- DL manuals
- Suzuki
- Automobile
- GRAND VITARA 1999
- Owner's Manual
Suzuki GRAND VITARA 1999 Owner's Manual
Important
WARNING/CAUTION/NOTE
Please read this manual and follow its instructions carefully. To emphasize special information, the words
WARNING, CAUTION and NOTE have special meanings. Pay special attention to the messages highlighted by
these signal words.
WARNING:
Indicates a potential hazard that could result in death or injury.
CAUTION:
Indicates a potential hazard that could result in vehicle damage.
NOTE:
Indicates special information to make maintenance easier or instructions clearer.
WARNING:
This service manual is intended for authorized Suzuki dealers and qualified service mechanics only.
Inexperienced mechanics or mechanics without the proper tools and equipment may not be able to
properly perform the services described in this manual.
Improper repair may result in injury to the mechanic and may render the vehicle unsafe for the driver
and passengers.
WARNING:
For vehicles equipped with a Supplemental Restraint (Air Bag) System:
• Service on and around the air bag system components or wiring must be performed only by an
authorized SUZUKI dealer. Refer to “Air Bag System Components and Wiring Location View” under
“General Description” in air bag system section in order to confirm whether you are performing ser-
vice on or near the air bag system components or wiring. Please observe all WARNINGS and “Ser-
vice Precautions” under “On-Vehicle Service” in air bag system section before performing service
on or around the air bag system components or wiring. Failure to follow WARNINGS could result in
unintentional activation of the system or could render the system inoperative. Either of these two
conditions may result in severe injury.
• If the air bag system and another vehicle system both need repair, Suzuki recommends that the air
bag system be repaired first, to help avoid unintended air bag system activation.
• Do not modify the steering wheel, instrument panel or any other air bag system component (on or
around air bag system components or wiring). Modifications can adversely affect air bag system
performance and lead to injury.
• If the vehicle will be exposed to temperatures over 93°C (200°F) (for example, during a paint baking
process), remove the air bag system components (air bag (inflator) modules, forward sensor(s),
SDM and/or seat belt pretensioners) beforehand to avoid component damage or unintended activa-
tion.
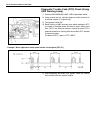
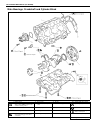
Summary of GRAND VITARA 1999
Page 1
Important warning/caution/note please read this manual and follow its instructions carefully. To emphasize special information, the words warning, caution and note have special meanings. Pay special attention to the messages highlighted by these signal words. Warning: indicates a potential hazard th...
Page 2: Foreword
Foreword this manual contains only different service information of the following applicable model as compared with sq416/sq420/sq625 service manual. Applicable model: grand vitara xl-7 therefore, whenever servicing the above applicable model, consult this manual first. And for any section, item or ...
Page 4: Table Of Contents
Table of contents general information transmission, clutch and differential 0a 7a1 general information 0a 0b 7b1 maintenance and lubrication 0b manual transmission 7a1 7c1 heating and air conditioning automatic transmission 7b1 1a 7d heater and ventilation 1a clutch 7c1 1b 7e air conditioning 1b tra...
Page 6: Section 0A
General information 0a-1 0a section 0a general information contents precautions......................................................0a-2 precaution for vehicles equipped with a supplemental restraint (air bag) system ...........................................0a-2 diagnosis............................
Page 7: Precautions
0a-2 general information precautions precaution for vehicles equipped with a sup- plemental restraint (air bag) system diagnosis • when troubleshooting air bag system, be sure to follow “diagnosis” in section 10b. Bypassing these proce- dures may result in extended diagnostic time, incorrect diagnos...
Page 8
General information 0a-3 servicing and handling warning: many of service procedures require disconnection of “air bag” fuse and all air bag (inflator) module(s) from initiator circuit to avoid an accidental deployment. Driver and passenger air bag (inflator) modules • for handling and storage of a l...
Page 9
0a-4 general information warning: sdm • during service procedures, be very careful when handling a sensing and diagnostic module (sdm). Never strike or jar the sdm. Never power up the air bag system when the sdm is not rigidly attached to the vehicle. All sdm and mounting bracket fasteners must be c...
Page 10
General information 0a-5 caution: • even when the accident was light enough not to cause air bags to activate, be sure to inspect sys- tem parts and other related parts according to instructions under “repair and inspection required after an accident” in section 10b. • when servicing parts other tha...
Page 11: Identification Information
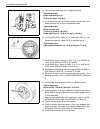
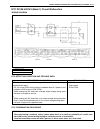
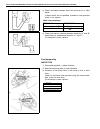
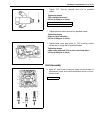
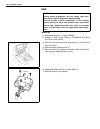
0a-6 general information identification information vehicle identification number the vehicle body number is on the left side of instrument panel and punched on the chassis inside the tire housing on the right front side..
Page 12
General information 0a-7 engine identification number the number is punched on the cylinder block. Engine identification number specification transmission identification number the a/t manufacture’s identification number is located on the transmission case as shown. However, the m/t identification n...
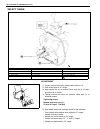
Page 13
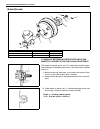
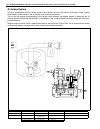
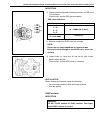
0a-8 general information warning, caution and information labels the figure below shows main labels among others that are attached to vehicle component parts. When servicing and handling parts, refer to warning/caution instructions printed on labels. If any warning/caution label is found stained or ...
Page 14: Section 0B
Maintenance and lubrication 0b-1 0b section 0b maintenance and lubrication contents maintenance schedule .................................. 0b-2 maintenance schedule under normal driving conditions ........................................ 0b-2 maintenance recommended under severe driving conditions ...
Page 15: Maintenance Schedule
0b-2 maintenance and lubrication maintenance schedule maintenance schedule under normal driving conditions note: • this interval should be judged by odometer reading or months, whichever comes first. • this table includes service as scheduled up to 90,000 km (54,000 miles) mileage. Beyond 90,000 km ...
Page 16
Maintenance and lubrication 0b-3 interval km ( × 1,000) 15 30 45 60 75 90 miles ( × 1,000) 9 18 27 36 45 54 months 12 24 36 48 60 72 chassis and body 6-1. Clutch (pedal and fluid level) – i – i – i 6-2. Brake discs and pads (thickness, wear, damage) i i i i i i brake drums and shoes (wear, damage) –...
Page 17
0b-4 maintenance and lubrication maintenance recommended under severe driving conditions if the vehicle is usually used under the conditions corresponding to any severe condition code given below, it is recommended that applicable maintenance operation be performed at the particular interval as give...
Page 18: Maintenance Service
Maintenance and lubrication 0b-5 maintenance service engine and emission control item 1-1 drive belt inspection and replacement water pump and generator drive belt inspec- tion 1) disconnect negative (–) cable at battery. 2) inspect belt for cracks, cuts, deformation, wear and cleanli- ness. If any ...
Page 19
0b-6 maintenance and lubrication power steering pump and/or a/c compressor drive belts (if equipped) inspection 1) disconnect negative (–) cable at battery. 2) inspect belt for cracks, cuts, deformation, wear and cleanli- ness. If any defect exists, replace. Check belt for tension. If belt tension i...
Page 20
Maintenance and lubrication 0b-7 1) drain engine oil by removing drain plug. 2) after draining oil, wipe drain plug clean. Reinstall drain plug, and tighten it securely as specified below. Tightening torque engine oil drain plug (a) : 50 n·m (5.0 kg-m, 36.5 lb-ft) 3) loosen oil filter by using oil f...
Page 21
0b-8 maintenance and lubrication 6) replenish oil until oil level is brought to full level mark on dipstick. (oil pan and oil filter capacity). The filler inlet is at the top of the cylinder head cover. It is recommended to use engine oil of se, sf, sg, sh or sj grade. Note: select the appropriate o...
Page 22: Section 1A
Heater and ventilation 1a-1 1a section 1a heater and ventilation contents general description ....................................... 1a-2 rear duct..................................................... 1a-3 warning: for vehicles equipped with supplement restraint (air bag) system: • service on and a...
Page 23: General Description
1a-2 heater and ventilation general description the heater, an in and out air selectable-type hot water heater, is so constructed that it is possible to assure an agreeable ventilation at all times by providing the ventilator air outlets at the center and both sides (right and left) of the instrumen...
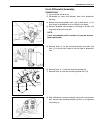
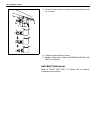
Page 24
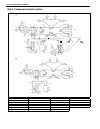
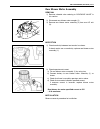
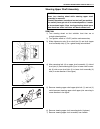
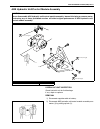
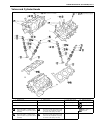
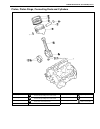
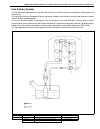
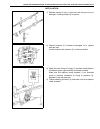
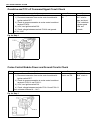
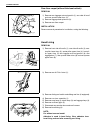
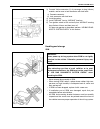
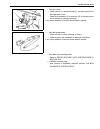
Heater and ventilation 1a-3 rear duct removal 1) disconnect negative (–) cable at battery. 2) remove front and second seats. 3) remove console box. 4) take off carpet till rear duct is totally exposed. 5) remove rear duct. Installation reverse removal sequence to install rear duct. 1. Heater unit 2....
Page 25
1a-4 heater and ventilation.
Page 26: Section 1B
Air conditioning (optional) 1b-1 1b section 1b air conditioning (optional) contents general description ....................................... 1b-3 refrigerant type .......................................... 1b-3 refrigerant flow of air conditioning system 1b-3 major components and location ..........
Page 27
1b-2 air conditioning (optional) charging .................................................... 1b-22 on-vehicle service ...................................... 1b-25 precaution.................................................. 1b-25 piping ..................................................... 1b-25 h...
Page 28: General Description
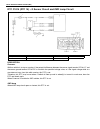
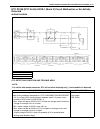
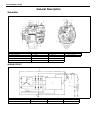
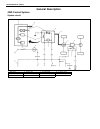
Air conditioning (optional) 1b-3 general description refrigerant type whether the a/c in the vehicle being serviced uses hfc-134a (r-134a) or cfc-12 (r-12) is indicated on label on the com- pressor. Also, it can be checked by the shape of the service (charge) valve. Refrigerant flow of air condition...
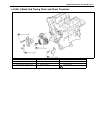
Page 29
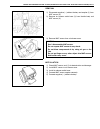
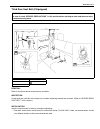
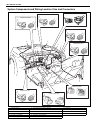
1b-4 air conditioning (optional) major components and location [a] : dual a/c model 6. Receiver/dryer 13. Suction pipe 20. Ventilation air [b] : single a/c model 7. Front expansion valve 14. Discharge pipe 21. Rear a/c air 1. Front cooling unit 8. Heater unit 15. Recirculation air 22. Room air 2. Fr...
Page 30
Air conditioning (optional) 1b-5 [a] : dual a/c lh steering model 4. Condenser 11. Low pressure charge valve [b] : dual a/c rh steering model 5. Sight glass 12. Floor liquid pipe [c] : single a/c lh steering model 6. Refrigerant (dual) pressure sensor 13. Floor suction pipe [d] : single a/c rh steer...
Page 31: Diagnosis
1b-6 air conditioning (optional) diagnosis general main a/c system (front a/c system) condition possible cause correction cool air does not come out (a/c system does not operative) no refrigerant perform recover, evacuation and charging. Fuse blown check “ig meter”, “rear defg” and “a/c” fuses, and ...
Page 32
Air conditioning (optional) 1b-7 cool air does not come out or insuffi- cient cooling (a/c sys- tem normal operative) insufficient or excessive charge of refrigerant check charge of refrigerant. Refrigerant leak in system check system for leaks. Condenser clogged check condenser. A/c evaporator clog...
Page 33
1b-8 air conditioning (optional) rear a/c system condition possible cause correction cool air dose not come out (rear blower motor normal operative) solenoid valve relay faulty check solenoid valve relay, and then replace if necessary solenoid valve faulty check solenoid valve, and then replace if n...
Page 34
Air conditioning (optional) 1b-9 quickly checking of refrigerant charge (if equipped with sight glass) the following procedure can be used for quickly checking whether the a/c system has a proper charge of refrigerant or not. 1) run engine at fast idle. 2) operate a/c at the following conditions for...
Page 35
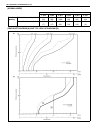
1b-10 air conditioning (optional) performance diagnosis 1) confirm that vehicle and environmental conditions are as fol- lows. • vehicle is not exposed to direct sun. • ambient temperature is within 15 - 35 °c (59 - 95 °f). 2) make sure that high pressure valve (1) and low pressure valve (2) of mani...
Page 36
Air conditioning (optional) 1b-11 9) check for each pressure of low side and high side if it is within shaded range of graph. If each gauge reading is out of specified pressure, correct defective part referring to “performance diagnosis table”. Example : 10) check inlet port temperature-to-outlet po...
Page 37
1b-12 air conditioning (optional) performance diagnosis table high pressure gauge low pressure gauge thermometer at center duct condition possible cause correction pressure high (“a” area of high side graph) refrigerant overcharged recharge. Expansion valve frozen or clogged check expansion valve. C...
Page 38
Air conditioning (optional) 1b-13 detail diagnosis table (at ambient temperature within 30 - 35 °c (85 - 95 °f)) condition possible cause correction manifold gauge mpa (kg/cm 2 ) (psi) detail lo hi 0.23 - 0.35 (2.3 - 3.5) (33 - 50) 1.4 - 1.75 (14 - 17.5) (200 - 249) normal condition – – negative pre...
Page 39
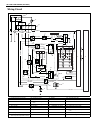
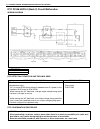
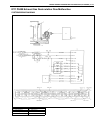
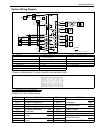
1b-14 air conditioning (optional) wiring circuit acg lt grn pnk pnk blk orn blk yel/grn red/blk blk/wht blu/wht pnk/blk pnk/grn red/blk wht/red yel/grn yel/blu a/c red/blu red/blu red/blk blk blu/orn blu/wht blu/wht pnk pnk/blu blk pnk/wht yel/blk gry/wht grn/blk blk/wht red/blk yel/grn blk blk blk ...
Page 40
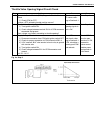
Air conditioning (optional) 1b-15 inspection of a/c controller and its circuits a/c controller (1) and its circuits can be checked at a/c controller wiring couplers by measuring voltage. Voltage check 1) remove a/c controller (1) from vehicle referring to “a/c controller” in this section. 2) remove ...
Page 41
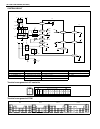
1b-16 air conditioning (optional) system circuit terminal arrangement of a/c controller terminal arrangement of ecm a: to “front blow” fuse 1. Front blower motor relay 6. Dual (refrigerant) pressure switch 11. Condenser cooling fan motor b: to “rear defg” fuse 2. Front blower motor 7. A/c thermistor...
Page 42
Air conditioning (optional) 1b-17 a/c controller voltage values table terminal wire circuit measurement ground normal value condition ac-a-1 blk/ wht controller main power supply ground to engine (fig b) 10 – 14 v ignition switch on with engine stopped ac-a-2 blk/ yel controller main ground ground t...
Page 43
1b-18 air conditioning (optional) terminal wire circuit measurement ground normal value condition ac-b-2 wht/ blk a/c evaporator temperature sensor (a/c evaporator ther- mistor) input ground to engine (fig b) 1.8 v (3520 Ω) a/c evaporator temperature sen- sor temperature at approx. 15 °c (59 °f) wit...
Page 44
Air conditioning (optional) 1b-19 refrigerant recovery, evacuation and charging operation procedure for charging a/c with refrigerant warning: • your eyes should not be exposed to refrigerant (liquid). Any liquid refrigerant-134a escaping by accident shows a temperature as low as approx. –6 °c (21.2...
Page 45
1b-20 air conditioning (optional) recovery note: • when discharging refrigerant out of a/c system, always recover it by using refrigerant recovery and recycling equipment (1). Discharging it into atmo- sphere would cause adverse effect to environments. • when handling recovery and recycling equipmen...
Page 46
Air conditioning (optional) 1b-21 evacuating evacuating procedure 1) connect high charging hose (1) and low charging hose (2) of manifold gauge set (3) respectively as follows: high charging hose (1) → high pressure charging valve (4) on discharge hose low charging hose (2) → low pressure charging v...
Page 47
1b-22 air conditioning (optional) checking system for pressure leaks after completing the evacuation, close manifold gauge high pres- sure valve (hi) and low-pressure valve (lo) and wait 10 minutes. Verify that low-pressure gauge reading has not changed. Charging caution: if the gauge reading moves ...
Page 48
Air conditioning (optional) 1b-23 the initial charging of the a/c system is performed from the high- pressure side with the engine stopped. And next, this method must be followed by charging from the low- pressure side with the engine running. 1) check to make sure that hoses are routed properly aft...
Page 49
1b-24 air conditioning (optional) c) purge any air existing in center charging hose when using refrigerant container tap valve, use following procedure to purge air. I) once fully tighten refrigerant container tap valve and then loosen (open) plate nut slightly. Ii) open low pressure valve of manifo...
Page 50: On-Vehicle Service
Air conditioning (optional) 1b-25 on-vehicle service precaution when servicing air conditioning system, the following rules must be observed. Piping • when connecting hoses and pipes, apply a few drops of compressor oil (refrigerant oil) to seats of coupling nuts and o-ring. Warning: should refriger...
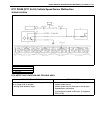
Page 51
1b-26 air conditioning (optional) • never use heat for bending pipes. When bending a pipe, try to make its bending radius as slight as possible. • keep internal parts of air conditioning free from moisture and dirt. When disconnecting any line from system, install a blind plug or cap to the fitting ...
Page 52
Air conditioning (optional) 1b-27 replenishing compressor oil when replacing air conditioning parts with new ones, it is neces- sary to replenish oil by the amount supposedly remaining in each part. When changing gas only when it is unavoidable to change gas without replacing any com- ponent part fo...
Page 53
1b-28 air conditioning (optional) rear a/c unit (rear a/c evaporator) removal 1) disconnect negative (–) cable at battery. 2) recover refrigerant by using recovery and recycling equip- ment. Be sure to follow the instruction manual for the equip- ment. The amount of compressor oil removed must be me...
Page 54
Air conditioning (optional) 1b-29 4) loosen floor suction pipe and floor liquid pipe mounting bolt (1). 5) remove rear a/c no.1 duct (1). 6) disconnect rear a/c unit wire couplers (2). 7) remove rear a/c unit mounting bolts (3), and then remove rear a/c unit (4). Inspection check the following. • cl...
Page 55
1b-30 air conditioning (optional) removal 1) remove rear a/c unit referring to “rear a/c unit” in this section. 2) disconnect solenoid valve connector (1). 3) loosen solenoid valve bracket mounting screws (2). 4) remove rear liquid pipe and rear suction pipe bolt (1), and then disconnect rear liquid...
Page 56
Air conditioning (optional) 1b-31 inspection 1) connect battery positive (+) cable to terminal “b” and battery negative (–) cable to terminal “c” as shown. 2) using ohmmeter, check continuity between terminal “a” and terminal “b” at specified temperature as shown. Rear a/c evaporator temperature con...
Page 57
1b-32 air conditioning (optional) solenoid valve removal 1) remove rear a/c unit referring to “rear a/c unit” in this section. 2) disconnect solenoid valve connector (1). 3) loosen solenoid valve flared nuts (2). 4) remove solenoid valve bracket mounting screws (3), and then remove rear liquid pipe ...
Page 58
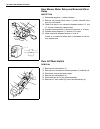
Air conditioning (optional) 1b-33 rear blower motor assembly removal 1) remove solenoid valve referring to “solenoid valve” in this section. 2) disconnect rear blower motor coupler (1). 3) remove rear blower motor assembly (2) from rear a/c unit (3). Inspection 1) check continuity between two termin...
Page 59
1b-34 air conditioning (optional) rear blower motor relay and solenoid valve relay inspection 1) disconnect negative (–) cable at battery. 2) remove rear blower motor relay (1) and/or solenoid valve relay (2) from vehicle. 3) check that there is no continuity between terminal “c” and “d”. If there i...
Page 60
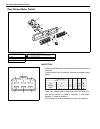
Air conditioning (optional) 1b-35 inspection • check rear a/c main switch for each terminal-to-terminal continuity. If check results are not specified, replace rear a/c main switch. Installation reverse removal procedure for installation. Rear blower motor resistor removal 1) remove rear a/c unit re...
Page 61
1b-36 air conditioning (optional) rear blower motor switch inspection • check rear blower motor switch for each terminal-to-terminal continuity. If check results are not specified, replace rear blower motor switch. • check rear blower motor switch bulb come on when con- nect battery positive (+) cab...
Page 62
Air conditioning (optional) 1b-37 rear a/c no.1 and no.2 duct rear a/c no.1 duct removal 1) remove rear a/c unit referring to “rear a/c unit” in this section. 2) remove rear a/c no.1 duct (1). Installation reverse removal procedure to install rear a/c no.1 duct (1). Rear a/c no.2 duct caution: never...
Page 63
1b-38 air conditioning (optional) compressor assembly inspection 1) install manifold gauge set (1) as shown in the figure. 2) close hi (4) and lo (5) side valves. 3) run engine at fast idle. 4) check compressor for the following items. If any of the above checks indicated a defect, repair com- press...
Page 64
Air conditioning (optional) 1b-39 removal 1) run engine at idle with a/c on for 10 minutes. 2) disconnect negative (–) cable at battery. 3) recover refrigerant from refrigeration system using recovery and recycling equipment. 4) remove p/s pump referring to step 4) to 7) of “removal” under “p/s pump...
Page 65
1b-40 air conditioning (optional) installation reverse removal procedure to install compressor assembly not- ing the following instructions. • if compressor was replaced, pour new compressor oil with the same amount as that drained from compressor. Refer to “replenishing compressor oil” in this sec-...
Page 66
Air conditioning (optional) 1b-41 magnet clutch inspection check the following items. • check no sigh of compressor oil leakage • check magnet clutch pulley bearing for noise and grease leakage. • check magnet clutch operation as follows : a) connect battery (1) and ammeter (2) to compressor (3) as ...
Page 67
1b-42 air conditioning (optional) 5) using special tool, remove circlip. Special tool (a) : 09900-06107 6) remove magnet clutch lead wire clamp screw, and remove magnet clutch read wire ground terminal. 7) remove magnet clutch with puller. 8) remove circlip using special tool. Special tool (a) : 099...
Page 68
Air conditioning (optional) 1b-43 4) install magnet clutch (1). A) set magnet clutch squarely over clutch installation boss. B) place special tool onto clutch bearing. Ensure that edge rests only on inner race of bearing. Special tool (a) : 09991-06010 c) install new circlip. 5) adjust clearance bet...
Page 69: Required Service Materials
1b-44 air conditioning (optional) required service materials tightening torque specification special tools material recommended suzuki product (part number) use compressor oil (refrigerant oil) compressor oil (nd-oil8, 250 cc) (99000-27080) • o-ring • each component fastening part tightening torque ...
Page 70: Section 3A
Front end alignment 3a-1 3a section 3a front end alignment contents general information ........................................3a-1 alignment service data (without load) .........3a-1 on-vehicle service ......................................... 3a-1 reference information ..............................
Page 71
3a-2 front end alignment.
Page 72: Section 3B1
Power steering (p/s) system 3b1-1 3b1 section 3b1 power steering (p/s) system contents general description ......................................3b1-2 power steering (p/s) pump ........................3b1-2 diagnosis .......................................................3b1-2 power steering pump dr...
Page 73: General Description
3b1-2 power steering (p/s) system general description power steering (p/s) pump power steering (p/s) pump specification : the specification of this power steering pump is the same as the specification of the same section in the service manual mentioned in this manual except for data of relieved pres...
Page 74
Power steering (p/s) system 3b1-3 hydraulic pressure in p/s circuit hydraulic pressure check 1) after cleaning joint of high pressure hose and p/s pump thoroughly, disconnect hose from pump and install special tool (oil pressure gauge, attachment and hose). Special tool (a) : 09915-77410 (b) : 09915...
