- DL manuals
- H3C
- Switch
- s5800 series
- High Availability Configuration Manual
H3C s5800 series High Availability Configuration Manual
Summary of s5800 series
Page 1
H3c s5820x&s5800 switch series high availability configuration guide hangzhou h3c technologies co., ltd. Http://www.H3c.Com software version: release 1211 document version: 6w100-20110415.
Page 2
Copyright © 2011, hangzhou h3c technologies co., ltd. And its licensors all rights reserved no part of this manual may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means without prior written consent of hangzhou h3c technologies co., ltd. Trademarks h3c, , aolynk, , h 3 care, , top g, , irf, n...
Page 3
Preface the h3c s5800&s5820x documentation set includes 12 configuration guides, which describe the software features for the s5800&s5820x switch series and guide you through the software configuration procedures. These configuration guides also provide configuration examples to help you apply softw...
Page 4
Configuration guide added and modified features cfd added features: itu-t y.1731 modified features: • change configuring the lb function in system view to configuring the lb function in any view • change configuring the lt function in system view to configuring the lt function in any view dldp — rrp...
Page 5
Gui conventions convention description boldface window names, button names, field names, and menu items are in boldface. For example, the new user window appears; click ok. > multi-level menus are separated by angle brackets. For example, file > create > folder. Symbols convention description warnin...
Page 6
Category documents purposes rps user manual describes the appearances, features, and specifications of the rps units available for the products. Lsw1fan and lsw1bfan installation manual describes the appearances, specifications, installation, and removal of the pluggable fan modules available for th...
Page 7
Category documents purposes pluggable sfp[sfp+][xfp] transceiver modules installation guide guides you through installing sfp/sfp+/xfp transceiver modules. • s5800-60c-pwr switch video installation guide • s5820x-28c switch video installation guide shows how to install the h3c s5800-60c-pwr and h3c ...
Page 8
I contents high availability overview··········································································································································· 1 availability requirements································································································...
Page 9
Ii displaying and maintaining cfd································································································································· 29 cfd configuration example ············································································································...
Page 10
Iii smart link collaboration mechanisms ················································································································· 96 smart link configuration task list ············································································································...
Page 11
Iv configuring router priority, preemptive mode and tracking function····························································136 configuring vf tracking······································································································································137 config...
Page 12
V configuring bfd for a vrrp backup to monitor the master············································································202 configuring bfd for the vrrp master to monitor the uplinks··········································································205 static routing-track-nqa co...
Page 13
1 high availability overview communication interruptions can seriously affect widely-deployed value-added services such as iptv and video conference. Therefore, the basic network infrastructures must be able to provide high availability. The following are the effective ways to improve availability: ...
Page 14
2 mttr = fault detection time + hardware replacement time + system initialization time + link recovery time + routing time + forwarding recovery time. A smaller value of each item means a smaller mttr and a higher availability. High availability technologies as previously mentioned, increasing mtbf ...
Page 15
3 technology introduction reference monitor link monitor link is a port collaboration function. It is usually used in conjunction with layer 2 topology protocols. The idea is to monitor the states of uplink ports and adapt the up/down state of downlink ports to the up/down state of uplink ports, tri...
Page 16
4 technology introduction reference frr fast reroute (frr) provides a quick per-link or per-node protection on an lsp. In this approach, once a link or node fails on a path, frr comes up to reroute the path to a new link or node to bypass the failed link or node. This can happen as fast as 50 millis...
Page 17
5 ethernet oam configuration this chapter includes these sections: • ethernet oam overview • ethernet oam configuration task list • configuring basic ethernet oam functions • configuring the ethernet oam connection detection timers • configuring oam remote loopback • displaying and maintaining ether...
Page 18
6 figure 1 formats of different types of ethernet oampdus table 4 description of the fields in an oampdu field description dest addr destination mac address of the ethernet oampdu it is a slow protocol multicast address 0180c2000002. As slow protocol packet cannot be forwarded by bridges, ethernet o...
Page 19
7 how ethernet oam works this section describes the working procedures of ethernet oam. Ethernet oam connection establishment ethernet oam connection is the base of all the other ethernet oam functions. Oam connection establishment is also known as the “discovery phase”, where an ethernet oam entity...
Page 20
8 exchange of event notification oampdus. When detecting a link error event listed in table 7 , the local oam entity sends an event notification oampdu to notify the remote oam entity. With the log information, network administrators can keep track of network status in time. Table 7 ethernet oam lin...
Page 21
9 note: • s5800&s5820x switch series is able to receive information oampdus carrying the critical link events listed in table 8 . • only the gigabit optical ports are able send information oampdus carrying link fault events. • s5800&s5820x switch series is able to send information oampdus carrying d...
Page 22
10 ethernet oam is enabled on an ethernet port, according to its ethernet oam mode, the ethernet port establishes an ethernet oam connection with its peer port. Follow these steps to configure basic ethernet oam functions: to do… use the command… remarks enter system view system-view — enter etherne...
Page 23
11 configuring link monitoring note: after ethernet oam connections are established, the link monitoring periods and thresholds configured in this section take effect on all ethernet ports automatically. Configuring errored symbol event detection an errored symbol event occurs when the number of det...
Page 24
12 to do… use the command… remarks configure the errored frame period event triggering threshold oam errored-frame-period threshold threshold-value optional 1 by default configuring errored frame seconds event detection an errored frame seconds event occurs when the number of error frame seconds det...
Page 25
13 to do… use the command… remarks enter system view system-view — enable ethernet oam remote loopback on a specified port oam loopback interface interface-type interface-number required disabled by default. Enable ethernet oam remote loopback in interface view follow these steps to enable ethernet ...
Page 26
14 to do… use the command… remarks enter system view system-view — enter layer 2 ethernet port view interface interface-type interface-number — reject the ethernet oam remote loopback request from a remote port oam loopback reject-request required by default, a port does not reject the ethernet oam ...
Page 27
15 configuration procedure 1. Configure switch a # configure gigabitethernet 1/0/1 to operate in passive ethernet oam mode and enable ethernet oam for it. System-view [switcha] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1 [switcha-gigabitethernet1/0/1] oam mode passive [switcha-gigabitethernet1/0/1] oam enable [...
Page 28
16 [switcha] display oam critical-event port : gigabitethernet1/0/1 link status : up event statistic : ------------------------------------------------------------------------- link fault :0 dying gasp : 0 critical event : 0 the output shows that no critical link event occurred on the link between s...
Page 29
17 cfd configuration this chapter includes these sections: • overview • cfd configuration task list • displaying and maintaining cfd • cfd configuration example overview connectivity fault detection (cfd), which conforms to ieee 802.1ag connectivity fault management (cfm) and itu-t y.1731, is an end...
Page 30
18 cfd exchanges messages and performs operations on a per-domain basis. By planning mds properly in a network, you can use cfd to locate failure points rapidly. Maintenance association a maintenance association (ma) is a set of maintenance points (mps) in an md. An ma is identified by the “md name ...
Page 31
19 as shown in figure 5 , an inward-facing mep does not send packets to its host port. Rather, it sends packets to other ports on the device. • mip a mip is internal to an md. It cannot send cfd packets actively; however, it can handle and respond to cfd packets. The ma and md to which a mip belongs...
Page 32
20 • loopback (lb) • linktrace (lt) • alarm indication signal (ais) • loss measurement (lm) • delay measurement (dm) • test (tst) cc connectivity faults are usually caused by device faults or configuration errors. Cc checks the connectivity between meps. This function is implemented through periodic...
Page 33
21 calculates and records the link transmission delay and jitter (delay variation) according to the transmission time and reception time. 1dm frames are multicast frames. 2. Two-way frame delay measurement the source mep sends a delay measurement message (dmm), which carries the transmission time, t...
Page 34
22 tasks remarks configuring cc on meps required configuring lb on meps optional configuring lt on meps optional configuring ais optional configuring lm optional configuring one-way dm optional configuring two-way dm optional configuring cfd functions configuring tst optional note: a port blocked by...
