- DL manuals
- Cabletron Systems
- Software
- SPECTRUM
- User Manual
Cabletron Systems SPECTRUM User Manual
Summary of SPECTRUM
Page 1
Title page portable management application for the emm-e6 user’s guide ®.
Page 3: Notice
I notice cabletron systems reserves the right to make changes in specifications and other information contained in this document without prior notice. The reader should in all cases consult cabletron systems to determine whether any such changes have been made. The hardware, firmware, or software de...
Page 4: Restricted Rights Notice
Ii restricted rights notice (applicable to licenses to the united states government only.) 1. Use, duplication, or disclosure by the government is subject to restrictions as set forth in subparagraph (c) (1) (ii) of the rights in technical data and computer software clause at dfars 252.227-7013. Cab...
Page 5: Contents
Iii contents chapter 1 introduction using the emm-e6 user’s guide ............................................................................... 1-1 what’s not in the emm-e6 user’s guide. . .................................................... 1-3 conventions ...........................................
Page 6
Contents iv chapter 3 alarm configuration using alarm configuration ......................................................................................... 3-2 configuring alarms............................................................................................... 3-3 setting repeater ala...
Page 7
V contents enabling security and traps...................................................................................... 7-12 repeater-level security and traps ..................................................................... 7-14 module-level security and traps.................................
Page 8
Contents vi.
Page 9: Chapter 1
1-1 chapter 1 introduction how to use the emm-e6 user’s guide; manual conventions; contacting the cabletron systems global call center; emm-e6 firmware versions supported by spma the emm-e6 (ethernet management module for ethernet with six ports) provides intelligence for cabletron systems’ multi-me...
Page 10
Introduction 1-2 using the emm-e6 user’s guide stand-alone launcher or the command line (if you are running in stand-alone mode); in addition, several applications can also be accessed from within the hub view, a graphical display of the emm-e6 and the hub it is managing. The emm-e6 user’s guide des...
Page 11
Using the emm-e6 user’s guide 1-3 introduction • chapter 8, front panel redundancy , describes how to configure redundancy for the two channel d epim ports on the emm-e6’s front panel. You can access the front panel redundancy application from the icon menu, the hub view, or the command line. • appe...
Page 12: Conventions
Introduction 1-4 conventions instructions on discovering cabletron devices, creating icons, and accessing the icon menus within your management platform are included in your installing and using spectrum for... Guide. If you are using spma for the emm-e6 in stand-alone mode — that is, without benefi...
Page 13
Conventions 1-5 introduction graphical interface in use. For the sake of consistency, the following conventions will be followed throughout this and other spma guides. Screen displays spma runs under a variety of different operating systems and graphical user interfaces. To maintain a consistent pre...
Page 14
Introduction 1-6 conventions some windows will also contain a button; selecting this button launches a history window ( figure 1-2 ) which lists all footer messages that have been displayed since the window was first invoked. This window can help you keep track of management actions you have taken s...
Page 15: Getting Help
Getting help 1-7 introduction if you’re using a two-button mouse, don’t worry. Spma doesn’t make use of mouse button 2. Just click the left button for button 1 and the right mouse button when instructed to use mouse button 3. Whenever possible, we will instruct you on which mouse button to employ; h...
Page 16: Emm-E6 Firmware
Emm-e6 firmware 1-8 introduction modem setting 8n1: 8 data bits, 1 stop bit, no parity for additional information about cabletron systems products, visit our world wide web site: http://www.Cabletron.Com/. For technical support, select service and support. Emm-e6 firmware spma for the emm-e6 has bee...
Page 17: Chapter 2
2-1 chapter 2 using the emm-e6 hub view navigating through the hub view; monitoring hub performance; managing the hub the heart of the spectrum portable management application (spma) for the emm-e6 is the hub view, a graphical interface that gives you access to many of the functions that provide con...
Page 18
Using the emm-e6 hub view 2-2 using the hub view navigating through the hub view within the hub view, you can click mouse buttons in different areas of the window to access various menus and initiate certain management tasks. The following diagrams describe the information displayed in the hub view ...
Page 19
Using the hub view 2-3 using the emm-e6 hub view contact status is a color code that shows the status of the connection between spma and the device: • green means a valid connection. • blue means that spma is trying to reach the device but doesn’t yet know if the connection will be successful. • red...
