- DL manuals
- Raritan
- Power distribution unit
- Dominion Px
- User Manual
Raritan Dominion Px User Manual
Summary of Dominion Px
Page 1
Copyright © 2011 raritan, inc. Dpx-0p-v1.5.1-e november 2011 255-80-6080-00 dominion px user guide release 1.5.1.
Page 2: Safety Guidelines
Warning! Read and understand all sections in this guide before installing or operating this product. Warning! Connect this product to an ac power source whose voltage is within the range specified on the product's nameplate. Operating this product outside the nameplate voltage range may result in el...
Page 3: Safety Instructions
1. Installation of this product should only be performed by a person who has knowledge and experience with electric power. 2. Make sure the line cord is disconnected from power before physically mounting or moving the location of this product. 3. This product is designed to be used within an electro...
Page 4
This document contains proprietary information that is protected by copyright. All rights reserved. No part of this document may be photocopied, reproduced, or translated into another language without express prior written consent of raritan, inc. © copyright 2011 raritan, inc. All third-party softw...
Page 5
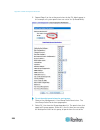
V contents safety guidelines ii safety instructions iii applicable models xiii what's new in the dominion px user guide xiv chapter 1 introduction 1 product models .............................................................................................................................. 1 product...
Page 6
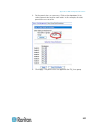
Contents vi mounting zero u models using claw-foot brackets................................................................... 12 mounting 1u or 2u models .......................................................................................................... 13 chapter 3 installation and configur...
Page 7
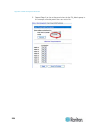
Contents vii circuit breaker status........................................................................................................49 outlets list......................................................................................................................... 50 all outlets control.....
Page 8
Contents viii disabling the pdu's ping response ...............................................................................108 setting up a digital certificate................................................................................................... 108 creating a certificate signing re...
Page 9
Contents ix snmp sets and configurable objects ............................................................................169 configuring the hysteresis ..............................................................................................170 disabling outlet switching.........................
Page 10
Contents x manual mode ...................................................................................................................198 inline monitor's web interface ................................................................................................... 198 menus ....................
Page 11
Contents xi appendix e using the ipmi tool set 230 channel commands .................................................................................................................. 230 authcap ..........................................................................230 info [channel number] ........
Page 12
Contents xii ipmi privilege levels ................................................................................................................. 243 appendix f additional pdu information 245 default hysteresis values for thresholds....................................................................
Page 13: Applicable Models
Xiii this user guide is applicable to the raritan pdus whose model names begin with dpxs, dpxr, dpcs, dpcr, or px. Note: for information on pdus whose model names begin with px2, see the "px-1000/2000 series" or "px2-3000/4000/5000 series" user guide or online help. Applicable models.
Page 14: Guide
Xiv the following sections have changed or information has been added to the dominion px user guide based on enhancements and changes to the equipment and/or user documentation. Product features (on page 3) circuit breaker orientation limitation (on page 6) connecting the dominion px to a power sour...
Page 15
What's new in the dominion px user guide xv please see the release notes for a more detailed explanation of the changes applied to this version of dominion px..
Page 16: Chapter 1
1 the dominion px is an intelligent power distribution unit (pdu) that allows you to reboot remote servers and other network devices and/or to monitor power in the data center. The intended use of the raritan dominion px is distribution of power to information technology equipment such as computers ...
Page 17
Chapter 1: introduction 2 zero u size 1u size 2u size.
Page 18
Chapter 1: introduction 3 product features the dominion px models vary in sizes and features. In general, the dominion px features include: for units with switching, the ability to power on, power off, and reboot the devices connected to each outlet. The ability to group outlets from multiple domini...
Page 19
Chapter 1: introduction 4 the ability to monitor the internal cpu temperature of the dominion px device the ability to display temperatures in both celsius and fahrenheit the ability to monitor environmental factors such as external temperature and humidity user-specified location attributes for env...
Page 20
Chapter 1: introduction 5 package contents the following sub-topics describe the equipment and other material included in the product package. Zero u products the dominion px device screws, brackets and/or buttons for zero u null-modem cable with rj-45 and db9f connectors on either end quick setup g...
Page 21: Chapter 2
6 this chapter describes how to rackmount a dominion px device. Only the most common rackmount method is displayed. Follow the procedure suitable for your model. In this chapter rackmount safety guidelines ...................................................................6 circuit breaker orientati...
Page 22
Chapter 2: rack-mounting the pdu 7 standard rackmount the zero u units are provided with high grade engineering polycarbonate isolation hardware to allow fixing in a variety of positions within the rack. For panel/flush mount, pull out fixing brackets are available on each end cap to allow mounting ...
Page 23
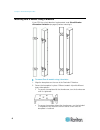
Chapter 2: rack-mounting the pdu 8 mounting zero u models using l-brackets if your pdu has circuit breakers implemented, read circuit breaker orientation limitation (on page 6) before mounting it. To mount zero u models using l-brackets: 1. Align the baseplates on the rear of the dominion px device....
Page 24
Chapter 2: rack-mounting the pdu 9 3. Align the l-brackets with the baseplates so that the five screw-holes on the baseplates line up through the l-bracket's slots. The rackmount side of brackets should face either the left or right side of the dominion px device. 4. Fasten the brackets in place wit...
Page 25
Chapter 2: rack-mounting the pdu 10 mounting zero u models using button mount if your pdu has circuit breakers implemented, read circuit breaker orientation limitation (on page 6) before mounting it. To mount zero-u models using button mount: 1. Align the baseplates on the rear of the dominion px de...
Page 26
Chapter 2: rack-mounting the pdu 11 4. Align the large mounting buttons with the mounting holes in the cabinet, fixing one in place and adjusting the other. 5. Depending on the type of your baseplates, either further tighten the thumbscrews or loosen the hex socket screws until the mounting buttons ...
Page 27
Chapter 2: rack-mounting the pdu 12 mounting zero u models using claw-foot brackets if your pdu has circuit breakers implemented, read circuit breaker orientation limitation (on page 6) before mounting it. To mount zero u models using claw-foot brackets: 1. Align the baseplates on the rear of the do...
Page 28
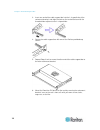
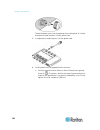
Chapter 2: rack-mounting the pdu 13 5. Using rack screws, fasten the dominion px device to the rack through the claw-foot brackets. Mounting 1u or 2u models using the appropriate brackets and tools, fasten the 1u or 2u dominion px device to the rack or cabinet. If your pdu has circuit breakers imple...
Page 29
Chapter 2: rack-mounting the pdu 14 3. Insert one end of the cable-support bar into the l-shaped hole of the rackmount bracket, and align the hole on the end of the bar with the threaded hole adjacent to the l-shaped hole. 4. Secure the cable-support bar with one of the raritan-provided cap screws. ...
Page 30: Chapter 3
15 this chapter explains how to install a dominion px device and configure it for network connectivity. In this chapter before you begin ....................................................................................15 connecting the dominion px to a power source ..................................
Page 31
Chapter 3: installation and configuration 16 note: if necessary, contact raritan technical support for the maximum operating temperature for your model. See maximum ambient operating temperature (on page 202). 2. Allow sufficient space around the dominion px device for cabling and outlet connections...
Page 32
Chapter 3: installation and configuration 17 configuring the dominion px there are two alternatives to initially configure a dominion px device: connect the dominion px device to a computer to configure it, using a serial connection between the dominion px and the computer. The computer must have a ...
Page 33
Chapter 3: installation and configuration 18 item # description 1 lan port 2 serial port 3 feature port 2. Connect the db9 end of the null-modem cable to the serial port (com) of the computer. Note: if you plan to use the serial connection to log in to the command line interface, leave the cable con...
Page 34
Chapter 3: installation and configuration 19 initial network and time configuration after the dominion px device is connected to your network, you must provide it with an ip address and some additional networking information. To configure the networking parameters: 1. Go to the computer that you con...
Page 35
Chapter 3: installation and configuration 20 static ip address - select none and assign the pdu a static ip address. You will be prompted for the address, network mask, and gateway. Note: the dominion px's ip address is automatically displayed in the system prompt. The default static ip address is...
Page 36
Chapter 3: installation and configuration 21 9. By default, the lan interface speed is set to auto, which allows the system to select the optimum speed. To keep the default, press enter. To set the speed to 10 or 100 mbps, type the speed you want and press enter. You are prompted to select the duple...
Page 37
Chapter 3: installation and configuration 22 then the system prompts you to specify the system location and contact person. 12. Now determine whether to enable or disable ntp servers for the date and time setting. synchronization with ntp servers: type y if you want the pdu's date and time to sync...