Page 35
23 configuring service instances before configuring the meps and mips, you must first configure service instances. A service instance is a set of service access points (saps), and belongs to an ma in an md. A service instance is indicated by an integer to represent an ma in an md. The md and ma defi...
Page 36
24 before creating meps, configure the mep list first. An mep list is a collection of local meps allowed to be configured in an ma and the remote meps to be monitored. Follow these steps to configure a mep: to do... Use the command... Remarks enter system view system-view — configure a mep list cfd ...
Page 38
26 the relationship between the interval field value in the ccm messages, the interval between ccm messages and the timeout time of the remote mep is illustrated in table 9 . Table 9 relationship of interval field value, interval between ccm messages, and timeout time of the remote mep interval fiel...
Page 40
28 caution: the lm function takes effect only in cfd ieee 802.1ag. Configuring one-way dm the one-way dm function measures the one-way frame delay between two meps, and monitors and manages the link transmission performance. Follow these steps to configure one-way dm: to do… use the command… remarks...
Page 43
31 figure 8 network diagram for cfd configuration configuration procedure 1. Configure a vlan and assign ports to it on each device shown in figure 8 , create vlan 100 and assign ports gigabitethernet 1/0/1 through gigabitethernet 1/0/4 to vlan 100. 2. Enable cfd # enable cfd on device a. System-vie...
Page 44
32 [devicec] cfd md md_b level 3 [devicec] cfd ma ma_b md md_b vlan 100 [devicec] cfd service-instance 2 md md_b ma ma_b 4. Configure meps # on device a, configure a mep list in service instance 1; create and enable inward-facing mep 1001 in service instance 1 on gigabitethernet 1/0/1. [devicea] cfd...
Page 45
33 # on device a, enable the sending of ccm frames for mep 1001 in service instance 1 on gigabitethernet 1/0/1. [devicea] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1 [devicea-gigabitethernet1/0/1] cfd cc service-instance 1 mep 1001 enable [devicea-gigabitethernet1/0/1] quit # on device b, enable the sending of ...
Page 46
34 2. Verify the lt function # identify the path between mep 1001 and mep 5001 in service instance 1 on device a. [devicea] cfd linktrace service-instance 1 mep 1001 target-mep 5001 linktrace to mep 5001 with the sequence number 1001-43462 mac address ttl last mac relay action 0010-fc00-6512 63 0010...
Page 47
35 [devicea] cfd dm two-way service-instance 1 mep 1001 target-mep 4002 frame delay: reply from 0010-fc00-6512: 10ms reply from 0010-fc00-6512: 9ms reply from 0010-fc00-6512: 11ms reply from 0010-fc00-6512: 5ms reply from 0010-fc00-6512: 5ms average: 8ms send dmm frames: 5 received: 5 lost: 0 frame ...
Page 48
36 dldp configuration this chapter includes these topics: • overview • dldp configuration task list • displaying and maintaining dldp • dldp configuration examples • troubleshooting dldp overview background unidirectional links occur when one end of a link can receive packets from the other end, but...
Page 49
37 figure 9 correct and incorrect fiber connections the device link detection protocol (dldp) detects unidirectional links (fiber links or twisted-pair links) and can be configured to shut down the related port automatically or prompt users to take actions to avoid network problems. As a data link l...
Page 50
38 state indicates… advertisement all neighbors are bi-directionally reachable or dldp has been in active state for more than five seconds. This is a relatively stable state where no unidirectional link has been detected. Probe dldp enters this state if it receives a packet from an unknown neighbor....
Page 51
39 dldp timer description enhanced timer in enhanced mode, this timer is triggered if no packet is received from a neighbor when the entry timer expires. Enhanced timer is set to 1 second. After the enhanced timer is triggered, the switch sends up to eight probe packets to the neighbor at a frequenc...
Page 52
40 figure 10 a scenario for enhanced dldp mode note: • in normal dldp mode, only fiber cross-connected unidirectional links can be detected. • in enhanced dldp mode, the following types of unidirectional links can be detected: fiber cross-connected links, and fiber pairs with one fiber or broken or ...
Page 53
41 dldp state type of dldp packets sent advertisement normal advertisement packet probe probe packet disable disable packet and then recoverprobe packet note: a switch sends flush packets when it transits to initial state from active, advertisement, probe, or delaydown state but does not send them w...
Page 54
42 packet type processing procedure if yes, no process is performed. Disable packet checks whether the local port is in disable state if not, the local port transits to disable state. If not, no process is performed. Recoverprobe packet checks whether the local port is in disable or advertisement st...
Page 55
43 table 16 description on dldp neighbor states dldp neighbor state description unknown a neighbor is in this state when it is just detected and is being probed. A neighbor is in this state only when it is being probed. It transits to two way state or unidirectional state after the probe operation f...
Page 56
44 to do… use the command… remarks enable dldp globally dldp enable required globally disabled by default enter ethernet port view interface interface-type interface-number enter ethernet port view or port group view enter port group view port-group manual port-group-name either of the two is requir...
Page 57
45 to do… use the command… remarks enter system view system-view — set the interval to send advertisement packets dldp interval time optional 5 seconds by default note: • the interval to send advertisement packets applies to all dldp-enabled ports. • to enable dldp to operate properly, make sure the...
Page 59
47 resetting dldp state in system view resetting dldp state in system view applies to all ports of the switch. Follow these steps to reset dldp in system view: to do… use the command… remarks enter system view system-view — reset dldp state dldp reset required resetting dldp state in port view or po...
Page 60
48 figure 11 network diagram for configuring automatic shutdown of unidirectional links correct fiber connection fiber link cross-connected fibers device a device b device a device b ethernet optical port tx end rx end ge1/0/49 ge1/0/50 ge1/0/49 ge1/0/50 ge1/0/49 ge1/0/50 ge1/0/49 ge1/0/50 configura...
Page 61
49 2. Configuration on device b # enable dldp globally, configure gigabitethernet 1/0/49 and gigabitethernet 1/0/50 to operate in full duplex mode and at 1000 mbps, and then enable dldp on the two ports. System-view [deviceb] dldp enable [deviceb] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/49 [deviceb-gigabiteth...
Page 62
50 neighbor port index : 60 neighbor state : two way neighbor aged time : 12 the output indicates that both gigabitethernet 1/0/49 and gigabitethernet 1/0/50 are in advertisement state, which means both links are bidirectional. # enable system information monitoring on device a, and enable the displ...
Page 63
51 manually shutting down unidirectional links network requirements • as shown in figure 12 , device a and device b are connected with two fiber pairs. • configure dldp to send information when a unidirectional link is detected, to remind the network administrator to manually shut down the faulty po...
Page 64
52 [devicea-gigabitethernet1/0/50] dldp enable [devicea-gigabitethernet1/0/50] quit # set the dldp mode to enhanced. [devicea] dldp work-mode enhance # set the port shutdown mode to manual. [devicea] dldp unidirectional-shutdown manual 2. Configuration on device b # enable dldp globally, configure g...
Page 65
53 interface gigabitethernet1/0/50 dldp port state : advertisement dldp link state : up the neighbor number of the port is 1. Neighbor mac address : 0023-8956-3600 neighbor port index : 60 neighbor state : two way neighbor aged time : 12 the output indicates that both gigabitethernet 1/0/49 and giga...
Page 66
54 the output indicates that the link status of both gigabitethernet 1/0/49 and gigabitethernet 1/0/50 is down. Assume that in this example, the unidirectional links are caused by cross-connected fibers. Correct the fiber connections, and then bring up the ports shut down earlier. # on device a, bri...
Page 67
55 rrpp configuration this chapter includes these sections: • rrpp overview • rrpp configuration task list • displaying and maintaining rrpp • rrpp configuration examples • troubleshooting rrpp overview the rapid ring protection protocol (rrpp) is a link layer protocol designed for ethernet rings. R...
