- DL manuals
- Suzuki
- Outboard Motor
- DF150
- Service Manual
Suzuki DF150 Service Manual
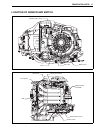
Summary of DF150
Page 1
Pre-production issue 1.
Page 2: Group Index
Group index general information 1 periodic maintenance 2 engine control system 3 engine electrical 4 fuel system 5 power unit 6 mid unit 7 power trim and tilt 8 lower unit [standard rotation (right-hand) model] 9 lower unit [counter rotation (left-hand) model] 10 wire/hose routing 11 © copyright suz...
Page 3: How To Use This Manual
How to use this manual to locate what you are looking for: 1. The text of this manual is divided into sections. 2. The section titles are listed on the previous page in a group index. Select the section needed for reference. 3. Holding the manual as shown at the right will allow you to find the firs...
Page 4
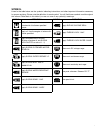
Symbol listed in the table below are the symbols indicating instructions and other important information necessary for proper servicing. Please note the definition for each symbol. You will find these symbols used throughout this manual. Refer back to this table if you are not sure of any symbol(s) ...
Page 5: Abbreviations
Abbreviations abbreviations used in this service manual are as follows: btdc : before top dead center ckp : crankshaft position cmp : camshaft position ctp : close throttle position dc : direct current dohc : double over head camshaft ecm : engine control module ex (ex.) : exhaust iac : idle air con...
Page 6: General Information
1 general information 1-1 contents general information warning/caution/note .........................................................................1- 2 general precautions ...........................................................................1- 2 identification number location ..................
Page 7: Warning/caution/note
1-2 general information warning/caution/note please read this manual and follow its instructions carefully. To emphasize special information, the symbol and the words warning, caution and note have special meanings. Pay special attention to the mes- sages highlighted by these signal words. ! Indicat...
Page 8
General information 1-3 " • if parts replacement is necessary, replace the parts with suzuki genuine parts or their equiv- alent. • when removing parts that are to be reused, keep them arranged in an orderly manner so that they may be reinstalled in the proper order and orientation. • be sure to use...
Page 9: Df 175
1-4 general information identification number location model, pre-fix, serial number the model, pre-fix and serial number of motor are stamped on a plate attached to the clamp bracket. Example engine serial number a second engine serial number plate is pressed into a boss on the cylinder block. Mode...
Page 10: Fuel And Oil
General information 1-5 fuel and oil gasoline recommendation suzuki highly recommends that you use alcohol-free unleaded gasoline with a minimum pump octane rating of 87 (r/2+m/2 method) or 91 (research method). However, blends of unleaded gasoline and alcohol with equivalent octane content may be u...
Page 11: Engine Break-In
1-6 general information engine break-in the first 10 hours are critically important to ensure correct run- ning of either a brand new motor or a motor that has been recon- ditioned or rebuilt. How the motor is operated during this time will have direct bearing on its life span and long-term durabili...
Page 12: Propellers
General information 1-7 propellers an outboard motor is designed to develop its rated power within a specified engine speed range. The maximum rated power delivered by the df150/175 models are shown below. If the standard propeller fails to meet the above requirement, use another pitch propeller to ...
Page 13: Cylinder Number
1-8 general information powerhead direction of rotation this outboard motor is designed with a l.H. (left hand) rotation powerhead utilizing an offset crankshaft. This design has the advantage of reducing the size of the motor and keeping the overall motor’s weight closer to the boat tran- som and t...
Page 14: * Specifications
General information 1-9 * specifications * these specifications are subject to change without notice. Dimensions & weight performance power head item unit data df150t df150z df175t df175z pre-fix 15001f 15001z 17501f 17501z overall length (front to back) mm (in.) 839 (33.0) overall width (side to si...
Page 15
1-10 general information fuel & oil bracket lower unit item unit data df150t df150z df175t df175z fuel suzuki highly recommends that you use alcohol-free unleaded gasoline with a minimum pump octane rating of 87 (r/2+m/2 method) or 91 (research method). However, blends of unleaded gasoline and alcoh...
Page 16
General information 1-11 reduction system item unit data df150t df150z df175t df175z propeller counter rotation models blade × dia. (in.) × pitch (in.) 3 × 15 and 1/2 × 17 3 × 15 and 1/4 × 19 3 × 15 × 21 3 × 14 and 3/4 × 23 3 × 14 and 1/2 × 25 3 × 14 and 1/2 × 27 3 × 16 × 17 3 × 16 × 18 and 1/2 3 × ...
Page 17: * Service Data
1-12 general information * service data * these service data are subject to change without notice. Powerhead ** figures shown are guidelines only, not absolute service limits. Item unit data df150t/z df175t/z recommended operating range r/min 5 000 – 6 000 5 500 – 6 100 idle speed r/min 650 ± 50 (in...
Page 18
General information 1-13 cylinder head/camshaft item unit data df150t/z df175t/z cylinder head distortion limit mm (in.) 0.03 (0.001) manifold seating faces dis- tortion limit mm (in.) 0.10 (0.004) cam height in std mm (in.) 42.520 – 42.680 (1.6740 – 1.6803) 44.420 – 44.580 (1.7488 – 1.7551) limit m...
