- DL manuals
- ABB
- Relays
- relion REF615
- Applications Manual
ABB relion REF615 Applications Manual
Summary of relion REF615
Page 1
Application manual feeder protection and control ref615.
Page 3
Document id: 1mrs756378 issued: 04.03.2009 revision: d product version: 2.0 © copyright 2009 abb. All rights reserved.
Page 4
Copyright this document and parts thereof must not be reproduced or copied without written permission from abb, and the contents thereof must not be imparted to a third party, nor used for any unauthorized purpose. The software or hardware described in this document is furnished under a license and ...
Page 5
Disclaimer the data, examples and diagrams in this manual are included solely for the concept or product description and are not to be deemed as a statement of guaranteed properties. All persons responsible for applying the equipment addressed in this manual must satisfy themselves that each intende...
Page 6
Conformity this product complies with the directive of the council of the european communities on the approximation of the laws of the member states relating to electromagnetic compatibility (emc council directive 2004/108/ec) and concerning electrical equipment for use within specified voltage limi...
Page 7
Table of contents section 1 introduction.......................................................................7 this manual........................................................................................7 intended audience........................................................................
Page 8
Functional diagrams for disturbance recorder and trip circuit supervision...................................................................42 functional diagrams for control and interlocking....................43 standard configuration b including directional earth-fault protection and cb condition...
Page 9
Applications.................................................................................93 functions.....................................................................................93 default i/o connections..........................................................95 functional diagrams.......
Page 10
Transient/intermittent earth-fault protection intrptef............154 identification.........................................................................154 functionality.........................................................................155 application.........................................
Page 11
Circuit breaker failure protection ccbrbrf..................................182 identification..............................................................................182 functionality..............................................................................182 application.....................
Page 12
Identification.........................................................................206 functions...................................................................................206 measurement function applications...........................................207 disturbance recorder................
Page 13
Section 1 introduction 1.1 this manual application manual contains application descriptions and setting guidelines sorted per function. The manual can be used to find out when and for what purpose a typical protection function can be used. The manual can also be used when calculating settings. 1.2 i...
Page 14
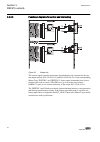
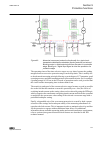
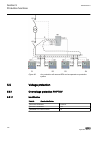
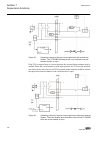
1.3 product documentation 1.3.1 product documentation set p la nni n g & p ur cha se e n gi nee ring in st al ling c om m iss io n ing o p e ra tio n m a in te na nc e d ec om m issi oni n g de inst a lli n g & d is pos a l application manual operation manual installation manual service manual engin...
Page 15
Operation manual contains instructions on how to operate the ied during normal service once it has been commissioned. The manual can be used to find out how to handle disturbances or how to view calculated and measured network data to determine the cause of a fault. Service manual contains instructi...
Page 16
1.3.3 related documentation name of the document document id modbus communication protocol manual 1mrs756468 dnp 3.0 communication protocol manual 1mrs756709 iec 60870-5-103 communication protocol manual 1mrs756710 installation manual 1mrs756375 operation manual 1mrs756708 technical manual 1mrs75637...
Page 17
In degraded process performance leading to personal injury or death. Therefore, comply fully with all warning and caution notices. 1.4.2 document conventions • abbreviations and acronyms in this manual are spelled out in glossary. Glossary also contains definitions of important terms. • push button ...
Page 18
Function iec 61850 iec 60617 iec-ansi non-directional earth-fault protection eflptoc1 i 0 > (1) 51n-1 (1) eflptoc2 i 0 > (2) 51n-1 (2) efhptoc1 i 0 >> 51n-2 efiptoc1 i 0 >>> 50n/51n directional earth-fault protection deflpdef1 i 0 > → (1) 67n-1 (1) deflpdef2 i 0 > → (2) 67n-1 (2) defhpdef1 i 0 >> → ...
Page 19
Function iec 61850 iec 60617 iec-ansi residual current measurement rescmmxu1 i 0 i n residual voltage measurement resvmmxu1 u 0 v n three-phase voltage measurement vmmxu1 3u 3u sequence voltage measurement vsmsqi1 u 1 , u 2 , u 0 u 1 , u 2 , u 0 three-phase power and energy measurement pemmxu1 p, e ...
Page 20
14.
Page 21
Section 2 ref615 overview 2.1 overview ref615 is a native iec 61850 feeder protection ied for selective short-circuit, overcurrent and earth-fault protection. It is applicable to all types of radial isolated neutral networks, resistant earthed networks and compensated networks. Ref615 is part of a p...
Page 22
2.1.1 product version history ied version release date product history 1.0 20.12.2007 product released 1.1 02.07.2008 • irig-b • support for parallel protocols added: iec 61850 and modbus • x130 bio added: optional for variants b and d • cb interlocking functionality enhanced • tcs functionality in ...
Page 23
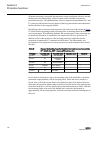
Table 2: standard configurations description std. Conf. Non-directional overcurrent and directional earth-fault protection a and b non-directional overcurrent and non-directional earth-fault protection c and d non-directional overcurrent and directional earth-fault protection with phase-voltage base...
Page 24
Functionality a b c d e f three-phase undervoltage, instance 1 - - - - - ● three-phase undervoltage, instance 2 - - - - - ● three-phase undervoltage, instance 3 - - - - - ● three-phase inrush current detection ● ● ● ● ● ● arc protection with three sensors ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ control circuit breaker control ...
Page 25
• arc protection • auto-reclosing • modbus tcp/ip or rtu/ascii • iec 60870-5-103 • dnp 3.0 tcp/ip or serial 2.3 physical hardware the ied consists of two main parts: plug-in unit and case. The plug-in unit content depends on the ordered functionality. Table 4: plug-in unit and case main unit slot id...
Page 26
The connection diagrams of different hardware modules are presented in this manual. See the installation manual for more information about the case and the plug-in unit. Table 5: number of physical connections in standard configurations conf. Analog channels binary channels ct vt bi bo a 4 1 3 6 b 4...
Page 27
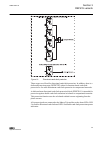
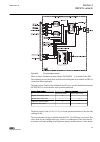
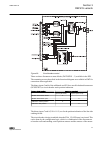
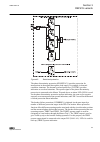
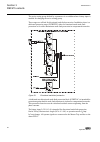
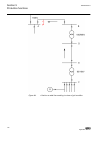
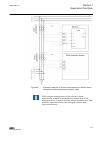
2.4 lhmi a070704 v2 en figure 1: lhmi the lhmi of the ied contains the following elements: • display • buttons • led indicators • communication port the lhmi is used for setting, monitoring and controlling. 2.4.1 lcd the lhmi includes a graphical lcd that supports two character sizes. The character ...
Page 28
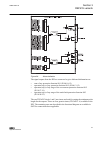
Character size rows in view characters on row small, mono-spaced (6x12 pixels) 5 rows 10 rows with large screen 20 large, variable width (13x14 pixels) 4 rows 8 rows with large screen min 8 the display view is divided into four basic areas: 1 2 3 4 a070705 v2 en figure 2: display layout 1 header 2 i...
Page 29
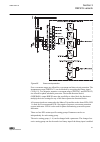
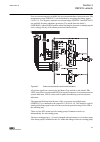
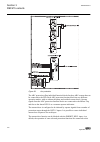
A071176 v1 en figure 3: lhmi keypad with object control, navigation and command push- buttons and rj-45 communication port 2.5 whmi the whmi enables the user to access the ied via a web browser. The supported web browser version is internet explorer 7.0 or later. Whmi is disabled by default. Whmi of...
Page 30
A070754 v3 en figure 4: example view of the whmi the whmi can be accessed: • locally by connecting your laptop to the ied via the front communication port. • remotely over lan/wan. 2.6 authorization the user categories have been predefined for the lhmi and the whmi, each with different rights and de...
Page 31
Table 6: predefined user categories username user rights viewer read only access operator • selecting remote or local state with (only locally) • changing setting groups • controlling • clearing alarm and indication leds and textual indications engineer • changing settings • clearing event list • cl...
Page 32
Optic lc connector (100base-fx). An optional serial interface is available for rs-232/rs-485 communication. Section 2 1mrs756378 d ref615 overview 26 ref615 application manual.
