- DL manuals
- Xirrus
- Wireless Access Point
- XR Series
- User Manual
Xirrus XR Series User Manual
Summary of XR Series
Page 1
August 11, 2015 release 7.5 wireless access point user’s guide.
Page 3: Wireless Access Points
All rights reserved. This document may not be reproduced or disclosed in whole or in part by any means without the written consent of xirrus, inc. Part number: 800-0022-001 (revision r) wireless access points xr and xd series.
Page 4
Trademarks is a registered trademark of xirrus, inc. All other trademarks and brand names are marks of their respective holders. Please see legal notices, warnings, compliance statements, and warranty and license agreements in “notices (xr-1000 to xr-6000 indoor models)” on page 563 . Xirrus, inc. 2...
Page 5: Table of Contents
Wireless access point i table of contents list of figures..................................................................................... Xv introduction ......................................................................................... 1 the xirrus family of products ......................
Page 6
Wireless access point ii applications enablement .............................................................................. 21 advanced feature sets .......................................................................................... 21 xirrus advanced rf performance manager (rpm) ...........
Page 7
Wireless access point iii power planning ............................................................................................... 55 power over ethernet ................................................................................ 55 security planning .........................................
Page 8
Wireless access point iv an overview .......................................................................................................... 86 structure of the wmi ............................................................................................. 87 user interface .......................
Page 9
Wireless access point v signal-to-noise ratio (snr) ........................................................................ 134 noise floor ..................................................................................................... 135 max by iap .............................................
Page 10
Wireless access point vi snmp .............................................................................................................. 197 dhcp server ................................................................................................. 200 proxy services .............................
Page 11
Wireless access point vii ssid management ........................................................................................ 276 ssid list (top of page) .......................................................................... 277 ssid limits and scheduling ......................................
Page 12
Wireless access point viii hotspot 2.0 ..................................................................................................... 366 understanding hotspot 2.0 .................................................................. 366 nai realms ..................................................
Page 13
Wireless access point ix network tools ........................................................................................ 422 progress bar and status frame ............................................................ 424 cli ........................................................................
Page 14
Wireless access point x interface .......................................................................................................... 470 load ................................................................................................................. 471 location ..........................
Page 15
Wireless access point xi configuring radio assurance mode (loopback tests) .......................... 507 appendices..................................................................................... 509 appendix a: quick reference guide ........................................... 511 factory defa...
Page 16
Wireless access point xii non-euclid location server ........................................................................ 531 upgrading the ap using the boot loader ....................................................... 533 sample output for the upgrade procedure: .................................
Page 17
Wireless access point xiii glossary of terms.......................................................................... 607 index................................................................................................ 619.
Page 18
Wireless access point xiv.
Page 19: List of Figures
Wireless access point list of figures xv list of figures figure 1. Xirrus ap ..................................................................................................... 1 figure 2. Wireless ap (xr series) ............................................................................ 4 figure...
Page 20
Wireless access point xvi list of figures figure 35. Network interfaces—xr-2000 series (left); xr-2005/2006 (right) .... 77 figure 36. Network interface ports—xr-4000 series ............................................ 78 figure 37. Network interface ports—xr-6000 series ...............................
Page 21
Wireless access point list of figures xvii figure 72. Controls for location map .................................................................... 130 figure 73. Station rssi values ................................................................................ 132 figure 74. Station rssi values ...
Page 22
Wireless access point xviii list of figures figure 109. Services..................................................................................................... 185 figure 110. Time settings (manual time)................................................................ 186 figure 111. Time setti...
Page 23
Wireless access point list of figures xix figure 146. Finding the domain name from active directory............................ 261 figure 147. Rogue control list ................................................................................. 263 figure 148. Oauth 2.0 management - token list ........
Page 24
Wireless access point xx list of figures figure 183. Dscp mappings...................................................................................... 379 figure 184. Roaming assist ....................................................................................... 381 figure 185. Wds ...........
Page 25
Wireless access point list of figures xxi figure 220. Disabling global iaps............................................................................ 500 figure 221. Enabling a specific iap.......................................................................... 501 figure 222. Disabling a specif...
Page 26
Wireless access point xxii list of figures.
Page 27: Introduction
Wireless access point introduction 1 introduction this chapter introduces the xirrus family of products, with an overview of its key features and benefits. “the xirrus family of products” on page 1 . “why choose the xirrus access point?” on page 3 . “wireless access point product overview” on page 4...
Page 28
Wireless access point 2 introduction xirrus management system (xms) xms is used for managing large wireless deployments from a centralized web-based interface. Xirrus offers xms-cloud—a software as a service option for xms, providing zero-touch provisioning and initial startup for new ap deployments...
Page 29
Wireless access point introduction 3 why choose the xirrus access point? The deployment of wireless is a necessity as businesses strive for greater flexibility in the workplace and the need for employee mobility rises. The user community is placing spiraling and often unanticipated demands on the wi...
Page 30
Wireless access point 4 introduction see also key features and benefits wireless access point product overview the xirrus family of products wireless access point product overview the wireless ap is a high capacity, multi-mode device designed with up to four times the coverage and eight times the ba...
Page 31
Wireless access point introduction 5 xr wireless ap product family xr-320 wall mounted 2-radio access points the xr-320 is a high performance gigabit wi-fi wall access point with integrated wired gigabit switch designed for in-room connectivity. This ap, built to support the latest 802.11ac wi-fi st...
Page 32
Wireless access point 6 introduction xr-500 series 2-radio access points these access points have one gigabit ethernet port and two multi-state radios (2.4ghz or 5ghz). They support 600mbps total, connecting up to 240 users at one time. The access point provides flexibility for delivering wireless s...
Page 33
Wireless access point introduction 7 xr-600 series 2-radio access points these access points provide robust wireless service in low-to-medium user density scenarios. They have two gigabit ethernet ports and two multi-state radios (2.4ghz or 5ghz), so that as more of your clients migrate to 802.11ac,...
Page 34
Wireless access point 8 introduction xr-1000 series 2-radio access points these aps include models with one gigabit ethernet port and two multi-state radios (2.4ghz or 5ghz) that can support 300mbps or 450mbps, connecting up to 480 users at one time. The xirrus xr-1000 series wireless ap is a two sl...
Page 35
Wireless access point introduction 9 xd4-130 4-radio high density access points these aps have two gigabit ethernet ports and four multi-state radios (2.4ghz or 5ghz) supporting 802.11ac and 802.11a/b/g/n. Each of the four 3x3 802.11ac radios supports 1.3gbps, connecting up to 780 users at one time ...
Page 36
Wireless access point 10 introduction xr-2006 series 2- and 4-radio high density access points these aps have two gigabit ethernet ports and two or four multi-state radios (2.4ghz or 5ghz) supporting 802.11ac and 802.11a/b/g/n. Each of the xr-2436’s four 3x3 802.11ac radios supports 1.3gbps, connect...
Page 37
Wireless access point introduction 11 xr-2005 series 2- and 4-radio access points these aps include models with one or two gigabit ethernet ports and two or four multi-state radios (2.4ghz or 5ghz) that can support 300mbps or 450mbps, connecting up to 960 users at one time. The xirrus xr-2005 series...
Page 38
Wireless access point 12 introduction xr-4006 series 4- to 8-radio high density access points these aps include models with two gigabit ethernet ports and four or eight multi-state radios (2.4ghz or 5ghz) supporting 802.11ac and 802.11a/b/g/n. Each of the xr-4836’s eight 3x3 802.11ac radios supports...
Page 39
Wireless access point introduction 13 xr-4000 series 4- to 8-radio high density access points (not ending in “6”) these aps include models with two gigabit ethernet ports and four or eight radios (iaps), connecting up to 1920 users at one time and offering a maximum wireless bandwidth of 3.6 gbps (u...
Page 40
Wireless access point 14 introduction xr-6000 series 8- to 16-radio high density access points these aps include models with four gigabit ethernet ports and up to sixteen radios, connecting up to 3840 users at one time and offering a maximum wireless bandwidth of 7.2 gbps (up to 450 mbps per radio)....
Page 41
Wireless access point introduction 15 feature sets , intrusion detection and prevention, site monitoring, and rf spectrum analysis are performed in the background by the ap automatically. Deployment flexibility xirrus’ unique multi-radio architecture (on all aps except the xr-500 series) generates 3...
Page 42
Wireless access point 16 introduction power over ethernet (poe) some smaller aps (xr-2000 models ending in “5” or “6”, and xr-500/600 series) are compatible with ieee802.3af and/or ieee802.3at poe+, and may be connected to appropriate powered switches. For example, the xirrus xt-5024 and xt-5048 are...
Page 43
Wireless access point introduction 17 configuration and control from a graphical console, plus a full complement of troubleshooting tools and statistics. Figure 5. Wmi: ap status in addition, a fully featured command line interface (cli) offers it professionals a familiar management and control envi...
Page 44
Wireless access point 18 introduction key features and benefits this section describes some of the key product features and the benefits you can expect when deploying the wireless ap (the xr-7630 product is used as an example in this section). High capacity and high performance figure 6. Layout of i...
Page 45
Wireless access point introduction 19 data rates in all directions. With a wireless ap deployed, far fewer access points are needed and wired-like resiliency is delivered throughout your wireless network. Your wireless ap deployment ensures: continuous connectivity if an iap (radio) fails. Continuou...
Page 46
Wireless access point 20 introduction 802.11a/b/g/n (monitor only) delivers 360° wireless coverage, with 2 dbi of gain. Non-overlapping channels complete use of non-overlapping channels limits interference and delivers maximum capacity. On the xr-7630, up to 16 non-overlapping channels are fully uti...
Page 47
Wireless access point introduction 21 applications enablement the wireless ap’s quality of service (qos) functionality combined with true switch capabilities enable high density video and voice over wireless lan deployments. Compliant with 802.1p and 802.1q standards. See also wireless access point ...
Page 48
Wireless access point 22 introduction with each of the ap’s multiple radios operating on a different channel, rpm selects the ideal radio for each station. High-speed stations are grouped together on radios with other high speed stations, while lower speed stations are combined with other lower spee...
Page 49
Wireless access point introduction 23 decryption into each ap, delivering line-rate encryption at the edge of the network instead of at a choke point within a centralized controller. The complete feature set of the rsm package includes: wireless ids/ips (intrusion detection/prevention system) wirele...
Page 50
Wireless access point 24 introduction packet analysis – integrated packet capture provides filterable views of all traffic traversing on the wired and wireless interfaces of the ap. Performance analysis – embedded traffic generation enables the throughput of the ap’s wireless or wired interfaces to ...
Page 51
Wireless access point introduction 25 about this user’s guide this user’s guide provides detailed information and procedures that will enable wireless network administrators to install, configure and manage the wireless ap so that end users can take full advantage of the product’s features and funct...
Page 52
Wireless access point 26 introduction firmware, uploading and downloading configurations and other files, using diagnostic tools, and resetting the ap to its factory defaults. The command line interface includes the commands and the command structure used by the wireless ap’s command line interface ...
Page 53
Wireless access point introduction 27 glossary of terms provides an explanation of terms directly related to xirrus product technology, organized alphabetically. Index the index is a valuable information search tool. Use the index to locate specific topics discussed in this user’s guide. Simply clic...
Page 54
Wireless access point 28 introduction.
Page 55: Installing The Wireless Ap
Wireless access point installing the wireless ap 29 installing the wireless ap the instructions for planning and completing a successful installation include the following topics: “installation prerequisites” on page 29 . “planning your installation” on page 32 . “installation workflow” on page 67 ....
Page 56
Wireless access point 30 installing the wireless ap depending on the model (see “xr wireless ap product family” on page 5 ). Secure shell (ssh) utility to establish secure remote command line access to the ap, you need a secure shell ( ssh ) utility, such as putty. The utility must be configured to ...
Page 57
Wireless access point installing the wireless ap 31 optional network components the following network components are optional. Xirrus management system (xms) the optional xms offers powerful management features for small or large wireless ap deployments. Client requirements the wireless ap should on...
Page 58
Wireless access point 32 installing the wireless ap planning your installation this section provides guidelines and examples to help you plan your xirrus wireless ap deployment to achieve the best overall coverage and performance. We recommend you conduct a site survey to determine the best location...
Page 59
Wireless access point installing the wireless ap 33 2. Be aware of the direct line between each device. For example, a wall that is 1.5 feet thick (half a meter) at 90° is actually almost 3 feet thick (or 1 meter) when viewed at a 45° angle. At an acute 2° degree angle the same wall is over 42 feet ...
Page 60
Wireless access point 34 installing the wireless ap coverage and capacity planning this section considers coverage and capacity for your deployment(s), including placement options, rf patterns and cell sizes, area calculations, roaming considerations, and channel allocations. Placement use the follo...
Page 61
Wireless access point installing the wireless ap 35 rf patterns the wireless ap allows you to control — automatically or manually — the pattern of wireless coverage that best suits your deployment needs. You can choose to operate with full coverage, half coverage, or custom coverage (by enabling or ...
Page 62
Wireless access point 36 installing the wireless ap custom coverage where there are highly reflective objects in proximity to the ap, you can turn off specific radios to avoid interference and feedback. Figure 12. Custom coverage capacity and cell sizes cell sizes should be estimated based on the nu...
Page 63
Wireless access point installing the wireless ap 37 fine tuning cell sizes adjusting the transmit power allows you to fine tune cell sizes. There are four standard sizes — small, medium, large, or max (the default is max). There is also an auto setting that automatically determines the best cell siz...
Page 64
Wireless access point 38 installing the wireless ap cell sizes are to be adjusted so that they are contained in each room. The goal is for stations to associate to the ap located in the same room with them. Figure 15. Auto cell size options multichannel auto cell is configured by turning off auto ce...
Page 65
Wireless access point installing the wireless ap 39 roaming considerations cells should overlap approximately 10 - 15% to accommodate client roaming. Figure 16. Overlapping cells allocating channels because the wireless ap is a multi-channel device, allocating the best channels to radios is importan...
Page 66
Wireless access point 40 installing the wireless ap allows the ap to come up for the first time and not interfere with existing equipment that may be already running, thereby limiting co-channel interference. More accurately tunes the rf characteristics of a wireless installation than manual configu...
Page 67
Wireless access point installing the wireless ap 41 other factors affecting throughput throughput of the ap can be affected by many factors such as distance, number of stations, obstacles, construction materials used at the site, etc. In addition, features applied to traffic may have an effect. Perf...
Page 68
Wireless access point 42 installing the wireless ap about ieee 802.11ac 802.11ac is a continuation of the ieee 802.11 standard. It multiplies the maximum data rate—eventually, up to ten times the 802.11n maximum. Along with increased data rates, it offers simultaneous transmission to multiple client...
Page 69
Wireless access point installing the wireless ap 43 “mu-mimo (multi-user multiple-in multiple-out)” on page 45 “higher precision in the physical layer” on page 47 “80 mhz and 160 mhz channel widths (bonding)” on page 48 “802.11ac data rates” on page 49 “acexpress™” on page 50 it is important to cons...
Page 70
Wireless access point 44 installing the wireless ap up to eight simultaneous data streams — spatial multiplexing spatial multiplexing transmits completely separate data streams on different antennas (in the same channel) that are recombined to produce new 802.11ac data rates. Previously used for 802...
Page 71
Wireless access point installing the wireless ap 45 802.11a/b/g radios, and degraded performance. In 802.11n and 802.11ac, these signals are used to enhance performance. Figure 19. Mimo signal processing 802.11ac increases the number of antennas and spatial streams from a maximum of four in 802.11n ...
Page 72
Wireless access point 46 installing the wireless ap one is directed to a mobile phone. When a transmission is complete, the antennas are reallocated. Figure 20. Mu-mimo with four antennas the table below illustrates how data streams might be allocated to multiple users on an 802.11ac transmitter wit...
Page 73
Wireless access point installing the wireless ap 47 higher precision in the physical layer wi-fi utilizes several digital modulation techniques and automatically switches between them to optimize for throughput or range. The basic unit of data transmitted is called a symbol. The number of points in ...
Page 74
Wireless access point 48 installing the wireless ap the higher the mcs value, the higher the data rate, as shown in the tablebelow. Xirrus aps support mcs7 -mcs9. Higher mcs levels require higher signal-to- noise ratios (i.E., a less noisy environment) and shorter transmission distances. 80 mhz and ...
Page 75
Wireless access point installing the wireless ap 49 be used: as eight 20 mhz channels; four 40 mhz channels; two 80 mhz channels; or one 160 mhz channel. Xirrus currently supports channels up to 80 mhz wide. Figure 22. Channel bonding (channels 36-64 shown) 802.11ac data rates figure 23. Maximum 802...
Page 76
Wireless access point 50 installing the wireless ap ieee 802.11ac data rates are dependent on the number of spatial streams obtained through the use of mu-mimo, 80 vs. 160mhz channel widths, the number of transmit antennas, and the type of modulation. Figure 23 shows the maximum data rate achievable...
Page 77
Wireless access point installing the wireless ap 51 data rates less than 100mbps as the effective bandwidth is shared among all devices connecting to a given radio. Migration to 802.11ac will take time. Older wi-fi technologies will continue to be with us for years. In order for 802.11ac to provide ...
Page 78
Wireless access point 52 installing the wireless ap when you add iaps to an ap or replace 802.11n iaps with 802.11ac modules, the access point determines its model number based on the count and types of radios. For example, if you add four 1300 mbps (3x3 mimo) iaps to an xr-4420, the ap will display...
Page 79
Wireless access point installing the wireless ap 53 in addition, the ap has full failover protection between the bonded-pair gigabit ports (see following table). The wireless ap gigabit ethernet ports actually support a number of modes: 802.3ad link aggregation load balancing broadcast link backup m...
Page 80
Wireless access point 54 installing the wireless ap switch failover protection to ensure that service is continued in the event of a switch failure, you can connect aps having multiple gigabit ports to more than one ethernet switch (not a hub). Figure 25. Switch failover protection see also coverage...
Page 81
Wireless access point installing the wireless ap 55 power planning all ap models support power over ethernet (poe) with an integrated splitter. Power over ethernet to deliver power to the ap, you must use xirrus-supplied power over ethernet (poe) modules or powered switches that are compatible with ...
Page 82
Wireless access point 56 installing the wireless ap security planning this section offers some useful guidelines for defining your preferred encryption and authentication method. For additional information, see “understanding security” on page 225 and the security section of “frequently asked questi...
Page 83
Wireless access point installing the wireless ap 57 pre-shared key uses a pass-phrase or key that is manually distributed to all authorized users. The same passphrase is given to client devices and entered into each ap. Mac access control lists (acls) mac access control lists provide a list of clien...
Page 84
Wireless access point 58 installing the wireless ap port requirements a number of ports are used by various ap features and by the xirrus management system (xms). The port requirements table on page 59 lists ports and the features that require them (xms port requirements are included in the table fo...
Page 85
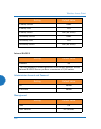
Wireless access point installing the wireless ap 59 the following table lists port requirements for the ap and for xms, how the ports are used, and whether they may be changed . Port application peer configurable ap icmp ping xms server no 20 tcp 21 tcp ftp client yes 22 tcp ssh client yes 23 tcp te...
Page 86
Wireless access point 60 installing the wireless ap xms icmp ping aps no 22 tcp ssh aps yes 25 tcp smtp mail server yes 123 udp ntp ntp server no 161 udp snmp aps no 162 udp snmp traphost 1 aps via xms config file 443 tcp https aps no 514 udp resident syslog server internal* via xms config file 1099...
Page 87
Wireless access point installing the wireless ap 61 see also management control external radius services vlan management.
