- DL manuals
- TDK-Lambda
- Power Supply
- G10-500
- User manual
TDK-Lambda G10-500 User manual
Series
Programmable DC Power Supplies
5kW in 1U 0-600V/ 0-500A
Built in LAN, USB, RS-232 & RS-485 Interface
Optional Interface: IEEE488.2 (GPIB)
USER MANUAL
This manual covers models
G10-500
G80-65
GB10-500
GB80-65
G20-250
G100-50
GB20-250
GB100-50
G30-170
G150-34
GB30-170
GB150-34
G40-125
G300-17
GB40-125
GB300-17
G60-85
G600-8.5
GB60-85
GB600-8.5
IA761-04-02
Summary of G10-500
Page 1
Series programmable dc power supplies 5kw in 1u 0-600v/ 0-500a built in lan, usb, rs-232 & rs-485 interface optional interface: ieee488.2 (gpib) user manual this manual covers models g10-500 g80-65 gb10-500 gb80-65 g20-250 g100-50 gb20-250 gb100-50 g30-170 g150-34 gb30-170 gb150-34 g40-125 g300-17 g...
Page 2: Table Of Contents
Table of contents chapter 1: specifications ................................................................................................. 1 1.1 5000w series specifications ...................................................................................... 1 1.2 standard unit low voltage outli...
Page 3
3.4 series operation ....................................................................................................... 36 3.4.1 series connection for increased output voltage ....................................... 36 3.4.2 series connection for positive and negative output voltage ..............
Page 4
5.7.2.2 lan command speed .................................................................. 61 5.7.3 select the control method ......................................................................... 62 5.7.3.1 control method options .............................................................. 6...
Page 5
5.10.2 numeric / data type parameters ............................................................... 88 5.10.3 command set categories ........................................................................... 88 5.10.4 identification commands ..........................................................
Page 6
6.2.3 trigger out ................................................................................................ 137 6.2.4 trigger delay ............................................................................................. 138 6.3 sequencer + trigger system examples ..........................
Page 7
8.4 multi drop connection ........................................................................................... 164 8.4.1 selecting a single power supply in a multi drop chain ............................ 164 8.5 communication cables ...............................................................
Page 8
This page intentionally left blank.
Page 9: Chapter 1:
1 chapter 1: specifications 1.1 5000w series specifications.
Page 10
2.
Page 11
3.
Page 12
4.
Page 13: 1.2
5 1.2 standard unit low voltage outline.
Page 14: 1.3
6 1.3 standard unit high voltage outline.
Page 15: 1.4
7 1.4 blank panel unit low voltage outline.
Page 16: 1.5
8 1.5 blank panel unit high voltage outline.
Page 17: 1.6
9 1.6 optional accessories 1.6.1 printed user manual • printed user manual, order p/n: g/m 1.6.2 serial port cables • for ordering serial port cables refer to chapter 5: 1.6.3 paralleling cable • paralleling cable: order p/n: g/p..
Page 18: Chapter 2:
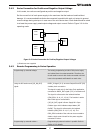
10 chapter 2: front/rear panel control & connectors 2.1 introduction the power supply series has a full set of controls, indicators and connectors that allow the user to setup and operate the unit. Before starting to operate the unit, please read the following sections for an explanation of the func...
Page 19
11 no. Control/indicator description 6 current display 4-digit 16-segment current display. Normally displays the output current. In preview mode, the display indicates the program setting of the output current. In menu navigation, the display indicates the selected parameter. 7 indicators bar refer ...
Page 20
12 no. Control/indicator description 12 conf button / indicator activates the configuration menu. The configuration menu provides power supply start mode control, voltage & current source control, analog programming / monitoring range selection, internal resistance function, constant power limit fun...
Page 21: 2.3
13 no. Control/indicator description 16 prev button / indicator press the prev button to display the output voltage and current limit settings. The display shows the settings for 5 seconds. If buttons are not pressed for 5 seconds, the display returns back to show actual output voltage and current. ...
Page 22
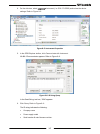
14 no. Control/indicator description section 1 voltage display 4-digit 16-segment voltage display. Normally displays the output voltage. In preview mode, the display indicates the program setting of the output voltage. In menu navigation, the display indicates the selected function. 2 operation mode...
Page 23
15 no. Control/indicator description section 10 rem indicator remote indicator. Rem is on if power supply is controlled by a remote communication (rs232/485, usb, lan, optional). 11 rs indicator recommended standard indicator. Rs232 or rs485 communication type is selected. 12 usb indicator universal...
Page 24: 2.4
16 2.4 rear panel connections and controls refer to figure 2–3 and table 2-3 for description of the rear panel connections and controls. Figure 2–3: rear panel connection and controls no. Connection description section 1 ac input connector connector type: pc 5/ 4-g-7,62. 2 ground stud functional gro...
Page 25: 2.5
17 note * lan connector leds (green & amber) and red status indicators might lit in power switch off state. Warning refer to the safety & installation manual for any connect/disconnect of any connector on the rear panel. 2.5 j1 connector terminal and function control and monitoring signals are selv....
Page 26
18 no. Connection description section 8 vpgm input for remote (analog) voltage/resistance programming of the output voltage. 9 not used 10 ena_in enable / disable the power supply output by dry-contact (short / open) or voltage source. Selectable signal polarity. 11 com common. Return for all signal...
Page 27: 2.6
19 2.6 front panel display messages table 2-5 shows the various messages shown on the display in different operating modes. Display text text description display text text description out output lock lock off off ulock unlock intfc interface sense sense rs232 rs232 local local rs485 rs485 rem remote...
