- DL manuals
- Cabletron Systems
- Software
- Spectrum EMM-E6
- User Manual
Cabletron Systems Spectrum EMM-E6 User Manual
EMM-E6
USER’S
GUIDE
EMM-E6
ETHERNET
EPIM-A
PWR
STBY
RCV
XMT
CLN
D C B A
CPU
RESET
SN
E
P
I
M
1
E
P
I
M
2
C
O
M
1
C
O
M
2
F
E
EPIM-A
PWR
LNK
YEL
STB DSR LNK
T1/FT1
TST RED SYN CTS TST
SYNC
BRIM-WT1
BRIM-A100
STY
LNK
XMT
RCV
BRIM-F6
CABLETRON SYSTEMS, P.O. Box 5005, Rochester, NH 83866-5005
CH1Book Page 1 Wednesday, March 20, 1996 7:48 AM
Summary of Spectrum EMM-E6
Page 1
Emm-e6 user’s guide emm-e6 ethernet epim-a pwr stby rcv xmt cln d c b a cpu reset sn e p i m 1 e p i m 2 c o m 1 c o m 2 f e epim-a pwr lnk yel stb dsr lnk t1/ft1 tst red syn cts tst sync brim-wt1 brim-a100 sty lnk xmt rcv brim-f6 cabletron systems, p.O. Box 5005, rochester, nh 83866-5005 ch1book pa...
Page 2: Notice
Emm-e6 user’s guide i notice cabletron systems reserves the right to make changes in specifications and other information contained in this document without prior notice. The reader should in all cases consult cabletron systems to determine whether any such changes have been made. The hardware, firm...
Page 3: Fcc Notice
Notice ii emm-e6 user’s guide fcc notice this device complies with part 15 of the fcc rules. Operation is subject to the following two conditions: (1) this device may not cause harmful interference, and (2) this device must accept any interference received, including interference that may cause unde...
Page 4: Vcci Notice
Notice emm-e6 user’s guide iii vcci notice this equipment is in the class i category (information equipment to be used in commercial and/or industrial areas) and conforms to the standards set by the voluntary control council for interference by information technology equipment (vcci) aimed at preven...
Page 5
Notice iv emm-e6 user’s guide cabletron software program license 1. License. You have the right to use only the one (1) copy of the program provided in this package subject to the terms and conditions of this license agreement. You may not copy, reproduce or transmit any part of the program except a...
Page 6: Exclusion Of Warranty and
Notice emm-e6 user’s guide v exclusion of warranty and disclaimer of liability 1. Exclusion of warranty. Except as may be specifically provided by cabletron in writing, cabletron makes no warranty, expressed or implied, concerning the program (including its documentation and media). Cabletron discla...
Page 7
Notice vi emm-e6 user’s guide united states government restricted rights the enclosed product (a) was developed solely at private expense; (b) contains “restricted computer software” submitted with restricted rights in accordance with section 52227-19 (a) through (d) of the commercial computer softw...
Page 8: Table of Contents
Emm-e6 user’s guide vii table of contents chapter 1 introduction 1.1 using this manual........................................................ 1-1 1.2 emm-e6 features .......................................................... 1-4 1.3 the mmac with flexible network bus ................. 1-10 1.4 ethe...
Page 9
Table of contents viii emme-e6 user’s guide chapter 2 requirements / configurations 2.1 network requirements ........................................... 2-1 2.1.1 10base-t twisted pair network ........................... 2-2 2.1.2 multimode fiber optic network ............................. 2-4 2.1.3...
Page 10
Table of contents emm-e6 user’s guide ix chapter 4 attaching a console 4.1 configuring your terminal .................................... 4-1 4.2 configuring a console cable ................................ 4-3 4.2.1 connecting to a vt series terminal ...................... 4-4 4.2.2 connecting to a...
Page 11
Table of contents x emme-e6 user’s guide chapter 10 router setup screen chapter 11 device statistics screen 11.1 device statistics......................................................... 11-2 11.2 device statistics screen commands .................. 11-3 11.2.1 selecting an update frequency ..........
Page 12
Table of contents emm-e6 user’s guide xi appendix a emm-e6 specifications a.1 bridging functionality ............................................. A-1 a.2 repeater functionality ........................................... A-2 a.3 com 1 port ..............................................................
Page 13: Chapter 1
Emm-e6 user’s guide 1-1 chapter 1 introduction welcome to the cabletron systems emm-e6 user’s guide . This manual explains how to set-up, configure, and locally manage the cabletron systems 6-port ethernet bridge/management module (emm-e6). 1.1 using this manual read through this manual completely t...
Page 14: Accessing Local Management
Chapter 1: introduction 1-2 emm-e6 user’s guide chapter 5, accessing local management , describes how to access lm after you attach the management console. Chapter 6, community names , explains how to use the community name table screen to set both local and remote access levels. Chapter 7, configur...
Page 15: Emm-E6 Specifications
Using this manual emm-e6 user’s guide 1-3 appendix a, emm-e6 specifications , details the properties of the emm-e6 and currently available epim modules. Appendix b, oid descriptions , supplies information detailing the object identifiers that may be accessed for managing the emm-e6. Following the ap...
Page 16: 1.2
Chapter 1: introduction 1-4 emm-e6 user’s guide 1.2 emm-e6 features • i960 processor design • ieee 802.1d compliant • available routing services • special filtering database • six port ethernet bridge • integrated brim technology • user configurable epims • expandable flash eeprom memory and runtime...
Page 17
Emm-e6 features emm-e6 user’s guide 1-5 i960 processor design the emm-e6 is equipped with an advanced intel i960 microprocessor that provides a scalable risc-based architecture. Ieee 802.1d compliant the emm-e6 is a fully ieee 802.1d compliant ethernet bridge. The emm-e6 supports both the ieee and d...
Page 18: Brim-E6
Chapter 1: introduction 1-6 emm-e6 user’s guide • brim-e6 : ethernet module with selectable epim connection • crbrim-w/e-ip : cisco router ethernet/wide area module for tcp/ip traffic. • crbrim-w/e-desktop : cisco router ethernet/wide area module for ip, ipx, decnet, and appletalk traffic. • crbrim-...
Page 19: Epim-T: 10Base-T Rj45 Port
Emm-e6 features emm-e6 user’s guide 1-7 • brim-a6: 100/155 mbps atm station connection with configurable connector. The brim-a6 uses atm port interface modules (apims). Apims allow a media flexibility for atm connections like that provided by fpims (described above). The following apim types are cur...
Page 20
Chapter 1: introduction 1-8 emm-e6 user’s guide flash memory allows for the downloading of firmware to the module without requiring that the module be shut down. The firmware download may be performed at any time during the operation of the module, and the new firmware image will be utilized at the ...
Page 21
Emm-e6 features emm-e6 user’s guide 1-9 dlm support the emm-e6 allows the option of using cabletron distributed lan monitor (dlm) software to locally poll and monitor any simple network management protocol (snmp) or internet protocol (ip) device. The emm-e6 itself tallies the polling results and can...
Page 22: 1.3
Chapter 1: introduction 1-10 emm-e6 user’s guide 1.3 the mmac with flexible network bus the multi media access center with flexible network bus (mmac-fnb) provides the operational platform for the emm-e6. The mmac-fnb (backplane) provides two physically separate buses - channel a (operating over the...
Page 23: Mmac Chassis
The mmac with flexible network bus emm-e6 user’s guide 1-11 table 1-1. Mmacs with shunting capabilities mmac chassis part # mmac-3fnb fc000000000 or above mmac-5fnb cc000000000 or above mmac-8fnb cg000000000 or above mmac-m8fnb dk000000000 or above mmac-m5fnb all mmac-m3fnb all if your mmac does not...
