- DL manuals
- Icom
- Transceiver
- IC-7100
- Basic Manual
Icom IC-7100 Basic Manual
BASIC MANUAL
i7100
HF/VHF/UHF ALL MODE TRANSCEIVER
This device complies with Part 15 of the FCC Rules. Operation
is subject to the following two conditions: (1) this device may
not cause harmful interference, and (2) this device must accept
any interference received, including interference that may cause
undesired operation.
WARNING: MODIFICATION OF THIS DEVICE TO RECEIVE
C E L L U L A R R A D I OT E L E P H O N E S E RV I C E S I G N A L S I S
PROHIBITED UNDER FCC RULES AND FEDERAL LAW.
Summary of IC-7100
Page 1
Basic manual i7100 hf/vhf/uhf all mode transceiver this device complies with part 15 of the fcc rules. Operation is subject to the following two conditions: (1) this device may not cause harmful interference, and (2) this device must accept any interference received, including interference that may ...
Page 2
I foreword thank you for purchasing this fine icom product. The ic-7100 hf / vhf / uhf all mode transceiver is designed and build with icom’s superior technology and craftsmanship combining tra- ditional analog technologies with the new digital technology, digital smart technologies for amateur radi...
Page 3
Ii precautions r danger high voltage! Never touch an an- tenna or internal antenna connector during transmission. This may result in an electrical shock or burn. R warning rf exposure! This device emits radio frequency (rf) energy. Extreme caution should be observed when operating this device. If yo...
Page 4
Iii e supplied accessories the following accessories are supplied with the transceiver. Q hand microphone ............................................... 1 w control cable ....................................................... 1 e ferrite emi filter ....................................................
Page 5: Section 3 Basic Operation
Controller — front panel ........................................................1-2 controller — function display ...............................................1-7 controller — multi-function keys ...........................................1-10 m-1 (m-1 menu) display d ...............................
Page 6: Controller — Front Panel
1 panel description 1-2 controller — front panel q power switch•af volume [pwr]•[af] (p. 3-2) push to turn on the transceiver power. ➥ • first, confirm the dc power source is turned on. Hold down for 1 second to turn off the power. ➥ rotate to adjust the audio output level. ➥ increases decreases w r...
Page 7
1 panel description 1-3 e tx/rx led lights green when the squelch opens, or a signal ➥ is received. Lights red when transmitting. ➥ r memory bank control [bank] ❍ when both the pbt and rit leds are off rotate to select a memory bank. ❍ when the pbt led (y) lights green (mode: ssb/cw/rtty/am) rotate ...
Page 8
1 panel description 1-4 !2 noise blanker key nb (fm sec. 5) (mode: ssb/cw/rtty/am) push to turn the noise blanker on or off. ➥ the noise blanker reduces pulse-type noise such as that generated by vehicle ignition systems. The noise blanker is not effective for non-pulse-type noise. • “nb” appears wh...
Page 9
1 panel description 1-5 !6 notch key notch (fm sec. 5) (mode = auto notch: ssb/am/fm manual notch: ssb/cw/rtty/am) ➥ in the ssb and am modes, push to toggle the notch function between auto, manual and off. • either the auto or manual notch function can be turned off in the “[notch] switch (ssb)/(am)...
Page 10
1 panel description 1-6 @2 speech•lock key speech ❍ speech key operation (p. 3-20) push to audibly announce the s-meter level, the displayed frequency and the operating mode. • the s-level announcement can be turned off in the “s-level speech” item of the “speech” set mode. (p. 6-4) set > speech > s...
Page 11
1 panel description 1-7 q tx icon indicates either the displayed frequency can be transmitted, or not. ➥ “ ” appears while the operating frequency is in an amateur band. ➥ “ ” appears while the operating frequency is not in an amateur band. However, when the “band edge beep” item is set to “off” in ...
Page 12
1 panel description 1-8 o clock readout shows the current time. • utc time or local time can be selected. !0 split icon (fm sec. 6) “ ” appears when the split function is turned on. !1 lock icon (fm sec. 5) “ ” appears when the lock function is activated. 1 ⁄ 4 tuning dial speed icon (p. 3-10) (mode...