Page 33
Section 3 ref615 variants 3.1 ref615 variant list ref615 is intended for protection and control mainly in mv feeder applications. The product has a number of standard configurations covering a wide range of primary circuit configurations in distribution networks based on different system earthing me...
Page 34
Signal matrix tool with smt the user can modify the standard configuration according to the actual needs. The ied is delivered from the factory with default connections described in the functional diagrams for bi's, bo's, function to function connections and alarm leds. Smt has a number of different...
Page 35
Functionality a b c d e f non-directional earth fault, high-set stage - - ● ● - - non-directional earth fault, instantaneous stage - - ● ● - - non-directional sensitive earth fault - - ● ● - - negative-sequence overcurrent, instance 1 ● ● ● ● ● ● negative-sequence overcurrent, instance 2 ● ● ● ● ● ●...
Page 36
Functionality a b c d e f residual voltage ● ● - - ● ● power, including power factor - - - - ● ● energy - - - - ● ● ● = included,○ = optional at the time of the order 1) basic interlocking functionality: closing of the circuit breaker can be enabled by a binary input signal. The actual interlocking ...
Page 37
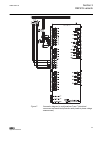
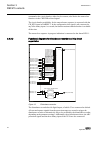
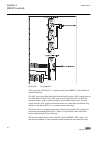
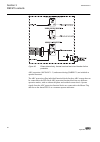
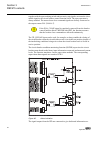
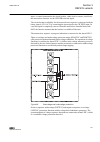
3.2.2 connection diagrams a071288 v4 en figure 5: connection diagram for configurations a and b (overcurrent and directional earth-fault protection) [1] [1] additional bio-module (x110 in the diagram) is included in the ied variant b 1mrs756378 d section 3 ref615 variants ref615 31 application manua...
Page 38
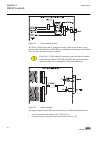
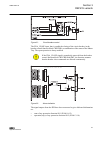
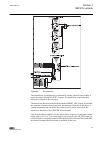
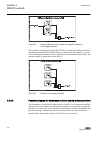
A071290 v3 en figure 6: connection diagram for configurations c and d (overcurrent and non-directional earth-fault protection) [2] [2] additional bio-module (x110 in the diagram) is included in the ied variant d section 3 1mrs756378 d ref615 variants 32 ref615 application manual.
Page 39
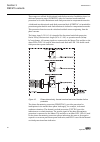
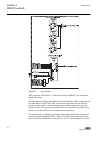
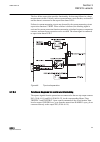
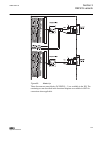
Guid-f7601942-acf2-47e2-8f21-cd9c1d2bc1f0 v2 en figure 7: connection diagram for configurations e and f (directional overcurrent and earth-fault protection with phase-to-phase voltage measurement) 1mrs756378 d section 3 ref615 variants ref615 33 application manual.
Page 40
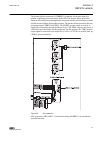
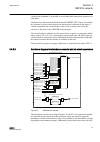
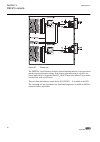
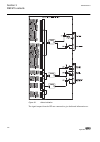
Guid-5d0135b3-3890-497a-8aaa-0362730c8682 v1 en figure 8: connection diagram for configurations e and f (directional overcurrent and earth-fault protection with phase-to-earth voltage measurement) 3.3 standard configuration a including directional earth- fault protection 3.3.1 applications the stand...
Page 41
3.3.2 functions table 9: functions included in the ref615 standard configuration with directional earth-fault protection function iec 61850 iec ansi three-phase non-directional overcurrent protection, low stage phlptoc1 3i> 51p-1 three-phase non-directional overcurrent protection, high stage, instan...
Page 42
3.3.2.1 default i/o connections binary input default usage connector-pins x120-bi1 blocking of overcurrent instantaneous stage x120-1,2 x120-bi2 circuit breaker closed position indication x120-3,2 x120-bi3 circuit breaker open position indication x120-4,2 binary output default usage connector-pins x...
Page 43
The analog channels are assigned to different functions as shown in the functional diagrams. The common signal marked with 3i represents the three phase currents. The signal marked with i 0 represents the measured residual current via a core balance ct. The signal marked with u 0 represents the meas...
Page 44
Four overcurrent stages are offered for overcurrent and short-circuit protection. The instantaneous stage (phiptoc1) can be blocked by energizing the binary input 1 (x120:1-2). Two negative sequence overcurrent stages (nsptoc1 and nsptoc2) are offered for phase unbalance protection. The inrush detec...
Page 45
A071318 v4 en figure 10: directional earth-fault protection three stages are offered for directional earth-fault protection. In addition, there is a dedicated protection stage (intrptef) either for transient based earth-fault protection or for cable intermittent earth-fault protection in compensated...
Page 46
A071320 v4 en figure 11: phase discontinuity, thermal overload and circuit breaker failure protection the phase discontinuity protection (pdnpstoc1) provides protection for interruptions in the normal three-phase load supply, for example, in downed conductor situations. The thermal overload protecti...
Page 47
A071322 v4 en figure 12: arc protection arc protection (arcsarc1-3) and autoreclosing (darrec1) are included as optional functions. The arc protection offers individual function blocks for three arc sensors that can be connected to the ied. Each arc protection function block has two different operat...
Page 48
Command to the circuit breaker, either local or remote, also blocks the autoreclose function via the cbxcbr-selected signal. The circuit breaker availability for the autoreclosure sequence is expressed with the cb_rdy input in darrec1. In the configuration, this signal is not connected to any of the...
Page 49
Two separate tcs functions have been included: tcsscbr1 for po3 (x100:16-19) and tcsscbr2 for po4 (x100:20-23). Both functions are blocked by the master trip and the circuit breaker open position signal. The tcs alarm indication is connected to led 9. 3.3.3.3 functional diagrams for control and inte...
Page 50
A071328 v3 en figure 15: circuit breaker control the ena_close input, that is, enable the closing of the circuit breaker, in the breaker control function block cbxcbr is a combination of the status of the master trip. The open operation is always enabled. If the ena_close signal is completely remove...
Page 51
The tpgapc1 is a timer and used for setting the minimum pulse length for the outputs. There are four generic timers (tpgapc1..4) available in the ied. The remaining ones not described in the functional diagram are available in smt for connection where applicable. 3.4 standard configuration b includi...
Page 52
Function iec 61850 iec ansi negative-sequence overcurrent protection, instance 2 nsptoc2 i 2 > (2) 46 (2) phase discontinuity pdnsptoc1 i 2 /i 1 > 46pd three-phase inrush detector inrphar1 3i2f> 68 three-phase thermal protection for feeders, cables and distribution transformers t1pttr1 3ith> 49f aut...
Page 53
Binary output default usage connector-pins x110-so1 upstream overcurrent blocking x110-14,15,16 x110-so2 overcurrent operate alarm x110-17,18,19 x110-so3 earth fault operate alarm x110-20,21,22 led default usage 1 non-directional overcurrent operate 2 directional/intermittent earth fault operate 3 d...
Page 54
A071332 v4 en figure 17: overcurrent protection four overcurrent stages are offered for overcurrent and short-circuit protection. The instantaneous stage (phiptoc1) can be blocked by energizing the binary input 1 (x120:1-2). Two negative sequence overcurrent stages (npstoc1 and npstoc2) are offered ...
Page 55
There are four ied variant specific setting groups. Parameters can be set independently for each setting group. The active setting group (1...4) can be changed with a parameter. The change of an active setting group can also be made via a binary input if the binary input is enabled for this. To enab...
Page 56
Three stages are offered for directional earth-fault protection. In addition, there is a dedicated protection stage (intrptef) either for transient based earth-fault protection or for cable intermittent earth-fault protection in compensated networks. A dedicated non-directional earth-fault protectio...
Page 57
The breaker failure protection (ccbrbrf1) is initiated via the start input by a number of different protection stages in the ied. The breaker failure protection function offers different operating modes associated with the circuit breaker position and the measured phase and residual currents. The br...
Page 58
The arc protection offers individual function blocks for three arc sensors that can be connected to the ied. Each arc protection function block has two different operation modes, with or without the phase and residual current check. Operate signals from the arc protection function blocks are connect...