Page 38
Chapter 3: installation and configuration 23 13. If synchronization with ntp servers is enabled in the previous step, a list of time zones is displayed and the dominion px prompts you to select a time zone. Type the number or the name of the desired time zone..
Page 39
Chapter 3: installation and configuration 24 14. When prompted to enable the daylight savings time, type yes to enable it if the daylight savings time is applicable to the selected time zone, or type no to disable it. 15. You must determine which ntp servers are used if the ntp synchronization is en...
Page 40
Chapter 3: installation and configuration 25 if you want to terminate the configuration process, type c and press enter. The configuration is thus canceled and you are returned to the opening prompt. 17. If you entered y to confirm the configuration, you will be returned to the opening prompt afte...
Page 41
Chapter 3: installation and configuration 26 raritan sensor hubs cannot be cascaded so at most a sensor hub can be connected to each sensor port on the dominion px device. This diagram illustrates a configuration with a sensor hub connected. The dominion px device raritan-provided phone cable rarita...
Page 42
Chapter 3: installation and configuration 27 about contact closure sensors raritan's contact closure sensor (dpx-cc2-tr) can detect the open-and-closed status of the connected detectors/switches. It requires the integration of at least a discrete (on/off) detector/switch to work properly. The types ...
Page 43
Chapter 3: installation and configuration 28 note: each button controls the spring of each corresponding termination point. 3. Fully insert each wire of both third-party detectors/switches into each termination point. plug both wires of a detector/switch into the two termination points to the left...
Page 44
Chapter 3: installation and configuration 29 normally open: the open status of the connected detector/switch is considered normal. normally closed: the closed status of the connected detector/switch is considered normal. This is the default. 5. To set the normal state for channel 2, repeat step ...
Page 45
Chapter 3: installation and configuration 30 how to connect differential air pressure sensors you can have a raritan differential air pressure sensor connected to the dominion px device if the differential air pressure data is desired. With this sensor, the temperature around the sensor can be also ...
Page 46: Chapter 4
31 this chapter explains how to use the dominion px device. It describes the leds and ports on the pdu, and explains how to use the led display panel. It also explains how the circuit breaker (overcurrent protector) works and when the beeper sounds. In this chapter panel components ....................
Page 47
Chapter 4: using the pdu 32 outlets the total number of outlets varies from model to model. A small led is adjacent to each outlet to indicate the outlet or pdu state. The pdu is shipped from the factory with all outlets turned on. The table below explains how to interpret different outlet led state...
Page 48
Chapter 4: using the pdu 33 port used for... The serial (com) port on the computer. The serial port is also used to interface with some raritan access products (such as the dominion kx) through the use of a power cim. Feature connection to raritan's environmental sensors. Lan connecting the dominion...
Page 49
Chapter 4: using the pdu 34 three-digit row the three-digit row shows the readings for the selected component. Values that may appear include: current, voltage, or active power of the selected outlet current of the selected line or circuit breaker the text “fup,” which indicates that the firmware up...
Page 50
Chapter 4: using the pdu 35 xb: this indicates either the l2 current, or l2-n or l2-l3 voltage of the selected outlet/inlet, where x is the outlet/inlet number. For example, 1b represents the outlet/inlet 1's l2 current, or l2-n or l2-l3 voltage. xc: this indicates either the l3 current, or l3-n...
Page 51
Chapter 4: using the pdu 36 tip: a quick way to distinguish between voltage, current, and power is the placement of the decimal point in the display. Voltage has no decimal point, active power has a decimal point between the first and second digits, and current has a decimal point between the second...
Page 52
Chapter 4: using the pdu 37 resetting the button-type circuit breaker your button-type circuit breakers may look slightly different from the images shown in this section, but the reset procedure remains the same. To reset the button-type breakers: 1. Locate the breaker whose on button is up, indicat...
Page 53
Chapter 4: using the pdu 38 3. Examine your dominion px device and the connected equipment to remove or resolve the cause that results in the overload or short circuit. This step is required, or you cannot proceed with the next step. 4. Pull up the operating handle until the colorful rectangle or tr...
Page 54: Chapter 5
39 this chapter explains how to use the web interface to administer a dominion px device. In this chapter logging in to the web interface ..............................................................39 web interface elements .............................................................................
Page 55
Chapter 5: using the web interface 40 2. If any security alert message appears, click ok or yes to accept. The login page then opens. 3. Type your user name and password in the username and password fields. Note: both the user name and password are case sensitive, so make sure you capitalize them co...
Page 56
Chapter 5: using the web interface 41 note: depending on your model type and hardware configuration, elements shown on your home page may appear differently from this image. The web interface allows a maximum of 16 users to log in simultaneously. You must enable javascript in the web browser for pro...
Page 57
Chapter 5: using the web interface 42 changing your password to change your password: 1. Choose user management > change password. The change password page opens. 2. Type the current password in the old password field. 3. Type your new password in the new password and confirm new password fields. Pa...
Page 58
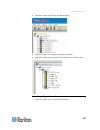
Chapter 5: using the web interface 43 alerts alert configuration alert policies alert policy editor alert destinations user management change password users & groups user/group system permissions user/group outlet permissions device settings pdu setup network security certificate date/time authentic...
Page 59
Chapter 5: using the web interface 44 outlet group editor diagnostics network interface network statistics ping host trace route to host device diagnostics help about dominion px to select a menu item: there are two ways to select an option from a menu: click the menu name to display a page listing ...
Page 60
Chapter 5: using the web interface 45 status panel the status panel appears on the left of every page in the interface. It shows: present date and time information about the user, including: user name user's present state (active, idle, and so on) ip address of the user's computer date and time of t...
Page 61
Chapter 5: using the web interface 46 information about all the users currently connected, including user name, ip address, and present state. Your active session is included in this list. Status of dominion px's serial port, indicating whether the serial port is supplying power to the connected rar...
Page 62
Chapter 5: using the web interface 47 note: if any psoc update failure occurs during the firmware upgrade process, the failure is reported in the status panel. See psoc firmware upgrade failure (on page 70). Status messages when you perform an operation from the web interface, such as creating a use...
Page 63
Chapter 5: using the web interface 48 default asterisk if a field has an asterisk after it, as shown below, then this field is currently set to its default value. If you change the default, the asterisk disappears. If you reset it to the default, the asterisk returns. Refresh many pages provide a re...
Page 64
Chapter 5: using the web interface 49 the status of each line is represented by a status bar. As the load on the line increases, the colored portion grows to fill the bar. A status bar that is nearly full indicates that the particular line is approaching its rated current limit. The colored portion ...
Page 65
Chapter 5: using the web interface 50 outlets list the outlets list displays each outlet on the dominion px device as a table row with a view of the power status, the rms current, and the rms power through the individual outlet. Note: rms refers to root mean square, a statistical method for measurin...
Page 66
Chapter 5: using the web interface 51 displaying additional details to display additional details about an outlet, click the outlet name. This displays the outlet details page. This page shows the name, status and line pair of the outlet, as well as: rms current power factor maximum rms current volt...
Page 67
Chapter 5: using the web interface 52 measurement accuracy voltage (per outlet): range 0-255v, +/-5%, resolution 1v current (per outlet): range 0-25a, +/-5%, resolution 0.01a tip: active energy per outlet is available using either the web interface or command line interface except for the models wit...
Page 68
Chapter 5: using the web interface 53 2. The device information panel displays the product name, serial number, and ip and mac addresses of the dominion px device, as well as detailed information about the firmware running in the pdu. 3. To open or save an xml file providing details for raritan tech...
Page 69
Chapter 5: using the web interface 54 displaying model configuration information to display information specific to the dominion px device that you are using, such as inlet or outlet types, trigger the device information dialog. To display the model configuration panel: 1. Choose maintenance > devic...
Page 70
Chapter 5: using the web interface 55 naming the dominion px device by default, the dominion px has a device name of its serial number. You may want to give it a more recognizable name for identification. The pdu's default host name is identical to the device name. Assign a different host name if ne...
Page 71
Chapter 5: using the web interface 56 tip: device name shown in the web interface should be identical to the snmp system name. However, the snmp system name becomes inconsistent with the device name when the device name is changed. To make both names identical, you must restart the dominion px devic...
Page 72
Chapter 5: using the web interface 57 role of a dns server as internet communications are carried out on the basis of ip addresses, appropriate dns server settings are required for mapping domain names (host names) to corresponding ip addresses, or the dominion px may fail to connect to the given ho...
Page 73
Chapter 5: using the web interface 58 modifying the network service settings the dominion px supports these network communication services: https, http, telnet and ssh. Https and http enable the access to the web interface, and telnet and ssh enable the access to the command line interface (see " us...