Page 19
1-14 general information valve/valve guide item unit data df150t/z df175t/z valve diameter in mm (in.) 35.9 (1.4) ex mm (in.) 31.4 (1.2) tappet clearance (cold engine condition) in std mm (in.) 0.23 – 0.27 (0.009 – 0.011) ex std mm (in.) 0.30 – 0.34 (0.012 – 0.013) valve seat angle in — 15°, 45°, 60...
Page 20
General information 1-15 cylinder/piston/piston ring item unit data df150t/z df175t/z cylinder distortion limit mm (in.) 0.03 (0.001) piston to cylinder clearance std mm (in.) 0.085 – 0.105 (0.0033 – 0.0041) limit mm (in.) 0.15 (0.0059) cylinder bore std mm (in.) 97.000 – 97.020 (3.8189 – 3.8197) cy...
Page 21
1-16 general information crankshaft/conrod item unit data df150t/z df175t/z conrod small end inside diameter std mm (in.) 21.968 – 21.979 (0.8649 – 0.8653) conrod big end oil clearance std mm (in.) 0.045 – 0.063 (0.0018 – 0.0025) limit mm (in.) 0.080 (0.0031) conrod big end inside diam- eter std mm ...
Page 22
General information 1-17 electrical item unit data df150t/z df175t/z ignition timing degrees at r/min btdc 5 – 26 ± 3 over revolution limiter r/min 6 200 6 300 ckp sensor resistance Ω at 20 °c 168 – 252 cmp sensor resistance Ω at 20 °c — ignition coil resistance primary Ω at 20 °c — secondary k Ω at...
Page 23
1-18 general information starter motor ptt motor self-diagnostic system indication when the abnormality occurs in a signal from sensor, switch, etc., the “check engine” lamp on the moni- tor-tachometer flashes (lights intermittently) according to the each code pattern with buzzer sounding. Max. Cont...
Page 24
General information 1-19 * if more than two items fail at once, the self-diagnostic indication appears according to priority order. The indication repeats three times. Priority * failed item code lamp flashing pattern fail-safe sys- tem activating 10 fuel injector 4 – 3 on off no 11 throttle positio...
Page 25: Tightening Torque
1-20 general information tightening torque tightening torque – important fasteners item thread diameter tightening torque n·m kg-m lb-ft cylinder head cover bolt 6 mm 11 1.1 8.0 cylinder head bolt 8 mm 23 2.3 16.6 12 mm 86 8.6 62.0 crankcase bolt outside 10 mm 37 3.7 26.8 inside 11 mm 58 5.8 41.9 cr...
Page 26
General information 1-21 tightening torque – general bolt note: these value are only applicable when torque for a general bolt is not listed in the “important fasteners” table. Item thread diameter tightening torque n·m kg-m lb-ft gearcase bolt 10 mm 54 5.5 40.0 12 mm 83 8.3 60.0 propeller shaft bea...
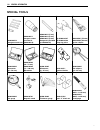
Page 27: Special Tools
1-22 general information special tools 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 09900-00410 hexagon wrench set 09900-00411 hexagon socket (included in 09900-00410) 09900-00413 (5 mm) 09900-00414 (6 mm) 09900-00415 (8 mm) hexagon bit (included in 09900-00410) (a) 09900-06107 (b) 09900-06108 snap ring pliers 09900-20101 (150 m...
Page 28
General information 1-23 16. 17. 18. 19. 09900-26006 engine tachometer 09900-28403 hydrometer 09910-39610 piston pin remover and installer 09912-58413: fuel pressure gauge set (1) 09912-58442: fuel pressure gauge (2) 09912-58432: fuel pressure hose (3) 09912-58490: 3-way joint & hose 20. 21. 22. 23....
Page 29
1-24 general information 35. 36. 37. 38. 39. Valve seat cutter (45°) (neway 128) valve seat cutter (15°) (neway 212) 09916-34550 valve guide reamer ( # 5.5 mm) 09916-34542 valve guide reamer handle 09916-37320 valve guide reamer ( # 10.5 mm) 40. 41. 42. 43. 44. 09916-44310 valve guide remover 09916-...
Page 30
General information 1-25 55. 56. 57. 58. 59. 09930-76420 timing light 09930-89220 3-pin connector test cord 09930-89240 4-pin connector test cord 09930-89260 injector test cord a 09930-89340 26-pin & 34-pin test cord 60. 61. 62. 63. 64. 09930-99320 digital tester 09932-79910 diagnostic harness 09932...
Page 31: Materials Required
1-26 general information note: * marked part no. Is in u.S. Market only. Materials required note: * marked part no. Is in u.S. Market only. 74. 75. 76. 99954-53008-820* digital voltmeter 99954-53873* stevens cd-77 peak reading volt- meter 99954-53883* gear oil filler suzuki outboard motor gear oil s...
Page 32: Periodic Maintenance
2 6 periodic maintenance 2-1 contents periodic maintenance periodic maintenance schedule .......................................................2- 2 periodic maintenance chart .....................................................2- 2 maintenance and tune-up procedures ..................................
Page 33
2-2 periodic maintenance periodic maintenance schedule the chart below lists the recommended intervals for all the required periodic service work necessary to keep the motor operating at peak performance and economy. Maintenance intervals should be judged by number of hours or months, whichever come...