Page 59
3.4.3.2 functional diagram for disturbance recorder and trip circuit supervision phlptoc1-start phhptoc1-start phhptoc2-start phiptoc1-start nsptoc1-start nsptoc2-start deflpdef1-start deflpdef2-start defhpdef1-start intrptef1-start efhptoc1-start pdnsptoc1-start t1pttr1-start ccrbrf1-trret ccrbrf1-...
Page 60
3.4.3.3 functional diagrams for control and interlocking a071326 v4 en figure 22: master trip the operate signals from the protections described above are connected to the two trip output contacts po3 (x100:16-19) and po4 (x100:20-23) via the corresponding master trips trpptrc1 and trpptrc2. Open co...
Page 61
A071344 v4 en figure 23: circuit breaker control there are three disconnector status blocks (dcsxswi1…3) available in the ied. The remaining two not described in the functional diagram are available in smt for connection where applicable. The binary inputs 5 and 6 of the additional card x110 are use...
Page 62
Trip logics and gas pressure alarm and circuit breaker spring charging. The okpos output from the dcsxswi block defines if the disconnector or breaker truck is definitely either open/in test position or close/in service position. This, together with the open earthing switch and non-active trip signa...
Page 63
A071346 v4 en figure 24: alarm indication the signal outputs from the ied are connected to give dedicated information on: • start of any protection function so1 (x100:10-12) • operation (trip) of any protection function so2 (x100:13-15) • operation (trip) of any stage of the overcurrent protection f...
Page 64
3.5 standard configuration c including non-directional earth-fault protection 3.5.1 applications the standard configuration for non-directional earth-fault protection is mainly intended for cable and overhead line feeder applications in directly or resistance earthed distribution networks. The ied w...
Page 65
Function iec 61850 iec ansi master trip trpptrc1 trpptrc2 master trip (1) master trip (2) 94/86 (1) 94/86 (2) trip circuit supervision, instance 1 tcsscbr1 tcs (1) tcm (1) trip circuit supervision, instance 2 tcsscbr2 tcs (2) tcm (2) disturbance recorder rdre1 - - three-phase current measurement cmm...
Page 66
3.5.3 functional diagrams the functional diagrams describe the default input, output, alarm led and function- to-function connections. The default connections can be viewed with smt and changed according to the application requirements, if necessary. The analog channels, measurements from cts and vt...
Page 67
A071348 v3 en figure 25: overcurrent protection four overcurrent stages are offered for overcurrent and short-circuit protection. The instantaneous stage (phiptoc1) can be blocked by energizing the binary input 1 (x120:1-2). Two negative sequence overcurrent stages (npstoc1 and npstoc2) are offered ...
Page 68
For this. To enable the change of an active setting group via a binary input, connect a free binary input with smt to the actsg input of the sgcb-block. Table 14: binary input states and corresponding active setting groups bi state active setting group off 1 on 2 the active setting group defined by ...
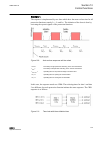
Page 69
A071352 v4 en figure 27: phase discontinuity, thermal overload and circuit breaker failure protection the phase discontinuity protection (pdnsptoc1) provides protection for interruptions in the normal three-phase load supply, for example, in downed conductor situations. The thermal overload protecti...
Page 70
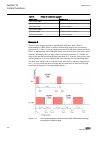
A071354 v4 en figure 28: arc protection arc protection (arcsarc1...3) and autoreclosing (darrec1) are included as optional functions. The arc protection offers individual function blocks for three arc sensors that can be connected to the ied. Each arc protection function block has two different oper...
Page 71
Input. A control command to the circuit breaker, either local or remote, also blocks the autoreclose function via the cbxcbr-selected signal. The circuit breaker availability for the autoreclosure sequence is expressed with the cb_rdy input in darrec1. In the configuration, this signal is not connec...
Page 72
(trpptrc1 and trpptrc2) and the circuit breaker open position signal. The tcs alarm indication is connected to led 9. 3.5.3.3 functional diagrams for control and interlocking a071358 v4 en figure 30: master trip the operate signals from the protections described above are connected to both of the tw...
Page 73
A071360 v3 en figure 31: circuit breaker control the ena_close input, that is, enable the closing of the circuit breaker, in the breaker control function block cbxcbr is a combination of the status of the master trip. The open operation is always enabled. If the ena_close signal is completely remove...
Page 74
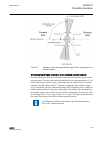
The two tpgapc blocks 1 and 2 are timers and used for setting the minimum pulse length for the outputs. There are four generic timers (tpgapc1..4) available in the ied. The remaining ones not described in the functional diagram are available in smt for connection where applicable. 3.6 standard confi...
Page 75
Function iec 61850 iec ansi three-phase inrush detector inrphar1 3i2f> 68 three-phase thermal protection for feeders, cables and distribution transformers t1pttr1 3ith> 49f autoreclosure darrec1 o → i 79 circuit breaker failure protection ccbrbrf1 3i>/i 0 >bf 51bf/51nbf master trip trpptrc1 trpptrc2...
Page 76
Led default usage 1 non-directional overcurrent operate 2 non-directional earth fault operate 3 sensitive earth fault operate 4 negative seq. Overcurrent/phase discontinuity operate 5 thermal overload alarm 6 breaker failure operate 7 disturbance recorder triggered 8 circuit breaker condition monito...
Page 77
A071364 v4 en figure 33: overcurrent protection four overcurrent stages are offered for overcurrent and short-circuit protection. The instantaneous stage (phiptoc1) can be blocked by energizing the binary input 1 (x120:1-2). Two negative sequence overcurrent stages (npstoc1 and npstoc2) are offered ...
Page 78
The active setting group (1...4) can be changed with a parameter. The change of an active setting group can also be made via a binary input if the binary input is enabled for this. To enable the change of an active setting group via a binary input, connect a free binary input with smt to the actsg i...
Page 79
A071352 v4 en figure 35: phase discontinuity, thermal overload and circuit breaker failure protection the phase discontinuity protection (pdnsptoc1) provides protection for interruptions in the normal three-phase load supply, for example, in downed conductor situations. The thermal overload protecti...
Page 80
A071370 v4 en figure 36: arc protection arc protection (arcsarc1-3) and autoreclosing (darrec1) are included as optional functions. The arc protection offers individual function blocks for three arc sensors that can be connected to the ied. Each arc protection function block has two different operat...
Page 81
External start command. It is possible to create individual autoreclose sequences for each input. The autoreclose function can be blocked with the inhibit_recl input. As a default, the operation of some selected protection functions are connected to this input. A control command to the circuit break...
Page 82
Protection signals and the three binary inputs from x120 are also connected, as well as the autorecloser external start command from the binary input 2 (x110:3-4). Two separate tcs functions are included: tcsscbr1 for po3 (x100:16-19) and tcsscbr2 for po4 (x100:20-23). Both functions are blocked by ...
Page 83
A071376 v4 en figure 39: circuit breaker control there are three disconnector status blocks (dcsxswi1…3) available in the ied. The remaining two not described in the functional diagram are available in smt for connection where applicable. The binary inputs 5 and 6 of the additional card x110 are use...
Page 84
Trip logics and gas pressure alarm and circuit breaker spring charging. The okpos output from the dcsxswi block defines if the disconnector or breaker truck is definitely either open/in test position or close/in service position. This, together with the open earthing switch and non-active trip signa...
Page 85
A071378 v4 en figure 40: alarm indication the signal outputs from the ied are connected to give dedicated information on: • start of any protection function so1 (x100:10-12) • operation (trip) of any protection function so2 (x100:13-14) • operation (trip) of any stage of the overcurrent protection f...
Page 86
3.7 standard configuration e including directional earth- fault protection with phase-voltage measurement 3.7.1 applications the standard configuration for directional earth-fault protection is mainly intended for cable and overhead line feeder applications in isolated and resonant-earthed distribut...
Page 87
Function iec 61850 iec ansi autoreclosure darrec1 o → i 79 circuit breaker failure protection ccbrbrf1 3i>/i 0 >bf 51bf/51nbf master trip trpptrc1 trpptrc2 master trip (1) master trip (2) 94/86 (1) 94/86 (2) trip circuit supervision, instance 1 tcsscbr1 tcs (1) tcm (1) trip circuit supervision, inst...