Page 28: 2.7
20 display text text description display text text description panel panel trig trigger e.Vol external voltage init init e.Res external resistance abort abort c.Src current source load load range range trg.In trigger input r.Int internal resistance ext external c.Pwr constant power bus bus power pow...
Page 29
21 rs232 rs485 usb lan intfc 0 adr 1 31 9.6k 38.4k 57.6k 115.2k baud gen lang scpi g :xx.Xxx rev. Voltage encoder 1 step rotate current encoder 1 step rotate opt --------------------- built_in --------------------- --- optional --- ip1 0 255 ip4 reset 1--4 ip mac1 mac6 1--6 mac 0 255 00 ff 00 ff lan...
Page 30
22 ovp min uvl max pro t e n t e r current encoder voltage encoder 0 max off uvp on 0.1 uvp.Dl 25.5 fold off fld.Dl cv uvp on fold cc/cv cc 0.1 25.5 protection menu ocl off on uvp off fold off voltage encoder 1 step rotate current encoder 1 step rotate function (voltage display) parameter (current d...
Page 31
23 start co nf e n t e r current encoder voltage encoder v.Src panel e.Res 5 range 10 e.Vol configuration menu r.Src v.Src c.Src panel e.Res e.Vol r.Int off on res 0.001 1.000 power min max c.Pow on c.Pwr off on safe auto r.Src v.Src slew off volt curr csl.Up 0.0001 999.99 vsl.Up csl.Dn 0.0001 999.9...
Page 32
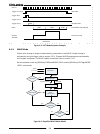
24 figure 2–8: system menu diagram dm.Dl sense panel sys t/ e n t e r current encoder voltage encoder system menu local rem ena off on ilc off on pso.Dl 0.000 10.000 save 1 2 3 4 recal 1 2 3 4 frst deflt no sure yes e n t e r pin 1 off on pin 2 off on prel disp brt d m.B rt dm.Dl note: max dm.Brt va...
Page 33
25 trig pro g e n t e r current encoder t r i g voltage encoder trg.Ou off trig ext trg.In bus fstr program menu init abort aborted / no inita ilzed inita ilzed load 1 2 3 4 off cont on 0.000 trg.Dl 10.00 voltage encoder 1 step rotate current encoder 1 step rotate function (voltage display) paramete...
Page 34: Chapter 3:
26 chapter 3: local operation 3.1 introduction this chapter describes the operating modes that do not require programming and monitoring the power supply via its communication interfaces: lan, usb, rs232/rs485, optional communication or by remote analog signals. Ensure that the rem indicator on the ...
Page 35
27 warnung bei einsatz einer stromversorgung mit einer ausgangsspannung von über 60vdc besteht am lastseitigen sense-punkt die potentielle gefahr eines elektrischen schlags. Stellen sie sicher, dass die anschlüsse an der last abgedeckt sind, um versehentlichen kontakt mit gefährlicher spannung zu ve...
Page 36
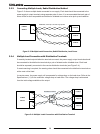
28 3.2.3 connecting multiple loads, radial distribution method figure 3–3 shows multiple loads connected to one supply. Each load should be connected to the power supply’s output terminals using separate pairs of wires. It is recommended that each pair of wires will be as short as possible and twist...
Page 37
29 3.2.5 constant voltage mode and voltage setting in constant voltage mode, the power supply regulates the output voltage at the selected value, while the load current varies as required by the load. While the power supply operates in constant voltage mode, the cv indicator on the display illuminat...
Page 38
30 1. Adjust the output current, when the power supply output is enabled (output on) or disabled (output off). There are three options to set output voltage: (a) when the output is enabled, rotate the current encoder knob to program the output current. This method affects output current immediately....
Page 39: 3.3
31 3.2.9 safe-start and auto-restart modes at ac turn on, the power supply can start at the last setting of the output voltage and current limit with the output enabled (auto-restart), or it can start with the output disabled (safe mode). 1. Press the configuration button. Display shows start safe o...
Page 40
32 3.3.2 over voltage protection the ovp circuit protects the load in the event of a remote or local programming error or a power supply failure. The protection circuit monitors the voltage at the power supply sense points thus providing the protection level at the load. Upon detection of an over vo...
Page 41
33 3.3.3 under voltage protection and under voltage limit the uvl function prevents output voltage setting below the uvl set value, and prevents an adjustment of the output voltage below a certain limit. The uvp function prevents power supply operation, if the output voltage is below the uvl set val...
Page 42
34 3.3.4 foldback protection foldback protection will shut down the power supply output if power supply operation mode crosses over from cc to cv or from cv to cc, according to a selected operation mode. There are three states of foldback protection. • off (default) • cv • cc for cc (or cp) to cv pr...
Page 43
35 3.3.5 protection delay foldback protection delay is the time between feedback transition (cv to cc transition or vice versa) event occurrences to output shutdown. Uvp protection delay is the time between uvl crossover point events to output shutdown. Note at output off -> on transition, additiona...
Page 44: 3.4
36 3.4 series operation power supplies of the same model can be connected in series to obtain an increased output voltage. Split connection of the power supplies gives positive and negative output voltage. Warning when power supplies are connected in series, and the load or one of the output termina...
Page 45
37 3.4.2 series connection for positive and negative output voltage in this mode, two units are configured as positive and negative output. Set the current limit of each power supply to the maximum that the load can handle without damage. It is recommended that diodes be connected in parallel with e...
Page 46: 3.5
38 programming via serial communication ports (rs232/rs485, usb): the communication ports are referenced to the com_selv, which is isolated from the power supply output potential. Therefore, power supplies connected in series can be chained using the remote-in and remote- out connectors. Refer to se...
