- DL manuals
- Icom
- Transceiver
- IC-7100
- Advanced Instructions
Icom IC-7100 Advanced Instructions
ADVANCED INSTRUCTIONS
i7100
2 INSTALLATION AND CONNECTIONS
HF/VHF/UHF ALL MODE TRANSCEIVER
The IC-7100 is not certified for vehicle installa-
tion in European countries. (As of June 2013)
Summary of IC-7100
Page 1
Advanced instructions i7100 20 control command 15 voice tx function 14 voice memory function 13 using an sd card 12 scan operation 11 memory operation 10 gps/gps-a operation 9 d-star operation 8 d-star operation 7 d-star introduction 6 functions for transmit 5 functions for receive 4 receive and tra...
Page 2: Introduction
I 3 basic operation 3-13 previous view setting frequency (continued) band edge warning beep d you can hear a beep tone when you tune into or out of an amateur band’s frequency range. A regular beep sounds when you tune into a range, and an lower tone error beep sounds when you tune out of a range. P...
Page 3: Introduction
Ii introduction functions and features of adobe ® reader ® the following functions and features can be used with adobe ® reader ® . • keyword search click “find (ctrl+f)” or “advanced search (shift+ctrl+f)” in the edit menu to open the search screen. This is convenient when search- ing for a particu...
Page 4: Introduction
Iii about the touch screen the following functions and features can be used with adobe ® reader ® . A brief touch d if the monitor is touched briefly, a beep sounds. Touch for 1 second d if the monitor is touched for more than 1 second, a beep sounds. • the operation is enabled as the beep sounds. T...
Page 5: Section
1-1 section 1 panel description 1-1 controller — front panel ........................................................1-2 controller — function display ...............................................1-8 controller — multi-function keys ...........................................1-11 m-1 (m-1 menu) di...
Page 6: Controller — Front Panel
1 panel description 1-2 controller — front panel q power switch•af volume [pwr]•[af] (p. 3-2) push to turn on the transceiver power. ➥ • first, confirm the dc power source is turned on. Hold down for 1 second to turn off the power. ➥ rotate to adjust the audio output level. ➥ increases decreases w r...
Page 7
1 panel description 1-3 e tx/rx led lights green when the squelch opens, or a signal ➥ is received. Lights red when transmitting. ➥ r memory bank control [bank] ❍ when both the pbt and rit leds are off rotate to select a memory bank. ❍ when the pbt led ( y ) lights green (mode: ssb/cw/rtty/am) rotat...
Page 8
1 panel description 1-4 o antenna tuner/call key tuner/call ❍ antenna tuner key operation (p. 16-4) (frequency band: hf/50 mhz) ➥ push to turn an optional automatic antenna tuner on or off (bypass). ➥ hold down for 1 second to manually tune the antenna tuner. • if the tuner cannot tune the antenna w...
Page 9
1 panel description 1-5 !5 preamp•attenuator key p.Amp att ❍ preamp key operation (p. 5-2) (frequency band: hf, 50/70 mhz) push to select one of two receive rf preampli- fiers, or to bypass them. • “p. Amp1” is a wide dynamic range preamplifier. It is most effective for the 1.8 to 21 mhz bands. • “p...
Page 10
1 panel description 1-6 !7 dr mode key dr (section 7,8,9) ➥ push to select the dr mode. • when the dr mode is selected, the transceiver auto - matically selects the dv mode. ➥ in the dr mode, push to cancel it. • the transceiver returns to the previous screen before entering the dr mode. !8 set mode...
Page 11
1 panel description 1-7 @2 speech•lock key speech ❍ speech key operation (p. 3-20) push to audibly announce the s-meter level, the displayed frequency and the operating mode. • the s-level announcement can be turned off in the “s-level speech” item of the “speech” set mode. (p. 17-15) set > speech >...
Page 12
1 panel description 1-8 q tx icon indicates either the displayed frequency can be transmitted, or not. ➥ “ ” appears while the operating frequency is in an amateur band. ➥ “ ” appears while the operating frequency is not in an amateur band. However, when the “band edge beep” item is set to “off” in ...
Page 13
1 panel description 1-9 o clock readout shows the current time. • utc time or local time can be selected. !0 split icon (p. 6-8) “ ” appears when the split function is turned on. !1 lock icon (p. 5-12) “ ” appears when the lock function is activated. 1 ⁄ 4 tuning dial speed icon (p. 3-10) (mode: ssb...
Page 14
1 panel description 1-10 !9 function icons “vox” appears when the vox function is activat- ➥ ed. (p. 6-2) the break-in icons appear when the break-in ➥ function is turned on. (p. 6-3) • “f-bkin” appears when the full break-in function is turned on. • “bk-in” appears when the semi break-in function i...
Page 15
1 panel description 1-11 push ➥ menu to change the set of functions assigned to touch keys. • toggles the function display menu between m-1, m-2 and m-3 menus or d-1 and d-2 menus. • functions vary, depending on the operating mode. • in the dr mode, the d-1 and d-2 menus can be select - ed. Touch or...
Page 16
1 panel description 1-12 d function keys on m-1 display scan key [scan] (p. 12-4) touch to display the “scan” screen. • push menu to return to the previous screen. Split key [split] (p. 6-8) ➥ touch to turn the split function on or off. • “ ” appears when the split function is on. ➥ touch for 1 seco...
Page 17
1 panel description 1-13 function keys on m-2 display (continued) d rtty decoder key [dec] (p. 4-12) touch to display the rtty decoder screen. • push menu to return to the previous screen. Speech compressor key [comp] (p. 6-5) (mode: ssb) ➥ touch to turn the speech compressor func- tion on or off. •...
Page 18
1 panel description 1-14 d function keys on d-1 display (mode: dv) (when the dr mode is selected) scan key [scan] (p. 12-4) ➥ touch to start or cancel the access re- peater scan. ➥ touch for 1 second to enter the “scan set” mode screen. • push menu to return to the previous screen. Skip key [skip] (...
Page 19
1 panel description 1-15 controller — rear and bottom panels q headphone/speaker jack [phones/sp] plug in standard stereo headphones (impedance: 8 to 16 ø ). • output power: more than 5 mw with an 8 ø load. • when headphones are connected, the internal speaker, and any external speaker, are disabled...
Page 20: Main Unit — Front Panel
1 panel description 1-16 main unit — front panel q cooling fan this is a cooling fan for heat dissipation. Depending on the internal temperature, it rotates at a low, mid or high speed. W sd card slot [sd card] insert an sd card of up to 32 gb sdhc. See section 13 for details. Q w previous view.
Page 21: Main Unit — Rear Panel
1 panel description 1-17 main unit — rear panel q antenna connector 1 [ant1] w antenna connector 2 [ant2] (p. 2-3) connect a 50 ø antenna with a pl-259 plug con- nector. • [ant1] is used for the hf, 50/70 mhz frequency bands. • [ant2] is used for the 144/430 mhz frequency bands. • [ant1] is used bel...
Page 22
1 panel description 1-18 !2 usb (universal serial bus) port [usb] using a usb cable, connect a pc to do the follow- ing: - input modulation - remotely control the transceiver using ci-v com- mands (p. 20-2) - send the received audio to the pc - send the decoded characters to the pc - low-speed data ...
Page 23
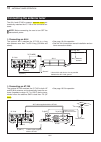
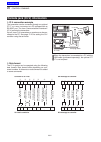
1 panel description 1-19 main unit — rear panel (continued) d acc socket information • acc socket acc pin no. Name description specifications 1 2 3 4 8 7 6 5 9 10 11 12 13 rear panel view color refers to the cable strands of the supplied cable. Q brown w red e orange r yellow t green y blue u purple...
Page 24
1 panel description 1-20 main unit — rear panel (continued) d data2 socket information data2 pin no. Name description specifications q w e r t y rear panel view 1 data in input terminal for data transmit. ( 1200 bps: afsk/ 9600 bps: g3ruh, gmsk) input level (1200 bps): input level (9600 bps): 100 mv...
Page 25: Microphone
1 panel description 1-21 microphone q ptt switch hold down to transmit, release to receive. W up/down keys [up]/[dn] push either key to change the operating frequen- ➥ cy, memory channel, set mode setting, and so on. (pp. 3-9, 4-11, 11-3) hold down either key for 1 second to start scan- ➥ ning. E up...
Page 26
1 panel description 1-22 microphone (continued) q ptt switch hold down to transmit, release to receive. W ptt lock switch push to lock the ptt switch in the transmit mode. E up/down switches [up]/[dn] change the selected readout frequency or memory channel. • holding down continuously changes the fr...
Page 27
1 panel description 1-23 q spch/lock key [spch/lock] ❍ speech key operation (p. 3-20) push to audibly announce the s-meter level, the displayed frequency and the operating mode. • the s-level announcement can be turned off in the “s-level speech” item of the “speech” set mode. (p. 17-15) set > speec...
Page 28
1 panel description 1-24 u mode key [mode] push to cycle through the operating modes: ➥ usb/lsb ➧ cw/cw-r ➧ rtty/rtty-r ➧ am ➧ fm ➧ wfm ➧ dv hold down for 1 second to toggle the following ➥ operating modes: usb ↔ lsb cw ↔ cw-r rtty ↔ rtty-r i power led lights green when transceiver’s power is on. O ...
Page 29: Section
2-1 section 2 installation and connections selecting a location .................................................................2-2 grounding ................................................................................2-2 antenna connection .........................................................
Page 30: Selecting A Location
2 installation and connections 2-2 select a location for the transceiver that allows ad- equate air circulation, free from extreme heat, cold, vibrations, away from tv sets, tv antenna elements, radios and other electromagnetic sources. The base of the transceiver has adjustable feet for the desktop...
Page 31: Antenna Connection
2 installation and connections 2-3 antenna connection for radio communications, the antenna is of critical im- portance, along with output power and receiver sensi- tivity. Select a well-matched 50 ø antenna and coaxial cable feedline. We recommend 1.5:1 or better voltage standing wave ratio (vswr) ...
Page 32
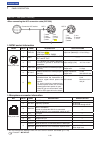
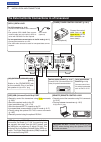
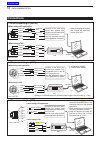
2 installation and connections 2-4 controller rear panel to the [controller] connector controller cable ferrite emi filter to the [main unit] connector connect controller to transceiver the main unit becomes hot when transmitted for long period of time. Do not place anything on the transceiver. It m...
Page 33
2 installation and connections 2-5 dash dot com [phones/sp] ( headphones/external speaker) jack [mic] connector controller set the switch on the bottom of the controller to “phones” to use headphones and set it to “sp” to use a speaker. Bottom of the controller the transceiver accepts head- phones w...
Page 34
2 installation and connections 2-6 required connections to a transceiver [ant2] 144/430mhz bands connector (p. 2-3) connect a 50 Ω antenna for the 144/430 mhz frequency bands or 74.8 mhz and above. Ic-7100 [ant1] hf, 50/70 mhz bands connector (p. 2-3) connect a 50 Ω antenna for the hf, 50/70 mhz fre...
Page 35
2 installation and connections 2-7 [data1] data1 jack for gps operation (p. 10-2) • connect a gps receiver to the transceiv - er. • the optional opc-1529r (data commu - nication cable) and a 3rd party's gps re- ceiver with rs-232c port are required. For low-speed data communication in the dv mode (p...
Page 36: Power Supply Connections
2 installation and connections 2-8 make sure the [power] switch is off before connect- ing the dc power cable. • we recommend using icom’s optional power supply (ps-126: dc13.8 v/25 a). D connecting the ps-126 power supply rear panel gnd ps-126 use the attached ac cable to con- nect to ac outlet. To...
Page 37: Linear Amplifier Connections
2 installation and connections 2-9 exciter 1 1&2 remote control cable acc cable to an antenna [acc-1] [remote] [ant] ic-pw1/euro non-european versions: 100–120 / 200–240 v european version: 230 v [input1] 7-pin side [remote] coaxial cable [ant1] ic-7100 opc-599 conversion cable [acc] gnd gnd gnd lin...
Page 38
2 installation and connections 2-10 d connecting a non-icom linear amplifier gnd hsend (orange) /vsend alc (blue) 13.8 v (gray) relay rf in rf out alc send non-icom linear amplifier to an antenna [ant1]* 2 13-pin plug with acc cable switching diode acc ic-7100 to connect a non-icom hf, 50/70* 1 mhz ...
Page 39: Section
3-1 section 3 basic operation 3-1 power on .................................................................................. 3- 2 before first applying power d ......................................................3-2 tuning on the power d ..............................................................
Page 40: Power On
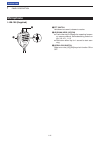
3 basic operation 3-2 pbt rit tx / rx pwr af rf/sql clr m-ch bank rit tuner/call menu mic/rf pwr nb speed/pitch set quick notch dr auto tune rx cs xfc speech mpad nr p.Amp att i7100 note: when turning off the power, the transceiver memorizes the settings. Thus the transceiver restarts with the set...
Page 41: Selecting A Function Menu
3 basic operation 3-3 selecting a function menu push menu ( c ) one or more times to select the “m-1” screen (m-1 menu), “m-2” screen (m-2 menu) or “m-3” screen (m-3 menu). • in the dr mode, push menu ( c ) once or twice to select the “d-1” screen (d-1 menu) or “d-2” screen (d-2 menu). • functions v...
Page 42: Selecting Vfo/memory Mode
3 basic operation 3-4 selecting vfo/memory mode ic-7100 has vfo and memory modes. In the vfo mode, rotate the dial to select the disired frequency. In the memory mode, rotate [m-ch] ( l ) to select the preprogrammed memory channel. Push menu ( c ) one or more times to select the “m-1” screen (m-1 me...
