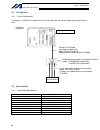
- DL manuals
- IAI
- Controller
- X-SEL
- Operation Manual
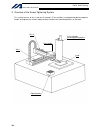
IAI X-SEL Operation Manual
Summary of X-SEL
Page 1
Operation manual fourth edition x-sel controller p/q type.
Page 2: Caution
Caution operator alarm on low battery voltage this controller is equipped with the following backup batteries for retention of data in the event of power failure: [1] system-memory backup battery for retention of position data, global variables/flags, error list, strings, etc. [2] absolute-encoder b...
Page 3: Caution
Caution drive-source cutoff relay error (detection of fused relay: e6d) as a condition limited to x-sel-p type controllers of standard single-phase specification, a “drive-source cutoff relay error (e6d)” may generate if the power is turned off and then turned on again (reconnected) too quickly. Thi...
Page 4: Safety Precautions
Intelligent actuator safety precautions please read the information in “safety precautions” carefully before selecting a model and using the product. The precautions described below are designed to help you use the product safely and avoid bodily injury and/or property damage. Directions are classif...
Page 5
Intelligent actuator [installation] z do not use this product in a place exposed to ignitable, inflammable or explosive substances. The product may ignite, burn or explode. Z avoid using the product in a place where the main unit or controller may come in contact with water or oil droplets. Z never ...
Page 6
Intelligent actuator z if the product is generating heat, smoke or a strange smell, turn off the power immediately. Continuing to use the product may result in product damage or fire. Z if any of the internal protective devices (alarms) of the product has actuated, turn off the power immediately. Co...
Page 7
Intelligent actuator z before installing or adjusting the product or performing other operations on the product, display a sign that reads, “work in progress. Do not turn on power.” if the power is turned on inadvertently, injury may result due to electric shock or sudden activation of an actuator. ...
Page 8: Ce Mark
Intelligent actuator ce mark 1. Ec directives the ec directives are a new set of directives issued by the european commission that are intended to protect the health and safety of users and consumers of products distributed within the eu (european union) zone, while ensuring free movements of these ...
Page 9
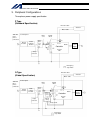
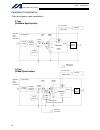
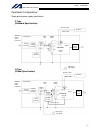
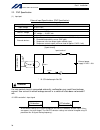
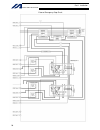
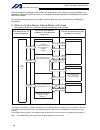
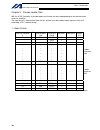
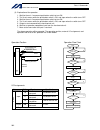
Intelligent actuator 3. Peripheral configurations three-phase power supply specification p type (standard specification) q type (global specification) 200-vac three- phase power bus control panel circuit breaker earth leakage breaker surge protector three- phase noise filter ring core clamp filters ...
Page 10
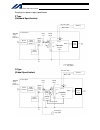
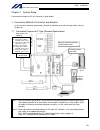
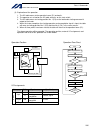
Intelligent actuator single-phase power supply specification p type (standard specification) q type (global specification) 200-vac single- phase power bus control panel circuit breaker earth leakage breaker surge protector single- phase noise filter ring core clamp filters encoder cable motor cable ...
Page 11
Intelligent actuator (1) environment use your x-sel-p/q controller in an environment conforming to pollution degree 2 or 1 as specified in iec 60664-1. Example) install the controller in a control panel having a structure resistant to intrusion of water, oil, carbon, dust, etc (ip54). (2) power sour...
Page 12
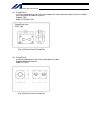
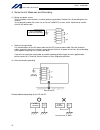
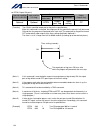
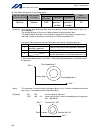
Intelligent actuator (5) three-phase noise filter install a noise filter in the three-phase ac power line. Supplier: densei-lambda model: mc1320 [fig. 1] external view of noise filter (three-phase specification) (6) single-phase noise filter install a noise filter in the single-phase ac power supply...
Page 13
Intelligent actuator (7) ring core install a ring core on the secondary side of the noise filter. Supplier: nec tokin model: esd-r-25 [fig. 3] external view of ring core shape/dimensions esd-r series.
Page 14
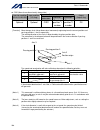
Intelligent actuator (8) clamp filter a install the following noise filter to the control power ac cable and motor cable (if there are multiple axes, connect to the cables of all axes). Supplier: tdk model: zcat3035-1330 [fig. 4] external view of clamp filter (9) clamp filter b install the following...
Page 15
Intelligent actuator (10) surge protector install a surge protector on the primary side of the noise filter. Supplier: okaya electric industries model: r xaxv-781bxz-4 (three-phase) r xaxv-781bwz-4 (single-phase) external dimensions [fig. 6] external view of surge protector resin case lead wire.
Page 16
Intelligent actuator (11) cables the restrictions and cautions regarding the cables are summarized below. A) all cables connected to the x-sel-p/q controller, such as the motor cable, encoder cable and various network cables, must be kept to a length below 30 m. B) for the brake power cable, use a s...
Page 17
Intelligent actuator prohibited handling of cables caution when designing an application system using actuators and controllers, incorrect wiring or connection of each cable may cause unexpected problems such as a disconnected cable or poor contact, or even a runaway system. This section explains pr...
Page 18
Intelligent actuator 7. Do not let the cable get tangled or kinked in a cable bearer or flexible tube. When bundling the cable, keep a certain degree of flexibility (so that the cable will not become too taut when bent). 8. Do not cause the cables to occupy more than 60% of the space in the cable be...
Page 19: Before Use
Intelligent actuator before use caution caution 1. Be sure to read this operation manual to ensure the proper use of this product. 2. Unauthorized use or reproduction of a part or all of this operation manual is prohibited. 3. Always handle or operate the product in manners specified in this operati...
Page 20: Table of Contents
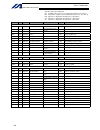
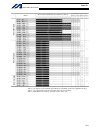
Intelligent actuator table of contents table of contents introduction................................................................................................... 1 part 1 installation ....................................................................................... 3 chapter 1 safety pr...
Page 21
Intelligent actuator table of contents part 2 operation....................................................................................... 83 chapter 1 operation .......................................................................................................................... 83 1. Start...
Page 22
Intelligent actuator table of contents 1.14 structural do .............................................................................................................. 209 1.15 multi-branching..............................................................................................................
Page 23
Intelligent actuator table of contents appendix .................................................................................................. 311 actuator specification list....................................................................................................................311 ho...
Page 24
Intelligent actuator table of contents absolute reset of a synchro controller.............................................................................................. 352 1. Synchro axes ...............................................................................................................
Page 25
1 intelligent actuator introuduction introduction thank you for purchasing the x-sel controller. Inappropriate use or handling will prevent this product from demonstrating its full function and may even cause unexpected failure or result in a shortened service life. Please read this manual carefully...
Page 26
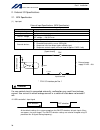
2 intelligent actuator introduction this controller receives two types of power from external power sources: one for driving the motor (three- phase or single-phase, 200 to 220 v) and the other for control (single-phase, 200 to 220 v). * a single-phase power source is required only for controllers o...
Page 27
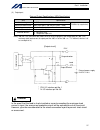
3 intelligent actuator part 1 installation part 1 installation caution chapter 1 safety precautions the x-sel controller can be combined with a maximum of six actuators of different types, and is able to provide integrated control over the entire system including peripherals. In other words, the x-s...
Page 28
4 intelligent actuator part 1 installation chapter 2 warranty period and scope of warranty the x-sel controller you have purchased passed our strict outgoing inspection. This unit is covered by the following warranty: 1. Warranty period the warranty period shall be either of the following periods, w...
Page 29
5 intelligent actuator part 1 installation chapter 3 installation environment and selection of auxiliary power devices 1. Installation environment (1) when installing and wiring the controller, do not block the ventilation holes provided for cooling. (insufficient ventilation will not only prevent t...
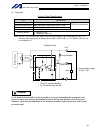
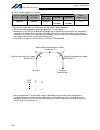
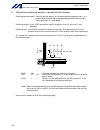
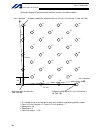
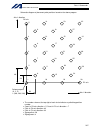
Page 30
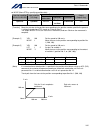
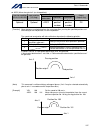
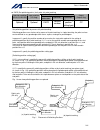
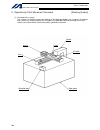
6 intelligent actuator part 1 installation 2. Heat radiation and installation design the control panel size, controller layout and cooling method so that the ambient temperature around the controller will be kept at or below 40°c. Install the controller vertically on a wall, as illustrated below. Th...
Page 31
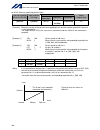
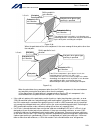
7 intelligent actuator part 1 installation 3. Selection of auxiliary power devices this section provides selection guidelines for breakers, earth leakage breakers, contactors, surge absorbers and noise filters that can be used with the ac power-supply line of the x-sel controller. These devices must...
Page 32
8 intelligent actuator part 1 installation (4) auxiliary power devices [1] breaker or electromagnetic contactor install a circuit breaker or earth leakage breaker in the ac power-supply line (primary side) of the controller in order to prevent damage due to power switching and short current. One cir...
Page 33
9 intelligent actuator part 1 installation [3] surge absorber with both the global specification and standard specification, the motor drive part of the x-sel controller has no built-in surge absorber to protect the equipment against surge noises that may generate in the controller due to lightning,...
Page 34
10 intelligent actuator part 1 installation peripheral configurations three-phase power supply specification p type (standard specification) q type (global specification) 200-vac three- phase power bus control panel circuit breaker earth leakage breaker surge protector three- phase noise filter ring...
Page 35
11 intelligent actuator part 1 installation peripheral configurations single-phase power supply specification p type (standard specification) q type (global specification) 200-vac single- phase power bus control panel circuit breaker earth leakage breaker surge protector single- phase noise filter r...
Page 36
12 intelligent actuator part 1 installation 4. Noise control measures and grounding (1) wiring and power source pe on the power terminal block is used for protective grounding. Provide class d grounding from this terminal. Use a grounding cable with a wire size of 1.0 mm 2 (#awg17) or more, which sh...
Page 37
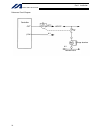
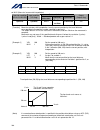
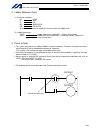
13 intelligent actuator part 1 installation (3) noise sources and noise elimination there are many noise sources, but solenoid valves, magnet switches and relays are of particular concern when building a system. Noise from these parts can be eliminated using the measures specified below: a. Ac solen...
Page 38
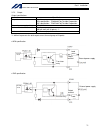
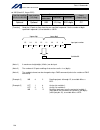
14 intelligent actuator part 1 installation reference circuit diagram controller surge absorber solenoid valve out com cr +24 v 0 v 100 vac cr 0 v.
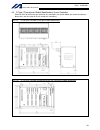
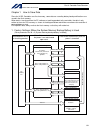
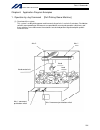
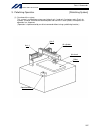
Page 39
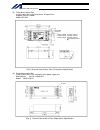
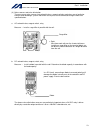
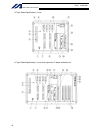
15 intelligent actuator part 1 installation chapter 4 name and function of each part 1. Front view of controller p type (standard specification), 4 axes p type (standard specification), 4 axes with expansion i/o board and brake unit.
Page 40
16 intelligent actuator part 1 installation q type (global specification), 4 axes q type (global specification), 4 axes with expansion i/o board and brake unit.
Page 41
17 intelligent actuator part 1 installation (1) fg terminal this terminal is used to ground fg on the enclosure. The enclosure is connected to pe in the ac input part inside the controller. Fg terminal specifications item description m4 3-point sems screw, 5 mm name fg cable size 2.0 ~ 5.5 mm 2 min....
Page 42
18 intelligent actuator part 1 installation (3) ac-power input connector a 200-vac, single-phase or three-phase input connector consisting of six terminals including motor power terminals, control power terminals and a pe terminal. Note) take note that the single-phase input specification and three-...
Page 43
19 intelligent actuator part 1 installation (6) encoder/axis-sensor connector this connector is used to connect the actuator encoder and axis sensors such as ls, creep and ot. * ls, creep and ot sensors are optional. Encoder/axis-sensor connector specifications item description details connector hal...
Page 44
20 intelligent actuator part 1 installation (7) motor connector this connector is used to drive the motor inside the actuator. Motor connector specifications item description details connector gic2.5/4-stf-7.62 4-pin, 2-piece connector by phoenix contact connector name m1 ~ 6 motor connector cable s...
Page 45
21 intelligent actuator part 1 installation (9) teaching connector the teaching interface connects iai’s teaching pendant or a pc (pc software) to enable operation and setting of your equipment from the teaching pendant/pc. The physical interface consists of a rs232c system based on a 25-pin, d-sub ...
Page 46
22 intelligent actuator part 1 installation interface specifications of teaching serial interface item no. Direction signal name details 1 fg frame ground 2 out txd transmitted data 3 in rxd received data 4 out rts request to send 5 in cts clear to send 6 out dsr equipment ready 7 sg signal ground 8...
Page 47
23 intelligent actuator part 1 installation (10) system i/o connector this i/o connector is used to control the safety actions of the controller. With the global specification, a safety circuit conforming to a desired safety category of up to level 4 can be configured using this connector and an ext...
Page 48
24 intelligent actuator part 1 installation (11) panel window this window consists of a 4-digit, 7-segment led display and five led lamps that indicate the status of the equipment. For the information shown on the display, refer to 2, “explanation of codes displayed on the panel window” or the “erro...
Page 49
25 intelligent actuator part 1 installation the functions are at the time of shipment. The functions assigned to port nos. 000 to 015, 300 to 310, 313 and 314 can be changed via i/o parameters. (refer to nos. 30 to 56, no. 59 and 60 in 1, “i/o parameters,” of appendix, “list of parameters.”) i/o int...
Page 50
26 intelligent actuator part 1 installation (14) general rs232c port connector 1 channel 1 of the two-channel rs232c port provided for connection of general rs232c equipment. (refer to i/o parameter nos. 201 to 203.) (15) general rs232c port connector 2 channel 2 of the two-channel rs232c port provi...
Page 51
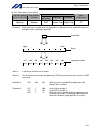
27 intelligent actuator part 1 installation (19) brake-power input connector this connector is used to input the drive power for the actuator brake. 24 vdc must be supplied externally. If the specified brake power is not supplied, the actuator brake cannot be released. Be sure to supply the brake po...