Page 34
Periodic maintenance 2-3 maintenance and tune-up procedures this section describes servicing procedures for each periodic maintenance requirement. Engine oil/engine oil filter engine oil level check 1. Place outboard motor upright on a level surface. 2. Remove motor cover. 3. Remove oil level dipsti...
Page 35
2-4 periodic maintenance engine oil change/engine oil filter replacement note: • engine oil should be changed while engine is warm. • when replacing engine oil filter, change engine oil at the same time. 1. Place outboard motor upright on a level surface. 2. Remove oil filler cap. 3. Place a contain...
Page 36
Periodic maintenance 2-5 (3) screw new filter on by hand until filter o-ring contacts the mounting surface. (4) tighten filter 3/4 turn from point of contact with mounting surface using an oil filter wrench. " engine oil filter: 14 n·m (1.4 kg-m, 10.0 lb-ft), 3/4 turn (5) install stbd side cover. 6....
Page 37
2-6 periodic maintenance gear oil 1. Place outboard motor upright on a level surface. 2. Place a container under the lower unit. 3. Remove lower gear oil drain plug first, then remove air vent plug and drain gear oil. 4. Fill with recommended gear oil through oil drain hole until oil just starts to ...
Page 38
Periodic maintenance 2-7 lubrication apply suzuki water resistant grease to the following points. $ 99000-25160: suzuki water resistant grease inspect every 50 hours (3 months). Swivel bracket propeller shaft throttle body/cable throttle cable/link shift link swivel bracket swivel bracket.
Page 39
2-8 periodic maintenance spark plug standard spark plug: ngk bkr6e # removal • disconnect ignition coil connector, then remove the bolt securing the ignition coil. • remove the ignition coil and spark plug. Carbon deposit inspect for a carbon deposit on spark plug base. If carbon is present, remove ...
Page 40
Periodic maintenance 2-9 installation installation is reverse order of removal. " spark plug: 28 n·m (2.8 kg-m, 20.0 lb-ft) tappet clearance the tappet clearance specification is different for intake and exhaust valves. Too small a tappet clearance may reduce engine power, too large a tappet clearan...
Page 41
2-10 periodic maintenance 4. Rotate crankshaft counterclockwise to bring cam nose verti- cal to shim surface. 5. Measure tappet clearances by inserting thickness gauge between cam and shim surface. Tappet clearance (cold engine condition): in.: 0.23 – 0.27 mm (0.009 – 0.011 in) ex.: 0.30 – 0.34 mm (...
Page 42
Periodic maintenance 2-11 4. Rotate top of cam 90 degree counterclockwise and remove shim from cut-away at tappet. (two tappets can be adjusted at the same time.) # 5. After removing shim, measure thickness of original shim and determine correct thickness of shim for proper tappet clear- ance as cal...
Page 43
2-12 periodic maintenance 6. Install shim. Identification number should face down (towards tappet). 7. Rotate crankshaft to be open (lift up) valve. 8. Remove tappet holder 1 and tighten camshaft housing bolts to specified torque. " camshaft housing bolt: 12 n·m (1.2 kg-m, 8.7 lb-ft) 9. Recheck tapp...
Page 44
Periodic maintenance 2-13 • tighten cylinder head cover bolts to specification. " cylinder head cover bolts: 11 n·m (1.1 kg-m, 8.0 lb-ft) ocv (oil control valve) • install gasket and ocv, and then tighten bolts securely. Note: position the ocv gasket tab as shown the right. # " ocv bolt: 12 n·m (1.2...
Page 45
2-14 periodic maintenance shim i.D . No. Present shim siz e (mm) t appet c learance (mm) 218 220 223 225 228 230 233 235 238 240 243 245 248 250 253 255 258 260 263 265 268 270 273 275 278 280 283 285 288 290 293 295 298 300 220 223 225 228 230 233 235 238 240 243 245 248 250 253 255 258 260 263 265...
Page 46
Periodic maintenance 2-15 shim id no. Present shim siz e (mm) t appet c learance (mm) 218 220 223 225 228 230 233 235 238 240 243 245 248 250 253 255 258 260 263 265 268 270 273 275 278 280 283 285 288 290 293 295 298 300 223 218 220 225 228 230 233 235 238 240 243 245 248 250 253 255 258 260 263 26...
Page 47
2-16 periodic maintenance idle speed note: • before checking idle speed, engine must be warmed up. • check and/or adjust idle speed after engine speed has stabi- lized. • before checking idle speed, check throttle link mechanism and throttle valve for smooth operation. 1. Remove bolt and no. 1 ignit...
Page 48
Periodic maintenance 2-17 9. During this fixed mode of iac valve duty, adjust engine speed to 650 ± 50 r/min. By turning by-pass air screw. Turning air screw counterclockwise: engine speed will increase. Turning air screw clockwise: engine speed will decrease. 10. When finished adjusting the idle sp...
Page 49
2-18 periodic maintenance breather and fuel line if leakage, cracks, swelling or other damage is found, replace the breather hose and/or fuel line. • inspect initially after 20 hours (1 month) and every 50 hours (3 months). • replace every 2 years..
Page 50
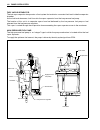
Periodic maintenance 2-19 low pressure fuel filter if leakage, cracks or other damage is found, replace the fuel fil- ter. Inspect and cleaning % 1. Turn the engine off. 2. To remove the cover 1, pull the upper part outward, then lift up. 3. Disconnect the inlet hose 2 and outlet hose 3 from fuel fi...