Page 68
56 basic concepts in rrpp figure 13 rrpp networking diagram rrpp domain interconnected devices with the same domain id and control vlans constitute an rrpp domain. An rrpp domain contains the following elements—primary ring, subring, control vlan, master node, transit node, primary port, secondary p...
Page 69
57 ip address configuration is prohibited on the control vlan interfaces. 2. Data vlan a data vlan is a vlan dedicated to transferring data packets. Both rrpp ports and non-rrpp ports can be assigned to a data vlan. Node each device on an rrpp ring is a node. The role of a node is configurable. Rrpp...
Page 70
58 as shown in figure 13 , device b and device c lie on ring 1 and ring 2. Device b’s port 1 and port 2 and device c’s port 1 and port 2 access the primary ring, so they are common ports. Device b’s port 3 and device c’s port 3 access only the subring, so they are edge ports. Rrpp ring group to redu...
Page 71
59 rrpp timers when rrpp checks the link state of an ethernet ring, the master node sends hello packets out the primary port according to the hello timer, and determines whether its secondary port receives the hello packets based on the fail timer. • the hello timer specifies the interval at which t...
Page 72
60 ring recovery after the ports belonging to the rrpp domain on the transit nodes, the edge nodes, or the assistant-edge nodes are brought up again, the master node may find the ring is restored after a period of time. A temporary loop may arise in the data vlan during this period, resulting in a b...
Page 73
61 • the master node sends fast-hello packets out its primary port at the interval specified by the fast-hello timer. If the secondary port receives the fast-hello packets sent by the local master node before the fast-fail timer expires, the entire ring is in the health state; otherwise, the ring tr...
Page 74
62 figure 15 schematic diagram for a tangent-ring network intersecting rings as shown in figure 16 , two or more rings are in the intersecting-ring network topology, with two common nodes between rings. You only need to define an rrpp domain, and configure one ring as the primary ring and the other ...
Page 75
63 figure 17 schematic diagram for a dual-homed-ring network single-ring load balancing in a single-ring network, you can achieve load balancing by configuring multiple domains. As shown in figure 18 , ring 1 is configured as the primary ring of both domain 1 and domain 2. Domain 1 and domain 2 are ...
Page 76
64 figure 19 schematic diagram for an intersecting-ring load balancing network protocols and standards rfc 3619, extreme networks' ethernet automatic protection switching (eaps) version 1 rrpp configuration task list caution: • rrpp does not have an auto election mechanism, so you must configure eac...
Page 77
65 task remarks configuring rrpp timers optional perform this task on the master node in the rrpp domain. Enabling fast detection optional perform this task on the master node, edge node, and assistant-edge node in the rrpp domain. Configuring rrpp fast detection configuring fast detection timers op...
Page 78
66 note: • when you configure existing vlans as control vlans, the system prompts errors. • to ensure proper forwarding of rrppdus, do not enable qinq or vlan mapping on the control vlans. • to ensure that rrppdus can be sent and received correctly, do not configure the default vlan of a port access...
Page 79
67 configuring rrpp ports perform this configuration on each node’s ports intended for accessing rrpp rings. Follow these steps to configure rrpp ports: to do… use the command… remarks enter system view system-view — enter port view interface interface-type interface-number — configure the link type...
Page 80
68 specifying a master node perform this configuration on a device to be configured as a master node. Follow these steps to specify a master node: to do… use the command… remarks enter system view system-view — enter rrpp domain view rrpp domain domain-id — specify the current device as the master n...
Page 81
69 specifying an assistant-edge node when configuring an assistant-edge node, you must first configure the primary ring before configuring the subrings. Perform this configuration on a device to be configured as an assistant-edge node. Follow these steps to specify an assistant-edge node: to do… use...
Page 82
70 caution: • the fail timer value must be equal to or greater than three times the hello timer value. • to avoid temporary loops when the primary ring fails in a dual-homed-ring network, ensure that the difference between the fail timer value on the master node of the subring and that on the master...
Page 83
71 to do… use the command… remarks enter system view system-view — enter rrpp domain view rrpp domain domain-id — configure the fast-fail timer timer fast-fail-timer fast-fail-value optional by default, the fast-fail timer is 600ms. Configure the fast-hello timer timer fast-hello-timer fast-hello-va...
Page 85
73 configuration procedure 1. Configuration on device a # create vlans 1 through 30, map these vlans to msti 1, and activate the mst region configuration. System-view [devicea] vlan 1 to 30 [devicea] stp region-configuration [devicea-mst-region] instance 1 vlan 1 to 30 [devicea-mst-region] active re...
Page 86
74 [deviceb-mst-region] quit # disable physical state change suppression and stp on gigabitethernet 1/0/1 and gigabitethernet 1/0/2, configure the two ports as trunk ports, and assign them to vlans 1 through 30, and configure them to trust the 802.1p precedence of the received packets. [deviceb] int...
Page 87
75 • device a, device b, device c and device d form primary ring 1, and device b, device c and device e form subring 2. • device a is the master node of primary ring 1, with gigabitethernet 1/0/1 as the primary port and gigabitethernet 1/0/2 the secondary port. • device e is the master node of subri...
Page 88
76 [devicea] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/2 [devicea-gigabitethernet1/0/2] undo link-delay [devicea-gigabitethernet1/0/2] undo stp enable [devicea-gigabitethernet1/0/2] port link-type trunk [devicea-gigabitethernet1/0/2] port trunk permit vlan 1 to 30 [devicea-gigabitethernet1/0/2] qos trust dot1p ...
Page 89
77 [deviceb-gigabitethernet1/0/3] undo stp enable [deviceb-gigabitethernet1/0/3] port link-type trunk [deviceb-gigabitethernet1/0/3] port trunk permit vlan 1 to 30 [deviceb-gigabitethernet1/0/3] qos trust dot1p [deviceb-gigabitethernet1/0/3] quit # create rrpp domain 1, configure vlan 4092 as the pr...
Page 90
78 [devicec-gigabitethernet1/0/2] quit [devicec] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/3 [devicec-gigabitethernet1/0/3] undo link-delay [devicec-gigabitethernet1/0/3] undo stp enable [devicec-gigabitethernet1/0/3] port link-type trunk [devicec-gigabitethernet1/0/3] port trunk permit vlan 1 to 30 [devicec-gi...
Page 91
79 [deviced-gigabitethernet1/0/2] port link-type trunk [deviced-gigabitethernet1/0/2] port trunk permit vlan 1 to 30 [deviced-gigabitethernet1/0/2] qos trust dot1p [deviced-gigabitethernet1/0/2] quit # create rrpp domain 1, configure vlan 4092 as the primary control vlan of rrpp domain 1, and config...
Page 92
80 [devicee-rrpp-domain1] protected-vlan reference-instance 1 # configure device e as the master node of subring 2, with gigabitethernet 1/0/1 as the primary port and gigabitethernet 1/0/2 as the secondary port, and enable ring 2. [devicee-rrpp-domain1] ring 2 node-mode master primary-port gigabitet...
Page 93
81 figure 22 network diagram for intersecting-ring load balancing configuration configuration procedure 1. Configuration on device a # create vlans 10 and 20, map vlan 10 to msti 1 and vlan 20 to msti 2, and activate mst region configuration. System-view [devicea] vlan 10 [devicea-vlan10] quit [devi...
Page 94
82 [devicea-gigabitethernet1/0/2] port link-type trunk [devicea-gigabitethernet1/0/2] undo port trunk permit vlan 1 [devicea-gigabitethernet1/0/2] port trunk permit vlan 10 20 [devicea-gigabitethernet1/0/2] qos trust dot1p [devicea-gigabitethernet1/0/2] quit # create rrpp domain 1, configure vlan 10...
Page 95
83 [deviceb-gigabitethernet1/0/1] undo link-delay [deviceb-gigabitethernet1/0/1] undo stp enable [deviceb-gigabitethernet1/0/1] port link-type trunk [deviceb-gigabitethernet1/0/1] undo port trunk permit vlan 1 [deviceb-gigabitethernet1/0/1] port trunk permit vlan 10 20 [deviceb-gigabitethernet1/0/1]...