Page 75
3b1-4 power steering (p/s) system 5) check relief pressure. A) increase engine speed to about 1500 r/min (rpm). Close gauge valve gradually while watching pressure increase indicated by gauge and take reading of relief pressure (maximum hydraulic pressure). When it is higher than specified values, p...
Page 76: Section 3C1
Air bag steering wheel and column 3c1-1 3c1 section 3c1 air bag steering wheel and column contents general description ..................................... 3c1-2 diagnosis ...................................................... 3c1-3 inspection and repair required after accident .......................
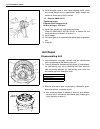
Page 77: General Description
3c1-2 air bag steering wheel and column general description this double tube type steering column has the following three important features in addition to the steering func- tion: • the column is energy absorbing, designed to compress in a front-end collision. • the ignition switch and lock are mou...
Page 78: Diagnosis
Air bag steering wheel and column 3c1-3 diagnosis for diagnosis of the steering wheel and steering column, refer to section 3. For diagnosis of the air bag system, refer to section 10b. Inspection and repair required after accident after an accident, whether the air bag has been deployed or not, be ...
Page 79
3c1-4 air bag steering wheel and column steering column removal 1) disconnect negative (–) cable at battery. 2) disable air bag system. Refer to “disabling air bag system” under “service precautions” in section 10b. 3) remove steering wheel and contact coil and combination switch assembly, if necess...
Page 80
Air bag steering wheel and column 3c1-5 6) remove steering upper shaft upper joint bolt (1) and nut (2) and disconnect steering upper shaft upper joint removing in arrow direction in the figure. 7) remove steering column (1) mounting bolts (2 pieces) (2) and nuts (2 pieces) (3). 8) if equipped with ...
Page 81
3c1-6 air bag steering wheel and column 3) install steering column assembly (1) with contacting upper side of lower bracket slits to mounting bolts. Tighten steering column lower mounting nuts (3) first and then upper mount- ing bolts (2) to specified torque. Tightening torque steering column mounti...
Page 82
Air bag steering wheel and column 3c1-7 steering upper shaft assembly removal 1) turn steering wheel so that vehicle’s front tires are at straight-ahead position. 2) turn ignition switch to “lock” position and remove key. 3) make alignment marks (3) on shaft joint (2) and shaft (upper shaft assembly...
Page 83
3c1-8 air bag steering wheel and column inspection check steering shaft damage and operation referring to check steering column and steering upper shaft for accident damage later in this section. Installation 1) be sure that front tires and steering wheel are in straight ahead position. 2) install s...
Page 84
Air bag steering wheel and column 3c1-9 6) install steering upper shaft upper joint bolt (2) and nut (1). Tighten steering upper shaft upper joint nut (1) to specified torque. Tightening torque steering upper shaft upper joint nut (a) : 23 n·m (2.3 kg-m, 17.0 lb-ft) steering lower shaft assembly rem...
Page 85
3c1-10 air bag steering wheel and column installation 1) be sure that front wheels and steering wheel are in straight ahead position. 2) align flat part “a” of lower shaft assembly (1) with bolt hole “b” of shaft joint as shown in the figure. Then insert shaft joint (1) into lower shaft assembly (2)...
Page 86
Air bag steering wheel and column 3c1-11 checking steering column and steering upper shaft for accident damage • check that 2 capsules are attached to steering column bracket securely. Check clearance between capsules and steering column bracket. Clearance should be 0 mm (0 in.) on both sides. If fo...
Page 87
3c1-12 air bag steering wheel and column • take measurement “b” as shown in the figure. If it is shorter than specified length, replace steering upper shaft assembly with new one. Steering upper shaft assembly length “b” : 419.0 ± 1.0 mm (16.50 ± 0.04 in.) tightening torque specification “b” fasteni...
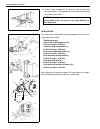
Page 88: Section 3D
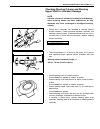
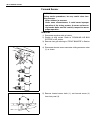
Front suspension 3d-1 3d section 3d front suspension contents on-vehicle service......................................... 3d-1 suspension control arm/bushings .............. 3d-1 tightening torque specification .................. 3d-2 on-vehicle service suspension control arm/bushings installation f...
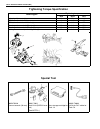
Page 89
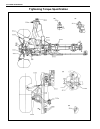
3d-2 front suspension tightening torque specification.
Page 90: Section 3E
Rear suspension 3e-1 3e section 3e rear suspension contents on-vehicle service......................................... 3e-1 rear axle shaft and wheel bearing ............ 3e-1 rear axle shaft inner oil seal ..................... 3e-5 rear axle housing ....................................... 3e-5 ti...
Page 91
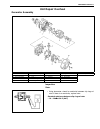
3e-2 rear suspension 2) remove circlip from axle shaft. 3) in order to remove retainer ring (1) from axle shaft (3), grind with a grinder two portion (2) of bearing retainer ring as illus- trated till it becomes thin. 4) break with a chisel (1) the thin ground sensor rotor and retainer ring, and it ...
Page 92
Rear suspension 3e-3 6) remove stud bolt(s) (1) by using hydraulic press (2). Installation install removed parts in reverse order of removal procedure, not- ing the following. 1) aligning serrations between new stud bolt(s) (1) and flange (4), install new stud bolt(s) (1) by tightening nut (2) as sh...
Page 93
3e-4 rear suspension 5) apply grease “a” to axle shaft inner oil seal lip as shown in the figure. “a” : grease 99000-25010 6) apply water tight sealant “b” to mating surfaces of brake back plate and rear axle hub (2). “b” : water tight sealant 99000-31110 7) install rear axle shaft to rear axle hous...
Page 94
Rear suspension 3e-5 rear axle shaft inner oil seal installation 1) using special tool drive in oil seal until it contacts oil seal pro- tector in axle housing. Special tool (a) : 09924-74510 (b) : 09944-88210 “a” : grease 99000-25010 “b” : sealant 99000-31110 2) for procedure hereafter, refer to st...
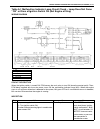
Page 95: Required Service Material
3e-6 rear suspension 5) apply thread lock cement to thread of propeller shaft flange bolt if reused. Install propeller shaft to joint flange aligning match marks and torque flange nuts to specification. “a” : cement 99000-32110 tightening torque propeller shaft nut (a) : 60 n·m (6.0 kg-m, 43.5 lb-ft...
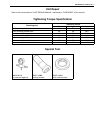
Page 96: Special Tool
Rear suspension 3e-7 special tool 09921-57810 09924-74510 09926-88310 09927-18411 counter shaft holder bush remover handle oil seal installer universal puller 09942-15510 09943-35512 09944-88210 sliding hammer brake drum remover bearing installer.
Page 97
3e-8 rear suspension.
Page 98: Section 3F
Wheels and tires 3f-1 3f section 3f wheels and tires contents general description ....................................... 3f-1 tires ............................................................. 3f-1 wheels ......................................................... 3f-1 general description tires this...
Page 99
3f-2 wheels and tires.
Page 100: Section 4A2
Front drive shaft/shaft bearing, oil seal 4a2-1 4a2 section 4a2 front drive shaft/shaft bearing, oil seal contents on-vehicle service....................................... 4a2-2 drive shaft ................................................. 4a2-2 required service material ..............................
Page 101: On-Vehicle Service
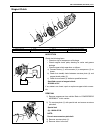
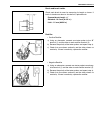
4a2-2 front drive shaft/shaft bearing, oil seal on-vehicle service drive shaft assembly 1) fully apply joint grease to wheel side joint. Use joint grease in the tube included in spare part. “a” : joint grease (about 85- 95 g (3.0 - 3.4 oz) (yellow)) 2) fit wheel side boot (1) on shaft. Fill up insid...
Page 102
Front drive shaft/shaft bearing, oil seal 4a2-3 6) install circlip (1) by using snap ring plier. 7) apply grease to entire surface of cage. Use joint grease in tube included in spare part. 8) insert cage into outer race and fit circlip (1) into groove of outer race. 9) apply grease in tube included ...
Page 103: Required Service Material
4a2-4 front drive shaft/shaft bearing, oil seal required service material material recommended suzuki product (part number) use lithium grease suzuki super grease a (99000-25010) • drive shaft oil seal • wheel spindle part of differential side drive shaft (rh) sealant sealing compound 366e (99000-31...
Page 104: Section 4B
Propeller shafts 4b-1 4b section 4b propeller shafts contents general description ....................................... 4b-1 on-vehicle service......................................... 4b-2 propeller shaft ............................................. 4b-2 tightening torque specification ............
Page 105: On-Vehicle Service
4b-2 propeller shafts on-vehicle service propeller shaft for the descriptions other than those mentioned below, refer to the same item in the same section of the service manual men- tioned in the foreword of this manual. Installation use the following specification to torque universal joint flange n...
Page 106: Section 5
Brakes 5-1 5 section 5 brakes contents diagnosis .......................................................... 5-2 diagnosis table ............................................. 5-2 warning: for vehicles equipped with supplemental restraint (air bag) system: • service on and around the air bag system co...
Page 107: Diagnosis
5-2 brakes diagnosis diagnosis table for the item not found in this column, refer to the same item of the same section in the service manual men- tioned in the foreword of this manual. Condition possible cause correction brake warning light turns on after engine start parking brake applied release p...
Page 108: Section 5A
Brakes pipe/hose/master cylinder 5a-1 5a section 5a brakes pipe/hose/master cylinder contents general description ....................................... 5a-2 master cylinder assembly............................ 5a-2 on-vehicle service......................................... 5a-3 front brake hose/p...
Page 109: General Description
5a-2 brakes pipe/hose/master cylinder general description master cylinder assembly the master cylinder has two pistons and three piston cups. Its hydraulic pressure is produced in the primary (“a” in the figure below) and secondary (“b”) chambers. The hydraulic pressure produced in the primary chamb...
Page 110: On-Vehicle Service
Brakes pipe/hose/master cylinder 5a-3 on-vehicle service front brake hose/pipe removal 1) raise and suitably support vehicle. Remove tire and wheel. This operation is not necessary when removing pipes connecting master cylinder and flexible hose. 2) clean dirt and foreign material from both hose end...
Page 111
5a-4 brakes pipe/hose/master cylinder for rh steering vehicle [d]: view d 1. E-ring [a]: clamp a 2. Flexible hose [b]: clamp b 3. Hose washer [c]: clamp d 4. Hose bolt t: top side 5. Brake caliper f: front side 6. 2 way joint.
Page 112
Brakes pipe/hose/master cylinder 5a-5 for lh steering vehicle [d]: view d 1. E-ring [a]: clamp a 2. Flexible hose [b]: clamp b 3. Hose washer [d]: clamp d 4. Hose bolt t: top side 5. Brake caliper f: front side 6. 2 way joint.
Page 113
5a-6 brakes pipe/hose/master cylinder master cylinder reservoir removal 1) disconnect reservoir lead wire at coupler. 2) clean outside of reservoir (1). 3) take out fluid with syringe or such. 4) remove reservoir stopper (3). 5) remove reservoir (1). Installation 1) when using new grommets, lubricat...
Page 114
Brakes pipe/hose/master cylinder 5a-7 master cylinder assembly removal 1) disconnect reservoir lead wire (1) at coupler. 2) clean around reservoir cap (2) and take out fluid with syringe or such. 3) disconnect brake pipes from master cylinder (3) and abs actuator (4). Inspection inspect distance “a”...
Page 115
5a-8 brakes pipe/hose/master cylinder brake booster clearance between booster piston rod and master cylinder piston check and adjustment the length of booster piston rod (1) is adjusted to provide speci- fied clearance “0” between piston rod (1) end and master cylinder piston (2). 1) before measurin...
Page 116
Brakes pipe/hose/master cylinder 5a-9 4) if measured depth is out of above specifications, adjust to specifications below by turning adjusting screw of piston rod. Special tool (f) : 09952-16021 depth “d” of piston rod for adjustment : 16.3 – 16.6 mm (0.642 – 0.653 in.).
Page 117: Special Tool
5a-10 brakes pipe/hose/master cylinder tightening torque specification special tool fastening part tightening torque n•m kg-m lb-ft brake flexible hose bolt (brake caliper/2 way joint) 23 2.3 17.0 brake hose / pipe bracket bolt 10 1.0 7.5 abs actuator bracket bolt 10 1.0 7.5 master cylinder attachin...
Page 118: Section 5C
Parking and rear brake 5c-1 5c section 5c parking and rear brake contents general description ....................................... 5c-2 drum brake assembly ................................. 5c-2 on-vehicle service......................................... 5c-3 parking brake cable ....................
Page 119: General Description
5c-2 parking and rear brake general description drum brake assembly the drum brake assembly has a self shoe clearance adjusting system so that drum-to-shoe clearance is main- tained appropriate at all times. Rear brake is a drum type. It uses leading trailing operation when brake pedal is depressed ...
Page 120: On-Vehicle Service
Parking and rear brake 5c-3 on-vehicle service parking brake cable brake drum inspection brake drum inspect drum for cleanliness. Check wear of its braking surface by measuring its inside diameter. Whenever brake drums are removed, they should be thoroughly cleaned and inspected for cracks, scores, ...
Page 121
5c-4 parking and rear brake cracked, scored, or grooved drum a cracked, drum is unsafe for further service and must be replaced. Do not attempt to weld a cracked drum. Smooth up any slight scores. Heavy or extensive scoring will cause excessive brake lining wear and it will probably be neces- sary t...
Page 122
Parking and rear brake 5c-5 wheel cylinder installation for the details, refer to the same item of the same section in the service manual mentioned in the foreword of this manual not- ing the following points. • take off bleeder plug cap from brake pipe and connect pipe (or pipes) to wheel cylinder ...
Page 123
5c-6 parking and rear brake 4) tighten brake back plate nuts to specified torque. Tightening torque brake back plate nut (a) : 50 n·m (5.0 kg-m, 36.5 lb-ft) 5) install wheel cylinder, and tighten wheel cylinder bolts and brake pipe flare nut (or nuts) to specified torque. Tightening torque wheel cyl...
Page 124
Parking and rear brake 5c-7 tightening torque specification fastening part tightening torque n•m kg-m lb-ft wheel cylinder bleeder plug 7.5 0.75 5.5 parking brake lever bolt 23 2.3 17.0 wheel cylinder bolt 13.5 1.35 10.0 brake pipe flare nut 16 1.6 12.0 brake back plate nut 50 5.0 36.5 wheel nut 100...
Page 125
5c-8 parking and rear brake.
Page 126: Section 5E2
Antilock brake system (abs) 5e2-1 5e2 section 5e2 antilock brake system (abs) contents general description ..................................... 5e2-3 components/parts location ....................... 5e2-3 abs hydraulic unit/control module assembly......................................................
Page 127
5e2-2 antilock brake system (abs) sensor circuit or sensor ring ................. 5e2-22 dtc c1031 (dtc 31), dtc c1032 (dtc 32) – right-rear wheel speed sensor circuit or sensor ring ................. 5e2-22 dtc c1035 (dtc 35), dtc c1036 (dtc 36) – left-rear wheel speed sensor circuit or sensor ring...
Page 128: General Description
Antilock brake system (abs) 5e2-3 general description components/parts location the abs (antilock brake system) controls the fluid pressure applied to the wheel cylinder of each brake from the master cylinder so that each wheel is not locked even when hard braking is applied. This abs has also the f...
Page 129
5e2-4 antilock brake system (abs) abs hydraulic unit/control module assembly abs control module is a component of abs hydraulic unit/control module assembly and has the following functions. Self-diagnosis function abs control module diagnoses conditions of the system compo- nent parts (whether or no...
Page 130: Diagnosis
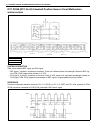
Antilock brake system (abs) 5e2-5 diagnosis to ensure that the trouble diagnosis is done accurately and smoothly, observe “precautions in diagnosing trou- bles” and follow “abs diagnostic flow table”. Precautions in diagnosing troubles • if the vehicles was operated in any of the following ways, abs...
Page 131
5e2-6 antilock brake system (abs) abs diagnostic flow table refer to the following pages for the details of each step. Step action yes no 1 1) perform “customer complaint analysis”. 2) perform “problem symptom confirmation”. 3) perform “diagnostic trouble code check, record and clearance”. Is there ...
Page 132
Antilock brake system (abs) 5e2-7 1) malfunction analysis a) customer complaint analysis record details of the problem (failure, complaint) and how it occurred as described by the customer. For this purpose, use of such a questionnaire form as shown below will facilitate collecting information to th...
Page 133
5e2-8 antilock brake system (abs) b) problem symptom confirmation check if what the customer claimed in “customer questionnaire” is actually found in the vehicle and if that symptom is found, whether it is identified as a failure. (this step should be shared with the cus- tomer if possible.) check w...
Page 134
Antilock brake system (abs) 5e2-9 abs warning lamp check 1) turn ignition switch on. 2) check that abs warning lamp (1) comes on for about 2 sec- onds and then goes off. If any faulty condition is found, advance to diagnostic flow table-a, b, c or d. Ebd warning lamp (brake warning lamp) check 1) tu...
Page 135
5e2-10 antilock brake system (abs) diagnostic trouble code (dtc) check (using abs warning lamp) 1) perform abs warning lamp check described above. 2) using service wire (4), connect diagnosis switch terminal (2) of monitor coupler (1) to ground (3). 3) turn ignition switch on. 4) read flashing of ab...
Page 136
Antilock brake system (abs) 5e2-11 diagnostic trouble code (dtc) check (using suzuki scan tool) 1) after setting cartridge for abs to suzuki scan tool, connect suzuki scan tool to data link connector. Special tool (a) : suzuki scan tool 2) turn ignition switch on. 3) read dtc according to instructio...
Page 137
5e2-12 antilock brake system (abs) 4) repeat disconnecting and reconnecting of service wire between diagnosis and ground terminals 5 times or more at about 1sec. Interval within 10 seconds. 5) turn ignition switch off and disconnect service wire from monitor coupler. 6) perform “driving test” (step ...
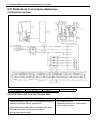
Page 138
Antilock brake system (abs) 5e2-13 c1022 22 rf wheel speed sensor circuit or sensor ring c1026 26 lf c1032 32 rr c1036 36 lr c1041 41 rf inlet solenoid valve circuit c1042 42 outlet solenoid valve circuit c1045 45 lf inlet solenoid valve circuit c1046 46 outlet solenoid valve circuit c1055 55 rear i...
Page 139
5e2-14 antilock brake system (abs) system circuit 1. Battery 11. Abs fail-safe transistor (solenoid valve transistor) 21. To ecm and sdm (if equipped) 2. Main fuses 12. Abs pump motor transistor 22. Stop lamp 3. Ignition switch 13. Pump motor 23. Stop lamp switch 4. Circuit fuses 14. Solenoid valves...
Page 140
Antilock brake system (abs) 5e2-15 table-a abs warning lamp circuit check – lamp does not come “on” at ignition switch on circuit description operation (on/off) of abs warning lamp is controlled by abs control module through lamp driver module in combination meter. If the antilock brake system is in...
Page 141
5e2-16 antilock brake system (abs) table-b abs warning lamp circuit check – lamp comes “on” steady refer to table – a for system circuit diagram and circuit description. Inspection step action yes no 1 perform diagnostic trouble code check. Is there any dtc (including code no.12, no codes on suzuki ...
Page 142
Antilock brake system (abs) 5e2-17 table-c abs warning lamp circuit check – the lamp flashes continuously while ignition switch is on circuit description when diagnosis switch terminal is shorted or connected to the ground with ignition switch on, diagnosis trouble code (dtc) is indicated by flashin...
Page 143
5e2-18 antilock brake system (abs) table-d code (dtc) is not outputted even with diagnosis switch terminal connected to ground circuit description when diagnosis switch terminal is connected to ground with ignition switch turned on, the abs control module outputs diagnostic trouble code by flashing ...
Page 144
Antilock brake system (abs) 5e2-19 table-e ebd warning lamp (brake warning lamp) check – lamp comes “on” steady circuit description ebd warning lamp (brake warning lamp) is controlled by parking brake switch, brake fluid level switch and abs control module/hydraulic unit assembly through lamp driver...
Page 145
5e2-20 antilock brake system (abs) dtc c1015 (dtc 15) – g sensor circuit and 4wd lamp circuit description g sensor while a vehicle is at stop or running, if the potential difference between the sensor signal terminal “e136-11” and the sensor ground terminal “e136-13” is not within the specified volt...
Page 146
Antilock brake system (abs) 5e2-21 inspection step action yes no 1 1) turn ignition switch on. Does 4wd lamp turn on when 4wd switch turns on? Go to step 2. Replace bulb or repair its circuit. 2 1) ignition switch off. 2) check for proper connection to ecm (pcm) and 4wd switch. 3) if ok, then check ...
Page 147
5e2-22 antilock brake system (abs) dtc c1021 (dtc 21), dtc c1022 (dtc 22) – right-front wheel speed sensor circuit or sensor ring dtc c1025 (dtc 25), dtc c1026 (dtc 26) – left-front wheel speed sensor circuit or sensor ring dtc c1031 (dtc 31), dtc c1032 (dtc 32) – right-rear wheel speed sensor circu...
Page 148
Antilock brake system (abs) 5e2-23 inspection step action yes no 1 1) disconnect applicable abs wheel speed sensor coupler with ignition switch off. 2) measure resistance between terminals of abs wheel speed sensor. Refer to “front wheel speed sen- sor” and/or “rear wheel speed sensor” in this secti...
Page 149
5e2-24 antilock brake system (abs) dtc c1041 (dtc 41) – right-front inlet solenoid circuit dtc c1045 (dtc 45) – left-front inlet solenoid circuit dtc c1055 (dtc 55) – rear inlet solenoid circuit dtc c1042 (dtc 42) – right-front outlet solenoid circuit dtc c1046 (dtc 46) – left-front outlet solenoid ...
Page 150
Antilock brake system (abs) 5e2-25 dtc c1057 (dtc 57) – power source circuit description the abs control module monitors the power source voltage at terminal “e136-18”. When the power source volt- age becomes extremely high or low, this dtc will be set. As soon as the voltage rises or lowers to the ...
Page 151
5e2-26 antilock brake system (abs) dtc c1061 (dtc 61) – abs pump motor circuit description the abs control module monitors the voltage at monitor terminal of pump motor circuit constantly with the igni- tion switch turned on. It sets this dtc when the voltage at the monitor terminal does not become ...
Page 152
Antilock brake system (abs) 5e2-27 dtc c1063 (dtc 63) – abs fail-safe relay circuit description abs control module monitors the voltage at the terminal of solenoid circuit constantly with ignition switch turned on. Also, immediately after ignition switch is turned on, perform initial check as follow...
Page 153
5e2-28 antilock brake system (abs) dtc c1071 (dtc 71) – abs control module description this dtc will be set when an internal malfunction is detected in the abs control module. Inspection 1. Abs hydraulic unit/control module assembly 3. Abs pump motor 5. Abs hydraulic unit/control module connector 2....
Page 154: On-Vehicle Service
Antilock brake system (abs) 5e2-29 on-vehicle service precautions when connector are connected to abs hydraulic unit/control module assembly, do not disconnect connectors of sensors and turn ignition switch on. Then dtc will be set in abs control mod- ule. Abs hydraulic unit operation check (using s...
Page 155
5e2-30 antilock brake system (abs) 9) perform following checks with help of another person. 10) brake pedal (1) should be depressed. A) ignition switch turned to on position by one person. B) wheel should be turned by another person’s hand. At this time, check that: • operation sound of solenoid is ...
Page 156
Antilock brake system (abs) 5e2-31 abs hydraulic unit/control module assembly hydraulic unit inspection check hydraulic unit for fluid leakage. If any, repair or replace. Removal 1) disconnect negative cable at battery. 2) disconnect abs hydraulic unit/control module assembly con- nector (1) by pull...
Page 157
5e2-32 antilock brake system (abs) 3) using special tool, loosen flare nuts (1) and disconnect brake pipes (2) from abs hydraulic unit/control module assembly (3). Special tool 09950-78220 4) remove three bolts and take out abs hydraulic unit/control module assembly (1) from bracket using flat end r...
