- DL manuals
- IAI
- Controller
- ssel
- Operation Manual
IAI ssel Operation Manual
Summary of ssel
Page 1
Ssel controller operation manual fifteenth edition.
Page 3
Please read before use thank you for purchasing our product. This operation manual describes all necessary information items to operate this product safely such as the operation procedure, structure and maintenance procedure. Before the operation, read this manual carefully and fully understand it t...
Page 5
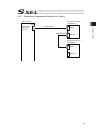
Construction of operation manual for each controller model and this manual ssel-cs z basic specifications • program mode operation ssel controller (this manual) me0157 • positioner mode operation ★ types to select from • pio control • fieldbus control (i) devicenet devicenet me0124 (ii) cc-link cc-l...
Page 7: Caution
Caution operator alarm on low battery voltage this controller can be equipped with the following optional backup batteries for retention of data in the event of power failure: [1] system-memory backup battery (optional) for retention of position data, global variables/flags, error list, strings, etc...
Page 8: Caution
Caution optional system-memory backup battery the ssel controller can be used with the optional system-memory backup battery. Caution: when installing the system-memory backup battery, “other parameter no. 20” must be set to “2.” installing the system-memory backup battery will add the following fun...
Page 9: Caution
Caution note on controller with expanded memory *1 *1 positions and programs have increased to 20000 and 128, respectively, among others. For a controller with expanded memory, use the pc software or teaching pendant of an applicable version as specified below. Teaching tool version xsel pc software...
Page 10
Table of contents safety guide......................................................................................................................1 modes in ssel controller .................................................................................................8 caution in handling .........
Page 11
2.4 installing the absolute-data backup battery (optional) ...............................................76 2.5 installing the absolute-data backup battery (optional) ...............................................77 chapter 3 program mode operation.....................................................
Page 12
7.11 permission of sio/pio program startup with password............................................254 7.12 parameter setting (applied).......................................................................................255 7.12.1 want to operate the system tentatively without using i/os............
Page 13
Chapter 10 warranty......................................................................................................391 10.1 warranty period..........................................................................................................391 10.2 scope of the warranty......................
Page 15
1 safety guide “safety guide” has been written to use the machine safely and so prevent personal injury or property damage beforehand. Make sure to read it before the operation of this product. Safety precautions for our products the common safety precautions for the use of any of our robots in each...
Page 16
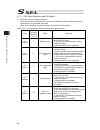
2 no. Operation description description 2 transportation ● when carrying a heavy object, do the work with two or more persons or utilize equipment such as crane. ● when the work is carried out with 2 or more persons, make it clear who is to be the leader and who to be the follower(s) and communicate...
Page 17
3 no. Operation description description (2) cable wiring ● use our company’s genuine cables for connecting between the actuator and controller, and for the teaching tool. ● do not scratch on the cable. Do not bend it forcibly. Do not pull it. Do not coil it around. Do not insert it. Do not put any h...
Page 18
4 no. Operation description description 4 installation and start (4) safety measures ● when the work is carried out with 2 or more persons, make it clear who is to be the leader and who to be the follower(s) and communicate well with each other to ensure the safety of the workers. ● when the product...
Page 19
5 no. Operation description description 6 trial operation ● when the work is carried out with 2 or more persons, make it clear who is to be the leader and who to be the follower(s) and communicate well with each other to ensure the safety of the workers. ● after the teaching or programming operation...
Page 20
6 no. Operation description description 8 maintenance and inspection ● when the work is carried out with 2 or more persons, make it clear who is to be the leader and who to be the follower(s) and communicate well with each other to ensure the safety of the workers. ● perform the work out of the safe...
Page 21: Alert Indication
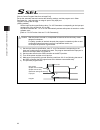
7 alert indication the safety precautions are divided into “danger”, “warning”, “caution” and “notice” according to the warning level, as follows, and described in the operation manual for each model. Level degree of danger and damage symbol danger this indicates an imminently hazardous situation wh...
Page 22
8 modes in ssel controller there are two types of modes in ssel controller, “program mode” to operate the program created in sel language and “positioner mode” to have an operation by indicating the position number from a controller such as host plc. There are five types of modes prepared in positio...
Page 23
9 caution in handling 1 make sure to follow the usage condition, environment and specification range of the product. Operation out of the guarantee could cause a drop in performance or malfunction of the product. 2. Wait for 5 seconds or more before rebooting the power. For the reason of controller ...
Page 24
10 6. Transference of pio signal between controllers please note the following when conducting transference of pio signal between controllers. To certainly transfer the signal between controllers with different scan time, it is necessary to have longer scan time than the one longer than the other co...
Page 25
11 international standards compliances this product complies with the following overseas standard. Refer to overseas standard compliance manual (me0287) for more detailed information. Rohs directive ce marking ○ ○.
Page 26
12.
Page 27
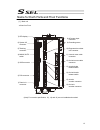
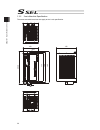
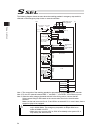
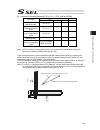
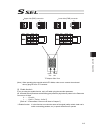
13 name for each parts and their functions [1] main unit ● view from front (note) for one axis specification, 12), 14) and 16) are not installed and masked. 8) ac power input connector 9) grounding screw 10) regenerative resister unit connector 11) 1st axis motor cable connector 12) 2nd axis motor c...
Page 28
14 ● view from bottom bat2 bat1 ● view from top sbat 19) 1st axis absolute-data backup battery connector 18) 2nd axis absolute-data backup battery connector 17) 1st/2nd axis absolute-data backup battery holder 21) system-memory backup battery holder 20) system-memory backup battery connector.
Page 29
15 1) panel unit connector [refer to 2.3.5] it is a connector to connect the panel unit pu-1 (option) to display the controller status and error numbers. [for details of panel unit, refer to 1.4.3 panel unit: pu-1] 2) pio connector [refer to 2.3.4] it is the pio interface with 24 points of input and...
Page 30
16 8) ac power input connector [refer to 2.3.1] it is a connector to input the main power supply 100v to 115v ac or single-phase 200v to 230v ac. It consists of five terminals, motor power terminals, control power terminals and pe terminals. Warning: do not attempt to touch this connector or wires w...
Page 31
17 18) 2nd axis absolute-data backup battery connector it is the connector to connect the absolute battery in order to have a backup of the 2nd absolute encoder data. (to mount the absolute data backup battery in the absolute encoder specification) 19) 1st axis absolute-data backup battery connector...
Page 32
18 [2] panel unit: pu-1 (option) this is the display board consists of four digits of seven-segment displays and led lamps. The status of a controller such as the error codes can be checked on it if it is connected to ssel controller. Also, if connected to an extension i/o unit, the condition of eac...
Page 33
19 [3] brake box: rcb-110-ra13-0 (option) it is a brake control unit necessary when the following actuators are in brake-equipped specification. Ultra high-thrust rod type rcs2-ra13r mzms/mzmm/lzms/lzmm types in ball screw nut rotary type ns series brakes for two axes can be controlled with one brak...
Page 34
20 2) brake power input connector[refer to 2.3.7] it is a connector to connect the power line. Supply 24v dc (19.76va/axis). 3) power on led it turns on (green) when 24v dc gets supplied. 4) brake release switch connector 2[refer to 2.3.7] signals of a switch prepared externally can ...
Page 35
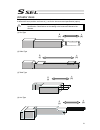
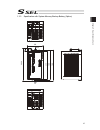
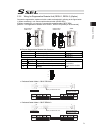
21 actuator axes refer to the pictures below for the actuator axes that can be controlled. 0 defines the home position, and items in ( ) are for the home-reversed specification (option). (1) rod type (2) slider type (3) table type (4) arm type caution: there are some actuators that are not applicabl...
Page 36
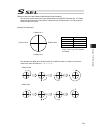
22 (5) gripper type finger attachment (6) rotary type (300-degree rotation specification) (360-degree rotation specification) (360-degree rotation specification) for multiple rotation specification with the origin reversed specification, the directions of + and – are the other way around.
Page 37
23 starting procedures when using this product for the first time, work while making sure to avoid omission and incorrect wiring by referring to the procedure below. Warning: make sure to put the brake release switch on the controller on the right (nom) when booting the power. If it is on the left (...
Page 38
24 2. Positioner mode it is necessary to select a mode for operation from the five types of positioner modes, and have the setting done in other parameter no. 25. [refer to chapter 4 for the operating methods.] no→ check item any vibration or abnormal noise? → test run adjustment 2 1) set the manu/a...
Page 39
Chapter 1 specifications check 25 chapter 1 specifications check 1.1 product check the standard configuration of this product is comprised of the following parts. If you find any faulty or missing parts, contact your local iai distributor. 1.1.1 components (excluding options) no. Item model quantity...
Page 40
Chapter 1 specifications check 26 1.1.2 teaching tool (optional) the pc software or teaching pendant is necessary to perform setup operations such as position and parameter settings through teaching or other means. Use either of them. No. Item model 1 pc software (with rs232c cable + emergency stop ...
Page 41
Chapter 1 specifications check 27 1.1.4 how to read the model plate 1.1.5 how to read the model mode serial number model ssel-c-2-200a-100ab-np-2-1 serial no. 600061190 made in japan ssel – cs - 2 - 200a - 100ab - np - 2 - 1 n o p q q r s t type specification table f details of axis 1 to axis 2 c se...
Page 42
Chapter 1 specifications check 28 linear actuators connectable to ssel controller the linear actuators lsa and lsas available to connect to ssel controller are as shown below. ○: connectable ×: not connectable linear actuator model single-phase 100v input specification single-phase 200v input specif...
Page 43
Chapter 1 specifications check 29 calculation of actuator wattage connectable to ssel controller the total wattage of two axes of connectable actuators should be 400w or less for the single-phase 100v input specification. It should be 800w or less for the single-phase 200v input specification. Howev...
Page 44
Chapter 1 specifications check 30 1.2 basic specifications 1.2.1 specification list specification item single-phase 100v input specification single-phase 200v input specification number of controlled axes 1-axis to 2-axis applicable motor capacity 20w to 750w total connectable wattage 400w 800w cont...
Page 45
Chapter 1 specifications check 31 specification item single-phase 100v input specification single-phase 200v input specification insulation resistance 10mΩ or more (between power terminal and i/o terminal and also all external terminals and case at the power supply of 500v dc) insulation strength 1,...
Page 46
Chapter 1 specifications check 32 1.2.2 power capacity and heat output calculate the power capacity and heat output using the following formulas. Rated power capacity [va] = rated motor power capacity on 1st axis [va] + rated motor power capacity on 2nd axis [va] + control power capacity [va] peek m...
Page 47
Chapter 1 specifications check 33 table 2 capacity and heat output of the control power supply control power capacity [va] heat output at control power source [w] 60 36 table 3 brake power supply power supply voltage [v] 24 rated current [a] 0.5 peek maximum current [a] 1 heat output at rated power ...
Page 48
Chapter 1 specifications check 34 1.2.3 selection of the circuit breaker for the selection of the circuit breaker, perform it according to the following items. • 3 times of the rated current flows to the controller during the acceleration/deceleration. Select one that does not trip when the above cu...
Page 49
Chapter 1 specifications check 35 1.3 external dimensions 1.3.1 2-axis specification the same external dimensions also apply to the 1-axis specification. 100 177 186 195 bat2 bat1 sbat 126 φ4.5.
Page 50
Chapter 1 specifications check 36 1.3.2 2-axis absolute specification the same external dimensions also apply to the 1-axis specification. 195 186 177 100 126 202.6 bat2 bat1 sbat φ4.5.
Page 51
Chapter 1 specifications check 37 1.3.3 specification with system memory backup battery (option) bat1 bat2 16.6 202.6 195 186 177 100 sbat φ4.5.
Page 52
Chapter 1 specifications check 38 1.4 option 1.4.1 pio board [1] type display polarity input and output points np npn input 24 points, output 8 points pn pnp input 24 points, output 8 points [2] input and output interfaces input output input voltage 24v dc ±10% load voltage 24v dc ±10% input current...
Page 53
Chapter 1 specifications check 39 caution: if a non-contact circuit is connected externally, malfunction may result from leakage current. Use a circuit in which leakage current in a off state does not exceed 1 ma. ~ pio board input signal on duration off duration at the default settings, the system ...
Page 54
Chapter 1 specifications check 40 1.4.2 field network board type overview details devicenet devicenet field network board this board communicates the i/o data as the remote i/o terminal. Refer to the separate instruction manual. (me0124) cc-link cc-link field network board this board communicates th...
Page 55
Chapter 1 specifications check 41 1.4.3 panel unit: pu-1 this is the display board consists of four digits of seven-segment displays and led lamps. The status of a controller such as the error codes can be checked on it if it is connected to ssel controller. Also, if connected to an extension i/o un...
Page 56
Chapter 1 specifications check 42 1.4.4 brake box: rcb-110-ra13-0 this is required when the following actuator has the brake. • ball screw nut rotary type ns series mzms/mzmm/lzms/lzmm • robo cylinder high-thrust rod type rcs2-ra13r one brake box can control the brakes for two axes. [specification] ...
Page 57
Chapter 1 specifications check 43 1.4.5 regenerative resister unit: resu-1 and resu-2 regenerative resister unit: a unit that converts to heat the regenerative current generated when the motor decelerates. [specification] item specification internal regenerative resistor 235Ω 80w resu-1 controller c...
Page 58
Chapter 1 specifications check 44 [number of connectable] to calculate the total number of necessary units, figure out from the table below considering the total wattage of two axes of actuators connected to ssel controller. It is a reference under a condition that the actuator is operated at the ma...
Page 59
Chapter 1 specifications check 45 1.5 installation and storage environment this product is capable for use in the environment of pollution degree 2*1 or equivalent. *1 pollution degree 2: environment that may cause non-conductive pollution or transient conductive pollution by frost (iec60664-1). [1]...
Page 60
Chapter 1 specifications check 46 1.6 noise prevention and the installation (1) protective ground for the grounding, the grounding resistance should be set to 100Ω or less. The wiring should apply a twist line or an annealed copper wire of 2.0 mm 2 (awg14) or more. L1 l2 l1c l2c nc pe utilize the gr...
Page 61
Chapter 1 specifications check 47 (2) noise elimination grounding (frame ground) have grounding on the frame when security grounding is not to be conducted. For grounding, make sure to conduct class d grounding (grounding resistance 100Ω or less). Apply annealed twist wire or copper wire cables with...
Page 62
Chapter 1 specifications check 48 (5) heat radiation and installation design the control panel size, controller layout and cooling method so that the surrounding air temperature around the controller will be kept at or below 40°c. Install the controller vertically on a wall, as shown below. This con...
Page 63
Chapter 1 specifications check 49 (6) panel unit (option) installation utilize the hook hole on the back side to hang on a tool such as l-shaped hook. Hook hole such as l-shaped hook 6 3.2 10 rear side 9 1.2 rear side.