Page 24: 1.4
Chapter 1: introduction 1-12 emm-e6 user’s guide 1.4 ethernet channels a, b, c, d, e, and f the emm-e6 manages all ethernet bridging traffic within its resident hub. This means that the emm-e6 controls up to six of the ethernet bridging channels - a, b, c, d, e, and, in the future, f. These channels...
Page 25: 1.4.2
Ethernet channels a, b, c, d, e, and f emm-e6 user’s guide 1-13 1.4.2 ethernet channels b and c the cabletron systems multichannel family of mims includes the repeater interface controller media interface module (ric mim), an ieee 802.3 compliant multi-port repeater. You can configure these modules ...
Page 26: 1.4.3
Chapter 1: introduction 1-14 emm-e6 user’s guide when frames have destination addresses for a different bus: • the sending ric mim transmits the frames over its designated ethernet bus; • the other ric mims on this bus receive the frames, and repeat them; • the emm-e6, after determining the source a...
Page 27: •
Ethernet channels a, b, c, d, e, and f emm-e6 user’s guide 1-15 fddi and token ring modules - the emm-e6 recognizes the following fddi and token ring modules, but the emm-e6 management does not provide control or statistics. • crm-3t • snacmim • trmim-32a • trmim-34a • trrmim-f2t • trrmim-f3t with t...
Page 28: 1.5
Chapter 1: introduction 1-16 emm-e6 user’s guide only one epim operates at any given time. However, using both epim slots in a redundancy configuration ensures that if the primary bridging port fails, or the connecting cable segment becomes inoperable, the backup port automatically takes over the br...
Page 29: 1.6
Bridges emm-e6 user’s guide 1-17 1.6 bridges an ethernet bridge is a device that allows the expansion of a network beyond the limitations of the ieee 802.3 specified limits for repeated ethernet networks. If an ethernet network has a repeater hop of four repeaters or a round trip propagation delay n...
Page 30: 1.6.1
Chapter 1: introduction 1-18 emm-e6 user’s guide the bridge is considered a node on the network and performs store and forward functions for packets on each network. This contrasts with a repeater which repeats the signal bit by bit from one side of the network to the other. The bridge actually read...
Page 31: 1.6.2
Bridges emm-e6 user’s guide 1-19 1.6.2 spanning tree algorithm the spanning tree algorithm (sta) is used by bridges to detect data loops (duplicate data paths). The bridges will then automatically break the loop and use the now open path as a backup in case the primary path fails. When a bridge is p...
Page 32: 1.7
Chapter 1: introduction 1-20 emm-e6 user’s guide 1.7 local management features local management for the emm-e6 provides tools that allow you to manage the device and its attached segments. Through local management you can: • assign an ip address and subnet mask to the emm-e6 bridge via the configura...
Page 33: 1.8
Community names emm-e6 user’s guide 1-21 1.8 community names when using local or remote management tools to access the emm-e6 it is important that the network manager has the ability to maintain network security. Community names provide some network security by acting as passwords into the device an...
Page 34: 1.9.1
Chapter 1: introduction 1-22 emm-e6 user’s guide 1.9.1 mibs the management information bases (mibs) are a database resident on the emm-e6. Objects in the information base are uniquely identified by administratively assigned identifiers (called object identifiers or oids), and can be viewed, retrieve...
Page 35: 1.10.2
Review of addressing emm-e6 user’s guide 1-23 as mac addresses are often used to perform management and control functions for networking hardware, it is important to be able to identify a mac address when it is requested or returned by network management. Since most mac addresses are set at manufact...
Page 36
Chapter 1: introduction 1-24 emm-e6 user’s guide table 1-2. Class a table 1-3. Class b table 1-4. Class c range of network ids: 1 - 126. Host. Host. Host [1 octet for the network id (127 reserved)] binary translation: (of first octet) 0000001 - 01111111 [first bit is always 0] range for the host id:...
Page 37: 1.10.3
Review of addressing emm-e6 user’s guide 1-25 1.10.3 identifying ip address classes in the event that you have an existing ip address and need to quickly determine what fields are available for host ip address configuration, make that determination based on the binary value of the first ddn field. T...
Page 38: 1.10.5
Chapter 1: introduction 1-26 emm-e6 user’s guide subnet addresses, when used with routing, allow discrimination between devices and groups of devices based on ip addresses. Networks of different subnets, even those on the same physical network segment, may be isolated, from a functional standpoint, ...
Page 39
Review of addressing emm-e6 user’s guide 1-27 the binary 1’s in the mask “mask-out” the network id and the 0’s show where the host id is located. When using part of the host id as a subnet address, define a subnet mask that will mask-out the bits of the host id that are being used as a subnet addres...
Page 40
Chapter 1: introduction 1-28 emm-e6 user’s guide the example in figure 1-3 masks out the three high order bits of the only octet available for modification, the last octet. This provides for up to six subnets and up to 30 host ids within each subnet. Modifying the default mask for a class b address ...
Page 41
Review of addressing emm-e6 user’s guide 1-29 table 1-7. Examples of class b subnet masks decimal mask binary equivalent available subnet addresses host ids per subnet 192. 0 11000000 00000000 64 and 192 16,382 224. 0 11100000 00000000 32, 64, 96, 128, 192, 224 8,190 240. 0 11110000 00000000 16 - 24...
Page 42: 1.10.6
Chapter 1: introduction 1-30 emm-e6 user’s guide 1.10.6 operation of the subnet mask the subnet mask defines how your emm-e6 treats snmp trap ip destination addresses in its trap table (see chapter 7, trap table screen, for additional information on traps). When using the subnet mask, the emm-e6 log...
Page 43: 1.10.8
Review of addressing emm-e6 user’s guide 1-31 1.10.8 addressing example a network manager, planning for the configuration of a network of 60 hosts, desires to implement subnets to create logical divisions between different groups of workstations and devices. The internet assigned numbers authority h...
Page 44
Chapter 1: introduction 1-32 emm-e6 user’s guide for any snmp trap-generating network devices not residing on the same subnet as the network management station, the default subnet mask utilized on that device must be altered to match the subnet scheme. In the above example, the default subnet mask i...
Page 45: 1.11
Lanview leds and reset switch emm-e6 user’s guide 1-33 1.11 lanview leds and reset switch the emm-e6 incorporates the cabletron systems lanview status monitoring and diagnostics system. Lanview leds can help diagnose any problems, such as a power failure or a cable fault. The module includes the fol...
Page 46
Chapter 1: introduction 1-34 emm-e6 user’s guide lanview secure modules also provide a “full security” configuration, under which broadcast and multicast packets contain modified data fields such as those used in eavesdrop prevention (described above). Ports set to full security mode will not see or...
Page 47: 1.13
Getting help emm-e6 user’s guide 1-35 1.13 getting help if you need additional support related to installation, configuration, or management of the emm-e6, or if you have any questions, comments, or suggestions concerning this manual, contact cabletron systems technical support: by phone...............
Page 48: Chapter 2
Emm-e6 user’s guide 2-1 chapter 2 requirements / configurations this chapter contains general networking guidelines. Before attempting to install the emm-e6 or any additional epims or brims, review the requirements and specifications outlined in this chapter. 2.1 network requirements take care in pl...
Page 49: 2.1.1
Chapter 2: requirements / configurations 2-2 emm-e6 user’s guide 2.1.1 10base-t twisted pair network when connecting a 10base-t segment at any of the 10base-t hub ports or a 10base-t ethernet port interface module (epim-t), ensure that the network meets the following requirements: • length - the iee...
Page 50
Network requirements emm-e6 user’s guide 2-3 • jitter -intersymbol interference and reflections can cause jitter in the bit cell timing, resulting in data errors. 10base-t links must not generate more than 5.0 ns of jitter. Make sure your cable meets 10base-t link impedance requirements to rule out ...