Page 96
84 # configure device b as the assistant-edge node of subring 3 in rrpp domain 1, with gigabitethernet 1/0/4 as the edge port, and enable subring 3. [deviceb-rrpp-domain1] ring 3 node-mode assistant-edge edge-port gigabitethernet 1/0/4 [deviceb-rrpp-domain1] ring 3 enable [deviceb-rrpp-domain1] quit...
Page 97
85 [devicec-gigabitethernet1/0/2] undo link-delay [devicec-gigabitethernet1/0/2] undo stp enable [devicec-gigabitethernet1/0/2] port link-type trunk [devicec-gigabitethernet1/0/2] undo port trunk permit vlan 1 [devicec-gigabitethernet1/0/2] port trunk permit vlan 10 20 [devicec-gigabitethernet1/0/2]...
Page 98
86 [devicec-rrpp-domain2] control-vlan 105 [devicec-rrpp-domain2] protected-vlan reference-instance 2 # configure device c as the transit node of primary ring 1 in rrpp domain 2, with gigabitethernet 1/0/1 as the primary port and gigabitethernet 1/0/2 as the secondary port, and enable ring 1. [devic...
Page 99
87 # create rrpp domain 1, configure vlan 100 as the primary control vlan of rrpp domain 1, and configure the vlan mapped to msti 1 as the protected vlan of rrpp domain 1. [deviced] rrpp domain 1 [deviced-rrpp-domain1] control-vlan 100 [deviced-rrpp-domain1] protected-vlan reference-instance 1 # con...
Page 100
88 [devicee-gigabitethernet1/0/2] port link-type trunk [devicee-gigabitethernet1/0/2] undo port trunk permit vlan 1 [devicee-gigabitethernet1/0/2] port trunk permit vlan 20 [devicee-gigabitethernet1/0/2] qos trust dot1p [devicee-gigabitethernet1/0/2] quit # create rrpp domain 2, configure vlan 105 a...
Page 101
89 # create rrpp domain 1, configure vlan 100 as the primary control vlan, and configure the vlan mapped to msti 1 as the protected vlan. [devicef] rrpp domain 1 [devicef-rrpp-domain1] control-vlan 100 [devicef-rrpp-domain1] protected-vlan reference-instance 1 # configure device f as the master node...
Page 102
90 figure 23 network diagram for fast detection configuration configuration procedure 1. Configuration on device a # disable physical state change suppression and stp on gigabitethernet 1/0/1 and gigabitethernet 1/0/2, configure the two ports as trunk ports, and assign them to all vlans, and configu...
Page 103
91 # enable fast detection, and set the fast-hello timer and fast-fail timer to 100 milliseconds and 300 milliseconds respectively. The value of the fast-fail timer must be equal to or greater than three times the fast-hello timer. [devicea-rrpp-domain1] fast-detection enable [devicea-rrpp-domain1] ...
Page 104
92 [deviced-gigabitethernet1/0/2] port link-type trunk [deviced-gigabitethernet1/0/2] port trunk permit vlan all [deviced-gigabitethernet1/0/2] qos trust dot1p [deviced-gigabitethernet1/0/2] quit # create rrpp domain 1, configure vlan 4092 as the primary vlan of rppp domain 1, and configure the vlan...
Page 105
93 smart link configuration this chapter includes these sections: • smart link overview • configuring a smart link device • configuring an associated device • displaying and maintaining smart link • smart link configuration examples smart link overview background to avoid single-point failures and g...
Page 106
94 the problem with stp, however, is that stp convergence time is long, which makes it not suitable for users who have high demand on convergence speed. Rrpp can meet users’ demand on convergence speed, but it involves complicated networking and configurations and is mainly used in ring-shaped netwo...
Page 107
95 messages in the receive control vlan and refresh their mac address forwarding entries and arp/nd entries. Flush message flush messages are used by a smart link group to notify other devices to refresh their mac address forwarding entries and arp/nd entries when link switchover occurs in the smart...
Page 108
96 you can configure protected vlans for a smart link group by referencing mstis. Smart link collaboration mechanisms collaboration between smart link and monitor link smart link cannot sense by itself when faults occur on the uplink of the upstream devices, or when faults are cleared. To monitor th...
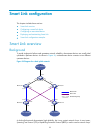
Page 109
97 note: • a smart link device is a network device that supports smart link and is configured with a smart link group and a transmit control vlan for flush message transmission. Device c and device d in figure 24 are two examples of smart link devices. • an associated device is a network device that...
Page 111
99 to do… use the command… remarks enable flush update in the specified control vlan flush enable [ control-vlan vlan-id ] optional by default, flush update is enabled, and vlan 1 is the control vlan. Caution: • the control vlan configured for a smart link group must be different from that configure...
Page 112
100 to do… use the command… remarks enter system view system-view — enter ethernet port view or layer 2 aggregate port view interface interface-type interface-number — configure the control vlans for receiving flush messages smart-link flush enable [ control-vlan vlan-id-list ] required by default, ...
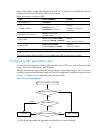
Page 113
101 figure 25 network diagram for single smart link group configuration device a device e device d device c device b ge 1/0 /1 ge 1/0 /2 ge 1/0 /1 ge 1/0 /1 ge 1/0 /2 ge 1/0 /2 ge1/0/3 ge1/0/1 ge1/0/2 ge1/0/3 ge1/0/1 ge1/0/2 master link slave link smart link group configuration procedure 1. Configur...
Page 114
102 # in smart link group 1, enable flush message sending, and specify vlan 10 as the control vlan. [devicec-smlk-group1] flush enable control-vlan 10 [devicec-smlk-group1] quit # bring up ports gigabitethernet 1/0/1 and gigabitethernet 1/0/2. [devicec] interface gigabitethernet1/0/1 [devicec-gigabi...
Page 115
103 [deviced] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/2 [deviced-gigabitethernet1/0/2] undo shutdown [deviced-gigabitethernet1/0/2] quit 3. Configuration on device b # create vlans 1 through 30. System-view [deviceb] vlan 1 to 30 # configure gigabitethernet 1/0/1, gigabitethernet 1/0/2, and gigabitethernet 1/...
Page 116
104 5. Configuration on device a # create vlans 1 through 30. System-view [devicea] vlan 1 to 30 # configure gigabitethernet 1/0/1 and gigabitethernet 1/0/2 as trunk ports that permit vlans 1 through 30, enable flush message receiving on them, and specify vlan 10 and vlan 20 as the control vlans for...
Page 117
105 • device c is a smart link device, and device a, device b, and device d are associated devices. Traffic of vlans 1 through 200 on device c are dually uplinked to device a by device b and device d. • implement dual uplink backup and load sharing on device c: ○ traffic of vlans 1 through 100 is up...
Page 118
106 # create smart link group 1, and configure all vlans mapped to msti 1 as the protected vlans for smart link group 1. [devicec] smart-link group 1 [devicec-smlk-group1] protected-vlan reference-instance 1 # configure gigabitethernet 1/0/1 as the master port and gigabitethernet 1/0/2 as the slave ...
Page 119
107 [deviceb-gigabitethernet1/0/2] port link-type trunk [deviceb-gigabitethernet1/0/2] port trunk permit vlan 1 to 200 [deviceb-gigabitethernet1/0/2] smart-link flush enable control-vlan 10 101 [deviceb-gigabitethernet1/0/2] quit 3. Configuration on device d # create vlan 1 through vlan 200. System-...
Page 120
108 preemption mode: role control vlan: 10 protected vlan: reference instance 1 member role state flush-count last-flush-time ----------------------------------------------------------------------------- gigabitethernet1/0/1 master actvie 5 16:37:20 2010/02/21 gigabitethernet1/0/2 slave standby 1 17...
Page 121
109 monitor link configuration this chapter includes these sections: • overview • configuring monitor link • displaying and maintaining monitor link • monitor link configuration example overview monitor link is a port collaboration function. Monitor link usually works together with layer 2 topology ...
