- DL manuals
- H3C
- Switch
- s5800 series
- Configuration Manual
H3C s5800 series Configuration Manual
Summary of s5800 series
Page 1
H3c s5820x&s5800 series ethernet switches layer 3 - ip services configuration guide hangzhou h3c technologies co., ltd. Http://www.H3c.Com document version: 6w103-20100716 product version: release 1110
Page 2
Copyright © 2009-2010, hangzhou h3c technologies co., ltd. And its licensors all rights reserved no part of this manual may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means without prior written consent of hangzhou h3c technologies co., ltd. Trademarks h3c, , aolynk, , h 3 care, , top g, , i...
Page 3: Preface
Preface the h3c s5800&s5820x documentation set includes 11 configuration guides, which describe the software features for the s5800&s5820x series ethernet switches and guide you through the software configuration procedures. These configuration guides also provide configuration examples to help you ...
Page 4
Conventions this section describes the conventions used in this documentation set. Command conventions convention description boldface bold text represents commands and keywords that you enter literally as shown. Italic italic text represents arguments that you replace with actual values. [ ] square...
Page 5
Category documents purposes psr750-a [ psr750-d ] power modules user manual describes the appearances, features, specifications, installation, and removal of the pluggable 750w power modules available for the products. Rps user manual describes the appearances, features, and specifications of the rp...
Page 6
Category documents purposes z s5800 series ethernet switches installation manual z s5820x series ethernet switches installation manual provides a complete guide to hardware installation and hardware specifications. Pluggable sfp[sfp+][xfp] transceiver modules installation guide guides you through in...
Page 7: Table of Contents
I table of contents 1 arp configuration·····································································································································1-1 arp overview················································································································...
Page 8
Ii ip addressing configuration example·····························································································4-4 displaying and maintaining ip addressing ·····························································································4-6 5 dhcp overview············...
Page 9
Iii dynamic ip address assignment configuration example ····························································6-19 self-defined option configuration example··················································································6-21 troubleshooting dhcp server configuration ·········...
Page 10
Iv protocols and standards ···············································································································10-2 configuring an interface to dynamically obtain an ip address through bootp ·······························10-2 displaying and maintaining bootp client config...
Page 11
V displaying and maintaining udp helper·······························································································14-2 udp helper configuration examples····································································································14-3 udp helper configuratio...
Page 12
Vi displaying and maintaining dhcpv6 ····································································································16-6 dhcpv6 configuration examples·········································································································16-7 stateless dhcpv6 co...
Page 13
Vii configuration example ················································································································17-39 configuring a gre over ipv6 tunnel··································································································17-41 configuration prer...
Page 14: Arp Configuration
1-1 1 arp configuration this chapter includes these sections: z arp overview z configuring arp z displaying and maintaining arp z arp configuration example arp overview arp function the address resolution protocol (arp) is used to resolve an ip address into a physical address (ethernet mac address, ...
Page 15
1-2 z sender hardware address: this field specifies the hardware address of the device sending the message. Z sender protocol address: this field specifies the protocol address of the device sending the message. Z target hardware address: this field specifies the hardware address of the device the m...
Page 16
1-3 arp request, in which the target ip address is the ip address of host b. After obtaining the mac address of host b, the gateway sends the packet to host b. Arp table after obtaining the mac address of a host, the device puts the ip-to-mac mapping into its own arp table. This mapping is used for ...
Page 17: Configuring Arp
1-4 configuring arp configuring a static arp entry a static arp entry is effective when the device is working normally. However, when the vlan or vlan interface to which a static arp entry corresponds is deleted, the entry, if long, will be deleted, and if short and resolved, will become unresolved....
Page 18
1-5 to do… use the command… remarks set the maximum number of dynamic arp entries that an interface can learn arp max-learning-num number optional 16384 by default for s5800 series ethernet switches 8192 by default for s5820x series ethernet switches setting the aging time for dynamic arp entries to...
Page 19: Configuration Gratuitous Arp
1-6 configuration gratuitous arp introduction to gratuitous arp in a gratuitous arp packet, the sender ip address and the target ip address are both the ip address of the device issuing the packet, the sender mac address is the mac address of the device, and the target mac address is the broadcast a...
Page 20
1-7 address of the vrrp group is associated with the real mac address of an interface, the sender mac address in the gratuitous arp packet is the mac address of the interface on the master router. For more information about vrrp, see vrrp configuration in the high availability configuration guide. C...
Page 22
1-9 figure 1-3 network diagram for configuring static arp entries configuration procedure configure the switch # create vlan 10. System-view [switch] vlan 10 [switch-vlan10] quit # add interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1 to vlan 10. [switch] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1 [switch-gigabitethernet1/0/1] ...
Page 23: Proxy Arp Configuration
2-1 2 proxy arp configuration this chapter includes these sections: z proxy arp overview z enabling proxy arp z displaying and maintaining proxy arp proxy arp overview a host may send an arp request for the mac address of another host that is isolated from the sending host at layer 2. Alternatively,...
Page 24: Enabling Proxy Arp
2-2 because host a considers that host b is on the same network, it broadcasts an arp request for the mac address of host b. Host b, however, cannot receive this request because it locates in a different broadcast domain. You can solve the problem by enabling proxy arp on switch. After that, switch ...
Page 25
2-3 to do… use the command… remarks enable proxy arp proxy-arp enable required disabled by default. Follow these steps to enable local proxy arp in vlan interface view: to do… use the command… remarks enter system view system-view — enter interface view interface interface-type interface-number — en...
Page 26
2-4 figure 2-3 network diagram for proxy arp configuration procedure # create vlan 2. System-view [switch] vlan 2 [switch-vlan2] quit # specify the ip address of interface vlan-interface 1. [switch] interface vlan-interface 1 [switch-vlan-interface1] ip address 192.168.10.99 255.255.255.0 # enable p...
Page 27
2-5 figure 2-4 network diagram for local proxy arp between isolated ports configuration procedure 1) configure switch b # add gigabitethernet1/0/3, gigabitethernet1/0/1 and gigabitethernet1/0/2 to vlan 2. Configure port isolation on host a and host b. System-view [switchb] vlan 2 [switchb-vlan2] por...
Page 28
2-6 local proxy arp configuration example in isolate-user-vlan network requirements as shown in figure 2-5 , switch b is attached to switch a. Vlan 5 on switch b is an isolate-user-vlan, which includes uplink port gigabitethernet1/0/1 and two secondary vlans, vlan 2 and vlan 3. Gigabitethernet1/0/2 ...
Page 29
2-7 [switcha-vlan5] quit [swticha-vlan5] interface vlan-interface 5 [swticha-vlan-interface5] ip address 192.168.10.100 255.255.0.0 the ping operation from host a to host b is unsuccessful because they are isolated at layer 2. # configure local proxy arp to implement layer 3 communication between vl...