Page 51: 2.1.2
Chapter 2: requirements / configurations 2-4 emm-e6 user’s guide 2.1.2 multimode fiber optic network when connecting a multimode fiber optic link segment to the hub (via epim-f1/f2), ensure the network meets the following requirements: • cable type - use the epim-f1 and epim-f2 for the following mul...
Page 52: 2.1.3
Network requirements emm-e6 user’s guide 2-5 2.1.3 single mode fiber optic network when connecting a single mode fiber optic link segment to the hub (via epim-f3), ensure the network meets the following requirements: • cable type - fiber optic link segments should consist of 8/125 to 12/125 µ m sing...
Page 53: 2.1.4
Chapter 2: requirements / configurations 2-6 emm-e6 user’s guide 2.1.4 thin-net network when connecting a thin-net (coaxial) segment to your hub (via an epim-c), ensure your network meets the following requirements: • cable type - use only 50 ohm rg-58a/u type coaxial cable for thin-net cable segmen...
Page 54: 2.3
Repeater media interface modules emm-e6 user’s guide 2-7 2.3 repeater media interface modules the emm-e6 communicates with the repeater mims over ethernet channels b and c of the mmac-fnb. The following repeater mims are currently available: • cxrmim: coaxial repeater mim; twelve 10base-2 coaxial co...
Page 55: 2.4
Chapter 2: requirements / configurations 2-8 emm-e6 user’s guide 2.4 port assignment modules • tpxmim-20/tpxmim-22: twisted pair port and bank assignment repeater mim; rj45 connectors (tpxmim-20 has nine, tpxmim- 22 has twenty-one); one epim. • tpxmim-32/tpxmim-36: twisted pair port and bank assignm...
Page 56: 2.5
Sample network configurations emm-e6 user’s guide 2-9 2.5 sample network configurations this section provides you with several examples for configuring networks with the emm-e6. These examples illustrate the flexibility and advantages to using the emm-e6 and ric mim technology: 2.5.1 three networks ...
Page 57: 2.5.1
Chapter 2: requirements / configurations 2-10 emm-e6 user’s guide 2.5.1 three networks with a single mmac-fnb one of the basic applications of the emm-e6 is for configuring three separate networks within one mmac. This provides you with the advantages of having three separate networks in one wiring ...
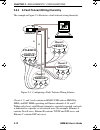
Page 58: 2.5.3
Sample network configurations emm-e6 user’s guide 2-11 2.5.3 adding users to a separate segment the example in figure 2-3 compares two methods of connecting 48 additional users to a network. Figure 2-3. Adding new users to place additional users on a new network with an emm-e6, you only need to add ...
Page 59: 2.5.4
Chapter 2: requirements / configurations 2-12 emm-e6 user’s guide 2.5.4 a fault tolerant wiring hierarchy the example in figure 2-4 illustrates a fault tolerant wiring hierarchy. Figure 2-4. Configuring a fault tolerant wiring scheme closets 1, 2, and 3 each contain an mmac-fnb with an emm-e6, mims,...
Page 60
Sample network configurations emm-e6 user’s guide 2-13 the star hub, which is an mmac-fnb that uses a configuration similar to the closet hubs, is the central repeater interconnect for the closets, but does not constitute a single point of failure. The emm-e6 in each mmac-fnb utilizes the 802.1d spa...
Page 61: 2.5.5
Chapter 2: requirements / configurations 2-14 emm-e6 user’s guide 2.5.5 the emm-e6 and brims the example in figure 2-5 illustrates just one possible emm-e6 and brim configuration. The emm-e6/brim combination provides various connection possibilities, depending on the brim(s) you use. Refer to indivi...
Page 62: Chapter 3
Emm-e6 user’s guide 3-1 chapter 3 installation this chapter contains instructions for: • unpacking and inventorying the contents of the emm-e6 carton • locating, identifying and setting the emm-e6 mode switches • adding/replacing optional modules (i.E., single in-line memory modules and ethernet por...
Page 63: 3.1
Chapter 3: installation 3-2 emm-e6 user’s guide 3.1 unpacking the emm-e6 unpack the emm-e6 as follows: 1. Remove the shipping material covering the emm-e6. 2. Verify the contents of the packing carton. The carton is shipped with the following items: 3. Carefully remove the module from the shipping b...
Page 64: 3.2
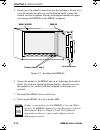
Setting mode switches emm-e6 user’s guide 3-3 3.2 setting mode switches the bank of dip switches located at the top of the emm-e6 (figure 3-1) are set to their default positions prior to shipping. Check these switches to ensure that they are in the correct position for normal emm-e6 operation. Figur...
Page 65
Chapter 3: installation 3-4 emm-e6 user’s guide switch definitions are as follows: • switch 1 - cabletron systems use only. • switch 2 - cabletron systems use only. • switch 3 - for manufacturing use only. Keep in off position. • switch 4 - mimrev (management interface module revision). This switch ...
Page 66
Setting mode switches emm-e6 user’s guide 3-5 after changing the state of switch 6 and repowering the device, the emm-e6 will request a new image until it either receives the image, or you reset the emm-e6 again by: - using the reset button on the front panel - removing the emm-e6 from the chassis b...
Page 67: 3.3
Chapter 3: installation 3-6 emm-e6 user’s guide 3.3 simm upgrades the emm-e6 allows memory upgrades for sdram, ldram, and flash eeprom. This section explains how to locate and add or replace a single in-line memory module (simm) for any of these memory types. 3.3.1 locating simms each memory type ha...
Page 68
Simm upgrades emm-e6 user’s guide 3-7 figure 3-2. Simm slot locations local dynamic random access memory (ldram) simm slot flash memory simm slot shared dynamic random access memory (sdram) simm slot emm-e6 direction of install ch1book page 7 wednesday, march 20, 1996 7:48 am.
Page 69: 3.3.2
Chapter 3: installation 3-8 emm-e6 user’s guide 3.3.2 installing simms installing a simm is a simple two step process. After finding the proper simm slot location, refer to figure 3-3 and the following instructions to install your simm. Figure 3-3. Installing a simm to install a simm: 1. Insert the ...
Page 70: 3.4
Adding/replacing epims emm-e6 user’s guide 3-9 3.4 adding/replacing epims this section contains procedures on how to add/replace an ethernet port interface module (epim) to upgrade or change the capabilities of your hub. After installing your new epim, refer to appropriate epim sections in this chap...
Page 71: 3.5
Chapter 3: installation 3-10 emm-e6 user’s guide 3.5 locating brims this section points out bridge router interface module (brim) connector locations on your emm-e6 board. Refer to your brim guide for installation procedures and additional information. The following diagram (figure 3-5) shows brim c...
Page 72: 3.6
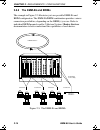
Pre-installation test emm-e6 user’s guide 3-11 3.6 pre-installation test before installing the emm-e6 in a live network, test the module in a controlled situation to ensure that it is repeating and bridging packets. You can perform this test with two workstations (see figure 3-6), using an mmac-fnb,...
Page 73
Chapter 3: installation 3-12 emm-e6 user’s guide 6. Send packets between the two workstations to verify the proper operation of the emm-e6. If a failure occurs, refer to chapter 14, troubleshooting. Figure 3-6. Pre-installation test note: if using unix workstations, a “ping” test verifies the emm-e6...
Page 74: 3.7
Installing the emm-e6 emm-e6 user’s guide 3-13 3.7 installing the emm-e6 installing the emm-e6 into any mmac hub is an easy operation and requires no special skills or tools. However, when you install your device, keep the following in mind: • you must install the emm-e6 in slots 1 and 2 (furthest s...