Page 122
110 uplink/downlink ports uplink port and downlink port are two port roles in monitor link groups: • uplink ports are the monitored ports. The state of a monitor link group adapts to that of its member uplink ports. When a monitor link group contains no uplink port or all the uplink ports are down, ...
Page 124
112 figure 28 network diagram for monitor link configuration device a device d device b ge 1/0 /1 ge 1/0 /2 ge 1/0 /1 ge 1/0 /1 ge 1/0 /2 ge 1/0 /2 device c ge 1/0 /1 ge 1/0 /2 configuration procedure 1. Configuration on device c # create vlans 1 through 30, map these vlans to msti 1, and activate m...
Page 125
113 # create vlans 1 through 30. System-view [devicea] vlan 1 to 30 # configure gigabitethernet 1/0/1 and gigabitethernet 1/0/2 as trunk ports, assign them to vlans 1 through 30, and enable flush message receiving on them. [devicea] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1 [devicea-gigabitethernet1/0/1] port...
Page 126
114 [deviced-gigabitethernet1/0/1] smart-link flush enable [deviced-gigabitethernet1/0/1] quit [deviced] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/2 [deviced-gigabitethernet1/0/2] port link-type trunk [deviced-gigabitethernet1/0/2] port trunk permit vlan 1 to 30 [deviced-gigabitethernet1/0/2] smart-link flush e...
Page 127
115 vrrp configuration this chapter includes these sections: • vrrp overview • vrrp standard protocol mode • vrrp load balancing mode • configuring vrrp for ipv4 • configuring vrrp for ipv6 • ipv4-based vrrp configuration examples • ipv6-based vrrp configuration examples • troubleshooting vrrp note:...
Page 128
116 configuring a default route for network hosts facilitates your configuration, but also requires high performance stability of the device that acts as the gateway. Using more egress gateways is a common way to improve system reliability, but introduces the problem of routing among the egresses. V...
Page 129
117 figure 30 network diagram for vrrp host a host b host c router a router b router c virtual router network as shown in figure 30 , router a, router b, and router c form a virtual router, which has its own ip address. Hosts on the ethernet use the virtual router as the default gateway. The router ...
Page 130
118 authentication mode to avoid attacks from unauthorized users, vrrp adds authentication keys into packets for authentication. Vrrp provides two authentication modes: • simple—simple text authentication a router sending a packet fills an authentication key into the packet, and the router receiving...
Page 131
119 figure 31 format of a vrrpv2 packet ... Figure 32 format of a vrrpv3 packet ... Version type virtual rtr id priority count ipv6 addrs auth type adver int checksum ipv6 address 1 authentication data 1 authentication data 2 ipv6 address n 0 7 15 23 31 3 a vrrp packet comprises the following fields...
Page 132
120 • ip address/ipv6 address—virtual ipv4 or ipv6 address entry of the vrrp group. The count ip addrs or count ipv6 addrs field defines the number of the virtual ip v4 or ipv6 addresses. • authentication data—authentication key. This field is used only for simple authentication and is 0 for any oth...
Page 133
121 tracking a track entry by monitoring a track entry, you can: • monitor an uplink and change the priority of the router according to the state of the uplink. If the uplink fails, hosts in the lan cannot access external networks through the router. In this case, the state of the monitored track en...
Page 134
122 figure 34 vrrp in load sharing mode host a host b host c router a backup router b backup router c master vrrp group 2 vrrp group 3 vrrp group 1 master backup backup backup master backup network a router can be in multiple vrrp groups and hold a different priority in a different group. As shown i...
Page 135
123 note: vrrp load balancing mode is based on vrrp standard protocol mode, so mechanisms, such as master election, preemption, and tracking functions, in the standard protocol mode are also supported in the load balancing mode. In addition, vrrp load balancing mode has new mechanisms, which are int...
Page 136
124 figure 36 answer arp requests 3. Different hosts send packets to different routers according to the requested virtual mac addresses. For example, as shown in figure 37 , host a regards the virtual mac address of router a as the gateway mac address, so it sends packets to router a for forwarding;...
Page 137
125 virtual forwarder creating a virtual forwarder virtual mac addresses help different hosts transmit packets to different routers in a vrrp group. To enable the routers in the vrrp group to forward the packets, create virtual forwarders (vfs) on the routers. Each vf associates with a virtual mac a...
Page 138
126 figure 38 vf information figure 38 illustrates the vf information on each router in the vrrp group and how the routers back up one another. The master, router a, assigns virtual mac addresses 000f-e2ff-0011, 000f-e2ff-0012, and 000f-e2ff-0013 to itself, router b, and router c respectively. The v...
Page 139
127 • timeout timer—the duration that the new avf takes over the vf owner. Before this timer times out, all the routers in the vrrp group keep the failed avf, and the new avf forwards the packets destined for the virtual mac address corresponding to the failed avf. When this timer times out, all the...
Page 140
128 task remarks specifying the type of mac addresses mapped to virtual ip addresses optional when vrrp works in load balancing mode, this configuration is not effective. Creating a vrrp group and configuring virtual ip address required configuring router priority, preemptive mode and tracking funct...
Page 141
129 a mapping is adopted, the hosts in the internal network do not need to update the mapping between the ip address and mac address when the master changes. • real mac address of an interface when an ip address owner exists in a vrrp group, if the virtual ip address is mapped to the virtual mac add...
Page 142
130 to do… use the command… remarks enter the specified vlan interface view or layer 3 ethernet interface view interface interface-type interface-number — create a vrrp group and configure a virtual ip address for the vrrp group vrrp vrid virtual-router-id virtual-ip virtual-address required vrrp gr...
Page 143
131 to do… use the command… remarks enter system view system-view — enter vlan interface view or layer 3 ethernet interface view interface interface-type interface-number — configure router priority in the vrrp group vrrp vrid virtual-router-id priority priority-value optional 100 by default. Config...
Page 144
132 to do… use the command… remarks enter the specified vlan interface view or layer 3 ethernet interface view interface interface-type interface-number — configure the vf to monitor a specified track entry and specify the amount by which the weight decreases vrrp vrid virtual-router-id weight track...
Page 145
133 note: • you might configure different authentication modes and authentication keys for the vrrp groups on an interface. However, members of the same vrrp group must use the same authentication mode and authentication key. • excessive traffic might cause a backup to trigger a change of its status...
Page 146
134 configuring vrrp for ipv6 vrrp for ipv6 configuration task list complete these tasks to configure vrrp for ipv6: task remarks configuring a vrrp working mode optional specifying the type of mac addresses mapped to virtual ipv6 addresses optional when vrrp works in load balancing mode, this confi...
Page 148
136 to do… use the command… remarks configure the vrrp group with a virtual ipv6 address, which is a global unicast address vrrp ipv6 vrid virtual-router-id virtual-ip virtual-address optional by default, no global unicast address is configured as the virtual ipv6 address of a vrrp group. Note: • wh...
Page 149
137 to do… use the command… remarks configure the interface to be tracked vrrp ipv6 vrid virtual-router-id track interface interface-type interface-number [ reduced priority-reduced ] optional no interface is being tracked by default. Configure vrrp to track a specified track entry vrrp ipv6 vrid vi...
Page 150
138 note: • you can configure the vf tracking function when vrrp works in either standard protocol mode or load balancing mode; however, the vf tracking function is effective only when vrrp works in load balancing mode. • by default, the weight of a vf is 255, and its lower limit of failure is 10. •...
Page 152
140 configuration procedure 1. Configure switch a # configure vlan 2. System-view [switcha] vlan 2 [switcha-vlan2] port gigabitethernet 1/0/5 [switcha-vlan2] quit [switcha] interface vlan-interface 2 [switcha-vlan-interface2] ip address 202.38.160.1 255.255.255.0 # create vrrp group 1 and set its vi...
Page 153
141 virtual ip : 202.38.160.111 virtual mac : 0000-5e00-0101 master ip : 202.38.160.1 # display the detailed information of vrrp group 1 on switch b. [switchb-vlan-interface2] display vrrp verbose ipv4 standby information: run mode : standard run method : virtual mac total number of virtual routers ...