Page 43: Vfo Operation
3 basic operation 3-5 vfo operation the ic-7100 has two vfos; “a” and “b,” and are conve- nient for quickly selecting two frequencies, or split fre- quency operation. You can use either vfo to call up a frequency and operating mode. Vfo is an abbreviation of variable frequency oscilla- tor. D select...
Page 44: Selecting A Frequency Band
3 basic operation 3-6 band register 1 register 2 register 3 1.8 mhz* 1 1.900000 mhz cw 1.910000 mhz cw 1.915000 mhz cw 3.5 mhz* 1 3.550000 mhz lsb 3.560000 mhz lsb 3.580000 mhz lsb 7 mhz 7.050000 mhz lsb 7.060000 mhz lsb 7.020000 mhz cw 10 mhz* 1 10.120000 mhz cw 10.130000 mhz cw 10.140000 mhz cw 14...
Page 45: Setting Frequency
3 basic operation 3-7 setting frequency you can select the transceiver’s frequency by using the dial, or you can enter it on the direct input screen. D tuning with the dial q on the band selection screen, select the desired fre- quency band. (p. 3-6) w rotate the dial to set the desired frequency. •...
Page 46
3 basic operation 3-8 d quick tuning function the operating frequency can be changed in ‘khz’ or ‘mhz’ steps for quick tuning. Select the desired tuning step in each operating fre- quency band and mode. Q touch the khz digits to select the ‘khz’ quick tuning function step, or turn it off. Or touch t...
Page 47
3 basic operation 3-9 d selecting ‘ khz ’ step when the ‘khz’ quick tuning is selected, the frequen- cy can be changed in the selected ‘khz’ steps. The steps can be memorized, depending on the operating modes. On the mode selection screen, select the desired op- q erating mode. (p. 3-17) touch the k...
Page 48
3 basic operation 3-10 setting frequency (continued) d 1⁄4 tuning step function (mode: ssb-d/cw/rtty) the dial speed is reduced to 1 ⁄ 4 of the normal speed when the 1 ⁄ 4 tuning function is on, for finer tuning con- trol. You can set the 1 ⁄ 4 tuning function in each operating frequency band. This ...
Page 49
3 basic operation 3-11 setting frequency (continued) d direct frequency input the transceiver has a direct input screen for direct fre- quency entry, as described below. • operating frequency input touch the mhz digits to enter the band selection dis- q play. Touch [f-inp]( w d ) to enter the direct...
Page 50
3 basic operation 3-12 setting frequency (continued) direct frequency input (continued) d • split offset frequency input touch the mhz digits to enter the band selection dis- q play. Touch [f-inp]( w d ) to enter the direct input screen. If the shift direction is minus, touch “• (–).” e • [split] ch...
Page 51
3 basic operation 3-13 setting frequency (continued) d band edge warning beep you can hear a beep tone when you tune into or out of an amateur band’s frequency range. A regular beep sounds when you tune into a range, and an lower tone error beep sounds when you tune out of a range. Push q set ( c ) ...
Page 52
3 basic operation 3-14 setting frequency (continued) d programming the user band edge when “on (user)” or “on (user) & tx limit” is selected in the “band edge beep” item, the “user band edge” item appears in the “function” set mode. A total of 30 band edge frequencies can be programmed in the “user ...
Page 53
3 basic operation 3-15 setting frequency (continued) programming the user band edge (continued) d • inserting a band edge enter the “user band edge” screen. Q set ( c ) > function > user band edge touch for 1 second the band edge that you want to w insert a new band edge above it. • if the desired b...
Page 54
3 basic operation 3-16 setting frequency (continued) programming the user band edge (continued) d • changing the band edge frequencies enter the “user band edge” screen. Q set ( c ) > function > user band edge touch the band edge to be changed. W • if the desired band edge is not displayed, touch [ ...
Page 55: Selecting The Operating Mode
3 basic operation 3-17 mode selection operating mode ssb lsb usb cw cw cw-r rtty rtty rtty-r am am * fm fm wfm wfm (only rx) dv dv data lsb lsb data usb usb data am am data fm fm data selecting the operating mode the usable operating modes in the ic-7100 are listed to the right below. You can select...
Page 56: Selecting The Audio Volume
3 basic operation 3-18 selecting the audio volume rotate [af] ➥ ( l ) control clockwise to increase the audio output level, counterclockwise to decrease it. [af] increases decreases the l , r , c or d in the instructions indicate the part of the controller. L : left side r : right side c : center bo...
Page 57
3 basic operation 3-19 squelch and receive (rf) sensitivity adjusts the rf gain and squelch threshold level. The squelch removes noise output to the speaker when no signal is received (closed squelch). • the squelch is particularly effective for am and fm, but also works in other modes. • the 12 to ...
Page 58: Voice Synthesizer Operation
3 basic operation 3-20 voice synthesizer operation the ic-7100 has a built-in voice synthesizer to an- nounce the operating frequency, mode and s-meter level in a clear, electronically-generated voice, in eng- lish or japanese. First, select the desired parameters to be announced in the “speech” set...
Page 59
3 basic operation 3-21 voice synthesizer operation (continued) d tuning off the s-meter announcement the s-meter announcement can be turned off. Push q set ( c ) to enter the set mode. Touch the “s-level speech” item of the “speech” w set mode. Speech > s-level speech • if the specified item is not ...
Page 60: Meter Display Selection
3 basic operation 3-22 meter display selection the transmit meter can be toggled between four func- tions for your convenience. ➥ touch the meter one or more times to select the tx meter function, rf power meter, swr meter, alc meter or comp meter. • po : displays the relative rf output power. • swr...
Page 61: Basic Transmit Operation
3 basic operation 3-23 basic transmit operation before transmitting, monitor the operating fre- quency to make sure transmitting won’t cause interference to other stations on the same fre- quency. It’s good amateur practice to listen first, and then, even if nothing is heard, ask “is the fre- quency...
Page 62
3 basic operation 3-24 basic transmit operation (continued) d microphone gain adjustment (mode: ssb/am/fm/dv) push q mic/rf pwr ( c ) to open the mic gain/rf power adjustment display. Push [ptt] to transmit. W • speak into the microphone at your normal voice level. Rotate [m-ch] e ( l ) to adjust th...
Page 63: Section
Operating ssb ......................................................................... 4- 2 operating cw ........................................................................... 4-3 about the cw reverse mode d ...................................................4-4 about keying speed d .............
Page 64: Operating Ssb
4 receive and transmit 4-2 select the desired frequency band. (p. 3-6) q on the mode selection screen, touch “ssb” to select w the lsb or usb mode. • when operating above 10 mhz, usb is selected first; when operating below 10 mhz, lsb is selected first. • after selecting lsb or usb, touch “ssb” agai...
Page 65: Operating Cw
4 receive and transmit 4-3 operating cw select the desired frequency band. (p. 3-6) q on the mode selection screen, touch “cw” to select w the cw mode. • after the cw mode is selected, touch “cw” again to tog - gle between cw and cw-r modes, if necessary. Rotate the dial to tune a desired signal. E ...
Page 66
4 receive and transmit 4-4 operating cw (continued) d about the cw reverse mode the cw reverse mode receives signals with a reverse side cw carrier point similar to voice lsb and usb modes. Use when interfering signals are near a desired signal and you want to reduce the interfering tone. On the mod...
Page 67
4 receive and transmit 4-5 d cw auto tune function the automatic tuning function automatically tunes the displayed frequency when an off-frequency signal is received. This function is active while in the cw mode is selected. Push ➥ auto tune rx cs ( r ) to automatically adjust for a zero beat with...
Page 68: Electronic Keyer Functions
4 receive and transmit 4-6 electronic keyer functions you can access a number of convenient built-in elec- tronic keyer functions in the memory keyer menu. Q in the cw mode, push menu ( c ) one or more times to select the “m-2” screen (m-2 menu). Touch [keyer]( w d ), and then push menu ( c ) to dis...
Page 69
4 receive and transmit 4-7 electronic keyer functions (continued) d memory keyer send menu preset characters can be sent using the keyer send screen. Contents of the memory keyer are enterd in the keyer memory (edit) screen. • transmitting q in the cw mode, turn on the break-in function. (p. 6-3) • ...
Page 70
4 receive and transmit 4-8 d editing a memory keyer the contents of the memory keyer memories can be set on the keyer memory (edit) screen. The memory keyer can memorize and retransmit 4 cw key codes for often-used cw sentences, contest numbers or a count up trigger. The total capacity of the memory...
Page 71
4 receive and transmit 4-9 d contest number set mode this mode is used to set the contest number, count up trigger and present number. • setting contents q in the cw mode, push menu ( c ) one or more times to select the “m-2” screen (m-2 menu). W push [keyer]( d ) to display the “keyer send” screen....
Page 72
4 receive and transmit 4-10 d keyer set mode this set mode is used to set the cw sidetone, memory keyer repeat time, dash weight, paddle specifications, keyer type, and so on. • setting contents q in the cw mode, push menu ( c ) one or more times to select the “m-2” screen (m-2 menu). W push [keyer]...
Page 73
4 receive and transmit 4-11 side tone level (default: 50%) select the cw sidetone output level. • 0 to 100% can be selected. Side tone level limit (default: on) set the cw sidetone level limit. When the [af] ( l ) control is rotated above a specified level, the cw sidetone does not increase. • off: ...
Page 74: Operating Rtty (Fsk)
4 receive and transmit 4-12 when using your rtty terminal or tnc, consult the manual that comes with the equipment. Select the desired frequency band. (p. 3-6) q on the mode selection screen, touch “rtty” to se- w lect the rtty mode. • after the rtty mode is selected, touch “rtty” again to toggle be...
Page 75
4 receive and transmit 4-13 the functions for rtty operation d about rtty reverse mode received characters are occasionally garbled when the mark and space signals are reversed. This reversal can be caused by incorrect tnc connections, setting or commands. To correctly receive reversed rtty signals,...
Page 76
4 receive and transmit 4-14 d rtty set mode the rtty set mode is used to set the twin peak filter function, mark and shift frequencies and the keying po- larity. • setting contents in the rtty mode, push q menu ( c ) one or more times to select the “m-2” screen (menu m-2). Touch [rtty]( w d ) to dis...
Page 77
4 receive and transmit 4-15 the functions for rtty operation (continued) d rtty decoder the transceiver has an rtty decoder for baudot (mark frequency: 2125 hz, shift frequency: 170 hz, 45 bps). An external terminal unit (tu) or terminal node con- nector (tnc) is not necessary for receiving a baudot...
Page 78
4 receive and transmit 4-16 decode usos (default: on) turn the usos (unshift on space) function on or off. This function decodes a letter code after receiving a “space.” • off: decodes as a character code • on: decodes as a letter code decode new line (default: cr,lf,cr+lf) select the internal rtty ...
Page 79
4 receive and transmit 4-17 the functions for rtty operation (continued) rtty memory screen (rt1–rt4) rtty memory screen (rt5–rt8) d transmitting an rtty memory previously entered characters can be sent using the rtty memory. Contents of the memory are enter in the rtty memory (edit) screen. In the ...
Page 80
4 receive and transmit 4-18 • preprogrammed contents ch contents rt1 ↵ de icom icom k ↵ rt2 ↵ de icom icom icom k ↵ rt3 ↵ qsl ur 599–599 bk ↵ rt4 ↵ qsl de icom icom ur 599–599 bk ↵ rt5 ↵ 73 gl sk ↵ rt6 ↵ cq cq cq de icom icom icom k ↵ rt7 ↵ my transceiver is ic–7100 & antenna is a 3–element triband ...
Page 81
4 receive and transmit 4-19 • rtty decode log sd card icon d turning on the rtty decode log turn on the rtty decode log to store your rtty op- erating record, both tx and rx, into an sd card. Be sure to insert the sd card, otherwise this function does not work properly. The sd card is not supplied b...
Page 82
4 receive and transmit 4-20 rtty decode log set mode d rtty decode log set mode the rtty decode log set mode is used to set the file type and the time stamps. Q in the rtty mode, push menu ( c ) one or more times to select the “m-2” screen (m-2 menu). Touch [dec]( w d ) to display the rtty decoder s...
Page 83: Operating Am/fm
4 receive and transmit 4-21 select the desired frequency band. (p. 3-6) q on the mode selection screen, touch “am” or “fm” to w select the am or fm mode. • to select the data mode, after selecting am or fm, touch “data” to select the data mode, if needed. Rotate the dial to tune a desired signal. E ...
Page 84: Tone Squelch Operation
4 receive and transmit 4-22 the tone squelch opens only when you receive a signal containing a matching subaudible tone. You can silently wait for calls from others using the same tone. Select the desired frequency band. (p. 3-6) q on the mode selection screen, touch “fm” to select w the fm mode. Pu...
Page 85: Dtcs Operation
4 receive and transmit 4-23 the dtcs function is another method of communica- tions using selective calling. Only received signals hav- ing a matching 3-digit code will open the squelch. Select the desired frequency band. (p. 3-6) q on the mode selection screen, touch “fm” to select w the fm mode. P...
Page 86
4 receive and transmit 4-24 to search for a repeater’s sub-audible tone frequency, a tone scan is available. By monitoring a repeater signal with a tone squelch or dtcs, you can determine the tone frequency neces- sary to open the repeater or the squelch. Select the desired frequency band. (p. 3-6) ...
Page 87: Repeater Operation
4 receive and transmit 4-25 a repeater receives transmitted signals and retransmits them on a different frequency. When using a repeater, the transmit frequency is shifted from the receive fre- quency by a frequency offset. A repeater can be accessed using the duplex function by setting the frequenc...
Page 88
4 receive and transmit 4-26 repeater operation (continued) d repeater access tone frequency setting some repeaters require a subaudible tone to be ac- cessed. Subaudible tones are superimposed on your normal signal and must be set first. You can select 50 tones from 67.0 hz to 254.1 hz. In the fm mo...