Page 13
1 panel description 1-9 !9 function icons “vox” appears when the vox function is activat- ➥ ed. (fm sec. 6) the break-in icons appear when the break-in ➥ function is turned on. (fm sec. 6) • “f-bkin” appears when the full break-in function is turned on. • “bk-in” appears when the semi break-in funct...
Page 14
1 panel description 1-10 push ➥ menu to change the set of functions assigned to touch keys. • toggles the function display menu between m-1, m-2 and m-3 menus or d-1 and d-2 menus. • functions vary, depending on the operating mode. • in the dr mode, the d-1 and d-2 menus can be select- ed. Touch or ...
Page 15
1 panel description 1-11 agc key [agc] (fm sec. 5) (mode: ssb/ssb-d/cw/rtty/am/am-d) ➥ touch to select the time constant of the agc circuit. ➥ touch for 1 second to display the “agc” screen. • push menu to return to the previous screen. Tone squelch key [tone] (fm sec. 4) (mode: fm) ➥ touch to selec...
Page 16
1 panel description 1-12 controller — multi-function keys function keys on m-3 display (continued) d vox key [vox] (fm sec. 6) (mode: ssb/am/fm/dv) ➥ touch to turn the vox function on or off. ➥ touch for 1 second to display the “vox” screen. • push menu to return to the previous screen. ✔ what is th...
Page 17
1 panel description 1-13 controller — rear and bottom panels q headphone/speaker jack [phones/sp] plug in standard stereo headphones (impedance: 8 to 16 ø ). • output power: more than 5 mw with an 8 ø load. • when headphones are connected, the internal speaker, and any external speaker, are disabled...
Page 18: Main Unit — Front Panel
1 panel description 1-14 main unit — front panel q cooling fan this is a cooling fan for heat dissipation. Depending on the internal temperature, it rotates at a low, mid or high speed. W sd card slot [sd card] insert an sd card of up to 32 gb sdhc. See fm sec. 13 for details. Main unit — rear panel...
Page 19
1 panel description 1-15 u straight key jack [key] (p. 2-5) connect a straight key or external electronic keyer using a standard 3.5(d) mm/ 1 ⁄ 8 inch plug. • to use the internal electronic keyer for cw operation, connect to [elec-key] on the front panel of the con- troller. (p. 1-13) (+) (_) i acce...
Page 20
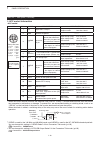
1 panel description 1-16 main unit — rear panel (continued) acc socket information d • acc socket acc pin no. Name description specifications 1 2 3 4 8 7 6 5 9 10 11 12 13 rear panel view color refers to the cable strands of the supplied cable. Q brown w red e orange r yellow t green y blue u purple...
Page 21
1 panel description 1-17 data2 socket information d data2 pin no. Name description specifications q w e r t y rear panel view 1 data in input terminal for data transmit. ( 1200 bps: afsk/ 9600 bps: g3ruh, gmsk) input level (1200 bps): input level (9600 bps): 100 mv 0.2 to 0.5 vp-p 2 gnd common groun...
Page 22: Microphone
1 panel description 1-18 microphone q ptt switch hold down to transmit, release to receive. W up/down keys [up]/[dn] push either key to change the operating frequen- ➥ cy, memory channel, set mode setting, and so on. (p. 3-9, fm sec. 4, 11) hold down either key for 1 second to start scan- ➥ ning. E ...
Page 23
1 panel description 1-19 q spch/lock key [spch/lock] ❍ speech key operation (p. 3-20) push to audibly announce the s-meter level, the displayed frequency and the operating mode. • the s-level announcement can be turned off in the “s-level speech” item of the “speech” set mode. (p. 6-4) set > speech ...
Page 24
1 panel description 1-20 u mode key [mode] push to cycle through the operating modes: ➥ usb/lsb ➧ cw/cw-r ➧ rtty/rtty-r ➧ am ➧ fm ➧ wfm ➧ dv hold down for 1 second to toggle the following ➥ operating modes: usb ↔ lsb cw ↔ cw-r rtty ↔ rtty-r i power led lights green when transceiver’s power is on. O ...
Page 25: Section
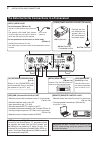
2-1 section 2 installation and connections selecting a location .................................................................2-2 grounding ................................................................................2-2 antenna connection .........................................................
