- DL manuals
- Cabletron Systems
- Switch
- MICROMMAC-22T
- User Manual
Cabletron Systems MICROMMAC-22T User Manual
Summary of MICROMMAC-22T
Page 1
Micrommac-22t/24t/42t/44t user’s guide booktitle2 optional.
Page 3: Notice
I notice cabletron systems reserves the right to make changes in specifications and other information contained in this document without prior notice. The reader should in all cases consult cabletron systems to determine whether any such changes have been made. The hardware, firmware, or software de...
Page 4
Notice ii doc notice this digital apparatus does not exceed the class a limits for radio noise emissions from digital apparatus set out in the radio interference regulations of the canadian department of communications. Le présent appareil numérique n’émet pas de bruits radioélectriques dépassant le...
Page 5
Notice iii cabletron software program license 1. License. You have the right to use only the one (1) copy of the program provided in this package subject to the terms and conditions of this license agreement. You may not copy, reproduce or transmit any part of the program except as permitted by the ...
Page 6
Notice iv declaration of conformity application of council directive(s): 89/336/eec 73/23/eec manufacturer’s name: cabletron systems, inc. Manufacturer’s address: 35 industrial way po box 5005 rochester, nh 03867 european representative name: mr. J. Solari european representative address: cabletron ...
Page 7: Contents
V contents preface chapter 1 introduction 1.1 micrommac-t models................................................................. 1-1 1.2 micrommac-t features .............................................................. 1-2 1.2.1 lobe port features ....................................................
Page 8
Contents vi 3.2 installing accessories ..................................................................3-5 3.2.1 removing the chassis cover.........................................3-5 3.2.2 removing protection panels ...........................................3-6 3.2.3 connectors and ports on the ...
Page 9
Contents vii appendix a system specifications a.1 operating specifications..............................................................A-1 a.2 power supply specifications .......................................................A-1 a.3 environmental specifications .......................................
Page 10
Contents viii.
Page 11: Figures
Ix figures figure 1-1 the micrommac-t . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-1 figure 2-1 micrommac-t operational components . . . . . . . . . . . 2-2 figure 2-2 connecting to a power source. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-3 figure 2-3 ring speed switch . . . . . . . . . . ...
Page 12
Figures x figure 4-10 connecting to the tpim-t2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4-14 figure 4-11 connecting to the tpim-f2/-f3 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4-16 figure 4-12 micrommac-t/sth stack configuration . . . . . . . . . . .4-17 figure 5-1 power up diagnostic screen . . . . . . . . ...
Page 13: Tables
Xi tables table 4-1 maximum lobe cable lengths . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-5 table 4-2 maximum trunk cable lengths . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-5 table 4-3 connector pinout cross-reference . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-8 table 4-4 tpim models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ...
Page 14
Tables xii.
Page 15: Preface
Xiii preface welcome to the cabletron systems micrommac-22t/24t/42t/44t user’s guide . This guide describes how to install, configure, and operate the micrommac-t family of intelligent, stackable token ring wiring hubs. This guide is intended for all users of the micrommac-t, who should have a basic...
Page 16: Using This Manual
Preface xiv using this manual this manual’s contents is organized as follows: chapter 1, introduction , describes micrommac-t model types and features. Chapter 2, operation , describes how to connect the micrommac-t to a power source, how to work with operational components, and the functions of mic...
Page 17: Related Documentation
Preface xv related documentation this section lists installation and operation manuals included with the micrommac-t and sth hubs and accessories typically used with the micrommac-t. Refer to documentation listed for the device you are working with for specific information about installing, operatin...
Page 18: Getting Help
Preface xvi getting help if you need technical assistance with your micrommac-t or have any questions, comments, or suggestions concerning this manual, contact cabletron systems technical support using any of the following methods: before calling cabletron systems technical support, have the followi...
Page 19: Chapter 1
1-1 chapter 1 introduction the micrommac-t, shown in figure 1-1 , is an ieee 802.5-based, ibm-compatible, snmp-compliant, intelligent, stackable multi-media access center (mmac). The micrommac-t is a versatile wiring hub into which you can install a variety of products designed to provide a range of...