Page 20
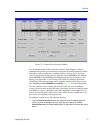
Using the emm-e6 hub view 2-4 using the hub view figure 2-2. Emm-e6 hub view device menu the device menu lets you perform the following: • open the device status window • access the ip address table • open the polling intervals window • change the port display form • launch the global find mac addre...
Page 21
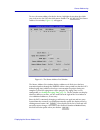
Using the hub view 2-5 using the emm-e6 hub view if you need to call the cabletron systems global call center about a problem with the hub view application, you’ll need the information provided in the info window: figure 2-3. Hub information window clicking mouse button 1 on the quit button closes a...
Page 22
Using the emm-e6 hub view 2-6 using the hub view figure 2-4. Emm-e6 ports using the mouse in a hub view module each media interface module, or mim, installed in the emm-e6-controlled hub will be displayed in the hub view; use the mouse as indicated in the illustration below to access network, module...
Page 23
Using the hub view 2-7 using the emm-e6 hub view figure 2-5. Mousing around a module display hub view port color codes the port status boxes in the hub view are color coded to indicate the port’s connection status. The colors are consistent for all port display forms except admin status and fnb chan...
Page 24: Monitoring Hub Performance
Using the emm-e6 hub view 2-8 monitoring hub performance • green indicates that the port is active; that is, the port has been enabled by management, has a valid link signal (if applicable), and is able to communicate with the station at the other end of the port’s cable segment. Note that an aui or...
Page 25
Monitoring hub performance 2-9 using the emm-e6 hub view figure 2-6. The emm-e6’s device, network, module, and port menus hub performance data available through these menus includes: • device, network, module, and port status descriptions. • network, module, and port statistics, which provide a comp...
Page 26
Using the emm-e6 hub view 2-10 monitoring hub performance changing the port display form via the device menu will affect all manageable ports in the hub; using the network menu will affect all ports on a specific channel, or network; and using the module menu will affect all ports on the appropriate...
Page 27
Monitoring hub performance 2-11 using the emm-e6 hub view • oow (out-of-window) collisions for error type descriptions, see checking statistics on page 2-20 . Protocols displays a percentage for each active port that represents what portion of that port’s traffic is of a particular protocol type. Yo...
Page 28
Using the emm-e6 hub view 2-12 monitoring hub performance - seg (segmented) indicates that the port has been segmented by the repeater due to an excessive collision level. • admin status displays either on or off, an indication of whether management has the port enabled or disabled. A port can be on...
Page 29
Monitoring hub performance 2-13 using the emm-e6 hub view checking device status and updating front panel info the device status window is where you change the information displayed on the hub view front panel and where you can see summary information about the current state of the hub. To open the ...
Page 30
Using the emm-e6 hub view 2-14 monitoring hub performance chassis type indicates the type of hub that houses this emm-e6 — mmac-m3fnb, mmac-m5fnb, and so forth — and whether or not the hub contains a shunting backplane. To change the name, location, contact, date, or time: 1. Highlight the appropria...
Page 31
Monitoring hub performance 2-15 using the emm-e6 hub view or click mouse button 3 on the appropriate network connection box to open the network menu. 2. Drag down to status and release. Figure 2-8. Emm-e6 network status window note that the information in the network status window applies to all mim...
Page 32
Using the emm-e6 hub view 2-16 monitoring hub performance checking module status you can open a module status window for any manageable module in the emm-e6-controlled hub. To open the module status window: 1. Click button 1 in the module type box. Or click button 3 in the module index, module type,...
Page 33
Monitoring hub performance 2-17 using the emm-e6 hub view checking port status you can open a port status window for any port on any manageable module installed in the hub. To open the port status window: 1. Click button 3 in the port index or port status box to display the port menu. 2. Drag down t...
Page 34
Using the emm-e6 hub view 2-18 monitoring hub performance • not supported — the selected port does not support the link feature, so the emm-e6 cannot determine link status; this value will show only for thin coax (bnc), aui, or transceiver ports. • unknown — the emm-e6 can’t determine a link status....
Page 35
Monitoring hub performance 2-19 using the emm-e6 hub view • aui epim • transceiver port aui epim • twisted pair: rj45 epim • multi-mode fiber: sma epim • multi-mode fiber: st epim • single-mode fiber: st epim • hardwired aui epim • unknown (for boards that don’t support media type) topology type ind...