Page 47: 3.6
39 for signal details, refer to table 3-2. So signal level (j1-1 – j1-11) power supply output daisy_out level (j1-2 – j1-11) ps_ok level (j1-3 – j1-11) 2-30v or open 0-0.6v or short on off (so fault) high low low high (open collector) table 3-2: daisy_in signal definition 3.6 rear panel (j1 connecto...
Page 48
40 3.6.2 enable in function ena_in signal serves as power supply output enable control. Connection to the signal is made via pin j1-10 (ena_in) and pin j1-11 (com_selv), which are isolated from the power supply output. Ena_in is reported by a display message ena fault, red alarm led is blinking 1/2 ...
Page 49
41 note safe start mode - if the interlock fault condition clears while units are in the safe start mode, the power supply returns to output off mode. Auto-restart mode - the output will automatically return to the previous setting. The following faults will require \ena_in recycle: uvp, ovp or fold...
Page 50
42 3.6.5 power supply ok signal power supply ok signal (\ps_ok_out) indicates power supply output state (on/off). It is an open collector signal at j1-3, referenced to com_selv at j1-11 (isolated interface common). When a fault condition occurs or power supply output is off, \ps_ok_out level is high...
Page 51: 3.7
43 3.7 parameter setting memory power supply has the following memory configuration modes: 3.7.1 default setting this function sets all parameters to their default state, as defined in table 3-5 and table 3-6. Factory reset settings can be restored via front panel menu or communication command. The ...
Page 52
44 user can recall up to 4 sets of parameters. Refer to table 3-5 for available recall parameter sets. To recall the front panel setting, perform the following steps: 1. Press the syst button. Syst (green) led illuminates. Rotate voltage encoder until recal 1 appears on the display. 2. Rotate curren...
Page 53
45 function factory reset (default settings) reset last setting save & recall enable (ena) polarity rev - + - power supply ok (ps_ok) delay [s] 00.01 - + - preload on - + - communication interface usb - + - communication power supply address 06 - + - communication baud rate [baud] 115200 - + - commu...
Page 54: Chapter 4:
46 chapter 4: remote analog programming 4.1 introduction the rear panel connector j1 allows the user to program the power supply output voltage and current with an analog device. J1 also provides monitoring signals for output voltage and output current. The programming range and monitoring signals r...
Page 55: 4.4
47 4.4 remote voltage programming of output voltage and current for voltage analog programming wiring, refer to figure 4–1. Set the remote programming settings as follows: 1. Short the pin j1-6 to j1-11. 2. Press the conf button. Conf (green) led illuminates. 3. Rotate the voltage encoder until v.Sr...
Page 56: 4.5
48 4.5 remote resistor programming of output voltage and output current for resistive programming, the internal current sources for output voltage and/or output current control, supply 1ma current through external programming resistors connected between j1-8 and j1-18 and between j1-7 and j1-18. The...
Page 57: 4.6
49 notes: 1. The power supply can be programmed to up to 108% of the rated output voltage and current. However, it is forbidden to operate the power supply over its voltage and current ratings. Performance is not guaranteed when operating the power supply above its ratings. 2. Communication: in the ...
Page 58: Chapter 5:
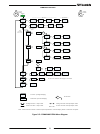
50 chapter 5: serial rs232/rs485, usb & lan interfaces 5.1 introduction this chapter describes the set-up, operation, commands, and communication protocols of the power supplies via serial communication interfaces: rs232, rs485, or usb, and lan. 5.2 configuration function level display parameter lev...
Page 59
51 5.2.3 address setting the power supply address can be set to any address in the range of 0 to 31. 1. Press the comm button. Comm led illuminates. Intfc message appears on the voltage display. 2. Rotate the voltage encoder 1 step clockwise. Adr message appears on the voltage display. 3. Rotate the...
Page 60
52 5.2.5 baud rate setting five optional rates are possible: 9600, 19200, 38400, 57600 and 115200. 1. Press the comm button. Comm led illuminates. Intfc message appears on the voltage display. 2. Rotate the voltage encoder 2 steps clockwise *. Baud message appears on the voltage display. 3. Rotate t...
Page 61
53 5.2.7 setting unit in remote, local lockout or local mode if power supply is in local mode, it can receive communication commands & queries. If a command is received, power supply will execute and change its mode to remote. If a query is received, power supply will reply and remain in the local m...
Page 62: 5.3
54 5.3 rear panel rs232/rs485 in connector rs232/485 in the interface is accessible through the rear panel rs232/485 in connector. The connector is eight contacts, shielded rj-45 type. The connector is used to connect power supplies in rs232 or rs485 configurations. Refer to figure 5–1 for the conne...
Page 63: 5.4
55 5.4 rear panel rs485 out connector rs485 out interface is accessible through the rear panel rs485 out connector. The connector is eight contacts, shielded rj-45 type. The connector is used to connect power supplies in rs485 daisy chain configuration. Refer to figure 5–2 for the connector descript...
Page 64: 5.5
56 5.5 connecting power supply to rs232 or rs485 bus connect rear panel rs232/rs485 in connector to the controller, or a pc rs232 or rs485 port using a suitable shielded cable. Refer to figure 5–3 and figure 5–4 for the available rs232 and rs485 cables. Db-9 connector 8 pin connector remarks pin no....
Page 65: 5.6
57 5.6 rear panel usb connector a standard usb type b connector is located on the rear panel of the usb communication interface. Refer to figure 5–5. Figure 5–5: usb connector 5.6.1 usb getting started figure 5–6: usb connection 1. Insert the software cd-rom shipped with the product into a cd-rom dr...
Page 66: 5.7
58 5.7 rear panel lan 5.7.1 introduction the local area network (lan) connection for the power supply series allows the user to remotely program, measure and check status of the power supply. A computer web page browser can be used to operate the power supply through a built-in web page server. For ...