Page 64
Chapter 1 specifications check 50
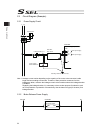
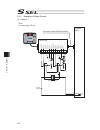
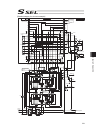
Page 65
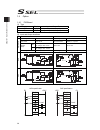
Chapter 2 wiring 51 chapter 2 wiring 2.1 wiring (connection of devices) diagram axis 1 axis 2 panel unit absolute-data backup batteries (option) usb rs232 conversion cable grounded regenerative resistance unit (option) auxiliary power equipment 24-vdc brake power supply (note 1)(note 2) teaching pen...
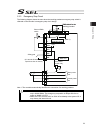
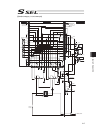
Page 66
Chapter 2 wiring 52 2.2 circuit diagram (example) 2.2.1 power supply circuit nac-10-472 pe l n l1 l2 l1c l2c pwr circuit breaker noise filter controller ac power supply input connector drive power supply drive power supply grounding resistance at 100Ω or less surge protector r/a/v-781bwz-2a leakage ...
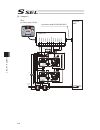
Page 67
Chapter 2 wiring 53 2.2.3 emergency stop circuit the following diagram shows the case when the teaching pendants emergency stop switch is reflected on the controller’s emergency stop circuit design. Motor power unit main cpu connection detection circuit external emg switch (*1) s1 +24v s2 emg+ emg- ...
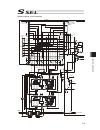
Page 68
Chapter 2 wiring 54 the following diagram shows the case when the teaching pendant’s emergency stop switch is reflected on the emergency stop circuits on several controllers. Main cpu emergency stop circuit +24v 0v (note 2) mc1 mc2 mcn cr cr safety gate s1 +24v s2 cr cr emg+ emg- enb+ enb- l1 l2 l1c...
Page 69
Chapter 2 wiring 55 2.2.4 motor encoder circuit [1] motor cable connection motor cable motor cable axis 1 mot1 mot2 axis 2 connector for the motor cable connector for the motor cable (note1) (note1) (note1) applicable motor cable model no. : cable length example) 030 = 3 m actuator cable single ...
Page 70
Chapter 2 wiring 56 2.2.5 pio circuit (note) refer to 4.1.3 pio pattern selection and pio signal in chapter 4 operation in positioner mode for the assignment of input and output ports in positioner mode. There are 2 types of pio as shown below. Polarity no. Of i/o points npn 24 input points / 8 outp...
Page 71
Chapter 2 wiring 57 pin no. Electric wire color port no. Function at standard setting (factory default) parameter no. Parameter name input function specification values (factory default) input function specification values function 7a orange 2 003 general-purpose input 33 input function select 003 0...
Page 72
Chapter 2 wiring 58 [2] output port assignment the set features will be assigned if the output function specification values (0 to 17, 24 and 25) are set in i/o parameter no. 46 to 53 (output function select 300 to 307). The features set at delivery can be changed. Pin no. Electric wire color port n...
Page 73
Chapter 2 wiring 59 [3] wiring (1) npn specification ● 24 input points / 8 output points 016 017 018 019 020 021 022 023 000 001 002 003 004 005 006 007 008 009 010 011 012 013 014 015 300 301 302 303 304 305 306 307 load (red-1 ) (orange-1) (yellow-1) (green-1) (blue-1) (purple-1) (gray-1) (white-1...
Page 74
Chapter 2 wiring 60 (2) pnp specification ● 24 input points / 8 output points 016 017 018 019 020 021 022 023 000 001 002 003 004 005 006 007 008 009 010 011 012 013 014 015 300 301 302 303 304 305 306 307 load (red-1 ) (orange-1) (yellow-1) (green-1) (blue-1) (purple-1) (gray-1) (white-1) (black-1)...
Page 75
Chapter 2 wiring 61 2.2.6 connection of regenerative resister unit (option) unit (resu-2) cb-sc-reu010 rb regenerative resister unit connector regenerative resister regenerative resister rb in rb out rb in rb out unit (resu-1) cb-st-reu010 ssel controller.
Page 76
Chapter 2 wiring 62 2.2.7 brake box (rcb-110-ra13-0) (option) ssel controller m1 brake box (rcb-110-ra13) 24vin 0v cb-x3- pa controller1 encoder input connector limit switch connector limit switch connector actuator1 encoder output connector 0v ns type (equipped with brake) +24v 24v dc 24v dc 0v cb-...
Page 77
Chapter 2 wiring 63 2.2.8 teaching port cd rd sd 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 er sg dr rs cs nc teaching connector tp attached emergency stop switch box pc software accessory cable pc ssel controller.
Page 78
Chapter 2 wiring 64 2.3 wiring method 2.3.1 wiring for power supply circuit to ssel controllers, supply the following power supplies. Power supply type specification remarks single-phase 100v specification single-phase 100v ac to 115v±10% motor power supply single-phase 200v specification single-pha...
Page 79
Chapter 2 wiring 65 (1) ac power supply input connector connector model remarks cable side mstb2.5/6-stf-5.08 (phoenix contact) enclosed in standard package controller side mstb2.5/6-gf-5.08 (phoenix contact) pin no. Signal name description applicable wire diameter 6 l1 motor power 200v ac or ac100v...
Page 80
Chapter 2 wiring 66 2.3.2 wiring the emergency stop circuit (system i/o) item description drive-source cutoff circuit built-in (hard-wired configuration) conforming category b, 1 to 4 (it is necessary to use tp adapter for 1 to 4.) [9.1 examples of safety circuits (refer to conforming to safety cate...
Page 81
Chapter 2 wiring 67 2.3.3 wiring for actuator the example of connection with a controller (1) motor cable connector specification connector model remarks cable side gic2.5/4-stf-7.62 (phoenix contact) controller side gic2.5/4-gf-7.62 (phoenix contact) terminal assignments pin no. Signal name descrip...
Page 82
Chapter 2 wiring 68 (2) encoder connector specifications connector model remarks cable side 10126-3000pe (sumitomo 3m) / hood (10326-52f0-008) controller side 10226-6202jl (sumitomo 3m) half-pitch i/o connector 26 pins pin no. Signal name description applicable wire diameter 1 nc not connected 2 nc ...
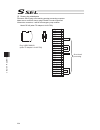
Page 83
Chapter 2 wiring 69 2.3.4 wiring for pio the connection of i/o to the controller is to be carried out using the dedicated i/o cable. The cable length is shown in the model code of the controller. Please check the controller model code. There are 2m for standard, 3m and 5m as an option. 10m is also a...
Page 84
Chapter 2 wiring 70 2.3.5 wiring for panel unit panel unit (option) can be used by connecting to ssel controller. Z panel unit connector connector model remarks cable side df11-8ds-2c (hirose) controller side df11-10ds-2c (hirose) 10 9 2 1 width color red (red) red ( white ) blue ( blue ) yellow(whi...
Page 85
Chapter 2 wiring 71 2.3.6 wiring for regenerative resister unit (resu-1, resu-2) (option) connect the regenerative resister unit with a cable enclosed with it referring to the figure below. 1) when connecting 1 unit: connect with enclosed cable (cb-sc-reu) 2) when connecting 2 or more units: connect...
Page 86
Chapter 2 wiring 72 2.3.7 wiring for the brake box (rcb-110-ra13-0) as shown in the figure below, connect the actuator, brake box and controller. (the figure is an example for connecting to the 1st axis.) controller rear view external brake connector box (rcb-110-ra13-0) encoder cable (cb-x3-pa) act...
Page 87
Chapter 2 wiring 73 (2) brake power input connector connector model remarks cable side mc1.5/2-st-3.5 (phoenix contact) brake box side mc1.5/2-g-3.5 (phoenix contact) pin no. Signal name description applicable wire diameter 1 0v 24v power ground 2 +24vin +24v power input 0.08 to 1.25mm 2 (awg28 to a...
Page 88
Chapter 2 wiring 74 2.3.8 wiring for the teaching tool the teaching connector is used to connect an iai teaching pendant or pc (pc software) so that the equipment can be operated, set up or otherwise manipulated from the teaching pendant/pc. Make sure to connect the enclosed dummy plug dp-3 (for sse...
Page 89
Chapter 2 wiring 75 z terminal assignments pin no. Direction signal name description 1 sg signal ground 2 out emgs emergency stop status 3 out vcc power output (5v power supply) 4 in dtr terminal ready (shorted to dsr) 5 nc 6 nc 7 nc 8 out rsvvcc power output (24v power supply) 9 in emgin emergency-...
Page 90
Chapter 2 wiring 76 2.4 installing the absolute-data backup battery (optional) 1) install the supplied battery holder at the bottom of the controller. 2) insert the battery into the holder. 3) connect the battery connector. Pay attention to the connector orientation. (the connector hook should face ...
Page 91
Chapter 2 wiring 77 2.5 installing the absolute-data backup battery (optional) 1) install the supplied battery holder at the top of the controller. 2) insert the battery into the holder. 3) connect the battery connector. Pay attention to the connector orientation. (the hook of the connector should f...
Page 92
Chapter 2 wiring 78.
Page 93
Chapter 3 program mode operation 79 chapter 3 program mode operation * program mode is executed when set to other parameter no. 25 = 0. 3.1 types of operations the ssel controller is a programming controller that can operate without a host controller. Programming for this controller uses iai’s dedic...
Page 94
Chapter 3 program mode operation 80 3.2 receiving and forwarding of i/o signals necessary for operation the i/o port can deliver the data with the xsel controller and external signals through interface. One port can exchange data for one contact (1 bit). Data is exchanged via pios (24v i/os) or over...
Page 95
Chapter 3 program mode operation 81 (1) i/o map the factory-set i/o port numbers and functions of the xsel controller are shown below. The functions of the i/o port can be changed using the parameter setting. [refer to 2.2.5 pio circuit and chapter 7. Parameter] port no. Function port no. Function 0...
Page 96
Chapter 3 program mode operation 82 3.3 controller data structure in the controller, there are various types of data existing in the memory such as program data, position data, parameters, etc. Ssel controller data structure parameters main sel language position data application programs parameters ...
Page 97
Chapter 3 program mode operation 83 3.3.1 how to save data the flow to save data in the ssel controller is illustrated below. When data is transferred from the pc software or teaching pendant to the controller, the data is only written to the main cpu memory as shown in the diagram below and will be...
Page 98
Chapter 3 program mode operation 84 [2] when the system-memory backup battery (optional) is used change the setting of other parameter no. 20 to 2 (system-memory backup battery installed). Battery backup memory positions sel global data (flags, variables, strings) error lists data edited on the pc o...
Page 99
Chapter 3 program mode operation 85 [3] points to note point to note when transferring data and writing to the flash memory never turn off the main power while data is being transferred or written to the flash memory. The data will be lost and the controller operation may be disabled. Point to note ...
Page 100
Chapter 3 program mode operation 86 control power motor power controller status pio power after the power is cut off, the power cutoff processing will start within approx. 0.5 to 1.5 ac cycles. Must be turned off simultaneously, as a rule. Power cutoff processing if the pio power is turned off durin...
Page 101
Chapter 3 program mode operation 87 3.4.2 panel unit pu-1 display the status of the controller is displayed in the led lamps on the controller panel. By connecting the panel unit to the controller, the status of the controller can be displayed in the 7-segment led in four digits. When the unit is st...
Page 102
Chapter 3 program mode operation 88 table 1 panel unit pu-1 (option) display list application control codes display priority (note 1) description 1 the ac power is cut off. (momentary power failure or power-supply voltage drop is also a possibility.) 1 a system-shutdown level error is present. 2 dat...
Page 103
Chapter 3 program mode operation 89 table 2 panel unit pu-1 (option) display list core control codes display priority (note 1) description 1 ac power cut off (momentary power failure or power-supply voltage drop may also be the cause.) 1 cold-start level error 1 cold-start level error 1 operation-ca...
Page 104
Chapter 3 program mode operation 90 3.4.3 position table and program creation and writing create a position table and create a program using the sel language. Perform the teaching, etc., and register the required coordinates in the position table. Also, create the program using the sel language. [re...
Page 105
Chapter 3 program mode operation 91 3.5 program operation for the operation there are two ways of start-up. One is the automatic start-up of the set program no. And the other is to start up with the program no. Selected externally. 3.5.1 auto start upon power on after the power is turned on, the pro...
Page 106
Chapter 3 program mode operation 92 [how to control program start from an input port] set up the automatic start and conduct the following settings, and the program set in other parameter no. 1 will start when on-edge is input to any input port. Program will stop with off-edge. (setting method) set ...
Page 107
Chapter 3 program mode operation 93 3.5.2 starting a program by specifying its program number the program to be started up, can be started with its number specified externally and start-up signal input. 1) connect the pc software and perform the setting, referring to the set values in the following ...
Page 108
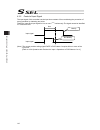
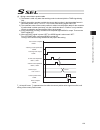
Chapter 3 program mode operation 94 3.5.3 input timing for software reset signal and servo-on signal [1] software reset signal the input function select 023 of i/o parameter no. 258 is assigned to the software reset signal input port at the delivery. It can be assigned to other input ports. T3 1 t 2...
Page 109
Chapter 4 operation in positioner mode 95 chapter 4 operation in positioner mode * positioner mode gets activated when set to other no. 25 = 1 to 4 and 16. 4.1 basic operation 4.1.1 basic operation methods the way of operation in positioner mode is to input the position number that positioning is re...
Page 110
Chapter 4 operation in positioner mode 96 1) by using a teaching tool such as the pc software, set the target position (coordinate value), velocity and acceleration/deceleration for the number of all necessary positioning points in the position table in manu mode (by setting auto/manu switch to manu...
Page 111
Chapter 4 operation in positioner mode 97 4.1.2 parameter settings it is necessary to define the control pattern by setting one in the five types of pio patterns of positioner mode in other parameter no. 25. [refer to 4.1.3 pio pattern selection and pio signal for the five types of pio patterns] (no...
Page 112
Chapter 4 operation in positioner mode 98 4.1.3 pio pattern selection and pio signal (1) pio pattern (control pattern) selection there are five types of pio patterns. Set the most suitable pio pattern with the actual use to parameter no. 25 “operation mode type”. Refer to “4.2 operation in positione...
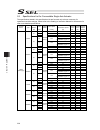
Page 113
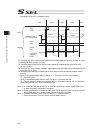
Chapter 4 operation in positioner mode 99 (2) pio patterns and signal assignment the signal assignment of i/o flat cable by the pio pattern is as shown below. Follow the following table to connect the external equipment (such as plc). Other parameter no.25 (pio pattern) selection 1 2 3 category pio ...
Page 114
Chapter 4 operation in positioner mode 100 note 1 c6f home-return incomplete error will occur if a start signal is generated under condition of home-return operation incomplete. Note 2 in the 2-axis independent mode, a system-battery voltage low warning will not be output. In this mode, it is recomm...