Page 36
Using the emm-e6 hub view 2-20 monitoring hub performance to view the ip address table: 1. Click on to access the device menu. 2. Drag down to ip address table and release. Figure 2-11. Emm-e6 ip address table note that the i/f description for the highlighted interface is repeated in the text box at...
Page 37
Monitoring hub performance 2-21 using the emm-e6 hub view to view hub statistics at the network, module, or port levels: 1. Display the network, module, or port menu by clicking mouse button 3 in the appropriate area (refer to figure 2-5 , page 2-7 ). 2. Drag down to statistics and then right to eit...
Page 38
Using the emm-e6 hub view 2-22 monitoring hub performance general/error statistics the general/errors statistics windows display the following fields: received bytes the total number of bytes of data received by this network (channel), module, or port since the statistics window was opened or the re...
Page 39
Monitoring hub performance 2-23 using the emm-e6 hub view “legal” collisions, as opposed to the oow collisions described below) are a natural by-product of a busy network; if you are experiencing high numbers of collisions, it may be time to redirect network traffic by using bridges or routers. Extr...
Page 40
Using the emm-e6 hub view 2-24 monitoring hub performance runt frames the total number of received packets smaller than the minimum ethernet frame size of 64 bytes (excluding preamble). This minimum size is tied to the maximum propagation time of an ethernet network segment — the maximum propagation...
Page 41
Monitoring hub performance 2-25 using the emm-e6 hub view protocols/frames statistics the protocols/frames statistics windows display the following fields: protocols • osi frames • novell frames • banyan frames • decnet frames • xns (xerox network systems) frames • ip frames • ctron frames • appleta...
Page 42
Using the emm-e6 hub view 2-26 monitoring hub performance figure 2-13. Port source address list the source address list window displays the mac addresses of all devices that have transmitted packets through the selected port within a time period less than the sat’s defined aging time (addresses that...
Page 43: Managing The Hub
Managing the hub 2-27 using the emm-e6 hub view managing the hub in addition to the performance information described in the preceding sections, the hub view also provides you with the tools you need to configure your hub and keep it operating properly. Hub management functions include setting polli...
Page 44
Using the emm-e6 hub view 2-28 managing the hub figure 2-14. Emm-e6 polling intervals 3. To activate the desired polling, click mouse button 1 on the selection box to the right of each polling type field. 4. To change a polling interval, highlight the value you would like to change, and enter a new ...
Page 45
Managing the hub 2-29 using the emm-e6 hub view device configuration this polling interval controls how often a survey is conducted of the type of equipment installed in the emm-e6-managed hub; information from this poll would change the hub view to reflect the addition and/or removal of a mim or mi...
Page 46
Using the emm-e6 hub view 2-30 managing the hub configuring ric mim connections because each ric mim repeats packets independently, you can insert it into the network via backplane channels b or c, or isolate it to act as a self-contained network. To change a ric mim’s channel assignment: 1. Click m...
Page 47
Managing the hub 2-31 using the emm-e6 hub view mode. When configured to operate on channels b or c, the tpxmim provides its own repeating; when operating on channel a, its ports depend on the emm-e6 for repeater functionality. All tpxmim ports default to channel b when first installed. To configure...
Page 48
Using the emm-e6 hub view 2-32 managing the hub if you have configured the ports on the tpxmim so that they are connected to different channels, the board’s network connection box will display a letter representing each channel to which a tpxmim port is connected. If the entire board is in stand-alo...
Page 49
Managing the hub 2-33 using the emm-e6 hub view to change a port’s topology status: 1. Click mouse button 3 on the appropriate port status box to open the port menu. 2. Drag down to trunk type, then right to force trunk or not forced, and release. Once source address locking is enabled, a port’s top...
Page 50
Using the emm-e6 hub view 2-34 managing the hub enabling/disabling mim ports you can enable and disable ports on any manageable mim from both the module menu, which affects all ports on a single module, and the port menu, which affects individual ports. To enable or disable all ports in a module: 1....
