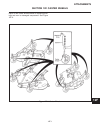
- DL manuals
- Jacobsen
- Lawn Mower
- HR 5111
- Service And Repair Instructions
Jacobsen HR 5111 Service And Repair Instructions
SERVICE & REPAIR
INSTRUCTIONS
HR5111
TM
HR5111
TM
Product No. 67760
with ROPS 69116
with CAB 69129
Includes Attachments
Litho in U.S.A.
3/97
Suggested Retail Price
$60.00
WARNING: If incorrectly used this machine can cause severe injury. Those who
use and maintain the machine should be trained in its proper use, warned of its
dangers and should read the entire manual before attempting to set up, operate,
adjust or service the machine.
!
Copyright 1997 Jacobsen Div. of Textron Inc.
“All rights reserved, including the right to reproduce
PUBLICATION REGISTRATION
Manual
Litho Date
Your Name
Address
City, State
Manual Purchased From:
Register Your Manual
Use the registration
card at the back of
this illustration.
Summary of HR 5111
Page 1
Service & repair instructions hr5111 tm hr5111 tm product no. 67760 with rops 69116 with cab 69129 includes attachments litho in u.S.A. 3/97 suggested retail price $60.00 warning: if incorrectly used this machine can cause severe injury. Those who use and maintain the machine should be trained in it...
Page 3: Introduction
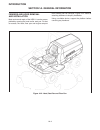
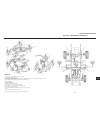
1 14 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 introduction controls engine drive train brake system steering wheels & tires hydraulics chassis electrical system preventive maintenance attachments options miscellaneous.
Page 5: Section 1
1 1a. General information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1a-1 contents . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1a...
Page 7
Contents this manual contains repair instructions for major trac- tor components, attachments and options. The table of contents at the start of each section lists contents of that section. Sections are identified by tabs in the right hand margin. This manual is to be used in conjunction with the op...
Page 8: Caution
General cleaning improper cleaning and lubrication of your machine re- sults in many equipment failures. Before any repairs are undertaken, thoroughly clean the exterior of the component to be removed. Use a clean surface to lay out parts being removed. Keep lubricants clean and cover containers not...
Page 9
Introduction section 1a. General information 1a-3 1a torque specifications standard sae grade #5 screws size torque values size torque values 8-32 27-33 in-lbs. (3-4 n.M) 1 ⁄ 2 -13 67-83 ft-lbs. (90-113 n.M) 8-36 28-34 in-lbs. (3-4 n.M) 1 ⁄ 2 -20 81-99 ft-lbs.(110-134 n.M) 10-24 39-47 in-lbs. (4-5 n...
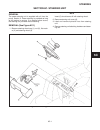
Page 10
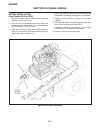
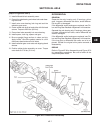
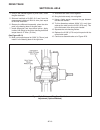
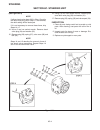
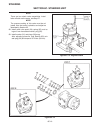
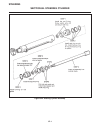
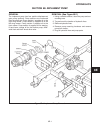
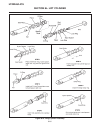
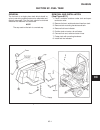
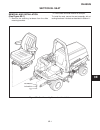
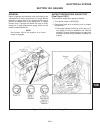
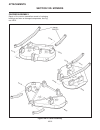
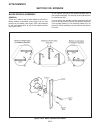
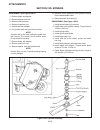
Introduction section 1a. General information 1a-4 fenders and hood removal and installation most service and repair of the hr5111 can be accom- plished by opening the hood and/or seat pan. For bet- ter access, the hood, floor pan and engine compart- ment cowling can be removed, figure 1a-2. Mark all...
Page 11: Section 2
2 2a. Repair and service tools and materials . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2a-1 2b. Failure analysis . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2b-1 general . . . ...
Page 13
Tools required: standard automotive hand tools. Cleaning materials: stoddard or equivalent solvent. Detergent and water. Lubricants: refer to section 11. Controls section 2a. Repair and service tools and materials 2a-1 2a.
Page 15
Controls section 2b. Failure analysis 2b-1 2b problem probable cause remedy 1. Engine does not turn a. Parking brake not set. A. Set parking brake. Over when ignition switch is engaged. B. Implement switch on. B. Turn off. C. 10 amp shut-off system circuit c. Reset. Breaker tripped. D. 50 amp tracto...
Page 16
Controls section 2b. Failure analysis problem probable cause remedy 8. Instrument(s) do not a. Faulty wiring or bad electrical a. Test (section 10c). Work. Ground. B. 10 amp gauge/panel light circuit b. Reset/test (section 10j). Breaker tripped. 9. No cruise control when a. 10 amp cruise/horn circui...
Page 17
Controls section 2b. Failure analysis 2b-3 2b problem probable cause remedy 16. Engine shuts down when a. No operator in seat. A. Set in seat. Implement switch is b. Faulty seat switch. B. Test (section 10g). Pulled to the on position. C. Faulty timing delay relay. C. Test/replace (section 10h). D. ...
Page 18
Controls section 2b. Failure analysis 2b-4 problem probable cause remedy 21. Engine does not shut a. Faulty electrical circuit. A. See section 10b. Down when operator leaves seat (implement switch on). 22. Panel lights do not come a. 10 amp gauge/panel light circuit a. Reset/test (section 10j). On w...
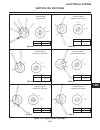
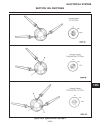
Page 19
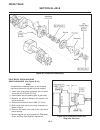
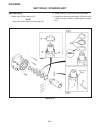
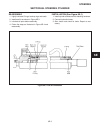
General the repair of controls is limited to adjustment of link- ages, straightening of bent rods or replacement of de- fective parts and hardware. Throttle (see figure 2c-1) located to the right of the operator’s seat, the throttle control is used to regulate engine speed. Replace a defective throt...
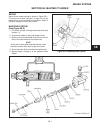
Page 20
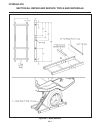
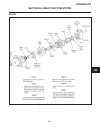
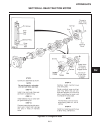
Traction pedal (see figure 2c-2) the traction pedal controls travel direction and speed. The traction pedal is connected by linkage to the hy- drostatic pump. Depending on which way the pedal is depressed, it controls “forward” or “reverse”. Repair of the traction pedal and linkage is limited to rep...
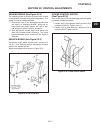
Page 21
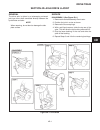
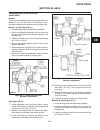
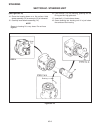
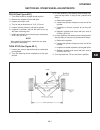
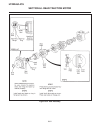
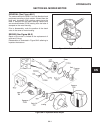
Traction pedal neutral adjustment if the tractor moves (“creeps”) in either direction while the engine is running, but traction pedal is not de- pressed, the hydro centering cylinder may need adjust- ing, see figure 2c-3 and adjust traction pedal linkage as follows: important place a small amount of...
Page 22: Warning
6. On the traction pump centering cylinder, loosen jam nut (1) and turn adjusting nut (2), moving thread- ed rod in or out as required to stop wheels from turning. 7. When the wheels stop turning, the traction pump is in “neutral”. Hold adjusting nut (2) in place and tighten locknut (1). Note check ...
Page 23
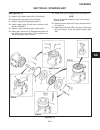
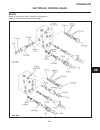
Parking brake (see figure 2c-4) the adjusting knob at the end of brake lever is used to compensate for brake lining and linkage wear, or to adjust to unusual holding demands. 1. Place brake lever in the disengaged position and turn knob in a clockwise direction, apply and re- lease brake lever every...
Page 24
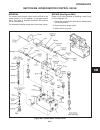
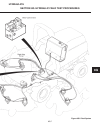
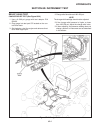
Repair note refer to section 10g for test/repair of switches. Repair of instruments is limited to replacement of faulty components. See figure 2d-1 and replace faulty com- ponent as follows: 1. Remove fuel tank to gain access. 2. Disconnect battery ground (black) cable. 3. Label wires for proper ide...
Page 25: Section 3
3 3a. Repair and service tools and materials . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3a-1 3b. Failure analysis . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3b-1 3c. General inst...
Page 27
Section 3a. Repair and service tools and materials 3a-1 3a general tools required: standard automotive hand tools. Cleaning materials: stoddard or equivalent solvent. Detergent and water. Anti-rust never-seize. Lubricants: refer to section 11. Other service items: compressed air source, engine hoist...
Page 29
Section 3b. Failure analysis 3b-1 3b general problem probable cause remedy 1. Engine cranks but a. Fuel tank empty. A. Check fuel level. Does not start. B. Fuel petcock at filter closed. B. Open petcocks. C. Air in fuel line. C. Purge air (section 3d). D. Electrical system malfunctioning. D. See sec...
Page 31
Contents the engine used in the hr5111 tractor is a kubota v-2203, 4 cylinder in-line, liquid cooled diesel engine. This section covers repairs to the engine associated components (eg. Exhaust system, air cleaners, radia- tors). Removal and installation of the engine is also covered, but engine repa...
Page 33: Warning
General a separate engine operator’s manual, prepared by the engine manufacturer is supplied with your tractor. Study the manual carefully until you are familiar with the main- tenance, operation and adjustment of your equipment. Proper attention to the engine manufacturer’s direc- tions will assure...
Page 34: Caution
Radiator (see figure 3d-2) changing coolant 1. Open drain cock (1) and radiator cap (2) and drain coolant into a clean container. 2. Flush the inside of the radiator (3) with clean water. Note always mix anti-freeze with the cooling water. Mixture ratios differ with the anti-freeze manu- facturer an...