Page 115
Chapter 4 operation in positioner mode 101 other parameter no.25 ”operation mode type” 4 16 category pio functions teaching mode ds-s-c1 compatible mode position quantity max. 2,047 (1,500 for controller before memory capacity increase) max. 20,000 (1,500 for controller before memory capacity increa...
Page 116
Chapter 4 operation in positioner mode 102 note 5 the actuator automatically conducts the home-return operation and then moves to the indicated position number if a start signal is generated under condition of home-return operation incomplete. Note 6 servo is turned on and then home-return operation...
Page 117
Chapter 4 operation in positioner mode 103 (3) list of pio signals the table below lists the functions of pio signals. Refer to the section shown in relevant sections for the details of the control of each signal. Category signal abbreviation signal name function description relevant sections standa...
Page 118
Chapter 4 operation in positioner mode 104 category signal abbreviation signal name function description relevant sections *alm alm alarm turns on when the controller is in normal condition, and turns off when an alarm is generated. (note) ds-s-c1 compatible mode is alm (active high). 4.2.3 [4] rdy ...
Page 119
Chapter 4 operation in positioner mode 105 4.2 operation in positioner mode in the positioner mode, the following 5 types of pio pattern can be selected with a proper parameter. Type setting value in other parameter no. 25 mode pio pattern 0 1 standard mode pio pattern 1 2 product switching mode pio...
Page 120
Chapter 4 operation in positioner mode 106 4.2.1 set of position table the values in the position table can be set as shown below. [1] setting at positioning operation caution: the input value is treated as the angle for the rotary actuator. Therefore; [mm] [deg]: ··············1.2 = 1.2deg [mm/s]...
Page 121
Chapter 4 operation in positioner mode 107 3) vel: velocity [mm/s]······ set the velocity in the operation. Do not attempt to input a value more than the maximum velocity. 4) acc: acceleration [g]···· set the acceleration at start. 5) dcl: deceleration [g]···· set the deceleration at stop. (referenc...
Page 122
Chapter 4 operation in positioner mode 108 [2] setting at pressing operation perform the setting as described below when having a pressing in standard mode of pio pattern 0 and type switchover mode of pio pattern 1. Pressing operation cannot be performed on two axes at the same time. For a controlle...
Page 123
Chapter 4 operation in positioner mode 109 7) pressing velocity [mm/s] ··· setup of the velocity during pressing operation is conducted. 8) pressing[%] ··················· setup of the pressing torque (current limit value) is conducted in %. The set value multiplied by 100 is the pressing torque (cu...
Page 124
Chapter 4 operation in positioner mode 110 4.2.2 control of input signal the input signal of this controller has the input time constant of 6ms considering the prevention of wrong operation by chattering and noise. Therefore, input each input signal for 6ms or more (note) continuously. The signal ca...
Page 125
Chapter 4 operation in positioner mode 111 4.2.3 operation ready and auxiliary signals = common item [1] servo on (son, sv, pend), ready (rdy) input output pio signal rdy son sv pend other than pattern 4 pio pattern 4 ds-s-c1 compatible mode : available, : unavailable (note) there is no servo-on si...
Page 126
Chapter 4 operation in positioner mode 112 [2] home return (home, hend, pend) input output pio signal home hend pend other than patterns 3 and 4 pio pattern 3 teaching mode note1 pattern 4 ds-s-c1 compatible mode note2 : available, : unavailable note 1: there is no home-return by home signal in pio...
Page 127
Chapter 4 operation in positioner mode 113 perform home-return operation by following the procedure explained below. * before commencing the procedure, confirm that the ready output signal rdy and alarm output signal +alm are on. 1) turn on the servo-on signal son 2) confirm that the servo-on status...
Page 128
Chapter 4 operation in positioner mode 114 [home-return operation of slider type / rod type actuators] 1) with the home signal being on, the actuator moves toward the mechanical end at the home return speed. The moving speed is 20mm/s for most actuators but less than 20mm/s for some actuators. Refer...
Page 129
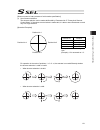
Chapter 4 operation in positioner mode 115 [actuator movement for spurious absolute specification] 1) with home signal on, the actuator moves towards the home-return direction set in parameter no.11 at 3mm/s (fixed). 2) move back and forth in approximately 16mm (to confirm the current position). 3) ...
Page 130
Chapter 4 operation in positioner mode 116 [operation of rotary actuator] 1) 2) home = 0° home sensor 1) with home signal on, the actuator rotates in ccw (counterclockwise) direction from the view point of the load side. The velocity is either 20deg/s or 5deg/s. (it depends on the setting of each ac...
Page 131
Chapter 4 operation in positioner mode 117 [operation of actuator of gripper type] 1) with home signal on, the actuator moves toward the mechanical end at the home return speed (20mm/s). 2) the actuator is turned at the mechanical end and stopped at the home position. The movement amount at this mom...
Page 132
Chapter 4 operation in positioner mode 118 [3] cancel (*canc, canc) input pio signal *canc, canc other than pio pattern 3 ○ pio pattern 3 teaching mode × ○: available, ×: unavailable 1) the actuator will decelerate and stop if the cancellation signal is turned off during movement. The remained movem...
Page 133
Chapter 4 operation in positioner mode 119 [5] error reset (res) output pio signal res other than pio pattern 4 ○ pio pattern 4 ds-s-c1 compatible mode × ○ : available, ×: unavailable 1) cancel the alarm signal *alm turned on when an error was generated. If an error is occurred, check the detail and...
Page 134
Chapter 4 operation in positioner mode 120 [6] cpu reset (cpres) output pio signal cpres other than pio pattern 4 × pio pattern 4 ds-s-c1 compatible mode ○ ○: available, ×: unavailable 1) it is the input signal to restart the controller. When an error is occurred, check the cause and get rid of it, ...
Page 135
Chapter 4 operation in positioner mode 121 [8] absolute battery error (aber) output pio signal aber in common for pio patterns 0, 1, 3 and 4 ○ pio pattern 2 2-axis independent mode × ○: available, ×: unavailable 1) it turns off when the absolute battery voltage is in normal condition. 2) it turns on...
Page 136
Chapter 4 operation in positioner mode 122 4.2.4 operation with the position no. Input = operations of pio patterns 0 to 4 this section describes the methods of operations of pio patterns 0 to 4. These patterns provide normal controller operation methods in which the controller is operated by turnin...
Page 137
Chapter 4 operation in positioner mode 123 [position indication in type switchover mode] the position indication in type switchover mode is to be conducted in position numbers and type numbers. With the same position number indication, different position movement can be performed for each type. Ther...
Page 138
Chapter 4 operation in positioner mode 124 e.G.) when parameter is set as stated below; other parameter no. 71 = 0 (binary) “position number input method indication” other parameter no. 72 = 6 “number of position number input bits” other parameter no. 73 = 50 “number of positions for one type” as th...
Page 139
Chapter 4 operation in positioner mode 125 [position indication in 2-axis independent mode] the position number uses the 13 bits from pc1 to 13 separately in 1st axis position number and 2nd axis position number. The way to divide is set in the parameter. Setting item parameter setting range way to ...
Page 140
Chapter 4 operation in positioner mode 126 sample use control method 1) first enter command position no. Pc1 to pc** with binary data. (note) it is necessary to turn off the teaching mode indication signal mode and set to positioner mode when positioning operation is to be made in teaching mode in p...
Page 141
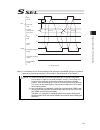
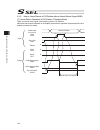
Chapter 4 operation in positioner mode 127 t1: at least 6 msec input start product/ position input servo on alarm ready positioning complete home return complete servo on status output 6) 7) 8) 9) 10) 4) 2) 1) b s a s 3) h h h t1 h h 5) p po o cstr son pc1 to pc** alm rdy pend hend svon (note) it is...
Page 142
Chapter 4 operation in positioner mode 128 [pio pattern 4 ds-s-c1 compatible mode] input start cstr position input pc1 to pc20000 alarm alm ready rdy positioning complete pend output stop move stop move stop t2 t2 t1 t1 pos a pos b l l h t3 t3 t4 t5 t5 t1: time after a position number signal is inpu...
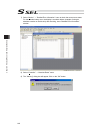
Page 143
Chapter 4 operation in positioner mode 129 [how to check positioner mode version] check the version of the positioner mode in operation mode in pos. Mode management info. Window after starting up in the positioner mode. Positioner mode administration information window opens if controller → pos. Mod...
Page 144
Chapter 4 operation in positioner mode 130 [ operation modes of rotary actuator in multiple rotation mode and command limitations] an actuator of multi-rotation specification includes two operation modes, or the normal mode enabling only a limited number of rotations and the index mode note 1 enabli...
Page 145
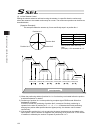
Chapter 4 operation in positioner mode 131 [shortcut control of rotary actuator of multi-rotation specification] (1) set of shortcut selection the shortcut selection can be made valid/invalid by parameter no.67 “rotary axis shortcut control select”. If the shortcut control select is made valid, it i...
Page 146
Chapter 4 operation in positioner mode 132 (2) infinite rotation control making the shortcut selection valid and moving the actuator in a specific direction continuously allows the actuator to be rotated continuously as a motor. The continuous operation can be done as described below. [operation exa...
Page 147
Chapter 4 operation in positioner mode 133 [2] interpolation operation[standard] (pc1 to pc**, cstr, line and pend) input output pio signal pc1 to pc** (note 1) cstr line pend pio pattern 0 standard mode pc1 to 16 ○ ○ ○ pio pattern 1 product switching mode pc1 to 16 ○ ○ ○ pio pattern 2 2-axis indepe...
Page 148
Chapter 4 operation in positioner mode 134 [3] pressing operation sample use velocity 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) positioning width 50 press-fitting process caulking process pressing operation cannot be performed on two axes at the same time. For 2-axis specification controller, set up the positio...
Page 149
Chapter 4 operation in positioner mode 135 t1: at least 6msec pressing operation complete judgment the time that the current more than the torque (current limit) set in % in “acc” in the larger position number has continued is identified in ‘pressing stop confirmation time in positioning (each axis ...
Page 150
Chapter 4 operation in positioner mode 136 caution: (1) the velocity before pressing start position is the value set in vel in the larger position number. The pressing velocity after starting pressing is the value set in vel in the smaller position number, and the pressing will be conducted in the v...
Page 151
Chapter 4 operation in positioner mode 137 [4] teaching by pio (mode, jog1+, jog1-, jog2+, jog2-, pwrt, tcmd, wend) input output pio signal mode jog1+ jog2+ jog1- jog2- pwrt tcmd wend other than pattern 3 pattern 3 teaching mode : existence of signal, : no signal (note) the feature is available onl...
Page 152
Chapter 4 operation in positioner mode 138 (2) jog/inching switch and jog input 1) the operation turns to the jog operation *1 when the four bits of inching ic001 to ic1 are set to 0. The operation turns to the inching operation *2 when setup is made in the four bits from inching ic001 to ic1. Four ...
Page 153
Chapter 4 operation in positioner mode 139 (3) writing current data to position table 1) the feature is valid only when the teaching mode is selected (with the tcmd signal being on). 2) specify the position number to which the current data is written in the binary data format in command position no....
Page 154
Chapter 4 operation in positioner mode 140 caution: (1) set the period taken from entering position no. To turning the pwrt on to 6ms or longer. In spite of 6ms timer process in the plc, commands may be input to the controller concurrently to cause writing to another position. Take the scanning time...
Page 155
Chapter 4 operation in positioner mode 141 [5] pause and operation interruption (*stp, *canc, pend) input output pio signal * stp * canc pend pattern 0 to 2 : existence of signal, : no signal input output pio signal * stp * canc pend pattern 3 teaching mode : existence of signal, : no signal input...
Page 156
Chapter 4 operation in positioner mode 142 control method pause is possible during movement. In addition, the remaining moving distance can be cancelled to interrupt the operation. The pause signal *stp is an input signal that is always on in the pio patterns except for in pio pattern 4. So, it is n...
Page 157
Chapter 4 operation in positioner mode 143 4.2.5 synchro operation it is a function to operate two axes of actuators at the same time. By setting one axis the master axis while the other as the slave axis, and by having the slave axis track the master one, two axes operate at the same time. The axis...
Page 158
Chapter 4 operation in positioner mode 144 4.2.6 how to home-return in pio pattern without home-return signal hend [1] home-return operation in pio pattern 3 teaching mode there is no home-return signal in the teaching mode in pio pattern 3. When the home-return operation is incomplete, home-return ...
Page 159
Chapter 4 operation in positioner mode 145 [2] home-return in pio pattern 4 ds-s-c1 compatible mode there is no home-return signal in ds-s-c1 compatible mode in pio pattern 4. The positioning complete signal is off if the home-return operation is in incomplete status after the power gets turned on. ...
Page 160
Chapter 4 operation in positioner mode 146.
Page 161
Chapter 5 absolute reset and absolute battery 147 chapter 5 absolute reset and absolute battery (note) conduct the absolute reset in manu mode. 5.1 absolute reset (absolute specification) 5.1.1 for pc software 1) turn off the controller power. 2) plug in the 9-pin d-sub connector on the connection c...
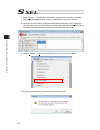
Page 162
Chapter 5 absolute reset and absolute battery 148 7) select “monitor” → “detailed error information” menu to check the current error status. For the encoder battery error, the display is as shown below. (example of using an absolute encoder on the 4th axis) after checking, close “detailed error info...
Page 163
Chapter 5 absolute reset and absolute battery 149 * conduct 10) to 15) and 20) to 22) for the versions earlier than main application v0.57 and earlier than xsel pc software v12.02.05.00. * conduct 16) to 22) for the versions of main application v0.57 or later and those of xsel pc software v12.02.05....
Page 164
Chapter 5 absolute reset and absolute battery 150 13) once the process of encoder multi rotation data reset is finished, the red arrow moves to the next item. Click on the buttons for the following processes one by one. (after completing every process, the red arrow moves to the next.) 1) reset cont...
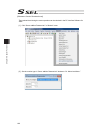
Page 165
Chapter 5 absolute reset and absolute battery 151 18) click on the “ × ” button in the absolute reset window to close it. 19) click × in “abs. Encoder reset” window to close the window and the screen switches to the confirmation window asking “write flash rom?”. Put a check mark on “parameter” and c...
Page 166
Chapter 5 absolute reset and absolute battery 152 23) now the process for absolute reset is complete. If a redo of the absolute reset is required, end the x-sel pc software once and conduct the whole process from the beginning again. (note) in some actuator, the current value does not show 0mm after...
Page 167
Chapter 5 absolute reset and absolute battery 153 5.1.2 for teaching pendant (1) sel-t/td/tg, ia-t-x/xd executes absolute data reset. Select the f1 (rabs) key on the controller item screen. Mode transition: ctl-rabs to execute absolute reset, press the f1 (yes) key. If not, press the f2 (no) key. Re...