Page 158
Antilock brake system (abs) 5e2-33 rear sensor rotor (retainer ring) removal 1) remove rear axle shaft assembly. Refer to “rear axle shaft” in section 3e. 2) in order to remove sensor rotor (retainer ring) (2) from shaft (1), grind with a grinder one part “a” of the sensor rotor (retainer ring) as s...
Page 159: Special Tool
5e2-34 antilock brake system (abs) tightening torque specification special tool fastening part tightening torque n•m kg-m lb-ft brake pipe flare nut : (a) 16 1.6 11.5 abs hydraulic unit bolt : (b) 9 0.9 6.5 abs hydraulic unit bracket bolt : (c) 10 1.0 7.5 wheel speed sensor bolt (front) : (d) 23 2.3...
Page 160
Antilock brake system (abs) 5e2-35 tech 2 kit (suzuki scan tool) (see note b.) note: a. This kit includes the following items and substitutes for the tech 2 kit. 1. Storage case, 2. Operator’s manual, 3. Tech 1a, 4. Dlc cable, 5. Test lead/probe, 6. Power source cable, 7. Dlc cable adapter, 8. Self-...
Page 161
5e2-36 antilock brake system (abs).
Page 162: Section 6-1
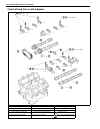
Engine general information and diagnosis (h27 engine) 6-1-1 6-1 section 6-1 engine general information and diagnosis (h27 engine) contents general information ...................................... 6-1-3 statement of cleanliness and care ............ 6-1-3 general information on engine service ........
Page 163
6-1-2 engine general information and diagnosis (h27 engine) table a-4 malfunction indicator lamp check – mil does not flash or just remains on even with grounding diagnosis switch terminal (vehicle with monitor connector) ................................... 6-1-45 table a-5 ecm (pcm) power and groun...
Page 164: General Information
Engine general information and diagnosis (h27 engine) 6-1-3 general information statement of cleanliness and care an automobile engine is a combination of many machined, honed, polished and lapped surfaces with tolerances that are measured in the thousands of an millimeter (ten thousands of inch). A...
Page 165
6-1-4 engine general information and diagnosis (h27 engine) • when disconnecting couplers, don’t pull wire harness but make sure to hold coupler itself. With lock type coupler, be sure to unlock before disconnection. Attempt to disconnect coupler without unlocking may result in damage to coupler. Wh...
Page 166
Engine general information and diagnosis (h27 engine) 6-1-5 fuel pressure relief procedure after making sure that engine is cold, relief fuel pressure as fol- lows. 1) place transmission gear shift lever in “neutral” (shift selector lever to “p” range for a/t vehicle), set parking brake, and block d...
Page 167: Engine Diagnosis
6-1-6 engine general information and diagnosis (h27 engine) engine diagnosis general description this vehicle is equipped with an engine and emission control system which are under control of ecm (pcm). The engine and emission control system in this vehicle are controlled by ecm (pcm). Ecm (pcm) has...
Page 168
Engine general information and diagnosis (h27 engine) 6-1-7 warm-up cycle a warm-up cycle means sufficient vehicle operation such that the coolant temperature has risen by at least 22°c (40°f) from engine starting and reaches a minimum temperature of 70 °c (160 °f). Driving cycle a “driving cycle” c...
Page 169
6-1-8 engine general information and diagnosis (h27 engine) priority of freeze frame data ecm (pcm) has 4 frames where the freeze frame data can be stored. The first frame stores the freeze frame data of the malfunction which was detected first. However, the freeze frame data stored in this frame is...
Page 170
Engine general information and diagnosis (h27 engine) 6-1-9 on-board diagnostic system (vehicle with monitor connector) ecm diagnosis troubles which may occur in the area including the following parts when the ignition switch is on and the engine is running, and indicates the result by turning on of...
Page 171
6-1-10 engine general information and diagnosis (h27 engine) data link connector (dlc) dlc (1) is in compliance with saej1962 in its installation posi- tion, the shape of connector and pin assignment. K line of iso 9141 is used for suzuki scan tool to communicate with ecm (pcm), abs control module a...
Page 172
Engine general information and diagnosis (h27 engine) 6-1-11 engine diagnostic flow table refer to following pages for the detail of each step. Step action yes no 1 customer complaint analysis 1) perform customer complaint analysis. Was customer complaint analysis performed? Go to step 2. Perform cu...
Page 173
6-1-12 engine general information and diagnosis (h27 engine) step 1. Customer complaint analysis record details of the problem (failure, complaint) and how it occurred as described by the customer. For this purpose, use of such an inspection form will facilitate collecting information to the point r...
Page 174
Engine general information and diagnosis (h27 engine) 6-1-13 step 2. Diagnostic trouble code (dtc)/freeze frame data check first, check dtc, referring to “diagnostic trouble code check” in this section. If dtc is indicated, record dtc and freeze frame data. After that clear dtc referring to “diagnos...
Page 175
6-1-14 engine general information and diagnosis (h27 engine) step 6. And 7. Rechecking and record of dtc refer to “dtc check” in this section for checking procedure. Step 8. Engine basic inspection and engine diagnosis table perform basic engine check according to the “engine basic inspection flow t...
Page 176
Engine general information and diagnosis (h27 engine) 6-1-15 step 9. Troubleshooting for dtc based on the dtc indicated in step 6 or 7 and referring to the applicable dtc diag. Flow table in this section, locate the cause of the trouble, namely in a sensor, switch, wire harness, connector, actuator,...
Page 177
6-1-16 engine general information and diagnosis (h27 engine) malfunction indicator lamp (mil) check 1) turn on ignition switch (but the engine at stop) and check that mil (1) lights. If mil does not light up, go to “diagnostic flow table a-1” for troubleshooting. 2) start engine and check that mil t...
Page 178
Engine general information and diagnosis (h27 engine) 6-1-17 [without using suzuki scan tool] (vehicle with monitor connector) 1) check malfunction indicator lamp referring to “malfunction indicator lamp check” in this section. 2) with the ignition switch off position, disconnect suzuki scan tool if...
Page 179
6-1-18 engine general information and diagnosis (h27 engine) [without using scan tool] 1) turn the ignition switch off position. 2) disconnect battery negative cable for specified time below to erase diagnostic trouble code stored in ecm memory and reconnect it. Time required to erase dtc: diagnosti...
Page 180
Engine general information and diagnosis (h27 engine) 6-1-19 p0133 ho2s circuit slow response (bank 1 - sensor 1) response time of ho2s-1 output volt- age between rich and lean is longer than specification. 2 driving cycles not applicable p0135 ho2s heater circuit malfunc- tion (bank 1 - sensor 1) t...
Page 181
6-1-20 engine general information and diagnosis (h27 engine) p0174 fuel system too lean (bank 2) short term fuel trim or total fuel trim (short and long terms added) is larger than specification for specified time or longer. (fuel trim toward rich side is large.) 2 driving cycles not applicable p017...
Page 182
Engine general information and diagnosis (h27 engine) 6-1-21 for a/t system (refer to section 7b1 for diagnosis) p0505 idle air control system mal- function difference between desired idle speed and actual idle speed continues to exceed specified value for longer than specified time. 2 driving cycle...
Page 183
6-1-22 engine general information and diagnosis (h27 engine) for immobilizer control system (refer to section 8g for diagnosis) p0753 (no.61) (no.62) shift solenoid a (#1) electrical monitor signal off is detected when shift solenoid a (#1) is on or monitor signal on is detected when it is off. 1 dr...
Page 184
Engine general information and diagnosis (h27 engine) 6-1-23 fail-safe table when any of the following dtcs is detected, ecm (pcm) enters fail-safe mode as long as malfunction continues to exist but that mode is canceled when ecm (pcm) detects normal condition after that. Dtc no. Trouble area fail s...
Page 185
6-1-24 engine general information and diagnosis (h27 engine) scan tool data as the data values given below are standard values estimated on the basis of values obtained from the normally operating vehicles by using a scan tool, use them as reference values. Even when the vehicle is in good condi- ti...
Page 186
Engine general information and diagnosis (h27 engine) 6-1-25 inj pulse width b2 at specified idle speed with no load after warming up. 2.0 – 3.3 msec ✱ at 2500 r/min with no load after warming up. 2.2 – 3.2 msec throttle pos (absolute throttle posi- tion) with ignition switch on/warmed up engine sto...
Page 187
6-1-26 engine general information and diagnosis (h27 engine) pnp signal (transmis- sion range switch) (for 4- a/t) with ignition switch on, selector lever in “p” or “n” position p/n range ✱ with ignition switch on, selector lever in “r”, “d”, “2” or “l” position d range fuel tank level ignition swit...
Page 188
Engine general information and diagnosis (h27 engine) 6-1-27 scan tool data definitions coolant temp (engine coolant temp., °c/°f) it is detected by engine coolant temp. Sensor. Intake air temp (°c/°f) it is detected by intake air temp. Sensor. Desire idle (desired idle speed rpm) the desired idle s...
Page 189
6-1-28 engine general information and diagnosis (h27 engine) tp sensor volt (tp sensor output voltage, v) throttle position sensor reading provides throttle valve opening information in the from of voltage. O2s b1 s1 (ho2s bank 1 sensor 1 output voltage, v) / o2s b2 s1 (ho2s bank 2 sensor 1 output v...
Page 190
Engine general information and diagnosis (h27 engine) 6-1-29 egr valve (%) this parameter indicates opening rate of egr valve which controls the amount of egr flow. A/c switch (on/off) on : command for operation being output from a/c amplifier to compressor. Off : command for operation not being out...
Page 191
6-1-30 engine general information and diagnosis (h27 engine) shift sol #2 con/mon (shift solenoid #2, b command/monitor, on/off) con-on : on command being output to shift solenoid #2, b. Con-off : on command not being output. Mon-on : electricity being passed to shift solenoid #2, b. Mon-off : elect...
Page 192
Engine general information and diagnosis (h27 engine) 6-1-31 engine diagnosis table perform troubleshooting referring to following table when ecm (pcm) has detected no dtc and no abnormality has been found in visual inspection and engine basic inspection previously. Condition possible cause correcti...
Page 193
6-1-32 engine general information and diagnosis (h27 engine) improper engine idling or engine fails to idle faulty spark plug spark plugs in section 6f2. Faulty ignition coil with ignitor ignition coil in section 6f2. Fuel pressure out of specification “diag. Flow table b-3” in this section. Engine ...
Page 194
Engine general information and diagnosis (h27 engine) 6-1-33 surges (engine power varia- tion under steady throttle or cruise. Feels like the vehicle speeds up and down with no change in the accelerator pedal.) defective spark plug (excess carbon deposits, improper gap, and burned electrodes, etc.) ...
Page 195
6-1-34 engine general information and diagnosis (h27 engine) poor gasoline mileage faulty spark plug (improper gap, heavy depos- its, and burned electrodes, etc.) spark plugs in section 6f2. Fuel pressure out of specification “diag. Flow table b-3” in this section. Faulty tp sensor, ect sensor or ma...
Page 196
Engine general information and diagnosis (h27 engine) 6-1-35 engine noise (note : before check- ing the mechanical noise, make sure the followings : ignition timing is properly adjusted, specified spark plug is used, specified fuel is used.) faulty hydraulic valve lash adjuster hydraulic valve lash ...
Page 197
6-1-36 engine general information and diagnosis (h27 engine) inspection of pcm (ecm) and its circuits pcm (ecm) and its circuits can be checked at pcm (ecm) wiring couplers by measuring voltage and resistance. Voltage check 1) remove pcm (ecm) cover from bracket referring to pcm (ecm) removal. 2) ch...
Page 198
Engine general information and diagnosis (h27 engine) 6-1-37 terminal circuit normal voltage condition e61-1 power source for co adjusting resistor (if equipped) 10 – 14 v ignition switch on e61-2 power source for back up 10 – 14 v ignition switch on and off e61-3 – – – e61-4 cruise control module (...
Page 199
6-1-38 engine general information and diagnosis (h27 engine) e61-22 a/c condenser fan motor relay (if equipped) 10 – 14 v ignition switch on, a/c not oper- ated and engine coolant temp. : less than 113°c, 235°f e61-23 fuel pump relay 0 – 2.5 v for 3 sec. After ignition switch on or while engine runn...
Page 200
Engine general information and diagnosis (h27 engine) 6-1-39 c51-3-9 throttle position sensor 0.5 – 1.2 v ignition switch on, throttle valve at idle position 3.4 – 4.7 v ignition switch on, throttle valve at full open position c51-3-10 mass air flow sensor 1.0 – 1.6 v ignition switch on and engine s...
Page 201
6-1-40 engine general information and diagnosis (h27 engine) c51-1-10 a/t input speed sensor (–) (a/t vehicle) about 2.5 v ignition switch on c51-1-11 a/t input speed sensor (+) (a/t vehicle) about 2.5 v ignition switch on c51-1-12 camshaft position sensor 1 deflects between 0 – 1 v and 4 – 6 v igni...
Page 202
Engine general information and diagnosis (h27 engine) 6-1-41 c51-2-1 fuel injector no.2 10 – 14 v ignition switch on c51-2-2 fuel injector no.1 c51-2-3 – – – c51-2-4 heater of ho2s-1 (bank 1) (if equipped) 10 – 14 v ignition switch on 0 – 2 v at specified idle speed after engine warmed up c51-2-5 he...
Page 203
6-1-42 engine general information and diagnosis (h27 engine) resistance check 1) disconnect couplers (1) from ecm/pcm with ignition switch off. 2) check resistance between each pair of terminals of discon- nected couplers (1) as listed in following table. Caution: never touch terminals of ecm/pcm it...
Page 204
Engine general information and diagnosis (h27 engine) 6-1-43 table a-1 malfunction indicator lamp circuit check – lamp does not come “on” or dims at ignition switch on (but engine at stop) wiring diagram circuit description when the ignition switch is turned on, ecm causes the main relay to turn on ...
Page 205
6-1-44 engine general information and diagnosis (h27 engine) table a-2 malfunction indicator lamp circuit check – lamp remains “on” after engine starts wiring diagram/circuit description refer to table a-1. Inspection 2 ecm power and ground circuit check : does engine start? Go to step 3. Go to “tab...
Page 206
Engine general information and diagnosis (h27 engine) 6-1-45 table a-3 malfunction indicator lamp check – mil flashes at ignition switch on (vehicle with monitor connector) wiring diagram/circuit description refer to table a-1. Troubleshooting table a-4 malfunction indicator lamp check – mil does no...
Page 207
6-1-46 engine general information and diagnosis (h27 engine) table a-5 ecm (pcm) power and ground circuit check – mil doesn’t light at ignition switch on and engine doesn’t start though it is cranked up wiring diagram circuit description when the ignition switch is turned on, the main relay turns on...
Page 208
Engine general information and diagnosis (h27 engine) 6-1-47 inspection step action yes no 1 main relay operating sound check : is operating sound of main relay heard at igni- tion switch on? Go to step 5. Go to step 2. 2 fuse check : is main “fi” fuse in good condition? Go to step 3. Check for shor...
Page 209
6-1-48 engine general information and diagnosis (h27 engine) dtc p0100 (dtc no.33, 34) mass air flow circuit malfunction wiring diagram dtc detecting condition and trouble area 1. Main fuse 2. Main relay 3. Ecm/pcm 4. Mass air flow sensor dtc detecting condition trouble area any one of the following...
Page 210
Engine general information and diagnosis (h27 engine) 6-1-49 dtc confirmation procedure 1) connect scan tool to dlc with ignition switch off. 2) turn on ignition switch and clear dtc, pending dtc and freeze frame data by using scan tool and run engine at idle speed for 20 sec. Or more. 3) check dtc ...
Page 211
6-1-50 engine general information and diagnosis (h27 engine) dtc p0110 (dtc no.23, 25) intake air temp. (iat) circuit malfunction wiring diagram dtc detecting condition and trouble area dtc confirmation procedure 1) connect scan tool to dlc with ignition switch off. 2) turn on ignition switch and cl...
Page 212
Engine general information and diagnosis (h27 engine) 6-1-51 troubleshooting step action yes no 1 was “engine diag. Flow table” per- formed? Go to step 2. Go to “engine diag. Flow table” in this section. 2 check iat sensor and its circuit : 1) connect scan tool with ignition switch off. 2) turn igni...
Page 213
6-1-52 engine general information and diagnosis (h27 engine) dtc p0115 (dtc no.14, 15) engine coolant temp. Circuit malfunction wiring diagram dtc detecting condition and trouble area dtc confirmation procedure 1) connect scan tool to dlc with ignition switch off. 2) turn on ignition switch and clea...
Page 214
Engine general information and diagnosis (h27 engine) 6-1-53 troubleshooting step action yes no 1 was “engine diag. Flow table” per- formed? Go to step 2. Go to “engine diag. Flow table” in this section. 2 check ect sensor and its circuit : 1) connect scan tool with ignition switch off. 2) turn igni...
Page 215
6-1-54 engine general information and diagnosis (h27 engine) dtc p0120 (dtc no.21, 22) throttle position circuit malfunction wiring diagram dtc detecting condition and trouble area dtc confirmation procedure 1) connect scan tool to dlc with ignition switch off. 2) turn on ignition switch and clear d...
Page 216
Engine general information and diagnosis (h27 engine) 6-1-55 troubleshooting step action yes no 1 was “engine diag. Flow table” per- formed? Go to step 2. Go to “engine diag. Flow table”. 2 check tp sensor and its circuit. 1) connect scan tool to dlc with ignition switch off and then turn ignition s...
Page 217
6-1-56 engine general information and diagnosis (h27 engine) dtc p0121 throttle position circuit range/performance problem wiring diagram/circuit description refer to dtc p0120. Dtc detecting condition and trouble area dtc confirmation procedure 1) connect scan tool to dlc with ignition switch off. ...
Page 218
Engine general information and diagnosis (h27 engine) 6-1-57 troubleshooting fig. For steps 4 and 5 step action yes no 1 was “engine diag. Flow table” performed? Go to step 2. Go to “engine diag. Flow table” in this section. 2 is there a dtc related to tp sensor (dtc p0120)? Go to applicable dtc dia...
Page 219
6-1-58 engine general information and diagnosis (h27 engine) dtc p0130 (dtc no.13) ho2s-1 (bank 1) circuit malfunction or no activity detected wiring diagram dtc detecting condition and trouble area 1. Ho2s heater relay 2. Ecm (pcm) 3. Ho2s-1 (bank-1) note: for vehicle with monitor connector, dtc wi...
Page 220
Engine general information and diagnosis (h27 engine) 6-1-59 dtc confirmation procedure 1) connect scan tool to dlc with ignition switch off. 2) turn on ignition switch and clear dtc, pending dtc and freeze frame data by using scan tool and start engine. 3) increase vehicle speed to 55 km/h (35 mph)...
Page 221
6-1-60 engine general information and diagnosis (h27 engine) fig. For step 2 dtc p0133 ho2s-1 (bank 1) circuit slow response wiring diagram/circuit description refer to dtc p0130. Dtc detecting condition and trouble area dtc confirmation procedure refer to dtc p0130. Troubleshooting 4 short term fue...
Page 222
Engine general information and diagnosis (h27 engine) 6-1-61 dtc p0135 ho2s-1 (bank 1) heater circuit malfunction wiring diagram refer to dtc p0130. Dtc detecting condition and trouble area dtc confirmation procedure 1) connect scan tool with ignition switch off. 2) turn on ignition switch and clear...
Page 223
6-1-62 engine general information and diagnosis (h27 engine) fig. For step 3 4 ho2s heater control circuit check : 1) with ignition switch off, install ho2s heater relay. 2) with ignition switch on leaving engine off, check voltage between c51-2-4 and ground. Is the voltage 10 – 14 v? Substitute a k...
Page 224
Engine general information and diagnosis (h27 engine) 6-1-63 dtc p0136 ho2s-2 (bank 1) circuit malfunction wiring diagram dtc detecting condition and trouble area dtc confirmation procedure 1. Ho2s heater relay 2. Ecm (pcm) 3. Ho2s-2 (bank-1) dtc detecting condition trouble area dtc will set when an...
Page 225
6-1-64 engine general information and diagnosis (h27 engine) 1) connect scan tool with ignition switch off. 2) turn on ignition switch and clear dtc, pending dtc and freeze frame data in ecm memory by using scan tool and start engine. 3) increase vehicle speed to 55 km/h (40 mph) or more. 4) keep dr...
Page 226
Engine general information and diagnosis (h27 engine) 6-1-65 dtc p0141 ho2s-2 (bank 1) heater circuit malfunction wiring diagram refer to dtc p0136. Dtc detecting condition and trouble area dtc confirmation procedure 1) connect scan tool with ignition switch off. 2) turn on ignition switch and clear...
Page 227
6-1-66 engine general information and diagnosis (h27 engine) troubleshooting fig. For step 2, 3 step action yes no 1 was “engine diag. Flow table” per- formed? Go to step 2. Go to “engine diag. Flow table” in this section. 2 ho2s-2 heater check : 1) disconnect ho2s-2 coupler with ignition switch off...
Page 228
Engine general information and diagnosis (h27 engine) 6-1-67 dtc p0150 (dtc no.26) ho2s-1 (bank 2) circuit malfunction or no activity detected wiring diagram dtc detecting condition and trouble area 1. Ho2s heater relay 2. Ecm (pcm) 3. Ho2s-1 (bank-2) note: for vehicle with monitor connector, dtc wi...
Page 229
6-1-68 engine general information and diagnosis (h27 engine) dtc confirmation procedure 1) connect scan tool to dlc with ignition switch off. 2) turn on ignition switch and clear dtc, pending dtc and freeze frame data by using scan tool and start engine. 3) increase vehicle speed to 55 km/h (35 mph)...
Page 230
Engine general information and diagnosis (h27 engine) 6-1-69 fig. For step 2 dtc p0153 ho2s-1 (bank 2) circuit slow response wiring diagram/circuit description refer to dtc p0150. Dtc detecting condition and trouble area dtc confirmation procedure refer to dtc p0150. Troubleshooting 4 short term fue...
Page 231
6-1-70 engine general information and diagnosis (h27 engine) dtc p0155 ho2s-1 (bank 2) heater circuit malfunction wiring diagram refer to dtc p0150. Dtc detecting condition and trouble area dtc confirmation procedure 1) connect scan tool with ignition switch off. 2) turn on ignition switch and clear...
Page 232
Engine general information and diagnosis (h27 engine) 6-1-71 fig. For step 2, 3 4 ho2s heater control circuit check : 1) with ignition switch off, install ho2s heater relay. 2) with ignition switch on leaving engine off, check voltage between c51-2-4 and ground. Is the voltage 10 – 14 v? Substitute ...
Page 233
6-1-72 engine general information and diagnosis (h27 engine) dtc p0156 ho2s-2 (bank 2) circuit malfunction wiring diagram dtc detecting condition and trouble area dtc confirmation procedure 1. Ho2s heater relay 2. Ecm (pcm) 3. Ho2s-2 (bank-2) dtc detecting condition trouble area dtc will set when an...
Page 234
Engine general information and diagnosis (h27 engine) 6-1-73 1) connect scan tool with ignition switch off. 2) turn on ignition switch and clear dtc, pending dtc and freeze frame data in ecm memory by using scan tool and start engine. 3) increase vehicle speed to 55 km/h (40 mph) or more. 4) keep dr...
Page 235
6-1-74 engine general information and diagnosis (h27 engine) dtc p0161 ho2s-2 (bank 2) heater circuit malfunction wiring diagram refer to dtc p0156. Dtc detecting condition and trouble area dtc confirmation procedure 1) connect scan tool with ignition switch off. 2) turn on ignition switch and clear...
Page 236
Engine general information and diagnosis (h27 engine) 6-1-75 troubleshooting fig. For step 2, 3 step action yes no 1 was “engine diag. Flow table” per- formed? Go to step 2. Go to “engine diag. Flow table” in this section. 2 ho2s-2 heater check : 1) disconnect ho2s-2 coupler with ignition switch off...
Page 237
6-1-76 engine general information and diagnosis (h27 engine) dtc p0171/p0172 fuel system too lean/rich (bank 1) dtc detecting condition and possible cause dtc confirmation procedure 1) connect scan tool to dlc with ignition switch off. 2) turn on ignition switch and clear dtc, pending dtc and freeze...