Page 35: Caution
Muffler removal and installation remove and install the muffler and engine as shown on figure 3d-3. Exhaust system inspection 1. Clean all sections of the exhaust system of dirt, dust or other foreign material. 2. Inspect exhaust system for cracks, holes, distor- tion or deformation. Engine section ...
Page 36: Caution
Fuel filter service (see figure 3d-4) the fuel filter is mounted on the left front of engine on the frame. Moisture and other foreign matter accumu- late in the fuel filter. Periodically clean and replace the filter element. (refer to section 11.) purge air from the fuel system after new filter has ...
Page 37
8. One at a time, loosen the high pressure fuel injec- tor line nuts at the injector while cranking the engine. 9. When bubbles disappear, tighten the fuel line nuts. Repeat steps 6 and 7 for the remaining fuel injec- tion lines. 10. When all the lines have been purged and the engine is running, lis...
Page 38
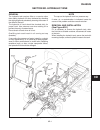
Engine installation (see figures 3d-6 to 3d-8) 1. Move the engine onto its approximate mounting position using a chain hoist. 2. Line up holes in hydrostatic pump drive plate with engine flywheel. Install bolts (1) and lockwashers (2). Torque to 37 ft-lbs. (51 n.M). 3. Slide engine forward, align an...
Page 39: Section 4
4 4a. Repair and service tools and materials . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4a-1 4b. Failure analysis . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4b-1 4c. Hydrostat dr...
Page 41
Tools required: standard automotive hand tools. Metric tools. Cleaning materials: stoddard solvent or equivalent. Loctite “chisel” gasket remover or equivalent. Lubricants: refer to section 11. Special tools: * bucher-guyer ag ch-8166 niederweningen fax: 01-857-26-55 * adjusting tool 150-10511-0. * ...
Page 43
Drive train section 4b. Failure analysis 4b-1 4b problem probable cause remedy 1. Differential lock does a. Torque on drive line. A. Stop tractor. Not disengage. B. Differential lock collar jammed. B. Repair (section 4e). C. Faulty differential lock piston. C. Repair (section 4e). D. Tractor in a tu...
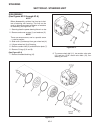
Page 45
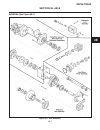
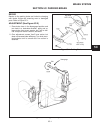
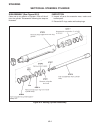
General the hydrostatic transmission is driven by a telescop- ing universal joint type drive shaft connected directly between the hydro and engine flywheel plate. Repair repairs are limited to renewing the cross and bearings. Service disassembly (see figure 4c-1) 1. Position the joint in a vise as s...
Page 47
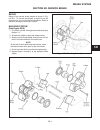
General the drive axle is driven by a telescoping universal joint type drive shaft connected directly between the hydro motor and axle. Note when removing, do not bend or damage the disc plate surface. Service disassembly (see figure 4d-1) 1. Remove drive shaft assembly from tractor. 2. Position the...
Page 48
Assembly (see figure 4d-1) note during reassembly be sure all the parts are clean and free of dirt. 1. Start one bushing in yoke ear and position center cross through yoke. 2. Drive the first bushing flush with outside surface of ear. Note do not bend ear of yoke. 3. Support the ear and using a sock...
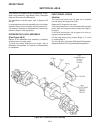
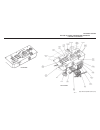
Page 49
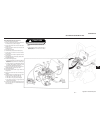
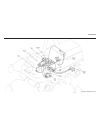
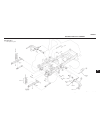
General (see figure 4e-1) drive train section 4e. Axle 4e-1 4e figure 4e-1. Axle assembly.
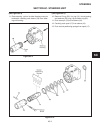
Page 50
This section is divided into four subsections; differ- ential lock assembly, input bevel pinion, reduction gear and drive axle and differential. For information on brake repair, refer to sections 5d and 5e. In most cases the entire axle assembly will not be disas- sembled. Refer only to the section ...
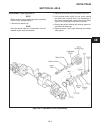
Page 51
Disassembly (see figure 4e-3) note before removing the input bevel pinion assembly from the axle, complete step 1. 1. Remove the elastic nut. Note once the elastic stop nut is loosened a new col- lapsible spacer must be installed. 2. Remove input bevel pinion assembly from axle. 3. If the original p...
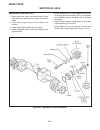
Page 52
Reassembly (see figure 4e-4) 1. Support the inner race of the bearing cone. Press input shaft into bearing cone, taper toward the inside. 2. Press bearing cups, tapers to the outside, into housing. 3. Install input shaft and bearing into housing. 4. Install collapsible sleeve and press bearing cone ...
Page 53
Break-away torque adjustment (see figure 4e-5) note the following adjustment is made with no seal installed in the pinion housing. 1. Tighten the elastic nut until a break-away torque of 4.5–6.3 in-lbs. (0.5–0.7 n.M) is obtained. Note apply a slow steady increasing pressure on the torque wrench. 2. ...
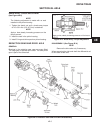
Page 54
Reassembly (see figure 4e-7) if the axle shaft(s) were not removed, proceed with step 5. 1. Press wheel axle bearing into axle housing. 2. Support the inner race of the bearing and press drive axle shaft into bearing. (step 3 for right axle only) 3. Remove the differential lock assembly housing. 4. ...
Page 55
(step 5 for right axle only) 5. Install differential lock assembly cover. 6. Press drive axle bearing and wheel axle outer bear- ing into cover. 7. Install outer cover bearing, lock ring and seal into reduction gear cover. 8. Fasten wheel axle shaft to brake disc with flat head screws. Torque to 29 ...
Page 56
Input bevel pinion and ring gear clearance (see figure 4e-10) note proceed with the following steps if a new matched input bevel pinion and ring gear are to be installed. 1. Install input bevel pinion assembly with no shims and torque it to 37 ft-lbs. (51 n.M). 2. Install special tool into bearing b...
Page 57
Pinion and ring gear backlash adjustment general there are two methods described to adjust backlash. Method “a” and “b” should be reviewed prior to per- forming the adjustment to determine which will be used. Method “a” (see figure 4e-11) 1. Press bearings onto the differential assembly. 2. Install ...
Page 58
4. Using a dial indicator against a pinion tooth, check the gear backlash. 5. Subtract backlash of 0.008" (0.2 mm) from the measurement obtained. Build a shim pack equal to the final dimension. 6. Remove the differential assembly, place the shim pack in the bearing bore of the gear case. 7. Install ...
Page 59: Section 5
5 5a. Repair and service tools and materials . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5a-1 5b. Failure analysis . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5b-1 5c. Parking brak...
Page 61
Brake system section 5a. Repair and service tools and materials 5a-1 5a tools required: standard automotive hand tools. Metric tools. Cleaning materials: stoddard solvent or equivalent. Lubricants: refer to section 11. Other service items: brake repair parts. Brake linings..
Page 63
Brake system section 5b. Failure analysis 5b-1 5b problem probable cause remedy 1. Parking brake does not a. Brake is not adjusted. A. Adjust brake (section 2c). Hold tractor in position. B. Worn brake linings. B. Replace lining (section 5c). C. Broken or worn cable. C. Replace (section 5c). 2. Serv...
Page 65
Repair repairs to the parking brake are limited to changing worn brake linings and renewing worn or damaged parts. Refer to figure 5c-1. Adjustment (see figure 5c-2) 1. Place brake lever in the disengaged position and turn knob in a clockwise direction, apply and re- lease brake lever every quarter ...
Page 67
Repair repair of the service brake calipers is shown in fig- ure 5d-1. To service the calipers, a repair kit can be ordered from your local jacobsen distributor. Refer to the parts catalog for the kit part number. Bleeding system (see figure 5d-2) 1. Fill master cylinder with approved brake fluid (s...
Page 69
Repair repair of the master cylinder is shown in figure 5e-1. To service the master cylinders, a repair kit can be ordered from your local jacobsen distributor. Refer to the parts catalog for the kit part number. Bleeding system (see figure 5e-2) 1. Fill master cylinder with approved brake fluid (se...
Page 71: Section 6
6 6a. Repair and service tools and materials . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6a-1 6b. Failure analysis . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6b-1 6c. Steering uni...
Page 73
Tools required: standard automotive hand tools. 6 mm hexagon socket wrench. 8 mm hexagon socket wrench. Cleaning materials: stoddard solvent or equivalent. Other service items: o-ring and kin ring tool sj 150-9000-11. Cardan shaft tool sj 150-9000-3. Above tool can be purchased from: danfoss, inc. 1...
Page 75
Steering section 6b. Failure analysis 6b-1 6b problem probable cause remedy 1. No turning of steering a. Insufficient oil supply. A. Check oil supply. Wheel. B. Insufficient oil pressure or no b. Check (section 8r). Oil pressure. C. Steering relief valve sticking c. Repair, clean and reset the open ...
Page 77
General the power steering unit is supplied with oil from the pump, section 3. Power steering is provided as long as the engine is running. If an engine failure occurs, the steering unit provides manual steering. Removal (see figure 6c-1) 1. Remove steering wheel cap (1), nut (2), flat wash- er (3) ...
Page 78
Disassembly (see figures 6c-2 through 6c-6) note before disassembly, scribe a line from top to bot- tom of steering unit housing. This line can be used to determine proper orientation of sections for assembly (see figure 6c-13). 1. Securely place the power steering fixture in a vise. 2. Remove end c...
Page 79
(see figure 6c-4) 9. Place steering unit on its side. Keeping cross pin horizontal, carefully push sleeve (14) from steer- ing unit housing. (see figure 6c-5) 10. Remove o-ring (22), kin ring (21), thrust bearing and washers (20), ring (19) and dust ring (23). 11. Push cross pin (15) out of sleeve (...
Page 80
(see figure 6c-6) note if either shock valve plugs (26) in step 15 and/or the relief valve plug (32) in step 17 are removed, the relief setting will be destroyed. If it is not necessary to remove these items, skip steps 14–17. 14. Use a 6 mm hex socket wrench. Remove shock valve plug (24) and washer...
