- DL manuals
- ABB
- Servo Drives
- ACS880-37
- Hardware Manual
ABB ACS880-37 Hardware Manual
Summary of ACS880-37
Page 1
Abb industrial drives hardware manual acs880-37 drives (160 to 3200 kw).
Page 2
List of related manuals you can find manuals and other product documents in pdf format on the internet. See section document library on the internet on the inside of the back cover. For manuals not available in the document library, contact your local abb representative. Drive hardware manuals and g...
Page 3: Hardware Manual
Hardware manual acs880-37 drives (160 to 3200 kw) 3axd50000020437 rev b en effective: 2017-03-27 2017 abb oy. All rights reserved. 1. Safety instructions 4. Mechanical installation table of contents 6. Electrical installation 9. Start-up.
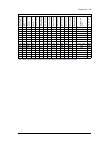
Page 5: Table Of Contents
5 table of contents 1. Safety instructions contents of this chapter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15 use of warnings and notes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15 general ...
Page 6
6 definitions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45 ip22 (standard) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45 ip42 (option +b054) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ...
Page 7
7 moving the crate with a forklift . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 63 removing the transport package . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 64 moving the unpacked drive cabinet . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ...
Page 8
8 signals in separate cables . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 86 signals allowed to be run in the same cable . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 86 relay cable type . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ...
Page 9
9 wiring the pt100 relays (option +nl514) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 106 powering the heating and lighting equipment (options +g300, +g301 and +g313) . 107 wiring ground fault monitoring for it ungrounded systems (option +q954) . . . . 108 connecting the motor cabl...
Page 10
10 9. Start-up contents of this chapter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 145 start-up procedure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 145 checks/settings with no voltage c...
Page 11
11 175 control panel . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 176 replacing the battery . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 176 cleaning . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ...
Page 12
12 electrical connections . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 198 mechanical connections . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 198 insulation supports . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ....
Page 13
13 units with main breaker (600 mm), top cable entry . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 226 location and size of output terminals (units without common motor terminal cubicle) . 227 frame 1×r8i + 1×r8i (without sine output filter) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ...
Page 14
14 planning the braking system . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 252 verifying the capacity of the braking equipment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 252 custom resistors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ...
Page 15: Safety Instructions
Safety instructions 15 1 safety instructions contents of this chapter this chapter contains the safety instructions which you must obey when you install and operate the drive and do maintenance on the drive. If you ignore the safety instructions, injury, death or damage can occur. Use of warnings an...
Page 16
16 safety instructions general safety in installation, start-up and maintenance these instructions are for all personnel that install the drive and do maintenance work on it. Warning! Obey these instructions. If you ignore them, injury or death, or damage to the equipment can occur. • secure the cab...
Page 17
Safety instructions 17 • beware of hot surfaces. Some parts, such as heatsinks of power semiconductors, remain hot for a while after disconnection of the electrical supply. • beware of hot air exiting from the air outlets. • keep the drive in its package or protect it otherwise from dust and burr fr...
Page 18
18 safety instructions • keep the cabinet doors closed when the drive is powered. With the doors open, a risk of a potentially fatal electric shock, arc flash or high-energy arc blast exists. If you cannot avoid working on a powered drive, obey the local laws and regulations on live working (includi...
Page 19
Safety instructions 19 electrical safety in installation, start-up and maintenance electrical safety precautions these warnings are for all personnel who do work on the drive, motor cable or motor. Warning! Obey these instructions. If you ignore them, injury or death, or damage to the equipment can ...
Page 20
20 safety instructions additional instructions and notes warning! Obey these instructions. If you ignore them, injury or death, or damage to the equipment can occur. • if you are not a qualified electrician, do not do electrical installation or maintenance work. • do not install a drive with emc fil...
Page 21
Safety instructions 21 grounding these instructions are for all personnel who are responsible for the grounding of the drive. Warning! Obey these instructions. If you ignore them, injury or death, or equipment malfunction can occur, and electromagnetic interference can increase. • if you are not a q...
Page 22: Drives
22 safety instructions additional instructions for permanent magnet motor drives safety in installation, start-up and maintenance these are additional warnings concerning permanent magnet motor drives. The other safety instructions in this chapter are also valid. Warning! Obey these instructions. If...
Page 23: Introduction To The Manual
Introduction to the manual 23 2 introduction to the manual contents of this chapter this chapter describes the manual. It contains a flowchart of steps in checking the delivery, installing and starting up the drive. The flowchart refers to chapters/sections in this manual and to other manuals. Targe...
Page 24: Related Documents
24 introduction to the manual electrical installation gives instructions on wiring the drive. Control units of the drive contains the default i/o connection diagrams, descriptions of the terminals and technical data for the control units of both the supply and inverter units. Installation checklist ...
Page 25: Flowchart
Introduction to the manual 25 quick installation, commissioning and operation flowchart task see plan the electrical installation and acquire the accessories needed (cables, fuses, etc.). Check the ratings, required cooling air flow, input power connection, compatibility of the motor, motor connecti...
Page 26: Terms And Abbreviations
26 introduction to the manual terms and abbreviations term/ abbreviation explanation bcu drive control unit. The drive contains two bcu control units. One controls the supply unit, the other controls the inverter unit. As standard, the external i/o control signals are connected to the control unit, ...
Page 27
Introduction to the manual 27 safety data (sil, pl) inverter unit the part of the drive that converts dc to ac for the motor. Consists of one or more inverter modules and their auxiliary components. The inverter unit is also capable of feeding energy from a decelerating motor into the dc link. I/o i...
Page 28
28 introduction to the manual.
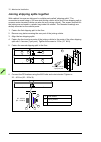
Page 29: Operation Principle And
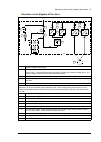
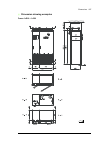
Operation principle and hardware description 29 3 operation principle and hardware description contents of this chapter this chapter briefly describes the operation principle and construction of the drive. Operation principle the acs880-37 is a low-harmonic, air-cooled, cabinet-installed drive for c...
Page 30
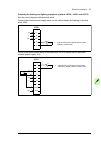
30 operation principle and hardware description the following figure shows the simplified main circuit diagram of the supply unit. Larger drives have supply units that consist of multiple supply modules connected in parallel. The supply unit is controlled by a type bcu control unit [a51]. Ac voltage...
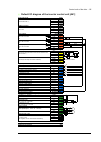
Page 31
Operation principle and hardware description 31 overview circuit diagram of the drive 1 auxiliary voltage transformer(s) 2 auxiliary voltage switch [q21]. Frame 1×r8i + 1×r8i has fuse disconnectors [f20.X] in place of an auxiliary voltage switch. The auxiliary voltage is switched by the main switch/...
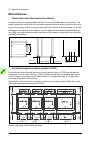
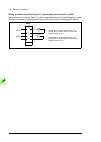
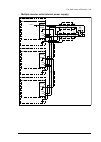
Page 32
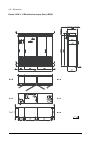
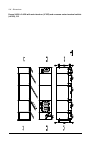
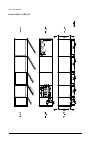
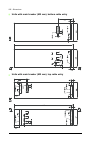
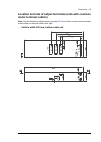
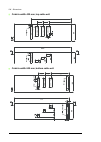
32 operation principle and hardware description cabinet line-up and layout examples frame 1×r8i + 1×r8i cabinet line-up example a auxiliary control cubicle (acu). Contains control electronics and customer i/o connections. See page 38 . B supply and inverter module cubicle. Contains the supply module...
Page 33
Operation principle and hardware description 33 cabinet layout example a auxiliary control cubicle (acu). See page 38 . 1 input cable lead-throughs, pe busbar 2 lcl filter module 3 input terminals (behind lcl filter module) 4 main switch/disconnector [q1.1] (behind mounting plate) 5 ac fuses (behind...