Page 88
Binary output default usage connector pins x100-po4 open circuit breaker/trip coil 2 x100-20-24 x110-so1 upstream overcurrent blocking x110-14,15 x110-so2 over current operate alarm x110-17,18 x110-so3 earth fault operate alarm x110-20,21 led default usage 1 non-directional overcurrent protection op...
Page 89
Four overcurrent stages are available for overcurrent and short-circuit protection. The instantaneous stage (phiptoc1) can be blocked by energizing the binary input 1 (x120:1-2). Two negative-sequence overcurrent stages (nsptoc1 and nsptoc2) are available for phase unbalance protection. The inrush d...
Page 90
Via a binary input, connect a free binary input with smt to the actsg input of the sgcb-block. Table 18: binary input states and corresponding active setting groups bi state active setting group off 1 on 2 the active setting group defined by a parameter is overridden when a binary input is enabled f...
Page 91
Guid-1f3c1f26-6f11-4250-9476-82c47c3ac570 v1 en figure 42: earth-fault protection the phase discontinuity protection (pdnsptoc1) provides protection for interruptions in the normal three-phase load supply, for example, in downed conductor situations. The thermal overload protection (t1pttr1) provide...
Page 92
Guid-8bd4614b-2c4d-475e-adc3-a376e213bf3c v1 en figure 43: phase discontinuity, thermal overload and circuit breaker failure protection arc protection (arcsarc1...3) and autoreclosing (darrec1) are included as optional functions. The arc protection offers individual function blocks for three arc sen...
Page 93
Guid-86a27183-ae21-4420-aa8d-b53a43c77bbe v1 en figure 44: arc protection the autorecloser is configured to be initiated by operate signals from a number of protection stages through the init1-5 inputs. It is possible to create individual autoreclose sequences for each input. The autoreclose functio...
Page 94
The autoreclose sequence in progress indication is connected to the alarm led 11. 3.7.3.2 functional diagram for disturbance recorder and trip circuit supervision guid-4be45287-d708-41f3-851a-084a9ac3265e v1 en figure 45: disturbance recorder the disturbance recorder has 64 digital inputs, of which ...
Page 95
The fuse failure supervision provides functionality for detecting failures in voltage measurement circuits. Failures, such as open miniature circuit breaker, are detected and the alarm is connected to the supervision alarm led 9. Failures in current measuring circuits are detected by the current mea...
Page 96
Guid-4963c315-60c2-4c60-be7f-b18d87a8d35e v1 en figure 47: master trip the trpptrc1 and 2 blocks provide the lockout/latching function, event generation and the trip signal duration setting. If the lockout operation mode is selected, one binary input can be re-assigned to the rst_lkout input of the ...
Page 97
Guid-4ded2926-a92a-4f6a-bcaa-7d9cd24acfc8 v1 en figure 48: circuit breaker control the binary inputs 5 and 6 of the additional card x110 are used for busbar disconnector (dcsxswi1) or circuit breaker truck position indication. Table 19: device positions indicated by binary inputs 5 and 6 primary dev...
Page 98
Together with the open earthing switch and non-active trip signals, activates the close- enable signal to the circuit breaker control function block. The open operation is always enabled. The autorecloser close command signals are directly connected to the output contact po1 (x100:6-7). If the ena_c...
Page 99
• start of any protection function so1 (x100:10-12) • operation (trip) of any protection function so2 (x100:13-14) • operation (trip) of any stage of the overcurrent protection function so2 (x110:17-19) • operation (trip) of any stage of the earth-fault protection function so3 (x110:20-22) the two t...
Page 100
Function iec 61850 iec ansi directional earth-fault protection, low stage, instance 1 deflpdef1 i 0 > → (1) 67n-1 (1) directional earth-fault protection, low stage, instance 2 deflpdef2 i 0 > → (2) 67n-1 (2) directional earth-fault protection, high stage defhpdef1 i 0 >> → 67n-2 transient/intermitte...
Page 101
3.8.2.1 default i/o connections binary input default usage connector pins x110-bi1 mcb open x110-1,2 x110-bi2 directional earth fault protection's basic angle control x110-3,4 x110-bi3 circuit breaker low gas pressure indication x110-5,6 x110-bi4 cb spring charged indication x110-7,6 x110-bi5 cb tru...
Page 102
3.8.3 functional diagrams the functional diagrams describe the default input, output, alarm led and function- to-function connections. The default connections can be viewed with smt and changed according to the application requirements. The analog channels, measurements from cts and vts, have fixed ...
Page 103
Guid-f0be506c-0a96-4aa2-ac55-ffd9bcd23951 v1 en figure 50: directional overcurrent protection and inrush indication all operate signals are connected to the master trip and to the alarm leds. Led 1 is used for overcurrent and led 4 for negative-sequence overcurrent protection operate indication. Led...
Page 104
The active setting group defined by a parameter is overridden when a binary input is enabled for changing the active setting group. Three stages are offered for directional earth-fault protection. In addition, there is a dedicated protection stage (intrptef) either for transient-based earth-fault pr...
Page 105
The phase discontinuity protection (pdnsptoc1) provides protection for interruptions in the normal three-phase load supply, for example, in downed conductor situations. The thermal overload protection (t1pttr1) provides indication on overload situations. The operate signal of the phase discontinuity...
Page 106
Guid-ec907a8e-9cf0-4150-a394-ffbaf30a8725 v1 en figure 53: arc protection the arc protection offers individual function blocks for three arc sensors that can be connected to the ied. Each arc protection function block has two different operation modes, with or without the phase and residual current ...
Page 107
Input. A control command to the circuit breaker, either local or remote, also blocks the autorreclose function via the cbxcbr-selected signal. The circuit breaker availability for the autorreclosure sequence is expressed with the binary input 4 (x110:6-7) by connecting the input signal to the cb_rdy...
Page 108
Guid-a77d0608-e3f2-4d3d-8907-15034fc42d51 v1 en figure 55: positive-sequence undervoltage and negative-sequence overvoltage protection the residual overvoltage protection (rovptov) provides earth fault protection by detecting abnormal level of residual voltage. It can be used, for example, as a non-...
Page 109
Guid-a2eba677-aef4-451b-807b-20f50d5894c7 v1 en figure 57: disturbance recorder two separate tcs functions are included: tcsscbr1 for po3 (x100:16-19) and tcsscbr2 for po4 (x100:20-23). Both functions are blocked by the master trip (trpptrc1 and trpptrc2) and the circuit breaker open position signal...
Page 110
Guid-f06a3fef-2c72-49a4-928f-d301335ec2c6 v1 en figure 58: trip circuit supervision 3.8.3.3 functional diagrams for control and interlocking the operate signals from the protections are connected to the two trip output contacts po3 (x100:16-19) and po4 (x100:20-23) via the corresponding master trips...
Page 111
Guid-300441a3-ae3c-4bbf-8c5a-b5ca8ba4ef53 v1 en figure 59: master trip three disconnector status blocks (dcsxswi1…3) are available in the ied. The remaining two not described in the functional diagram are available in smt for connection where applicable. 1mrs756378 d section 3 ref615 variants ref615...
Page 112
Guid-de498cfb-a256-4275-9a1f-5ef3b09046f4 v1 en figure 60: circuit breaker control the binary inputs 5 and 6 of the additional card x110 are used for busbar disconnector (dcsxswi1) or circuit-breaker truck position indication. Table 22: device positions indicated by binary inputs 5 and 6 primary dev...
Page 113
Together with the open earthing switch and non-active trip signals, activates the close- enable signal to the circuit breaker control function block. The open operation is always enabled. The auto-recloser close command signals are directly connected to the output contact po1 (x100:6-7). If the ena_...
Page 114
Guid-79eb68ee-f160-402e-a841-bc6d074e7294 v1 en figure 61: alarm indication the signal outputs from the ied are connected to give dedicated information on: section 3 1mrs756378 d ref615 variants 108 ref615 application manual.
Page 115
• start of any protection function so1 (x100:10-12) • operation (trip) of any protection function so2 (x100:13-14) • operation (trip) of any stage of the overcurrent protection function so2 (x110:17-19) • operation (trip) of any stage of the earth-fault protection function so3 (x110:20-22) • operati...
Page 116
110
Page 117
Section 4 basic functions 4.1 general parameters table 23: analog channel settings, phase currents parameter values (range) unit step default description secondary current 1=0.2a 2=1a 3=5a 2=1a rated secondary current primary current 1.0...6000.0 a 0.1 100.0 rated primary current amplitude corr. A 0...