Page 81: Caution
Assembly (see figures 6c-7 through 6c-12) 1. Coat all parts with oil. Make sure parts are clean. 2. Insert spool (17) into sleeve (16), guide in carefully. 3. Install two flat neutral position springs (18) into slot of spool (17). 4. Slide two curved springs (18) between the flat springs. 5. Press s...
Page 82
(see figure 6c-8) 7. Install ring (19) over sleeve (16). Note ring (19) should rotate free of springs (18). 8. Install cross pin (15) through sleeve and spool. 9. Install thrust bearing and washers (20) being sure inside chamber of heavy washer goes on spool first. Steering section 6c. Steering unit...
Page 83
(see figure 6c-9) 10. Place the steering unit on its side. Insert the outer sleeve of tool sj 150-9000-11 into the sleeve bore. 11. Lubricate o-ring (22) and kin ring (21). Place them on the guide tool as shown. 12. Using the inner tool, push and turn the guide through the outer tool sleeve until o-...
Page 84
(see figure 6c-10) 14. Place the housing down on a flat surface. Hold sleeve assembly (14) so cross pin (15) is horizontal. 15. Carefully insert sleeve assembly (14). Note sleeve to housing fit is very close. Do not force together. 16. Push sleeve (14) into housing, pushing out the o-ring and kin ri...
Page 85
(see figure 6c-11) 19. Install 3/16" suction valve balls (13) as shown. 20. Install suction valve pins (12) as shown. 21. Install o-ring (8) and distributor plate (7). 22. Install cardan shaft (9) and hold in position with tool sj 150-9000-3. 23. Install o-rings (4 and 6) to gear wheel set (5). 24. ...
Page 86
Note there are two shock valve assemblies. Instal- lation of both are the same, see step 27. Note the pressure setting of this valve must be ad- justed. Use the tractor hydraulics and adjust as described in section 8s. 28. Install relief valve spool (34), spring (33), and us- ing an 8 mm hex socket ...
Page 87
Installation (see figures 6c-1 and 6c-14) 1. Position and attach steering unit to tractor. 2. Connect hydraulic lines, see figure 6c-14. 3. Install insert (5), flat washer (3), steering wheel (4) and nut (1). Torque nuts to 25–30 ft-lbs. (34–41 n.M). 4. If steering unit was disassembled, adjust shoc...
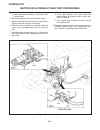
Page 89
Toe-in (see figure 6d-1) 1. Turn steer wheels to straight ahead position. 2. Remove the cylinder rod end ball joint. 3. Loosen the rod jam nuts. 4. Turn tie rod so wheels toe-in 1/16" (1.6 mm). 5. Loosen cylinder clamp on rod end of cylinder. 6. Lengthen or shorten rod end ball joint to line up with...
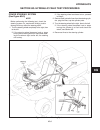
Page 91
Removal (see figure 6e-1) 1. Block the wheel and set the parking brake. 2. Tag and remove hydraulic lines. Cap the cylinder ports and plug the lines. 3. Remove attaching hardware and remove cylinder. Steering section 6e. Steering cylinder 6e-1 6e figure 6e-1. Steering cylinder removal and installati...
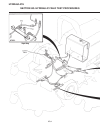
Page 92
Disassembly (see figure 6e-2) clean and air dry exterior of cylinder. Drain all the oil from the cylinder. Disassemble following the steps as illustrated. Inspection • inspect all parts for excessive wear, cracks and broken parts. • discard all o-rings, seals and backup rings. Steering section 6e. S...
Page 93
Reassembly 1. Lightly lubricate o-rings, backup rings and seals. 2. Install seal kit as shown in figure 6e-3. 3. Lubricate all parts before assembly. 4. Follow the steps as illustrated in figure 6e-4 and reassembly. Installation (see figure 6e-1) 1. Install cylinder and secure with attaching hardwar...
Page 94
Steering section 6e. Steering cylinder 6e-4 figure 6e-4. Steering cylinder assembly.
Page 95: Section 7
7 7a. Repair and service tools and materials . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7a-1 7b. Failure analysis . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7b-1 7c. Tire service...
Page 97
Tools required: standard automotive hand tools. Cleaning materials: stoddard solvent or equivalent. Other service items: commercially available tire sealant. Non-hardening. Tire pressure gauge. Compressed air with tire valve fitting. Wheels & tires section 7a. Repair and service tools and materials ...
Page 99
Wheels & tires section 7b. Failure analysis 7b-1 7b problem probable cause remedy 1. Tractor rides hard. A. Over inflated tires. A. Reduce tire pressure 20 to 24 psi (1.4 to 1.6 bars) front and 6 to 10 psi (.41 to .68 bars) rear. 2. Tractor wanders. A. Under inflated tires. A. Inflate tires to 20 to...
Page 101
General tires are subject to damage from sharp objects. If large punctures or tears occur, it is advisable to take the tire (installed on the wheel) to a qualified tire repair shop. The front drive wheels are bolted directly to the wheel hub which is part of the front axle assembly. See section 4 fo...
Page 103: Section 8
8 8a. Repair and service tools and materials . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8a-1 8b. Failure analysis . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8b-1 8c. General inst...
Page 104
8m. Mower motor control valve . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8m-1 general . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8m-1 repair...
Page 105
8 mower system . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8r-15 front mower . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8r-15 pum...
Page 107
Tools required: standard automotive hand tools, including torque wrench, seal drivers, snap ring pliers, bearing driver. Tachometer. Hydra sleuth or in-line tester equipped with load valve. Pressure test kit. Cleaning materials: stoddard or equivalent solvent. Detergent and water. Loctite “locquic” ...
Page 108
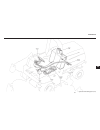
Hydraulics section 8a. Repair and service tools and materials 8a-2 figure 8a-1. Wheel restraint.
Page 109
Hydraulics section 8b. Failure analysis 8b-1 8b problem probable cause remedy traction system 1. Forward and reverse a. Dump valve not closed. A. Close valve. Slow (2 whd). B. Parking brake applied. B. Release. C. Traction linkage damaged or out c. Adjust/repair (section 2c). Of adjustment. D. No or...
Page 110
Hydraulics section 8b. Failure analysis 8b-2 problem probable cause remedy 7. No differential lock. A. Faulty cartridge valve. A. Replace (section 8k). Check led in differential b. Faulty 4 wheel drive control valve b. Repair/replace (section 8f). Lock solenoid plug: spool. On — switch solenoid c. I...
Page 111
Hydraulics section 8b. Failure analysis 8b-3 8b problem probable cause remedy 5. Front mower will not a. Valve detent spool sticks. A. Repair (section 8h). Lower. B. Restriction in oil return line. B. Test (section 8r). 6. Mower stops lowering a. Detent spool not locking in a. Repair (section 8h). W...
Page 112
Hydraulics section 8b. Failure analysis 8b-4 problem probable cause remedy 3. Left wing runs slow. A. Reel-to-bedknife too tight. A. Adjust (section 12e). B. Faulty reel or drive. B. Repair (section 12d). C. Faulty reel motor. C. Test (section 8r). D. Right wing motor excessive d. Test (section 8r)....
Page 113: Caution
General note component location illustrations and hydraulic diagrams are located at the end of this section. The following general instructions apply to all hy- draulic system service procedures. Carefully read and adhere to each precaution. • dirt in the hydraulic system will cause damage to system...
Page 114
3. Using a wrench, tighten the nut the amount shown in the chart below. The line will show which fittings have been tightened correctly and also indicates if a fitting is becoming loose. 37° flare torque recommendations special hose installation instructions 1. Hold the fixed portion of the hose cou...
Page 115
O-ring boss torque recommendations ors (face seal) fittings (see figure 8c-3) face seal fittings have o-ring grooves machined into the flat male face. This o-ring and flat surface mate against the mating fittings machined face. The swivel nut can be retracted to inspect the o-ring and fitting face w...
Page 117
General (see figure 8d-1) the traction pump supplies oil to the traction system of the tractor. The pump is engine driven through a drive shaft. It is a variable output pump. When disassembling pump, only disassemble the necessary components for repair. In some cases it is not necessary to completel...
Page 118: Caution
Repair (see figure 8d-2) refer to figure 8d-2 for disassembly and reassembly of the traction pump. Inspection 1. Inspect bronze surface of valve plate for scratch- es or gouged marks. 2. Inspect piston shoes for excessive wear, cracks or shoes that fall off pistons. 3. Inspect shaft for excessive we...
Page 119
Installation (see figure 8d-1) 1. Install the pump, rotating it back and forth to en- gage the splines, fasten the mounting plate. 2. Connect all control linkage. See section 2 for prop- er adjustments. 3. Install the implement pump. 4. Connect all hydraulic hoses and tubes. 5. Install seat and seat...
Page 121
General the implement pump has four positive displacement gear pump sections. Pump sections are numbered from the shaft end. Pump section 1 supplies oil to the right wing mower. Pump section 2 supplies oil to the left wing mower. Pump section 3 supplies oil to the front mower. Pump section 4 supplie...
Page 122: Caution
Repair disassembly (see figure 8e-2) 1. Before disassembly mark pump sections, starting at drive shaft end, to ensure correct order of part reassembly. Recommended method of marking body sections is to use a fine point metal punch, making one indentation in line on each section. Hydraulics section 8...
Page 123
2. After removing tie bolts, disassemble pump one section at a time. Before removing gear sets, mark a line across meshing teeth to ensure that gears are reassembled in the same position (see figure 8e-3). 3. Place parts in assembly order, on a clean work area as they are removed. 4. Discard seals a...
Page 125
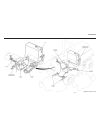
Repair repairs are limited to replacing the 4 wheel drive pilot cartridge or changing o-rings. Hydraulics section 8f. 4 wheel drive control valve 8f-1 8f figure 8f-1. 4 wheel drive control valve.