Page 74
Chapter 5: using the web interface 59 4. To use a different port for https, http, telnet, or ssh service, type a new port number in the corresponding text box. Valid range is 1 to 65535. Warning: different network services cannot share the same tcp port. 5. When you are finished, click apply. The se...
Page 75
Chapter 5: using the web interface 60 setting the date and time you can set the internal clock on the dominion px device manually, or link to a network time protocol (ntp) server and let it set the date and time for the dominion px. Important: if you are using raritan's power iq to manage the domini...
Page 76
Chapter 5: using the web interface 61 2. Enter a time zone by selecting an appropriate option from the time zone drop-down list. For example, select (gmt -3:00) argentina if you are located in argentina. 3. Choose one of the methods to set the date and time: to customize the date and time, select ...
Page 77
Chapter 5: using the web interface 62 to use the dhcp- or bootp-assigned ntp servers only, select the "use ntp servers provided by dhcp/bootp" checkbox, and leave the primary and secondary time server fields blank. The ntp servers will be automatically discovered. to make the dhcp- or bootp-assi...
Page 78
Chapter 5: using the web interface 63 5. Click apply. The settings are modified. Tip: the device altitude can be also set in meters by using the snmp set requests. Configuring the smtp settings the dominion px can be configured to send alerts or event messages to a specific administrator by email. T...
Page 79
Chapter 5: using the web interface 64 configuring the snmp settings you can enable or disable snmp communication between an snmp manager and the dominion px device. To configure the snmp communication: 1. Choose device settings > snmp settings. The snmp settings page opens. 2. Select the enable snmp...
Page 80
Chapter 5: using the web interface 65 note: to perform snmp v3 operations successfully, make sure the name of your user group does not contain any spaces. 5. Type the snmp mibii syslocation value in the system location field. 6. Type the snmp mibii syscontact value in the system contact field. 7. Cl...
Page 81
Chapter 5: using the web interface 66 4. When you finish, click apply. The retrieved data samples are stored immediately once this feature is enabled and the delay between samples is configured. After data retrieval is enabled, an external manager or application (such as raritan's power iq) can acce...
Page 82
Chapter 5: using the web interface 67 data for the inlet as shown below: inlet load unbalance, including the average, maximum and minimum inlet active power, including the average, maximum and minimum inlet apparent power, including the average, maximum and minimum inlet active energy, including the...
Page 83
Chapter 5: using the web interface 68 4. When the reset is complete, the login page opens. Now you can log back in to the dominion px device. Updating the firmware users must either use the admin account or have both the firmware update and unit reset privileges in order to successfully update the d...
Page 84
Chapter 5: using the web interface 69 3. Click upload. The firmware update page opens. It shows the current firmware version and the new firmware version, and gives you a last chance to terminate the update. Note: when upgrading a dominion px device over a low bandwidth network, after the firmware u...
Page 85
Chapter 5: using the web interface 70 psoc firmware upgrade failure all raritan pdus include two types of processors: the main pdu processor, which controls the unit's high level functionality, such as the web server, snmp agent, environmental sensor management and so on. The psoc (programmable syst...
Page 86
Chapter 5: using the web interface 71 in the firmware status report, the number prior to the square brackets refers to the inoperative psoc. The range of numbers within the square brackets indicates the impacted outlets. For example, "failed psocs: 2[o:5-8] 4[o:13-16] 6[o:21-24]" means: psoc 2 firmw...
Page 87
Chapter 5: using the web interface 72 copying configurations with bulk configuration the bulk configuration feature lets you save the settings of a configured dominion px device to your pc. You can use this configuration file to: copy that configuration to other dominion px devices of the same model...
Page 88
Chapter 5: using the web interface 73 saving a dominion px configuration a source device is an already configured dominion px device that is used to create a configuration file containing the settings that can be shared between dominion px devices. These settings include user and group configuration...
Page 89
Chapter 5: using the web interface 74 copying a dominion px configuration a target device is a dominion px device that loads another dominion px device's configuration file. Copying a dominion px configuration to a target device adjusts that dominion px device's settings to match those of the source...
Page 90
Chapter 5: using the web interface 75 setting up user profiles the dominion px is shipped with one built-in user profile: admin, which is used for initial login and configuration. This profile has full system and outlet permissions, and should be reserved for the system administrator. This profile c...
Page 91
Chapter 5: using the web interface 76 note: before entering any information in the user profile, make sure the user group is created and available for selection. See setting up user groups (on page 79). 2. In the user management panel, type the following information about the user in the correspondi...
Page 92
Chapter 5: using the web interface 77 3. Select a user group from the drop-down list in the user group field. The user group determines the system functions and outlets this user can access. if you select none, the user is not assigned to a user group. This means you have to set the user's permiss...
Page 93
Chapter 5: using the web interface 78 2. Select the user profile you want to modify from the existing users drop-down list. All information in the user profile is displayed except the password. 3. Make all necessary changes to the information shown. To change the password, type a new password in the...
Page 94
Chapter 5: using the web interface 79 2. Select the user from the "user (not in group)" drop-down list. The drop-down list shows all user profiles that have not been assigned to a user group. 3. Set the permissions as necessary. Click on the drop-down list to select a permission level for each permi...
Page 95
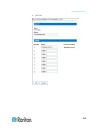
Chapter 5: using the web interface 80 creating a user group it is better to create a user group with appropriate permissions before creating new user profiles that will have these permissions. To create a user group: 1. Choose user management > users & groups. The user/group management page opens. T...
Page 96
Chapter 5: using the web interface 81 2. Select the user group from the group drop-down list. The permissions that apply to this group appear. If this is the first time you are setting the permissions for this group, all permissions are set to no. 3. Set the permissions as necessary. Click on the dr...
Page 97
Chapter 5: using the web interface 82 note: the "user (not in group)" field on this page is used to set individual user permissions. If you are setting group permissions, you may ignore this field. Some permissions must be enabled with other permissions for the effects to apply. Check the individual...
Page 98
Chapter 5: using the web interface 83 3. Set the permissions as necessary. Click on the drop-down list to select a permission level for each outlet. 4. When you are finished, click apply. The permissions are applied to the user group. Note: the "user (not in a group)" field on this page is used to s...
Page 99
Chapter 5: using the web interface 84 note: to modify a user group's system or outlet permissions, repeat the procedure for setting the system or outlet permissions and make any necessary changes. See setting the system permissions (on page 80) and setting the outlet permissions (on page 82). Deleti...
Page 100
Chapter 5: using the web interface 85 setting the global default outlet state set a global default for the power state of the outlets when the dominion px device is powered on. Setting an individual outlet's startup state to something other than device default overrides this default state for that o...
Page 101
Chapter 5: using the web interface 86 setting the global power cycling delay when an outlet is power cycled, it is turned off and then back on. The number you enter on the pdu setup page determines the length of time (in seconds) it takes for all outlets on the dominion px device to turn back on aft...
Page 102
Chapter 5: using the web interface 87 setting the outlet power-on sequence by default, the outlets are sequentially powered on in ascending order from outlet 1 to the highest-numbered outlet when turning on or power cycling all outlets on the dominion px device. You can change the order in which the...
Page 103
Chapter 5: using the web interface 88 naming and configuring outlets you can give each outlet a name to help you identify the it equipment connected to it. Besides, you can set the default state and power cycling delay for a specific outlet on the outlet setup page. Note: for configuring outlet thre...
Page 104
Chapter 5: using the web interface 89 viewing outlet details to display details about a particular outlet: 1. Choose details > outlet details. The outlet details page opens. 2. Select an outlet from the "show details of outlet" drop-down list. The page shows these details about the outlet: outlet ...
Page 105
Chapter 5: using the web interface 90 active power apparent power active energy (energy consumption, if applicable) note: to display the outlet setup page, click the setup link. See naming and configuring outlets (on page 88) for a picture of the outlet setup page. Power cycling an outlet power cycl...
Page 106
Chapter 5: using the web interface 91 setting up power thresholds and hysteresis the dominion px is shipped with certain pdu and outlet power thresholds already defined, and with a hysteresis value already set for all thresholds. You can change the default dominion px thresholds and hysteresis value...
Page 107
Chapter 5: using the web interface 92 threshold criterion upper non-critical threshold larger than or equal to the following formula: lower non-critical threshold + (2 x hysteresis) lower non-critical threshold larger than or equal to the following formula: lower critical threshold + hysteresis 4. W...
Page 108
Chapter 5: using the web interface 93 threshold criterion lower non-critical threshold larger than or equal to the following formula: lower critical threshold + hysteresis 5. When you are finished, click apply. The setup details are applied. Exception: for any 5a-rated outlet, default threshold valu...