Page 51
2-20 periodic maintenance water pump/water pump impeller inspect water pump case, inner sleeve and under panel. Replace if wear, cracks, distortion or corrosion is found. Suzuki recommends that replacing the water pump impeller every 200 hours (12 months). Inspect water pump impeller. Replace if van...
Page 52
Periodic maintenance 2-21 anodes anodes if 2/3 of zinc anode has corroded away, replace anode. The anode should be periodically cleaned with a wire brush to ensure maximum effectiveness. Note: the anode cover may be separated from the power unit body by inserting and turning a 10 mm bolt to function...
Page 53
2-22 periodic maintenance battery % recommended battery: 12 v 100 ah (360 kc) or larger connecting battery upon completion of connection, lightly apply grease to battery terminals. How to connect: 1. Connect positive (+) terminal first. 2. Connect negative (–) terminal second. How to disconnect: 1. ...
Page 54
Periodic maintenance 2-23 battery solution level check battery solution level should be between upper level and lower level. If level is low, add distilled water only. # battery solution gravity check measure the gravity of battery solution using a hydrometer. Battery solution gravity: 1.28 at 20 °c...
Page 55
2-24 periodic maintenance bolts and nuts check that all bolts and nuts listed below are tightened to their specified torque. Fuel mixture check (o2 feedback) to perform fuel mixture check (o2 feedback) operation, a bat- tery powered personal computer and the suzuki diagnostic sys- tem software/hardw...
Page 56: Oil Pressure
Periodic maintenance 2-25 oil pressure oil pressure (at normal operating temp.): 400 – 600 kpa (4.0 – 6.0 kg/cm 2 , 57 – 85 psi) at 3000 r/min. Note: the figure shown above is a guideline only, not an absolute ser- vice limit. If oil pressure is lower or higher than specification, the following caus...
Page 57
2-26 periodic maintenance 5. Install oil pressure gauge adaptor into oil pressure switch hole in place of oil pressure switch. ! 09915-77311: oil pressure gauge 09915-78211: oil pressure gauge adapter 6. Install the ring gear cover and air intake silencer case. 7. Start engine and allow to warm up a...
Page 58: Cylinder Compression
Periodic maintenance 2-27 cylinder compression cylinder compression: standard: 1 100 – 1 700 kpa (11 – 17 kg/cm 2 , 156 – 242 psi) max. Difference between cylinders: 100 kpa (1.0 kg/cm 2 , 14 psi) note: figures shown are guidelines only, not absolute service limits. Low compression pressure can indi...
Page 59: Engine Vacuum Check
2-28 periodic maintenance engine vacuum check engine vacuum is required for proper operation of the multi-stage induction system used on the df150 & df175. Engine vacuum is also an indicator of general engine condition. 1. Warm up engine to normal operating temperature. Make sure engine idle speed i...
Page 60: Engine Control System
3 6 engine control system 3-1 contents engine control system engine control system structure ..................................................... 3- 2 system structure 1 .......................................................................... 3- 2 system structure 2 .................................
Page 61
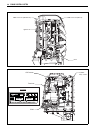
3-2 engine control system engine control system structure the df150/df175 models employ an integrated control system which performs the control functions for fuel injection, ignition, idle/trolling speed (idle air), etc. Through the ecm (engine control module). System structure 1 note: • df150 model...
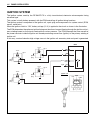
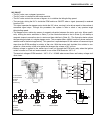
Page 62
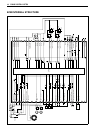
Engine control system 3-3 system structure 2 [df150/175] fuel t ank batter y ecm shift position sensor neutral s witc h emer g enc y stop s witc h star ter rela y main rela y silencer by-pass air scre w map sensor cylinder temp. Sensor *o 2 sensor spar k plug ex. Manif old temp. Sensor cmp sensor ck...
Page 63
3-4 engine control system components for system control engine control module (ecm) the ecm sends signals to control the actuators based on the information inputs from each sensor/switch. Major controls are as follows: note: information related to the caution system, self-diagnostic system, total op...
Page 64
Engine control system 3-5 ecm connector/terminals layout termi- nal wire color circuit termi- nal wire color circuit 1 g starter relay control 31 br/r ocv (–) 2 b/g o2 feedback 32 — — 3 — — 33 gr/g variable intake control valve (vsv) 4 r/b ckp sensor 34 p/w rev-limit lamp 5 y/bl cmp sensor #1 35 y/b...
Page 65
3-6 engine control system ecm internal structure batter y off ig. St . Reset s witch neutr al s witch star ter rela y engine s witch main rela y ecm pwr ecm gnd neutr al/cr anking s witch rela y control buzz er cancel s witch ckp sensor cmp sensor #2 vvt cmp sensor #1 sensor po w e r 5 v map sensor ...
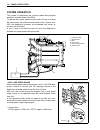
Page 66
Engine control system 3-7 location of sensor and switch cylinder temp. Sensor tps iac valve map sensor oil pressure switch iat sensor fuel injector vsv high pressure fuel pump shift position sensor neutral switch.