Page 52
28 intelligent actuator part 1 installation 2. Explanation of codes displayed on the panel window 2.1 application display priority (*1) description 1 ac power is cut off (including momentary power failure or drop in power- source voltage). 1 system-down level error 2 writing data to the flash rom. 3...
Page 53
29 intelligent actuator part 1 installation 2.2 core display priority (*1) description 1 ac power is cut off (including momentary power failure or drop in power- source voltage). 1 cold-start level error 1 cold-start level error 1 operation-cancellation level error 1 operation-cancellation level err...
Page 54
30 intelligent actuator part 1 installation 2.3 current monitor and variable monitor other parameter nos. 49 and 50 can be set up to monitor currents or variables on the panel window (main application version 0.09 or later). (1) current monitor currents of up to four axes having continuous axis numb...
Page 55
31 intelligent actuator part 1 installation (2) variable monitor the contents of global integer variables can be displayed on the panel window. Positive integers of 1 to 999 can be displayed. Parameter settings other parameter no. 49 = 2 other parameter no. 50 = variable number of the global integer...
Page 56
32 intelligent actuator part 1 installation chapter 5 specifications 1. Controller specifications 1.1. P type (standard specification) controller with 1 to 6 axes total output when maximum number of axes are connected single-phase specification: 1600w three-phase specification: 2400w control power i...
Page 57
33 intelligent actuator part 1 installation rs232c port for teaching serial interface enabled only in the manual operation mode. Iai’s dedicated teaching pendant or ansi teaching pendant (selected by a switch) rs232c port for general pc connection dedicated 2-channel rs232c, 9-pin dte specification ...
Page 58
34 intelligent actuator part 1 installation 1.2 q type (global specification) controller with 1 to 6 axes total output when maximum number of axes are connected single-phase specification: 1600w three-phase specification: 2400w control power input single-phase, 200 ~ 230 vac ± 10% motor power input ...
Page 59
35 intelligent actuator part 1 installation rs232c port for teaching serial interface enabled only in the manual operation mode. Iai’s dedicated teaching pendant or ansi teaching pendant (selected by a switch) rs232c port for general pc connection dedicated 2-channel rs232c, 9-pin dte specification ...
Page 60
36 intelligent actuator part 1 installation 2. External i/o specifications 2.1. Npn specification (1) input part external input specifications (npn specification) item specification input voltage 24 vdc ±10% input current 7 ma per circuit on/off voltage on voltage --- 16.0 vdc min. Off voltage --- 5...
Page 61
37 intelligent actuator part 1 installation (2) output part external output specifications (npn specification) item specification load voltage 24 vdc maximum load current 100 ma per point, 400 ma per 8 ports note) leakage current 0.1 ma max. Per point td62084 (or equivalent) insulation method photoc...
Page 62
38 intelligent actuator part 1 installation 2.2. Pnp specification (1) input part external input specifications (pnp specification) item specification input voltage 24 vdc ±10% input current 7 ma per circuit on/off voltage on voltage --- 8 vdc max. Off voltage --- 19 vdc min. Insulation method photo...
Page 63
39 intelligent actuator part 1 installation (2) output part external output specifications item specification load voltage 24 vdc maximum load current 100 ma per point, 400 ma per 8 ports note) leakage current 0.1 ma max. Per point td62784 (or equivalent) insulation method photocoupler insulation ex...
Page 64
40 intelligent actuator part 1 installation 3. Power-source capacity and heat output the power consumption and heat output of the x-sel controller will vary depending on the number of connected axes and i/o configuration. This section explains how to estimate the power-source capacity and heat outpu...
Page 65
41 intelligent actuator part 1 installation [1] control power-source capacity the power-source capacity of the control power supply is obtained by applying the efficiency coefficient and power factor to the sum of all power consumptions of controlled units, based on the applicable values shown in th...
Page 66
42 intelligent actuator part 1 installation (3) calculation example obtain the power-source capacities and heat outputs when a controller of the following specifications is used. Actuator for axis 1: 200 w actuator for axis 2: 200 w actuator for axis 3: 100 w with brake actuator for axis 4: 60 w sta...
Page 67
43 intelligent actuator part 1 installation 4. External dimensions 4.1 p/q type (three-phase standard specification, single-phase global specification, single-phase standard specification) 4-axis controller external views of enclosures for various 4-axis controllers are shown below (the external enc...
Page 68
44 intelligent actuator part 1 installation fig. 4-3 p/q type 4-axis controller with expansion i/o board (three-phase standard specification, single-phase global specification, single-phase standard specification) fig. 4-4 p/q type 4-axis controller with expansion i/o board + absolute brake unit (th...
Page 69
45 intelligent actuator part 1 installation 4.2 p/q type (standard specification) 6-axis controller (three-phase standard specification, single-phase global specification, single-phase standard specification) external views of enclosures for various 6-axis controllers are shown below (the external e...
Page 70
46 intelligent actuator part 1 installation fig. 4-7 p/q type 6-axis controller (three-phase standard specification, single-phase global specification, single-phase standard specification) fig. 4-8 p/q type 6-axis controller with expansion i/o board + absolute brake unit (three-phase standard specif...
Page 71
47 intelligent actuator part 1 installation 4.3 q type (three-phase global specification) 4-axis controller external views of enclosures for various 4-axis controllers are shown below (the external enclosure dimensions are the same for 1-axis to 4-axis controllers). Fig. 4-9 q type 4-axis controller...
Page 72
48 intelligent actuator part 1 installation fig. 4-11 q type 4-axis controller with expansion i/o board fig. 4-12 q type 4-axis controller with expansion i/o board + absolute brake unit.
Page 73
49 intelligent actuator part 1 installation 4.4 q type (three-phase global specification) 6-axis controller external views of enclosures for various 6-axis controllers are shown below (the external enclosure dimensions are the same for 5-axis and 6-axis controllers). Fig. 4-13 q type 6-axis controll...
Page 74
50 intelligent actuator part 1 installation fig. 4-15 q type 6-axis controller with expansion i/o board (three-phase global specification) fig. 4-16 q type 6-axis controller with expansion i/o board + absolute brake unit (three-phase global specification).
Page 75
51 intelligent actuator part 1 installation chapter 6 safety circuit the circuit configuration for embodying safety actions such as emergency stop is different between the standard specification and global specification of the x-sel controller. The standard controller has a built-in drive-source cut...
Page 76
52 intelligent actuator part 1 installation 2. Safety circuit for p type (standard specification) controller the p type controller has a built-in drive-source cutoff circuit just like iai’s other controllers. The drive-source cutoff circuit consists of a relay and conforms to safety category b. If y...
Page 77
53 intelligent actuator part 1 installation with the p type, use only the signals shown in the shaded fields of the table for connection with the safety switches. Exercise caution that opening the specified pins or wiring them differently may compromise the safety actions of the controller. The rdyo...
Page 78
54 intelligent actuator part 1 installation 3. Safety circuit for q type (global specification) controller the global controller has no internal drive-source cutoff circuit so that the user can configure a desired drive-source cutoff circuit externally to the controller to conform to the required sa...
Page 79
55 intelligent actuator part 1 installation terminal assignments pin no. Signal name overview details 9 det in to fused- contact detection circuit external contact error input (paired with no. 18) connected to the fused-contact detection contacts of the safety circuit. 8 in emergency-stop detection ...
Page 80
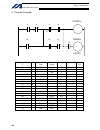
56 intelligent actuator part 1 installation • em1/emg2, enb1/enb2 emg1 (line+)/(line-) and emg2 (line+)/(line-) are redundant emergency-stop control lines. Enb1 (line+)/(line-) and enb2 (line+)/(line-) are redundant enabling control lines. Use these lines to cut off the external drive source. Since ...
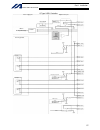
Page 81
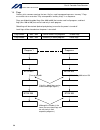
57 intelligent actuator part 1 installation q type x-sel controller power supply part digital control part not installed ac cutoff relay rectifier dc bus to power stage external emergency-stop reset contact output teaching pendant power-on reset mpsdwn bit power error mushroom emergency- stop swit c...
Page 82
58 intelligent actuator part 1 installation external emergency-stop circuit contactor (neo sc) relay contactor (neo sc) 200-vac, three- phase reset switch external emergency-stop switch external emg switch contact 1 external emg switch contact 2 safety relay unit (g9sa-301 by omron) safety gate swit...
Page 83
59 intelligent actuator part 1 installation chapter 7 system setup a connection example of a 2-axis controller is given below: 1. Connection method of controller and actuator in the case of an absolute specification, perform an absolute reset after the connection (refer to chapter 8). 1.1 connection...
Page 84
60 intelligent actuator part 1 installation 1.2 connection diagram for q type (global specification) note 1: with the absolute specification, set the absolute-data backup battery enable/disable switch to the bottom position for all axes before connecting the encoder/axis-sensor cables. (after the ca...
Page 85
61 intelligent actuator part 1 installation 1.3 startup procedure note: when installing multiple axes to the controller, be sure to connect the actuator cables to the right connectors. Check the type of the actuator connected to each connector. If the cables and connectors are not connected properly...
Page 86
62 intelligent actuator part 1 installation 2. I/o connection diagram 2.1 npn specification pin no. Category port no. Function 1 - +24-v input 2 000 program start 3 001 general-purpose input 4 002 general-purpose input 5 003 general-purpose input 6 004 general-purpose input 7 005 general-purpose inp...
Page 87
63 intelligent actuator part 1 installation 2.2 pnp specification pin no. Category port no. Function 1 - +24-v input 2 000 program start 3 001 general-purpose input 4 002 general-purpose input 5 003 general-purpose input 6 004 general-purpose input 7 005 general-purpose input 8 006 general-purpose i...
Page 88
64 intelligent actuator part 1 installation 2.3 i/o flat cable flat cable: kfx-50 (s) (color) (kaneko cord) no. Color no. Color no. Color no. Color no. Color 1 brown-1 11 brown-2 21 brown-3 31 brown-4 41 brown-5 2 red-1 12 red-2 22 red-3 32 red-4 42 red-5 3 orange-1 13 orange-2 23 orange-3 33 orange...
Page 89
65 intelligent actuator part 1 installation 3. Multi-point dio board this board is a multi-point dio board equipped with 48 input points and 48 output points for use with xsel controllers. 3.1 overview 3.1.1 features [1] one board provides a total of 96 input/output points. Multiple inputs/outputs o...
Page 90
66 intelligent actuator part 1 installation 3.2 configuration 3.2.1 system configuration this board is installed in the standard i/o slot or any expansion slot and exchanges signals with external dios. 3.3 specifications 3.3.1 input/output specifications item specification numbers of input/output po...
Page 91
67 intelligent actuator part 1 installation 3.4 external interface specifications 3.4.1 terminal assignment for external dio interface overview of multi-point dio interface specifications item overview remarks applicable connector half-pitch flat connector, 100 pins hif6-100pa-1.27ds (hirose) connec...
Page 92
68 intelligent actuator part 1 installation 3.5 connection cables for multi-point io board cable 1 cable 2 category pin no. Color port no. Function category pin no. Color port no. Function - 1 brown-1 - external power supply 24 vdc for pin nos. 2 to 25/51 to 74 51 brown-1 300 alarm output 2 red-1 00...
Page 93
69 intelligent actuator part 1 installation 3.6 connection cables for multi-point io board model: cb-x-pioh020 • cable with connectors on both ends model: cb-x-pioh020-h6 this connector is used to connect the multi-point dio board and an optional terminal block unit. Socket: hif6-100d-1.27r (hirose)...
Page 94
70 intelligent actuator part 1 installation 3.7 input/output circuits 3.7.1 input input specifications item specification (common to pnp/npn specifications) external power-supply voltage dc24v ± 10% input current 7 ma max. Per point leak current 1 ma max. Per point input circuit • npn specification ...
Page 95
71 intelligent actuator part 1 installation 3.7.2 output output specifications item specification output element transistor array npn specification: td62084af by toshiba corporation pnp specification: td62784af by toshiba corporation external power-supply voltage dc24 ± 10% maximum load current 50 m...
Page 96
72 intelligent actuator part 1 installation chapter 8 how to perform an absolute encoder reset (absolute specification) when the absolute-encoder battery voltage of the x-sel controller is abnormal or when the battery or encoder cable is disconnected, an encoder battery error will occur and an absol...
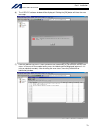
Page 97
73 intelligent actuator part 1 installation (6) the x-sel pc software window will be displayed. Clicking the [ok] button will clear the error message. (7) from the [monitor (m)] menu, select [detailed error information (e)] to check the current error status. In the case of an encoder battery error, ...
Page 98
74 intelligent actuator part 1 installation (8) from the [controller (c)] menu, select [absolute reset (a)]. (9) when a [warning] dialog box is displayed, click the [ok] button. (10) the [abs. Encoder reset] dialog box will be displayed. Click here to select the axis you wish to perform an absolute ...
Page 99
75 intelligent actuator part 1 installation (12) another [warning] dialog box will be displayed. Click the [yes] button. (13) when the processing of “encoder rotation data reset 1” is complete, the red arrow will move to the next item. Press the following processing buttons one by one (the red arrow...
Page 100
76 intelligent actuator part 1 installation (15) when the [confirmation] dialog box is displayed, click the [yes] button and restart the controller. (note) commencing the operation without first executing a software reset or reconnecting the power may generate the following errors: error no. C70: ab...
Page 101
77 intelligent actuator part 1 installation chapter 9 maintenance • routine maintenance and inspection are necessary so that the system will operate properly at all times. Be sure to turn off the power before performing maintenance or inspection. • the standard inspection interval is six months to o...
Page 102
78 intelligent actuator part 1 installation 3. Replacement procedure for system-memory backup battery backing up the system memory if “other parameter no. 20, backup-battery installation function type” is set to “2” (installed), the following sram data in the x-sel controller will be backed up by th...
Page 103
79 intelligent actuator part 1 installation battery replacement procedure 1) remove the 7-segment led panel from the controller. Slide the panel upward and pull it toward you to remove. 2) press the center of the battery using a finger, as shown. The battery will come off from the holder. 3) install...
Page 104
80 intelligent actuator part 1 installation (8) when the replacement of system-memory backup battery is complete, confirm that the battery is installed securely and then turn on the controller power. (9) revert “other parameter no. 20, backup-battery installation function type” to the value recorded...
Page 105
81 intelligent actuator part 1 installation 4. Replacement procedure for absolute-data backup battery the replacement procedure will vary depending on if errors are present at the time of replacement and if so, which errors are present (no.A23, 914, ca2). • if no error is present, perform steps (1) ...
Page 106
82 intelligent actuator part 1 installation (6) turn on the controller power. (7) set the absolute-data backup battery enable/disable switch to the top (enb) position. (note) this operation is not required if no error has generated or when an a23 error has generated. (8) turn off the controller powe...