Page 109
Chapter 5: using the web interface 94 monitoring unbalanced loads in a three-phase dominion px device, a load imbalance occurs when the current on a line differs from the average current of all three lines. The largest absolute difference in current is expressed as a percentage of the average curren...
Page 110
Chapter 5: using the web interface 95 configuring unbalanced load thresholds configuring these thresholds determines when the unbalanced load indicator changes colors from white to yellow or red. It also configures the unbalanced load event thresholds used in alert notifications. Unbalanced load det...
Page 111
Chapter 5: using the web interface 96 line details page to open the line details page, choose details > line details. The page opens and displays for each line the present current draw, the largest amount of current drawn since the dominion px device's last boot, and the amount of available current ...
Page 112
Chapter 5: using the web interface 97 each bank of outlets governed by a circuit breaker is listed as a table, and indicates what lines they draw power from. Each table contains the status of the circuit breaker, present current draw through that bank, the largest amount of current that was drawn by...
Page 113
Chapter 5: using the web interface 98 configuring the firewall the dominion px has a firewall that you can configure to prevent specific ip addresses and ranges of ip addresses from accessing the dominion px device. When the dominion px was initially configured, you were prompted to enable or disabl...
Page 114
Chapter 5: using the web interface 99 3. Click apply. The firewall is enabled. Changing the default policy after enabling the firewall, the default policy is to accept traffic from all ip addresses. This means only ip addresses discarded by a specific rule will not be permitted to access the dominio...
Page 115
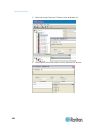
Chapter 5: using the web interface 100 to create firewall rules: 1. Choose device settings > security. The security settings page opens. Locate the panel labeled ip access control. 2. Ensure the enable ip access control checkbox is selected. 3. Create specific rules. See the table for different oper...
Page 116
Chapter 5: using the web interface 101 4. When finished, the rules appear in the ip access control panel. 5. Click apply. The rules are applied. Deleting firewall rules when any firewall rules become obsolete or unnecessary, remove them from the rules list. To delete a firewall rule: 1. Choose devic...
Page 117
Chapter 5: using the web interface 102 2. Set the default action. See changing the default action (on page 102). 3. Create rules that accept or drop traffic sending from specific addresses when they are associated with a specific user group. See creating group based access control rules (on page 103...
Page 118
Chapter 5: using the web interface 103 4. Click apply. The default action is applied. Creating group based access control rules group based access control rules accept or drop traffic intended for the dominion px device, based on the user's group membership. Like firewall rules, the order of rules i...
Page 119
Chapter 5: using the web interface 104 action do this... Field. click replace. This system replaces the existing rule with the one you just created. 4. When you are finished, click apply. The rules are applied. Deleting group based access control rules when any access control rule becomes unnecess...
Page 120
Chapter 5: using the web interface 105 enabling user blocking user blocking determines how many times a user can attempt to log in to the dominion px and fail authentication before the user's login is blocked. To enable user blocking: 1. Choose device settings > security. The security settings page ...
Page 121
Chapter 5: using the web interface 106 2. To prevent more than one person from using the same login at the same time, select the enable single login limitation checkbox. 3. To force users to change their passwords regularly, select the enable password aging checkbox, and then enter a number of days ...
Page 122
Chapter 5: using the web interface 107 enabling strong passwords use of strong passwords makes it more difficult for intruders to crack user passwords and access the dominion px device. By default, strong passwords should be at least eight characters long and contain upper- and lower-case letters, n...
Page 123
Chapter 5: using the web interface 108 4. When you are finished, click apply. The changes are applied. Disabling the pdu's ping response the dominion px device responds to the icmp ping request by default. You can have the pdu stop responding to any icmp ping request if necessary. To disable the pdu...
Page 124
Chapter 5: using the web interface 109 creating a certificate signing request follow this procedure to create the csr for your dominion px device. To create a csr: 1. Choose device setting > certificate. The first page of the ssl server certificate management page appears. 2. Provide the information...
Page 125
Chapter 5: using the web interface 110 field type this... Locality/city the city where your company is located. State/province the full name of the state or province where your company is located. Country (iso code) the country where your company is located. Use the standard iso country code. For a ...
Page 126
Chapter 5: using the web interface 111 installing a certificate after the ca provides a signed certificate according to the csr you submitted, you must install it on the dominion px device. To upload an ssl certificate, you must log in as the administrator (admin). To install the certificate: 1. Cho...
Page 127
Chapter 5: using the web interface 112 setting up external user authentication for security purposes, users attempting to log in to the dominion px must be authenticated. The dominion px supports the access using one of the following authentication mechanisms: local database of user profiles on the ...
Page 128
Chapter 5: using the web interface 113 the network port used by the ldap server the type of the ldap server, usually one of the following options: a generic ldap server novell directory service microsoft active directory ® (ad) if using a microsoft active directory server, consult your ad ad...
Page 129
Chapter 5: using the web interface 114 setting up ldap authentication to set up ldap authentication: 1. Choose device settings > authentication. The authentication settings page opens..
Page 130
Chapter 5: using the web interface 115 2. Select the ldap radio button to enable the ldap section of the page. 3. Type of external ldap/ldaps server. Choose from among the options available:.
Page 131
Chapter 5: using the web interface 116 generic ldap server. novell directory microsoft active directory. Active directory is an implementation of ldap/ldaps directory services by microsoft for use in windows environments. 4. User ldap server - type the ip address or dns name of your ldap/ldaps...
Page 132
Chapter 5: using the web interface 117 12. Bind dn - type the bind dn when bind dn and password are required. 13. Password - type the bind password when bind dn and password are required. 14. Base dn of user ldap server - enter the name you want to bind against the ldap/ldaps server (up to 255 chara...
Page 133
Chapter 5: using the web interface 118 2. Click the radius radio button. 3. Type the ip address of the radius server in the server field. 4. Type the shared secret in the shared secret field. The shared secret is necessary to protect communication with the radius server. 5. By default, the dominion ...
Page 134
Chapter 5: using the web interface 119 2. Log in to the dominion px web interface. The dominion px should have detected the connected sensors, and display them in the web interface. 3. Identify each sensor through the sensor's serial number. See identifying environmental sensors (on page 119). 4. Th...
Page 135
Chapter 5: using the web interface 120 the serial number for each sensor appears listed in the web interface after each sensor is detected by the dominion px. Match the serial number from the tag to those listed in the sensor table..
Page 136
Chapter 5: using the web interface 121 managing environmental sensors the dominion px starts to retrieve an environmental sensor's reading and/or state and records the state transitions after the environmental sensor is managed. The dominion px device can manage a maximum of 16 environmental sensors...
Page 137
Chapter 5: using the web interface 122 manually assign an id number to the sensor: a sensor becomes "managed" after you assign an id number to it. The default name is automatically assigned. If another sensor already occupied the id number at the time of assignment, that sensor becomes "unmanaged"...
Page 138
Chapter 5: using the web interface 123 2. If the sensor selected in the previous step is a raritan contact closure sensor connected with third-party detectors/switches, the on/off sensor subtype field is displayed for you to select the detector/switch type: contact: the detector/switch is designed...
Page 139
Chapter 5: using the web interface 124 4. Describe the sensor's location by assigning alphanumeric values to the x, y and z coordinates. See describing the sensor location (on page 126). All location fields are optional. 5. Configure the upper and lower thresholds for numeric sensors. the upper cr...
Page 140
Chapter 5: using the web interface 125 to enable the hysteresis, type a non-zero value, which must meet the rules described in the table: threshold criterion upper critical threshold larger than or equal to the following formula: upper non-critical threshold + hysteresis upper non-critical thresho...
Page 141
Chapter 5: using the web interface 126 describing the sensor location optional: use the x, y and z coordinates to describe each sensor's physical location. You can use these location values to track records of environmental conditions in fixed locations around your it equipment. The x, y and z value...
Page 142
Chapter 5: using the web interface 127 now you can use the number of rack units to describe the height of the sensor's location. See configuring environmental sensors (on page 122). Viewing sensor readings and states the home page shows the following information for environmental sensors: number of ...
Page 143
Chapter 5: using the web interface 128 states of managed sensors an environmental sensor shows the state after being managed. Available sensor states vary depending on the sensor type -- numeric or discrete. For example, a contact closure sensor is a discrete sensor so it switches between three stat...
Page 144
Chapter 5: using the web interface 129 "normal" state this state indicates the sensor is in the normal state. For a contact closure sensor, this state is the normal state you have set. If the normal state is set to normally closed, the normal state means the contact closure switch is closed. If the ...
Page 145
Chapter 5: using the web interface 130 "below lower non-critical" state only a numeric sensor shows this state. This state means the sensor reading is below the lower non-critical threshold as indicated below: lower critical threshold note: the symbol "above upper non-critical" state only a numeric ...