Page 67
3-8 engine control system cmp sensor #2 (df175) cmp sensor #1 (df150/175) ignition coil ocv cylinder temp. Sensor 30a 30a 10a 30a opt std main relay 10a starter relay 60a main select spare starter mtr ign coil,injector,ecm,f/p isolator ptt sw iac, cmp, vsv, vvt sp are sp are fuse box ckp sensor fuse...
Page 68
Engine control system 3-9 sensor and switch ckp (crankshaft position) sensor there is one (1) ckp sensor installed below the flywheel rotor. When the reluctor bars on the flywheel pass the sensor, a signal (voltage pulse) is generated and sent to the ecm. This is the fundamental signal used to judge...
Page 69
3-10 engine control system ecm cylinder identification: cylinders are identified by a calculation combined from two signals; one from the ckp sensor and one from the cmp sensor. Cmp (camshaft position) sensor #2 • for df175 model: cmp sensor #2 is mounted on the cylinder head cover with trigger vane...
Page 70
Engine control system 3-11 cylinder temperature sensor the cylinder temperature sensor is installed on the cylinder (top side) and used to detect the cylinder temperature. This is a thermistor type sensor (resistance of which changes depending on temperature) and inputs a signal to the ecm as a volt...
Page 71
3-12 engine control system tps (throttle position sensor) the tps is installed on the throttle body and detects the degree of throttle opening. The throttle shaft is interlocked with the tps shaft. This sensor is a variable resistor changing resistance (ohms) in accordance with the throttle opening....
Page 72
Engine control system 3-13 ecm main relay the ecm main relay is installed in the fuse box. When ener- gized by turning the ignition switch on, a circuit is formed which supplies battery voltage to the ecm, fuel injector, ignition coil, iac valve, cmp sensor, high pressure fuel pump, ocv (oil con- tr...
Page 73
3-14 engine control system sub battery cable (ecm power source line) the ecm is battery dependent and must be provided with its own dedicated 12v power supply. The electri- cal circuits which provide this supply are: 1. The sub battery cable to the white lead wire in the remote control extension har...
Page 74
Engine control system 3-15 o2 sensor (optional item) the o2 sensor is installed in the exhaust manifold only when the o2 feedback operation is performed. This sensor is a zirconia element (platinum plated) which changes output voltage depending on the oxygen concentration difference between its inte...
Page 75: Ignition System
3-16 engine control system ignition system the ignition system used by the df150/df175 is a fully transistorized, electronic microcomputer timing advanced type. This system is totally battery powered, with the ecm controlling all ignition timing functions. The ignition system is composed of the igni...
Page 76
Engine control system 3-17 ignition control system outline sensors at specific points on the engine monitor current engine conditions and send signals to the ecm. Based on these signals, the ecm determines the optimum ignition timing and releases voltage to the ignition coils. Specification ignition...
Page 77
3-18 engine control system ignition timing chart the following chart is an example for ignition at btdc 10°. Control mode when cranking: the ignition timing is fixed at btdc 5° until the engine starts. When idling/trolling: the ignition timing is controlled within the range of btdc 5° ± 5° to provid...
Page 78
Engine control system 3-19 electronic fuel injection system the fuel injection system used by the df150/df175 is a speed-density, multi-point, sequential, electronic fuel injection type. The fuel injection system is composed of the fuel line components, air intake components, and components for syst...
Page 79
3-20 engine control system fuel injection timing chart control mode before start: when the ignition switch is turned “on”, the ecm receives a map sensor signal, indicating the static baro- metric pressure of the intake manifold. This signal is used to compensate the fuel injection map for altitude. ...
Page 80
Engine control system 3-21 fuel delivery system components the fuel delivery system is composed of the low pressure fuel line components (fuel tank, filter, pump etc.), fuel vapor separator, high pressure fuel pump, high pressure fuel filter, fuel pressure regulator (located in the fuel vapor separa...
Page 81
3-22 engine control system fuel vapor separator the fuel vapor separator incorporates a float system that maintains a constant fuel level inside the separator chamber. As the fuel level decreases, fuel flows into the vapor separator from the low pressure fuel pump. The function of this unit is to se...
Page 82
Engine control system 3-23 fuel pressure regulator the fuel pressure regulator is located in the fuel vapor separator. The regulator’s function in the system is to maintain a constant fuel pressure relative to the injector while the engine is operating. The regulator diaphragm chamber is open to the...
Page 83
3-24 engine control system high pressure fuel pump control system outline to supply the optimum fuel amount, the ecm controls the fuel pump drive duty cycle, a repeated on/off signal, at a specified rate (1 000 times a second). Based on engine speed and battery voltage, the ecm determines the optimu...
Page 84
Engine control system 3-25 air intake components air, after entering through the silencer case, passes through the throttle body and flows into the surge tank where it is then distributed to the cylinder intake manifold. Intake manifold pressure, monitored by the map sensor, is an indirect measure o...
Page 85
3-26 engine control system by-pass air screw/passage since the throttle valve is almost fully closed when idling/trolling, the main flow of air necessary to maintain idling/trolling speed passes through the by-pass air passage. The by-pass air screw controls the flow of air through the pas- sage and...
Page 86
Engine control system 3-27 iac valve • the iac valve uses a stepper type motor. • the iac valve is installed on the intake manifold. • the iac valve controls the volume of bypass air to stabilize the idling/trolling speed. • the transistor driving the iac is inside the ecm and turns on/off when a si...
