certain situations such as when starting up the system for the first time. Normally the brake release switch on the front panel of the controller is set to the “rls” side to release the ...
Page 70
51 jog (jog+, jog-) this signal is enabled when the teaching type is selected. When the actuator is jogging (i.E., the jisl signal is off), it will jog toward the +/- software stroke limit upon detection of an off on rise edge of this signal. If an on off fall edge of this signal is detected whi...
Page 71
52 movement to each position (st0 to st2) [3-point type] since the number of positioning points is limited to three, the actuator can be controlled just like an air cylinder. While this signal is on, the actuator will move toward the target position. If the signal turns off while the actuator is mov...
Page 72
53 5.3.2 details of each output signal operating mode status (rmds) the internal operating mode of the controller is output based on the auto/manu selector switch on the controller and the rmod signal received by the input port. If the selector switch is set to “auto” and the rmod signal is off (aut...
Page 73
54 home return completion (hend) this signal is off immediately after the power is input, and turns on in either of the following two conditions: [1] home return operation has completed with respect to the first movement command issued with the start signal. [2] home return operation has completed f...
Page 74
55 movement complete at each position (pe0 to pe6) [7-point type] when pio pattern is “4,” a position number (0 through 6) corresponding to each movement command will be output upon completion of positioning. Simple alarm-code output function is not provided for these signals. If an alarm generates,...
Page 75
56 emergency stop (*emgs) this signal remains on while the controller is normal, and will turn off if the emergency stop circuit is cut off. Program the plc so that it will monitor this signal and implement appropriate safety measures for the entire system if the signal turns off. Load output judgme...
Page 76
57 1 = 2 = 10.00 30.00 0 -10.00 no [mm] position 6. Data entry to move the actuator to a specified position, a target position must be entered in the “position” field. A target position can be specified in the absolute mode where a distance from the home is entered, or in the incremental mode where ...
Page 77
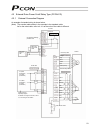
58 (4) acceleration/deceleration enter the acceleration/deceleration at which to move the actuator, in [g]. Basically, the acceleration and deceleration should be inside the rated acceleration/deceleration range specified in the catalog. The input range is greater than the rated range in the catal...
Page 78
59 “push & hold operation” this field defines the maximum push distance after reaching the target position in push & hold operation. Consider possible mechanical variation of the load and set an appropriate positioning band that will prevent the positioning from completing before the load is contact...
Page 79
60 (9) acceleration/deceleration mode this field is not used for this controller. The factory setting is “0.” (10) incremental this field defines whether the position is specified in the absolute mode or incremental mode. The factory setting is “0.” 0: absolute mode 1: incremental mode (11) comm...
Page 80
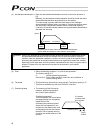
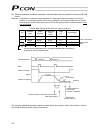
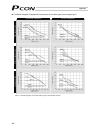
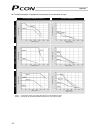
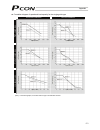
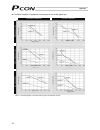
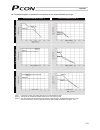
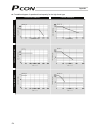
61 6.1.1 relationship of push force at standstill and current-limiting value when performing operation in the push & hold mode, enter the current-limiting value (%) in the push column of the position-data table. Determine the current-limiting value (%) from the push force to be applied to the load a...
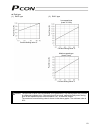
Page 81
62 (3) ss8c type caution: the precision of push force at standstill is not guaranteed. The above graphs are provided for reference purposes only. If the push force is too small, malfunction may occur during push & hold operation due to slide resistance, etc., so exercise caution. The maximum current...
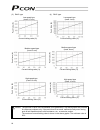
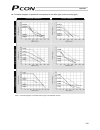
Page 82
63 rod type (1) ra2c type (2) ra3c type caution: the precision of push force at standstill is not guaranteed. The above graphs are provided for reference purposes only. If the push force is too small, malfunction may occur during push & hold operation due to slide resistance, etc., so exercise cauti...
Page 83
64 (3) ra4c type (4) ra6c type caution: the precision of push force at standstill is not guaranteed. The above graphs are provided for reference purposes only. If the push force is too small, malfunction may occur during push & hold operation due to slide resistance, etc., so exercise caution. The m...
Page 84
65 (5) ra10c/w-ra10c type caution: the precision of push force at standstill is not guaranteed. The above graphs are provided for reference purposes only. If the push force is too small, malfunction may occur during push & hold operation due to slide resistance, etc., so exercise caution. The maximu...