Page 89
4 receive and transmit 4-27 repeater operation (continued) d one-touch repeater function this function allows you to set the repeater operation by holding down one switch. First, set the frequency offset as well as the repeater access tone frequency (p. 4-26). Touch the memory channel indication onc...
Page 90
4 receive and transmit 4-28 repeater operation (continued) d transmit frequency monitor check you may be able to directly receive the other party’s transmitted signal without having to go through a re- peater. This function helps you to check whether direct communication can be made, or not. While r...
Page 91
4 receive and transmit 4-29 d storing a non standard repeater while the “m-1” menu is selected, touch [a/b]( q d ) to select vfo a. Rotate the dial to set the repeater output frequency. W touch [a/b]( e d ) to select vfo b. Rotate the dial to set the repeater input frequency. R t push menu ( c ) to ...
Page 92: Section
Preamp and attenuator ...........................................................5-2 preamplifier d .............................................................................5-2 attenuator d ................................................................................5-2 agc function ............
Page 93: Preamp and Attenuator
5 functions for receive 5-2 d preamplifier the preamplifier amplifies weak signals in the receiver front end, to improve the s/n ratio and sensitivity. Turn this function on when receiving weak signals. (frequency band: hf, 50/70 mhz) ➥ push p.Amp att ( c ) one or more times to set the pre- amp off,...
Page 94: Agc Function
5 functions for receive 5-3 the agc (auto gain control) controls receiver gain to produce a constant audio output level, even when the received signal strength greatly varies. The transceiver has 3 pre-set agc time constants: fast, mid and slow for ssb, cw, rtty and am modes. In the fm , wfm and dv ...
Page 95: Rit Function
5 functions for receive 5-4 rit function the rit (receive increment tuning) function compen- sates for off-frequency operation of the received sta- tion. The function shifts the receive frequency up to ±9.99 khz in 10 hz steps*, without changing the trans - mit frequency. * the [m-ch] ( l ) control ...
Page 96: Twin Pbt Operation
5 functions for receive 5-5 (mode: ssb/cw/rtty/am) to reject interference, pbt (passband tuning) electron - ically narrows the if passband width by shifting the if frequency slightly outside of the if filter passband. The ic-7100 uses dsp for the pbt function. Moving both twin-pbt ([m-ch/bank] ( l )...
Page 97: If Filter Selection
5 functions for receive 5-6 the transceiver has 3 passband width if filters for each mode. The filter selection is automatically memorized in each mode. The pbt shift frequencies are automatically memo- rized in each filter. D if filter selection on the mode selection screen, select the desired q mo...
Page 98: If (Dsp) Filter Shape
5 functions for receive 5-7 (mode: ssb/ssb-d/cw) a soft or sharp type of dsp filter shape for both ssb and cw can be independently selected. On the mode selection screen, select the ssb or q cw mode. (p. 3-17) touch the filter icon for 1 second to display the “fil- w ter” screen. Push [sharp] or [so...
Page 99: Noise Blanker
5 functions for receive 5-8 (mode: ssb/cw/rtty/am) the noise blanker eliminates pulse-type noise such as noise from car ignitions. Push ➥ nb ( d ) to turn the noise blanker function on or off. • “nb” is displayed when the noise blanker is on. When using the noise blanker function, received signals m...
Page 100: Noise Reduction
5 functions for receive 5-9 nr noise reduction the noise reduction function reduces random noise components and enhances audio signals which are buried in noise. The received signals are converted to digital signals and then the audio signals are separated from the noise. Push q nr ( c ) to turn on ...
Page 101: Notch Function
5 functions for receive 5-10 (mode = auto notch: ssb/am/fm manual notch: ssb/cw/rtty/am) this transceiver has auto and manual notch functions. ➥ in the ssb or am mode, push notch ( c ) to toggle the notch function between auto, manual and off. • either the auto or manual notch function can be turned...
Page 102
5 functions for receive 5-11 d manual notch function (mode = manual notch: ssb/cw/rtty/am) the manual notch function allows you to manually at- tenuate a frequency via the “notch control.” push q notch ( c ) once or twice to turn on the man- ual notch function. • “mn” appears. Hold down w notch ( c ...
Page 103: Lock Function
5 functions for receive 5-12 the ic-7100 has two kinds of lock functions; dial lock and panel lock. The dial lock function locks only the dial, and panel lock function locks controller opera- tion. The dial lock function prevents frequency changes by accidental movement of the dial by electronically...
Page 104: Meter Peak Hold Function
5 functions for receive 5-13 meter peak hold function appears for 0.5 seconds. The meter peak hold function is set to on by default, the peak level of a received signal strength or the out- put power is displayed for approximately 0.5 seconds. The function can be turned off in the “meter peak hold” ...
Page 105: Simple Band Scope
5 functions for receive 5-14 simple band scope the band scope function allows you to visually check the location and strength of signals around a specified frequency. The ic-7100’s band scope function can be used in any operating mode and any frequency band. Indicator description sweep icon while th...
Page 106: Section
Vox function ............................................................................6-2 using the vox function d ...........................................................6-2 adjusting the vox function d ......................................................6-2 break-in function .................
Page 107: Vox Function
6 functions for transmit 6-2 (mode: ssb/am/fm/dv) the vox (voice-operated transmission) function switches the transceiver between transmit and receive with your voice. This function provides hands-free op- eration. D using the vox function select the desired frequency band. (p. 3-6) q on the mode se...
Page 108: Break-In Function
6 functions for transmit 6-3 break-in function (mode: cw ) the break-in function is used in the cw mode to auto- matically toggle the transceiver between transmit and receive when keying. The ic-7100 is capable of full break-in or semi break-in. D semi break-in operation during semi break-in operati...
Page 109
6 functions for transmit 6-4 break-in function (continued) push q speed/pitch ( c ) to open the key speed/cw pitch adjustment window. Rotate [m-ch] w ( l ) to adjust the key speed. • the adjustable key speed is between 6 and 48 wpm (words per minute). Push e menu ( c ) to close the window. Speed/pit...
Page 110: Speech Compressor Function
6 functions for transmit 6-5 speech compressor function (mode: ssb ) the speech compressor function increases average rf output power, improving signal strength and read- ability. Select the desired frequency band. (p. 3-6) q on the mode selection screen, select the usb or w lsb mode. (p. 3-17) befo...
Page 111
6 functions for transmit 6-6 transmit filter width selection (mode: ssb ) the transmit filter width for the ssb mode can be se- lected from wide, mid or narrow. This setting can be memorized each for the speech compressor on and off. Select the desired frequency band. (p. 3-6) q on the mode selectio...
Page 112: Monitor Function
6 functions for transmit 6-7 monitor function the monitor function allows you to monitor your trans- mit if signals in any mode. Use this to check voice characteristics while adjusting transmit parameters. The cw side tone functions regardless of the “monitor” setting. Push q set ( c ) to enter the ...
Page 113: Split Frequency Operation
6 functions for transmit 6-8 l eft r ight c enter d isplay split frequency operation split frequency operation allows you to transmit and receive on two different frequencies. Split frequency operation is performed using frequencies in vfo a and vfo b. • the split frequency operation is automaticall...
Page 114
6 functions for transmit 6-9 split frequency operation (continued) d direct frequency shift input the frequency shift can directly be entered. Touch the mhz digits to enter the band selection dis- q play. Touch [f-inp]( w d ) to enter the direct input screen. If the shift direction is minus, touch “...
Page 115
6 functions for transmit 6-10 split frequency operation (continued) d split lock function the split lock function is convenient for changing only the transmit frequency. When the split lock function is not used, accidentally releasing xfc ( r ) while rotating the dial, changes the receive frequency....
Page 116: Quick Split Function
6 functions for transmit 6-11 quick split function when you touch [split]( d ) for 1 second, the split fre- quency operation is turned on. The undisplayed vfo is automatically changed according to the plus/minus frequency shift programmed in the “split offset” item of the “function” set mode (p. 17-...
Page 117
6 functions for transmit 6-12 quick split function (continued) d split frequency offset setting by setting an often-used split frequency offset in ad- vance, you can use the quick split function to select split operation at the touch of one key. Push q set ( c ) to enter the set mode. Touch the “spl...
Page 118: Measuring Swr
6 functions for transmit 6-13 measuring swr the ic-7100 has a built-in circuit for measuring antenna swr— no external equipment or special adjustments are necessary. The ic-7100 can measure swr two ways — spot mea- surement and plot measurement. D spot measurement this function is convenient to use ...
Page 119
6 functions for transmit 6-14 d plot measurement plot measurement allows you to measure the swr over an entire band. Measuring swr (continued) indicator description measurement start icon touch [ ]( d ) to start the measuring. While measuring, “ u ” is displayed. The measured fre- quency is displaye...
Page 120
6 functions for transmit 6-15 measuring swr plot measurement (continued) d select the desired frequency band. (p. 3-6) q on the mode selection screen, select the rtty or w rtty-r mode. (p. 3-17) if necessary, adjust the rf power to more than 30 w e on the mic gain/rf power adjustment display. • if y...
Page 121
6 functions for transmit 6-16 d swr graph set mode push q menu ( c ) one or more times to select the “m-3” screen (m-3 menu). Touch [swr]( w d ) to display the “swr” (swr graph) screen. Touch [set]( e d ) to enter the “swr graph set” screen. Touch the desired item to select. R • see below for detail...
Page 122: Dtmf Memory Encoder
6 functions for transmit 6-17 dtmf memory encoder dtmf tones are used for autopatching, controlling oth- er equipment, and so on. The transceiver has 16 dtmf memory channels for storage of often-used dtmf codes sequence of up to 24 digits. D programming a dtmf code select the desired frequency band....
Page 123
6 functions for transmit 6-18 d transmitting dtmf code to transmit dtmf code using a dtmf send window, program the desired code in advance. Select the desired frequency band. (p. 3-6) q on the mode selection screen, select the fm or dv w mode. (p. 3-17) • the dtmf encoder can be used in the fm or dv...
Page 124
6 functions for transmit 6-19 d transmitting dtmf code (direct input) select the desired frequency band. (p. 3-6) q on the mode selection screen, select the fm or dv w mode. (p. 3-17) • the dtmf encoder can be used in the fm or dv mode. Push e menu ( c ) one or more times to select the “m-3” screen ...
Page 125
6 functions for transmit 6-20 d setting dtmf transfer speed the dtmf transfer speed can be selected. On the mode selection screen, select the fm or dv q mode. (p. 3-17) • the dtmf encoder can be used in the fm or dv mode. Push w menu ( c ) one or more times to select the “m-3” screen (m-3 menu). • i...
Page 126: Section
7-1 section 7 d-star introduction important! • the repeater list described in this manual may differ from your transceiver’s preloaded contents. • although japanese repeaters are used in the setting examples, the japanese repeater node (port) letters are dif - ferent from those in other countries. B...
Page 127
7 d-star introduction 7-2 important! Before starting d-star, the following steps are needed. Step 1 entering your call sign (my) into the transceiver. Step 2 registering your call sign (my) to a gateway repeater. You have completed the steps!! “my” (your own call sign) programming you can store up t...
Page 128
7 d-star introduction 7-3 enter the call sign 2. Touch the desired block one or more times to select t the desired character. (example: j) • a to z, 0 to 9 and / are selectable. • touch “ab ⇔ 12” to toggle between the alphabet input and the number input mode. • touch [clr]( d ) to delete the selecte...
Page 129
7 d-star introduction 7-4 “my” (your own call sign) programming convenient! ✓ if necessary, enter a note of up to 4 characters, such as the model of the transceiver, name, area name, and so on, after your call sign. Touch [ q g ]( d ) one or more times until the cursor moves to the right of the “/”....
Page 130: D-Star Introduction
7 d-star introduction 7-5 • in the original d-star (digital smart technologies for amateur radio) plan, jarl envisioned a system of repeaters grouped together into zones. • the d-star repeater enables you to call a ham sta - tion on another repeater through the internet. • the transceiver can be ope...
Page 131
7 d-star introduction 7-6 the dr (d-star repeater) mode is one mode you can use for d-star repeater operation. In this mode, you can select a preprogrammed repeater or frequency in “from” (the access repeater or simplex), and ur call sign in “to” (destination), as shown to the right. Note: if the re...
Page 132
7 d-star introduction 7-7 in the dr mode, the transceiver has three communica- tion forms, as shown below. • local area call: to call through your local area (ac - cess) repeater. • gateway call: to call through your local area (ac - cess) repeater, repeater gateway and the internet to your destinat...
Page 133: Section
8-1 section 8 d-star operation important! • the repeater list, described in this manual, may differ from your transceiver’s preloaded contents. • although japanese repeaters are used in the setting examples, the japanese repeater node (port) letters are dif - ferent from other country’s. Be sure to ...
Page 134: D-Star Operating Procedures
8 d-star operation 8-2 d-star operating procedures this section describes the basic d-star procedures. • when it is the first time to operate d-star, check whether or not you can access your local area repeat- er (access repeater), and if your signal is successfully sent to a destination repeater. •...
Page 135
8 d-star operation 8-3 d-star operating procedures (continued) d making a gateway call set “from” (access repeater) 1. Push q dr ( c ) to select the dr mode. Check whether or not “from” is selected. W • if “from” is not selected, touch the “from” field. Touch the “from” field. E • the “from select” ...
Page 136
8 d-star operation 8-4 d-star operating procedures making a gateway call (continued) d set “to” (destination) 2. Check whether or not “to” is selected. U • if “to” is not selected, touch the “to” field. Touch the “to” field. I • the “to select” screen appears. Touch “gateway cq.” o • the “repeater g...