Page 87
3-28 engine control system control mode before start: the iac valve is initialized at 70% opening position when engine is not running (ignition switch off). When cranking: the iac valve is controlled to operate at approx. 40 – 100% duty. Duty change depends on cylinder temperature. After start (fast...
Page 88: Multi-Stage Induction
Engine control system 3-29 multi-stage induction outline the multi-stage induction system is designed to improve the intake efficiency by changing the intake tract volume in accor- dance with the engine speed. This system improves low and mid range torque and increases power output at the higher rpm...
Page 89
3-30 engine control system system operation this system is operated by the vacuum created during engine operation and controlled by the ecm. To operate the system (open/close the shut off valve to change the intake tract), the intake manifold, check valve, vacuum tank, vsv and depression chamber are...
Page 90
Engine control system 3-31 • high speed range when the engine speed is above the preset value (*), the ecm generates a signal to turn the vsv off, and vacuum is no longer applied to the depression chamber. Without vacuum the shut off valve return spring returns and holds the valve in its normal open...
Page 91
3-32 engine control system vvt (variable valve timing) system • the vvt system is designed to continuously vary intake valve timing to best fit the engines current oper- ating condition. • the intake cam timing sprocket assembly (vvt actuator) is located at the front end of the intake cam- shaft. Th...
Page 92
Engine control system 3-33 ocv (oil control valve) the ocv is used to regulate oil flow and is installed on the lower camshaft housing. Retard operation when the duty ratio of the ecm is small, the ocv spool valve is pushed away from the coil by spring force and engine oil pres- sure is applied to t...
Page 93: Caution System
3-34 engine control system caution system the following four caution systems alert the operator when an abnormality occurs on the engine. • over-revolution caution • low oil pressure caution • overheat caution • low battery voltage caution over-revolution caution system condition: the ecm controlled...
Page 94
Engine control system 3-35 low oil pressure caution system condition: immediate activation of system when the oil pressure switch is turned “on” due to an engine oil pressure drop below 100 kpa (1.0 kg/cm 2 , 14 psi). Action: reset: stop engine and check engine oil level. Refill engine oil to the co...
Page 95
3-36 engine control system overheat caution condition 1 (maximum temperature) immediate activation of system when: • cylinder temperature reaches 120 °c (248 °f) • exhaust manifold temperature reaches 114 °c (237.2 °f) condition 2 (temp. Rise vs time) immediate activation of system when: • the avera...
Page 96
Engine control system 3-37 low battery voltage caution system condition 1: system activated when battery voltage decreases to less than 9 volts for 30 seconds. Condition 2: system activated if battery voltage is less than 2 v for more than 2 seconds with the ignition switch turned “on” and engine no...
Page 97: Self-Diagnostic System
3-38 engine control system self-diagnostic system the self-diagnostic system alerts the operator when an abnor- mality occurs in a signal from sensor, switch, etc. When the system is activated, the “check engine” lamp flashes (lights intermittently) according to each code pattern along with a buzzer...
Page 98
Engine control system 3-39 note: • if more than two items fail at once, the self-diagnostic indication appears according to priority order. The indication repeats three times. • if the failed item remains, the self-diagnostic indication appears again after turning the ignition switch “on”. • after c...
Page 99
3-40 engine control system condition for self-diagnostic system operation failed item condition map sensor 1 • no signal (with engine running) • receiving an out of range “37 – 860 mmhg (1.46 – 33.86 inhg) (0.50 – 4.84 v)” signal (with engine running) iac valve/by-pass air screw adjustment • iac val...
Page 100
Engine control system 3-41 note 1: these conditions will be caused by iac valve failure or incorrect by-pass air screw adjustment. If iac valve is always closed or by-pass air is too low, the ecm controls the iac valve duty to increase to maintain the idling/trolling speed specified. Note 2: this co...
Page 101: Fail-Safe System
3-42 engine control system fail-safe system the fail-safe system is closely related to the self-diagnostic system. When an abnormality occurs in a sensor signal, the ecm ignores the out-of-range signal and assumes a pre-programmed value for the failed sensors. This allows the engine to continue runn...
Page 102
Engine control system 3-43 operating hour indication system when the ignition switch is initially turned “on” (from “off”), the ecm tests the caution system by turning on all four lamps in the monitor-tachometer and sounding the caution buzzer for an ini- tial two seconds. For the next three seconds...
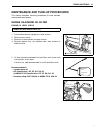
Page 103: Oil Change Reminder System
3-44 engine control system oil change reminder system this system informs the operator it is time to change engine oil based on the recommended maintenance schedule. When the total motor operating hours have reached the prepro- grammed hours, the “oil” lamp will flash, and the buzzer will begin a se...
Page 104
Engine control system 3-45 start-in-gear protection system ■ control by neutral switch a switch to detect neutral gear position is located on the throttle lever holder and operated by the clutch con- trol lever. This on/off type switch is on in neutral and off in forward or reverse. On starting the ...
Page 105: O2 Feedback System
3-46 engine control system o2 feedback system after extended usage, the engine components may become deteriorated or worn. This might make the a/f (air/fuel mixture ratio) incorrect which could affect exhaust emissions. To correct the a/f, an o2 sensor must be temporally installed in the exhaust man...
