- DL manuals
- Keithley
- Switch
- 2700
- User Manual
Keithley 2700 User Manual - General Information
1-2
Getting Started
Model 2700 Multimeter/Switch System User’s Manual
General information
Warranty information
Warranty information is located at the front of this manual. Should your Model 2700
require warranty service, contact the Keithley representative or authorized repair facility in
your area for further information. When returning the instrument for repair, be sure to fill
out and include the service form at the back of this manual to provide the repair facility
with the necessary information.
NOTE
The service form requires the serial number of the Model 2700. The serial num-
ber label is located inside the unit on the bottom panel. The serial number can
be viewed by removing the slot covers and/or switching modules from the main-
frame.
WARNING
Before removing (or installing) switching modules, make sure
to turn off the Model 2700 and disconnect the line cord. Also,
remove any other external power connected to the instrument
or switching module(s).
The serial number can also be read from the front panel by selecting the SNUM
item of the SETUP menu. Press SHIFT and then SETUP to access the menu. For
remote operation, the serial number can be read using the *IDN? command (see
Section 12 for details).
Contact information
Worldwide phone numbers are listed at the front of this manual. If you have any questions,
please contact your local Keithley representative or call a Keithley Application Engineer at
1-800-348-3735 (U.S. and Canada only).
Safety symbols and terms
The following symbols and terms may be found on the instrument or used in this manual:
The
symbol on an instrument indicates that the user should refer to the operating
instructions located in the manual.
The
symbol on the instrument shows that high voltage may be present on the termi-
nal(s). Use standard safety precautions to avoid personal contact with these voltages.
The
WARNING
heading used in this manual explains dangers that might result in per-
sonal injury or death. Always read the associated information very carefully before per-
forming the indicated procedure.
The
CAUTION
heading used in this manual explains hazards that could damage the
instrument. Such damage may invalidate the warranty.
!
Summary of 2700
Page 1
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual a g r e a t e r m e a s u r e o f c o n f i d e n c e test equipment depot - 800.517.8431 - 99 washington street melrose, ma 02176 - testequipmentdepot.Com.
Page 2: Warranty
Warranty keithley instruments, inc. Warrants this product to be free from defects in material and workmanship for a period of 3 years from date of shipment. Keithley instruments, inc. Warrants the following items for 90 days from the date of shipment: probes, cables, rechargeable batteries, diskette...
Page 4
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual ©2001, keithley instruments, inc. All rights reserved. Cleveland, ohio, u.S.A. Sixth printing, november 2002 document number: 2700-900-01 rev. F.
Page 5: Manual Print History
Manual print history the print history shown below lists the printing dates of all revisions and addenda created for this manual. The revision level letter increases alphabetically as the manual undergoes sub- sequent updates. Addenda, which are released between revisions, contain important change i...
Page 6: Afety Precautions
The following safety precautions should be observed before using this product and any associated instrumentation. Although some instruments and accessories would normally be used with non-hazardous voltages, there are situations where hazardous conditions may be present. This product is intended for...
Page 7
Bles or jumpers, installing or removing switching cards, or making internal changes, such as installing or removing jumpers. Do not touch any object that could provide a current path to the common side of the circuit under test or power line (earth) ground. Al- ways make measurements with dry hands ...
Page 8: Table of Contents
Table of contents 1 getting started general information ................................................................... 1-2 warranty information .......................................................... 1-2 contact information ............................................................ 1-2 saf...
Page 9
Remote programming information ........................................... 1-25 quick start exercises ................................................................. 1-25 basic dmm measurements — front panel inputs ............. 1-26 exercise 1 — basic dmm measurements ................. 1-27 closi...
Page 10: Basic Dmm Operation
Identifying installed modules and viewing closed channels .... 2-25 card menu ...................................................................... 2-25 switching module queries (remote operation) .................. 2-27 *opt? ...........................................................................
Page 11
Resistance measurements ( Ω 2 and Ω 4) .................................... 3-16 connections ....................................................................... 3-17 front panel inputs ....................................................... 3-17 model 7700 switching module .........................
Page 12
Remote programming for basic measurements ........................ 3-38 basic measurement commands ......................................... 3-38 basic measurement programming examples .................... 3-44 example #1 — continuous triggering ........................ 3-44 example #2 — one-shot tr...
Page 13
Remote programming — range ........................................... 4-3 range commands ......................................................... 4-3 range programming examples ..................................... 4-5 digits ...........................................................................
Page 14: Buffer
Ratio and channel average ........................................................ 5-15 basic operation .................................................................. 5-16 scanning .................................................................... 5-17 remote programming — ratio and channel av...
Page 15: Triggering
Saving the configured scan ......................................... 7-12 scan reset ........................................................................... 7-13 simple scan ....................................................................... 7-14 advanced scan ..................................
Page 16: Limits and Digital I/o
External triggering example ................................................ 8-9 model 2700 ................................................................ 8-10 model 7002 ................................................................ 8-10 external triggering with bnc connections ...................
Page 17
Gpib standards .................................................................. 10-4 selecting gpib and setting primary address ..................... 10-4 gpib connections .............................................................. 10-5 general bus commands ........................................
Page 18: Status Structure
Rs-232 interface operation .................................................... 10-18 sending and receiving data ............................................. 10-18 baud rate ......................................................................... 10-18 signal handshaking (flow control) ..............
Page 19: Common Commands
12 common commands description ................................................................. 12-3 description ................................................................. 12-4 description ................................................................. 12-6 13 scpi signal oriented measurem...
Page 20: Model 7700 Connection Guide
B model 7700 connection guide card configuration — schematic ............................................... B-2 connections and wiring ............................................................ B-4 screw terminals .................................................................. B-5 wiring proce...
Page 21: Measurement Considerations
Continuous measurement mode ....................................... D-12 scanning ........................................................................... D-13 e measurement considerations measurement considerations ..................................................... E-2 thermoelectric potentia...
Page 22: List of Illustrations
List of illustrations 1 getting started figure 1-1 model 2700 front panel .......................................................... 1-9 figure 1-2 model 2700 rear panel ......................................................... 1-12 figure 1-3 power module ..............................................
Page 23: Buffer
Figure 3-5 dci and aci connections using model 7700 switching module .............................................................................3-15 figure 3-6 Ω 2 and Ω 4 connections for front panel inputs ..................... 3-17 figure 3-7 Ω 2 and Ω 4 connections for model 7700 switching modu...
Page 24: Limits and Digital I/o
9 limits and digital i/o figure 9-1 default limits ......................................................................... 9-2 figure 9-2 digital i/o port ...................................................................... 9-5 figure 9-3 digital i/o port simplified schematic ......................
Page 25: Measurement Considerations
D signal processing sequence and data flow figure d-1 basic signal processing ......................................................... D-2 figure d-2 signal processing using instrument features ......................... D-3 figure d-3 signal processing using ratio or channel average .............. ...
Page 26: List of Tables
List of tables 1 getting started table 1-1 model 77xx series switching modules ................................. 1-7 table 1-2 fuse ratings .......................................................................... 1-15 table 1-3 display commands ........................................................
Page 27: Buffer
6 buffer table 6-1 buffer commands ................................................................... 6-9 7 scanning table 7-1 scanning commands ............................................................. 7-28 table 7-2 external trigger scan example .............................................. ...
Page 28: Scpi Reference Tables
15 scpi reference tables table 15-1 calculate command summary .......................................... 15-3 table 15-2 display command summary ............................................... 15-6 table 15-3 format command summary ............................................... 15-7 table 15-4 rout...
Page 30
1 getting started quick start — of the following section topics, three can be used immediately to quickly acquaint yourself with fundamental instrument operations. Use qs1 to familiarize your- self with front panel controls, use qs2 to power-up the instrument and finally, use qs3 to perform exercise...
Page 31: General Information
1-2 getting started model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual general information warranty information warranty information is located at the front of this manual. Should your model 2700 require warranty service, contact the keithley representative or authorized repair facility in your area ...
Page 32: Inspection
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual getting started 1-3 inspection model 2700 was carefully inspected electrically and mechanically before shipment. After unpacking all items from the shipping carton, check for any obvious signs of physical damage that may have occurred during transit....
Page 33
1-4 getting started model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual model 7703 — this differential multiplexer provides 32 channels of 2-pole input, or 16 channels of 4-pole input. Model 7705 — this control module provides 40 independent 1-pole switching (spst) channels that are isolated from the ...
Page 34: Model 2700 Features
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual getting started 1-5 rack mount kits model 4288-1 single fixed rack mount kit — mounts a single model 2700 in a standard 19-inch rack. Model 4288-2 side-by-side rack mount kit — mounts two instruments (models 182, 428, 486, 487, 2000, 2001, 2002, 2010...
Page 35: Plug-In Switching Modules
1-6 getting started model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual • buffer — store up to 55,000 readings in the internal buffer. • limits — two sets of high and low reading limits to test devices. • digital i/o port — five digital limit test output lines to control external circuitry. The digita...
Page 36
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual getting started 1-7 table 1-1 model 77xx series switching modules model 7700 model 7701 model 7702 model 7703 model 7705 2-pole operation 4-pole operation 1-pole operation measure volts measure amps measure ohms cold junction for thermo- couples rela...
Page 37: Pseudocards
1-8 getting started model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual pseudocards using remote programming, you can assign a pseudocard to an empty switching module slot. With a pseudocard installed, the model 2700 will operate as if the switching module is installed in the model 2700. This feature ...
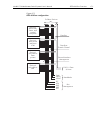
Page 38
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual getting started 1-9 figure 1-1 model 2700 front panel note most keys provide a dual function or operation. The nomenclature on a key indi- cates its unshifted function/operation which is selected by pressing the key. Nomenclature (in blue) above a ke...
Page 39
1-10 getting started model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual middle row unshifted extrig selects external triggering (front panel, bus, trigger link) as the trigger source. Trig triggers a measurement when in external triggering (ex trig). Store sets the number of readings to store and ena...
Page 40
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual getting started 1-11 4 display annunciators: * (asterisk) readings being stored in buffer. ↔ (more) indicates additional selections are available. ))) (speaker) beeper on for continuity or limits testing. Digital input/output or analog output active ...
Page 41: Rear Panel Summary
1-12 getting started model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual rear panel summary the rear panel of model 2700 is shown in figure 1-2 . As shown, a slot cover is installed on slot 2. Warning slot covers must be installed on unused slots to prevent personal con- tact with high voltage circuit...
Page 42: Power-Up
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual getting started 1-13 power-up line power connection follow the procedure below to connect the model 2700 to line power and turn on the instrument. 1. Check to see that the line voltage indicated in the window of the fuse holder assem- bly ( figure 1-...
Page 43: Line Frequency
1-14 getting started model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual figure 1-3 power module line frequency the model 2700 will operate at line frequencies from 45hz to 66hz, and 360hz to 440hz. There are no user-settings for line frequency. It is automatically sensed at power-up. The following co...
Page 44
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual getting started 1-15 setting line voltage and replacing fuse a rear panel fuse located next to the ac receptacle protects the power line input of the instrument. If the line voltage setting needs to be changed or the line fuse needs to be replaced, p...
Page 45: Power-Up Sequence
1-16 getting started model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual power-up sequence on power-up, the model 2700 performs self-tests on its eprom and ram and momen- tarily lights all segments and annunciators. If a failure is detected, the instrument momen- tarily displays an error message and t...
Page 46: Display
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual getting started 1-17 remote programming the following command controls keyclick: system:kclick ' enable or disable keyclick. Where: = on or off note keyclick on is the factory, *rst, and system:preset default. Display readings are displayed in engine...
Page 47
1-18 getting started model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual display:text:data define text message this command defines the text message for display. A message can be as long as 12 char- acters. A space counts as a character. Excess message characters results in an error. The characters mus...
Page 48: Defaults and User Setups
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual getting started 1-19 defaults and user setups model 2700 can be restored to one of two default setup configurations (factory or *rst), or four user-saved (sav0, sav1, sav2, or sav3). As shipped from the factory, model 2700 powers up to the factory (f...
Page 49: Saving and Restoring Setups
1-20 getting started model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual saving and restoring setups saving a user setup 1. Configure model 2700 for the desired measurement application. 2. Press shift and then save to access the save setup menu. 3. Press to place the cursor on the present setup (sav0,...
Page 50
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual getting started 1-21 table 1-4 default settings setting factory *rst set diff auto channel configuration no (off) no effect ✓ autozero on on buffer no effect no effect auto clear yes (on) no effect ✓ channel average off off closed channels none none ...
Page 51
1-22 getting started model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual setting factory *rst set diff limits off off lo limit 1 -1 -1 hi limit 1 +1 +1 lo limit 2 -2 -2 hi limit 2 +2 +2 line synchronization off off math mx+b off off scale factor 1.0 1.0 offset 0.0 0.0 units “x” “x” percent off off ref...
Page 52
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual getting started 1-23 setting factory *rst set diff rs-232 off off baud rate no effect no effect flow control xonxoff xonxoff terminator no effect no effect scanning disabled disabled auto scan no (off) no effect ✓ type (simple or advanced) no effect ...
Page 53
1-24 getting started model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual remote programming — default and user setups default and user setup commands are listed in table 1-5 . Note the system:preset and *rst defaults are listed in the scpi tables in section 15 . Programming example *sav 2 ' save prese...
Page 54: Quick Start Exercises
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual getting started 1-25 remote programming information remote programming information is integrated with front panel operation throughout this manual. Programming commands are listed in tables, and additional information that per- tains exclusively to r...
Page 55
1-26 getting started model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual basic dmm measurements — front panel inputs note see section 3 for details on basic dmm operation. The model 2700 is shipped from the factory to power-up to factory defaults. The instru- ment powers up to a setup that continuousl...
Page 56
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual getting started 1-27 exercise 1 — basic dmm measurements the exercise in table 1-6 measures acv on the 10v range and stores 15 readings in the buffer. Table 1-6 exercise 1—measure ac volts - store readings in buffer front panel operation command sequ...