Page 88
Wireless access point 62 installing the wireless ap network management planning network management can be performed using any of the following methods: centralized web-based management, using the optional xirrus management system (xms). Xms-cloud provides zero-touch provisioning and ongoing manageme...
Page 89
Wireless access point installing the wireless ap 63 wds planning wds (wireless distribution system) creates wireless backhaul connections between aps, allowing your wireless network to be expanded using multiple aps without the need for a wired backbone to link them (see figure 27 ). Wds features in...
Page 90
Wireless access point 64 installing the wireless ap figure 28. A multiple hop wds connection multiple wds links can provide link redundancy (failover capability - see figure 29 ). A network protocol (spanning tree protocol — stp) prevents aps from forming network loops. Figure 29. Wds failover prote...
Page 91
Wireless access point installing the wireless ap 65 wds links have a host/client relationship similar to the usual iap/station pattern for aps: a wds client link associates/authenticates to a host (target) ap in the same way that stations associate to iaps. The client side of the link must be config...
Page 92
Wireless access point 66 installing the wireless ap common deployment options the following table lists some typical and recommended deployment options for a number of the features that have been discussed in this chapter. See also coverage and capacity planning network management planning planning ...
Page 93
Wireless access point installing the wireless ap 67 installation workflow this workflow illustrates the steps that are required to install and configure the ap successfully. Review this flowchart before attempting to install the unit on a customer’s network. Cloud xms customers will skip the last tw...
Page 94
Wireless access point 68 installing the wireless ap failover planning installation prerequisites planning your installation power planning wireless access point product overview security planning.
Page 95
Wireless access point installing the wireless ap 69 installing your wireless ap this section provides information about the physical installation of your xirrus wireless ap. For complete instructions, please see the installation guide for your model of ap or access point. Choosing a location based o...
Page 96
Wireless access point 70 installing the wireless ap once you have determined the best location for your wireless ap, you must run cables to the location for the following services: power no separate power cable is required to the ap—xirrus wireless aps use poe (power over ethernet). See the installa...
Page 97
Wireless access point installing the wireless ap 71 important note about network connections see also failover planning installation prerequisites installation workflow mounting and connecting the ap power over ethernet (poe) ! The ap’s ethernet ports should be plugged into an ethernet switch, not a...
Page 98
Wireless access point 72 installing the wireless ap mounting and connecting the ap a detailed installation guide is available at support.Xirrus.Com that describes mounting your ap. Please follow the provided instructions carefully. Data and power connections to the ap are also detailed in the instal...
Page 99
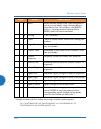
Wireless access point installing the wireless ap 73 ap led operating sequences use the following tables to review the operating sequences of the ap’s leds. “led boot sequence” on page 73 “led operation when ap is running” on page 74 led boot sequence the normal boot led sequence is as follows: ap ac...
Page 100
Wireless access point 74 installing the wireless ap led operation when ap is running the normal led operation when the ap is running is shown in the table below. Note that behavior may be modified using “led settings” on page 378 or via the cli . Led status reason iap led is off iap is down iap led ...
Page 101
Wireless access point installing the wireless ap 75 see also installation prerequisites installation workflow installing your wireless ap led settings zero-touch provisioning and ongoing management most customers employ the xirrus management system (xms) for the initial setup and continuing manageme...
Page 102
Wireless access point 76 installing the wireless ap if you are not using xms new devices can be auto-provisioned upon initial deployment via the xirrus mobilize platform (pre-order required) as shown in this video: www.Xirrus.Com/ tv/training/mobilize-training . Your welcome email will contain login...
Page 103
Wireless access point installing the wireless ap 77 ap management interfaces user interfaces with zero-touch setup provided by xms and mobilize, your xirrus network is ready for use a few minutes after deployment. We recommend that you use the xms for ongoing monitoring and fine-tuning of the networ...
Page 104
Wireless access point 78 installing the wireless ap figure 36. Network interface ports—xr-4000 series figure 37. Network interface ports—xr-6000 series using the serial port if using the serial port to make your connection, use serial settings of 8 bits, no parity, no flow control, 1 stop bit (8n1) ...
Page 105
Wireless access point installing the wireless ap 79 using the ethernet ports to access the ap by default, the ap's ethernet interfaces use dhcp to obtain an ip address. If the ap is booted and does not receive dhcp addresses on gigabit ethernet ports, then both gigabit1 and its bonded pair port (if ...
Page 106
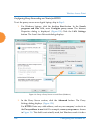
Wireless access point 80 installing the wireless ap starting the wmi use this procedure to log in to the wmi on a web browser. 1. Establish a network connection and open your web browser. 2. Connect to the wireless ap using its host name or ip address as described in the previous section. Http:// lo...
Page 107
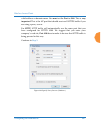
Wireless access point installing the wireless ap 81 if you need to enter the license manually, use the following procedure. It describes entering the license key using the wmi. If you are using the xms, you may use it to manage and upgrade large numbers of licenses for the wireless network. 1. This ...
Page 108
Wireless access point 82 installing the wireless ap securing low level access to the ap most local management of the xirrus ap is done via the wmi or cli—see “the command line interface” on page 433 . The ap also has a lower level interface: xbl(xirrus boot loader), which allows access to more primi...
Page 109
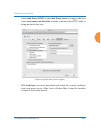
Wireless access point installing the wireless ap 83 on all other ap models (those with a console port), xircon access to both xbl and cli is disabled by default. If xircon is not going to be used to access an ap, we recommend leaving xircon access disabled. Procedure for securing low level ap access...
Page 110
Wireless access point 84 installing the wireless ap 4. If xircon access at the xbl level is to be allowed, use the following three commands to change the xbl username and password from the default values of admin/admin. In the example below, replace newusername and newpassword with your desired entr...
Page 111: The Web Management Interface
Wireless access point the web management interface 85 the web management interface this topic provides an overview of the xirrus wireless ap’s embedded web management interface (wmi), used for establishing your network’s configuration settings and wireless operating parameters. It also includes logi...
Page 112
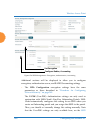
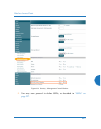
Wireless access point 86 the web management interface an overview the wmi is an easy-to-use graphical interface to your wireless ap. It allows you to configure the product to suit your individual requirements and ensure that the unit functions efficiently and effectively. Figure 38. Web management i...
Page 113
Wireless access point the web management interface 87 structure of the wmi the content of the wmi is organized by function and hierarchy, shown in the following table. Click on any item below to jump to the referenced destination. Status windows access point status windows access point summary acces...
Page 114
Wireless access point 88 the web management interface configuration windows express setup network interfaces bonds and bridging dns settings cisco discovery protocol (cdp) settings services time settings (ntp) netflow wi-fi tag location system log snmp dhcp server proxy services vlans vlan managemen...
Page 115
Wireless access point the web management interface 89 user interface figure 39. Wmi: frames the wmi has been designed with simplicity in mind, making navigation quick and easy. In the following example, you’ll see that windows are divided into left and right frames. ( figure 39 ) the left frame cont...
Page 116
Wireless access point 90 the web management interface showing a summary of its current configuration, as well as to show links for all of its associated wmi pages. Three log messages counters are located at the bottom of the menu. They provide a running total of messages generated by the arrayos sys...
Page 117
Wireless access point the web management interface 91 the command log shows the resulting commands for requests made through the wmi. Figure 41. Wmi command log utility buttons are located at the bottom right of each window — a feedback button, a print button and a help button. Figure 42. Wmi: utili...
Page 118
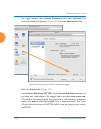
Wireless access point 92 the web management interface note that wmi provides an option that allows you to change its behavior. You may change: refresh interval — the refresh interval, if automatic refresh is selected. See “options” on page 431 for more information. Logging in use this procedure to l...
Page 119
Wireless access point the web management interface 93 applying configuration changes in most of the wmi configuration windows, your changes to settings are applied to the ap as you make them. In most cases, there is no separate apply button to click to make the changes take effect. There are a few e...
Page 120
Wireless access point 94 the web management interface.
Page 121
Wireless access point viewing status on the wireless ap 95 viewing status on the wireless ap these windows provide status information and statistics for your ap using the product’s embedded web management interface (wmi). You cannot make configuration changes to your ap from these windows. The follo...
Page 122
Wireless access point 96 viewing status on the wireless ap access point status windows the following ap status windows are available: access point summary — displays information on the configuration of all ap interfaces, including iaps. Access point information — provides version/serial number infor...
Page 123
Wireless access point viewing status on the wireless ap 97 content of the access point summary window the access point summary window is sub-divided into the ethernet interfaces section and the integrated access point(radio) section, providing you with the following information: ethernet settings su...
Page 124
Wireless access point 98 viewing status on the wireless ap bond settings summary this section provides information about the relationship that has been selected for the gigabit ports. For detailed explanations and to make configuration changes, see “bonds and bridging” on page 173 . • bond : lists a...
Page 125
Wireless access point viewing status on the wireless ap 99 figure 45. Disabled iap (partial view) • channel : shows which channel each iap is using, and the channel setting. To avoid co-channel interference, adjacent radios should not be using adjacent channels. To make channel selections for a spec...
Page 126
Wireless access point 100 viewing status on the wireless ap • rx threshold : shows the receive threshold for each iap. • stations : informs you how many client stations are currently associated with each iap. • wds link/distance : the wds link on this radio (if any), and whether the link has been se...
Page 127
Wireless access point viewing status on the wireless ap 101 notice that the compass heading field will only show a value if the ap model is one that includes a built-in compass. In order for this reading to be correct, the ap must be mounted with iap1 facing north. If the ap does not have an integra...
Page 128
Wireless access point 102 viewing status on the wireless ap access point information this is a status only window that shows you the current firmware versions utilized by the ap, serial numbers assigned to each module, mac addresses, licensing information, and recent boot timestamps. It will also sh...
Page 129
Wireless access point viewing status on the wireless ap 103 access point configuration this is a status only window that allows you to display the configuration settings assigned to the ap, based on the following filter options: running — displays the current configuration (the one running now). Sav...
Page 130
Wireless access point 104 viewing status on the wireless ap admin history it is useful to know who else is currently logged in to an ap while you're configuring it, or who has logged in since the ap booted. This status-only window shows you all administrator logins to the ap that have occurred since...
Page 131
Wireless access point viewing status on the wireless ap 105 network assurance — shows results of connectivity tests for network servers. Undefined vlans — shows vlans present on an 802.1q connection to the ap, that are not configured in the ap's vlan list. Network this window provides a snapshot of ...
Page 132
Wireless access point 106 viewing status on the wireless ap network map this window offers detailed information about this ap and all neighboring aps, including how the aps have been set up within your network. Figure 52. Network map the network map has a number of options at the top of the page tha...
Page 133
Wireless access point viewing status on the wireless ap 107 (iap) up : informs you how many iaps are currently up and running. To enable or disable all iaps, go to “express setup” on page 163 . To enable or disable individual iaps, go to “iap settings” on page 312 . Ssid : informs you how many ssids...
Page 134
Wireless access point 108 viewing status on the wireless ap scd firmware : the software version number of the scd firmware on each ap. Iap info (enabled by default) enable/disable display of the iap/up columns. Stations stations : tells you how many stations are currently associated to each ap. To d...
Page 135
Wireless access point viewing status on the wireless ap 109 spanning tree status multiple active paths between stations can cause loops in the network. If a loop exists in the network topology, the potential exists for the duplication of messages. The spanning tree protocol is a link management prot...
Page 136
Wireless access point 110 viewing status on the wireless ap routing table this status-only window lists the entries in the ap’s routing table. The table provides the ap with instructions for sending each packet to its next hop on its route across the network. Figure 54. Routing table see also vlans ...
Page 137
Wireless access point viewing status on the wireless ap 111 dhcp leases this status-only window lists the ip addresses (leases) that the ap has allocated to client stations. For each, it shows the ip address assigned from one of the defined dhcp pools, and the mac address and host name of the client...
Page 138
Wireless access point 112 viewing status on the wireless ap you may sort the rows based on any column that has an active column header, indicated when the mouse pointer changes to the hand icon . Click refresh to update the information at any time. Click auto refresh to instruct the ap to refresh th...
Page 139
Wireless access point viewing status on the wireless ap 113 lldp list this status-only window lists devices on the ap’s network that support the link layer discovery protocol (lldp). Figure 59. Lldp list the ap performs discovery on the network on an ongoing basis. This list shows the devices that h...
Page 140
Wireless access point 114 viewing status on the wireless ap network assurance must be enabled on the ap in order to perform these connectivity tests and display this information. See “management control” on page 237 . See also management control undefined vlans this status-only window lists vlans th...
Page 141
Wireless access point viewing status on the wireless ap 115 rf monitor windows every wireless ap includes an integrated rf spectrum analyzer as a standard feature. The spectrum analyzer allows you to characterize the rf environment by monitoring throughput, signal, noise, errors, and interference le...
Page 142
Wireless access point 116 viewing status on the wireless ap iap monitoring the rf monitor — iap monitoring window displays traffic statistics and rf readings observed by each ap iap (radio). Note that the data is an instantaneous snapshot for the iap — it is not an average or a cumulative total. To ...
Page 143
Wireless access point viewing status on the wireless ap 117 spectrum analyzer spectrum analysis on wireless aps is a distributed capability that automatically covers the entire wireless network, since a sensor is present in every unit. Aps monitor the network 24/7 and analyze interference anywhere i...
Page 144
Wireless access point 118 viewing status on the wireless ap figure 64. Rf spectrum analyzer the spectrum analyzer offers several display options: to display horizontal bar graphs, click the rotate checkbox at the bottom of the data window. In the rotated view, if you wish to view data as a numerical...
Page 145
Wireless access point viewing status on the wireless ap 119 at the bottom left of the frame, you may select whether to display only 2.4 ghz channels, 5 ghz channels, or both (the default is both). Note that the data is an instantaneous snapshot — it is not an average or a cumulative total. Spectrum ...
Page 146
Wireless access point 120 viewing status on the wireless ap no data rate information was available for the interval. A higher date rate (above 6 mbps) typically indicates user data traffic on the channel. Otherwise, the data rate reflects control packets at the lower basic rates. Rogues this window ...
Page 147
Wireless access point viewing status on the wireless ap 121 you can refresh the list at any time by clicking on the refresh button, or click in the auto refresh check box to instruct the ap to refresh the list automatically. See also network map rogue control list ssids ssid management.
Page 148
Wireless access point 122 viewing status on the wireless ap channel history the rf monitor — channel history window focuses on traffic statistics and rf readings observed for just one channel that you select in the channel field. A new set of readings is added every 10 seconds for a 5 ghz channel, o...
Page 149
Wireless access point viewing status on the wireless ap 123 figure 67. Rf monitor — channel history (rotated) if you select rotate and text together, data is presented as a numerical table. ( figure 68 ) click pause to stop collecting data, or resume to continue. Figure 68. Rf monitor — channel hist...
Page 150
Wireless access point 124 viewing status on the wireless ap radio assurance when radio assurance mode is enabled, the monitor radio performs loopback tests on the ap’s radios. When problems are encountered, the ap can take various actions to correct them by performing different levels of reset on th...
Page 151
Wireless access point viewing status on the wireless ap 125 see also iaps xirrus advanced rf analysis manager (ram) rf resilience radio assurance.
Page 152
Wireless access point 126 viewing status on the wireless ap station status windows the following station status windows are available: stations — this list describes all stations associated to the ap. Location map — displays a map showing the approximate locations of all stations associated to the a...
Page 153
Wireless access point viewing status on the wireless ap 127 stations this window shows client stations currently visible to the ap. You may choose to view only stations that have associated to the ap, or include stations that are unassociated by selecting the appropriate buttons above the list. The ...
Page 154
Wireless access point 128 viewing status on the wireless ap you may sort the rows based on any column that has an active column header. Click again to reverse the sort order. You may select one or more specific stations and perform one of the following actions by clicking the associated button: deny...
Page 155
Wireless access point viewing status on the wireless ap 129 location map the location map shows the approximate locations of stations relative to this ap. The location of each station is computed based on the rssi of its signal as received by the ap. The distance is adjusted based on the environment...
Page 156
Wireless access point 130 viewing status on the wireless ap completely obscure another. You may minimize a station that is not of interest by clicking it. There is also a minimize all button. You may replace the range-finder background image above with your own custom image of the floor plan of the ...
Page 157
Wireless access point viewing status on the wireless ap 131 display associated/unassociated : select whether to display stations that are associated to the ap, stations that are not associated, or both. Display 2.4 ghz/5 ghz : select whether to display 802.11bgn stations, or 802.11an stations, or bo...
Page 158
Wireless access point 132 viewing status on the wireless ap construction), or indoor dense (many walls or obstructions, or unusually dense walls). Scale : this view-only value shows the approximate distance represented by each hash mark on the default map background. Associated , unassociated, total...
Page 159
Wireless access point viewing status on the wireless ap 133 is shown on a representation of the ap, either colorized or numerically based on your selection. ( figure 74 ) the stations are listed to the left of the ap — click on a station to show its rssi values on the ap. Figure 74. Station rssi val...
Page 160
Wireless access point 134 viewing status on the wireless ap signal-to-noise ratio (snr) for each station that is associated to the ap, the signal-to-noise ratio (snr) window shows the station’s snr value as measured by each iap. In other words, the window shows the snr of the station’s signal at eac...
Page 161
Wireless access point viewing status on the wireless ap 135 the hand icon . Click on the refresh button to refresh the station list, or click in the auto refresh check box to instruct the ap to refresh this window automatically. See also station status windows rf monitor windows noise floor for each...
Page 162
Wireless access point 136 viewing status on the wireless ap figure 78. Station noise floor values — colorized graphical view in either graphical or tabular view, you may sort the rows based on any column that has an active column header, indicated when the mouse pointer changes to the hand icon . Cl...
Page 163
Wireless access point viewing status on the wireless ap 137 max by iap this status-only window shows the maximum number of client stations that have historically been associated to the ap. For each iap, the list shows the iap’s state and channel number, the current number of stations associated, and...
Page 164
Wireless access point 138 viewing status on the wireless ap station assurance station assurance monitors the quality of the connections that users are experiencing on the wireless network. This window shows client stations that have had connectivity issues. You may enable or disable the station assu...
Page 165
Wireless access point viewing status on the wireless ap 139 statistics windows the following ap statistics windows are available: iap statistics summary — provides an overview of the statistical data associated with all iaps. Expands to show links for displaying detailed statistics for individual ia...
Page 166
Wireless access point 140 viewing status on the wireless ap clicking on the appropriate button. You can also click in the auto refresh check box to instruct the ap to refresh this window automatically. See also system log window global settings global settings .11an global settings .11bgn iaps per-i...
Page 167
Wireless access point viewing status on the wireless ap 141 figure 82. Individual iap statistics page you can refresh the data (update the window with the latest information) or clear the data (reset all content to zero and begin counting again) at any time by clicking on the appropriate button. You...
Page 168
Wireless access point 142 viewing status on the wireless ap network statistics this is a status only window that allows you to review statistical data associated with each network (ethernet) interface and its activity. You can refresh the data (update the window with the latest information) or clear...
Page 169
Wireless access point viewing status on the wireless ap 143 vlan statistics this is a status only window that allows you to review statistical data associated with your assigned vlans. You can refresh the information that is displayed on this page at any time by clicking on the refresh button, or se...
Page 170
Wireless access point 144 viewing status on the wireless ap wds statistics the main wds statistics window provides statistical data for all wds client and host links. To access data about a specific wds client or host link, simply click on the desired link in the left frame to access the appropriate...
Page 171
Wireless access point viewing status on the wireless ap 145 ids statistics the xirrus ap employs a number of ids/ips (intrusion detection system/ intrusion prevention system) strategies to detect and prevent malicious attacks on the wireless network. This status-only window provides detailed intrusi...