Page 137
8 d-star operation 8-5 d-star operating procedures (continued) internet ja3yua calling to jp1yiu port a through jp3yhh port b. Jm1zlk, this is ja3yua. Thanks for the nice qso and i hope to talk to you again soon. This is ja3yua now clear of the jp3yhh repeater. Ja3yua, this is jm1zlk. Hello, how are...
Page 138
8 d-star operation 8-6 the transceiver includes a status message in the signal received back from the access repeater, after transmit- ting. D shows “ur?” the call was successfully sent, but no station’s signal was received within 3 seconds. The called station may have missed your call, so after wai...
Page 139: Capturing A Call Sign
8 d-star operation 8-7 after you receive the repeater’s signal, the calling sta- tion’s call sign can be captured by holding down the call sign capture key auto tune rx cs ( r ). Then you can quickly and easily reply to the received call. Capturing a call sign set the received call sign to the des...
Page 140
8 d-star operation 8-8 • when you know your access repeater from the repeater list (p. 8-9) when your access repeater is preloaded in your trans- ceiver’s repeater list, you can select it by selecting the repeater area or name. • when you don't know which repeater you can access. • when the “from” d...
Page 141
8 d-star operation 8-9 when your access repeater is preloaded in your trans- ceiver’s repeater list, you can select it from the repeater list. By only selecting the repeater from the list, the call sign, frequency, duplex and offset frequency settings are automatically set for easy operation. Exampl...
Page 142
8 d-star operation 8-10 d using the dr mode scan the dr mode scan is useful to find a repeater. To quickly find a repeater, the dr mode scan skips re- peaters that are not specified as an access repeater. (the “use (from)” setting is set to “no” (skip is set) on the repeater list.) example: select t...
Page 143
8 d-star operation 8-11 d using the repeater search function the transceiver searches for the nearest repeater by using your own and the repeater’s position. The nearest repeater in your transceiver’s repeater list is displayed as the available choices. To receive your own position, connect an exter...
Page 144
8 d-star operation 8-12 selecting the access repeater from the near re- 2. Peater list push q dr ( c ) to select the dr mode. Check whether or not “from” is selected. W • if “from” is not selected, touch the “from” field. Touch the “from” field. E • the “from select” screen appears. Touch “near repe...
Page 145
8 d-star operation 8-13 d using the tx history repeaters you transmitted to in the dr mode are stored in the tx history, and you can select a repeater from the tx history as your access repeater. The tx history stores up to 10 of the latest “from” (access repeater) repeaters. Push q dr ( c ) to sele...
Page 146
8 d-star operation 8-14 the destination repeater or station must be set to “to” when you transmit a call in the dv mode. You have eight ways to set the destination. Click the title shown below to jump to the specified page. How to switch the repeater group: when “local cq” or “gateway cq” is se- lec...
Page 147
8 d-star operation 8-15 d using the “local cq” (local area call) when “local cq” is selected in the “to select” screen, “cqcqcq” is set in “to.” example: making a local area call by accessing the “hirano” repeater. Push q dr ( c ) to select the dr mode. Check whether or not “to” is selected. W • if ...
Page 148
8 d-star operation 8-16 d using the “ gateway cq ” (gateway call) when “gateway cq” is selected in the “to select” screen, the repeater to make a gateway cq call can be selected from the repeater list. Example: making a gateway cq call to (japan; hama- cho) from the “hirano” repeater. Push q dr ( c ...
Page 149
8 d-star operation 8-17 d using the “your call sign” the “your call sign” memory stores the programmed “ur” (destination) call sign. When you select an individual station call sign for the “to” (destination) setting using “your call sign,” a gate- way call can be made. When you call the destination ...
Page 150
8 d-star operation 8-18 d using the rx history when a call is received in the dv mode, the call data is stored in the rx history. Up to 50 callers, and only the last called call signs can be stored. Example: select “tom” from rx history. Push q dr ( c ) to select the dr mode. Check whether or not “t...
Page 151
8 d-star operation 8-19 d using the tx history the tx history stores the name and/or call sign of up to 20 “to” (destination) settings that were used when you made the calls. Note: if you never transmit a call in the dv mode, you cannot select “to” (destination) from the tx his- tory. Example: selec...
Page 152
8 d-star operation 8-20 d directly inputting (ur) the destination station call sign can be directly input. Example: directly input the call sign “jm1zlk.” push q dr ( c ) to select the dr mode. Check whether or not “to” is selected. W • if “to” is not selected, touch the “to” field. Touch the “to” f...
Page 153
8 d-star operation 8-21 d directly inputting (rpt) the destination repeater call sign can be directly input. Example: directly input the call sign “jp3ydh” push q dr ( c ) to select the dr mode. Check whether or not “to” is selected. W • if “to” is not selected, touch the “to” field. Touch the “to” ...
Page 154: Section
9-1 section 9 d-star operation 9-1 important! • the repeater list, described in this manual, may differ from your transceiver’s preloaded contents. • although japanese repeat - ers are used in the setting ex- amples, the japanese repeater node (port) letters are different from other country’s. Be su...
Page 155: Message Operation
9 d-star operation 9-2 the l , r , c or d in the instructions indicate the part of the controller. L : left side r : right side c : center bottom d : display (touch screen) l eft r ight c enter d isplay the transceiver has a total of 5 message memories to store short messages to transmit during dv m...
Page 156
9 d-star operation 9-3 enter the tx message 2. Touch the desired block one or more times to select t the desired character or symbol. (example: j) selectable characters and symbols a to z, a to z, 0 to 9, ! # $ % & \ ? " ’ ` ^ + – ✱ ⁄ . , : ; = ( ) [ ] { } ¦ _ ¯ @ (space) • touch “ab ⇔ 12” to toggle...
Page 157
9 d-star operation 9-4 push set touch the entered tx message to set the message o to be used. !0 push set ( c ) to exit the set mode. 2. Enter the tx message (continued) the l , r , c or d in the instructions indicate the part of the controller. L : left side r : right side c : center bottom d : dis...
Page 158
9 d-star operation 9-5 the l , r , c or d in the instructions indicate the part of the controller. L : left side r : right side c : center bottom d : display (touch screen) l eft r ight c enter d isplay message operation (continued) d message transmission you can transmit a preprogrammed text messag...
Page 159
9 d-star operation 9-6 the l , r , c or d in the instructions indicate the part of the controller. L : left side r : right side c : center bottom d : display (touch screen) l eft r ight c enter d isplay message operation (continued) d tx message deleting the programmed tx message can be deleted, as ...
Page 160: Received Call Sign Viewing
9 d-star operation 9-7 when a dv call is received, the calling station and the repeater’s call signs are stored in the rx history screen. Up to 50 calls can be stored. Even if the transceiver is turned off, the rx record won’t be deleted. The stored call signs can be displayed in the following manne...
Page 161
9 d-star operation 9-8 the l , r , c or d in the instructions indicate the part of the controller. L : left side r : right side c : center bottom d : display (touch screen) l eft r ight c enter d isplay when the received call includes gps position data. You can delete the rx history data. Push ➥ qui...
Page 162: Bk Mode Communication
9 d-star operation 9-9 the bk (break-in) function allows you to break into a conversation, where the two other stations are commu- nicating with call sign squelch enabled. (default: off) note: the bk function is automatically turned off when transceiver is turned off. After receiving a dv conversati...
Page 163: Emr Communication
9 d-star operation 9-10 emr communication the emr (enhanced monitor request) communication mode can be used in only the dv mode. In the emr mode, no call sign setting is necessary. All transceivers that receive an emr mode signal auto- matically open their squelch to receive the signal. When an emr ...
Page 164
9 d-star operation 9-11 emr communication (continued) d adjusting the emr af level the audio output level when an emr signal is received is adjustable between 0 and 100. When an emr signal is received, the audio will be heard at the preset level, or the [af] ( l ) control level, whichever is higher....
Page 165: Display Type Setting
9 d-star operation 9-12 display type setting the display size in the dr mode, such as a repeater name, call sign, and so on, can be set to large. (default: normal) push q quick ( c ) to enter the quick set mode. Touch the “display type.” w • if the specified item is not displayed, touch [ ∫ ] or [ √...
Page 166: Dv Automatic Detection
9 d-star operation 9-13 if you receive an fm signal during dv mode operation, the “dv” and “fm” icons alternately blink to indicate the received signal is fm. When the dv auto detect function is turned on, the transceiver automatically selects the fm mode to tem- porarily monitor the signal. (defaul...
Page 167: Automatic Reply Function
9 d-star operation 9-14 when a call addressed to your own call sign is received, the automatic reply function automatically replies with your call sign. (default: off) depending on the setting, the recorded message may be transmitted with the call sign. Push q set ( c ) to enter the set mode. Touch ...
Page 168
9 d-star operation 9-15 the auto reply voice announcement can be recorded and saved on the sd card to reply to the call with your voice. Note: be sure to insert an sd card to the [sd] slot of the transceiver before starting to record a voice announcement. Push q set ( c ) to enter the set mode. Touc...
Page 169
9 d-star operation 9-16 automatic reply function (continued) q transmits to the destina- tion station destination station w transmits the auto reply posi- tion data transceiver can display the distance and direction when the “gps select” item in the “gps” set mode is set to “external gps” and the tr...
Page 170: Low-Speed Data Communication
9 d-star operation 9-17 in addition to digital voice communication, low-speed data communication can be made. Use the supplied usb cable or the optional opc- 1529r data communication cable with a third-party serial data communication software. Note: • only ascii code can be used for the low-speed da...
Page 171: Speech Function
9 d-star operation 9-18 the speech function announces the called station call sign, or the individual or station call sign that is selected from the rx history. It is convenient when you cannot watch the lcd, or you missed the call’s audio. This function helps you to know the call sign of the call- ...
Page 172
9 d-star operation 9-19 d to announce the rx>cs call sign the station call sign that is selected from the rx histo- ry by holding down auto tune rx cs ( r ), will be announced. Push q set ( c ) to enter the set mode. Touch the “rx>cs speech” item of the “speech” w set mode. Speech > rx > cs speech...
Page 173
9 d-star operation 9-20 d speech language selection the speech language can be set to english or japa- nese. This setting is used for all speech functions. Push q set ( c ) to enter the set mode. Touch the “speech language” item of the “speech” w set mode. Speech > speech language • if the specified...
Page 174
9 d-star operation 9-21 d speech speed selection the speech speed can be set to slow or fast. This setting is used for all speech functions. Push q set ( c ) to enter the set mode. Touch the “speech speed” item of the “speech” w set mode. Speech > speech speed • if the specified item is not displaye...
Page 175: Digital Squelch Functions
9 d-star operation 9-22 the digital squelch opens only when receiving a signal addressed to your own call sign, or a signal that in- cludes a matching digital code. You can silently wait for calls from others. You can independently set the digital squelch function in the vfo, memory, call channel, o...
Page 176
9 d-star operation 9-23 d digital code setting push q dr ( c ) to enter the dr mode. Push w menu ( c ) to select the “d-2” screen (d-2 menu). • to use the digital code squelch function in another mode, push menu ( c ) to select the “m-2” screen (m-2 menu). Touch [dsql]( e d ) for 1 second to display...
Page 177: Viewing The Call Signs
9 d-star operation 9-24 the call sign can be displayed or change in the in the “call sign” set mode. Set ( c ) > call sign while in the dv mode, shows the “call sign” screen in the “d-1” screen (d-1 menu). Push q dr ( c ) to enter the dr mode. Push w menu ( c ) to select the “d-1” screen (d-1 menu)....
Page 178
9 d-star operation 9-25 note in the “call sign” screen, touch “ur:” for 1 second to open the function window. The function window displays the “edit,” “clear” and “add to your memo- ry” items, and then touch the desired item. • touch “edit” to enter the call sign edit screen. • touch “clear” to dele...
Page 179
9 d-star operation 9-26 touch “edit” touch [cs] edit the call sign, then touch [ent]. Touch “r1:” for 1 second d for duplex (repeater) operation while in the dr mode, only “my” call sign can be set. Example : while in the dv mode, making a gateway call making a gateway cq call to hamacho repeater (j...
Page 180
9 d-star operation 9-27 touch “ur:” touch “gate- way cq” touch “usa midwest” touch “dallas” touch “r2:” touch “gw” gateway “r2” setting 2. Touch “r2:.” o • the “rpt2 select” screen is displayed. !0 touch “gw.” • the display returns to the “call sign” screen. • when you manually enter the call sign, ...
Page 181: Repeater List
9 d-star operation 9-28 you can store repeater information for quick and simple communication in up to 900 repeater memory channels (repeater list) in up to 25 groups. Programming the repeater list is required for dr mode operation. D repeater list contents the following contents are included in the...
Page 182: Repeater List Programming
9 d-star operation 9-29 d new repeater programming repeater group selection 1. Push q set ( c ) to enter the set mode. Touch the “repeater list” item of the “dv memory” w set mode. Dv memory > repeater list • if the specified item is not displayed, touch [ ∫ ] or [ √ ]( d ) one or more times to sele...
Page 183
9 d-star operation 9-30 repeater name programming 2. Y touch “name” to enter the repeater name edit mode. • a cursor appears and blinks. Touch the desired block one or more times to u select the desired character or symbol. Selectable characters and symbols a to z, a to z, 0 to 9, ! # $ % & \ ? " ’ ...
Page 184
9 d-star operation 9-31 repeater sub name programming 3. !1 touch “sub name” to enter the repeater sub name edit mode. • a cursor appears and blinks. !2 touch the desired block one or more times to select the desired character or symbol. Selectable characters and symbols a to z, a to z, 0 to 9, ! # ...
Page 185
9 d-star operation 9-32 repeater call sign programming 4. When used for simplex communication, go to [7. Access repeater setting]. !6 touch “call sign” to enter the repeater call sign edit mode. • a cursor appears and blinks. !7 touch the desired block one or more times to select the desired charact...