Page 107
83 intelligent actuator part 2 operation part 2 operation chapter 1 operation how to start a program with the x-sel controller, the stored programs can be started (run) using four methods. Of these methods, two are mainly used to debug programs or perform trial operations, while the remaining two ar...
Page 108
84 intelligent actuator part 2 operation 1. Starting a program by auto-start via parameter setting i/o parameter no. 33 (input function selection 003) = 1 (default factory setting) set the number of the program you wish to start automatically in other parameter no. 1 (auto-start program number). Set...
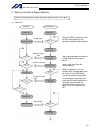
Page 109
85 intelligent actuator part 2 operation 2. Starting via external signal selection (1) flow chart when the ready signal turns on, the rdy lamp (green) on the controller front panel will illuminate. Input a desired program number as a bcd code from the external device. Input a start signal from the e...
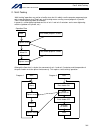
Page 110
86 intelligent actuator part 2 operation (2) timing chart ready output program number input external start input program 1 program 2 t1: duration after the ready output turns on until input of external start signal is permitted t1 = 10 msec min. T2: duration after the program number is input until i...
Page 111
87 intelligent actuator part 2 operation 3. Drive-source recovery request and operation-pause reset request (1) drive-source recovery request 1. How to request a drive-source recovery a drive-source recovery request can be issued using one of the following methods: • set i/o parameter no. 44 to “1” ...
Page 112
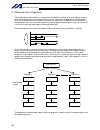
88 intelligent actuator part 3 controller data structure part 3 controller data structure the controller data consists of parameters as well as position data and application programs used to implement sel language. X-sel controller data structure the user must create position data and application pr...
Page 113
89 intelligent actuator part 3 controller data structure chapter 1 how to save data since the x-sel controller uses flash memory, some data are saved by battery backup while others are saved in the flash memory. When data is transferred from the pc software or teaching pendant to the controller, the...
Page 114
90 intelligent actuator part 3 controller data structure since the programs, parameters and symbols are read from the flash memory at restart, the data in the temporary memory will remain the same as the original data before edit unless the edited data are written to the flash memory. The controller...
Page 115
91 intelligent actuator part 3 controller data structure 3. Points to note point to note when transferring data and writing to the flash memory never turn off the main power while data is being transferred or written to the flash memory. The data will be lost and the controller operation may be disa...
Page 116
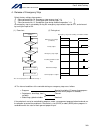
92 intelligent actuator part 3 controller data structure chapter 2 x-sel language data 1. Values and symbols used in sel language 1.1 list of values and symbols used the various functions required in a program are represented by values and symbols. Function global range local range remarks input por...
Page 117
93 intelligent actuator part 3 controller data structure z the variables and flags in the global range will be retained even after the controller power is turned off. (when other parameter no. 20 is set to “2.” refer to chapter 1, “how to save data,” of part 3.) z the variables and flags in the loca...
Page 118
94 intelligent actuator part 3 controller data structure 1.3 virtual i/o ports (1) virtual input ports port no. Function 7000 always off 7001 always on 7002 voltage low warning for system-memory backup battery 7003 abnormal voltage of system-memory backup battery 7004 (for future expansion = use str...
Page 119
95 intelligent actuator part 3 controller data structure (2) virtual output ports port no. Function 7300 latch cancellation output for a latch signal indicating that all-operation-cancellation factor is present (7011) (latch is cancelled only when operation-cancellation factor is no longer present) ...
Page 120
96 intelligent actuator part 3 controller data structure 1.4 flags contrary to its common meaning, the term “flag” as used in programming means “memory.” flags are used to set or reset data. They correspond to “auxiliary relays” in a sequencer. Flags are divided into global flags (nos. 600 to 899) t...
Page 121
97 intelligent actuator part 3 controller data structure 1.5 variables (1) meaning of variable “variable” is a technical term used in software programming. Simply put, it means “a box in which a value is put.” variables can be used in many ways, such as putting in or taking out a value and performin...
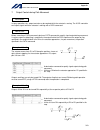
Page 122
98 intelligent actuator part 3 controller data structure (2) types of variables variables are classified into two types, as follows: 1. Integer variables these variables cannot handle decimal places. [example] 1234 integer variable number 200 ~ 299 1200 ~ 1299 can be used in all programs “global int...
Page 123
99 intelligent actuator part 3 controller data structure 3. Variables with “*” (asterisk) (indirect specification) an “*” (asterisk) is used to specify a variable. In the following example, the content of variable box 1 will be put in variable box 2. If variable box 1 contains “1234,” then “1234” wi...
Page 124
100 intelligent actuator part 3 controller data structure 1.6 tags the term “tag” means “heading.” tags are used in the same way you attach labels to the pages in a book you want to reference frequently. A tag is a destination specified in a jump command “goto.” command operand 1 tag tag number (int...
Page 125
101 intelligent actuator part 3 controller data structure 1.7 subroutines by taking out the parts of a program that are used repeatedly and registering them as “subroutines,” the same processing can be performed with fewer steps. (a maximum of 15 nests are accommodated.) they are used only in each p...
Page 126
102 intelligent actuator part 3 controller data structure 1.8 symbols in the x-sel controller, values such as variable numbers and flag numbers can be handled as symbols. For the method to edit symbols, refer to “editing symbols” in the operation manual for x- sel teaching pendant or “symbol edit wi...
Page 127
103 intelligent actuator part 3 controller data structure 1.10 axis specification axes can be specified based on axis number or axis pattern. (1) axis numbers and how axes are stated each of multiple axes is stated as follows: axis number how axis is stated 1 axis 1 2 axis 2 3 axis 3 4 axis 4 5 axis...
Page 128
104 intelligent actuator part 3 controller data structure (2) axis pattern whether or not each axis will be used is indicated by “1” or “0.” (upper) (lower) axis number axis 6 axis 5 axis 4 axis 3 axis 2 axis 1 used 1 1 1 1 1 1 not used 0 0 0 0 0 0 [example] when axes 1 and 2 are used axis 2 000011 ...
Page 129
105 intelligent actuator part 3 controller data structure x-sel language consists of a position part (position data = coordinates, etc.) and a command part (application program). 2. Position part as position data, coordinates, speeds, accelerations and decelerations are set and stored. Position no. ...
Page 130
106 intelligent actuator part 3 controller data structure 3. Command part the primary feature of sel language is its very simple command structure. Since the structure is simple, there is no need for a compiler (to translate into computer language) and high-speed operation is possible via an interpr...
Page 131
107 intelligent actuator part 3 controller data structure 3.2 extension condition conditions can be combined in a complex manner. (sel language) command extension condition input condition command operand 1 operand 2 output condition 1 a condition 2 a condition 3 command operand 1 operand 2 command ...
Page 132
108 intelligent actuator part 4 commands part 4 commands chapter 1 list of sel language command codes 1. By function variables can be specified indirectly in the operand 1, operand 2 and output fields. Symbols can be input in the condition, operand 1, operand 2 and output fields. The input items in ...
Page 133
109 intelligent actuator part 4 commands operation type in the output field cc: command was executed successfully, zr: operation result is zero, pe: operation is complete, cp: command part has passed, tu: time up eq: operand 1 = operand 2, ne: operand 1 ≠ operand 2, gt: operand 1 > operand 2, ge: op...
Page 134
110 intelligent actuator part 4 commands operation type in the output field cc: command was executed successfully, zr: operation result is zero, pe: operation is complete, cp: command part has passed, tu: time up eq: operand 1 = operand 2, ne: operand 1 ≠ operand 2, gt: operand 1 > operand 2, ge: op...
Page 135
111 intelligent actuator part 4 commands operation type in the output field cc: command was executed successfully, zr: operation result is zero, pe: operation is complete, cp: command part has passed, tu: time up eq: operand 1 = operand 2, ne: operand 1 ≠ operand 2, gt: operand 1 > operand 2, ge: op...
Page 136
112 intelligent actuator part 4 commands operation type in the output field cc: command was executed successfully, zr: operation result is zero, pe: operation is complete, cp: command part has passed, tu: time up eq: operand 1 = operand 2, ne: operand 1 ≠ operand 2, gt: operand 1 > operand 2, ge: op...
Page 137
113 intelligent actuator part 4 commands 2. Alphabetical order operation type in the output field cc: command was executed successfully, zr: operation result is zero, pe: operation is complete, cp: command part has passed, tu: time up eq: operand 1 = operand 2, ne: operand 1 ≠ operand 2, gt: operand...
Page 138
114 intelligent actuator part 4 commands operation type in the output field cc: command was executed successfully, zr: operation result is zero, pe: operation is complete, cp: command part has passed, tu: time up eq: operand 1 = operand 2, ne: operand 1 ≠ operand 2, gt: operand 1 > operand 2, ge: op...
Page 139
115 intelligent actuator part 4 commands operation type in the output field cc: command was executed successfully, zr: operation result is zero, pe: operation is complete, cp: command part has passed, tu: time up eq: operand 1 = operand 2, ne: operand 1 ≠ operand 2, gt: operand 1 > operand 2, ge: op...
Page 140
116 intelligent actuator part 4 commands operation type in the output field cc: command was executed successfully, zr: operation result is zero, pe: operation is complete, cp: command part has passed, tu: time up eq: operand 1 = operand 2, ne: operand 1 ≠ operand 2, gt: operand 1 > operand 2, ge: op...
Page 141
117 intelligent actuator part 4 commands operation type in the output field cc: command was executed successfully, zr: operation result is zero, pe: operation is complete, cp: command part has passed, tu: time up eq: operand 1 = operand 2, ne: operand 1 ≠ operand 2, gt: operand 1 > operand 2, ge: op...
Page 142
118 intelligent actuator part 4 commands chapter 2 explanation of commands 1. Commands 1.1 variable assignment z let (assign) command, declaration extension condition (ld, a, o, ab, ob) input condition (i/o, flag) command, declaration operand 1 operand 2 output (output, flag) optional optional let v...
Page 143
119 intelligent actuator part 4 commands z clr (clear variable) command, declaration extension condition (ld, a, o, ab, ob) input condition (i/o, flag) command, declaration operand 1 operand 2 output (output, flag) optional optional clr variable number variable number zr [function] clear the variabl...
Page 144
120 intelligent actuator part 4 commands 1.2 arithmetic operation z add (add) command, declaration extension condition (ld, a, o, ab, ob) input condition (i/o, flag) command, declaration operand 1 operand 2 output (output, flag) optional optional add variable number data zr [function] add the conten...
Page 145
121 intelligent actuator part 4 commands z mult (multiply) command, declaration extension condition (ld, a, o, ab, ob) input condition (i/o, flag) command, declaration operand 1 operand 2 output (output, flag) optional optional mult variable number data zr [function] multiply the content of the vari...
Page 146
122 intelligent actuator part 4 commands z mod (remainder of division) command, declaration extension condition (ld, a, o, ab, ob) input condition (i/o, flag) command, declaration operand 1 operand 2 output (output, flag) optional optional mod variable number data zr [function] assign, to the variab...
Page 147
123 intelligent actuator part 4 commands 1.3 function operation z sin (sine operation) command, declaration extension condition (ld, a, o, ab, ob) input condition (i/o, flag) command, declaration operand 1 operand 2 output (output, flag) optional optional sin variable number data zr [function] assig...
Page 148
124 intelligent actuator part 4 commands z tan (tangent operation) command, declaration extension condition (ld, a, o, ab, ob) input condition (i/o, flag) command, declaration operand 1 operand 2 output (output, flag) optional optional tan variable number data zr [function] assign the tangent of the...
Page 149
125 intelligent actuator part 4 commands z sqr (root operation) command, declaration extension condition (ld, a, o, ab, ob) input condition (i/o, flag) command, declaration operand 1 operand 2 output (output, flag) optional optional sqr variable number data zr [function] assign the root of the data ...
Page 150
126 intelligent actuator part 4 commands 1.4 logical operation z and (logical and) command, declaration extension condition (ld, a, o, ab, ob) input condition (i/o, flag) command, declaration operand 1 operand 2 output (output, flag) optional optional and variable number data zr [function] assign th...
Page 151
127 intelligent actuator part 4 commands z or (logical or) command, declaration extension condition (ld, a, o, ab, ob) input condition (i/o, flag) command, declaration operand 1 operand 2 output (output, flag) optional optional or variable number data zr [function] assign the logical or operation re...
Page 152
128 intelligent actuator part 4 commands z eor (logical exclusive-or) command, declaration extension condition (ld, a, o, ab, ob) input condition (i/o, flag) command, declaration operand 1 operand 2 output (output, flag) optional optional eor variable number data zr [function] assign the logical exc...
Page 153
129 intelligent actuator part 4 commands 1.5 comparison operation z cp (compare) command, declaration extension condition (ld, a, o, ab, ob) input condition (i/o, flag) command, declaration operand 1 operand 2 output (output, flag) eq ne gt ge optional optional cp variable number data lt le [functio...
Page 154
130 intelligent actuator part 4 commands 1.6 timer z timw (timer) command, declaration extension condition (ld, a, o, ab, ob) input condition (i/o, flag) command, declaration operand 1 operand 2 output (output, flag) optional optional timw time prohibited tu [function] stop the program and wait for ...
Page 155
131 intelligent actuator part 4 commands z timc (cancel timer) command, declaration extension condition (ld, a, o, ab, ob) input condition (i/o, flag) command, declaration operand 1 operand 2 output (output, flag) optional optional timc program number prohibited cp [function] cancel a timer in other...
Page 156
132 intelligent actuator part 4 commands z gttm (get time) command, declaration extension condition (ld, a, o, ab, ob) input condition (i/o, flag) command, declaration operand 1 operand 2 output (output, flag) optional optional gttm variable number prohibited cp [function] read system time to the va...
Page 157
133 intelligent actuator part 4 commands 1.7 i/o, flag operation z bt (output port, flag operation) command, declaration extension condition (ld, a, o, ab, ob) input condition (i/o, flag) command, declaration operand 1 operand 2 output (output, flag) optional optional bt output, flag (output, flag) ...
Page 158
134 intelligent actuator part 4 commands z btpn (output on pulse) command, declaration extension condition (ld, a, o, ab, ob) input condition (i/o, flag) command, declaration operand 1 operand 2 output (output, flag) optional optional btpn output port, flag timer setting cp [function] turn on the sp...
Page 159
135 intelligent actuator part 4 commands z btpf (output off pulse) command, declaration extension condition (ld, a, o, ab, ob) input condition (i/o, flag) command, declaration operand 1 operand 2 output (output, flag) optional optional btpf output port, flag timer setting cp [function] turn off the ...
Page 160
136 intelligent actuator part 4 commands z wt (wait for i/o port, flag) command, declaration extension condition (ld, a, o, ab, ob) input condition (i/o, flag) command, declaration operand 1 operand 2 output (output, flag) optional optional wt i/o, flag (time) tu [function] wait for the i/o port or ...