Page 146
Chapter 5: using the web interface 131 assigning or changing the id number instead of letting the dominion px assign an id number to the sensor, you can manually assign any id number (1 to 16) to a detected or managed sensor. With the feature, you can: have a sensor managed if it has not been manage...
Page 147
Chapter 5: using the web interface 132 components of an alert the alert is a condition statement: if "a" happens, then do "b". This condition statement describes what the dominion px does in certain situations and is composed of multiple parts: event: this is the "a" portion of an alert and describe...
Page 148
Chapter 5: using the web interface 133 creating alert destinations to set up new alerts, first create the necessary destinations on the alert destinations page. Choose alerts > alert destinations to open the page..
Page 149
Chapter 5: using the web interface 134 this table on the page lists the existing destinations configured on the dominion px. Two destinations, event log and switch outlets, are always available as part of the system. You can add and delete additional destinations. There are four destination types: e...
Page 150
Chapter 5: using the web interface 135 3. Type the ip address of the snmp manager in the destination ip field. This must be a numeric ip address. Dns names are not allowed. Tip: although you can specify snmp destinations in this field, it is highly recommended to specify the snmp destination on the ...
Page 151
Chapter 5: using the web interface 136 creating alert policies once your destinations are created, you can create policies based on notifying these destinations. This is done on the alert policies editor, which you can reach by choosing alerts > alert policy editor. On this page, you can select an e...
Page 152
Chapter 5: using the web interface 137 event log: causes the dominion px to record alert notifications in the system log. addresses listed under email: causes the dominion px to send alert notifications to the specified e-mail address. addresses listed under snmp: causes an snmp trap to be sen...
Page 153
Chapter 5: using the web interface 138 creating alerts the alert configuration page is where you specify how the dominion px responds to certain events. First describe an event that triggers an alert and then select the policy the dominion px should take in response. To create an alert: 1. Choose al...
Page 154
Chapter 5: using the web interface 139 3. If you selected a line, outlet, or circuit breaker segment, indicate the specific line, outlet, or circuit breaker using the new drop-down list that appears. 4. Select an alert event that occurs to the specified segment. The list of events depends on the sel...
Page 155
Chapter 5: using the web interface 140 note: it is possible for an alert to set the same outlet state twice. For example, a temperature threshold alert is created with the event direction set to assert & deassert. This alert calls a policy that turns the outlet off. In such a scenario, the alert tri...
Page 156
Chapter 5: using the web interface 141 sample unit-level alert in this example, we want the dominion px to shut down most of its outlets if the dominion px device becomes too hot. However, since mission-critical servers are plugged into outlets 1 and 2, we want to leave them running. Our alert would...
Page 157
Chapter 5: using the web interface 142 sample environmental alert 2 we can configure a complimentary alert that looks something like this: event: environmental temperature; temperature above non-critical threshold event direction: deassert policy: outlets on + facilities this powers on all the outle...
Page 158
Chapter 5: using the web interface 143 upper non-critical threshold hysteresis upper non-critical reset lower non-critical reset hysteresis lower non-critical threshold lower critical reset hysteresis lower critical threshold the hysteresis values define a reset threshold. For upper thresholds, the ...
Page 159
Chapter 5: using the web interface 144 example: when hysteresis is useful this example demonstrates when a deassertion hysteresis is useful. The current critical threshold for outlet 1 is set to 10 amps (a). The current draw rises to 11a, triggering a current critical alert. The current then continu...
Page 160
Chapter 5: using the web interface 145 configuring the local event log follow this procedure to determine whether the local logging function is enabled and which types of events are logged in the local log. To configure the local event log: 1. Choose device settings > event log. The event log settin...
Page 161
Chapter 5: using the web interface 146 5. By default, when the local event log is enabled, seven event types appear in the event log assignments panel to the right. All are enabled by default. To disable any of these event types, deselect the appropriate checkboxes. Note: see event types (on page 24...
Page 162
Chapter 5: using the web interface 147 viewing the local event log to display the internal event log, choose maintenance > view event log. Each event entry in the local log consists of: date and time of the event type of the event a description of the event (for example, for an authentication ...
Page 163
Chapter 5: using the web interface 148 configuring the nfs logging this procedure describes how to enable the network file system (nfs) logging function and determine which types of events are recorded in the nfs log file. To configure the nfs logging: 1. Choose device settings > event log. The even...
Page 164
Chapter 5: using the web interface 149 configuring the smtp logging you can enable the simple mail transfer protocol (smtp) logging function and determine which types of events are recorded in the smtp log file. To configure the smtp logging: 1. Ensure the smtp server settings have been configured p...
Page 165
Chapter 5: using the web interface 150 configuring the snmp logging event logging can be performed by sending snmp traps to a third-party snmp manager. See using snmp (on page 161) for instructions on enabling snmp event logging. Configuring the syslog forwarding to make the dominion px automaticall...
Page 166
Chapter 5: using the web interface 151 5. Click apply. Syslog forwarding is configured. Note: if you want to disable syslog forwarding, deselect all checked event types under the syslog column and click apply. Then deselect enable syslog forwarding. If event types are still selected in the syslog co...
Page 167
Chapter 5: using the web interface 152 identifying other dominion px devices to add outlets from other dominion px devices, you must first identify which dominion px devices are sharing their outlets. To identify other dominion px devices: 1. Choose outlet groups > outlet group devices. The outlet g...
Page 168
Chapter 5: using the web interface 153 grouping outlets together once the participating dominion px devices have been added to list of outlet group devices, their individual outlets can be grouped together. Outlets that are grouped together power on and power off in unison, using a control panel fro...
Page 169
Chapter 5: using the web interface 154 5. A list of available dominion px devices and their outlets appears under collection of real outlets. Select the checkbox representing the desired physical outlet to make it part of the outlet group. All outlets that are selected are grouped together when you ...
Page 170
Chapter 5: using the web interface 155 4. The page refreshes once to indicate that the desired command was performed, and again a few seconds later to update the status of the outlet group. Note: the page must finish loading or refreshing before selecting an action. If you select an action before th...
Page 171
Chapter 5: using the web interface 156 diagnostics the dominion px provides the following tools in the web interface for diagnosing potential networking issues. Network interface network statistics ping host trace route to host device diagnostics network interface page the dominion px provides infor...
Page 172
Chapter 5: using the web interface 157 network statistics page the dominion px provides statistics about your network interface. To view statistics about your network interface: 1. Choose diagnostics > network statistics. The network statistics page opens. 2. Click refresh. The relevant information ...
Page 173
Chapter 5: using the web interface 158 ping host page ping is a network tool used to test whether a particular host or ip address is reachable across an ip network. Using the ping host page, you can determine if a target server or another dominion px is accessible. To ping the host: 1. Choose diagno...
Page 174
Chapter 5: using the web interface 159 4. Click trace route. The trace route command is executed for the given hostname or ip address and the maximum hops. The output of trace route is displayed in the result field. Saving a device diagnostics file when instructed by raritan technical support, you c...
Page 175
Chapter 5: using the web interface 160 2. To view the content of any topic, click the topic in the left pane. Then its content is displayed in the right pane. 3. To select a different topic, do any of the following: to view the next topic, click the next icon in the toolbar. to view the previous...
Page 176: Chapter 6
161 this snmp section helps you set up the dominion px for use with an snmp manager. The dominion px can be configured to send traps to an snmp manager, as well as receive get and set commands in order to retrieve status and configure some basic settings. In this chapter enabling snmp .................
Page 177
Chapter 6: using snmp 162 enabling snmp to communicate with an snmp manager, you must first enable the snmp agent on the dominion px device. To enable snmp: 1. Choose device settings > snmp settings. The snmp settings page opens. 2. Select the enable snmp agent checkbox to enable the dominion px to ...
Page 178
Chapter 6: using snmp 163 note: to perform snmp v3 operations successfully, make sure the name of your user group does not contain any spaces. 5. Type the snmp mibii syslocation value in the system location field. 6. Type the snmp mibii syscontact value in the system contact field. 7. Click on the l...
Page 179
Chapter 6: using snmp 164 configuring users for encrypted snmp v3 the snmp v3 protocol allows for encrypted communication. To take advantage of this, users need to have an encryption phrase, which acts as a shared secret between them and the dominion px. This encryption phrase can be set on the user...
Page 180
Chapter 6: using snmp 165 4. To use the user's password as the encryption phrase, select the use password as encryption phrase checkbox. 5. To specify a different encryption phrase, deselect this checkbox. Type a new phrase in the snmp v3 encryption phrase field, then type it again in the confirm sn...