Page 238
Engine general information and diagnosis (h27 engine) 6-1-77 troubleshooting step action yes no 1 was “engine diag. Flow table” per- formed? Go to step 2. Go to “engine diag. Flow table” in this section. 2 is there dtc (s) other than “dtc p0171/ p0172”? Go to applicable dtc flow table. Go to step 3....
Page 239
6-1-78 engine general information and diagnosis (h27 engine) dtc p0174/p0175 fuel system too lean/rich (bank 2) dtc detecting condition and possible cause dtc confirmation procedure 1) connect scan tool to dlc with ignition switch off. 2) turn on ignition switch and clear dtc, pending dtc and freeze...
Page 240
Engine general information and diagnosis (h27 engine) 6-1-79 troubleshooting step action yes no 1 was “engine diag. Flow table” per- formed? Go to step 2. Go to “engine diag. Flow table” in this section. 2 is there dtc (s) other than “dtc p0174/ p0175”? Go to applicable dtc flow table. Go to step 3....
Page 241
6-1-80 engine general information and diagnosis (h27 engine) dtc p0300/p0301/p0302/p0303/p0304/p0305/p0306 random misfire/cylinder 1 misfire/cylinder 2 misfire/cylinder 3 misfire/cylinder 4 misfire detected/cyl- inder 5 misfire detected/cylinder 6 misfire detected system description ecm (pcm) measur...
Page 242
Engine general information and diagnosis (h27 engine) 6-1-81 troubleshooting step action yes no 1 was “engine diag. Flow table” per- formed? Go to step 2. Go to “engine diag. Flow table” in this section. 2 ignition system inspection : 1) check spark plug and ignition spark of cylin- der where misfir...
Page 243
6-1-82 engine general information and diagnosis (h27 engine) dtc p0325 (dtc no.43) knock sensor circuit malfunction circuit description dtc detecting condition and trouble area dtc confirmation procedure 1) connect scan tool to dlc with ignition switch off. 2) turn on ignition switch and clear dtc, ...
Page 244
Engine general information and diagnosis (h27 engine) 6-1-83 troubleshooting fig. For steps 2 and 3 step action yes no 1 was “engine diag. Flow table” per- formed? Go to step 2. Go to “engine diag. Flow table” in this section. 2 knock sensor and its circuit check : 1) with engine running, check volt...
Page 245
6-1-84 engine general information and diagnosis (h27 engine) dtc p0335 crankshaft position sensor circuit malfunction wiring diagram dtc detecting condition and trouble area dtc confirmation procedure 1) connect scan tool to dlc with ignition switch off. 2) turn on ignition switch and clear dtc, pen...
Page 246
Engine general information and diagnosis (h27 engine) 6-1-85 troubleshooting [a] fig. For step 3 / [b] fig. For step 4 step action yes no 1 was “engine diag. Flow table” performed? Go to step 2. Go to “engine diag. Flow table” in this section. 2 ckp sensor and its circuit resistance check : 1) with ...
Page 247
6-1-86 engine general information and diagnosis (h27 engine) dtc p0340 (dtc no.42) camshaft position sensor circuit malfunction wiring diagram system description cmp sensor detects ref signal and pos signal. • ref signal : 4 pulses/1 revolution of camshaft. There are 2 different kinds of wavelength....
Page 248
Engine general information and diagnosis (h27 engine) 6-1-87 dtc detecting condition and trouble area dtc confirmation procedure 1) connect scan tool to dlc with ignition switch off. 2) turn on ignition switch and clear dtc, pending dtc and freeze frame data by using scan tool. 3) crank engine for 3...
Page 249
6-1-88 engine general information and diagnosis (h27 engine) fig. For step 4 5 cmp sensor (ref) signal check : 1) with ignition switch off, connect cmp sensor coupler. 2) disconnect couplers from ignition coil assembly and fuel injectors. 3) with ignition switch on and crankshaft turned slowly, chec...
Page 250
Engine general information and diagnosis (h27 engine) 6-1-89 dtc p0400 exhaust gas recirculation flow malfunction system/wiring diagram 1. Egr valve 5. Ecm (pc) 2. Intake manifold 6. Map sensor 3. Exhaust gas 7. Main fuse 4. Sensed information 8. Main relay.
Page 251
6-1-90 engine general information and diagnosis (h27 engine) dtc detecting condition and trouble area dtc confirmation procedure 1) connect scan tool to dlc with ignition switch off. 2) turn on ignition switch and clear dtc, pending dtc and freeze frame data by using scan tool and warm up engine com...
Page 252
Engine general information and diagnosis (h27 engine) 6-1-91 troubleshooting step action yes no 1 was “engine diag. Flow table” per- formed? Go to step 2. Go to “engine diag. Flow table” in this section. 2 is there dtc p0403 (egr circuit malfunction)? Go to dtc p0403 diag. Flow table. Go to step 3. ...
Page 253
6-1-92 engine general information and diagnosis (h27 engine) dtc p0403 (dtc no.51) exhaust gas recirculation circuit malfunction wiring diagram dtc detecting condition and trouble area dtc confirmation procedure 1) connect scan tool to dlc with ignition switch off. 2) turn on ignition switch and cle...
Page 254
Engine general information and diagnosis (h27 engine) 6-1-93 troubleshooting step action yes no 1 was “engine diag. Flow table” per- formed? Go to step 2. Go to “engine diag. Flow table” in this section. 2 egr valve check : 1) with ignition switch off, disconnect connec- tor from egr valve. 2) check...
Page 255
6-1-94 engine general information and diagnosis (h27 engine) dtc p0420 catalyst system efficiency below threshold (bank 1) system diagram circuit description exhaust oxygen concentration at the pre-catalyst and the post-catalyst of wu-twc is detected from ho2s-1 and ho2s-2 respectively and according...
Page 256
Engine general information and diagnosis (h27 engine) 6-1-95 dtc confirmation procedure 1) connect scan tool to dlc with ignition switch off. 2) turn on ignition switch and clear dtc, pending dtc and freeze frame data by using scan tool. 3) increase vehicle speed to 80 – 90 km/h (50 – 56 mph). 4) ke...
Page 257
6-1-96 engine general information and diagnosis (h27 engine) dtc p0430 catalyst system efficiency below threshold (bank 2) system diagram circuit description exhaust oxygen concentration at the pre-catalyst and the post-catalyst of wu-twc is detected from ho2s-1 and ho2s-2 respectively and according...
Page 258
Engine general information and diagnosis (h27 engine) 6-1-97 dtc confirmation procedure 1) connect scan tool to dlc with ignition switch off. 2) turn on ignition switch and clear dtc, pending dtc and freeze frame data by using scan tool. 3) increase vehicle speed to 80 – 90 km/h (50 – 56 mph). 4) ke...
Page 259
6-1-98 engine general information and diagnosis (h27 engine) dtc p0443 evap control system purge control valve circuit malfunction system/wiring diagram dtc detecting condition and trouble area dtc confirmation procedure 1. Main fuse 3. Evap canister purge valve 2. Main relay 4. Ecm (pcm) dtc detect...
Page 260
Engine general information and diagnosis (h27 engine) 6-1-99 1) connect scan tool to dlc with ignition switch off. 2) turn on ignition switch and clear dtc, pending dtc and freeze frame data by using scan tool. 3) start engine and warm up it completely. 4) increase vehicle speed to 55 km/h (35 mph) ...
Page 261
6-1-100 engine general information and diagnosis (h27 engine) evap canister purge system inspection 1) warm up engine to normal operating temperature. 2) hoist vehicle so that all wheels rotate freely. 3) set m/t in “neutral” or a/t in “p” position and parking brake. 4) disconnect purge hose (1) fro...
Page 262
Engine general information and diagnosis (h27 engine) 6-1-101 vacuum hose inspection check hoses for connection, leakage, clog and deterioration. Replace as necessary. Evap canister purge valve and its circuit inspection 1) connect suzuki scan tool to dlc (1) with ignition switch off and disconnect ...
Page 263
6-1-102 engine general information and diagnosis (h27 engine) 5) connect 12 v-battery to evap canister purge valve (3) termi- nals. In this state, blow hose “a” (1). Air should come out of hose “b” (2). If check result is not as described, replace evap canister purge valve. 6) connect vacuum hoses. ...
Page 264
Engine general information and diagnosis (h27 engine) 6-1-103 dtc p0460 fuel level sensor circuit high input wiring diagram/circuit description dtc detecting condition and trouble area dtc confirmation procedure 1) connect scan tool to dlc with ignition switch off. 2) turn on ignition switch and cle...
Page 265
6-1-104 engine general information and diagnosis (h27 engine) troubleshooting step action yes no 1 was “engine diag. Flow table” per- formed? Go to step 2. Go to “engine diag. Flow table” in this section. 2 does fuel level meter in combination meter indi- cate “e” (empty)? Replenish fuel tank with f...
Page 266
Engine general information and diagnosis (h27 engine) 6-1-105 dtc p0500 (dtc no.24) vehicle speed sensor malfunction wiring diagram dtc detecting condition and trouble area 1. Speedometer 2. Vehicle speed sensor 3. Cruise control module (if equipped) 4. Ecm (pcm) dtc detecting condition trouble area...
Page 267
6-1-106 engine general information and diagnosis (h27 engine) dtc confirmation procedure 1) connect scan tool to dlc with ignition switch off. 2) turn on ignition switch and clear dtc, pending dtc and freeze frame data by using scan tool and warm up engine completely. 3) increase vehicle speed to 10...
Page 268
Engine general information and diagnosis (h27 engine) 6-1-107 [a] fig. For step 3 / [b] fig. For step 4, 6, 7 fig. For step 5 5 vss visual inspection: 1) remove vss referring to “transfer” section. 2) check vss drive and driven gears for damage and excessive wear. Are they in good condition? Poor vs...
Page 269
6-1-108 engine general information and diagnosis (h27 engine) dtc p0505 idle air control system malfunction system/wiring diagram dtc detecting condition and trouble area 1. Throttle body 3. Ecm (pcm) 5. Fia valve 7. Main relay 2. Idle air control valve 4. Sensed information 6. Main fuse dtc detecti...
Page 270
Engine general information and diagnosis (h27 engine) 6-1-109 dtc confirmation procedure 1) connect scan tool to dlc with ignition switch off. 2) turn on ignition switch and clear dtc, pending dtc and freeze frame data by using scan tool and warm up engine completely. 3) run engine at idle speed for...
Page 271
6-1-110 engine general information and diagnosis (h27 engine) dtc p0601 (dtc no.71) internal control module memory check sum error system description internal control module is installed in ecm (pcm). Dtc detecting condition and trouble area dtc confirmation procedure 1) connect scan tool to dlc wit...
Page 272
Engine general information and diagnosis (h27 engine) 6-1-111 dtc p1408 manifold absolute pressure sensor circuit malfunction wiring diagram dtc detecting condition and trouble area dtc confirmation procedure 1. Map sensor 2. Ecm (pcm) dtc detecting condition trouble area • while engine is running a...
Page 273
6-1-112 engine general information and diagnosis (h27 engine) 1) connect scan tool to dlc with ignition switch off. 2) turn on ignition switch and clear dtc, pending dtc and freeze frame data by using scan tool and warm up engine completely. 3) run engine at idle speed for 1 min. (engine coolant tem...
Page 274
Engine general information and diagnosis (h27 engine) 6-1-113 dtc p1450/p1451 barometric pressure sensor circuit malfunction/perfor- mance problem system description barometric pressure sensor is installed in ecm (pcm). Dtc detecting condition and trouble area dtc confirmation procedure for dtc p145...
Page 275
6-1-114 engine general information and diagnosis (h27 engine) dtc p1500 engine starter signal circuit malfunction wiring diagram dtc detecting condition and trouble area dtc confirmation procedure 1) connect scan tool to dlc with ignition switch off. 2) turn on ignition switch and clear dtc by using...
Page 276
Engine general information and diagnosis (h27 engine) 6-1-115 dtc p1510 ecm back-up power supply malfunction wiring diagram circuit description battery voltage is supplied to keep dtc memory, values that ecm has learned to control engine, etc. In ecm even when ignition switch is turned off. Dtc dete...
Page 277
6-1-116 engine general information and diagnosis (h27 engine) table b-1 fuel pump circuit inspection wiring diagram inspection 1. To ignition switch 4. Fuel pump relay 2. Main fuse 5. Fuel pump 3. Main relay 6. Ecm (pcm) caution: check to make sure that connection is made between correct terminals. ...
Page 278
Engine general information and diagnosis (h27 engine) 6-1-117 fig. For step 2 table b-2 fuel injectors and circuit inspection wiring diagram 3 fuel pump relay check : 1) check fuel pump relay referring to “fuel pump relay inspection” in section 6e2. Is it in good condition? “blk/wht” or “wht/ grn” c...
Page 279
6-1-118 engine general information and diagnosis (h27 engine) inspection step action yes no 1 check injector for operating sound : using sound scope, check each injector for operating sound at engine cranking. Do all 6 injectors make operating sound? Go to step 2. Go to step 3. 2 wire harness check ...
Page 280
Engine general information and diagnosis (h27 engine) 6-1-119 table b-3 fuel pressure inspection system diagram special tool (a) : 09912-58441 (b) : 09912-58431 (c) : 09919-58421 inspection 1. Injector 4. Fuel filter 2. Delivery pipe 5. Fuel pump 3. Fuel pressure regulator note: before using the fol...
Page 281
6-1-120 engine general information and diagnosis (h27 engine) 3 1) start engine and warm it up to normal oper- ating temperature. 2) keep it running at specified idle speed. Is fuel pressure then within 210 – 260 kpa (2.1 – 2.6 kg/cm 2 , 29.8 – 37.0 psi)? Normal fuel pressure. Clogged vacuum passage...
Page 282
Engine general information and diagnosis (h27 engine) 6-1-121 table b-4 idle air control system inspection wiring diagram inspection 1. Throttle body 3. Ecm (pcm) 5. Main fuse 2. Idle air control valve 4. Sensed information 6. Main relay step action yes no 1 check engine idle speed and iac duty refe...
Page 283
6-1-122 engine general information and diagnosis (h27 engine) 3 check iac valve referring to “iac valve inspection” in section 6e2. Is check result as specified? Go to step 4. Iac valve malfunction, “blu/ blk”, “lt grn/blk”, “ppl/ blk”, “gry/blu” or “ppl/ yel” wire open or short or poor coupler conn...
Page 284
Engine general information and diagnosis (h27 engine) 6-1-123 table b-5 a/c signal circuits inspection (if equipped) wiring diagram inspection 1. A/c control module (amplifier) 2. Ecm (pcm) step action yes no 1 check a/c signal circuit. 1) check voltage at terminal e61-17 with ignition switch on. A/...
Page 285
6-1-124 engine general information and diagnosis (h27 engine) table b-6 a/c condenser fan motor relay control system inspection (if equipped) wiring diagram inspection 1. To ignition switch 3. A/c fuse 5. A/c condenser fan motor 2. Main fuse 4. A/c condenser fan motor relay 6. Ecm (pcm) warning: kee...
Page 286: Special Tool
Engine general information and diagnosis (h27 engine) 6-1-125 special tool 09912-58441 09912-58431 09912-58490 09912-58421 pressure gauge pressure hose 3-way joint & hose checking tool set (see note “a”.) 09917-47011 09930-88521 09931-76011 vacuum pump gauge injector test lead tech 1a kit (suzuki sc...
Page 287
6-1-126 engine general information and diagnosis (h27 engine).
Page 288: Section 6A2
Engine mechanical (h27 engine) 6a2-1 6a2 section 6a2 engine mechanical (h27 engine) contents on-vehicle service........................................6a2-2 throttle body and intake manifold ..............6a2-2 exhaust manifold.........................................6a2-9 lh (no.1) bank 2nd timing ...
Page 289: On-Vehicle Service
6a2-2 engine mechanical (h27 engine) on-vehicle service throttle body and intake manifold 1. Air cleaner box 6. Intake manifold 11. Gasket 16. Throttle body bolt 2. Intake air hose 7. Intake manifold gasket 12. Iat sensor tightening torque 3. Intake air pipe 8. Throttle body assembly 13. Maf sensor ...
Page 290
Engine mechanical (h27 engine) 6a2-3 removal 1) release fuel pressure in fuel feed line by referring to section 6. 2) disconnect negative (–) cable at battery. 3) drain coolant. 4) remove strut tower bar (2). 5) disconnect coupler from intake air temp. Sensor, and maf sensor. 6) remove surge tank co...
Page 291
6a2-4 engine mechanical (h27 engine) 8) disconnect accelerator cable (1) and a/t throttle cable (2) (for a/t vehicle) from throttle body. 9) disconnect water hoses (3) from throttle body. 10) disconnect injector wire (1) coupler. 11) disconnect brake booster hose (2) from intake manifold. 12) discon...
Page 292
Engine mechanical (h27 engine) 6a2-5 19) disconnect hoses of heater, evap canister, fuel feed and fuel return. 20) remove throttle body (1) and intake collector (2) from intake manifold (3). 21) disconnect hoses of pcv valve and evap canister purge valve from intake collector. 22) remove throttle bo...
Page 293
6a2-6 engine mechanical (h27 engine) installation 1) install new intake manifold gaskets (1) to cylinder heads. 2) install intake manifold (1). Tighten bolts and nuts to specified torque. Tightening torque intake manifold bolt and nut (a) : 23 n·m (2.3 kg-m, 16.5 lb-ft) 3) install throttle body (2) ...
Page 294
Engine mechanical (h27 engine) 6a2-7 6) connect hoses of heater, evap canister, fuel feed and fuel return. 7) install egr pipe with new gaskets. 8) connect hoses of evap canister purge valve and heater. 9) connect hoses of pcv, breather and water. 10) connect couplers of manifold absolute pressure (...
Page 295
6a2-8 engine mechanical (h27 engine) 16) connect water hoses (3) to throttle body. 17) connect accelerator cable (1) and a/t throttle cable (2) (for a/t vehicle) to throttle body. 18) install surge tank pipe (2) to intake manifold with new gas- kets and intake air pipe (1) to throttle body. 19) inst...
Page 296
Engine mechanical (h27 engine) 6a2-9 26) upon completion of installation, verify that there is no fuel leakage at each connection according to procedure described in section 6. Exhaust manifold removal 1) disconnect negative (–) cable at battery. 2) remove air cleaner upper case and intake air hose ...
Page 297
6a2-10 engine mechanical (h27 engine) 4) disconnect egr pipe from right (no.2) bank exhaust mani- fold if right side exhaust manifold is removed. 5) remove oil level gauge guide (3) if left side exhaust manifold is removed. 6) detach p/s pump assembly as following, if left side exhaust manifold is r...
Page 298
Engine mechanical (h27 engine) 6a2-11 installation 1) install new manifold gaskets to cylinder heads and no.1 pipe gasket to exhaust no.1 pipe. 2) install exhaust manifolds. • always install new bolts with pre-coated adhesive to the locations with ✱ mark. • tighten both manifold nuts and bolts to sp...
Page 299
6a2-12 engine mechanical (h27 engine) 7) reverse removal procedure to install front propeller shaft if removed. When installing propeller shaft, align match mark (1). Use following specification to torque universal joint flange. Tightening torque universal joint flange bolt (c) : 55 n·m (5.5 kg-m, 4...
Page 300
Engine mechanical (h27 engine) 6a2-13 lh (no.1) bank 2nd timing chain and chain tensioner 1. Lh bank 2nd timing chain 5. Camshaft sprocket bolt 9. Timing chain tensioner adjuster no. 3 bolt 2. Timing chain tensioner adjuster no.3 6. Timing chain guide no.4 10. Timing chain tensioner adjuster no. 3 n...
Page 301
6a2-14 engine mechanical (h27 engine) camshaft and valve lash adjuster 1. Rh bank 2nd timing chain 6. Lh bank intake camshaft 11. Timing chain guide no.5 2. Rh bank exhaust camshaft 7. Lh bank exhaust camshaft 12. Valve lash adjuster 3. Rh bank intake camshaft 8. Lh bank intake camshaft holder 13. C...
Page 302
Engine mechanical (h27 engine) 6a2-15 inspection cam wear using a micrometer, measure cam height. If measured height is below its limit, replace camshaft. Intake cam height : standard : 40.402 – 40.562 mm (1.5906 – 1.5969 in.) limit : 40.300 mm (1.3581 in.) exhaust cam height : standard : 39.428 – 3...
Page 303
6a2-16 engine mechanical (h27 engine) 6) remove housing, and using scale (2) on gaging plastic (1) envelop, measure gaging plastic (1) width at its widest point. Camshaft journal clearance : standard : 0.045 – 0.099 mm (0.0018 – 0.0039 in.) limit : 0.12 mm (0.0047 in.) if measured camshaft journal c...
Page 304
Engine mechanical (h27 engine) 6a2-17 valves and cylinder heads 1. Cylinder block 6. Exhaust valve 11. Valve stem oil seal 16. Cylinder head bolt (hex hole bolt) 2. Rh bank cylinder head 7. Intake valve 12. Valve spring retainer tightening torque 3. Lh bank cylinder head 8. Valve spring seat 13. Val...
Page 305
6a2-18 engine mechanical (h27 engine) inspection valve guides using a micrometer and bore gauge, take diameter readings on valve stems and guides to check stem-to-guide clearance. Be sure to take reading at more than one place along the length of each stem and guide. If clearance exceeds limit, repl...
Page 306
Engine mechanical (h27 engine) 6a2-19 5) install cylinder head to block. After applying oil to cylinder head bolts, tighten them gradu- ally as follows. A) tighten all bolts to 53 n·m (5.3 kg-m, 38.5 lb-ft) according to numerical order in the figure. B) in the same manner as in a), tighten them to 8...
Page 307
6a2-20 engine mechanical (h27 engine) 12) install oil pan and oil pump strainer. Refer to “oil pan and oil pump strainer” in this sec- tion. 13) install cylinder head cover. Refer to “cylinder head cover” in this section. 14) install exhaust manifold. Refer to “exhaust manifold” in this section. 15)...
Page 308
Engine mechanical (h27 engine) 6a2-21 piston, piston rings, connecting rods and cylinders 1. Top ring 5. Connecting rod : clean bearing installing surface when install. 9. Piston pin circlip tightening torque 2. 2nd ring 6. Connecting rod bearing cap : clean bearing installing surface when install. ...
Page 309
6a2-22 engine mechanical (h27 engine) inspection cylinders • inspect cylinder walls for scratches, roughness, or ridges which indicate excessive wear. If cylinder bore is very rough or deeply scratched, or ridged, rebore cylinder and use over size piston. • using a cylinder gauge, measure cylinder b...
Page 310
Engine mechanical (h27 engine) 6a2-23 • piston clearance : measure cylinder bore diameter and piston diameter to find their difference which is piston clearance. Piston clearance should be within specification as given below. If it is out of specification, rebore cylinder and use oversize piston. Pi...
Page 311
6a2-24 engine mechanical (h27 engine) assembly 1) 2 sizes of piston are available as standard size spare part so as to ensure proper piston-to-cylinder clearance. When installing a standard size piston, make sure to match piston with cylinder as follows. A) each piston has stamped number (1 or 2) on...
Page 312
Engine mechanical (h27 engine) 6a2-25 3) install piston rings to piston : • as shown in the figure, 1st and 2nd rings have “rn” or “r” mark respectively. When installing these piston rings to pis- ton, direct marked side of each ring toward top of piston. • 1st rings differs from 2nd ring in thickne...
Page 313: Unit Repair Overhaul
6a2-26 engine mechanical (h27 engine) unit repair overhaul engine assembly removal 1) release fuel pressure in fuel feed line. Refer to “fuel pressure relief procedure” in section 6. 2) disconnect negative (–) cable at battery. 3) remove engine hood. 4) drain engine oil. 5) drain coolant. 6) remove ...
Page 314
Engine mechanical (h27 engine) 6a2-27 12) disconnect the following electric lead wires : • injector wire coupler • cmp sensor coupler • ignition coil couplers • ckp sensor coupler • map sensor coupler • tp sensor (1) coupler • iac valve (2) coupler • earth wire (3) from surge tank • evap canister pu...