Page 57
1-28 getting started model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual closing and opening channels — system channel operation note see section 2 for details on closing and opening switching module channels. Note the following discussion assumes a multiplexing switching module (i.E., model 7700) is ...
Page 58
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual getting started 1-29 figure 1-5 connection to dmm for 4-wire function (system channel 106 closed) note switching module channels can also be controlled using multiple channel opera- tion. This allows individual control of all module channels (switche...
Page 59
1-30 getting started model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual figure 1-6 front panel keys to close and open system channels for remote programming, the following three commands are used for basic system opera- tion to open and close input channels: route:close ' close specified system chann...
Page 60: Simple Scanning
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual getting started 1-31 exercise 2 — closing and opening channels (system channel operation) the exercise in table 1-7 demonstrates a sequence to close and open channels of a model 7700 installed in slot 1 of the mainframe. Simple scanning note see sect...
Page 61
1-32 getting started model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual for scan, the reading count also determines the number of scans to perform and is best explained by an example. Assume there are 10 channels in the scan list (i.E., 101 through 110). If you set the reading count to 10 or less, on...
Page 62
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual getting started 1-33 for remote programming, the following commands are used for simple scanning: route:scan ' define scan list*. Trigger:count ' specify number of scans (1 to 11000 or infinity). Sample:count ' specify number of channels to scan (1 t...
Page 63
1-34 getting started model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual trigger and return readings — remote programming there are several commands used to trigger and return readings. The proper commands and sequence to use depend on the trigger state (continuous or non-continuous) and what you are ...
Page 64
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual getting started 1-35 figure 1-8 exercise 4 — trigger and return a single reading init:cont off trig:coun 1 samp:coun 1 place 2700 in non-continuous trigger state set 2700 to perform one measurement 1. If a math function (mx+b, percent or 1/x) is enab...
Page 65
1-36 getting started model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual figure 1-9 exercise 5 — trigger and return multiple readings init:cont off trig:coun 1 samp:coun x read? Init fetch? Place 2700 in non-continuous trigger state set 2700 to perform “x” number of measurements (x = 2 to 110000) 2. I...
Page 66
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual getting started 1-37 figure 1-10 exercise 6 — return a single reading (continuous triggering) samp:coun 1 init:cont on data? Data:fresh? Fetch? Calc:data? Place 2700 in continuous trigger state. Or or return basic reading 2, 3 return result of math c...
Page 67
1-38 getting started model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual.
Page 68
2 closing and opening switching module channels • close/open overview — summarizes the two operating modes to control switch- ing modules: system channel operation and multiple channel operation. • switching module installation and connections — explains how to install a switching module (or pseudoc...
Page 69: Close/open Overview
2-2 close/open switching module channels model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual close/open overview note this section covers basic close/open operations for switching module channels. It also covers the operating characteristics that are unique to the model 7700 switching module. There ar...
Page 70: Module Installation
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual close/open switching module channels 2-3 switching module installation and connections in order to exercise close/open operations explained in this section, a switching module (or pseudocard) must be installed in the mainframe. A switching module can...
Page 71: Connections
2-4 close/open switching module channels model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual connections warning connection information for switching modules is intended for qualified service personnel. Do not attempt to connect dut or external circuitry to a switching module unless qualified to do so...
Page 72: Pseudocards
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual close/open switching module channels 2-5 pseudocards using remote programming, you can assign a pseudocard to an empty switching module slot. With a pseudocard installed, the model 2700 will operate as if the switching module is installed in the mode...
Page 73: System Channel Operation
2-6 close/open switching module channels model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual system channel operation the system channel is a closed measurement channel that is internally connected to the internal dmm input of the model 2700. The system channel number is displayed on the model 2700. F...
Page 74: 2-Wire Functions
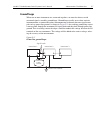
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual close/open switching module channels 2-7 2-wire functions figure 2-1 shows an example of how the system channel is connected to the dmm input of the model 2700. Assume a model 7700 switching module is installed in slot 1 of the mainframe. When channe...
Page 75
2-8 close/open switching module channels model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual 4-wire functions (paired channels) a 4-wire function, such as Ω 4, requires that another measurement channel be paired to the system channel. For example, if the switching module has 20 measurement channels, c...
Page 76
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual close/open switching module channels 2-9 controlling the system channel when a measurement channel is closed, a previous system channel (and, for a 4-wire func- tion, its paired channel) is first opened. The closed measurement channel becomes the sys...
Page 77
2-10 close/open switching module channels model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual close key (single menu option) the single menu option for the close key can be used to select a measurement chan- nel as the system channel ( figure 2-4 ). Perform the following steps to select the system cha...
Page 78
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual close/open switching module channels 2-11 open key (all menu option) the all menu option of the open key opens all channels for all switching modules installed in the model 2700 ( figure 2-5 ). For example, if a model 7700 switching module is install...
Page 79
2-12 close/open switching module channels model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual reference: a. Route:close this command functions the same as the front panel close key (single menu option) to select the system channel. Only one measurement channel can be specified in the . Trying to close...
Page 80: Multiple Channel Operation
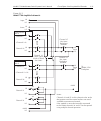
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual close/open switching module channels 2-13 remote programming example (system channel operation) the following example assumes a model 7700 installed in slot 1, and the Ω 4 function of the model 2700 is selected. This command sequence connects channel...
Page 81
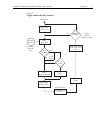
2-14 close/open switching module channels model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual controlling multiple channels warning when using multiple channel operation, you must be very careful when switching hazardous voltages. If you inadvertently close the wrong channel(s), you could create a sho...
Page 82
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual close/open switching module channels 2-15 close key (multi menu option) the multi menu option for the close key can be used to close any individual channel in the mainframe ( figure 2-6 ). Perform the following steps to close a channel: note channels...
Page 83
2-16 close/open switching module channels model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual 3. Press enter to display the prompt to open a channel (open mlt:xxx). 4. Using , , , and , key in the three-digit channel you want to select. 5. Press enter to open the channel. Note if the channel you open ...
Page 84
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual close/open switching module channels 2-17 reference: a. Route:multiple:close this command functions like the front panel close key (multi menu option) to close channels. When you send this command to close the channels specified in the , only those l...
Page 85
2-18 close/open switching module channels model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual remote programming example (multiple channel operation) the following example assumes a model 7700 installed in slot 1. This command sequence connects channel 101 to channel 111 (through channel 123). Note th...
Page 86
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual close/open switching module channels 2-19 anomaly #2 example — opening the paired channel assume 4-wire connections to a 1k Ω resistor using channels 1 and 11 of the model 7700 switching module. Also assume the Ω 4 function is selected. The following...
Page 87
2-20 close/open switching module channels model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual dual independent multiplexers using multiple channel operation, any multiplexer switching module can be configured as two independent multiplexers. For example, the model 7700 is normally used as a single 1 ×...
Page 88
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual close/open switching module channels 2-21 dual multiplexer application this application demonstrates how to use the model 7700 as a dual multiplexer to bias and measure 10 dut. An external source powers dut, while the dmm of the model 2700 measures t...
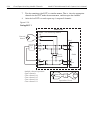
Page 89
2-22 close/open switching module channels model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual figure 2-9 dual multiplexer application connections ch 1 dut 1 h1 lo ch 2 dut 2 h1 lo ch 10 dut 10 h1 lo ch 11 h1 lo ch 12 h1 lo ch 20 h1 lo ch 23 (closed) ch 25 ch 24 h1 lo external source model 7700 switchi...
Page 90
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual close/open switching module channels 2-23 test procedure: notes the following test procedure assumes a model 7700 switching module installed in slot 1 of the mainframe. The procedure assumes that the instrument is operating in the continuous mea- sur...
Page 91
2-24 close/open switching module channels model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual 7. Test the remaining eight dut in a similar manner. That is, close the appropriate channels for the dut, make the measurement, and then open the channels. 8. After the last dut is tested, repeat step 1 to op...
Page 92: Viewing Closed Channels
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual close/open switching module channels 2-25 identifying installed modules and viewing closed channels on power-up, the model numbers of installed switching modules are displayed briefly. If a model 7700, 7701, 7702, 7703, 7705, 7708, or 7709 switching ...
Page 93
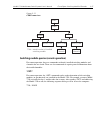
2-26 close/open switching module channels model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual slotx: 77xx — use to configure the switching module in slot x (where x = 1 or 2). If configuration is not necessary, the instrument will exit from the menu when enter is pressed. Note for switching modules th...
Page 94
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual close/open switching module channels 2-27 figure 2-11 card menu tree switching module queries (remote operation) for remote operation, there are commands to identify installed switching modules and channels that are closed. There are also commands to...
Page 95
2-28 close/open switching module channels model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual route:close? Route:multiple:close? Route:multiple:close:state? These query commands are used to determine closed switching module channels. Rout:clos? Is used to return a list of closed measurement channels i...
Page 96: Relay Closure Count
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual close/open switching module channels 2-29 relay closure count the model 2700 keeps an internal count of the number of times each module relay has been closed. The total number of relay closures are stored in eeprom on the card. This count will help y...
Page 97: Reading Relay Closure Count
2-30 close/open switching module channels model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual reading relay closure count to determine the closure count of specific channels, send this query via remote: route:close:count? Here, is the summary of channels. For example, to determine the closure count of...
Page 98: Model 7700 Switching Module
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual close/open switching module channels 2-31 model 7700 switching module note connection and wiring procedures for the model 7700 are to be performed by qualified service personnel. This information is provided in appendix b (model 7700 connection guide)...
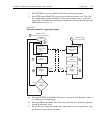
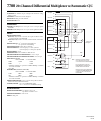
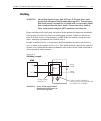
Page 99: Schematic Diagram
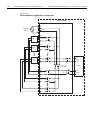
2-32 close/open switching module channels model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual with a 4-wire function/operation selected, channels are paired as follows: schematic diagram the simplified schematic diagram of the model 7700 is shown in figure 2-12 . Channels 1 through 20 are used for all...
Page 100
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual close/open switching module channels 2-33 figure 2-12 model 7700 simplified schematic notes: cold junction ref x3 channel 1 hi lo channel 10 hi lo (channels 2–9) channel 11 hi lo channel 20 hi lo (channels 12–19) channel 21 hi lo channel 22 hi lo amps...
Page 101
2-34 close/open switching module channels model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual.
Page 102
3 basic dmm operation • dmm measurement capabilities — summarizes the measurement capabilities of the model 2700 and covers maximum signal levels for switching modules. • high energy circuit safety precautions — provides safety information when per- forming measurements in high energy circuits. • pe...
Page 103: Dmm Measurement Capabilities
3-2 basic dmm operation model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual dmm measurement capabilities note accuracy specifications for all measurement functions and the model 7700 switching module are provided in appendix a . The dmm of the model 2700 can make the following measurements: dcv — dc vo...
Page 104
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual basic dmm operation 3-3 high energy circuit safety precautions to optimize safety when measuring voltage in high energy distribution circuits, read and use the directions in the following warning. Warning dangerous arcs of an explosive nature in a hi...
Page 105: Performance Considerations
3-4 basic dmm operation model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual performance considerations warm-up after the model 2700 is turned on, it must be allowed to warm up for at least two hours to allow the internal temperature to stabilize. If the instrument has been exposed to extreme temperatu...
Page 106
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual basic dmm operation 3-5 lsync (line cycle synchronization) synchronizing a/d conversions with the frequency of the power line increases common mode and normal mode noise rejection. When line cycle synchronization is enabled, the measurement is initia...
Page 107
3-6 basic dmm operation model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual remote programming — autozero and lsync autozero and lsync commands the commands to control display resolution (digits) are listed in table 3-1 . Table 3-1 autozero and lsync commands commands description default autozero comm...
Page 108: Channel List Parameter ()
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual basic dmm operation 3-7 channel list parameter () channels of one or more switching modules installed in the model 2700 can be scanned. Each scan channel can have its own unique setup. For example, a channel could be set to measure dcv on the 10v ran...
Page 109: Dcv Input Divider
3-8 basic dmm operation model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual voltage measurements (dcv and acv) the model 2700 can make dcv measurements from 0.1µv to 1000v and acv measure- ments from 0.1µv to 750v rms, 1000v peak. Dcv input resistance: 100v and 1000v ranges: 10m Ω 100mv, 1v, and 10v r...
Page 110
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual basic dmm operation 3-9 front panel input when using the front panel input terminals, connect the test leads to the input hi and lo terminals as shown in figure 3-2 . Figure 3-2 dcv and acv connections using front panel inputs input impedance = 1m Ω ...
Page 111
3-10 basic dmm operation model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual model 7700 switching module connections for the model 7700 switching module are shown in figure 3-3 . For basic dcv and acv measurements ( figure 3-3 a and b), channels 1 through 20 can be used. Ratio and channel average calc...
Page 112: Volts Measurement Procedure
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual basic dmm operation 3-11 volts measurement procedure note make sure the inputs switch is in the correct position. To use front panel inputs, it must be in the “f” (out) position. For switching modules, it must be in the “r” (in) position. 1. If a swi...
Page 113: Crest Factor
3-12 basic dmm operation model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual crest factor ac voltage (and current) accuracies are affected by the crest factor of the waveform, which is the ratio of the peak value to the rms value. Table 3-2 lists the fundamental fre- quencies at which the correspondin...
Page 114
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual basic dmm operation 3-13 thermal emfs thermal emfs (thermoelectric potentials) are generated by temperature differences between the junctions of dissimilar metals. These can be large compared to the signal that the model 2700 can measure. Thermal emf...
Page 115: Connections
3-14 basic dmm operation model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual current measurements (dci and aci) the model 2700 can make dci measurements from 10na to 3a and aci measurements from 1µa to 3a rms. Note see the previous discussion about crest factor in “voltage measurements (dcv and acv),”...
Page 116: Amps Measurement Procedure
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual basic dmm operation 3-15 model 7700 switching module connections for the model 7700 switching module are shown in figure 3-5 . Note that only channels 21 and 22 can be used for current measurements. Figure 3-5 dci and aci connections using model 7700...