Page 85
66 6.2 explanation of modes 6.2.1 positioning mode push = 0 the actuator moves to the target position set in the “position” field of the position table. 6.2.2 push & hold mode push = other than 0 (1) load was contacted successfully upon reaching the target position set in the “position” field of the...
Page 86
67 (2) load was not contacted (missed) if the actuator does not still contact the load after having moved the distance specified in the “positioning band” field, the position complete signal will not turn on. Therefore, include timeout check processing in the sequence circuit on the plc side. it i...
Page 87
68 (4) positioning band was entered with a wrong sign take note that if a value with a wrong sign is set in the “positioning band” field of the position table, the operation will deviate by a distance corresponding to “positioning band x 2,” as shown below. 6.2.3 torque check function in push & hold...
Page 88
69 warning this function is available only with the pcon-cf controller. (it cannot be used with the pcon-c or pcon-cg controller.) if the actuator contacts the load before reaching the target position, a servo error alarm will generate. Pay due attention to the relationship of the target positio...
Page 89
70 6.2.4 speed change during movement speed control involving multiple speed levels is possible in a single operation. The actuator speed can be decreased or increased at a certain point during movement. However, the position at which to implement each speed change must be set. 6.2.5 operation at di...
Page 90
71 on on off *stp actuator operation target position zone output (zone1) actuator operation + direction home value set in parameter no. 2 value set in parameter no. 1 6.2.6 pause the actuator can be paused during movement using an external input signal (*stp). The pause signal uses the contact b log...
Page 91
72 6.2.8 home return after the power is turned on, home return must be performed to establish the home position. The method of home return varies depending on the pio pattern. When a dedicated input is used [pio pattern 5] home return is performed using the home return (home) input. The actuator w...
Page 92
73 6.2.9 overview of teaching type depending on your system, it may be desirable to be able to use a touch panel, etc., to perform jogging operation or write the current position to the “position” field of the position table, without using a pc or teaching pendant. The teaching type is provided to s...
Page 93
74 6.2.10 overview of 7-point type the number of positioning points is kept small, or specifically to seven or less. This type assumes simple applications where the plc ladder sequence only requires a simple circuit configuration. I/o signals provide separate command inputs and movement complete out...
Page 94
75 [2] 64-point type command position 1 input (pc1) command position 2 input (pc2) command position 4 input (pc4) “5” is indicated by a binary code. * all other command position inputs (pc8, pc16 and pc32) turn off. At least 6 msec of delay time is needed (ensured by a timer setting on the plc side)...
Page 95
76 6.2.11 overview of 3-point type this type provides a control method adjusted to that of an air cylinder by assuming that the controller is used as an air cylinder. The key differences between this controller and an air cylinder are summarized in the table below. Program appropriate controls by re...
Page 96
77 item air cylinder rcp2 position check upon power on determined by an external detection sensor, such as a reed switch. Immediately after the power is turned on, the controller cannot identify the current position because the mechanical coordinates have been lost. Accordingly, a rear end command m...
Page 97
78 6.3 notes on the robo gripper (1) finger operation [1] definition of position the specified stroke of the 2-finger type indicates the sum of travel distances of both fingers. In other words, the travel distance of one finger is one half the specified stroke. A position you specify defines the dis...
Page 98
79 (2) removing the gripped load this gripper is designed to maintain the load-gripping force via a self-lock mechanism even when the servo is turned off or the controller power is cut off. If the gripped load must be removed while the power is cut off, do so by turning the open/close screw or remov...
Page 99
80 6.4 power-saving modes at standby positions one general feature of pulse motors is that their holding current in standstill state is greater than ac servo motors. Therefore, this product provides energy-saving modes to reduce power consumption in situations where the actuator remains standstill f...
Page 100
81 full servo control mode the pulse motor is servo-controlled to reduce the holding current. Although the exact degree of current reduction varies depending on the actuator model, load condition, etc., the holding current decreases to approx. 1/2 to 1/4. Since the servo remains on, position deviati...
Page 101
82 warning: if the next movement command is specified in the incremental mode (based on constant pitch feed), never use the automatic servo-off mode. The current position may deviate slightly as the servo turns off and then on again. Caution: in push & hold operation, both the full servo control mod...
Page 102
83 6.5 using a rotary actuator in multi-rotation specification rotary actuators of multi-rotation specification models let you select multi-rotation operation or limited- rotation operation using a parameter. 6.5.1 how to use (1) home return when a home return command is issued, a signal from the li...