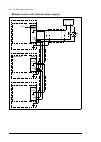
Page 34
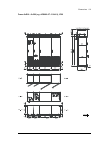
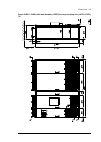
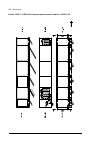
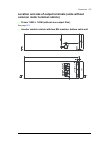
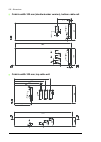
34 operation principle and hardware description frame 2×r8i + 2×r8i cabinet line-up example a auxiliary control cubicle (acu). Contains control electronics and customer i/o connections. See page 38 . B incoming cubicle. Contains the input terminals, switchgear and charging equipment. C supply module...
Page 35
Operation principle and hardware description 35 cabinet layout example a auxiliary control cubicle (acu). See page 38 . 1 input cable lead-throughs, pe busbar 2 input terminals 3 main switch-disconnector [q1.1] 4 grounding/earthing switch [q9.1] (option +f259) 5 ac fuses 6 charging resistors and con...
Page 36
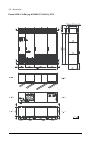
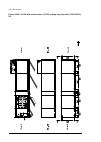
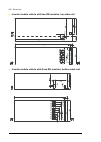
36 operation principle and hardware description frame 3×r8i + 3×r8i (with main breaker) cabinet line-up example a auxiliary control cubicle (acu). Contains control electronics and customer i/o connections. See page 38 . B incoming cubicle. Contains the input terminals, switchgear and charging equipm...
Page 37
Operation principle and hardware description 37 cabinet layout example a auxiliary control cubicle (acu). See page 38 . 1 input cable lead-throughs, pe busbar 2 input terminals 3 charging resistors 4 incoming cubicle cooling fans (behind the charging resistor mounting plate) 5 main breaker [q1] 6 ch...
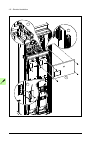
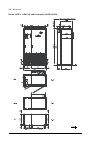
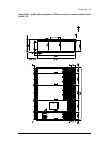
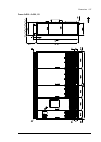
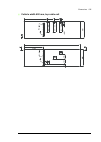
Page 38
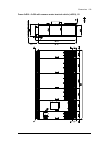
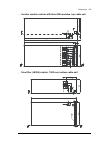
38 operation principle and hardware description auxiliary control cubicle (acu) layout a layout example of the auxiliary control cubicle (acu) is shown below. 1 fuse-disconnectors f101. On the primary of transformer t101 (item 27 ). 19 lead-through for control cables 2 fuse-disconnectors f27 for mot...
Page 39
Operation principle and hardware description 39 6 switch f90 for ground fault monitoring (item 12 ) 24 motor fan starters and contactors (options +m602…610) 7 fso-xx safety functions module (option +q973 and other options requiring fso-xx) 25 terminal blocks x601 for motor fan connections (options +...
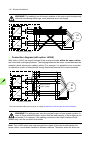
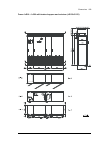
Page 40
40 operation principle and hardware description overview of power and control connections the diagram shows the power connections and control interfaces of the drive. 1 2 3 4 option modules can be inserted into slots 1, 2, 3 and 4 as follows: additional modules can be installed on an optional fea-03...
Page 41
Operation principle and hardware description 41 10 terminal blocks for customer connections installed in the drive cabinet. For the locations, see auxiliary control cubicle (acu) layout (page 38 ). Wiring details are given starting on page 103 . 11 supply unit (consisting of one or more supply modul...
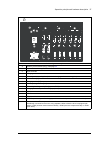
Page 42: Door Switches And Lights
42 operation principle and hardware description door switches and lights label in english label in local language description 1 ready - ready light (option +g327) 2 run - run light (option +g328) 3 fault - fault light (option +g329) 4 run/enbl - run enable signal switch for the supply unit 5 e-stop ...
Page 43
Operation principle and hardware description 43 main disconnecting device [q1.1] depending on the configuration of the drive, the main disconnecting device of the drive is either a switch-disconnector or a main circuit breaker. Units with a switch-disconnector also have a main contactor. The main di...
Page 44
44 operation principle and hardware description control panel the acs-ap-w is the user interface of the drive. It provides the essential controls such as start/stop/direction/reset/reference, and the parameter settings for the inverter control program. The control panel can be removed by pulling it ...
Page 45: Descriptions Of Options
Operation principle and hardware description 45 descriptions of options note: all options are not available for all drive types, do not coexist with certain other options, or may require additional engineering. Check actual availability with abb. Degree of protection definitions according to iec/en ...
Page 46
46 operation principle and hardware description marine construction (option +c121) the option includes the following accessories and features: • reinforced mechanics • grab railings • door flush bolt which allows the door to open 90 degrees and prevents it from slamming close • self-extinctive mater...
Page 47
Operation principle and hardware description 47 resistor braking (options +d150 and +d151) see chapter resistor braking on page 249 . Emc filters (option + e202) see section type designation key on page 55 and sections compliance with the european emc directive on page 193 and compliance with en 618...
Page 48
48 operation principle and hardware description output for motor space heater (option +g313) the option contains: • load switch for providing electrical isolation during service • miniature circuit breaker for overcurrent protection • terminal block for external supply and heating element(s) connect...
Page 49
Operation principle and hardware description 49 additional wire markings the following additional wire markings are available. Bottom cable entry/exit (options +h350 and +h352) for ul listed (+c129) units, the default input and output cabling direction is through the roof of the cabinet. The bottom ...
Page 50
50 operation principle and hardware description note that this option is not available with option +e206 (sine filters) – in this case, the motor cables are connected to the sine filter cubicle. Common output terminal (option +h366) as standard, each inverter module must be individually cabled to th...
Page 51
Operation principle and hardware description 51 +l505, +2l505, +l513, +2l513 option +l505 provides a thermistor relay and a terminal block. The terminal block has connections for the measuring circuit (one to three ptc sensors in series), the output indication of the relay, and an optional external ...
Page 52
52 operation principle and hardware description thermal protection with pt100 relays (options +nl506 and +nl514) pt100 temperature monitoring relays are used for overtemperature supervision of motors equipped with pt100 sensors. For example, there can be three sensors to measure the temperature of t...
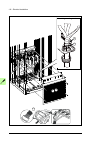
Page 53
Operation principle and hardware description 53 starter for auxiliary motor fan (options +m602…+m610) what the option contains the option provides switched and protected connections for 3-phase auxiliary motor fans. Each fan connection is equipped with • fuses • a manual motor starter switch with an...
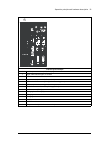
Page 54: Type Designation Label
54 operation principle and hardware description type designation label the type designation label includes ratings, appropriate markings, a type designation and a serial number, which allow the identification of each unit. A sample label is shown below. Quote the complete type designation and serial...
Page 55: Type Designation Key
Operation principle and hardware description 55 type designation key the type designation contains information on the specifications and configuration of the drive. The first digits from left express the basic configuration (eg, acs880-37-1210a-3). The optional selections are given thereafter, separ...
Page 56
56 operation principle and hardware description line options f255 main (air circuit) breaker (instead of line contactor) f259 grounding (earthing) switch cabinet equipment g300 cabinet and module heating elements (external supply) (page 47 ) g301 cabinet lighting (page 47 ) g307 terminals for connec...
Page 57
Operation principle and hardware description 57 l514 atex-certified thermal protection with pt100 relays (3, 5 or 8 pcs) (page 52 ) l515 fea-03 i/o extension adapter l516 fen-21 resolver interface module l517 fen-01 ttl incremental encoder interface module l518 fen-11 ttl absolute encoder interface ...
Page 58
58 operation principle and hardware description q978 emergency stop (configurable for category 0 or 1) with fso-xx safety functions module, by opening the main breaker/contactor q979 emergency stop (configurable for category 0 or 1) with fso-xx safety functions module, by activating the safe torque ...
Page 59: Mechanical Installation
Mechanical installation 59 4 mechanical installation contents of this chapter this chapter describes the mechanical installation procedure of the drive. Examining the installation site examine the installation site: • the installation site is sufficiently ventilated or cooled to transfer away the dr...
Page 60: Necessary Tools
60 mechanical installation necessary tools the tools required for moving the unit to its final position, fastening it to the floor and wall and tightening the connections are listed below: • crane, fork-lift or pallet truck (check load capacity!), slate/spud bar, jack and rollers • pozidriv and torx...