Page 26: Selecting A Location
2 installation and connections 2-2 select a location for the transceiver that allows ad- equate air circulation, free from extreme heat, cold, vibrations, away from tv sets, tv antenna elements, radios and other electromagnetic sources. The base of the transceiver has adjustable feet for desktop use...
Page 27
2 installation and connections 2-3 connect controller to transceiver the main unit becomes hot when transmitted for long period of time. Do not place anything on the transceiver. It may ob- struct radiation and cause mechanical trouble. Using ferrite emi filter* depending on the installed condition ...
Page 28
2 installation and connections 2-4 dash dot com [phones/sp] (headphone/external speaker)jack [mic] connector controller set the switch under con- troller to “phones” to use headphone and set “sp” to use speaker. Bottom of the controller sp-35 (optional) a jack to connect the paddle with electrode co...
Page 29
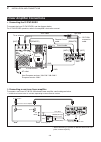
2 installation and connections 2-5 required connections to a transceiver [ant2] 144/430mhz bands connector (p. 2-2) connect a 50 Ω antenna for the 144/430 mhz frequency bands or 74.8 mhz and above. Ic-7100 [ant1] hf, 50/70 mhz bands connector (p. 2-3) connect a 50 Ω antenna for the hf, 50/70 mhz fre...
Page 30
2 installation and connections 2-6 the external units connections to a transceiver [data1] data1 jack for gps operation ( fm sec. 10 ) • connect a gps receiver to the transceiv- er. • the optional opc-1529r (data commu- nication cable) and a 3rd party's gps re- ceiver with rs-232c port are required....
Page 31: Power Supply Connections
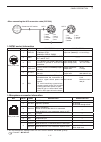
2 installation and connections 2-7 power supply connections connect to power supply for european versions opc-2095 gnd dc power socket make sure the [pwr] (l) switch is off before con- necting the dc power cable. • we recommend using icom’s optional power supply (ps-126: dc13.8 v/25 a). D connecting...
Page 32: Linear Amplifier Connections
2 installation and connections 2-8 linear amplifier connections exciter 1 1&2 remote control cable acc cable to an antenna [acc-1] [remote] [ant] ic-pw1/euro non-european versions: 100–120 / 200–240 v european version: 230 v [input1] 7-pin side [remote] coaxial cable [ant1] ic-7100 opc-599 conversio...
Page 33: Section
3-1 section 3 basic operation 3-1 section 3 basic operation 3-1 power on ..................................................................................3-2 before first applying power d ......................................................3-2 tuning on the power d ..................................
Page 34: Power On
3 basic operation 3-2 pbt rit tx / rx pwr af rf/sql clr m-ch bank rit tuner/call menu mic/rf pwr nb speed/pitch set quick notch dr auto tune rx cs xfc speech mpad nr p.Amp att i7100 note: when turning off the power, the transceiver memorizes the settings. Thus the transceiver restarts with the set...
Page 35: Selecting A Function Menu
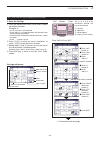
3 basic operation 3-3 selecting a function menu push menu (c) one or more times to select the “m-1” screen (m-1 menu), “m-2” screen (m-2 menu) or “m-3” screen (m-3 menu). • in the dr mode, push menu (c) once or twice to select the “d-1” screen (d-1 menu) or “d-2” screen (d-2 menu). • functions vary,...
Page 36: Selecting Vfo/memory Mode
3 basic operation 3-4 selecting vfo/memory mode ic-7100 has vfo and memory modes. In the vfo mode, rotate the dial to select the disired frequency. In the memory mode, rotate [m-ch] (l) to select the preprogrammed memory channel. Push menu (c) one or more times to select the “m-1” screen (m-1 menu)....
Page 37: Vfo Operation
3 basic operation 3-5 vfo operation the ic-7100 has two vfos; “a” and “b,” and are conve- nient for quickly selecting two frequencies, or split fre- quency operation. You can use either vfo to call up a frequency and operating mode. Vfo is an abbreviation of variable frequency oscilla- tor. Selectin...