Page 30: Arp Snooping Configuration
3-1 3 arp snooping configuration this chapter includes these sections: z arp snooping overview z configuring arp snooping z displaying and maintaining arp snooping arp snooping overview introduction arp snooping is used in layer 2 switching networks. It creates arp snooping entries using arp packets...
Page 32: Ip Addressing Configuration
4-1 4 ip addressing configuration this chapter includes these sections: z ip addressing overview z configuring ip addresses z displaying and maintaining ip addressing ip addressing overview this section covers these topics: z ip address classes z special ip addresses ip address classes on an ip netw...
Page 33
4-2 table 4-1 ip address classes and ranges class address range remarks a 0.0.0.0 to 127.255.255.255 the ip address 0.0.0.0 is used by a host at bootstrap for temporary communication. This address is never a valid destination address. Addresses starting with 127 are reserved for loopback test. Packe...
Page 34: Configuring Ip Addresses
4-3 figure 4-2 subnet a class b network subnetting is a tradeoff between subnets and accommodated hosts. For example, a class b network has 65,534 (2 16 – 2) addresses before being subnetted. After you break it down into 512 (2 9 ) subnets by using the first 9 bits of the host id, you have only 7 bi...
Page 36
4-5 figure 4-3 network diagram for ip addressing configuration configuration procedure # assign a primary ip address and a secondary ip address to vlan-interface 1. System-view [switch] interface vlan-interface 1 [switch-vlan-interface1] ip address 172.16.1.1 255.255.255.0 [switch-vlan-interface1] i...
Page 37
4-6 reply from 172.16.2.2: bytes=56 sequence=4 ttl=255 time=26 ms reply from 172.16.2.2: bytes=56 sequence=5 ttl=255 time=26 ms --- 172.16.2.2 ping statistics --- 5 packet(s) transmitted 5 packet(s) received 0.00% packet loss round-trip min/avg/max = 25/25/26 ms the output information shows that the...
Page 38: Dhcp Overview
5-1 5 dhcp overview introduction to dhcp the fast expansion and growing complexity of networks have resulted in scarce ip addresses assignable to hosts. Meanwhile, as many people need to take their laptops across networks, the ip addresses need to be changed accordingly. Therefore, related configura...
Page 39
5-2 z dynamic allocation: dhcp assigns an ip address to a client for a limited period of time, which is called a lease. Most dhcp clients obtain their addresses in this way. Dynamic ip address allocation process figure 5-2 dynamic ip address allocation process as shown in figure 5-2 , a dhcp client ...
Page 40: Dhcp Message Format
5-3 ip address lease extension the ip address dynamically allocated by a dhcp server to a client has a lease. When the lease expires, the ip address is reclaimed by the dhcp server. If the client wants to use the ip address longer, it has to extend the lease duration. When the half lease duration el...
Page 41: Dhcp Options
5-4 z giaddr: ip address of the first relay agent a request message traveled. Z chaddr: client hardware address. Z sname: server host name, from which the client obtained configuration parameters. Z file: bootfile name and path information, defined by the server to the client. Z options: optional pa...
Page 42
5-5 z option 33: static route option. It specifies a list of classful static routes (the destination addresses in these static routes are classful) that a client should add to its routing table. If option 121 exists, option 33 is ignored. For more information about dhcp options, refer to rfc 2132. S...
Page 43
5-6 figure 5-6 format of the value field of the acs parameter sub-option z the value field of the service provider identifier sub-option contains the service provider identifier. Z figure 5-7 shows the format of the value field of the pxe server address sub-option. Currently, the value of the pxe se...
Page 44
5-7 figure 5-8 sub-option 1 in normal padding format z sub-option 2: padded with the mac address of the dhcp relay agent interface or the mac address of the dhcp snooping device that received the client’s request. The following figure gives its format. The value of the sub-option type is 2, and that...
Page 45: Protocols and Standards
5-8 z sub-option 1: ip address of the primary network calling processor, which is a server serving as the network calling control source and providing program downloads. Z sub-option 2: ip address of the backup network calling processor that dhcp clients will contact when the primary one is unreacha...
Page 46: Dhcp Server Configuration
6-1 6 dhcp server configuration when configuring the dhcp server, go to these sections for information you are interested in: z introduction to dhcp server z dhcp server configuration task list z configuring an address pool for the dhcp server z enabling dhcp z enabling the dhcp server on an interfa...
Page 47
6-2 in addition to assigning ip addresses to dhcp clients on public networks, a multi-vpn-instance customer edge (mce) device serving as the dhcp server can also assign ip addresses to dhcp clients on private networks. Note that the ip address ranges of public and private networks or those of privat...
Page 48
6-3 address to the client. For the configuration of this address pool, refer to section configuring manual address allocation . 2) if the receiving interface has an extended address pool referenced, the dhcp server will assign an ip address from this address pool. If no ip address is available in th...
Page 49
6-4 dhcp server configuration task list complete the following tasks to configure the dhcp server: task remarks configuring an address pool for the dhcp server required enabling dhcp required enabling the dhcp server on an interface required applying an extended address pool on an interface required...
Page 50
6-5 creating a dhcp address pool when creating a dhcp address pool, specify it as a common address pool or an extended address pool. Follow these steps to create a dhcp address pool: to do… use the command… remarks enter system view system-view — create a dhcp address pool and enter its view dhcp se...
Page 53
6-8 to do… use the command… remarks enter extended address pool view dhcp server ip-pool pool-name extended — specify the ip address range network ip range min-address max-address required not specified by default. Specify the ip address mask network mask mask required not specified by default. Spec...
Page 54
6-9 configuring dns servers for the client when a dhcp client wants to access a host on the internet via the host name, it contacts a domain name system (dns) server holding host name-to-ip address mappings to get the host ip address. You can specify up to eight dns servers in the dhcp address pool....
Page 56
6-11 configuring option 184 parameters for the client with voice service to assign voice calling parameters along with an ip address to dhcp clients with voice service, you need to configure option 184 on the dhcp server. If option 55 in the request from a dhcp client contains option 184, the dhcp s...
Page 57
6-12 2) after getting related parameters, the dhcp client will send a tftp request to obtain the configuration file from the specified tftp server for system initialization. If the client cannot get such parameters, it will perform system initialization without loading any configuration file. To imp...
Page 59
6-14 enabling the dhcp server on an interface with the dhcp server enabled on an interface, upon receiving a client’s request, the dhcp server will assign an ip address from its address pool to the dhcp client. Follow these steps to enable the dhcp server on an interface: to do… use the command… rem...
Page 60
6-15 to do… use the command… remarks apply an extended address pool on the interface dhcp server apply ip-pool pool-name optional by default, the dhcp server has no extended address pool applied on its interface, and assigns an ip address from a common address pool to a requesting client. Only an ex...
Page 61
6-16 with the unauthorized dhcp server detection enabled, the device puts a record once for each dhcp server. The administrator needs to find unauthorized dhcp servers from the log information. Configuring ip address conflict detection to avoid ip address conflicts, the dhcp server checks whether th...