Page 117: Resistance Measurements (
3-16 basic dmm operation model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual amps fuse replacement (front panel amps input) warning make sure the instrument is disconnected from the power line and other equipment before replacing the amps fuse. 1. Turn off the power and disconnect the power line and t...
Page 118: Connections
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual basic dmm operation 3-17 connections note when using the front panel inputs, the inputs switch must be in the “f” (out) position. For switching modules, it must be in the “r” (in) position. Front panel inputs connections for resistance measurements a...
Page 119
3-18 basic dmm operation model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual model 7700 switching module connections for the switching module are shown in figure 3-7 . As shown in figure 3-7 a, each of the 20 channels can be used to perform Ω 2 measurements. For Ω 4 measurements, a channel pair is use...
Page 120
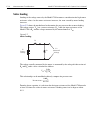
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual basic dmm operation 3-19 shielding to achieve a stable reading, it helps to shield resistances greater than 100k Ω . As shown in figure 3-6 and figure 3-7 , place the resistance in a shielded enclosure and connect the shield to the input low terminal...
Page 121: Offset-Compensated Ohms
3-20 basic dmm operation model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual 6. Observe the displayed reading. If the “overflow” message is displayed, select a higher range until a normal reading is displayed (or press auto for autorang- ing). For manual ranging, use the lowest possible range for the ...
Page 122
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual basic dmm operation 3-21 enabling/disabling offset-compensated ohms offset-compensated ohms is enabled by pressing shift and then ocomp. When enabled, the ocomp annunciator is on. Offset-compensated ohms is disabled by again pressing shift and then o...
Page 123: Temperature Measurements
3-22 basic dmm operation model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual temperature measurements the model 2700 can measure temperature using thermocouples, thermistors, and 4-wire rtds. When deciding which temperature sensor to use, keep in mind that the thermocou- ple is the most versatile, the...
Page 124
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual basic dmm operation 3-23 reference junctions a reference junction is the cold junction in a thermocouple circuit which is held at a sta- ble, known temperature. It is at the cold junction where dissimilar wire connections must be made. As long as the...
Page 125: Thermistors
3-24 basic dmm operation model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual external reference junction for switching modules that do not have built-in sensors to measure temperature, each module can use a thermistor or 4-wire rtd to acquire the reference temperature. Connect a thermistor to channel ...
Page 126: 4-Wire Rtds
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual basic dmm operation 3-25 4-wire rtds for 4-wire rtds, the temperature measurement range is -200°c to 630°c (0.01°c resolu- tion). Rtd types that are supported include d100, f100, pt385, and pt3916. A user type is available to modify rtd parameters, s...
Page 127
3-26 basic dmm operation model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual with open thermocouple detection disabled, the model 2700 can calculate the average temperature of two thermocouple channels using channel average (see section 5 for details). As shown in figure 3-8 d, one thermocouple is con...
Page 128
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual basic dmm operation 3-27 table 3-3 color codes — thermocouple wires t/c type positive (+) negative (-) t/c type positive (+) negative (-) j u.S. White red e u.S. Purple red british yellow blue british brown blue din red blue din red black japanese re...
Page 129
3-28 basic dmm operation model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual thermistor connections a thermistor can be connected directly to the front panel inputs or to any of the 20 input channels of the model 7700 switching module as shown in figure 3-9 . Figure 3-9 thermistor connections 4-wire r...
Page 130
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual basic dmm operation 3-29 temperature measurement configuration the model 2700 is configured to measure temperature from the temperature measurement configuration menu. Use the following general rules to navigate through the menu structure: • press shi...
Page 131
3-30 basic dmm operation model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual thermistor temperature measurement configuration the steps to configure thermistor measurements are provided in table 3-5 . After pressing shift and then sensor, the menu starts at step 1 to select measurement units. Each time...
Page 132
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual basic dmm operation 3-31 4-wire rtd temperature measurement configuration the alpha, beta, delta, and Ω at 0°c parameters for the five basic rtd types are provided in table 3-6 . Note that these parameters can be modified using remote programming. The...
Page 133
3-32 basic dmm operation model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual temperature measurement procedure note make sure the inputs switch is in the correct position. To use front panel inputs, it must be in the “f” (out) position. For switching modules, it must be in the “r” (in) position. 1. If...
Page 134: Trigger Level
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual basic dmm operation 3-33 frequency and period measurements the model 2700 can make frequency measurements from 3hz to 500khz on voltage ranges of 100mv, 1v, 10v, 100v, and 750v. Period (1 / frequency) measurements can be taken from 2µs to 333ms on th...
Page 135: Connections
3-34 basic dmm operation model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual connections note when using the front panel inputs, the inputs switch must be in the “f” (out) position. For switching modules, it must be in the “r” (in) position. Front panel input when using the front panel input terminals...
Page 136
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual basic dmm operation 3-35 frequency and period measurement procedure note make sure the inputs switch is in the correct position. To use front panel inputs, it must be in the “f” (out) position. For switching modules, it must be in the “r” (in) positi...
Page 137: Continuity Testing
3-36 basic dmm operation model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual continuity testing the model 2700 can test continuity using the 2-wire 1k Ω range. After selecting continu- ity, you will be prompted to enter the threshold resistance level (1 to 1000 Ω ). When the measured circuit is below ...
Page 138: Continuity Testing Procedure
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual basic dmm operation 3-37 continuity testing procedure note make sure the inputs switch is in the correct position. To use front panel inputs, it must be in the “f” (out) position. For switching modules, it must be in the “r” (in) position. 1. Apply t...
Page 139: Basic Measurement Commands
3-38 basic dmm operation model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual remote programming for basic measurements basic measurement commands note when measurements are performed, the readings are fed to other enabled pro- cessing operations. Appendix d explains “data flow (remote operation)” and t...
Page 140
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual basic dmm operation 3-39 commands 1 description default ref temp function [sense[1]] optional root command. :temperature:transducer [, ] select temperature transducer; = tcouple, frtd, or thermistor. Tc :temperature:tcouple:type [, ] select t/c type;...
Page 141
3-40 basic dmm operation model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual commands 1 description default ref period function :period:threshold:voltage:range [, ] select threshold voltage range; = 0 to 1010. 10 f :period:aperture [, ] set gate time for period measurements in secs; = 0.01 to 1.0. 1.0...
Page 142
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual basic dmm operation 3-41 reference a. Function [, ] note that the parameters in the table are enclosed in single quotes (‘ ’). However, double quotes (“ ”) can instead be used. For example: func ‘volt:ac’ = func “volt:ac” scan configuration — when usi...
Page 143
3-42 basic dmm operation model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual e. Temperature:frtd:rzero [, ] temperature:frtd:alpha [, ] temperature:frtd:beta [, ] temperature:frtd:delta [, ] these commands are used to set the parameters for the user rtd type. Note that the rzero command sets the “ Ω a...
Page 144
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual basic dmm operation 3-43 data:fresh? Can only be used once to return the same reading string. That is, the reading must be “fresh.” sending this command again to retrieve the same reading string will generate error -230 (data corrupt or stale), or ca...
Page 145
3-44 basic dmm operation model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual basic measurement programming examples example #1 — continuous triggering the following command sequence places the model 2700 in a continuous trigger mode to measure acv. Whenever data? Is sent, the last measured reading wil...
Page 146: Measurement Queries
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual basic dmm operation 3-45 example #4 — scan configuration (model 7700) the following commands configure scan channels 101, 102, and 121 of a model 7700 installed in slot 1. When channel 101 is scanned, dcv will be selected. When channel 102 is scanned,...
Page 147: :read?
3-46 basic dmm operation model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual :read? What it does this command performs three actions. It will reset the trigger model to the idle layer (equivalent to the :abort command), take the trigger model out of idle (equivalent to the :init command), and return a...
Page 148: [:sense[1]]:data:fresh?
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual basic dmm operation 3-47 [:sense[1]]:data:fresh? What it does this query is similar to :fetch? In that it returns the latest reading from the instrument, but it has the advantage of making sure that it does not return the same reading twice. Limitati...
Page 149: Examples
3-48 basic dmm operation model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual examples one-shot reading, dc volts, no trigger, fastest rate *rst :initiate:continuous off;:abort :sense:function ‘voltage:dc’ :sense:voltage:dc:range 10 // use fixed range for fastest readings. :sense:voltage:dc:nplc 0.01 /...
Page 150
4 range, digits, rate, bandwidth, and filter • range — provides details on measurement range selection. Includes the com- mands for remote programming. • digits — provides details on selecting display resolution. Includes the commands for remote programming. • rate and bandwidth — provides details o...
Page 151: Range
4-2 range, digits, rate, bandwidth, and filter model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual range the range setting is “remembered” by each measurement function. When you select a function, the instrument will return to the last range setting for that function. Measurement ranges and maximum re...
Page 152: Manual Ranging
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual range, digits, rate, bandwidth, and filter 4-3 manual ranging to change range, press the range or key. The instrument changes one range per key press. The selected range is displayed for one second. Note that the manual range keys have no effect on t...
Page 153
4-4 range, digits, rate, bandwidth, and filter model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual manual ranging the range is selected by specifying the expected reading as an absolute value using the parameter for the appropriate :range command. The model 2700 will then go to the most sensitive rang...
Page 154: Digits
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual range, digits, rate, bandwidth, and filter 4-5 range programming examples example #1 — the following commands select range for dcv, Ω 2 and dci: volt:rang 0.5 ' select 1v range for dcv. Res:rang 2e3 ' select 10k Ω range for Ω 2. Curr:rang 0.1 ' selec...
Page 155
4-6 range, digits, rate, bandwidth, and filter model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual remote programming — digits digits commands the commands to control display resolution (digits) are listed in table 4-3 . Additional information on these commands follow the table. Note query commands ar...
Page 156: Rate and Bandwidth
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual range, digits, rate, bandwidth, and filter 4-7 digits programming examples example #1 — the following commands set digits for dcv and aci: volt:dig 5.5 ' set dcv to 5 ½ digits. Curr:ac:dig 4 ' set aci to 3 ½ digits. Example #2 — the following command...
Page 157
4-8 range, digits, rate, bandwidth, and filter model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual the front panel rate settings for all but the ac functions are explained as follow: • fast sets integration time to 0.1 plc. Use fast if speed is of primary impor- tance (at the expense of increased read...
Page 158: Bandwidth
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual range, digits, rate, bandwidth, and filter 4-9 setting measurement speed — the rate key is used to set measurement speed from the front panel. Simply press rate until the desired speed annunciator (fast, med, or slow) turns on. Note the model 2700 us...
Page 159
4-10 range, digits, rate, bandwidth, and filter model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual remote programming — rate and bandwidth rate and bandwidth commands the commands to set the integration rate and bandwidth are listed in table 4-5 . Additional information on these commands follows the ...
Page 160
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual range, digits, rate, bandwidth, and filter 4-11 aperture aperture is a different way to specify the integration rate. As previously explained, 1 plc sets the integration rate to 16.67msec (assuming 60hz line power). You can instead use an aperture co...
Page 161
4-12 range, digits, rate, bandwidth, and filter model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual to set bandwidth, simply specify (approximately) the frequency of the input signal. The instrument will automatically set the bandwidth as follows: = 3 to 29 3hz to 300khz = 30 to 299 30hz to 300khz = 3...
Page 162: Filter
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual range, digits, rate, bandwidth, and filter 4-13 filter the digital filter is used to stabilize noisy measurements. The displayed, stored, or trans- mitted reading is a windowed-average of a number of reading conversions (from 1 to 100). The filter se...
Page 163
4-14 range, digits, rate, bandwidth, and filter model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual filter window — the digital filter uses a window to control filter threshold. As long as the input signal remains within the selected window, a/d conversions continue to be placed in the stack. If the s...
Page 164
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual range, digits, rate, bandwidth, and filter 4-15 figure 4-2 moving and repeating filters filter example filter type - moving filter window = 0.01% of range filter count = 10 filter state = on ten readings fill the stack to yield a filtered reading. Now...
Page 165
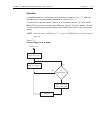
4-16 range, digits, rate, bandwidth, and filter model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual note bit 8 of the operation event status register sets when the filter window has properly settled (or the filter is disabled). See section 11 , “ status structure ,” for details. Filter control and config...
Page 166
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual range, digits, rate, bandwidth, and filter 4-17 figure 4-3 filter configuration flow chart scanning the moving filter cannot be used when scanning. A scan channel cannot be configured to use the moving filter. Also, the filter window is not used when s...
Page 167
4-18 range, digits, rate, bandwidth, and filter model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual remote programming — filter filter commands the filter commands are listed in table 4-6 . Additional information on these commands follow the table. Note query commands are not included in table 4-6 . Al...
Page 168
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual range, digits, rate, bandwidth, and filter 4-19 commands 1, 4 description 5 default Ω 2 filter commands [sense[1]] optional root command. :resistance:average:tcontrol select filter type; = moving or repeat. (note 2) :resistance:average:window set filt...
Page 169
4-20 range, digits, rate, bandwidth, and filter model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual filter programming examples example #1 — the following command sequence configures filtering for the dci function: curr:tcon mov ' select the moving filter. Curr:aver:wind 0.01 ' set filter window to 0....
Page 170
5 relative, math, ratio, channel average, and db • relative — explains how to null an offset or establish a baseline value. Includes the commands for remote programming. • math — covers the three basic math operations: mx+b, percent, and reciprocal (1/x). Includes the commands for remote programming...
Page 171: Relative
5-2 rel, math, ratio, channel average, db model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual relative the rel (relative) function can be used to null offsets or subtract a baseline reading from present and future readings. When rel is enabled, the instrument uses the present reading as a relative val...
Page 172
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual rel, math, ratio, channel average, db 5-3 pressing rel a second time disables rel. You can input a rel value manually using the mx+b function. Set m for 1 and b for any value you want. The mx+b function is covered in this section (see “math,” page 5-...