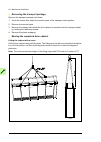
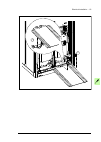
Page 61
Mechanical installation 61 moving and unpacking the drive move the drive in its original packaging to the installation site as shown below to avoid damaging the cabinet surfaces and door devices. When you are using a pallet truck, check its load capacity before you move the drive. The drive cabinet ...
Page 62
62 mechanical installation lifting the crate with a crane max 20 position each sling as close to a transverse board as possible. We recommend the use of transverse spreader bars. Lifting point.
Page 63
Mechanical installation 63 moving the crate with a forklift free width for fork tines: 750 mm (29.5”).
Page 64
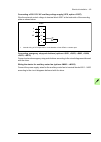
64 mechanical installation removing the transport package remove the transport package as follows: 1. Undo the screws that attach the wooden parts of the transport crate together. 2. Remove the wooden parts. 3. Remove the clamps with which the drive cabinet is mounted onto the transport pallet by un...
Page 65
Mechanical installation 65 moving the cabinet on rollers warning: do not move marine versions (option +c121) on rollers. Lay the cabinet on the rollers and move it carefully until close to its final location. Remove the rollers by lifting the unit with a crane, forklift, pallet truck or jack. Moving...
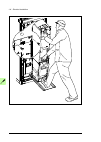
Page 66
66 mechanical installation final placement of the cabinet move the cabinet into its final position with a slate bar (spud bar). Place a piece of wood between the edge of the cabinet and the bar to protect the cabinet frame..
Page 67: (Non-Marine Units)
Mechanical installation 67 fastening the cabinet to the floor and wall or roof (non-marine units) general rules • the drive must be installed in an upright vertical position. • the cabinet can be installed with its back against a wall (a), or back-to-back with another unit (b). • leave 400 mm (15.75...
Page 68
68 mechanical installation fastening methods fasten the cabinet to the floor by using the clamps included along the edge of the cabinet bottom, or by bolting the cabinet to the floor through the holes inside (if they are accessible). Alternative 1 – clamping alternative 2 – using the holes inside th...
Page 69: Units, +C121)
Mechanical installation 69 fastening the cabinet to the floor and roof/wall (marine units, +c121) follow the general rules given in section general rules on page 67 . See the dimension drawing delivered with the drive for the locations of the fastening holes in the flat bars below the cabinet and fo...
Page 70
70 mechanical installation joining shipping splits together wide cabinet line-ups are delivered in multiple parts called “shipping splits”. The connection is made using a 200 mm wide joining cubicle at the end of one shipping split (a common motor terminal cubicle can also act as a joining cubicle)....
Page 71
Mechanical installation 71 7. Remove the shroud covering the dc busbars in the joining cubicle. 8. Use the joint pieces to connect the dc busbars. Tighten the bolts to 55…70 n·m (40…50 lbf·ft). Warning! Make sure you install the washers in the correct order as shown. For example, placing an unpassiv...
Page 72: Miscellaneous
72 mechanical installation miscellaneous cable duct in the floor below the cabinet a cable duct can be constructed below the 500 mm wide middle part of the cabinet. The cabinet weight lies on the two 50 mm wide transverse sections which the floor must carry. Prevent the cooling air flow from the cab...
Page 73
Mechanical installation 73 the air duct must be able to supply a sufficient volume of cooling air. The minimum air flow values are given in section cooling data, noise (page 187 ). Top cable entry adapter and joining cubicles have no air inlet. Warning! Make sure that the incoming air is sufficientl...
Page 74
74 mechanical installation arc welding fastening the cabinet by arc welding is not recommended. However, if arc welding is the only mounting option, connect the return conductor of the welding equipment to the cabinet frame at the bottom within 0.5 meters (1’6”) of the welding point. Note : the thic...
Page 75: Electrical Installation
Guidelines for planning the electrical installation 75 5 guidelines for planning the electrical installation contents of this chapter this chapter contains instructions for planning the electrical installation of the drive. Some instructions are mandatory to follow in every installation, others prov...
Page 76
76 guidelines for planning the electrical installation examining the compatibility of the motor and drive use an asynchronous ac induction motor, permanent magnet synchronous motor or ac induction servomotor with the drive. Several induction motors can be connected to the drive at a time. Select the...
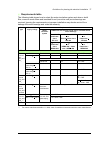
Page 77
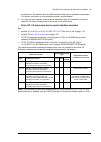
Guidelines for planning the electrical installation 77 requirements table the following table shows how to select the motor insulation system and when a d u /d t filter, common mode filters and insulated n-end (non-drive end) motor bearings are required. Ignoring the requirements or improper install...
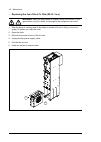
Page 78
78 guidelines for planning the electrical installation the abbreviations used in the table are defined below. Additional requirements for explosion-safe (ex) motors if you will use an explosion-safe (ex) motor, follow the rules in the requirements table above. In addition, consult the motor manufact...
Page 79
Guidelines for planning the electrical installation 79 additional requirements for abb motors of types other than m2_, m3_, m4_, hx_ and am_ use the selection criteria given for non-abb motors. Additional requirements for braking applications when the motor brakes the machinery, the intermediate cir...
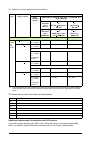
Page 80
80 guidelines for planning the electrical installation additional data for calculating the rise time and the peak line-to-line voltage if you need to calculate the actual peak voltage and voltage rise time considering the actual cable length, proceed as follows: • peak line-to line voltage: read the...
Page 81: Selecting The Power Cables
Guidelines for planning the electrical installation 81 selecting the power cables general rules select the input power and motor cables according to local regulations: • select a cable capable of carrying the drive nominal current. See section ratings (page 179 ) for the rated currents, and section ...
Page 82
82 guidelines for planning the electrical installation typical cable sizes input (supply) cable sizes the table below gives copper and aluminum cable types with concentric copper shield for nominal current. For drawings of the terminals, see chapter dimensions (page 201 ). 1. The cable sizing is bas...
Page 83
Guidelines for planning the electrical installation 83 or earth (directly buried). For other conditions, size the cables according to local safety regulations, appropriate input voltage and the load current of the drive. Output (motor) cable sizes the table below gives copper and aluminum cable type...
Page 84
84 guidelines for planning the electrical installation on top of the other, ambient temperature 30 °c, pvc insulation, surface temperature 70 °c (iec/en 60204- 1 and iec 60364-5-52/2001). For other conditions, size the cables according to local safety regulations, appropriate input voltage and the l...
Page 85
Guidelines for planning the electrical installation 85 motor cable shield if the motor cable shield is used as the sole protective earth conductor of the motor, make sure that the conductivity of the shield is sufficient. See subsection general rules above, or iec 61800-5-1. To effectively suppress ...
Page 86: Routing The Cables
86 guidelines for planning the electrical installation planning the braking system see chapter resistor braking . Selecting the control cables shielding all control cables must be shielded. Use a double-shielded twisted pair cable for analog signals. This type of cable is recommended for the pulse e...
Page 87
Guidelines for planning the electrical installation 87 a diagram of the cable routing is shown below. Separate control cable ducts lead 24 v and 230 v (120 v) control cables in separate ducts unless the 24 v cable is insulated for 230 v (120 v) or insulated with an insulation sleeving for 230 v (120...
Page 88: Protection
88 guidelines for planning the electrical installation implementing thermal overload and short-circuit protection protecting the drive and input power cable in short-circuits the drive is equipped with internal ac fuses as standard. Protect the input cable with fuses or a suitable circuit breaker. S...
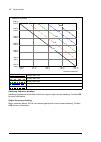
Page 89: Function
Guidelines for planning the electrical installation 89 residual current device compatibility the drive is suitable to be used with residual current devices of type b. Note : the emc filter of the drive includes capacitors connected between the main circuit and the frame. These capacitors and long mo...
Page 90
90 guidelines for planning the electrical installation implementing the functions provided by the fso-xx safety functions module (option +q972 or +q973) the drive can be equipped with an fso-xx safety functions module (option +q972 or +q973) which enables the implementation of functions such as safe...