Page 62
6-17 configuring the handling mode for option 82 follow these steps to enable the dhcp server to handle option 82: to do… use the command… remarks enter system view system-view — enable the server to handle option 82 dhcp server relay information enable optional enabled by default. To support option...
Page 63
6-18 to do… use the command… remarks clear information about dhcp server statistics reset dhcp server statistics available in user view using the save command does not save dhcp server lease information. Therefore, when the system boots up or the reset dhcp server ip-in-use command is executed, no l...
Page 64
6-19 system-view [switcha] interface vlan-interface 2 [switcha-vlan-interface2] ip address 10.1.1.1 25 [switcha-vlan-interface2] quit 2) configure the dhcp server # enable dhcp. [switcha] dhcp enable # enable the dhcp server on vlan-interface 2. [switcha] interface vlan-interface 2 [switcha-vlan-int...
Page 65
6-20 z the domain name and dns server address on subnets 10.1.1.0/25 and 10.1.1.128/25 are the same. Therefore, the domain name suffix and dns server address can be configured only for subnet 10.1.1.0/24. Subnet 10.1.1.128/25 can inherit the configuration of subnet 10.1.1.0/24. In this example, the ...
Page 66
6-21 [switcha] dhcp server ip-pool 0 [switcha-dhcp-pool-0] network 10.1.1.0 mask 255.255.255.0 [switcha-dhcp-pool-0] domain-name aabbcc.Com [switcha-dhcp-pool-0] dns-list 10.1.1.2 [switcha-dhcp-pool-0] quit # configure dhcp address pool 1 (address range, gateway, lease duration, and wins server). [s...
Page 67
6-22 system-view [switcha] dhcp enable # enable the dhcp server on vlan-interface 2. [switcha] interface vlan-interface 2 [switcha-vlan-interface2] dhcp select server global-pool [switcha-vlan-interface2] quit # configure dhcp address pool 0. [switcha] dhcp server ip-pool 0 [switcha-dhcp-pool-0] net...
Page 68
7-1 7 dhcp relay agent configuration when configuring the dhcp relay agent, go to these sections for information you are interested in: z introduction to dhcp relay agent z dhcp relay agent configuration task list z configuring the dhcp relay agent z displaying and maintaining dhcp relay agent confi...
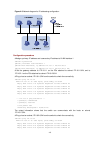
Page 69
7-2 figure 7-1 dhcp relay agent application ip network dhcp server dhcp relay agent dhcp client dhcp client dhcp client dhcp client no matter whether a relay agent exists or not, the dhcp server and client interact with each other in a similar way. The following describes the forwarding process on t...
Page 70
7-3 if a client’s requesting message has… handling strategy padding format the dhcp relay agent will… drop random drop the message. Keep random forward the message without changing option 82. Normal forward the message after replacing the original option 82 with the option 82 padded in normal format...
Page 71
7-4 configuring the dhcp relay agent enabling dhcp enable dhcp before performing other dhcp-related configurations. Follow these steps to enable dhcp: to do… use the command… remarks enter system view system-view — enable dhcp dhcp enable required disabled by default. Enabling the dhcp relay agent o...
Page 72
7-5 to do… use the command… remarks enter system view system-view — create a dhcp server group and add a server into the group dhcp relay server-group group-id ip ip-address required not created by default. Enter interface view interface interface-type interface-number — correlate the dhcp server gr...
Page 73
7-6 to do… use the command… remarks enter system view system-view — create a static binding dhcp relay security static ip-address mac-address [ interface interface-type interface-number ] optional no static binding is created by default. Enter interface view interface interface-type interface-number...
Page 75
7-8 to do… use the command… remarks configure the dhcp relay agent to send a dhcp-release request dhcp relay release ip client-ip required configuring the dhcp relay agent to support option 82 prerequisites you need to complete the following tasks before configuring the dhcp relay agent to support o...
Page 78
7-11 # enable dhcp. System-view [switcha] dhcp enable # add dhcp server 10.1.1.1 into dhcp server group 1. [switcha] dhcp relay server-group 1 ip 10.1.1.1 # enable the dhcp relay agent on vlan-interface 1. [switcha] interface vlan-interface 1 [switcha-vlan-interface1] dhcp select relay # correlate v...
Page 79
7-12 [switcha-vlan-interface1] dhcp select relay # correlate vlan-interface 1 to dhcp server group 1. [switcha-vlan-interface1] dhcp relay server-select 1 # enable the dhcp relay agent to support option 82, and perform option 82-related configurations. [switcha-vlan-interface1] dhcp relay informatio...
Page 80: Dhcp Client Configuration
8-1 8 dhcp client configuration when configuring the dhcp client, go to these sections for information you are interested in: z introduction to dhcp client z enabling the dhcp client on an interface z displaying and maintaining the dhcp client z dhcp client configuration example when multiple vlan i...
Page 81
8-2 z an interface can be configured to acquire an ip address in multiple ways, but these ways are mutually exclusive. The latest configuration will overwrite the previous one. Z after the dhcp client is enabled on an interface, no secondary ip address can be configured for the interface. Z if the i...
Page 82
8-3 figure 8-1 network diagram for dhcp client configuration example configuration procedure 1) configure switch a # specify the ip address of vlan-interface 2. System-view [switcha] interface vlan-interface 2 [switcha-vlan-interface2] ip address 10.1.1.1 24 [switcha-vlan-interface2] quit # enable t...
Page 83
8-4 destination: 20.1.1.0, mask: 255.255.255.0, nexthop: 10.1.1.2 dns server: 20.1.1.1 client id: 3030-3066-2e65-3230- 302e-3030-3032-2d45- 7468-6572-6e65-7430- 2f30 t1 will timeout in 4 days 23 hours 59 minutes 50 seconds. # use the display ip routing-table command to view the route information on ...
Page 84: Dhcp Snooping Configuration
9-1 9 dhcp snooping configuration when configuring dhcp snooping, go to these sections for information you are interested in: z dhcp snooping overview z configuring dhcp snooping basic functions z configuring dhcp snooping to support option 82 z displaying and maintaining dhcp snooping z dhcp snoopi...
Page 85
9-2 clients, ports that connect to dhcp clients, and vlans to which the ports belong. With dhcp snooping entries, dhcp snooping can implement the following: z arp detection: whether arp packets are sent from an authorized client is determined based on dhcp snooping entries. This feature prevents arp...
Page 86
9-3 figure 9-2 configure trusted ports in a cascaded network table 9-1 describes roles of the ports shown in figure 9-2 . Table 9-1 roles of ports device untrusted port trusted port disabled from recording binding entries trusted port enabled to record binding entries switch a gigabitethernet 1/0/1 ...
Page 87
9-4 if a client’s requesting message has… handling strategy padding format the dhcp snooping device will… drop — drop the message. Keep random forward the message without changing option 82. Normal forward the message after replacing the original option 82 with the option 82 padded in normal format....