Page 38: Selecting A Frequency Band
3 basic operation 3-6 band register 1 register 2 register 3 1.8 mhz* 1 1.900000 mhz cw 1.910000 mhz cw 1.915000 mhz cw 3.5 mhz* 1 3.550000 mhz lsb 3.560000 mhz lsb 3.580000 mhz lsb 7 mhz 7.050000 mhz lsb 7.060000 mhz lsb 7.020000 mhz cw 10 mhz* 1 10.120000 mhz cw 10.130000 mhz cw 10.140000 mhz cw 14...
Page 39: Setting Frequency
3 basic operation 3-7 setting frequency you can select the transceiver’s frequency by using the dial, or you can enter it on the direct input screen. Tuning with the dial d q on the band selection screen, select the desired fre- quency band. (p. 3-6) w rotate the dial to set the desired frequency. •...
Page 40
3 basic operation 3-8 quick tuning function d the operating frequency can be changed in ‘khz’ or ‘mhz’ steps for quick tuning. Select the desired tuning step in each operating fre- quency band and mode. Q touch the khz digits to select the ‘khz’ quick tuning function step, or turn it off. Or touch t...
Page 41
3 basic operation 3-9 selecting d ‘ khz’ step when the ‘khz’ quick tuning is selected, the frequen- cy can be changed in the selected ‘khz’ steps. The steps can be memorized, depending on the operating modes. On the mode selection screen, select the desired op- q erating mode. (p. 3-17) touch the kh...
Page 42
3 basic operation 3-10 setting frequency (continued) 1/4 tuning step function d (mode: ssb-d/cw/rtty) the dial speed is reduced to 1 ⁄ 4 of the normal speed when the 1 ⁄ 4 tuning function is on, for finer tuning con- trol. You can set the 1 ⁄ 4 tuning function in each operating frequency band. This ...
Page 43
3 basic operation 3-11 setting frequency (continued) direct frequency input d the transceiver has a direct input screen for direct fre- quency entry, as described below. • operating frequency input touch the mhz digits to enter the band selection dis- q play. Touch [f-inp]( w d ) to enter the direct...
Page 44
3 basic operation 3-12 setting frequency (continued) direct frequency input (continued) d • split offset frequency input touch the mhz digits to enter the band selection dis- q play. Touch [f-inp]( w d ) to enter the direct input screen. If the shift direction is minus, touch “• (–).” e • [split] ch...
Page 45
3 basic operation 3-13 setting frequency (continued) band edge warning beep d you can hear a beep tone when you tune into or out of an amateur band’s frequency range. A regular beep sounds when you tune into a range, and an lower tone error beep sounds when you tune out of a range. Push q set (c) to...
Page 46
3 basic operation 3-14 setting frequency (continued) programming the user band edge d when “on (user)” or “on (user) & tx limit” is selected in the “band edge beep” item, the “user band edge” item appears in the “function” set mode. A total of 30 band edge frequencies can be programmed in the “user ...
Page 47
3 basic operation 3-15 setting frequency (continued) programming the user band edge (continued) d • inserting a band edge enter the “user band edge” screen. Q set (c) > function > user band edge touch for 1 second the band edge that you want to w insert a new band edge above it. • if the desired ban...
Page 48
3 basic operation 3-16 setting frequency (continued) programming the user band edge (continued) d • changing the band edge frequencies enter the “user band edge” screen. Q set (c) > function > user band edge touch the band edge to be changed. W • if the desired band edge is not displayed, touch [y] ...
Page 49: Selecting The Operating Mode
3 basic operation 3-17 mode selection operating mode ssb lsb usb cw cw cw-r rtty rtty rtty-r am am * fm fm wfm wfm (only rx) dv dv data lsb lsb data usb usb data am am data fm fm data selecting the operating mode the usable operating modes in the ic-7100 are listed to the right below. You can select...
Page 50: Selecting The Audio Volume
3 basic operation 3-18 selecting the audio volume rotate [af] ➥ (l) control clockwise to increase the audio output level, counterclockwise to decrease it. [af] increases decreases the l, r, c or d in the in- structions indicate the part of the controller. L : left side r : right side c : center bott...
Page 51
3 basic operation 3-19 squelch and receive (rf) sensitivity adjusts the rf gain and squelch threshold level. The squelch removes noise output to the speaker when no signal is received (closed squelch). • the squelch is particularly effective for am and fm, but also works in other modes. • the 12 to ...