Page 67
59 rear panel features • ethernet rj-45 connector (standard 8-pin phone jack for lan) • link, activity led and speed led on rj-45 connector • lan status leds show lan fault and “blink identify” on rear panel, close to lan rj-45 connector rs-485 multi-drop chain • allows connection of up to 31 power ...
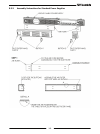
Page 68
60 lan protocols tcp lan packets follow transmission control protocol ipv4 internet protocol version 4 instrument protocols vxi-11 supports core channel, not abort or interrupt channels visa vxi-11 compliant, uses rpc and portmapper, scpi commands tcp sockets send scpi commands to port 8003 udp sock...
Page 69
61 supply configurations local control supply may be controlled from the front panel even if lan is monitoring lan remote control supply may be controlled and monitored through lan rs232, rs485, usb or option control lan interface is disabled if the standard rs-232, rs-485, usb or optional communica...
Page 70
62 5.7.3 select the control method 5.7.3.1 control method options the power supply with may be operated through four interfaces. This section describes how to enable each option. Mode mode description 1 lan control using an ethernet connection lan disables serial, analog and optional communication p...
Page 71
63 • duplicate ip: blinking green if there are two (or more) instruments with the same ip address, green led is blinking. • lan fault/disconnected: steady red shows that the lan interface is not selected, lan connection is disconnected or broken. 5.7.4 connect to a network 5.7.4.1 lan cable the lan ...
Page 72
64 • peer-to-peer network in this type of configuration, the power supply is connected directly to a computer that is not a network server. The power supply configures its own ip address and other settings. Figure 5–8: peer-to-peer network 5.7.4.3 power-up the lan power supply the power supply lan o...
Page 73
65 5.7.4.4 ip addresses the simplest and most reliable way to open a network connection is via the power supply’s ip address, which is represented by a group of four numbers separated by periods (i.E. 10.1.15.123). The power supply can receive an ip address in three modes: dhcp auto-ip static ip ip ...
Page 74
66 if the rating has decimal point, substitute “p” for the decimal point. For example: model default hostname g10-40 g10-40 gh100-4.5 gh100-4p5 a custom host name can be created through the web pages (refer to section 5.7.6.6). For example, host name can be set to lambda. In this case, the control p...
Page 75
67 a lan reset does not change the service name, even if it is a custom name, but it may remove the dash and the number if a service name conflict has been removed. To restore the factory default service name, open the lan modify web page and enter a blank for the new service name (refer to sectio...
Page 76
68 to change the ip address: 1. Press comm button. Rotate voltage encoder until ip appears on the voltage display, 1 appears on the current display. 2. Press current encoder to enter ip configuration. Rotate voltage encoder to view the ip address. Voltage display shows ip1-ip4 by rotating voltage en...
Page 77
69 keep-alive: 1800 seconds (30 minutes) auto-negotiate: automatically select network speed vxi-11 discovery: enabled password: none multicast dns: enabled 5.7.6 web pages 5.7.6.1 benefits of web pages the web pages are useful for: • reading the power supply model, identity, revision and lan setup i...
Page 78
70 5.7.6.3 the home page the following page appears when the web page is opened for the first time or when it is refreshed: figure 5–9: home page visa name using ip address for automation programming, visa is a type of communication driver. For lan instruments, the ip address may be used in the visa...
Page 79
71 multicast dns the lan broadcasts its hostname even if no network server is present. This is useful for connecting over simple peer-to-peer networks. Logging in to change power supply output or lan settings, a user must first log in. When the dc power tab or lan tab is clicked, a login box appears...
Page 80
72 5.7.6.5 dc power page when the dc power tab is selected, the following web page opens. This page and its sub-menus allow a user to operate the power supply and adjust its output settings. A. Dc power ➔ output page when the dc power tab is selected, the output page opens by default (gui). Figure 5...
Page 81
73 settings this section displays the selected power supply’s output voltage, current limit and output on/off settings. The settings cannot be changed until you have logged-in as 'admin'. To change a settings, perform the following: 1. Tick check to modify. 2. Set desired settings. After settings ar...
Page 82
74 c. Dc power ➔ system page on the dc power tab, the system button is available at the top of the panel. When opened, the window allows the user to operate four functions: • reset one instrument (this resets only the supply selected in the rs-485 list box). • reset all instruments (this resets all ...
Page 83
75 5. To read system errors, send syst:err:enab command to enable the error system (has to be sent once prior reading errors). 0. The settings can be changed only by logging-in as 'admin'. Figure 5–14: dc power - utility tab 5.7.6.6 lan page when the lan tab is selected, the following web page opens...
Page 84
76 address of the network router to allow the power supply to communicate outside of the local subnet. • dns server address of the server running the domain naming service. This is used for hostname addressing. • hostname the power supply hostname may be used instead of the ip address to create a co...
Page 85
77 note: after changing the lan settings, you are requested to close the web browser. Re-open the web page . If the change duplicates ip, the lan status green led and the front panel display will blink, ip address will revert to the previous state. Press any front panel button or encoder to stop the...
Page 86
78 c. Lan ➔ advanced & lan->advanced->modify page click the lan ➔ advanced button to view advanced lan settings: figure 5–17: lan – advanced tab these settings can be changed only by logging-in as 'admin'. Figure 5–18: lan – changing settings • lan timeout if the user is logged in via the web page o...
Page 87
79 • apply click this button to save the new settings. A pop-up box will ask you to close or refresh the page. ‘admin’ log-in will be logged-out. • close click this button to return to the lan configure page shown in section a. D. Lan ➔ users page this page allows creating password protection for th...