Page 127
Repair repair is limited to cleaning only. Use a punch, manu- ally push poppet off its seat and flush with cleaning solvent. If the problem still exists, replace valve. Hydraulics section 8g. Anti-siphon valve 8g-1 8g figure 8g-1. Anti-siphon valve.
Page 129
General the lift and lower control valve is used to raise and lower the cutting units. Left control is for the left wing. Right control is for the right wing. Center control is for the three front cutting units. Removal 1. Drain and remove the fuel line. 2. Tag and mark hydraulic lines on valve. 3. ...
Page 130
Hydraulics section 8h. Lift and lower control valve 8h-2 figure 8h-3. Spool assembly removal figure 8h-4. Relief valve removal.
Page 131: Caution
Inspection 1. Remove all nicks and burrs from parts. 2. Inspect parts for excessive wear or damage, re- place parts as necessary. 3. Inspect poppet seats for burrs or roughness. 4. Discard old o-rings and replace with new ones. Reassembly see figures 8h-5 to 8h-7. Hydraulics section 8h. Lift and low...
Page 132
Hydraulics section 8h. Lift and lower control valve 8h-4 figure 8h-7. Detent and lockout reassembly.
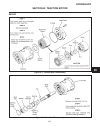
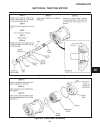
Page 133
Repair hydraulics section 8i. Traction motor 8i-1 8i figure 8i-1. Traction motor disassembly figure 8i-2. Drive shaft disassembly.
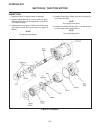
Page 134
Inspection 1. Inspect all parts for signs of wear or damage. 2. Inspect needle bearing in housing and lock plate. Needles should be free of excess play and remain in the bearing cage. 3. Inspect pistons and shoes. Pistons should be snug and shoes should be flat and have no signs of flaking. Note do ...
Page 135
Hydraulics section 8i. Traction motor 8i-3 8i figure 8i-4. Drive shaft reassembly figure 8i-5. Traction motor reassembly.
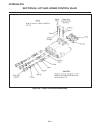
Page 137
Repair hydraulics section 8j. Rear traction motor 8j-1 8j figure 8j-1. Rear traction motor.
Page 138
Hydraulics section 8j. Rear traction motor 8j-2 figure 8j-2. Seal assembly.
Page 139
Hydraulics section 8j. Rear traction motor 8j-3 8j figure 8j-3. O-rings and seals.
Page 141
Repair repair of the control valve is limited to changing car- tridges or renewing o-ring on each cartridge. Hydraulics section 8k. Control valve 8k-1 8k figure 8k-1. Control valve.
Page 143: Caution
General the hr5111 tractor uses four hydraulic cylinders to raise and lower the cutting units. The two wing cylin- ders are the same and are different from the two cylin- ders which are the same. Front cylinders disassembly (see figure 8l-1) 1. Clean and air dry exterior of cylinder. 2. Drain all th...
Page 144
Inspection 1. Inspect all parts for excessive wear, cracks and broken parts. 2. Discard all o-rings, seals and seal ring. Reassembly 1. Lightly lubricate o-rings, seal ring and seals. 2. Install seal kit as shown in figure 8l-2. 3. Lubricate all parts before assembly. 4. Follow the steps as illustra...
Page 145
Hydraulics section 8l. Lift cylinder 8l-3 8l figure 8l-3. Lift cylinder assembly.
Page 146
Wiring cylinders disassembly (see figure 8l-4) 1. Clean and air dry exterior of cylinder. 2. Drain all the oil from the cylinder. 3. Disassemble following the steps in figure 8l-4. 4. Disassemble remainder of cylinder as shown in fig- ure 8l-4. Hydraulics section 8l. Lift cylinder 8l-4 figure 8l-4. ...
Page 147
Inspection 1. Inspect all parts for excessive wear, cracks and broken parts. 2. Discard all o-rings, seals and backup rings. Reassembly 1. Lightly lubricate o-rings, backup rings and seals. 2. Install seal kit as shown in figure 8l-5.. Note do not install rod o-ring at this time. 3. Lubricate all pa...
Page 148
Hydraulics section 8l. Lift cylinder 8l-6 figure 8l-6. Wing cylinder assembly.
Page 149
General the mower motor control valves control oil flow to the mower motors. It is a 2 position, 4 way open center valve. The valve is solenoid operated. See section 10i for solenoid test. The following illustration shows one of the three valves. Repair (see figure 8m-1) repair of the valve consists...
Page 150
Inspection 1. Inspect all parts for signs of excessive wear or damage. 2. O-rings should be discarded and a new kit o-ring installed. 3. Check spool making sure it slides smoothly in valve body. 4. Check plunger making sure it slides easily in the outer flux sleeve. 5. Check for broken or cracked re...
Page 151
General (see figure 8n-1) the motors used on the hr5111 are uni-directional and positioned according to their rotation. Viewed from the shaft end, clockwise (cw) rotating motors have the letter c stamped on the motor housing. Motors that are counterclockwise (ccw) rotating have the letter a stamped ...
Page 152: Caution
Disassembly 1. Clean exterior of motor with suitable solvent be- fore removing the bolts. 2. Before disassembly mark motor sections, starting at drive shaft end, to ensure correct order and po- sition of parts when reassembling. Recommended method of marking body sections is to use a fine point meta...
Page 153
Repair the bypass is located at the bottom left side of the hydraulic tank. Repair is limited to cleaning only. Disassemble and flush with a cleaning solvent. Hydraulics section 8o. Oil cooler cold oil bypass 8o-1 8o figure 8o-1. Bypass.
Page 155
Repair repair of the flotation control is renewing o-ring or replacing the control cartridge. Hydraulics section 8p. Flotation control 8p-1 8p figure 8p-1. Back pressure control valve.
Page 157
General the purpose of this section is to provide a guide for field testing the hydraulic system. More extensive test procedures, using test instruments, are presented in section 8r. Component location illustrations, hydrau- lic schematics and diagrams are presented in section 8s. Before performing ...
Page 158
• if the engine does not labor, a fault exists in the traction pump. 4. Reconnect hydraulic lines to the traction pump. 5. Remove both hydraulic lines from the 4 wheel valve. Plug the hoses and cap the valve ports. 6. With the tractor on asphalt or concrete, chain the tractor to an unmovable object ...
Page 159
Power steering system (see figure 8q-3) note before performing the following test, check the steering system for mechanical binding and/or damage that may affect the steering effort. 1. Turn the steering wheel completely to the right, then to the left. • if the steering wheel becomes hard or stops t...
Page 160
Hydraulics section 8q. Hydraulic field test procedures 8q-4.
Page 161
Hydraulics section 8q. Hydraulic field test procedures 8q-5 8q figure 8q-4. Lift and lower control lift and lower control (see figure 8q-4) note be sure engine is above 2000 rpm. 1. Isolate the circuit at fault by operating each han- dle of the control valve separately. Note if all circuits are affe...
Page 162: Danger
Mower system (see figure 8q-5) the mower circuits can be divided into three separate circuits. Mower pump section 1 supplies oil to motor control valve. Then to right wing motors. Mower pump section 2 supplies oil to a motor control valve. The motor control valve controls the left wing. Mower pump s...
Page 163
Hydraulics section 8q. Hydraulic field test procedures 8q-7 figure 8q-5. Reel system 8q.
Page 164
4. Follow the procedure listed under the circuit hav- ing the problem. Front mowers if all motors are affected, check the case drain line on the left motor. If the case drain line feels warmer than the two remaining motors, it may have excessive internal leakage, see section 8n. If only the right an...
Page 165: Caution
General the tests in this section are provided as a means of isolating a problem in the hydraulic system. This section consists of two test methods. The first; relief valve tests, using pressure gauges only. Using this method results in some test conclusions not being final. Second; starting with th...
Page 166
Relief valve test charge relief test (see figure 8r-2) 1. Use a 0–500 psi gauge with test adapter p/n 551433. 2. Plug gauge into test port cd located on the con- trol valve block. 3. Set the brake, start the engine and advance throt- tle to 2800 engine rpm. • charge relief should read 190–250 psi. N...
Page 167
Hydraulics section 8r. Instrument test 8r-3 8r figure 8r-3. Steering system relief steering system relief (see figure 8r-3) 1. Use a 0–2000 psi gauge with test adapter p/n 551433. 2. Plug gauge into test port sd located on the con- trol valve block. 3. Set the brake, start the engine and advance thr...
Page 168
Hydraulics section 8r. Instrument test 8r-4 lift system relief (see figure 8r-4) 1. Use a 0–2000 psi gauge with test adapter p/n 551433. 2. Plug gauge into test port ld located on the con- trol valve block. 3. Set the brake, start the engine and advance throt- tle to 2800 engine rpm. 4. Raise cuttin...
Page 169
Hydraulics section 8r. Instrument test 8r-5 8r figure 8r-5. Traction system relief traction system relief forward (see figure 8r-5) 1. Use a 0–5000 psi gauge with test adapter p/n 551433. 2. Plug gauge into test port ad located on the top left of the 4 wheel drive valve. 3. Set the parking brake, st...
Page 170
Hydraulics section 8r. Instrument test 8r-6 figure 8r-6. Mower system relief front motors mower system relief there are three relief valves, one located under the coil on each motor control valve. The procedure below is the same for each circuit, front, right or left wings. Identify which circuit ha...
Page 171
Hydraulics section 8r. Instrument test 8r-7 8r charge pump test (see figure 8r-7) 1. Remove outlet line from pump section 4 (pump section closest to the front axle). 2. Connect the in port of the tester to the pump out- let port. 3. Connect hose from the out port of tester to the pump outlet line. 4...
Page 172
Hydraulics section 8r. Instrument test 8r-8 priority valve test (see figure 8r-8) note a charge pump test must be performed before proceeding with this test. 9. At the top of the traction pump, remove the outlet line of the charge filter from the fitting. 10. Connect the in port of the tester to the...