Page 168
Chapter 5 absolute reset and absolute battery 154 3) servo on f1 (ok) key. 4) homing f1 (ok) key. 5) servo off after executing absolute reset, be sure to reset software or reconnect the power. Do not press the f1 (ok) key but press the page up key. Then move to 6) encoder multi-rotation data reset 2...
Page 169
Chapter 5 absolute reset and absolute battery 155 (2) tb-01 select absolute reset from controller menu. To have an absolute reset, either touch yes button or press f1 (yes) key. When not to have an absolute reset, either touch no button or press f2 (no) key. The display returns to the previous scree...
Page 170
Chapter 5 absolute reset and absolute battery 156 1) encoder rotation data reset 1 touch ok button or press f1 (ok) key. 2) reset controller error touch ok button or press f1 (ok) key. 3) servo-on touch ok button or press f1 (ok) key..
Page 171
Chapter 5 absolute reset and absolute battery 157 4) returning home touch ok button or press f1 (ok) key. 5) servo-off touch ok button or press f1 (ok) key. 6) encoder rotation data reset 2 touch ok button or press f1 (ok) key..
Page 172
Chapter 5 absolute reset and absolute battery 158 return to the axis no. Input screen. When you want to have another axis conduct absolute reset, input the axis number and touch ok button or press f1 (ok) key. To finish absolute reset, either touch re-start controller button or press esc key. Restar...
Page 173
Chapter 5 absolute reset and absolute battery 159 5.2 absolute reset (battery-less absolute specification) main application: v0.57 or later xsel pc software: v12.02.05.00 or later 1) turn off the controller power. 2) plug in the 9-pin d-sub connector on the connection cable to the communication port...
Page 174
Chapter 5 absolute reset and absolute battery 160 7) select “monitor” → “detailed error information” menu to check the current error status. After checking the absolute error , close the “detailed error information” window. 8) make sure to have a backup of the parameters before conducting. Select “p...
Page 175
Chapter 5 absolute reset and absolute battery 161 11) “abs. Encoder reset” appears. Select the tab for the axis that requires the absolute reset. 12) press “start” button, and the warning window appears. Release the emergency stop, check the content and click “yes”. Home-return operation of the indi...
Page 176
Chapter 5 absolute reset and absolute battery 162 5.3 data retaining battery 5.3.1 system-memory backup battery (option) [1] specifications with an option, it is available to have a backup of sel global data and error list in a battery so the data is retained even after the power to the robot is tur...
Page 177
Chapter 5 absolute reset and absolute battery 163 voltage alarm 3.1v (reference value) battery voltage drop warning (error no.A01) 2.5v (reference value) battery voltage error (error no. A02) normal 3.6v 3.1v 2.5v w arning signal output alarm occurrence battery voltage drop warning (error no. A01) b...
Page 178
Chapter 5 absolute reset and absolute battery 164 [2] replacement for system-memory backup battery caution: the following contents of sram will be retained for 30 minutes after the power is turned off (when the super capacitance inside the controller is fully charged) if the system memory backup bat...
Page 179
Chapter 5 absolute reset and absolute battery 165 5) replace the system memory backup battery. Remove the battery connector and pull out the battery. 6) put the new battery in the holder, and locate the snap feature on the right to connect the connector. 7) when the replacement of system-memory back...
Page 180
Chapter 5 absolute reset and absolute battery 166 12) set “other parameter no. 20 system-memory backup battery mounting feature type” back to what was recorded in step 9), transfer the data to the controller, and then write the parameter to the flash rom. * the ways to edit the parameter and to writ...
Page 181
Chapter 5 absolute reset and absolute battery 167 5.3.2 absolute encoder backup [1] specifications since the backup for the absolute position data is conducted by the battery, it will be maintained even if the power to the robot is turned off. Batteries have a life, so it is recommended that you rep...
Page 182
Chapter 5 absolute reset and absolute battery 168 voltage alarm 3.1v (reference value) battery voltage drop warning (error no.A23) 2.5v (reference value) battery voltage error (error no.914, ca2) normal 3.6v 3.1v 2.5v w arning signal output alarm occurrence absolute reset is not necessary battery vo...
Page 183
Chapter 5 absolute reset and absolute battery 169 [2] replacement for absolute battery the replacement process may differ depending on the error (no. A23, 914, ca2) occurred during replacement. • have from 1) to 4) conducted when there is no error has occurred or absolute data backup battery voltage...
Page 184
Chapter 5 absolute reset and absolute battery 170 5) plug in the 9-pin d-sub connector on the pc software connection cable to the communication port on the pc (or plug in the usb connector to the usb port on the pc). Join the 25-pin d-sub connector on the other end to the teaching port on the contro...
Page 185
Chapter 5 absolute reset and absolute battery 171 * conduct 11) for the versions earlier than main application v0.57 and earlier than xsel pc software v12.02.05.00. * conduct 12) for the versions of main application v0.57 or later and those of xsel pc software v12.02.05.00 or later. 11) the absolute...
Page 186
Chapter 5 absolute reset and absolute battery 172 13) select controller → software reset in the menu to reboot the controller. (note) without restarting the controller by having the software reset or rebooting the power, it may cause; • error no. C70 abs coordinate unconfirmed error, or • error no. ...
Page 187
Chapter 6 special functions 173 chapter 6 special functions 6.1 synchro function 6.1.1 overview [1] common items (applicable to both the battery-less absolute specification, absolute specification and incremental specification) it is a function to operate two axes of actuators at the same time. By s...
Page 188
Chapter 6 special functions 174 [caution for when using synchro function] • in case the current positions of the master axis and the slave axis are not in the right place during the servo is on, an automatic adjustment will be performed in slow speed. • in case the current positions of the master ax...
Page 189
Chapter 6 special functions 175 [2] incremental specification with the incremental specification, the relative positioning of the master-axis and slave-axis sliders remains fixed while the power is on. (if the sliders were moved while the power was turned off, synchro movement will begin from the po...
Page 190
Chapter 6 special functions 176 6.1.2 preparation for operation of synchro specification prepare for operation with the steps described below. 1) positioning of synchro axes sliders [refer to [1] in this section] 2) absolute reset [refer to [2] in this section] it is not necessary when both the mast...
Page 191
Chapter 6 special functions 177 [2] how to absolute reset on synchronizing specification the way how to perform the absolute reset differs in case the two axes are both battery-less absolute specification and absolute specification and in case it is the combination of battery-less absolute specifica...
Page 192
Chapter 6 special functions 178 (1) method for when 2 axes are battery-less absolute specification and absolute specification described below is the steps when master axis = 1 and slave axis = 1 in “axis-specific parameter no. 38 encoder abs/inc type”. (note) when having the absolute reset conducted...
Page 193
Chapter 6 special functions 179 * conduct 3) for the versions earlier than main application v0.57 and earlier than xsel pc software v12.02.05.00. * conduct 4) for the versions of main application v0.57 or later and those of xsel pc software v12.02.05.00 or later. 3) have the absolute reset conducted...
Page 194
Chapter 6 special functions 180 4) conduct he absolute reset in the following steps. A. Have only “encoder rotation data reset” done on the slave axis. B. For the master axis, conduct in the order shown in the screen. C. Again, conduct “encoder multi-rotation data reset” on (1) slave axis. After hav...
Page 195
Chapter 6 special functions 181 5) set the value of the slave axis recorded in 1) in “axis-specific parameter no. 83, abs synchro-slave axis coordinate initialization cancell.” select [transfer to controller] → [write to flash rom] → [restart controller] (software reset). 6) set home preset values a...
Page 196
Chapter 6 special functions 182 c. Input the value figured out in b. To “axis-specific parameter no. 12 home preset value” on the slave axis. Select [transfer to controller] → [write to flash rom] → [restart controller] (software reset). 7) after turning the servo on, move the master axis with jog o...
Page 197
Chapter 6 special functions 183 (2) method for combination of battery-less absolute specification or absolute specification and incremental specification described below is the steps when master-axis = 1 and slave-axis = 0 in “axis-specific parameter no. 38 encoder abs/inc type”. After completing 6....
Page 198
Chapter 6 special functions 184 6.1.3 procedure for re-execution of absolute reset in case that absolute reset has to be conducted again for such reasons as a trouble, follow the instruction below to perform the reset. • proceed to step (1) when the mechanical joint condition is in the same as at th...
Page 199
Chapter 6 special functions 185 caution: if a change is necessary on the home preset value for a fine-tuning of a slave axis at the startup, record and keep the home preset value before the change by following the method mentioned in 6.1.2 [2] (1) 6). When the absolute reset is executed again, put t...
Page 200
Chapter 6 special functions 186 6.2 multiple-slider near-miss detection (collision prevention) function supported versions : ssel controller main application version 0.12 or later : pc software version v7.0.4.0 or later when multiple sliders are used, this function prevents jogging or positioning ax...
Page 201
Chapter 6 special functions 187 [1] setting method 1) set the mating axis number for each axis in axis-specific parameter no. 104, “target axis specification for multiple-slider near-miss detection.” (the example below assumes that an interlocked slider exists on the positive side of the coordinate ...
Page 202
Chapter 6 special functions 188 related parameters (axis-specific parameters) no. Parameter name default value (reference) input range unit remarks 104 target axis specification for multiple-slider near-miss detection 0h 0h to ffffffffh bits 0 to 3: mating axis number of near-miss detection target (...
Page 203
Chapter 6 special functions 189 6.3 driver overload warning function setting the motor estimated raised temperature that causes the driver overload error as 100%, the driver overload warning (message level error) will be detected when the load rate (hereafter described as the overload level) exceede...
Page 204
Chapter 6 special functions 190 [reference: check of overload level] the overload level during the motor operation can be checked in the pc interface software for xsel. [1] click “servo addition datamonitor” in “monitor” menu. [2] set the monitor type in “servo addition datamonitor” window to “01: m...
Page 205
Chapter 6 special functions 191 ● axis-specific parameters no. Parameter name default value (reference) input range unit access right remarks 113 olwl (used be ovld) driver overload warning load level ratio 100 50 to 100 % f set in % from the driver overload error load level (invalid when 100) * to ...
Page 206
Chapter 6 special functions 192.
Page 207
Chapter 7 i/o parameter 193 chapter 7 i/o parameter parameter data should be set appropriately according to the applicaiton requirements. When a change is required to the parameters, make sure to back up the data before the change so the settings can be returned anytime. With using pc software, it i...
Page 208
Chapter 7 i/o parameter 194 ◎ parameters set in bits • how to use bits refer below for how to turn on the bits (in case the last digit of the set value is h). Set the value of hexadecimal number transformed from the binary number. ■ binary number in the binary number system, the figure is expressed ...
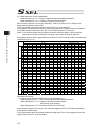
Page 209
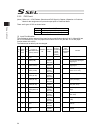
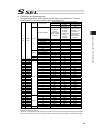
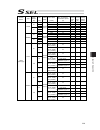
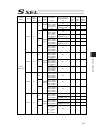
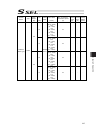
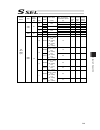
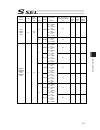
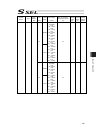
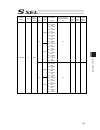
Chapter 7 i/o parameter 195 7.1 i/o parameter (all types) no. Parameter name default value (reference) input range unit remarks 1 i/o port assignment type 1 0 to 20 0: fixed assignment 1: automaticassignment 2 i/o slot 1 fix-allocated input port start no. 000 -1 to 299 0+(multiple of 8)(invalid if a...
Page 210
Chapter 7 i/o parameter 196 i/o parameter (all types) no. Parameter name default value (reference) input range unit remarks 24 i/o setting bit pattern 1 10000h 0h to ffffffffh bits 0 to 3: rdy out function selection (system io) (0: sysrdy (software = pio trigger program can be run) and hardware is n...
Page 211
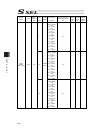
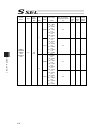
Chapter 7 i/o parameter 197 i/o parameter (all types) no. Parameter name default value (reference) input range unit remarks 45 input function selection 015 0 0 to 99 input function specification value * refer to 7.2 i/o function lists 46 output function selection 300 2 0 to 99 outputt function speci...
Page 212
Chapter 7 i/o parameter 198 i/o parameter (all types) no. Parameter name default value (reference) input range unit remarks 74 number of tp user output ports used (hand, etc.) 0 0 to 8 referenced by tp. (invalid if “0” is set) 75 tp user output port start number (hand, etc.) 0 0 to 599 referenced by...
Page 213
Chapter 7 i/o parameter 199 i/o parameter (all types) no. Parameter name default value (reference) input range unit remarks 107 reserved by the system (change is prohibited) 0 0h to ffffffffh 108 reserved by the system (change is prohibited) 0 0h to ffffffffh 109 reserved by the system (change is pr...
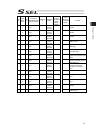
Page 214
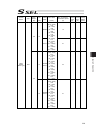
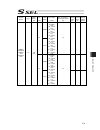
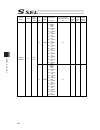
Chapter 7 i/o parameter 200 i/o parameter (all types) no. Parameter name default value (reference) input range unit remarks 123 network attribute 4 0h 0h to ffffffffh bits 0 to 3: ethernet tcp/ip message communication selection whether to permit 0.0.0.0 (ip address of connection destination can be i...
Page 215
Chapter 7 i/o parameter 201 i/o parameter (all types) no. Parameter name default value (reference) input range unit remarks 125 network attribute 6 1e1eh 0h to ffffffffh bits 0 to 7: reserved by the system bits 8 to 15: reserved by the system bits 16 to 23: increment of “pc/tp reconnection delay at ...
Page 216
Chapter 7 i/o parameter 202 i/o parameter (all types) no. Parameter name default value (reference) input range unit remarks 151 iai protocol b/tcp: ip address of connection destination (manu mode) (ml) 0 0 to 255 152 iai protocol b/tcp: ip address of connection destination (manu mode) (l) 100 0 to 2...
Page 217
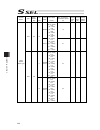
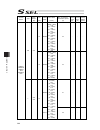
Chapter 7 i/o parameter 203 i/o parameter (all types) no. Parameter name default value (reference) input range unit remarks 178 (for expansion) 0 179 (for expansion) 0 180 (for expansion) 0 181 (for expansion) 0 182 (for expansion) 0 183 (for expansion) 0 184 (for expansion) 0 185 (for expansion) 0 ...
Page 218
Chapter 7 i/o parameter 204 i/o parameter (all types) no. Parameter name default value (reference) input range unit remarks 220 reserved by the sio system 00000000h 0h to ffffffffh 221 reserved by the sio system 00000000h 0h to ffffffffh 222 reserved by the sio system 00000000h 0h to ffffffffh 223 r...
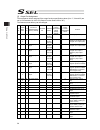
Page 219
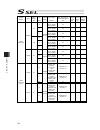
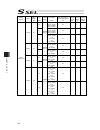
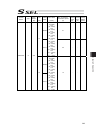
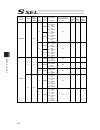
Chapter 7 i/o parameter 205 i/o parameter (all types) no. Parameter name default value (reference) input range unit remarks 253 input function selection 018 11 0 to 99 input function specification value * refer to 7.2 i/o function lists 254 input function selection 019 12 0 to 99 input function spec...