Page 103
84 7. Operation 7.1 how to start 7.1.1 timings after power on procedure after initial startup until actuator adjustment [1] connect the motor relay cable to the mot connector and encoder relay connector to the pg connector. [2] connect the supplied flat cable to the pio connector (for connection bet...
Page 104
85 [10] perform home return. Overview of operation on the teaching pendant on the rcm-t, select the “edit/teach” screen, bring the cursor to “*home” in the sub display area, and then press the return key. on the rcm-e, select the “teach/play” screen, scroll until “*home return” is displayed, and...
Page 105
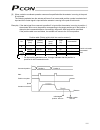
86 procedure of normal operation the operating procedure in normal condition is specified below: [1] reset the emergency stop or enable the supply of motor drive power. [2] supply the 24-vdc i/o power. [3] supply the 24-vdc controller power. * if the monitor led [sv/alm] on the front panel illuminat...
Page 106
87 home position mechanical end power on p osition emergency stop not actuated (motor drive power supplied) safety circuit condition supply of 24-vdc i/o power supply of 24-vdc controller power mode selector switch operation mode status output (rmds) pause input (home) servo on input (son) monitor l...
Page 107
88 warning: since the drive motor uses a pulse motor, excited-phase detection is performed when the servo is first turned on after the power on. Therefore, the actuator must be able to move when the servo turns on. If the slider or rod is contacting a mechanical end or the load is contacting any sur...
Page 108
89 full-scale operation this product provides energy-saving modes to reduce power consumption in situations where the actuator remains standstill for a long period at a standby position. You can also select the status of position complete signal to be applied if the servo turns off or “position devi...
Page 109
90 7.2 home return operation 7.2.1 method using the home input signal (pio pattern = 0 to 4) since the home return signal (home) is provided in pio patterns 0 to 4, perform home return using this signal. when the home return signal (home) turns on, the actuator starts moving toward the mechanical ...
Page 110
91 command position 1 to 256 input (pc1 ~ pc256) start input (cstr) home return complete output (hend) completed position output (pm1 ~ pm256) position complete output (pend) moving output (move) mechanical end home position target position actuator movement (note) if the home is not yet established...
Page 111
92 7.2.2 method used when no home input signal is available (pio pattern = 5) since no home return signal (home) is available in pio pattern 5, input the rear end move command (st0) first to perform home return. when the rear end movement command (st0) turns on, the actuator starts moving toward t...
Page 112
93 7.3 positioning mode (back and forth movement between two points) example of use in operation) the actuator moves back and forth between two positions. The position 250 mm from the home is set as position 1, and the position 100 mm from the home is set as position 2. The travel speed to position ...
Page 113
94 start position complete moving actuator movement is complete. Position table (field(s) within thick line must be entered.) no. Position [mm] speed [mm/s] acceleration [g] deceleration [g] push [%] positioning band [mm] 0 * * * * * * 1 250.00 200.00 0.30 0.30 0 0.10 2 100.00 100.00 0.30 0.30 0 0.1...
Page 114
95 7.4 push & hold mode example of use in operation) the actuator is caused to move back and forth in the push & hold mode and positioning mode. The position 280 mm from the home is set as position 1, and the position 40 mm from the home is set as position 2. Movement to position 1 is performed in t...
Page 115
96 position table (field(s) within thick line must be entered.) no. Position [mm] speed [mm/s] acceleration [g] deceleration [g] push [%] positioning band [mm] 0 * * * * * * 1 280.00 200.00 0.30 0.30 50 15.00 2 40.00 100.00 0.30 0.30 0 0.10 : t1: 6 msec or more; time after selecting/entering a comma...
Page 116
97 speed return action returned position 250.34 mm target position 280 mm position where the push & hold operation completed 290.34 mm 7.4.1 return action after push & hold by relative coordinate specification positioning mode the reference position is the target position for the position number use...
Page 117
98 7.5 speed change during movement example of use in operation) the actuator speed is reduced at a certain point during movement. The position 150 mm from the home is set as position 1, and the position 200 mm from the home is set as position 2. The actuator is initially located between the home an...
Page 118
99 position table (field(s) within thick line must be entered.) no. Position [mm] speed [mm/s] acceleration [g] deceleration [g] push [%] positioning band [mm] 0 * * * * * * 1 150.00 200.00 0.30 0.30 0 10.00 2 200.00 100.00 0.30 0.30 0 0.10 : t1: 6 msec or more; time after selecting/entering a comma...
Page 119
100 7.6 operation at different acceleration and deceleration settings example of use in operation) positioning is performed to the position 150 mm from the home (position 1) at a speed of 200 mm/sec. The acceleration is 0.3 g and the deceleration is 0.1 g. Method) set 0.3 [g] in the “acceleration” f...