Page 173
Hydraulics section 8r. Instrument test 8r-9 8r lift system test (see figure 8r-9) front mower cylinders and lift valve isolation test 15. Raise the front mower and block it in the up posi- tion. 16. Disconnect the two return hoses (rod end port) from the front left cylinder. 17. Remove the blocking ...
Page 174
Hydraulics section 8r. Instrument test 8r-10 figure 8r-10. Lift system test, wing mower circuit left wing cylinder and lift valve isolation test (see figure 8r-10) 15. Raise left wing mower and lock in transport posi- tion. 16. At the left cylinder, remove return line from the rod end of cylinder. 1...
Page 175
Hydraulics section 8r. Instrument test 8r-11 8r traction system traction pump test (see figure 8r-11) 1. Raise front wheels off the ground. 2. Remove 4 wheel drive hose from the left side of the traction pump, cap tee and plug line. 3. Remove front traction motor hose from left side of traction pump...
Page 176
Hydraulics section 8r. Instrument test 8r-12 figure 8r-12. Front hydrostatic motor test front traction motor test (see figure 8r-12) note a traction pump test must be performed before proceeding with this test. 17. Connect both front traction motor hoses to the left and right side tees on pump. 18. ...
Page 177
Hydraulics section 8r. Instrument test 8r-13 8r 4 wheel drive valve test (see figure 8r-13) note a traction pump and front motor test must be performed before proceeding with this test. 22. Connect 4 wheel drive hose to left side of traction pump. 23. At the 4 wheel drive valve, remove hoses from l1...
Page 178
Hydraulics section 8r. Instrument test 8r-14 figure 8r-14. Rear traction motor test 40. Slowly close tester load valve until 3000 psi is ob- tained and allow oil to heat up to 150°f. 41. Read/record gpm flow. Subtract from flow obtained for the left rear motor test. Record engine rpm. • if flow drop...
Page 179
Hydraulics section 8r. Instrument test 8r-15 mower system front mower pump test (see figure 8r-15) 1. Remove outlet line from pump section 3. 2. Connect the in port of the tester to the pump out- let port, plug pump outlet line. 3. Put the hose from the out port of tester into the hydraulic tank. 4....
Page 180
Hydraulics section 8r. Instrument test 8r-16 motor valve test (see figure 8r-16) note a pump test must be performed before proceed- ing with this test. 8. Reconnect outlet line to pump. 9. Remove hydraulic line from the a port of the left motor and install a tee to hose. Cap motor port. 10. Connect ...
Page 181
8r-17 right motor test note a pump, valve, center motor and left motor test must be performed before proceeding with this test. 32. Move wooden block to right motor blade. 33. Open tester load valve, start engine, advance throt- tle to 2800 engine rpm. 34. Push center mower reel switch into cut and ...
Page 182
Hydraulics section 8r. Instrument test 8r-18 figure 8r-17. Pump test wing motor wing mowers pump test (see figure 8r-17) pump section 1 supplies oil to the right wing and pump section 2 to the left wing. The test procedure is the same for both circuits. Test the circuit having the fault. 1. Remove o...
Page 183
Hydraulics section 8r. Instrument test 8r-19 8r right wing motor valve test (see figure 8r-18) note a pump section 1 test must be performed before proceeding with this test. 8. Reconnect outlet line to pump, section 1. 9. Remove hydraulic line from the a port of the inside motor and install a tee to...
Page 184
Hydraulics section 8r. Instrument test 8r-20 left wing motor valve test (see figure 8r-19) note a pump section 2 test must be performed before proceeding with this test. 8. Reconnect outlet line to pump, section 2. 9. Remove hydraulic line from the port c of the left wing inside motor and install a ...
Page 185
Hydraulics section 8r. Instrument test 8r-21 8r figure 8r-19. Left wing motor circuit tests.
Page 186
Hydraulics section 8r. Instrument test 8r-22 this page intentionally left blank.
Page 187
Hydraulic instrument test data sheet relief valve tests actual settings charge relief _____ psi 190–250 psi steering relief _____ psi 1500 psi lift system relief _____ psi 1500 psi traction system relief forward _____ psi 3500 psi reverse _____ psi 3500 psi mower system relief front motors _____ psi...
Page 188
Hydraulics section 8r. Instrument test 8r-24 flow tests (continued) traction system traction pump no load ________ gpm @ engine rpm ________ no load @ ________ gpm @ engine rpm ________ @ 3000 psi – ________ gpm @ engine rpm – ________ conclusion = ________ gpm drop @ engine rpm drop = ________ fron...
Page 189
Hydraulics section 8r. Instrument test 8r-25 8r flow tests (continued) mower system tests (continued) front mower pump (continued) center motor no load ________ gpm @ engine rpm ________ center motor test ________ gpm @ 3000 psi – ________ gpm @ engine rpm – ________ conclusion = ________ gpm drop @...
Page 190
Hydraulics section 8r. Instrument test 8r-26 flow tests (continued) mower system tests (continued) front mower pump (continued) right wing mower pump (section 1) no load ________ gpm @ engine rpm ________ @ 2500 psi – ________ gpm @ engine rpm – ________ conclusion = ________ gpm drop @ engine rpm d...
Page 191
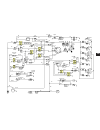
Hydraulics 8s-1 8s figure 8s-1. Flow diagram.
Page 192
Hydraulics 8s-3 figure 8s-2. Schematic (early).
Page 193
Hydraulics 8s-5 8s figure 8s-3. Schematic (later).
Page 194
T p l r 2300 psi 2300 psi 1500 psi 435 psi 3000 psi t p a b c 435 psi 3000 psi t p a b c 435 psi 3000 psi t p a b c 4 3 2 1 inside inside outside outside lh ctr rh 50 psi bypass 25 psi bypass oil cooler suction filter diff lock weight transfer control priority valve control valve 17 ltr charge relie...
Page 195
T p l r 2300 psi 2300 psi 1500 psi 435 psi 3000 psi t p a b c 435 psi 3000 psi t p a b c 4 3 2 1 inside inside outside outside lh ctr rh 50 psi bypass 25 psi bypass oil cooler suction filter diff lock weight transfer control priority valve control valve 17 ltr charge relief valve 250psi 1500 psi lif...
Page 196
T p l r 2300 psi 2300 psi 1500 psi 435 psi 3000 psi t p a b c 435 psi 3000 psi t p a b c 4 3 2 1 inside inside outside outside lh ctr rh 50 psi bypass 25 psi bypass oil cooler suction filter diff lock weight transfer control priority valve control valve 17 ltr charge relief valve 250psi 1500 psi lif...
Page 197
T p l r 2300 psi 2300 psi 1500 psi 435 psi 3000 psi t p a b c 435 psi 3000 psi t p a b c 4 3 2 1 inside inside outside outside lh ctr rh 50 psi bypass 25 psi bypass oil cooler suction filter diff lock weight transfer control priority valve control valve 17 ltr charge relief valve 250psi 1500 psi lif...
Page 198
T p l r 2300 psi 2300 psi 1500 psi 435 psi 3000 psi t p a b c 435 psi 3000 psi t p a b c 4 3 2 1 inside inside outside outside lh ctr rh 50 psi bypass 25 psi bypass oil cooler suction filter diff lock weight transfer control priority valve control valve 17 ltr charge relief valve 250psi 1500 psi lif...
Page 199
T p l r 2300 psi 2300 psi 1500 psi 435 psi 3000 psi t p a b c 435 psi 3000 psi t p a b c 4 3 2 1 inside inside outside outside lh ctr rh 50 psi bypass 25 psi bypass oil cooler suction filter diff lock weight transfer control priority valve control valve 17 ltr charge relief valve 250psi 1500 psi lif...
Page 200
T p l r 2300 psi 2300 psi 1500 psi 435 psi 3000 psi t p a b c 435 psi 3000 psi t p a b c 4 3 2 1 inside inside outside outside lh ctr rh 50 psi bypass 25 psi bypass oil cooler suction filter diff lock weight transfer control priority valve control valve 17 ltr charge relief valve 250psi 1500 psi lif...
Page 201
T p l r 2300 psi 2300 psi 1500 psi 435 psi 3000 psi t p a b c 4 3 2 1 inside inside outside outside lh ctr rh 50 psi bypass 25 psi bypass oil cooler suction filter diff lock weight transfer control priority valve control valve 17 ltr charge relief valve 250psi 1500 psi lift valve lh center rh 4wd va...
Page 202
Hydraulics 8s-7 figure 8s-4. Traction system (1 of 4).
Page 203
Hydraulics 8s-9 8s figure 8s-5. Power steering system (2 of 4).
Page 204
Hydraulics 8s-11 figure 8s-6. Lift system (3 of 4).
Page 205
Hydraulics 8s-13 8s figure 8s-7. Mower system (4 of 4).
Page 207: Section 9
9 9a. Repair and service tools and materials . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9a-1 9b. Failure analysis . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9b-1 9c. Fuel tank . ...
Page 209
Tools required: standard automotive hand tools including bearing pullers. Cleaning and stoddard or equivalent solvent. Refinishing materials: detergent and water. Paint, jacobsen orange. Paint, jacobsen black. Anti-rust never-seize. Lubricants: grease gun grease (eg. Sunray dx671 or gulf supreme no....
Page 211
Chassis section 9b. Failure analysis 9b-1 9b problem probable cause remedy 1. Lift/lower functions do a. Engine rpm not above 2000. A. Increase engine rpm. Not occur when lever is b. Lever linkage is worn. B. Repair or replace linkage actuated. (section 2c). C. Mechanical binding. C. Lubricate/repai...
Page 213
General the fuel tank is a single piece tank which should re- quire no servicing unless punctured or otherwise acci- dentally damaged. The fuel tank should be drained whenever the machine is to be stored. Note the cap used on the tank is a vented cap. Removal and installation (see figure 9c-1) 1. Pl...