Page 220
Chapter 7 i/o parameter 206 i/o parameter (all types) no. Parameter name default value (reference) input range unit remarks 301 to 600 (for extension) 601 reserved by the system 0 0 to 4 (main application version 0.48 or 0.55 or later. Sram16mbit version only) 602 ia net occupied station top number ...
Page 221
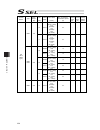
Chapter 7 i/o parameter 207 i/o parameter (all types) no. Parameter name default value (reference) input range unit remarks 609 ia net attribute 2 f05h 0h to ffffffffh bits 0 to 7: iai protocol b/sio, iai protocol b/tcp non-communication confirmation timer value (sec) (time to become receivable cond...
Page 222
Chapter 7 i/o parameter 208 i/o parameter (all types) no. Parameter name default value (reference) input range unit remarks 633 reserved by the system 0h 0h to ffffffffh (main application version 0.48 or 0.55 or later. Sram16mbit version only) 634 reserved by the system 0h 0h to ffffffffh (main appl...
Page 223
Chapter 7 i/o parameter 209 i/o parameter (all types) no. Parameter name default value (reference) input range unit remarks 664 reserved by the system 0 0 to 99999999 (main application version 0.48 or 0.55 or later. Sram16mbit version only) 665 reserved by the system 0h 0h to ffffffffh (main applica...
Page 224
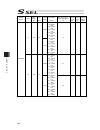
Chapter 7 i/o parameter 210 i/o parameter (all types) no. Parameter name default value (reference) input range unit remarks 695 communication shared memory reference work pattern among ia net controllers (95-64) 0h 0h to ffffffffh (same as i/o parameter no. 693) (main application version 0.48 or 0.5...
Page 225
Chapter 7 i/o parameter 211 i/o parameter (all types) no. Parameter name default value (reference) input range unit remarks 708 extension output port start number at extension i/o unit slot 1 fixed assignment -1 -1 to 599 300+(multiples of 8) (invalid when a negative value or applicable slot do not ...
Page 226
Chapter 7 i/o parameter 212 i/o parameter (all types) no. Parameter name default value (reference) input range unit remarks 713 extension input port start number at extension i/o unit slot 4 fixed assignment -1 -1 to 299 0+(multiples of 8) (invalid when a negative value or applicable slot di not in ...
Page 227
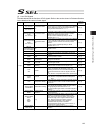
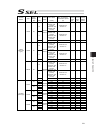
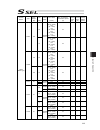
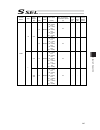
Chapter 7 i/o parameter 213 7.2 i/o function lists [1] input function list input function specification value function name remarks 0 general-purpose input 1 program start signal (bcd) (on edge) specify a bcd program number using the ports to which start-program number specification bits x (input fu...
Page 228
Chapter 7 i/o parameter 214 i/o function lists [1] input function specification value function name remarks 22 axis 1 forced brake-release input when the applicable port turns on, the brake will be unlocked forcibly (pay attention to falling load). * brake release of the synchronized slave axis conf...
Page 229
Chapter 7 i/o parameter 215 [2] output function list output function specification value function name remarks 0 general-purpose output 1 operation-cancellation level or higher error output (on) * the following output functions cannot be assigned at the same time: • operation-cancellation level or h...
Page 230
Chapter 7 i/o parameter 216 i/o function lists [2] output function specification value function name remarks 20 to 23 reserved by the system for expansion 24 axis 1 servo-on status output 25 axis 2 servo-on status output 26 to 29 reserved by the system for expansion.
Page 231
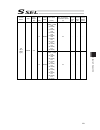
Chapter 7 i/o parameter 217 7.3 parameters common to all axes no. Parameter name default value (reference) input range unit remarks 1 valid axis pattern 1b or 11b 0b to 11111111b off bit: setting of driver not mounted 2 default override 100 1 to 100 used if not specified in program. (invalid for sio...
Page 232
Chapter 7 i/o parameter 218 parameters common to all axes no. Parameter name default value (reference) input range unit remarks 18 maximum operation acceleration/deceleration check timing 1 0 to 1 0: check at input pc/tp checks the input in all axes parameter no. 22 “maximum acceleration” and “no. 2...
Page 233
Chapter 7 i/o parameter 219 parameters common to all axes no. Parameter name default value (reference) input range unit remarks 29 all axes setting bit pattern 1 10000 0h to ffffffffh bits 0 to 3: selection of use of last pc/tp inching distance (0: do not use, 1: use) *referenced by the pc/tp bits 4...
Page 234
Chapter 7 i/o parameter 220 parameters common to all axes no. Parameter name default value (reference) input range unit remarks 69 (for expansion) 0 70 (for expansion) 0 71 (for expansion) 0 72 (for expansion) 0 73 (for expansion) 0 74 (for expansion) 0 75 (for expansion) 0 76 (for expansion) 0 77 (...
Page 235
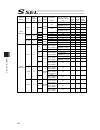
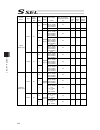
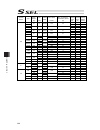
Chapter 7 i/o parameter 221 7.4 axis-specific parameters no. Parameter name default value (reference) input range unit remarks 1 axis operation type 0 0 to 1 0: linear movement axis 1: rotation movement axis (angle control) 2 acmx+acceleration 1 30 1 to 999 0.01g acceleration speed when acmx command...
Page 236
Chapter 7 i/o parameter 222 axis-specific parameters no. Parameter name default value (reference) input range unit remarks 21 offset movement amount in home-return 1000 -99999999 to 99999999 0.001mm offset movement amount from the z-phase ideal position (positive value = direction to go against the ...
Page 237
Chapter 7 i/o parameter 223 axis-specific parameters no. Parameter name default value (reference) input range unit remarks 38 encoder abs/inc type 1 0 to 1 0: incremental 1: absolute 39 magnetic pole sensor mount indication (for future expansion = setting change forbidden) 1 0 to 1 0: not equipped 1...
Page 238
Chapter 7 i/o parameter 224 axis-specific parameters no. Parameter name default value (reference) input range unit remarks 54 pressing stop detection movement amount in home-return 20 1 to 99999 0.001mm used in pressing check in home-return operation 55 pressing stop detection movement amount in pre...
Page 239
Chapter 7 i/o parameter 225 axis-specific parameters no. Parameter name default value (reference) input range unit remarks 76 home-adjustment parameter set selection 1 0 to 1 0: p21 = phase-z evacuation distance at inc home return p12 = ideal phase-z position coordinate 1: p32 is read automatically ...
Page 240
Chapter 7 i/o parameter 226 axis-specific parameters no. Parameter name default value (reference) input range unit remarks 91 zone 2 output no. 0 0 to 899 physical output port or global flag or extended output ports (output invalid when set to 0, invalid when duplicated) 92 zone 3 max. 0 -99999999 t...
Page 241
Chapter 7 i/o parameter 227 axis-specific parameters no. Parameter name default value (reference) input range unit remarks 107 multi-slider setting bit pattern 1 12h 0h to ffffffffh bits 0 to 3: multi-slider actual position overapproach detection margin (mm) (valid only on multi-slider master axis p...
Page 242
Chapter 7 i/o parameter 228 axis-specific parameters no. Parameter name default value (reference) input range unit remarks 134 maximum operation acceleration for each axis 0 0 to 999 0.01g invalid when set to 0. Limited by all axes parameter no. 22 “maximum acceleration” when set to invalid (main ap...
Page 243
Chapter 7 i/o parameter 229 axis-specific parameters no. Parameter name default value (reference) input range unit remarks 186 (for expansion) 0 187 (for expansion) 0 188 (for expansion) 0 189 (for expansion) 0 190 (for expansion) 0 191 (for expansion) 0 192 (for expansion) 0 193 (for expansion) 0 1...
Page 244
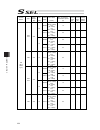
Chapter 7 i/o parameter 230 7.5 driver parameters no. Parameter name default value (reference) input range unit remarks 1 type (upper) (manufacturing information) space 2 type (middle) (manufacturing information) space 3 type (lower) (manufacturing information) space 4 manufacturing data (manufactur...
Page 245
Chapter 7 i/o parameter 231 driver parameters (all types) no. Parameter name default value (reference) input range unit remarks 26 motor • encoder configuration information (compatible with e, priority on e)(configuration information) 0000h 0000h to ffffh motor encoder identificati on number high-or...
Page 246
Chapter 7 i/o parameter 232 driver parameters (all types) no. Parameter name default value (reference) input range unit remarks 45 torque filter time constant 0 0 to 2500 [refer to 7.13 servo adjustment] 46 current control band number 4 0 to 15 * change prohibited unless any indication from the supp...
Page 247
Chapter 7 i/o parameter 233 driver parameters (all types) no. Parameter name default value (reference) input range unit remarks 76 current control query information 09 0h 0000h to ffffh lower word of linear motor lead 77 current control query information 10 0h 0000h to ffffh bits 0 to 3: linear moto...
Page 248
Chapter 7 i/o parameter 234 7.6 encoder parameters no. Parameter name default value (reference) input range unit remarks 1 type (upper) (manufacturing information) space 2 type (middle) (manufacturing information) space 3 type (lower) (manufacturing information) space 4 manufacturing data (manufactu...
Page 249
Chapter 7 i/o parameter 235 encoder parameters (all types) no. Parameter name default value (reference) input range unit remarks 19 (function information) 0000h 0000h to ffffh 20 (function information) 0000h 0000h to ffffh 21 (function information) 0000h 0000h to ffffh 22 (function information) 0000...
Page 250
Chapter 7 i/o parameter 236 7.7 i/o devices parameters no. Parameter name default value (reference) input range unit remarks 1 type (upper) (manufacturing information) space 2 type (middle) (manufacturing information) space 3 type (lower) (manufacturing information) space 4 manufacturing data (manuf...
Page 251
Chapter 7 i/o parameter 237 i/o devices parameters (all types) no. Parameter name default value (reference) input range unit remarks 32 device parameter (by board type) 00000000h 00000000h to ffffffffh 33 device parameter (by board type) 00000000h 00000000h to ffffffffh 34 device parameter (by board...
Page 252
Chapter 7 i/o parameter 238 i/o devices parameters (all types) no. Parameter name default value (reference) input range unit remarks 63 query information 11 (by board type) 0000h 0000h to ffffh 64 query information 12 (by board type) 0000h 0000h to ffffh 65 query information 13 (by board type) 0000h...
Page 253
Chapter 7 i/o parameter 239 7.8 other parameters no. Parameter name default value (reference) input range unit remarks 1 auto-start program number 0 0 to 64 (not applied for memory capacity increase) 0 to 128 (applicable for memory capacity increase) (invalid if “0” is set) 2 i/o processing program ...
Page 254
Chapter 7 i/o parameter 240 other parameters (all types) no. Parameter name default value (reference) input range unit remarks 10 emergency-stop recovery type 0 0 to 4 0: abort operations/programs 1: recovery after reset 2: operation continued (only during automatic operation. * operation commands f...
Page 255
Chapter 7 i/o parameter 241 other parameters (all types) no. Parameter name default value (reference) input range unit remarks 27 (for expansion) 0 28 (for expansion) 0 29 (for expansion) 0 30 option password 00 0h 0h to ffffffffh reserved (change is prohibited) * change is prohibited unless instruc...
Page 256
Chapter 7 i/o parameter 242 other parameters (all types) no. Parameter name default value (reference) input range unit remarks 40 eeprom information check type 03h 0h to ffffffffh 0: disable checksum, 1: enable checksum bit 0 = (reserved by the system) bit 1 = encoder bits 2 to 7 = (reserved by the ...
Page 257
Chapter 7 i/o parameter 243 other parameters (all types) no. Parameter name default value (reference) input range unit remarks 47 other setting bit pattern 2 1h 0h to ffffffffh bits 0 to 7: reserved by the system.(data for other models) bits 8 to 11: whether to use servo monitoring io monitor functi...
Page 258
Chapter 7 i/o parameter 244 other parameters (all types) no. Parameter name default value (reference) input range unit remarks 61 (for expansion) 0 62 (for expansion) 0 63 (for expansion) 0 64 (for expansion) 0 65 (for expansion) 0 66 (for expansion) 0 67 (for expansion) 0 68 (for expansion) 0 69 (f...
Page 259
Chapter 7 i/o parameter 245 7.9 feature setup for i/o any input and output port can be made to the dedicated input and output or the general input and output. Set the input function specification value to the io parameter (input function select n) applicable to the input and output port number that ...
Page 260
Chapter 7 i/o parameter 246 [input function specification values] input function specification value 0: general-purpose input the applicable input can be used freely in programs as a generalpurpose input. Input function specification value 1: program start signal (bcd) (on edge) the applicable signa...
Page 261
Chapter 7 i/o parameter 247 input function specification value 9: start-program number specification bit 1 (least significant bit) this bit specifies the least significant bit of a program number. Note: start-program number specification bits x (input function specification values 9 through 15) cann...
Page 262
Chapter 7 i/o parameter 248 input function specification value 21: remote-mode control input this signal can be used to switch between the auto mode and manual mode. Note: switching is enabled only when the mode switch is set to “auto.” input function specification value 22: axis 1 forced brake rele...
Page 263
Chapter 7 i/o parameter 249 [ output function specification value] output function specification value 0: general-purpose output the applicable output can be used freely in programs as a generalpurpose output. Output function specification value 1: operation-cancellation level or higher error output...
Page 264
Chapter 7 i/o parameter 250 output function specification value 10: auto mode output a signal will be output during the auto mode. Output function specification value 11: auto operation status output a signal will be output during auto program operation. Output function specification value 12: all-v...
Page 265
Chapter 7 i/o parameter 251 7.10 parameters for linear / rotation controls shown in the list below are the combinations of parameters for linear and rotation controls: inpu t uni t • dist ance mm • s pe ed m m /se c • a ccelera tion / d ecel eration g • angle mm → de g • an gular velocity mm/s ec → ...
Page 266
Chapter 7 i/o parameter 252 [parameters related to rotary axis movement] ● rotation movement axis mode select (axis-specific parameter no.66) set the rotation axis mode. When setting of the axis operation type (axis-specific parameter no. 1) is rotary movement axis: 1, the current value expression i...
Page 267
Chapter 7 i/o parameter 253 [shortcut control for multi-rotation specification rotary actuator] the shortcut control select can be set valid/invalid in axis-specific parameter no. 67 “rotary movement axis shortcut control select”. Movement can be performed in one way when the shortcut select is set ...
Page 268
Chapter 7 i/o parameter 254 7.11 permission of sio/pio program startup with password by setting to parameter “manual operation type” (other parameter no. 21), the parameter can be changed so sio program startup and pio program startup cannot be conducted without inputting a password. (1) pc software...