Page 173: Remote Programming — Rel
5-4 rel, math, ratio, channel average, db model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual remote programming — rel rel commands the rel commands to set range are listed in table 5-1 . Additional information on these commands follow the table. Note query commands are not included in table 5-1 . All...
Page 174
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual rel, math, ratio, channel average, db 5-5 commands 1 description default rel commands for Ω 2 [sense[1]] optional root command. :resistance:reference [, ] specify rel value; = 0 to 120e6 ( Ω ). 0 :resistance:reference:state [, ] enable/disable rel; =...
Page 175
5-6 rel, math, ratio, channel average, db model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual “pressing rel” using rel commands when the front panel rel key is pressed, the displayed reading is used as the rel value. Subsequent readings are then the result of the actual input value and the rel value. ...
Page 176: Math
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual rel, math, ratio, channel average, db 5-7 math the model 2700 has three built-in math calculations that are accessed from the math menu: mx+b, percent, and reciprocal (1/x). Figure 5-1 shows the math menu tree. Note that the settings shown in the men...
Page 177: Mx+B
5-8 rel, math, ratio, channel average, db model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual mx+b this math operation lets you manipulate normal display readings (x) mathematically according to the following calculation. Y = mx + b where: x is the normal display reading. M and b are the user-entered ...
Page 178: Percent
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual rel, math, ratio, channel average, db 5-9 mx+b rel the mx+b function can be used to manually establish a rel value. To do this, set the scale factor (m) to 1 and set the offset (b) to the rel value. Each subsequent reading will be the difference betw...
Page 179: Reciprocal (1/x)
5-10 rel, math, ratio, channel average, db model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual reciprocal (1/x) the reciprocal of a reading is displayed when the reciprocal (1/x) math function is enabled: reciprocal = 1/x where: x is the normal input reading the displayed units designator for reciproc...
Page 180: Basic Operation
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual rel, math, ratio, channel average, db 5-11 basic operation note if using switching module inputs, make sure the front panel inputs switch is set to the rear position (in). If using the front panel inputs, the switch must be in the front position (out...
Page 181: Remote Programming — Math
5-12 rel, math, ratio, channel average, db model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual remote programming — math math commands note when measurements are performed, the readings are fed to other enabled pro- cessing operations, including math. Appendix d explains “data flow (remote operation),”...
Page 182
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual rel, math, ratio, channel average, db 5-13 setting mx+b units the parameter for calculate:kmath:munits must be one character enclosed in single or double quotes. It can be any letter of the alphabet, the degrees symbol (°) or the ohms symbol ( Ω ). T...
Page 183
5-14 rel, math, ratio, channel average, db model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual math programming examples example #1 — the following command sequence performs the mx+b calculation for channels 101 and 102 of the model 7700. Keep in mind that after calc:data? Is sent, the model 2700 has ...
Page 184: Ratio and Channel Average
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual rel, math, ratio, channel average, db 5-15 ratio and channel average with a switching module installed in the model 2700, the ratio or average of two channels can be calculated and displayed. The ratio calculation can be done on the dcv function, and...
Page 185: Basic Operation
5-16 rel, math, ratio, channel average, db model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual basic operation note make sure the inputs switch is set to the rear position (in). 1. Select and configure (range, filter, rel, etc.) a valid measurement function. For ratio, the only valid function is dcv. ...
Page 186
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual rel, math, ratio, channel average, db 5-17 scanning ratio and channel average can be used in an advanced scan. The 2-channel scan for the calculation is performed for every primary channel that is scanned. For example, assume the model 7700 is instal...
Page 187
5-18 rel, math, ratio, channel average, db model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual remote programming — ratio and channel average ratio and channel average commands the ratio and channel average are listed in table 5-3 . Details on these commands follow the table. Note queries are not incl...
Page 188
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual rel, math, ratio, channel average, db 5-19 ratio and channel average programming examples example #1 — the following command sequence performs the ratio calculation using primary channel 102 of the model 7700. After read? Is sent, the model 2700 must...
Page 189: Remote Programming — Db
5-20 rel, math, ratio, channel average, db model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual scanning typically a scan using db is configured and run using remote programming. However, once db is selected using remote programming, a simple db scan can be configured and run from the front panel. When...
Page 190
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual rel, math, ratio, channel average, db 5-21 programming examples — db example #1 — the following command sequence configures the model 2700 to perform dcv db measurements. A 1v input will be measured as 0db. Func 'volt' ' select dcv function. Unit:vol...
Page 191
5-22 rel, math, ratio, channel average, db model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual.
Page 192
6 buffer • buffer overview — summarizes basic buffer (data store) capabilities. • front panel buffer — explains how to store and recall readings, and discusses the various statistics available on buffer data including minimum and maximum val- ues, average (mean), standard deviation, and peak-to-peak...
Page 193: Buffer Overview
6-2 buffer model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual buffer overview the model 2700 has a data store (buffer) to store from 2 to 55,000 readings. The instru- ment stores the readings that are displayed during the storage process. Each timestamped reading includes the buffer location number a...
Page 194: Timestamps
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual buffer 6-3 note if the buffer is empty when the model 2700 is turned off, buffer auto clear will enable when it is turned back on. If the buffer is not empty, the instrument will power up to the last auto clear set- ting. Keep in mind that if the ins...
Page 195
6-4 buffer model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual note with auto clear disabled and the relative timestamp selected, every stored read- ing is referenced to the first reading (#0), even if the buffer is stopped and started again. For example, assume you stored 10 readings in the buffer, an...
Page 196: Storing Readings
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual buffer 6-5 selecting timestamp perform the following steps to select either the real-time clock timestamp or the relative timestamp: note changing the timestamp will clear the buffer if a storage is in process. The mes- sage “buf cleared” will be dis...
Page 197: Recalling Readings
6-6 buffer model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual recalling readings readings stored in the buffer are displayed by pressing the recall key. The readings are positioned at the left side of the display, while the buffer location number (reading num- ber) and timestamps are positioned at th...
Page 198: Buffer Statistics
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual buffer 6-7 figure 6-2 recalling buffer data — real-time clock timestamp buffer statistics minimum and maximum this mode displays the minimum and maximum readings stored in the buffer. The buffer location number and timestamp are also provided for the...
Page 199: Buffer Commands
6-8 buffer model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual standard deviation this mode displays the standard deviation of buffered readings. The following equation is used to calculate standard deviation: where: y is the standard deviation. X i is a stored reading. N is the number of stored readi...
Page 200
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual buffer 6-9 note optional command words and most queries are not included in table 6-1 . The unabridged tables for all scpi commands are provided in section 15 . Table 6-1 buffer commands command description default 1 ref system:time set clock time in...
Page 201
6-10 buffer model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual a. System:time set clock time use to set the clock time in the 24-hour format (hr/min/sec). Seconds can be set to 0.01 sec resolution. Examples: syst:time 13, 23, 36 'set time to 1:23:36 pm. Syst:time 3, 25, 28.5 'set time to 3:25:28.5 am...
Page 202
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual buffer 6-11 f. Trace:points 2 to 55000 set buffer size with buffer auto-clear enabled, you can set the buffer to store from 2 to 55,000 readings. A buffer size of zero or one is not valid (error -222). With buffer auto-clear disabled, you cannot use ...
Page 203
6-12 buffer model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual j. Trace:data:selected? , specify readings to return trace:next? Query location of last buffer reading use the trace:data:selected? Command to specify which stored readings to return. The parameter specifies the first stored reading to re...
Page 204
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual buffer 6-13 the data returned by trace:data? Can include from one to all five data elements shown in the above item list. For example, if you want the units and reading number included with the reading, you would send this command: format:elements re...
Page 205: Programming Example
6-14 buffer model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual note if the standard deviation calculation is being performed on a buffer that has more than 1000 readings, the “calculating” message will flash to indicate that the model 2700 is busy. While busy with the calculation, remote program- ming...
Page 206
7 scanning • scanning fundamentals — explains channel assignments (slot/channel program- ming format), the difference between sequential and non-sequential scans, and the basic scan process. Block diagrams (known as trigger models) are provided to help explain the step and scan operations. • scan co...
Page 207: Scanning Fundamentals
7-2 scanning model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual scanning fundamentals the model 2700 can scan the channels of up to five installed keithley switching modules. Each scan channel can have its own unique setup. Aspects of operation that can be uniquely set for each channel include functi...
Page 208: Scan Process
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual scanning 7-3 the mainframe. The first digit (1 or 2) indicates the slot number, and the next two digits indicate the channel number of the switching module. Examples: channel 101 slot 1, channel 1 channel 112 slot 1, channel 12 channel 220 slot 2, ch...
Page 209: Trigger Models
7-4 scanning model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual calculations using channel pairs — ratio and channel average performs measurements on two channels and then calculates (and displays) the result. Therefore, these 2-channel calculations also use paired channels. The scan process is to (1...
Page 210
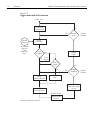
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual scanning 7-5 figure 7-1 trigger model with step function enable scan control source immediate external timer event detection output trigger another reading ? Trigger counter (reading count) yes no close first chan in list open last chan close next ch...
Page 211
7-6 scanning model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual figure 7-2 trigger model with scan function enable scan control source immediate external timer manual* bus* event detection another scan? Trigger counter yes no close first chan in list open last chan close next chan in list ratio/chan ...
Page 212
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual scanning 7-7 step operation overview — when the step key is pressed, the model 2700 leaves the idle state, closes the first channel, and waits for the programmed trigger event. After the trigger is detected, the instrument may be subjected to one or ...
Page 213
7-8 scanning model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual immediate control source with immediate triggering, event detection is immediate allowing channels to be scanned. Timer control source with the timer source enabled (selected), event detection is immediately satisfied. On the initial pas...
Page 214
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual scanning 7-9 the auto delay period cannot be adjusted by the user. It is a fixed delay for the selected function and range ( table 8-1 ). Note when scanning, the auto delay times in table 8-1 are valid for all control sources (immediate, external, ti...
Page 215
7-10 scanning model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual scan operation — when a scan is started, one or more complete scans will be per- formed. The number of channels in the scan list determines the number of channels for each scan. The reading count determines the number of scans to perfor...
Page 216: Scan Configuration
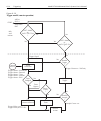
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual scanning 7-11 scan configuration a scan is configured from the scan configuration menu which is accessed by pressing shift and then config. Figure 7-3 shows the basic flowchart to configure a scan. After entering the menu structure you can configure a...
Page 217
7-12 scanning model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual there are two scan configurations: simple and advanced. When you configure the simple scan, the instrument uses the present instrument setup for each channel in the scan. For the advanced scan, each channel can have its own unique setup...
Page 218: Scan Reset
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual scanning 7-13 assume a model 7700 module configured for a10-channel scan and a reading count of 30. For this configuration, the instrument will scan through the scan list three times. Now assume the scan setup is saved in sav1, and sav1 is the power-...
Page 219: Simple Scan
7-14 scanning model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual simple scan for a simple scan, you specify a starting channel (min chan) and an ending channel (max chan) for the scan. These settings determine the number of channels in the scan. For example, if you set min chan to 101 and max chan to...
Page 220: Advanced Scan
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual scanning 7-15 advanced scan for an advanced scan, each enabled channel can have its own unique setup. Channels that are disabled are excluded from the scan list. When you enter the channel setup menu, the displayed information indicates the present s...
Page 221
7-16 scanning model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual when you press the Ω 4 function key for a primary channel, the subsequently paired channels will be displayed briefly. Model 7700 example: if you press Ω 4 for channel 108, channels 109 and 110 will also assume the Ω 4 function, and the...
Page 222
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual scanning 7-17 3. If you did not disable the channel, make your setup changes (if any) for the selected function. These changes do not affect the following channels. 4. Using the or keys or the close key to select the channel, repeat steps 2-2 and 2-3...
Page 223: Setting Delay
7-18 scanning model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual setting delay as shown in figure 7-1 and figure 7-2 , a delay (auto or manual) can be set by the user. With auto delay selected, the delay period depends on function and range ( table 8-1 ). With manual delay selected, the delay period ...
Page 224: Auto Channel Configuration
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual scanning 7-19 inadvertently trigger a monitor scan (see “ scan operation — monitor scan,” page 7-35 ). The monitor channel must be a channel that is in the scan list. If the monitor channel is removed from the scan list, the lowest channel in the sca...
Page 225
7-20 scanning model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual as with normal operation, when you use the , , or close to close a channel (or chan- nel pair), any other closed channels are first opened. Perform the following steps to enable or disable auto channel configuration. 1. Press shift and ...
Page 226: Saving Setup
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual scanning 7-21 saving setup up to four instrument setups can be saved in memory using the shift > save menu (sav0, sav1, sav2, or sav3). A user-saved setup can also be used as the power-on setup. A user-saved setup can be restored from the shift > set...
Page 227: Scan Operation
7-22 scanning model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual scan operation a basic scan is controlled solely by the step and scan keys. When one of these keys is pressed, the step or scan operation will be performed. For the manual/external trigger scan, the trig key or triggers received from an...
Page 228: Manual/external Trigger Scan
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual scanning 7-23 manual/external trigger scan the only difference between a manual/external trigger scan and the basic scan is control. The basic scan runs as soon as the step or scan key is pressed. The manual/external trigger scan is controlled by the...
Page 229
7-24 scanning model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual monitor scan (analog trigger) a channel can be assigned as a monitor channel. When the monitor channel detects that a reading limit has been reached, the scan will be triggered to start. There are four reading limits that can be used to...
Page 230
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual scanning 7-25 a. Press the or key to enable or disable low limit 1 (llim1 scan:n/y), and press enter. B. Press the or key to enable or disable high limit 1 (hlim1 scan:n/y), and press enter. C. Press the or key to enable or disable low limit 2 (llim2...
Page 231: Trigger Model
7-26 scanning model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual remote programming — scanning note scanning examples (remote programming and front panel operation) are pro- vided at the end of this section. Trigger model the trigger model for bus operation is shown in figure 7-2 . Bus operation is s...