Page 75
Chapter 3: installation 3-14 emm-e6 user’s guide 4. Firmly press the module connections into the backplane. Do not try to force the module into place or use the knurled knobs to draw the module into the backplane. Forcing a misaligned module into place can damage the emm-e6 or the mmac backplane. Fi...
Page 76: Emm-E6
Installing the emm-e6 emm-e6 user’s guide 3-15 7. Observe the status of the lanview leds on the emm-e6. When the cpu led is flashing, the stby (standby) leds indicate the module’s boot state. During this period (up to 5 minutes), the leds cycle through a series of internal diagnostics. (see figure 3...
Page 77: 3.8
Chapter 3: installation 3-16 emm-e6 user’s guide 3.8 installation check-out after connecting to the network, verify that packets can pass over the network segments via the emm-e6. Again, you can use two workstations set up as file server and client. Keep the server workstation stationary in the wiri...
Page 78
Installation check-out emm-e6 user’s guide 3-17 figure 3-9. Installation checkout tpt file server workstation mmac-m3fnb with emm-e6 and tprmim office locations client workstation emm-e6 mmac-m3fnb t tprmim-33 ch1book page 17 wednesday, march 20, 1996 7:48 am.
Page 79: 3.9
Chapter 3: installation 3-18 emm-e6 user’s guide 3.9 connecting to the network this section gives procedures for connecting the emm-e6 to the network using the various epims available. When the emm-e6 is first powered up, the epim 1 port acts as the bridge port and the epim 2 port is off. Once you h...
Page 80: 3.9.1
Connecting to the network emm-e6 user’s guide 3-19 3.9.1 connecting a twisted pair segment to an epim-t before connecting a segment to the epim-t, check each end of the segment to determine wire cross-over. If the wires do not cross over, use the switch on the epim-t to internally cross over the rj4...
Page 81
Chapter 3: installation 3-20 emm-e6 user’s guide 2. Check that the lnk led for the port is on. If the led is not on, perform each of the following steps until it is: a. Check that the 10base-t device at the other end of the twisted pair segment is powered. B. Verify that the rj45 connectors on the t...
Page 82: 3.9.2
Connecting to the network emm-e6 user’s guide 3-21 3.9.2 connecting an aui cable to an epim-x to connect an epim-x to a device not requiring sqe: 1. Verify that the sqe led on the epim-x is off. If the sqe led is on, set the position of the sqe switch to off. 2. Attach one end of an aui cable, no lo...
Page 83: 3.9.3
Chapter 3: installation 3-22 emm-e6 user’s guide 3.9.3 connecting to an epim-f1/f2, or epim-f3 when connecting a fiber optic link segment to an epim-f1/f2, or epim-f3 keep the following in mind: • when connecting a fiber optic link segment with sma 906 connectors to an epim-f1 with sma ports, make s...
Page 84
Connecting to the network emm-e6 user’s guide 3-23 we recommend that you label the fiber optic cables to indicate receive and transmit ends. Cabletron systems prelabels its cable. At one end of the cable, one fiber is labeled 1, and the other fiber is labeled 2. This pattern repeats at the other end...
Page 85
Chapter 3: installation 3-24 emm-e6 user’s guide figure 3-13. The epim-f1/f2 and epim-f3 5. Check that the lnk led on the applicable module port is on. If the led is not on, perform each of the following steps until it is: a. Check that the device at the other end of the link is powered. B. Verify p...
Page 86: 3.9.4
Connecting to the network emm-e6 user’s guide 3-25 3.9.4 connecting a thin-net segment to an epim-c to connect a thin-net segment to an epim-c: 1. Set the internal termination switch (figure 3-14), located above the port (when the epim has been inserted into the emm-e6) and labeled term to: • the on...
Page 87
Chapter 3: installation 3-26 emm-e6 user’s guide figure 3-14. The epim-c attach thin-net segment directly to bnc connector when internal termination switch is set to on ( ). When internal termination switch is set to off ( ): connect bnc t-connector to port. Attach a terminator or terminated thin-ne...
Page 88: 3.9.5
Connecting to the network emm-e6 user’s guide 3-27 3.9.5 connecting an aui cable to an epim-a to connect an epim-a to an external network segment: 1. Check that the pwr led on the epim-a is on. If the pwr led is not on, contact cabletron systems technical support. 2. Attach an external transceiver t...
Page 89
Chapter 3: installation 3-28 emm-e6 user’s guide 5. Lock the aui connector into place using the connector slide latch. 6. If the transceiver pwr led is off with the aui cable connected: a. Check the aui connections for proper pinouts. Appendix a lists the pinouts for the transceiver connection. B. C...
Page 90: Chapter 4
Emm-e6 user’s guide 4-1 chapter 4 attaching a console this chapter describes how to attach a local management console to the emm-e6, and lists the setup and configuration requirements for: • console/terminal • console cable • console cable connections. 4.1 configuring your terminal the following ins...
Page 91
Chapter 4: attaching a console 4-2 emm-e6 user’s guide table 4-1. Vt terminal setup display setup menu columns .......................... -> controls ........................... -> auto wrap ........................ -> scroll ................................ -> text cursor....................... -> ...
Page 92: 4.2
Configuring a console cable emm-e6 user’s guide 4-3 4.2 configuring a console cable this section outlines the proper cable configurations for connecting the emm-e6 to a local management terminal. For information on the appropriate pinouts, refer to appendix a of this user’s guide. You need the follo...
Page 93: 4.2.1
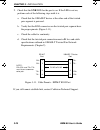
Chapter 4: attaching a console 4-4 emm-e6 user’s guide 4.2.1 connecting to a vt series terminal to connect a vt series terminal to a cabletron module console port (figure 4-1): 1. Connect the rj45 connector at one end of the cable to the console port on the cabletron module. 2. Plug the rj45 connect...
Page 94: 4.2.2
Configuring a console cable emm-e6 user’s guide 4-5 4.2.2 connecting to an ibm pc or compatible to connect an ibm pc or compatible running vt terminal emulation to a cabletron module console port (figure 4-2): 1. Connect the rj45 connector at one end of the cable to the console port on the cabletron...
Page 95: 4.3
Chapter 4: attaching a console 4-6 emm-e6 user’s guide 4.3 pinout descriptions 4.4 configuring a ups cable to configure an uninterruptible power supply (ups) cable: 1. Plug a straight-through twisted pair, rs232, cable into the emm-e6 rj45 com 1 port. 2. Plug the other end of the rs232 cable into th...
Page 96: Chapter 5
Emm-e6 user’s guide 5-1 chapter 5 accessing local management with your terminal properly configured, and the correct physical cable connections in place, you can access the local management interface. To access local management: 1. Turn the terminal on, and press the return key. The emm-e6 password ...
Page 97
Chapter 5: accessing local management 5-2 emm-e6 user’s guide 2. Enter your password and press return. The default super-user access password is the return key (which defaults internally to ‘public’). • if you enter an invalid password, the emm-e6 ignores the entry, and the cursor returns to the beg...
Page 98
Emm-e6 user’s guide 5-3 3. Use the arrow keys to highlight an option, and press return (or simply use the corresponding function key). The selected screen appears. If you do nothing on lm for 15 minutes, the password screen reappears. At this point, you must re-enter the password to continue using e...
Page 99: Chapter 6
Emm-e6 user’s guide 6-1 chapter 6 community names the community name table option lets you set local management community names. These names act as passwords to lm and provide security for your emm-e6. You can control emm-e6 access by establishing up to four different levels of security authorizatio...
Page 100: 6.2
Chapter 6: community names 6-2 emm-e6 user’s guide 6.2 community name table screen fields this section briefly explains each community name table screen field. Community name displays the community name through which a user can access lm. All community names act as passwords to local management. Dep...