Page 181
Chapter 6: using snmp 166 configuring the snmp traps the dominion px automatically keeps an internal log of events that occur. See setting up event logging (on page 144). These events can also be used to send snmp traps to a third party manager. Note that the dominion px sends traps via snmp v2c pro...
Page 182
Chapter 6: using snmp 167 6. When snmp logging is enabled, eight event types appear in the event log assignments panel to the right. All are disabled by default. To enable any of these event types, select the appropriate checkboxes. 7. Click apply. Snmp logging is configured. 8. From the maintenance...
Page 183
Chapter 6: using snmp 168 a false circuit breaker trip trap if the dominion px generates an snmp trap of voltage measurement failure for the circuit breaker, it indicates a false circuit breaker trip caused by the hardware failure. In that case, you have to return the pdu to raritan for fixing the p...
Page 184
Chapter 6: using snmp 169 layout opening the mib reveals the custom objects that describe the dominion px system at the unit level as well as at the individual-outlet level. As standard, these objects are first presented at the beginning of the file, listed under their parent group. The objects then...
Page 185
Chapter 6: using snmp 170 configuring the hysteresis you can configure the hysteresis values using the snmp set command. Different from the dominion px web interface, snmp accepts only integer values as the hysteresis values so decimal point values will be rejected. To set a decimal point value, you...
Page 186
Chapter 6: using snmp 171 changing id numbers of environmental sensors all id numbers of existing environmental sensors can be rearranged at a time by using the snmp mib variable "reorderexternalsensorstableentries" and a comma-separated list. Below are the guidelines of using this variable: id numb...
Page 187
Chapter 6: using snmp 172 6 to 9 7 to 16 11 remains unchanged since the original id numbers are not consecutive because of missing numbers 1, 3, 4, 8, 9 and 10, you must mark each missing number with a comma in the comma-separated list. Position 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 original id numbers 2, 5...
Page 188: Chapter 7
173 this section explains how to use the command line protocol (clp) interface to administer a dominion px device. In this chapter about the clp interface ........................................................................173 logging in to the clp interface ........................................
Page 189
Chapter 7: using the clp interface 174 with hyperterminal you can use any terminal emulation programs for local access to the command line interface. This section illustrates hyperterminal, which is part of windows operating systems prior to windows vista. To log in using hyperterminal: 1. Connect y...
Page 190
Chapter 7: using the clp interface 175 5. Type a name and press enter. The login name is case-sensitive, so make sure you capitalize the correct letters. Then you are prompted to enter a password. 6. Type a password and press enter. The password is case sensitive, so make sure you capitalize the cor...
Page 191
Chapter 7: using the clp interface 176 then you are prompted to enter a password. 4. Type a password and press enter. The password is case sensitive, so make sure you capitalize the correct letters. After properly entering the password, the clp:/-> system prompt appears. 5. You are now logged in to ...
Page 192
Chapter 7: using the clp interface 177 syntax the following is the syntax for the show command: clp:/-> show /system1/outlet where is the number of the outlet. To display information for all outlets, type the wildcard asterisk (*) instead of a number. Attributes you can use the name and powerstate a...
Page 193
Chapter 7: using the clp interface 178 example 1 - no attributes the diagram shows the output of the show command without any attributes entered. Example 2 - name attribute the diagram shows the output of the show command with the name attribute. Example 3 - powerstate attribute the diagram shows th...
Page 194
Chapter 7: using the clp interface 179 showing in-depth outlet information use the show command to display the rms current, power factor, max current, active power and apparent power of a specific outlet. To show in-depth outlet information: 1. Perform the show command on an outlet. This displays th...
Page 195
Chapter 7: using the clp interface 180 examples of showing in-depth outlet information 1. Perform the show command on the outlet without additional attributes. 2. Perform the show command on the associated sensors. Switching an outlet the set command can turn an outlet on or off..
Page 196
Chapter 7: using the clp interface 181 turning an outlet on using the keyword on turns the outlet on. Clp:/-> set /system1/outlet powerstate=on where is the number of the outlet. Turning an outlet off using the keyword off turns the outlet off. Clp:/-> set /system1/outlet powerstate=off where is the...
Page 197
Chapter 7: using the clp interface 182 showing environmental sensor information the following is the syntax for the show command for environmental sensors: clp:/-> show /system1/externalsensor where is the id number assigned to the environmental sensor while having the environmental sensor managed. ...
Page 198
Chapter 7: using the clp interface 183 example 1 - no attributes this diagram shows the output of the show command without any attributes entered for a humidity sensor, whose id number is 1..
Page 199
Chapter 7: using the clp interface 184 the diagram shows the output of the show command without any attributes entered for a contact closure sensor, whose id number is 3. Example 2 - name attribute the diagram shows the output of the show command with the name attribute for the environmental sensor ...
Page 200
Chapter 7: using the clp interface 185 configuring the thresholds for environmental sensors the following shows the syntax for configuring the thresholds of numeric environmental sensors, such as temperature sensors. Note that a discrete (on/off) sensor does not have threshold properties. Clp:/-> se...
Page 201
Chapter 7: using the clp interface 186 querying the pdu's serial number the show command with the keyword serialnumber queries the serial number of the dominion px device. Clp:/-> show -d properties=serialnumber /system1 resetting the dominion px device the reset command restarts the dominion px man...
Page 202
Chapter 7: using the clp interface 187 example 2 - getting in-depth help information to show detailed help information, add the option -output verbose between the help command and the queried command. The diagram shows the output of the help information for the show command in details..
Page 203: Chapter 8
188 the model name of a dominion px inline monitor follows this format: px-3nnn, where n is a numeric digit. Unlike most of the dominion px devices, an inline monitor may have multiple inlets. Each inlet is connected to an outlet only, so an inlet's rating is the same as an outlet's rating. Raritan ...
Page 204
Chapter 8: inline monitors 189 models with power sockets this diagram shows an inline monitor whose inlets and outlets are in the form of power sockets or receptacles. The total number of inlets and outlets varies depending on the model you purchased. Number description 1 inlets (the side labeled li...
Page 205
Chapter 8: inline monitors 190 number description 1 inlets (the side labeled line) 2 top cover 3 outlets (the side labeled load) 4 front panel with the led display 5 rear panel cord installation usually an inline monitor requires you to install power cords on both of its inlets and outlets unless th...
Page 206
Chapter 8: inline monitors 191 installation guidelines keep in mind that electricity is transmitted only between the inlet and outlet labeled with the same number. That is, electricity flows from the inlet labeled "ch1" to the outlet labeled "ch1," from the inlet labeled "ch2" to the outlet labeled ...
Page 207
Chapter 8: inline monitors 192 cord installation for a cable-gland type the cord installation procedure for all 1u cable-gland models is similar regardless of the inline monitor's ratings and total number of inlets and outlets. Description in this section is applicable to the following 1u models: si...
Page 208
Chapter 8: inline monitors 193 the cord is made from stranded copper wire. (use of aluminum wire is not permitted.) the inner diameter of each ring terminal on each wire is 5.3 mm. the cord diameter matches the cable gland's diameter. Model cable gland diameter single-phase models 11-17mm y-wi...
Page 209
Chapter 8: inline monitors 194 thread the power wires into the opening of the cable gland. A y-wired three-phase model requires a 5-wire power cord. 5. A single-phase model requires a 3-wire power cord. 6. Fasten power wires to appropriate wire terminals. A. Connect the ground wire (green or green/y...
Page 210
Chapter 8: inline monitors 195 single-phase model: y-wired three-phase model: b. Remove the clear plastic cover from the terminal block adjacent to the ground terminal. C. Connect the cord's remaining wires to the terminal block..
Page 211
Chapter 8: inline monitors 196 single-phase model: connect the l1 wire to the terminal labeled l1, and the l2 wire to the one labeled l2. Ensure both are tightened securely with screws to a torque of 1.96 n·m. y-wired three-phase model: connect the l1 wire to the terminal labeled l1, the l2 wire...
Page 212
Chapter 8: inline monitors 197 8. Locate the outlet whose ch number is identical to that of the inlet where the power cord was just installed. For example, if the inlet where you installed a power cord is labeled ch1, now you must locate the outlet labeled ch1 for cord installation. 9. Slightly loos...
Page 213
Chapter 8: inline monitors 198 manual mode you can switch between voltage, active power and current readings of the selected outlet in the manual mode on an inline monitor. To enter the manual mode, press the up or down button. To operate the led display of an inline monitor: 1. Press the up or down...
Page 214
Chapter 8: inline monitors 199 menus an inline monitor is not implemented with the overcurrent protection mechanism and outlet-switching function, so its menu items are slightly different from those of a regular dominion px pdu. The following list shows each menu with their own set of menu items. De...