Page 88
80 5.7.7 programming using visa drivers 5.7.7.1 visa description in the test and measurement industry, virtual instrument software architecture (visa) is a popular framework that includes hardware drivers, configuration utilities and connection managers. Varieties of communication busses are support...
Page 89
81 5.7.8 programming using sockets 5.7.8.1 socket description the visa drivers for the power supply are commonly used in the test and measurement industry. For customers who cannot use visa because of installation, licensing issues or because the controller (i.E.: industrial plc) does not support vi...
Page 90
82 5.7.8.4 input buffer requirements with a controller using tcp or udp sockets, the power supply can receive commands much faster than it can process. To make sure the lan is not overloaded, it is required that the controller sometimes sends a query and then waits for the response. The response is ...
Page 91
83 5.7.8.7 using udp sockets this is a simpler socket type with reduced network traffic. It is a ‘connectionless’ protocol because messages are sent and there is no acknowledgement that they have been received. Open udp socket port 8005 to send scpi commands. Responses to queries are sent back autom...
Page 92: 5.8
84 5.8 multi power supply connection (daisy-chain) to rs232, rs485, usb or lan a daisy-chain configuration of up to 32 units can be connected to rs232, rs485, usb, lan or optional communication (i.E. Ieee). The first unit connects to the controller or pc via rs232, rs485, usb, lan or optional commun...
Page 93
85 note: if a custom cable is used, connect only the pins listed in the table above. Keep pins 1, 2 and 7 not connected. Caution when using multiple lan controllers with multi-drop, only one power supply may be “selected” at a time because one controller may change the selected address and the other...
Page 94
86 all the supplies on the multi-drop chain will be set to 70 volts, except for the supply at rs-485 address 4 that will be set to 90 volts. Note: rs-485 retransmit baud-rate is automatically set to 115,200 bps if usb, lan or optional communication (i.E. Ieee) is selected..
Page 95: 5.9
87 5.9 gen protocol (gen series communication language) gen communication language is supported to provide compatibility to the legacy genesys programmable power supplies series. To use the advanced functions of the power supply, refer to scpi language, section 5.12. Recommended time delay between c...
Page 96
88 • in commands with an argument, a space must appear between the command and the argument. • for any command that sets a numeric value, the value may be up to 12 characters long. • carriage return: if the cr character (ascii 13) is received by itself, the power supply will respond with an ”ok” and...
Page 97
89 5.10.4 identification commands idn? Query returns the power supply model identification as an ascii string (one comma, no spaces) returns example tdk-lambda,g100-50 rev? Query returns the software version as an ascii string returns example g:xx.Xxx sn? Query returns the supply’s serial number. Up...
Page 98
90 rst function reset setting. Refer to table 3-5. Returns ok \ function repeat last command. If \ is received, the power supply will repeat the last command returns ok frst function restore factory reset parameters. Refer to table 3-5 & table 3-6 returns none note: factory reset does not affect adv...
Page 99
91 mp? Query returns the measured output power returns 5 digits format dvc? Query displays voltage and current data. Data returns as a string of ascii characters. A comma separates different fields. Fields order: measured voltage, programmed voltage, measured current, programmed current, over voltag...
Page 100
92 ovp function sets the over-voltage protection level. An attempt to adjust from the front panel or program the ovp below this level will result in the execution error response (‘e04’) and the ovp setting will stay unchanged parameters range is limited by the ovp programming range and voltage progr...
Page 103
95 model rated output voltage (v) minimum (v) maximum (v) 10 0.5 12 20 1.0 24 30 1.5 36 300 15 330.75 600 30 661.5 table 5-6: ovp programming range model rated output voltage (v) minimum (v) maximum (v) 10 0 9.5 20 0 19 30 0 28.5 300 0 285 600 0 570 table 5-7: uvl programming range 5.10.8 auxiliary ...
Page 105
97 flt? Query returns the value of the questionable group condition register, a read-only register holding the real-time power supply faults. Returns example 09fa fena function sets the value of the questionable group enable register. This register is a mask to enable specific bits from the conditio...
Page 106
98 5.11 serial communication test set-up basic set-up to test serial communication operation. 1 equipment pc with a serial communication terminal software installed, power supply and rs232 or usb cable. 2 pc set-up bits per second: 115200 data bits: 8 parity: none stop bits: 1 flow control: none 3 p...
Page 107: 5.12 Scpi Protocol
99 5.12 scpi protocol note: selecting the power supply (instrument:nselect other command. 5.12.1 data format serial data format is 8 bit, one start bit and one stop bit. No parity bit. 5.12.2 end of message the end of message is the carriage return character (ascii 13, 0x0d). Power supply ignores th...
Page 108
100 5.12.6 scpi command hierarchy scpi is an ascii-based command language designed for use in test and measurement equipment. The command structure is organized around common roots, or nodes, which are the building blocks of the scpi subsystems. An example of a common root is output. Some of the com...
Page 110
102 *ese function this command programs the standard event status enable register bits. The programming determines which events of the standard event status event register (see *esr? Below) are allowed to set the esb (event summary bit) of the status byte register. "1" in the bit position enables th...
Page 111
103 *esr? Query returns the value of the standard event status event register. The event register is a read-only register, which stores (latches) all standard events. Reading the standard event status event register clears it. Bit configuration of the standard event status event register is as follo...
Page 112
104 *opt? Query returns the type of an optional card installed. Returns 0, no option installed 1, gpib *psc function the power on status clear (psc) command controls automatic power on clear of the service request enable register, the standard event status enable register, and device specific event ...
Page 113
105 *sre function sets the condition of the service request enable register. This register determines which bits from the status byte register are allowed to set the request for service (rqs) summary bit. A "1" in any service request enable register bit position enables the corresponding status byte...