Page 118
Parameter values (range) unit step default description amplitude corr. A 0.900...1.100 0.001 1.000 phase a voltage phasor magnitude correction of an external voltage transformer amplitude corr. B 0.900...1.100 0.001 1.000 phase b voltage phasor magnitude correction of an external voltage transformer...
Page 119
Table 28: alarm led settings parameter values (range) unit step default description alarm led mode 0=follow-s 1) 1=follow-f 2) 2=latched-s 3) 3=latchedack-f-s 4) 0=follow-s alarm mode for led 1 description alarm leds led 1 description of alarm alarm led mode 0=follow-s 1=follow-f 2=latched-s 3=latch...
Page 120
Parameter values (range) unit step default description description alarm leds led 10 description of alarm alarm led mode 0=follow-s 1=follow-f 2=latched-s 3=latchedack-f-s 0=follow-s alarm mode for led 11 description alarm leds led 11 description of alarm 1) non-latched mode 2) non-latched blinking ...
Page 121
Table 31: ethernet front port settings parameter values (range) unit step default description ip address 192.168.000.254 ip address for front port (fixed) mac address xx-xx-xx-xx- xx-xx mac address for front port table 32: ethernet rear port settings parameter values (range) unit step default descri...
Page 122
Table 35: iec 60870-5-103 settings parameter values (range) unit step default description serial port 1 0=not in use 1=com 1 2=com 2 0=not in use com port for instance 1 address 1 1...255 1 unit address for instance 1 start delay 1 0...20 char 4 start frame delay in chars for instance 1 end delay 1 ...
Page 123
Parameter values (range) unit step default description class1ovind 1 0=no indication 1=both edges 2=rising edge 2=rising edge overflow indication for instance 1 class1ovftype 1 0...255 10 function type for class 1 overflow indication for instance 1 class1ovinfno 1 0...255 255 information number for ...
Page 124
Parameter values (range) unit step default description frame3inuse 2 -1=not in use 0=user frame 1=standard frame 1 2=standard frame 2 3=standard frame 3 4=standard frame 4 5=standard frame 5 6=private frame 6 7=private frame 7 -1=not in use active class2 frame 3 for instance 2 frame4inuse 2 -1=not i...
Page 125
Table 37: modbus settings parameter values (range) unit step default description serial port 1 0=not in use 1=com 1 2=com 2 0=not in use com port for serial interface 1 parity 1 0=none 1=odd 2=even 2=even parity for serial interface 1 address 1 1...255 1 modbus unit address on serial interface 1 lin...
Page 126
Parameter values (range) unit step default description ctlstructpwd7 **** password for modbus control struct 7 ctlstructpwd8 **** password for modbus control struct 8 internal overflow 0=false 1=true 0=false modbus internal overflow: true-system level overflow occured (indication only) table 38: dnp...
Page 127
Table 39: serial communication settings parameter values (range) unit step default description fiber mode 0=no fiber 1=fiber light on loop 2=fiber light off loop 3=fiber light on star 4=fiber light off star 0=no fiber fiber mode for com1 serial mode 1=rs485 2wire 2=rs485 4wire 3=rs232 no handshake 4...
Page 128
Table 41: time settings parameter values (range) unit step default description date 0 date time 0 time time format 1=24h:mm:ss:ms 2=12h:mm:ss:ms 1=24h:mm:ss:ms time format date format 1=dd.Mm.Yyyy 2=dd/mm/yyyy 3=dd-mm-yyyy 4=mm.Dd.Yyyy 5=mm/dd/yyyy 6=yyyy-mm-dd 7=yyyy-dd-mm 8=yyyy/dd/mm 1=dd.Mm.Yyyy...
Page 129
Table 42: generic timers, tpgapc1...4 parameter values (range) unit step default description pulse time 0...60000 ms 1 150 minimum pulse time table 43: x100 psm binary output signals name type default description x100-po1 boolean 0=false connectors 6-7 x100-po2 boolean 0=false connectors 8-9 x100-so...
Page 130
Table 46: x110 bio binary input settings parameter values (range) unit step default description input 1 filter time 5...1000 ms 5 connectors 1-2 input 2 filter time 5...1000 ms 5 connectors 3-4 input 3 filter time 5...1000 ms 5 connectors 5-6c input 4 filter time 5...1000 ms 5 connectors 7-6c input ...
Page 131
Parameter values (range) unit step default description input 2 inversion 0=false 1=true 0=false connectors 3-2c input 3 inversion 0=false 1=true 0=false connectors 4-2c input 4 inversion 0=false 1=true 0=false connectors 5-6 table 49: x130 bio binary output signals name type default description x130...
Page 132
Parameter values (range) unit step default description input 4 inversion 0=false 1=true 0=false connectors 6-5c input 5 inversion 0=false 1=true 0=false connectors 7-8c input 6 inversion 0=false 1=true 0=false connectors 9-8c table 52: x130 aim binary input signals name type description x130-input 1...
Page 133
4.2.1 internal faults internal fault indications have the highest priority on the lhmi. None of the other lhmi indications can override the internal fault indication. An indication about the fault is shown as a message on the lhmi. The text internal fault with an additional text message, a code, dat...
Page 134
Fault indication fault code additional information internal fault conf. Error,x120 65 card in slot x120 is wrong type, is missing or does not belong to the original composition. Internal fault conf. Error,x130 66 card in slot x130 is wrong type, is missing or does not belong to the original composit...
Page 135
Warning indication warning code additional information warning modbus error 21 error in the modbus communication. Warning dnp3 error 22 error in the dnp3 communication. Warning dataset error 24 error in the data set(s). Warning report cont. Error 25 error in the report control block(s). Warning goos...
Page 136
The ied supports sntp, irig-b, dnp 3.0, modbus and iec 60870-5-103 to update the real-time clock. Irig-b with gps provides the best accuracy. With modbus tcp or dnp 3.0 over tcp/ip, sntp time synchronization should be used for better synchronization accuracy. When the sntp server ip setting is chang...
Page 137
To enable active setting group changing via binary input, connect any of the (free) binary inputs to sgcb-block input named actsg using pcm600 and set the setting sg follow input to “true”. Table 56: active setting group binary input state bi state active setting group off 1 on 2 the setting group p...
Page 138
132.
Page 139
Section 5 protection functions 5.1 three-phase current protection 5.1.1 three-phase non-directional overcurrent protection phxptoc 5.1.1.1 identification table 58: function identification different stages: low stage high stage instantaneous stage iec 61850 identification: phlptoc phhptoc phiptoc iec...
Page 140
• selective overcurrent and short-circuit protection of feeders in distribution and subtransmission systems • back-up overcurrent and short-circuit protection of power transformers and generators • overcurrent and short-circuit protection of various devices connected to the power system, for example...
Page 141
Account the selectivity requirements, switching-in currents, and the thermal and mechanical withstand of the transformer and outgoing feeders. Traditionally, overcurrent protection of the transformer has been arranged as shown in figure 62 . The low-set stage phlptoc operates time-selectively both i...
Page 142
Of busbar protection is increased, because there is now a dedicated, selective and fast busbar protection functionality, which is based on the blockable overcurrent protection principle. The additional time selective stages on the transformer hv- and lv-sides provide increased security degree of bac...
Page 143
A070980 v1 en figure 63: numerical overcurrent protection functionality for a typical sub- transmission/distribution substation (feeder protection not shown). Blocking output = digital output signal from the start of a protection stage, blocking in = digital input signal to block the operation of a ...
Page 144
Radial outgoing feeder overcurrent protection the basic requirements for feeder overcurrent protection are adequate sensitivity and operation speed taking into account the minimum and maximum fault current levels along the protected line, selectivity requirements, inrush currents and the thermal and...
Page 145
A070982 v1 en figure 64: functionality of numerical multiple-stage overcurrent protection the coordination plan is an effective tool to study the operation of time selective operation characteristics. All the points mentioned earlier, required to define the overcurrent protection parameters, can be ...
Page 146
A070984 v1 en figure 65: example coordination of numerical multiple-stage over current protection 5.1.2 three-phase directional overcurrent protection dphxpdoc 5.1.2.1 identification iec 61850 identification: dphxpdoc iec 60617 identification: 3i> ->, 3i>> -> ansi/ieee c37.2 device number: 67-1, 67-...