Page 172
Wireless access point 146 viewing status on the wireless ap contains 1 will show entries for iap1, iap10, iap11, and iap12. Click the reset button to return to showing all entries. Figure 87. Filtered ids statistics many of the column headers may be clicked to sort the entries in ascending or descen...
Page 173
Wireless access point viewing status on the wireless ap 147 filter statistics the filter statistics window provides statistical data for all configured filters. The name, state (enabled — on or off), and type (allow or deny) of each filter is shown. For enabled filters, this window shows the number ...
Page 174
Wireless access point 148 viewing status on the wireless ap click on a column header to sort the rows based on that column. You can refresh the data (update the window with the latest information) at any time by clicking the refresh button . You can also click in the auto refresh check box to instru...
Page 175
Wireless access point viewing status on the wireless ap 149 per-station statistics this window provides detailed statistics for the selected station. This window is accessed from the station statistics window — click the mac address of the desired entry in the station column to display its per-stati...
Page 176
Wireless access point 150 viewing status on the wireless ap application control windows the application control feature provides real-time visibility of application usage by users across the wireless network. Network usage has changed enormously in the last few years, with the increase in smart phon...
Page 177
Wireless access point viewing status on the wireless ap 151 application control can track application usage over time to monitor trends. Usage may be tracked by ap, vlan, or station. Many hundreds of applications are recognized and grouped into a number of categories. The distributed architecture of...
Page 178
Wireless access point 152 viewing status on the wireless ap application control this display-only window provides a snapshot of the application usage on your ap. In order to view the application control window, the ap must have a license that supports this feature, and you must have enabled the appl...
Page 179
Wireless access point viewing status on the wireless ap 153 the application control window has three sections: selection criteria allow you to choose the type of data to show, and to filter for a single vlan or station. Pie charts present a color coded at-a-glance view of the top ten applications be...
Page 180
Wireless access point 154 viewing status on the wireless ap by category : check this box if you wish to analyze and list traffic by the types of applications in use, such as games or collaboration. Auto refresh instructs the ap to periodically refresh this window automatically. Use the refresh butto...
Page 181
Wireless access point viewing status on the wireless ap 155 traffic tables figure 93. Application control (station traffic) these tables provide detailed information about how your wireless bandwidth is being used. There are tables for station traffic and/or ap management traffic, depending on which...
Page 182
Wireless access point 156 viewing status on the wireless ap when you find risky or unproductive applications consuming bandwidth on the network, you can easily create filters to control them. See “filter management” on page 393 . You may use filters to: block problematic traffic, such as bittorrent ...
Page 183
Wireless access point viewing status on the wireless ap 157 system log window this is a status only window that allows you to review the system log, where system alerts and messages are displayed. Although there are no configuration options available in this window, you do have the usual choice of d...
Page 184
Wireless access point 158 viewing status on the wireless ap ids event log window this status only window displays the intrusion detection system (ids) event log, listing any detected attacks on your network. For descriptions of the types of attacks detected, as well as the settings to fine-tune ids ...
Page 185
Wireless access point viewing status on the wireless ap 159 period — the length of the window used to determine whether the count of this type of event exceeded the threshold. Current — the count of this type of event for the current period. Average — the average count per period of this type of eve...
Page 186
Wireless access point 160 viewing status on the wireless ap.
Page 187: Configuring The Wireless Ap
Wireless access point configuring the wireless ap 161 configuring the wireless ap the following topics include procedures for configuring the ap using the product’s embedded web management interface (wmi). Procedures have been organized into functional areas that reflect the flow and content of the ...
Page 188
Wireless access point 162 configuring the wireless ap this chapter only covers using the configuration windows on the ap. To view status or use system tools on the ap, please see: “viewing status on the wireless ap” on page 95 “using tools on the wireless ap” on page 409 if you have added modular ia...
Page 189
Wireless access point configuring the wireless ap 163 express setup initial ap configuration via xms sets items such as ssids and security, as described in “zero-touch provisioning and ongoing management” on page 75 . This page allows you to see many of these values, or change them locally. Figure 9...
Page 190
Wireless access point 164 configuring the wireless ap when finished, click the save button if you wish to make your changes permanent. Procedure for performing an express setup 1. License key : an unlicensed ap will automatically contact xirrus to obtain its license, if it has internet connectivity....
Page 191
Wireless access point configuring the wireless ap 165 c. Ip settings : if you choose the static ip addressing option, enter the following: • address : enter a valid ip address for this ap. To use a remote connection (web, snmp , or ssh ), a valid ip address must be used. • subnet mask : enter a vali...
Page 192
Wireless access point 166 configuring the wireless ap • wep (wired equivalent privacy) — an optional ieee 802.11 function that offers frame transmission privacy similar to a wired network. Wep generates secret shared encryption keys that both source and destination stations can use to alter frame bi...
Page 193
Wireless access point configuring the wireless ap 167 5. Admin settings: this section allows you to change the default admin username, password, and privileges for the ap. You may change the password and leave the user name as is, but we suggest that you change both to improve ap security. A. New ad...
Page 194
Wireless access point 168 configuring the wireless ap to your deployment, select it and click apply. For example, the high- density option uses best practices to configure the ap for high density settings such as lecture halls, convention centers, stadiums, etc. 8. Iap settings: figure 98. Leds are ...
Page 195
Wireless access point configuring the wireless ap 169 network this is a status-only window that provides a snapshot of the configuration settings currently established for the ethernet interfaces. Dns settings and other settings are summarized as well. You must go to the appropriate configuration wi...
Page 196
Wireless access point 170 configuring the wireless ap network status windows spanning tree status network statistics interfaces xr-500, xr-1000, and some xr-2000 series aps have one gigabit ethernet interface, while xr- 600, xr-4000 and some xr-2000 series aps have two, and xr-6000 series models hav...
Page 197
Wireless access point configuring the wireless ap 171 network interface ports for the location of network interface ports on an ap, see the illustrations in “user interfaces” on page 77 . Procedure for configuring the network interfaces configure the gigabit network interfaces. The fields for each o...
Page 198
Wireless access point 172 configuring the wireless ap negotiate feature is disabled, you can manually choose half or full duplex for your data transmission preference. B. Mtu : the maximum transmission unit size. This is the largest packet size (in bytes) that the interface can pass along. C. Speed ...
Page 199
Wireless access point configuring the wireless ap 173 dns settings network network statistics spanning tree status bonds and bridging on models with more than one gigabit port these ports may be bonded, i.E. Configured to work together in sets. For example, one port may provide active backup or load...
Page 200
Wireless access point 174 configuring the wireless ap of duplicating one bond’s traffic to another bond is very useful for troubleshooting with a network analyzer. Procedure for configuring network bonds configure the bonding behavior of the gigabit network interfaces. The fields for each of these b...
Page 201
Wireless access point configuring the wireless ap 175 traffic received on gigx is transmitted by gigy; similarly, traffic received on gigy is transmitted by gigx. The ap acts as a wired bridge—this allows aps to be chained and still maintain wired connectivity. When bridging is enabled, it configure...
Page 202
Wireless access point 176 configuring the wireless ap may be bonded. You may also include just one single port in a bond—this is useful for mirroring one gigabit port to another port ( step c on page 178 ). In aps that have four gigabit ports, you have the option of bonding three or four ports toget...
Page 203
Wireless access point configuring the wireless ap 177 b. Aggregate traffic from gig ports using 802.3ad — the ap sends network traffic across all member gigabit ports to increase link speed to the network. These ports act as a single logical interface, using a load balancing algorithm to balance tra...
Page 204
Wireless access point 178 configuring the wireless ap d. Load balance traffic between gig ports — this option provides trunking, similar to option (b) — aggregate traffic from gig1 & gig2 using 802.3ad , but it does not use 802.3ad and it uses a different load balancing algorithm to determine the ou...
Page 205
Wireless access point configuring the wireless ap 179 on bondx is passed on to the onboard processor as well as out bondy. All traffic received on bondy is passed on to the onboard processor as well as out bondx. This allows a network analyzer to be plugged into bondy to capture traffic for troubles...
Page 206
Wireless access point 180 configuring the wireless ap dns settings this window allows you to establish your dns (domain name system) settings. The ap uses these dns servers to resolve host names into ip addresses. The ap also registers its own host name with these dns servers, so that others may add...
Page 207
Wireless access point configuring the wireless ap 181 server that assigns an ip address to the ap, rather than using the dns server fields above. You may also configure that dhcp server to assign a host name to the ap. 6. Click the save button if you wish to make your changes permanent. See also dhc...
Page 208
Wireless access point 182 configuring the wireless ap 2. Cdp interval : the ap sends out cdp announcements advertising its presence at this interval. The default is 60 seconds. 3. Cdp hold time : cdp information received from neighbors is retained for this period of time before aging out of the ap’s...
Page 209
Wireless access point configuring the wireless ap 183 procedure for configuring lldp settings 1. Enable lldp: when lldp is enabled, the ap sends out lldp announcements of the ap’s presence, and gathers lldp data sent by neighbors. When disabled, it does neither. Lldp is disabled by default. 2. Lldp ...
Page 210
Wireless access point 184 configuring the wireless ap xr-2225/2226 (two 2x2 radios) = 22.5w xr-2235/2236 (two 3x3 radios) = 26.1w xr-2425/2426 (four 2x2 radios) = 30w note that request power is not available on the xr-2435/2436. Additionally, it is not available on certain other aps, including t...
Page 211
Wireless access point configuring the wireless ap 185 services this is a status-only window that allows you to review the current settings and status for services on the ap, including dhcp, snmp, syslog, and network time protocol (ntp) services. For example, for the dhcp server, it shows each dhcp p...
Page 212
Wireless access point 186 configuring the wireless ap “system log” on page 193 “snmp” on page 197 “dhcp server” on page 200 “proxy services” on page 202 time settings (ntp) this window allows you to manage the ap’s time settings, including synchronizing the ap’s clock with a universal clock from an ...
Page 213
Wireless access point configuring the wireless ap 187 3. Auto adjust daylight savings : check this box to have the system adjust for daylight savings automatically, else leave it unchecked (default). 4. Use network time protocol: select whether to set time manually or use ntp to manage system time. ...
Page 214
Wireless access point 188 configuring the wireless ap b. Ntp primary authentication : (optional) if you are using authentication with ntp, select the type of key: md5 or sha1. Select none if you are not using authentication (this is the default). C. Ntp primary authentication key id : enter the key ...
Page 215
Wireless access point configuring the wireless ap 189 netflow this window allows you to enable or disable the sending of netflow information to a designated collector. Netflow is a proprietary but open network protocol developed by cisco systems for collecting ip traffic information. When netflow is...
Page 216
Wireless access point 190 configuring the wireless ap wi-fi tag this window enables or disables wi-fi tag capabilities. When enabled, the ap listens for and collects information about wi-fi rfid tags sent on the designated channel. These tags are transmitted by specialized tag devices (for example, ...
Page 217
Wireless access point configuring the wireless ap 191 location the ap offers an integrated capability for capturing and uploading visitor analytics data, eliminating the need to install a standalone sensor network. This data can be used to characterize information such as guest or customer traffic a...
Page 218
Wireless access point 192 configuring the wireless ap 3. Location server url : if location support is enabled, enter the url of the location/analytics server. If this url contains the string euclid, then the ap knows that data is destined for a euclid location server. For a euclid analytics server, ...
Page 219
Wireless access point configuring the wireless ap 193 system log this window allows you to enable or disable the syslog server, define primary, secondary, and tertiary servers, set up email notification, and set the level for syslog reporting for each server and for email notification — the syslog s...
Page 220
Wireless access point 194 configuring the wireless ap 2. Console logging : if you enabled syslog, select whether or not to echo syslog messages to the console as they occur. If you enable console logging, be sure to set the console logging level (see step 9 below). 3. Local file size (1-2000 lines):...
Page 221
Wireless access point configuring the wireless ap 195 e. Email syslog smtp recipient addresses : specify the entire email address of the recipient of the email notification. You may specify additional recipients by separating the email addresses with semicolons (;). 7. Station formatting : if you ar...
Page 222
Wireless access point 196 configuring the wireless ap console. If you set this level too low, the volume of messages may make it very difficult to work with the cli or view other output on the console. B. Local file : for records to be stored on the ap’s internal syslog file, choose your preferred l...
Page 223
Wireless access point configuring the wireless ap 197 see also system log services snmp time settings (ntp) snmp this window allows you to enable or disable snmp v2 and snmp v3 and define the snmp parameters. Snmp allows remote management of the ap by the xms and other snmp management tools. Snmp v3...
Page 224
Wireless access point 198 configuring the wireless ap complete snmp details for the ap, including trap descriptions, are found in the xirrus mib, available at support.Xirrus.Com , in the downloads section (login is required to download the mib). Note: if you are managing your aps with xms (the xirru...
Page 225
Wireless access point configuring the wireless ap 199 7. Context engine id : the unique identifier for this snmp server. We recommend that you do not change this value. The context engine id must be set if data collection is to be done via a proxy agent. This id helps the proxy agent to identify the...
Page 226
Wireless access point 200 configuring the wireless ap 15. Send auth failure traps : click the checkbox to the left of the enabled label to enable or disable log authentication failure traps. 16. Keepalive trap interval (minutes): traps are sent out at this interval to indicate the presence of the ap...
Page 227
Wireless access point configuring the wireless ap 201 dhcp usage is determined in several windows — see ssid management , group management , and vlan management . Procedure for configuring the dhcp server 1. New internal dhcp pool : enter a name for the new dhcp pool, then click on the create button...
Page 228
Wireless access point 202 configuring the wireless ap 11. Dns servers (1 to 3): enter the ip address of the primary dns server, secondary dns server and tertiary dns server. These dns server addresses will be passed to stations when they associate, along with the assigned ip address. Note that if yo...
Page 229
Wireless access point configuring the wireless ap 203 about proxy forwarding figure 118. Proxy forwarding example when you configure proxy forwarding settings on the ap, it forwards each http request to the proxy server (for example, blue coat) at the specified url, which checks if the policies that...
Page 230
Wireless access point 204 configuring the wireless ap proxy forwarding on the ap is configured as described in “procedure for configuring proxy forwarding on the ap” on page 210 . This proxies all http traffic to the specified server. If you wish to proxy https traffic as well, you must take the add...
Page 231
Wireless access point configuring the wireless ap 205 summary of proxy forwarding behavior on the ap if proxy forwarding is not enabled in the ap and the client browser is not configured to use a proxy: http traffic (port 80) and https traffic (port 443) pass transparently through the ap in the usua...
Page 232
Wireless access point 206 configuring the wireless ap configuring proxy forwarding on clients for https to set the proxy server on an apple laptop, skip to step 3 . 1. For windows laptops, click the desktop start button. In the search programs and files field, enter configure proxy server. The inter...
Page 233
Wireless access point configuring the wireless ap 207 valid address or domain name. You must set the port to 4388. This is very important ! This is the ap port that should receive all https traffic if you are using a proxy server. For http: http traffic will automatically use the same port that you ...
Page 234
Wireless access point 208 configuring the wireless ap 3. For apple laptops, open system preferences and select network. The network dialog is displayed. ( figure 121 ) click the advanced button. Figure 121. Set up a proxy server on each client (apple) 4. Select the proxies tab. ( figure 122 ) check ...
Page 235
Wireless access point configuring the wireless ap 209 check web proxy (http): under web proxy server, we suggest that you enter www.Xirrus.Com port 4388 to make it obvious that http traffic is being proxied in this way. Figure 122. Specify proxy servers (apple) 5. Ssl certificate : you must download...
Page 236
Wireless access point 210 configuring the wireless ap procedure for configuring proxy forwarding on the ap 1. Enable: if you wish to use proxy forwarding, select the proxy server type—blue coat or netbox blue. Figure 123. Proxy forwarding 2. Bluecoat url : if you selected blue coat above, enter the ...
Page 237
Wireless access point configuring the wireless ap 211 mask of the proxy server. If this server requires authentication, you may enter a user name and password as well. Socks : other management functions use this form of socket to send traffic. For example, this socket is used by the xms-cloud config...
Page 238
Wireless access point 212 configuring the wireless ap socks, an fqdn is not allowed—an ip address is required. The default port settings are standard defaults for these ports. 3. Username/password : for each proxy client, if the proxy server requires authentication, enter the username and password h...
Page 239
Wireless access point configuring the wireless ap 213 vlans this is a status-only window that allows you to review the current status of configured vlans and vlan pools. Vlans are virtual lans used to create broadcast domains. Vlan pools are provided for special situations where clients are to be as...
Page 240
Wireless access point 214 configuring the wireless ap understanding virtual tunnels xirrus aps support layer 2 tunneling. This allows an ap to use tunnels to transport traffic for one or more ssid-vlan pairs onto a single destination network through the layer 3 core network. Tunnels may be implement...
Page 241
Wireless access point configuring the wireless ap 215 tunnels can be configured to come up on demand but this is a poor choice for wireless, since tunnel setup can take roughly 5-20 seconds and present a problem for authentication. Vlan pools a vlan pool is a set of vlans. Using a pool allows a clie...
Page 242
Wireless access point 216 configuring the wireless ap vlan management this window allows you to set up vlans and vlan pools. After creating a new vlan (added to the list of vlans), you can modify the configuration parameters of an existing vlan or delete a selected vlan. For arrayos 6.6 and later re...
Page 243
Wireless access point configuring the wireless ap 217 procedure for managing vlans 1. Default route: this option sets a default route from the ap. The ap supports a default route on native and tagged interfaces. Once the default route is configured the ap will attempt to use address resolution proto...
Page 244
Wireless access point 218 configuring the wireless ap 4. First, create all of the vlans that will belong to this pool. See step 5 below. Click in the field for the new pool to display a list of vlans. Add the desired vlans to this pool, one at a time. This field also provides a search feature—type i...
Page 245
Wireless access point configuring the wireless ap 219 11. Gateway : if the dhcp option is disabled, enter the ip gateway address for this vlan association. 12. Tunnel server : if this vlan is to be tunneled, enter the ip address or host name of the tunnel server that will perform the tunneling. For ...
Page 246
Wireless access point 220 configuring the wireless ap tunnels this read-only window allows you to review the tunnels that have been defined on the ap. It lists all tunnels and their settings, including the type of authentication and the local and remote endpoints for each tunnel. Figure 127. Tunnel ...
Page 247
Wireless access point configuring the wireless ap 221 802.1q vlan tags for final layer 2 processing. The process occurs in reverse for packets traveling in the other direction. One tunnel is able to transport up to 16 vlans. Tunnel management this window allows you to create tunnels. Figure 128. Tun...
Page 248
Wireless access point 222 configuring the wireless ap includes ap bssid, ssid name, and ssid encryption type. You may use this option here or on the ssid management page, but not in both places. Information is inserted as a colon-separated text string in the circuit id value field in this format: [a...
Page 249
Wireless access point configuring the wireless ap 223 ssid assignments this window allows you to select the ssids to be bridged by each tunnel. Station traffic for ssids assigned will be bridged through a tunnel regardless of whether these ssids have vlans defined for them. If there is a vlan define...
Page 250
Wireless access point 224 configuring the wireless ap security this status-only window allows you to review the ap’s security parameters. It includes the assigned network administration accounts, access control list (acl) values, management settings, encryption and authentication protocol settings, ...
Page 251
Wireless access point configuring the wireless ap 225 “about creating user accounts on the radius server” on page 254 security settings are configured with the following windows: “admin management” on page 230 “admin privileges” on page 232 “admin radius” on page 234 “management control” on page 237...