Page 186
9 d-star operation 9-33 repeater list programming (continued) gateway repeater call sign programming 5. The 8th digit in the call sign, programmed in ‘4. Re- peater call sign programming’ as described above, is automatically set to “g” as the gateway port. And you can skip this setting and go to the...
Page 187
9 d-star operation 9-34 repeater list programming (continued) access repeater setting 7. The programmed repeaters can be used as an ac- cess repeaters in the dr mode. For simplex operation, or when the programmed repeater is not used as an access repeater, select “no.” in this case, the programmed r...
Page 188
9 d-star operation 9-35 duplex direction setting 9. • this item appears only when “yes” is selected in ‘7. Access repeater setting.’ • “dup – ” is automatically set when the access re- peater frequency is programmed in ‘8. Access re- peater frequency programming.’ • if necessary, you can change the ...
Page 189
9 d-star operation 9-36 repeater list programming (continued) position data accuracy level setting 11. When the repeater search function is not used, or the distance between your position and a repeater is not displayed, select “off.” $0 touch “position”. $1 touch the position data accuracy level. •...
Page 190
9 d-star operation 9-37 repeater list programming (continued) utc offset programming 14. Utc (universal time coordinated) offset is the time difference between utc and repeater local time. This item enables you to check the destination repeater’s time when you make a gateway call. (p. 9-44) $8 touch...
Page 191: Editing A Repeater List
9 d-star operation 9-38 this function reprograms a repeater’s data. This is use- ful when already-programmed data is incorrect, has changed or some data should be added to the list. Push q set ( c ) to enter the set mode. Touch the “repeater list” item of the “dv memory” w set mode. Dv memory > repe...
Page 192: Deleting A Repeater List
9 d-star operation 9-39 the l , r , c or d in the instructions indicate the part of the controller. L : left side r : right side c : center bottom d : display (touch screen) l eft r ight c enter d isplay the programmed repeater contents can be deleted from the repeater list. Push q set ( c ) to ente...
Page 193
9 d-star operation 9-40 you can move the programmed repeaters to rearrange their display order in the selected repeater group. The programmed repeater cannot be moved out of their assigned repeater group. Push q set ( c ) to enter the set mode. Touch the “repeater list” item of the “dv memory” w set...
Page 194
9 d-star operation 9-41 this section describes how to add a new repeater infor- mation to the repeater list using the rx history. Push q dr ( c ) to enter the dr mode. Touch [cd]( w d ). • the “rx history” screen are displayed. Touch e [ ∫ ] or [ √ ]( d ) to select the root item (“rx his- tory”). To...
Page 195
9 d-star operation 9-42 you can set unnecessary repeaters as scan skip tar- gets. The selected repeaters are skipped during scan- ning for faster selection and scanning. You can set the skip setting to all repeaters in the se- lected repeater group, or the individual repeater. When a repeater is spe...
Page 196
9 d-star operation 9-43 push q set ( c ) to enter the set mode. Touch the “repeater list” item of the “dv memory” w set mode. Dv memory > repeater list • if the specified item is not displayed, touch [ ∫ ] or [ √ ]( d ) one or more times to select the page . • the repeater groups are displayed. Touc...
Page 197: Repeater Detail Screen
9 d-star operation 9-44 according to the programmed contents, such as posi- tion data, utc offset, and so on, the distance between your position and the repeater or repeater time can be displayed on the repeater detail screen. The detail screen can also be entered in the “ from select” screen. Push ...
Page 198
9 d-star operation 9-45 a your (destination) call sign can be manually pro- grammed. The your (destination) call sign is set to “to,” you can make a call to a station, even if you don’t know where the station is currently located. Up to 200 your call signs can be programmed. Push q set ( c ) to ente...
Page 199
9 d-star operation 9-46 !0 touch “call sign” to enter the your call sign edit mode. • a cursor appears and blinks. !1 touch the desired block one or more times to select the desired character or symbol. (for example: j) • a to z, 0 to 9, / and a space can be selected. • touch “ab ⇔ 12” to toggle bet...
Page 200
9 d-star operation 9-47 editing a your (destination) call sign touch “edit.” this function reprograms a your (destination) call sign’s data. This is useful when already-programmed data is incorrect, has changed or some data should be added to the list. Push q set ( c ) to enter the set mode. Touch t...
Page 201
9 d-star operation 9-48 you can move your call signs to rearrange their display order. It is easy to find stations that you often communicate if the stations are moved to the top of the memory. Push q set ( c ) to enter the set mode. Touch the “your call sign” item of the “dv memory” w set mode. Dv ...
Page 202
9 d-star operation 9-49 select the call sign you want to delete. The l , r , c or d in the instructions indicate the part of the controller. L : left side r : right side c : center bottom d : display (touch screen) l eft r ight c enter d isplay the your (destination) call signs can be deleted from t...
Page 203: Your Setting Is Correct?
9 d-star operation 9-50 if you make a local area call with the gateway call set- ting, the destination repeater, selected in “to,” will be busy while you transmit. So the station that uses that repeater as their access repeater cannot access it, as shown below. Be sure to set cqcqcq in “to” when you...
Page 204: Section
10-1 section 10 gps/gps-a operation 10-1 gps operation ........................................................................ 10- 2 gps receive setting d ...............................................................10-2 checking gps position .........................................................
Page 205: Gps Operation
10 gps/gps-a operation 10-2 gps operation you can display your own gps data in all operating modes. You can also transmit gps data when in the dv mode. To receive gps data, connect a third-party gps receiver that has an rs-232c output and nmea data format. D gps receive setting push q set ( c ) to e...
Page 206: Checking Gps Position
10 gps/gps-a operation 10-3 checking gps position you can check your current position. D displaying position data push q quick ( c ). Touch [ w ∫ ]/[ √ ]( d ) one or more times and select “gps position.” touching [ e ∫ ]/[ √ ]( d ) allows you change between my ( my ) screen, the received ( rx ) scre...
Page 207: Pm75Ts
10 gps/gps-a operation 10-4 checking gps position (continued) d changing the gps memory and alarm gps memory and gps alarm contents can be changed in the “gps position” screen. While displaying the q mem or alm screen, push quick ( c ). While displaying the w mem screen, touch [gps mem- ory select],...
Page 208
10 gps/gps-a operation 10-5 checking gps position (continued) d saving your own or received position data with this function, you can save the position informa- tion of your station from wherever you are, and also the position information of the station you received it from. The gps memory is capabl...
Page 209: Checking Gps Information (
10 gps/gps-a operation 10-6 this screen is used to receive gps satellite informa- tion when the gps indicator does not stop blinking for a long time. Gps information displays the quantity, signal power and position of the gps satellites. The sky view screen shows the position of gps sat- ellites. Th...
Page 210: Adding Or Editing Gps Memory
10 gps/gps-a operation 10-7 adding or editing gps memory d gps memory you can add gps data to gps memory. You can add your own position, other station’s positions or any positions that are manually programmed. The gps memory is capable of storing a total of 100 channels, and conveniently stored in u...
Page 211
10 gps/gps-a operation 10-8 add a gps memory (continued) d 2. Gps memory name programming touch [name:] to enter the name programming y mode. Enter the name touching the desired block one or u more times to select the desired character, number or symbol. Selectable characters and symbols a to z, a t...
Page 212
10 gps/gps-a operation 10-9 adding or editing gps memory (continued) 4. Gps memory time programming !4 touch “time:” to enter the time programming mode. !5 touch or hold down [+] or [-] under the changing sub- ject between hour, minute, and second to program the time. • you can also change by using ...
Page 213
10 gps/gps-a operation 10-10 adding or editing gps memory (continued) 7. Gps memory group programming @7 touch “group:” to enter the group programming mode. @8 touch the desired group between (no group) or a to z. • when the group is selected, automatically returns to the “gps memory edit” screen. •...
Page 214
10 gps/gps-a operation 10-11 adding or editing gps memory (continued) d gps group name programming you can register the name of each gps group. Push q set ( c ) to enter the set mode. Touch the “gps memory” item of the “gps” set w mode. Gps > gps memory • if the specified item is not displayed, touc...
Page 215
10 gps/gps-a operation 10-12 adding or editing gps memory (continued) d clearing a gps data gps memories can be cleared (erased). Please note that erased gps memories cannot be re- stored. There are two ways to clear the memories; • erasing all gps memory in a group. • erasing a specific memory chan...
Page 216
10 gps/gps-a operation 10-13 d moving a gps data you can move programmed gps memories to rear- range their display order in the selected gps memory group. In order to move the gps memory out of their assigned memory group, edit and move, and then save. Push q set ( c ) to enter the set mode. Touch t...
Page 217
10 gps/gps-a operation 10-14 d gps alarm setting a gps alarm can sound when a target position comes into the alarm area. This function can be set to the caller station, all gps memory channels, a specified memory group or a specified memory channel. Adding or editing gps memory (continued) 0.25’ 0.2...
Page 218
10 gps/gps-a operation 10-15 gps alarm setting (continued) d example: alarm area (rx/memory) alarm setting is set to rx. Push q set ( c ) to enter the set mode. Touch the “gps alarm” item of the “gps” set w mode. Gps > gps alarm • if the specified item is not displayed, touch [ ∫ ] or [ √ ]( d ) one...
Page 219: Transmitting Gps Data
10 gps/gps-a operation 10-16 transmitting gps data set a gps sentence to transmit gps data in the dv mode. D gps data sentence setting push q set ( c ) to enter the set mode. Touch the “gps tx mode” item of the “gps” set w mode. Gps > gps tx mode • if the specified item is not displayed, touch [ ∫ ]...
Page 220
10 gps/gps-a operation 10-17 gps transmitting data (continued) d gps message programming enter a gps message of up to 20 characters to be transmitted with the position data. Example: adding “hello how are you?” push q set ( c ) to enter the set mode. Touch the “gps tx mode” item of the “gps” set w m...
Page 221: Transmitting Gps-A Data
10 gps/gps-a operation 10-18 transmitting gps-a data gps-a mode is an operating mode supported with the d-prs to transmit position data. In gps-a operation, the following codes are transmit- ted to the pc connected to the ic-7100. Gps-a code is based on aprs ® code. (aprs ® : automatic packet report...
Page 222
10 gps/gps-a operation 10-19 transmitting gps-a data (continued) d setting gps-a set to transmit in the gps-a mode. 1. Setting gps-a in the gps tx mode push q set ( c ) to enter the set mode. Touch the “gps tx mode” item of the “gps” set w mode. Gps > gps tx mode • if the specified item is not displ...
Page 223
10 gps/gps-a operation 10-20 6. Setting gps-a symbol select the desired gps-a symbol that represents your operating situation. The selected gps-a symbol channel's symbols (1~4) are transmitted along with the position data. !2 touch [ ∫ ]/[ √ ]( d ) to change the gps-a (dv-a) set- ting page. !3 touch...
Page 224
10 gps/gps-a operation 10-21 transmitting gps-a data (continued) 8. Comment programming program your comment and transmit it with the gps-a position data. The number of characters you can enter differs, de- pending on the settings of data extension and altitude (p. 10-19). Data extension altitude th...
Page 225
10 gps/gps-a operation 10-22 in the dv mode, this function automatically transmits the gps receiver’s current position data, at a selected interval, and should only be used in simplex transmis- sion. Note: • your own call sign must be entered to activate the gps automatic transmission. • when the “g...
Page 226: Section
11-1 section 11 memory operation 11-1 general description ...............................................................11-2 memory channel contents d .....................................................11-2 selecting a memory channel ................................................11- 3 selecting...
Page 227: General Description
11 memory operation 11-2 the transceiver has a total of 495 memory channels (99 channels in each of 5 memory banks, a to e), 6 scan edge channels (3 pairs) and two call channels (c1/c2) each for the 144 and 430 mhz frequency bands. The memory mode is useful to quickly select often- used frequencies....
Page 228: Selecting A Memory Channel
11 memory operation 11-3 d selecting in the vfo mode touch the memory channel number indication once q or twice to select the vfo mode. (p. 3-4) rotate [bank]( w l ) to select a memory bank that contains the channel you want to select. Rotate [m-ch]( e l ) to select a memory channel num- ber. • rota...
Page 229: Selecting A Call Channel
11 memory operation 11-4 two call channels (c1/c2) are selectable in each of the 144 and 430 mhz frequency bands. Factory default frequencies and operating modes are programmed into the call channels. Change these to suit your operating needs. Select q the 144 or 430 mhz frequency band. (p. 3-6) pus...
Page 230: Programming A Memory Channel
11 memory operation 11-5 memory channels can be programmed in either the vfo mode or the memory mode. Note: if you perform the operations as described below in a pre-programmed channel, the previous channel content will be overwritten. D programming in the vfo mode touch the memory channel number in...
Page 231
11 memory operation 11-6 programming a memory channel (continued) d programming in the dr mode push q dr to select the dr mode. (section 8) set the desired contents. (section 8) w push e menu ( c ) one or more times to select the “d- 2” screen. Touch [mw]( r d ). • the “mw” screen appears. Rotate [b...
Page 232
11 memory operation 11-7 programming a memory channel (continued) d checking the programmed memory con- tents the programmed memory channels can be checked on the “memory list” screen. When the “m-3” (menu 3) screen is selected, touch q [memo]( d ) to display the “memo” (memory) screen. Rotate [bank...
Page 233: Clearing A Memory Channel
11 memory operation 11-8 any no longer used regular memory channels can be cleared, and then become blank channels. Touch the memory channel number indication once q or twice to select the memory mode. (p. 3-4) rotate [bank]( w l ) or [m-ch]( l ) to select the mem- ory channel to be cleared. Push e ...
Page 234: Copying Memory Contents
11 memory operation 11-9 the memory channel contents (frequency, operating mode, and so on.) can be copied to the vfo. D copying in the memory mode touch the memory channel number indication once q or twice to select the memory mode. (p. 3-4) rotate [bank]( w l ) or [m-ch]( l ) to select the mem- or...