Page 120
101 start position complete moving actuator movement is complete. Position table (field(s) within thick line must be entered.) no. Position [mm] speed [mm/s] acceleration [g] deceleration [g] push [%] positioning band [mm] 0 * * * * * * 1 150.00 200.00 0.30 0.10 0 0.10 : t1: 6 msec or more; time aft...
Page 121
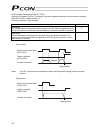
102 7.7 pause example of use in operation) pause the actuator during movement. [effective in pio pattern = 0 to 4] method) use the pause input. Controller pio signal name start command position 1 command position 2 command position 4 command position 8 command position 16 command position 32 *pause ...
Page 122
103 command position start position complete completed position pause moving actuator movement 6 msec or more command position start position complete completed position pause reset moving actuator movement approx. 1 msec t1: 6 msec or more; time after selecting/entering a command position until the...
Page 123
104 7.8 zone signal output two types of zone output signals are available: zone output (zone1) and position zone output (pzone). The boundaries defining the signal on range are set differently for each zone output. [1] zone output (zone1) --- set by parameter no. 1/no. 2. [2] position zone output (p...
Page 124
105 controller [5] [2] [1] [9] [8] [3] [7] [6] [10] [4] pio signal name start command position 1 command position 32 completed position 1 completed position 32 position complete zone moving category input output reference flow select/enter a desired command position. [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] [6] [7] [8] ...
Page 125
106 t1: 6 msec or more; time after selecting/entering a command position until the start input turns on (the scan time of the host controller must be considered.) caution: when the start signal turns on, the position complete output will turn off and the moving output will turn on. Always turn off t...
Page 126
107 [13][10][5][2] [1] [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] [6] [7] [8] [10] [9] [7] [15] [14][11][6][3] [16][11][8][4] [9] [11] [12] [13] [14] [15] [16] 7.9 incremental moves example of use in operation) move the actuator from the home to the 30-mm position by issuing an absolute position command (position no. 1), ...
Page 127
108 start position complete moving actuator position table (field(s) within thick line must be entered.) t1: 6 msec or more; time after selecting/entering a command position until the start input turns on (the scan time of the host controller must be considered.) caution 1: when the start signal t...
Page 128
109 7.9.1 judgment method of end position although completion judgment is based on the applicable count managed by the plc, the zone output signal can be used additionally to double-check the completion of movement. Program the plc so that the on/off status of the zone output signal is checked when ...
Page 129
110 7.9.2 notes on incremental mode if an operation command is issued based on relative coordinate specification while the actuator is moving (in the normal positioning mode or push & hold mode), how the actuator will operate varies depending on whether or not push action is specified in the operati...
Page 130
111 [2] when a relative coordinate operation command is specified while the actuator is moving in the push & hold mode the following explains how the actuator will move if an incremental position number is selected and input and then a start signal is input while the actuator is moving in the push &...
Page 131
112 (2) when the relative coordinate operation command specifies an operation in the push & hold mode example) if a position 2 command is input followed by a start signal while the actuator is moving to position 1, a new target position will be set by adding the incremental distance to the current p...
Page 132
113 7.10 jogging/teaching using pio if the teaching type is selected, you can jog the actuator via operation from the plc. You can also write the current actuator position to the “position” field of the position table under a specified position number via operation from the plc. If the actuator posi...
Page 133
114 jogging/teaching timing t1: 20 msec or more; time after the current-position write input is turned on until writing of the current position is started when the operation mode (mode) input is turned on, the current operation mode (modes) output will turn on and the teaching mode permitting pio te...
Page 134
115 7.11 operation in 7-point type separate movement command inputs are provided for the target positions for position nos. 0 to 6, so simply turn on the input signal corresponding to the position you wish to move the actuator to, and the actuator will start moving. Example of use in operation) move...
Page 135
116 caution: movement commands are executed based on the rise edge, so input each signal continuously for 6 msec or more. (even if the level mode is selected for the movement command input (parameter no. 27), the movement command is still executed based on the rise edge.) if two or more movement com...
Page 136
117 the movement command input operates in two modes. You can select the operation condition of the movement command input (st0 to st6) in parameter no. 27. The factory setting is “0: [level mode].” description of the movement command input setting level mode: the actuator starts moving when the inp...
Page 137
118 handling of the pause (*stp) signal this signal is a contact b signal, meaning that it must remain on while the actuator is moving. If the pause signal turns off while the actuator is moving, the actuator will decelerate to a stop. The actuator will start moving when the signal turns on again. U...