Page 101: 6.3
Establishing community names emm-e6 user’s guide 6-3 6.3 establishing community names in order for any community name table edits to take effect, you must have super-user access. In other words, when you log into lm, you must do so with a super-user password. A password from any of the other levels ...
Page 102: Chapter 7
Emm-e6 user’s guide 7-1 chapter 7 configuration screen in the emm-e6 configuration screen you can assign an ip address and subnet mask to the emm-e6. You can also: • set the default interface • set the default gateway • override locked ports • enable all ports. 7.1 accessing the configuration screen...
Page 103: 7.2
Chapter 7: configuration screen 7-2 emm-e6 user’s guide 7.2 configuration screen fields the following briefly explains each configuration screen field. I/f displays the interface number (1 to 6) corresponding to a particular emm-e6 channel. This number allows the emm-e6 to accurately identify mib ii...
Page 104
Configuration screen fields emm-e6 user’s guide 7-3 subnet mask displays the subnet mask for each of the six emm-e6 channels in dotted decimal notation. Mac address displays the physical address of each bridge interface. Default interface displays the default interface number for the emm-e6 default ...
Page 105: 7.3
Chapter 7: configuration screen 7-4 emm-e6 user’s guide 7.3 setting the host ip address the table on the configuration screen allows you to assign an ip address and subnet mask to the emm-e6. To set the host ip: 1. Use the arrow keys to highlight the ip address field. 2. Enter the ip address into th...
Page 106: 7.4
Modifying a subnet mask emm-e6 user’s guide 7-5 7.4 modifying a subnet mask the emm-e6 automatically enters the natural subnet mask for any ip address that you enter. A natural subnet mask is a logical separation between network and host identifiers within the ip address. The emm-e6 allows you to mo...
Page 107: 3. Press The Return Key.
Chapter 7: configuration screen 7-6 emm-e6 user’s guide • the emm-e6 does not provide a natural subnet mask that fits your host/network identifier scheme. To modify the subnet mask: 1. Use the arrow keys to highlight the appropriate subnet mask field. 2. Enter the subnet mask in this field in the fo...
Page 108
Setting default gateway and interface emm-e6 user’s guide 7-7 to set the default gateway and its associated default interface: 1. Use the arrow keys to highlight the default interface field. 2. Enter the interface number of the emm-e6 for the default gateway in this field. The interface number will ...
Page 109: 7.6
Chapter 7: configuration screen 7-8 emm-e6 user’s guide 7.6 connecting/disconnecting a ups the emm-e6 provides the option of connecting to an uninterruptible power supply (ups) using local management. To enable the ups connection using emm-e6/lm: 1. Use the arrow keys to highlight the com 1 applicat...
Page 110: 7.7
Unlocking ports emm-e6 user’s guide 7-9 7.7 unlocking ports when you lock the chassis for security reasons (e.G., using remote inband management), unauthorized devices cannot communicate through an mmac-fnb chassis station port. The port lock override function provides fail-safe recovery if you cann...
Page 111: Chapter 8
Emm-e6 user’s guide 8-1 chapter 8 trap table screen as an snmp compliant device, the emm-e6 can authenticate an snmp request. The trap table defines the management stations to receive snmp traps for alarm/event notification. 8.1 accessing the trap table screen to access the trap table screen: 1. Fro...
Page 112: 8.2
Chapter 8: trap table screen 8-2 emm-e6 user’s guide 8.2 trap table screen fields the trap table contains three modifiable fields. The fields, shown in figure 8-1, allow the user to direct trap information to users on the network. The three fields are: snmp community name displays the community name...
Page 113
Configuring the trap table emm-e6 user’s guide 8-3 6. Using the arrow keys, highlight the desired trap ip address field. 7. Enter the ip address of the workstation to which you want the emm-e6 to send traps. Use the xxx.Xxx.Xxx.Xxx format with the value of xxx ranging from 0 to 254. 8. Using the arr...
Page 114: Chapter 9
Emm-e6 user’s guide 9-1 chapter 9 snmp tools screen this section describes specific commands and features within the snmp tools screen. This screen allows you to access management information bases (mibs), and varies according to your level of security access. The following descriptions outline the ...
Page 115: 9.2
Chapter 9: snmp tools screen 9-2 emm-e6 user’s guide 9.2 snmp tools screen fields the following describes the snmp tools screen fields and commands. Community name identifies the community name mib access level password. Oid prepend specifies the number prefix common to all object identifiers (oids)...
Page 116: 9.3
The security access level emm-e6 user’s guide 9-3 cycles allows you to specify the number of get next requests to walk through and how much time elapses between each request. Repeat repeats the get command, allowing you to monitor any changes to a specific oid. 9.3 the security access level each mib...
Page 117: Community Name.
Chapter 9: snmp tools screen 9-4 emm-e6 user’s guide in order to access a specific mib’s components, you must set the appropriate mib password in the community name field. To set the snmp tools screen community name: 1. Use the arrow keys to highlight the field to the right of community name. 2. Ent...
Page 118: 3. Enter The Oid.
Getting and setting oids emm-e6 user’s guide 9-5 4. Press the return key. If there is no instance of that oid, the emm-e6 displays “mib_no_instance.” otherwise, the emm-e6 displays that oid’s data type, length, and value. To get the next oid: 1. Highlight getnext, using the arrow keys. 2. Press the ...
Page 119: 9.5
Chapter 9: snmp tools screen 9-6 emm-e6 user’s guide 5. Enter the oid’s data type. 6. Press the return key. The emm-e6 displays “snmp oid data.” 7. Enter the data, or value of the oid. 8. Press the return key. If the emm-e6 accepts the entry, it displays “ operation code: xxxx ”; otherwise, an error...
Page 122: Chapter 10
Emm-e6 user’s guide 10-1 chapter 10 router setup screen this chapter shows the router setup screen, figure 10-1, below. Using this screen the user can select the protocol to be used by any routing services previously installed in the emm-e6. The user should use the routing services manual to make th...
Page 123: Chapter 11
Emm-e6 user’s guide 11-1 chapter 11 device statistics screen this chapter describes the features of the device statistics screen. Using this screen, you can view error, collision, and traffic statistics for the entire network, a selected slot, or a selected port. This screen also provides the option...
Page 124: 11.1
Chapter 11: device statistics screen 11-2 emm-e6 user’s guide 11.1 device statistics this section describes device statistics screen data fields. Bytes received displays the number of bytes received. Frames received displays the number of frames received. Frames filtered displays the total number of...
Page 125: 11.2
Device statistics screen commands emm-e6 user’s guide 11-3 runt packets displays the number of runt packets received from the network. A runt packet is less than the minimum ethernet frame size of 64 bytes, not including preamble. Giant packets displays the number of giant packets receivedfrom the n...
Page 126: 11.2.1
Chapter 11: device statistics screen 11-4 emm-e6 user’s guide network this command lets you select the network you want to monitor. The choices range from a to f, depending on the configuration of your network and the options available from this configuration. For example, if you do not have a media...
Page 127: 11.2.2
Device statistics screen commands emm-e6 user’s guide 11-5 11.2.2 selecting a network/slot/port when the device statistics screen first appears, statistics are displayed for network 1, slot 1, and port 1. To view statistics for another network, slot, and port, use the network x, slot x, or port x co...
Page 128: 11.2.4
Chapter 11: device statistics screen 11-6 emm-e6 user’s guide 11.2.4 disabling ports the disable port command lets you disable the port selected in the port command. You must first use the port command to select the desired port. To set the port disable command: 1. Use the arrow keys to highlight th...
Page 129: Chapter 12
Emm-e6 user’s guide 12-1 chapter 12 command line interface screen the command line interface (cli) screen, figure 12-1, will function in future releases of the emm-e6. Figure 12-1. Emm-e6 cli information screen emm-e6-960 local management cabletron emm-e6 revision 0.00.00 cli information c o m m u n...