Page 235: Programming A Memory Name
11 memory operation 11-10 all memory channels, including scan edges and call channels, can be tagged with alphanumeric names of up to 16 characters each. [example]: programming a memory name into mem- ory channel 99 of bank a. Touch the memory channel number indication once q or twice to select the ...
Page 236
11 memory operation 11-11 touch [ o f ]( d ) to move the cursor backwards, or touch [ g ]( d ) to move the cursor forwards. !0 repeat steps i and o to program up to 16 char- acters memory name, and then touch [ent]( d ) to save the name, and return to the “memory list” screen. !1 touch [ ]( d ) to r...
Page 237
11 memory operation 11-12 while in the memory mode, the programmed memory name can be displayed. Touch the memory channel number indication once q or twice to select the memory mode. (p. 3-4) push w quick ( d ) to open the quick menu window. Touch [name display]. E touch the desired display type opt...
Page 238: Memo Pad Function
11 memory operation 11-13 the transceiver has a memo pad function to store the displayed content for easy writing and recalling. The memo pads are separate from the memory channels. The default number of memo pads is 5. However, you can increase the number to 10 in the “memopad num- bers” item of th...
Page 239
11 memory operation 11-14 memo pad function (continued) you can call up a memo pad by pushing mpad ( r ) one or more times while in either the vfo or memory mode. • the memo pad content is called up, starting from the most recently written. When you call up a memo pad, the previously displayed conte...
Page 240: Section
12-1 section 12 scan operation 12-1 12-1 scan types ..............................................................................12-2 preparation .............................................................................12- 3 scan set mode ...........................................................
Page 241: Scan Types
12 scan operation 12-2 scan – ∂ f frequency + ∂ f frequency center frequency (start frequency) jump mch 1 mch 5 mch 2 mch 3 mch 4 mch 6 mch 7 mch 99 means the select memory channels. means the select memory channels. mch 1 mch 5 mch 2 mch 3 mch 4 mch 6 mch 7 mch 99 fm fm usb ...
Page 242: Preparation
12 scan operation 12-3 for a programmed scan: program scan edge frequencies into program scan edge channels “1a–3a” and “1b–3b.” (p. 12-7) for a memory scan: program two or more memory channels. (program scan edge channels will not be scanned.) (p. 11-5) for a mode select scan: program two or more m...
Page 243: Scan Set Mode
12 scan operation 12-4 scan set mode the scan speed, scan resume function, pause timer, resume timer and the dial function can be set in the scan set mode. Push q menu ( c ) one or more times to select the “m- 1” (menu 1) screen. Touch [scan]( w d ) to display the “scan” screen. Touch [set]( e d ) t...
Page 244
12 scan operation 12-5 scan speed (default: fast) select the desired scan speed between slow and fast. • slow: the scan is slower. • fast: the scan is faster. Scan resume (default: on) set the scan resume function on or off. • off: when a signal is detected, the scan is can - celled. • on: when a si...
Page 245
12 scan operation 12-6 voice squelch control function (mode: ssb/am/fm) this function is useful when you do not want unmodu- lated signals pausing or cancelling a scan. When the voice squelch control (vsc) function is on, the receiv- er checks received signals for voice components. The scan pauses, ...
Page 246: Scan Edge Programming
12 scan operation 12-7 memory channels 1a–3a and 1b–3b are the program scan edge channels. They are used to program the up- per and lower frequency edges for programmed scans. (see section 11) factory default frequency and operating modes are programmed into the scan edge channels: 1a/1b are for hf,...
Page 247: Programmed Scan (Vfo Mode)
12 scan operation 12-8 a programmed scan searches for signals between pro- gram scan edge channels “1a–3a” and “1b–3b.” before starting the programmed scan, scan edges must be programmed into these channels. See the previous page for scan edge programming. If the same frequencies are programmed into...
Page 248
12 scan operation 12-9 fine programmed scan (vfo mode) when a signal is received during a fine programmed scan, the scanning tuning step is temporarily set to 10 hz and the scan speed decreases. Start the programmed scan. Q • follow steps q through u as described on page 12-8. While scanning, touch ...
Page 249: Memory Scan (Memory Mode)
12 scan operation 12-10 d memory scan a memory scan searches for signals through memory channels 1 to 99. Blank (unprogrammed) memory channels are skipped. Note: for a memory scan to start, two or more memory channels must be programmed. (p. 11-5) touch the memory channel number indication once q or...
Page 250
12 scan operation 12-11 d mode select scan repeatedly scans all memory channels with the same operating mode as the displayed mode. Note: for a mode select scan to start, two or more memory channels must be programmed, and their operating mode must be the same as the displayed mode. Follow steps q q...
Page 251
12 scan operation 12-12 d select memory scan the select memory scan searches for signals through memory channels specified as “ ” (select). Note: for a select memory scan to start, two or more memory channels must be designated as se- lect memory channels. (see below) follow steps q q through e as d...
Page 252
12 scan operation 12-13 memory scan (memory mode) (continued) all memory channels can be set as select memory chan- nels, except for the scan edge and call channels. When the “scan” screen or the “memo” screen ➥ (memory menu) is displayed, touch [sel]( d ) to set or cancel the displayed memory chann...
Page 253: F Scan and Fine
12 scan operation 12-14 d about the ∂ f scan ∂ f (delta frequency) scan searches for signals within the specified range with the displayed vfo frequency or memory channel frequency as the center frequency. The frequency range is specified by the width of the selected span. Touch the memory channel n...
Page 254
12 scan operation 12-15 d about the fine ∂ f scan when a signal is received during a fine ∂ f scan, the scanning tuning step is temporarily set to 10 hz and the scan speed decreases. Start q ∂ f scan. • follow steps q through y as described on page 12-14. While scanning, touch [fine]( w d ) to switc...
Page 255
12 scan operation 12-16 the receive frequency and the operating mode setting set the priority channel (example: a05) quick [bank]/ [m-ch] select the vfo mode select the memory mode touch “prio watch on” while priority scanning vfo frequency and a priority channel checks the selected priority channel...
Page 256
12 scan operation 12-17 the receive frequency and the operating mode setting [bank]/ [m-ch] dr when the vfo frequency is set as the priority channel select the repeater to receive (example: hirano43) select the dr mode touch “prio watch on” appears while the priority scanning set the receive frequen...
Page 257
12 scan operation 12-18 dr mode and a priority channel (continued) note: when the dr mode screen is displayed, you can normally use the dr mode; “from” (access repeater)/“to” (destination) selection, the dr mode scanning and so on. To start the dr mode scan, touch [scan] in the “d-1” screen. When a ...
Page 258: Section
13-1 section 13 using an sd card about the sd card ................................................................. 13- 2 saving data onto the sd card ............................................... 13-3 inserting the sd card ............................................................ 13-4 formatt...
Page 259: About The Sd Card
13 using an sd card 13-2 the sd and sdhc cards are not available from icom. Purchase locally. An sd card of up to 2 gb or an sdhc of up to 32 gb, can be used with the ic-7100. Icom has checked the compatibility with the following sd and sdhc cards. (as of june 2013) brand type memory size sandisk ® ...
Page 260: Saving Data Onto The Sd Card
13 using an sd card 13-3 the following data can be stored onto the card: • data settings of the transceiver memory channel contents, and repeater lists stored in the transceiver. • communication contents the transmitted and received audio. • communication log the communication and receive history lo...
Page 261: Inserting The Sd Card
13 using an sd card 13-4 turn off the transceiver. Q insert the card into the slot until it locks in place, and w makes a ‘click’ sound. • “ ” appears when the sd card is inserted. • “ ” and “ ” alternately blink while accessing the sd card. Note: before inserting, be sure to check the card directio...
Page 262: Removing The Sd Card
13 using an sd card 13-5 turn off the power. Q push in the sd card until a click sounds, and then w carefully pull it out. Removing the sd card d removing the sd card while the trans- ceiver’s power is on push q set ( c ) to enter the set mode. Touch the “sd card” set mode. W • if the specified item...
Page 263
13 using an sd card 13-6 memory channels, set mode item settings, and repeat- er lists can be saved on the sd card. Saving data settings on the sd card allows you to eas- ily restore the transceiver to its previous settings, even if an all reset is performed. For your information ✓ data settings are...
Page 264
13 using an sd card 13-7 saving with a different file name push q set ( c ) to enter the set mode. Touch the “save setting” item of the “sd card” set w mode. (sd card > save setting ) • if the specified item is not displayed, touch [ ∫ ] or [ √ ]( d ) one or more times to select the page. Touch “>.”...
Page 265
13 using an sd card 13-8 the saved memory channels, set mode item settings and repeater lists can be copied to the transceiver. This function is convenient when copying the saved data, such as memory channels, or repeater lists, to another ic-7100 and then operating with the same data. Saving the cu...
Page 266
13 using an sd card 13-9 touch [yes]( y d ) to start the file check. • while checking the file, “checking file” and a prog - ress bar are displayed. After checking, settings data loading begins. U • while loading, “loading” and a progress bar are dis - played. After loading ends, “completed!” appear...
Page 267
13 using an sd card 13-10 a backup file allows easy restoring even if the setting data in the sd card is accidentally deleted. Depending on your pc, a memory card reader (pur- chase locally) may be additionally required to read the sd card. D about the sd card’s folder contents the folder in the sd ...
Page 268
13 using an sd card 13-11 d making a backup file on your pc windows 7 is used for these instructions. Insert the sd card into the sd card drive on your q pc. • if no sd card drive is built-in, connect a memory card reader (purchase locally) and then insert the sd card into it. Click the “open folder...
Page 269: Updating The Repeater List
13 using an sd card 13-12 for easy operation, the repeater list is preloaded into your transceiver. This section describes how to manually update the re- peater list using an sd card. The latest setting file, which includes the repeater list, can be downloaded from the icom website. Downloading the ...
Page 270
13 using an sd card 13-13 inserting the sd card 4. Y remove the sd card from your pc, and insert the card into the transceiver’s slot. See page 13-4 for details of inserting the sd card into the transceiver. Saving the current data is recommended before loading other data into the transceiver. Updat...
Page 271
13 using an sd card 13-14 !1 touch [yes], [no] or [cancel]( d ). • when [yes]( d ) is touched, the skip settings of the re- peater list are retained. (p. 9-34) • when [no]( d ) is touched, the skip settings of the re- peater list are not retained. (p. 9-34) • when [cancel]( d ) is touched, returns t...
Page 272
13 using an sd card 13-15 cloning transceiver-to-transceiver using an sd card this topic describes the cloning method using the sd card. Memory channel contents, set mode item settings and repeater list can be saved onto an sd card. Recorded voice memories are not included in the clon- ing data. To ...
Page 273: Section
14-1 section 14 voice memory function recording a qso audio ........................................................ 14- 2 to start recording d ..................................................................14-2 to stop recording d ....................................................................
Page 274: Recording A Qso Audio
14 voice memory function 14-2 the voice memory function records a qso (communi- cation) audio onto the sd card. This function enables you to record both received and transmitted audio, a qso with a dx’pedition, and play- back the recorded audio after the qso. Note: be sure to insert an sd card into ...
Page 275: Changing The Recording Mode
14 voice memory function 14-3 you can change the recording mode in the set mode to record only the received audio. The default setting is “tx&rx” (both transmit and receive signals are recorded). Push q set ( c ) to enter the set mode. Touch the “rec mode” item of the “voice memo” set w mode. ( voic...
Page 276
14 voice memory function 14-4 push q set ( c ) to enter the set mode. Touch the “play files” item of the “voice memo” set w mode. ( voice memo > qso recorder > play files ) • if the specified item is not displayed, touch [ ∫ ] or [ √ ]( d ) one or more times to select the page. • the folder list is ...
Page 277: Operation While Playing Back
14 voice memory function 14-5 you can fast forward or rewind while playing back. D fast forward while playing touch to fast forward to the skip time point. (default: 10 seconds) if you want to change the skip time, see “changing the skip time.” (p. 14-6) d rewind while playing touch to rewind to the...
Page 278: Changing The Skip Time
14 voice memory function 14-6 you can change the fast forward and rewind skip time while playing. Push q set ( c ) to enter the set mode. Touch the “skip time” item of the “voice memo” set w mode. ( voice memo > qso recorder > player set > skip time ) • if the specified item is not displayed, touch ...
Page 279
14 voice memory function 14-7 push q set ( c ) to enter the set mode. Touch the “play files” item of the “voice memo” set w mode. ( voice memo > qso recorder > play files ) • if the specified item is not displayed, touch [ ∫ ] or [ √ ]( d ) one or more times to select the page. • the folder list is ...
Page 280: Deleting The Folder
14 voice memory function 14-8 note: all the files in the folder are also deleted. Push q set ( c ) to enter the set mode. Touch the “play files” item of the “voice memo” set w mode. ( voice memo > qso recorder > play files ) • if the specified item is not displayed, touch [ ∫ ] or [ √ ]( d ) one or ...
Page 281
14 voice memory function 14-9 in the default settings, the transceiver records audio only while receiving signals (the squelch is open). If you want to continue recording even if no signal is received, do the following steps. Push q set ( c ) to enter the set mode. Touch the “rx rec condition” item ...
Page 282
14 voice memory function 14-10 the transceiver can record the transmit and receive au- dio into the same file. Push q set ( c ) to enter the set mode. Touch the “file split” item of the “voice memo” set w mode. ( voice memo > qso recorder > recorder set > file split ) • if the specified item is not ...
Page 283
14 voice memory function 14-11 the transceiver starts to record the transmitted audio when the [ptt] switch is pushed. After transmitting, when the transceiver receives a sig- nal in a given amount of time, it also records the re- ceived audio. Therefore, you can record all communica- tion audio usi...