Page 269
Chapter 7 i/o parameter 255 7.12 parameter setting (applied) you can add functions or set dedicated functions to i/o ports by changing parameter values. Setting examples under different operating conditions are explained below. When executing the desired operation, change the parameter settings in t...
Page 270
Chapter 7 i/o parameter 256 7.12.1 want to operate the system tentatively without using i/os if you want to perform a test operation before wiring the i/os and fieldbus, disable the error monitor functions for i/os and fieldbus. (the i/os and fieldbus whose error monitor function was disabled cannot...
Page 271
Chapter 7 i/o parameter 257 7.12.5 want to enable auto recovery (restart) upon cancellation of emergency stop you can automatically restart the system (via software reset) when the emergency stop is cancelled, and execute the program. Parameter no. Set value description other parameter no.1 executio...
Page 272
Chapter 7 i/o parameter 258 7.12.9 want to turn on the servo externally have the on-edge (off → on) input to an input port and the servo turns on, and off-edge (on → off) and the servo turns off. Parameter no. Set value description i/o parameter no.N (n = 30 to 45, 251 to 258) 4 set i/o parameter “i...
Page 273
Chapter 7 i/o parameter 259 7.12.13 want to pause the xsel controller externally when off is input to an input port, it makes a pause. To release the pause, turn on one of the input ports that the operation pause signal has been set and input on-edge (off → on) to another input port that the operati...
Page 274
Chapter 7 i/o parameter 260 7.12.17 want to output that all the single axis actuators are at the home position it can be confirmed that all the single axis actuators are at the home position. Current position any output port home on other than home off parameter no. Set value description i/o paramet...
Page 275
Chapter 7 i/o parameter 261 7.12.19 want to output that a single axis actuator got into the area (zone) which has been set four areas (zones) and output ports can be set to each axis of single axis actuators. It can be confirmed that the actuator got into the area (zone) which has been set. A signal...
Page 276
Chapter 7 i/o parameter 262 7.12.20 want to output the error level an error level being generated can be shown by combination of on/off of output ports. Set the output function specification values 1 to 4 and 5 to 7. • output function specification value 1: operation-cancellation level or higher err...
Page 277
Chapter 7 i/o parameter 263 7.12.22 want to know the current operation mode current operation mode can be checked with conditions of output ports. Current operation mode any output port auto on manu off parameter no. Set value description i/o parameter no.N (n = 46 to 53) 10 set i/o parameter “outpu...
Page 278
Chapter 7 i/o parameter 264 7.12.25 want to know the current at this moment on panel unit pu-1 (option) without connecting to teaching tool current can be monitored on the panel unit pu-1 (option). [setting] parameter no. Default value description other parameter no. 49 1 other parameter no. 50 1 ex...
Page 279
Chapter 7 i/o parameter 265 7.12.26 want to monitor the global integral variables on panel unit pu-1 (option) without connecting to teaching tool global integer variables can be displayed on the panel window. Positive integers of 1 to 999 can be displayed. The display shows u--- after 999. Parameter...
Page 280
Chapter 7 i/o parameter 266 7.13 servo adjustment at the delivery from the factory, the parameter settings are established to obtain the stable operational characteristics in an operation within the rated (maximum) transportable weight defined for the actuator. However, the preset setting cannot alw...
Page 281
Chapter 7 i/o parameter 267 no. Phenomenon that requires adjustment how to adjust 4 abnormal noise is generated. It is desired to minimize high noise generated especially during stop or operation with low speed (500mm/sec or less). Input driver parameter no. 45 “torque filter time constant”. Try to ...
Page 282
Chapter 7 i/o parameter 268.
Page 283
Chapter 8 troubleshooting 269 chapter 8 troubleshooting 8.1 action to be taken upon occurrence of problem when a trouble is occurred, take an action following the steps described below in order to have a rapid recovery and to avoid the recurrence of the same trouble. 1) check on led lamps on control...
Page 284
Chapter 8 troubleshooting 270 table 1 panel unit pu-1 (option) display list application control codes display priority (note 1) description 1 the ac power is cut off. (momentary power failure or power-supply voltage drop is also a possibility.) 1 a system-shutdown level error is present. 2 data is b...
Page 285
Chapter 8 troubleshooting 271 table 2 panel unit pu-1 (option) display list core control codes display priority (note 1) description 1 ac power cut off (momentary power failure or power-supply voltage drop may also be the cause.) 1 cold-start level error 1 cold-start level error 1 operation-cancella...
Page 286
Chapter 8 troubleshooting 272 8.2 error level control program run (application only) error level system error assignment source error no. (hex) display (7-segme nt display, etc.) error list (applicati on only) error led output (main only) other parameter no. 4 = 0 other parameter no. 4 = 1 error res...
Page 287
Chapter 8 troubleshooting 273 program run (application only) error level system error assignment source error no. (hex) display (7-segme nt display, etc.) error list (applicati on only) error led output (main only) other parameter no. 4 = 0 other parameter no. 4 = 1 error reset (applicat ion only) r...
Page 288
Chapter 8 troubleshooting 274 8.3 error list (main application) in the panel unit pu-1 (option), the error numbers follow e in the display. Error no. Error name description, action, etc. 200 encoder parameter data version mismatch warning the version of encoder parameter data is not supported by thi...
Page 289
Chapter 8 troubleshooting 275 in the panel unit pu-1 (option), the error numbers follow e in the display. Error no. Error name description, action, etc. 21f written data size excess flash rom writing denied error the data (program data, etc.) size written to the flash rom has exceeded the size capab...
Page 290
Chapter 8 troubleshooting 276 in the panel unit pu-1 (option), the error numbers follow e in the display. Error no. Error name description, action, etc. 406 flash busy reset timeout error erasing/writing the flash rom 407 control constant table management information mismatch error the management in...
Page 291
Chapter 8 troubleshooting 277 in the panel unit pu-1 (option), the error numbers follow e in the display. Error no. Error name description, action, etc. 548 ia net resize overlapping error several stations executed resizing. There could be several stations exist that has executed resizing. Check on ...
Page 292
Chapter 8 troubleshooting 278 in the panel unit pu-1 (option), the error numbers follow e in the display. Error no. Error name description, action, etc. Operatio n-can cellati on l evel errors 573 abs encoder abnormality detection [detail & cause] there is an error on the absolute encoder. The follo...
Page 293
Chapter 8 troubleshooting 279 in the panel unit pu-1 (option), the error numbers follow e in the display. Error no. Error name description, action, etc. 605 forced discharge error abnormal forced discharge. The drive-source cutoff relay may be abnormal. The power must be reconnected. 606 regenerativ...
Page 294
Chapter 8 troubleshooting 280 in the panel unit pu-1 (option), the error numbers follow e in the display. Error no. Error name description, action, etc. 634 feedback pulse synchronization error (detected in the position loop) abnormal feedback pulse synchronization (detected in the position loop). 6...
Page 295
Chapter 8 troubleshooting 281 in the panel unit pu-1 (option), the error numbers follow e in the display. Error no. Error name description, action, etc. 64f encoder error reset error at servo on (serial encoder command) turn off the servo before resetting an encoder error. 650 encoder receive timeou...
Page 296
Chapter 8 troubleshooting 282 in the panel unit pu-1 (option), the error numbers follow e in the display. Error no. Error name description, action, etc. 661 encoder/motor combination mismatch error (linear/rotary type) the linear/rotary type does not match between the encoder and motor. Check the “m...
Page 297
Chapter 8 troubleshooting 283 in the panel unit pu-1 (option), the error numbers follow e in the display. Error no. Error name description, action, etc. 677 abz encoder phase-z clear position error check if the encoder cable is connected. 680 magnetic-pole detection parameter error invalid parameter...
Page 298
Chapter 8 troubleshooting 284 in the panel unit pu-1 (option), the error numbers follow e in the display. Error no. Error name description, action, etc. 801 scif overrun status (iai protocol reception) communication failure. Check for noise, connected equipment and communication setting. 802 scif re...
Page 299
Chapter 8 troubleshooting 285 in the panel unit pu-1 (option), the error numbers follow e in the display. Error no. Error name description, action, etc. 813 maintenance information 3 maintenance information (for analysis) 814 maintenance information 4 maintenance information (for analysis) 815 maint...
Page 300
Chapter 8 troubleshooting 286 in the panel unit pu-1 (option), the error numbers follow e in the display. Error no. Error name description, action, etc. 900 blank step shortage error there are not enough blank steps to save step data. Provide enough blank steps needed to save step data. 901 step num...
Page 301
Chapter 8 troubleshooting 287 in the panel unit pu-1 (option), the error numbers follow e in the display. Error no. Error name description, action, etc. A0d head sector number specification error error erasing the flash rom a0e sector count specification error error erasing the flash rom a0f write-d...
Page 302
Chapter 8 troubleshooting 288 in the panel unit pu-1 (option), the error numbers follow e in the display. Error no. Error name description, action, etc. A28 reorganization disable error during program run a program-area reorganization operation was attempted while a program was running. End all acti...
Page 303
Chapter 8 troubleshooting 289 in the panel unit pu-1 (option), the error numbers follow e in the display. Error no. Error name description, action, etc. A4b monitoring-record count specification error the specified number of records for monitoring data query is invalid. A4c monitoring-operation spec...
Page 304
Chapter 8 troubleshooting 290 in the panel unit pu-1 (option), the error numbers follow e in the display. Error no. Error name description, action, etc. A6e refusal error during write a processing not permitted while data is being written to the flash rom or slave parameters are being written was at...
Page 305
Chapter 8 troubleshooting 291 in the panel unit pu-1 (option), the error numbers follow e in the display. Error no. Error name description, action, etc. B00 scha setting error the setting of scha command is invalid. B01 tpcd setting error the setting of tpcd command is invalid. B02 slen setting erro...
Page 306
Chapter 8 troubleshooting 292 in the panel unit pu-1 (option), the error numbers follow e in the display. Error no. Error name description, action, etc. B92 excessive arc interpolation radius error the radius for arc interpolation is too large. Use cir, arc or other command. C02 executable program c...
Page 307
Chapter 8 troubleshooting 293 in the panel unit pu-1 (option), the error numbers follow e in the display. Error no. Error name description, action, etc. C16 create stack failed initialization of the input-condition-status storage stack has failed. C17 expansion-condition code error input program ste...
Page 308
Chapter 8 troubleshooting 294 in the panel unit pu-1 (option), the error numbers follow e in the display. Error no. Error name description, action, etc. C39 subroutine number error the subroutine number is invalid. C3a user-open communication channel number error the channel number of the communicat...
Page 309
Chapter 8 troubleshooting 295 in the panel unit pu-1 (option), the error numbers follow e in the display. Error no. Error name description, action, etc. C57 flash-rom verify error (flash rom erase) error erasing the flash rom c58 flash-rom ack timeout error (flash rom erase) error erasing the flash ...
Page 310
Chapter 8 troubleshooting 296 in the panel unit pu-1 (option), the error numbers follow e in the display. Error no. Error name description, action, etc. C6f home-return incomplete error home return has not completed yet. This error may also occur if operation is performed immediately after changing ...
Page 311
Chapter 8 troubleshooting 297 in the panel unit pu-1 (option), the error numbers follow e in the display. Error no. Error name description, action, etc. C86 driver servo ready off error the ready signal for the driver of the applicable axis is off. C87 sel unsupported function error an attempt was m...
Page 312
Chapter 8 troubleshooting 298 in the panel unit pu-1 (option), the error numbers follow e in the display. Error no. Error name description, action, etc. Ca2 abnormal absolute-data backup battery voltage (main analysis) check the connection of the absolute-data backup battery/replace the battery and/...
Page 313
Chapter 8 troubleshooting 299 in the panel unit pu-1 (option), the error numbers follow e in the display. Error no. Error name description, action, etc. Cba reference-axis/py/py-axis mismatch error at palletizing angle acquisition angle cannot be calculated because the reference axis for angle calcu...
Page 314
Chapter 8 troubleshooting 300 in the panel unit pu-1 (option), the error numbers follow e in the display. Error no. Error name description, action, etc. D01 encoder eeprom-write timeout error the encoder is faulty or failure occurred in the encoder communication. D02 encoder eeprom-read timeout erro...
Page 315
Chapter 8 troubleshooting 301 in the panel unit pu-1 (option), the error numbers follow e in the display. Error no. Error name description, action, etc. D35 abs encoder abnormality detection2 [detail & cause] initialization of the absolute encoder did not complete. [countermeasure] reboot the power ...
Page 316
Chapter 8 troubleshooting 302 in the panel unit pu-1 (option), the error numbers follow e in the display. Error no. Error name description, action, etc. D5d fieldbus error (fbrs link error) a fbrs link error was detected. Check the statuses of monitor leds on the front panel of the board by referrin...
Page 317
Chapter 8 troubleshooting 303 in the panel unit pu-1 (option), the error numbers follow e in the display. Error no. Error name description, action, etc. D78 encoder initialization error an encoder initialization error generated. D79 encoder hardware error an encoder hardware error generated. D7a enc...
Page 318
Chapter 8 troubleshooting 304 in the panel unit pu-1 (option), the error numbers follow e in the display. Error no. Error name description, action, etc. E15 sci overrun error communication failure. Check for noise, shorting, circuit failure and slave card. E16 program end confirmation timeout error ...
Page 319
Chapter 8 troubleshooting 305 in the panel unit pu-1 (option), the error numbers follow e in the display. Error no. Error name description, action, etc. E33 slave response logic error the slave response logic is invalid. E34 slave block number out of range the slave block number is out of range. E37...
Page 320
Chapter 8 troubleshooting 306 in the panel unit pu-1 (option), the error numbers follow e in the display. Error no. Error name description, action, etc. E5f length conversion parameter error check axis-specific parameter nos. 47, 50, 51, 42, 1, etc. E60 slave maximum receive size over error the slav...
Page 321
Chapter 8 troubleshooting 307 in the panel unit pu-1 (option), the error numbers follow e in the display. Error no. Error name description, action, etc. E7e parameter error the parameter is invalid. E7f stroke parameter error check axis-specific parameter nos. 7, 8, 1, etc. E80 unsupported card erro...
Page 322
Chapter 8 troubleshooting 308 in the panel unit pu-1 (option), the error numbers follow e in the display. Error no. Error name description, action, etc. F00 shutdown error (hi_sysdwn () definition) a shutdown error (hi_sysdwn () definition) was detected. F03 to f59 shutdown error (os call error) a s...
Page 323
Chapter 8 troubleshooting 309 ◎ error list (main core) in the panel unit pu-1 (option), the error numbers follow e in the display. Error no. Error name description, action, etc. A70 scif overrun error communication error. Check for noise, connected equipment and communication setting. (when updating...
Page 324
Chapter 8 troubleshooting 310 in the panel unit pu-1 (option), the error numbers follow e in the display. Error no. Error name description, action, etc. A86 absolute-encoder backup battery voltage-low warning (driver detection) the voltage of the absolute-data backup battery is low. Check the batter...