Page 154
142 vrid : 1 adver timer : 1 admin status : up state : master config pri : 110 running pri : 110 preempt mode : yes delay time : 5 auth type : none virtual ip : 202.38.160.111 virtual mac : 0000-5e00-0101 master ip : 202.38.160.1 the output shows that after switch a resumes normal operation, it beco...
Page 155
143 [switcha-vlan-interface2] ip address 202.38.160.1 255.255.255.0 # create a vrrp group 1 and set its virtual ip address to 202.38.160.111. [switcha-vlan-interface2] vrrp vrid 1 virtual-ip 202.38.160.111 # configure the priority of switch a in the vrrp group to 110, which is higher than that of sw...
Page 156
144 interface vlan-interface2 vrid : 1 adver timer : 4 admin status : up state : master config pri : 110 running pri : 110 preempt mode : yes delay time : 5 auth type : simple key : hello virtual ip : 202.38.160.111 virtual mac : 0000-5e00-0101 master ip : 202.38.160.1 vrrp track information: track ...
Page 157
145 # when vlan-interface 3 on switch a is not available, the detailed information of vrrp group 1 on switch b is displayed. [switchb-vlan-interface2] display vrrp verbose ipv4 standby information: run mode : standard run method : virtual mac total number of virtual routers : 1 interface vlan-interf...
Page 158
146 configuration procedure 1. Configure switch a # configure vlan 2. System-view [switcha] vlan 2 [switcha-vlan2] port gigabitethernet 1/0/5 [switcha-vlan2] quit [switcha] interface vlan-interface 2 [switcha-vlan-interface2] ip address 202.38.160.1 255.255.255.128 # create a vrrp group 1 and set it...
Page 159
147 [switchb-vlan-interface3] vrrp vrid 2 priority 110 3. Verify the configuration to verify your configuration, use the display vrrp verbose command. # display the detailed information of the vrrp group on switch a. [switcha-vlan-interface3] display vrrp verbose ipv4 standby information: run mode :...
Page 160
148 virtual mac : 0000-5e00-0102 master ip : 202.38.160.131 the output shows that in vrrp group 1 switch a is the master, switch b is the backup and hosts with the default gateway of 202.38.160.100/25 accesses the internet through switch a; in vrrp group 2 switch a is the backup, switch b is the mas...
Page 161
149 [switcha-vlan2] port gigabitethernet 1/0/5 [switcha-vlan2] quit # configure vrrp to work in load balancing mode. [switcha] vrrp mode load-balance # create vrrp group 1 and configure its virtual ip address as 10.1.1.1. [switcha] interface vlan-interface 2 [switcha-vlan-interface2] ip address 10.1...
Page 162
150 # configure the vfs to monitor track entry 1, making the weight of switch b decrease by more than 245—250 in this example—when track entry 1 turns to negative. In such a case, another router with a higher weight can take over. [switchb] interface vlan-interface 2 [switchb-vlan-interface2] vrrp v...
Page 163
151 10.1.1.3 (backup) 10.1.1.4 (backup) forwarder information: 3 forwarders 1 active config weight : 255 running weight : 255 forwarder 01 state : active virtual mac : 000f-e2ff-0011 (owner) owner id : 0000-5e01-1101 priority : 255 active : local forwarder 02 state : listening virtual mac : 000f-e2f...
Page 164
152 priority : 127 active : 10.1.1.2 forwarder 02 state : active virtual mac : 000f-e2ff-0012 (owner) owner id : 0000-5e01-1103 priority : 255 active : local forwarder 03 state : listening virtual mac : 000f-e2ff-0013 (learnt) owner id : 0000-5e01-1105 priority : 127 active : 10.1.1.4 forwarder weig...
Page 165
153 state : active virtual mac : 000f-e2ff-0013 (owner) owner id : 0000-5e01-1105 priority : 255 active : local forwarder weight track information: track object : 1 state : positive weight reduced : 250 the output shows that in vrrp group 1, switch a is the master and switch b and switch c are the b...
Page 166
154 track object : 1 state : negative weight reduced : 250 # use the display vrrp verbose command to display the detailed information of vrrp group 1 on switch c. [switchc-vlan-interface2] display vrrp verbose ipv4 standby information: run mode : load balance run method : virtual mac total number of...
Page 167
155 # when the timeout timer—about 1800 seconds—expires, display the detailed information of vrrp group 1 on switch c. [switchc-vlan-interface2] display vrrp verbose ipv4 standby information: run mode : load balance run method : virtual mac total number of virtual routers : 1 interface vlan-interfac...
Page 168
156 auth type : none virtual ip : 10.1.1.1 member ip list : 10.1.1.3 (local, master) 10.1.1.4 (backup) forwarder information: 2 forwarders 1 active config weight : 255 running weight : 255 forwarder 02 state : active virtual mac : 000f-e2ff-0012 (owner) owner id : 0000-5e01-1103 priority : 255 activ...
Page 169
157 figure 43 network diagram for single vrrp group configuration configuration procedure 1. Configure switch a # configure vlan 2. System-view [switcha] ipv6 [switcha] vlan 2 [switcha-vlan2] port gigabitethernet 1/0/5 [switcha-vlan2] quit [switcha] interface vlan-interface 2 [switcha-vlan-interface...
Page 170
158 [switchb] interface vlan-interface 2 [switchb-vlan-interface2] ipv6 address fe80::2 link-local [switchb-vlan-interface2] ipv6 address 1::2 64 # create a vrrp group 1 and set its virtual ipv6 addresses to fe80::10 and 1::10. [switchb-vlan-interface2] vrrp ipv6 vrid 1 virtual-ip fe80::10 link-loca...
Page 171
159 when switch a fails, you can still ping host b on host a. To view the detailed information of the vrrp group on switch b, use the display vrrp ipv6 verbose command. # when switch a fails, the detailed information of vrrp group 1 on switch b is displayed. [switchb-vlan-interface2] display vrrp ip...
Page 172
160 • when switch a operates normally, packets sent from host a to host b are forwarded by switch a. If vlan-interface 3 through which switch a connects to the internet is not available, packets sent from host a to host b are forwarded by switch b. • to prevent attacks to the vrrp group by illegal u...
Page 173
161 [switcha-vlan-interface2] vrrp ipv6 vrid 1 preempt-mode timer delay 5 # set vlan-interface 3 on switch a to be tracked, and configure the amount by which the priority value decreases to be more than 10—30 in this example, so that when vlan interface 3 fails, the priority of switch a in vrrp grou...
Page 174
162 virtual ip : fe80::10 1::10 virtual mac : 0000-5e00-0201 master ip : fe80::1 vrrp track information: track interface: vlan3 state : up pri reduced : 30 # display the detailed information of vrrp group 1 on switch b. [switchb-vlan-interface2] display vrrp ipv6 verbose ipv6 standby information: ru...
Page 175
163 run mode : standard run method : virtual mac total number of virtual routers : 1 interface vlan-interface2 vrid : 1 adver timer : 400 admin status : up state : master config pri : 100 running pri : 100 preempt mode : yes delay time : 5 auth type : simple key : hello virtual ip : fe80::10 1::10 v...
Page 176
164 configuration procedure 1. Configure switch a # configure vlan 2. System-view [switcha] ipv6 [switcha] vlan 2 [switcha-vlan2] port gigabitethernet 1/0/5 [switcha-vlan2] quit [switcha] interface vlan-interface 2 [switcha-vlan-interface2] ipv6 address fe80::1 link-local [switcha-vlan-interface2] i...
Page 177
165 # enable switch b to send ra messages, so that hosts in vlan 2 can learn the default gateway address. [switchb-vlan-interface2] undo ipv6 nd ra halt [switchb-vlan-interface2] quit # configure vlan 3. [switchb] vlan 3 [switchb-vlan3] port gigabitethernet 1/0/6 [switchb-vlan3] quit [switchb] inter...