Page 51: Chapter 3
3-1 chapter 3 alarm configuration using alarm configuration; setting repeater alarm configuration; setting port and module alarm configuration alarms work in conjunction with your network management system to let you know when defined thresholds have been reached. You define the conditions that will...
Page 52: Using Alarm Configuration
Alarm configuration 3-2 using alarm configuration using alarm configuration to open the alarms window from the icon: 1. Click on the appropriate emm-e6 icon to display the icon menu. 2. Drag down to alarm configuration and release. From the hub view: 1. In the hub view, click on to display the devic...
Page 53
Using alarm configuration 3-3 alarm configuration configuring alarms while configuring alarms for your emm-e6 you must set the threshold and timebase that will factor in triggering the alarm. From the repeater alarms window you set an alarm timebase that applies to all enabled alarms at the repeater...
Page 54: Setting Repeater Alarms
Alarm configuration 3-4 setting repeater alarms alignment if this check box is selected, all misaligned packets will be included in calculating the overall percentage of errors. A misaligned packet is one with an non-integral number of bytes; these are also sometimes referred to as framing errors. R...
Page 55
Setting repeater alarms 3-5 alarm configuration setting and changing alarms 1. In the alarms window, click mouse button 1 on a repeater selection in the scroll list. 2. Click mouse button 1 on to open the set repeater alarms window. Figure 3-2. Set repeater alarms window 3. In the set repeater alarm...
Page 56
Alarm configuration 3-6 setting module and port alarms setting module and port alarms the following sections describe procedures for setting module and port alarm limits. Module-level alarms are based on the combined traffic within a particular module, while port-level alarms are based on an individ...
Page 57
Setting module and port alarms 3-7 alarm configuration figure 3-3. Set module alarms window 3. Select one or more modules in the scroll list. To apply one set of conditions to all modules, you can either select each module in the list or use the set alarm for box at the bottom of the window to choos...
Page 58
Alarm configuration 3-8 setting module and port alarms 7. If you select yes for disable module on alarm, the defined condition will cause the device to disable the module. 8. Click mouse button 1 on . Setting port alarms 1. In the alarms window, click mouse button 1 on a repeater selection in the sc...
Page 59
Setting module and port alarms 3-9 alarm configuration 3. Select one or more ports in the scroll list. To apply one set of conditions to all ports, you can either select each port in the list or use the set alarm for box at the bottom of the window to choose either selected ports, which applies the ...
Page 60
Alarm configuration 3-10 setting module and port alarms.
Page 61: Chapter 4
4-1 chapter 4 link/seg traps what are link and segmentation traps; enabling and disabling these traps at the device, module, and port levels among the traps which cabletron devices are designed to generate are traps that indicate when a repeater port gains or loses a link signal, when the repeater s...
Page 62: What Is A Link Trap?
Link/seg traps 4-2 what is a link trap? What is a link trap? Some cabletron ethernet repeater ports — including rj45 twisted pair and fiber optic ports — generate a link signal to monitor the status of their connection with the device at the other end of the cable segment. If the cable is removed or...
Page 63
Enabling and disabling link/seg traps 4-3 link/seg traps from the hub view: 1. Click on to display the device menu. 2. Drag down to link/seg traps and release. From the command line (stand-alone mode): 1. From the appropriate directory, type spmarun r4hwtr the main repeater link/seg traps window, fi...
Page 64
Link/seg traps 4-4 enabling and disabling link/seg traps configuring link/seg traps for the repeater to enable or disable link and segmentation traps for all ports on a repeater: 1. In the repeater link/seg traps window, click mouse button 1 on the repeater interface for which you would like to conf...
Page 65
Enabling and disabling link/seg traps 4-5 link/seg traps figure 4-3. The module traps window 3. In the module traps window, click mouse button 1 to select the module for which you wish to configure link and segmentation traps. If the set trap status for field displays selected modules (the default s...
Page 66
Link/seg traps 4-6 enabling and disabling link/seg traps viewing and configuring link/seg traps for ports to enable or disable link and segmentation traps for individual ports: 1. In the repeater link/seg traps window, select a repeater in the scroll list. 2. Click mouse button 1 on ; the port traps...
Page 67
Enabling and disabling link/seg traps 4-7 link/seg traps 5. Click on the appropriate selection in the segmenting traps field to enable or disable segmenting traps, as desired. 6. Click on to save your changes; click on to exit the window..