Page 232: Channel Setup
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual scanning 7-27 channel setup the parameter is used to set up scan channels. For example, the following exam- ples show how to set up scan channel 101: func 'volt', (@101) ' set 101 for dcv. Volt:rang 10, (@101) ' set 101 for 10v range. Volt:dig 4.5, (...
Page 233
7-28 scanning model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual table 7-1 scanning commands commands description default ref scan commands route:scan specify list of channels to be scanned. A route:scan? Returns list of channels to be scanned. Route:scan:tsource select trigger(s) to start scan; = im...
Page 234
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual scanning 7-29 reference a. Route:scan — channels will be scanned in the order that they are listed. The following example shows the proper format for specifying channels in a scan list for a sequential scan: rout:scan (@101:110,201,204,206) for the a...
Page 235
7-30 scanning model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual example 1 — after channel 105 is scanned, the unit backs up to scan channel 103, then proceeds forward to scan channels 106 through 110. Example 2 — the scan starts with channel 110, then proceeds backward to channel 101. Notes non-sequ...
Page 236
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual scanning 7-31 b. Route:scan:tsource = immediate = hlimit1, hlimit2, llimit1, llimit2 as with front panel operation, the scan can start immediately when it is enabled and triggered, or it can be started by a reached reading limit detected by the mon- ...
Page 237: Scanning Programming Example
7-32 scanning model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual scanning programming example the following program will scan 10 channels (101 through 110): trac:cle ' clear buffer. Init:cont off ' disable continuous initiation. Trig:sour imm ' select the immediate control source. Trig:coun 1 ' set t...
Page 238
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual scanning 7-33 operation a simplified model of external trigger scan operation is shown in figure 7-4 , while the procedure steps and programming commands are listed in table 7-2 . As shown in the operation model, when the scan is enabled, channel 101...
Page 239
7-34 scanning model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual table 7-2 external trigger scan example front panel operation remote programming 1 restore defaults: restore defaults (shift setup > restore: fact). *rst 2 for front panel operation, proceed to step 3. For remote programming, clear buff...
Page 240: Monitor Scan
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual scanning 7-35 monitor scan for this example, channel 101 of the model 7700 is used to monitor temperature. When the temperature reading reaches 30°c, it will start the scan. For this 4-channel scan, chan- nel 101 measures temperature, while channels ...
Page 241
7-36 scanning model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual figure 7-5 monitor scan example ≥ 30˚c ? 4 measurements ? Measure temp close monitor channel (101) no yes measure open last chan close next chan close first channel return to monitor mode no yes scan monitor mode: scan mode:.
Page 242
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual scanning 7-37 table 7-3 monitor scan example front panel operation remote programming 1 restore defaults (shift setup > restore: fact). Syst:pres 2 for front panel operation, proceed to step 3. For remote programming, clear the buffer: trac:cle 3 con...
Page 243
7-38 scanning model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual.
Page 244
8 triggering • trigger model — explains the various components of the front panel trigger model, which controls the triggering operations of the instrument. • reading hold — explains the reading hold feature which is used to screen out readings that are not within a specified reading window. • exter...
Page 245: Trigger Model
8-2 triggering model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual trigger model the flow chart in figure 8-1 summarizes triggering as viewed from the front panel. It is called a trigger model because it is modeled after the scpi commands used to control triggering. Note for scanning, the trigger mode...
Page 246: Delay (Auto Or Manual)
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual triggering 8-3 control source and event detection the control source holds up operation until the programmed event occurs and is detected. The control sources are described as follows: • immediate — with this control source, event detection is immedi...
Page 247
8-4 triggering model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual the delay function is accessed by pressing shift and then delay. The present delay setting (auto or manual) is displayed. Press the or key to display the desired set- ting and press enter. If manual is chosen, also enter the duration o...
Page 248: Device Action
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual triggering 8-5 device action the primary device action is a measurement. However, the device action block could include the following additional actions ( figure 8-2 ): figure 8-2 device action • filtering — if the repeating filter is enabled, the in...
Page 249: Reading Hold (Autosettle)
8-6 triggering model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual reading hold (autosettle) with hold enabled (hold annunciator on), the first processed reading becomes the “seed” reading and operation loops back within the device action block. After the next reading is processed, it is checked to se...
Page 250: External Triggering
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual triggering 8-7 external triggering the ex trig key selects triggering from three external sources: trigger link, digital i/o, and the trig key. When ex trig is pressed, the trig annunciator lights and dashes are displayed to indicate the instrument i...
Page 251: External Trigger
8-8 triggering model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual external trigger the ext trig input requires a falling-edge, ttl-compatible pulse with the specifica- tions shown in figure 8-4 . In general, external triggers can be used to control measure operations. For the model 2700 to respond to...
Page 252: External Triggering Example
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual triggering 8-9 external triggering example for a test system that requires a large number of switching channels, the model 2700 can be used with external scanners such as the keithley models 7001 and 7002. For example, 10 model 7011s installed in the...
Page 253
8-10 triggering model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual for this example, the models 2700 and 7002 are configured as follows: model 2700 factory defaults restored (accessed from shift-setup) external triggers (accessed from ex trig) buffer enabled and set to store 400 readings model 7002 f...
Page 254
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual triggering 8-11 1. Press ex trig to place the model 2700 in the external trigger mode. 2. Press step on the model 7002 to take it out of idle and start the scan. The scan- ner’s output pulse triggers the model 2700 to take a reading, store it, and se...
Page 255
8-12 triggering model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual d. After the relay settles, the model 7002 outputs a channel ready pulse. Since the instrument is programmed to scan 400 channels, operation loops back up to point b, where it waits for an input trigger. E & f. Model 2700 operation is...
Page 256
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual triggering 8-13 remote programming — triggering trigger model (remote operation) the following paragraphs describe how the model 2700 operates for remote operation. The flow chart in figure 8-10 summarizes operation over the bus. The flow chart is ca...
Page 257
8-14 triggering model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual figure 8-10 trigger model (remote operation) control source event detection no start :init (:imm) or :init:cont on ? Yes :abort *rcl 0 :syst:pres *rst :init (:imm) or :init:cont on ? No yes idle and initiate :trigger:source immediate ...
Page 258: Trigger Model Operation
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual triggering 8-15 trigger model operation once the instrument is taken out of idle, operation proceeds through the trigger model down to the device action. In general, the device action includes a measurement and, when scanning, closes the next channel...
Page 259: Triggering Commands
8-16 triggering model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual output trigger — the model 2700 will send one or more output triggers. The output trigger is applied to the trigger link connector on the rear panel. It can be used to trigger an external instrument to perform an operation. The trigge...
Page 260
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual triggering 8-17 reference a. Abort — with continuous initiation disabled, the 2700 goes into the idle state. With continuous initiation enabled, operation continues at the top of the trigger model. B. Initiate — whenever the instrument is operating w...
Page 261: Programming Example
8-18 triggering model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual programming example the following program fragment triggers (and stores in the buffer) 10 readings. Note that in order to send the readings to the computer, you must address the model 2700 to talk after sending read?. *rst ' restore *...
Page 262
9 limits and digital i/o • limits — explains how to perform limit tests on measured readings. • digital i/o — covers the digital i/o port. Explains how the five digital outputs respond to the results of limit tests. • remote programming — limits and digital output — summarizes the com- mands to perf...
Page 263: Limits
9-2 limits and digital i/o model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual limits note limits cannot be used with the cont function. When using limits, you can set and control the values that determine the high/in/low status of subsequent measurements. The limit test is performed on the result of ...
Page 264
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual limits and digital i/o 9-3 overflow readings — a reading that exceeds the present measurement range causes the “ovrflw” message to be displayed. The “in,” “1,” and “2” messages are not displayed while in the overflow condition. The high annunciator w...
Page 265: Scanning
9-4 limits and digital i/o model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual scanning when a simple scan is configured, the present limit values and state will apply to all chan- nels in the scan. When an advanced scan is configured, each channel can have its own unique limits configuration. Details...
Page 266: Digital I/o
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual limits and digital i/o 9-5 digital i/o model 2700’s digital i/o port is accessed at a male db-9 connector located on the rear panel. The connector location and pin designations are shown in figure 9-2 . Figure 9-2 digital i/o port digital input (trig...
Page 267: Digital Outputs
9-6 limits and digital i/o model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual digital outputs the digital i/o port has five digital outputs. Each digital output can be used as a sink to control devices (e.G., relays), or as a source to provide input to external logic (ttl or cmos) circuitry. The simp...
Page 268
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual limits and digital i/o 9-7 logic sense the selected logic sense (active high or active low) determines if an output is pulled high or low when the limit is reached. If logic sense is set high, the output line will be pulled high when the reading reac...
Page 269
9-8 limits and digital i/o model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual sink mode — controlling external devices each output can be operated from an external supply (voltage range from +5v to +33v applied through the external device being driven). The high current sink capacity of the output dr...
Page 270
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual limits and digital i/o 9-9 figure 9-4 controlling externally powered relays 4.75k pull up resistor pin 9 - digital ground digital output pin 7 - diode clamp relay coil relay coil + + - - external power (+5v to +33v) external power (+5v to +33v) model...
Page 271
9-10 limits and digital i/o model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual source mode — logic control the digital outputs can be used as logic inputs to active ttl, low-power ttl, or cmos inputs. For this mode of operation, the output lines can source up to 200µa. Caution each output line can so...
Page 272: Setting Digital Output
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual limits and digital i/o 9-11 setting digital output the output menu (shown in table 9-1 ) is used to control and configure digital outputs. Menu items for the digital output include: • doutput — use to enable (on) or disable (off) the digital outputs....
Page 273: Scanning
9-12 limits and digital i/o model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual perform the following steps to enable and configure digital outputs: 1. Press shift and then output. 2. If the digital output is already on (doutput: on), proceed to step 3. Otherwise, press to move the cursor to the right...
Page 274
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual limits and digital i/o 9-13 remote programing — limits and digital output limits and digital output commands the limits and digital output commands are provided in table 9-2 . Table 9-2 limits and digital i/o commands commands * description def ref l...
Page 275
9-14 limits and digital i/o model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual note when measurements are performed, the readings are fed to other enabled oper- ations, including limits. Appendix d explains “ data flow (remote operation) ” and the commands used to read the result of limit tests. Refer...
Page 276
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual limits and digital i/o 9-15 b. Calculate3:limit1:fail? Calculate3:limit2:fail? These commands are used to query the results of limit 1 and limit 2: 0 = passing (reading within the high and low limits) 1 = failing (reading has reached or exceeded the ...
Page 277: Limits
9-16 limits and digital i/o model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual application — sorting resistors for this application, the idea is to sort a batch of 100 Ω resistors into three bins. Bin 1 is for resistors that are within 1% of the nominal value. Bin 2 is for resistors that exceed 1% to...
Page 278
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual limits and digital i/o 9-17 limit 1 will be used to test for the 1% tolerance and limit 2 will be used to test for the 5% tolerance. The resistance values for the 1% and 5% tolerances are calculated as follows: r 1% = 100 Ω × 1% r 5% = 100 Ω × 5% = 1...
Page 279: Digital Outputs
9-18 limits and digital i/o model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual remote operation — for remote operation, make sure both limit 1 and limit 2 are enabled. The following table evaluates the three possible pass/fail combinations for this example. Keep in mind that a fail condition must be ...
Page 280
10 remote operations • operation enhancements — summarizes some of the more important operations that can only be performed using remote operation. • gpib setup — covers gpib bus standards, selecting the gpib, primary address selection, and bus connections. • general bus commands — describes general...
Page 281: Operation Enhancements
10-2 remote operations model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual operation enhancements there are some operations you can do over the ieee-488 bus and rs-232 interface that you cannot do from the front panel. The more important ones are summarized below. Pseudocards using remote operation, y...
Page 282: Separate Function Setups
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual remote operations 10-3 separate function setups a few settings from the front panel are global. That is, the setting on one function also applies to the other functions. For example, if you set dcv for 3 ½ digits, all the other functions will also be...
Page 283: Gpib Setup
10-4 remote operations model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual gpib setup the following provides information about gpib standards, selecting the gpib, setting the primary address, and bus connections. Gpib standards the gpib is the ieee-488 instrumentation data bus with hardware and progra...
Page 284: Gpib Connections
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual remote operations 10-5 gpib connections to connect the model 2700 to the gpib bus, use a cable equipped with standard ieee-488 connectors as shown in figure 10-1 . Figure 10-1 ieee-488 connector to allow many parallel connections to one instrument, s...
Page 285
10-6 remote operations model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual figure 10-2 shows a typical connecting scheme for a multi-unit test system. Figure 10-2 ieee-488 connections to avoid possible mechanical damage, stack no more than three connectors on any one unit. Note to minimize interferenc...
Page 286
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual remote operations 10-7 to connect the model 2700 to the ieee-488 bus, follow these steps: 1. Line up the cable connector with the connector located on the rear panel. The con- nector is designed so it will fit only one way. Figure 10-3 shows the loca...
Page 287: General Bus Commands
10-8 remote operations model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual general bus commands general commands are those commands, such as dcl, that have the same general mean- ing regardless of the instrument. Table 10-1 lists the general bus commands. Ren (remote enable) the remote enable command ...
Page 288: Llo (Local Lockout)
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual remote operations 10-9 llo (local lockout) use the llo command to prevent local operation of the instrument. After the unit receives llo, all of its front panel controls except output off are inoperative. In this state, pressing local will not restor...
Page 289: Front Panel Gpib Operation
10-10 remote operations model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual front panel gpib operation this section describes aspects of the front panel that are part of gpib operation, including messages, status indicators, and the local key. Error and status messages see appendix c for a list of err...
Page 290: Local Key
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual remote operations 10-11 srq you can program the instrument to generate a service request (srq) when one or more errors or conditions occur. When this indicator is on, a service request has been generated. This indicator stays on until the serial poll...