Page 106: Inspection
Engine control system 3-47 inspection precaution on system inspection " # note: • the self-diagnostic codes memory in ecm will remain even if battery is disconnected. • as each terminal voltage is affected by battery voltage, use a full-charged battery. • make sure all ground points have good electr...
Page 107
3-48 engine control system inspection for ecm circuit voltage # ! 09930-89340: 26-pin & 34-pin test cord 09930-99320: digital tester $ tester range: % dcv (see chart for range.) 1. Turn ignition switch off. 2. Connect the 26-pin & 34-pin test cord between ecm and wire harness as shown in figure. 3. ...
Page 108
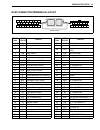
Engine control system 3-49 circuit voltage table terminal wire color circuit standard voltage condition/remarks 1 g starter relay control approx. 1.3 v ignition switch on, shift in neutral, stop switch plate out approx. 0.5 v ignition switch on, shift in neutral, stop switch plate in 2 b/g o2 feedba...
Page 109
3-50 engine control system * :when 12 v is displayed at no. 55 (57) terminal, 0 (zero) v is displayed at no. 58 (56) terminal. Con- versely, if 0 v is displayed at no. 55 (57) terminal, 12 v will be displayed at no. 58 (56) terminal. Terminal wire color circuit standard voltage condition/remarks 26 ...
Page 110
Engine control system 3-51 inspection for resistance ! 09930-99320: digital tester & tester range: Ω (resistance, see chart for range.) note: make sure ignition switch is always off when measuring resis- tance. 1. Turn ignition switch off. 2. Disconnect battery cables from battery. 3. Disconnect wir...
Page 111
3-52 engine control system note 3: disconnect 10 amp. (iac, cmp) fuse from fuse box and connect tester probe to fuse terminal “ c” of fuse box side. Resistance table item terminal for tester probe connection standard resistance (at 20 °c) ckp sensor 4 (r/b) to 49 (b/w) 168 – 252 Ω fuel injector no. ...
Page 112
Engine control system 3-53 component inspections high pressure fuel pump 6 sec operating sound 1. Install the emergency stop switch lock plate in position. 2. Shift into neutral. 3. Turn ignition switch on and check for fuel pump operating sound. Fuel pump operating sound: sounds for approx. 6 secon...
Page 113
3-54 engine control system fuel injector operating signal ! 09930-89340: 26-pin & 34-pin test cord peak voltmeter stevens cd-77 ' tester range: neg 50 1. Disconnect all ignition coil connectors. 2. Connect test cord between ecm and wire harness as shown in figure then turn ignition switch on. 3. Con...
Page 114
Engine control system 3-55 ignition coil operating signal ! 09930-89340: 26-pin & 34-pin test cord peak voltmeter stevens cd-77 ' tester range: sen 50 1. Connect test cord between ecm and wire harness as shown in figure then turn ignition switch on. 2. Connect the tester probe (“ +”, red) to each te...
Page 115
3-56 engine control system ignition coil assembly ! 09930-99320: digital tester $ tester range: % dcv (see chart for range.) note: the ignition coil power transistor and high-tension lead are an integral part of the coil’ internal circuit. Using resistance mea- surements to check for a defect on eit...
Page 116
Engine control system 3-57 cmp sensor signal ! 09930-89340: 26-pin & 34-pin test cord 09930-99320: digital tester $ tester range: % dcv (see chart for range.) 1. Turn ignition switch off. 2. Remove cmp sensor. (see page 3-69.) 3. Connect the 26-pin & 34-pin test cord between ecm and wire harness as ...
Page 117
3-58 engine control system map sensor output voltage change ! 09917-47011: vacuum pump gauge 09930-89340: 26-pin & 34-pin test cord 09930-99320: digital tester $ tester range: % dcv (see chart for range.) 1. Remove flywheel. (see page 3-66.) 2. Remove the three bolts and fuel hose guard. 3. Remove b...
Page 118
Engine control system 3-59 8. If out of specification, check wire harnesses for open and short. If wire harnesses are in good condition, replace map sensor and recheck. Tps (throttle position sensor) ! 09930-99320: digital tester 09930-89340: 26-pin & 34-pin test cord $ tester range: %(dcv (see char...
Page 119
3-60 engine control system shift position sensor ! 09930-99320: digital tester 09930-89220: 3-pin test cord $ tester range: %(dcv (see chart for range.) 1. Turn ignition switch off. 2. Connect 3-pin test cord between shift position sensor and wire harness as shown in figure. 3. Turn the ignition swi...
Page 120
Engine control system 3-61 oil pressure switch note: before checking the oil pressure switch, make sure the engine oil pressure is within specification. 1. Remove the blue lead wire from oil pressure switch. 2. Check the continuity between the switch terminal and engine body ground. ! 09930-99320: d...
Page 121
3-62 engine control system iac valve 1. Disconnect connector from iac valve. 2. Check each coil of iac valve for resistance. If out of specification, replace iac valve. 3. Remove iac valve from intake manifold. (see page 3-69.) 4. Connect connector to iac valve. 5. When the ignition switch is turned...
Page 122
Engine control system 3-63 multi-stage induction system inspection • ensure the depression chamber rod pulls the shut off valves to the complete close position after engine start. • ensure the shut off valve return spring returns the shut off valves to the full open position when the engine is turne...