Page 252
Wireless access point 226 configuring the wireless ap choosing an encryption method : wireless data encryption prevents eavesdropping on data being transmitted or received over the airwaves. The ap allows you to establish the following data encryption configuration options: • open — this option offe...
Page 253
Wireless access point configuring the wireless ap 227 the encryption mode (wep, wpa, etc.) is selected in the ssids >ssid management window (see “ssid management” on page 276 ). The encryption standard used with wpa or wpa2 (aes or tkip) is selected in the security>global settings window under wpa s...
Page 254
Wireless access point 228 configuring the wireless ap address in the deny list. The wireless ap will accept up to 1,000 acl entries. Pci dss or fips 140-2 security — to implement the requirements of these security standards on the ap, please see “auditing pci dss” on page 593 or “implementing fips s...
Page 255
Wireless access point configuring the wireless ap 229 using the ap’s default certificate figure 131. Import xirrus certificate authority the ap’s certificate is signed by a xirrus ca that is customized for your ap and its current host name. By default, browsers will not trust the ap’s certificate. Y...
Page 256
Wireless access point 230 configuring the wireless ap using an external certificate authority if you prefer, you may install a certificate on your ap signed by an outside ca. The ap’s certificate is used for security when stations attempt to associate to an ssid that has web page redirect (captive p...
Page 257
Wireless access point configuring the wireless ap 231 procedure for creating or modifying network administrator accounts 1. Admin id: enter the login name for a new network administrator id. The length of the id must be between 5 and 50 characters, inclusive. 2. Read/write : choose 1:read-write if y...
Page 258
Wireless access point 232 configuring the wireless ap admin privileges this window provides a detailed level of control over the privileges of ap administrators. Administrators may be assigned one of eight privilege levels. You may define the privilege level of each major feature (configuration sect...
Page 259
Wireless access point configuring the wireless ap 233 privilege level 0 is read-only. As a minimum, all administrators have permission for read access to all areas of ap configuration. Higher privilege levels may be used to define additional privileges for specific configuration sections. If you are...
Page 260
Wireless access point 234 configuring the wireless ap admin radius this window allows you to set up authentication of network administrators via radius. Using radius to control administrator accounts for logging in to aps has these benefits: centralized control of administrator accounts. Less effort...
Page 261
Wireless access point configuring the wireless ap 235 figure 134. Admin radius procedure for configuring admin radius use this window to enable/disable administrator authentication via radius, and to set up primary and secondary servers to use for authentication of administrators attempting to log i...
Page 262
Wireless access point 236 configuring the wireless ap c. Timeout (seconds) : define the maximum idle time (in seconds) before the radius server’s session times out. The default is 600 seconds. 2. Admin radius primary server : this is the radius server that you intend to use as your primary server. A...
Page 263
Wireless access point configuring the wireless ap 237 management control this window allows you to enable or disable the ap management interfaces and set their inactivity time-outs. The range is 300 (default) to 100,000 seconds. Figure 135. Management control procedure for configuring management con...
Page 264
Wireless access point 238 configuring the wireless ap upload a text file. Click choose file and browse to the file. Click upload when done. Figure 136. Pre-login banner d. Post-login banner : text that you enter here will be displayed in a message box after a user logs in to the wmi. If you wish to ...
Page 265
Wireless access point configuring the wireless ap 239 figure 137. Management transports 2. Ssh a. On/off : choose on to enable management of the ap over a secure shell (ssh-2) connection, or off to disable this feature. Be aware that only ssh-2 connections are supported by the ap. Ssh clients used f...
Page 266
Wireless access point 240 configuring the wireless ap disconnected. The value you enter here must be between 30 seconds and 100,000 seconds. C. Port : enter a value in this field to define the port used by telnet. The default port is 23. 4. Xircon the xircon utility connects to xirrus aps that do no...
Page 267
Wireless access point configuring the wireless ap 241 5. Console a. On/off : choose on to enable management of the ap via a serial connection, or choose off to disable this feature. B. Connection timeout 30-100000 (seconds) : enter a value in this field to define the timeout (in seconds) before your...
Page 268
Wireless access point 242 configuring the wireless ap a. Network assurance : click the on button to enable this mode. Network assurance checks network connectivity to each server that you configure, such as the ntp server, radius servers, snmp trap hosts, etc. By proactively identifying network reso...
Page 269
Wireless access point configuring the wireless ap 243 pci dss requirements. For more information, see “auditing pci dss” on page 593 . The pci-audit command checks items such as: • telnet is disabled. • admin radius is enabled (admin login authentication is via radius server). • an external syslog s...
Page 270
Wireless access point 244 configuring the wireless ap 8. Https (x.509) certificate , figure 139. Https (x.509) certificate a. Import xirrus authority into browser : this feature imports the xirrus certificate authority (ca) into your browser (for a discussion, please see “certificates and connecting...
Page 271
Wireless access point configuring the wireless ap 245 service by turning it off and on again using the cli), it automatically creates a security certificate for that host name. That certificate uses xirrus as the signing authority. Thus, in order to avoid having certificate errors on your browser wh...
Page 272
Wireless access point 246 configuring the wireless ap this step and step 10 allow you to obtain a certificate from an external authority and install it on an ap. “using an external certificate authority” on page 230 discusses reasons for using an external ca. For example, to obtain and install a cer...
Page 273
Wireless access point configuring the wireless ap 247 address. Click the create button to create the certificate signing request. See step 9 above to use this request. 11. Click the save button if you wish to make your changes permanent. See also interfaces - to enable/disable management over an eth...
Page 274
Wireless access point 248 configuring the wireless ap there is also a per-ssid acl (see “per-ssid access control list” on page 298 ). If the same mac address is listed in both the global acl and in an ssid’s acl, and if either acl would deny that station access to that ssid, then access will be deni...
Page 275
Wireless access point configuring the wireless ap 249 global settings this window allows you to establish the security parameters for your wireless network, including wep, wpa, wpa2 and radius authentication. When finished, click the save button if you wish to make your changes permanent. For additi...
Page 276
Wireless access point 250 configuring the wireless ap • active directory defines wireless user accounts on an active directory server external to the ap. See “active directory” on page 259 . Wpa settings these settings are used if the wpa or wpa2 encryption type is selected on the ssids >ssid manage...
Page 277
Wireless access point configuring the wireless ap 251 wep settings these settings are used if the wep encryption type is selected on the ssids > ssid management window or the express setup window (on this window, encryption type is set in the ssid settings: wireless security field). Click the show c...
Page 278
Wireless access point 252 configuring the wireless ap see also admin management external radius internal radius access control list management control security security planning ssid management.
Page 279
Wireless access point configuring the wireless ap 253 external radius this window allows you to define the parameters of an external radius server for user authentication. To set up an external radius server, you must choose external radius as the authentication server mode in “global settings” on p...
Page 280
Wireless access point 254 configuring the wireless ap about creating user accounts on the radius server an attribute of user (wireless client) accounts is controlled by radius vendor specific attributes (vsas) defined by xirrus. In particular, use the vsa named xirrus-admin-role to set the privilege...
Page 281
Wireless access point configuring the wireless ap 255 3. Settings (radius dynamic authorization) : some radius servers have the ability to contact the ap (referred to as an nas, see below) to terminate a user with a disconnect message (dm). Or radius may send a change-of-authorization (coa) message ...
Page 282
Wireless access point 256 configuring the wireless ap ssid to which the client wishes to connect. If your site is using purple wifi, you must use ethernet-mac, which identifies the ap using its wired network mac address rather than a particular iap. See “web page redirect for purple wifi venues” on ...
Page 283
Wireless access point configuring the wireless ap 257 g. Secondary shared secret / verify secret : if using a secondary accounting server, enter the shared secret that it will be using, then re- enter the shared secret to verify that you typed it correctly. 6. Click the save button if you wish to ma...
Page 284
Wireless access point 258 configuring the wireless ap procedure for creating a new user 1. User name: enter the name of the user that you want to authenticate to the internal radius server. You may enter up to 1000 users (up to 256 on the xr-500 series, or up to 480 on two-radio aps). 2. Ssid restri...
Page 285
Wireless access point configuring the wireless ap 259 4. Verify password : (optional) retype the user password to verify that you typed it correctly. 5. If you want to delete one or more users, click their delete buttons. 6. Click the save button if you wish to make your changes permanent. See also ...
Page 286
Wireless access point 260 configuring the wireless ap figure 145. Active directory server procedure for use of an active directory server 1. Choose active directory as the authentication server mode in “global settings” on page 249 . 2. Domain administrator : enter the administrator account name for...
Page 287
Wireless access point configuring the wireless ap 261 after you have made a change requiring validation (i.E., entering a new hostname or changing an existing entry to a different hostname). If you return to this page at a later time, the checkmark will not be present. 5. Workgroup/domain : enter th...
Page 288
Wireless access point 262 configuring the wireless ap tools. The domain controller will give the ap a secret that may be used as a key to fetch information. The secret may be checked with the check secret test tool, below. You may click leave domain to ask the domain controller to remove the ap from...
Page 289
Wireless access point configuring the wireless ap 263 rogue control list this window allows you to set up a control list for rogue aps, based on a type that you define. You may classify rogue aps as blocked, so that the ap will take steps to prevent stations from associating with the blocked ap. See...
Page 290
Wireless access point 264 configuring the wireless ap 3. Match only : select the match criterion to compare the rogue bssid/ ssid string against: bssid, manufacturer, or ssid. The bssid field contains the mac address. 4. Click create to add this rogue ap to the rogue control list. 5. Rogue control l...
Page 291
Wireless access point configuring the wireless ap 265 figure 148. Oauth 2.0 management - token list procedure for obtaining a token and accessing restful api on the ap 1. Present user credentials for a permanent token a user-developed application must register by presenting the following information...
Page 292
Wireless access point 266 configuring the wireless ap please see “api documentation” on page 426 for a description of the features available in the api..
Page 293
Wireless access point configuring the wireless ap 267 ssids this status-only window allows you to review ssid (service set identifier) assignments. It includes the ssid name, whether or not an ssid is visible on the network, any security and qos parameters defined for each ssid, associated vlan ids,...
Page 294
Wireless access point 268 configuring the wireless ap the read-only limits section of the ssids window allows you to review any limitations associated with your defined ssids. For example, this window shows the current state of an ssid (enabled or not), how much ssid and station traffic is allowed, ...
Page 295
Wireless access point configuring the wireless ap 269 bss. A group of bsss can be formed to allow stations in one bss to communicate to stations in another bss via a backbone that interconnects each access point. The extended service set (ess) refers to the group of bssids that are grouped together ...
Page 296
Wireless access point 270 configuring the wireless ap understanding qos priority on the wireless ap figure 150. Four traffic classes the wireless ap’s quality of service priority feature ( qos ) allows traffic to be prioritized according to your requirements. For example, you typically assign the hi...
Page 297
Wireless access point configuring the wireless ap 271 figure 151. Priority level—ieee 802.1p (layer 2) ieee802.1p uses three bits in an ethernet frame header to define eight priority levels at the mac level (layer 2) for wired networks. Each data packet may be tagged with a priority level, i.E., a u...
Page 298
Wireless access point 272 configuring the wireless ap end-to-end qos handling wired qos - ethernet port: egress: outgoing wired packets are ieee 802.1p tagged at the ethernet port for upstream traffic, thus enabling qos at the edge of the network. Ingress: incoming wired packets are assigned qos pri...
Page 299
Wireless access point configuring the wireless ap 273 wireless qos - radios: each ssid can be assigned a separate qos priority (i.E., traffic class) from 0 to 3, where 3 is highest priority and 2 is the default. See “ssid management” on page 276 . If multiple ssids are used, packets from the ssid wi...
Page 300
Wireless access point 274 configuring the wireless ap • all other dscp values are set to qos level 0 (the lowest level— best effort). Packet filtering qos classification filter rules can be used to redefine the qos priority level to override defaults. See “filter management” on page 393 . This allow...
Page 301
Wireless access point configuring the wireless ap 275 or it may be dead-ended by defining a specific dead-end vlan on the honeypot ssid to “trap” stations (see “vlans” on page 213 ). Use the honeypot feature carefully as it could interfere with legitimate ssids and prevent clients from associating t...
Page 302
Wireless access point 276 configuring the wireless ap ssid management this window allows you to manage ssid s (create, edit, schedule, rename, and delete), assign security parameters and vlan s on a per ssid basis, and configure the web page redirect (wpr captive portal) functionality. Figure 153. S...
Page 303
Wireless access point configuring the wireless ap 277 procedure for managing ssids 1. New ssid: to create a new ssid, enter a new ssid name. Ssid names are case sensitive and may only consist of the characters a-z, a-z, 0-9, dash, and underscore. You may create up to 16 ssids (up to 8 on the xr-500 ...
Page 304
Wireless access point 278 configuring the wireless ap 7. Qos : (optional) select a value in this field for qos (quality of service) priority filtering. The qos value must be one of the following: • 0 — the lowest qos priority setting, where qos makes its best effort at filtering and prioritizing dat...
Page 305
Wireless access point configuring the wireless ap 279 10. Filter list : if you wish to apply a set a filters to this ssid’s traffic, select the desired filter list. See “filters” on page 389 . 11. Authentication : the following authentication options are available (only valid encryption/authenticati...
Page 306
Wireless access point 280 configuring the wireless ap . Figure 154. Ssid management—encryption, authentication, accounting additional sections will be displayed to allow you to configure encryption, authentication server, and radius accounting settings. • the wpa configuration encryption settings ha...
Page 307
Wireless access point configuring the wireless ap 281 management page (i.E., they are configured per ssid rather than in global settings ). Easypass onboarding facilitates “bring your own device (byod)” usage. Xms-cloud’s onboarding lets you create user accounts in advance, and a user can self-regis...
Page 308
Wireless access point 282 configuring the wireless ap 15. Wpr (web page redirect , also called captive portal): check the checkbox to enable the web page redirect functionality, or clear it to disable this option. If enabled, wpr configuration fields will be displayed under the ssid limits section. ...
Page 309
Wireless access point configuring the wireless ap 283 the lower part of the window contains a few sections of additional settings to configure for the currently selected ssid, depending on the values chosen for the settings described above. “ssid limits and scheduling” on page 283 “web page redirect...
Page 310
Wireless access point 284 configuring the wireless ap 21. Rename ssid : use this field if you wish to change the name of an ssid without changing any of its other settings. For example, a convention center might wish to change the ssid name based on the name of the current exhibition. Scheduling 22....
Page 311
Wireless access point configuring the wireless ap 285 25. Use date off to specify a date to take the ssid out of service without deleting it. At the specified date, the ap will turn the enabled flag off. Leave expiration and date off set to none (the default) if you want this ssid to remain in servi...
Page 312
Wireless access point 286 configuring the wireless ap web page redirect (captive portal) configuration if you enable wpr, the ssid management window displays additional fields that must be configured. If enabled, wpr displays a splash or login page when a client associates to the wireless network an...
Page 313
Wireless access point configuring the wireless ap 287 this option displays a login page (residing on the ap) instead of the first user-requested url. There is an upload function that allows you to replace the default login page, if you wish. Please see “web page redirect (captive portal)” on page 42...
Page 314
Wireless access point 288 configuring the wireless ap external login page this option redirects the user to a login page on an external web server for authentication, instead of the first user-requested url. Login information (user name and password) must be obtained by that page, and returned to th...
Page 315
Wireless access point configuring the wireless ap 289 after the splash page, the user is redirected to the captured url. If you want the user redirected to a specific landing page instead, enter its address in landing page url. Cloud this option is only used in conjunction with the guest access feat...
Page 316
Wireless access point 290 configuring the wireless ap when users connect to the ssid that runs the easypass personal portal, they are redirected to a login page hosted in the cloud by xms. After successful authentication, a user is redirected to a personal wi-fi setup page to specify necessary param...
Page 317
Wireless access point configuring the wireless ap 291 customizing an internal login or splash page you may customize these pages with a logo and/or background image, and header and/or footer text, as shown below in figure 156 . Figure 156. Customizing an internal login or splash page background imag...
Page 318
Wireless access point 292 configuring the wireless ap whitelist configuration for web page redirect on a per-ssid basis, the whitelist allows you to specify internet destinations that stations can access without first having to pass the wpr (captive portal) login/ splash page. Note that a whitelist ...
Page 319
Wireless access point configuring the wireless ap 293 the station will still be required to pass through the configured wpr flow for all other internet addresses. The whitelist will work against all traffic -- not just http or https indirect access to other web sites is not permitted. For example, i...
Page 320
Wireless access point 294 configuring the wireless ap http://purpleportal.Net/access/ • redirect secret : enter the password provided to you by purple wifi. 3. In the next section on the same page, create wpr whitelist configuration entries as directed by purple wifi for web sites that should not be...
Page 321
Wireless access point configuring the wireless ap 295 5. Regardless of whether you selected a global authentication server in step 13 on page 279 , you need the following setting for compatibility with purple wifi. On the security > external radius page, in the radius attribute formatting section: •...
Page 322
Wireless access point 296 configuring the wireless ap 7. If radius authenticates successfully, then the end user is given access to the full internet, outside of your internal network. Future connections to the same access point are automatically authenticated with no user action required. Wpa confi...
Page 323
Wireless access point configuring the wireless ap 297 airwatch active iaps by default, when a new ssid is created, that ssid is active on all iaps. This window allows you to specify which iaps will offer that ssid. Put differently, you can specify which ssids are active on each iap. This feature is ...
Page 324
Wireless access point 298 configuring the wireless ap per-ssid access control list this window allows you set up access control lists (acls) on a per-ssid basis, to control whether a station with a particular mac address may associate to a particular ssid. You may create access control list entries ...
Page 325
Wireless access point configuring the wireless ap 299 • deny list : denies the listed mac addresses permission to associate to the ap. All others are allowed. The minus symbol appears before the ssid name for a deny list. • disabled : a red dot appears before the ssid name for a disabled list. A gre...
Page 326
Wireless access point 300 configuring the wireless ap figure 161. Honeypot whitelist procedure for configuring honeypot whitelists 1. Create a honeypot: if you have not already created an ssid named honeypot , you will be asked whether you wish to create one. Click yes. You must have an ssid named h...
Page 327
Wireless access point configuring the wireless ap 301 3. Honeypot broadcasts : this section only appears if you have created an ssid named honeypot. You may define one or more alias names for this ssid. They will be broadcast instead of the name honeypot. Personal wi-fi the settings on this page wil...
Page 328
Wireless access point 302 configuring the wireless ap is optional. For example, enter 2016:09:29 08:00. If the hour and minute are omitted, they are assumed to be 23:59. Use after duration to specify the length of time before the ssid expires, in days, hours, and minutes. Use the format dd [hh:mm], ...
Page 329
Wireless access point configuring the wireless ap 303 groups this is a status-only window that allows you to review user (i.E., wireless client) group assignments. It includes the group name, radius id, device id, vlan ids and qos parameters and roaming layer defined for each group, and dhcp pools a...
Page 330
Wireless access point 304 configuring the wireless ap security parameters, web page redirect (wpr), and traffic limits. When a new user is created, you can apply all of these settings just by making the user a member of the group. The group allows you to apply a uniform configuration to a set of use...
Page 331
Wireless access point configuring the wireless ap 305 see also external radius internal radius ssids understanding qos priority on the wireless ap web page redirect (captive portal) configuration understanding fast roaming group management this window allows you to manage groups (create, edit and de...
Page 332
Wireless access point 306 configuring the wireless ap 3. Enabled : check this box to enable this group or leave it blank to disable it. When a group is disabled, users that are members of the group will behave as if the group did not exist. In other words, the options configured for the ssid will ap...