Page 88
9-5 to do… use the command… remarks enter ethernet interface view interface interface-type interface-number — specify the port as trusted dhcp-snooping trust [ no-user-binding ] required untrusted by default. Z you need to specify the ports connected to the authorized dhcp servers as trusted to ensu...
Page 90
9-7 z you can enable dhcp snooping to support option 82 on layer 2 ethernet interfaces and layer 2 aggregation interfaces only. Z if a layer 2 ethernet interface is added to an aggregation group, enabling dhcp snooping to support option 82 on the interface will not take effect. After the interface q...
Page 91
9-8 dhcp snooping configuration examples dhcp snooping configuration example network requirements as shown in figure 9-3 , switch b is connected to a dhcp server through gigabitethernet 1/0/1, and to two dhcp clients through gigabitethernet 1/0/2 and gigabitethernet 1/0/3. Gigabitethernet 1/0/1 forw...
Page 92
9-9 [switchb] dhcp-snooping # specify gigabitethernet 1/0/1 as trusted. [switchb] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1 [switchb-gigabitethernet1/0/1] dhcp-snooping trust [switchb-gigabitethernet1/0/1] quit # configure gigabitethernet 1/0/2 to support option 82. [switchb] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/2 [...
Page 93: Bootp Client Configuration
10-1 10 bootp client configuration while configuring a bootp client, go to these sections for information you are interested in: z introduction to bootp client z configuring an interface to dynamically obtain an ip address through bootp z displaying and maintaining bootp client configuration if seve...
Page 94: Through Bootp
10-2 obtaining an ip address dynamically a dhcp server can take the place of the bootp server in the following dynamic ip address acquisition. A bootp client dynamically obtains an ip address from a bootp server in the following steps: 1) the bootp client broadcasts a bootp request, which contains i...
Page 95
10-3 displaying and maintaining bootp client configuration to do… use the command… remarks display bootp client information display bootp client [ interface interface-type interface-number ] available in any view bootp client configuration example network requirement as shown in figure 6-2 . Switch ...
Page 96: Ipv4 Dns Configuration
11-1 11 ipv4 dns configuration when configuring dns, go to these sections for information you are interested in: z dns overview z configuring the ipv4 dns client z configuring the dns proxy z displaying and maintaining ipv4 dns z ipv4 dns configuration examples z troubleshooting ipv4 dns configurati...
Page 97
11-2 figure 11-1 dynamic domain name resolution figure 11-1 shows the relationship between the user program, dns client, and dns server. The resolver and cache comprise the dns client. The user program and dns client can run on the same device or on different devices. The dns server and the dns clie...
Page 98
11-3 dns proxy introduction to dns proxy a dns proxy forwards dns requests and replies between dns clients and a dns server. As shown in figure 11-2 , a dns client sends a dns request to the dns proxy, which forwards the request to the designated dns server, and conveys the reply from the dns server...
Page 99
11-4 configuring the ipv4 dns client configuring static domain name resolution configuring static domain name resolution refers to specifying the mappings between host names and ipv4 addresses. Static domain name resolution allows applications such as telnet to contact hosts by using host names inst...
Page 100: Configuring The Dns Proxy
11-5 z you can configure up to six dns servers, including those with ipv6 addresses. Z you can specify up to ten dns suffixes. Configuring the dns proxy follow these steps to configure the dns proxy: to do… use the command… remarks enter system view system-view — enable dns proxy dns proxy enable re...
Page 101
11-6 figure 11-3 network diagram for static domain name resolution configuration procedure # configure a mapping between host name host.Com and ip address 10.1.1.2. System-view [sysname] ip host host.Com 10.1.1.2 # use the ping host.Com command to verify that the switch can use static domain name re...
Page 102
11-7 configuration procedure z before performing the following configuration, make sure that the switch and the host are accessible to each another via available routes, and the ip addresses of the interfaces are configured as shown figure 11-4 . Z this configuration may vary with different dns serv...
Page 103
11-8 figure 11-6 add a host in figure 11-6 , right click zone com, and then select new host to bring up a dialog box as shown in figure 11-7 . Enter host name host and ip address 3.1.1.1. Figure 11-7 add a mapping between domain name and ip address 2) configure the dns client # enable dynamic domain...
Page 104
11-9 system-view [sysname] dns resolve # specify the dns server 2.1.1.2. [sysname] dns server 2.1.1.2 # configure com as the name suffix. [sysname] dns domain com 3) configuration verification # use the ping host command on the switch to verify that the communication between the switch and the host ...
Page 105
11-10 configuration procedure before performing the following configuration, assume that switch a, the dns server, and the host are reachable to each other and the ip addresses of the interfaces are configured as shown in figure 11-8 . 1) configure the dns server this configuration may vary with dif...
Page 106
11-11 troubleshooting ipv4 dns configuration symptom after enabling the dynamic domain name resolution, the user cannot get the correct ip address. Solution z use the display dns dynamic-host command to verify that the specified domain name is in the cache. Z if the specified domain name does not ex...
Page 107: Ipv6 Dns Configuration
12-1 12 ipv6 dns configuration introduction to ipv6 dns ipv6 dns is responsible for translating domain names into ipv6 addresses. Similar to ipv4 dns, ipv6 dns involves static domain name resolution and dynamic domain name resolution. The functions and implementations of the two types of domain name...
Page 108
12-2 to do… use the command… remarks enable dynamic domain name resolution dns resolve required disabled by default. Specify a dns server dns server ipv6 ipv6-address [ interface-type interface-number ] required not specified by default. If the ipv6 address of a dns server is a link-local address, y...
Page 109
12-3 ipv6 dns configuration examples static domain name resolution configuration example network requirements as shown in figure 12-1 , static domain name resolution is configured on the switch and thus the switch can use the domain name host.Com to access the host whose ipv6 address is 1::2. Figure...
Page 110
12-4 dynamic domain name resolution and the domain name suffix are configured on the switch that serves as a dns client, and thus the switch can use domain name host to access the host with the domain name host.Com and the ipv6 address 1::1/64. Figure 12-2 network diagram of dynamic domain name reso...
Page 111
12-5 as shown in figure 12-3 , right click forward lookup zones, select new zone, and then follow the instructions to create a new zone named com. Figure 12-3 create a zone # create a mapping between the host name and the ipv6 address. As shown in figure 12-4 , right click zone com. Figure 12-4 crea...
Page 112
12-6 in figure 12-4 , select other new records to bring up a dialog box as shown in figure 12-5 . Select ipv6 host (aaa) as the resource record type. Figure 12-5 select the resource record type as shown in figure 12-6 , type host name host and ipv6 address 1::1, and then click ok..
Page 113
12-7 figure 12-6 add a mapping between domain name and ipv6 address 2) configure the dns client # enable dynamic domain name resolution. System-view [switch] dns resolve # specify the dns server 2::2. [switch] dns server ipv6 2::2 # configure com as the dns suffix. [switch] dns domain com 3) configu...