Page 161
137 intelligent actuator part 4 commands z in (read i/o, flag as binary) command, declaration extension condition (ld, a, o, ab, ob) input condition (i/o, flag) command, declaration operand 1 operand 2 output (output, flag) optional optional in i/o, flag i/o, flag cc [function] read the i/o ports or...
Page 162
138 intelligent actuator part 4 commands z inb (read i/o, flag as bcd) command, declaration extension condition (ld, a, o, ab, ob) input condition (i/o, flag) command, declaration operand 1 operand 2 output (output, flag) optional optional inb i/o, flag bcd digits cc [function] read the i/o ports or...
Page 163
139 intelligent actuator part 4 commands z out (write output, flag as binary) command, declaration extension condition (ld, a, o, ab, ob) input condition (i/o, flag) command, declaration operand 1 operand 2 output (output, flag) optional optional out output, flag output, flag cc [function] write the...
Page 164
140 intelligent actuator part 4 commands z outb (write output, flag as bcd) command, declaration extension condition (ld, a, o, ab, ob) input condition (i/o, flag) command, declaration operand 1 operand 2 output (output, flag) optional optional outb output, flag bcd digits cc [function] write the va...
Page 165
141 intelligent actuator part 4 commands z fmio (set in, inb, out, outb command format) command, declaration extension condition (ld, a, o, ab, ob) input condition (i/o, flag) command, declaration operand 1 operand 2 output (output, flag) optional optional fmio format type prohibited cp [function] s...
Page 166
142 intelligent actuator part 4 commands (4) operand 1 = 3 data is read or written after its upper 16 bits and lower 16 bits are reversed every 32 bits and its upper eight bits and lower eight bits are reversed every 16 bits. (i/o, flag number upper) (i/o, flag number lower) 01234567h ⇔ 67h 45h 23h ...
Page 167
143 intelligent actuator part 4 commands [example 2] variable 99 = 00001234h (decimal: 4660, bcd: 1234) 00001234h variable 99 4660 (in/out command) 1234 (inb/outb command) (i/o, flag number upper) (i/o, flag number lower) fmio = 0 00h 00h 12h 34h ⇔ 0000 0000 0000 0000 0001 0010 0011 0100 fmio = 1 00...
Page 168
144 intelligent actuator part 4 commands 1.8 program control z goto (jump) command, declaration extension condition (ld, a, o, ab, ob) input condition (i/o, flag) command, declaration operand 1 operand 2 output (output, flag) optional optional goto tag number prohibited cp [function] jump to the pos...
Page 169
145 intelligent actuator part 4 commands z exsr (execute subroutine) command, declaration extension condition (ld, a, o, ab, ob) input condition (i/o, flag) command, declaration operand 1 operand 2 output (output, flag) optional optional exsr subroutine number prohibited cp [function] execute the su...
Page 170
146 intelligent actuator part 4 commands z edsr (end subroutine) command, declaration extension condition (ld, a, o, ab, ob) input condition (i/o, flag) command, declaration operand 1 operand 2 output (output, flag) prohibited prohibited edsr prohibited prohibited cp [function] declare the end of a ...
Page 171
147 intelligent actuator part 4 commands 1.9 task management z exit (end program) command, declaration extension condition (ld, a, o, ab, ob) input condition (i/o, flag) command, declaration operand 1 operand 2 output (output, flag) optional optional exit prohibited prohibited cp [function] end the ...
Page 172
148 intelligent actuator part 4 commands z expg (start other program) command, declaration extension condition (ld, a, o, ab, ob) input condition (i/o, flag) command, declaration operand 1 operand 2 output (output, flag) optional optional expg program number (program number) cc [function] start the ...
Page 173
149 intelligent actuator part 4 commands z abpg (abort other program) command, declaration extension condition (ld, a, o, ab, ob) input condition (i/o, flag) command, declaration operand 1 operand 2 output (output, flag) optional optional abpg program number (program number) cc [function] forcibly e...
Page 174
150 intelligent actuator part 4 commands z sspg (pause program) command, declaration extension condition (ld, a, o, ab, ob) input condition (i/o, flag) command, declaration operand 1 operand 2 output (output, flag) optional optional sspg program number (program number) cc [function] pause the progra...
Page 175
151 intelligent actuator part 4 commands z rspg (resume program) command, declaration extension condition (ld, a, o, ab, ob) input condition (i/o, flag) command, declaration operand 1 operand 2 output (output, flag) optional optional rspg program number (program number) cc [function] resume the prog...
Page 176
152 intelligent actuator part 4 commands 1.10 position operation z pget (read position data) command, declaration extension condition (ld, a, o, ab, ob) input condition (i/o, flag) command, declaration operand 1 operand 2 output (output, flag) optional optional pget axis number position number cc [f...
Page 177
153 intelligent actuator part 4 commands z pput (write position data) command, declaration extension condition (ld, a, o, ab, ob) input condition (i/o, flag) command, declaration operand 1 operand 2 output (output, flag) optional optional pput axis number position number cp [function] write the valu...
Page 178
154 intelligent actuator part 4 commands z pclr (clear position data) command, declaration extension condition (ld, a, o, ab, ob) input condition (i/o, flag) command, declaration operand 1 operand 2 output (output, flag) optional optional pclr position number position number cp [function] clear the ...
Page 179
155 intelligent actuator part 4 commands z pcpy (copy position data) command, declaration extension condition (ld, a, o, ab, ob) input condition (i/o, flag) command, declaration operand 1 operand 2 output (output, flag) optional optional pcpy position number position number cp [function] copy the po...
Page 180
156 intelligent actuator part 4 commands z pred (read current position) command, declaration extension condition (ld, a, o, ab, ob) input condition (i/o, flag) command, declaration operand 1 operand 2 output (output, flag) optional optional pred axis pattern position number cp [function] read the cu...
Page 181
157 intelligent actuator part 4 commands z prdq (read current axis position (1 axis direct)) command, declaration extension condition (ld, a, o, ab, ob) input condition (i/o, flag) command, declaration operand 1 operand 2 output (output, flag) optional optional prdq axis number variable number cp th...
Page 182
158 intelligent actuator part 4 commands z ptst (check position data) command, declaration extension condition (ld, a, o, ab, ob) input condition (i/o, flag) command, declaration operand 1 operand 2 output (output, flag) optional optional ptst axis pattern position number cc [function] check if vali...
Page 183
159 intelligent actuator part 4 commands z pvel (assign speed data) command, declaration extension condition (ld, a, o, ab, ob) input condition (i/o, flag) command, declaration operand 1 operand 2 output (output, flag) optional optional pvel speed position number cp [function] write the speed specif...
Page 184
160 intelligent actuator part 4 commands z pacc (assign acceleration data) command, declaration extension condition (ld, a, o, ab, ob) input condition (i/o, flag) command, declaration operand 1 operand 2 output (output, flag) optional optional pacc acceleration position number cp [function] write th...
Page 185
161 intelligent actuator part 4 commands z pdcl (assign deceleration data) command, declaration extension condition (ld, a, o, ab, ob) input condition (i/o, flag) command, declaration operand 1 operand 2 output (output, flag) optional optional pdcl deceleration position number cp [function] assign t...
Page 186
162 intelligent actuator part 4 commands z paxs (read axis pattern) command, declaration extension condition (ld, a, o, ab, ob) input condition (i/o, flag) command, declaration operand 1 operand 2 output (output, flag) optional optional paxs variable number position number cp [function] store the ax...
Page 187
163 intelligent actuator part 4 commands z psiz (check position data size) command, declaration extension condition (ld, a, o, ab, ob) input condition (i/o, flag) command, declaration operand 1 operand 2 output (output, flag) optional optional psiz variable number prohibited cp [function] set an app...
Page 188
164 intelligent actuator part 4 commands z gvel (get speed data) command, declaration extension condition (ld, a, o, ab, ob) input condition (i/o, flag) command, declaration operand 1 operand 2 output (output, flag) optional optional gvel variable number position number cp [function] obtain speed da...
Page 189
165 intelligent actuator part 4 commands z gacc (get acceleration data) command, declaration extension condition (ld, a, o, ab, ob) input condition (i/o, flag) command, declaration operand 1 operand 2 output (output, flag) optional optional gacc variable number position number cp [function] obtain a...
Page 190
166 intelligent actuator part 4 commands z gdcl (get deceleration data) command, declaration extension condition (ld, a, o, ab, ob) input condition (i/o, flag) command, declaration operand 1 operand 2 output (output, flag) optional optional gdcl variable number position number cp [function] obtain d...
Page 191
167 intelligent actuator part 4 commands 1.11 actuator control declaration z vel (set speed) command, declaration extension condition (ld, a, o, ab, ob) input condition (i/o, flag) command, declaration operand 1 operand 2 output (output, flag) optional optional vel speed prohibited cp [function] set...
Page 192
168 intelligent actuator part 4 commands z ovrd (override) command, declaration extension condition (ld, a, o, ab, ob) input condition (i/o, flag) command, declaration operand 1 operand 2 output (output, flag) optional optional ovrd speed ratio prohibited cp [function] reduce the speed in accordance...
Page 193
169 intelligent actuator part 4 commands z acc (set acceleration) command, declaration extension condition (ld, a, o, ab, ob) input condition (i/o, flag) command, declaration operand 1 operand 2 output (output, flag) optional optional acc acceleration prohibited cp [function] set the travel accelera...
Page 194
170 intelligent actuator part 4 commands z dcl (set deceleration) command, declaration extension condition (ld, a, o, ab, ob) input condition (i/o, flag) command, declaration operand 1 operand 2 output (output, flag) optional optional dcl deceleration prohibited cp [function] set the travel decelera...
Page 195
171 intelligent actuator part 4 commands z scrv (set sigmoid motion ratio) command, declaration extension condition (ld, a, o, ab, ob) input condition (i/o, flag) command, declaration operand 1 operand 2 output (output, flag) optional optional scrv ratio prohibited cp [function] set the ratio of sig...
Page 196
172 intelligent actuator part 4 commands z ofst (set offset) command, declaration extension condition (ld, a, o, ab, ob) input condition (i/o, flag) command, declaration operand 1 operand 2 output (output, flag) optional optional ofst axis pattern offset value cp [function] reset the target value by...
Page 197
173 intelligent actuator part 4 commands z deg (set arc angle) command, declaration extension condition (ld, a, o, ab, ob) input condition (i/o, flag) command, declaration operand 1 operand 2 output (output, flag) optional optional deg angle prohibited cp [function] set a division angle for the inte...
Page 198
174 intelligent actuator part 4 commands z base (specify axis base) command, declaration extension condition (ld, a, o, ab, ob) input condition (i/o, flag) command, declaration operand 1 operand 2 output (output, flag) optional optional base axis number prohibited cp [function] count the axes sequen...
Page 199
175 intelligent actuator part 4 commands z grp (set group axes) command, declaration extension condition (ld, a, o, ab, ob) input condition (i/o, flag) command, declaration operand 1 operand 2 output (output, flag) optional optional grp axis pattern prohibited cp [function] allow only the position d...
Page 200
176 intelligent actuator part 4 commands z hold (hold: declare axis port to pause) command, declaration extension condition (ld, a, o, ab, ob) input condition (i/o, flag) command, declaration operand 1 operand 2 output (output, flag) optional optional hold (input port, global flag) (hold type) cp [f...
Page 201
177 intelligent actuator part 4 commands z canc (cancel: declare axis port to abort) command, declaration extension condition (ld, a, o, ab, ob) input condition (i/o, flag) command, declaration operand 1 operand 2 output (output, flag) optional optional canc (input port, global flag) (canc type) cp ...
Page 202
178 intelligent actuator part 4 commands z vlmx (specify vlmx speed) command, declaration extension condition (ld, a, o, ab, ob) input condition (i/o, flag) command, declaration operand 1 operand 2 output (output, flag) optional optional vlmx prohibited prohibited cp [function] set the actuator trav...
Page 203
179 intelligent actuator part 4 commands z dis (set division distance at spline movement) command, declaration extension condition (ld, a, o, ab, ob) input condition (i/o, flag) command, declaration operand 1 operand 2 output (output, flag) optional optional dis distance prohibited cp [function] set...
Page 204
180 intelligent actuator part 4 commands z potp (set path output type) command, declaration extension condition (ld, a, o, ab, ob) input condition (i/o, flag) command, declaration operand 1 operand 2 output (output, flag) optional optional potp 0 or 1 prohibited cp [function] set the output type in ...
Page 205
181 intelligent actuator part 4 commands z papr (set push-motion approach distance, speed) command, declaration extension condition (ld, a, o, ab, ob) input condition (i/o, flag) command, declaration operand 1 operand 2 output (output, flag) optional optional papr distance speed cp [function] set th...
Page 206
182 intelligent actuator part 4 commands z qrtn (set quick-return mode) command, declaration extension condition (ld, a, o, ab, ob) input condition (i/o, flag) command, declaration operand 1 operand 2 output (output, flag) optional optional qrtn 0 or 1 prohibited cp [function] set and cancel the qui...
Page 207
183 intelligent actuator part 4 commands 1.12 actuator control command z sv (turn on/off servo) command, declaration extension condition (ld, a, o, ab, ob) input condition (i/o, flag) command, declaration operand 1 operand 2 output (output, flag) optional optional sv axis pattern prohibited pe [func...
Page 208
184 intelligent actuator part 4 commands z home (return to home) command, declaration extension condition (ld, a, o, ab, ob) input condition (i/o, flag) command, declaration operand 1 operand 2 output (output, flag) optional optional home axis pattern prohibited pe [function] perform home return of ...
Page 209
185 intelligent actuator part 4 commands z movp (move ptp by specifying position data) command, declaration extension condition (ld, a, o, ab, ob) input condition (i/o, flag) command, declaration operand 1 operand 2 output (output, flag) optional optional movp position number prohibited pe [function...
Page 210
186 intelligent actuator part 4 commands z movl (move by specifying position data) command, declaration extension condition (ld, a, o, ab, ob) input condition (i/o, flag) command, declaration operand 1 operand 2 output (output, flag) optional optional movl position number prohibited pe [function] mo...
Page 211
187 intelligent actuator part 4 commands z mvpi (move via incremental ptp) command, declaration extension condition (ld, a, o, ab, ob) input condition (i/o, flag) command, declaration operand 1 operand 2 output (output, flag) optional optional mvpi position number prohibited pe [function] move the a...
Page 212
188 intelligent actuator part 4 commands z mvli (move via incremental interpolation) command, declaration extension condition (ld, a, o, ab, ob) input condition (i/o, flag) command, declaration operand 1 operand 2 output (output, flag) optional optional mvli position number prohibited pe [function] ...