Page 333
Wireless access point configuring the wireless ap 307 • 0 — the lowest qos priority setting, where qos makes its best effort at filtering and prioritizing data, video and voice traffic without compromising the performance of the network. Use this setting in environments where traffic prioritization ...
Page 334
Wireless access point 308 configuring the wireless ap the authentication options that are offered on the ssid management page are not offered here. Since the group membership of a user is provided to the ap by a radius server, this means the user has already been authenticated. You may create a wpr ...
Page 335
Wireless access point configuring the wireless ap 309 15. Traffic per station : check the unlimited checkbox if you do not want to place a restriction on the traffic per station for this group, or enter a value in the packets/sec or kbps field and make sure that the unlimited box is unchecked to for...
Page 336
Wireless access point 310 configuring the wireless ap iaps this status-only window summarizes the status of the integrated access points. For each iap, it shows whether it is up or down, the channel and wireless mode, the antenna that it is currently using, its cell size and transmit and receive pow...
Page 337
Wireless access point configuring the wireless ap 311 aps have a fast roaming feature, allowing them to maintain sessions for applications such as voice, even while users cross boundaries between aps. Fast roaming is set up in the global settings window and is discussed in: “understanding fast roami...
Page 338
Wireless access point 312 configuring the wireless ap a user to maintain the same ip address through an entire real-time data session. The user may be associated to any of the vlans defined on the ap. The layer 3 session is maintained by establishing a tunnel back to the originating ap. You should d...
Page 339
Wireless access point configuring the wireless ap 313 you may also access this window by clicking on the ap image at the lower left of the wmi window — click the xirrus logo in the center of the ap. See “user interface” on page 89 . Procedure for auto configuring iaps you can auto-configure channel ...
Page 340
Wireless access point 314 configuring the wireless ap one of the iaps must be set to monitor mode if you wish to support spectrum analyzer , radio assurance (loopback testing), and intrusion detection features. Monitoring has a timeshare mode option, which is especially useful for small aps with two...
Page 341
Wireless access point configuring the wireless ap 315 6. Set channel lock to block auto-channel assignment if you want to lock in your channel selection so that an autochannel operation (see advanced rf settings ) can’t change it. A locked padlock will be displayed for the iap. 7. The bond field wor...
Page 342
Wireless access point 316 configuring the wireless ap 8. In the cell size field, select auto to allow the optimal cell size to be automatically computed (see also, “rf power and sensitivity” on page 360 ). To set the cell size yourself, choose either small, medium, large , or max to use the desired ...
Page 343
Wireless access point configuring the wireless ap 317 10. The antenna field displays the antenna that has automatically been selected for this iap. 11. If desired, enter a description for this iap in the description field. 12. You may reset all of the enabled iaps by clicking the reset channels butt...
Page 344
Wireless access point 318 configuring the wireless ap global settings figure 168. Global settings (iaps) this window allows you to establish global iap settings. Global iap settings include enabling or disabling all iaps (regardless of their operating mode), and changing settings for beacons, statio...
Page 345
Wireless access point configuring the wireless ap 319 procedure for configuring global iap settings 1. Country : this is a display-only value. Once a country has been set, it may not be changed. The channels that are available for assignment to iaps will differ, depending on the country of operation...
Page 346
Wireless access point 320 configuring the wireless ap beacon configuration 6. Beacon interval : when the ap sends a beacon, it includes with it a beacon interval, which specifies the period of time before it will send the beacon again. Enter the desired value in the beacon interval field, between 20...
Page 347
Wireless access point configuring the wireless ap 321 11. Wmm power save : click on to enable wireless multimedia power save support, as defined in ieee802.11e. This option saves power and increases battery life by allowing the client device to doze between packets to save power, while the ap buffer...
Page 348
Wireless access point 322 configuring the wireless ap 15. Station timeout period : specify a time (in seconds) in this field to define the timeout period for station associations. 16. Max station association per access point : this option allows you to define how many station associations are allowe...
Page 349
Wireless access point configuring the wireless ap 323 advanced traffic optimization figure 169. Multicast processing 20. Multicast processing: this sets how multicast traffic is handled. Multicast traffic can be received by a number of subscribing stations at the same time, thus saving a great deal ...
Page 350
Wireless access point 324 configuring the wireless ap • for compatibility with ordinary operation, i.E., there is no optimization or modification of multicast traffic. • if you have an application where many subscribers need to see the multicast—a large enough number that it would be less efficient ...
Page 351
Wireless access point configuring the wireless ap 325 (mdns) are in use. For example, apple bonjour finds local network devices such as printers or other computers using mdns. By default, the list contains the ipv4 multicast address for apple bonjour mdns: 224.0.0.251. For an additional discussion o...
Page 352
Wireless access point 326 configuring the wireless ap • in multicast vlan forwarding, enter a list of vlans that participate in the multicast forwarding. • in mdns filter, specify the mdns service types that are allowed to be forwarded. • if you leave this field blank, then there is no filter, and m...
Page 353
Wireless access point configuring the wireless ap 327 multicast addresses - host names are not allowed. To remove an entry, select it in the list and click delete. To remove all entries from the list, click reset. 23. Multicast vlan forwarding: this is a list of vlans that participate in the multica...
Page 354
Wireless access point 328 configuring the wireless ap 24. Mdns filter: there are many different types of services that may be specified in multicast query and response packets. The mdns filters let you restrict forwarding, so that multicast packets are forwarded only for the services that you explic...
Page 355
Wireless access point configuring the wireless ap 329 apple-tv , ichat, iphoto, itunes, itunes-home-sharing, internet- printing , mobile-device-sync, and secure-telnet. For example, to allow mirroring of an ipad on an apple-tv, select apple- tv . You may define your own type if you do not see the se...
Page 356
Wireless access point 330 configuring the wireless ap designed network (having -70db or better everywhere), where virtually every client should have a 54mbps connection. In this case, broadcasts and multicasts will all go out at 54mbps vs. The standard rate. Thus, with broadcast rate optimization on...
Page 357
Wireless access point configuring the wireless ap 331 if you select on and an iap is not the best choice for network performance, that iap will send an “ap full” message in response to probe, association, or authentication requests. This deters persistent clients from forcing their way onto overload...
Page 358
Wireless access point 332 configuring the wireless ap note that the ap has a broadcast optimization feature that is always on (it is not configurable). Broadcast optimization restricts all broadcast packets (not just arp broadcasts) to only those radios that need to forward them. For instance, if a ...
Page 359
Wireless access point configuring the wireless ap 333 • ports 15000 to 17999 — reserved for layer 3 roaming (tunneling between subnets). 31. Share roaming info with : three options allow your ap to share roaming information with all aps; just with those that are within range; or with specifically ta...
Page 360
Wireless access point 334 configuring the wireless ap global settings . 11an this window allows you to establish global 802.11a iap settings. These settings include defining which 802.11a data rates are supported, enabling or disabling all 802.11an iaps, auto-configuration of channel allocations for...
Page 361
Wireless access point configuring the wireless ap 335 2. Data rate presets : the wireless ap can optimize your 802.11a data rates automatically, based on range or throughput. Click optimize range to optimize data rates based on range, or click optimize throughput to optimize data rates based on thro...
Page 362
Wireless access point 336 configuring the wireless ap • non-radar : give preference to channels that are not required to use dynamic frequency selection (dfs) to avoid communicating in the same frequency range as some radar (also see step 8 on page 320 ). • negotiate : negotiate air-time with other ...
Page 363
Wireless access point configuring the wireless ap 337 • full scan : perform a full traffic scan on all channels on all iaps to determine the best channel allocation. • include wds : automatically assign 5ghz to wds client links. 5. Set cell size : cell size may be set globally for all 802.11an iaps ...
Page 364
Wireless access point 338 configuring the wireless ap 8. Auto cell size overlap (%) : enter the percentage of cell overlap that will be allowed when the ap is determining automatic cell sizes. For 100% overlap, the power is adjusted such that neighboring aps that hear each other best will hear each ...
Page 365
Wireless access point configuring the wireless ap 339 ssids — ssid management window also have station limit settings — max station association per iap ( page 322 ) and station limit ( page 283 ), respectively. If multiple station limits are set, all will be enforced. As soon as any limit is reached...
Page 366
Wireless access point 340 configuring the wireless ap global settings . 11bgn this window allows you to establish global 802.11b/g iap settings. These settings include defining which 802.11b and 802.11g data rates are supported, enabling or disabling all 802.11b/g iaps, auto-configuring 802.11b/g ia...
Page 367
Wireless access point configuring the wireless ap 341 procedure for configuring global 802.11b/g iap settings 1. 802.11g data rates: the ap allows you to define which data rates are supported for all 802.11g radios. Select (or deselect) 11g data rates by clicking in the corresponding supported and b...
Page 368
Wireless access point 342 configuring the wireless ap environment. In this case, it will pick a set of compatible channel assignments at random. The following options may be selected for auto configuration: • negotiate : negotiate air-time with other aps before performing a full scan. • full scan : ...
Page 369
Wireless access point configuring the wireless ap 343 8. Auto cell period (seconds) : you may set up auto-configuration to run periodically, readjusting optimal cell sizes for the current conditions. Enter a number of seconds to specify how often auto-configuration will run. If you select none, then...
Page 370
Wireless access point 344 configuring the wireless ap 13. Auto cell configuration : click auto configure to instruct the ap to determine and set the best cell size for each enabled 802.11b/g iap whose cell size is auto on the iap settings window, based on changes in the environment. This is the reco...
Page 371
Wireless access point configuring the wireless ap 345 17. 802.11b preamble : the preamble contains information that the ap and client devices need when sending and receiving packets. All compliant 802.11b systems have to support the long preamble. A short preamble improves the efficiency of a networ...
Page 372
Wireless access point 346 configuring the wireless ap global settings . 11n this window allows you to establish global 802.11n iap settings. These settings include enabling or disabling 802.11n mode for the entire ap, specifying the number of transmit and receive chains (data stream) used for spatia...
Page 373
Wireless access point configuring the wireless ap 347 procedure for configuring global 802.11n iap settings 1. 802.11n data rates : the ap allows you to define which data rates are supported for all 802.11n radios. Select (or deselect) 11n data rates by clicking in the corresponding supported and ba...
Page 374
Wireless access point 348 configuring the wireless ap 7. 5 ghz channel bonding : select dynamic to have auto-configuration for bonded 5 ghz channels be automatically updated as conditions change. For example, if there are too many clients to be supported by a bonded channel, dynamic mode will automa...
Page 375
Wireless access point configuring the wireless ap 349 global settings . 11ac this window allows you to establish global 802.11ac iap settings. These settings include enabling or disabling 802.11ac mode for the entire ap, specifying the number of data streams used in spatial multiplexing, and setting...
Page 376
Wireless access point 350 configuring the wireless ap procedure for configuring global 802.11ac iap settings 1. 802.11ac mode : select enabled to allow the ap to operate in 802.11ac mode. If you select disabled, then 802.11ac operation is disabled on the ap. 2. 80 mhz guard interval : this is the le...
Page 377
Wireless access point configuring the wireless ap 351 global settings . 11u understanding 802.11u as the number of access points available in public venues increases, mobile devices users have a harder time distinguishing usable ssids from the tens, if not hundreds of access points visible. Using th...
Page 378
Wireless access point 352 configuring the wireless ap cellular networks. The service network may have arrangements with one or more cellular service providers who can transparently provide wireless and internet connectivity. Figure 175. 802.11u global settings.
Page 379
Wireless access point configuring the wireless ap 353 procedure for configuring 802.11u settings use this window to establish the 802.11u configuration. 1. 802.11u internetworking. Click on to enable 802.11u protocol operation. 2. Access network type : this indicates the type of network supported by...
Page 380
Wireless access point 354 configuring the wireless ap 7. Hessid . Enter the globally unique homogeneous ess id. This ssid is marked as being hotspot 2.0 capable. This ssid attribute is global—if 802.11u is enabled and hotspot 2.0 is enabled, then all ssids will have hotspot 2.0 capability. 8. Ipv4 a...
Page 381
Wireless access point configuring the wireless ap 355 10. Roaming consortium. Each of the roaming consortia has an organizational identifier (oi) obtained from ieee that unique identifies the organization. This is similar to the oui part of a mac address. Use this control to build up a list of ois f...
Page 382
Wireless access point 356 configuring the wireless ap when add is clicked the authentication type and optional url will appear in the list. An authentication type may be deleted by selecting it in the list and clicking delete. All authentication types may be deleted by clicking reset. 14. Venue name...
Page 383
Wireless access point configuring the wireless ap 357 advanced rf settings this window allows you to establish rf settings, including automatically configuring channel allocation and cell size, and configuring radio assurance and standby modes. Changes you make on this page are applied to all iaps, ...
Page 384
Wireless access point 358 configuring the wireless ap applications. In standby mode, an ap monitors beacons from the target ap. When the target has not been heard from for 40 seconds, the standby ap enables its radios until it detects that the target ap has come back online. Standby mode is off by d...
Page 385
Wireless access point configuring the wireless ap 359 rf resilience 2. Radio assurance mode : when this mode is enabled, the monitor radio performs loopback tests on the ap. This mode requires rf monitor mode to be enabled (dedicated or timeshare mode, see step 1 ) to support self- monitoring functi...
Page 386
Wireless access point 360 configuring the wireless ap rf power and sensitivity for an overview of rf power and cell size settings, please see “capacity and cell sizes” on page 36 and “fine tuning cell sizes” on page 37 . 5. Set cell size : cell size may be set globally for all enabled iaps to auto, ...
Page 387
Wireless access point configuring the wireless ap 361 10. Auto cell configuration : click this button to instruct the ap to determine and set the best cell size for each enabled iap whose cell size is auto on the iap settings window, based on changes in the environment. This is the recommended metho...
Page 388
Wireless access point 362 configuring the wireless ap range set to yes, and it must have at least one active iap with an ssid that has broadcast enabled. Auto band runs separately from auto channel configuration. If a radio’s band is changed, associated stations will be disconnected and will then re...
Page 389
Wireless access point configuring the wireless ap 363 • full scan : perform a full traffic scan on all channels on all iaps to determine the best channel allocation. • non-radar : give preference to channels without radar-detect. See table in “procedure for configuring global 802.11an iap settings” ...
Page 390
Wireless access point 364 configuring the wireless ap specified time. If you do not specify am or pm, time is interpreted in 24- hour military time. For example, sat 11:00 pm and saturday 23:00 are both acceptable and specify the same time. 17. Channel list selection : this list selects which channe...
Page 391
Wireless access point configuring the wireless ap 365 figure 177. Station assurance (advanced rf settings) 19. Enable station assurance : this is enabled by default. Click no if you wish to disable it, and click yes to re-enable it. When station assurance is enabled, the ap will monitor connection q...
Page 392
Wireless access point 366 configuring the wireless ap 26. Min received signal strength : (db) station assurance detects whether the strength of the signal received from the station falls below this threshold during a period. 27. Min signal to noise ratio : (db) station assurance detects whether the ...
Page 393
Wireless access point configuring the wireless ap 367 procedure for hotspot 2.0 settings use this window to establish the hotspot 2.0 configuration. 1. Hotspot 2.0. Click enabled to enable hotspot 2.0 operation. 2. Downstream group-addressed forwarding. Click enabled to allow the access point to for...
Page 394
Wireless access point 368 configuring the wireless ap figure 178. Hotspot 2.0 settings 5. English/chinese operator friendly name. Enter an english or chinese name into one of the fields. An incorrectly entered name can be deleted by clicking the corresponding delete. 6. Connection capabilities. A ho...
Page 395
Wireless access point configuring the wireless ap 369 b. A protocol number. For example 1 for icmp, 6 for tcp, 17 for udp, and 50 for encapsulated security protocol in ipsec vpn connections. C. Port number for udp/tcp connection. D. Status : one of open, closed or unknown. Any of the entries may be ...
Page 396
Wireless access point 370 configuring the wireless ap procedure for nai realms settings use this window to establish the names of the supported realms. 1. Enter the realm name. Enter the name of a realm in the box to the left of the create button and click create. The realm will be added to the nai ...
Page 397
Wireless access point configuring the wireless ap 371 • eap-aka • eap-aka’ (eap-aka prime) • eap-fast • eap-mschap-v2 • eap-sim • eap-tls • eap-ttls • gtc • md5-challenge • none • peap 3. Specify authentication parameters. Each of the authentication methods may specify up to five authentication para...
Page 398
Wireless access point 372 configuring the wireless ap intrusion detection the xirrus ap employs a number of ids/ips (intrusion detection system/ intrusion prevention system) strategies to detect and prevent malicious attacks on the wireless network. Use this window to adjust intrusion detection sett...
Page 399
Wireless access point configuring the wireless ap 373 the ap provides a suite of intrusion detection and prevention options to improve network security. You can separately enable detection of the following types of problems: rogue access point detection and blocking unknown aps are detected, and may...
Page 400
Wireless access point 374 configuring the wireless ap disassociation flood flooding the ap with forged disassociation packets. Deauthentication flood flooding the ap with forged deauthenticates. Eap handshake flood flooding an ap with eap-start messages to consume resources or crash the target. Null...
Page 401
Wireless access point configuring the wireless ap 375 about blocking rogue aps if you classify a rogue ap as blocked (see “rogue control list” on page 263 ), then the ap will take measures to prevent stations from staying associated to the rogue. When the monitor radio is scanning, any time it hears...
Page 402
Wireless access point 376 configuring the wireless ap procedure for configuring intrusion detection rf intrusion detection and auto block mode 1. Intrusion detection mode: this option allows you to choose the standard intrusion detection method, or you can choose off to disable this feature. See “ap...
Page 403
Wireless access point configuring the wireless ap 377 without a controlling access point, also called an independent basic service set — ibss). • ess/infrastructure only — only consider auto blocking rogue aps if they are in infrastructure mode rather than ad hoc mode. 6. Auto block whitelist: use t...
Page 404
Wireless access point 378 configuring the wireless ap 8. Duration attack nav (ms) : for the duration attack, you may also modify the default duration value that is used to determine whether a packet may be part of an attack. If the number of packets having at least this duration value exceeds the th...
Page 405
Wireless access point configuring the wireless ap 379 choose on radio enabled or on first association, as desired. You may also choose disabled to keep the leds from being lit. The leds will still light during the boot sequence, then turn off. 2. Led blink behavior : this option allows you to select...
Page 406
Wireless access point 380 configuring the wireless ap the dscp mappings page shows the default mapping of each of the 64 dscp values to one of the ap’s four qos levels, and allows you to change these mappings. For a detailed discussion of the operation of qos and dscp mappings on the ap, please see ...
Page 407
Wireless access point configuring the wireless ap 381 rssi of client = -75 -75 another example: threshold = -15 rssi of neighbor ap = -60 rssi of station = -70 -70 > (-15 + -60) : client will not roam figure 184. Roaming assist procedure for configuring roaming assist 1. Enable roaming assist: use ...
Page 408
Wireless access point 382 configuring the wireless ap 3. Roaming threshold : this is the difference in signal strength between radios that will trigger a deauthentication, as described in the discussion above. In most cases, this will be a negative number. Triggering occurs regardless of whether the...
Page 409
Wireless access point configuring the wireless ap 383 wds this is a status-only window that provides an overview of all wds links that have been defined. Wireless distribution system (wds) is a system that enables the interconnection of access points wirelessly, allowing your wireless network to be ...
Page 410
Wireless access point 384 configuring the wireless ap in the link. When the client link is created, each member iap will associate to a radio on the host ap. You may wish to consider configuring the wds link iaps so that only the wds link ssids are active on them. See “active iaps” on page 297 . Fig...
Page 411
Wireless access point configuring the wireless ap 385 long distance links if you are using wds to provide backhaul over an extended distance, use the wds dist. (miles) setting to prevent timeout problems associated with long transmission times. (see “iap settings” on page 312 ) set the approximate d...