Page 91: Drive
Guidelines for planning the electrical installation 91 using power factor compensation capacitors with the drive power factor compensation is not needed with ac drives. However, if a drive is to be connected in a system with compensation capacitors installed, note the following restrictions. Warning...
Page 92
92 guidelines for planning the electrical installation 1) relay outputs; 2) varistor; 3) rc filter; 4) diode connecting a motor temperature sensor to the drive i/o warning! Iec 60664 requires double or reinforced insulation between live parts and the surface of accessible parts of electrical equipme...
Page 93
Guidelines for planning the electrical installation 93 connectors of the module. See the table below for the sensor insulation requirement. For sensor connection to the extension module, see its manual. 4. You can connect a sensor to an external thermistor relay the insulation of which is rated for ...
Page 94
94 guidelines for planning the electrical installation.
Page 95: Electrical Installation
Electrical installation 95 6 electrical installation contents of this chapter this chapter gives instructions on the wiring of the drive. Warnings warning! Only qualified electricians are allowed to carry out the work described in this chapter. Follow the safety instructions on the first pages of th...
Page 96
96 electrical installation motor and motor cable 1. Check that the motor cable is disconnected from the drive output terminals u2, v2 and w2. 2. Measure the insulation resistance between each phase conductor and the protective earth conductor using a measuring voltage of 1000 v dc. The insulation re...
Page 97
Electrical installation 97 t21 and t101 tap settings (400…500 v units) t21 and t101 tap settings (690 v units) 500 v 1 480 v 2 460 v 3 440 v 4 415 v 5 400 v 6 380 v 7 u1 8 tp1 9 tp2 10 t21_x1 or t101_x1 t21_x2 or t101_x2 1 230 v 2 3 4 n 5 Θ 690 v 1 660 v 2 600 v 3 575 v 4 540 v 5 525 v 6 7 u1 8 tp1 ...
Page 98
98 electrical installation t111 tap settings 3~ input 3~ input 3~ output supply voltage terminals tap settings terminals a1– b1– c1– 400 v (50 hz) 320/340 v (60 hz) 690 v a1, b1, c1 c2 a2 b2 a1, b1, c1 a2, b2, c2 660 v a1, b1, c1 c2 a2 b2 a1, b1, c1 a2, b2, c2 600 v a1, b1, c1 c3 a3 b3 a1, b1, c1 a2...
Page 99
Electrical installation 99 connecting the control cables see chapter control units of the drive (page 131 ) for the default i/o connections of the inverter unit (with the acs880 primary control program). The default i/o connections can be different with some hardware options, see the circuit diagram...
Page 100
100 electrical installation note 1 : keep the shields continuous as close to the connection terminals as possible. Secure the cables mechanically at the lead-through strain relief. Note 2: if the outer surface of the shield is non-conductive: • cut the shield at the midpoint of the bare part. Be car...
Page 101
Electrical installation 101 5. Arrange the bunches according to size from thickest to the thinnest between the emi conductive cushions. 6. If more than one cable go through a grommet, seal the grommet by applying loctite 5221 (catalogue number 25551) inside the grommet. Routing the control cables in...
Page 102
102 electrical installation at the other end of the cable, leave the shields unconnected or ground them indirectly via a high-frequency capacitor with a few nanofarads, eg. 3.3 nf / 630 v. The shield can also be grounded directly at both ends if they are in the same ground line with no significant v...
Page 103
Electrical installation 103 connecting a 230/115 v ac auxiliary voltage supply (ups, option +g307) wire the external control voltage to terminal block x307 at the back side of the mounting plate as shown below. Connecting emergency stop push buttons (options +q951, +q952, +q963, +q964, +q978, +q979)...
Page 104
104 electrical installation wiring the ptc thermistor relay(s) (options +l505, +2l505, +l513, +2l513) the external wiring of option +2l505 and +2l513 (two thermistor relays) is shown below. For example, one relay can be used to monitor the motor windings, the other to monitor the bearings. The maxim...
Page 105
Electrical installation 105 wiring the pt100 relays (option +nl506) external wiring of eight pt100 sensors is shown below. The maximum contact load capacity is 250 v ac 10 a. For the actual wiring, see the circuit diagram delivered with the drive. 1 2 3 4 5 6 … 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 x506 1 × pt...
Page 106
106 electrical installation wiring the pt100 relays (option +nl514) external wiring of three pt100 sensors is shown below. The maximum contact load capacity is 250 v ac 10 a. For the actual wiring, see the circuit diagram delivered with the drive. For instructions on commissioning option +nl514, see...
Page 107
Electrical installation 107 powering the heating and lighting equipment (options +g300, +g301 and +g313) see the circuit diagrams delivered with drive. Connect the external power supply wires for the cabinet heater and lighting to terminal block x300. Connect the motor heater wiring to terminal bloc...
Page 108
108 electrical installation wiring ground fault monitoring for it ungrounded systems (option +q954) we recommend to connect alarm 1 for drive tripping and alarm 2 for alarm signals in order to avoid unnecessary trippings due to the ground fault monitor self testing with alarm 2. 1 2 3 4 x954 alarm 1...
Page 109
Electrical installation 109 connecting the motor cables (units without common motor terminal cubicle or sine output filter) on units without a common motor terminal cubicle or a sine output filter, the motor cables connect to busbars located behind the inverter module(s). The location and dimensions...
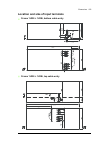
Page 110
110 electrical installation warning! The cabling from all inverter modules to the motor must be physically identical considering cable type, cross-sectional area, and length. Connection diagram (with option +h366) with option +h366, the output busbars of the inverter modules within the same cubicle ...
Page 111
Electrical installation 111 multiple inverter cubicles (ie. Two cubicles of two modules each), make sure that the motor cabling is identical for both cubicles. Procedure removing the inverter module(s) to allow more room for cabling work, the inverter module can be removed completely instead of only...
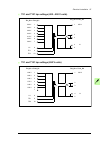
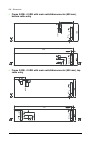
Page 112
112 electrical installation 5 6 4 3.
Page 113
Electrical installation 113 7 8 8.
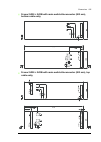
Page 114
114 electrical installation 9 10
Page 115
Electrical installation 115 removing and reinstalling the fan carriage of an inverter module refer to the drawings below. Warning! Obey the instructions in chapter safety instructions . If you ignore them, injury or death, or damage to the equipment can occur. 1. Do the steps in section electrical s...
Page 116
116 electrical installation 4 5 3 6 7.
Page 117
Electrical installation 117 connecting the motor cables refer to the drawings below. Warning! Obey the instructions in chapter safety instructions . If you ignore them, injury or death, or damage to the equipment can occur. 1. Do the steps in section electrical safety precautions (page 19 ) before y...
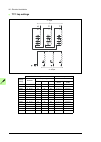
Page 118
118 electrical installation 2 360° grounding detail 11 b pe 10 7 5 6 8 a.
Page 119
Electrical installation 119 re-installing the fan carriage of an inverter module (if the inverter module was removed completely instead of only the fan carriage, proceed to section re-inserting the inverter module into the cubicle below.) the re-installation of the fan carriage is the removal proced...
Page 120
120 electrical installation connecting the motor cables (units with common motor terminal cubicle or sine filter) output busbars if the drive is equipped with option +h359, the motor cables connect to a common motor terminal cubicle. Similarly, if the drive is equipped with option +e206 (sine output...
Page 121
Electrical installation 121 3. Lead the cables into the cubicle. Make the 360° earthing arrangement at the cable entry as shown. 4. Cut the cables to suitable length. Strip the cables and conductors. 5. Twist the cable screens into bundles and connect the bundles to the pe busbar in the cubicle. 6. ...
Page 122
122 electrical installation connecting the input power cables connection diagram notes: 1) fuses or other protection means. Use a separate pe conductor in addition if the conductivity of the shield does not meet the requirement for the pe conductor. See section selecting the power cables (page 81 )....