Page 138
119 7.12 operation in 3-point type after the power has been turned on, input the rear end move command first to complete home return, and then perform continuous operation. refer to 7.2.2, “method used when no home input signal is available.” example of use in operation) how to move the actuator f...
Page 139
120 meaning of position detected output signals (ls0, ls1, ls2) these signals are handled in the same manner as limit switches (lss), and turn on when the following conditions are met: [1] the home return complete output signal (hend) is on. [2] the current position is within the positioning band fr...
Page 140
121 speed change during movement if the load is made of soft material or is a bottle or otherwise topples easily due to its shape, one of the following two methods can be used to prevent the load from receiving vibration or impact when it stops: [1] reduce the deceleration to make the deceleration c...
Page 141
122 pause during movement since move commands are based on level mode, the actuator continues to move while a move command is on. Once the move command turns off, the actuator will decelerate to a stop and complete the operation. Therefore, turn off the move command if the actuator must be stopped t...
Page 142
123 8. Parameters 8.1 parameter table category: a: parameter relating to the actuator stroke range b: parameter relating to the actuator operating characteristics c: parameter relating to the external interface d: servo gain adjustment no. Category symbol name unit default factory setting 1 a zonm z...
Page 143
124 no. Category symbol name unit default factory setting 41 c fpio operating-mode input disable selection [0: enable / 1: disable] - 0 [enable] 42 b enbl enable function [0: enable/1: disable] - 1 [disable] 43 b hmc polarity of home check sensor input [0: contact a / 1: contact b] - set individuall...
Page 144
125 8.2 detail explanation of parameters if a parameter has been changed, always restart the controller using a software reset command or by reconnecting the power. 8.2.1 parameters relating to the actuator stroke range soft limit (no.3/4 limm/liml) set the soft limit in the positive direction in pa...
Page 145
126 zone boundary (1: no.1/2 zonm/zonl 2: no.23/24 znm2/znl2) these parameters set the zone within which the zone output signal (zone1) turns on when the selected pio pattern is “0” (standard type), “4” (7-point type) or “5” (3-point type). The zone output signal turns on when the current position i...
Page 146
127 home return direction (no.5 org) unless specified by the user, the home return direction is set to the motor direction at the factory. Should a need arise to change the home direction after the actuator has been assembled into your system, reverse the setting in parameter no. 5 between “0” and “...
Page 147
128 default acceleration/deceleration (no.9 acmd) the factory setting is the rated acceleration/deceleration of the actuator. When a target position is written to an unregistered position table or the current position is read in the teaching mode, the setting in this parameter will be used as the ac...
Page 148
129 default direction of excited-phase signal detection (no.28 phsp) when the servo is turned on for the first time after the power on, excited-phase detection is performed this parameter defines the direction of this detection. The parameter need not be changed in normal conditions. In certain situ...
Page 149
130 move command servo status actuator movement servo on automatic servo-off mode (a green led blinks.) target position t: delay time (seconds) after positioning is completed until the servo turns off automatic servo-off delay time (no.36 aso1/no.37 aso2/no.38 aso3) this parameter defines the delay ...
Page 150
131 push speed (no.34 pshv) this parameter defines the push speed to be applied after the actuator reaches the target position in push & hold operation. Before the shipment, this parameter has been set to the default value selected in accordance with the characteristics of the actuator. Set an appro...
Page 151
132 enable function (no.42 fdio4) whether to enable or disable the deadman switch function on an ansi-type teaching pendant is defined by parameter no. 42. * an ansi-type teaching pendant will be developed in the future. Setting enable (use) 0 disable (do not use) 1 the factory setting is “1 [disabl...
Page 152
133 torque check range (no.51 trqz) this parameter sets whether or not to use the check range when determining if the threshold has been exceeded. The default value is “0,” i.E., to enable the check range. Setting enable (use the check range to make judgment) 0 disable (do not use the check range to...
Page 153
134 if the actuator is moved in the order to positions 1 2 3 4, the actuator will operate differently depending on whether or not shortcut is selected, as explained below. When shortcut is not selected when shortcut is selected absolute unit (no.83 etyp) parameter no. 83 sets whether or not an...
Page 154
135 8.2.3 parameters relating to the external interface pio pattern selection (no.25 iopn) select the pio operation pattern in parameter no. 25. This setting forms the basis of operation, so be sure to set this parameter at the beginning. The factory setting is “0 [standard type].” parameter no. 25 ...
Page 155
136 movement command type (no.27 fpio) when the pio pattern is set to “7-point type,” define the operation condition of the movement command input (st0 to st6) in parameter no. 27. The factory setting is “0 [level mode].” description of the movement command input setting level mode: the actuator sta...