Page 20: 1.2 Micrommac-T Features
Introduction 1-2 1.2 micrommac-t features this section provides an overview of micrommac-t features. 1.2.1 lobe port features this section overviews lobe port features. Repeater circuitry repeater circuitry in the micrommac-t enables lobe ports to regenerate, reshape, and filter the incoming signal,...
Page 21
Introduction 1-3 the chief benefit provided by out-of-band access capability is that it allows you to manage your network in the event that the in-band network communication infrastructure that supports remote communication with the micrommac-t becomes inoperable. You can also access lm from an in-b...
Page 22
Introduction 1-4 1.2.4 monitoring and diagnostic indicators cabletron systems front-panel lanview led (light emitting diode) system conveys information about the operational status of the micrommac-t and the network. See section 5.1 for information about using leds to monitor micrommac-t functions a...
Page 23
Introduction 1-5 if the offending station cannot be definitively removed from the ring by the recovery process (that is, if the offending station repeatedly attempts to re-insert before the recovery process has concluded), a trap notifies the nms that the condition was not corrected and also identif...
Page 24
Introduction 1-6 1.2.7 distributed monitoring capabilities the micrommac-t includes all ten rmon groups for token ring and distributed lan monitor (dlm) software. These resources enable you to configure the micrommac-t to perform various management functions, get more precise information about the o...
Page 25
Introduction 1-7 • capture component - filter group – compares packets on ring to criteria specified in a filter expression to determine whether packets need to be captured for analysis. - packet capture group – performs the capture of packets meeting criteria specified by the filter group. Distribu...
Page 26: 1.2.9 Accessories
Introduction 1-8 1.2.8 ups monitoring capability you can configure either of the micrommac-t’s front-panel com ports to support connection to an american power conversion (apc) uninterruptible power supply (ups). See the micrommac-t local management guide for instructions. This connection enables re...
Page 27
Introduction 1-9 tpims – media-flexible trunk cable expansion cabletron systems hot-swappable, active tpims are designed for installation in the micrommac-t’s ring in and ring out (ri/ro) receptacles. Each tpim provides a specific media interface: stp, utp, and fiber (single-mode and multimode), all...
Page 28
Introduction 1-10
Page 29: Chapter 2
2-1 chapter 2 operation this chapter describes micrommac-t control, monitoring, and connection components shown in figure 2-1 . Specifically, it covers the following areas: • connecting to a power source – turning the hub on and off • working with console switches and buttons - setting the ring spee...
Page 30
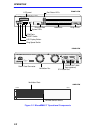
Operation 2-2 figure 2-1 micrommac-t operational components r display reset cpu 16mb/s act mgmt ro 2 4 2 3 2 2 2 1 2 0 1 9 1 8 1 7 1 6 1 5 1 4 1 3 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 micrommac-24t token ring hub with lanview supporting 100 ohm utp cable com 1 com 2 ri cabletron micrommac-24t 24 23 22 21 20 1...
Page 31
Operation 2-3 2.1 turning the hub on and off you turn on the micrommac-t by connecting it to a power source, and you turn it off by disconnecting it from the power source. The micrommac-t’s universal power supply permits use of power sources from 100 vac to 250 vac, 50/60hz. Use the power cord inclu...
Page 32: Micrommac-24T
Operation 2-4 2.2 control switches and buttons this section describes how to use micrommac-t switches and buttons to perform various hub-configuration and monitoring operations. 2.2.1 setting the ring speed use the speed, or ring speed switch, shown in figure 2-3 , to set the ring operating speed to...
Page 33: Micrommac-24T
Operation 2-5 2.2.2 resetting the micrommac-t use the reset switch, shown in figure 2-4 , to restart the micrommac-t when, for example, you want to implement a ring speed change or revert to default operational settings after toggling the nvram switch. Figure 2-4 the reset switch to reset the microm...