Page 115
107 5.14.2 initiate subsystem initiate[:immediate] function initialize trigger system. If initialized, trigger in system is active (system is ready to receive trigger signal). If not initialized, all trigger signals are ignored. Initiate:continuous function continously re-initiates a trigger. If ina...
Page 116
108 global:*rcl function refers to *rcl command description. Parameters 1,2,3,4 global:*rst function: refers to *rst command description. Global:*save function refers to *sav command description. Parameters 1,2,3,4 global:current[:amplitude] function refers to [source]:current[:level][:immediate][:a...
Page 120
112 [program]:list:dwell ,{} function: specifies the time interval of each value (point) in a list to remain in effect. The function accepts up to 100 parameters. Parameters 0.001 to 129,600 unit s query [program]:list:dwell? Return ,{} example list:dwel .6,1.5,1.5,.4 note: a delay of ~100msec is re...
Page 121
113 notes: delay of ~20msec is required after the load command, prior to sending any additional command. Uvl and ovp level settings clamp sequence-programmed values. Loading an empty sequence results in error -286,”data load empty”. Loading a sequence while any sequence is running, results in error ...
Page 122
114 note: a delay of ~100msec is required after the [program]:wave:current command if long sequences are used, prior sending any additional command. [program]:wave:time ,{} function: specifies the time interval of each slope between 2 points of a wave. The function defines up to 100 parameters. Para...
Page 124
116 [source]:current:slew:up function sets a digital current reference up programming slew rate. Parameters 0.0001 ~ 999.99 unit a/ms query [source]:current:slew:up? Return example :curr:slew:up 1 sets a digital current reference up programming slew to 1a/ms. :curr:slew:up? Returns a digital current...
Page 125
117 [source]:voltage:slew:down function sets a digital voltage reference down programming slew rate. Parameters 0.0001 ~ 999.99 unit v/ms query [source]:voltage:slew:down? Return example :volt:slew:down 1 sets a digital voltage reference down programming slew to 1v/ms. :volt:slew:down? Returns a dig...
Page 128
120 5.14.9 status subsystem status:operation[:event]? Query returns the value of the operational condition group event register. The value is according to the operational condition group condition register and operational condition group enable register. The event register is a read-only register. E...
Page 129
121 status:operation:condition? Query returns the value of the operational condition group condition register, which is a read-only register that holds the real-time operational status of the power supply. Bit configuration of the operational condition group condition register is as follows: positio...
Page 130
122 status:operation:enable function sets the value of the operational condition group enable register. This register is a mask for enabling specific bits from the condition register to the event register. Refer to status:operation[:event]? Command for the complete list of the registers that can be ...
Page 131
123 status:questionable:condition? Query returns the value of the questionable condition group condition register, which is a read-only register that holds the real-time conditional status of the power supply. Refer to status:questionable[:event]? Command for the complete registers list. Returns 0…6...
Page 132
124 5.14.10 system subsystem system[:communicate]:address function sets the power supply communication address. Parameters 0…31 query system[:communicate]:address? Return 0…31 note: power supply addressing is lost after an address change. System[:communicate]:baudrate function sets a serial communic...
Page 134
126 system:frst function restores factory default parameters. Refer to table 3-5 & table 3-6 note: factory reset does not affect advanced parallel configuration acknowledgment (does not affect power supply configuration (single, master or slave roles does not change). System:firmware[:version]? Func...
Page 136
128 system:remote[:state] function sets the power supply control source (front panel or communication) to local, remote, or llo mode. Local – enables the front panel control. Remote – disables the front panel settings change. Llo – same as remote + disable front panel unlock by the front panel. Deac...
Page 137
129 5.14.11 trigger subsystem note: the trigger subsystem must be enabled from the initiate subsystem. If disabled, commands from the trigger subsystem will not affect power supply output. Trigger[:immediate] function if trigger is enabled (by initiate command), trig generates an immediate trigger s...
Page 138
130 5.15 scpi commands summary common commands scpi command *cls *ese (?) *esr? *idn? *opc (?) *opt? *psc (?) *rcl *rst *sav *sre *stb? *trg *tst? *wai abort subsystem commands scpi command [:]display [:window]:state (?) [:window]:flash (?) [:window]:test (?) [:]initiate [:immediate] :continuous (?)...
Page 140
132 :questionable [:event]? :condition? :enable (?) [:]system [:communicate] :address (?) :baudrate (?) :interface (?) :lan :host? :idled :ip (?) :mac? :res :language (?) :error:enable :error? :frst :firmware [:version]? :panel :lock? :parallel:acknowledge :parallel? :pon :time? :time :ac? :preload ...
Page 141: Chapter 6:
133 chapter 6: advanced functions 6.1 sequencer the sequencer allows advanced waveforms programming of power supply output in steps of one mille-second. Up to four sequences, 100 points each, can be stored inside power supply memory. There are two programmable modes: list and wave. These programmabl...
Page 142
134 figure 6–2: list mode sequence example 6.1.2 wave mode output value change in slopes is determined by parameters in the wave. Output change is activated by the input trigger (refer to section 6.2.2). Program wave parameters are activated by the program subsystem. For wave related commands, refer...
Page 143
135 figure 6–4: wave mode sequence example 6.1.3 sequencer functions 6.1.3.1 counter defines the number of performed iterations. The counter can be set to 1 ~ 9999. Any number above 9999 sets the number of iterations to infinity. Counter setting is available via the communication command [program]:c...
Page 144
136 6.1.3.6 step execute a single step from a sequence in the list or wave mode. Step function is available via the front panel menu (refer to section 2.7) or via the communication command [program]:step . 6.1.3.7 abort stop sequencer wave or list mode execution. Return sequencer system to idle stat...