Page 123
Electrical installation 123 5. Prepare the ends of the cables. 6. If fire insulation is used, make an opening in the mineral wool sheet according to the diameter of the cable. 7. Remove the rubber grommets from the lead-through plate for the cables to be connected. Cut adequate holes into the rubber...
Page 124
124 electrical installation pe 10 7 4 8 10
Page 125: Connecting A Pc
Electrical installation 125 connecting a pc a pc (with eg. The drive composer pc tool) can be connected to the inverter unit as follows: 1. Connect an acs-ap-x control panel to the inverter control unit either by using an ethernet (eg. Cat5e) networking cable, or by inserting the panel into the pane...
Page 126: Panel)
126 electrical installation panel bus (control of several drives from one control panel) one control panel (or pc) can be used to control several drives by constructing a panel bus. This is done by daisy-chaining the panel connections of the drives. Some drives have the necessary panel connectors in...
Page 127: Installing Option Modules
Electrical installation 127 installing option modules mechanical installation of i/o extension, fieldbus adapter and pulse encoder interface modules see page 40 for the available slots for each module. Install the option modules as follows: warning! Obey the instructions in chapter safety instructio...
Page 128
128 electrical installation mechanical installation of an fso-xx safety functions module this procedure describes the mechanical installation of an fso-xx safety functions module onto the inverter control unit. (the fso-xx can alternatively be installed beside the control unit, which is the standard...
Page 129
Electrical installation 129 2. Tighten the fso-xx electronics grounding screw. 3. Connect the fso-xx data cable between fso-xx connector x110 and to bcu-x2 connector x12. Wiring of option modules see the appropriate option module manual for specific installation and wiring instructions. 3 2.
Page 130
130 electrical installation.
Page 131: Control Units Of The Drive
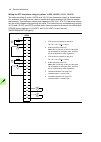
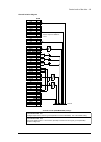
Control units of the drive 131 7 control units of the drive what this chapter contains this chapter • describes the connections of the control units used in the drive, • contains the specifications of the inputs and outputs of the control units. General the acs880 drive utilizes bcu-x2 control units...
Page 132
132 control units of the drive control unit layout and connections description i/o i/o terminals (see following diagram) slot 1 i/o extension, encoder interface or fieldbus adapter module connection. (this is the sole location for an fdpi-02 diagnostics and panel interface.) slot 2 i/o extension, en...
Page 133
Control units of the drive 133 description xai analog inputs xao analog outputs xdi digital inputs, digital input interlock (diil) xdio digital input/outputs xd2d drive-to-drive link xd24 +24 v output (for digital inputs) xeth ethernet port (eg. For pc communication) xpow external power input xro1 r...
Page 134
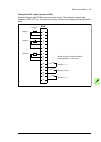
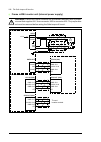
134 control units of the drive default i/o diagram of the supply control unit [a51] the diagram below shows the default i/o connections on the supply control unit [a51], and describes the use of the signals/connections in the supply unit. Under normal circumstances, the factory-made wiring should no...
Page 135
Control units of the drive 135 default i/o diagram of the inverter control unit [a41] drive-to-drive link xd2d drive-to-drive link 1) b 1 a 2 bgnd 3 shield 4 rs485 connection x485 not in use b 5 a 6 bgnd 7 shield 8 relay outputs xro1…xro3 ready 250 v ac / 30 v dc 2 a nc 11 com 12 no 13 running 250 v...
Page 136
136 control units of the drive notes: the wire size accepted by all screw terminals (for both stranded and solid wire) is 0.5 … 2.5 mm 2 (24…12 awg). The torque is 0.5 n·m (5 lbf·in). 1) see section drive-to-drive link (xd2d) (page 137 ). 2) see chapter the safe torque off function (page 237 ). 3) 0...
Page 137
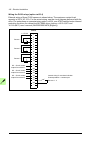
Control units of the drive 137 ai1 or ai2 as a pt100, pt1000, ptc or kty84 sensor input three pt100/pt1000/ptc sensors or one kty84 sensor for motor temperature measurement can be connected between an analog input and output as shown below. (alternatively, you can connect the kty to an fio-11 or fai...
Page 138
138 control units of the drive use shielded twisted-pair cable (~100 ohm, for example, profibus-compatible cable) for the wiring. For best immunity, high quality cable is recommended. Keep the cable as short as possible; the maximum length of the link is 50 meters (164 ft). Avoid unnecessary loops a...
Page 139
Control units of the drive 139 control unit connector data power supply (xpow) connector pitch 5 mm, wire size 2.5 mm 2 24 v (±10%) dc, 2 a external power input. Two supplies can be connected for redundancy. Relay outputs ro1…ro3 (xro1…xro3) connector pitch 5 mm, wire size 2.5 mm 2 250 v ac / 30 v d...
Page 140
140 control units of the drive analog outputs ao1 and ao2 (xao) connector pitch 5 mm, wire size 2.5 mm 2 0…20 ma, r load frequency range: 0…500 hz resolution: 11 bit + sign bit inaccuracy: 2% of full scale range drive-to-drive link (xd2d) connector pitch 5 mm, wire size 2.5 mm 2 physical layer: rs-4...
Page 141
Control units of the drive 141 ground isolation diagram xpow +24vi 1 gnd 2 +24vi 3 gnd 4 xai +vref 1 -vref 2 agnd 3 ai1+ 4 ai1- 5 ai2+ 6 ai2- 7 xao ao1 1 agnd 2 ao2 3 agnd 4 xd2d b 1 a 2 bgnd 3 shield 4 xro1, xro2, xro3 nc 11 com 12 no 13 nc 21 com 22 no 23 nc 31 com 32 no 33 xd24 +24vd 5 dicom 6 +2...
Page 142
142 control units of the drive.
Page 143: Installation Checklist
Installation checklist 143 8 installation checklist contents of this chapter this chapter contains an installation checklist which you must complete before you start up the drive. Warnings warning! Obey the instructions in chapter safety instructions . If you ignore them, injury or death, or damage ...
Page 144
144 installation checklist there is an adequately sized protective earth (ground) conductor between the drive and the switchboard, and the conductor has been connected to appropriate terminal. Proper grounding has also been measured according to the regulations. There is an adequately sized protecti...
Page 145: Start-Up
Start-up 145 9 start-up contents of this chapter this chapter contains the start-up procedure of the drive. Start-up procedure the tasks which are needed in certain cases only are marked with underlining, and option codes are given in brackets. Default device designations (if any) are given in brack...
Page 146
146 start-up action safety warning! Obey the safety instructions during the start-up procedure. See chapter safety instructions on page 15. Checks/settings with no voltage connected ensure that the disconnector of the supply transformer is locked to the off (0) position, ie. No voltage is, and canno...
Page 147
Start-up 147 switch on the auxiliary voltage [q21]. Drives of frame size 1×r8i + 1×r8i: close the main switch-disconnector [q1.1]. This will power up the main circuit of the drive as well as the auxiliary voltage circuit. Setting up the supply unit parameters check the voltage range setting in param...
Page 148
148 start-up check that the motor starts, stops and follows the speed reference in the correct direction when controlled through the customer-specific i/o or fieldbus. Drives in which the safe torque off control circuit is in use: test and validate the operation of the safe torque off function. See ...
Page 149: Fault Tracing
Fault tracing 149 10 fault tracing contents of this chapter this chapter describes the fault tracing possibilities of the drive. Leds warning and fault messages see the firmware manual for the descriptions, causes and remedies of the drive control program warning and fault messages. Where led color ...
Page 150
150 fault tracing.
Page 151: Maintenance
Maintenance 151 11 maintenance contents of this chapter this chapter contains preventive maintenance instructions..
Page 152: Maintenance Intervals
152 maintenance maintenance intervals the table below shows the maintenance tasks which can be done by the end user. The complete maintenance schedule is available on the internet ( www.Abb.Com/drivesservices ). For more information, consult your local abb service representative ( www.Abb.Com/search...
Page 153: Cabinet
Maintenance 153 cabinet cleaning the interior of the cabinet warning! Obey the instructions in chapter safety instructions . If you ignore them, injury or death, or damage to the equipment can occur. Warning! Use a vacuum cleaner with an antistatic hose and nozzle, and wear a grounding wristband. Ot...