Page 130: Chapter 13
Emm-e6 user’s guide 13-1 chapter 13 mib navigator this chapter describes the procedures required to access the mib navigator residing on the emm-e6. The mib navigator command set is described and examples of each command are provided. 13.1 managing device mibs the mib navigator allows access to a co...
Page 131: 13.2
Chapter 13: mib navigator 13-2 emm-e6 user’s guide 13.2 accessing the mib navigator the mib navigator function resides on your cabletron device (emm-e6, etwmim, esxmim, etc.). Access the mib navigator in-band, through a device (i.E., workstation) connected to the same network or internetwork, using ...
Page 132: 13.3
Mib navigator command set overview emm-e6 user’s guide 13-3 13.3 mib navigator command set overview there are three categories of commands in the command set. • navigation commands - allows the user to access and manage the mib for the device running the mib navigator. Some of commands also provide ...
Page 133: 13.3.2
Chapter 13: mib navigator 13-4 emm-e6 user’s guide • to abort the output or interrupt a process the escape character is ^c (where ^ equals the control key). • a slash (/) proceeding an oid issues that command from the root directory regardless of where you are in the mib. If no slash precedes the oi...
Page 134: Navigation Commands
Mib navigator command set overview emm-e6 user’s guide 13-5 navigation commands (cont’d) cd use this command to change directories within a mib subtree. The path specified must be valid. This command has two special subtree options: .. - moves you to one subtree above the current one. / - moves you ...
Page 135: Navigation Commands
Chapter 13: mib navigator 13-6 emm-e6 user’s guide navigation commands (cont’d) dir, ls each of these commands displays the contents of a specified sub-tree (the current directory displays if you do not specify a sub-tree). Options can be used separately or combined. When no option is used the ascii...
Page 136: Navigation Commands
Mib navigator command set overview emm-e6 user’s guide 13-7 navigation commands (cont’d) help the help command provides a list of available mib navigator commands. The command also provides help for individual mib navigator commands. Format: help (general help) help (specific help) example mibnav> h...
Page 137: Navigation Commands
Chapter 13: mib navigator 13-8 emm-e6 user’s guide navigation commands (cont’d) pwd the pwd command displays the full path name for the directory in which you are currently working. Format: pwd example mibnav> pwd # /iso/org/dod/internet/mgmt/mib-2 set the set command enables you to set the value of...
Page 138: Navigation Commands
Mib navigator command set overview emm-e6 user’s guide 13-9 navigation commands (cont’d) su the su command enables you to change your community name to allow for different access to the mib. The community name that you enter allows you either basic read, read only, read/write, or super-user access t...
Page 139: Navigation Commands
Chapter 13: mib navigator 13-10 emm-e6 user’s guide navigation commands (cont’d) whoami the whoami command displays your community string and access privileges to the mib. When using the whoami command one of these four access levels will display: basic read, read only, read/write, and super user. F...
Page 140: 13.3.3
Mib navigator command set overview emm-e6 user’s guide 13-11 13.3.3 built-in commands the following provides a brief description, the proper format, and an example of each built-in command. Arp the arp command provides access to the arp (address resolution protocol) cache, enabling you to view cache...
Page 141: Built-In Commands
Chapter 13: mib navigator 13-12 emm-e6 user’s guide built-in commands (cont’d) netstat the netstat provides a display of general network statistics for the managed device. The netstat command must be used with one of the following two display options: -i displays status and capability information fo...
Page 142: Built-In Commands
Mib navigator command set overview emm-e6 user’s guide 13-13 built-in commands (cont’d) snmp- branch the snmpbranch command enables you to query another snmp device. The command provides a display of objects that match the specified object-id. If no match is made, no object will display. Format: snm...
Page 143: Built-In Commands
Chapter 13: mib navigator 13-14 emm-e6 user’s guide built-in commands (cont’d) snmpset the snmpset command enables you to set the value of an object in other snmp devices. This command requires the appropriate community string and oid. When defining a new leaf, the set command prompts you for a valu...
Page 144: Built-In Commands
Mib navigator command set overview emm-e6 user’s guide 13-15 built-in commands (cont’d) traceroute the traceroute command generates a traceroute request to a specified ip address and provides a display of all next-hop routers in the path to the device. If the device is not reached, the command displ...
Page 145: 13.3.4
Chapter 13: mib navigator 13-16 emm-e6 user’s guide 13.3.4 special commands the following provides a brief description, the proper format, and an example applicable to each special command. Done, quit, exit these commands enable you to exit from the mib navigator and return to the operating system. ...
Page 146: Chapter 14
Using lanview emm-e6 user’s guide 14-1 chapter 14 troubleshooting this chapter includes information for troubleshooting network and emm- e6 operational problems. The following sections describe the emm-e6’s lanview leds, provide a troubleshooting checklist, and explain how and when to reset the emm-...
Page 147
Chapter 14: troubleshooting 14-2 emm-e6 user’s guide table 14-1. Lanview leds led color description error condition/ recommended action cpu multicolor green red flashing green indicates that the board is operating properly. If off, or red, the board has a problem. Press the reset switch on the emm-e...
Page 148
Using lanview emm-e6 user’s guide 14-3 xmt a,b,c,d (transmit) green led flashes to indicate that a segment is transmitting a frame. If not connected to the lan, the led flashes every two seconds to indicate it is transmitting bpdu frames. If none of the transmit leds is flashing, the emm-e6 is not t...
Page 149: 14.2
Chapter 14: troubleshooting 14-4 emm-e6 user’s guide 14.2 troubleshooting checklist if your emm-e6 is not operating properly, the following checklist describes some of the problems that may occur with the emm-e6 installed in an mmac, possible causes for the problem, and suggestions for resolving the...
Page 150
Troubleshooting checklist emm-e6 user’s guide 14-5 table 14-2. Troubleshooting checklist problem possible causes recommended action no leds on. Loss of power to the mmac. Emm-e6 not properly installed. Check the proper installation of the mmac power supply module and its access to a live outlet. Che...
Page 151
Chapter 14: troubleshooting 14-6 emm-e6 user’s guide a port on a mim managed by the emm-e6 cannot access the network, while other ports on the same mim are able to access. The port is either off or segmented. Port cable is defective. Enable the port via local or remote management. Try connecting the...
Page 152: 14.3
Using the reset switch emm-e6 user’s guide 14-7 14.3 using the reset switch the emm-e6 incorporates a recessed reset switch, located above the leds (see figure 14-1). This reset switch initializes the emm-e6 processor. This switch does not initialize non-volatile random access memory (nvram), the no...
Page 153: Chapter 15
Emm-e6 user's guide 15-1 chapter 15 image file download this chapter provides instructions for downloading an image file to the emm-e6 using three different methods; altering hardware switch settings to force the module to accept new firmware, through unix operating system commands, and by setting s...
Page 154: 15.1
Chapter 15: image file download 15-2 emm-e6 user's guide 15.1 getting started cabletron ships backup copies of image files for all of its intelligent devices. The first file, suffixed with .Hex (after it has been decompressed from a .Zip) is for standard local downloading (any port, except the brim)...
Page 155: 15.2
Forced download with unix emm-e6 user's guide 15-3 15.2 forced download with unix downloading an emm-e6 image file with a unix workstation requires setting up a management station, and forcing the download. To force a download, you can use mode switch 6 on the emm-e6 or set specific mib oids. Due to...
Page 156: (E.G., Unix% Rarpd -A).
Chapter 15: image file download 15-4 emm-e6 user's guide 2. Edit the /etc/hosts file by adding the emm-e6 mac address and follow it with the same unique name you used in step one above. (e.G., 00:00:1d:32:0c:1b emme6). 3. If you already have a /tftpboot directory, confirm the rarp setup of your work...