Page 412
Wireless access point 386 configuring the wireless ap procedure for setting up wds client links 1. Host link stations : check the allow checkbox to instruct the ap to allow stations to associate to iaps on a host ap that participates in a wds link. The wds host iap will send beacons announcing its a...
Page 413
Wireless access point configuring the wireless ap 387 storedrssi = (storedrssi * roamingavgweight + newrssireading * (100 - roamingavgweight)) / 100 this prevents erroneous or out-of-line rssi readings from causing the wds link to jump to a new ap. Such readings can result from temporary obstructio...
Page 414
Wireless access point 388 configuring the wireless ap 11. Username : enter a username for this wds link. A username and password is required if the ssid is using peap for wds authentication from the internal radius server. 12. Password : enter a password for this wds link. 13. Clear settings : click...
Page 415
Wireless access point configuring the wireless ap 389 filters the wireless ap’s integrated firewall uses stateful inspection to speed the decision of whether to allow or deny traffic. Filters are used to define the rules used for blocking or passing traffic. Filters can also set the vlan and qos lev...
Page 416
Wireless access point 390 configuring the wireless ap under the filter list to which they belong. Each filter entry is a link that takes you to its filter management entry, and the list includes information about the type of filter, the protocol it is filtering, which port it applies to, source and ...
Page 417
Wireless access point configuring the wireless ap 391 procedure for managing filter lists 1. Stateful filtering: stateful operation of the integrated firewall can be enabled or disabled. If you have a large number of filters and you don’t want to apply them in a stateful manner, you may use this opt...
Page 418
Wireless access point 392 configuring the wireless ap custom application control list 9. Create new list : enter a name for the new application control list in this field, followed by the enter key. The new list is added to the application control lists table, and this list may be used to create fil...
Page 419
Wireless access point configuring the wireless ap 393 filter management this window allows you to create and manage filters that belong to a selected filter list, based on the filter criteria you specify. Filters are an especially powerful feature when combined with the intelligence provided by the ...
Page 420
Wireless access point 394 configuring the wireless ap non- critical traffic from applications like youtube may be given lower priority (qos) or bandwidth allowed may be capped per station or for all stations. Traffic flows for specific applications may be controlled by sending them into vlans that a...
Page 421
Wireless access point configuring the wireless ap 395 viewing or modifying existing filter entries: 4. Filter : select a filter entry if you wish to modify it. Source and destination details are displayed below the bottom of the list. 5. On : use this field to enable or disable this filter. 6. Log :...
Page 422
Wireless access point 396 configuring the wireless ap 13. Qos : (optional) set packets ingressing from the wired network that match the filter criteria to this qos level (0 to 3) before sending them out on the wireless network. Select the level from the pull-down list. Level 0 has the lowest priorit...
Page 423
Wireless access point configuring the wireless ap 397 the category games from 9:00 to 12:00, and another could deny them from 13:00 to 18:00. Similarly, you might create two rules for different days—one to deny games mon-fri 8:00 to 18:00, and another to deny them on sat. From 8:00 to 12:00. 20. Sou...
Page 424
Wireless access point 398 configuring the wireless ap 24. Application lists : if you wish this filter to apply to a previously configured custom application control list , select the desired list. You may not select a category or an application in addition to the list. 25. Click the save button if y...
Page 425
Wireless access point configuring the wireless ap 399 clusters clusters allow you to configure multiple aps at the same time. Using wmi (or cli), you may define a set of aps that are members of the cluster. Then you may enter cluster mode for a selected cluster, which sends all successive configurat...
Page 426
Wireless access point 400 configuring the wireless ap are shown, along with the number of aps currently in each. Up to 16 clusters may be created, with up to 50 aps in each. Figure 193. Cluster management procedure for managing cluster definition 1. New cluster name: enter a name for the new cluster...
Page 427
Wireless access point configuring the wireless ap 401 note that the ap on which you are currently running wmi is not automatically a member of the cluster. If you would like it to be a member, you must add it explicitly. Procedure for managing clusters 1. Edit cluster: expand the entry for the clust...
Page 428
Wireless access point 402 configuring the wireless ap 4. Some status and statistics windows will present information for all aps in the cluster. 5. Click the save button when done if you wish to save changes on the cluster member aps. 6. Exit: click the button to the right of the operating cluster t...
Page 429
Wireless access point configuring the wireless ap 403 you may terminate cluster mode operation by clicking the button to the right of the row..
Page 430
Wireless access point 404 configuring the wireless ap mobile mobile device management (mdm) servers enable you to manage large-scale deployments of mobile devices. They may include capabilities to handle tasks such as enrolling devices in your environment, configuring and updating device settings ov...
Page 431
Wireless access point configuring the wireless ap 405 the ap settings entered on this page are mostly taken from airwatch. Once you have entered these settings, your users will be constrained to follow a set of steps to access the wireless network, as described in “user procedure for wireless access...
Page 432
Wireless access point 406 configuring the wireless ap 8. Redirect url : obtain this from your airwatch server. Go to the system / advanced / site urls page, and copy the enrollment url string into this field. When a mobile device that is not currently enrolled with airwatch attempts to connect to th...
Page 433
Wireless access point configuring the wireless ap 407 5. If the device is not enrolled, all user traffic will be blocked, except that http traffic is redirected to an intermediate page on the ap that tells the user to download and install the airwatch agent. The page displays a link to the airwatch-...
Page 434
Wireless access point 408 configuring the wireless ap.
Page 435
Wireless access point using tools on the wireless ap 409 using tools on the wireless ap these wmi windows allow you to perform administrative tasks on your ap, such as upgrading software, rebooting, uploading and downloading configuration files, and other utility tasks. Tools are described in the fo...
Page 436
Wireless access point 410 using tools on the wireless ap system tools figure 196. System tools this window allows you to manage files for software images, configuration, and web page redirect (wpr), manage the system’s configuration parameters, reboot the system, and use diagnostic tools. The page c...
Page 437
Wireless access point using tools on the wireless ap 411 when upgrading the ap for a new major release, the ap needs the new license key that enables the operation of that release before upgrading. If you do not obtain the new license first, the ap will display a message and revert to the previous s...
Page 438
Wireless access point 412 using tools on the wireless ap system note that the top line of this section shows the current software version running on the ap. See figure 196 . 1. License key if you need an updated license (for example, if you are upgrading an ap to a new major release—say, from 7.0 to...
Page 439
Wireless access point using tools on the wireless ap 413 x, your license will be updated for you automatically; with other xms versions, you can easily upgrade all members of a profile network to a new arrayos release. See “about licensing and upgrades” on page 410 for details. Click the choose file...
Page 440
Wireless access point 414 using tools on the wireless ap remote boot services (automatic updates from remote image or configuration file) figure 197. Remote boot services the ap software image or configuration file can be downloaded from an external server. In large deployments, all aps can be point...
Page 441
Wireless access point using tools on the wireless ap 415 3. Remote configuration: when the ap boots up, it fetches the specified configuration file from the tftp server defined above, and applies this configuration after the local configuration is applied. The remote configuration must be an ap conf...
Page 442
Wireless access point 416 using tools on the wireless ap perform network-wide updates), you may obtain one through auto- provisioning . Click the start button, and the ap will contact the xirrus mobilize server with its serial number and mac address to obtain and install its latest license. If the a...
Page 443
Wireless access point using tools on the wireless ap 417 • history/saved-yyyymmdd-hhmm.Conf : the setting values that were explicitly saved using the set restore point button (see step 4 below). Click update to update your configuration settings by appending to the current ap configuration. Click re...
Page 444
Wireless access point 418 using tools on the wireless ap apply . For example, the high-density option uses best practices to configure the ap for high density settings such as lecture halls, convention centers, stadiums, etc. 6. Download current configuration: click on the link titled xs_current.Con...
Page 445
Wireless access point using tools on the wireless ap 419 diagnostics 8. Diagnostic log : click the create button to update the ap information for use by xirrus customer support personnel. The name of the log file ends with diagnostic.Log , and may have an additional prefix. ( figure 199 ) figure 199...
Page 446
Wireless access point 420 using tools on the wireless ap 10. Archiving log : this log saves internal status information that may be needed by xirrus customer support personnel. Click the start button to start accumulating this information. The size of the file is self-limiting so that you do not nee...
Page 447
Wireless access point using tools on the wireless ap 421 11. Upload signature file : first, download the latest signature file from the xirrus customer support site: arrayos - xr platform latest release to your file system. Click the browse button, then browse to locate the new signature file. Click...
Page 448
Wireless access point 422 using tools on the wireless ap 12. Upload file : use this to install files for your own custom wpr splash/ login page (as described above) on the ap. Note that uploaded files are not immediately used - you must reboot the ap first. At that time, the ap looks for and uses th...
Page 449
Wireless access point using tools on the wireless ap 423 the radius ping command is a simple utility that tests connectivity to a radius server by attempting to log in with the specified username and password. When using a radius server, this command allows you to verify that the server configuratio...
Page 450
Wireless access point 424 using tools on the wireless ap 16. Ip address : for ping or trace route, enter the ip address of the target device. 17. Timeout : for ping or trace route, enter a value (in seconds) before the action times out. 18. Execute system command : click execute to start the specifi...
Page 451
Wireless access point using tools on the wireless ap 425 to enter a command, simply type it in. The command is echoed and output is shown in the normal way — that is, the same way it would be if you were using the cli directly. You may use the extra scroll bar inside the right edge of the window to ...
Page 452
Wireless access point 426 using tools on the wireless ap api documentation aps provide an api interface conforming to the restful api model. Developers may use this read-only api to read status, statistics, and settings from the ap. The interactive api documentation page provides documentation for t...
Page 453
Wireless access point using tools on the wireless ap 427 the api documentation page lists all of the apis that are available, lists their calling parameters, if any, and allows you to perform sample calls and view sample output. Status/settings the restful api on the ap is broken into these two main...
Page 454
Wireless access point 428 using tools on the wireless ap the figure above shows the get request for ethernet-stats{name}. Click again to collapse (hide) the api details. High-level details are shown, including the response class name and the response content type (limited to json at this time). Tryi...
Page 455
Wireless access point using tools on the wireless ap 429 figure 207. Api — get request response the figure above shows the response for ethernet-stats{name}. The response is produced in the human-readable json format. The status and statistics data shown are as described in “viewing status on the wi...
Page 456
Wireless access point 430 using tools on the wireless ap api documentation toolbar figure 208. Api documentation toolbar the status and settings sections each have a toolbar as shown above, offering the following options. Show/hide —expands or collapses this list of get requests. Hiding and then sho...
Page 457
Wireless access point using tools on the wireless ap 431 options this window allows you to customize the behavior of the wmi. Figure 209. Wmi display options procedure for configuring options 1. Refresh interval in seconds : many of the windows in the status section of the wmi have an auto refresh o...
Page 458
Wireless access point 432 using tools on the wireless ap logout click on the logout button to terminate your session. When the session is terminated, you are presented with the login window. Figure 210. Login window.
Page 459: The Command Line Interface
Wireless access point the command line interface 433 the command line interface this section covers the commands and the command structure used by the ap’s command line interface (cli), and provides a procedure for establishing an ssh connection to the ap. Topics discussed include: “establishing a s...
Page 460
Wireless access point 434 the command line interface administrator assign a reserved address to the ap for ease of access in the future. • if the network does not use dhcp, use the factory default address 10.0.2.1 to access either the gigabit 1 or gigabit 2 ethernet port. You may need to change the ...
Page 461
Wireless access point the command line interface 435 getting started with the cli the root command prompt ( root command prompt ) is the first prompt you see after logging in to the cli. If you are at a level other than the root command prompt you can return to this prompt at any time by using the e...
Page 462
Wireless access point 436 the command line interface the help command is only available at the root command prompt. Initiating this command generates a window that provides information about the types of help that are available with the cli. Figure 212. Help window ? Command this command is availabl...
Page 463
Wireless access point the command line interface 437 figure 214 shows an example of how the help system can provide the argument and format when specifying the time zone under the date-time command. Figure 214. Partial help.
Page 464
Wireless access point 438 the command line interface top level commands this section offers an at-a-glance view of all top level commands — organized alphabetically. Top level commands are defined here as commands that are directly accessible from the root command prompt that consists of the name of...
Page 465
Wireless access point the command line interface 439 configure commands the following table shows the second level commands that are available with the top level configure command [myap(config)#]. Show display information about the selected item. See “show commands” on page 443 . Statistics display ...
Page 466
Wireless access point 440 the command line interface cluster make configuration changes to multiple aps. Contact-info contact information for assistance on this ap. Date-time configure date and time settings. Dhcp-server configure the dhcp server. Dns configure the dns settings. End exit the configu...
Page 467
Wireless access point the command line interface 441 netflow configure netflow data collector. No disable (if enabled) or set to default value. Proxy-fwd configure proxy forwarding settings. Quick-config apply configuration template for typical deployment scenario. Quit exit the command line interfa...
Page 468
Wireless access point 442 the command line interface syslog enable, disable or configure the syslog server. Tunnel configure tunnels. Uptime display time since the last boot. Vlan configure vlan parameters. Wifi-tag configure vlan parameters. Xms-override override xms managed mode and allow local co...
Page 469
Wireless access point the command line interface 443 show commands the following table shows the second level commands that are available with the top level show command [myap# show]. Command description acl display the access control list. Active-directory show active directory information. Admin d...
Page 470
Wireless access point 444 the command line interface country-list display countries that the ap can be set to support. Date-time display date and time settings summary. Dhcp-leases display ip addresses (leases) assigned to stations by the dhcp server. Dhcp-pool display internal dhcp server settings ...
Page 471
Wireless access point the command line interface 445 lastboot-config display ap configuration at the time of the last boot-up. Lldp link layer discovery protocol information. Location- reporting location server reporting information. Mac-table mac address bridging table management display settings f...
Page 472
Wireless access point 446 the command line interface self-test display self test results. Snmp display snmp summary information. Spanning-tree display spanning tree information. Spectrum- analyzer display spectrum analyzer measurements. Ssid display ssid summary information. Station- assurance stati...
Page 473
Wireless access point the command line interface 447 display configuration or status information. Iap-name iap1, iap2 iap interface information command description.
Page 474
Wireless access point 448 the command line interface statistics commands the following table shows the second level commands that are available with the top level statistics command [myap# statistics]. Command description ethernet display statistical data for all ethernet interfaces. Filter display ...
Page 475
Wireless access point the command line interface 449 ethernet name eth0 , gig1, gig2 display statistical data for the defined ethernet interface (either eth0, gig1 or gig2). Format: statistics gig1 iap-name iap1, iap2 iap interface information command description.
Page 476
Wireless access point 450 the command line interface configuration commands all configuration commands are accessed by using the configure command at the root command prompt (myap#). This section provides a brief description of each command and presents sample formats where deemed necessary. The com...
Page 477
Wireless access point the command line interface 451 admin the admin command [myap(config-admin)#] is used to configure the administrator list. Command description add add a user to the administrator list. Format: admin add [userid] del delete a user to the administrator list. Format: admin del [use...
Page 478
Wireless access point 452 the command line interface auth the auth command [myap(config)# auth] is used to configure oauth tokens. See also, “oauth 2.0 management” on page 264 . Cdp the cdp command [myap(config)# cdp] is used to configure the cisco discovery protocol. Command description del delete ...
Page 479
Wireless access point the command line interface 453 interval the ap sends out cdp announcements at this interval. Format: cdp interval [# seconds] off disable the cisco discovery protocol format: cdp off on enable the cisco discovery protocol format: cdp on command description.
Page 480
Wireless access point 454 the command line interface clear the clear command [myap(config)# clear] is used to clear requested elements. Command description arp clear the arp table entry for a requested ip address, or clear all entries if no ip address is entered. Format: clear arp [ipaddress] authen...
Page 481
Wireless access point the command line interface 455 syslog clear all syslog messages, but continue to log new messages. Format: clear syslog undefined-vlan clear undefined vlan information. Format: clear undefined-vlan command description.
Page 482
Wireless access point 456 the command line interface cluster the cluster command [myap(config)# cluster] is used to create and operate clusters. Clusters allow you to configure multiple aps at the same time. Using cli (or wmi), you may define a set of aps that are members of the cluster. Then you ma...
Page 483
Wireless access point the command line interface 457 contact-info the contact-info command [myap(config)# contact-info] is used for managing administrator contact information. Command description email add an email address for the contact (must be in quotation marks). Format: contact-info email [“co...
Page 484
Wireless access point 458 the command line interface date-time the date-time command [myap(config-date-time)#] is used to configure the date and time parameters. Your ap supports the network time protocol (ntp) in order to ensure that the ap’s internal time is accurate. Ntp is set to utc time by def...
Page 485
Wireless access point the command line interface 459 dhcp-server the dhcp-server command [myap(config-dhcp-server)#] is used to add, delete and modify dhcp pools. Command description add add a dhcp pool. Format: dhcp-server add [dhcp pool] del delete a dhcp pool. Format: dhcp-server del [dhcp pool] ...
Page 486
Wireless access point 460 the command line interface dns the dns command [myap(config-dns)#] is used to configure your dns parameters. Command description domain enter your domain name. Format: dns domain [www.Mydomain.Com] server1 enter the ip address of the primary dns server. Format: dns server1 ...
Page 487
Wireless access point the command line interface 461 file the file command [myap(config-file)#] is used to manage files. Command description active-image validate and commit a new ap software image. Backup-image validate and commit a new backup software image. Cat list file contents. Check-image val...
Page 488
Wireless access point 462 the command line interface http-get perform an http file download. This is the preferred method of downloading files for xms cloud. Format: http-get [no-cert-check] [] no-cert-check causes the ap to download the file even if the ssl certificate is invalid, expired, or not s...
Page 489
Wireless access point the command line interface 463 remote-config when the ap boots up, it fetches the specified configuration file from the tftp server defined in the file remote-server command, and uses this configuration. This must be an ap configuration file with a .Conf extension. A partial co...
Page 492
Wireless access point 466 the command line interface air cleaner the air cleaner feature offers a number of predetermined filter rules that eliminate a great deal of unnecessary wireless traffic, resulting in improved performance. You may select all of the air cleaner rules for the greatest effect, ...
Page 493
Wireless access point the command line interface 467 if you select all, the rules shown in figure 215 are added to the predefined filter list named global. These rules assume that you have station-to-station blocking enabled, that a dhcp server is on the ap’s wired connection, and that you want to b...
Page 494
Wireless access point 468 the command line interface radios. These rogue dhcp servers are blocked from doing any damage with this filter. There have been quite a few cases in public venues like schools and conventions where such traffic is seen. Air-cleaner-mcast.1 drops all multicast traffic with a...
Page 495
Wireless access point the command line interface 469 group the group command [myap(config)# group] is used to create and configure user groups. User groups allow administrators to assign specific network parameters to users through radius privileges rather than having to map users to a specific ssid...
Page 496
Wireless access point 470 the command line interface interface the interface command [myap(config)# interface] is used to select the interface that you want to configure. To see a listing of the commands that are available for each interface, use the ? Command at the selected interface prompt. For e...
Page 497
Wireless access point the command line interface 471 load the load command [myap(config)# load] loads a configuration file. Location the location command [myap(config)# location] is used to set the location descriptive string for the ap. Command description factory.Conf load the factory settings con...
Page 498
Wireless access point 472 the command line interface location-reporting the location-reporting command [myap(config)# location-reporting] is used to configure location server settings. See also, “location” on page 191 . Command description cust-key set location server customer key. Format: location-...
Page 499
Wireless access point the command line interface 473 management the management command [myap(config)# management] enters management mode, where you may configure management parameters. The following types of settings may be configured in management mode: command description enter management mode. Fo...