Page 315
6a2-28 engine mechanical (h27 engine) 24) remove a/t fluid hose clamps (1) from engine mounting bracket (2). (for a/t vehicle) 25) remove clutch housing lower plate. 26) remove torque converter bolts (for a/t vehicle). 27) remove starter motor. 28) lower vehicle. 29) support transmission. For a/t ve...
Page 316
Engine mechanical (h27 engine) 6a2-29 3) tighten bolts and nuts fastening cylinder block and transmis- sion to specified torque. Tightening torque transmission to cylinder block bolt and nut (b) : 85 n·m (8.5 kg-m, 61.5 lb-ft) 4) remove lifting device 5) tighten torque converter bolts to specified t...
Page 317
6a2-30 engine mechanical (h27 engine) main bearings, crankshaft and cylinder block 1. Cylinder block 6. Rear oil seal 11. O-ring [a]: sealant application amount 2. Lower crankcase : apply sealant 99000-31150 to lower crankcase mating surface. 7. Flywheel (m/t) drive plate (a/t) 12. Clutch housing pl...
Page 318
Engine mechanical (h27 engine) 6a2-31 main bearing clearance check clearance by using gaging plastic (1) according to the fol- lowing procedure. 1) remove crankcase. 2) clean bearings and main journals. 3) place a piece of gaging plastic to full width of bearing (paral- lel to crankshaft) on journal...
Page 319
6a2-32 engine mechanical (h27 engine) selection of main bearings • standard bearing : if bearing is in malcondition, or bearing clearance is out of specification, select a new standard bearing according to the following procedure and install it. 1) first check journal diameter. As shown in the figur...
Page 320
Engine mechanical (h27 engine) 6a2-33 3) there are 5 kinds of standard bearings differing in thickness. To distinguish them, they are painted in following colors at the position as shown in the figure. Each color indicates the following thickness at the center of bearing. Standard size main bearing ...
Page 321
6a2-34 engine mechanical (h27 engine) • undersize bearing (0.25 mm) : 0.25 mm undersize bearing is available, in 5 kinds varying in thickness. To distinguish them, each bearing is painted in the following colors at such position as shown in the figure. Each color represents the following thickness a...
Page 322
Engine mechanical (h27 engine) 6a2-35 inspection honing or reboring cylinders 1) when any cylinder needs reboring, all other cylinders must also be rebored at the same time. 2) select oversized piston according to amount of cylinder wear. Oversize piston specification : 3) using micrometer, measure ...
Page 323: Special Tool
6a2-36 engine mechanical (h27 engine) special tool 09911-97810 09913-75510 09915-47310 09915-64510 oil seal installer bearing installer oil filter wrench compression gauge 09915-64530 09915-67010 09915-67310 09915-77310 compression gauge hose compression gauge attachment (c) vacuum gauge oil pressur...
Page 324
Engine mechanical (h27 engine) 6a2-37 09916-84511 09917-68221 09917-87810 09917-98221 forceps camshaft lock holder valve guide installer valve stem seal installer 09918-08210 09919-28610 09924-17810 09926-58010 vacuum gauge hose joint protective sleeve flywheel holder bearing puller attachment 09944...
Page 325
6a2-38 engine mechanical (h27 engine).
Page 326: Section 6B
Engine cooling 6b-1 6b section 6b engine cooling contents maintenance ....................................................6b-2 coolant.......................................................... 6b-2 note: • for the descriptions (items) not found in this section, refer to the descriptions of h25 engin...
Page 327: Maintenance
6b-2 engine cooling maintenance coolant anti-freeze proportioning chart : coolant capacity : freezing temperature °c –16 –36 °f 3 –33 antifreeze/anticorrosion coolant concentration % 30 50 ratio of compound to cooling water ltr. 2.7/6.4 4.6/4.6 us pt 5.8/13.7 9.8/9.8 imp. Pt. 4.8/11.3 8.1/8.1 engine...
Page 328: Section 6C
Engine fuel 6c-1 6c section 6c engine fuel contents general description ....................................... 6c-1 fuel system ................................................. 6c-1 on-vehicle service ........................................ 6c-2 fuel tank ............................................
Page 329: On-Vehicle Service
6c-2 engine fuel on-vehicle service fuel tank removal 1) relieve fuel pressure in fuel feed line referring to section 6 or section 6-1. 2) disconnect negative (–) cable at battery. 3) before disconnecting fuel filler hose, give match marks on fuel filler hose and fuel filler neck. 4) disconnect fuel...
Page 330
Engine fuel 6c-3 10) disconnect fuel vapor hose and return hose from pipes. 11) remove fuel tank protector (if equipped) from vehicle. 12) lower fuel tank gradually while holding it horizontally and pull out coupler at fuel pump. Inspection after removing fuel tank, check hoses and pipes connected t...
Page 331
6c-4 engine fuel installation 1) install fuel pump assembly, fuel cut valve and vapor control valve to fuel tank. Refer to “fuel pump” in this section. 2) connect fuel hoses to fuel tank, fuel cut valve, and vapor control valve, check valve and fuel pump assembly. After connecting, clamp hoses secur...
Page 332
Engine fuel 6c-5 fuel lines due to the fact that fuel feed line is under high pressure, this sys- tem requires special consideration for service. The feed pipe uses screw couplings and hose clamps. Inspection visually inspect fuel lines for evidence of fuel leakage, hose cracking and deterioration, ...
Page 333
6c-6 engine fuel.
Page 334: Section 6E2
Engine and emission control system (sequential multiport fuel injection for h27 engine) 6e2-1 6e2 section 6e2 engine and emission control system (sequential multiport fuel injection for h27 engine) contents general description ..................................... 6e2-2 system flow.....................
Page 335: General Description
6e2-2 engine and emission control system (sequential multiport fuel injection for h27 engine) fuel injector.......................................... 6e2-26 electronic control system........................ 6e2-31 engine control module (ecm)/ powertrain control module (pcm) ........ 6e2-31 mass air ...
Page 336
Engine and emission control system (sequential multiport fuel injection for h27 engine) 6e2-3 system flow.
Page 337
6e2-4 engine and emission control system (sequential multiport fuel injection for h27 engine) system diagram.
Page 338
Engine and emission control system (sequential multiport fuel injection for h27 engine) 6e2-5 1. Air cleaner 22. Fuel level sensor 39. A/c controller (if equipped) 2. Intake air temp. Sensor 23. Monitor connector (if equipped) 40. Data link connector/immobilizer control mod- ule (if equipped) 3. Mas...
Page 339
6e2-6 engine and emission control system (sequential multiport fuel injection for h27 engine) air intake system the main components of the air intake system are air cleaner, mass air flow sensor, air cleaner, intake air pipe, throttle body, intake collector, idle air control valve and intake manifol...
Page 340
Engine and emission control system (sequential multiport fuel injection for h27 engine) 6e2-7 fuel delivery system the fuel delivery system consists of the fuel tank, fuel pump, fuel filter, fuel pressure regulator, delivery pipe and fuel injectors. The fuel in the fuel tank is pumped up by the fuel...
Page 341
6e2-8 engine and emission control system (sequential multiport fuel injection for h27 engine) electronic control system the electronic control system consists of 1) various sensors which detect the state of engine and driving condi- tions, 2) ecm (pcm) which controls various devices according to the...
Page 342
Engine and emission control system (sequential multiport fuel injection for h27 engine) 6e2-9 orn/blu ppl/wht gry/yel red/wht gry/red gry/red gry/blk red/grn gry/red gry/yel orn/blk lt blu gry/yel pnk/blu gry pnk/blk gry/wht yel/blk pnk/wht blk/red red/yel grn/wht blu/orn wht orn blu/yel blu/grn orn...
Page 343
6e2-10 engine and emission control system (sequential multiport fuel injection for h27 engine) terminal arrangement of ecm (pcm) connector (viewed from harness side) 1. Fuel injector no.1 17. “o/d off” lamp (a/t) 34. Power steering pressure switch 2. Fuel injector no.2 18. “power” lamp (a/t) 35. Sto...
Page 344
Engine and emission control system (sequential multiport fuel injection for h27 engine) 6e2-11 terminal circuit terminal circuit terminal circuit c51-3-1 intake air temp. (iat) sensor c51-3-13 power source for tp sensor c51-3-25 ground for iat sensor, map sensor and oxygen sensor (if equipped) c51-3...
Page 345: Diagnosis
6e2-12 engine and emission control system (sequential multiport fuel injection for h27 engine) engine and emission control input/output table diagnosis refer to section 6-1. Ignition coil with igniter ho2s heater control input output function main relay control fuel pump control injection control ig...
Page 346: On-Vehicle Service
Engine and emission control system (sequential multiport fuel injection for h27 engine) 6e2-13 on-vehicle service general when hoses are disconnected and system components are removed for service, reinstall components properly, and route and connect hoses correctly after service. Refer to figure on ...
Page 347
6e2-14 engine and emission control system (sequential multiport fuel injection for h27 engine) accelerator cable adjustment 1) with throttle valve closed, check accelerator pedal play which should be within following specification. If measured value is out of specification, adjust accelerator cable ...
Page 348
Engine and emission control system (sequential multiport fuel injection for h27 engine) 6e2-15 idle speed/idle air control (iac) duty inspec- tion before idle speed/iac duty check, make sure of the following. • lead wires and hoses of engine/emission control systems are connected securely. • acceler...
Page 349
6e2-16 engine and emission control system (sequential multiport fuel injection for h27 engine) [not using suzuki scan tool] (vehicle with monitor connector) 1) disconnect scan tool from dlc if connected. 2) warm up engine to normal operating temperature. 3) stop engine and connect duty meter (3) bet...
Page 350
Engine and emission control system (sequential multiport fuel injection for h27 engine) 6e2-17 idle mixture inspection/adjustment (vehicle without heated oxygen sensor) all vehicles not equipped with heated oxygen sensor are shipped with their co % factory adjusted as follows. Engine idle mixture (c...
Page 351
6e2-18 engine and emission control system (sequential multiport fuel injection for h27 engine) air intake system throttle body removal 1) disconnect negative (–) cable at battery. 2) drain cooling system. 3) remove strut tower bar. 4) disconnect accelerator cable (1) and or a/t throttle cable (2) fr...
Page 352
Engine and emission control system (sequential multiport fuel injection for h27 engine) 6e2-19 6) remove surge tank cover. Remove intake air pipe (1) and surge tank pipe (2). 7) disconnect connectors of tp sensor and iac valve. 8) disconnect ground wire at connector. 9) remove clamp bracket (1) and ...
Page 353
6e2-20 engine and emission control system (sequential multiport fuel injection for h27 engine) cleaning clean throttle body bore and bypass air passages (1) by blowing compressed air. Installation 1) clean mating surfaces and install throttle body gasket to intake collector (1) with new gasket (2). ...
Page 354
Engine and emission control system (sequential multiport fuel injection for h27 engine) 6e2-21 14) install strut tower bar (1) and tighten bolts. 15) refill cooling system. 16) connect negative (–) cable at battery. 17) adjust accelerator cable and a/t throttle cable, refer to “accelerator cable adj...
Page 355
6e2-22 engine and emission control system (sequential multiport fuel injection for h27 engine) 3) remove air cleaner outlet hose and remove iac valve from throttle body. 4) connect connector to iac valve. 5) check that plunger (1) of iac valve moves once and then stops as soon as ignition switch (2)...
Page 356
Engine and emission control system (sequential multiport fuel injection for h27 engine) 6e2-23 fuel delivery system fuel pressure inspection 1) relieve fuel pressure in fuel feed line referring to “fuel pressure relief procedure” in section 6-1. 2) disconnect fuel feed hose from (3) delivery fuel fe...
Page 357
6e2-24 engine and emission control system (sequential multiport fuel injection for h27 engine) 8) after checking fuel pressure, remove fuel pressure gauge (1). 9) remove fuel pressure gauge, hose and 3-way joint. 10) connect fuel feed hose and clamp it securely. 11) with engine “off” and ignition sw...
Page 358
Engine and emission control system (sequential multiport fuel injection for h27 engine) 6e2-25 removal remove fuel tank from body according to procedure described in section 6c and remove fuel pump from fuel tank. Inspection check fuel pump filter for evidence of dirt and contamination. If present, ...
Page 359
6e2-26 engine and emission control system (sequential multiport fuel injection for h27 engine) installation for installation, reverse removal procedure and note the follow- ings. • use new o-ring. • apply thin coat of gasoline to o-ring to facilitate installation. • tighten fuel pressure regulator (...
Page 360
Engine and emission control system (sequential multiport fuel injection for h27 engine) 6e2-27 removal 1) relieve fuel pressure in fuel feed line referring to “fuel pressure relief procedure” in section 6-1. 2) remove throttle body intake collector, refer to “throttle body” in this section. 3) disco...
Page 361
6e2-28 engine and emission control system (sequential multiport fuel injection for h27 engine) 1) install injector (1) and fuel pressure regulator (2) to special tool (injector checking tool). Special tool (a) : 09912-58421 2) connect special tools (hoses and attachment) to pipes of vehicle. Special...
Page 362
Engine and emission control system (sequential multiport fuel injection for h27 engine) 6e2-29 installation 1) replace injector o-ring (1) with new one using care not to damage it. Install grommet (2) to injector. 2) check if insulator (1) is scored or damaged. If it is, replace with new one. Instal...
Page 363
6e2-30 engine and emission control system (sequential multiport fuel injection for h27 engine) 5) install fuel connect pipe (1) and tighten union bolts to speci- fied torque with new gaskets (3). Tightening torque fuel connect pipe union bolt (b) : 30 n·m (3.0 kg-m, 22.0 lb-ft) 6) install fuel feed ...
Page 364
Engine and emission control system (sequential multiport fuel injection for h27 engine) 6e2-31 electronic control system engine control module (ecm)/powertrain control module (pcm) removal 1) disconnect negative (–) cable from battery. 2) disable air bag system (if equipped) referring to “dis- ablin...
Page 365
6e2-32 engine and emission control system (sequential multiport fuel injection for h27 engine) mass air flow sensor (maf sensor) inspection 1) connect voltmeter (1) to “b+” terminal of maf sensor (2) coupler disconnected and ground (3). 2) turn ignition switch on and check that voltage is battery vo...
Page 366
Engine and emission control system (sequential multiport fuel injection for h27 engine) 6e2-33 removal 1) disconnect negative (–) cable at battery and coupler (1) from maf sensor (3). 2) remove air cleaner outlet hose (2) from throttle body and maf sensor (3). 3) remove maf sensor from air cleaner c...
Page 367
6e2-34 engine and emission control system (sequential multiport fuel injection for h27 engine) intake air temperature (iat) sensor removal 1) disconnect negative (–) cable at battery. 2) disconnect iat sensor coupler. 3) remove iat sensor from air cleaner case. Inspection immerse temperature sensing...
Page 368
Engine and emission control system (sequential multiport fuel injection for h27 engine) 6e2-35 throttle position sensor (tp sensor) inspection 1) disconnect negative (–) cable at battery and coupler from tp sensor (4). 2) using ohmmeter, check resistance between terminals under each condition given ...
Page 369
6e2-36 engine and emission control system (sequential multiport fuel injection for h27 engine) engine coolant temperature sensor (ect sensor) removal 1) disconnect negative (–) cable from battery. 2) drain cooling system. 3) disconnect coupler from ect sensor (1). 4) remove ect sensor from water out...
Page 370
Engine and emission control system (sequential multiport fuel injection for h27 engine) 6e2-37 heated oxygen sensor (sensor 1) removal 1) disconnect negative (–) cable from battery. 2) disconnect coupler of oxygen sensor (s). 3) remove oxygen sensor (s) from exhaust manifold (s). Installation revers...
Page 371
6e2-38 engine and emission control system (sequential multiport fuel injection for h27 engine) heater inspection 1) disconnect ho2s-1 or -2 coupler. 2) using ohmmeter, measure resistance between terminals “vb” and “gnd” of ho2s coupler (1). If found faulty, replace ho2s. Resistance of ho2s heater: 1...
Page 372
Engine and emission control system (sequential multiport fuel injection for h27 engine) 6e2-39 heater inspection refer to “heated oxygen sensor (sensor 1) heater inspection” vehicle speed sensor (vss) on-vehicle inspection 1) hoist vehicle. 2) release parking brake lever, set transmission in neutral...
Page 373
6e2-40 engine and emission control system (sequential multiport fuel injection for h27 engine) inspection 1) check sensor o-ring (1) for damage and deterioration. Replace as necessary. 2) arrange 3 new 1.5 v batteries (2) in series and connect its positive terminal to “vin” terminal of map sensor (1...
Page 374
Engine and emission control system (sequential multiport fuel injection for h27 engine) 6e2-41 installation 1) confirm that vacuum passage on intake manifold is free from clog. 2) apply engine oil to o-ring of sensor. 3) install sensor (1) to intake manifold (2). 4) connect connector to sensor (1) s...
Page 375
6e2-42 engine and emission control system (sequential multiport fuel injection for h27 engine) 3) check resistance between each two terminals as in table below. If check results are as specified, proceed to next operation check. If not, replace. Main relay resistance: 4) check that there is continui...
Page 376
Engine and emission control system (sequential multiport fuel injection for h27 engine) 6e2-43 fuel cut operation inspection 1) warm up engine to normal operating temperature. 2) while listening to sound of injector by using sound scope (1) or such, increase engine speed to higher than 3,000 r/min. ...
Page 377
6e2-44 engine and emission control system (sequential multiport fuel injection for h27 engine) emission control system egr system (if equipped) egr system inspection (using suzuki scan tool) 1) connect suzuki scan tool to data link connector (dlc) (1) with ignition switch off. Special tool (a) : suz...
Page 378
Engine and emission control system (sequential multiport fuel injection for h27 engine) 6e2-45 inspection 1) check resistance between following terminals of egr valve (1) in each pair. If found faulty, replace egr valve assembly. Egr valve resistance: 2) remove carbon from egr valve gas passage. 3) ...
Page 379
6e2-46 engine and emission control system (sequential multiport fuel injection for h27 engine) 1) disconnect vacuum hoses from evap canister and remove evap canister. 2) when air is blown into tank pipe, there should be no restric- tion of flow through purge pipe and air pipe. If operation differs f...
Page 380
Engine and emission control system (sequential multiport fuel injection for h27 engine) 6e2-47 pcv system pcv hose inspection check hoses for connection, leakage, clog, and deterioration. Replace as necessary. Pcv valve on-vehicle inspection 1) disconnect pcv valve from cylinder head cover and plug ...
Page 381: Special Tool
6e2-48 engine and emission control system (sequential multiport fuel injection for h27 engine) pcv system pcv hose check hoses for connection, leakage, clog, and deterioration. Replace as necessary. Tightening torque specification special tool note: be sure to check that there is no obstruction in p...
Page 382
Engine and emission control system (sequential multiport fuel injection for h27 engine) 6e2-49 09917-47010 09930-88521 09931-76011 vacuum pump gauge injector test lead tech 1a kit (suzuki scan tool) (see note “b”.) mass storage cartridge for tech 1a 09931-76030 14/16 pin dlc cable for tech 1a tech 2...
Page 383
6e2-50 engine and emission control system (sequential multiport fuel injection for h27 engine).
Page 384: Section 6F2
Ignition system (for h27 engine) 6f2-1 6f2 section 6f2 ignition system (for h27 engine) contents general description ...................................... 6f2-2 components ................................................ 6f2-2 system wiring ............................................. 6f2-3 diagno...
Page 385: General Description
6f2-2 ignition system (for h27 engine) general description the ignition system is a direct ignition system. It consists of the parts as described below and has an electronic ignition control system. • ecm (or pcm) it detects the engine condition through the signals from the sensors, determines the m...
Page 386
Ignition system (for h27 engine) 6f2-3 system wiring note: for ecm (pcm) terminal assignment, refer to section 6e2. 1. To ignition switch 8. Ignition coil assembly (for no.3 cylinder) 2. “ig coil meter” fuse 9. Ignition coil assembly (for no.4 cylinder) 3. Ecm (or pcm) 10. Spark plug 4. Cmp sensor 1...
Page 387: Diagnosis
6f2-4 ignition system (for h27 engine) diagnosis diagnostic flow table condition possible cause correction engine cranks, but will not start or hard to start (no spark) blown fuse for ignition coil assembly replace. Loose connection or disconnection of lead wire connect securely. Faulty spark plug (...
Page 388
Ignition system (for h27 engine) 6f2-5 reference oscilloscope waveforms of cmp sensor ref signal and no.1 ignition trigger signal are as shown in figure when connecting oscilloscope between terminal c51-1-13 of ecm (pcm) connec- tor connected to ecm (pcm) and ground, and between terminal c51-2-28 an...
Page 389
6f2-6 ignition system (for h27 engine) ignition spark check 1) remove surge tank cover. 2) disconnect injector coupler (1). 3) remove spark plug and check it for condition and type, refer- ring to “spark plug” in this section. 4) if ok, connect ignition coil coupler to ignition coil assembly and con...
Page 390
Ignition system (for h27 engine) 6f2-7 5) set timing light to ignition harness for no.1 cylinder. 6) using timing light, check that timing observed from viewpoint is within specification. Initial ignition timing of viewpoint (when it is fixed by suzuki scan tool) : 5 ± 1° btdc ignition order : 1-6-5...
Page 391: On-Vehicle Service
6f2-8 ignition system (for h27 engine) on-vehicle service ignition coil assembly (igniter and ignition coil) removal 1) remove ignition coil cover. 2) disconnect ignition coil coupler. 3) remove ignition coil bolt (1), and then pull out ignition coil assembly (2). Inspection check ignition coil asse...
Page 392
Ignition system (for h27 engine) 6f2-9 inspection inspect them for electrode wear, carbon deposits and insulator damage. If any abnormality is found, replace them with specified new plug. Spark plug air gap “a” : 1.0 – 1.1 mm (0.039 – 0.043 in.) spark plug type : denso k20pr-u11/sk16pr11 ngk bkr6e-1...
Page 393
6f2-10 ignition system (for h27 engine) cmp sensor removal 1) disconnect cmp sensor coupler (2). 2) remove a/t fluid level gauge and filler tube. 3) remove cmp sensor (1) by removing bolt (3). Installation 1) install a new o-ring (2) with engine oil applied to cmp sen- sor (1). Caution: disassembly ...
Page 394
Ignition system (for h27 engine) 6f2-11 2) install cmp sensor to camshaft. Fit the dog of cmp sensor coupling into the slots of cam- shaft, when installing. The dogs of cmp sensor coupling are offset. Therefore, if the dogs can not be fitted into the slots, turn the cmp sensor shaft by 180 degree an...
Page 395
6f2-12 ignition system (for h27 engine) noise suppressor removal 1) disconnect coupler of noise suppressor (1). 2) remove noise suppressor (1) from harness (2). Inspection using ohmmeter, check to be sure that capacitor (condenser) in noise suppressor is not conductive. If check result is not satisf...
Page 396: Special Tool
Ignition system (for h27 engine) 6f2-13 special tool 09930-76420 09931-76011 09931-76030 timing light (dry cell type) tech 1a kit (suzuki scan tool) (see note “a”.) 16/14 pin dlc cable for tech 1a mass storage cartridge for tech 1a tech 2 kit (suzuki scan tool) (see note “b”.) note: “a”: this kit in...
Page 397
6f2-14 ignition system (for h27 engine).
Page 398: Section 6H
Charging system 6h-1 6h section 6h charging system contents general description ....................................... 6h-2 generator ..................................................... 6h-2 unit repair overhaul ..................................... 6h-3 generator assembly ..........................
Page 399: General Description
6h-2 charging system general description generator wiring circuit b : generator output (battery terminal) l : lamp terminal 5. Stator core 10. Rear end frame d : dummy terminal 1. Pulley 6. Field coil 11. Drive end frame e : ground 2. Pulley nut 7. Rectifier f : field coil terminal 3. Rotor fan 8. B...
Page 400: Unit Repair Overhaul
Charging system 6h-3 unit repair overhaul generator assembly inspection rotor • using ohmmeter, check for continuity between slip rings of rotor. If there is no continuity, replace rotor. Standard resistance between slip rings of rotor : 1.6 – 2.0 Ω Ω Ω Ω at 20°c (68°f) 1. Pulley nut 6. Driver end b...
Page 401
6h-4 charging system • using ohmmeter, check that there is no continuity between slip ring and rotor. If there is continuity, replace rotor. • check slip rings for roughness or scoring. If rough or scored, replace rotor. Using a vernier caliper, measure the slip ring diameter. If the diameter is les...