Page 156
137 pause input disable selection (no.15 fpio) parameter no. 15 defines whether the pause input signal is disabled or enabled. Setting enable (use) 0 disable (do not use) the signal 1 the factory setting is “0 [enable].” servo on input disable selection (no.21 fpio) parameter no. 21 defines whether ...
Page 157
138 output mode of position complete signal (no.39 fpio) this parameter is effective when any pio pattern other than “5” [3-point type] is selected. It defines the status of completed position number signals [pm1 to pm256], movement complete signals at respective positions [pe0 to pe6] and position ...
Page 158
139 silent interval multiplier (no.45 sivm) this parameter is not used for this controller. It is applied to controllers of rs485 serial communication type. If specified, this parameter defines the multiplier to be applied to the silent interval time for delimiter judgment in the rtu mode. The defau...
Page 159
140 8.2.4 servo gain adjustment before the shipment, the servo has been adjusted in accordance with the standard specification of the actuator. Accordingly, the servo settings need not be changed in normal conditions. Nonetheless, the parameters relating to servo adjustment are made accessible by th...
Page 160
141 speed loop integral gain (no.32 vlpt) parameter no. Unit input range default 32 --- 1 ~ 217270 set individually in accordance with the actuator characteristics. This parameter determines the response when a speed control loop is used. Increasing the set value lowers the response with respect to ...
Page 161
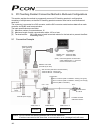
142 teaching pendant [con-t, rcm-t] pc software (optional) rs232c cross cable (provided by the user) components: sio converter (with built-in terminal resistor) vertical type horizontal type input power supply controller power supply terminal resistor r = 220 adrs switch: 0 controller 1 adrs switch:...
Page 162
143 9.2 sio converter (optional) this unit is a rs232c-rs485 converter. When multiple controllers are linked, you can connect a teaching pendant to the mini din 8-pin connector to move all axes together or edit the parameters of all axes at once. Explanation of function [1] power/emergency-stop term...
Page 163
144 [4] d-sub, 9-pin connector (rs232c) a connection port with a plc’s communication module. It can also be connected to a pc. For the communication cable, use the rs232c cross cable specified below. [5] mini din, 8-pin connector (rs485) a connection port with a teaching pendant or pc. For the commu...
Page 164
145 9.3 address switch set an address (0 to 15) as a hexadecimal (0 to f) using the adrs switch on the front panel of each controller to define the slave number for the controller. Assign “0” to the controller nearest the host, and then assign 1, 2, 3, …, e and f to the remaining controllers in the ...
Page 165
146 9.5 detail connection diagram (note) the user must provide the two-paired shielded cable. If cables other than the recommended brands are connected to [a] and [b], use those with a cable-sheath outer diameter of 1.35 to 1.60 mm. Accessories (optional): [1] controller link cable cb-rcb-ctl002 (co...
Page 166
147 10. Troubleshooting 10.1 action to be taken upon occurrence of problem upon occurrence of a problem, take an appropriate action according to the procedure below in order to ensure speedy recovery and prevent recurrence of the problem. A. Check the status indicator lamps. Sv (green) --- the servo...
Page 167
148 10.2 alarm level classification alarms are classified into two levels based on the corresponding symptoms. Alarm level alm lamp *alm signal what happens when alarm generates how to reset operation cancellation lit output the actuator decelerates to a stop and then the servo turns off. Input an a...
Page 168
149 10.3 alarm description output using pio in pio patterns 0 to 3 (64 to 512-point positioning type), alarm information can be output using the ports for completed position output signals (four bits of pm1 to pm8) so that when an alarm occurs, the nature of the alarm can be identified on the plc si...
Page 169
150 10.4 alarm description and cause/action (1) message level alarms code error name cause/action 080 movement command when servo off cause: a movement command was input as a numerical command when the servo was off. Action: input a son signal to turn the servo on (the sv signal or pend signal shoul...
Page 170
151 code error name cause/action 0a3 position command information data error cause: the speed or acceleration/deceleration effective when the numerical command was issued exceeded the maximum settable value. Action: change the speed or acceleration/deceleration to an appropriate value. If a position...
Page 171
152 code error name cause/action 0c1 servo error this error indicates that the motor could not be operated for 2 seconds or more after the move command was accepted and before the target position was reached. Cause: [1] the motor relay cable connector is loose or open. [2] if the actuator is equippe...