Page 34: 2.2.3 Clearing Nvram
Operation 2-6 2.2.3 clearing nvram nvram (non-volatile random access memory) stores system parameters specified in management applications, including the ip address, community passwords, ring security list, beacon recovery settings, and stack and port configuration settings. Use the nvram switch, sh...
Page 35: 2.3 Indicators
Operation 2-7 2. Flip the nvram switch from its current position with a non-conductive instrument inserted through the right-most lower circulation vent on the right side panel. 3. Reset the micrommac-t as described in section 2.2.2 . 2.3 indicators this section describes micrommac-t indicators: • l...
Page 36
Operation 2-8 except for the 16mb/s, or ring speed, led, which lights yellow when the ring speed is set for 16 mbps and does not light when the ring speed is set for 4 mbps, all leds are capable of emitting multiple colors. For example, the mgmt led lights green when the management agent in the micr...
Page 37: Micrommac-24T
Operation 2-9 • to display messages that provide information about the micrommac-t firmware image and the server from which the image was downloaded, press the display button two second to display the first message. Press and immediately release to view each additional message. See section 5.2 for a...
Page 38: 2.4 Ports
Operation 2-10 2.4 ports this section describes micrommac-t ports and their functions. 2.4.1 com ports the micrommac-t’s two rj45 com ports shown in figure 2-8 support rs-232c serial communication with other dte (data terminal equipment) devices. Figure 2-8 com ports this following sections describe...
Page 39: 2.4.2 Lobe Ports
Operation 2-11 com 2 only • power up diagnostic screen see figure 5.3.1 for information about the screen. 2.4.2 lobe ports token ring stations connect to lobe ports to insert into the token ring. Lobe ports can also be converted through management to ring out ports to support connection to passive m...
Page 40: 2.4.4 Sth Stack Ports
Operation 2-12 2.4.3 ring in/ring out ports the ring out (ro) and ring in (ri) ports on the micrommac-t, shown in figure 2-11 , support trunk cable connection to ring ports on other token ring concentrators. Ri/ro connections can be established with any of the standard media types supported by the t...
Page 41: Chapter 3
3-1 chapter 3 installation this chapter describes how to install the micrommac-t and accessories (12-port daughterboard, microsnac-t, crbrim-w/t, ldram simm) in the micrommac-t. 3.1 installing the micrommac-t this section describes installation requirements and procedures for installing the micromma...
Page 42
Installation 3-2 3.1.2 attaching the strain-relief bar the strain-relief bar absorbs the brunt of strain exerted on cabling that might otherwise be exerted directly on connector/port interfaces, as shown in figure 3-1 . To protect your network equipment, install the strain-relief bar, especially if ...
Page 43
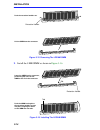
Installation 3-3 figure 3-2 attaching the strain-relief bar 3.1.3 installing the micrommac-t in a rack to install the micrommac-t: 1. Remove the two 3/8-inch flathead cover screws from the front side edges of the micrommac-t as shown in figure 3-3 . Figure 3-3 remove front side screws 2. Align the h...
Page 44
Installation 3-4 3. Position the micrommac-t between the rack columns, and then attach with the mounting screws included with the rack as shown in figure 3-5 . Figure 3-5 installing the micrommac-t in a rack 3.1.4 free-standing installation for an enclosed-shelf or table-top installation, put the hu...
Page 45: 3.2 Installing Accessories
Installation 3-5 3.2 installing accessories this section describes how to remove the micrommac-t chassis cover and install the following accessories in the micrommac-t: • 12-port daughterboard • microsnac-t daughterboard • crbrim-w/t module • 8 mb ldram single in-line memory module (simm) see the pr...
Page 46
Installation 3-6 2. Slide the cover straight back from the front panel, and then lift and remove as shown in figure 3-8 . Figure 3-8 removing the chassis cover 3.2.2 removing protection panels this section describes how to remove the protection panels covering the micrommac-t’s front-panel aperture ...
Page 47
Installation 3-7 figure 3-9 removing the front panel this unit is configured as a: micrommac-42t to upgrade to a micrommac44t order part number: tr-stp-ugkit 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16 15 14 13 ri support post ...