Page 157
Forced download with unix emm-e6 user's guide 15-5 7. Edit the /etc/inetd.Conf file by removing anything prior to the tftpboot daemon (e.G., the # sign) that comments-out the line. 8. Kill the inetd process (e.G., unix% kill -hup ‘process id number’), and then restart the process (e.G., unix% inetd)...
Page 158
Chapter 15: image file download 15-6 emm-e6 user's guide to force a download using the emm-e6 download switch: 1. Remove the safety bars from the mmac chassis. 2. Unscrew the knurled knobs at the top and bottom of the emm-e6 front panel. 3. Slide the mim out of the chassis until you can easily acces...
Page 159: 15.3
Standard local download emm-e6 user's guide 15-7 15.3 standard local download table 15-1 provides a step by step procedure for downloading the firmware image file. This section provides specific mib oids, their names, and the required setting for proper image file download. Refer to your specific mi...
Page 160: 15.4
Chapter 15: image file download 15-8 emm-e6 user's guide 15.4 remote runtime download table 15-2 provides a step by step procedure for downloading the firmware image file. This section provides specific mib oids, their names, and the required setting for proper image file download. Refer to your spe...
Page 161
Remote runtime download emm-e6 user's guide 15-9 table 15-2. Runtime download procedure step oid name oid number data type snmp oid data (1). Ctdltftprequesthost 1.3.6.1.4.1.52.4.1.5.8.1.18.0 ip address enter the ip address of the tftp server. (2). Ctdltftprequest 1.3.6.1.4.1.52.4.1.5.8.1.19.0 strin...
Page 162
Chapter 15: image file download 15-10 emm-e6 user's guide note: if you selected forcedownloadreset at step 3, then do not continue, you have completed all necessary settings. Note: if you selected forcedownload at step 3, then you can reset the emm-e6 at a later time. You can reset the emm-e6 remote...
Page 163: Appendix A
Emm-e6 user’s guide a-1 appendix a emm-e6 specifications this appendix provides the operating specifications for the cabletron systems emm-e6. Cabletron systems reserves the right to change these specifications at any time without notice. A.1 bridging functionality flash memory: 2 mb (expandable to ...
Page 164: A.2
Appendix a: emm-e6 specifications a-2 emm-e6 user’s guide a.2 repeater functionality delay times (port x in to port x out) start of packet: 1,450 ns max. Collision to jam: 1,550 ns max. Preamble input: minimum of 40 bits to a max. Of 64 bits required. Output: 64 bits min . (last 2 bits = 1 , 1) . Ja...
Page 165: A.3
Emm-e6 user’s guide a-3 a.3 com 1 port type: standard rj45 port pin 1 transmit data (xmt) from com 1 port 2 data set ready (dsr) to com 1 port 3 not used 4 receive data (rcv) to com 1 port 5 signal ground (gnd) 6 data terminal ready (dtr) from com 1 port 7 not used 8 not used a.4 com 2 port type: st...
Page 166: A.6
Appendix a: emm-e6 specifications a-4 emm-e6 user’s guide a.6 safety this unit meets the safety requirements of ul 1950 (without d3 deviations), csa c22.2 no. 950, and en 60950; the emi requirements of fcc part 15 class a, en 55022 class a, and vcci class i; and the emc requirements of en 50082-1, i...
Page 167: A.8
Emm-e6 user’s guide a-5 a.8 epim-t (10base-t twisted pair port) internal transceiver: cabletron systems tpt 10base-t twisted pair transceiver type: 8 pin rj45 jack (figure a-1). Figure a-1. Epim-t (with rj45 port) a slide switch on the epim-t determines the cross-over status of the cable pairs. The ...
Page 168: A.9
Appendix a: emm-e6 specifications a-6 emm-e6 user’s guide a.9 epim-f1/f2 (multimode fiber optic port) internal transceiver: cabletron systems fot-f fiber optic transceiver type: epim-f1: sma fiber optic ports (figure a-3) epim-f2: st fiber optic ports (figure a-3) figure a-3. Epim-f1 and epim-f2 tab...
Page 169: A.10
Emm-e6 user’s guide a-7 a.10 epim-f3 (single mode fiber optic port) internal transceiver: cabletron systems fot-f3 fiber optic transceiver type: st fiber optic ports (figure a-4) figure a-4. Epim-f3 transmitter power is inversely proportional to temperature rise. Use the output power coefficient to ...
Page 170: Parameter
Appendix a: emm-e6 specifications a-8 emm-e6 user’s guide table a-2. Epim-f3 statistics parameter typical minimum maximum transmitter peak wave length: 1300 nm 1270 nm 1330 nm spectral width: 60 nm — 100 nm rise time: 3.0 ns 2.7 ns 5.0 ns fall time: 2.5 ns 2.2 ns 5.0 ns duty cycle: 50.1% 49.6% 50.7%...
Page 171: A.11
Emm-e6 user’s guide a-9 a.11 epim-c (bnc port) internal transceiver: cabletron systems tms-3 transceiver type: bnc receptacle, with gold center contact, for use with bnc type t-connectors and rg-58 thin-net cable (figure a-5). Figure a-5. Epim-c (with bnc port) termination: using the switch to the s...
Page 172: A.12
Appendix a: emm-e6 specifications a-10 emm-e6 user’s guide a.12 epim-a and epim-x (aui port) interface connector: db-15 port (female connector for epim-a, male connector for epim-x) (figure a-6). Type: 15 position d type receptacle figure a-6. Epim-a and epim-x (aui port) table a-3. Db-15 pinouts co...
Page 173: Appendix B
Emm-e6 user's guide b-1 appendix b emm-e6 oids this appendix contains a selected number of oid strings that are among the most frequently needed. The oids are implemented by using either the snmp tools procedures detailed in chapter 9 or the mib navigator procedures located in chapter 13. Note that ...
Page 174: B.2
Appendix b: commonly-used oids b-2 emm-e6 user's guide b.2 configuring arp request packets the emm-e6’s snmp tools screen allows you to generate an address resolution protocol (arp) request packet utilizing specific framing through local management. An arp request is used to send an snmp trap to a d...
Page 175: B.3
Port group security emm-e6 user's guide b-3 b.3 port group security the next seven oids are used for port group security features. Rptrsrcaddrmgmtportlock description: setting this object to lock activates the network port security lock. Setting a value of portmismatch (3) is invalid. A read of port...
Page 176: Rptrportsecuritylockstatus
Appendix b: commonly-used oids b-4 emm-e6 user's guide rptrportsecuritylockstatus description: defines the lock status for this particular port entry. Object identifier: 1.3.6.1.4.1.52.4.1.1.1.4.3.9.1.1.3 data type: integer values: 1 unlock 2 lock access policy: read-write rptrportsecuritylockaddadd...
Page 177
Port group security emm-e6 user's guide b-5 rptrportsecuritydisableonviolation description: designates whether port is disabled if source address is violated. A source address violation occurs when an address is detected which is not in the source address list for this port. If this port is disabled...
Page 178: B.4
Appendix b: commonly-used oids b-6 emm-e6 user's guide b.4 enabling & disabling snmp traps the emm-e6 supports the collection and reporting of snmp traps of several types and at several levels. Snmp trap sending may be enabled or disabled for the following trap types: segmentation, link, and source ...
Page 179: Rptrsatrapsetscraddr
Enabling & disabling snmp traps emm-e6 user's guide b-7 rptrsatrapsetscraddr description: enables and disables source address traps for this network (i.E., channel a, b, or c). Object identifier: 1.3.6.1.4.1.52.4.1.1.1.4.1.6.2.1 data type: integer values: 1 disable 2 enable access policy: read-write...