Page 147
In radial networks, the phase overcurrent relays are often sufficient for the short circuit protection of lines, transformers and other equipment. The current-time characteristic should be chosen according to the common practice in the network. It is recommended to use the same current-time characte...
Page 148
Guid-74662396-1bad-4ac2-adb6-f4a8b3341860 v1 en figure 67: overcurrent protection of parallel operating transformers closed ring network topology the closed ring network topology is used in applications where electricity distribution for the consumers is secured during network fault situations. The ...
Page 149
Guid-276a9d62-bd74-4335-8f20-ec1731b58889 v1 en figure 68: closed ring network topology where feeding lines are protected with directional overcurrent relays 5.1.3 three-phase thermal overload protection for overhead lines and cables t1pttr 5.1.3.1 identification table 60: function identification ie...
Page 150
An alarm level gives an early warning to allow operators to take action before the line trips. The early warning is based on the three-phase current measuring function using a thermal model with first order thermal loss with the settable time constant. If the temperature rise continues the function ...
Page 151
5.2 earth-fault protection 5.2.1 non-directional earth-fault protection efxptoc 5.2.1.1 identification table 61: function identification different stages: low stage high stage instantaneous stage iec 61850 identification: eflptoc efhptoc efiptoc iec 60617 identification: i 0 > i 0 >> i 0 >>> ansi/ie...
Page 152
• low (eflptoc) • high (efhptoc) • instantaneous (efiptoc). Eflptoc contains several types of time-delay characteristics. Efhptoc and efiptoc are used for fast clearance of serious earth faults. 5.2.2 directional earth-fault protection defxpdef 5.2.2.1 identification table 62: function identificatio...
Page 153
To turn the directional characteristic, if the expected fault current angle does not coincide with the polarizing quantity to produce the maximum torque. That is, rca is the angle between the maximum torque line and polarizing quantity. If the polarizing quantity is in phase with the maximum torque ...
Page 154
Guid-f3a658d8-b667-4e85-9528-e1d024954b32 v1 en figure 70: definition of the relay characteristic angle, rca=+60 degrees in a solidly earthed network example 3. The "phase angle" mode is selected, isolated network (φrca = -90 deg) => characteristic angle = -90 deg section 5 1mrs756378 d protection f...
Page 155
Guid-a052b527-ce4e-4f2f-b0e6-6a4b0c445c60 v1 en figure 71: definition of the relay characteristic angle, rca=–90 degrees in an isolated network directional earth-fault protection in an isolated neutral network in isolated networks, there is no intentional connection between the system neutral point ...
Page 156
A070441 v1 en figure 72: earth-fault situation in an isolated network directional earth-fault protection in a compensated network in compensated networks, the capacitive fault current and the inductive resonance coil current compensate each other. The protection cannot be based on the reactive curre...
Page 157
Compensated networks or of the earthing resistor in earthed networks. As a result the characteristic angle is set automatically to suit the earthing method used. The rca_ctl input can be used to change the i 0 characteristic: table 63: relay characteristic angle control in i 0 sin(φ) and i 0 cos(φ) ...
Page 158
A070443 v2 en figure 74: extended operation area in directional earth-fault protection 5.2.2.4 application the directional earth-fault protection (defxpdef) is designed for protection and clearance of earth faults and for earth-fault protection of different equipment connected to the power systems, ...
Page 159
Reference residual voltage (-u 0 ). In compensated networks, the phase angle criterion with extended operating sector can also be used. When the relay characteristic angle rca is 0 degrees, the negative quadrant of the operation sector can be extended with the min forward angle setting. The operatio...
Page 160
Core balance current transformers should have a transformation ratio of at least 70:1. Lower transformation ratios such as 50:1 or 50:5 are not recommended. Attention should be paid to make sure the measuring transformers are connected correctly so that defxpdef is able to detect the fault current d...
Page 161
5.2.3.2 functionality the transient/intermittent earth-fault protection (intrptef) is a sample based function designed for the protection and clearance of intermittent and transient earth faults in distribution and sub-transmission networks. Fault detection is done from the residual current and resi...
Page 162
Protection for feeder earth faults when it is applied to the trip feeders feeding the busbar. In intermittent earth-fault situations, this may cause the back-up protection to trip without the dedicated intermittent earth-fault protection function for the corresponding feeder. Intrptef can be used in...
Page 163
A070760 v2 en figure 77: intermittent earth-fault situation in neutral compensated network transient earth fault in networks transient earth fault is a special type of fault which can be detected by using the intrptef function in transient mode. In this mode the fault direction is detected from the ...
Page 164
A070976 v1 en figure 78: transient earth-fault situation and operation of intrptef during a fault 5.3 unbalance protection 5.3.1 negative phase-sequence current protection nsptoc 5.3.1.1 identification table 66: function identification iec 61850 identification: nsptoc iec 60617 identification: i2> a...
Page 165
5.3.1.2 functionality the negative phase-sequence current protection nsptoc is used for increasing sensitivity to detect single phasing situations, unbalanced loads due to, for example, broken conductors or to unsymmetrical feeder voltages. The function is based on the measurement of the negative ph...
Page 166
5.3.2.2 functionality the phase discontinuity protection pdnsptoc is used for detecting unbalance situations caused by broken conductors. The function starts and operates when the unbalance current i 2 /i 1 exceeds the set limit. To prevent faulty operation at least one phase current needs to be abo...
Page 167
Iratio i i = 2 1 a070702 v1 en (equation 3) a situation when a phase a conductor is broken is shown in figure 79 ieca070699 v1 en figure 79: broken conductor fault in phase a in a distribution or or subtransmission feeder current quantities during the broken fault in phase a, together with the ratio...
Page 168
5.4 arc protection arcsarc 5.4.1 identification table 68: function identification iec 61850 identification: arcsarc iec 60617 identification: arc ansi/ieee c37.2 device number: 50l/50nl 5.4.2 functionality the arc protection (arcsarc) detects arc situations in air insulated metal-clad switchgears ca...
Page 169
The lens sensors can be placed, for example, in the busbar compartment, the breaker compartment, and the cable compartment of the metal-clad cubicle. The light detected by the lens sensors is compared to an automatically adjusted reference level. Light sensor 1, light sensor 2, and light sensor 3 in...
Page 170
A040362 v1 en figure 81: arc protection with one ied arc protection with several ieds when using several ieds, the ied protecting the outgoing feeder trips the circuit breaker of the outgoing feeder when detecting an arc at the cable terminations. If the ied protecting the outgoing feeder detects an...
Page 171
A040363 v2 en figure 82: arc protection with several ieds arc protection with several ieds and a separate arc protection system when realizing an arc protection with both ieds and a separate arc protection system, the cable terminations of the outgoing feeders are protected by ieds using one lens se...
Page 172
A040364 v1 en figure 83: arc protection with several ieds and a separate arc protection system 5.5 voltage protection 5.5.1 overvoltage protection phptov 5.5.1.1 identification table 69: function identification iec 61850 identification phptov iec 60617 identification 3u> ansi/ieee c37.2 device numbe...
Page 173
5.5.1.2 functionality the three-phase overvoltage protection phptov is applied on power system elements, such as generators, transformers, motors and power lines to protect the system from excessive voltages that could damage the insulation and cause insulation breakdown. The three-phase overvoltage...
Page 174
5.5.2.2 functionality the three-phase undervoltage protection phptuv is used to disconnect devices from the network, for example, electric motors which get damaged when subjected to service under low voltage conditions. Phptuv includes a settable value for the detection of undervoltage either in a s...
Page 175
5.5.3 residual overvoltage protection rovptov 5.5.3.1 identification table 71: function identification iec 61850 identification: rovptov iec 60617 identification: u0> ansi/ieee c37.2 device number: 59g 5.5.3.2 functionality the residual overvoltage protection rovptov is used in distribution networks...
Page 176
5.5.4 negative sequence overvoltage protection nsptov 5.5.4.1 identification table 72: function identification iec 61850 identification: nsptov iec 60617 identification: u2> ansi/ieee c37.2 device number: 47o- 5.5.4.2 functionality the negative sequence overvoltage protection nsptov is used to detec...
Page 177
This scheme also prevents connecting the machine to the network if the phase sequence of the network is not correct. An appropriate value for the setting parameter voltage start value is approximately 3 percent of u n . A suitable value for the setting parameter operate delay time depends on the app...