Page 291
10-12 remote operations model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual these brackets indicate that immediate is implied (optional) and does not have to be used. Thus, the above command can be sent in one of two ways: initiate or initiate:immediate notice that the optional command is used without...
Page 292: Query Commands
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual remote operations 10-13 angle brackets angle brackets () are used to denote a parameter type. Do not include the brackets in the program message. For example: ratio the indicates a boolean-type parameter is required. Therefore, to enable channel rati...
Page 293: Short-Form Rules
10-14 remote operations model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual long-form and short-form versions an scpi command word can be sent in its long-form or short-form version. The command subsystem tables in section 15 provide the long-form version. However, the short-form version is indicated ...
Page 294: Program Messages
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual remote operations 10-15 program messages a program message is made up of one or more command words sent by the computer to the instrument. Each common command is a three letter acronym preceded by an asterisk (*). Scpi commands are categorized in the...
Page 295
10-16 remote operations model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual command path rules • each new program message must begin with the root command, unless it is optional (e.G., [sense]). If the root is optional, simply treat a command word on the next level as the root. For fastest operation, ...
Page 296: Response Messages
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual remote operations 10-17 response messages a response message is the message sent by the instrument to the computer in response to a query command program message. Sending a response message after sending a query command, the response message is place...
Page 297: Rs-232 Interface Operation
10-18 remote operations model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual rs-232 interface operation sending and receiving data the rs-232 interface transfers data using eight data bits, one stop bit, and no parity. Make sure the controller you connect to the multimeter also uses these settings. You...
Page 298: Terminator
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual remote operations 10-19 signal handshaking (flow control) signal handshaking between the controller and the instrument allows the two devices to communicate to each other regarding being ready or not ready to receive data. The model 2700 does not supp...
Page 299
10-20 remote operations model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual selecting and configuring rs-232 interface after selecting (enabling) the rs-232 interface, you will then set the baud rate, flow con- trol, and terminator. 1. Press the shift key and then the rs-232 key. The rs 232 on or rs 23...
Page 300: Rs-232 Connections
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual remote operations 10-21 rs-232 connections the rs-232 serial port is connected to the serial port of a computer using a straight- through rs-232 cable terminated with db-9 connectors. Do not use a null modem cable . The serial port uses the transmit ...
Page 301: Error Messages
10-22 remote operations model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual table 10-3 provides pinout identification for the 9-pin (db-9) or 25-pin (db-25) serial port connector on the computer (pc). Error messages see appendix c for rs-232 error messages (+800 through +808). Table 10-3 pc serial por...
Page 302
11 status structure • overview — provides an operational overview of the status structure for the model 2700. • clearing registers and queues — covers the actions that clear (reset) registers and queues. • programming and reading registers — explains how to program enable registers and read any regi...
Page 303: Overview
11-2 status structure model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual overview the model 2700 provides a series of status registers and queues allowing the operator to monitor and manipulate the various instrument events. The status structure is shown in figure 11-1 . The heart of the status struc...
Page 304
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual status structure 11-3 figure 11-1 model 2700 status register structure (always zero) logical or (always zero) idle state status byte register logical or *stb? *sre / *sre? Master summary status (mss) msb = measurement summary bit eav = error availabl...
Page 305
11-4 status structure model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual clearing registers and queues when the model 2700 is turned on, the bits of all registers in the status structure are cleared (reset to 0), and the two queues are empty. Commands to reset the event and event enable registers, an...
Page 306: Programming Enable Registers
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual status structure 11-5 programming and reading registers programming enable registers the only registers that can be programmed by the user are the enable registers. All other registers in the status structure are read-only registers. The following ex...
Page 307: Reading Registers
11-6 status structure model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual reading registers any register in the status structure can be read by using the appropriate query (?) com- mand. The following explains how to interpret the returned value (response message). The actual query commands are covere...
Page 308: Status Byte Register
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual status structure 11-7 status byte register the summary messages from the status registers and queues are used to set or clear the appropriate bits (b0, b2, b3, b4, b5, and b7) of the status byte register. These summary bits do not latch, and their st...
Page 309: Serial Polling and Srq
11-8 status structure model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual service request enable register the generation of a service request is controlled by the service request enable register. This register is programmed by you and is used to enable or disable the setting of bit b6 (rqs/mss) by the...
Page 310
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual status structure 11-9 status byte and service request commands the commands to program and read the status byte register and service request enable register are listed in table 11-2 . For details on programming and reading registers, see “programming...
Page 311
11-10 status structure model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual ' $include: 'ieeeqb.Bi' cls ' clear pc output screen. Const addr = 16 ' set instrument address. ' ' init gpib. ' call initialize(21, 0) call transmit("unt unl listen " + str$(addr) + " sdc unl", status%)' send device clear. Cal...
Page 312: Status Register Sets
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual status structure 11-11 status register sets as shown in figure 11-1 , there are four status register sets in the status structure of the model 2700: standard event status, operation event status, measurement event status, and questionable event statu...
Page 313
11-12 status structure model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual • bit b1 — not used. • bit b2, query error (qye) — set bit indicates that you attempted to read data from an empty output queue. • bit b3, battery-backed ram error (bre) — set bit indicates that the scan can- not be resumed (er...
Page 314
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual status structure 11-13 operation event register the bits of the operation event register ( figure 11-5 ) are described as follows: • bits b0 through b3 — not used. • bit b4, measuring (meas) — set bit indicates that the instrument is performing a mea...
Page 315
11-14 status structure model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual measurement event register the used bits of the measurement event register ( figure 11-6 ) are described as follows: • bit b0, reading overflow (rof) — set bit indicates that the reading exceeds the measurement range of the ins...
Page 316
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual status structure 11-15 figure 11-6 measurement event status (b15) ml (b14) btf (b13) bqf (b12) hl (b11) bof (b10) bf (b9) bhf (b8) bav (b7) bn (b6) rav (b5) hl2 (b4) ll2 (b3) hl1 (b2) ll1 (b1) rof (b0) (b15) ml (b14) btf (b13) bqf (b12) hl (b11) bof ...
Page 317
11-16 status structure model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual questionable event register the used bits of the questionable event register ( figure 11-7 ) are described as follows: • bits b0 through b3 — not used. • bit b4, temperature summary (temp) — set bit indicates that an invalid re...
Page 318: Condition Registers
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual status structure 11-17 condition registers as figure 11-1 shows, each status register set (except the standard event register set) has a condition register. A condition register is a real-time, read-only register that constantly updates to reflect th...
Page 319: Event Enable Registers
11-18 status structure model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual event enable registers as figure 11-1 shows, each status register set has an enable register. Each event register bit is logically anded (&) to a corresponding enable bit of an enable register. Therefore, when an event bit is s...
Page 320: Queues
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual status structure 11-19 queues the model 2700 uses two queues, which are first-in, first-out (fifo) registers: • output queue — used to hold reading and response messages. • error queue — used to hold error and status messages. The model 2700 status m...
Page 321
11-20 status structure model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual on power-up, all error messages are enabled and will go into the error queue as they occur. Status messages are not enabled and will not go into the queue. As listed in table 11-6 , there are commands to enable and/or disable m...
Page 322
12 common commands.
Page 323
12-2 common commands model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual common commands (summarized in table 12-1 ) are device commands that are common to all devices on the bus. These commands are designated and defined by the ieee-488.2 standard. Table 12-1 ieee-488.2 common commands and queries mn...
Page 324
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual common commands 12-3 a *idn? — identification query reads identification code the identification code includes the manufacturer, model number, serial number, and firm- ware revision levels and is sent in the following format: keithley instruments inc.,...
Page 325
12-4 common commands model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual note the following commands take a long time to process and may benefit from using *opc or *opc?: • *rst and syst:pres • *rcl and *sav • rout:mult:clos and rout:mult:open – only if the is long. • calc2:imm and calc2:imm?– only whe...
Page 326
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual common commands 12-5 note the following commands take a long time to process and may benefit from using *opc or *opc?: • *rst and syst:pres • *rcl and *sav • rout:mult:clos and rout:mult:open – only if the is long. • calc2:imm and calc2:imm?– only whe...
Page 327
12-6 common commands model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual f *rst — reset return model 2700 to rst defaults when the *rst command is sent, model 2700 performs the following operations: 1. Returns model 2700 to the rst default conditions (see “default” column of scpi tables). 2. Cancels a...
Page 328
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual common commands 12-7 • sequential commands – a command whose operations are allowed to finish before the next command is executed. • overlapped commands – a command that allows the execution of subsequent com- mands while device operations of the ove...
Page 329
12-8 common commands model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual.
Page 330
13 scpi signal oriented measurement commands.
Page 331
13-2 scpi signal oriented commands model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual the signal oriented measurement commands are used to acquire readings. You can use these high level instructions to control the measurement process. These commands are summarized in table 13-1 . Note when measuremen...
Page 332: Configure: [], [], []
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual scpi signal oriented commands 13-3 configure: [], [], [] configure:voltage[:dc] [], [], [] configure dcv configure:voltage:ac [], [], [] configure acv configure:current[:dc] [], [], [] configure dci configure:current:ac [], [], [] configure aci configure...
Page 333
13-4 scpi signal oriented commands model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual query configure? Query the selected function. Description included — when the parameter is included with configure command, the specified channel(s) for the scanlist assumes the *rst default settings for the specifi...
Page 334: Fetch?
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual scpi signal oriented commands 13-5 fetch? Description this command requests the latest post-processed reading. After sending this command and addressing the model 2700 to talk, the reading is sent to the computer. This command does not affect the ins...
Page 335: Read?
13-6 scpi signal oriented commands model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual read? Description this command is typically used with the instrument in the “one-shot” measurement mode to trigger and acquire a specified number of read- ings. The sample:count command is used to specify the number...
Page 336: Measure:? [], [], []
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual scpi signal oriented commands 13-7 measure:? [], [], [] measure:voltage[:dc]? [], [], [] measure dcv measure:voltage:ac? [], [], [] measure acv measure:current[:dc]? [], [], [] measure dci measure:current:ac? [], [], [] measure aci measure:resistance...
Page 337
13-8 scpi signal oriented commands model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual when a measure? Command is sent, the specified function is selected. If specified, range and resolution will also set. All other instrument set- tings related to the selected function are reset to the *rst defaults....
Page 338
14 format and miscellaneous system commands • format commands — covers the scpi commands to configure the format that readings are sent over the bus. • miscellaneous system commands — covers miscellaneous system commands..
Page 339: Format Commands
14-2 format and misc system commands model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual format commands the commands in this subsystem are used to select the format for transferring data, table 14-1 , over the bus. Format[:data] [,] parameters ascii = ascii format sreal = binary ieee-754 single preci...
Page 340
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual format and misc system commands 14-3 figure 14-1 ascii data format ieee-754 single precision format real, 32, or sreal will select the binary ieee-754 single precision data format. Figure 14-2 a shows the normal byte order format for each data elemen...
Page 341
14-4 format and misc system commands model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual figure 14-2 ieee-754 data formats s # 0 7 0 7 0 7 0 7 0 e f header byte 1 byte 2 byte 3 byte 4 s = sign bit (0 = positive, 1 = negative) e = exponent bits (8) f = fraction bits (23) normal byte order shown. For sw...
Page 342: Format:elements
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual format and misc system commands 14-5 format:elements parameters reading = dmm reading units = units tstamp = timestamp rnumber = reading number channel = channel number limits = limits reading the specified elements are included in the data string in...
Page 343: Format:border
14-6 format and misc system commands model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual limits — for the ascii data format, limit test results are returned as a 4-bit binary num- ber “abcd” where: a = high limit 2 b = low limit 2 c = high limit 1 d = low limit 1 a “0” indicates that the limit has pas...
Page 344: System:preset
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual format and misc system commands 14-7 miscellaneous system commands system commands not covered in other sections of the manual are documented here. Table 15-7 lists all system commands and provides references on where to find more information. System...
Page 345: System:beeper[:state]
14-8 format and misc system commands model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual this command is used to simulate front panel key presses. For example, to select the volts measurement function, send the following command to simulate pressing the “dcv” key: system:key 2. The key-press codes are...
Page 346
15 scpi reference tables.
Page 347: Reference Tables
15-2 scpi reference tables model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual reference tables table 15-1 through table 15-10 summarize the commands to operate the model 2700 and model 7700 switching module. Note the commands listed in the following tables pertain to operation of the model 2700 and t...
Page 348
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual scpi reference tables 15-3 table 15-1 calculate command summary command description default parameter ref scpi calculate[1] subsystem to control calc 1: sec 5 ✓ :format [] select math format (none, mxb, percent, or reciprocal). Percent ✓ :format? [] ...
Page 349
15-4 scpi reference tables model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual calculate3 subsystem to control calc 3 (limit test): sec 9 ✓ :mlimit path for master limit command: :latched enable or disable master limit latch. Off :output path for limit output commands: [:state] enable or disable limit...
Page 350
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual scpi reference tables 15-5 calculate3 :limit2 path to control limit 2 test: ✓ :upper path to configure upper limit: ✓ [:data] [, ] set upper limit (-4294967295 to +4294967295). 2 ✓ [:data]? [] query upper limit. ✓ :lower path to configure lower limit...
Page 351
15-6 scpi reference tables model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual table 15-2 display command summary command description default parameter ref scpi display (see note) sec 1 [:window[1]] ✓ :text path to control user text messages. ✓ :data ascii message “a” (up to 12 characters). (none) ✓ :...
Page 352
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual scpi reference tables 15-7 table 15-3 format command summary command description default parameter ref scpi format sec 14 [:data] [,] select data format (ascii, sreal or dreal). Ascii [:data]? Query data format. ✓ :elements specify data elements (rea...
Page 353
15-8 scpi reference tables model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual table 15-4 route command summary command description default parameter ref scpi route :monitor specify one channel to be monitored. Sec 7 :state enable or disable channel monitoring. Off :state? Query state of channel monit...