Page 52: Voice Synthesizer Operation
3 basic operation 3-20 voice synthesizer operation the ic-7100 has a built-in voice synthesizer to an- nounce the operating frequency, mode and s-meter level in a clear, electronically-generated voice, in eng- lish or japanese. First, select the desired parameters to be announced in the “speech” set...
Page 53
3 basic operation 3-21 voice synthesizer operation (continued) tuning off the s-meter announcement d the s-meter announcement can be turned off. Push q set (c) to enter the set mode. Touch the “s-level speech” item of the “speech” w set mode. Speech > s-level speech • if the specified item is not di...
Page 54: Meter Display Selection
3 basic operation 3-22 meter display selection the transmit meter can be toggled between four func- tions for your convenience. ➥ touch the meter one or more times to select the tx meter function, rf power meter, swr meter, alc meter or comp meter. • po : displays the relative rf output power. • swr...
Page 55: Basic Transmit Operation
3 basic operation 3-23 basic transmit operation before transmitting, monitor the operating fre- quency to make sure transmitting won’t cause interference to other stations on the same fre- quency. It’s good amateur practice to listen first, and then, even if nothing is heard, ask “is the fre- quency...
Page 56
3 basic operation 3-24 basic transmit operation (continued) microphone gain adjustment d (mode: ssb/am/fm/dv) push q mic/rf pwr (c) to open the mic gain/rf power adjustment display. Push [ptt] to transmit. W • speak into the microphone at your normal voice level. Rotate [m-ch] e (l) to adjust the mi...
Page 57: Section
4-1 section 4 d-star introduction important! • the repeater list described in this manual may differ from your trans- ceiver’s preloaded contents. • although japanese repeaters are used in the setting examples, the japanese repeater node (port) letters are different from those in other countries. Be...
Page 58
4 d-star introduction 4-2 important! Before starting d-star, the following steps are needed. Step 1 entering your call sign (my) into the transceiver. Step 2 registering your call sign (my) to a gateway repeater. You have completed the steps!! “my” (your own call sign) programming you can store up t...
Page 59
4 d-star introduction 4-3 enter the call sign 2. Touch the desired block one or more times to select t the desired character. (example: j) • a to z, 0 to 9 and / are selectable. • touch “ab⇔12” to toggle between the alphabet input and the number input mode. • touch [clr](d) to delete the selected ch...
Page 60
4 d-star introduction 4-4 “my” (your own call sign) programming convenient! ✓ if necessary, enter a note of up to 4 characters, such as the model of the transceiver, name, area name, and so on, after your call sign. Touch [ q g ](d) one or more times until the cursor moves to the right of the “/”. R...
Page 61: D-Star Introduction
4 d-star introduction 4-5 • in the original d-star (digital smart technologies for amateur radio) plan, jarl envisioned a system of repeaters grouped together into zones. • the d-star repeater enables you to call a ham sta- tion on another repeater through the internet. • the transceiver can be oper...
Page 62
4 d-star introduction 4-6 in the dr mode, the transceiver has three communica- tion forms, as shown below. • local area call: to call through your local area (ac- cess) repeater. • gateway call: to call through your local area (ac- cess) repeater, repeater gateway and the internet to your destinatio...
Page 63: Section
5-1 section 5 d-star operation d-star operating procedures .............................................5-2 making a local area call d ........................................................5-2 making a gateway call d ..........................................................5-3 about “ur?” and “rp...
Page 64: D-Star Operating Procedures
5 d-star operation 5-2 d-star operating procedures this section describes the basic d-star procedures. • when it is the first time to operate d-star, check whether or not you can access your local area repeat- er (access repeater), and if your signal is successfully sent to a destination repeater. •...
Page 65
5 d-star operation 5-3 d-star operating procedures (continued) making a gateway call d set “from” (access repeater) 1. Push q dr (c) to select the dr mode. Check whether or not “from” is selected. W • if “from” is not selected, touch the “from” field. Touch the “from” field. E • the “from select” sc...
Page 66
5 d-star operation 5-4 d-star operating procedures (continued) internet ja3yua calling to jp1yiu port a through jp3yhh port b. Jm1zlk, this is ja3yua. Thanks for the nice qso and i hope to talk to you again soon. This is ja3yua now clear of the jp3yhh repeater. Ja3yua, this is jm1zlk. Hello, how are...