Page 114
12-8 bytes=56 sequence=3 hop limit=126 time = 1 ms reply from 1::1 bytes=56 sequence=4 hop limit=126 time = 1 ms reply from 1::1 bytes=56 sequence=5 hop limit=126 time = 1 ms --- host.Com ping statistics --- 5 packet(s) transmitted 5 packet(s) received 0.00% packet loss round-trip min/avg/max = 1/1/...
Page 115: Overview
13-1 13 ip performance optimization configuration this chapter includes these sections: z overview z enabling reception and forwarding of directed broadcasts to a directly connected network z configuring cut-through forwarding z enabling the syn cookie feature z configuring tcp attributes z configur...
Page 116
13-2 enabling forwarding of directed broadcasts to a directly connected network follow these steps to enable the device to forward directed broadcasts: to do… use the command… remarks enter system view system-view — enter interface view interface interface-type interface-number — enable the interfac...
Page 117
13-3 [switcha-vlan-interface2] ip address 2.2.2.2 24 z configure switch b # enable switch b to receive directed broadcasts. System-view [switchb] ip forward-broadcast # configure a static route to the host. [switchb] ip route-static 1.1.1.1 24 2.2.2.2 # configure an ip address for vlan-interface 2. ...
Page 118: Configuring Tcp Attributes
13-4 the syn cookie feature can prevent syn flood attacks. After receiving a tcp connection request, the server directly returns a syn ack message, instead of establishing an incomplete tcp connection. Only after receiving an ack message from the client can the server establish a connection, and the...
Page 119
13-5 to do… use the command… remarks configure the tcp finwait timer tcp timer fin-timeout time-value optional 675 seconds by default. Configure the size of tcp receive/send buffer tcp window window-size optional 8 kb by default. The actual length of the finwait timer is determined by the following ...
Page 120
13-6 3) icmp destination unreachable packets if the device receives an ip packet whose destination is unreachable, it drops the packet and sends an icmp destination unreachable error packet to the source. Conditions for sending icmp destination unreachable packets: z if a packet matches no route, th...
Page 121
13-7 the device stops sending “ttl timeout” icmp error packets if you disable sending of icmp timeout packets. However, “reassembly timeout” error packets are still sent normally. Displaying and maintaining ip performance optimization to do… use the command… remarks display current tcp connection st...
Page 122: Udp Helper Configuration
14-1 14 udp helper configuration this chapter includes these sections: z introduction to udp helper z configuring udp helper z displaying and maintaining udp helper z udp helper configuration examples currently, only vlan interfaces support udp helper related configuration. Introduction to udp helpe...
Page 124
14-3 udp helper configuration examples udp helper configuration example network requirements on switch a, configure udp helper to forward broadcast packets with udp destination port number 55 and destination ip address 255.255.255.255 or 10.110.255.255 to the destination server 10.2.1.1/16. Figure 1...
Page 125: Ipv6 Basics Configuration
15-1 15 ipv6 basics configuration this chapter includes these sections: z ipv6 overview z ipv6 basics configuration task list z configuring basic ipv6 functions z configuring ipv6 ndp z configuring pmtu discovery z configuring ipv6 tcp properties z configuring icmpv6 packet sending z displaying and ...
Page 126
15-2 figure 15-1 ipv4 packet header format and basic ipv6 packet header format larger address space the source and destination ipv6 addresses are 128 bits (or 16 bytes) long. Ipv6 can provide 3.4 x 10 38 addresses to meet the requirements of hierarchical address division and the allocation of public...
Page 127
15-3 router discovery messages, and icmpv4 redirect messages and provides a series of other functions. Flexible extension headers ipv6 cancels the options field in the header and introduces optional extension headers to provide scalability and improve efficiency. The options field in the ipv4 packet...
Page 128
15-4 identified by that address. The nearest interface is chosen according to the routing protocols' measure of distance. There are no broadcast addresses in ipv6. Their function is replaced by multicast addresses. The type of an ipv6 address is designated by the first several bits called the format...
Page 129
15-5 z the unspecified address is 0:0:0:0:0:0:0:0 (or ::). It cannot be assigned to any node. Before acquiring a valid ipv6 address, a node fills this address in the source address field of ipv6 packets. The unspecified address cannot be used as a destination ipv6 address. Multicast addresses ipv6 m...
Page 130
15-6 figure 15-2 convert a mac address into an eui-64 address-based interface identifier z on a tunnel interface the lower 32 bits of the eui-64 address-based interface identifier are the source ipv4 address of the tunnel interface. The higher 32 bits of the eui-64 address-based interface identifier...
Page 131
15-7 icmpv6 message type function responds to an rs message. Router advertisement (ra) message 134 advertises information such as the prefix information options and flag bits (with the ra message suppression function disabled). Redirect message 137 informs the source host of a better next hop on the...
Page 132
15-8 ipv4). Dad is accomplished through ns and na message exchange. Figure 15-4 shows the dad process. Figure 15-4 duplicate address detection the dad process is: 1) host a sends an ns message whose source address is the unspecified address and whose destination address is the corresponding solicite...
Page 133
15-9 z in addition to an address prefix, the prefix information option also contains the preferred lifetime and valid lifetime of the address prefix. Nodes update the preferred lifetime and valid lifetime accordingly through periodic ra messages. Z an automatically generated address is applicable wi...
Page 134
15-10 2) if the mtu supported by a forwarding interface is smaller than the packet, the device discards the packet and returns an icmpv6 error packet containing the interface mtu to the source host. 3) after receiving the icmpv6 error packet, the source host uses the returned mtu to limit the packet...
Page 135
15-11 z rfc 1981: path mtu discovery for ip version 6 z rfc 2375: ipv6 multicast address assignments z rfc 2460: internet protocol, version 6 (ipv6) specification. Z rfc 2461: neighbor discovery for ip version 6 (ipv6) z rfc 2462: ipv6 stateless address autoconfiguration z rfc 2463: internet control...
Page 136
15-12 z eui-64 format: when the eui-64 format is used, the ipv6 address prefix of an interface is the configured prefix, and the interface identifier is generated automatically by the interface. Z manual configuration: ipv6 site-local addresses or global unicast addresses are configured manually. Z ...
Page 137
15-13 to do... Use the command... Remarks manually assign a link-local address for the interface ipv6 address ipv6-address link-local configured for an interface, a link-local address will be generated automatically. Note that: z an interface can have only one link-local address, but can have multip...
Page 138: Configuring Ipv6 Ndp
15-14 configuring ipv6 ndp configuring a static neighbor entry the ipv6 address of a neighboring node can be resolved into a link-layer address dynamically through ns and na messages or through a manually configured static neighbor entry. The device uniquely identifies a static neighbor entry by the...