Page 354
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual scpi reference tables 15-9 route :multiple path to control multiple channels: sec 2 :open open channel(s) specified in list. Unlisted channels not affected. :close close channel(s) specified in list 4 . Unlisted channels not affected. :state? Query c...
Page 355
15-10 scpi reference tables model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual table 15-5 sense command summary command description default parameter ref scpi [sense[1]] :function [, ] select function: ‘voltage[:dc]’, ‘voltage :ac’, ‘current[:dc]’, ‘current:ac’, ‘resistance’, ‘fresistance’, ‘temperat...
Page 356
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual scpi reference tables 15-11 [sense[1]] :voltage[:dc] path to configure dc voltage. Sec 3 ✓ :aperture [, ] set integration rate in seconds (60hz; 1.67e-4 to 1, 50hz; 2e-4 to 1). (note 2) sec 4 :aperture? [] query aperture integration rate. :nplcycles ...
Page 357
15-12 scpi reference tables model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual [sense[1]] :voltage:ac path to configure ac voltage. Sec 3 ✓ :aperture [, ] set integration rate in seconds (60hz; 1.67e-4 to 1, 50hz; 2e-4 to 1). (note 2) sec 4 :aperture? [] query aperture integration rate. :nplcycles [,...
Page 358
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual scpi reference tables 15-13 [sense[1]] :current[:dc] path to configure dc current. Sec 3 ✓ :aperture [, ] set integration rate in seconds (60hz; 1.67e-4 to 1, 50hz; 2e-4 to 1). (note 2) sec 4 :aperture? [] query aperture integration rate. :nplcycles ...
Page 359
15-14 scpi reference tables model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual [sense[1]] :current:ac path to configure ac current. Sec 3 ✓ :aperture [, ] set integration rate in seconds (60hz; 1.67e-4 to 1, 50hz; 2e-4 to 1). (note 2) sec 4 :aperture? [] query aperture integration rate. :nplcycles [,...
Page 360
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual scpi reference tables 15-15 [sense[1]] :resistance path to configure resistance. Sec 3 ✓ :aperture [, ] set integration rate in seconds (60hz; 1.67e-4 to 1, 50hz; 2e-4 to 1). (note 2) sec 4 :aperture? [] query aperture integration rate. :nplcycles [,...
Page 361
15-16 scpi reference tables model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual [sense[1]] :fresistance path to configure four-wire resistance. Sec 3 ✓ :aperture [, ] set integration rate in seconds (60hz; 1.67e-4 to 1, 50hz; 2e-4 to 1). (note 2) sec 4 :aperture? [] query aperture integration rate. :n...
Page 362
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual scpi reference tables 15-17 [sense[1]] :temperature path to configure temperature: sec 3 ✓ :aperture [, ] set integration rate in seconds (60hz; 1.67e-4 to 1, 50hz; 2e-4 to 1). (note 2) sec 4 :aperture? [] query aperture integration rate. :nplcycles ...
Page 363
15-18 scpi reference tables model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual [sense[1]] :temperature :tcouple path to configure thermocouple: 5 sec 3 :type [, ] select t/c type (j, k, t, e, r, s, b, n). K :type? [] query t/c type. :odetect enable or disable t/c open detector. Off :odetect? Query st...
Page 364
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual scpi reference tables 15-19 [sense[1]] :frequency path to configure frequency. Sec 3 :aperture [, ] sets gate time for frequency measurements in seconds (0.01 to 1.0). 1.0 sec 4 :aperture? [] query frequency gate time. :digits [, ] specify measuremen...
Page 365
15-20 scpi reference tables model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual [sense[1]] :continuity path to configure continuity test: sec 3 :threshold set threshold resistance in ohms (1 to 1000). 10 :threshold? Query threshold resistance. Notes: 1. Caverage:delay and ratio:delay are coupled. Chan...
Page 366
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual scpi reference tables 15-21 table 15-6 status command summary command description default parameter ref scpi status (note 1) sec 11 ✓ :measurement path to control measurement event registers: [:event]? Read the event register. (note 2) :enable progra...
Page 367
15-22 scpi reference tables model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual table 15-7 system command summary command description default parameter ref scpi system :preset return to :syst:pres defaults. Sec 14 ✓ :posetup select power-on setup: (rst, preset, sav0, sav1, sav2, or sav3). Sec 1 :poset...
Page 368
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual scpi reference tables 15-23 [:start]? Request lowest numbered volts/2-wire channel (usually 1); 0 = voltage measurements not supported. :end? Request highest numbered volts/2-wire channel. 0 = voltage measurements not supported. :achannel path to que...
Page 369
15-24 scpi reference tables model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual :csohms? Query whether card supports common-side 4-wire ohms (i.E., 7701). :time sec> set system time using 24-hour format. Sec 6 :time? Query system time. :date day> set system date (yr = 1999 or 20xx). Sec 6 : date? Quer...
Page 371
15-26 scpi reference tables model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual table 15-9 trigger command summary command description default parameter ref scpi initiate subsystem command path: sec 8 ✓ [:immediate] initiate one trigger cycle. ✓ :continuous enable or disable continuous initiation. (no...
Page 372
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual scpi reference tables 15-27 table 15-10 unit command summary command description default parameter ref scpi unit :temperature select temperature units (c, cel, f, far, or k). C sec 3 ✓ :temperature? Query temperature units. ✓ :voltage path to configu...
Page 373
15-28 scpi reference tables model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual.
Page 374
A specifications.
Page 375
Hw 11/07/02 revision e page 1 of 4 2700 multimeter/data acquisition system dc characteristics 1 conditions: med (1 plc) 2 or 10 plc or med (1 plc) with digital filter of 10 accuracy: ± (ppm of reading + ppm of range) (ppm = parts per million) e.G., 10ppm = 0.001%) function range resolution test curr...
Page 376
Hw 11/07/02 revision e page 2 of 4 2700 multimeter/data acquisition system dc speed vs. Noise rejection rate filter readings/s 12 digits rms noise 10v range nmrr cmrr 14 10 50 0.1 (0.08) 6.5 110 db 13 140 db 1 off 15 (12) 6.5 90 db 13 140 db 0.1 off 500 (400) 5.5 - 80 db 0.01 off 2000 (1800) 4.5 - 8...
Page 377
Hw 11/07/02 revision e page 3 of 4 2700 multimeter/data acquisition system ac specifications 1 accuracy: ±(% of reading + % of range), 23°c ±5°c function range resolution calibration cycle 3 hz- 10 hz 10 hz- 20 khz 20 khz- 50 khz 50 khz- 100 khz 100 khz- 300 khz voltage 2 100.0000 mv 0.1 µv 90 days ...
Page 378
Hw 11/07/02 revision e page 4 of 4 2700 multimeter/data acquisition system general specifications expansion slots: 2 power supply: 100v / 120v / 220v / 240v +10%. Line frequency: 45hz to 66hz and 360hz to 440hz, automatically sensed at power-up. Power consumption: 28va. Operating environment: specif...
Page 379: 7700
Hw 10/10/02 rev. B general 20 channels: 20 channels of 2-pole relay input. All channels config- urable to 4-pole. 2 channels: 2 channels of current only input. Relay type: latching electromechanical. Actuation time: capabilities channels 1-20: multiplex one of 20 2-pole or one of 10 4-pole signals i...
Page 380: Accuracy Calculations
Specifications a-7 accuracy calculations the information below discusses how to calculate accuracy for both dc and ac characteristics. Calculating dc characteristics accuracy dc characteristics accuracy is calculated as follows: accuracy = ±(ppm of reading + ppm of range) (ppm = parts per million, a...
Page 381
A-8 specifications calculating dbm characteristics accuracy as an example of how to calculate the actual reading limits for a 13dbm measurement with a reference impedance of 50 Ω , assume an applied signal of 0.998815v. The relationship between voltage and dbm is as follows: from the previous exampl...
Page 382: Additional Derating Factors
Specifications a-9 thus, the actual reading accuracy is 10mv ±36mv or 10.036mv to 9.964mv. Applying the voltage reading accuracy into the db equation yields: thus, the actual reading accuracy is -60db + 0.031213db to -60db - 0.031326db. Dbm and db for other voltage inputs can be calculated in exactl...
Page 383: Optimizing Measurement Speed
A-10 specifications optimizing measurement speed the configurations listed below assume that the multimeter has had factory setups restored. Dc voltage, dc current, and resistance: • select 3 ½ digits, 0.01 plc, filter off, fixed range. Ac voltage and ac current: • select 3 ½ digits, 0.01 plc, filte...
Page 384
B model 7700 connection guide.
Page 385
B-2 model 7700 connection guide model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual card configuration — schematic figure b-1 shows a simplified schematic diagram of the model 7700 module. As shown, the model 7700 has channels that are grouped into two banks of ten channels (twenty channels total). Bac...
Page 386
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual model 7700 connection guide b-3 figure b-1 simplified schematic for model 7700 notes: cold junction ref x3 channel 1 hi lo channel 10 hi lo (channels 2–9) channel 11 hi lo channel 20 hi lo (channels 12–19) channel 21 hi lo channel 22 hi lo amps hi lo ...
Page 387: Connections and Wiring
B-4 model 7700 connection guide model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual connections and wiring warning the following information is intended for qualified service personnel. Do not make or break switching module connections unless qualified to do so. Warning to prevent electric shock that ...
Page 388: Screw Terminals
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual model 7700 connection guide b-5 screw terminals figure b-2 shows how to access the screw terminals on the model 7700. Channel designa- tions for the screw terminals are contained in figure b-3 . Figure b-2 screw terminal access sense (ohms, 4-wire) i...
Page 389: Wiring Procedure
B-6 model 7700 connection guide model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual figure b-3 model 7700 screw terminal channel designations wiring procedure use the following procedure to wire the model 7700 module. Make all connections using correct wire size (up to 20 awg). Also, make sure to add ...
Page 390: Typical Connections
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual model 7700 connection guide b-7 figure b-4 wire dressing typical connections the following examples show typical wiring connections for the following types of measurements: • thermocouple connections, figure b-5 • Ω 2-wire and thermistor connections,...
Page 391
B-8 model 7700 connection guide model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual figure b-5 thermocouple connections figure b-6 Ω 2-wire and thermistor connections channel 1 hi lo channel 20 hi lo (channels 2-19) thermocouple channel 1 hi lo channel 20 hi lo (channels 2-19) resistor or thermistor.
Page 392
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual model 7700 connection guide b-9 figure b-7 Ω 4-wire and rtd connections figure b-8 current connections (ac or dc) channel 1 hi lo channel 10 hi lo (channels 2-9) channel 11 hi lo channel 20 hi lo (channels 12-19) resistor or 4-wire rtd resistor or 4-...
Page 393: Connection Log
B-10 model 7700 connection guide model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual figure b-9 voltage connections (dc or ac) connection log make a copy of table b-1 and affix it to the cover of the model 7700. Use this to record connection information and channel descriptions as needed. Channel 1 hi...
Page 394
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual model 7700 connection guide b-11 table b-1 connection log model 7700 channel color description amps com h l input h l sense h l ch1 h l ch2 h l ch3 h l ch4 h l ch5 h l ch6 h l ch7 h l ch8 h l ch9 h l ch10 h l ch11 h l ch12 h l ch13 h l ch14 h l ch15 ...
Page 395
B-12 model 7700 connection guide model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual.
Page 396
C status and error messages.
Page 397
C-2 status and error messages model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual table c-1 status and error messages number description event -440 -430 -420 -410 -363 -350 -330 -314 -315 -285 -284 -282 -281 -260 -241 -230 -225 -224 -223 -222 -221 -220 -215 -214 -213 -212 -211 -210 -202 -201 -200 -178...
Page 398
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual status and error messages c-3 -148 -144 -141 -140 -128 -124 -123 -121 -120 -114 -113 -112 -111 -110 -109 -108 -105 -104 -103 -102 -101 -100 character data not allowed character data too long invalid character data character data error numeric data no...
Page 399
C-4 status and error messages model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual +101 +121 +122 +123 +124 +125 +126 +161 +171 +174 +180 +301 +302 +303 +304 +305 +306 +307 +308 +309 +310 +311 +312 +313 +314 operation complete device calibrating device settling device ranging device sweeping device mea...
Page 400
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual status and error messages c-5 +400 +401 +402 +403 +404 +405 +406 +407 +408 +409 +410 +411 +412 +413 +414 +415 +416 +417 +418 +419 +420 +421 +422 +423 +424 +425 +426 +427 +428 +429 +430 +438 +439 +450 +451 +452 +453 +454 +455 calibration messages: 10v...
Page 401
C-6 status and error messages model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual +456 +457 +458 +459 +460 +461 +462 +463 +464 +465 +466 +467 +468 +469 +470 +471 +472 +473 +474 +475 +476 +477 +478 +479 +480 +481 +482 +483 +484 +485 +486 +487 +488 +489 +490 +491 +492 +493 +494 +495 1 vac zero error 1 v...
Page 402
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual status and error messages c-7 note scpi-confirmed messages are described in volume 2: command reference of the standard commands for programmable instruments. Refer to the system:error? Command. +496 +497 +498 +500 +510 +511 +512 +513 +514 +515 +516 +...
Page 403
C-8 status and error messages model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual.
Page 404
D signal processing sequence and data flow.
Page 405: Signal Processing Sequence
D-2 signal processing sequence and data flow model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual signal processing sequence basic signal processing the signal is applied to the multimeter input via front panel input terminals or a switching module. When a channel is closed or scanned, the signal conne...
Page 406
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual signal processing sequence and data flow d-3 signal processing using instrument features figure d-2 shows the processing sequence for an input signal with various instrument fea- tures enabled. If a feature is not enabled, the reading simply falls th...
Page 407
D-4 signal processing sequence and data flow model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual ocomp (offset-compensated ohms) the model 2700 performs a normal ohms measurement by sourcing a known current (i), measuring the voltage (v), and then calculating the resistance (r = v/i). Offset- compensa...