Page 154: Module Heatsinks
154 maintenance cleaning the door air inlets (ip54) 1. Remove the fasteners at the top of the grating. 2. Lift the grating and pull it away from the door. 3. Remove the air filter mat. 4. Place the new filter mat in the grating the metal wire side facing the door. 5. Reinstall the grating in reverse...
Page 155
Maintenance 155 warning! Obey the instructions in chapter safety instructions . If you ignore them, injury or death, or damage to the equipment can occur. Warning! Use a vacuum cleaner with antistatic hose and nozzle. Using a normal vacuum cleaner creates static discharges which can damage circuit b...
Page 156: Fans
156 maintenance fans the lifespan of the cooling fans of the drive depends on the running time, ambient temperature and dust concentration. See the firmware manual for the actual signal which indicates the running time of the cooling fan. Reset the running time signal after fan replacement. Replacem...
Page 157
Maintenance 157 replacing the fan(s) in the incoming cubicle warning! Obey the instructions in chapter safety instructions . If you ignore them, injury or death, or damage to the equipment can occur. 1. Stop the drive and do the steps in section electrical safety precautions (page 19 ) before you st...
Page 158
158 maintenance replacing a roof fan (ip54/ul type 12) warning! Obey the instructions in chapter safety instructions . If you ignore them, injury or death, or damage to the equipment can occur. 1. Stop the drive and do the steps in section electrical safety precautions (page 19 ) before you start th...
Page 159
Maintenance 159 replacing a supply or inverter module cooling fan warning! Obey the instructions in chapter safety instructions . If you ignore them, injury or death, or damage to the equipment can occur. 1. Stop the drive and do the steps in section electrical safety precautions (page 19 ) before y...
Page 160
160 maintenance replacing the circuit board compartment fan (frame r8i) the r8i module is equipped with a fan blowing air through the circuit board compartment. The fan is accessible from the front of the module. Warning! Obey the instructions in chapter safety instructions . If you ignore them, inj...
Page 161
Maintenance 161 8. Put the fan onto the threaded studs on the fan holder with the airflow direction arrow pointing towards the fan holder. 9. Install and tighten the four nuts removed earlier. 10. Connect the fan cable. 11. Align and push the fan holder into the module. 12. Install and tighten the t...
Page 162
162 maintenance replacing the fan of the lcl filter (blcl-1x-x) warning! Obey the instructions in chapter safety instructions . If you ignore them, injury or death, or damage to the equipment can occur. 1. Stop the drive (if running) and do the steps in section electrical safety precautions (page 19...
Page 163
Maintenance 163 replacing the fan of the lcl filter (blcl-2x-x) warning! Obey the instructions in chapter safety instructions . If you ignore them, injury or death, or damage to the equipment can occur. 1. Stop the drive (if running) and do the steps in section electrical safety precautions (page 19...
Page 164
164 maintenance supply and inverter modules cleaning the module heatsink fins pick up dust from the cooling air. The module runs into overtemperature warnings and faults if the heatsink is not clean. In a “normal” environment (neither especially dusty nor clean), the heatsink should be checked annua...
Page 165
Maintenance 165 reduced run a “reduced run” function is available for supply and inverter units consisting of parallel- connected modules. The function makes it possible to continue operation with limited current even if one (or more) module is out of service, for example, because of maintenance wor...
Page 166
166 maintenance 6. If the control unit (a41 or a51) is powered from the faulty module, connect the power supply wiring using the extension wire set included to another module. 7. If the safe torque off (sto) function is in use, install the jumper wire set included in the sto wiring in place of the m...
Page 167
Maintenance 167 returning the module 1. Remove the air baffle and install the module in reverse order. Use the following tightening torques: • dc busbar assembly to upper insulators (2 × m8): 9 n·m (6.6 lbf·ft) • dc busbar assembly to lower insulators (2 × m10): 18 n·m (13.3 lbf·ft) • fuses to dc bu...
Page 168: Lcl Filter
168 maintenance lcl filter replacing the lcl filter warning! Ignoring the following instructions can cause physical injury, or damage to the equipment: • use extreme caution when maneuvering modules that run on wheels. The modules are heavy and have a high center of gravity. They topple over easily ...
Page 169
Maintenance 169 12. Replace the module: install the module in reverse order. Mind you fingers. Keep a constant pressure with one foot on the base of the module to prevent the module from falling on its back. Note: be careful not to break the fastening screws: tighten the fastening screws of the modu...
Page 170
170 maintenance 6 8 7 11 10 9.
Page 171: Capacitors
Maintenance 171 capacitors the dc circuit of the power modules of the drive contain several electrolytic capacitors. Their lifespan depends on the operating time of the drive, loading and ambient temperature. Capacitor life can be prolonged by lowering the ambient temperature. Capacitor failure is u...
Page 172: Fuses
172 maintenance fuses replacing the ac fuses in the incoming cubicle units without a main breaker have ac fuses in the incoming cubicle (or, in the case of frame 1×r8i + 1×r8i, in the combined supply and inverter module cubicle). Warning! Obey the instructions in chapter safety instructions . If you...
Page 173
Maintenance 173 replacing the dc fuses in the supply module cubicle (frame 2×r8i + 2×r8i and up) there are dc fuses at the output of each supply module (labeled 4b in the drawing below). Note that there are also dc fuses at the input of each inverter module; see page 175 . This procedure can also be...
Page 174
174 maintenance 3 4b 4a 4b 8.
Page 175
Maintenance 175 replacing the dc fuses in the inverter module cubicle (frame 2×r8i + 2×r8i and up) parallel-connected inverter modules have dc fuses fitted above each module. Warning! Obey the instructions in chapter safety instructions . If you ignore them, injury or death, or damage to the equipme...
Page 176: Control Panel
176 maintenance control panel replacing the battery 1. Turn the lid on the back of the panel counter-clockwise until the lid opens. 2. Replace the battery with a new cr2032 battery. 3. Put the lid back and tighten it by turning it clockwise. 4. Dispose of the old battery according to local disposal ...
Page 177: Control Units
Maintenance 177 control units bcu control unit types there are three variants of the bcu control unit used in acs880 drives: bcu-02, bcu-12 and bcu-22. These have a different number of converter module connections (2, 7 and 12 respectively) but are otherwise identical. The three bcu types are interc...
Page 178
178 maintenance control unit battery replace the real-time clock battery if the batt ok led is not illuminated when the control unit is powered. For information on the led, see control unit layout and connections on page 132 . 1. Do the steps in section electrical safety precautions (page 19 ) befor...
Page 179: Technical Data
Technical data 179 12 technical data contents of this chapter this chapter contains the technical specifications of the drive, for example, the ratings, fuse data, sizes and technical requirements, provisions for fulfilling the requirements for ce and other markings. Ratings the nominal ratings for ...
Page 180
180 technical data definitions u n = 500 v 0420a-5 390 420 550 250 350 364 403 250 300 314 200 250 0570a-5 529 570 750 400 500 494 547 355 450 426 250 350 0780a-5 724 780 1020 560 700 675.5 749 500 600 583 400 500 1010a-5 937 1010 1320 710 900 875 970 630 800 755 500 600 1110a-5 1030 1110 1450 800 1...
Page 181
Technical data 181 derating ambient temperature derating in the temperature range +40…50 °c (+104…122 °f), the rated output current is derated by 1% for every added 1 °c (1.8 °f). The output current can be calculated by multiplying the current given in the rating table by the derating factor (k) : a...
Page 182
182 technical data switching frequency derating switching frequencies other than default can require output current derating. Contact abb for more information. Output frequency derating motor operation above 150 hz can require type-specific output current derating. Contact abb for more information. ...
Page 183
Technical data 183 frame sizes and power module types drive type acs880-37-… frame size supply module(s) used lcl filter(s) used inverter modules used qty type acs880-104-… qty type qty type acs880-104-… u n = 400 v 0450a-3 1×r8i + 1×r8i 1 0470a-3+e205+n8201 1 blcl-13-5 1 0470a-3+e205 0620a-3 1×r8i ...