Page 213
189 intelligent actuator part 4 commands z path (move along path) command, declaration extension condition (ld, a, o, ab, ob) input condition (i/o, flag) command, declaration operand 1 operand 2 output (output, flag) optional optional path start position number end position number pe [function] move...
Page 214
190 intelligent actuator part 4 commands z j w (jog) command, declaration extension condition (ld, a, o, ab, ob) input condition (i/o, flag) command, declaration operand 1 operand 2 output (output, flag) optional optional j w axis pattern input, output, flag number pe [function] the axes in the axis...
Page 215
191 intelligent actuator part 4 commands z stop (stop movement) command, declaration extension condition (ld, a, o, ab, ob) input condition (i/o, flag) command, declaration operand 1 operand 2 output (output, flag) optional optional stop axis pattern prohibited cp [function] decelerate and stop the ...
Page 216
192 intelligent actuator part 4 commands z pspl (move along spline) command, declaration extension condition (ld, a, o, ab, ob) input condition (i/o, flag) command, declaration operand 1 operand 2 output (output, flag) optional optional pspl start position number end position number pe [function] co...
Page 217
193 intelligent actuator part 4 commands z push (move by push motion) command, declaration extension condition (ld, a, o, ab, ob) input condition (i/o, flag) command, declaration operand 1 operand 2 output (output, flag) optional optional push target position number prohibited pe [function] perform ...
Page 218
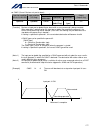
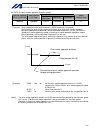
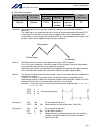
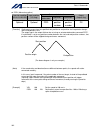
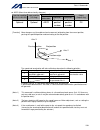
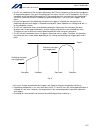
194 intelligent actuator part 4 commands [example] papr 100 20 movp 2 push 10 set the push-motion approach distance to 100 mm and push-motion approach speed to 20 mm/sec. Move from the current position to position no. 2. Perform push-motion movement from position nos. 2 to 10. The diagram below desc...
Page 219
195 intelligent actuator part 4 commands z ptrq (change push torque limit parameter) command, declaration extension condition (ld, a, o, ab, ob) input condition (i/o, flag) command, declaration operand 1 operand 2 output (output, flag) optional optional ptrq axis pattern ratio cc [function] change t...
Page 220
196 intelligent actuator part 4 commands z cir2 (move along circle 2 (arc interpolation)) command, declaration extension condition (ld, a, o, ab, ob) input condition (i/o, flag) command, declaration operand 1 operand 2 output (output, flag) optional optional cir2 passing position 1 number passing po...
Page 221
197 intelligent actuator part 4 commands z arc2 (move along circle 2 (arc interpolation)) command, declaration extension condition (ld, a, o, ab, ob) input condition (i/o, flag) command, declaration operand 1 operand 2 output (output, flag) optional optional arc2 passing position number end position...
Page 222
198 intelligent actuator part 4 commands z cirs (move three-dimensionally along circle) command, declaration extension condition (ld, a, o, ab, ob) input condition (i/o, flag) command, declaration operand 1 operand 2 output (output, flag) optional optional cirs passing position 1 number passing posi...
Page 223
199 intelligent actuator part 4 commands z arcs (move three-dimensionally along arc) command, declaration extension condition (ld, a, o, ab, ob) input condition (i/o, flag) command, declaration operand 1 operand 2 output (output, flag) optional optional arcs passing position number end position numb...
Page 224
200 intelligent actuator part 4 commands z chvl (change speed) command, declaration extension condition (ld, a, o, ab, ob) input condition (i/o, flag) command, declaration operand 1 operand 2 output (output, flag) optional optional chvl axis pattern speed cp [function] change the speed of the axes o...
Page 225
201 intelligent actuator part 4 commands z arcd (move along arc via specification of end position and center angle (arc interpolation)) command, declaration extension condition (ld, a, o, ab, ob) input condition (i/o, flag) command, declaration operand 1 operand 2 output (output, flag) optional opti...
Page 226
202 intelligent actuator part 4 commands z arcc (move along arc via specification of center position and center angle (arc interpolation)) command, declaration extension condition (ld, a, o, ab, ob) input condition (i/o, flag) command, declaration operand 1 operand 2 output (output, flag) optional o...
Page 227
203 intelligent actuator part 4 commands z pbnd (set positioning band) command, declaration extension condition (ld, a, o, ab, ob) input condition (i/o, flag) command, declaration operand 1 operand 2 output (output, flag) optional optional pbnd axis pattern distance cp [function] set the position co...
Page 228
204 intelligent actuator part 4 commands z cir (move along circle) command, declaration extension condition (ld, a, o, ab, ob) input condition (i/o, flag) command, declaration operand 1 operand 2 output (output, flag) optional optional cir passing position 1 number passing position 2 number pe [func...
Page 229
205 intelligent actuator part 4 commands z arc (move along arc) command, declaration extension condition (ld, a, o, ab, ob) input condition (i/o, flag) command, declaration operand 1 operand 2 output (output, flag) optional optional arc passing position number end position number pe [function] move ...
Page 230
206 intelligent actuator part 4 commands 1.13 structural if z if (structural if) command, declaration extension condition (ld, a, o, ab, ob) input condition (i/o, flag) command, declaration operand 1 operand 2 output (output, flag) optional optional if variable number data cp [function] compare the ...
Page 231
207 intelligent actuator part 4 commands z is (compare strings) command, declaration extension condition (ld, a, o, ab, ob) input condition (i/o, flag) command, declaration operand 1 operand 2 output (output, flag) optional optional is column number column number, character literal cp [function] com...
Page 232
208 intelligent actuator part 4 commands z else (else) command, declaration extension condition (ld, a, o, ab, ob) input condition (i/o, flag) command, declaration operand 1 operand 2 output (output, flag) prohibited prohibited else prohibited prohibited cp [function] an else command is used arbitra...
Page 233
209 intelligent actuator part 4 commands 1.14 structural do z dw (do while) command, declaration extension condition (ld, a, o, ab, ob) input condition (i/o, flag) command, declaration operand 1 operand 2 output (output, flag) optional optional dw variable number data cp [function] compare the conte...
Page 234
210 intelligent actuator part 4 commands z iter (repeat) command, declaration extension condition (ld, a, o, ab, ob) input condition (i/o, flag) command, declaration operand 1 operand 2 output (output, flag) optional optional iter prohibited prohibited cp [function] forcibly switch the control to ed...
Page 235
211 intelligent actuator part 4 commands 1.15 multi-branching z slct (start selected group) command, declaration extension condition (ld, a, o, ab, ob) input condition (i/o, flag) command, declaration operand 1 operand 2 output (output, flag) optional optional slct prohibited prohibited cp [function...
Page 236
212 intelligent actuator part 4 commands z wh (select if true; variable) command, declaration extension condition (ld, a, o, ab, ob) input condition (i/o, flag) command, declaration operand 1 operand 2 output (output, flag) prohibited prohibited wh variable number data cp [function] this command is ...
Page 237
213 intelligent actuator part 4 commands z ws (select if true; character) command, declaration extension condition (ld, a, o, ab, ob) input condition (i/o, flag) command, declaration operand 1 operand 2 output (output, flag) prohibited prohibited ws column number column number, character literal cp ...
Page 238
214 intelligent actuator part 4 commands z othe (select other) command, declaration extension condition (ld, a, o, ab, ob) input condition (i/o, flag) command, declaration operand 1 operand 2 output (output, flag) prohibited prohibited othe prohibited prohibited cp [function] this command is used be...
Page 239
215 intelligent actuator part 4 commands 1.16 system information acquisition z axst (get axis status) command, declaration extension condition (ld, a, o, ab, ob) input condition (i/o, flag) command, declaration operand 1 operand 2 output (output, flag) optional optional axst variable number axis num...
Page 240
216 intelligent actuator part 4 commands z pgst (get program status) command, declaration extension condition (ld, a, o, ab, ob) input condition (i/o, flag) command, declaration operand 1 operand 2 output (output, flag) optional optional pgst variable number program number cp [function] store in the...
Page 241
217 intelligent actuator part 4 commands z syst (get system status) command, declaration extension condition (ld, a, o, ab, ob) input condition (i/o, flag) command, declaration operand 1 operand 2 output (output, flag) optional optional syst variable number prohibited cp [function] store the system ...
Page 242
218 intelligent actuator part 4 commands 1.17 zone z wzna (wait for zone on, with and) command, declaration extension condition (ld, a, o, ab, ob) input condition (i/o, flag) command, declaration operand 1 operand 2 output (output, flag) optional optional wzna zone number axis pattern cp [function] ...
Page 243
219 intelligent actuator part 4 commands z wzno (wait for zone on, with or) command, declaration extension condition (ld, a, o, ab, ob) input condition (i/o, flag) command, declaration operand 1 operand 2 output (output, flag) optional optional wzno zone number axis pattern cp [function] wait for th...
Page 244
220 intelligent actuator part 4 commands z wzfa (wait for zone off, with and) command, declaration extension condition (ld, a, o, ab, ob) input condition (i/o, flag) command, declaration operand 1 operand 2 output (output, flag) optional optional wzfa zone number axis pattern cp [function] wait for ...
Page 245
221 intelligent actuator part 4 commands z wzfo (wait for zone off, with or) command, declaration extension condition (ld, a, o, ab, ob) input condition (i/o, flag) command, declaration operand 1 operand 2 output (output, flag) optional optional wzfo zone number axis pattern cp [function] wait for t...
Page 246
222 intelligent actuator part 4 commands 1.18 communication z open (open channel) command, declaration extension condition (ld, a, o, ab, ob) input condition (i/o, flag) command, declaration operand 1 operand 2 output (output, flag) optional optional open channel number prohibited cp [function] open...
Page 247
223 intelligent actuator part 4 commands z read (read) command, declaration extension condition (ld, a, o, ab, ob) input condition (i/o, flag) command, declaration operand 1 operand 2 output (output, flag) optional optional read channel number column number cc [function] read a character string from...
Page 248
224 intelligent actuator part 4 commands (note1) a read command must be executed before the other side sends the end character. (note2) channel nos. 31 to 34 (available with the ethernet option) cannot be specified for dummy read (operand 2: 0). Scha 10 open 1 read 1 2 other side clos 1 • return cod...
Page 249
225 intelligent actuator part 4 commands z tmrw (set read/writ timeout value) command, declaration extension condition (ld, a, o, ab, ob) input condition (i/o, flag) command, declaration operand 1 operand 2 output (output, flag) optional optional tmrw read timer setting (write timer setting) cp [fun...
Page 250
226 intelligent actuator part 4 commands z writ (write) command, declaration extension condition (ld, a, o, ab, ob) input condition (i/o, flag) command, declaration operand 1 operand 2 output (output, flag) optional optional writ channel number column number cc (note 1) [function] write the characte...
Page 251
227 intelligent actuator part 4 commands z scha (set end character) command, declaration extension condition (ld, a, o, ab, ob) input condition (i/o, flag) command, declaration operand 1 operand 2 output (output, flag) optional optional scha character code prohibited cp [function] set the end charac...
Page 252
228 intelligent actuator part 4 commands 1.19 string operation z scpy (copy character string) command, declaration extension condition (ld, a, o, ab, ob) input condition (i/o, flag) command, declaration operand 1 operand 2 output (output, flag) optional optional scpy column number column number, cha...
Page 253
229 intelligent actuator part 4 commands z scmp (compare character strings) command, declaration extension condition (ld, a, o, ab, ob) input condition (i/o, flag) command, declaration operand 1 operand 2 output (output, flag) optional optional scmp column number column number, character literal eq ...
Page 254
230 intelligent actuator part 4 commands z sget (get character) command, declaration extension condition (ld, a, o, ab, ob) input condition (i/o, flag) command, declaration operand 1 operand 2 output (output, flag) optional optional sget variable number column number, character literal cp [function]...
Page 255
231 intelligent actuator part 4 commands z sput (set character) command, declaration extension condition (ld, a, o, ab, ob) input condition (i/o, flag) command, declaration operand 1 operand 2 output (output, flag) optional optional sput column number data cp [function] set the data specified in ope...
Page 256
232 intelligent actuator part 4 commands z str (convert character string; decimal) command, declaration extension condition (ld, a, o, ab, ob) input condition (i/o, flag) command, declaration operand 1 operand 2 output (output, flag) optional optional str column number data cc [function] copy to the...
Page 257
233 intelligent actuator part 4 commands z strh (convert character string; hexadecimal) command, declaration extension condition (ld, a, o, ab, ob) input condition (i/o, flag) command, declaration operand 1 operand 2 output (output, flag) optional optional strh column number data cc [function] copy ...
Page 258
234 intelligent actuator part 4 commands z val (convert character string data; decimal) command, declaration extension condition (ld, a, o, ab, ob) input condition (i/o, flag) command, declaration operand 1 operand 2 output (output, flag) optional optional val variable number column number, characte...
Page 259
235 intelligent actuator part 4 commands z valh (convert character string data; hexadecimal) command, declaration extension condition (ld, a, o, ab, ob) input condition (i/o, flag) command, declaration operand 1 operand 2 output (output, flag) optional optional valh variable number column number, ch...
Page 260
236 intelligent actuator part 4 commands z slen (set length) command, declaration extension condition (ld, a, o, ab, ob) input condition (i/o, flag) command, declaration operand 1 operand 2 output (output, flag) optional optional slen character string length prohibited cp [function] set the length t...
Page 261
237 intelligent actuator part 4 commands 1.20 palletizing-related z bgpa (declare start of palletizing setting) command, declaration extension condition (ld, a, o, ab, ob) input condition (i/o, flag) command, declaration operand 1 operand 2 output (output, flag) optional optional bgpa palletizing nu...
Page 262
238 intelligent actuator part 4 commands z papi (set palletizing counts) command, declaration extension condition (ld, a, o, ab, ob) input condition (i/o, flag) command, declaration operand 1 operand 2 output (output, flag) optional optional papi count count cp set counts in the palletizing-axis dir...
Page 263
239 intelligent actuator part 4 commands z pase (declare palletizing axes) command, declaration extension condition (ld, a, o, ab, ob) input condition (i/o, flag) command, declaration operand 1 operand 2 output (output, flag) optional optional pase axis number axis number cp set the two axes to be u...
Page 264
240 intelligent actuator part 4 commands z past (set palletizing reference point) command, declaration extension condition (ld, a, o, ab, ob) input condition (i/o, flag) command, declaration operand 1 operand 2 output (output, flag) optional optional past (position number) prohibited cp set the refe...
Page 265
241 intelligent actuator part 4 commands z paps (set palletizing points) for 3-point & 4-point teaching command, declaration extension condition (ld, a, o, ab, ob) input condition (i/o, flag) command, declaration operand 1 operand 2 output (output, flag) optional optional paps position number (palle...