Page 48
Installation 3-8 removing the rear protection panel to remove the rear protection panel: 1. Remove the micrommac-t chassis cover as described in section 3.2.1 . 2. Remove the screws securing the rear protection panel to the micrommac-t rear panel, and then remove the protection panel from the apertu...
Page 49
Installation 3-9 figure 3-11 connectors and ports for accessories 3.2.4 installing the 12-port daughterboard you can double the micrommac-22/42t’s lobe-port count from 12 to 24 ports by installing a 12-port daughterboard. A utp daughterboard is included with the upgrade kit, tr-utp-ugkit, required f...
Page 50
Installation 3-10 2. Lower the daughterboard on to the support posts as shown in figure 3-12 , aligning the front of the 12-port daughterboard flush against the aperture and inserting the daughterboard connector pins completely into the connector. The pins should insert easily into the connector. Yo...
Page 51
Installation 3-11 3.2.5 installing the microsnac-t the microsnac-t is a sna/wan network access converter that you can install in the micrommac-t to integrate sna and lan data. The microsnac-t includes its own operating code and com-port-accessible management tools. The microsnac-t installs above the...
Page 52
Installation 3-12 figure 3-13 installing the microsnac-t daughterboard 3.2.6 installing the crbrim-w/t the crbrim-w/t bridge/router module provides wan connectivity to remote networks. To install the crbrim-w/t: 1. Remove the micrommac-t chassis cover as described in section 3.2.1 and the rear prote...
Page 53
Installation 3-13 figure 3-14 installing the crbrim-w/t 3. Connect the lan-traffic ports using the cable included with the crbrim-w/t. 3.2.7 installing the ldram simm this section describes how to replace of the factory-installed 4 mb ldram simm with the 8 mb ldram simm required by the micrommac-t t...
Page 54
Installation 3-14 figure 3-15 removing the ldram simm 2. Install the 8 mb simm as shown in figure 3-16 figure 3-16 installing the ldram simm push the retraction handles out. Lift the simm from the connector. Retraction handle push the simm back against lower the simm into the connector, positioning ...
Page 55: Chapter 4
4-1 chapter 4 cabling this chapter describes basic token ring cabling terminology and guidelines and procedures for establishing cable connections between the micrommac-t and other network devices. See appendix b for media design and performance specifications not included in this chapter. 4.1 token...
Page 56
Cabling 4-2 4.1.2 describing lobe cabling lobe cabling is used to connect stations to lobe (or tcu) ports on wiring concentrators to connect stations to the ring. Micrommac-t models support both utp and stp lobe cabling. A station can transmit data to and receive data from other stations on the ring...
Page 57: 4.2.1 Signal Interference
Cabling 4-3 4.2.1 signal interference this section describes some of the conditions that can degrade token ring signals and related corrective measures. Crosstalk crosstalk is interference caused by signal coupling between different cable pairs contained within a multi-pair cable bundle. Multi-pair ...
Page 58
Cabling 4-4 4.2.3 determining the maximum signal-drive distance one of the most important physical-design factors to consider when establishing a token ring network is the maximum signal-drive distance accommodated by the different media types that can be used for the installation. Basically, the dr...
Page 59
Cabling 4-5 table 4-2 lists the maximum recommended lengths allowed for utp, stp, and multimode fiber optic trunk cable supporting 4 mbps and 16 mbps data-transmission rates. Table 4-1 maximum lobe cable lengths cable type 4 mbps 16 mbps stp (ibm types 1 & 2) 300 meters (984 feet) 150 meters (493 fe...
Page 60
Cabling 4-6 adjusted ring length (arl) optimal design of the network installation requires contingency planning for worst-case scenarios involving the physical removal of a trunk cable segment in the installation. Arl is the variable factored into the design equation to account for the diminishment ...
Page 61
Cabling 4-7 figure 4-2 utp lobe cabling example using a mic connector shielded patch cables that adapt a shielded rj45 cable to a medium interface connector (mic) are available from cabletron systems. These ibm type 6 and 9 adapter/patch cables allow you to connect the note the cabletron systems trm...