Page 145: 6.2
137 6.2 trigger system the trigger system, consisting of trigger in and trigger out functions, provides the ability to synchronize sequencer arbitrary waveforms. In addition, the trigger out function provides the ability to generate trigger signal, if power supply output state or voltage / current p...
Page 146: 6.3
138 programming mode wave or list (for current or voltage mode) • off mode – no trigger output signal. • trig mode – trigger is generated if the list or wave sequence is completed. • fstr mode – trigger is generated every step (after completion). To enable trigger out signal functionality, refer to ...
Page 147
139 6.3.3 list mode example volt: mode list select list mode sequence list:volt 2,4,2,8,5,4 set voltage values ”2,4,2,8,5,4” volts list:dwel 0.5,0.5,1,1,1,1 set dwell values ”0.5,0.5,1,1,1,1” seconds step auto set auto step execution mode ”auto” coun 1 set list execution iterations ”1” trig:sour bus...
Page 148
140 6.3.4 wave mode example volt: mode wave select sequence mode ”wave” wave: volt 2,4,4,9,9,3,3 set voltage values ”2,4,4,9,9,3,3” volts wave:time 1,0.5,0.5,0.5,0.5,1.5,1.5 set time values ”1,0.5,0.5,0.5,0.5,1.5,1.5” seconds step auto set auto step execution mode ”auto” coun 1 set wave execution it...
Page 149: 6.4
141 6.4 internal resistance internal resistance function is primarily used to simulate battery voltage drop, as a response to load current. In addition, it can be used in cases of voltage drop over long load wires. Power supply output voltage v out is set according to voltage setting minus actual lo...
Page 150: 6.5
142 6.5 constant power limit the constant power limit function limits the output power provided by the power supply. The constant power limit function is enabled via the front panel menu (refer to section 2.7) or the communication command [source]:power:state . Constant power setting range is limite...
Page 151: 6.6
143 to limit voltage and current values (in addition to constant power limit), set voltage limit and current limit, as shown in figure 6–9. Figure 6–9: constant power - example 2 6.6 preload control preload control function provides the ability to enable/disable internal preload circuitry. This func...
Page 152: 6.7
144 6.7 ocl – analog programming over current limit analog programming over current limit (ocl) function provides the ability to limit analog programming of maximum current programming value. Setting ocl to on state clamps maximum current programming value to digital programming value (set by front ...
Page 153: 6.8
145 6.8 slew-rate control slew-rate control function provides the ability to control voltage or current reference slew rate. Slew rate function is enabled via the front panel menu (refer to section 2.7) or the communication commands system:slew[:state] . • select volt for voltage reference slew cont...
Page 154: 6.9
146 6.9 advanced parallel up to four units of the same voltage and current ratings can be connected in parallel to provide up to four times of the output current capability. One of the units operates as a master while the remaining units operate as slaves. The configuration of the system (master-sla...
Page 155
147 figure 6–12: parallel connection with remote sensing caution make sure the connection between –v terminals is reliable to prevent disconnection during operation. Disconnection may cause damage to the power supply. Note with local sensing, it is important to minimize wire length to decrease wire ...
Page 156
148 6.9.3.1 acknowledge via the front panel 1. To acknowledge a parallel system via the front panel, turn on the master unit, and wait for 5 seconds. The following appears on the master display: wait ack. 2. To acknowledge, press the current encoder. Display blinks, indicating that the parallel syst...
Page 157
149 note constant power limit minimum limit setting is dependent on the number of units connected in parallel. Single unit minimum value is 1w. Connecting additional units in parallel results in 1w multiplied by n, while n is the number of units connected in parallel (including the master unit). 6.9...
Page 158: Chapter 7:
150 chapter 7: status, fault and srq registers 7.1 general this section describes various status errors (faults) and srq register structures. The registers can be read or set via communication commands. Two individual sets of registers are managed, one set for the scpi language, another set for the ...
Page 159
151 scpi register tree shown in figure 7–1 describes the structure of status, events, faults, messaging and service request registers. Condition registers hold a snapshot of the actual state. The enable registers can be set by the user to enable srq (service request) in case of a condition change. E...
Page 160
152 7.2.3 operational condition (status register) group structure operational condition status register group holds a snapshot of the actual status state of the power supply at a present time. Power supply status might quickly change condition before the controlling pc detects it. Events can be stor...
Page 161
153 7.2.4 standard event status group structure standard event status group latches error groups. Power switch on and operation complete events status might quickly change its condition before the controlling pc detects it. Events can be stored in the event register if the enable register allows it....
Page 162
154 7.2.5 output queue the output queue is a queue that stores the message sent from the power supply to the controlling pc until the message is read. The output queue is cleared at power on and by the *cls command. Whenever the queue holds a message, it sets the mav bit in the status byte register ...
Page 163
155 error number error description error event -300 “device-specific error” generic device dependent error -301 “message timeout” timeout of 15 sec. Before receiving a terminator (cr or lf) has occurred -302 “general error” unrecoverable system error, recycle ac. If problem persists, contact service...
Page 164
156 error number error description error event 335 “internal resistance is on” an attempt to set constant power mode, analog programming, slew rate or sequencer while internal resistance is on 336 “constant power mode is on” an attempt to set internal resistance, analog programming, slew rate or seq...
Page 165
157 7.2.7 service request enable group structure service request enable group register summarizes questionable condition group, standard event status group and operational condition group events, if these are enabled. The group also contains busy bit and message available bit and service request bit...
Page 166
158 7.2.8 determining the cause of a service interrupt a service request (srq) is set if the contents of at least one of the event registers has changed (from logical zero to logical one). To determine the reason for an srq, perform the following actions: 1. Poll by *stb? Query to determine which bi...