Page 215
Chapter 8: inline monitors 200 maintenance device information view event log update firmware bulk configuration unit reset diagnostics network interface network statistics ping host trace route to host device diagnostics help about dominion px home page the power status of each outlet on an inline m...
Page 216
Chapter 8: inline monitors 201 snmp and clp interfaces same as regular dominion px models, an inline monitor allows remote access through either snmp or clp interface. See using snmp (on page 161) and using the clp interface (on page 173)..
Page 217: Appendix A Specifications
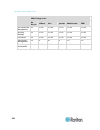
202 in this chapter maximum ambient operating temperature ..........................................202 dominion px serial rj-45 port pinouts ................................................202 dominion px feature rj-12 port pinouts.............................................202 maximum ambient ope...
Page 218
Appendix a: specifications 203 rj-12 pin/signal definition 1 +12v ― power (500ma, fuse protected) 2 gnd ― signal ground 3 rs485 (data +) bi-direction al data line + 4 rs485 (data -) bi-direction al data line - 5 gnd ― signal ground 6 1-wire used for feature port.
Page 219
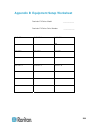
204 dominion px series model ____________ dominion px series serial number ____________ outlet 1 outlet 2 outlet 3 model model model serial number serial number serial number use use use outlet 4 outlet 5 outlet 6 model model model serial number serial number serial number use use use appendix b equ...
Page 220
Appendix b: equipment setup worksheet 205 outlet 7 outlet 8 outlet 9 model model model serial number serial number serial number use use use outlet 10 outlet 11 outlet 12 model model model serial number serial number serial number use use use outlet 13 outlet 14 outlet 15 model model model serial nu...
Page 221
Appendix b: equipment setup worksheet 206 outlet 16 outlet 17 outlet 18 model model model serial number serial number serial number use use use outlet 19 outlet 20 outlet 21 model model model serial number serial number serial number use use use.
Page 222
Appendix b: equipment setup worksheet 207 outlet 22 outlet 23 outlet 24 model model model serial number serial number serial number use use use types of adapters _________________________________________________________ types of cables _________________________________________________________ name o...
Page 223
208 you may connect the dominion px device to a raritan access product (kvm switch) via a power cim, such as d2cim-pwr. Serial port support of the power cim must be enabled in order to enable communications to the kvm switch. By default, serial port support for the power cim is enabled. If no connec...
Page 224: Appendix D Integration
209 product direct access interfaces access through cc-sg interfaces connectivity max # of px units supported association control association control dominion sx >= 3.1: sx gui; rsc into px serial port cc gui cc gui cscspcs-1 or cscspcs-10 max = number of serial ports product direct access interface...
Page 225
Appendix d: integration 210 product direct access interfaces access through cc-sg interfaces connectivity max # of px units supported association control association control paragon ii (ust) paragon manager, osd osd ip-reach + osd ip-reach + osd p2cim-pwr max = number of channel ports paragon ii (us...
Page 226
Appendix d: integration 211 power iq configuration raritan's power iq is a software application that collects and manages the data from different pdus installed in your server room or data center. With this software, you can: do bulk configuration for multiple pdus name outlets on different pdus swi...
Page 227
Appendix d: integration 212 for snmp version 1/2c pdus, enter an snmp community string that has at least read permissions to this pdu. This enables polling the pdu for data. Enter an snmp community string that has both read and write permissions to the pdu to enable power control, outlet renaming,...
Page 228
Appendix d: integration 213 dominion kx ii power strip configuration dominion kx ii integration requires d2cim-pwr and straight cat5 cable. For more information on dominion kx ii, see either of the following: dominion kx ii user guide: available on the raritan website's firmware and documentation se...
Page 229
Appendix d: integration 214 naming the rack pdu in the kx ii or lx (port page for power strips) note: px rack pdus (power strips) can be named in the px as well as in kx ii and lx. Once a raritan remote rack pdu is connected to the kx ii or lx, it will appear on the port configuration page. Click on...
Page 230
Appendix d: integration 215 3. Click ok..
Page 231
Appendix d: integration 216 associating outlets with target servers on kx ii and lx the port page opens when you click on a port on the port configuration page. From this page, you can make power associations, change the port name to something more descriptive, and update target server settings if y...
Page 232
Appendix d: integration 217 removing power associations when disconnecting target servers and/or rack pdus from the device, all power associations should first be deleted. When a target has been associated with a rack pdu and the target is removed from the device, the power association remains. When...
Page 233
Appendix d: integration 218 connecting the power strip 1. Connect the male rj-45 of the p2cim-pwr to the female rj-45 connector on the serial port power strip. 2. Connect the female rj-45 connector of the p2cim-pwr to any of the available female system port connectors on the dominion kx using a stra...
Page 234
Appendix d: integration 219 4. Click on the outlet drop-down that is associated the selected power strip. A list of available outlets is displayed. Select the outlet to which the device is connected. Repeat these steps for all devices plugged into multiple outlets. Once outlets have been assigned, r...
Page 235
Appendix d: integration 220 2. Select up to eight dominion px devices from drop-down list. 3. Select up to a total of four outlets from the dominion px devices..
Page 236
Appendix d: integration 221 4. Notice the target icon change to indicate power. 5. Notice the outlet icon change to indicate association. 6. Notice the outlet name automatically changes to the target's name. Controlling a target server's power 1. Select the target server associated with outlets..
Page 237
Appendix d: integration 222 2. Select from power on, power off, or cycle power options. Paragon ii paragon ii integration requires p2cim-pwr and straight cat5 cable. You can associate up to four outlets to a target server, and all four outlets can be from separate dominion px devices, if necessary. ...
Page 238
Appendix d: integration 223 adding a dominion px in paragon ii add a dominion px device exactly as you would add any second-tier device. Your paragon ii auto-detects the dominion px device and changes the device type to pcr8, pcs12, pcs20, dpx16, or dpx24. On the osd screen, press f5 to enter the ch...
Page 239
Appendix d: integration 224 controlling a target server's power after associating the outlets with target servers, you can turn on, turn off or power cycle a target by controlling the outlets. To control a target server's power: 1. Select a target server from the selection menu or selection menu by ...
Page 240
Appendix d: integration 225 3. Select an outlet and press x, o, or r: if there is no permission to the outlet, the message "no outlets / access denied" appears. if o, execute on command. if x or r, “are you sure (yes/no)?” is displayed. Users must type yes (case insensitive) in order for comma...
Page 241
Appendix d: integration 226 2. Click add. The power strip configuration screen appears. 3. Type a name and description in the name and description fields. 4. Select the number of outlets from the number of outlets drop-down menu. 5. Type the port number in the port field. 6. Click ok..
Page 242
Appendix d: integration 227 power control 1. Choose power control > power strip power control. The outlet control screen appears. 2. Check the box of outlet number you wish to control, and click on/off buttons to power on/off the selected outlet(s). 3. A confirmation message appears, indicating succ...
Page 243
Appendix d: integration 228 checking power strip status 1. Choose power control > power strip status. 2. A status box appears, displaying details of the controlled dominion px, including power state of each outlet on the device. Dominion ksx dominion ksx does not support connectivity with dominion p...
Page 244
Appendix d: integration 229 commandcenter secure gateway you can manage a dominion px from a commandcenter secure gateway (cc-sg) if it is connected through any of the following raritan products: dominion sx dominion kx paragon ii see the cc-sg administrators guide for more details. Note: if you hav...
Page 245
230 the ipmi tool set is command-line that allows users to display channel information, print sensor data, and set lan configuration parameters. The following explains the available ipmi commands. Note: the open source ipmi tool can be downloaded from sourceforge, and compiled on linux system .Then ...
Page 246
Appendix e: using the ipmi tool set 231 info [channel number] displays information about the selected channel. If no channel is given it displays information about the currently used channel: example $ ipmitool -i lan -h 192.168.51.58 -u admin -a channel info getaccess [userid] configures the given ...
Page 247
Appendix e: using the ipmi tool set 232 sends a pre-defined event to the system event log. The currently supported values for are: temperature: upper critical: going high voltage threshold: lower critical: going low memory: correctable ecc error detected note: these pre-defined events usually do not...
Page 248
Appendix e: using the ipmi tool set 233 set sets the given parameter on the given channel. Valid parameters are: ipaddr sets the ip address for this channel. Netmask sets the netmask for this channel. Macaddr sets the mac address for this channel. Defgw ipaddr sets the default gateway ip address. De...
Page 249
Appendix e: using the ipmi tool set 234 x cipher suite unused c callback u user o operator a admin o oem sensor commands the sensor commands allow you to display detailed sensor information. List lists sensors and thresholds in a wide table format. Example $ ipmitool -i lan -h allen-dpxpcr20-20 -u a...