Page 215
General the hydraulic tank requires little or no service other than adding hydraulic oil when indicated by checking the sight gauge and periodically cleaning the screen in the outlet of the tank. The hydraulic oil level should be checked daily for proper level. Use extreme care when adding oil to pr...
Page 217
Removal and installation (see figure 9e-1) 1. Remove the attaching hardware from the slide mounting brackets. 2. Lift the seat and slide mounts off seat pan. To install the seat, secure the seat assembly with at- taching hardware. Lubricate as described in section 11. Chassis section 9e. Seat 9e-1 9...
Page 219
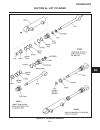
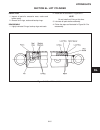
Chassis section 9f. Deck lift assembly 1 9f figure 9f-1. Lift assembly lift assembly (see figure 9f-1) 1. Lower implement to ground..
Page 220
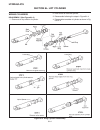
Transport lock mechanism (see figure 9f-2) the wing transport lock mechanism should not require adjustments unless the arms have been disassembled. Repair is limited to replacing damaged or worn parts. Note when installing the center lock nut, do not tight- en against latch hook. Latch hook must mov...
Page 221
General repair of the rear axle is limited to replacement of bro- ken parts and servicing bushings and bearings. (see steer cylinder service section 6f and adjustments section 6d.) removal and installation (see figure 9g-1) 1. Block front wheels to prevent tractor movement. 2. Raise the rear of the ...
Page 222
Spindle removal and installation (see figure 9g-1) 1. Disconnect tie rod and head end of the steering cylinder from the right hand steering assembly and tie rod from the left steering assembly. 2. Remove hydraulic lines from motor. Cap and plug all fittings. 3. Remove hydraulic motors. 4. Remove the...
Page 223: Section 10
10 10a. Repair and service tools and materials . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10a-1 10b. Failure analysis . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10b-1 10c. General inst...
Page 224
Hydraulic charge filter switch test . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10g-18 field test . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10g-18 switch test . . . . ....
Page 225: 10A
Tools required: multimeter. Jumper wires. 60 amp ammeter. Cleaning materials: baking soda and water. Other service items: electrical insulation compound p/n 365422. Electrical system section 10a. Repair and service tools and materials 10a-1 10a.
Page 227: 10B
Electrical system section 10b. Failure analysis 10b-1 10b problem probable cause remedy 1. Engine will not turn over a. Battery dead. A. Charge or replace (section 10d). When ignition switch is b. Parking brake not set. B. Set brake. Engaged. C. Implement switch not in the off c. Push into off posit...
Page 228
Electrical system section 10b. Failure analysis 10b-2 problem probable cause remedy glow plug circuit 1. Glow plugs do not a. Parking brake not set. A. Set brake. Come on. B. Implement switch not in the off b. Push into off position. Position. C. 50 amp tractor circuit breaker c. Reset/test (section...
Page 229: 10B
Electrical system section 10b. Failure analysis 10b-3 10b problem probable cause remedy implement circuits (continued) 3. Only one wing does not a. Arm interlock switch not closing. A. Check switch/adjust (section 2c). Come on. B. Faulty arm interlock switch. B. Test switch (section 10g). C. Faulty ...
Page 230
Electrical system section 10b. Failure analysis 10b-4 problem probable cause remedy gauges and panel lights (continued) 3. Panel light does not come a. 10 amp gauge/panel light circuit a. Reset/test (section 10j). On when test switch is breaker tripped. Pushed to the on position. B. Battery dead. B....
Page 231: 10B
Electrical system section 10b. Failure analysis 10b-5 10b problem probable cause remedy gauges and panel lights (continued) 10. Horn does not sound a. 10 amp cruise/horn circuit a. Reset/test (section 10j). When test switch is breaker tripped. Pushed to the on b. Faulty horn relay. B. Test/replace (...
Page 232
Electrical system section 10b. Failure analysis 10b-6 problem probable cause remedy cab circuits (continued) 4. Cab work lights do not a. Bulb burned out. A. Replace. Work. B. Faulty wiring or bad electrical b. Test (section 10c). Ground. C. Faulty light switch. C. Test (section 10g). 5. Tail light ...
Page 233: 10C
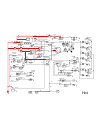
General repair of the electrical system, for the most part, is limited to the replacement of faulty components or wir- ing. Wiring diagrams and component location illus- trations are provided in section 10n for troubleshoot- ing and/or testing the electrical system. Specific repair and replacement i...
Page 234
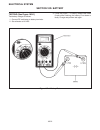
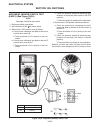
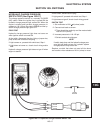
Resistance test (see figure 10c-2) 1. Set the multimeter to an Ω (ohms) scale. 2. Touch the leads to the terminals on the wire or switch. 3. Read the Ω (ohms) on the multimeter. • contacts of a switch or a wire should have less than 0.5 Ω (ohms) reading. • if Ω (ohms) readings are above 0.5 the swit...
Page 235: 10D
General for normal service, use a battery rated 12v, 770 cold cranking amps at 0°f (–18°c) aabm group #78nf. Charging a maintenance free battery note remove battery from tractor. 1. Be sure charger is “off”. 2. Connect charger leads to battery. Connect the pos- itive (+) connector from the charger t...
Page 236
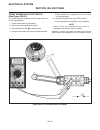
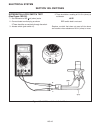
Testing (see figure 10d-1) test battery voltage as follows: 1. Connect dc multimeter to battery terminals. 2. Set voltmeter to 20 vdc. 3. Crank the engine — if battery voltage falls below 9 volts while cranking, the battery is run-down or faulty. Charge and perform test again. Electrical system sect...
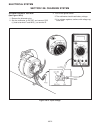
Page 237: 10E
General the 35 amp charging system consists of an alternator and separate regulator. See the engine manufacturer’s service manual for de- tailed repairs of the alternator. Alternator field test output current (see figure 10e-1) 1. Remove the red wire from terminal b of the alter- nator. 2. Connect a...
Page 238
Alternator input voltage (see figure 10e-2) 1. Remove the alternator plug. 2. Set the multimeter to 20 vdc and connect pos (+) lead to terminal f and neg (–) to terminal e. 3. Turn on the ignition switch. • the multimeter should read battery voltage. • if no voltage registers, continue with voltage ...
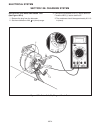
Page 239: 10E
No load test (see figure 10e-3) 1. Remove the electrical plug from the alternator. 2. Using a jumper wire, connect the f terminal to the b terminal. 3. Ground the e terminal. 4. Set the multimeter to 200 vdc. 5. Start and run engine at approximately 1500 rpm. 6. Disconnect the battery neg (–) cable....
Page 240
Rotor coil, slip ring and brush test (see figure 10e-4) 1. Remove the plug from the alternator. 2. Set the multimeter to 200 Ω (ohms) range. 3. Connect the multimeter pos (+) lead to terminal f and the neg (–) lead to terminal e. • the resistance should be approximately 6.5–10 Ω (ohms). Electrical s...
Page 241: 10E
No load regulating voltage test (see figure 10e-5) 1. Set the multimeter to the 20 vdc range. 2. Connect the multimeter pos (+) lead to the b ter- minal and the neg (–) lead to the ground. 3. Start and run the engine at idle. 4. Remove the neg (–) battery cable. 5. Gradually accelerate the engine an...
Page 242
Regulator test (see figure 10e-6) the regulator regulates the output voltage and current according to the electrical demand. Electrical system section 10e. Charging system 10e-6 figure 10e-6. Regulator test.
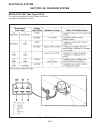
Page 243: 10F
General the repair of the starter is covered in the engine man- ufacturer’s service manual which can be obtained through your local jacobsen distributor. Field test pull in solenoid (see figure 10f-1) 1. Disconnect the neg (–) battery cable. 2. Disconnect the red and brn leads from the coil and tape...
Page 244
Starter motor (see figure 10f-2) 1. Disconnect the neg (–) battery cable. 2. Disconnect the pur/wht solenoid wire from the starter solenoid. 3. Remove starter. 4. Connect the cable to starter as shown. 5. Connect cable to pos (+) terminal of battery. 6. Touch the neg (–) cable to the neg (–) termina...
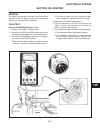
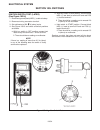
Page 245: 10G
General this section provides instructions for testing the vari- ous switches that are part of the electrical system. Repair is limited to replacement of components found faulty during testing. See figure 10n for location of components. Seat switch test (see figure 10g-1) 1. Disconnect seat switch c...
Page 246
Ignition switch test (early) (see figure 10g-2) 1. Disconnect ground (black) neg (–) cable at bat- tery. 2. Disconnect wiring connector at switch. 3. Set multimeter to 200 Ω (ohms) scale. 4. See figure 10i-3 and check all switch positions as follows: a. With key switch in off position connect test l...
Page 247: 10G
Electrical system section 10g. Switches 10g-3 10g figure 10g-3. Ignition switch test step 4 contacts open no continuity contacts closed continuity 0–0.5 ohms contacts closed continuity 0–0.5 ohms contacts closed continuity 0–0.5 ohms contacts closed continuity 0–0.5 ohms contacts closed continuity 0...
Page 248
Ignition switch test (later) (see figure 10g-4) 1. Disconnect ground (black) neg (–) cable at battery. 2. Disconnect wiring connector at switch. 3. Set multimeter to 200 Ω (ohms) scale. 4. See figure 10g-5 and check all switch positions as follows: a. With key switch in off position connect test lea...
Page 249: 10G
Electrical system section 10g. Switches 10g-5 10g figure 10g-5. Ignition switch test step 4.