Page 500
Wireless access point 474 the command line interface network- assurance enable/disable network assurance. Pci-audit enable/disable pci (payment card industry) audit mode. See “auditing pci dss” on page 593 . Quick-config apply quick configuration template. Quit exit the command line interface. Reaut...
Page 501
Wireless access point the command line interface 475 mdm the mdm command [myap(config)# mdm] is used to configure mobile device management server settings. See also, “mobile” on page 404 . Xircon enable/disable xircon access. See xircon user’s guide for more information. Command description airwatch...
Page 502
Wireless access point 476 the command line interface more the more command [myap(config)# more] is used to turn terminal pagination on or off. Command description disable off turn off terminal pagination. Format: more off enable on turn on terminal pagination. Format: more on.
Page 503
Wireless access point the command line interface 477 netflow the netflow command [myap(config-netflow)#] is used to enable or disable, or configure sending ip flow information (traffic statistics) to the collector you specify. Command description collector set the netflow collector ip address or ful...
Page 504
Wireless access point 478 the command line interface no the no command [myap(config)# no] is used to disable a selected element or set the element to its default value. Command description 2.4ghz disable all 2.4ghz iaps. 5ghz disable all 5ghz iaps. Acl disable the access control list. Format: no acl...
Page 505
Wireless access point the command line interface 479 quick-config the quick-config command is used to apply configuration templates to the ap for typical deployment scenarios. Snmp disable snmp features. Format: no snmp spanning-tree disable spanning tree. Ssh disable ssh access. Format: no ssh sysl...
Page 506
Wireless access point 480 the command line interface quit the quit command [myap(config)# quit] is used to exit the command line interface. Authentication-server the authentication-server command [myap(config-authserver)#] is used to configure the external and internal radius server parameters. Comm...
Page 507
Wireless access point the command line interface 481 use choose the active radius server (either external or internal). Format: authentication-server use external (or internal) command description.
Page 508
Wireless access point 482 the command line interface reboot the reboot command [myap(config)# reboot] is used to reboot the ap. If you have unsaved changes, the command will notify you and give you a chance to cancel the reboot. Reset the reset command [myap(config)# reset] is used to reset all sett...
Page 509
Wireless access point the command line interface 483 restore the restore command [myap(config)# restore] is used to restore configuration to a version that was previously saved locally. Command description ? Use this to display the list of available config files. Format: restore ? Enter the name of ...
Page 510
Wireless access point 484 the command line interface roaming-assist the roaming-assist command [myap(config)# roaming-assist] is used to configure roaming assistance settings. See also, “roaming assist” on page 380 . Command description data-rate set minimum packet data rate before roaming, in mbps....
Page 511
Wireless access point the command line interface 485 run-tests the run-tests command [myap(run-tests)#] is used to enter run-tests mode, which allows you to perform a range of tests on the ap. Command description @ execute command from history ad-authenticate test domain user authentication. Ad-chec...
Page 514
Wireless access point 488 the command line interface snmp the snmp command [myap(config-snmp)#] is used to enable, disable, or configure snmp. Command description trap configure traps for snmp. Up to four trap destinations may be configured, and you may specify whether to send traps for authenticati...
Page 515
Wireless access point the command line interface 489 ssid the ssid command [myap(config-ssid)#] is used to establish your ssid parameters. Command description add add an ssid. Format: ssid add [newssid] del delete an ssid. Format: ssid del [oldssid] edit edit an existing ssid. Format: ssid edit [exi...
Page 516
Wireless access point 490 the command line interface syslog the syslog command [myap(config-syslog)#] is used to enable, disable, or configure the syslog server. Command description console enable or disable the display of syslog messages on the console, and set the level to be displayed. All messag...
Page 517
Wireless access point the command line interface 491 tunnel the tunnel command [myap(config-tunnel)#] is used to establish your tunnel parameters. Primary set the ip address of the primary syslog server and/or the severity level of messages to be logged. Format: syslog primary [1.2.3.4] level [0-7] ...
Page 518
Wireless access point 492 the command line interface uptime the uptime command [myap(config)# uptime] is used to display the elapsed time since you last rebooted the ap. Vlan the vlan command [myap(config-vlan)#] is used to establish your vlan parameters. Edit modify an existing tunnel. Format: tunn...
Page 519
Wireless access point the command line interface 493 wifi-tag the wifi-tag command [myap(config-wifi-tag)#] is used to enable or disable wi-fi tag capabilities. When enabled, the ap listens for and collects information default-route assign a vlan for the default route (for outbound management traffi...
Page 520
Wireless access point 494 the command line interface about wi-fi rfid tags sent on the designated channels. See also “wi-fi tag” on page 190 . Command description disable off disable wifi-tag. Format: wifi-tag disable enable on enable wifi-tag. Format: wifi-tag enable refresh disable and enable wifi...
Page 521
Wireless access point the command line interface 495 sample configuration tasks this section provides examples of some of the common configuration tasks used with the wireless ap, including: “configuring a simple open global ssid” on page 496. “configuring a global ssid using wpa-peap” on page 497. ...
Page 522
Wireless access point 496 the command line interface configuring a simple open global ssid this example shows you how to configure a simple open global ssid. Figure 216. Configuring a simple open global ssid.
Page 523
Wireless access point the command line interface 497 configuring a global ssid using wpa-peap this example shows you how to configure a global ssid using wpa-peap encryption in conjunction with the ap’s internal radius server. Figure 217. Configuring a global ssid using wpa-peap.
Page 524
Wireless access point 498 the command line interface configuring an ssid-specific ssid using wpa-peap this example shows you how to configure an ssid-specific ssid using wpa- peap encryption in conjunction with the ap’s internal radius server. Figure 218. Configuring an ssid-specific ssid using wpa-...
Page 525
Wireless access point the command line interface 499 enabling global iaps this example shows you how to enable all iaps (radios), regardless of the wireless technology they use. Figure 219. Enabling global iaps.
Page 526
Wireless access point 500 the command line interface disabling global iaps this example shows you how to disable all iaps (radios), regardless of the wireless technology they use. Figure 220. Disabling global iaps.
Page 527
Wireless access point the command line interface 501 enabling a specific iap this example shows you how to enable a specific iap (radio). In this example, the iap that is being enabled is a1 (the first iap in the summary list). Figure 221. Enabling a specific iap.
Page 528
Wireless access point 502 the command line interface disabling a specific iap this example shows you how to disable a specific iap (radio). In this example, the iap that is being disabled is a2 (the second iap in the summary list). Figure 222. Disabling a specific iap.
Page 529
Wireless access point the command line interface 503 setting cell size auto-configuration for all iaps this example shows how to set the cell size for all enabled iaps to be auto- configured (auto). (see “fine tuning cell sizes” on page 37 .) the auto_cell option may be used with global_settings, gl...
Page 530
Wireless access point 504 the command line interface setting the cell size for all iaps this example shows you how to establish the cell size for all iaps (radios), regardless of the wireless technology they use. Be aware that if the intrude-detect feature is enabled on the monitor radio the cell si...
Page 531
Wireless access point the command line interface 505 setting the cell size for a specific iap this example shows you how to establish the cell size for a specific iap (radio). In this example, the cell size for a2 is being set to medium. You have the option of setting iap cell sizes to small, medium...
Page 532
Wireless access point 506 the command line interface configuring vlans on an open ssid this example shows you how to configure vlans on an open ssid. Figure 226. Configuring vlans on an open ssid setting the default route enables the ap to send management traffic, such as syslog messages and snmp in...
Page 533
Wireless access point the command line interface 507 configuring radio assurance mode (loopback tests) the ap uses its built-in monitor radio to monitor other radios in the ap. Tests include sending probes on all channels and checking for a response, and checking whether beacons are received from th...
Page 534
Wireless access point 508 the command line interface figure 227. Configuring radio assurance mode (loopback testing).
Page 535: Appendices
Wireless access point appendices 509 appendices.
Page 536
Wireless access point 510 appendices page is intentionally blank.
Page 537
Wireless access point 511 appendix a: quick reference guide this section contains product reference information. Use this section to locate the information you need quickly and efficiently. Topics include: “factory default settings” on page 511 . “keyboard shortcuts” on page 517 . Factory default se...
Page 538
Wireless access point 512 gigabit 1 and gigabit 2 server settings ntp syslog setting default value enabled yes dhcp yes default ip address 10.0.2.1 default ip mask 255.255.255.0 default gateway none auto negotiate on duplex full speed 1000 mbps mtu size 1500 management enabled yes setting default va...
Page 539
Wireless access point 513 snmp dhcp local syslog level information maximum internal records 500 primary server none primary syslog level information secondary server none secondary syslog level information setting default value enabled yes read-only community string (v2) xirrus_read_only read-write ...
Page 540
Wireless access point 514 default ssid security global settings - encryption ip start range 192.168.1.4 ip end range 192.168.1.254 nat disabled ip gateway none dns domain none dns server (1 to 3) none setting default value id xirrus vlan none encryption off encryption type none qos 2 enabled yes bro...
Page 541
Wireless access point 515 external radius (global) wep key length null (all 4 keys) default key id 1 wpa enabled no tkip enabled yes aes enabled yes eap enabled yes psk enabled no pass phrase null group rekey disabled setting default value enabled yes primary server none primary port 1812 primary se...
Page 542
Wireless access point 516 internal radius administrator account and password management primary server none primary port 1813 primary secret null (no secret) secondary server none secondary port 1813 secondary secret null (no secret) setting default value enabled no the user database is cleared upon...
Page 543
Wireless access point 517 keyboard shortcuts the following table shows the most common keyboard shortcuts used by the command line interface. Telnet off telnet timeout 300 seconds serial on serial timeout 300 seconds management over iaps off http timeout 300 seconds action shortcut cut selected data...
Page 544
Wireless access point 518.
Page 545
Wireless access point 519 appendix b: faq and special topics this appendix provides valuable support information that can help you resolve technical difficulties. Before contacting xirrus, review all topics below and try to determine if your problem resides with the wireless ap or your network infra...
Page 546
Wireless access point 520 see also multiple ssids security vlan support frequently asked questions this section answers some of the most frequently asked questions, organized by functional area. Multiple ssids q. What are bssids and ssids? A. Bssid (basic service set identifier) refers to an individ...
Page 547
Wireless access point 521 the wireless quality of service (qos) desired for this ssid. The wired vlan associated with this ssid. As an example, one ssid named accounting might require the highest level of security, while another ssid named guests might have low security requirements. Another example...
Page 548
Wireless access point 522 8. If you need to edit any of the ssid settings, you can do so from the ssid management page. See also general hints and tips security ssids ssid management vlan support security q. How do i ensure that i meet fips requirements? A. To meet the level 2 security requirements ...
Page 549
Wireless access point 523 configuration auditing do not change approved configuration settings. The optional xms offers powerful management features for small or large wireless ap deployments, and can audit your configuration settings automatically. In addition, using the xms eliminates the need for...
Page 550
Wireless access point 524 older wireless clients). Because aes is the strongest encryption standard currently available, it is highly recommended for enterprise networks. Any of the above encryption modes can be used (and can be used at the same time). Q. Which user authentication method should i us...
Page 551
Wireless access point 525 number of users — in this case, enter the mac addresses of each user in the allow list. In the event of a lost or stolen mac adapter, enter the affected mac address in the deny list. Q. Why do i need to authenticate my wireless ap units? A. When deploying multiple wireless ...
Page 552
Wireless access point 526 particular vlan according to the ieee 802.1q standard, with vlan switches processing packets according to the tag. Q. What would i use vlans for? A. Logically separating different types of users, systems, applications, or other logical division aids in performance and manag...
Page 553
Wireless access point 527 ap monitor and radio assurance capabilities all models of the wireless ap have integrated monitoring capabilities to check that the ap’s radios are functioning correctly, and act as a threat sensor to detect and prevent intrusion from rogue access points. Enabling monitorin...
Page 554
Wireless access point 528 intrusion detectio n is enabled or disabled separately from monitoring. See step 1 in “intrusion detection” on page 372 . Radio assurance the ap is capable of performing continuous, comprehensive tests on its radios to assure that they are operating properly. Testing is ena...
Page 555
Wireless access point 529 • when no stations are associated to the ap • midnight radio assurance options if the monitor detects a problem with an ap radio as described above, it will take action according to the preference that you have specified in the radio assurance mode setting on the advanced r...
Page 556
Wireless access point 530 radius vendor specific attribute (vsa) for xirrus a radius vsa is defined for xirrus aps to control administrator privilege settings for user accounts. The radius vsa is used by aps to define the following attribute for administrator accounts: ap administrators — the xirrus...
Page 557
Wireless access point 531 location service data formats xirrus aps are able to capture and upload visitor analytics data, acting as a sensor network in addition to providing wireless connectivity. This data is sent to the location server in different formats, based on the type of server. The locatio...
Page 558
Wireless access point 532 ** sample format with five radios receiving a station’s probe request: "pr":{"00:0f:7d:44:03:20":-69,"00:0f:7d:44:03:30":-68,"00:0f:7d:44:03:40":-70, "00:0f:7d:44:03:60":-68,"00:0f:7d:44:03:70":-60} bi bssid bssid that the station is on (aes encrypted if cust-key is not bla...
Page 559
Wireless access point 533 upgrading the ap using the boot loader if you are experiencing difficulties communicating with the ap using the web management interface, the ap provides lower-level facilities that may be used to accomplish an upgrade via the boot loader (xbl). 1. Log in to your xirrus cus...
Page 560
Wireless access point 534 user’s guide here . You may also find this useful: how can i access my ap if it does not seem to be accessible via ip? How do i access an ap via console or xircon? Attach a network cable to the ap’s gig1 port, if it is not already part of your network. Boot your ap and watc...
Page 561
Wireless access point 535 sample output for the upgrade procedure: the user actions are highlighted in the output below, for clarity. Output will be in the form shown below, but may not be exactly the same. Username: admin password: ***** xr50326004f89# configure xr50326004f89(config)# reboot are yo...
Page 562
Wireless access point 536 username: admin password: ***** xbl>dhcp [dhcp ] device : eth0 - 1000 mbps full duplex [dhcp ] ip addr : 10.100.44.48 xbl>dir [usb 0 ] directory of / date time size file or directory name ----------- -------- ---------- --------------------------- 2014-dec-12 18:47:16 17776...
Page 563
Wireless access point 537 [tftp ] loading : ################################################ done [tftp ] complete: 7.4 sec, 10.1 mb/sec [tftp ] bytes : 78027656 (4a69b88 hex), 10226 kbytes/sec [usb 0 ] file : xs-7.2.3-5452.Bin [usb 0 ] address : 0x6000000 [usb 0 ] saving : #########################...
Page 564
Wireless access point 538 [flash ] saving : environment 4 kb xbl>boot [usb 0 ] file : xs-7.2.3-5452.Bin [usb 0 ] address : 0x6000000 [usb 0 ] loading : ################################################## [usb 0 ] loading : ################################################ done [usb 0 ] complete: 6.5 s...
Page 565: Series Only)
Wireless access point 539 appendix c: notices (xd4 and xr500/600 series only) this appendix contains the following information: “notices” on page 539 “eu directive 1999/5/ec compliance information” on page 543 “compliance information (non-eu)” on page 550 “safety warnings” on page 552 “translated sa...
Page 566
Wireless access point 540 this equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a class b digital device, pursuant to part 15 of the fcc rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful interference in a residential installation. This equipment gener...
Page 567
Wireless access point 541 modifications to the device will void the warranty and may violate fcc regulations. Cable runs for power over gigabit ethernet (poge) if using poge, the ap must be connected to poge networks without routing cabling to the outside plant — this ensures that cabling is not exp...
Page 568
Wireless access point 542 ce dispositif est conforme à la norme cnr-210 d'industrie canada applicable aux appareils radio exempts de licence. Son fonctionnement est sujet aux deux conditions suivantes: (1) le dispositif ne doit pas produire de brouillage préjudiciable, et (2) ce dispositif doit acce...
Page 569
Wireless access point 543 eu directive 1999/5/ec compliance information this section contains compliance information for the xirrus wireless ap family of products. The compliance information contained in this section is relevant to the european union and other countries that have implemented the eu ...
Page 570
Wireless access point 544 français [french] cet appareil est conforme aux exigences essentielles et aux autres dispositions pertinentes de la directive 1999/5/ec. ĺ slenska [icelandic] Þetta tæki er samkvæmt grunnkröfum og öðrum viðeigandi ákvæðum tilskipunar 1999/5/ec. Italiano [italian] questo app...
Page 571
Wireless access point 545 assessment criteria the following standards were applied during the assessment of the product against the requirements of the directive 1999/5/ec: radio: en 301 893 and en 300 328 (if applicable) emc: en 301 489-1 and en 301 489-17 safety: en 50371 to en 50385 and en 60601 ...
Page 572
Wireless access point 546 weee compliance natural resources were used in the production of this equipment. This equipment may contain hazardous substances that could impact the health of the environment. In order to avoid harm to the environment and consumption of natural resources, we encourage you...
Page 573
Wireless access point 547 national restrictions in the majority of the eu and other european countries, the 2.4 ghz and 5 ghz bands have been made available for the use of wireless lans. The following table provides an overview of the regulatory requirements in general that are applicable for the 2....
Page 574
Wireless access point 548 les liasons sans fil pour une utilisation en extérieur d’une distance supérieure à 300 mèters doivent être notifiées à l’institut belge des services postaux et des télécommunications (ibpt). Visitez www.Bipt.Be pour de plus amples détails. Greece a license from eett is requ...
Page 575
Wireless access point 549 antennas the xirrus wireless ap employs integrated antennas that cannot be removed and which are not user accessible. Nevertheless, as regulatory limits are not the same throughout the eu, users may need to adjust the conducted power setting for the radio to meet the eirp l...
Page 576
Wireless access point 550 compliance information (non-eu) this section contains compliance information for the xirrus wireless ap family of products. The compliance information contained in this section is relevant to the listed countries (outside of the european union and other countries that have ...
Page 577
Wireless access point 551 declaration of conformity mexico xr-520: dictamen #: 1402d00742 xr-600: dictamen #: 1402ce08098 xr-520: cofetel cert #: rcpxixr13-1003 thailand this telecommunication equipment conforms to ntc technical requirement..
Page 578
Wireless access point 552 safety warnings translated safety warnings appear on the following page. This appendix contains notices, warnings, and compliance information for the xd4 and xr500/600 series only. For other models, see the notes under “notices (xr-1000 to xr-6000 indoor models)” on page 56...
Page 579
Wireless access point 553 translated safety warnings avertissements de sécurité this appendix contains notices, warnings, and compliance information for the xd4 and xr500/600 series only. For other models, see the notes under “notices (xr-1000 to xr-6000 indoor models)” on page 563. ! Sécurité lisez...
Page 580
Wireless access point 554 software license and product warranty agreement this software license agreement (the “agreement”) is a legal agreement between you (“customer”) and licensor (as defined below) and governs the use of the software installed on the product (as defined below). If you are an emp...
Page 581
Wireless access point 555 the product in accordance with the accompanying documentation and for no other purpose. 2.2 ownership. The license granted under sections 2.1 above with respect to the software does not constitute a transfer or sale of licensor's or its suppliers' ownership interest in or t...
Page 582
Wireless access point 556 3.0 limited warranty and limitation of liability 3.1 limited warranty & exclusions. Licensor warrants that the software will perform in substantial accordance with the specifications therefore set forth in the documentation for a period of ninety [90] days after customer's ...
Page 583
Wireless access point 557 3.4 limitation of liability. (a) total liability. Notwithstanding anything else herein, all liability of licensor and its suppliers under this agreement shall be limited to the amount paid by customer for the relevant software, or portion thereof, that gave rise to such lia...