Page 178
Loses synchronism during the network fault. A sufficiently fast trip of the utility circuit breaker of the power station can avoid these risks. The lower the three-phase symmetrical voltage of the network is, the higher is the probability that the generator loses the synchronism. The positive sequen...
Page 179
Single-phase earth fault guid-8d2e499e-dcff-4f01-ada0-53f24b5e32c9 v1 en (equation 7) z k1 , z k2 and z k0 respective positive, negative and zero-sequence impedances of the faulted circuit z f fault impedance the approximations are based on the assumption that the sequence impedances consist mainly ...
Page 180
The disadvantage of the fast operation of the psptuv operation is that it issues a trip even if the fault is on one of the medium voltage lines fed by the power station. This is an undue trip since such a fault would not lead to an islanding condition. This drawback is smaller than the benefit of ha...
Page 181
X d ’ transient reactance of the generator of the power station. If x d ' 0.15 s n 5 mva u n 10 kv x kg 2 Ω the setting is then calculated: x x u s v va d d n n ’ ’ . ( ) ( ) = = × = 2 2 0 15 10000 5000000 3 Ω guid-d691182a-75bd-4204-8c1d-8c5ac95333f2 v1 en u x x x g kg kg d 1 0 5 0 6 0 5 0 6 2 2 3 ...
Page 182
Guid-dd28b178-6102-4cef-bf81-93a3cfe8d55e v1 en figure 84: a fault on a radial line resulting in a loss-of-grid condition section 5 1mrs756378 d protection functions 176 ref615 application manual.
Page 183
Guid-e424e267-ca5c-4fae-ad20-a7472421e3a6 v1 en figure 85: the equivalent circuit used in the calculation. U 1f is the positive- sequence component of the voltage during a fault at the farthest point of a potential island near the substation a. X kg is the short circuit reactance between the measuri...
Page 184
Guid-a6d0d737-9e83-47b4-a8e6-1543d03f45e9 v1 en figure 86: overreaching distance relays give rise to a loss-of-grid situation at a line fault guid-7d702bf5-3937-4273-8964-ee8995601b3c v1 en figure 87: equivalent circuit used in the calculation section 5 1mrs756378 d protection functions 178 ref615 a...
Page 185
The equivalent circuit is now used in the calculation. The u 1 value of the fault-point voltage at a single phase-to-earth fault is u 1f = 0.67 p.U. The positive phase-sequence component of the transient source voltage of a generator can be approximated by 1.1 p.U. The u 1 voltage appearing at the m...
Page 186
The value reduced to the 10 kv voltage level is x y ’ = 0.3 × (10/150)² Ω = 0.0013 Ω. The setting can now be calculated: u x x x x x x g y kb kg kg d y 1 0 67 1 0 67 1 1 0 67 1 0 67 = + − + + + − − − . . (( . . ) ( . ( ) ’ ’ ’ ’ )) ) ’ ’ ’ x x x y kb y + = guid-e8ce42ab-e53c-478e-b907-828ffbb19cac v...
Page 187
Section 6 protection related functions 6.1 three-phase inrush detector inrphar 6.1.1 identification table 74: function identification iec 61850 identification: inrphar iec 60617 identification: 3i2f> ansi/ieee c37.2 device number: 68 6.1.2 functionality the transformer inrush detection inrphar is us...
Page 188
A070695 v1 en figure 88: inrush current in transformer 6.2 circuit breaker failure protection ccbrbrf 6.2.1 identification table 75: function identification iec 61850 identification: ccbrbrf iec 60617 identification: 3i>i 0 >bf ansi/ieee c37.2 device number: 51bf/51nbf 6.2.2 functionality the breake...
Page 189
External commands through binary inputs. The start command is always a default for three-phase operation. Ccbrbrf includes a three-phase conditional or unconditional re-trip function, and also a three-phase conditional back-up trip function. Ccbrbrf uses the same levels of current detection for both...
Page 190
Up breakers. The circuit breakers are normally upstream breakers which feed fault current to a faulty feeder. The back-up trip always includes a current check criterion. This means that the criterion for a breaker failure is that there is a current flow through the circuit breaker after the set back...
Page 191
6.3.3 application all trip signals from different protection functions are routed through the trip logic. The most simplified alternative of a logic function is linking the trip signal and ensuring that the signal is long enough. The tripping logic in the protection relay is intended to be used in t...
Page 192
Lock-out trpptrc is provided with possibilities to activate a lockout. When activated, the lockout can be manually reset after checking the primary fault by activating the rst_lkout input or from the lhmi clear menu parameter. When using the “latched” mode, the resetting of the trip output can done ...
Page 193
Section 7 supervision functions 7.1 trip circuit supervision tcsscbr 7.1.1 identification table 77: function identification iec 61850 identification: tcsscbr iec 60617 identification: tcs ansi/ieee c37.2 device number: tcm 7.1.2 functionality the trip circuit supervision function (tcsscbr) is design...
Page 194
A051097 v4 en figure 91: operating principle of the trip-circuit supervision with an external resistor. The tcsscbr blocking switch is not required since the external resistor is used. If the tcs is required only in a closed position, the external shunt resistance may be omitted. When the circuit br...
Page 195
Trip-circuit supervision and other trip contacts it is typical that the trip circuit contains more than one trip contact in parallel, for example in transformer feeders where the trip of a buchholz relay is connected in parallel with the feeder terminal and other relays involved. The constant test c...
Page 196
A070970 v1 en figure 94: improved connection for parallel trip contacts several trip-circuit supervision functions parallel in circuit not only the trip circuit often have parallel trip contacts, it is also possible that the circuit has multiple tcs circuits in parallel. Each tcs circuit causes its ...
Page 197
In the protection ied monitors the healthy auxiliary relay coil, not the circuit breaker coil. The separate trip circuit supervision relay is applicable for this to supervise the trip coil of the circuit breaker. Dimensioning of the external resistor under normal operating conditions, the applied ex...
Page 198
Using power output contacts without trip-circuit supervision if tcs is not used but the contact information of corresponding power outputs are required, the internal resistor can be by-passed. The output can then be utilized as a normal power output. When bypassing the internal resistor, the wiring ...
Page 199
A070972 v3 en figure 96: incorrect connection of trip-circuit supervision a connection of three protection ieds with a double pole trip circuit is shown in the following figure. Only the ied r3 has an internal tcs circuit. In order to test the operation of the ied r2, but not to trip the circuit bre...
Page 200
A070974 v3 en figure 97: incorrect testing of ieds 7.2 current circuit supervision ccrdif 7.2.1 identification table 79: function identification iec 61850 identification: ccrdif iec 60617 identification: mcs 3i ansi/ieee c37.2 device number: mcs 3i 7.2.2 functionality the current circuit supervision...
Page 201
Currents (i_a, i_b and i_c) and it is to be externally summated, that is, outside the ied. Ccrdif detects a fault in the measurement circuit and issues an alarm or blocks the protection functions to avoid unwanted tripping. It must be remembered that the blocking of protection functions at an occurr...
Page 202
Guid-88fc46c8-8d14-45de-9e36-e517ea3886aa v1 en figure 98: connection diagram for reference current measurement with core balanced current transformer current measurement with two independent three-phase sets of ct cores the figures show diagrams of connections where the reference current is measure...
Page 203
Guid-8dc3b17a-13fe-4e38-85c6-a228bc03206b v1 en figure 99: connection diagram for current circuit supervision with two sets of three-phase current transformer protection cores when using the measurement core for reference current measurement, it should be noted that the saturation level of the measu...
Page 204
Guid-c5a6bb27-36f9-4652-a5e4-e3d32cfea77b v1 en figure 100: connection diagram for current circuit supervision with two sets of three-phase current transformer cores (protection and measurement) example of incorrect connection the currents must be measured with two independent cores, that is, the ph...
Page 205
Guid-bbf3e23f-7ce4-43a3-8986-5aaca0433235 v1 en figure 101: example of incorrect reference current connection 7.3 fuse failure supervision seqrfuf 7.3.1 identification table 80: function identification iec 61850 identification: seqrfuf iec 60617 identification: fusef ansi/ieee c37.2 device number: 6...
Page 206
A criterion based on the delta current and the delta voltage measurements can be added to seqrfuf to detect the three-phase fuse failures which, in practice, are more associated with the voltage transformer switching during station operations. 7.3.3 application some protection functions operate on t...