Page 284
14 voice memory function 14-12 the transceiver can display the folder’s name, number of the files in the folder, total capacity of the files and date. Push q set ( c ) to enter the set mode. Touch the “ w play files” item of the “voice memo” set mode. ( voice memo > qso recorder > play files ) • if ...
Page 285: Viewing The File Information
14 voice memory function 14-13 the transceiver can display the recorded file’s frequen- cy, mode, date, and so on. Push q set ( c ) to enter the set mode. Touch the “ w play files” item of the “voice memo” set mode. ( voice memo > qso recorder > play files ) • if the specified item is not displayed,...
Page 286
14 voice memory function 14-14 viewing the file information (continued) • receive information screen ( receiving in the dr mode) example of file information screens (the display items differ, depending on the recording contents.) • transmit information screen (your own position) ( transmitting in th...
Page 287
14 voice memory function 14-15 push q set ( c ) to enter the set mode. Touch the “sd card” item. W • if the specified item is not displayed, touch [ ∫ ] or [ √ ]( d ) one or more times to select the page. Touch the “sd card info” item. E • the information screen appears. Touch [ r ]( c ) to cancel t...
Page 288
14 voice memory function 14-16 you can also playback the voice memory data on a pc. However, the recorded information (frequency, date, and so on) are not displayed. • mircosoft ® windows ® 7 is used for the description. Example: connect a memory card reader (3rd party product) to the pc, and insert...
Page 289: Section
15-1 section 15 voice tx function recording the voice audio ....................................................15-2 playing back the recorded voice audio ...............................15- 3 programming a memory name .............................................15- 4 transmitting the recorded voice...
Page 290: Recording The Voice Audio
15 voice tx function 15-2 the voice tx function transmits the recorded audio on an sd card once, or repeatedly, for up to 10 minutes at the specified interval. Up to 4 memories are available for repeated cq and exchange transmissions in contests, as well as when making repeated calls to dx’peditions...
Page 291
15 voice tx function 15-3 playing back the recorded voice audio the recorded voice audio for the voice tx function can be played back. Push q menu ( c ) one or more times to select the “m- 2” (menu 2) screen. • in the dr mode, select the “d1” screen. Touch [voice]( w d ) to select the voice tx mode....
Page 292: Programming A Memory Name
15 voice tx function 15-4 each voice tx memory, [t1] through [t4], can be pro- grammed with an alphanumeric name of up to 16 char- acters. [example]: programming the memory name “con- test” in [t1]. Push q menu ( c ) one or more times to select the “m- 2” (menu 2) screen. • in the dr mode, select th...
Page 293
15 voice tx function 15-5 programming a memory name (continued) after programming, touch [ent] touch [ ] to can- cel the “voice tx record” screen touch [ i f ]( d ) to move the cursor backwards, or touch [ g ]( d ) to move the cursor forwards. Repeat steps o u and i to program up to 16 char- acters ...
Page 294
15 voice tx function 15-6 push q menu ( c ) one or more times to select the “m- 2” (menu 2) screen. • in the dr mode, select the “d1” screen. Touch [voice]( w d ) to select the voice tx mode. • “voice tx” screen is displayed. Push e menu ( c ) to display the “voice” screen. R > touch the desired mem...
Page 295
15 voice tx function 15-7 d adjusting the tx volume level push q menu ( c ) one or more times to select the “m-2” (menu 2) screen. • in the dr mode, select the “d1” screen. Touch [voice]( w d ) to select the voice tx mode. • “voice tx” screen is displayed. Touch [level]( e d ) to display the “tx lev...
Page 296: Voice Tx Set Mode
15 voice tx function 15-8 repeat time (default: 5sec) set the repeat interval to between 1 and 15 seconds (in 1 second steps) for the voice repeat transmission. The transceiver repeatedly transmits the recorded voice audio at this interval. Auto monitor (default: on) turn the tx monitor function on ...
Page 297: Section
16-1 section 16 antenna tuner operation connecting the antenna tuner ..............................................16-2 connecting an ah-4 d ..............................................................16-2 connecting an at-180 d ...........................................................16-2 conne...
Page 298: Connecting The Antenna Tuner
16 antenna tuner operation 16-2 connecting the antenna tuner to long wire to optional ah-2b ground ah-4 to [ant1] ic-7100 to [tuner] ground* ant antenna element to [transceiver] to [ant1] to [acc] at-180 to [ant] to [acc]* ground hf/6 m antenna coaxial cable supplied with the at-180 acc cable suppli...
Page 299
16 antenna tuner operation 16-3 d connector information for the at-180 acc(2) socket pin layout pin no./ name description specifications acc 2 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 (rear panel view) 8 v q regulated 8 v output when the band voltage modification is performed. Same as acc pin q . Gnd w connects to ground. – h...
Page 300: Operating The Ah-4
16 antenna tuner operation 16-4 operating the ah-4 d before operating r danger high voltage! Never touch the antenna element while tuning or transmitting. Always place it in a secure place. Never operate the ah-4 without an antenna connect- ed. The tuner and transceiver will be damaged. Never operat...
Page 301: Operating The At-180
16 antenna tuner operation 16-5 operating the at-180 d before operating about using antenna: 1. Caution: • never connect the antenna worth than 3:1 anten- na. Even if the antenna tuner tune this antenna, it causes to damage the antenna tuner. • never transmit with the tuner on if no antenna is conne...
Page 302
16 antenna tuner operation 16-6 d operating the at-180 automatic antenna tuner automatically matches to your antenna. Once the tuner matches the antenna, the variable capacitor settings are memorized as a preset point for each frequency range (100 khz steps). Therefore, when you change the frequency...
Page 303
16 antenna tuner operation 16-7 setting the at-180 internal switches the optional at-180 has 3 operating configurations for hf band operation. Select a suitable configurations for your antenna system. Q remove the top cover of the at-180. W set the tuner switches to the desired positions ac- cording...
Page 304: Section
17-1 section 17 set mode set mode description ............................................................17-2 the set mode settings d ..........................................................17-2 set mode items and default settings ...................................17- 3 voice memo set mode ........
Page 305: Set Mode Description
17 set mode 17-2 the set mode is used to program infrequently changed values or function settings. Note: the set mode is constructed in a tree struc- ture. You may go to the next tree level, or go back a level, depending on the selected item. Set d the set mode settings push q set ( c ) to enter the...
Page 306
17 set mode 17-3 note: the default settings shown below in bold are for the usa version. The default settings may differ, depending on your transceiver version. Call sign (section 9) ➥ rx history (section 9) ➥ my station (section 7) ➥ gps (section 10) ➥ sd card (section 13) ➥ voice memo in this item...
Page 307
17 set mode 17-4 speech in this item, set the speech options. Rx call sign speech off, on (kerchunk) or on (all) selects the rx call sign speech function option while on, or turn it off. Rx>cs speech off or on turns the rx>cs speech function on or off. S-level speech off or on turns the signal stren...
Page 308
17 set mode 17-5 function in this item, set the function options. Monitor off or on selects whether or not to monitor your transmit signal in any mode other than cw. Monitor level 0%~ 50% ~100% sets the monitor level. Beep level 0%~ 50% ~100% sets the beep output level. Beep level limit off or on se...
Page 309
17 set mode 17-6 ptt start off or on turns the ptt tuner start function on or off. [tuner] switch manual or auto selects whether or not to store the at-180’s sta- tus by each band. [speech/lock] switch speech/lock , lock/speech selects the function for speech when pushed or held down. Lock function ...
Page 310
17 set mode 17-7 tone control in this item, set the rx/tx tone control options. Rx ssb rx hpf/lpf ---- – ---- , 100~2000 – 500~2400 sets the high-pass filter or low-pass filter of the receive audio. Rx bass –5~ 0 ~+5 sets the bass level of the receive audio. Rx treble –5~ 0 ~+5 sets the treble level...
Page 311
17 set mode 17-8 connectors in this item, set the external connector’s options. Usb audio sql off (open) or on selects whether or not to output the audio from the [usb] connector, according to the squelch state (open or closed). Acc/usb output select af or if sets the [usb] connector and the [acc] s...
Page 312
17 set mode 17-9 display in this item, set the transceiver’s display options. Lcd contrast 0%~ 50% ~100% sets the contrast level of the lcd. Lcd backlight 0%~ 50% ~100% sets the backlight level of the lcd. Key backlight 0%~ 50% ~100% sets the backlight level of the key. Meter peak hold off or on tur...
Page 313
17 set mode 17-10 others in this item, set other options. Information version shows the transceiver’s firmware version num- ber. Clone clone mode reads or writes the cs-7100 data to or from the pc, and/or receives data from a master trans- ceiver. Clone master mode writes your ic-7100 (master) data ...
Page 314: Voice Memo Set Mode
17 set mode 17-11 > voice memo > qso recorder > > insert an sd card into the transceiver before select- ing this item. Touch [>] to start voice recording. • “recording started.” appears. • [>] is displayed while recording. Once recording has started, the recording will con- tinue, even the transceiv...
Page 315
17 set mode 17-12 file split (default: on) voice memo > qso recorder > recorder set > file split (file split) turn the file split function on or off. • off: when the recording starts, a new file is auto - matically created in the folder of the sd card. The audio is continuously recorded into the fil...
Page 316: Dv Set Mode
17 set mode 17-13 standby beep (default: on) dv set > standby beep (standby beep) turn the standby beep function on or off. This function sounds a beep after a received signal dis- appears. • off: turns the function off. • on: turns the function on to sound a beep. • on (to me: high tone): turns the...
Page 317
17 set mode 17-14 dv auto detect (default: off) dv set > dv auto detect (dv auto detect) turn the dv mode automatic detect function on or off. If you receive a non-digital signal during dv mode op- eration, this function automatically switches to the fm mode. • off: turns the function off. The opera...
Page 318: Speech Set Mode
17 set mode 17-15 rx call sign speech (default: on (kerchunk)) speech > rx call sign speech (rx call sign speech) turn the rx call sign speech function on or off for calls received in the dv mode. • off: no announcement is made even when a call is received. • on (kerchunk): the caller station’s call...
Page 319: Qso/rx Log Set Mode
17 set mode 17-16 qso log (default: off) qso/rx log > qso log (qso log) select whether or not to make a communication log on the sd card. The communication log is saved in the “csv” format. Be sure to insert the sd card into the transceiver be- fore making a communication log. • off: the qso log fun...
Page 320
17 set mode 17-17 the qso log contents are shown below: content example description tx/rx tx rx transmission and reception date 12/23/2012 13:51:48 12/23/2012 13:51:48 date and time the call was started. Frequency 438.010000 438.010000 operating frequencies ( when duplex is set, the frequencies of t...
Page 321: Function Set Mode
17 set mode 17-18 monitor (default: off) function > monitor (monitor) turn the monitor function on or off. This function allows you to monitor your transmit signal in any mode other than cw. • off: turns the function off. • on: monitors your transmit signal. Monitor level (default: 50%) function > m...
Page 322
17 set mode 17-19 tx delay (default: all bands; off) function > tx delay (tx delay) sets the transmission’s timing for each operating band. When an external device, such as a vacuum tube linear amplifier or a receiver preamplifier, is connected to the transceiver and you use the send line, a problem...
Page 323
17 set mode 17-20 auto repeater function > split/dup > auto repeater (auto repeat- er) this item appears only in the korean and u.S.A. Ver- sion transceivers. The auto repeater function automatically turns the du- plex operation and tone encoder* on or off. The offset and repeater tone* are not chan...
Page 324
17 set mode 17-21 main dial auto ts (default: high) function > main dial auto ts (main dial auto ts) set the auto tuning step function for the dial. When rapidly rotating the dial, the tuning step auto- matically changes as selected. There are two types of auto tuning steps: low (faster) and high (f...
Page 325
17 set mode 17-22 mic af out (default: off) function > mic af out (mic af out) select the [mic] connector output function. • off: the [mic] connector does not output the re - ceived audio. When using the optional hm-151 remote con - trol mic , select “off.” • on: the [mic] connector outputs the rece...
Page 326: Tone Control Set Mode
17 set mode 17-23 rx hpf/lpf (default: [----] - ----) tone control > rx > (mode) > rx hpf/lpf (rx hpf/ lpf) (mode: ssb/cw/rtty/am/fm/dv) first select the operating mode, then set the receive audio high-pass filter to between 100 hz and 2000 hz in 100 hz steps. Rx hpf/lpf (default: ---- - [----]) ton...
Page 327: Connectors Set Mode
17 set mode 17-24 usb audio sql (default: off (open)) connectors > usb audio sql (usb audio sql) select whether or not to output the audio from the [usb] connector on the rear panel, according to the squelch state. The same audio signals are output from the [usb] con- nector and the [acc] socket. • ...
Page 328
17 set mode 17-25 keyer (default: off) connectors > external keypad > keyer (external keypad (keyer)) select whether or not to enable transmitting keyer memory contents using the external keypad. • off: the external keypad is disabled. • on: transmits the desired keyer memory contents in m1 to m4 du...
Page 329
17 set mode 17-26 dv data/gps out baud (default: 4800) connectors > usb2/data1 function > dv data/gps out baud (dv data/gps out baud) set the dv or gps data transfer speed to 4800 or 9600 bps. Rtty decode baud (default: 9600) connectors > usb2/data1 function > rtty decode baud (rtty decode baud) set...
Page 330: Display Set Mode
17 set mode 17-27 display contrast (default: 50%) display > lcd contrast (lcd contrast) set the display contrast level to between 0% and 100%. Lcd backlight (default: 50%) display > lcd backlight (lcd backlight) set the lcd backlight brightness to between 0% and 100%. Key backlight (default: 50%) di...