Page 178
166 # display the detailed information of the vrrp group on switch b. [switchb-vlan-interface3] display vrrp ipv6 verbose ipv6 standby information: run mode : standard run method : virtual mac total number of virtual routers : 2 interface vlan-interface2 vrid : 1 adver timer : 100 admin status : up ...
Page 179
167 figure 46 network diagram for vrrp load balancing mode ip: 1::4/64 gateway ip: 1::10 host a host b host c switch a switch b switch c vlan-int2 ip: fe80::1; 1::1/64 vip: fe80::10; 1::10 network vlan-int2 ip: fe80::2; 1::2/64 vip: fe80::10; 1::10 vlan-int2 ip: fe80::3; 1::3/64 vip: fe80::10; 1::10...
Page 180
168 [switcha-vlan-interface2] undo ipv6 nd ra halt [switcha-vlan-interface2] quit # create track entry 1 to associate with the physical status of vlan-interface 3 on switch a. When the track entry becomes negative, it means that the interface fails. [switcha] track 1 interface vlan-interface 3 # con...
Page 181
169 [switchc] vlan 2 [switchc-vlan2] port gigabitethernet 1/0/5 [switchc-vlan2] quit # configure vrrp to work in load balancing mode. [switchc] vrrp mode load-balance # create vrrp group 1 and configure its virtual ipv6 addresses as fe80::10 and 1::10. [switchc] interface vlan-interface 2 [switchc-v...
Page 182
170 config weight : 255 running weight : 255 forwarder 01 state : active virtual mac : 000f-e2ff-4011 (owner) owner id : 0000-5e01-1101 priority : 255 active : local forwarder 02 state : listening virtual mac : 000f-e2ff-4012 (learnt) owner id : 0000-5e01-1103 priority : 127 active : fe80::2 forward...
Page 183
171 forwarder 02 state : active virtual mac : 000f-e2ff-4012 (owner) owner id : 0000-5e01-1103 priority : 255 active : local forwarder 03 state : listening virtual mac : 000f-e2ff-4013 (learnt) owner id : 0000-5e01-1105 priority : 127 active : fe80::3 forwarder weight track information: track object...
Page 184
172 virtual mac : 000f-e2ff-4013 (owner) owner id : 0000-5e01-1105 priority : 255 active : local forwarder weight track information: track object : 1 state : positive weight reduced : 250 the output shows that in vrrp group 1, switch a is the master and switch b and switch c are the backups. Each of...
Page 185
173 track object : 1 state : negative weight reduced : 250 # use the display vrrp ipv6 verbose command to display the detailed information of vrrp group 1 on switch c. [switchc-vlan-interface2] display vrrp ipv6 verbose ipv6 standby information: run mode : load balance run method : virtual mac total...
Page 186
174 # when the timeout timer—about 1800 seconds—expires, display the detailed information of vrrp group 1 on switch c. [switchc-vlan-interface2] display vrrp ipv6 verbose ipv6 standby information: run mode : load balance run method : virtual mac total number of virtual routers : 1 interface vlan-int...
Page 187
175 preempt mode : yes delay time : 5 auth type : none virtual ip : fe80::10 1::10 member ip list : fe80::2 (local, master) fe80::3 (backup) forwarder information: 2 forwarders 1 active config weight : 255 running weight : 255 forwarder 02 state : active virtual mac : 000f-e2ff-4012 (owner) owner id...
Page 188
176 • if the ping succeeds, check that their configurations are consistent in terms of number of virtual ip addresses, virtual ip addresses, advertisement interval, and authentication. Frequent vrrp state transition. Analysis: the vrrp advertisement interval is set too short. Solution: increase the ...
Page 189
177 stateful failover configuration this chapter includes these sections: • overview • introduction to stateful failover configuration • enabling stateful failover • configuring the backup vlan • displaying and maintaining stateful failover • stateful failover configuration example • configuration g...
Page 190
178 3. If one device fails, the other device can take over the services by using vrrp or a dynamic routing protocol (such as ospf) to avoid service interruption. In this document, the stateful failover feature supports backing up portal, and dhcp services. Figure 48 network diagram for stateful fail...
Page 191
179 introduction to stateful failover configuration to implement stateful failover on two devices, you need to perform the following configurations: • routing configuration. Configure vrrp or a dynamic routing protocol on the devices and the uplink/downlink devices to ensure that the traffic can aut...
Page 192
180 configuring the backup vlan after you specify a vlan as a backup vlan, the interfaces added to the vlan can serve as stateful failover interfaces to transmit stateful failover packets. Follow these steps to configure a backup vlan: to do… use the command… remarks enter system view system-view — ...
Page 193
181 figure 50 network diagram for stateful failover configuration procedure 1. Configure device a. # create vlan 100. System-view [devicea] vlan 100 # assign gigabitethernet 1/0/1 to vlan 100. [devicea-vlan100] port gigabitethernet 1/0/1 [devicea-vlan100] quit # specify vlan 100 as a backup vlan. [d...
Page 194
182 4. The configurations on device d are similar to those on device a (omitted). Configuration guidelines • stateful failover can be implemented only between two devices rather than among more than two devices. • the same numbered interfaces must exist on the two devices. Otherwise, session backup ...
Page 195
183 bfd configuration this chapter includes these sections: • introduction to bfd • configuring bfd basic functions • enabling trap • displaying and maintaining bfd note: the term router or router icon in this document refers to both routers and layer 3 switches. Introduction to bfd devices must qui...
Page 196
184 operation of bfd figure 51 bfd session establishment (on ospf routers) bfd session establishment: 1. A protocol sends hello messages to discover neighbors and establish neighborships. 2. After establishing neighborships, the protocol notifies bfd of the neighbor information, including destinatio...
Page 197
185 bfd detection methods • single-hop detection: detects the ip connectivity between two directly connected systems. • multi-hop detection: detects any of the paths between two systems. These paths have multiple hops and may be overlapped. • bidirectional detection: sends detection packets at two s...
Page 198
186 echo packets have a format similar to the format of bfd control packets (except that the desired min tx interval and required min rx interval fields are null) with udp port number 3785. Figure 2 illustrates the packet format. Figure 1 bfd packet format • vers: protocol version. The protocol vers...
Page 199
187 • demand (d): if set, demand mode is active in the transmitting system (the system wishes to operate in demand mode, knows that the session is up in both directions, and is directing the remote system to cease the periodic transmission of bfd control packets). If clear, demand mode is not active...
Page 200
188 • draft-ietf-bfd-multihop-08, bfd for multihop paths • draft-ietf-bfd-generic-05, generic application of bfd configuring bfd basic functions the bfd basic function configuration is the basis for configuring bfd for other protocols. Configuration prerequisites before configuring bfd basic functio...
Page 201
189 to do… use the command… remarks configure the minimum interval for receiving bfd control packets bfd min-receive-interval value optional for relevant information, see the description of the required min rx interval field in “ bfd packet format .” the value defaults to 400. Configure the detectio...
Page 202
190 note: • for the description of the snmp-agent trap enable bfd command, see the snmp-agent trap enable command ( network management and monitoring command reference ). • for the information center configuration, see the network management and monitoring configuration guide . Displaying and mainta...
Page 203
191 track configuration this chapter includes these sections: • track overview • track configuration task list • associating the track module with a detection module • associating the track module with an application module • displaying and maintaining track entries • track configuration examples tr...
Page 204
192 • if the tracked object functions normally, for example, the target interface is up or the target network is reachable, the state of the track entry is positive. • if the tracked object functions abnormally, for example, the target interface is down or the target network is unreachable, the stat...
Page 205
193 complete these tasks to configure the track module: task remarks associating track with nqa associating track with bfd associating the track module with a detection module associating track with interface management required use any of the approaches. Associating track with vrrp associating trac...
Page 206
194 associating track with bfd bfd supports the control packet mode and echo mode. Only echo-mode bfd can be associated with a track entry. When associated with a track entry, the bfd functions as follows: • if bfd detects the link fails, it informs the track entry of the link failure. The track mod...