Page 207
Section 8 condition monitoring functions 8.1 circuit breaker condition monitoring sscbr 8.1.1 identification table 81: function identification iec 61850 identification: sscbr iec 60617 identification: cbcm ansi/ieee c37.2 device number: cbcm 8.1.2 functionality the circuit breaker condition monitori...
Page 208
Breaker contact travel time high travelling times indicate the need for maintenance of the circuit breaker mechanism. Therefore, detecting excessive travelling time is needed. During the opening cycle operation, the main contact starts opening. The auxiliary contact a opens, the auxiliary contact b ...
Page 209
A071114 v2 en figure 103: trip curves for a typical 12 kv, 630 a, 16 ka vacuum interrupter nr = the number of closing-opening operations allowed for the circuit breaker ia = the current at the time of tripping of the circuit breaker calculation of directional coef the directional coefficient is calc...
Page 210
The equation shows that there are 30,000 possible operations at the rated operating current of 630 a and 20 operations at the rated fault current 16 ka. Therefore, if the tripping current is 10 ka, one operation at 10 ka is equivalent to 30,000/500=60 operations at the rated current. It is also assu...
Page 211
Section 9 measurement functions 9.1 basic measurements 9.1.1 three-phase current cmmxu 9.1.1.1 identification table 82: function identification iec 61850 identification: cmmxu iec 60617 identification: 3i ansi/ieee c37.2 device number: 3i 9.1.2 three-phase voltage vmmxu 9.1.2.1 identification table ...
Page 212
Table 85: function identification iec 61850 identification: resvmmxu iec 60617 identification: u0 ansi/ieee c37.2 device number: u0 9.1.5 sequence current csmsqi 9.1.5.1 identification table 86: function identification iec 61850 identification: csmsqi iec 60617 identification: i1, i2, i0 ansi/ieee c...
Page 213
The three-phase voltage measurement function, vmmxu, is used for monitoring and metering the phase-to-phase voltages of the power system. The phase-to-earth voltages are also available in vmmxu. The residual current measurement function, rescmmxu, is used for monitoring and metering the residual cur...
Page 214
The limit supervision indicates, if the measured signal exceeds or goes below the set limits. Depending on the measured signal type, up to two high limits and up to two low limits can be set for the limit supervision the deadband supervision reports a new measurement value if the input signal has go...
Page 215
The disturbance recorder follows the 1999 version of the comtrade standard and uses the binary data file format. 1mrs756378 d section 9 measurement functions ref615 209 application manual.
Page 216
210
Page 217
Section 10 control functions 10.1 circuit breaker control cbxcbr 10.1.1 identification table 89: function identification iec 61850 identification: cbxcbr iec 60617 identification: i0 cb ansi/ieee c37.2 device number: i0 cb 10.1.2 functionality the circuit breaker control function cbxcbr is intended ...
Page 218
A070879 v2 en figure 104: status indication based interlocking via goose messaging 10.2 disconnector dcsxswi and earthing switch essxswi 10.2.1 identification table 90: function identification iec 61850 identification: dcsxswi essxswi iec 60617 identification: i0 dc i0 es ansi/ieee c37.2 device numb...
Page 219
10.2.3 application in the field of distribution and sub-transmission automation, the reliable control and status indication of primary switching components both locally and remotely is in a significant role. These features are needed especially in modern remote controlled substations. The applicatio...
Page 220
10.4 auto recloser darrec 10.4.1 identification table 91: function identification iec 61850 logical node name: darrec iec 60617 identification: o-->i ansi/ieee c37.2 device number: 79 10.4.2 functionality about 80 to 85 percent of faults in the mv overhead lines are transient and automatically clear...
Page 221
Only a short interruption is needed for extinguishing the arc. These faults are transient by nature. A semi-transient fault can be caused for example by a bird or a tree branch falling on the overhead line. The fault disappears on its own if the fault current burns the branch or the wind blows it aw...
Page 222
A070884 v1 en figure 106: simplified cbb initiation diagram init_1...6 = initiation lines cbb1...Cbb2 = first two cycle building blocks the operation of a cbb consists of two parts: initiation and execution. In the initiation part, the status of the initiation lines is compared to the cbb settings. ...
Page 223
A070885 v1 en figure 107: simplified cbb diagram each cbb has individual init signals cbb_ and blk signals cbb_ settings. Therefore, each initiation line can be used for both initiating and blocking any or all auto-reclose shots. Other conditions that must be fulfilled before any cbb can be initiate...
Page 224
• only such cbbs that are set for the next shot in the sequence can be accepted for execution. For example, if the next shot in the sequence should be shot 2, a request from cbb set for shot 3 is rejected. • any cbb that is set for the next shot or any of the following shots can be accepted for exec...
Page 225
Example 1. The sequence is implemented by two shots which have the same reclose time for all protection functions, namely i>>, i> and i 0 >. The initiation of the shots is done by activating the operate signals of the protection functions. A070887 v1 en figure 109: auto-reclose sequence with two sho...
Page 226
Table 93: settings for configuration example 1 setting name setting value shot number cbb1 1 init signals cbb1 7 (lines 1,2 and 3 = 1+2+4 = 7) first reclose time 0.3s (an example) shot number cbb2 2 init signals cbb2 7 (lines 1,2 and 3 = 1+2+4 = 7) second reclose time 15.0s (an example) example 2 th...
Page 227
T hsar = time delay of high-speed auto-reclosing, here: first reclose time t dar = time delay of delayed auto-reclosing, here: second reclose time t l>> operating time for the i>> protection stage to clear the fault t l> or lo> operating time for the i> or i 0 > protection stage to clear the fault t...
Page 228
• del_init_2 • del_init_3 • del_init_4 del_init_2 and init_2 are connected together with an or-gate, as are inputs 3 and 4. Inputs 1, 5 and 6 do not have any delayed input. From the auto-reclosing point of view, it does not matter whether init_x or del_init_x line is used for shot initiation or bloc...
Page 229
10.4.3.5 shot initiation from protection start signal in it simplest, all auto-reclose shots are initiated by protection trips. As a result, all trip times in the sequence are the same. This is why using protection trips may not be the optimal solution. Using protection start signals instead of prot...
Page 230
Parameter to "1" and connecting the protection start information to the corresponding del_init_ input. When the function detects a closing of the circuit breaker, that is, any other closing except the reclosing done by the function itself, it always prohibits shot initiation for the time set with th...
Page 231
Section 11 requirements for measurement transformers 11.1 current transformers 11.1.1 current transformer requirements for non-directional overcurrent protection for reliable and correct operation of the overcurrent protection, the ct has to be chosen carefully. The distortion of the secondary curre...
Page 232
The ct accuracy primary limit current describes the highest fault current magnitude at which the ct fulfils the specified accuracy. Beyond this level, the secondary current of the ct is distorted and it might have severe effects on the performance of the protection relay. In practise, the actual acc...
Page 233
The factor 0.7 takes into account the protection relay inaccuracy, current transformer errors, and imperfections of the short circuit calculations. The adequate performance of the ct should be checked when the setting of the high set stage o/c protection is defined. The operate time delay caused by ...
Page 234
A071142 v1 en figure 114: example of three-stage overcurrent protection the maximum three-phase fault current is 41.7 ka and the minimum three-phase short circuit current is 22.8 ka. The actual accuracy limit factor of the ct is calculated to be 59. The start current setting for low-set stage (3i>) ...
Page 235
Section 12 glossary 100base-fx a physical media defined in the ieee 802.3 ethernet standard for local area networks (lans). 100base-fx uses fibre-optic cabling. 100base-tx a physical media defined in the ieee 802.3 ethernet standard for local area networks (lans). 100base-tx uses twisted-pair cablin...
Page 236
Iec 61850-8-1 a communication protocol based on the iec 61850 standard series and a standard for substation modelling. Ied intelligent electronic device ip address internet protocol address is a set of four numbers between 0 and 255, separated by periods. Each server connected to the internet is ass...
Page 237
Tcs trip-circuit supervision vt voltage transformer wan wide area network whmi web human-machine interface section 12 glossary ref615 231 application manual.
Page 238
232.
Page 239
233.
Page 240
1mrs756378 d © copyright 2009 abb. All rights reserved. Abb oy distribution automation p.O. Box 699 fi-65101 vaasa, finland phone +358 10 22 11 fax +358 10 22 41094 www.Abb.Com/substationautomation.