Page 62
Cabling 4-8 micrommac-42t/44t to an existing patch panel equipped with ibm data connectors. Figure 4-3 illustrates an example stp lobe cabling configuration demonstrating how the adapter is used. Figure 4-3 stp lobe cabling example connector pinouts table 4-3 lists provides a cross-reference of pino...
Page 63
Cabling 4-9 connection procedure to attach a lobe cable segment to a micrommac-t lobe port, insert the rj45 connector on the cable into an rj45 lobe port on the micrommac-t, as shown in figure 4-4 . The associatedport statusled lights: • green when the port is enabled and the station is inserted int...
Page 64: 4.4.1 Describing Tpims
Cabling 4-10 4.4 connecting trunk cabling this section describes how to configure and install tpims to construct the ri/ro ports for the micrommac-t and also how to connect trunk cable to the ports. 4.4.1 describing tpims tpims, shown in figure 4-5 , are hot swappable (that is, you do not have to po...
Page 65
Cabling 4-11 4.4.2 configuring tpims for ri/ro application tpims are shipped configured for ri/ro application. (they can also be configured for station-port application for other cabletron devices.) before installing a tpim in a ri/ro receptacle to build a ring port for attachment to a cabletron sys...
Page 66: 4.4.3 Installing A Tpim
Cabling 4-12 4.4.3 installing a tpim to install a tpim into a ri/ro receptacle: 1. Remove the plastic cover from the receptacle. Keep the cover handy for future reattachment. 2. Slide the tpim into the receptacle slot, as indicated in figure 4-7 , until the connector pins in the slot are fully inser...
Page 67
Cabling 4-13 4.4.4 connecting twisted pair trunk cable segments this section describes how to connect twisted pair trunk cable segments to micrommac-t ri/ro ports. It also describes how to check the status of the connection using the lnk led. Connecting stp use the tpim-t1 to connect an stp trunk ca...
Page 68
Cabling 4-14 connecting utp use the tpim-t2 to connect a utp trunk cable segment with an rj45 connector as shown in figure 4-10 . Figure 4-10 connecting to the tpim-t2 checking the connection thelnk led on the tpim-t1/t2/t4 lights: • green if a connection between the micrommac-t and another token ri...
Page 69
Cabling 4-15 4.4.5 connecting fiber optic trunk cable segments use the tpim-f2/ f3 to connect fiber optic trunk cable segments. When connecting a fiber optic link segment to the tpim-f2 or tpim-f3 consider the following: • ensure that the alignment key on the st (stab and twist) connector on the fib...
Page 70
Cabling 4-16 figure 4-11 connecting to the tpim-f2/-f3 3. Attach the other end of the fiber strand connected to the micrommac-t rx port to the tx port on the other hub. Attach the other end of the strand connected to the micrommac-t tx port to the rx port on the other hub. Thelnk led on the tpim-f2/...
Page 71
Cabling 4-17 4.5 connecting sth stackable hubs this section describes how to connect the cabletron systems sth hubstack series of active, non-intelligent, stackable hubs to the micrommac-t. You can connect up to four sth hubs to the micrommac-t, as shown in figure 4-12 . Figure 4-12 micrommac-t/sth ...
Page 72
Cabling 4-18 2. Attach the other end of interconnect cable securely to the stack port on the sth. (the sth port labeled reserve is non-functional and cannot support the connection.) the sth’s stack led lights: • green if you have correctly connected the micrommac-t and sth hub and both hubs are set ...
Page 73: Chapter 5
5-1 chapter 5 monitoring and troubleshooting this chapter describes how to use lanview leds, the lcd system, and the power up diagnostic screen to monitor micrommac-t and network performance. It also includes a troubleshooting checklist. 5.1 using lanview leds lanview leds are part of the overall di...
Page 74: 5.2 Using The Lcd System
Monitoring and troubleshooting 5-2 5.2 using the lcd system the lcd panel displays information about the micrommac-t and its operational activities and events and conditions occurring on the token ring managed by the micrommac-t. That information is grouped into the following categories: • static sy...