Page 180: Rptrportgrphwtrapsetseg
Appendix b: commonly-used oids b-8 emm-e6 user's guide rptrportgrphwtrapsetseg description: enables and disables segmentation traps for the specified port group at the board level. Object identifier: 1.3.6.1.4.1.52.4.1.1.1.4.2.5.1.1.1.3. Data type: integer values: 1 disable 2 enable access policy: r...
Page 181: Rptrporthwtrapsetlink
Enabling & disabling snmp traps emm-e6 user's guide b-9 rptrporthwtrapsetlink description: enables and disables link traps for this port. Object identifier: 1.3.6.1.4.1.52.4.1.1.1.4.3.8.1.1.1.3.. Data type: integer values: 1 disable 2 enable access policy: read-write rptrporthwtrapsetseg description...
Page 182: B.5
Appendix b: commonly-used oids b-10 emm-e6 user's guide b.5 activating rmon groups the initial configuration of the emm-e6 at installation does not provide the activation of the rmon default and host groups. These management groups may be activated or deactivated through local management using oid s...
Page 183: B.6
Bridging emm-e6 user's guide b-11 b.6 bridging the following oid is used to enable and disable the interface for the bridging function. Dot1dstpportenable description: the enabled/disabled status of the port. Object identifier: 1.3.6.1.2.1.17.2.15.1.4 data type: integer values: 1 enable 2 disable ac...
Page 184: B.8
Appendix b: commonly-used oids b-12 emm-e6 user's guide b.8 channel selection the following two oids are needed to select channel assignments (a, b, or c) for all boards or individual ports. These oids are needed for products supporting multichannel connectivity. Fnbconnect description: denotes the ...
Page 185: B.9
Oid hashing on source addreses emm-e6 user's guide b-13 b.9 oid hashing on source addreses the following oid allows the enabling and disabling of dec hashing, which may be necessary or desired in decnet and mixed ieee 802.3/ decnet environments. Rptrsrcaddrmgmthashtype description: this enables and ...
Page 186: Glossary
Emm-e6 user’s guide gl-1 glossary this glossary provides brief descriptions of some of the recurrent terms in the main text, as well as related terms used in discussions of the relevant networking discussions. These descriptions are not intended to be comprehensive discussions of the subject matter....
Page 187
Attenuation to brim gl-2 emm-e6 user’s guide attenuation loss of signal power (measured in decibels) due to transmission through a cable. Attenuation is dependent on the type, manufacture and installation quality of cabling, and is expressed in units of loss per length, most often db/m. Aui attachme...
Page 188
Broadcast to connectivity emm-e6 user’s guide gl-3 broadcast a type of network transmission; a broadcast transmission is one which is sent to every station on the network, regardless of location, identification, or address. Buses physical portions of the backplane of a modular chassis which pass inf...
Page 189
Console to decryption gl-4 emm-e6 user’s guide console see terminal. Cross-over a length of multi-stranded cable in which the transmit wire(s) of one end is/are crossed over within the cable to connect to the receive wire(s) of the other end. Cross- overs are used to connect devices to like devices,...
Page 190
Dedicated to fault-tolerance emm-e6 user’s guide gl-5 dedicated assigned to one purpose or function. Default gateway the ip address of the network or host to which all packets addressed to unknown network or host are sent device (network) any discrete electronic item connected to a network which eit...
Page 191
Fddi to host gl-6 emm-e6 user’s guide fddi fiber distributed data interface. A high-speed networking architecture. Fddi requires that stations only transmit data when they have been given permission by the operation of the network, and dictates that stations will receive information at pre-determine...
Page 192
Hot swap to ip emm-e6 user’s guide gl-7 hot swap hot swap capability indicates that a product is capable of being removed from an operating modular chassis and reinserted or replaced without requiring that the chassis and all associated modules be powered down. Hub see modular chassis. Iana internet...
Page 193
Ip address to mbps gl-8 emm-e6 user’s guide ip address internet protocol address. The ip address is associated, by the network manager or network designer, to a specific interface. The availability of ip addresses is controlled by the iana. Iso international organization for standardization. The iso...
Page 194
Media to nanometer emm-e6 user’s guide gl-9 media physical cabling or other method of interconnection through which network signals are transmitted and received. Mib management information base. A database of data related to a specific management or manageable network device, which may be viewed or ...
Page 195
Node to port assignment gl-10 emm-e6 user’s guide node any single end station on a network capable of receiving, processing, and transmitting packets. Nvram non-volatile random access memory. Memory which is protected from elimination during shutdown and between periods of activity, frequently throu...
Page 196
Protocol to sdram emm-e6 user’s guide gl-11 protocol a set of rules governing the flow of information within a communications infrastructure. Protocols control operations such as frame format, timing, and error correction. See also architecture. Pvc polyvinyl chloride. A material commonly used in th...
Page 197
Segment to sqe gl-12 emm-e6 user’s guide segment a portion of a network which is separated from other networks. A segment may be one portion of a bridged, switched, or routed network. Segments must be capable of operating as their own networks, without requiring the services of other portions of the...
Page 198
St to throughput emm-e6 user’s guide gl-13 st straight-tip. A modular connector and port system used with both multimode and single mode fiber optic cabling. The st connector utilizes an insert and twist-lock mechanism. Station see node. Stp shielded twisted pair. Refers to a type of cabling, most c...
Page 199
Token to utp gl-14 emm-e6 user’s guide token a particular type of frame which informs a station in the token ring and fddi network architectures that it may transmit data for a specified length of time. Once that time has expired, the station must stop transmitting and pass the token along to the ne...
Page 200: Numerics
Emm-e6 user’s guide index-i numerics 10baset 3-19 a a channel 1-12 address classes identifying 1-25 addressing 1-22 arp b-2 arp 13-11 attenuation multimode 2-4 singlemode 2-5 twisted pair 2-3 b b channel 1-13 backplane 1-10 basic read only 1-21 basic-read 6-2 baud rate default 3-4 bootp 3-4 bpdu 1-1...
Page 201
Index-ii emm-e6 user’s guide e e channel 1-16 eavesdrop prevention 1-33 emm-e6 features 1-4 enabling ports 7-9 epims 1-7 errors, statistics 11-2 exit 13-16 f f channel 1-16 fault tolerant wiring 2-12 filter 1-18 filter rate a-1 firmware upgrades 15-1 flash memory 1-7 flexible network bus 1-10 forced...
Page 202
Emm-e6 user’s guide index-iii m mac address 1-22 memory 3-6, a-1 eeprom 1-7 local dynamic 1-8 shared dynamic 1-8 mib 1-22 access 13-2 description 13-1 hierarchy 13-1 managing devices 13-1 mib2 13-7 mode switches 3-3 multi media access center 1-10 n natural mask 1-26 netstat 13-12 network id 1-23 nex...
Page 203
Index-iv emm-e6 user’s guide s safety a-4 sample configurations 2-9 security 1-33 community names 1-21 set 1-21 set 13-8 simm upgrade 3-6 slash notation 13-4 snmp 1-21 snmp tools screen 9-1 snmp traps 8-1 snmpbranch 13-13 snmpget 13-13 snmpset 13-14 snmptree 13-14 spanning tree algorithm 1-19 specif...
Page 204: Emm-E6
Emm-e6 quick reference card emm-e6 quick reference card led description cpu flashing green: board operating properly. Red: cpu error condition. Stby a, b, c, d amber indicates port or interface placed in standby state. Rcv a, b, c, d green indicates valid link from station to emm-e6 interface. Amber...
Page 205
Emm-e6 quick reference card emm-e6 quick reference card • slide the emm-e6 into the first and second slots of the mmac chassis (as shown below). • secure the module by tightening the knurled knobs at the top and bottom of the module. • power on the mmac chassis. Monitor the state of the cpu led. • t...