Page 402
Charging system 6h-5 brush and brush holder check each brush for wear by measuring its length as shown. If brush is found worn down to service limit, replace brush. Exposed brush length “a” standard : 10.5 mm (0.413 in.) limit : 1.5 mm (0.059 in.) rectifier • positive rectifier a) using an ohmmeter,...
Page 403: Specifications
6h-6 charging system specifications battery generator tightening torque specification battery type 55d23l 75d23l 95d26l rated capacity ah/5hr, 12 volts 48 52 66 electrolyte l (us/imp.Pt) 3.9 (8.24/6.86) 3.9 (8.24/6.86) 4.0 (8.53/7.04) electrolyte s.G. 1.28 when fully charged at 20°c (68°f) type 105 ...
Page 404: Section 6K
Exhaust system 6k-1 6k section 6k exhaust system contents on-vehicle service..........................................6k-2 components.................................................. 6k-2 caution: be sure to use unleaded fuel for the catalytic converter equipped vehicle. Use of leaded fuel will aff...
Page 405: On-Vehicle Service
6k-2 exhaust system on-vehicle service components type with weld bolt at muffler front flange 1-1 exhaust manifold (without wu-twc) 4. Heated oxygen sensor-1 (if equipped) 7. Exhaust pipe bolt 11. Muffler tail pipe 1-2 exhaust manifold (with wu-twc) 5. Exhaust pipe gasket 8. Muffler 12. Muffler gask...
Page 406
Exhaust system 6k-3 type without weld bolt at muffler front flange 1-1 exhaust manifold (without wu-twc) 4. Heated oxygen sensor-1 (if equipped) 7. Exhaust pipe bolt 12. Muffler gasket 1-2 exhaust manifold (with wu-twc) 5. Exhaust pipe gasket 8. Muffler 13. No.1 exhaust pipe stiffener 2. Seal ring 6...
Page 407
6k-4 exhaust system.
Page 408: Section 7A1
Manual transmission 7a1-1 7a1 section 7a1 manual transmission contents unit repair .....................................................7a1-1 unit repair note: for the descriptions (items) not found in this section, refer to the same section of the service manual mentioned in the foreword of this ma...
Page 409
7a1-2 manual transmission.
Page 410: Section 7B1
Automatic transmission (4 a/t) 7b1-1 7b1 section 7b1 automatic transmission (4 a/t) contents general description ......................................7b1-3 electronic shift control system...................7b1-4 automatic gear shift diagram...................7b1-5 diagnosis ...........................
Page 411
7b1-2 automatic transmission (4 a/t) stall test ................................................... 7b1-38 line pressure test.................................... 7b1-39 road test ................................................. 7b1-40 manual road test..................................... 7b1-41 tim...
Page 412: General Description
Automatic transmission (4 a/t) 7b1-3 general description item specifications torque converter type 3-element, 1-step, 2-phase type (with tcc (lock-up) mechanism) stall torque ratio 2.0 oil pump type trochoid type oil pump drive system engine driven gear change device type forward 4-step, reverse 1-s...
Page 413
7b1-4 automatic transmission (4 a/t) electronic shift control system 1. Pcm (ecm) 9. Transmission range sensor 17. Mil (“service engine soon” lamp) 2. Vss 10. Shift solenoid-a 18. O/d off switch 3. Cmp sensor 11. Shift solenoid-b 19. P/n change switch 4. Tp sensor 12. Tcc solenoid 20. 4wd low switch...
Page 414
Automatic transmission (4 a/t) 7b1-5 automatic gear shift diagram automatic shift schedule as a result of shift control is shown below. In case that select lever is shifted to l at a higher than 55 km/h or 34 mile/h speed, 2nd or 3rd gear is operated and then down shifts to 1st at a speed lower than...
Page 415
7b1-6 automatic transmission (4 a/t) [normal mode] gear shift diagram [a] and tcc lock-up diagram [b] shift 1 → → → → 2 2 → → → → 3 3 → → → → 4 4 → → → → 3 3 → → → → 2 2 → → → → 1 throttle opening full throttle km/h (mile/h) 46 (29) 93 (58) 160 (100) 150 (94) 83 (52) 36 (23) closed throttle km/h (mi...
Page 416: Diagnosis
Automatic transmission (4 a/t) 7b1-7 diagnosis this vehicle is equipped with an electronic transmission control system, which control the automatic shift up and shift down timing, tcc operation, etc. Suitably to vehicle driving conditions. Pcm (ecm) has an on-board diagnosis system which detects a m...
Page 417
7b1-8 automatic transmission (4 a/t) on-board diagnostic system (vehicle with monitor connector) for automatic transmission control system, pcm (ecm) has fol- lowing functions. Refer to section 6/6-1 for details. • when the ignition switch is turned on with the engine at a stop, malfunction indicato...
Page 418
Automatic transmission (4 a/t) 7b1-9 precaution in diagnosing trouble • don’t disconnect couplers from pcm (ecm), battery cable from battery, pcm ground wire harness from engine or main fuse before checking the diagnosis information (dtc, freeze frame data, etc.) stored in pcm memory. Such disconnec...
Page 419
7b1-10 automatic transmission (4 a/t) automatic transmission diagnostic flow table refer to the following pages for the details of each step. Step action yes no 1 customer complaint analysis 1) perform customer complaint analysis refer- ring to the next page. Was customer complaint analysis performe...
Page 420
Automatic transmission (4 a/t) 7b1-11 step 1. Customer complaint analysis record details of the problem (failure, complaint) and how it occurred as described by the customer. For this purpose, use of such a inspection form will facilitate collecting information to the point required for proper analy...
Page 421
7b1-12 automatic transmission (4 a/t) step 10. Check for intermittent problem check parts where an intermittent trouble is easy to occur (e.G., wire harness, connector, etc.), referring to “intermittent and poor connection” in section 0a and related circuit of dtc recorded in step 2. Step 11. Final ...
Page 422
Automatic transmission (4 a/t) 7b1-13 malfunction indicator lamp (mil) check refer to the same item in section 6-1 for checking procedure. “o/d off” lamp check 1) check that o/d off switch button is at off position (pushed). 2) turn ignition switch on. 3) check that “o/d off” lamp lights for about 2...
Page 423
7b1-14 automatic transmission (4 a/t) diagnostic trouble code table refer to the same item in section 6-1. Fail safe table refer to the same item in section 6-1. Visual inspection visually check following parts and systems. A/t basic check this inspection is important for troubleshooting when pcm (e...
Page 424
Automatic transmission (4 a/t) 7b1-15 trouble diagnosis table 1 trouble diagnosis table 2 transmission fluid running condition 4 perform stall test, time rag test, line pressure test, engine brake test and “p” range test referring to “stall test”, “line pressure test”, “engine brake test” and ““p” r...
Page 425
7b1-16 automatic transmission (4 a/t) gear shift trouble diagnosis table 3 transmission fluid running condition condition possible cause correction poor 1–2 shift, exces- sive slippage regulator valve sticking replace. 1–2 shift valve sticking replace. Shift solenoid valve-b sticking replace. Interm...
Page 426
Automatic transmission (4 a/t) 7b1-17 gear shift abnormal noise scan tool data refer to section 6-1. Inspection of pcm and its circuit refer to section 6-1. Wire harness and connectors refer to section 6-1. Condition possible cause correction poor 1–2 shift, exces- sive slippage fluid pressure leaka...
Page 427
7b1-18 automatic transmission (4 a/t) table a-1 : no tcc lock-up occurs system description pcm turns tcc solenoid off under any of the following conditions. • brake pedal switch : on • 4wd low switch : on • cruise control module : tcc off command signal is output (if equipped). • ect : ect troublesh...
Page 428
Automatic transmission (4 a/t) 7b1-19 5 “4wd low” switch signal inspection : with ignition switch on, check voltage between c51-1-26 terminal of pcm coupler and ground. “4wd low” switch specification transfer gear position “4l” or “n” : 0 v transfer gear position “4h” or “2h” : battery voltage is th...
Page 429
7b1-20 automatic transmission (4 a/t) table a-2 : no gear shift to o/d system description pcm does not shift to o/d gear under any of the following conditions. • o/d off switch : on • 4wd low switch : on • cruise control module : o/d off command signal is output (if equipped). • ect : ect troublesho...
Page 430
Automatic transmission (4 a/t) 7b1-21 5 “4wd low” switch signal inspection : with ignition switch on, check voltage between c51-1-26 terminal of pcm coupler and ground. “4wd low” switch specification transfer gear position “4l” or “n” : 0 v transfer gear position “4h” or “2h” : battery voltage is th...
Page 431
7b1-22 automatic transmission (4 a/t) table b-1 : “o/d off” light circuit check (“o/d off” light doesn’t light at ignition switch on but engine starts up) wiring diagram troubleshooting 1. Pcm 4. P/n change switch 2. Fuse 5. J/c 3. O/d off switch 6. J/c step action yes no 1 “o/d off” light circuit c...
Page 432
Automatic transmission (4 a/t) 7b1-23 table b-2 : “o/d off” light circuit check (“o/d off” light comes on steadily) wiring diagram refer to “table b-1” in this section. Troubleshooting [a] for step 1/[b] for step 4 step action yes no 1 check o/d off switch status. Press o/d off switch button (1). Do...
Page 433
7b1-24 automatic transmission (4 a/t) table b-3 : “power” light circuit check (“power” light doesn’t light at ignition switch on but engine starts up) wiring diagram troubleshooting 1. Pcm 4. P/n change switch 2. Fuse 5. J/c 3. O/d off switch step action yes no 1 “power” light circuit check : 1) wit...
Page 434
Automatic transmission (4 a/t) 7b1-25 table b-4 : “power” light circuit check (“power” light comes on steadily) wiring diagram refer to “table b-3” in this section. Troubleshooting [a] for step 1/[b] for step 4 step action yes no 1 check power/normal change switch position. Is switch button at norma...
Page 435
7b1-26 automatic transmission (4 a/t) dtc p0705 (dtc no.72) - transmission range sensor (switch) circuit mal- function wiring diagram dtc detecting condition and trouble area 1. Pcm 3. J/c 2. Fuse 4. Transmission range sensor (switch) dtc detecting condition trouble area • transmission range switch ...
Page 436
Automatic transmission (4 a/t) 7b1-27 dtc confirmation procedure 1) connect scan tool to dlc with ignition switch off, if available. 2) clear dtc, pending dtc and freeze frame data in pcm memory by using scan tool and start engine. 3) shift a/t selector lever to each of l, 2, d, n, r and p ranges fo...
Page 437
7b1-28 automatic transmission (4 a/t) fig. For step 2. 6 check transmission range switch for installation posi- tion. 1) shift select lever to “n” range. 2) check that “n” reference line on switch and center line on shaft are aligned. Are they aligned? Go to step 7. Adjust. 7 check transmission rang...
Page 438
Automatic transmission (4 a/t) 7b1-29 dtc p0715 (dtc no.76) - input/turbine speed sensor circuit malfunction wiring diagram dtc detecting condition and trouble area 1. Pcm 2. Input shaft speed sensor dtc detecting condition trouble area input speed sensor detected speed is lower than spec- ification...
Page 439
7b1-30 automatic transmission (4 a/t) dtc confirmation procedure 1) connect scan tool to dlc with ignition switch off, if available. 2) clear dtc, pending dtc and freeze frame data by using scan tool. 3) start engine and turn o/d cut switch on. 4) shift select lever to d range and start vehicle. 5) ...
Page 440
Automatic transmission (4 a/t) 7b1-31 reference connect oscilloscope between c51-1-11 (+) and c51-1-10 (–) of pcm connector connected to pcm and check input speed sensor signal. 4 check visually input speed sensor and over- drive clutch drum for the followings. • no damage • no foreign material atta...
Page 441
7b1-32 automatic transmission (4 a/t) dtc p0720 (dtc no.75) output speed sensor circuit malfunction wiring diagram dtc detecting condition and trouble area dtc confirmation procedure 1) connect scan tool to dlc with ignition switch off, if available. 2) clear dtc, pending dtc and freeze frame data i...
Page 442
Automatic transmission (4 a/t) 7b1-33 troubleshooting reference connect oscilloscope between c51-1-23 (+) and c51-1-22 (–) of pcm connector connected to pcm and check output speed sen- sor signal. Step action yes no 1 was “a/t diagnostic flow table” in this section performed? Go to step 2. Go to “a/...
Page 443
7b1-34 automatic transmission (4 a/t) dtc p0743 (dtc no.65/66) - tcc (lock-up) solenoid electrical wiring diagram dtc detecting condition and trouble area 1. Pcm 2. Shift solenoid-a 3. Shift solenoid-b 4. Tcc solenoid dtc detecting condition trouble area voltage at terminal c51-1-8 of pcm is high wh...
Page 444
Automatic transmission (4 a/t) 7b1-35 dtc confirmation procedure 1) connect scan tool to dlc with ignition switch off, if available. 2) clear dtc, pending dtc and freeze frame data in pcm memory by using scan tool. 3) start engine, warm it up to normal operating temperature and shift transfer lever ...
Page 445
7b1-36 automatic transmission (4 a/t) dtc p0753 (dtc no.61/62) shift solenoid-a (#1) electrical dtc p0758 (dtc no.63/64) shift solenoid-b (#2) electrical wiring diagram dtc detecting condition and trouble area 1. Pcm 2. Shift solenoid-a 3. Shift solenoid-b 4. Tcc solenoid dtc detecting condition tro...
Page 446
Automatic transmission (4 a/t) 7b1-37 dtc confirmation procedure 1) connect scan tool to dlc with ignition switch off, if available. 2) clear dtc, pending dtc and freeze frame data in pcm memory by using scan tool. 3) start engine and shift transfer lever to “2h” or “4h” range. 4) shift selector lev...
Page 447
7b1-38 automatic transmission (4 a/t) stall test this test is to check overall performance of automatic transmission and engine by measuring stall speed at “d” and “r” ranges. Be sure to perform this test only when transmission fluid is at normal operating temperature and its level is between full a...
Page 448
Automatic transmission (4 a/t) 7b1-39 line pressure test purpose of this test is to check operating conditions of each part by measuring fluid pressure in fluid pressure line. Line pressure test requires following conditions. • automatic fluid is at normal operating temperature (70 to 80 ° c/158 – 1...
Page 449
7b1-40 automatic transmission (4 a/t) troubleshooting road test this test is to check if upshift and downshift take place at specified speed while actually driving vehicle on a level road. 1) warm up engine. 2) with engine running at idle, shift select lever “d”. 3) accelerate vehicle speed by depre...
Page 450
Automatic transmission (4 a/t) 7b1-41 manual road test this test check the gear being used in “l”, “2” or “d” range when driven with unoperated gear shift control system. Test drive vehi- cle on a level road. 1) disconnect shift solenoid coupler (1) valves on transmission. 2) with select lever in “p...
Page 451
7b1-42 automatic transmission (4 a/t) troubleshooting engine brake test 1) while driving vehicle in 3rd gear of “d” range, shift select lever down to “2” range and check if engine brake operates. 2) in the same way as in step 1, check engine brake for operation when select lever is shifted down to “...
Page 452: On-Vehicle Service
Automatic transmission (4 a/t) 7b1-43 on-vehicle service maintenance service fluid level level check at normal operating temperature 1) stop vehicle and place it level. 2) apply parking brake and place chocks against wheels. 3) with selector at p position, start engine. 4) warm up engine till fluid ...
Page 453
7b1-44 automatic transmission (4 a/t) level check at room temperature the fluid level check at room temperature (20 – 30 °c (68 – 86 °f)) performed after repair or fluid change before test driving is just preparation for level check of normal operating temperature. The checking procedure itself is t...
Page 454
Automatic transmission (4 a/t) 7b1-45 a/t throttle cable adjustment 1) pull inner cable (3) by force of 2 n (0.2 kg, 0.45 lb) or less to be no slack of inner cable with a/t throttle cable (1) curved as shown in the figure. 2) fix stopper (2) to inner cable (3) with clearance “c”. A/t throttle cable ...
Page 455
7b1-46 automatic transmission (4 a/t) manual selector assembly removal 1) disconnect negative (–) cable at battery. 2) remove console box. 3) disconnect connector for illumination lamp, shift lock sole- noid (if equipped) and overdrive off switch (if equipped). 4) remove selector assembly mounting b...
Page 456
Automatic transmission (4 a/t) 7b1-47 inspection • check select lever for smooth and clear-cut movement and position indicator for correct indication. For operation of select lever, refer to left figure..
Page 457
7b1-48 automatic transmission (4 a/t) select cable adjustment 1) loosen manual shift lever (select cable side) nut (1). 2) shift select lever to “n” range. 3) align center line (2) on manual valve shaft (3) to “n” refer- ence line (4) as shown. 4) tighten manual shift lever nut (selector cable side)...
Page 458: Unit Repair
Automatic transmission (4 a/t) 7b1-49 unit repair sub-assembly repair overdrive (case side) disassembly 1) measure clearance between retaining ring (1) and brake backing plate (2) with thickness gauge. If it is not within standard range, replace brake disc or brake plate. Clearance between retaining...
Page 459
7b1-50 automatic transmission (4 a/t) 4) blow air into fluid hole in o/d case (2) and remove brake pis- ton (1). 5) remove brake piston inner ring and brake piston outer ring from brake piston. 6) unsnap seal ring (1). 7) remove 2 seal rings (1). Forward clutch note: be careful not to open seal ring...
Page 460
Automatic transmission (4 a/t) 7b1-51 disassembly 1) after removing retaining ring (1), remove direct clutch input hub (2) and forward clutch hub (3). 2) remove bearing race and thrust bearing. 3) install direct clutch input hub (1) and retaining ring (2). 4) install forward clutch (2) to o/d case (...
Page 461
7b1-52 automatic transmission (4 a/t) 5) remove retaining ring (1) and then remove direct clutch input hub. 6) remove retaining ring and then remove all clutch discs. 7) using special tool and hydraulic press, compress forward clutch piston return spring and remove retaining return spring. Special t...
Page 462
Automatic transmission (4 a/t) 7b1-53 direct clutch disassembly 1) install direct clutch assembly (1) to center support (2) and with 4 – 8 kg/cm 2 air pressure applied to second fluid hole from the left, measure stroke of direct clutch piston as shown in figure. If it is not within standard range, u...
Page 463
7b1-54 automatic transmission (4 a/t) 6) install direct clutch cylinder to center support. Remove direct clutch piston by blowing air into the second hole from the left as shown in the figure. Also, remove direct clutch inner piston by blowing air into hole at the extreme right. And then remove o-ri...
Page 464
Automatic transmission (4 a/t) 7b1-55 lower valve body 1. Lower valve body 7. Tcc (lock-up) control valve plate 13. Primary regulator valve sleeve 2. Spring 8. Tcc (lock-up) control valve gasket 14. Primary regulator valve plunger 3. Pressure relief valve ball 9. Tcc (lock-up) control sleeve 15. Pri...
Page 465
7b1-56 automatic transmission (4 a/t) disassembly 1) remove bypass valve (1), bypass valve spring, check ball valve damping spring, valve body ball (2) and ball valve spring. 2) remove lower valve body plate (1) and lower valve body plate gasket. 3) remove tcc (lock-up) control valve plate (2) and t...
Page 466
Automatic transmission (4 a/t) 7b1-57 6) after removing shift solenoid valve (a & b) (1), remove sole- noid valve gasket, low coast modulator valve spring (2), inter coast modulator valve spring (3) and 2 intermediate coast modulator valves (4). 7) pressing tcc (lock-up) control sleeve with finger a...
Page 467
7b1-58 automatic transmission (4 a/t) assembly assemble each component by reversing disassembly procedure and noting the following points. • coil outer diameter and free length of each valve spring should be as listed below. Be sure to use each one of correct size. Coil outer diameter and free lengt...
Page 468
Automatic transmission (4 a/t) 7b1-59 • tighten tcc (lock-up) solenoid valve bolt to specified torque. Tightening torque tcc solenoid valve bolt : 5.5 n·m (0.55 kg-m, 4.0 lb-ft) • tighten pressure relief valve bolt to specified torque. Tightening torque pressure relief valve bolt : 5.5 n·m (0.55 kg-...
Page 469
7b1-60 automatic transmission (4 a/t) accumulator piston and spring specification : tightening torque specification used for piston outer diameter “a” spring free length “b” direct clutch accumulator (2) 31.80 – 31.85 mm (1.252 – 1.254 in.) upper spring 43.56 mm (1.715 in.) lower spring 30.00 mm (1....
Page 470: Special Tool
Automatic transmission (4 a/t) 7b1-61 special tool 09925-37811-001 09931-76030 09931-76011 oil pressure gauge 16/14 pin dlc cable for tech 1a mass storage cartridge for tech 1a tech 1a kit (suzuki scan tool) (see note “a”.) 09940-53111 bearing installer tech 2 kit (suzuki scan tool) (see note “b”.) ...
Page 471
7b1-62 automatic transmission (4 a/t).
Page 472: Section 7C1
Clutch 7c1-1 7c1 section 7c1 clutch note: the clutch of this model is the same as that of h25 engine in the construction and operation. Refer to the same section of the service manual mentioned in the foreword of this manual for ser- vice procedure..
Page 473
7c1-2 clutch.
Page 474: Section 7E
Differential (front) 7e-1 7e section 7e differential (front) contents general description ........................................7e-2 4wd control system.....................................7e-2 system circuit ............................................7e-2 diagnosis ..................................
Page 475: General Description
7e-2 differential (front) general description 4wd control system system circuit 1. 4wd switch 4. Release valve 7. Front differential 10. To ignition switch 2. Air pump assembly 5. Pressure switch 8. Air hose and pipe 11. Ecm or pcm 3. Pump motor 6. Transfer 9. 4wd indicator lamp.
Page 476: Diagnosis
Differential (front) 7e-3 diagnosis differential assembly diagnosis table 4wd control system diagnostic flow table before performing the trouble diagnosis, check that the transfer and front differential are in good condition and there is no air leakage from air hoses and the actuator. Refer to “4wd ...
Page 477
7e-4 differential (front) flow table step action yes no 1 turn on ignition switch (but engine at stop) and check malfunction indicator lamp. Does lamp light up? Go to step 2. A trouble has occurred at some place. Repair it referring to malfunction indi- cator lamp (“check engine” lamp) check in diag...
Page 478
Differential (front) 7e-5 4wd control system circuit inspection voltage check check for input or output voltage (voltage between each circuit and body ground) of ecm (pcm) with ecm (pcm) connector connected and ignition switch turned on. Ter- minal circuit wire color normal voltage condition e61-19 ...
Page 479
7e-6 differential (front) 4wd control system inspection 1) install special tool to air hose connecting between air pump assembly and differential (actuator) as shown in figure. Tighten adjusting screw (2) of special tool as far as it stops. Close air check side opening by using fuel hose (1) as blin...
Page 480: On-Vehicle Service
Differential (front) 7e-7 on-vehicle service differential mountings removal and installation 1) lift up vehicle and turn steering wheel all way to the right. 2) separate front mounting bracket r (2) from differential hous- ing (3) by removing bolts (1) from its lower part. 3) remove front mounting b...
Page 481
7e-8 differential (front) 6) position slit in each bush (2) as shown when press-fitting it. Bush instillation position (angle “a”) : 45 ° (slit alignment) 7) position each bush to bracket as shown in the figure bush installation position (length “a”) : 3.0 mm (0.12 in.) 8) tighten differential front...
Page 482
Differential (front) 7e-9 front differential assembly dismounting 1) lift up vehicle and drain oil. 2) disconnect air hose and breather hose from differential housing. 3) before removing propeller shaft, give match marks (1) on joint flange and propeller shaft as shown in the figure. 4) remove prope...
Page 483
7e-10 differential (front) 9) using 2 large screwdrivers (4) as levers, pull out right side drive shaft joint (1) from differential (2) and dismount housing assembly from vehicle. Remounting for remounting, reverse dismounting procedure and use the fol- lowing tightening torque. Tightening torque fr...
Page 484: Unit Repair
Differential (front) 7e-11 unit repair refer to the same section of “unit repair manual” mentioned in “foreword” of this manual. Tightening torque specification special tool fastening part tightening torque n•m kg-m lb-ft front mounting bolts 85 8.5 61.5 front mounting bracket bolts 50 5.0 36.5 fron...