Page 266
242 intelligent actuator part 4 commands • if palletizing positions are set by means of 4-point teaching and a certain level of palletizing accuracy is required in a condition where all four points used in the setting of palletizing positions are known to be on a plane, it is recommended that pallet...
Page 267
243 intelligent actuator part 4 commands when the point data of any component other than the pz-axis component is the same between any two points among the three points other than the end point (in the above figure, the point data of a component other than the pz-axis component is the same between t...
Page 268
244 intelligent actuator part 4 commands z psli (set zigzag) command, declaration extension condition (ld, a, o, ab, ob) input condition (i/o, flag) command, declaration operand 1 operand 2 output (output, flag) optional optional psli offset amount (count) cp set a zigzag palletizing. The value spec...
Page 269
245 intelligent actuator part 4 commands z pchz (declare palletizing z-axis) only when there are at least three axes. Command, declaration extension condition (ld, a, o, ab, ob) input condition (i/o, flag) command, declaration operand 1 operand 2 output (output, flag) optional optional pchz (axis nu...
Page 270
246 intelligent actuator part 4 commands z ptrg (set palletizing arch triggers) command, declaration extension condition (ld, a, o, ab, ob) input condition (i/o, flag) command, declaration operand 1 operand 2 output (output, flag) optional optional ptrg position number position number cp set the arc...
Page 271
247 intelligent actuator part 4 commands z pext (set palletizing composition) command, declaration extension condition (ld, a, o, ab, ob) input condition (i/o, flag) command, declaration operand 1 operand 2 output (output, flag) optional optional pext (position number) prohibited cp set palletizing ...
Page 272
248 intelligent actuator part 4 commands z achz (declare arch-motion z-axis) command, declaration extension condition (ld, a, o, ab, ob) input condition (i/o, flag) command, declaration operand 1 operand 2 output (output, flag) optional optional achz axis number prohibited cp specify the axis number...
Page 273
249 intelligent actuator part 4 commands z atrg (set arch triggers) command, declaration extension condition (ld, a, o, ab, ob) input condition (i/o, flag) command, declaration operand 1 operand 2 output (output, flag) optional optional atrg position number position number cp set the arch triggers u...
Page 274
250 intelligent actuator part 4 commands z aext (set arch-motion composition) command, declaration extension condition (ld, a, o, ab, ob) input condition (i/o, flag) command, declaration operand 1 operand 2 output (output, flag) optional optional aext (position number) prohibited cp set arch-motion ...
Page 275
251 intelligent actuator part 4 commands 1.21 palletizing calculation command z ptng (get palletizing position number) command, declaration extension condition (ld, a, o, ab, ob) input condition (i/o, flag) command, declaration operand 1 operand 2 output (output, flag) optional optional ptng palleti...
Page 276
252 intelligent actuator part 4 commands z pdec (decrement palletizing position number by 1) command, declaration extension condition (ld, a, o, ab, ob) input condition (i/o, flag) command, declaration operand 1 operand 2 output (output, flag) optional optional pdec palletizing number prohibited cc ...
Page 277
253 intelligent actuator part 4 commands z parg (get palletizing angle) command, declaration extension condition (ld, a, o, ab, ob) input condition (i/o, flag) command, declaration operand 1 operand 2 output (output, flag) optional optional parg palletizing number axis number cp obtain the palletizi...
Page 278
254 intelligent actuator part 4 commands 1.22 palletizing movement command z pmvp (move to palletizing points via ptp) command, declaration extension condition (ld, a, o, ab, ob) input condition (i/o, flag) command, declaration operand 1 operand 2 output (output, flag) optional optional pmvp palleti...
Page 279
255 intelligent actuator part 4 commands z pmvl (move to palletizing points via interpolation) command, declaration extension condition (ld, a, o, ab, ob) input condition (i/o, flag) command, declaration operand 1 operand 2 output (output, flag) optional optional pmvl palletizing number (position nu...
Page 280
256 intelligent actuator part 4 commands z pach (palletizing-point arch motion) command, declaration extension condition (ld, a, o, ab, ob) input condition (i/o, flag) command, declaration operand 1 operand 2 output (output, flag) optional optional pach palletizing number position number pe perform ...
Page 281
257 intelligent actuator part 4 commands • the pz-axis coordinate of the end point will become the pz-axis component of the position coordinates of the palletizing point, if any, plus the palletizing z-axis offset. If there is no pz component, the pz-axis coordinate of the end point will become the ...
Page 282
258 intelligent actuator part 4 commands z arch (arch motion) command, declaration extension condition (ld, a, o, ab, ob) input condition (i/o, flag) command, declaration operand 1 operand 2 output (output, flag) optional optional arch position number position number pe perform arch motion from the ...
Page 283
259 intelligent actuator part 4 commands • the arch-motion z-axis will come down after a rise-process command value is output. Therefore, the operation may follow the locus in fig. 5 given in the aforementioned explanation of pach command, depending on the settings of arch-trigger points and z point...
Page 284
260 intelligent actuator part 4 commands 1.23 building of pseudo-ladder task z chpr (change task level) command, declaration extension condition (ld, a, o, ab, ob) input condition (i/o, flag) command, declaration operand 1 operand 2 output (output, flag) optional optional chpr 0 or 1 prohibited cp [...
Page 285
261 intelligent actuator part 4 commands z tslp (task sleep) command, declaration extension condition (ld, a, o, ab, ob) input condition (i/o, flag) command, declaration operand 1 operand 2 output (output, flag) prohibited prohibited tslp time prohibited cp [function] set the time during which the a...
Page 286
262 intelligent actuator part 4 commands 1.24 extended commands z ecmd1 (get motor current value (as percentage of rated current)) command, declaration extension condition (ld, a, o, ab, ob) input condition (i/o, flag) command, declaration operand 1 operand 2 output (output, flag) optional optional ...
Page 287
263 intelligent actuator part 4 commands z ecmd2 (get home sensor status) command, declaration extension condition (ld, a, o, ab, ob) input condition (i/o, flag) command, declaration operand 1 operand 2 output (output, flag) optional optional ecmd 2 axis number cc this command is supported by contro...
Page 288
264 intelligent actuator part 4 commands z ecmd3 (get overrun sensor status) command, declaration extension condition (ld, a, o, ab, ob) input condition (i/o, flag) command, declaration operand 1 operand 2 output (output, flag) optional optional ecmd 3 axis number cc this command is supported by con...
Page 289
265 intelligent actuator part 4 commands z ecmd4 (get creep sensor status) command, declaration extension condition (ld, a, o, ab, ob) input condition (i/o, flag) command, declaration operand 1 operand 2 output (output, flag) optional optional ecmd 4 axis number cc this command is supported by contr...
Page 290
266 intelligent actuator part 4 commands z ecmd250 (set torque limit/“torque limit over” detection time) command, declaration extension condition (ld, a, o, ab, ob) input condition (i/o, flag) command, declaration operand 1 operand 2 output (output, flag) optional optional ecmd 250 integer variable ...
Page 291
267 intelligent actuator part 4 commands * when reverting the conditions to their defaults [example2] let 290 3 set the target axis pattern (axes 1 and 2) in integer variable 290. Let 291 1000 set a steady-state torque limit (maximum limit set for each axis) in integer variable 291. Let 292 20000 cl...
Page 292
268 intelligent actuator part 4 commands chapter 3 key characteristics of actuator control commands and points to note 1. Continuous movement commands [path, cir, arc, pspl, cir2, arc2, arcd, arcc, cirs, arcs] (1) by running a program with continuous movement commands input in a series of continuous...
Page 293
269 intelligent actuator part 4 commands path 21 23 312 [example 3] if an input condition is specified, the output will turn on upon completion of operation in the step before the one in which the input condition is specified. Output field timing potp 1 308 turn on as p1 approaches. 309 turn on as p...
Page 294
270 intelligent actuator part 4 commands 2. Path/pspl commands when executing a path or pspl command, pay attention to the locus because it will change if the acceleration/deceleration is different between points. The locus can be fine-tuned by changing the acceleration/deceleration, but different a...
Page 295
271 intelligent actuator part 4 commands chapter 4 palletizing function the sel language used by the x-sel controller provides palletizing commands that support palletizing operation. These commands allow simple specification of various palletizing settings and enable arch motion ideal for palletizi...
Page 296
272 intelligent actuator part 4 commands (2) palletizing pattern --- command: papn select a pattern indicating the palletizing order. The two patterns illustrated below are available. The encircled numbers indicate the order of palletizing and are called “palletizing position numbers.” fig. 1 papn 2...
Page 297
273 intelligent actuator part 4 commands a. 3-point teaching method to set the palletizing positions by 3-point teaching, store desired positions in position data fields as three continuous position data and then specify the first position number using a paps command. This method allows you to set t...
Page 298
274 intelligent actuator part 4 commands b. Method to set palletizing positions in parallel with the actuators palletizing reference point: store the position data of the start point (palletizing position no. 1) in a position data field and specify the applicable position number using a past command...
Page 299
275 intelligent actuator part 4 commands (5) zigzag setting --- command: psli use a psli command to set a zigzag layout as shown below. Zigzag offset: offset amount in the preferential-axis direction, which will be applied when even- numbered rows are placed. “even-numbered rows” refer to the rows o...
Page 300
276 intelligent actuator part 4 commands (7) palletizing arch-motion setting (a) palletizing z-direction axis number --- command: pchz (b) palletizing z-axis offset --- command: ofpz (c) palletizing composition --- command: pext composition data refers to position data of any additional axis you wis...
Page 301
277 intelligent actuator part 4 commands 3. Palletizing calculation the items that can be operated or obtained using palletizing calculation commands are shown below: (1) palletizing position number commands --- pset, pinc, pdec, ptng number showing the ordinal number of a palletizing point. (in fig...
Page 302
278 intelligent actuator part 4 commands 4. Palletizing movement palletizing movement commands include those used to move to a palletizing point and one used to move to an end point specified by position data. (1) movement commands to palletizing point --- pmvp, pmvl, pach position coordinates of a ...
Page 303
279 intelligent actuator part 4 commands (2) movement comment based on end point specified by point data --- arch perform arch motion using an end point specified by position data. In the case of a linear movement in parallel with an actuator, operation can be performed only with two axes including ...
Page 304
280 intelligent actuator part 4 commands 5. Program examples (1) simple program example (two-axis specification) using paps (set by 3-point teaching) the example below specifies movement only and does not cover picking operation. Step e n cnd cmnd operand 1 operand 2 pst comment 1 bgpa 1 start setti...
Page 305
281 intelligent actuator part 4 commands (2) simple program example (two-axis specification) using papt, past and pase the example below specifies movement only and does not cover picking operation. Step e n cnd cmnd operand 1 operand 2 pst comment 1 bgpa 1 start setting palletizing no. 1. 2 papi 3 ...
Page 306
282 intelligent actuator part 4 commands (3) simple program example using paps (set by 3-point teaching) the example below specifies movement only and does not cover picking operation. Step e n cnd cmnd operand 1 operand 2 pst comment 1 bgpa 1 start setting palletizing no. 1. 2 3 papi 5 7 palletizin...
Page 307
283 intelligent actuator part 4 commands step e n cnd cmnd operand 1 operand 2 pst comment 31 movp 8 move to picking position. 32 33 tag 1 beginning of loop processing 34 pach 1 9 palletizing arch motion 35 z point specified by position no. 9 36 arch 8 9 arch motion 37 z point specified by position ...
Page 308
284 intelligent actuator part 4 commands schematic diagram of placement-point positions based on the above program • the number shown at the top right of each circle indicates a palletizing position number. • count in px-axis direction = 5, count in py-axis direction = 7 • zigzag offset: 20 • zigzag...
Page 309
285 intelligent actuator part 4 commands (4) simple program example using pase, papt and past the example below specifies movement only and does not cover picking operation. Step e n cnd cmnd operand 1 operand 2 pst comment 1 bgpa 1 start setting palletizing no. 1. 2 3 papi 5 7 palletizing counts: 5...
Page 310
286 intelligent actuator part 4 commands step e n cnd cmnd operand 1 operand 2 pst comment 31 tag 1 beginning of loop processing 32 pach 1 9 palletizing arch motion 33 z point specified by position no. 9 34 arch 8 9 arch motion 35 z point specified by position no. 9 36 pinc 1 600 increment palletizi...
Page 311
287 intelligent actuator part 4 commands schematic diagram of placement-point positions based on the above program • the number shown at the top right of each circle indicates a palletizing position number. • count in px-axis direction = 5, count in py-axis direction = 7 • pitch in px-axis direction...
Page 312
288 intelligent actuator part 4 commands chapter 5 pseudo-ladder task with the x-sel controller, a pseudo-ladder task function can be used depending on the command and extension condition. The input format is shown below. Note that this function must be used by expert engineers with a full knowledge...
Page 313
289 intelligent actuator part 4 commands 2. Ladder statement field (1) extension conditions ld load a and o or ab and block ob or block all of the above extension conditions can be used in non-ladder tasks. (2) ladder commands outr ladder output relay (operand 1 = output, flag number) timr ladder ti...
Page 314
290 intelligent actuator part 4 commands 4. Program example extension condition input condition command operand 1 operand 2 output e n cnd cmnd pst ld 7001 chpr 1 tpcd 1 tag 1 ld 8 a n 9 o 10 ld n 11 a 12 ld 13 a n 14 ob ab outr 314 a 15 timr 900 0.5 ld 7001 tslp 3 ld 7001 goto 1 ld 7001 exit outr31...
Page 315
291 intelligent actuator part 4 commands chapter 6 application program examples 1. Operation by jog command [doll-picking game machine] (1) overview of the system this system is a doll-picking game machine consisting of axis-1 and axis-2 actuators. Pushbutton switches corresponding to the two axes a...
Page 316
292 intelligent actuator part 4 commands (2) explanation of the operation 1. Wait for the axis-1 movement pushbutton switch to turn on. 2. The x-axis moves while the pushbutton switch is on, and stops when the switch turns off. 3. Wait for the axis-2 movement pushbutton switch to turn on. 4. The y-a...
Page 317
293 intelligent actuator part 4 commands (3) x-sel controller application program step e n cnd cmnd operand 1 operand 2 pst comment 1 home 11 axes 1 and 2 return to home (servo on). 2 vel 400 set speed to 400 mm/s. 3 tag 1 4 wton 16 wait for input from axis-1 movement switch. 5 jfwn 1 16 move forwar...
Page 318
294 intelligent actuator part 4 commands 2. Operation by point movement command [riveting system] (1) overview of the system this system is a riveting system consisting of an xy-table operated by axis-1 and axis-2 actuators and a riveter. By setting a load on the xy-table at the operation home and t...