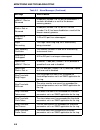
Page 75
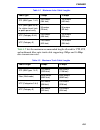
Monitoring and troubleshooting 5-3 5.2.2 viewing saved alarm messages saved alarm messages listed in table 5-3 describe events and conditions that occur on the ring. The lcd panel displays messages about the events and conditions as they occur. The micrommac-t stores the messages produced since the ...
Page 76
Monitoring and troubleshooting 5-4 ummac-t port xx removed a lobe port (number 1 to 24) on the micrommac-t has been disabled as a result of the beacon recovery process. Stack x port xx removed a lobe port (number 1 to 24) on an sth hub (number 2 to 5) has been disabled as a result of the beacon reco...
Page 77
Monitoring and troubleshooting 5-5 stn threshold: line errors the line error count has exceeded the threshold parameters set in an snmp application for one or more stations on the ring. Stn threshold: internal errors the internal error count has exceeded the threshold parameters set in an snmp appli...
Page 78
Monitoring and troubleshooting 5-6 5.2.3 viewing unsaved initialization messages an unsaved initialization message appears on the lcd as the event that produces it occurs, but it is not saved for future retrieval. Table 5-4 lists normal unsaved initialization messages. Table 5-5 lists unsaved failur...
Page 79
Monitoring and troubleshooting 5-7 5.2.4 viewing saved system messages saved system messages listed in table 5-6 provide information about servers from which image files were downloaded and the image files. To view saved system messages: 1. Enter the saved alarm messages queue as described in sectio...
Page 80
Monitoring and troubleshooting 5-8 5.3 monitoring the initialization process you can use any of the following methods to monitor the initialization process that occurs when the micrommac-t is powered up or reset: • power up diagnostic screen • led cycle • lcd messages 5.3.1 power up diagnostic scree...
Page 81
Monitoring and troubleshooting 5-9 in the event of a system error, the test screen provides you with the following response options: continue proceeds with the remainder of the tests. Retry executes a single retry of the test producing the error message. Loop repeatedly retries the test producing th...
Page 82
Monitoring and troubleshooting 5-10 exiting the screen to exit the power up diagnostic screen and access the local management password screen, press the enter key. 5.3.2 leds and the lcd panel table 5-7 lists the information conveyed by the led system and the lcd panel during initialization phases f...
Page 83
Monitoring and troubleshooting 5-11 5.4 general troubleshooting checklist this section provides a checklist of troubleshooting procedures to help you resolve the most typically encountered problems that can occur with a token ring network installation. To check the micrommac-t installation: 1. Trace...
Page 84
Monitoring and troubleshooting 5-12.
Page 85: Appendix A
A-1 appendix a system specifications cabletron systems reserves the right to change specifications at any time without notice. A.1 operating specifications data buffer memory (ram): 8 mb (expandable, see chapter 3) internal processor: intel 80c960cf at 24 mhz controller: texas instruments tms380c26 ...
Page 86: A.4 Physical Specifications
System specifications a-2 a.3 environmental specifications operating temperature: +5 ° to +40 ° c (41 ° to 104 ° f) storage temperature: -30 ° to +90 ° c (-22 ° to 194 ° f) operating humidity: 5 to 95% (non-condensing) a.4 physical specifications dimensions: 2.8h x 17.0w x 13.5d inches (7.2h x 43.6w...
Page 87: Appendix B
B-1 appendix b tpim specifications b.1 tpim-t1/t2/t4 pinouts figure b-1 shows tpim-t1/t2/t4 pinouts for ri/ro applications. Figure b-1 tpim-t1/t2/t4 pinouts tpim-t1 tpim-t2/t4 ring in ring out 1. Transmit + 2. Ground 3. +5v at 250ma 4. Ground 5. Receive - 6. Transmit - 7. Ground 8. Ground 9. Receive...