Page 485
7e-12 differential (front).
Page 486: Section 7F
Differential (rear) 7f-1 7f section 7f differential (rear) contents general description ........................................ 7f-2 diagnosis ......................................................... 7f-2 diagnosis table ............................................ 7f-2 on-vehicle service............
Page 487: General Description
7f-2 differential (rear) general description the differential assembly using a hypoid bevel pinion and gear is installed to the rear axle. It is set in the conven- tional type axle housing. The differential assembly is decisive in that the drive power is concentrated there. Therefore, use of genuine...
Page 488: On-Vehicle Service
Differential (rear) 7f-3 on-vehicle service 1. Universal joint flange 9. Differential carrier assembly 17. Bearing adjuster 25. Bolt 2. Hypoid gear set 10. Differential pinion 18. Lock plate 26. Bolt 3. Bevel pinion spacer apply thread lock cement 99000-32110 referring to “differential case” in this...
Page 489
7f-4 differential (rear) precaution for maintenance service • when having driven through water, check immediately if water has entered (if so, oil is cloudy). Water mixed oil must be changed at once. • whenever vehicle is hoisted for any other service work than oil change, also be sure to check for ...
Page 490
Differential (rear) 7f-5 rear differential assembly dismounting 1) lift up vehicle and drain oil from rear differential housing. 2) remove rear brake drums and pull out right and left rear axle shafts. (refer to “rear axle shaft removal” of section 3e.) 3) before removing propeller shaft, give match...
Page 491: Unit Repair
7f-6 differential (rear) 3) install propeller shaft to joint flange aligning match marks and torque flange nuts to specification. Apply thread lock cement to thread part of bolt if reused. “a” : cement 99000-32110 tightening torque propeller shaft flange nuts (a) : 60 n·m (6.0 kg-m, 43.5 lb-ft) 4) i...
Page 492
Differential (rear) 7f-7 b) remove differential left case (2) from differential right case (1). C) remove pinion shafts, differential gears, washers, differen- tial pinions, spring washers, thrust washers. 4) using special tools, pull out differential side bearings (1). Special tool (c) : 09913-8523...
Page 493
7f-8 differential (rear) b) make mating marks (1) on drive bevel pinion and compan- ion flange. C) remove companion flange from drive bevel pinion. Use special tool if it is hard to remove. Special tool (f) : 09913-65135 d) remove drive bevel pinion with rear bearing, shim and spacer from carrier. I...
Page 494
Differential (rear) 7f-9 6) using a hammer and brass bar (1), drive out front bearing outer race with bearing (2) and oil seal (3). 7) drive out rear bearing outer race in the same way as in the step 6). Component inspection • check companion flange for wear or damage. • check bearings for wear or d...
Page 495
7f-10 differential (rear) differential carrier for press-fitting drive bevel pinion bearing outer races, use spe- cial tools as shown in the figure. Special tool (a) : 09924-74510 (b) : 09926-68310 (c) : 09913-75510 differential case 1) after applying differential oil to differential gear (4), pinio...
Page 496
Differential (rear) 7f-11 4) in the same manner as described in step 1), install thrust washer (2), spring washer (1) and differential gear (4). 5) install differential left case (1) and then tighten screws to specified torque. “a” : cement 99000-32110 tightening torque differential case screw (a) :...
Page 497
7f-12 differential (rear) 9) install special tool to differential case assembly and check that preload is within specification below. If preload exceeds specified value, check if foreign matter is caught or gear is damaged. Special tool (b) : 09928-06510 side gear preload : max. 2.5 n·m (0.25 kg-m, ...
Page 498
Differential (rear) 7f-13 drive bevel pinion to engage drive bevel pinion and gear correctly, it is pre-required to install drive bevel pinion to differential carrier properly by using adjusting shim as described on the followings. Shown below is relative positions of drive bevel pinion, differentia...
Page 499
7f-14 differential (rear) 1) install special tools with bearings and universal joint flange (2) to differential carrier (1). Special tool (e) : 09951-46010 (f) : 09926-78311-002 2) tighten flange nut (1) so that specified bearing preload is obtained. Special tool (c) : 09922-75222 (f) : 09926-78311-...
Page 500
Differential (rear) 7f-15 3) set dial gauge to mounting dummy and make 0 (zero) adjustment on surface plate. Special tool (a) : 09900-20606 (b): 09926-78320 4) place zero-adjusted mounting dummy and dial gauge set on pinion mounting dummy and take measurement between zero position and extended dial ...
Page 501
7f-16 differential (rear) 6) select adjusting shim(s) (2) closest to calculated value from among following available sizes and put it in place and then press-fit rear bearing (1). Calculated valve “f” : closest value to “e” (refer to step 5).) special tool (g) : 09925-18011 (h) : 09927-66010 availab...
Page 502
Differential (rear) 7f-17 9) while tightening flange nut gradually with special tool and power wrench (4 - 10 magnification) (1), set preload of pinion to specification. Pinion bearing preload : 0.9 – 1.7 n·m (9.0 – 17.0 kg-cm, 7.8 – 14.7 lb-in.) spring measure reading with special tool : 16 – 30 n ...
Page 503
7f-18 differential (rear) assembling unit 1) place bearing outer races on their respective bearings. Used left and right outer races are not interchangeable. 2) install case assembly in carrier. 3) install side bearing adjusters on their respective carrier, making sure adjuster are threaded properly...
Page 504
Differential (rear) 7f-19 7) measure preload of pinion bearing with spring balance (1) or torque wrench (2) and check composite preload of pinion bearing and side bearing. Composite preload of pinion bearing and side bearing : 1.1 – 2.0 n·m (11.0 – 20.0 kg-cm, 9.5 – 17.4 lb-in.) spring measure readi...
Page 505
7f-20 differential (rear) tooth contact pattern diagnosis and remedy normal high contact pinion is positioned too far from the center of drive bevel gear. 4) increase thickness of pinion height adjusting shim and position pinion closer to gear center. 5) adjust drive bevel gear backlash to specifica...
Page 506: Required Service Material
Differential (rear) 7f-21 10) upon completion of gear tooth contact check in step 9), caulk flange nut (2) with caulking tool (1) and hammer. Tightening torque specification required service material fastening part tightening torque n•m kg-m lb-ft differential oil level/filler plug 50 5.0 36.5 diffe...
Page 507: Special Tool
7f-22 differential (rear) special tool 09900-20606 09900-20701 09913-61510 09913-65135 dial gauge magnetic stand bearing puller bearing puller 09922-76570 09913-75510 09913-85230 09922-66021 attachment bearing installer bearing removing jig flange holder 09922-75222 09922-76560 09924-74510 09925-180...
Page 508
Differential (rear) 7f-23 09928-06510 09930-40113 09930-40120 09944-66020 differential torque checking tool rotor holder attachment bearing installer 09951-16060 09951-18210 09951-46010 lower arm bush remover oil seal remover & installer no. 2 drive shaft oil seal installer note: this tool is consti...
Page 509
7f-24 differential (rear).
Page 510: Section 8
Body electrical system 8-1 6f1 6f2 6g 6h 6k 7a 8 6k 7c1 7d 7e 7f 8a 8d 8e 9 10 10a 10b section 8 body electrical system wiring system (harnesses, connectors, fuses, relay, switches, grounds, system circuit diagram) .......... Section 8a lighting system ..................................................
Page 511: General Description
8-2 body electrical system general description wire color symbols there are two kinds of colored wire used in this vehicle. One is single-colored wire and the other is dual-colored (striped) wire. The single-colored wire uses only one color symbol (i.E. “grn”). The dual-colored wire uses two color s...
Page 512: Section 8C
Instrumentation/driver information 8c-1 8c section 8c instrumentation/driver information contents general description ........................................8c-2 combination meter ........................................8c-2 on-vehicle service ..........................................8c-4 fuel met...
Page 513: General Description
8c-2 instrumentation/driver information general description combination meter 1. Tachometer 8. Multifunction indicator light 15. Charge warning light 2. Speedometer 9. Turn signal pilot light (rh) 16. Brake fluid level, parking brake and ebd warning light 3. Fuel level meter 10. Air bag warning ligh...
Page 514
Instrumentation/driver information 8c-3 combination meter internal circuits combination meter couplers [a] : coupler a [b] : coupler b [c] : coupler c 1. To cruise control module (if equipped) gry/yel 1. To door switch (drive side) blk/blu 1. To ground blk 2. Blank – 2. To transmission range switch ...
Page 515: On-Vehicle Service
8c-4 instrumentation/driver information on-vehicle service fuel meter/fuel gauge unit fuel level sensor (sender gauge) inspection remove fuel pump assembly referring to section 6c. Use an ohmmeter to confirm that resistance of sender gauge unit changes with change of float position. If measured valu...
Page 516
Instrumentation/driver information 8c-5 engine coolant temperature (ect) meter and sensor engine coolant temperature sensor removal and installation refer to “ect sensor” in section 6e2. Oil pressure light oil pressure switch removal and installation refer to “oil pressure check” in section 6a2. Bra...
Page 517
8c-6 instrumentation/driver information.
Page 518: Section 8D
Windows, mirrors, security and locks 8d-1 8d section 8d windows, mirrors, security and locks contents general description ....................................... 8d-2 rear wiper and washer (if equipped) ......... 8d-2 on-vehicle service......................................... 8d-3 windshield wipers...
Page 519: General Description
8d-2 windows, mirrors, security and locks general description rear wiper and washer (if equipped).
Page 520: On-Vehicle Service
Windows, mirrors, security and locks 8d-3 on-vehicle service windshield wipers front wiper and washer wiper motor • as shown in the figure, use a 12 v battery to connect its (+) terminal to terminal “a”, and its (–) terminal to “black” lead wire (2). If motor (1) rotates at a low revolution speed of...
Page 521
8d-4 windows, mirrors, security and locks rear window wiper and washer (for vehicle with cruise control system) inspection rear wiper and washer switch 1) disconnect negative (–) cable at battery. 2) disconnect combination switch lead wire coupler. 3) use a circuit tester to check the continuity at ...
Page 522: Section 8E
Cruise control system 8e-1 6f1 6f2 6g 6h 6k 7a 7a1 7b1 7c1 7d 7e 8e 8a 8b 8c 8d 8b 9 10 10a 10b section 8e cruise control system contents general description ....................................... 8e-2 cautions in servicing ................................... 8e-2 symbols and marks....................
Page 523: General Description
8e-2 cruise control system general description cautions in servicing refer to section 8. Symbols and marks refer to section 8a. Abbreviations refer to section 8a. Wiring color symbols refer to section 8. Joint connector refer to section 8. Fuse box and relay refer to section 8a. Power supply diagram...
Page 524
Cruise control system 8e-3 cruise control system the cruise control system is a device which maintains a preset vehicle speed while driving at a high speed, e.G., on a highway. It allows the driver to drive his vehicle at a constant speed of 40 km/h (25 mile/h) or higher without depressing the accel...
Page 525
8e-4 cruise control system components and functions component function cruise control actuator assembly with control mod- ule cruise control module: executes centralized control by means of a microcomputer over all functions including setting a constant speed, resuming it, setting coast, limiting mi...
Page 526: Diagnosis
Cruise control system 8e-5 cancel conditions constant cruising is cancelled under the following conditions. • ignition switch is turned off. • cruise main switch is turned off. • vehicle speed has slowed down to lower than minimum operating speed (40 km/h (25 mile/h)). • *vehicle speed varies beyond...
Page 527
8e-6 cruise control system vehicle speed can not be set. Actuator cable play maladjusted or actua- tor cable faulty refer to “cruise cable play inspection and adjustment” in this section. Main switch, “coast/set”, “resume/ accel” and “cancel” switch circuits faulty refer to “cruise main switch, coat...
Page 528
Cruise control system 8e-7 note on system circuit inspection refer to “precaution for electrical circuit service” in section 0a. “resume/accel” switch fails to resume preset vehicle speed after cruise control is cancelled. Main switch, “coast/set”, “resume/ accel” and “cancel” switch circuits faulty...
Page 529
8e-8 cruise control system cruise main switch indicator lamp circuit check fig. For step 2 step action yes no 1 check circuit for short. 3) disconnect connector from cruise control module with ignition switch off. 4) turn ignition switch on. Does cruise main switch indicator lamp turn on? “lt grn/wh...
Page 530
Cruise control system 8e-9 “cruise” indicator lamp circuit check fig. For step 2 step action yes no 1 check circuit for short. 1) disconnect connector from cruise control module with ignition switch off. 2) turn ignition switch on. Does “cruise” indicator lamp turn on? “grn/yel” circuit is shorted t...
Page 531
8e-10 cruise control system cruise main switch, coast/set, resume/accel and cancel switches circuits check fig. For step 1 step action yes no 1 switch circuit check 1) disconnect connector from cruise control module with ignition switch off. 2) check for proper connection to cruise control module at...
Page 532
Cruise control system 8e-11 vss circuit check fig. For step 1 step action yes no 1 vehicle speed sensor circuit check 1) disconnect connector from cruise control module with ignition switch off. 2) check for proper connection to cruise control module at terminal e132-1. 3) if ok, check for continuit...
Page 533
8e-12 cruise control system stop lamp switch (with pedal position switch) circuits check fig. For step 1 step action yes no 1 stop lamp switch (with pedal position switch) circuits check 1) disconnect connector from cruise control module with ignition switch off. 2) check for proper connection to cr...
Page 534
Cruise control system 8e-13 transmission range switch circuit check fig. For step 1 step action yes no 1 transmission range switch circuit check 1) disconnect connector from cruise control module with ignition switch off. 2) check for proper connection to cruise control module at terminal e132-9. 3)...
Page 535
8e-14 cruise control system clutch pedal position switch circuit check fig. For step 1 step action yes no 1 clutch pedal position switch circuit check 1) disconnect connector from cruise control module with ignition switch off. 2) check for proper connection to cruise control module at terminal e132...
Page 536
Cruise control system 8e-15 throttle valve opening signal circuit check fig. For step 2 step action yes no 1 powertrain control module (pcm) diagnostic trouble code check 1) check pcm for dtc. Is there a dtc related to throttle position sensor? Check and repair tp sensor refer- ring to section 6-1. ...
Page 537
8e-16 cruise control system overdrive and tcc off command signal circuit check fig. For step 1 cruise control module power and ground circuits check fig. For step 1 step action yes no 1 overdrive off command signal circuit check 1) disconnect connector from cruise control module with ignition switch...
Page 538
Cruise control system 8e-17 cruise control module and its circuit inspection voltage check check for input or output voltage of control module (voltage between each circuit and body ground) with cruise control module connector connected. Caution: cruise control module can not be checked by itself. I...
Page 539
8e-18 cruise control system resistance check 4) disconnect cruise control module connector from cruise con- trol module with ignition switch off. 5) check resistance between each pair of terminals of discon- nected connectors as shown in the following table. Caution: never touch terminals of cruise ...
Page 540: On-Vehicle Service
Cruise control system 8e-19 cruise cable play inspection and adjustment inspection and adjustment 1) remove actuator cap. 2) with actuator lever (1) returned at original position (2) (where lever does not move clockwise any further), check cruise cable for play. If it is out of specification, adjust...
Page 541
8e-20 cruise control system coast/set, resume/accel and cancel switches these switches are built in the combination switch assembly. Removal and installation refer to “combination switch” in section 3c1. Inspection 1) disable air bag system referring to “disabling air bag system” in section 10b. 2) ...
Page 542
Cruise control system 8e-21 clutch pedal position (cpp) switch removal 1) disconnect cpp switch connector with ignition switch off. 2) remove cpp switch from pedal bracket. Inspection check for resistance between terminals under each condition below. If check result is not satisfactory, replace. Cpp...
Page 543
8e-22 cruise control system stop lamp switch (with pedal position switch) inspection 1) disconnect negative (–) cable at battery. 2) disconnect stop lamp switch connector and remove stop lamp switch from pedal bracket. 3) check switch (2 contacts) for resistance under each of the following each cond...
Page 544
Cruise control system 8e-23 cruise control actuator assembly (with con- trol module) removal 1) disconnect negative (–) cable at battery. 2) disconnect connector from actuator assembly (2) (with con- trol module). 3) remove actuator cap (1) from actuator assembly (2). 4) disconnect cruise cable (3) ...
Page 545
8e-24 cruise control system cruise cable removal 1) disconnect cruise cable from cruise control arm and accelerator bracket. 2) remove actuator cap and disconnect cruise cable from actuator. 3) release cable from all clamps. 4) remove cable from vehicle. Installation install cruise cable by reversin...
Page 546: Section 9
Body service 9-1 9 section 9 body service contents glass, windows and mirror.............................. 9-2 quarter window .............................................. 9-2 body structure .................................................. 9-3 under body dimensions ..................................
Page 547: Glass, Windows and Mirror
9-2 body service glass, windows and mirror quarter window removal and installation refer to “windshield” in this section as removal and installa- tion procedures are basically the same. However, note the follow- ings. • before applying primer to glass edge, install molding accord- ing to installing ...
Page 548: Body Structure
Body service 9-3 body structure under body dimensions hole to hole distance : a. Front bumper side installation hole i. 3rd mounting installation hole b. 1st mounting installation hole j. Lower rod installation hole c. Suspension frame front installation hole k. Upper rod installation inside hole d....
Page 549
9-4 body service body dimensions hole to hole distance : a. Front bumper installation clip hole g. Center member installation hole b (b’). Front bumper installation hole h (h’). Fender installation reference hole c (c’). Headlight installation hole i (i’). Fender installation hole d (d’). Headlight ...
Page 550
Body service 9-5 hole to hole distance : a. Garnish installation clip hole i (i’). Hole in rear door lower hinge in lower part b (b’). Front end of front windshield lower installation section j (j’). Rear scuff installation hole (at front end) c (c’). Front end of front windshield upper installation...
Page 551
9-6 body service hole to hole distance: a. Hole in front door upper hinge at rear g. Hole in rear door lower hinge in lower part b. Hole in front door lower hinge at rear h. Assistant grip front installation hole c. Trim installation clip hole i. Trim installation hole d. φ7 jig hole j. Door striker...
Page 552
Body service 9-7 hole to hole distance : a. Clip hole in the center of head lining rear installation section e. Installation hole in uppermost part of lower hinge b (b’). Innermost end of roof panel installation section f (f’). Innermost end of rear floor tail member installation section c. Installa...
Page 553: Seat
9-8 body service seat second seat removal 1) remove adjuster extension cover. 2) remove adjuster extension bracket. 3) remove front and rear adjuster inside covers. 4) remove adjuster outside covers. 5) remove second seat mounting bolts. 6) disassemble and repair seat as necessary. Installation reve...
Page 554
Body service 9-9 third seat (if equipped) removal 1) raise the front portion of seat cushion to remove rear seat cushion. 2) remove 6 mounting bolts to remove seat back. 3) disassemble and repair seat if necessary. Installation reverse removal procedure to install rear seat noting the following inst...
Page 555: Paint And Coatings
9-10 body service paint and coatings sealant application area 1. Side body inner panel 6. Center floor panel 11. Main floor extension panel 2. Rear wheel housing outer rear panel 7. Front floor panel 12. Rear floor cap 3. Rear wheel housing panel 8. Center floor member “a” : apply sealant 4. Rear fl...
Page 556
Body service 9-11 1. Cowl top panel “a” : apply sealant 2. Dash panel “b” : brush treatment 3. Cowl front panel 4. Front floor panel 5. Front pillar inner lower panel e e d d “a” (“b”) “a” “a” “a” (“b”) “a” view:z d – d e – e 3 1 2 4 5 2.
Page 557
9-12 body service 1. Rear quarter inner panel 5. Roof panel 9. Air outlet panel 2. Side body outer panel 6. Front pillar upper reinforcement “a” : apply sealant 3. Back pillar outer panel 7. Rear wheel housing panel “b” : brush treatment 4. Front pillar inner panel 8. Fuel inlet box n “a” (“b”) “a” ...
Page 558
Body service 9-13 1. Side body outer panel 3. Center floor gusset “a” : apply sealant 2. Rear wheel housing outer panel 4. Center floor panel “b” : brush treatment “a” “a” “a” “a” 1 1 2 3 “a” “a” qq qq “a” (“b”) “a” (“b”) “a” (“b”) “a” (“b”) “a” (“b”) “a” (“b”) m m 4 view:u view:x view:v (lh) m – m ...
Page 559
9-14 body service “a” : apply sealant “b” : sealant width (more than 5 mm (0.20 in.) between “a” and “b”) “c” : wipe off sealant in this section “d” : be free from protrude of sealant outside from this line “e” : smooth out sealant with a brush “a” “c” view:dd view:ff view:bb view:cc view:ee gg – gg...
Page 560
Body service 9-15 “a” : apply sealant “c” : wipe off sealant in this section “b” : smooth out sealant with a brush “d” : sealant width (more than 5 mm (0.20 in.) between “a” and “b”) “c” “b” “a” “b” “b” “a” “a” “a” “a” “a” “a” “a” “b” “a” “c” “d” “d” jj kk ll “a” “a” “a” pp pp mm nn nn mm hh hh “b” ...
Page 561
9-16 body service “a” : apply sealant “b” : smooth out sealant with a brush “c” : sealant width c more than 5 mm (0.20 in.) kk kk “a” “a” “b” “b” ll ll “c” ll – ll kk – kk.
Page 562
Body service 9-17 undercoating/anti-corrosion compound application area “a” : 200 mm (7.87 in.) 1. Side body outer “b” : 100 mm (3.94 in.) 2. Side sill inner “a” : apply rust proof wax (hot wax 50 µm or more) 3. Frame “b” : apply rust proof wax (high viscosity wax 50 µm or more) 4. Main floor 5. Sid...
Page 563
9-18 body service “a” : 30 mm (1.18 in.) 1. Main floor 6. Extension floor “b” : 100 mm (3.94 in.) 2. Front fender 7. Center floor “a” : apply undercoating (pvc, 400 µm or more) 3. Front wheel housing 8. Rear floor “b” : add undercoating (pcv) to cover edges and mating parts 4. Frame 9. Side sill inn...
Page 564: Exterior And Interior Trim
Body service 9-19 exterior and interior trim floor carpet front floor carpet removal 1) remove front and second seats. 2) remove third seat cushion (if equipped). 3) remove front and second seat belt lower anchor bolts. 4) remove dash side trims (1), front side sill scuffs (2), center pillar inner l...
Page 565
9-20 body service rear floor carpet (without third seat vehicle) removal 1) remove rear luggage mat end garnish (1), rear side sill scuff and rear quarter lower trims (2). 2) remove luggage hook plate nut (3). 3) remove rear floor carpet. Installation reverse removal procedure for installation, noti...
Page 566
Body service 9-21 installation reverse removal procedure to install head lining noting the follow- ing instructions. • set roof harness (1) and rear washer hose (2) to head lining (3) with adhesive tape as shown. • for without sunroof model apply double coated tape (4) to head lining as shown. • tig...
Page 567
9-22 body service.
Page 568: Section 10
Restraint system 10-1 10 section 10 restraint system seat belt......................................................................................................................................... Section 10a air bag system.............................................................................
Page 569: General Description
10-2 restraint system general description seat belt with elr the seat belt with emergency locking retractor (elr) is designed so that it locks immediately (to prevent the webbing from being pulled out of the retractor any further) when any of the following items is detected as exceeding each set val...
Page 570: Section 10A
Seat belt 10a-1 10a section 10a seat belt contents on-vehicle service....................................... 10a-2 service precautions ................................... 10a-2 service and diagnosis ............................ 10a-2 disabling air bag system ........................ 10a-2 enabling a...
Page 571: On-Vehicle Service
10a-2 seat belt on-vehicle service service precautions service and diagnosis before servicing or replacing seat belts, refer to following precautionary items. • seat belts should be normal relative to strap retractor and buckle portions. • keep sharp edges and damaging objects away from belts. Avoid...
Page 572
Seat belt 10a-3 front seat belt inspection on vehicle seat belts with alr as to seat belts with alr (other than driver side seat belt), check them as follows in addition to above check. • with vehicle at stop, pull seat belt all the way out, let it retract a little and try to pull it. It should not ...