Page 184: Fuses
184 technical data fuses ac fuses notes: • see also implementing thermal overload and short-circuit protection (page 88 ) and electrical power network specification (page 189 ). • fuses with higher current rating than the recommended ones must not be used. • fuses from other manufacturers can be use...
Page 185
Technical data 185 dc fuses drives with parallel-connected supply and inverter modules (ie. Frames 2×r8i + 2×r8i and above) have dc fuses at the output of each supply module and at the input of each inverter module. Notes: • fuses with higher current rating than the recommended ones must not be used...
Page 186: Dimensions And Weights
186 technical data fuses on cvar varistor board the cvar board is used in units for ul and csa installations. The fuse type is ferraz a070grb10t13/g330010 (10 a 700 v ac). Brake chopper dc fuses optional (+d150) brake choppers have two dc fuses each. The fuse type is bussmann 170m8635 (630 a 1000 v)...
Page 187: Cooling Data, Noise
Technical data 187 cooling data, noise drive type air flow heat dissipation noise m 3 /h ft 3 /min kw db(a) u n = 400 v acs880-37-0450a-3 3760 2215 14 75 acs880-37-0620a-3 3760 2215 18 75 acs880-37-0870a-3 3760 2215 27 75 acs880-37-1110a-3 7220 4250 31 77 acs880-37-1210a-3 7220 4250 34 77 acs880-37-...
Page 188: Sine Output Filter Data
188 technical data sine output filter data sine output filters are available as option +e206. The table below shows the types and technical data of the filters and filter cubicles used in acs880-37 drives. The standard filters listed require no current derating. For availability of sine output filte...
Page 189: Motor Connection Data
Technical data 189 electrical power network specification voltage ( u 1 ) acs880-37-xxxxx-3: 380…415 v ac 3-phase ± 10%. This is indicated in the type designation label as typical input voltage level (3~ 400 v ac). Acs880-37-xxxxx-5: 380…500 v ac 3-phase ± 10%. This is indicated in the type designat...
Page 190: Efficiency
190 technical data frequency 0…±598 hz (0…±120 hz with sine output filters [option +e206]) • for higher operational output frequencies, please contact your local abb representative. • operation above 150 hz may require type-specific derating. For more information, contact your local abb representati...
Page 191: Materials
Technical data 191 contamination iec/en 60721-3-3:2002: classification of environmental conditions - part 3-3: classification of groups of environmental parameters and their severities - stationary use of weather protected locations iec 60721-3-1:1997 iec 60721-3-2:1997 chemical gases class 3c2 clas...
Page 192
192 technical data package standard package: • timber, polyethylene sheet (thickness 0.15 mm), stretch film (thickness 0.023 mm), pp tape, pet strap, sheet metal (steel) • for land and air transport when planned storage time is less than 2 months or when storage can be arranged in clean and dry cond...
Page 193: Applicable Standards
Technical data 193 applicable standards ce marking a ce mark is attached to the drive to verify that the drive complies with the provisions of the european low voltage and emc directives. The ce marking also verifies that the drive, in regard to its safety functions (such as safe torque off), confor...
Page 194
194 technical data the machinery directive. These functions of the drive comply with european harmonized standards such as en 61800-5-2. The related declarations of conformity are shown below. Declaration of conformity.
Page 195
Technical data 195.
Page 196
196 technical data compliance with en 61800-3:2004 definitions emc stands for e lectro m agnetic c ompatibility. It is the ability of electrical/electronic equipment to operate without problems within an electromagnetic environment. Likewise, the equipment must not disturb or interfere with any othe...
Page 197: Ul And Csa Markings
Technical data 197 category c4 if the provisions under category c3 cannot be met, the requirements of the standard can be met as follows: 1. It is ensured that no excessive emission is propagated to neighboring low-voltage networks. In some cases, the natural suppression in transformers and cables i...
Page 198: Rcm Marking
198 technical data • protect the input cable with fuses. Suitable iec (class ar) fuses and ul fuses are listed starting on page 184 . Circuit breakers must not be used without fuses in the usa. For suitable circuit breakers, contact your local abb representative. • for installation in the united sta...
Page 199: Disclaimers
Technical data 199 insulation supports cable lugs disclaimers generic disclaimer the manufacturer shall have no obligation with respect to any product which (i) has been improperly repaired or altered; (ii) has been subjected to misuse, negligence or accident; (iii) has been used in a manner contrar...
Page 200
200 technical data.
Page 201: Dimensions
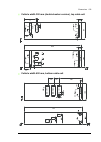
Dimensions 201 13 dimensions what this chapter contains this chapter contains the following dimension data: • composition of cabinet line-ups in tabular form for each frame size with options (page 202 ) • approximate weights of basic line-ups (page 206 ) • dimension drawing examples of selected line...
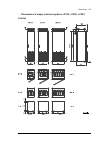
Page 202: Cabinet Line-Up Dimensions
202 dimensions cabinet line-up dimensions the drive consists of cubicles built into a cabinet line-up. The tables below show the composition of cabinet line-ups for each frame size and the standard combinations of options. The dimensions are in millimeters (for inches, divide by 25.4). Notes: • the ...
Page 203
Dimensions 203 acs880-37-1110a-3, -1010a-5, -1110a-5, -0660a-7, -0770a-7, -0950a-7, -1130a-7 a ux ili ar y c o nt ro l cu bi cl e (a cu) in co mi ng c u bi cl e (i cu) su p pl y m o du le cub icl e in ve rt er mo du le cub icl e joi ni ng cu bi cl e co m m o n m o to r te rm in al cu bi cl e s ine f...
Page 204
204 dimensions acs880-37-1210a-3, -1430a-3, -1700a-3, -1530a-5 a ux ili ar y c o nt ro l cu bi cl e (a cu) in co mi ng c u bi cl e (i cu) a da pt e r f or t op en tr y su p pl y m o du le cub icl e in ve rt er mo du le cub icl e joi ni ng cu bi cl e *c o m mo n mo to r te rm in al cu bi cl e s ine f...
Page 205
Dimensions 205 4×r8i + 4×r8i auxiliary control cubicle (acu) incoming cubicle (icu) adapter for top entry supply module cubicle 1 supply module cubicle 2 inverter module cubicle 1 common motor terminal cubicle inverter module cubicle 2 shipping split widths line-up width 400 600 800 800 600 600 3800...
Page 206
206 dimensions weights the table below lists the approximate basic weights of the drive types. Drive type acs880-37-… weight kg lbs 0450a-3 0620a-3 0870a-3 0420a-5 0570a-5 0780a-5 0320a-7 0390a-7 0580a-7 1180 2600 1110a-3 1010a-5 1110a-5 0660a-7 0770a-7 0950a-7 1130a-7 1970 4340 1210a-3 1430a-3 1700...
Page 207
Dimensions 207 dimension drawing examples frame 1×r8i + 1×r8i.
Page 208
208 dimensions frame 1×r8i + 1×r8i, top cable entry/exit (+h351+h353).
Page 209
Dimensions 209 frame 1×r8i + 1×r8i with brake choppers and resistors (+d150+d151).
Page 210
210 dimensions frame 1×r8i + 1×r8i with sine output filter (+e206).
Page 211
Dimensions 211 frame 2×r8i + 2×r8i (eg. Acs880-37-1110a-3), ip22.
Page 212
212 dimensions frame 2×r8i + 2×r8i (eg. Acs880-37-1210a-3), ip54.
Page 213
Dimensions 213 frame 2×r8i + 2×r8i with main breaker (+f255) and common motor terminal cubicle (+h359), 1/2.
Page 214
214 dimensions frame 2×r8i + 2×r8i with main breaker (+f255) and common motor terminal cubicle (+h359), 2/2.
Page 215
Dimensions 215 frame 2×r8i + 2×r8i with main breaker (+f255) and top entry/top exit (+h351+h353), 1/2.
Page 216
216 dimensions frame 2×r8i + 2×r8i with main breaker (+f255) and top entry/top exit (+h351+h353), 2/2.
Page 217
Dimensions 217 frame 3×r8i + 3×r8i, 1/2.
Page 218
218 dimensions frame 3×r8i + 3×r8i, 2/2.