Page 68
Link/seg traps 4-8 enabling and disabling link/seg traps.
Page 69: Chapter 5
5-1 chapter 5 repeater redundancy this chapter describes how to configure and enable redundant circuits setting network circuit redundancy the redundancy application gives you the ability to define redundant circuits for your emm-e6 to ensure that critical network connections remain operational. Eac...
Page 70
Repeater redundancy 5-2 setting network circuit redundancy from the command line (stand-alone mode) 1. From the appropriate directory, type: spmarun r4red the main repeater redundancy window, figure 5-1 , will appear. Figure 5-1. The repeater redundancy window configuring a redundant circuit to esta...
Page 71
Setting network circuit redundancy 5-3 repeater redundancy figure 5-2. The channel x redundancy window 2. If you want to change a circuit’s name or the number of retries, highlight the appropriate circuit and click . The change circuit window, figure 5-3 , will appear. Figure 5-3. The change circuit...
Page 72
Repeater redundancy 5-4 setting network circuit redundancy in the appropriate boxes, enter a new circuit name (up to 16 alphanumeric characters) and/or number of retries; retries is the number of times the emm-e6 tests the connection to the first ip address listed in the circuit addresses window bef...
Page 73
Setting network circuit redundancy 5-5 repeater redundancy 5. By default, all ports are created as inactive backup ports. You should set one port to be the primary port and one port to be the active port. Typically, the same port is both primary and active but this is not required. To select primary...
Page 74: Monitoring Redundancy
Repeater redundancy 5-6 monitoring redundancy monitoring redundancy once you have configured your redundant circuits, you can use the fields in the all circuits box to set the parameters that the emm-e6 uses to periodically test each of the circuits. The emm-e6 automatically polls all enabled circui...
Page 75: Chapter 6
6-1 chapter 6 source addressing displaying the source address list; setting the aging time; selecting the hash type; effects of source address locking; configuring source address traps; finding a source address displaying the source address list the source address list, or table (sat), contains the ...
Page 76
Source addressing 6-2 displaying the source address list the repeater source address window, figure 6-1 , will appear. Figure 6-1. The repeater source address window the repeater source address window provides a list of the repeater interfaces available on the emm-e6, as well as command buttons that...
Page 77
Displaying the source address list 6-3 source addressing to view the source address list for the device, highlight the interface for which you wish to view the sat, then click mouse button 1 on ; the source address list window, figure 6-2 , will appear. Figure 6-2. The source address list window the...
Page 78: Setting The Hash Type
Source addressing 6-4 setting the hash type setting the aging time the source address list aging time determines the minimum amount of time an inactive source address will remain in the source address table before it is purged. The source address timer runs continuously beginning at the time the dev...
Page 79: Locking Source Addresses
Locking source addresses 6-5 source addressing 2. Click mouse button 1 on ; the channel x source address list window, figure 6-2 ( page 6-3 ), will appear. 3. In the hash type field, click mouse button 1 on the appropriate selection to apply dec or nondec hashing toall ports on the selected repeater...
Page 80
Source addressing 6-6 locking source addresses in addition to activating the security measures as configured via the security application, locking source addresses has the following effects: • on devices running older versions of firmware, unlinked ports will be disabled immediately after locking ha...
Page 81
Configuring source address traps 6-7 source addressing • a port’s topology status (station or trunk) remains fixed while locking is in effect, even if the number of detected addresses changes. • any ports disabled due to a violation (or because they were unlinked when locking was enabled) must be ma...
Page 82
Source addressing 6-8 configuring source address traps other traps that will be sent in response to changes in source addressing (even when the above traps have been disabled) include: • porttypechanged traps are issued when a port’s topology status changes from station to trunk, or vice versa. The ...
Page 83
Configuring source address traps 6-9 source addressing module- and port-level traps to set module- and port-level source addressing traps, select the appropriate channel in the repeater source address window, then click on to enable and disable module-level traps, or on to enable and disable port-le...
Page 84
Source addressing 6-10 configuring source address traps figure 6-3. The module source address traps window to enable or disable port-level traps: 1. In the port source address traps window ( figure 6-4 , below), click mouse button 1 to select the port or ports for which you wish to enable or disable...