Page 167: 7.3
159 7.3 gen language 7.3.1 gen register tree figure 7–2: gen registers tree diagram gen register tree shown in figure 7–2 describes the structure of the status, faults, messaging and service request registers. Condition registers hold a snapshot of the actual state. Enable registers.
Page 168
160 can be set by the user to enable srq (service request) in case a condition change occurs. Event registers latch condition registers state if the corresponding enable registers are set to logical one. Event registers remain set (latched) until the user reads the register, reading the register cle...
Page 169
161 7.3.3 operational group (status register) structure operational condition status register group holds a snapshot of the actual status state of the power supply at a present time. Power supply status might quickly change its condition before the controlling pc detects it. Events can be stored in ...
Page 170
162 7.3.5 execution error (“exx”) power supply responds with an execution error if it receives a valid command, but it cannot execute the command at that time, because another setting prevents it. The execution error response format is ‘enn‘ where ‘nn’ is ‘01’ to ‘08’. The following error commands a...
Page 171: Chapter 8:
163 chapter 8: ieee option 8.1 general the internal factory, general purpose interface bus (gpib), installed as an option, allows operation of the power supply from a controller/computer via ieee-488. The interface allows the user a remote control of the power supply, including output voltage, curre...
Page 172: 8.4
164 8.4 multi drop connection one ieee interface can control more than one power supply. A maximum of 31 units can be connected via rs485 interface to a power supply with the installed ieee option. Refer to figure 8–2.The power supply connected to a pc via the gpib cable must be configured to an iee...
Page 173: 8.5
165 8.5 communication cables • gpib cable - use standard ieee-488, 26 awg gpib cable up to 3 meters in length. • rs485 link cable - use serial link cable with rj-45 shielded connectors (p/n: gen/rj45). 8.6 ieee controller configuration a typical ieee controller is a personal computer with an ieee in...
Page 174: 8.9
166 8.9 communication example this section provides an example of how to communicate with the ieee option power supply using the national instruments™ max application. 1. Run the national instruments™ max (measurement & automation explorer). Figure 8–3: national instruments™ max – desktop icon 2. On...
Page 175
167 4. On the side tree, select instrument (i.E. G30-170-gpib) and review the device settings. Refer to figure 8–5. Figure 8–5: instrument properties 5. In the gpib explorer toolbar, click communicate with instrument. Ni-488.2 communicator appears. Refer to figure 8–6. Figure 8–6: id string query in...
Page 176: Chapter 9:
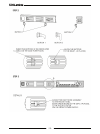
168 chapter 9: air filter option 9.1 general the air filter kit is supplied separately, by customer request. The usage of the air filter is according to customers’ needs. 9.2 specifications when using the air filter kit, all the specifications of the power supply remain the same as for standard powe...
Page 177
169 9.3.2 assembly instructions for standard power supplies.
Page 178
170
Page 179
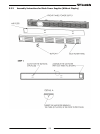
171 9.3.3 assembly instructions for blank power supplies (without display).
Page 180
172.
Page 181: Chapter 10:
173 chapter 10: maintenance 10.1 introduction this chapter provides information about maintenance, calibration and troubleshooting. 10.2 units under warranty units requiring repair during the warranty period should be returned to a tdk lambda authorized service facility. Refer to the address listing...
Page 182: 10.6 Troubleshooting
174 10.5 parts replacement and repairs as repairs are made only by the manufacturer or by authorized service facilities, no parts replacement information is provided in the manual. In case of failure, unusual or erratic operation of the unit, contact the tdk lambda sales or service facility nearest ...
Page 183: 10.7 Fuse Rating
175 symptom check action ref. If analog programming is used, check if the ovp is set lower than the output. No output. Display indicates so check if the rear panel j1 output daisy is in function. 3.6.1 no output. Front panel alarm led is on. Display indicates ilc_fault check the rear panel j1 interl...
Page 184: 10.1 Einleitung
176 10.1 einleitung dieses kapitel enthält informationen über instandhaltung, kalibrierung und fehlersuche. 10.2 geräte unter gewährleistung geräte, die während des gewährleistungszeitraums einer reparatur bedürfen, müssen an eine zugelassenen tdk-lambda-servicestätte zurückgeschickt werden. Die adr...
Page 185
177 frontgesteuerten betrieb und führen sie die angeführten tests im kapitel 3.7 durch, um festzustellen, ob das problem am netzgerät liegt. Die tabelle 10-1 enthält die grundlegenden tests zur ausführung einer problemdiagnose und liefert hinweise auf abschnitte dieses handbuches, welche weiterführe...
Page 186: 10.7 Netzsicherungswert
178 feststellung prÜfen nächster schritt bezug display zeigt ”ena_fault” an. An der rückseite den ena-anschluss und deren funktion am j1-stecker prüfen. 3.7.2 kein ausgang. Frontseitige alarm led blinkt an der frontplatte mit 0.5hz. Display zeigt ”fold fault” an. Foldback-einstellung und laststrom p...
Page 187: Chapter 11:
179 chapter 11: index address setting, 51 adjustments and calibration, 173 advanced functions, 133 advanced paralle slave units, 149 advanced parallel operation, 148 advanced parallel, 146, 147 connection, 146 system identification, 149 air filter, 168 alarm ac fail, 35 alarms, 31 analog indication ...
Page 188
180 controls, 10 front, 10, 13 rear, 10, 16 parameter setting memory, 43 parts replacement and repairs, 174 periodic maintenance, 173 preload control, 143 programming remote resistor, 48 remote voltage, 47 programming remote analog, 46 protection delay, 35 foldback, 34 over temperature, 35 over volt...