Page 408
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual signal processing sequence and data flow d-5 math next in the signal processing sequence is a math operation (mx+b, percent, or recipro- cal). These math operations allow you to mathematically manipulate the reading (x) that is applied to this block ...
Page 409
D-6 signal processing sequence and data flow model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual signal processing using ratio or ch avg with a switching module installed, the ratio or average of two channels can be calculated. Figure d-3 shows where ratio or ch avg is calculated in the signal process...
Page 410
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual signal processing sequence and data flow d-7 data flow (remote operation) remote operation can be used with triggering configured to perform a specified number of measurements and then stop. The various read commands (sens:data?, fetch?, read?, meas?,...
Page 411: Sense and Sample Buffer
D-8 signal processing sequence and data flow model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual note for the following discussion, a “data array” is defined as the group of data ele- ments that are included with each measured reading. Each data array includes the reading as well as the channel, readin...
Page 412: [Sens[1]]:data[Latest]?
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual signal processing sequence and data flow d-9 [sens[1]]:data[latest]? [sens[1]]:data:fresh? These commands are used to return (read) the last processed data array stored in the sam- ple buffer. [sens[1]]:data[:latest]? This command returns (reads) one...
Page 413: Fetch?
D-10 signal processing sequence and data flow model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual fetch? Read? Measure? Calc[1]:data[latest]? Calc[1]:data:fresh? As shown in figure d-4 , these commands are used to read data arrays output from the calc1 math block. However, if there is no math function...
Page 414: Calc3:lim1:fail?
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual signal processing sequence and data flow d-11 measure? The measure? Command places the instrument in a “one-shot” measurement mode (which places one data array in the sample buffer) and then performs a read?. With no math function enabled, the one da...
Page 415: Calc2:imm?
D-12 signal processing sequence and data flow model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual calc2:imm? Calc2:imm calc2:data? Statistical information (minimum, maximum, mean, standard deviation, and peak-to-peak) is available for the readings stored in the buffer (data store). When the desired ca...
Page 416: Scanning
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual signal processing sequence and data flow d-13 scanning for remote operation, scanning is normally performed with continuous initiation disabled (init:cont off). The sample count (samp:count) specifies the number of channels to scan and store in the b...
Page 417
D-14 signal processing sequence and data flow model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual.
Page 418
E measurement considerations.
Page 419: Measurement Considerations
E-2 measurement considerations model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual measurement considerations low-level voltage measurements made using the model 2700 can be adversely affected by various types of noise or other unwanted signals that can make it very difficult to obtain accurate voltag...
Page 420: Thermoelectric Generation
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual measurement considerations e-3 thermoelectric generation figure e-1 shows a representation of how thermal emfs are generated. The test leads are made of the a material, while the source under test is the b material. The temperatures between the junct...
Page 421: Minimizing Thermal Emfs
E-4 measurement considerations model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual minimizing thermal emfs to minimize thermal emfs, use only copper wires, lugs, and test leads for the entire test setup. Also, it is imperative that all connecting surfaces are kept clean and free of oxides. As noted in...
Page 422: Source Resistance Noise
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual measurement considerations e-5 source resistance noise noise present in the source resistance is often the limiting factor in the ultimate resolution and accuracy of model 2700 measurements. The following paragraphs discuss the genera- tion of johnso...
Page 423: Magnetic fields
E-6 measurement considerations model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual magnetic fields when a conductor loop cuts through magnetic lines of force, a very small current is gener- ated. This phenomenon will frequently cause unwanted signals to occur in the test leads of a test system. If the ...
Page 424: Ground Loops
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual measurement considerations e-7 ground loops when two or more instruments are connected together, care must be taken to avoid unwanted signals caused by ground loops. Ground loops usually occur when sensitive instrumentation is connected to other inst...
Page 425
E-8 measurement considerations model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual figure e-3 shows how to connect several instruments together to eliminate this type of ground loop problem. Here, only one instrument is connected to power line ground. Ground loops are not normally a problem with instr...
Page 426: Shielding
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual measurement considerations e-9 shielding warning do not float input lo more than 30v rms, 42.4v peak above earth ground with an exposed shield connected to input lo. To avoid a pos- sible shock hazard, surround the lo shield with a second safety shie...
Page 427: Meter Loading
E-10 measurement considerations model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual meter loading loading of the voltage source by the model 2700 becomes a consideration for high source resistance values. As the source resistance increases, the error caused by meter loading increases. Figure e-5 shows...
Page 428
F temperature equations • thermocouple equation — documents the its-90 inverse function polynomial and the coefficients to calculate thermocouple temperature. • thermistor equation — documents the steinhart-hart equation which is used to calculate thermistor temperature. • rtd equation — documents t...
Page 429: Thermocouple Equation
F-2 temperature equations model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual thermocouple equation the model 2700 uses the its-90 inverse function coefficients for the polynomial to calcu- late thermocouple temperature. The model 2700 measures the thermocouple voltage, and then calculates temperature...
Page 430
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual temperature equations f-3 table f-2 type e inverse function polynomial -200°c to 0°c (-8,825µv to 0µv) 0°c to 1,000°c (0µv to 76,373µv) c 0 = 0.0 0.0 c 1 = 1.697 728 8 × 10 -2 1.705 703 5 × 10 -2 c 2 = -4.351 497 0 × 10 -7 -2.330 175 9 × 10 -7 c 3 = ...
Page 431
F-4 temperature equations model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual table f-4 type k inverse function polynomial -200°c to 0°c (-5,891µv to 0µv) 0°c to 500°c (0µv to 20,644µv) 500°c to 1,372°c (20,644µv to 54,886µv) c 0 = 0.0 0.0 -1.318 058 × 10 2 c 1 = 2.517 346 2 × 10 -2 2.508 355 2 × 10 -...
Page 432
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual temperature equations f-5 table f-6 type r inverse function polynomial -50°c to 250°c (-226µv to 1,923µv) 250°c to 1,200°c (1,923µv to 13,228µv) 1,064°c to 1,664.5°c (11,361µv to 19,739µv) 1,664.5°c to 1,768.1°c (19,739µv to 21,103µv) c 0 = 0.0 1.334...
Page 433: Thermistor Equation
F-6 temperature equations model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual thermistor equation temperature (in kelvin) is calculated using the steinhart-hart equation as follows: where: t k is the calculated temperature in kelvin. Lnr is the natural log of the measured resistance of the thermistor....
Page 434: Rtd Equation
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual temperature equations f-7 selecting a thermistor — the thermistor manufacturers specified curve fitting values (a, b, and c) may not be exactly the same as the ones used by the model 2700. If they are not exactly the same, perform the following steps...
Page 435
F-8 temperature equations model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual r rtd = r 0 [1 + at + bt 2 + ct 3 (t-100)] where: r rtd is the calculated resistance of the rtd r 0 is the known rtd resistance at 0°c t is the temperature in °c a = alpha [1 + (delta/100)] b = -1 (alpha)(delta)(1e-4) c = -1...
Page 436
G ieee-488 bus overview.
Page 437: Introduction
G-2 ieee-488 bus overview model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual introduction the ieee-488 bus is a communication system between two or more electronic devices. A device can be either an instrument or a computer. When a computer is used on the bus, it serves as a supervisor of the communi...
Page 438
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual ieee-488 bus overview g-3 figure g-1 ieee-488 bus configuration device 1 able to talk, listen, and control (computer) device 2 able to talk and listen 2700 device 3 only able to listen (printer) device 4 only able to talk dav nrfd ndac ifc atn srq ren...
Page 439: Bus Lines
G-4 ieee-488 bus overview model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual there are two categories of controllers: system controller and basic controller. Both are able to control other instruments, but only the system controller has the absolute authority in the system. In a system with more than...
Page 440: Bus Management Lines
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual ieee-488 bus overview g-5 bus management lines the five bus management lines help to ensure proper interface control and management. These lines are used to send the uniline commands. Atn (attention) — the atn state determines how information on the ...
Page 441: Bus Commands
G-6 ieee-488 bus overview model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual once all ndac and nrfd are properly set, the source sets dav low, indicating to accept- ing devices that the byte on the data lines is now valid. Nrfd will then go low, and ndac will go high once all devices have accepted th...
Page 442
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual ieee-488 bus overview g-7 table g-1 ieee-488 bus command summary command type command state of atn line comments uniline multiline universal addressed unaddressed common scpi ren (remote enable) eoi ifc (interface clear) atn (attention) srq llo (loca...
Page 443: Uniline Commands
G-8 ieee-488 bus overview model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual uniline commands atn, ifc, and ren are asserted only by the controller. Srq is asserted by an external device. Eoi may be asserted either by the controller or other devices depending on the direction of data transfer. The fo...
Page 444: Addressed Multiline Commands
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual ieee-488 bus overview g-9 addressed multiline commands addressed commands are multiline commands that must be preceded by the device listen address before that instrument will respond to the command in question. Note that only the addressed device wi...
Page 445: Common Commands
G-10 ieee-488 bus overview model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual common commands common commands are commands that are common to all devices on the bus. These com- mands are designated and defined by the ieee-488.2 standard. Generally, these commands are sent as one or more ascii charact...
Page 446
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual ieee-488 bus overview g-11 figure g-3 command codes d 7 d 6 d 5 d 4 x 0 0 0 command x 0 0 1 command x 0 1 0 primary address x 0 1 1 primary address x 1 0 0 primary address x 1 0 1 primary address x 1 1 0 x 1 1 1 bits d 3 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1...
Page 447: Typical Command Sequences
G-12 ieee-488 bus overview model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual typical command sequences for the various multiline commands, a specific bus sequence must take place to properly send the command. In particular, the correct listen address must be sent to the instrument before it will res...
Page 448: Ieee Command Groups
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual ieee-488 bus overview g-13 ieee command groups command groups supported by the model 2700 are listed in table g-5 . Common com- mands and scpi commands are not included in this list. Table g-5 ieee command groups handshake command group ndac = not da...
Page 449: Interface Function Codes
G-14 ieee-488 bus overview model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual interface function codes the interface function codes, which are part of the ieee-488 standards, define an instru- ment’s ability to support various interface functions and should not be confused with pro- gramming commands...
Page 450
Model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual ieee-488 bus overview g-15 pp (parallel poll function) — the instrument does not have parallel polling capabilities (pp0). Dc (device clear function) — dc1 defines the ability of the instrument to be cleared (initialized). Dt (device trigger function...
Page 451
G-16 ieee-488 bus overview model 2700 multimeter/switch system user’s manual.
Page 452: Index
Index symbols scpi signal oriented measurement measure:? [], [], 13-7 Ω symbol 5-13 Ω 2 and Ω 4 connections for front panel inputs 3-17 Ω 2 and Ω 4 connections for model 7700 switching module 3-18 numerics 2-wire functions 2-7 4-wire functions 2-8 4-wire rtds 3-25 connections 3-28 temperature measur...
Page 453
C cables 1-4 leakage 3-19 card menu 2-25 card: config 2-25 card: view 2-26 tree 2-27 carrying case 1-5 channel average 5-15, 5-18 basic operation 5-16 commands 5-18 delay 5-18 enabling/disabling 5-18 programming examples 5-19 remote programming 5-18 scanning 5-17 channel list parameter () 3-7 channe...
Page 454
Connectors digital i/o 1-12 ieee-488 1-12, 10-5 rs-232 interface 1-12, 10-21 trig link 1-12 contact information 1-2 continuity connections 3-36 continuity testing 3-36 connections 3-36 front panel input 3-36 model 7700 switching module 3-36 procedure 3-37 control sources 7-7 external trigger 7-8 imm...
Page 455
Math programming examples 5-14 multiple channel remote programming example 2-18 program and read register set programming example 11-18 range programming examples 4-5 rate and bandwidth programming examples 4-12 ratio and channel average programming examples 5-19 read error queue 11-20 rel programmi...
Page 456
I idle 7-7, 8-2, 8-13 ieee g-3 ieee command groups g-13 ieee-488 bus configuration g-3 bus overview g-1 connector 1-12, 10-5 ieee-488.2 common commands see common commands ieee-754 single precision format 14-3 inputs front panel 1-11, 1-26 inputs switch 1-11 inspection 1-3 interface function codes g...
Page 457
Current see current measurements (dci and aci) frequency and period see frequency and period measurements one-shot mode 13-6 ranges 4-2 resistance see resistance measurements ( Ω 2 and Ω 4) 3-16 setting speed 4-9 temperature see temperature measure- ments voltage see voltage measurements (dcv and ac...
Page 458
R rack mount kits 1-5 radio frequency interference e-6 range 4-2 auto ranging 4-3, 4-4 commands 4-3 keys 1-10 manual ranging 4-3, 4-4 measurement 4-2 programming examples 4-5 remote programming 4-3 scanning 4-3 range, digits, rate, bandwidth, and filter 4-1 rate 4-7 aperture 4-11 bandwidth 4-11 band...
Page 459
Triggering 8-13 resistance measurements ( Ω 2 and Ω 4) 3-16 connections 3-17 cable leakage 3-19 front panel inputs 3-17 model 7700 switching module 3-18 shielding 3-19 offset-compensated ohms 3-20 resistors sorting 9-16 response messages 10-17 multiple 10-17 sending 10-17 terminator (rmt) 10-17 rs-2...
Page 460
Source mode logic control 9-10 spe, spd (serial polling) 11-8 specifications a-5 speed setting measurement speed 4-9 vs. Noise characteristics 4-7 standard event status 11-11 status and error messages c-1 status byte and service request (srq) 11-6 commands 11-9 status indicators gpib 10-10 status st...
Page 461
U user setups see setups v voltage measurements (dcv and acv) 3-8 connections 3-8 front panel input 3-9 model 7700 switching module 3-10 dcv input divider 3-8 procedure 3-11 voltmeter complete 8-8 w warm-up 3-4 warranty information 1-2.
Page 462
Specifications are subject to change without notice. All keithley trademarks and trade names are the property of keithley instruments, inc. All other trademarks and trade names are the property of their respective companies. Keithley instruments, inc. Belgium: keithley instruments b.V. Bergensesteen...