Page 123
3-64 engine control system vacuum passage inspection 1. Disconnect vacuum hose 1 from vacuum switching valve 2. 2. Start engine and run it at idle speed. Place a finger over vacuum hose end 1 and engine vacuum is present. 3. If vacuum is not present, clean vacuum passage with com- pressed air, start...
Page 124
Engine control system 3-65 vsv (vacuum switching valve) 1. With ignition switch off, disconnect connector from vsv. 2. Check resistance between vsv terminals. Resistance of vsv: 37 – 44 Ω 3. Disconnect two hoses from vsv. 4. With 12 v applied between the vsv terminals, check that port (e) connects t...
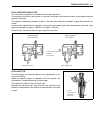
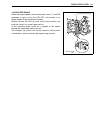
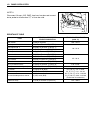
Page 125: Removal/installation
3-66 engine control system removal/installation flywheel removal 1. Remove ring gear cover and air intake silencer case. (see page 6-2.) 2. To lock the flywheel 1 when removing attaching bolts, use special tool shown in figure. Use screws and threaded holes on top of cylinder to attach special tool....
Page 126
Engine control system 3-67 3. Remove eight (8) flywheel bolts 2. 4. Remove flywheel 1 and dowel pin 3. Installation installation is reverse order of removal with special attention to the following steps. • install dowel pin 3. • install flywheel 1 onto crankshaft making sure to align dowel pin hole....
Page 127
3-68 engine control system ckp sensor removal 1. Remove flywheel. (see page 3-66.) 2. Remove the electric parts holder. (see page 4-30.) 3. Disconnect ckp sensor lead wire connector in electric parts holder. 4. Remove two (2) screws 1 and ckp sensor 2. Installation installation is reverse order of r...
Page 128
Engine control system 3-69 cmp sensor removal 1. Disconnect cmp sensor lead wire connector at sensor. 2. Remove bolt, cmp sensor and sensor cover. Installation installation is reverse order of removal. • install cmp sensor and sensor cover, then tighten sensor mounting screw securely. • connect sens...
Page 129
3-70 engine control system oil pressure switch removal 1. Remove the ring gear cover and air intake silencer case 1. (see page 6-2.) 2. Remove the three bolts and fuel hose guard 2. 3. Loosen screw 3 and disconnect blue lead wire 4 from switch. 4. Remove oil pressure switch from cylinder block. Inst...
Page 130
Engine control system 3-71 ocv (oil control valve) removal 1. To remove the cover 1, pull the upper part outward, then lift up. 2. Disconnect ocv lead wire connector at ocv. 3. Remove the four (4) bolts securing ocv, then remove ocv and discard ocv gasket. Installation installation is reverse order ...
Page 131: Troubleshooting
3-72 engine control system troubleshooting " in this section, troubleshooting procedures are based on the assumption that “low pressure fuel system” and “mechanical components (power unit, lower unit, etc.)” are normal. Note: for troubleshooting of “starter motor will not run”, see page (4-13). Char...
Page 132
Engine control system 3-73 chart 3: self-diagnostic code “1-4” cylinder temp. Sensor chart 4: self-diagnostic code “2-3” iat sensor chart 5: self-diagnostic code “4-2” ckp sensor chart 6: self-diagnostic code “2-4” cmp sensor start no yes cylinder temp. Sensor failure check cylinder temp. Sensor res...
Page 133
3-74 engine control system chart 7: self-diagnostic code “2-2” air intake system chart 8: self-diagnostic code “3-2” map sensor 2 chart 9: self-diagnostic code “1-5” ex. Mani. Temp. Sensor start no yes throttle position sensor failure check throttle position sensor output voltage change. Is result o...
Page 134
Engine control system 3-75 chart 10: self-diagnostic code “4-3” fuel injector chart 11: self-diagnostic code “2-1” throttle position sensor chart 12: self-diagnostic code “1-2” shift position sensor start no yes yes check “28” “36” “53” “54” terminal voltage. Is result ok? (see page 3-48.) • ecm fai...
Page 135
3-76 engine control system chart 13: self-diagnostic code “2-6” cmp sensor (vvt) chart 14: self-diagnostic code “5-2” vvt advance chart 15: self-diagnostic code “3-3” neutral switch start no yes check cmp sensor (vvt) signal. Is result ok? (see page 3-57.) possible cause: • ecm failure • wire contin...
Page 136
Engine control system 3-77 chart 16: self-diagnostic code “4-1” model discrimination chart 17: self-diagnostic code “6-2” ocv chart 18: self-diagnostic code “1-1” over charging note: this self-diagnostic code indication may be canceled by turning ignition switch on, because ecm detects battery volta...
Page 137
3-78 engine control system chart 19: engine cranked, but not start (or stops shortly after starting) before starting the troubleshooting, make sure that: • there is no self-diagnostic code indication. • emergency stop switch plate is set in place. Start no yes yes yes yes no check “23” terminal volt...
Page 138
Engine control system 3-79 chart 20: unstable idling/trolling (or engine tends to stall) note 1 if shift position sensor has failed (while engine running), engine will tend to stall when shifting into gear. Note 2 if throttle position sensor has failed, engine will tend to stall when decelerating. N...