Page 88
Tpim specifications b-2 b.2 tpim-f2/f3 specifications the tpim-f2 supports multimode fiber optic cabling, and the tpim-f3 supports single mode fiber optic cabling. Tpim-f2 the tpim-f2 is designed to operate with 50/125 µ m, 62.5/125 µ m, and 100/140 µ m fiber optic cable. Table b-1 lists receiver se...
Page 89
Tpim specifications b-3 tpim-f3 the tpim-f3 is designed to operate with 8.3/125 µ m fiber optic cable. Table b-3 lists tpim-f3 specifications transmitter power and receive sensitivity levels, shown in table b-1 , table b-2 , and table b-3 are peak power levels after optical overshoot. A peak power m...
Page 90
Tpim specifications b-4.
Page 91: Appendix C
C-1 appendix c media specifications this appendix describes design and performance specifications for each of the media types used with the micrommac-t. C.1 twisted pair copper cable twisted pair copper cable is used for baseband data transmission. It consists of multiple pairs of entwined solid cop...
Page 92: C.1.2 Stp
Media specifications c-2 media filters a media filter is required when connecting a utp lobe segment from a micrommac-22t or micrommac-24t to a station supporting stp cabling. Cabletron systems, inc. Offers the following media filters: • the trmf media filter has an embedded female rj45 (utp) port a...
Page 93: C.2 Fiber Optic Cable
Media specifications c-3 ibm types 6 and 9 are used primarily for lobe connections from stations to wall jacks or patch panels. Table c-2 lists stp cable performance specifications. . C.2 fiber optic cable fiber optic cable is used for both baseband and broadband data transmission. Although construc...
Page 94: C.2.1 Multimode
Media specifications c-4 c.2.1 multimode table c-3 lists signal tolerance specifications for multimode fiber optic cable supported by the tpim-f2. C.2.2 single-mode table c-4 lists signal tolerance specifications for single-mode fiber optic cable supported by the tpim-f3. Table c-3 signal tolerances...
Page 95: Index
Ix-1 index a accessories, described 12-port daughterboard 1-9 crbrim-w/t 1-8 microsnac-t 1-8 tpim 1-9, 4-10 accessories, installation 12-port daughterboard 3-9 to 3-10 crbrim-w/t 3-12 to 3-13 ldram simm 3-13 to 3-14 microsnac-t 3-11 to 3-12 tpim 4-12 act led 5-1 automatic beacon recovery process (ab...
Page 96
Index ix-2 distributed lan monitor (dlm) 1-7 distributed monitoring dlm 1-7 rmon 1-6 document conventions used xiii organizational structure xiv documentation, for related products xv e eeprom 1-3 emc requirements a-2 environmental specifications a-2 f fiber optic cable connecting to ring port 4-15 ...
Page 97
Index ix-3 leds. See lanview leds lnk led (tpim), indications 4-12, 4-14, 4-16, 5-1 lobe cabling connecting 4-6 to 4-9 described 4-2 maximum lengths 4-5 lobe port status leds 5-1 lobe port, applications 2-11 lobe ports connecting to 4-6 to 4-9 pinouts 2-11 repeater circuitry 1-2 ring out capability ...
Page 98
Index ix-4 power on/off procedure 2-3 power supply specifications a-1 power up diagnostic screen 5-8 power up diagnostic tests monitoring with power up diagnostic screen 5-8 responding to error messages 5-9, 5-10 protection panel, removing front panel 3-6 rear panel 3-8 r reset switch 2-5 resetting ...
Page 99
Index ix-5 when connecting fiber trunk-cable segments 4-16 when connecting lobe segments 4-9 when connecting sth hub 4-18 when connecting twisted-pair trunk-cable segments 4-14 trunk cabling connecting 4-10 to 4-16 described 4-1 maximum lengths 4-5 u uninterruptible power supply (ups) 1-8 unshielded...
Page 100
Index ix-6.
Page 101: Power Supply Cord
Power supply cord the mains cord used with this equipment must be a 2 conductor plus ground type with minimum 0.75 mm square conductors and must incorporate a standard iec appliance coupler on one end and a mains plug on the other end which is suitable for the use and application of the product and ...