Page 67
5 d-star operation 5-5 the transceiver includes a status message in the signal received back from the access repeater, after transmit- ting. Shows “ur?” d the call was successfully sent, but no station’s signal was received within 3 seconds. The called station may have missed your call, so after wai...
Page 68: Capturing A Call Sign
5 d-star operation 5-6 after you receive the repeater’s signal, the calling sta- tion’s call sign can be captured by holding down the call sign capture key auto tune rx cs (r). Then you can quickly and easily reply to the received call. Capturing a call sign set the received call sign to the destina...
Page 69
5 d-star operation 5-7 • when you know your access repeater from the repeater list (p. 5-8) when your access repeater is preloaded in your trans- ceiver’s repeater list, you can select it by selecting the repeater area or name. • when you don't know which repeater you can access. • when the “from” d...
Page 70
5 d-star operation 5-8 when your access repeater is preloaded in your trans- ceiver’s repeater list, you can select it from the repeater list. By only selecting the repeater from the list, the call sign, frequency, duplex and offset frequency settings are automatically set for easy operation. Exampl...
Page 71
5 d-star operation 5-9 using the dr mode scan d the dr mode scan is useful to find a repeater. To quickly find a repeater, the dr mode scan skips re- peaters that are not specified as an access repeater. (the “use (from)” setting is set to “no” (skip is set) on the repeater list.) example: select th...
Page 72
5 d-star operation 5-10 using the repeater search function d the transceiver searches for the nearest repeater by using your own and the repeater’s position. The nearest repeater in your transceiver’s repeater list is displayed as the available choices. To receive your own position, connect an exter...
Page 73
5 d-star operation 5-11 selecting the access repeater from the near re- 2. Peater list push q dr (c) to select the dr mode. Check whether or not “from” is selected. W • if “from” is not selected, touch the “from” field. Touch the “from” field. E • the “from select” screen appears. Touch “near repeat...
Page 74
5 d-star operation 5-12 using the tx history d repeaters you transmitted to in the dr mode are stored in the tx history, and you can select a repeater from the tx history as your access repeater. The tx history stores up to 10 of the latest “from” (access repeater) repeaters. Push q dr (c) to select...
Page 75
5 d-star operation 5-13 the destination repeater or station must be set to “to” when you transmit a call in the dv mode. You have eight ways to set the destination. Click the title shown below to jump to the specified page. How to switch the repeater group: when “local cq” or “gateway cq” is se- lec...
Page 76
5 d-star operation 5-14 using the “local cq” (local area call) d when “local cq” is selected in the “to select” screen, “cqcqcq” is set in “to.” example: making a local area call by accessing the “hirano” repeater. Push q dr (c) to select the dr mode. Check whether or not “to” is selected. W • if “t...
Page 77
5 d-star operation 5-15 using the d “ gateway cq” (gateway call) when “gateway cq” is selected in the “to select” screen, the repeater to make a gateway cq call can be selected from the repeater list. Example: making a gateway cq call to (japan; hama- cho) from the “hirano” repeater. Push q dr (c) t...
Page 78
5 d-star operation 5-16 using the “your call sign” d the “your call sign” memory stores the programmed “ur” (destination) call sign. When you select an individual station call sign for the “to” (destination) setting using “your call sign,” a gate- way call can be made. When you call the destination ...
Page 79
5 d-star operation 5-17 using the rx history d when a call is received in the dv mode, the call data is stored in the rx history. Up to 50 callers, and only the last called call signs can be stored. Example: select “tom” from rx history. Push q dr (c) to select the dr mode. Check whether or not “to”...
Page 80
5 d-star operation 5-18 using the tx history d the tx history stores the name and/or call sign of up to 20 “to” (destination) settings that were used when you made the calls. Note: if you never transmit a call in the dv mode, you cannot select “to” (destination) from the tx his- tory. Example: selec...
Page 81
5 d-star operation 5-19 directly inputting (ur) d the destination station call sign can be directly input. Example: directly input the call sign “jm1zlk.” push q dr (c) to select the dr mode. Check whether or not “to” is selected. W • if “to” is not selected, touch the “to” field. Touch the “to” fie...