Page 250
Implement (mower) switch test (early) (see figure 10g-6) note see page 10g-23 for later switch. 1. Disconnect switch connectors. 2. Set multimeter to 200 Ω (ohms) scale. 3. With switch in off position, test as follows: a. Connect one multimeter test lead to terminal a and the other lead to b. • ther...
Page 251: 10G
Wing mower control and lighting switch test (see figure 10g-7) 1. Disconnect switch connectors. 2. Set multimeter to 200 Ω (ohms) scale. 3. With switch in off position, test as follows: a. Check for continuity across all remaining com- binations of terminals (with switch in the off position). • ther...
Page 252
Front mower control switch test (see figure 10g-8) 1. Disconnect switch connectors. 2. Set multimeter to 200 Ω (ohms) scale. 3. With switch in off position, test as follows: a. Check for continuity across all combinations of terminals (with switch in the off position). • there should be no reading o...
Page 253: 10G
4 wheel drive switch test (see figure 10g-9) 1. Disconnect switch connectors. 2. Set multimeter to 200 Ω (ohms) scale. 3. With switch in off position, test as follows: a. Check for continuity across all combinations of terminals (with switch in the off position). • there should be no reading on the ...
Page 254
Cruise control switch test (see figure 10g-10) 1. Disconnect switch connectors. 2. Set multimeter to 200 Ω (ohms) scale. 3. With switch in off position, test as follows: a. Check for continuity across terminals (with switch in the off position). • there should be no reading on the multimeter. 4. Pla...
Page 255: 10G
Glow plug switch test test switch test (see figure 10g-11) the glow plug switch is pushed by the operator to allow current flow to the glow plugs, prior to starting the machine. See figure 10g-11 and test switch as follows: 1. Disconnect leads at switch. 2. Set multimeter to 200 Ω (ohms) scale. 3. C...
Page 256
Front mower shut-off switch (see figure 10g-12) the switch prevents operation of the mower when it is in the raised position. 1. Lower mower reels to the ground. 2. Disconnect wire connector at switch. 3. Set multimeter to 200 Ω (ohms) scale. 4. Connect multimeter test leads to switch terminals. • t...
Page 257: 10G
Brake switch test wing mower shut-off switch test parking brake switch test reverse sensing switch test (later) (see figure 10g-13) note before testing, check to see if the switch is just out of adjustment. See section 2c for adjustment procedures. 1. Remove the wires from the switch. 2. Set multime...
Page 258
Neutral and reverse sensing switch test (see figure 10g-14) 1. Disconnect ground cable at battery. 2. Identify (label) and disconnect electrical leads at switch. 3. Set multimeter to 200 Ω (ohms) scale. 4. Connect leads as shown. • there should be a reading on multimeter (conti- nuity). 5. Depress s...
Page 259: 10G
Horn switch test (see figure 10g-15) the horn switch sounds the tractor horn when the op- erator pushes on the switch. It also can be used to test the lights on the monitor panel. 1. Remove the plug from the switch. 2. Set multimeter to 200 Ω (ohms) scale. 3. Connect leads to switch as shown. • ther...
Page 260
Differential lock switch test (see figure 10g-16) 1. Set multimeter to 200 Ω (ohms) scale. 2. Connect leads to switch plug as shown. • there should be no continuity through the switch. 3. Actuate switch (push switch in). • there should be a reading of 0–0.5 Ω (ohms) at multimeter. Note red switch le...
Page 261: 10G
Hydraulic charge pressure switch test (see figure 10g-17) the charge pressure switch is a normally closed (nc) switch. When the ignition key is turned on the hydraulic charge pressure light comes on. When the engine is started and hydraulic charge pressure in- creases to 118–132 psi, the switch open...
Page 262
Hydraulic charge filter switch test (see figure 10g-18) the charge filter switch is a normally open (no) switch. When the hydraulic oil pressure at the inlet of the charge oil filter increases above 20 psi the switch closes and the hydraulic charge filter light comes on. Field test at the switch, re...
Page 263: 10G
Hydraulic return oil filter switch test (see figure 10g-19) the hydraulic return oil filter switch is a normally open (no) switch. When the hydraulic oil pressure at the inlet of the filter increases above 20–25 psi the switch closes and the hydraulic oil filter light comes on. Field test at the swi...
Page 264
Engine oil pressure switch test (see figure 10g-20) the engine oil pressure switch is a normally closed (nc) switch. When the ignition key is turned on the engine oil pressure light comes on. When the engine is started and oil pressure increases above 10 psi, the switch opens and the engine oil pres...
Page 265: 10G
Hydraulic oil temperature engine cooling water tempera- ture switch test (see figure 10g-21) the temperature switch is a normally open (no) switch. When the cooling water reaches 230°f (110°c) the switch will close. Field test using a jumper wire, remove the grn wire and ground it. Turn the ignition...
Page 266
Air cleaner service indicator switch test (see figure 10g-22) the air cleaner service indicator switch is a normally open (no) switch. When the air filter becomes re- stricted and 25" h2o of vacuum is reached, the switch will close. Field test using a jumper wire, remove both the blu/wht and blk wir...
Page 267: 10G
Implement (mower) switch test (see figure 10g-23) 1. Disconnect switch connectors. 2. Set multimeter to 200 Ω (ohms) scale. 3. With switch in off position, test as follows: a. Connect one multimeter test lead to terminal 4 and the other lead to 5. • there should be 0–0.5 Ω (ohms) on the mul- timeter...
Page 269: 10H
Engine (fuel) solenoid horn cruise engage cab (see figure 10h-1) 1. Set multimeter to 200 Ω (ohms) scale. 2. Connect red pos (+) lead to one of the terminals 87, then to the second terminal 87. 3. Connect black neg (–) lead from multimeter to terminal 30. • there should be no continuity on both term...
Page 270
Cruise disengage (brake relay) (see figure 10h-2) 1. Set multimeter to 200 Ω (ohms) scale. 2. Connect black neg (–) lead from multimeter to terminal 30. 3. Connect red pos (+) lead from multimeter to ter- minal 87a. • there should be continuity. If there is no conti- nuity, replace relay. 4. Move th...
Page 271: 10H
Seat delay relay test (see figure 10h-3) 1. Connect white and brown wires to +12 vdc (bat). 2. Leave black wire grounded or connect to bat neg (–) terminal, if relay is removed from machine. 3. Set dmm to 20 vdc. 4. Connect red lead from dmm to yellow wire and black lead to ground neg (–) terminal a...
Page 273: 10I
Fuel solenoid (see figure 10i-1) when the ignition switch is turned to the start posi- tion, the solenoid plunger retracts approximately 1" (25.4 mm). This opens the fuel system. With the plunger retracted there should be a gap between the lever and top. Test solenoid does not retract when ignition ...
Page 274
Adjustment (see figure 10i-2) 1. Disconnect solenoid rod at lever. 2. Turn ignition switch to start momentarily with- out starting engine. This will seat solenoid plunger. Leave ignition switch in run position. 3. Adjust and connect rod at stop lever as necessary so that there is a gap between lever...
Page 275: 10I
Differential lock 4 wheel drive (see figure 10i-3) 1. Energize the solenoid. 2. Notice if the led (light emitting diode) is lit. • if led is lit, proceed with step 3. • if led does not light, check interlock switches and wiring. 3. Remove the hirshman connector from solenoid. 4. Set multimeter to 20...
Page 276
(see figure 10i-4) 7. Set multimeter to 200 Ω (ohms) range. 8. Connect multimeter leads to coil as shown. • coil Ω (ohms) reading should be approximately 10 Ω (ohms) if reading is correct. Valve car- tridge may be faulty. • coil Ω (ohm) reading not to specification, change coil. Electrical system se...
Page 277: 10I
Glow plug solenoid test (see figure 10i-5) 1. Connect a 12 vdc battery to terminals 1 and 2. • there should be an audible “click”. 2. Set multimeter to 200 Ω (ohms) scale. 3. Connect multimeter test leads to terminals 3 and 4. • multimeter reading should be less than 0.5 Ω (ohms). Replace a solenoid...
Page 278
Deck motor valve solenoid (see figure 10i-6) 1. Energize the solenoid. 2. Notice of the led (light emitting diode) is lit. • if led is lit, proceed with step 3. • if led does not light, check interlock switches and wiring. 3. Remove the hirshman connector from solenoid. 4. Set multimeter to 20 vdc r...
Page 279: 10I
(see figure 10i-7) 7. Set multimeter to 200 Ω (ohms) range. 8. Connect multimeter leads to coil as shown. • coil Ω (ohms) reading should be approximately 2.98–3.65 Ω (ohms) if reading is correct. Valve cartridge may be faulty. • coil Ω (ohms) reading is not to specification, change coil. Electrical ...
Page 281: 10J
Circuit breaker test see figure 10j-1 and test circuit breaker as follows: 1. Set multimeter to 200 Ω (ohms) scale. 2. Connect meter leads to terminals as shown. • with the circuit breaker open (tripped) there should be no continuity on the meter scale. 3. Depress button (close). • there should be a...
Page 282
Fuse test see figure 10j-2 and test fuse as follows: 1. Set multimeter to 200 Ω (ohms) scale. 2. Connect meter leads to fuse as shown. • there should be a reading (continuity) on the meter scale. If not, replace fuse. Electrical system section 10j. Circuit breakers and fuse 10j-2 power off on 200m 2...
Page 283: 10K
General repair of gauges and sending units are limited to the replacement of faulty components or wiring. Before replacing a gauge that is not working make sure to perform a voltage check at the gauge wire. If voltage checks okay, a gauge that does not work is faulty except for a water temperature g...
Page 285: 10L
Glow plug test see figure 10l-1 and test a suspected faulty glow plug as follows: 1. Shut down and allow engine to cool. 2. Disconnect glow plug lead wire. 3. Set multimeter to 200 Ω (ohms) scale. 4. Connect one multimeter test lead to glow plug ter- minal and the other to housing. • the multimeter ...