Page 325
Chapter 8 troubleshooting 311 in the panel unit pu-1 (option),, the error numbers follow e in the display. Error no. Error name description, action, etc. E90 core code flash-rom status error the core program is invalid. Contact iai. E91 application code flash-rom status error the application program...
Page 326
Chapter 8 troubleshooting 312.
Page 327
Chapter 9 appendix 313 chapter 9 appendix 9.1 example of safety circuit (conforming to safety category) use the teaching pendant tb-01-d or tb-01-dr when constructing a system complied with safety categories (iso12100-1). Also, for ssel-cs, tp adapter (model code: ia-lb-tgs) is required. In this sec...
Page 328
Chapter 9 i appendix 314 9.1.2 wiring and setting of safety circuit [1] power supply to use safty relays and/or contactors of 24v dc specification in the safety circuit, the control power supply should be used only for the circuit as much as possible. For example, to supply power to the safety circu...
Page 329
Chapter 9 appendix 315 upper side (emg) connector lower side (enb) connector tp adapter side view wiring color signal no. Yellow yellow yellow yellow wiring color signal no. Yellow yellow yellow yellow upper side lower side (note) when operating the controller with auto mode, make sure to connect th...
Page 330
Chapter 9 i appendix 316 9.1.3 examples of safety circuits [1] category 1 connection cable cb-sel26h-lbs*** controller ssel ia-lb-tgs enbout enbin enb2+ enb2- enb1+ enb1- emgout emgin emg2+ emg2- emg1+ emg1- 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 l1 l2 emergency stop switch reset switch enable switc h r y r y 2...
Page 331
Chapter 9 appendix 317 [detailed category 1 circuit example] detailed category 1 circuit example l1 l2 ssel 1.S1 2.S2 3.Emg+ 4.Emg- tpcs vp24 r y r y vp7v tp connection detecting manuin vp5 5 7 6 5 7 6 5-6 : tp non- detecting 7-6 : tp detecting vp5 vp5 5-6 : auto 7-6 : manu 5.Enb+ 6.Enb- e24v vp5 tp...
Page 332
Chapter 9 i appendix 318 [2] category 2 tb-01 (or dummy plug: dp-4s) connection cable cb-sel26h-lbs*** controller ssel ia-lb-tgs enbout enbin enb2+ enb2- enb1+ enb1- emgout emgin emg2+ emg2- emg1+ emg1- 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 l1 l2 reset switch enable switch emergency stop switch 24v 24v 24v 24v...
Page 333
Chapter 9 appendix 319 [detailed category 2 circuit example] l1 l2 ssel 1.S1 2.S2 3.Emg+ 4.Emg- tpcs vp24 r y r y vp7v tp connection detecting manuin vp5 5 7 6 5 7 6 vp5 vp5 5-6 : auto 7-6 : manu 5.Enb+ 6.Enb- e24v vp5 tpenbok r y e24g sdwn *emgstr 2.Emgs 3.Vcc 4.Dtr 8.Rsv2vcc 13.Rts 14.Cts 15.Txd 1...
Page 334
Chapter 9 i appendix 320 [3] category 3 or 4 tb-01 (or dummy plug: dp-4s) connection cable cb-sel26h-lbs*** controller ssel ia-lb-tgs enbout enbin enb2+ enb2- enb1+ enb1- emgout emgin emg2+ emg2- emg1+ emg1- 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 l1 l2 reset switch enable switch emergency stop switch 24v 24v 24...
Page 335
Chapter 9 appendix 321 [detailed category 3 or 4 circuit example] l1 l2 ssel 1.S1 2.S2 3.Emg+ 4.Emg- tpcs vp24 r y r y vp7v tp connection detecting manuin vp5 5 7 6 5 7 6 vp5 vp5 5-6 : auto 7-6 : manu 5.Enb+ 6.Enb- e24v vp5 tpenbok r y e24g sdwn *emgstr 2.Emgs 3.Vcc 4.Dtr 8.Rsv2vcc 13.Rts 14.Cts 15....
Page 336
Chapter 9 i appendix 322 9.1.4 tp adapter and related parts [1] tp adapter external dimensions.
Page 337
Chapter 9 appendix 323 [2] connection cable related parts • controller/tp adaptor connection cable use this cable to connect the controller and tp adapter. Maximum cable length : 2.0m (standard cable length : 0.5m) cn1 cn2 cb-sel26h-lb color signal yellow pink white orange gray white gray gray gray ...
Page 338
Chapter 9 i appendix 324 [3] dummy plug related parts connect a dummy plug to the teaching pendant connecting connector. Make sure to connect a dummy plug if the auto mode is specified. Without the connection, it will be the emergency stop condition. Model: dp-4s (when tp adapter is ia-lb-tgs) gnd e...
Page 339
Chapter 9 appendix 325 9.2 stopping method and recovery 9.2.1 stopping method actuator operation can be stopped in two methods: normal operation stop and emergency stop. 1) normal operation stop normal position control is active: set a deceleration operation plan and cause the actuator to decelerate...
Page 340
Chapter 9 i appendix 326 9.2.2 recovery [1] drive-source recovery request (1) method of drive-source recovery request recovery of drive source can be requested by one of the following methods: determine the port number to input the drive cutoff cancellation input, and set the input select function s...
Page 341
Chapter 9 appendix 327 [2] operation-pause reset request (1) method of operation-pause reset request reset of operation pause can be requested by one of the following methods: d determine the port number to input the operation pause signal, and set the input select function specification value 7 (op...
Page 342
Chapter 9 i appendix 328 9.3 specifications list for connectable single axis actuator the specifications stated in this specifications list are focused only to those necessary for operational condition settings. Please refer to the catalog or instruction manual for the actuator for other more detail...
Page 343
Chapter 9 appendix 329 motor output lead max. Speed max. Acceleration/ deceleration speed min. Pressing force max. Pressing force rated pressing speed actuator series type [w] [mm] mounting direction [mm/s] [g] [n] [n] [mm/s] 12 600 0.3 - - - 6 300 0.3 - - - 20 3 150 0.2 - - - 12 600 0.3 - - - 6 300...
Page 344
Chapter 9 i appendix 330 motor output lead max. Speed max. Acceleration/ deceleration speed min. Pressing force max. Pressing force rated pressing speed actuator series type [w] [mm] mounting direction [mm/s] [g] [n] [n] [mm/s] 16 800 (at 50 ~ 250st) 755 (at 300st) 0.3 - - - 8 400 (at 50 ~ 250st) 37...
Page 345
Chapter 9 appendix 331 motor output lead max. Speed max. Acceleration/ deceleration speed min. Pressing force max. Pressing force rated pressing speed actuator series type [w] [mm] mounting direction [mm/s] [g] [n] [n] [mm/s] 10 horizontal: 280 vertical: 230 (at 50st) horizontal: 380 vertical: 330 (...
Page 346
Chapter 9 i appendix 332 motor output lead max. Speed max. Acceleration/ deceleration speed min. Pressing force max. Pressing force rated pressing speed actuator series type [w] [mm] mounting direction [mm/s] [g] [n] [n] [mm/s] 0.3 - - - 10 665 high accel/ deceleration type: 1.0 - - - 0.3 - - - 5 33...
Page 347
Chapter 9 appendix 333 motor output lead max. Speed max. Acceleration/ deceleration speed min. Pressing force max. Pressing force rated pressing speed actuator series type [w] [mm] mounting direction [mm/s] [g] [n] [n] [mm/s] 0.3 - - - horizontal 1300 (at 50 ~ 500st) 1160 (at 550st) 990 (at 600st) h...
Page 348
Chapter 9 i appendix 334 motor output lead max. Speed max. Acceleration/ deceleration speed min. Pressing force max. Pressing force rated pressing speed actuator series type [w] [mm] mounting direction [mm/s] [g] [n] [n] [mm/s] 16 800 (at 50 ~ 600st) 640 (at 700st) 480 (at 800st) 0.3 - - - 8 400 (at...
Page 349
Chapter 9 appendix 335 motor output lead max. Speed max. Acceleration/ deceleration speed min. Pressing force max. Pressing force rated pressing speed actuator series type [w] [mm] mounting direction [mm/s] [g] [n] [n] [mm/s] 20 1000 (at 50 ~ 600st) 960 (at ~ 700st) 765 (at ~ 800st) 625 (at ~ 900st)...
Page 350
Chapter 9 i appendix 336 motor output lead max. Speed max. Acceleration/ deceleration speed min. Pressing force max. Pressing force rated pressing speed actuator series type [w] [mm] mounting direction [mm/s] [g] [n] [n] [mm/s] horizontal 1300 (at 50 ~ 500st) 1160 (at 550st) 990 (at 600st) 0.3 - - -...
Page 351
Chapter 9 appendix 337 motor output lead max. Speed max. Acceleration/ deceleration speed min. Pressing force max. Pressing force rated pressing speed actuator series type [w] [mm] mounting direction [mm/s] [g] [n] [n] [mm/s] 20 1000 (at 50 ~ 600st) 960 (at ~ 700st) 765 (at ~ 800st) 625 (at ~ 900st)...
Page 352
Chapter 9 i appendix 338 motor output lead max. Speed max. Acceleration/ deceleration speed min. Pressing force max. Pressing force rated pressing speed actuator series type [w] [mm] mounting direction [mm/s] [g] [n] [n] [mm/s] 5 300 (at 50 ~ 650st) 260 (at ~ 700st) 230 (at ~ 750st) 200 (at ~ 800st)...
Page 353
Chapter 9 appendix 339 motor output lead max. Speed max. Acceleration/ deceleration speed min. Pressing force max. Pressing force rated pressing speed actuator series type [w] [mm] mounting direction [mm/s] [g] [n] [n] [mm/s] horizontal 1.0 - - - 100 30 vertical 1800 (at 50 ~ 650st) 1610 (at ~ 700st...
Page 354
Chapter 9 i appendix 340 motor output lead max. Speed max. Acceleration/ deceleration speed min. Pressing force max. Pressing force rated pressing speed actuator series type [w] [mm] mounting direction [mm/s] [g] [n] [n] [mm/s] horizontal 1.0 - - - sa8 150 30 vertical 1800 (at 50 ~ 650st) 1610 (at ~...
Page 355
Chapter 9 appendix 341 motor output lead max. Speed max. Acceleration/ deceleration speed min. Pressing force max. Pressing force rated pressing speed actuator series type [w] [mm] mounting direction [mm/s] [g] [n] [n] [mm/s] 20 horizontal/ vertical 1200 (at 50 ~ 600st) 1105 (at ~ 650st) 970 (at ~ 7...
Page 356
Chapter 9 i appendix 342 motor output lead max. Speed max. Acceleration/ deceleration speed min. Pressing force max. Pressing force rated pressing speed actuator series type [w] [mm] mounting direction [mm/s] [g] [n] [n] [mm/s] 20 horizontal/ vertical 1200 (at 50 ~ 600st) 1105 (at ~ 650st) 970 (at ~...
Page 357
Chapter 9 appendix 343 motor output lead max. Speed max. Acceleration/ deceleration speed min. Pressing force max. Pressing force rated pressing speed actuator series type [w] [mm] mounting direction [mm/s] [g] [n] [n] [mm/s] 5 300 (at 50 ~ 650st) 250 (at ~ 700st) 220 (at ~ 750st) 190 (at ~ 800st) 1...
Page 358
Chapter 9 i appendix 344 motor output lead max. Speed max. Acceleration/ deceleration speed min. Pressing force max. Pressing force rated pressing speed actuator series type [w] [mm] mounting direction [mm/s] [g] [n] [n] [mm/s] horizontal 1.0 - - - 100 30 vertical 1800 (at 50 ~ 650st) 1510 (at ~ 700...
Page 359
Chapter 9 appendix 345 motor output lead max. Speed max. Acceleration/ deceleration speed min. Pressing force max. Pressing force rated pressing speed actuator series type [w] [mm] mounting direction [mm/s] [g] [n] [n] [mm/s] horizontal 1.0 - - - sa8 150 30 vertical 1800 (at 50~ 650st) 1510 (at ~ 70...
Page 360
Chapter 9 i appendix 346 motor output lead max. Speed max. Acceleration/ deceleration speed min. Pressing force max. Pressing force rated pressing speed actuator series type [w] [mm] mounting direction [mm/s] [g] [n] [n] [mm/s] 20 horizontal/ vertical 1200 (at 50 ~ 600st) 1105 (at ~ 650st) 970 (at ~...
Page 361
Chapter 9 appendix 347 motor output lead max. Speed max. Acceleration/ deceleration speed min. Pressing force max. Pressing force rated pressing speed actuator series type [w] [mm] mounting direction [mm/s] [g] [n] [n] [mm/s] 20 horizontal/ vertical 1200 (at 50 ~ 600st) 1105 (at ~ 650st) 970 (at ~ 7...
Page 362
Chapter 9 i appendix 348 motor output lead max. Speed max. Acceleration/ deceleration speed min. Pressing force max. Pressing force rated pressing speed actuator series type [w] [mm] mounting direction [mm/s] [g] [n] [n] [mm/s] 10 horizontal: 280 vertical: 230 (at 50st) horizontal: 380 vertical: 330...
Page 363
Chapter 9 appendix 349 motor output lead max. Speed max. Acceleration/ deceleration speed min. Pressing force max. Pressing force rated pressing speed actuator series type [w] [mm] mounting direction [mm/s] [g] [n] [n] [mm/s] horizontal 1.0 - - - 16 vertical 960 0.7 - - - horizontal 0.6 - - - 8 vert...
Page 364
Chapter 9 i appendix 350 motor output lead max. Speed max. Acceleration/ deceleration speed min. Pressing force max. Pressing force rated pressing speed actuator series type [w] [mm] mounting direction [mm/s] [g] [n] [n] [mm/s] 10 vertical 600 (at 100 ~ 700st) 430 (at 800st) 345 (at 900st) 280 (at 1...
Page 365
Chapter 9 appendix 351 motor output lead max. Speed max. Acceleration/ deceleration speed min. Pressing force max. Pressing force rated pressing speed actuator series type [w] [mm] mounting direction [mm/s] [g] [n] [n] [mm/s] 30 horizontal 1800 (at 800 ~ 1100st) 1650 (at 1200st) 1500 (at 1300st) 142...
Page 366
Chapter 9 i appendix 352 motor output lead max. Speed max. Acceleration/ deceleration speed min. Pressing force max. Pressing force rated pressing speed actuator series type [w] [mm] mounting direction [mm/s] [g] [n] [n] [mm/s] horizontal 1.0 - - - 20 vertical 1200 (at 100 ~ 800st) 920 (at ~ 900st) ...
Page 367
Chapter 9 appendix 353 motor output lead max. Speed max. Acceleration/ deceleration speed min. Pressing force max. Pressing force rated pressing speed actuator series type [w] [mm] mounting direction [mm/s] [g] [n] [n] [mm/s] 200 20 horizontal 1200 (at 1000 ~ 1200st) 1150 (at 1300st) 1000 (at 1400st...