Page 584
Wireless access point 558 protective of a party's right in such confidential information as those set forth herein. 4.2 return of materials. Customer agrees to (i) destroy all confidential information (including deleting any and all copies contained on any of customer's designated hardware or the pr...
Page 585
Wireless access point 559 6. Miscellaneous if customer is a corporation, partnership or similar entity, then the license to the software and documentation that is granted under this agreement is expressly conditioned upon and customer represents and warrants to licensor that the person accepting the...
Page 586
Wireless access point 560 hardware warranty agreement please read this agreement carefully before using this product by using this product, you acknowledge that you have read and understood all the terms and conditions of this agreement and that you are consenting to be bound by this agreement. If y...
Page 587
Wireless access point 561 whether in contract, tort (including negligence), or otherwise, exceed the price paid by customer. The foregoing limitations shall apply even if the above-stated warranty fails of its essential purpose. Some states do not allow limitation or exclusion of liability for conse...
Page 588
Wireless access point 562.
Page 589: Appendix D: Notices
Wireless access point 563 appendix d: notices (xr-1000 to xr-6000 indoor models) this appendix contains the following information: “notices” on page 563 “eu directive 1999/5/ec compliance information” on page 567 “compliance information (non-eu)” on page 574 “safety warnings” on page 576 “translated...
Page 590
Wireless access point 564 provide reasonable protection against harmful interference in a residential installation. This equipment generates, uses and can radiate rf energy and, if not installed and used in accordance with the instructions, may cause harmful interference to radio communications. How...
Page 591
Wireless access point 565 battery warning ul statement use only with listed ite product. Rf radiation hazard warning to ensure compliance with fcc and industry canada rf exposure requirements, this device must be installed in a location where the antennas of the device will have a minimum distance o...
Page 592
Wireless access point 566 conformément à la réglementation d'industrie canada, le présent émetteur radio peut fonctionner avec une antenne d'un type et d'un gain maximal (ou inférieur) approuvé pour l'émetteur par industrie canada. Dans le but de réduire les risques de brouillage radioélectrique à l...
Page 593
Wireless access point 567 eu directive 1999/5/ec compliance information this section contains compliance information for the xirrus wireless array family of products. The compliance information contained in this section is relevant to the european union and other countries that have implemented the ...
Page 594
Wireless access point 568 français [french] cet appareil est conforme aux exigences essentielles et aux autres dispositions pertinentes de la directive 1999/5/ec. ĺ slenska [icelandic] Þetta tæki er samkvæmt grunnkröfum og öðrum viðeigandi ákvæðum tilskipunar 1999/5/ec. Italiano [italian] questo app...
Page 595
Wireless access point 569 assessment criteria the following standards were applied during the assessment of the product against the requirements of the directive 1999/5/ec: radio: en 301 893 and en 300 328 (if applicable) emc: en 301 489-1 and en 301 489-17 safety: en 50371 to en 50385 and en 60601 ...
Page 596
Wireless access point 570 weee compliance natural resources were used in the production of this equipment. This equipment may contain hazardous substances that could impact the health of the environment. In order to avoid harm to the environment and consumption of natural resources, we encourage you...
Page 597
Wireless access point 571 national restrictions in the majority of the eu and other european countries, the 2.4 ghz and 5 ghz bands have been made available for the use of wireless lans. The following table provides an overview of the regulatory requirements in general that are applicable for the 2....
Page 598
Wireless access point 572 les liasons sans fil pour une utilisation en extérieur d’une distance supérieure à 300 mèters doivent être notifiées à l’institut belge des services postaux et des télécommunications (ibpt). Visitez www.Bipt.Be pour de plus amples détails. Greece a license from eett is requ...
Page 599
Wireless access point 573 antennas the xirrus wireless array employs integrated antennas that cannot be removed and which are not user accessible. Nevertheless, as regulatory limits are not the same throughout the eu, users may need to adjust the conducted power setting for the radio to meet the eir...
Page 600
Wireless access point 574 compliance information (non-eu) this section contains compliance information for the xirrus wireless array family of products. The compliance information contained in this section is relevant to the listed countries (outside of the european union and other countries that ha...
Page 601
Wireless access point 575 declaration of conformity —brazil xr-1000 xr-2000 xr-4000
Page 602
Wireless access point 576 safety warnings translated safety warnings appear on the following page. This appendix contains notices, warnings, and compliance information for all array models except for the xr-500/600 series and models ending in h . For notices, warnings, and compliance information for...
Page 603
Wireless access point 577 translated safety warnings avertissements de sécurité this appendix contains notices, warnings, and compliance information for all array models except for the xr-500/600/xd series and models including the letter h . For notices, warnings, and compliance information for thos...
Page 604
Wireless access point 578 software license and product warranty agreement this software license agreement (the “agreement”) is a legal agreement between you (“customer”) and licensor (as defined below) and governs the use of the software installed on the product (as defined below). If you are an emp...
Page 605
Wireless access point 579 the product in accordance with the accompanying documentation and for no other purpose. 2.2 ownership. The license granted under sections 2.1 above with respect to the software does not constitute a transfer or sale of licensor's or its suppliers' ownership interest in or t...
Page 606
Wireless access point 580 3.0 limited warranty and limitation of liability 3.1 limited warranty & exclusions. Licensor warrants that the software will perform in substantial accordance with the specifications therefore set forth in the documentation for a period of ninety [90] days after customer's ...
Page 607
Wireless access point 581 3.4 limitation of liability. (a) total liability. Notwithstanding anything else herein, all liability of licensor and its suppliers under this agreement shall be limited to the amount paid by customer for the relevant software, or portion thereof, that gave rise to such lia...
Page 608
Wireless access point 582 protective of a party's right in such confidential information as those set forth herein. 4.2 return of materials. Customer agrees to (i) destroy all confidential information (including deleting any and all copies contained on any of customer's designated hardware or the pr...
Page 609
Wireless access point 583 6. Miscellaneous if customer is a corporation, partnership or similar entity, then the license to the software and documentation that is granted under this agreement is expressly conditioned upon and customer represents and warrants to licensor that the person accepting the...
Page 610
Wireless access point 584 hardware warranty agreement please read this agreement carefully before using this product by using this product, you acknowledge that you have read and understood all the terms and conditions of this agreement and that you are consenting to be bound by this agreement. If y...
Page 611
Wireless access point 585 whether in contract, tort (including negligence), or otherwise, exceed the price paid by customer. The foregoing limitations shall apply even if the above-stated warranty fails of its essential purpose. Some states do not allow limitation or exclusion of liability for conse...
Page 612
Wireless access point 586.
Page 613
Wireless access point 587 appendix e: medical usage notices xirrus xr‐1000/2000/4000/6000 series wireless devices have been tested and found to comply with the requirements of iec 60601‐1‐2. Section 5.2.1.1 ‐ the xirrus wireless device needs special precautions regarding emc and must be installed an...
Page 614
Wireless access point 588 section 5.2.2.1 (f) table 2 guidance and manufacturer’s declaration – electromagnetic immunity xirrus wireless devices are intended for use in the electromagnetic environment specified below. The customer or the user of the xirrus wireless device should assure that it is us...
Page 615
Wireless access point 589 section 5.2.2.1 (g) xirrus wireless devices have no essential performance per iec 60601‐1‐2. Section 5.2.2.2 – tables 4 and 6 table 4 for non‐life supporting equipment guidance and manufacturer’s declaration – electromagnetic immunity xirrus wireless devices are intended fo...
Page 616
Wireless access point 590 table 6 for non‐life supporting equipment note 1 at 80 mhz and 800 mhz, the higher frequency range applies. Note 2 these guidelines may not apply in all situations. Electromagnetic propagation is affected by absorption and reflection from structures, objects and people. A f...
Page 617
Wireless access point 591 section 5.2.2.5 both single channels (20mhz bandwidth) and bonded channels (40mhz bandwidth) are supported. Section 5.2.2.6 the types of modulation used include cck, qspk, bpsk, dss, ofdm, 16‐qam, and 64‐qam. The regulatory limits for maximum output power are specified in e...
Page 618
Wireless access point 592 maximum eirp 2.4ghz 36dbm 5150-5250mhz 23dbm 5250-5350mhz 30dbm 5470-5725mhz 30dbm 5725-5850mhz 36dbm.
Page 619: Appendix F: Auditing Pci Dss
Wireless access point 593 appendix f: auditing pci dss the payment card industry (pci) data security standard (dss) was developed by major credit card companies to help those that process credit card transactions (or cardholder information) in order to secure cardholder information and protect it fr...
Page 620
Wireless access point 594 pci dss and wireless the xirrus ap provides numerous security features that allow it to be a component of a pci dss-compliant network. The following sections indicate the specific features that allow the ap to operate in a pci dss mode. Objective: maintain a vulnerability m...
Page 621
Wireless access point 595 the xirrus ap pci compliance configuration the check list below is designed to help ensure that aps are configured in a manner that is supportive of pci data security standards. Detailed configuration steps for each item are found in the referenced section of the user’s gui...
Page 622
Wireless access point 596 the pci-audit command the ap provides a cli command, pci-audit (part of the management command), that checks whether the ap’s configuration satisfies pci dss wireless requirements. This command does not change any parameters, but will inform you of any violations that exist...
Page 623
Wireless access point 597 the pci-audit command checks items such as: telnet is disabled. Admin radius is enabled (admin login authentication is via radius server). An external syslog server is in use. All ssids must set encryption to wpa or better (which also enforces 802.1x authentication) sample ...
Page 624
Wireless access point 598.
Page 625
Wireless access point 599 appendix g: implementing fips security aps may be configured to satisfy the requirements for level 2 of federal information processing standard (fips) publication 140-2 . This appendix lists simple steps that must be followed exactly to implement fips 140-2, level 2 on xirr...
Page 626
Wireless access point 600 important : before you apply the tamper-evident seal, clean the area of any grease, dirt, or oil. We recommend using alcohol-based cleaning pads for this. Each seal must be applied to straddle both sides of an opening or seam so that it will show if an attempt has been made...
Page 627
Wireless access point 601 figure 230. Tamper evident seal application close-up 2. Apply four seals, near the middle of each of the sides of the enclosure and straddling the slight gap between the metal back and the plastic dome cover as shown below. Important: make sure that each seal straddles a se...
Page 628
Wireless access point 602 2. First verify that the software release running on the unit has been certified for fips (see the note on page 599 ). Click status > access point in the menu on the left of the wmi window. Then click information. In the software configuration section, check the system soft...
Page 629
Wireless access point 603 figure 232. Security - management control window 5. You may now proceed to define ssids, as described in âssidsâ on page 227 ..
Page 630
Wireless access point 604 to implement fips 140-2, level 2 using cli: for details of the settings that are enforced for fips level 2, see “about fips configuration” on page 605 . 1. Use the following command to check that the system software version running on the unit is one that has been certified...
Page 631
Wireless access point 605 in the cli, enter show management and check the fips 140-2 mode setting. See also the web management interface the command line interface about fips configuration when you put the ap in fips mode, it checks that the following settings are in effect, and changes the...
Page 632
Wireless access point 606 11. These additional features are not allowed in fips mode: ftp, tftp, and zero-touch activation. Only fips approved ciphers are used for ssh/ https in fips mode. 12. When fips mode is enabled/disabled, csps (critical security parameters) are zeroed, configuration is saved ...
Page 633: Glossary of Terms
Wireless access point glossary of terms 607 glossary of terms 802.11a a supplement to the ieee 802.11 wlan specification that describes radio transmissions at a frequency of 5 ghz and data rates of up to 54 mbps. 802.11ac a supplement to the ieee 802.11 wlan specification. Operates in the 5 ghz rang...
Page 634
Wireless access point 608 glossary of terms aes (advanced encryption standard) a data encryption scheme that uses three different key sizes (128-bit, 192-bit, and 256-bit). Aes was adopted by the u.S. Government in 2002 as the encryption standard for protecting sensitive but unclassified electronic ...
Page 635
Wireless access point glossary of terms 609 cdp (cisco discovery protocol) cdp is a layer 2 network protocol which runs on most cisco equipment and some other network equipment. It is used to share information with other directly connected network devices. Information such as the model, network capa...
Page 636
Wireless access point 610 glossary of terms dns (domain name system) a system that maps meaningful domain names with complex numeric ip addresses. Dns is actually a separate network — if one dns server cannot translate a domain name, it will ask a second or third until a server is found with the cor...
Page 637
Wireless access point glossary of terms 611 edcf (enhanced distributed coordinator function) a qos extension which uses the same contention-based access mechanism as current devices but adds “offset contention windows” that separate high priority packet s from low priority packets (by assigning a la...
Page 638
Wireless access point 612 glossary of terms gigabit 1 through 4 the gigabit ethernet interfaces on xr series aps. Xr-4000 series aps have two gigabit interfaces, while xr-6000 series and higher models have four gigabit interfaces. See also, gigabit ethernet . Gigabit ethernet a version of ethernet w...
Page 639
Wireless access point glossary of terms 613 mtu (maximum transmission unit) the largest physical packet size — measured in bytes — that a network can transmit. Any messages larger than the mtu are divided into smaller packet s before being sent. Every network has a different mtu, which is set by the...
Page 640
Wireless access point 614 glossary of terms preamble preamble (sometimes called a header) is a section of data at the head of a packet that contains information that the access point and client devices need when sending and receiving packets. Plcp has two structures, a long and a short preamble. All...
Page 641
Wireless access point glossary of terms 615 sdma (spatial division multiple access) a wireless communications mode that optimizes the use of the radio spectrum and minimizes cost by taking advantage of the directional properties of antennas. The antennas are highly directional, allowing duplicate fr...
Page 642
Wireless access point 616 glossary of terms subnet mask a mask used to determine what subnet an ip address belongs to. An ip address has two components: (1) the network address and (2) the host address. For example, consider the ip address 150.215.017.009. Assuming this is part of a class b network,...
Page 643
Wireless access point glossary of terms 617 multiple switches from different vendors. This interoperability and traffic containment across different switches is the result of a switch's ability to use and recognize 802.1q tag headers — called vlan tagging. Switches that implement 802.1q tagging add ...
Page 644
Wireless access point 618 glossary of terms wpa2 (wi-fi protected access 2) wpa2 is the follow-on security method to wpa for wireless networks and provides stronger data protection and network access control. It offers enterprise and consumer wi-fi users with a high level of assurance that only auth...
Page 645: Index
Wireless access point index 619 index numerics 11ac see 802.11ac 349 802.11a 3 , 4 , 312 , 334 802.11a/b/g 32 802.11a/b/g/n 18 802.11a/n 18 , 72 , 276 802.11ac wmi page 349 802.11b 3 , 4 , 340 802.11b/g 312 , 340 802.11b/g/n 18 , 72 , 276 802.11e 21 802.11g 3 , 4 , 340 802.11i 4 , 81 , 163 802.11n 4...
Page 646
Wireless access point 620 index wmi options 431 application control custom list 390 , 392 update (signature file) 420 approved setting rogues 120 aps 66 , 120 , 263 , 264 , 522 rogues, blocking 375 aps, rogue see rogue aps 357 , 376 aps, xr overview 4 arp filtering 331 arp table window 110 array 34 ...
Page 647
Wireless access point index 621 rogue aps 375 blocking rogue aps 357 bond mode, bridging 173 boot 413 bridging aps 173 broadcast 332 fast roaming 332 browser certificate error 228 , 244 bss 520 bssid 120 , 520 buttons 91 byod (bring your own device) 280 c capacity of 802.11n 50 cascading style sheet...
Page 648
Wireless access point 622 index top level commands 438 command, utilities ping, traceroute, radius ping 422 commands acl 450 admin 451 auth, authentication 452 cdp 452 clear 454 cluster 456 configure 439 contact-info 457 date-time 458 dhcp-server 459 dns 460 file 461 filter 465 group 456 , 469 hostn...
Page 649
Wireless access point index 623 defaults reset configuration to factory de- faults 418 delivery traffic indication message 318 denial of service see dos attack 377 deny traffic see filters 389 deployment 32 , 62 , 66 , 69 , 522 ease of 20 detection intrusion 376 see dos attack 377 see impersonation ...
Page 650
Wireless access point 624 index express setup 72 , 81 , 163 express setup 81 , 163 extended service set 520 extensible authentication protocol 522 f factory default settings 511 factory defaults 512 , 513 , 514 , 516 dhcp 513 reset configuration to 415 factory.Conf 415 fail-over standby mode 357 fai...
Page 651
Wireless access point index 625 hyperterminal 30 , 69 i iap 34 , 72 , 163 , 312 active ssids 297 naming 2 see also radio 310 settings 312 iap led 72 ids see intrusion detection 372 ids event log viewing window 158 ieee 3 , 81 , 163 ieee 802.11ac wmi page 349 ieee 802.11n capacity, increased 50 multi...
Page 652
Wireless access point 626 index settings 378 license key upgrading 80 , 412 limits group 308 interactions 308 station 308 traffic 308 link layer discovery protocol (lldp) 182 list custom application control list 390 , 392 list, access control see access control list 247 , 298 list, mac access see ac...
Page 653
Wireless access point index 627 mobilize 20 monitor mode for auto cell 337 , 343 monitoring intrusion detection 120 see intrusion detection 376 mounting 72 mounting plate 72 mounting the unit 72 mtu 170 size 170 multiple data streams 44 n nat table - see connection tracking 111 neighbors, cdp 112 ne...
Page 654
Wireless access point 628 index ping 422 planning 52 , 55 , 56 , 62 failover 52 network management 62 port failover 52 power 55 security 56 switch failover 52 wds 63 poge 29 poge power injectors 1 port failover 52 port requirements 58 power request power (lldp) 183 power outlet 29 power over gigabit...
Page 655
Wireless access point index 629 ram (rf analysis manager) 23 reauthentication 318 reboot 413 active software image 413 redirect (wpr) 421 refresh interval wmi 431 remote boot image automatic update from remote tftp server 414 remote configuration automatic update from remote server 414 remote tftp s...
Page 656
Wireless access point 630 index secret 512 secure shell 30 secure shell 29 security fips 599 pci dss 593 security 4 , 20 , 224 , 520 , 522 certificate, see certificate 244 security manager see rsm 22 see group 303 self-monitoring 376 radio assurance 507 radio assurance options 358 , 359 self-test ra...
Page 657
Wireless access point index 631 station timeout period 318 stations 520 stations limits and interactions 308 rogues 120 statistics 147 statistics per station 149 statistics 163 filters 147 netflow 189 per-station 149 stations 147 wds 144 status bar 86 submitting comments 91 subnet 29 , 52 , 81 , 170...
Page 658
Wireless access point 632 index unknown setting rogues 120 update signature file (application control) 420 upgrade active software image 413 license key 80 , 412 software image 412 u-psk, easypass onboarding 280 user accounts 259 setting radius vsas 254 user group 303 qos 306 user group limits and i...
Page 659
Wireless access point index 633 sample wpr files 422 ssid settings 282 ssid settings, about 286 , 296 whitelist settings, about 292 , 293 wep 20 , 56 , 81 , 163 , 224 , 276 , 514 , 522 wep (wired equivalent privacy) encryption method 226 wep encryption and xr arrays 251 whitelist honeypot 299 , 300 ...
Page 660
Wireless access point 634 index.
Page 662
1.800.947.7871 toll free in the us +1.805.262.1600 sales +1.805.262.1601 fax 2101 corporate center drive thousand oaks, ca 91320, usa to learn more visit: xirrus.Com or email info@xirrus.Com © 201 xirrus, inc. All rights reserved. The xirrus logo is a registered trademark of xirrus, inc. All other t...