Page 172
153 code error name cause/action 0d9 software stroke limit overtravel error cause: [1] the actuator installed vertically overshot and exceeded a software stroke limit due to a large load or high deceleration setting when the target position was set to a point near the software stroke limit. [2] the ...
Page 173
154 code error name cause/action 0ef absolute encoder error (3) cause: the current value changed at a speed equal to or greater than the specified rotational speed due to an external factor or for other reason while the power was cut off. Action: change the speed setting in the simple absolute unit ...
Page 174
155 (2) cold-start level alarms code error name cause/action 0a1 parameter data error cause: the input range of parameter range data is not appropriate. (example) this error occurs when the magnitude relationship of a pair of range parameters is inappropriate, such as when the value of soft limit- i...
Page 175
156 code error name cause/action 0e8 phase-a/b disconnection detection 0e9 phase-a disconnection detection 0ea phase-b disconnection detection encoder signals cannot be detected correctly. Cause: [1] loose or disconnected encoder-relay cable connector [2] piano switch 4 on the simple absolute unit i...
Page 176
157 10.5 messages displayed during operation using the teaching pendant this section explains the warning messages that may be displayed during operation using the teaching pendant. Code message name description 112 invalid data an inappropriate value was entered in a parameter. (example) 9601 was e...
Page 177
158 code message name description 180 address change ok 181 controller initialization ok 182 home change all clear 183 i/o function changed these messages are displayed to confirm operation. (they don’t indicate an operation error or other abnormality.) 202 emergency stop this message indicates that...
Page 178
159 code message name description 30c no connected axis this message indicates that no controller address is recognized. Cause: [1] the controller is not operating properly. [2] only the supplied communication cable (sga/sgb) is disconnected. [3] if a sio converter is used, 24v is supplied to the co...
Page 179
160 10.6 specific problems i/o signals cannot be exchanged with the plc. Cause: [1] the 24-v i/o power supply is connected in reverse. [2] if the problem is with an output circuit, a circuit component may have been damaged due to a large load that caused the current flowing into the circuit to excee...
Page 180
161 home return ends in the middle in a vertical application. Cause: [1] the load exceeds the rating. [2] the ball screw is receiving torsional stress due to the affixing method of the actuator, tightening of bolts only on one side, etc. [3] the slide resistance of the actuator itself is large. Acti...
Page 181
162 a servo error occurred while the actuator was moving (robo gripper). Cause: the load was not positioned properly and contacted the finger attachment in the positioning mode. Action: adjust the starting position of push action and the thickness of finger attachment (including buffer material) by ...
Page 182
163 abnormal operation results when the servo is turned on after the power on. Cause: excitation phase detection was not performed correctly when the servo was turned on, because one of the following conditions existed when the power was input: [1] the slider or rod was contacting the mechanical end...
Page 183
164 appendix * appendix list of supported actuator specifications slider, ball screw drive model stroke (mm) and maximum speed (mm/sec) (note 1) load capacity (note 2) rated acceleration horizontal vertical horizontal vertical motor s trai ght motor rev e rs in g (note 1) the figure in the elongated...
Page 184
165 appendix rod type model stroke (mm) and maximum speed (mm/sec) (note 1) load capacity (note 2) rated acceleration horizontal vertical horizontal vertical standard spl as h-proof single-guide double-guide (note 1) the figure in the elongated circle indicates the maximum speed for each stroke the ...
Page 185
166 appendix gripper type stroke maximum gripping force maximum speed lead rated acceleration rcp2-grs-i-pm-1-10-p1 10 mm (5 mm per side) 21 n 33.3 mm/s (one side) 1.0 mm 0.3 g 2- finger rcp2-grm-i-pm-1-14-p1 14 mm (7 mm per side) 80 n 36.7 mm/s (one side) 1.1 mm 0.3 g rcp2-gr3ss-i-pm-30-10-p1 10 mm...
Page 186
167 appendix slider type table type model stroke (mm) and maximum speed (mm/sec) (note 1) load capacity (note 2) rated acceleration horizontal vertical horizontal vertical model stroke (mm) and maximum speed (mm/sec) (note 1) rated acceleration horizontal vertical horizontal vertical load capacity (...
Page 187
168 appendix correlation diagram of speed and load capacity for the slider type (motor-straight type) (note) in the above graphs, the number after the type code indicates the lead. Horizontal installation vertical installation high -spee d type medium -spee d type low-spee d type speed (mm/sec) loa ...
Page 188
169 appendix correlation diagram of speed and load capacity for the slider type (motor-reversing type) (note) in the above graphs, the number after the type code indicates the lead. Horizontal installation vertical installation high -spee d type medium -spee d type low-spee d type speed (mm/sec) loa...