Page 139
15-15 to do… use the command… remarks enter system view system-view — enter interface view interface interface-type interface-number — configure the maximum number of neighbors dynamically learned by the interface ipv6 neighbors max-learning-num number optional by default, an interface on an s5800 s...
Page 140
15-16 parameters description o flag this field determines whether hosts use the stateful autoconfiguration to acquire other configuration information. If the o flag is set to 1, hosts use the stateful autoconfiguration (for example, through a dhcp server) to acquire other configuration information. ...
Page 141
15-17 to do… use the command… remarks disable the ra message suppression undo ipv6 nd ra halt required by default, ra messages are suppressed. Configure the maximum and minimum intervals for sending ra messages ipv6 nd ra interval max-interval-value min-interval-value optional by default, the maximu...
Page 142
15-18 to do… use the command… remarks set the ns retransmission timer ipv6 nd ns retrans-timer value optional by default, the local interface sends ns messages at 1000 ms intervals, and the value of the retrans timer field in ra messages sent by the local interface is 0. Set the reachable time ipv6 ...
Page 143: Configuring Pmtu Discovery
15-19 to do… use the command… remarks configure the number of attempts to send an ns message for dad ipv6 nd dad attempts value optional 1 by default. When the value argument is set to 0, dad is disabled. Configuring pmtu discovery configuring a static pmtu for a specified ipv6 address you can confi...
Page 144
15-20 z synwait timer: when a syn packet is sent, the synwait timer is triggered. If no response packet is received before the synwait timer expires, the ipv6 tcp connection establishment fails. Z finwait timer: when the ipv6 tcp connection status is fin_wait_2, the finwait timer is triggered. If no...
Page 146
15-22 to do… use the command… remarks enable sending of icmpv6 time exceeded messages ipv6 hoplimit-expires enable optional enabled by default. Displaying and maintaining ipv6 basics configuration to do… use the command… remarks display the ipv6 fib entries display ipv6 fib [ slot slot-number ] [ ip...
Page 148
15-24 system-view [switcha] ipv6 # specify a global unicast address for vlan-interface 2. [switcha] interface vlan-interface 2 [switcha-vlan-interface2] ipv6 address 3001::1/64 [switcha-vlan-interface2] quit # specify a global unicast address for vlan-interface 1, and allow it to advertise ra messag...
Page 149
15-25 nd dad is enabled, number of dad attempts: 1 nd reachable time is 30000 milliseconds nd retransmit interval is 1000 milliseconds hosts use stateless autoconfig for addresses ipv6 packet statistics: inreceives: 25829 intooshorts: 0 intruncatedpkts: 0 inhoplimitexceeds: 0 inbadheaders: 0 inbadop...
Page 150
15-26 ipv6 packet statistics: inreceives: 272 intooshorts: 0 intruncatedpkts: 0 inhoplimitexceeds: 0 inbadheaders: 0 inbadoptions: 0 reasmreqds: 0 reasmoks: 0 infragdrops: 0 infragtimeouts: 0 outfragfails: 0 inunknownprotos: 0 indelivers: 159 outrequests: 1012 outforwdatagrams: 35 innoroutes: 0 into...
Page 151
15-27 inbadheaders: 0 inbadoptions: 0 reasmreqds: 0 reasmoks: 0 infragdrops: 0 infragtimeouts: 0 outfragfails: 0 inunknownprotos: 0 indelivers: 117 outrequests: 83 outforwdatagrams: 0 innoroutes: 0 intoobigerrors: 0 outfragoks: 0 outfragcreates: 0 inmcastpkts: 28 inmcastnotmembers: 0 outmcastpkts: 7...
Page 152
15-28 round-trip min/avg/max = 3/3/3 ms as shown in the output information, switch b can ping switch a and host. Troubleshooting ipv6 basics configuration symptom the peer ipv6 address cannot be pinged. Solution z use the display current-configuration command in any view or the display this command ...
Page 153: Dhcpv6 Configuration
16-1 16 dhcpv6 configuration this chapter includes these sections: z dhcpv6 configuration overview z configuring the dhcpv6 client z configuring the dhcpv6 relay agent z displaying and maintaining dhcpv6 z dhcpv6 configuration examples dhcpv6 configuration overview the dynamic host configuration pro...
Page 154
16-2 typical dhcpv6 network application figure 16-2 network diagram for dhcpv6 figure 16-2 shows a typical dhcpv6 network. A dhcpv6 client uses a multicast address to contact the dhcpv6 server on the local link to obtain an ipv6 address and other configuration parameters. If the dhcpv6 server reside...
Page 155
16-3 with an ipv6 address obtained through stateless address autoconfiguration, a device automatically enables the stateless dhcpv6 function after it receives an ra message with the managed address configuration flag (“m” flag) set to 0 and with the other stateful configuration flag (“o” flag) set t...
Page 156
16-4 2) after receiving the request, the dhcpv6 relay agent encapsulates the request into the relay message option of a relay-forward message, and sends the message to the dhcpv6 server. 3) after obtaining the request from the relay-forward message, the dhcpv6 server selects an ipv6 address and othe...
Page 157
16-5 z for detailed information about the ipv6 address auto command, see ipv6 basics configuration commands in the layer 3 - ip services command reference. Z with an ipv6 address obtained through stateless address autoconfiguration, a device automatically enables the stateless dhcpv6 function to obt...
Page 158
16-6 z executing the ipv6 dhcp relay server-address command repeatedly can specify multiple dhcpv6 servers, and up to eight dhcpv6 servers can be specified for an interface. After receiving requests from dhcpv6 clients, the dhcpv6 relay agent forwards the requests to all the specified dhcpv6 servers...
Page 159
16-7 dhcpv6 configuration examples stateless dhcpv6 configuration example network requirements as shown in figure 16-5 , through stateless dhcpv6, switch a obtains the dns server address, domain name, and other information from the server. Switch b acts as the gateway to send ra messages periodicall...
Page 160
16-8 [switcha-vlan-interface2] display ipv6 dhcp client interface vlan-interface 2 vlan-interface2 is in stateless dhcpv6 client mode state is open preferred server: reachable via address : fe80::213:7fff:fef6:c818 duid : 0003000100137ff6c818 dns servers : 1:2:3::5 1:2:4::7 domain names : abc.Com sy...
Page 161
16-9 configuration procedure 1) configure switch a as a dhcpv6 relay agent # enable the ipv6 packet forwarding function. System-view [switcha] ipv6 # configure the ipv6 addresses of vlan-interface 1 and vlan-interface 2 respectively. [switcha] interface vlan-interface 2 [switcha-vlan-interface2] ipv...
Page 162: Tunneling Configuration
17-1 17 tunneling configuration this chapter includes these sections: z tunneling overview z tunneling configuration task list z configuring an ipv6 manual tunnel z configuring a 6to4 tunnel z configuring an isatap tunnel z configuring an ipv4 over ipv4 tunnel z configuring an ipv4 over ipv6 tunnel ...