Page 219
Dimensions 219 frame 3×r8i + 3×r8i with common motor terminal cubicle (+h359), 1/2.
Page 220
220 dimensions frame 3×r8i + 3×r8i with common motor terminal cubicle (+h359), 2/2.
Page 221
Dimensions 221 dimensions of empty cubicles (options +c199, +c200, +c201) ip22/ip42.
Page 222
222 dimensions ip54.
Page 223
Dimensions 223 location and size of input terminals frame 1×r8i + 1×r8i, bottom cable entry frame 1×r8i + 1×r8i, top cable entry.
Page 224
224 dimensions frame 2×r8i + 2×r8i with main switch/disconnector (400 mm), bottom cable entry frame 2×r8i + 2×r8i with main switch/disconnector (400 mm), top cable entry.
Page 225
Dimensions 225 frame 2×r8i + 2×r8i with main switch/disconnector (600 mm), bottom cable entry frame 2×r8i + 2×r8i with main switch/disconnector (600 mm), top cable entry.
Page 226
226 dimensions units with main breaker (600 mm), bottom cable entry units with main breaker (600 mm), top cable entry.
Page 227
Dimensions 227 location and size of output terminals (units without common motor terminal cubicle) frame 1×r8i + 1×r8i (without sine output filter) see page 223 . Inverter module cubicle with two r8i modules, bottom cable exit.
Page 228
228 dimensions inverter module cubicle with two r8i modules, top cable exit inverter module cubicle with three r8i modules, bottom cable exit.
Page 229
Dimensions 229 inverter module cubicle with three r8i modules, top cable exit sine filter (+e206) cubicle, 1000 mm, bottom cable exit.
Page 230
230 dimensions sine filter (+e206) cubicle, 1000 mm, top cable exit.
Page 231: Motor Terminal Cubicle)
Dimensions 231 location and size of output terminals (units with common motor terminal cubicle) note: see the dimension tables starting on page 202 as to which common motor terminal cubicle width is used with which drive type. Cubicle width 300 mm, bottom cable exit.
Page 232
232 dimensions cubicle width 300 mm (double-busbar version), bottom cable exit cubicle width 300 mm, top cable exit.
Page 233
Dimensions 233 cubicle width 300 mm (double-busbar version), top cable exit cubicle width 400 mm, bottom cable exit.
Page 234
234 dimensions cubicle width 400 mm, top cable exit cubicle width 600 mm, bottom cable exit.
Page 235
Dimensions 235 cubicle width 600 mm, top cable exit.
Page 236
236 dimensions.
Page 237: Contents Of This Chapter
The safe torque off function 237 14 the safe torque off function contents of this chapter this chapter describes the safe torque off (sto) function of the inverter (ie. The inverter unit of the drive) and gives instructions for its use. Description the safe torque off function can be used, for examp...
Page 238
238 the safe torque off function the function also corresponds to prevention of unexpected start-up as specified by en 1037:1995 + a1:2008 and uncontrolled stop (stop category 0) as specified in en/iec 60204-1. Compliance with the european machinery directive see page 193 . Iec 61508-1:2010 function...
Page 239: Wiring
The safe torque off function 239 wiring the following diagrams present examples of safe torque off wiring for • a frame n×r8i inverter unit (page 240 ) • multiple inverter units (page 241 ) • multiple inverter units when an external 24 v dc power supply is used (page 242 ). For information on the sp...
Page 240
240 the safe torque off function frame n×r8i inverter unit (internal power supply) warning! Frame r8i inverter modules are as standard delivered with a jumper wire set that supplies 24 v from connector x53 to connector x52. The jumper wire set must be removed before wiring the safe torque off circui...
Page 241
The safe torque off function 241 multiple inverter units (internal power supply) +24 v out1 sgnd in1 in2 out1 sgnd in1 in2 out1 sgnd in1 in2 k xsto control unit xsto control unit xsto control unit inverter unit inverter unit inverter unit.
Page 242
242 the safe torque off function multiple inverter units (external power supply) out1 sgnd in1 in2 out1 sgnd in1 in2 out1 sgnd in1 in2 +24 v control unit 24 v dc – + k xsto control unit xsto control unit xsto inverter unit inverter unit inverter unit.
Page 243: Operation Principle
The safe torque off function 243 operation principle 1. The safe torque off activates (the activation switch is opened, or safety relay contacts open). 2. The sto inputs on the inverter control unit de-energize. 3. The control unit cuts off the control voltage from the inverter igbts. 4. The control...
Page 244
244 the safe torque off function acceptance test procedure after wiring the safe torque off function, validate its operation as follows. Notes: • if the drive is equipped with safety option +q950, +q951, +q952, +q957, +q963, +q964, +q978 or +q979, do the procedure shown in the documentation of the o...
Page 245: Use
The safe torque off function 245 use 1. Open the activation switch, or activate the safety functionality that is wired to the sto connection. 2. Sto inputs on the inverter control unit de-energize, and the inverter control unit cuts off the control voltage from the inverter igbts. 3. The control pro...
Page 246: Maintenance
246 the safe torque off function number of pole pairs. Notes : • if a running drive is stopped by using the safe torque off function, the drive will cut off the motor supply voltage and the motor will coast to a stop. If this causes danger or is not otherwise acceptable, stop the drive and machinery...
Page 247: Safety Data
The safe torque off function 247 the diagnostics of the safe torque off function cross-compare the status of the two sto channels. In case the channels are not in the same state, a fault reaction function is performed and the inverter trips on an “sto hardware failure” fault. An attempt to use the s...
Page 248
248 the safe torque off function abbreviations declaration of conformity see section compliance with the european machinery directive (page 193 ). Abbr. Reference description cat. En iso 13849-1 classification of the safety-related parts of a control system in respect of their resistance to faults a...
Page 249: Resistor Braking
Resistor braking 249 15 resistor braking contents of this chapter this chapter tells how to select, protect and wire brake choppers and resistors. The chapter also contains the related technical data. Operating principle the brake chopper handles the energy generated by a decelerating motor. The cho...
Page 250
250 resistor braking factory-installed brake choppers and resistors the following brake choppers (option +d150) and resistors (+d151) are available for the acs880-37 as factory-installed. It is also possible to use option +d150 with a custom resistor assembly. Consult your local abb representative f...
Page 251: Technical Data
Resistor braking 251 technical data ratings of chopper/resistor combinations safur resistors the safur resistors available as factory-installed (option +d151) are also available separately. Terminals and cable lead-through data of factory-installed chopper/resistor cubicles see the dimension drawing...
Page 252
252 resistor braking planning the braking system verifying the capacity of the braking equipment 1. Calculate the maximum power generated by the motor during braking ( p max ). 2. Ensure that the braking power of the chopper is equal to or greater than p max . The p brmax values specified in the rat...
Page 253
Resistor braking 253 calculating the maximum braking power ( p br ) • braking energy transferred during any ten minute period must be less than or equal to the energy transferred during the reference braking cycle. • the braking power must not exceed the rated maximum value p brmax . Example 1 the d...
Page 254
254 resistor braking selecting and routing the cables of a custom resistor use the same cable type for the resistor cabling as for the drive input cabling to ensure that the input fuses also protect the resistor cable. Alternatively, a two conductor shielded cable with the same cross-sectional area ...
Page 255
Resistor braking 255 thermal protection of the resistors the standard resistors available as option +d151 are equipped with a thermal switch. The switches of the resistors are wired in series and connected to the enable input of the brake chopper. The relay output of the chopper is wired to the supp...
Page 256: Start-Up
256 resistor braking connection procedure warning! Obey the instructions in chapter safety instructions . If you ignore them, injury or death, or damage to the equipment can occur. • do the steps in section electrical safety precautions (page 19 ) before you start the work. • connect the resistor ca...
Page 257
Further information product and service inquiries address any inquiries about the product to your local abb representative, quoting the type designation and serial number of the unit in question. A listing of abb sales, support and service contacts can be found by navigating to www.Abb.Com/searchcha...
Page 258
Www.Abb.Com/drives www.Abb.Com/drivespartners 3axd50000020437 rev b (en) 2017-03-27 contact us.