Page 207
195 to do… use the command… remarks create a track entry, associate it with the interface management module to monitor the physical status of an interface, and specify the delay time for the track module to notify the associated application module when the track entry status changes track track-entr...
Page 208
196 to do… use the command… remarks enter system view system-view — enter interface view interface interface-type interface-number — create a vrrp group and configure its virtual ip address vrrp vrid virtual-router-id virtual-ip virtual-address required no vrrp group is created by default. Associate...
Page 209
197 associating track with static routing a static route is a manually configured route. With a static route configured, packets to the specified destination are forwarded through the path specified by the administrator. The disadvantage of using static routes is that they cannot adapt to network to...
Page 210
198 associating track with pbr policy-based routing (pbr) is a routing mechanism based on user-defined policies. Different from the traditional destination-based routing mechanism, pbr enables you to use a policy (based on the source address, and other criteria) to route packets. Pbr cannot detect t...
Page 212
200 # configure the test type as icmp-echo. [switcha-nqa-admin-test] type icmp-echo # configure the destination address as 10.1.2.2. [switcha-nqa-admin-test-icmp-echo] destination ip 10.1.2.2 # set the test frequency to 100 ms. [switcha-nqa-admin-test-icmp-echo] frequency 100 # configure reaction en...
Page 213
201 6. Verify the configuration after configuration, ping host b on host a, and you can see that host b is reachable. Use the display vrrp command to view the configuration result. # display detailed information about vrrp group 1 on switch a. [switcha-vlan-interface2] display vrrp verbose ipv4 stan...
Page 214
202 admin status : up state : backup config pri : 110 running pri : 80 preempt mode : yes delay time : 5 auth type : simple key : hello virtual ip : 10.1.1.10 master ip : 10.1.1.2 vrrp track information: track object : 1 state : negative pri reduced : 30 # display detailed information about vrrp gro...
Page 215
203 figure 55 network diagram for monitoring the master on the backup internet virtual router virtual ip address: 192.168.0.10 vlan-int2 192.168.0.101/24 vlan-int2 192.168.0.102/24 switch a master switch b backup l2 switch vrrp packets bfd probe packets configuration procedure 1. Create vlans, and a...
Page 216
204 [switchb] interface vlan-interface 2 [switchb-vlan-interface2] vrrp vrid 1 virtual-ip 192.168.0.10 [switchb-vlan-interface2] vrrp vrid 1 track 1 switchover [switchb-vlan-interface2] return 6. Verify the configuration # display the detailed information of vrrp group 1 on switch a. Display vrrp ve...
Page 217
205 local ip : 192.168.0.102 the output shows that when the status of the track entry becomes positive, switch a is the master and switch b the backup. # enable vrrp state debugging and bfd event debugging on switch b. Terminal debugging terminal monitor debugging vrrp state debugging bfd event # wh...
Page 218
206 figure 56 network diagram for monitoring uplinks using bfd internet master uplink device backup uplink device uplink virtual router virtual ip address: 192.168.0.10 vlan-int2 192.168.0.101/24 vlan-int2 192.168.0.102/24 switch a master switch b backup vlan-int3 1.1.1.1/24 vlan-int3 1.1.1.2/24 l2 ...
Page 219
207 [switchb] interface vlan-interface 2 [switchb-vlan-interface2] vrrp vrid 1 virtual-ip 192.168.0.10 [switchb-vlan-interface2] return 6. Verify the configuration # display the detailed information of the vrrp group on switch a. Display vrrp verbose ipv4 standby information: run mode : standard run...
Page 220
208 the output shows that when the status of track entry 1 becomes positive, switch a is the master and switch b the backup. # when the uplink of switch a goes down, the status of track entry 1 becomes negative. Display track 1 track id: 1 status: negative duration: 0 days 0 hours 1 minutes 40 secon...
Page 221
209 static routing-track-nqa collaboration configuration example network requirements as shown in figure 57 , switch a, switch b, switch c, and switch d are connected to two segments 20.1.1.0/24 and 30.1.1.0/24. Configure static routes on these switches so that the two segments can communicate with ...
Page 222
210 # configure a static route to 30.1.1.0/24, with the address of the next hop as 10.1.1.2 and the default priority 60. This static route is associated with track entry 1. System-view [switcha] ip route-static 30.1.1.0 24 10.1.1.2 track 1 # configure a static route to 30.1.1.0/24, with the address ...
Page 223
211 system-view [switchd] ip route-static 20.1.1.0 24 10.2.1.2 track 1 # configure a static route to 20.1.1.0/24, with the address of the next hop as 10.4.1.3 and the priority 80. [switchd] ip route-static 20.1.1.0 24 10.4.1.3 preference 80 # configure a static route to 10.1.1.1, with the address of...
Page 224
212 10.3.1.0/24 direct 0 0 10.3.1.1 vlan3 10.3.1.1/32 direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 inloop0 20.1.1.0/24 direct 0 0 20.1.1.1 vlan6 20.1.1.1/32 direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 inloop0 30.1.1.0/24 static 60 0 10.1.1.2 vlan2 127.0.0.0/8 direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 inloop0 127.0.0.1/32 direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 inloop0 the output shows...
Page 225
213 reply from 30.1.1.1: bytes=56 sequence=1 ttl=254 time=2 ms reply from 30.1.1.1: bytes=56 sequence=2 ttl=254 time=1 ms reply from 30.1.1.1: bytes=56 sequence=3 ttl=254 time=1 ms reply from 30.1.1.1: bytes=56 sequence=4 ttl=254 time=2 ms reply from 30.1.1.1: bytes=56 sequence=5 ttl=254 time=1 ms -...
Page 226
214 • configure static routing-track-bfd collaboration to determine whether the master route is available in real time. If the master route is unavailable, bfd can quickly detect the route failure to make the backup route take effect, and switch b forwards packets to 20.1.1.0/24 through switch c and...
Page 227
215 # configure a static route to 30.1.1.0/24, with the address of the next hop as 10.4.1.2. System-view [switchc] ip route-static 30.1.1.0 24 10.4.1.2 # configure a static route to 20.1.1.0/24, with the address of the next hop as 10.3.1.1. [switchb] ip route-static 20.1.1.0 24 10.3.1.1 5. Verify th...
Page 228
216 bfd session: packet type: echo interface : vlan-interface2 remote ip : 10.2.1.2 local ip : 10.2.1.1 # display the routing table of switch a. [switcha] display ip routing-table routing tables: public destinations : 9 routes : 9 destination/mask proto pre cost nexthop interface 10.2.1.0/24 direct ...
Page 229
217 5 packet(s) received 0.00% packet loss round-trip min/avg/max = 1/1/2 ms vrrp-track-interface management collaboration configuration example (the master monitors the uplink interface) network requirements • as shown in figure 59 , host a needs to access host b on the internet. The default gatewa...
Page 230
218 4. Configure vrrp on switch b. System-view [switchb] interface vlan-interface 2 # create vrrp group 1, and configure the virtual ip address 10.1.1.10 for the group. [switchb-vlan-interface2] vrrp vrid 1 virtual-ip 10.1.1.10 5. Verify the configuration after configuration, ping host b on host a, ...
Page 231
219 # after shutting down the uplink interface on switch a, display detailed information about vrrp group 1 on switch a. [switcha-vlan-interface3] display vrrp verbose ipv4 standby information: run mode : standard run method : virtual mac total number of virtual routers : 1 interface vlan-interface2...
Page 232
220 index a b c d e h i m o r s t v a activating an rrpp domain, 69 associating the track module with a detection module, 193 associating the track module with an application module, 195 availability evaluation, 1 availability requirements, 1 b background, 5 c cfd configuration example, 30 cfd confi...
Page 233
221 resetting dldp state, 46 rrpp configuration examples, 72 rrpp configuration task list, 64 rrpp overview, 55 s setting dldp mode, 44 setting the delaydown timer, 45 setting the interval for sending advertisement packets, 44 setting the port shutdown mode, 45 smart link configuration examples, 100...