Page 368
Chapter 9 i appendix 354 motor output lead max. Speed max. Acceleration/ deceleration speed min. Pressing force max. Pressing force rated pressing speed actuator series type [w] [mm] mounting direction [mm/s] [g] [n] [n] [mm/s] lxmx 400 20 horizontal 1200 (at 1000 ~ 1200st) 1150 (at 1300st) 1000 (at...
Page 369
Chapter 9 appendix 355 motor output lead max. Speed max. Acceleration/ deceleration speed min. Pressing force max. Pressing force rated pressing speed actuator series type [w] [mm] mounting direction [mm/s] [g] [n] [n] [mm/s] 40 horizontal 2400 (at 1000 ~ 1200st) 2300 (at 1300st) 2000 (at 1400st) 19...
Page 370
Chapter 9 i appendix 356 motor output lead max. Speed max. Acceleration/ deceleration speed min. Pressing force max. Pressing force rated pressing speed actuator series type [w] [mm] mounting direction [mm/s] [g] [n] [n] [mm/s] horizontal 1.0 - - - 40 vertical 2400 (at 100 ~ 800st) 1840 (at 900st) 1...
Page 371
Chapter 9 appendix 357 motor output lead max. Speed max. Acceleration/ deceleration speed min. Pressing force max. Pressing force rated pressing speed actuator series type [w] [mm] mounting direction [mm/s] [g] [n] [n] [mm/s] 40 horizontal 2400 (at 900 ~ 1200st) 2200 (at 1300st) 1965 (at 1400st) 172...
Page 372
Chapter 9 i appendix 358 motor output lead max. Speed max. Acceleration/ deceleration speed min. Pressing force max. Pressing force rated pressing speed actuator series type [w] [mm] mounting direction [mm/s] [g] [n] [n] [mm/s] 50 horizontal 2000 (at 900 ~ 1700st) 1930 (at 1800st) 1740 (at 1900st) 1...
Page 373
Chapter 9 appendix 359 motor output lead max. Speed max. Acceleration/ deceleration speed min. Pressing force max. Pressing force rated pressing speed actuator series type [w] [mm] mounting direction [mm/s] [g] [n] [n] [mm/s] horizontal 1.0 - - - 40 vertical 2000 (at 100 ~ 700st) 1965 (at ~ 800st) 1...
Page 374
Chapter 9 i appendix 360 motor output lead max. Speed max. Acceleration/ deceleration speed min. Pressing force max. Pressing force rated pressing speed actuator series type [w] [mm] mounting direction [mm/s] [g] [n] [n] [mm/s] 40 horizontal 2000 (at 1000 ~ 1300st) 1965 (at 1400st) 1725 (at 1500st) ...
Page 375
Chapter 9 appendix 361 motor output lead max. Speed max. Acceleration/ deceleration speed min. Pressing force max. Pressing force rated pressing speed actuator series type [w] [mm] mounting direction [mm/s] [g] [n] [n] [mm/s] 50 horizontal 2000 (at 1000 ~ 1700st) 1930 (at 1800st) 1740 (at 1900st) 15...
Page 376
Chapter 9 i appendix 362 motor output lead max. Speed max. Acceleration/ deceleration speed min. Pressing force max. Pressing force rated pressing speed actuator series type [w] [mm] mounting direction [mm/s] [g] [n] [n] [mm/s] horizontal 0.5 4 vertical 240 (at 100 ~ 600st) 165 (at ~ 700st) 130 (at ...
Page 377
Chapter 9 appendix 363 motor output lead max. Speed max. Acceleration/ deceleration speed min. Pressing force max. Pressing force rated pressing speed actuator series type [w] [mm] mounting direction [mm/s] [g] [n] [n] [mm/s] horizontal 0.5 5 vertical 300 (at 100 ~ 700st) 215 (at ~ 800st) 170 (at ~ ...
Page 378
Chapter 9 i appendix 364 motor output lead max. Speed max. Acceleration/ deceleration speed min. Pressing force max. Pressing force rated pressing speed actuator series type [w] [mm] mounting direction [mm/s] [g] [n] [n] [mm/s] horizontal 0.5 5 vertical 300 (at 120 ~ 670st) 215 (at ~ 770st) 170 (at ...
Page 379
Chapter 9 appendix 365 motor output lead max. Speed max. Acceleration/ deceleration speed min. Pressing force max. Pressing force rated pressing speed actuator series type [w] [mm] mounting direction [mm/s] [g] [n] [n] [mm/s] 20 horizontal 1200 (at 800 ~ 1100st) 1100 (at ~ 1200st) 1000 (at ~ 1300st)...
Page 380
Chapter 9 i appendix 366 motor output lead max. Speed max. Acceleration/ deceleration speed min. Pressing force max. Pressing force rated pressing speed actuator series type [w] [mm] mounting direction [mm/s] [g] [n] [n] [mm/s] horizontal 0.7 10 vertical 600 (at 100 ~ 800st) 460 (at ~ 900st) 380 (at...
Page 381
Chapter 9 appendix 367 motor output lead max. Speed max. Acceleration/ deceleration speed min. Pressing force max. Pressing force rated pressing speed actuator series type [w] [mm] mounting direction [mm/s] [g] [n] [n] [mm/s] horizontal 0.7 10 vertical 600 (at 120 ~ 770st) 460 (at ~ 870st) 380 (at ~...
Page 382
Chapter 9 i appendix 368 motor output lead max. Speed max. Acceleration/ deceleration speed min. Pressing force max. Pressing force rated pressing speed actuator series type [w] [mm] mounting direction [mm/s] [g] [n] [n] [mm/s] 200 400 20 horizontal 1200 (at 1000 ~ 1200st) 1150 (at ~ 1300st) 1000 (a...
Page 383
Chapter 9 appendix 369 motor output lead max. Speed max. Acceleration/ deceleration speed min. Pressing force max. Pressing force rated pressing speed actuator series type [w] [mm] mounting direction [mm/s] [g] [n] [n] [mm/s] horizontal 0.7 - - - 10 vertical 600 (at ~ 600st) 560 (at ~ 650st) 490 (at...
Page 384
Chapter 9 i appendix 370 motor output lead max. Speed max. Acceleration/ deceleration speed min. Pressing force max. Pressing force rated pressing speed actuator series type [w] [mm] mounting direction [mm/s] [g] [n] [n] [mm/s] horizontal 0.7 - - - 10 vertical 600 (at ~ 700st) 530 (at ~ 750st) 480 (...
Page 385
Chapter 9 appendix 371 motor output lead max. Speed max. Acceleration/ deceleration speed min. Pressing force max. Pressing force rated pressing speed actuator series type [w] [mm] mounting direction [mm/s] [g] [n] [n] [mm/s] horizontal sspa mxm 400 40 vertical 2400 (at ~ 700st) 2150 (at ~ 750st) 19...
Page 386
Chapter 9 i appendix 372 motor output lead max. Speed max. Acceleration/ deceleration speed min. Pressing force max. Pressing force rated pressing speed actuator series type [w] [mm] mounting direction [mm/s] [g] [n] [n] [mm/s] horizontal 240 (at ~ 500st) 230 (at ~ 550st) 200 (at ~ 600st) 0.5 4 vert...
Page 387
Chapter 9 appendix 373 motor output lead max. Speed max. Acceleration/ deceleration speed min. Pressing force max. Pressing force rated pressing speed actuator series type [w] [mm] mounting direction [mm/s] [g] [n] [n] [mm/s] horizontal 300 (at ~ 600st) 270 (at ~ 650st) 240 (at ~ 700st) 215 (at ~ 75...
Page 388
Chapter 9 i appendix 374 motor output lead max. Speed max. Acceleration/ deceleration speed min. Pressing force max. Pressing force rated pressing speed actuator series type [w] [mm] mounting direction [mm/s] [g] [n] [n] [mm/s] horizontal 1200 (at ~ 600st) 1085 (at ~ 650st) 960 (at ~ 700st) 855 (at ...
Page 389
Chapter 9 appendix 375 motor output lead max. Speed max. Acceleration/ deceleration speed min. Pressing force max. Pressing force rated pressing speed actuator series type [w] [mm] mounting direction [mm/s] [g] [n] [n] [mm/s] 20 horizontal 1200 (at ~ 1100st) 1100 (at ~ 1200st) 1000 (at ~ 1300st) 950...
Page 390
Chapter 9 i appendix 376 motor output lead max. Speed max. Acceleration/ deceleration speed min. Pressing force max. Pressing force rated pressing speed actuator series type [w] [mm] mounting direction [mm/s] [g] [n] [n] [mm/s] horizontal 1200 (at ~ 650st) 1165 (at ~ 700st) 1045 (at ~ 750st) 940 (at...
Page 391
Chapter 9 appendix 377 motor output lead max. Speed max. Acceleration/ deceleration speed min. Pressing force max. Pressing force rated pressing speed actuator series type [w] [mm] mounting direction [mm/s] [g] [n] [n] [mm/s] 20 horizontal 1200 (at ~ 1200st) 1150 (at ~ 1300st) 1000 (at ~ 1400st) 950...
Page 392
Chapter 9 i appendix 378 motor output lead max. Speed max. Acceleration/ deceleration speed min. Pressing force max. Pressing force rated pressing speed actuator series type [w] [mm] mounting direction [mm/s] [g] [n] [n] [mm/s] horizontal 0.5 - - - 5 vertical 300 (at ~ 600st) 270 (at ~ 650st) 240 (a...
Page 393
Chapter 9 appendix 379 motor output lead max. Speed max. Acceleration/ deceleration speed min. Pressing force max. Pressing force rated pressing speed actuator series type [w] [mm] mounting direction [mm/s] [g] [n] [n] [mm/s] horizontal 20 vertical 1200 (at ~ 600st) 1085 (at ~ 650st) 960 (at ~ 700st...
Page 394
Chapter 9 i appendix 380 motor output lead max. Speed max. Acceleration/ deceleration speed min. Pressing force max. Pressing force rated pressing speed actuator series type [w] [mm] mounting direction [mm/s] [g] [n] [n] [mm/s] 20 horizontal 1200 (at 800 ~ 1100st) 1100 (at ~ 1200st) 1000 (at ~ 1300s...
Page 395
Chapter 9 appendix 381 motor output lead max. Speed max. Acceleration/ deceleration speed min. Pressing force max. Pressing force rated pressing speed actuator series type [w] [mm] mounting direction [mm/s] [g] [n] [n] [mm/s] horizontal 20 vertical 1200 (at ~ 650st) 1165 (at ~ 700st) 1045 (at ~ 750s...
Page 396
Chapter 9 i appendix 382 motor output lead max. Speed max. Acceleration/ deceleration speed min. Pressing force max. Pressing force rated pressing speed actuator series type [w] [mm] mounting direction [mm/s] [g] [n] [n] [mm/s] 20 horizontal 1200 (at 1000~ 1200st) 1150 (at ~ 1300st) 1000 (at ~ 1400s...
Page 397
Chapter 9 appendix 383 motor output lead max. Speed max. Acceleration/ deceleration speed min. Pressing force max. Pressing force rated pressing speed actuator series type [w] [mm] mounting direction [mm/s] [g] [n] [n] [mm/s] horizontal 0.7 - - - 10 vertical 600 (at ~ 550st) 540 (at ~ 600st) 480 (at...
Page 398
Chapter 9 i appendix 384 motor output lead max. Speed max. Acceleration/ deceleration speed min. Pressing force max. Pressing force rated pressing speed actuator series type [w] [mm] mounting direction [mm/s] [g] [n] [n] [mm/s] horizontal s 200 30 vertical 1600 (at ~ 650st) 1450 (at ~ 650st) 1290 (a...
Page 399
Chapter 9 appendix 385 motor output lead max. Speed max. Acceleration/ deceleration speed min. Pressing force max. Pressing force rated pressing speed actuator series type [w] [mm] mounting direction [mm/s] [g] [n] [n] [mm/s] horizontal 20 vertical 1100 (at ~ 650st) 1040 (at ~ 700st) 940 (at ~ 750st...
Page 400
Chapter 9 i appendix 386 motor output lead max. Speed max. Acceleration/ deceleration speed min. Pressing force max. Pressing force rated pressing speed actuator series type [w] [mm] mounting direction [mm/s] [g] [n] [n] [mm/s] horizontal 25 vertical 1100 (at ~ 900st) 1060 (at ~ 1000st) 900 (at ~ 11...
Page 401
Chapter 9 appendix 387 motor output lead max. Speed max. Acceleration/ deceleration speed min. Pressing force max. Pressing force rated pressing speed actuator series type [w] [mm] mounting direction [mm/s] [g] [n] [n] [mm/s] 10 horizontal 500 (at ~ 600st) 455 (at ~ 700st) 365 (at ~ 800st) 300 (at ~...
Page 402
Chapter 9 i appendix 388 motor output lead max. Speed max. Acceleration/ deceleration speed min. Pressing force max. Pressing force rated pressing speed actuator series type [w] [mm] mounting direction [mm/s] [g] [n] [n] [mm/s] sxms-a - - - sxms-i 60 12 horizontal 720 0.8 - - - sxmm-a - - - sxmm-i 6...
Page 403
Chapter 9 appendix 389 motor output lead max. Speed max. Acceleration/ deceleration speed min. Pressing force max. Pressing force rated pressing speed actuator series type [w] [mm] mounting direction [mm/s] [g] [n] [n] [mm/s] decelera tion ratio 1/50 360 - - - 30 30 decelera tion ratio 1/100 180 - -...
Page 404
Chapter 9 i appendix 390
Page 405
Chapter 10 w arranty 391 chapter 10 warranty 10.1 warranty period one of the following periods, whichever is shorter: 18 months after shipment from our company 12 months after delivery to the specified location 10.2 scope of the warranty our products are covered by warranty when all of the following...
Page 406
Chapter 10 w arranty 392 10.5 conditions of conformance with applicable standards/regulations, etc., and applications (1) if our product is combined with another product or any system, device, etc., used by the customer, the customer must first check the applicable standards, regulations and/or rule...
Page 407
Trouble report sheet 393 trouble report sheet 2. Vertical 3..
Page 408
Trouble report sheet 394.
Page 409
Change history 395 change history revision date revision description 2015.10 fourteenth edition revised overall 2015.12 edition 14b pg. 64 note corrected corrected wiring of bk +, bk- and 24v, 0v. 2016.02 2016.02 2016.11 2017.01 2017.03 2017.07 2017.09 2017.11 edition 14c pg. 163 change made in syst...
Page 410
Change history 396 revision date revision description 2017.11 edition 15f pg. 119, 141, 142 note added stating remaining movement can be cancelled with error reset (res) signal in version v0014 and later in teaching mode.
Page 412
Manual no.: me0157-15f (november 2017) the information contained in this document is subject to change without notice for purposes of product improvement. Copyright © 2017. Nov. Iai corporation. All rights reserved. 17.11.000 head office: 577-1 obane shimizu-ku shizuoka city shizuoka 424-0103, japan...