Page 163
17-2 z the term tunnel used throughout this document refers to an ipv4/ipv6 transition tunnel, ipv4 over ipv4 tunnel or ipv6 over ipv6 tunnel unless otherwise specified. Z for information about vpn, see mce configuration in the layer 3 - ip routing configuration guide. Introduction to ipv4/ipv6 tran...
Page 164
17-3 the devices at both ends of an ipv6 over ipv4 tunnel must support the ipv4/ipv6 dual stack. Figure 17-1 ipv6 over ipv4 tunnel the ipv6 over ipv4 tunnel processes packets in the following way: 1) a host in the ipv6 network sends an ipv6 packet to the device at the source end of the tunnel. 2) af...
Page 165
17-4 type according to the way an ipv6 packet is encapsulated, ipv6 over ipv4 tunnels are divided into the following types: tunnel type tunnel mode manually configured tunnel ipv6 manual tunnel 6to4 tunnel automatic tunnel intra-site automatic tunnel addressing protocol (isatap) tunnel the configura...
Page 166
17-5 with the application of the ipv6 technology, there will be more and more ipv6 hosts in the existing ipv4 network. The isatap tunneling technology provides a satisfactory solution for ipv6 application. An isatap tunnel is a point-to-point automatic tunnel. The destination of a tunnel can automat...
Page 167
17-6 2) the ip protocol stack determines how to route the packet according to the destination address in the ip header. If the packet needs to be routed to the ipv4 host connected to router b, the packet is sent to router a’s tunnel interface that is connected to router b. 3) after the tunnel interf...
Page 168
17-7 5) if the passenger protocol is ipv4 or ipv6, the packet is sent to the tunnel processing module for decapsulation. 6) the decapsulated packet is sent to the corresponding protocol module for the secondary routing process. Gre tunnel generic routing encapsulation (gre) is a protocol designed fo...
Page 169
17-8 figure 17-7 format of an x packet encapsulated for transmission over an ip tunnel these are the terms involved: z payload: packet that needs to be encapsulated and transmitted. Z passenger protocol: protocol that the payload packet uses, ipx in the example. Z encapsulation or carrier protocol: ...
Page 170
17-9 task remarks configuring a tunnel interface required configuring an ipv6 manual tunnel configuring a 6to4 tunnel configuring an ipv6 over ipv4 tunnel configuring an isatap tunnel optional use one as needed. Configuring an ipv4 over ipv4 tunnel optional configuring an ipv4 over ipv6 tunnel optio...
Page 171
17-10 to do… use the command… remarks reference a service loopback group service-loopback-group number required by default, the tunnel does not reference any service loopback group. Set the mtu of the interface mtu size optional 64000 by default shut down the tunnel interface shutdown optional by de...
Page 172
17-11 to do… use the command… remarks a site-local address ipv6 address ipv6-address/prefix-length eui-64 by default, no ipv6 global unicast address or site-local address is configured for the tunnel interface. Ipv6 address auto link-local interface configure a link-local ipv6 address ipv6 address i...
Page 173
17-12 configuration example network requirements as shown in figure 17-8 , two ipv6 networks are connected to an ipv4 network through switch a and switch b respectively. Configure an ipv6 manual tunnel between switch a and switch b to make the two ipv6 networks reachable to each other. Figure 17-8 n...
Page 174
17-13 [switcha] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/3 [switcha-gigabitethernet1/0/3] undo stp enable [switcha-gigabitethernet1/0/3] port service-loopback group 1 [switcha-gigabitethernet1/0/3] quit # reference service loopback group 1 on the tunnel. [switcha] interface tunnel 0 [switcha-tunnel0] service-l...
Page 175
17-14 line protocol current state :up ipv6 is enabled, link-local address is fe80::c0a8:6401 global unicast address(es): 3001::1, subnet is 3001::/64 joined group address(es): ff02::1:ff00:0 ff02::1:ff00:1 ff02::1:ffa8:6401 ff02::2 ff02::1 mtu is 1480 bytes nd reachable time is 30000 milliseconds nd...
Page 176: Configuring A 6To4 Tunnel
17-15 5 packet(s) transmitted 5 packet(s) received 0.00% packet loss round-trip min/avg/max = 1/1/1 ms configuring a 6to4 tunnel configuration prerequisites z configure ip addresses for interfaces (such as the vlan interface, and loopback interface) on the device to ensure normal communication. Z sp...
Page 178
17-17 figure 17-9 network diagram for a 6to4 tunnel configuration procedure make sure that switch a and switch b have the corresponding vlan interfaces created and can reach each other. Z configuration on switch a # enable ipv6. System-view [switcha] ipv6 # configure an ipv4 address for vlan-interfa...
Page 179
17-18 [switcha-gigabitethernet1/0/3] quit # reference service loopback group 1 on the tunnel. [switcha] interface tunnel 0 [switcha-tunnel0] service-loopback-group 1 [switcha-tunnel0] quit # configure a static route whose destination address is 2002::/16 and next-hop is the tunnel interface. [switch...
Page 180: Configuring An Isatap Tunnel
17-19 reply from 2002:501:101:1::2: bytes=32 time=1ms reply from 2002:501:101:1::2: bytes=32 time=1ms reply from 2002:501:101:1::2: bytes=32 time ping statistics for 2002:501:101:1::2: packets: sent = 4, received = 4, lost = 0 (0% loss), approximate round trip times in milli-seconds: minimum = 0ms, ...
Page 181
17-20 to do… use the command… remarks specify the isatap tunnel mode tunnel-protocol ipv6-ipv4 isatap required by default, the tunnel is a gre over ipv4 tunnel. The same tunnel mode should be configured at both ends of the tunnel. Otherwise, packet delivery will fail. Configure a source address or i...
Page 182
17-21 figure 17-10 network diagram for an isatap tunnel configuration procedure z make sure that the corresponding vlan interfaces have been created on the switch. Z make sure that vlan-interface 101 on the isatap switch and the isatap host are reachable to each other. Z configuration on the switch ...
Page 183
17-22 # reference service loopback group 1 on the tunnel. [switch] interface tunnel 0 [switch-tunnel0] service-loopback-group 1 [switch-tunnel0] quit # configure a static route to the isatap host. [switch] ipv6 route-static 2001:: 16 tunnel 0 z configuration on the isatap host the specific configura...
Page 184
17-23 default site prefix length 48 # by comparison, it is found that the host acquires the address prefix 2001::/64 and automatically generates the address 2001::5efe:2.1.1.2. Meanwhile, “uses router discovery” is displayed, indicating that the router discovery function is enabled on the host. At t...
Page 185
17-24 to do… use the command… remarks specify the ipv4 over ipv4 tunnel mode tunnel-protocol ipv4-ipv4 optional by default, the tunnel is a gre over ipv4 tunnel. The same tunnel mode should be configured at both ends of the tunnel. Otherwise, packet delivery will fail. Configure a source address or ...