Page 319
295 intelligent actuator part 4 commands (2) explanation of the operation 1. The xy-table moves to the operation home (p1) and waits. 2. The operator sets a load on the xy-table and turns on the start switch. 3. The xy-table moves to riveting position no. 1 (p2) on the load and a riveting command is...
Page 320
296 intelligent actuator part 4 commands (3) x-sel controller application program step e n cnd cmnd operand 1 operand 2 pst comment 1 home 11 xy-table returns to home (servo on). 2 vel 400 set speed to 400 mm/s. 3 tag 1 4 movl 1 move to position no. 1 (origin of work). 5 let 1 2 set 2 in load counte...
Page 321
297 intelligent actuator part 4 commands 3. Palletizing operation [palletizing system] (1) overview of the system this system is a palletizing system consisting of axis-1 and axis-2 actuators and a z-axis air cylinder. It clamps a load at the load feed point and transfers it onto a pallet, and repea...
Page 322
298 intelligent actuator part 4 commands (2) explanation of the operation 1. Move to the standby point and wait for a start input. 2. Move to the load feed point after a start input is received. 3. The z-axis comes down and the air chuck clamps the load. 4. The z-axis rises and moves to above the pa...
Page 323
299 intelligent actuator part 4 commands (3) x-sel controller application program step e n cnd cmnd operand 1 operand 2 pst comment 1 home 11 axes 1 and 2 return to home. 2 vel 100 set speed to 100 mm/s. 3 acc 0.2 acceleration/deceleration: 0.2 g 4 tag 1 5 let 300 0 clear variable. 6 let 301 0 clear...
Page 324
300 intelligent actuator part 5 multi-tasking part 5 multi-tasking chapter 1 real-time multi-tasking 1. Sel language the x-sel controller allows integrated control of actuators and peripherals with a single controller using its 32-bit risc cpu and high-speed real-time operating system. There is no n...
Page 325
301 intelligent actuator part 5 multi-tasking 2. Multi-tasking “multi-tasking” operation may not be a familiar term, but it is widely used in computer programming to refer to parallel processing. Simply put, multi-tasking means running several programs in parallel. Take a screw-tightening robot, for...
Page 326
302 intelligent actuator part 5 multi-tasking 3. Difference from a sequencer the parallel processing method has evolved from the traditional method of using a sequence control circuit consisting of relays to a more recent one using a sequencer equipped with a microcomputer. Since a microcomputer bas...
Page 327
303 intelligent actuator part 5 multi-tasking 4. Release of emergency stop default factory settings of parameters “other parameter no. 10, emergency-stop recovery type” = 0 “other parameter no. 11, safety-gate open recovery type” = 0 “other parameter no. 12, recognition type during automatic operati...
Page 328
304 intelligent actuator part 5 multi-tasking 5. Program switching various methods are available to switch between programs, depending on the purpose of programs. The representative methods are explained below. External start program switching program single-tasking exit command multi-tasking expg c...
Page 329
305 intelligent actuator part 5 multi-tasking chapter 2 example of building a system how to build hardware and software is explained in details by using a screw-tightening robot as an example. 1. Equipment screw-tightening machine (for z-axis) actuators (for axes 1 and 2) iai’s 60-w servo motor with...
Page 330
306 intelligent actuator part 5 multi-tasking 3. Overview of the screw-tightening system this system consists of axis-1 and axis-2 actuators, z-axis cylinder, screw-tightening device and parts feeder, and tightens the screws fed by the parts feeder at the specified positions on the load. Axis 1 axis...
Page 331
307 intelligent actuator part 5 multi-tasking 4. Hardware (1) i/o assignments i/o connector (50-pin) pin no. Category port no. Function cable color 1 - general-purpose: nc, compact: +24-v input brown – 1 2 000 program start red – 1 3 001 general-purpose input orange – 1 4 002 general-purpose input y...
Page 332
308 intelligent actuator part 5 multi-tasking (2) layout diagram pin no. Category port no. Function 1 - general-purpose: nc, compact: +24-v input 2 000 program start 3 001 general-purpose input 4 002 general-purpose input 5 003 general-purpose input 6 004 general-purpose input 7 005 general-purpose ...
Page 333
309 intelligent actuator part 5 multi-tasking 5. Software (1) control flow chart main program: screw-tightening machine program 1 start program 2 align origin start screw tightening (pushbutton) move z-axis air cylinder down start screw tightening screw tightening complete z-axis air cylinder up 6 s...
Page 334
310 intelligent actuator part 5 multi-tasking (2) main program screw-tightening program no. 1 application program extension condition input condition command output condition comment and, or i/o, flag command operand 1 operand 2 output port, flag comment 1 expg 2 start program 2. 2 home 11 align hom...
Page 335
311 intelligent actuator appendix appendix ~ actuator specification list (note 1) the figure in each elongated circle indicates the maximum speed for the applicable stroke(s). (note 2) the load capacity is based on operation at the rated acceleration. (note 3) rcs2-r**7 series actuators cannot be us...
Page 336
312 intelligent actuator appendix (note 1) the figure in each elongated circle indicates the maximum speed for the applicable stroke(s). (note 2) the load capacity is based on operation at the rated acceleration. Stroke (mm) and maximum speed (mm/sec) (note 1) load capacity (note 2) horizontal model...
Page 337
313 intelligent actuator appendix (note 1) the figure in each elongated circle indicates the maximum speed for the applicable stroke(s). (note 2) the load capacity is based on operation at the rated acceleration. (note 3) rcs-rb75 series actuators cannot be used as axis 5 or 6. Model stroke (mm) and...
Page 338
314 intelligent actuator appendix (note 1) the figure in each elongated circle indicates the maximum speed for the applicable stroke(s). (note 2) the load capacity is based on operation at the rated acceleration. Model stroke (mm) and maximum speed (mm/sec) (note 1) load capacity (note 2) rated acce...
Page 339
315 intelligent actuator appendix (note 1) the figure in each elongated circle indicates the maximum speed for the applicable stroke(s). (note 2) the load capacity is based on operation at the rated acceleration. Model stroke (mm) and maximum speed (mm/sec) (note 1) load capacity (note 2) rated acce...
Page 340
316 intelligent actuator appendix (note 1) the maximum speed may not be reached with short stroke models. (note 2) the actual value may vary depending on the operating condition. (note 3) lsa type actuators cannot be used as axis 5 or 6. Lsa ( l inear typ e ) model stroke (mm) horizontal (kg) load c...
Page 341
317 intelligent actuator appendix ~ how to create a program 1. Position table position table the x-sel controller p/q types can handle up to 4,000 registered positions. Positions are registered using the pc software or teaching pendant. (example of 6-axis system) no.: specify a number, and the actua...
Page 342
318 intelligent actuator appendix 2. Programming format program edit screen (pc software) the x-sel controllers support programs consisting of up to 6,000 steps. Programs are edited using the pc software or teaching pendant. No.: step number b: set a breakpoint (this field becomes editable during on...
Page 343
319 intelligent actuator appendix 3. Positioning to five positions description move the actuator to positions 1 through 5 at a speed of 100 mm/sec after homing. Use of only 1 axis is assumed. Flowchart • homing must be performed and a speed must be set, before the actuator can be operated. • the act...
Page 344
320 intelligent actuator appendix 4. How to use tag and goto description use goto and tag commands to repeat the same operation within the program or to jump to a desired step if a condition is satisfied. A tag command can be written in a step either before or after a goto command. Example of use 1 ...
Page 345
321 intelligent actuator appendix 5. Moving back and forth between two points description moves back and forth between two points. Flowchart • the actuator moves back and forth between p1 and p2 indefinitely. • use of only 1 axis is assumed. • enter tag in the first of the steps to be repeated, and ...
Page 346
322 intelligent actuator appendix 6. Path operation description move continuously through four arbitrary points without stopping (path movement). The actuator moves along the path shown at right, without stopping at p2 and p3. Compared with movp and movl, this command does not require the actuator t...
Page 347
323 intelligent actuator appendix 7. Output control during path movement description in spray operation, etc., output control may be required while the actuator is moving. The x-sel controller can output signals while the actuator is moving with a path command. How to use before executing a path com...
Page 348
324 intelligent actuator appendix 8. Circle/arc operation description the actuator moves along a two-dimensional circle or arc. How to use to specify a circle, specify three points the actuator will pass. To specify an arc, specify the starting point, passing point and end point. Example of use 1 ci...
Page 349
325 intelligent actuator appendix 9. Home return completion output description output a signal to confirm completion of homing (incremental specification). With the x-sel controller, a home return completion signal can be output using an i/o parameter. However, the following explains how to output a...
Page 350
326 intelligent actuator appendix 10. Axis movement by input waiting and completion output description how to perform input waiting and output a processing completion signal is explained. Flowchart example of use the actuator waits until input port 10 turns on, and then moves to p1. The actuator wai...
Page 351
327 intelligent actuator appendix 11. Changing the moving speed description change the moving speed. How to use with the x-sel controller, the speed can be set using the following two methods: a: use a vel command within the application program b: use a speed setting in the position data table examp...
Page 352
328 intelligent actuator appendix 12. Changing the speed during operation description use a path command to change the speed while the actuator is moving. For example, this command is useful in a paint dispensing application where the application volume changes in the middle. Example of use the actu...
Page 353
329 intelligent actuator appendix 13. Local/global variables and flags description the internal variables and flags used in the sel language are classified into local and global types. The data range used commonly by all programs is called the global range, while the data range used only by each pro...
Page 354
330 intelligent actuator appendix 14. How to use subroutines description a subroutine is a group of steps that are called and executed several times within a program. Subroutines are used to reduce the number of program steps and make the program easy to read. Up to 99 subroutines can be used in one...
Page 355
331 intelligent actuator appendix 15. Pausing the operation description use a declaration command hold to pause the moving axis temporarily via external input. How to use a pause interruption operation can be executed to a moving axis (to decelerate the axis to a stop) by declaring a hold command wi...
Page 356
332 intelligent actuator appendix 16. Canceling the operation 1 (canc) description use a declaration command canc to decelerate the moving axis to a stop and cancel the remaining operation. How to use while can is input, all movement commands in the same program are cancelled. Example of use canc co...
Page 357
333 intelligent actuator appendix 17. Canceling the operation 2 (stop) description decelerate the moving axis to a stop and cancel the remaining operation. (stop) how to use execute a stop command from other program to forcibly stop the operation (in the multi-tasking mode). Specify the axis you wan...
Page 358
334 intelligent actuator appendix 18. Movement by position number specification description load externally input bcd codes as position numbers to execute movements. Example of use use an inb command to load a position number as a bcd code from an input port. A position number can be specified using...
Page 359
335 intelligent actuator appendix 19. Movement by external position data input description receive target position data as absolute values from a host device to execute movements. Example of use use an inb command to load position data as a bcd code from an input port. Each bcd value should consist ...
Page 360
336 intelligent actuator appendix 20. Outputting coordinates description read the current actuator coordinate in real time and output the reading from an output port as bcd data. Example of use use a prdq command to load the current coordinate position of axis 1. The current coordinate data of axis ...
Page 361
337 intelligent actuator appendix 21. Conditional jump description select the destination to jump to via goto using the external input, output and/or internal flag statuses as a condition. The controller waits for multiple inputs, and performs processing according to the received input(s). Example o...
Page 362
338 intelligent actuator appendix 22. Waiting multiple inputs description the controller waits for multiple different inputs and performs processing upon reception of any of these inputs. Point a wton command permits processing only when the specified input is received. The controller cannot wait fo...
Page 363
339 intelligent actuator appendix 23. How to use offset description with an ofst command, an offset can be specified for position data when you want to shift (offset) all teaching points by several millimeters because the actuator was not installed exactly in the specified position or for other reas...
Page 364
340 intelligent actuator appendix 24. Executing an operation n times description execute a specific operation n times. Example of use the actuator moves back and forth between p1 and p2 ten times, and then the program ends. Use a cpeq command to compare the number of times the movement has been actu...
Page 365
341 intelligent actuator appendix 25. Constant-pitch feed description feed the actuator by a specified pitch n times from a reference point. The pitch and number of repetitions are specified by variables in advance. Flowchart example of use use an ofst command to perform pitch feed. The number of ti...
Page 366
342 intelligent actuator appendix 26. Jogging description the slider moves forward or backward while an input is on or off. Instead of an input, an output or global flag can be used as a cue. The slider will move directly to the next step if the specified input does not satisfy the condition when th...
Page 367
343 intelligent actuator appendix 27. Switching programs description use expg/abpg commands to switch programs using a program. Example of use 1 start program 2 once the processing of program 1 is completed, and then end program 1. Program 1 program 2 example of use 2 start a program via an external...
Page 368
344 intelligent actuator appendix 28. Aborting a program description abort a program currently running. Execute an abpg command (command to abort other program) from other program in the multi-tasking mode. Caution * if the target program was executing a movement command, the actuator immediately de...
Page 369
345 intelligent actuator appendix ~ battery backup function the x-sel controller uses the following two batteries. System-memory backup battery a coin-type battery is used to back up the position data, sel program variables, etc., in the controller. Each controller is shipped with the system-memory ...
Page 370
346 intelligent actuator appendix to replace the system-memory backup battery, open the panel window on the front side of the controller and replace the coin-type battery in the battery holder. It is recommended that the battery be replaced regularly in accordance with the power-on frequency/duratio...
Page 371
347 intelligent actuator appendix 2. Absolute-data backup battery if the x-sel controller is to drive an absolute-type actuator, an absolute-data backup battery must be installed in the controller. An absolute encoder is designed to retain rotation data and detect rotations using the power supplied ...
Page 372
348 intelligent actuator appendix the x-sel controller provides an enable switch for absolute-data backup battery for each controller axis. When replacing any absolute-data backup battery following a battery error, turn the absolute-data backup battery enable/disable switch of the target axis to off...
Page 373
349 intelligent actuator appendix ~ expansion i/o board (optional) type: ia-103-x-32 type: ia-103-x-16 pin no. Category port no. Function pin no. Port no. Function 1 - +24-v input 1 - +24-v input 2 32 general-purpose input 2 32 general-purpose input 3 33 general-purpose input 3 33 general-purpose in...
Page 374
350 intelligent actuator appendix ~ number of regenerative resistors to be connected regenerative energy that generates when the actuator decelerates to a stop or moves downward in a vertical installation is absorbed through the capacitor or resistor inside the controller. Excess regenerative energy...
Page 375
351 intelligent actuator appendix ~ synchro function 1. Common items (applicable to both the absolute specification and incremental specification) synchro axes consist of a master axis and a slave axis. The axis with the smaller axis number becomes the master axis. A combination of master-axis and s...
Page 376
352 intelligent actuator appendix ~ absolute reset of a synchro controller if you have specified the synchro specification at the time of order, the controller has been shipped with their parameters set for the synchro specification. To perform an absolute reset, however, the parameters must be chan...