Page 82
5 d-star operation 5-20 directly inputting (rpt) d the destination repeater call sign can be directly input. Example: directly input the call sign “jp3ydh” push q dr (c) to select the dr mode. Check whether or not “to” is selected. W • if “to” is not selected, touch the “to” field. Touch the “to” fi...
Page 83: Section
6-1 section 6 set mode set mode description ............................................................6-2 the set mode settings d ..........................................................6-2 set mode items and default settings ...................................6-3 ‘fm’ means ‘full manual.’ ‘sec....
Page 84: Set Mode Description
6 set mode 6-2 the set mode is used to program infrequently changed values or function settings. Note: the set mode is constructed in a tree struc- ture. You may go to the next tree level, or go back a level, depending on the selected item. The set mode settings d push q set (c) to enter the set mod...
Page 85
6 set mode 6-3 note: the default settings shown below in bold are for the usa version. The default settings may differ, depending on your transceiver version. Call sign (fm sec. 9) ➥ rx history (fm sec. 9) ➥ my station (section 4) ➥ gps (fm sec. 10) ➥ sd card (fm sec. 13) ➥ voice memo in this item, ...
Page 86
6 set mode 6-4 speech in this item, set the speech options. Rx call sign speech off, on (kerchunk) or on (all) selects the rx call sign speech function option while on, or turn it off. Rx>cs speech off or on turns the rx>cs speech function on or off. S-level speech off or on turns the signal strengt...
Page 87
6 set mode 6-5 function in this item, set the function options. Monitor off or on selects whether or not to monitor your transmit signal in any mode other than cw. Monitor level 0%~ 50%~100% sets the monitor level. Beep level 0%~ 50%~100% sets the beep output level. Beep level limit off or on select...
Page 88
6 set mode 6-6 ptt start off or on turns the ptt tuner start function on or off. [tuner] switch manual or auto selects whether or not to store the at-180’s sta- tus by each band. [speech/lock] switch speech/lock, lock/speech selects the function for speech when pushed or held down. Lock function mai...
Page 89
6 set mode 6-7 tone control in this item, set the rx/tx tone control options. Rx ssb rx hpf/lpf ---- – ----, 100~2000 – 500~2400 sets the high-pass filter or low-pass filter of the receive audio. Rx bass –5~ 0~+5 sets the bass level of the receive audio. Rx treble –5~ 0~+5 sets the treble level of t...
Page 90
6 set mode 6-8 connectors in this item, set the external connector’s options. Usb audio sql off (open) or on selects whether or not to output the audio from the [usb] connector, according to the squelch state (open or closed). Acc/usb output select af or if sets the [usb] connector and the [acc] soc...
Page 91
6 set mode 6-9 display in this item, set the transceiver’s display options. Lcd contrast 0%~ 50%~100% sets the contrast level of the lcd. Lcd backlight 0%~ 50%~100% sets the backlight level of the lcd. Key backlight 0%~ 50%~100% sets the backlight level of the key. Meter peak hold off or on turns th...
Page 92
6 set mode 6-10 others in this item, set other options. Information version shows the transceiver’s firmware version num- ber. Clone clone mode reads or writes the cs-7100 data to or from the pc, and/or receives data from a master trans- ceiver. Clone master mode writes your ic-7100 (master) data to...
Page 93: Section
7-1 section 7 ce installation notes ...................................................................7-2 country code list ...................................................................7-3.
Page 94: Installation Notes
7-2 7 ce for amateur base station installations it is recom- mended that the forward clearance in front of the an- tenna array is calculated relative to the eirp (effective isotropic radiated power). The clearance height below the antenna array can be determined in most cases from the rf power at th...
Page 95: Country Code List
7-3 7 ce country code list • iso 3166-1 country codes country codes 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 austria belgium bulgaria croatia czech republic cyprus denmark estonia finland france germany greece hungary iceland ireland italy latvia at be bg hr cz cy dk ee fi fr de gr hu is ie it lv 1...
Page 96
1-1-32 kamiminami, hirano-ku, osaka 547-0003, japan a-7085h-1ex-q printed in japan © 2013 icom inc. At fi it pl gb ro be fr lv pt is tr cy de lt sk li hr cz gr lu si no dk hu mt es ch ee ie nl se bg at fi it pl gb ro be fr lv pt is tr cy de lt sk li hr cz gr lu si no dk hu mt es ch ee ie nl se bg at...