Page 250
Appendix e: using the ipmi tool set 235 oem commands you can use the oem commands to manage and control the operation of the dominion px device. Oem net-fn is as defined below: #define ipmi_netfn_oem_pp 0x3c the table lists each oem command and gives its id. The sections that follow explain each com...
Page 251
Appendix e: using the ipmi tool set 236 a note about group commands when sending group commands, a valid group number (0 through 23, or 255) must be used. Only the group number itself can be sent, alpha-numeric expressions for group numbers are incorrect, and cause the command to be ignored. For exa...
Page 252
Appendix e: using the ipmi tool set 237 decimal binary decimal binary 2 0000 0010 14 0000 1110 3 0000 0011 15 0000 1111 4 0000 0100 16 0001 0000 5 0000 0101 17 0001 0001 6 0000 0110 18 0001 0010 7 0000 0111 19 0001 0011 8 0000 1000 20 0001 0100 9 0000 1001 21 0001 0101 10 0000 1010 22 0001 0110 11 0...
Page 253
Appendix e: using the ipmi tool set 238 get power on delay command request data - - response data 1 completion code 2 delay in 1/10 seconds set receptacle state command this command is used to switch on/off and recycle individual receptacles. Request data 1 # of receptacle [7 - 5] reserved [4 - 0] #...
Page 254
Appendix e: using the ipmi tool set 239 get receptacle state and data command request data 1 # of receptacle [7 - 5] reserved [4 - 0] # of receptacle, 0 based, highest valid # depends on device model response data 1 completion code 2 current receptacle state and visual state [7] reserved [6] 1b = bl...
Page 255
Appendix e: using the ipmi tool set 240 set group membership command request data 1 # of group [7 - 5] reserved [4 - 0] group #, valid numbers: 0 - 23, 255 2 [7 - 1] reserved [0] 1b = enable group, 0b = disable group 3 [7] 1b = receptacle 7 belongs to group ... [0] 1b = receptacle 0 belongs to group...
Page 256
Appendix e: using the ipmi tool set 241 ... [0] 1b = receptacle 16 belongs to group set group power on delay command request data 1 # of group [7 - 5] reserved [4 - 0] group #, valid numbers: 0 - 23, 255 2 delay in 1/10 seconds this delay overwrites the global delay for all receptacles in that group...
Page 257
Appendix e: using the ipmi tool set 242 response data 1 completion code get receptacle acl request data 1 # of receptacle response data 1 completion code 2 number of acl entries to follow 3 +n acl entry [7] 0b = deny, 1b = allow [6] 0b = user id, 1b = privilege level [5 - 0] user id or privilege lev...
Page 258
Appendix e: using the ipmi tool set 243 response data 1 completion code get power cycle delay command request data 1 # of receptacle (0xff for global unit delay) response data 1 completion code 2 delay (seconds), 1-255, 0 if not set (receptacle only) note: values greater than 255 cannot be sent to t...
Page 259
Appendix e: using the ipmi tool set 244 ipmi privilege level: no access callback user operator administrator oem ssl certificate management no yes/no yes/no yes/no yes/no yes/no security settings no yes/no yes/no yes/no yes/no yes/no unit reset no yes/no yes/no yes/no yes/no yes/no user/group manage...
Page 260
245 in this chapter default hysteresis values for thresholds .............................................245 event types...........................................................................................245 mac address ...........................................................................
Page 261
Appendix f: additional pdu information 246 event type examples outlet control outlet(#) switched on by user outlet(#) switched off by user outlet(#) cycled by user outlet/unit/environmental sensors assertion: environmental temperature (#) above upper non-critical threshold deassertion: environmental...
Page 262
Appendix f: additional pdu information 247 mac address a label is affixed to a dominion px device, near the led display, showing both the serial number and mac address of the pdu. If necessary, you can find the pdu's ip address through the mac address by using commonly-used network tools. Contact yo...
Page 263
Appendix f: additional pdu information 248 data for btu calculation if you need to calculate the heat (btu/hr) generated by the dominion px device, use the following power data in the btu calculation formula. Model name maximum power (watt) px-nnnn, dpxs, dpxr, dpcs and dpcr series 24 the letter "n"...
Page 264
249 this section provides an ldap example for illustrating the configuration procedure using microsoft active directory ® (ad). To configure ldap authentication, four main steps are required: a. Determine user accounts and groups intended for the dominion px b. Create user groups for the dominion px...
Page 265
Appendix g: ldap configuration illustration 250 step b. Configure user groups on the ad server you must create the groups for the dominion px on the ad server, and then make appropriate users members of these groups. In this illustration, we assume: the groups for the dominion px are named px_admin ...
Page 266
Appendix g: ldap configuration illustration 251 step c. Configure ldap authentication on the dominion px device you must enable and set up ldap authentication properly on the dominion px device to use external authentication. In the illustration, we assume: the dns server settings have been configur...
Page 267
Appendix g: ldap configuration illustration 252 base dn of user ldap server - type dc=techadssl,dc=com as the starting point where your search begins on the ad server. name of login-name attribute - type samaccountname because the ldap server is microsoft active directory. name of user-entry o...
Page 268
Appendix g: ldap configuration illustration 253 active directory domain - type techadssl.Com. Note: for more information on ldap configuration, see setting up ldap authentication (on page 114). 4. Click apply. The ldap authentication is activated..
Page 269
Appendix g: ldap configuration illustration 254 note: if the dominion px clock and the ldap server clock are out of sync, the certificates are considered expired and users are unable to authenticate using ldap. To ensure proper synchronization, administrators should configure the dominion px and the...
Page 270
Appendix g: ldap configuration illustration 255 2. Select px_user from the group drop-down list. The permissions that apply to this group appear. Since this is the first time you are setting the system permissions for this group, all permissions are set to no. 3. Set the permissions as necessary. Cl...
Page 271
Appendix g: ldap configuration illustration 256 5. Repeat steps 2 to 4 to set the permissions for the px_admin group. In this example, all system permissions are set to yes (or read-write). To set the outlet permissions for each group: 1. Choose user management > user/group outlet permissions. The u...
Page 272
Appendix g: ldap configuration illustration 257 3. Set the permissions as necessary. Click on the drop-down list to select a permission level for each outlet. In this example, all outlet permissions are set to no. 4. Click apply. The permissions are applied to the px_user group..
Page 273
Appendix g: ldap configuration illustration 258 5. Repeat steps 2 to 4 to set the permissions for the px_admin group. In this example, all outlet permissions are set to yes..
Page 274
259 you can reset the dominion px settings, including the administrator password, at the local serial console. To establish a serial connection, see connecting the dominion px to a computer (on page 17). In this chapter resetting to factory defaults .....................................................
Page 275
Appendix h: resetting the pdu settings 260 5. Type your user name and password to log in to the clp interface when prompted. See with hyperterminal (on page 174). 6. Type the following command and press enter. Clp:/-> set /system1 factorydefaults=true 7. Wait until the welcome message appears, indic...
Page 276: Index
261 • 232 1 1u products • 5 1u size • 2 2 2u products • 5 2u size • 2 a a false circuit breaker trip trap • 168 a note about group commands • 236 a note about measurement units • 172 a note about outlet numbers • 236 a note about the non-critical temperature threshold alarm • 38 a note about untrigg...
Page 277
Index 262 connecting the dominion px to a computer • 17, 18, 259, 260 connecting the dominion px to a power source • xiv, 16 connecting the dominion px to your network • 18 connecting the power strip • 218 connecting third-party detectors/switches to dpx-cc2-tr • 27 connection ports • 32 contact clo...
Page 278
Index 263 g gathering information for ldap configuration • 112 get ... [] • 234 get group membership command • 240 get group power on delay command • 241 get power cycle delay command • 243 get power on delay command • 238 get receptacle acl • 242 get receptacle state and data command • 239 get rece...
Page 279
Index 264 o oem commands • 235 outlet grouping • 151 outlet permissions • 79 outlet sensor properties • 179 outlets • 32 outlets list • 50 overview • 188 p package contents • 5, 15 panel components • 31 paragon ii • 222 paragon manager application • 225 ping host page • 158 power control • 227 power...
Page 280
Index 265 showing environmental sensor information • 182 showing in-depth outlet information • 179 showing outlet information • 177 snmp and clp interfaces • 201 snmp gets and sets • 168 snmp sets and configurable objects • 169 specifications • 6, 202 specifying the device altitude • xiv, 62 standar...
Page 281
U.S./canada/latin america monday - friday 8 a.M. - 6 p.M. Et phone: 800-724-8090 or 732-764-8886 for commandcenter noc: press 6, then press 1 for commandcenter secure gateway: press 6, then press 2 fax: 732-764-8887 email for commandcenter noc: tech-ccnoc@raritan.Com email for all other products: te...