Page 287: 10M
Diode test see figure 10m-1 and test diode as follows: 1. Set meter to scale. 2. Connect meter leads to diode as shown. • there should be a reading (continuity on the meter scale. 3. Reverse the pos (+) and neg (–) test leads. • there should be no continuity. • if continuity registers in both positi...
Page 289
Electrical system section 10n. Wiring diagrams and component location illustration 10n-1 10n fogire 10n-1. Wiring diagram (1 of 2).
Page 290
Electrical system section 10n. Wiring diagrams and component location illustration 10n-3 figure 10n-2. Wiring diagram (1 of 2).
Page 291
Electrical system section 10n. Wiring diagrams and component location illustration 10n-5 10n figure 10n-3. Wiring diagram for figures 10n-1 and 10n-2 (2 of 2).
Page 293
Alternator a b i s x y volt meter ignition switch fuel solenoid h p glow plugs cb7 cb6 cb1 cb4 cb5 cb2 cb3 time delay relay seat switch pto switch parking brake switch glow plug switch front deck switch left deck switch right deck switch 50 amp 50 amp 30 amp 10 amp 30 amp 10 amp 10 amp starter wing ...
Page 294
Alternator a b i s x y volt meter ignition switch fuel solenoid h p glow plugs cb7 cb6 cb1 cb4 cb5 cb2 cb3 time delay relay seat switch pto switch parking brake switch glow plug switch front deck switch left deck switch right deck switch 50 amp 50 amp 30 amp 10 amp 30 amp 10 amp 10 amp starter wing ...
Page 295
A b i s x y volt meter ignition switch fuel solenoid h p glow plugs cb7 cb6 cb1 cb4 cb5 cb2 cb3 time delay relay seat switch pto switch parking brake switch glow plug switch front deck switch left deck switch right deck switch 50 amp 50 amp 30 amp 10 amp 30 amp 10 amp 10 amp starter wing mower switc...
Page 296
Alternator a b i s x y volt meter ignition switch fuel solenoid h p glow plugs cb7 cb6 cb1 cb4 cb5 cb2 cb3 time delay relay seat switch pto switch parking brake switch glow plug switch front deck switch left deck switch right deck switch 50 amp 50 amp 30 amp 10 amp 30 amp 10 amp 10 amp starter wing ...
Page 297
Alternator a b i s x y volt meter ignition switch fuel solenoid h p glow plugs cb7 cb6 cb1 cb4 cb5 cb2 cb3 time delay relay seat switch pto switch parking brake switch glow plug switch front deck switch left deck switch right deck switch 50 amp 50 amp 30 amp 10 amp 30 amp 10 amp 10 amp starter wing ...
Page 298
Electrical system section 10n. Wiring diagrams and component location illustration 10n-7 figure 10n-4. Component location (1 of 3).
Page 299
Electrical system section 10n. Wiring diagrams and component location illustration 10n-9 10n figure 10n-5. Component location (2 of 3).
Page 300
Electrical system section 10n. Wiring diagrams and component location illustration 10n-11 figure 10n-6. Component location (3 of 3).
Page 301: Section 11
11 11a. General . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11a-1 preventive maintenance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1...
Page 303: 11A
Preventive maintenance preventive maintenance (pm) is maintenance per- formed to prevent malfunctions and parts breakdowns by periodically and systematically checking equipment and its systems. Preventive maintenance will cut back corrective main- tenance. Scheduling each machine should be scheduled...
Page 304
11a-2 pmmrs preventive maintenance management record system order blank name _____________________________________ address _________________________________ city ______________________________________ state _____________________ zip ___________ distributor p.O. No. ________________________ check no....
Page 305: 11B
General this section contains lubrication and maintenance charts. For easy reference a 25" x 19" wall chart can be obtained from your jacobsen distributor. Footnotes are found on page 11c-4 and are shown in bold type; example: a, b, etc. Lubrication schedules the following lubrication charts outline...
Page 306
Preventive maintenance section 11b. Lubrication schedules and charts 11b-2 ref. Qty. Description remarks 40 hours (every week) 1 8 a hydraulic lift cylinder ends 2 4 a mower arm pivots 4 8 a wing mower unit pivots 5 8 a caster wheel pivots 6 10 a caster wheel axle mower lubrication chart.
Page 307: 11C
General the following charts summarize maintenance to be per- formed daily, weekly, every two weeks, monthly, every three months, and annually. The maintenance charts give recommended hours of operation between various procedures. Intervals are based on a 40 hour week. Reference numbers are keyed to...
Page 308
Preventive maintenance section 11c. Maintenance schedules 11c-2 ref. Qty. Description engine 25 1 fuel x check. Fuel oil #2 cetane rating 45. 26 fuel filter x clean 100 hours. X replace 500 hours. Fuel lines and clamps x check 50 hours. X replace every 2 years. D engine oil x check. X change first 2...
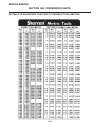
Page 309
Preventive maintenance section 11c. Maintenance schedules 11c-3 11c footnotes a use pressure gun grease (nlgi grade 0). Apply with grease gun. B use hand grease gun (nlgi grade 0). C system capacity: 20 gallons. Jacobsen hydraulic oil. Part no. 502696 carton containing two 2-1/2 gallons (9.5 liters)...
Page 311: Section 12
12 12a. Repair and service tools and materials . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12a-1 12b. Failure analysis . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12b-1 12c. Genera...
Page 313: 12A
Tools required: standard automotive hand tools, including driving tools, and seal spreaders; blade grinder. Cleaning materials: stoddard or equivalent solvent. Detergent and water. Lubricants: non-metallic additive wheel bearing grease (eg. Sunray dx 692 or enco fibrox 280). Grease gun grease (eg. S...
Page 315: 12B
Attachments section 12b. Failure analysis 12b-1 problem probable cause remedy 1. Blades do not turn. A. Blades jammed. A. Clean underside of deck. B. Spindle bearing failure. B. Check bearings, repair (section 12d). C. Drive assembly malfunctioning. C. Inspect, repair (section 12d). D. Drive motor m...
Page 317: 12C
Preparation for repair thoroughly clean decks prior to removal, disassembly and/or repair. Coat bare metal parts with light oil to prevent rust and corrosion. Decks are exposed to water, grass clippings, sand, corrosive fertilizers, and foreign objects. It may be necessary to use bearing pullers and...
Page 319: 12D
Pivot housing and push arms removal and installation of the pivot housings and push arms are illustrated in figure 12d-1. Attachments section 12d. Mowers 12d-1 12d figure 12d-1. Pivot housings and push arms.
Page 320
Carrier assembly repair of the carrier assemblies consist of replacing bushings and worn or damaged components, see fig- ure 12d-2. Attachments section 12d. Mowers 12d-2 figure 12d-2. Carrier assembly.
Page 321: 12D
Deck fittings removal and installation of deck fittings are illustrated in figure 12d-3. Attachments section 12d. Mowers 12d-3 12d figure 12d-3. Deck fittings.
Page 322
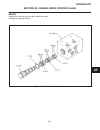
Blade spindle assembly general there are 7 motors, one for each blade on the hr111. Motor rotation is identified in two ways, first: by their position on the decks, see figure 12d-4 and second: by the code letter which is part of the model number, see figure 12d-5. In this section service of the mot...
Page 323: 12D
Attachments section 12d. Mowers 12d-5 12d figure 12d-5. Motor rotation by code letter.
Page 324
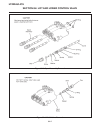
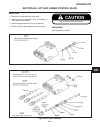
Disassembly (see figure 12d-6) 1. Remove blade and adapter. 2. Remove square drive key. 3. Remove shaft protector. 4. Remove large lock ring. 5. Install blade with adapter. 6. Pull spindle shaft and guide from housing. Note a suction will be felt when pulling the guide from the housing. The suction ...
Page 325: 12E
General every 50 hours examine the cutter bars to make sure they are in good operating condition. See figure 12e-1. 1. The blades should follow along a straight line and should not be bent. Replace all bent blades. The damage may include a microscopic crack which could grow, allowing a piece of the ...
Page 326
Blade installation (see figure 12e-4) when installing blades make sure blade is positioned correctly. Torque center blade mounting screw to 75 ft-lbs. (102 n.M) and the two blade mounting adapter screws to 35–40 ft-lbs. (47–54 n.M). Attachments section 12e. Blades 12e-2 figure 12e-4. Blade installat...
Page 327: 12F
Repair of the caster wheels consist of replacing bush- ings and worn or damaged components. See figure 12f-2. Attachments section 12f. Caster wheels 12f-1 12f figure 12f-1. Caster wheels.
Page 328
Attachments section 12f. Caster wheels 12f-2 figure 12f-2. Caster wheel repair.
Page 329: Section 13
13 this section intentionally left blank section 13 options.
Page 331: Section 14
14 14a. Precaution decal locations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14a-1 tractor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14a...
Page 333: 14A
Miscellaneous section 14a. Precaution decal locations 14a-1 14a tractor part no. 964907 1 part no. 365339 2 part no. 365919 3.
Page 334
Miscellaneous section 14a. Precaution decal locations 14a-2 part no. 361175 4 part no. 861883 9 part no. 339237 5 part no. 365956 6 part no. 339460 7 part no. 363134 8 part no. 366160 10 part no. 366527 11.
Page 335: 14A
Miscellaneous section 14a. Precaution decal locations 14a-3 14a mower part no. J-t338141 1.
Page 337: 14B
Miscellaneous section 14b. Conversion charts 14b-1 14b millimeters to decimals.
Page 338
Miscellaneous section 14b. Conversion charts 14b-2 decimals to millimeters, fractions to decimals to millimeters.
Page 339: 14B
Miscellaneous section 14b. Conversion charts 14b-3 14b to convert into divide by linear miles kilometers 1.609 measurement yards meters 0.9144 feet meters 0.3048 feet centimeters 30.48 inches meters 0.0254 inches centimeters 2.54 inches millimeters 25.4 area square miles square kilometers 2.59 squar...