Page 189
170 appendix correlation diagram of speed and load capacity for the standard rod type (note) in the above graphs, the number after the type code indicates the lead. (note 1) the figures for horizontal installation assume use of an external guide. Horizontal installation (note 1) vertical installatio...
Page 190
171 appendix correlation diagram of speed and load capacity for the single-guide type (note) in the above graphs, the number after the type code indicates the lead. Horizontal installation vertical installation high -spee d type medium -spee d type low-spee d type speed (mm/sec) loa d ca paci ty ( k...
Page 191
172 appendix correlation diagram of speed and load capacity for the double-guide type (note) in the above graphs, the number after the type code indicates the lead. Horizontal installation vertical installation high -spee d type medium -spee d type low-spee d type speed (mm/sec) loa d ca paci ty ( k...
Page 192
173 appendix correlation diagram of speed and load capacity for the dustproof/splash-proof type (note) in the above graphs, the number after the type code indicates the lead. (note 1) the figures for horizontal installation assume use of an external guide. (note 2) use of the actuator at the maximum...
Page 193
174 appendix correlation diagram of speed and load capacity for the high-thrust type horizontal installation vertical installation high -spee d type medium -spee d type speed (mm/sec) loa d ca paci ty ( kg) speed (mm/sec) loa d ca paci ty ( kg) speed (mm/sec) loa d ca paci ty ( kg) speed (mm/sec) lo...
Page 194
175 appendix correlation diagram of speed and load capacity for the rcp3 slider type horizontal installation vertical installation speed (mm/sec) loa d ca paci ty ( kg) lead 2 speed (mm/sec) loa d ca paci ty ( kg) speed (mm/sec) loa d ca paci ty ( kg) speed (mm/sec) loa d ca paci ty ( kg) speed (mm/...
Page 195
176 appendix correlation diagram of speed and load capacity for the rcp3 table type horizontal installation vertical installation speed (mm/sec) loa d ca paci ty ( kg) speed (mm/sec) loa d ca paci ty ( kg) speed (mm/sec) loa d ca paci ty ( kg) speed (mm/sec) loa d ca paci ty ( kg) speed (mm/sec) loa...
Page 196
177 appendix fault check and replacement of the cooling fan a cooling fan is installed in the large-capacity type (pcon-cf). To check if the fan is faulty, or when replacing the fan, follow the procedure below: 1) unplug all connectors and wires connected to the controller, and take out the controll...
Page 197
178 appendix 3) check if the fan is normal. (note) to extend the service life of the fan, a temperature sensor is used to detect the temperature around the power transistor. The fan will operate when the detected temperature reaches 60 c or above, and stop when the temperature drops to 50c or belo...
Page 198
179 appendix example of basic pcon positioning sequence given below is an example of basic sequence for creating a positioning sequence using the pcon. Indicates pio signals of the controller. Timer1 pend pm1 pm2 pm4 pm8 timer1 pend sv home a b c d e f h i j k l pm1 pm2 pm4 pm8 timer1 pm1 pm2 pm4 pm...
Page 199
180 appendix pend m n n o s s j m n m (a) p p o o q q q p p b j o s r o r r current positioning completed position (positioning circuit for position 2) positioning start request to position 2 positioning start request to position 2 auxiliary start signal for next positioning positioning start pulse ...
Page 200
181 appendix s pc1 pc2 pc4 pc8 timer 2 cstr timer 2 j o position 3 set signal position 5 set signal command position 1 command position 2 position 6 set signal position 3 set signal command position 4 command position 8 (start signal circuit) waiting for start start command for positioning to other ...
Page 201
182 appendix recording of parameters recorded date: category: a: parameter relating to the actuator stroke range b: parameter relating to the actuator operating characteristics c: parameter relating to the external interface d: servo gain adjustment no. Category name unit recorded data 1 a zone boun...
Page 202
183 appendix no. Category name unit recorded data 41 c operating-mode input disable selection [0: enable / 1: disable] - 42 b enable function [0: enable / 1: disable] - 43 b polarity of home check sensor input [0: contact a / 1: contact b] - 45 c silent interval multiplier - 46 b speed override % 47...
Page 203
184.
Page 204
185.
Page 205
Catalog no.: me0170-6a head office: 2690 w. 237th street, torrance, ca 90505 tel (310) 891-6015 fax (310) 891-0815 chicago office: 1261 hamilton parkway, itasca, il 60143 tel (630) 467-9900 fax (630) 467-9912 atlanta office: 1220-e kennestone circle, marrietta, ga 30066 tel (678) 354-9470 fax (678) ...