Page 573
10a-4 seat belt removal 1) disconnect negative cable at battery. 2) disable air bag system referring to “disabling air bag system” of “service precautions” under “on-vehicle service” in section 10b, if necessary. 3) remove front pillar lower trim. 4) disconnect yellow connector for seat belt pretens...
Page 574
Seat belt 10a-5 seat belt switch check driver side seat belt strap switch for continuity by using ohmmeter. Seat belt strap switch specification without inserted buckle tongue to buckle catch: terminal “a” and “b” : continuity with inserted buckle tongue to buckle catch: terminal “a” and “b” : no co...
Page 575
10a-6 seat belt second rear seat belt removal refer to the figure above to remove rear seat belts. Inspection check second rear seat belt in the same way as when inspecting front seat belt except pretesioner inspection. (refer to “front seat belt” in this section.) installation install in reverse or...
Page 576
Seat belt 10a-7 third rear seat belt (if equipped) removal refer to the figure above to remove rear seat belts. Inspection check third rear seat belt in the same way as when inspecting second rear seat belt. (refer to “second rear seat belt” in this section.) installation install in reverse order of...
Page 577
10a-8 seat belt tightening torque specification fastening part tightening torque n•m kg-m lb-ft upper and lower anchor bolt 35 3.5 25.5 retractor assembly bolt 35 3.5 25.5 retractor assembly screw 5.5 0.55 4.0 buckle bolt 35 3.5 25.5.
Page 578: Section 10B
Air bag system 10b-1 10b section 10b air bag system contents general description ......................................10b-3 system components and wiring location view and connectors ..................................10b-4 system wiring diagram...............................10b-5 diagnosis ............
Page 579
10b-2 air bag system dtc b1031 – power source voltage high........................................................... 10b-33 dtc b1032 – power source voltage low ........................................................... 10b-33 dtc b1035 – rh forward sensor circuit open or short to ground ............
Page 580: General Description
Air bag system 10b-3 general description with the air bag system which includes air bags for both the driver’s and passenger’s sides as well as the seat belt pretension- ers (if equipped), the sag of the seat belt is taken up (for seat belt with pretensioner), the driver air bag (inflator) module is...
Page 581
10b-4 air bag system system components and wiring location view and connectors 1. Air bag harness 7. Passenger air bag (inflator) module 13. Grommet 2. “air bag” fuse box 8. Sdm 14. Instrument panel harness 3. “air bag” monitor coupler 9. Seat belt pretensioner (retractor assembly) (if equipped) 15....
Page 582
Air bag system 10b-5 system wiring diagram terminal arrangement of sdm (viewed from harness side) connector “q01” (sdm connector) 1 2 3 5 4 blk/blu blu/blk blu/red blk/wht blu blu grn/red grn grn wht wht grn yel/red yel pnk wht brn lt grn 6 12v 5v 5v ppl/red orn/grn orn/blu yel/grn yel/blu orn/grn o...
Page 583: Diagnosis
10b-6 air bag system diagnosis diagnostic trouble code (dtc) the air bag diagnostic system check must always be the starting point of any air bag system diagno- sis. The air bag diagnostic system check checks for proper “air bag” warning lamp operation and checks for air bag diagnostic trouble codes...
Page 584
Air bag system 10b-7 special tool (b) : 09932-75010 (air bag driver/passenger load tool) this tool is used only when called for in this section. It is used as a diagnostic aid and safety device to prevent inadvertent air bag (inflator) module deployment. The load tool has three connectors attached t...
Page 585
10b-8 air bag system intermittents and poor connections most intermittents are caused by faulty electrical connections or wiring. When a check for proper connection is requested in a diagnostic flow table, perform careful check of suspect circuits for: • poor mating of connector halves, or terminals...
Page 586
Air bag system 10b-9 air bag diagnostic system check the diagnostic procedures used in this section are designed to find and repair air bag system malfunctions. To get the best results, it is important to use the diagnostic flow tables and follow the sequence listed below. 1) perform the air bag dia...
Page 587
10b-10 air bag system air bag diagnostic system check flow table step action yes no 1 1) make sure that battery voltage is about 11v or higher. 2) note “air bag” warning lamp as ignition switch is tuned on. Does “air bag” warning lamp come on when ignition switch is tuned on? Go to step 2. Proceed t...
Page 588
Air bag system 10b-11 dtc check using suzuki scan tool 1) turn ignition switch to off position. 2) after setting cartridge to suzuki scan tool, connect it to data link connector (dlc) located on underside of instru- ment panel at driver’s seat side. Special tool (a) : suzuki scan tool 3) turn igniti...
Page 589
10b-12 air bag system example : when driver air bag initiator circuit resistance high (dtc b1021) is set dtc clearance using suzuki scan tool 1) turn ignition switch to off position. 2) connect suzuki scan tool to data link connector (dlc) (1) in the same manner as when making this connection for dt...
Page 590
Air bag system 10b-13 not using suzuki scan tool 1) turn ignition switch to on position and wait about 6 seconds or more. 2) using service wire, repeat shorting and opening between diagnosis switch terminal on “air bag” monitor coupler and body ground 5 times at about 1 second intervals. 3) perform ...
Page 591
10b-14 air bag system dtc table dtc “air bag” warning lamp flashing pattern diagnosis no. Mode – 12 normal – b1015 15 passenger air bag circuit resistance high diagnose trou- ble according to diagnostic flow table corre- sponding to each code no. B1016 16 resistance low b1018 18 short to ground b101...
Page 592
Air bag system 10b-15 dtc “air bag” warning lamp flashing pattern diagnosis no. Mode b1041 41 driver preten- sioner circuit resistance high diagnose trou- ble according to diagnostic flow table corre- sponding to each code no. B1042 42 resistance low b1043 43 short to ground b1044 44 short to power ...
Page 593
10b-16 air bag system table a - “air bag” warning lamp comes on steady table b - “air bag” warning lamp does not come on table c - “air bag” warning lamp flashes table d - “air bag” warning lamp cannot indicate flashing pattern of dtc wiring diagram 1. From main fuse 5. “air bag” fuse 9. To ecm, tcm...
Page 594
Air bag system 10b-17 table test description table a : step 1 : check “air bag” fuse. Step 2 : check power source circuit. Step 3 : check “air bag” warning lamp circuit. Table b : step 1 : check combination meter power feed circuit. Step 2 : check electrical connection check mechanism in sdm connect...
Page 595
10b-18 air bag system table b : note: upon completion of inspection and repair work, perform following items. • reconnect all air bag system components, ensure all components are properly mounted. • repeat air bag diagnostic system check to confirm that the trouble has been corrected. Step action ye...
Page 596
Air bag system 10b-19 [a] fig. For step 2/[b] fig. For step 3 and 5/[c] fig. For step 4 special tool (a) : 09932-75020 table c : fig. For step 2 special tool (a) : 09932-75020 1. 16-pin connector (for combination meter) 2. “blu” wire terminal note: upon completion of inspection and repair work, perf...
Page 597
10b-20 air bag system table d : fig. For step 2 special tool (a) : 09932-75020 step action yes no 1 1) inspect connection between diagnostic switch terminal on “air bag” monitor cou- pler and body ground by service wire. Is it securely connected between them by ser- vice wire? Go to step 2. Properly...
Page 598
Air bag system 10b-21 table e - sdm cannot communicate through the serial data circuit wiring diagram table test description step 1 : an improper connection to the data link connector (dlc) will prevent communications from being established. Step 2 : this test checks whether it is possible to commun...
Page 599
10b-22 air bag system diagnostic flow table fig. For step 3 special tool (a) : 09932-75020 step action yes no 1 1) make sure that suzuki scan tool is free from malfunc- tion and correct cartridge for air bag system is used. 2) ignition switch off. 3) check proper connection of suzuki scan tool to dl...
Page 600
Air bag system 10b-23 dtc b1015 - passenger air bag initiator circuit resistance high dtc b1016 - passenger air bag initiator circuit resistance low dtc b1018 - passenger air bag initiator circuit short to ground dtc b1019 - passenger air bag initiator circuit short to power circuit wiring diagram d...
Page 601
10b-24 air bag system diagnostic flow table dtc b1015 : [a] fig. For step 1 and 2/[b] fig. For step 2 special tool (a) : 09932-75020 (b) : 09932-75010 step action yes no 1 1) with ignition switch off, disconnect passenger air bag (inflator) module connector behind the glove box. 2) check proper conn...
Page 602
Air bag system 10b-25 dtc b1016: [a] fig. For step 1 and 2/[b] fig. For step 2 special tool (a) : 09932-75020 (b) : 09932-75010 step action yes no 1 1) with ignition switch off, disconnect passenger air bag (inflator) module connector behind the glove box. 2) check proper connection to passenger air...
Page 603
10b-26 air bag system dtc b1018: [a] fig. For step 1, 2 and 3/[b] fig. For step 2/[c] fig. For step 3 special tool (a) : 09932-75020 (b) : 09932-75010 step action yes no 1 1) with ignition switch off, disconnect passenger air bag (inflator) module connector behind the glove box. 2) check proper conn...
Page 604
Air bag system 10b-27 dtc b1019: [a] fig. For step 1, 2 and 3/[b] fig. For step 2/[c] fig. For step 3 special tool (a) : 09932-75020 (b) : 09932-75010 step action yes no 1 1) with ignition switch off, disconnect passenger air bag (inflator) module connector behind the glove box. 2) check proper conn...
Page 605
10b-28 air bag system dtc b1021 – driver air bag initiator circuit resistance high dtc b1022 – driver air bag initiator circuit resistance low dtc b1024 – driver air bag initiator circuit short to ground dtc b1025 – driver air bag initiator circuit short to power circuit wiring diagram dtc will set ...
Page 606
Air bag system 10b-29 diagnostic flow table dtc b1021 : [a] fig. For step 1 and 2/[b] fig. For step 2/[c] fig. For step 3 special tool (a) : 09932-75020 (b) : 09932-75010 step action yes no 1 1) with ignition switch off, disconnect contact coil con- nector located near the base of the steering colum...
Page 607
10b-30 air bag system dtc b1022 : [a] fig. For step 1 and 2/[b] fig. For step 2/[c] fig. For step 3 special tool (a) : 09932-75020 (b) : 09932-75010 step action yes no 1 1) with ignition switch off, disconnect contact coil con- nector located near the base of the steering column. 2) check proper con...
Page 608
Air bag system 10b-31 dtc b1024 : [a] fig. For step 1 and 2/[b] fig. For step 2/[c] fig. For step 3 special tool (a) : 09932-75020 (b) : 09932-75010 step action yes no 1 1) with ignition switch off, disconnect contact coil connector located near the base of the steering col- umn. 2) check proper con...
Page 609
10b-32 air bag system dtc b1025 : [a] fig. For step 1 and 2/[b] fig. For step 2/[c] fig. For step 3 special tool (a) : 09932-75020 (b) : 09932-75010 step action yes no 1 1) with ignition switch off, disconnect contact coil con- nector located near the base of the steering column. 2) check proper con...
Page 610
Air bag system 10b-33 dtc b1031 – power source voltage high dtc b1032 – power source voltage low wiring diagram dtc will set when dtc b1031 : the power source voltage to sdm is above specified value for specified time. Dtc b1032 : the power source voltage is below an approx. 8 v for specified time. ...
Page 611
10b-34 air bag system diagnostic flow table dtc b1031 : fig. For step 1 special tool (a) : 09932-75020 dtc b1032 : step action yes no 1 1) with ignition switch off, disconnect sdm connector. 2) check proper connection to sdm at “q01-4” terminal. 3) if ok then ignition switch on, and then check volta...
Page 612
Air bag system 10b-35 fig. For step 2 special tool (a) : 09932-75020 3 1) with ignition switch off, reconnect sdm connector. With ignition switch on, is dtc b1032 current? Substitute a known-good sdm and recheck. Check charging system and repair as necessary. (refer to diagnosis in section 6h) step ...
Page 613
10b-36 air bag system dtc b1035 – rh forward sensor circuit open or short to ground dtc b1036 – rh forward sensor circuit short between two wires or short to power circuit dtc b1037 – lh forward sensor circuit open or short to ground dtc b1038 – lh forward sensor circuit short between two wires or s...
Page 614
Air bag system 10b-37 dtc b1036 and b1038 : step 1 : check whether malfunction is in forward sensor. Step 2 : check if forward sensor circuit is shorted between two wires. Step 3 : check if forward sensor circuit is shorted to power circuit. Diagnostic flow table dtc b1035 and b1037 : step action ye...
Page 615
10b-38 air bag system [a] fig. For step 1/[b] fig. For step 2/[c] fig. For step 3 special tool (a) : 09932-75020 dtc b1036 and b1038 : note: upon completion of inspection and repair work, perform following items. • reconnect all air bag system components, ensure all components are properly mounted. ...
Page 616
Air bag system 10b-39 [a] fig. For step 1/[b] fig. For step 2/[c] fig. For step 3 special tool (a) : 09932-75020 3 1) measure voltage from “q01-13” terminal to body ground and “q01-14” terminal to body ground, or from “q01-18” terminal to body ground and “q01-19” terminal to body ground. With igniti...
Page 617
10b-40 air bag system dtc b1041 – driver pretensioner initiator circuit resistance high dtc b1042 – driver pretensioner initiator circuit resistance low dtc b1043 – driver pretensioner initiator circuit short to ground dtc b1044 – driver pretensioner initiator circuit short to power circuit dtc b104...
Page 618
Air bag system 10b-41 dtc will set when dtc b1041 and b1045 : the resistance of driver or passenger seat belt pretensioner initiator circuit is above a specified value for speci- fied time. Dtc b1042 and b1046 : the resistance of driver or passenger seat belt pretensioner initiator circuit is below ...
Page 619
10b-42 air bag system fig. For step 1 and 2 fig. For step 2 special tool (a) : 09932-75020 (b) : 09932-75010 dtc b1042 and b1046 : 1. Pretensioner harness [a] : for dtc b1041 [b] : for dtc b1045 note: upon completion of inspection and repair work, perform following items. • reconnect all air bag sys...
Page 620
Air bag system 10b-43 fig. For step 1 and 2 fig. For step 2 special tool (a) : 09932-75020 (b) : 09932-75010 2 1) with ignition switch off, disconnect sdm. 2) check proper connection to sdm at termi- nals “q01-11” and “q01-12” or “q01-6” and “q01-5”. 3) if ok then measure resistance between “q01-11”...
Page 621
10b-44 air bag system dtc b1043 and b1047 : fig. For step 1 and 2 fig. For step 2 special tool (a) : 09932-75020 (b) : 09932-75010 step action yes no 1 1) with ignition switch off, remove center pil- lar inner garnish of applicable side then dis- connect seat belt pretensioner connector. 2) check pr...
Page 622
Air bag system 10b-45 dtc b1044 and b1048 : fig. For step 1 and 2 note: upon completion of inspection and repair work, perform following items. • reconnect all air bag system components, ensure all components are properly mounted. • clear diagnostic trouble codes (refer to dtc clearance), if any. • ...
Page 623
10b-46 air bag system fig. For step 2 special tool (a) : 09932-75020 (b) : 09932-75010 dtc b1051 – frontal crash detected (system activation command output- ted) dtc will set when the sdm detects a frontal crash of sufficient force to warrant activation of the air bag system. (sdm outputs a deployme...
Page 624
Air bag system 10b-47 dtc b1061 – “air bag” warning lamp circuit failure wiring diagram dtc will set when: the voltage at the “air bag” warning lamp circuit terminal “q01-2” does not match the commanded state of the warning lamp driver for specified time. 2 1) inspect front of vehicle and undercar- ...
Page 625
10b-48 air bag system table test description step 1 : this test rechecks “air bag” warning lamp operation. Step 2 : this test rechecks whether an abnormality is in sdm. Dtc b1061 : dtc b1071 – internal sdm fault dtc will set when an internal sdm fault is detected by sdm. Dtc b1013 – system specifica...
Page 626: On-Vehicle Service
Air bag system 10b-49 on-vehicle service service precautions service and diagnosis warning/caution labels are attached on each part of air bag system components (sdm, air bag (inflator) modules and seat belt pretensioners). Be sure to follow the instructions. • many of service procedures require dis...
Page 627
10b-50 air bag system disabling air bag system 1) turn steering wheel so that vehicle's wheels (front tires) and pointing straight ahead. 2) turn ignition switch to “lock” position and remove key. 3) remove “air bag” fuse from “air bag” fuse box (1). 4) disconnect yellow connector (2) of contact coi...
Page 628
Air bag system 10b-51 3) connect yellow connector (1) of passenger air bag (inflator) module, and be sure to lock connector with lock lever. A) connect connector. B) lock connector with lock lever. 4) install glove box. 5) install “air bag” fuse to “air bag” fuse box. 6) turn ignition switch to on a...
Page 629
10b-52 air bag system live (undeployed) air bag (inflator) modules special care is necessary when handling and storing a live (unde- ployed) air bag (inflator) modules. The rapid gas generation produced during deployment of the air bag could cause the air bag (inflator) module, or an object in front...
Page 630
Air bag system 10b-53 live (inactivated) seat belt pretensioner special care is necessary when handling and storing a live (inac- tivated) seat belt pretensioners. Also, when the seat belt pretensioners activate, gas is generated and the seat belt (1) is retracted into the retractor assembly (2) qui...
Page 631
10b-54 air bag system deployed air bag (inflator) module and acti- vated seat belt pretensioner refer to the procedure described under “deployed air bag (inflator) module and activated seat belt preten- sioner disposal” in this section for disposal. Warning: • for handling and storage of a live seat...
Page 632
Air bag system 10b-55 air bag wire harness and connector air bag wire harness (1) can be identified easily as it is covered with a yellow protection tube. Be very careful when handling it. • when an open in air bag wire harness (1), damaged wire harness, connector or terminal is found, replace wire ...
Page 633
10b-56 air bag system repairs and inspections required after an accident accident with deployment/activation - component replacement certain air bag system components must be replaced. Those components are: • driver and passenger air bag (inflator) modules – replace with new one. • driver and passen...
Page 634
Air bag system 10b-57 accident with or without deployment/activation - component inspections certain air bag and restraint system components must be inspected after any crash, whether the air bag system activated or not. Those components are: • steering column and shaft joints – check for length, da...
Page 635
10b-58 air bag system • instrument panel member, reinforcement and knee bolster & panel (1) (passenger) – check for any distortion, bending, cracking or other dam- age. • if any faulty condition is found in above checks, replace. • passenger air bag (inflator) module – check for dents, cracks, damag...
Page 636
Air bag system 10b-59 • forward sensor – check sensor (1), sensor bracket (2), and front panel (3) for damage bend or rust. – check that connector (4) or lead wire (5) of forward sensor has a scorching, melting or damage. If any faulty condition is found in above checks, replace. • seat belt pretens...
Page 637
10b-60 air bag system sdm removal 1) disconnect negative (–) cable at battery. 2) disable air bag system. Refer to “disabling air bag system” in this section. 3) remove rear and front center console box (1) by removing screw and clips. 4) remove center garnish panel (2). 5) remove ashtray (3) and tu...
Page 638
Air bag system 10b-61 inspection • check sdm and sdm plate for dents, cracks or deformation. • check sdm connector for damage, cracks or lock mecha- nism. • check sdm terminal for bent, corrosion or rust. If any faulty condition is found in above checks, replace. Installation 1) check that none of f...
Page 639
10b-62 air bag system forward sensor removal 1) disconnect negative cable at battery. 2) disable air bag system. Refer to “disabling air bag system” in this section. 3) remove front grill referring to “front bumper” in section 9. 4) disconnect forward sensor connector sliding connector outer (1) as ...
Page 640
Air bag system 10b-63 inspection • check sensor (1) and its bracket (2) for dents, cracks, defor- mation or rust. • check sensor connector (sensor side and harness side) or lock mechanism for damage or crack. • check connector terminals for bent, corrosion or rust. • check sensor for resistance. Sen...
Page 641
10b-64 air bag system 3) connect forward sensor connector pushing connector inner (1) as shown. 4) connect negative cable at battery. 5) enable air bag system. Refer to “enabling air bag sys- tem” in this section. Seat belt pretensioner refer to “front seat belt” in section 10a for removal, inspecti...
Page 642
Air bag system 10b-65 air bag (inflator) module and seat belt pretensioner disposal do not dispose of the live (undeployed) air bag (inflator) modules and seat belt pretensioners. The method employed depends upon the final disposition of the particular vehicle, as noted in “deployment/ activation ou...
Page 643
10b-66 air bag system deployment/activation outside vehicle use this procedure when the vehicle itself is used again (only the air bag (inflator) module(s) and seat belt pretensioner(s) are dis- posed). 1) turn ignition switch to “lock”, position remove key and put on safety glasses. 2) check that t...
Page 644
Air bag system 10b-67 5) set air bag (inflator) module or seat belt pretensioner as fol- lows. [in case of driver air bag (inflator) module] a) clear a space on the ground about 185 cm (6 ft) (3) in diameter where the driver air bag (inflator) module (1) is to be deployed. A paved, outdoor location ...
Page 645
10b-68 air bag system c) fill plastic reservoir in fixture (special tool) with water or sand. This is necessary to provide sufficient stabilization of the fixture during deployment. D) attach the passenger air bag (inflator) module in the fixture (special tool) using mounting attachment, hold-down b...
Page 646
Air bag system 10b-69 6) stretch the deployment harness from the driver or passenger air bag (inflator) module to its full length 10 m (33 ft) (1). Special tool (a) : 09932-75030 7) place a power source (3) near the shorted end of the deploy- ment harness. Recommended application: 12 volts mini- mum...
Page 647
10b-70 air bag system 12) separate (1) the two banana plugs on the deployment har- ness. 13) connect the deployment harness to the power source (12v vehicle battery) (2) to immediately deploy/activate the air bag or seat belt pretensioner. 14) disconnect the deployment harness from power source (12v...
Page 648
Air bag system 10b-71 18) dispose of the deployed air bag (inflator) module and the activated seat belt pretensioner through normal refuse chan- nels after it has cooled for at least 10 minutes and tightly seal the air bag (inflator) module and the seat belt pretensioner in a strong vinyl bag. (refe...
Page 649
10b-72 air bag system deployment/activation inside vehicle use this procedure when scrapping the entire vehicle including the air bag (inflator) modules and seat belt pretensioners. 1) turn ignition switch to “lock” position, remove key and put on safety glasses. 2) remove all loose objects from fro...
Page 650
Air bag system 10b-73 5) check that there is no open, short or damage in special tool (deployment harness). If any faulty condition is found, do not use it and be sure to use new deployment harness. Special tool (a) : 09932-75030 6) short (1) the two deployment harness leads together by fully seatin...
Page 651
10b-74 air bag system 8) route deployment harness out the vehicle. 9) verify that the inside of the vehicle and the area surrounding the vehicle are clear of all people and loose or flammable objects. 10) stretch the deployment harness to its full length 10 m (33 ft) (1). Special tool (a) : 09932-75...
Page 652
Air bag system 10b-75 14) separate the two banana plugs on the deployment harness. 15) connect (1) the deployment harness to the power source (12 v vehicle battery) (2) to immediately deploy/activate the air bag or the pretensioner. 16) disconnect the deployment harness from the power source (12 v v...
Page 653
10b-76 air bag system deployed air bag (inflator) module and acti- vated seat belt pretensioner disposal deployed air bag (inflator) module and the activated seat belt pre- tensioner can be disposed of through normal refuse channels just like any other parts. For their disposal, however, following p...
Page 654: Special Tool
Air bag system 10b-77 tightening torque specification special tool fastening part tightening torque n•m kg-m lb-ft sdm bolt 6 0.6 4.5 passenger air bag (inflator) module screw 5.5 0.55 4.0 passenger air bag (inflator) module bolt 23 2.3 16.5 forward sensor bolt 10 1.0 7.2 driver air bag (inflator) m...
Page 655
10b-78 air bag system warning: be sure to use the specified digital multimeter. Otherwise, air bag deployment or personal injury may result. Note: • “a” : this kit includes the following items and substitutes for the tech-2 kit. 1. Storage case, 2. Operator’s manual, 3. Tech 1a, 4. Dlc cable, 5. Tes...
Page 656
Prepared by overseas service department 1st ed. June, 2001 2nd ed. Oct., 2001 printed in japan printing: january, 2002 652.