Page 85: Finding A Source Address
Finding a source address 6-11 source addressing figure 6-4. The port source address traps window 2. Click on the appropriate selection in the trap status field to enable or disable traps for the selected port(s), as desired. 3. Click on to save your changes. Finding a source address you can use the ...
Page 86
Source addressing 6-12 finding a source address figure 6-5. Find source address window 2. In the mac address field, enter the source address you wish to locate in a hexadecimal (xx:xx:xx:xx:xx:xx) format. 3. Click on . If the address is in the table at the time the search is initiated, the remaining...
Page 87: Chapter 7
7-1 chapter 7 security launching the security application; lanview secure defined; configuring security; enabling security and traps at the repeater, module, and port levels; security on non-lanview secure mims the security application allows you to configure and manage the lanview secure feature in...
Page 88: What Is
Security 7-2 what is lanviewsecure? From the command line (stand-alone mode): 1. From the appropriate directory, type spmarun r4sec the repeater security window, figure 7-1 , will appear. Figure 7-1. The repeater security window the repeater security window provides a list of the repeater interfaces...
Page 89
What is lanviewsecure? 7-3 security when the lanview secure feature is enabled, it provides two kinds of protection: intruder protection will prevent any unauthorized source addresses from communicating with the network via a secure port, and can be configured to secure both station and trunk ports;...
Page 90: Lanview
Security 7-4 what is lanviewsecure? Configurable violation response before lanview secure , any locked port which experienced a violation was shut down automatically; now, you can choose to allow ports to remain enabled even after an unsecured address has attempted to access a locked port. If you ch...
Page 91: Lanview
What is lanviewsecure? 7-5 security forced non-secure status with the original version of lanview secure , all ports except those which had been forced to trunk status could be locked, and would be locked automatically if locking were enabled at the repeater or module level. With the enhanced versio...
Page 92: Configuring Security
Security 7-6 configuring security configurable violation response you can still choose to allow ports to remain enabled even after an unsecured address has attempted to access a locked port. If you choose not to disable a port which has experienced a violation, however, the port’s only response to a...
Page 93
Configuring security 7-7 security figure 7-2. Channel x port security window the top portion of the window contains a list box which displays each port communicating on the selected channel, designated by module and port number. Each port’s current lock status, violation response, security level, an...
Page 94
Security 7-8 configuring security 2. In the on violation field, click to select disable if you want the port or ports to be disabled if any unauthorized source address is detected, or select nodisable if you wish the port to remain operational after a violation. Note that selecting the nodisable opt...
Page 95
Configuring security 7-9 security figure 7-3. The addresses window 3. On the left side of the window, the learned addresses list box will display all source addresses detected by the selected port during the last aging interval (see chapter 6, source address, for more information on the aging interv...
Page 96
Security 7-10 configuring security figure 7-4. Add mac address window d. Enter the desired mac address in an xx:xx:xx:xx:xx:xx format, then click on . A confirmation window will appear; if you click on yes to secure the address, it will appear in the secure addresses list box. 4. To secure addresses...
Page 97
Configuring security 7-11 security resetting learned addresses you can clear all learned and secured addresses out of a port’s address table, and allow that port to begin learning (and securing) new addresses, as follows: 1. In the repeater security window, click mouse button 1 on the repeater inter...
Page 98: Enabling Security And Traps
Security 7-12 enabling security and traps transmitted clean to all ports on that channel unless security has been enabled there, too. Packets bridged to channel a will always be transmitted clean to all ports, regardless of lock status; however, careful bridge configuration and prudent use of each p...
Page 99
Enabling security and traps 7-13 security • a newsourceaddress trapis generated when a station port — one receiving packets from zero, one, or two source addresses — receives a packet from a source address that is not currently in its source address table. Information included in this trap includes ...
Page 100
Security 7-14 enabling security and traps repeater-level security and traps locking ports at the repeater, or channel, level applies all applicable security (as configured via the port security window) to every port on the channel. To enable or disable security and traps for all ports on a repeater:...
Page 101
Enabling security and traps 7-15 security 5. Click mouse button 1 on to save your changes; the new status will be displayed in each field to the right of the field name. Click on to exit the window. Module-level security and traps locking ports at the module level applies all applicable protections ...