Page 186
17-25 figure 17-11 network diagram for an ipv4 over ipv4 tunnel configuration procedure make sure that switch a and switch b have the corresponding vlan interfaces created and are reachable to each other. Z configuration on switch a # configure an ipv4 address for vlan-interface 100. System-view [sw...
Page 187
17-26 [switcha-gigabitethernet1/0/3] port service-loopback group 1 [switcha-gigabitethernet1/0/3] quit # reference service loopback group 1 on the tunnel. [switcha] interface tunnel 1 [switcha-tunnel1] service-loopback-group 1 [switcha-tunnel1] quit # configure a static route from switch through the...
Page 188
17-27 tunnel1 current state: up line protocol current state: up description: tunnel1 interface the maximum transmit unit is 1480 internet address is 10.1.2.1/24 primary encapsulation is tunnel, service-loopback-group id is 1. Tunnel source 2.1.1.1, destination 3.1.1.1 tunnel protocol/transport ip/ip...
Page 189
17-28 configuring an ipv4 over ipv6 tunnel configuration prerequisites z configure ip addresses for interfaces (such as the vlan interface, and loopback interface) on the device to ensure normal communication. Z specify one of the above interfaces as the source interface of the tunnel. Z ensure reac...
Page 190
17-29 z to encapsulate and forward ipv4 packets whose destination address does not belong to the network segment where the receiving tunnel interface resides, you need to configure a static route or dynamic routing for forwarding those packets through this tunnel interface. If you configure a static...
Page 191
17-30 [switcha] ipv6 # configure an ipv4 address for vlan-interface 100. [switcha] interface vlan-interface 100 [switcha-vlan-interface100] ip address 30.1.1.1 255.255.255.0 [switcha-vlan-interface100] quit # configure an ipv6 address for vlan-interface 101 [switcha] interface vlan-interface 101 [sw...
Page 192
17-31 # create the interface tunnel 2. [switchb] interface tunnel 2 # configure an ipv4 address for the interface tunnel 2. [switchb-tunnel2] ip address 30.1.2.2 255.255.255.0 # configure the tunnel encapsulation mode. [switchb-tunnel2] tunnel-protocol ipv4-ipv6 # configure the source address for th...
Page 193
17-32 description: tunnel2 interface the maximum transmit unit is 1460 internet address is 30.1.2.2/24 primary encapsulation is tunnel, service-loopback-group id is 1. Tunnel source 2002::0002:0001, destination 2002::0001:0001 tunnel protocol/transport ip/ipv6 last clearing of counters: never last 3...
Page 195
17-34 z to encapsulate and forward ipv6 packets whose destination address does not belong to the network segment where the receiving tunnel interface resides, you need to configure a static route or dynamic routing for forwarding those packets through this tunnel interface. If you configure a static...
Page 196
17-35 make sure that switch a and switch b have the corresponding vlan interfaces created and can reach each other. Z configuration on switch a # enable ipv6. System-view [switcha] ipv6 # configure an ipv6 address for vlan-interface 100. [switcha] interface vlan-interface 100 [switcha-vlan-interface...
Page 197
17-36 system-view [switchb] ipv6 # configure an ipv6 address for vlan-interface 100. [switchb] interface vlan-interface 100 [switchb-vlan-interface100] ipv6 address 2002:3::1 64 [switchb-vlan-interface100] quit # configure an ipv6 address for vlan-interface 101. [switchb] interface vlan-interface 10...
Page 198
17-37 ff02::1:ff00:0 ff02::2 ff02::1 mtu is 1460 bytes nd reachable time is 30000 milliseconds nd retransmit interval is 1000 milliseconds hosts use stateless autoconfig for addresses ipv6 packet statistics: ... Display ipv6 interface tunnel 2 verbose tunnel2 current state :up line protocol current ...
Page 199
17-38 configuring a gre over ipv4 tunnel configuration prerequisites interfaces on a device, such as vlan interfaces, and loopback interfaces, are configured with ipv4 addresses and can communicate. These interfaces can be used as the source of a virtual tunnel interface to ensure the reachability o...
Page 200
17-39 z the source address and destination address of a tunnel uniquely identify a path. They must be configured at both ends of the tunnel and the source address at one end must be the destination address at the other end and vice versa. Z tunnel interfaces using the same encapsulation protocol mus...
Page 201
17-40 [switcha] interface tunnel 1 # configure an ipv4 address for interface tunnel 1. [switcha-tunnel1] ip address 10.1.2.1 255.255.255.0 # configure the tunnel encapsulation mode. [switcha-tunnel1] tunnel-protocol gre # configure the source address of interface tunnel 1 to be the ip address of the...
Page 202
17-41 [switchb] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/3 [switchb-gigabitethernet1/0/3] undo stp enable [switchb-gigabitethernet1/0/3] port service-loopback group 1 # apply service loopback group 1 to the tunnel in tunnel interface view. [switchb-gigabitethernet1/0/3] quit [switchb] interface tunnel 1 [switc...
Page 204
17-43 figure 17-15 network diagram for a gre over ipv6 tunnel configuration procedure before the configuration, make sure that switch a and switch b can reach each other. 1) configure switch a system-view # enable ipv6. [switcha] ipv6 # configure interface vlan-interface 100. [switcha] interface vla...
Page 205
17-44 # add interface gigabitethernet 1/0/3 to service loopback group 1. [switcha] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/3 [switcha-gigabitethernet1/0/3] undo stp enable [switcha-gigabitethernet1/0/3] port service-loopback group 1 # apply service loopback group 1 to the tunnel in tunnel interface view. [swi...
Page 206
17-45 [switchb-tunnel0] quit # configure a static route from switch b through interface tunnel 0 to group 1. [switchb] ip route-static 10.1.1.0 255.255.255.0 tunnel 0 displaying and maintaining tunneling configuration to do… use the command… remarks display information about tunnel interfaces displa...
Page 207: Index
18-1 18 index 6to4 tunnel configuration example 17-16 a allocation mechanisms 5-1 application environment of trusted ports 9-2 arp function 1-1 arp message format 1-1 arp operation 1-2 arp table 1-3 assigning an ip address to an interface 4-3 b basic concepts 16-1 bootp application 10-1 c configurat...
Page 208
18-2 d dhcp address pool 6-2 dhcp options overview 5-4 dhcp relay agent configuration example 7-10 dhcp relay agent option 82 support configuration example 7-11 dhcp relay agent support for option 82 7-2 dhcp snooping configuration example 9-8 dhcp snooping option 82 support configuration example 9-...
Page 209
18-3 proxy arp 2-1 s self-defined option configuration example 6-21 self-defined options 5-5 setting the aging time for dynamic arp entries 1-5 special ip addresses 4-2 stateless dhcpv6 configuration example 16-7 stateless dhcpv6 configuration 16-2 static domain name resolution 11-1 static ip addres...