Page 331
17 set mode 17-28 tx call sign display (default: your call sign) display > tx call sign display (tx call sign display) select whether or not to display your own or the desti- nation station’s call sign while transmitting. • off: does not display the call sign. • your call sign: displays and scrolls ...
Page 332
17 set mode 17-29 choose your language carefully when the system language of the transceiver is set to japanese, the ic- 7100 has the capability to display both english and japanese characters. However, if you select japanese as the display language (p. 17-28), all menu items throughout the ic-7100 ...
Page 333: Time Set Set Mode
17 set mode 17-30 date time set > date/time > date (date) manually set the date. Time time set > date/time > time (time) manually set the time that is displayed on the right hand corner of the screen to between 0:00 and 23:59. The time is displayed in the 24 hour format. Gps time correct (default: a...
Page 334: Others Set Mode
17 set mode 17-31 version others > information > version (version) shows the transceiver firmware’s version number. Clone mode others > clone > clone mode select to read or write the cs-7100 data from or to the pc, and/or to receive data from a master transceiver. See page 19-5 for details. Clone ma...
Page 335: Section
18-1 section 18 data communication connections ...........................................................................18-2 when connecting to [data2] d .................................................18-2 when connecting to [acc] d ....................................................18-2 when c...
Page 336: Connections
18 data communication 18-2 tnc data in data out(9600bps) gnd af out(1200bps) pttp rear panel view tx audio rx audio ptt gnd sql* q r w t e y sql data in data out(9600bps) gnd af out(1200bps) pttp tx audio rx audio ptt gnd sql* q r w t e y sql pc rs-232c • when using a tnc • when using a pc applicati...
Page 337: Packet (Afsk) Operation
18 data communication 18-3 before operating packet (afsk), be sure to consult the operating manual that came with your tnc. Connect the tnc and pc. (p. 18-2) q select the desired band. (p. 3-6) w select the data mode of ssb, am or fm. (p. 3-17) e rotate the dial to tune the desired signal and de- r ...
Page 338
18 data communication 18-4 in the fm data mode, the data transmission speed can be set to 9600 bps only when the data is output from pin 3 of the [data2] socket. Push q set ( c ) to enter the set mode. Touch the “9600bps mode” item of the “connectors” w set mode. (connectors > 9600bps mode ) • if th...
Page 339
18 data communication 18-5 when the data transmission speed is set to 9600 bps, the data signal coming from the tnc is applied exclu- sively to the internal limiter circuitry to automatically maintain band width. Never apply data levels from the tnc of over 0.6 vpp. Otherwise the transceiver will no...
Page 340: Section
19-1 section 19 maintenance cleaning ................................................................................. 19- 2 replacing the fuses ............................................................... 19- 2 circuitry fuse replacement d ....................................................19-2...
Page 341: Cleaning
19 maintenance 19-2 if the transceiver becomes dusty or dirty, wipe it clean with a dry, soft cloth. Do not use harsh solvents such as benzine or alcohol when cleaning, as they will dam- age the transceiver surfaces. Cleaning if a fuse blows, and the transceiver stops functioning, find the source of...
Page 342: Resetting The Cpu
19 maintenance 19-3 resetting the cpu d partial reset push q set ( c ) to enter the set mode. Touch the “reset” item of the “others” set mode. W (others > reset ) • if the specified item is not displayed, touch [ ∫ ] or [ √ ]( d ) one or more times to select the page. Touch “partial reset.” e when t...
Page 343
19 maintenance 19-4 resetting the cpu (continued) d all reset recommended! ✓ after an all reset, you cannot use the transceiver in the dr mode because the repeater list will be cleared. So we recommend you save the programmed data onto an sd card, or to your pc using the optional clon- ing software ...
Page 344: Data Cloning
19 maintenance 19-5 connect a mini plug cable to the [remote] jack of q the master and sub transceivers. To [remote] to [remote] mini plug cable (purchase separately) push [pwr] w ( l ) to turn on the power, and then touch the “clone” item of the “others” set mode. ( set ( c ) > others > clone ) ope...
Page 345
19 maintenance 19-6 data cloning (continued) d cloning using a cloning software the optional cs-7100 cloning software is also avail- able to clone/edit contents with a pc using icf format files. The programmed data can be write to the transceiver using an sd card or a pc. This section describes how ...
Page 346
19 maintenance 19-7 data cloning (continued) initial setup using an sd card d after starting up the first time, “initial setup” appears. Q click w click r click to make the initial setup using the saved data in the card, follow the steps below. Q click the [sd] radio button. W click [open...] to sho...
Page 347
19 maintenance 19-8 importing the repeater list in a csv format file reading the data from the transceiver 1. Click ➥ , or select “read to start reading the data from the transceiver. Before importing, make a backup file of all the transceiver’s data onto your pc in case of data loss. Repeater list ...
Page 348
19 maintenance 19-9 programming the repeater list 1. Q select the desired repeater group in the “repeater list” folder on the tree view screen of the cs-7100. W program each item of the repeater list, using the cs- 7100. • see the help file of the cs-7100 for assistance. Exporting the repeater list ...
Page 349: Protection Function
19 maintenance 19-10 the tuning tension of the dial may be adjusted to suit your preference. The tension adjustment is located on the side of the front panel, as shown to the right. Slide the tension adjustment to a comfortable level while turning the dial continuously and evenly in one direction. I...
Page 350: External Keypad Connections
19 maintenance 19-11 w mic u/d u gnd 1.5k ø ±5% 1.5k ø ±5% 2.2k ø ±5% 4.7k ø ±5% s1 s2 s3 s4 user box external keypad i q 1.9mhz rotary switch diode vr 4.7k ø 4.7k ø 4.7k ø 100µh 100µh 4700pf 4700pf 4700pf band 8v 8v external power souce acc socket of an optional unit gnd 10k ø 10k ø 22k ø vr open v...
Page 351: Troubleshooting
19 maintenance 19-12 transceiver power d problem possible cause solution ref. Power does not turn on when [pwr] is pushed. • the power cable is improperly connect - ed. • a fuse is blown. • power output voltage is not correct. • reconnect the dc power cable correctly. • correct the cause, then repla...
Page 352
19 maintenance 19-13 problem possible cause solution ref. The antenna is not prop- erly tuned. • the antenna swr is adjusted too high. • check the coaxial cable. • adjust the antenna swr. • change the length of the coaxial cable. Sec. 6 sec. 2 the supply voltage de- creases when transmit- ting. • th...
Page 353
19 maintenance 19-14 d while operating d-star problem possible cause solution ref. After your call, the repeat- er does not return a status reply. • the access repeater setting is wrong. • the repeater setting is wrong. • your transmission did not reach the re - peater. • select the correct repeater...
Page 354: Section
20-1 section 20 control command remote jack (ci-v) information ............................................ 20- 2 ci-v connection example d ......................................................20-2 data format d ............................................................................20-2 comman...
Page 355
20 control command 20-2 controller to ic-7100 fe fe 88 e0 cn sc data area fd preamb le code (fix ed) tr ansceiv er’ s def ault address controller’ s def ault address command number (see the command tab le) sub command number (see the command tab le) bcd code data such as for frequency , memor y numb...
Page 356
20 control command 20-3 d command table remote jack (ci-v) information (continued) cmd. Sub cmd. Data description 00 see p. 20-11 send the operating frequency for transceive 01 see p. 20-11 send the operating mode for transceive 02 see p. 20-12 read the band edge frequencies 03 see p. 20-11 read the...
Page 357
20 control command 20-4 command table (continued) d remote jack (ci-v) information cmd. Sub cmd. Data description 14 0e 0000 to 0255 send/read the comp level (0000=0 to 0255=10) 0f 0000 to 0255 send/read the break-in delay setting (0000=2.0d to 0255=13.0d) 12 0000 to 0255 send/read nb level (0000=0%...
Page 358
20 control command 20-5 command table (continued) d remote jack (ci-v) information cmd. Sub cmd. Data description 19 00 read the transceiver id 1a 00 see p. 20-16 send/read the memory channel contents 01 see p. 20-12 send/read the band stacking regis- ter contents 02 see p. 20-13 send/read the memor...
Page 359
20 control command 20-6 command table (continued) d remote jack (ci-v) information cmd. Sub cmd. Data description 1a 05 0035 00/01 send/read the speaker output setting (00=off, 01=on) 0036 00/01 send/read the mic af output set- ting (00=off, 01=on) 0037 00 to 22 send/read the function of [f-1] on th...
Page 360
20 control command 20-7 command table (continued) d remote jack (ci-v) information cmd. Sub cmd. Data description 1a 05 0074 see p. 20-11 send/read the wide ssb tx bandwidth 0075 see p. 20-11 send/read the mid ssb tx band- width 0076 see p. 20-11 send/read the narrow ssb tx bandwidth 0077 00 to 10 s...
Page 361
20 control command 20-8 command table (continued) d remote jack (ci-v) information cmd. Sub cmd. Data description 1a 05 0116 00/01 send/read the opening message (00=off, 01=on) 0117 00/01 send/read the power on check setting (00=off, 01=on) 0118 00/01 send/read the display language (00=english, 01=j...
Page 362
20 control command 20-9 command table (continued) d remote jack (ci-v) information cmd. Sub cmd. Data description 1a 05 0162 00 to 15 send/read nr level for the dr mode (00=0 to 15=15) 0163 0000 to 0255 send/read the vox gain (0000=0% to 0255=100%) 0164 0000 to 0255 send/read the anti-vox gain (0000...
Page 363
20 control command 20-10 command table (continued) d remote jack (ci-v) information cmd. Sub cmd. Data description 1a 05 0211 see p. 20-14 send/read the gps-a comment 0212 00 to 08 send/read the gps auto tx inter- val setting ( 00=off, 01=5 sec., 02=10 sec., 03=30 sec., 04=1 min., 05=3 min., 06=5 mi...
Page 364
20 control command 20-11 • operating frequency command: 00, 03, 05 q x x x x x w e x r t x x x x 10 hz digit: 0–9 1 hz digit: 0–9 1 khz digit: 0–9 100 hz digit: 0–9 100 khz digit: 0–9 10 khz digit: 0–9 10 mhz digit: 0–9 1 mhz digit: 0–9 1000 mhz digit: 0 (fix ed) 100 mhz digit: 0–4 • operating mode ...
Page 365
20 control command 20-12 • character code setting command: 1a 00, 1a 05 0200, 1a 05 0201, 1a 05 0206, 1a 05 0207, 1a 05 0208, 1a 05 0209, 1a 05 0211, 1f 02, 20 0001, 20 0002 character ascii code character ascii code a–z 41–5a a–z 61–7a 0–9 30–39 space 20 ! 21 # 23 $ 24 % 25 & 26 \ 5c ? 3f " 22 ’ 27 ...
Page 366
20 control command 20-13 • memory keyer contents command: 1a 02 x q : channel data w – &1 : text data x x x …… x x 01 : m1 02 : m2 03 : m3 04 : m4 • character’s code character ascii code description 0–9 30–39 number a–z 41–5a alphabetical characters a–z 61–7a alphabetical characters space 20 word sp...
Page 367
20 control command 20-14 • gps-a symbol setting command : 1a 05 0206, 0207, 0208, 0209 x x x x second digit first digit ⁄, \, 0 to 9, a to z can be used for the first digit char - acter. See ‘character code setting’ for the second digit character. (p. 20-12) • comment setting command: 1a 05 0211 set...
Page 368
20 control command 20-15 • dv rx call sign setting command : 20 0001, 20 0002 x x x x x x x x x x x x …… !5 – @2 e – !0 !1 – !4 x x x x …… q 、 w x x …… x x @3 – #0 x x …… x x #1 – #8 header flag data (first byte) q data description bit 7 0 (fixed) — 6 0 (fixed) — 5 0 (fixed) — 4 0/1 0= voice, 1= dat...
Page 369
20 control command 20-16 data content description (continued) d remote jack (ci-v) information bank number q 01: a, 02: b, 03: c, 04: d, 05: e w , e memory channel number 0001–0099: memory channel 1 to 99 0100: programmed scan edge 1a 0101: programmed scan edge 1b 0102: programmed scan edge 2a 0103:...
Page 370: Section
Specifications ..........................................................................21-2 general d ....................................................................................21-2 transmitter d ...............................................................................21-2 receiver ...
Page 371: Specifications
21 specifications and options 21-2 specifications general d • frequency coverage: (unit: mhz) receive 0.030000 – 199.999999* 1 * 2 400.000000 – 470.000000* 1 * 2 transmit 1.800000 – 1.999999* 2 , 3.500000 – 3.999999* 2 , 5.255000 – 5.405000* 1 * 3 , 5.332000* 3 * 4 , 5.348000* 3 * 4 , 5.358500* 3 * ...
Page 372
21 specifications and options 21-3 receiver d • receive system ssb/cw/rtty/am/fm/dv: triple superheterodyne system wfm: double superheterodyne system • intermediate frequencies 1st: 124.487 mhz (ssb/cw/rtty/am/fm/dv) 134.732 mhz (wfm) 2nd: 455 khz (ssb/cw/rtty/am/fm/dv) 10.7 mhz (wfm) 3rd: 36 khz (s...
Page 373: Options
21 specifications and options 21-4 options at-180 hf / 50 mh z automatic antenna tuner fully automatic antenna tuner with pre- set memories for each 100 khz. Unique “automatic tuner on” function is avail- able. See page 16-3 for at-180 speci- fications. Ah-4 hf automatic antenna tuner specially desi...
Page 374
21 specifications and options 21-5 • hm-103 hand microphone hand microphone equipped with [up]/[down] switches. • hm-151 hand microphone remote control microphone. • hm-198 hand microphone hand microphone equipped with [up]/[down] switches. The same as that supplied with the transceiver. • mb-62 mob...
Page 375
1-1-32 kamiminami, hirano-ku, osaka 547-0003, japan a-7091-2ex © 2013 icom inc..