Page 102
Security 7-16 enabling security and traps figure 7-6. Channel x module security window 3. Use the set security for field or the mouse to select the module or modules for which you wish to configure security (note that the settings in the set security for field will change automatically as you click ...
Page 103
Enabling security and traps 7-17 security port-level security and traps to enable or disable security and/or traps at the port level: 1. In the repeater security window, click to selected the desired repeater interface, or channel, in the scroll list. 2. Click ; the channel x port security window, f...
Page 104
Security 7-18 enabling security and traps 4. In the security mode field, click mouse button 1 on the appropriate selection to apply full or continuous lock status to the selected port(s), or to unlock selected ports. (note that if your emm-e6 does not support the newest security enhancements, or if ...
Page 105: Chapter 8
8-1 chapter 8 front panel redundancy this chapter describes setting up front panel redundancy setting front panel redundancy when you configure front panel redundancy, you designate one of the emm-e6’s redundant front panel ports as the active port and the other port as the backup. Once a redundancy...
Page 106
Front panel redundancy 8-2 setting front panel redundancy the front panel redundancy window, figure 8-1 , will appear. Figure 8-1. Front panel redundancy window configuring a redundant circuit to configure a redundant circuit for the front panel: notes the spmarun script invoked first in the above c...
Page 107
Setting front panel redundancy 8-3 front panel redundancy 1. Use mouse button 1 to highlight a port, either aui #1 or aui #2. 2. Click on to access the add circuit address window, figure 8-2 . Figure 8-2. Add circuit address window 3. In the add circuit address window, enter the ip address of a netw...
Page 108
Front panel redundancy 8-4 setting front panel redundancy.
Page 109: Appendix A
A-1 appendix a emm-e6 mib structure emm-e6 management information base configuration ietf mib support in addition to its proprietary features, the emm-e6 currently supports the following ietf mibs: • rfc 1213 mib for network management of tcp/ip-based internets: mib-ii • rfc 1271 remote network moni...
Page 110
Emm-e6 mib structure a-2 emm-e6 mib structure mib components the emm-e6 mib components are described below. Note, however, that at any given time the component list displayed by your emm-e6 may not include some of the components described below, since the emm-e6 has the ability to alter the componen...
Page 111
Emm-e6 mib structure a-3 emm-e6 mib structure repeater one, repeater two, and repeater three the repeater mib components control all repeater functionality on the emm-e6’s three internal repeater channels: a, b, and c. These functions include port count, port enable/disable, port status, board numbe...
Page 112
Emm-e6 mib structure a-4 emm-e6 mib structure distributed lan monitor the distributed lan monitor, or dlm, mib component is a proprietary feature that allows you to delegate a management station’s polling responsibilities to one or more strategically placed “smart hub” devices — like an emm-e6 — on ...
Page 113
Emm-e6 mib structure a-5 emm-e6 mib structure a brief word about mib components and community names as mentioned above, the arrangement of the emm-e6’s mib into a series of components provides a tremendous amount of flexibility in controlling access to the emm-e6’s configuration and statistical info...
Page 114
Emm-e6 mib structure a-6 emm-e6 mib structure.
Page 115: Index
Index-1 index a active port 5-5 active ports 2-12 add circuit address 5-4 admin status 2-12 advanced router config 1-4 aging time 6-3, 6-4 aging time 2-26 alarm 3-5 alarm configuration 2-4, 3-2 alarm threshold 3-5 alarm types 3-5 alignment errors 2-23 atm_mib a-3 audible chassis alarm 2-14 avg packe...
Page 116
Index index-2 h history window 1-6 host services a-3 hostname 2-1 i ietf mibs, supported by emm-e6 a-1 inactive backup ports 5-5 intruder protection 7-3 ip address 2-3 ip address table 2-4 ip services a-3 isolated 2-30, 2-31 l lanviewsecure 7-2 on non-secure mims 7-5 learnmodechange trap 7-13 learns...
Page 117
Index-3 index rmon host a-4 runt frames 2-24 s sat 6-1 secure address assignment 7-3, 7-5 secure addresses 7-8 securestatechange trap 7-13 security 2-4, 6-5 security level 7-8 security parameters 7-6 security violation response 7-4, 7-6 segmentation traps 4-1 segmented 2-8 set trap status for 4-5, 4...
Page 118
Index index-4.