Page 377
353 intelligent actuator appendix 2. Position adjustment of synchro-axis sliders the positions of synchro-axis sliders are adjusted (physically adjusted for parallelism). (1) with the axes and controller not connected by cables (main controller power is off), adjust the relative positioning of the m...
Page 378
354 intelligent actuator appendix (3) perform an absolute reset using the special procedure (forced reset by ignoring the on-screen instructions) as explained below: 1. Perform “encoder rotation data reset 1” for the slave axis. 2. Perform “encoder rotation data reset 1” through “encoder rotation da...
Page 379
355 intelligent actuator appendix (4) enter the value of the slave axis recorded in (1) in “axis-specific parameter no. 83, abs synchro slave-axis coordinate initialization cancellation.” → select [transfer to controller] → [write to flash rom] → [restart controller] (software reset). (5) set home p...
Page 380
356 intelligent actuator appendix 3. Enter the calculation result obtained in step 2 above in the slave-axis field of “axis-specific parameter no. 12, home preset value.” → select [transfer to controller] → [write to flash rom] → [restart controller] (software reset). (6) turn on the servo and check...
Page 381
357 intelligent actuator appendix 5. Notes on use of the synchro function • as a rule, the synchro function must be implemented by coupling the master-axis and slave-axis sliders using a bracket, etc. • if the current position of the master axis is not aligned with that of the slave axis when the se...
Page 382
358 intelligent actuator appendix ~ multiple-slider near-miss detection (collision prevention) function * applicable versions: x-sel-pq controllers of main application version 0.51 or later teaching pendant main application (ia-t-x, ia-t-xd) version 1.41 or later teaching pendant main application (i...
Page 383
359 intelligent actuator appendix related parameters (axis-specific parameters) no. Parameter name default value input range unit remarks 104 target axis specification for multiple-slider near-miss detection 0h 0h ~ ffffffffh bits 0 to 3: mating axis number of near-miss detection target (on the posi...
Page 384
360 intelligent actuator appendix ~ general-purpose rs232 (2-channel rs232 unit) (1) specifications the 2-channel rs232 unit is a dedicated d-sub, 9-pin rs232 interface. This unit can be used when a general-purpose rs232 device is connected. Rs232 connector specifications item overview details appli...
Page 385
361 intelligent actuator appendix.
Page 386
362 intelligent actuator appendix (3) parameter settings the sio channel numbers and specifications are set as follows based on the factory settings for applicable parameters: the details are set based on the following parameters: channel 1 → i/o parameter nos. 201 to 203 channel 2 → i/o parameter n...
Page 387
363 intelligent actuator appendix no. Parameter name default value input range unit 202 attribute 2 of sio channel 1 opened to user (standard mount) 00000001h 0h ~ ffffffffh none 214 attribute 2 of sio channel 2 opened to user (standard mount) 00000001h 0h ~ ffffffffh none z settings bits 28 to 31: ...
Page 388
364 intelligent actuator appendix (4) programs [1] string processing commands a string refers to a character string. This controller uses global strings and local strings. Global strings are common strings that can be read or written from any program. Local strings are valid only in the program in w...
Page 389
365 intelligent actuator appendix [3] explanation of strings characters sent per the aforementioned transmission format are stored in a “string,” which, simply put, is a dedicated container for characters. Strings are divided into global strings that can be read or written in all programs, and local...
Page 390
366 intelligent actuator appendix [4] determination of transmission format in this example of application program, three types of transmission formats are used including home return command, movement command and movement completion. These formats are determined as specified below. Take note that the...
Page 391
367 intelligent actuator appendix [5] processing procedure the processing procedure to be followed when programming this application example is explained below: a. Set “lf” as a character indicating the end of a character string (terminator character). B. Open channel 1 of the rs232 unit so that thi...
Page 392
368 intelligent actuator appendix ~ list of parameters if you have any question regarding changing the parameters, please contact iai’s sales engineering section. After changing a parameter, record the new and old parameter settings. If you have purchased the pc software, we recommend that you back ...
Page 393
369 intelligent actuator appendix 1. I/o parameters no. Parameter name default value (reference) input range unit remarks 1 i/o port assignment type 1 0 ~ 20 0: fixed assignment 1: automatic assignment (priority: network i/f module → slot 1 (standard i/o) ~; * ports are assigned only for the install...
Page 394
370 intelligent actuator appendix i/o parameters no. Parameter name default value (reference) input range unit remarks 18 network i/f module error monitor 1 0 ~ 5 0: do not monitor 1: monitor * some exceptions apply. 19 (for expansion) 0 20 input filtering periods 2 1 ~ 9 msec input signal is recogn...
Page 395
371 intelligent actuator appendix i/o parameters no. Parameter name default value (reference) input range unit remarks 30 input function selection 000 1 0 ~ 5 0: general-purpose input 1: program start signal (on edge) (007 to 013: bcd-specified program number) 2: program start signal (on edge) (007 ...
Page 396
372 intelligent actuator appendix i/o parameters no. Parameter name default value (reference) input range unit remarks 46 output function selection 300 2 0 ~ 20 0: general-purpose output 1: output error of operation-cancellation level or higher (on) 2: output error of operation-cancellation level or...
Page 397
373 intelligent actuator appendix i/o parameters no. Parameter name default value (reference) input range unit remarks 59 output function selection 313 0 0 ~ 5 0: general-purpose output 1: system-memory backup battery voltage-low warning level or lower 60 output function selection 314 0 0 ~ 5 0: gen...
Page 398
374 intelligent actuator appendix i/o parameters no. Parameter name default value (reference) input range unit remarks 75 tp user output port start number (hand, etc.) 0 0 ~ 599 referenced by tp. 76 auto mode physical output port number 0 0 ~ 599 (invalid if “0” is set) 77 input port number permitte...
Page 399
375 intelligent actuator appendix i/o parameters no. Parameter name default value (reference) input range unit remarks 100 attribute 1 of sio channel 3 opened to user (expanded) 28100010h 0h ~ ffffffffh bits 28 to 31: baud rate type (0: 9.6, 1: 19.2, 2: 38.4, 3: 57.6, 4: 76.8, 5: 115.2 kbps) bits 24...
Page 400
376 intelligent actuator appendix i/o parameters no. Parameter name default value (reference) input range unit remarks 120 network attribute 1 1h 0h ~ ffffffffh bits 0 to 3: cc-link remote register area h/l byte swap selection (0: do not swap, 1: swap) * the number of used ports and number of occupi...
Page 401
377 intelligent actuator appendix i/o parameters no. Parameter name default value (reference) input range unit remarks 126 network attribute 7 7d007d0h 0h ~ ffffffffh ethernet tcp/ip message communication attribute bits 0 to 15: min timeout value (msec) bits 16 to 31: mout timeout value (msec) 127 n...
Page 402
378 intelligent actuator appendix i/o parameters no. Parameter name default value (reference) input range unit remarks 144 iai protocol b/tcp: own port number (manu mode) 64511 1025 ~ 65535 145 channel 31 opened to user (tcp/ip): own port number 64512 1025 ~ 65535 146 channel 32 opened to user (tcp/...
Page 403
379 intelligent actuator appendix i/o parameters no. Parameter name default value (reference) input range unit remarks 201 attribute 1 of sio channel 1 opened to user (standard mount) 28100001h 0h ~ ffffffffh bits 28 to 31: baud rate type (0: 9.6, 1: 19.2, 2: 38.4, 3: 57.6, 4: 76.8, 5: 115.2 kbps) *...
Page 404
380 intelligent actuator appendix i/o parameters no. Parameter name default value (reference) input range unit remarks 204 attribute 4 of sio channel 1 opened to user (standard mount) 00000000h 0h ~ ffffffffh 205 attribute 5 of sio channel 1 opened to user (standard mount) 00000000h 0h ~ ffffffffh 2...
Page 405
381 intelligent actuator appendix i/o parameters no. Parameter name default value (reference) input range unit remarks 215 attribute 3 of sio channel 2 opened to user (standard mount) 01118040h 0h ~ ffffffffh bits 28 to 31: flow control type (0: none, 1: xon/xoff, 2: hardware) * valid only in full-d...
Page 406
382 intelligent actuator appendix 2. Parameters common to all axes no. Parameter name default value (reference) input range unit remarks ~ 1 valid axis pattern 0000b 00b ~ 11111111b an off bit indicates that no driver is installed. 2 default override 100 1 ~ 100 used if not specified in program. (in...
Page 407
383 intelligent actuator appendix parameters common to all axes no. Parameter name default value (reference) input range unit remarks 28 selection of inching → jog auto-switching prohibition 0 reference only 0: execute auto-switching (continuous button on timer), 1: prohibited * referenced by the pc...
Page 408
384 intelligent actuator appendix parameters common to all axes no. Parameter name default value (reference) input range unit remarks 103 driver initialization communication type setting (axes 1 to 4) 0h reference only bits 0 to 7: driver initialization communication type of axis 1 bits 8 to 15: dri...
Page 409
385 intelligent actuator appendix 3. Axis-specific parameters no parameter name default value (reference) input range unit remarks ~ 1 axis operation type 0 0 ~ 1 0: linear movement axis, 1: rotational movement axis (angle control) 2 ~ 5 (for expansion) 0 ~ 6 coordinate/physical- operation direction...
Page 410
386 intelligent actuator appendix axis-specific parameters no parameter name default value (reference) input range unit remarks 30 servo on check time 150 0 ~ 5000 msec brake equipped: time after receiving a servo-on start response until start of brake unlocking brake not equipped: time after receiv...
Page 411
387 intelligent actuator appendix no parameter name default value (reference) input range unit remarks • if an “error no. C72/d6b, overrun error” generates, adjust the relationship of the installed positions of both synchro axes or set “axis-specific parameter no. 15, overrun-sensor input polarity” ...
Page 412
388 intelligent actuator appendix axis-specific parameters no parameter name default value (reference) input range unit remarks 76 home-adjustment parameter set selection 1 reference only (change prohibited) 0: p21 = phase-z evacuation distance at inc home return p12 = ideal phase-z position coordin...
Page 413
389 intelligent actuator appendix axis-specific parameters no parameter name default value (reference) input range unit remarks 97 zone 4 output number 0 0 ~ 899 physical output port or global flag (output is invalid if “0” is input; multiple specification is invalid) 98 ~ 103 (for expansion) 0 ~ 10...
Page 414
390 intelligent actuator appendix 4. Driver card parameters no. Parameter name default value (reference) input range unit remarks 1 type (upper) (manufacturing information) space reference only for adjustment by the manufacturer 2 type (middle) (manufacturing information) space reference only for ad...
Page 415
391 intelligent actuator appendix driver card parameters no. Parameter name default value (reference) input range unit remarks 29 motor/encoder characteristic word (compatible with e, priority on e) (configuration information) 0004h reference only for adjustment by the manufacturer 30 motor/encoder ...
Page 416
392 intelligent actuator appendix driver card parameters no. Parameter name default value (reference) input range unit remarks 61 ~ 67 (for expansion) 0h 0000h ~ ffffh 68 current control query information 01 0h reference only for adjustment by the manufacturer 69 current control query information 02...
Page 417
393 intelligent actuator appendix 5. Encoder parameters no. Parameter name default value (reference) input range unit remarks 1 type (upper) (manufacturing information) space reference only 2 type (middle) (manufacturing information) space reference only 3 type (lower) (manufacturing information) sp...
Page 418
394 intelligent actuator appendix 6. I/o devices no. Parameter name default value (reference) input range unit remarks 1 type (upper) (manufacturing information) space reference only for adjustment by the manufacturer 2 type (middle) (manufacturing information) space reference only for adjustment by...
Page 419
395 intelligent actuator appendix 7. Other parameters no. Parameter name default value (reference) input range unit remarks 1 auto-start program number 0 0 ~ 64 (invalid if “0” is set) 2 i/o processing program number at operation/program abort 0 0 ~ 64 the start trigger is determined from the “i/o p...
Page 420
396 intelligent actuator appendix other parameters no. Parameter name default value (reference) input range unit remarks 12 automatic operation recognition type 0 0 ~ 3 0: program is running and all-operation-cancellation factor is not present 1: [program is running or in auto mode] and all- operati...
Page 421
397 intelligent actuator appendix other parameters no. Parameter name default value (reference) input range unit remarks 36 pc/tp data protect setting (program) 0h 0h ~ ffffffffh bits 0 to 3: protect type (0: read/write, 1: read only, 2: no read/write) bits 4 to 7: protect release method (0: special...
Page 422
398 intelligent actuator appendix other parameters no. Parameter name default value (reference) input range unit remarks 40 eeprom information check type 83h reference only 0: disable checksum, 1: enable checksum bit 0 = driver bit 1 = encoder bit 2 = i/o board bits 3 to 6 = (for future expansion) b...
Page 423
399 intelligent actuator appendix other parameters no. Parameter name default value (reference) input range unit remarks 46 other setting bit pattern 1 2001h 0h ~ ffffffffh bits 0 to 3: variable-value format type in response message to real-number/variable query (0: big endian with four upper/lower ...
Page 424
400 intelligent actuator appendix other parameters no. Parameter name default value (reference) input range unit remarks 49 panel 7-segment display data type 0 0 ~ 9 0: display controller status 1: display motor current indicator the current pattern of each axis is displayed instead of “ready status...
Page 425
401 intelligent actuator appendix 8. Manual operation types the selectable operation types will vary depending on the setting of the “manual operation type” parameter (other parameter no. 21). (1) pc software 1. Setting = 0 (always enable edit and sio/pio start) functions operation type password edi...
Page 426
Appendi x intelli gent a c tuat or 402 9. Use examples of key parameters you can add functions to those available under the factory settings or set dedicated functions to i/o ports, by changing the parameter values. Before changing a parameter, be sure to read the corresponding section in the list o...
Page 427
Appendi x intelli gent a c tuat or 403 description action parameter setting manipulation/operation want to execute home return using an external input signal. Input port no. 15 can be used as an home return input. I/o parameter no. 45 = 1 home return will be executed at the on edge of input port no....
Page 428
Appendi x intelli gent a c tuat or 404 description action parameter setting manipulation/operation want to output signal when all valid axes are at their home. Output port no. 304 can be set as a signal indicating that all valid axes are at their home. Note: do not use a home command when the contro...
Page 429
Appendi x intelli gent a c tuat or 405 description action parameter setting manipulation/operation want to start programs while emergency-stop signal is input or the safety gate is open. Programs to be started are i/o processing or calculation programs that do not command actuator operation (pio pro...
Page 430
Appendi x intelli gent a c tuat or 406 description action parameter setting manipulation/operation want to continue actuator operation after the emergency stop is reset (want to resume actuator operation from the part stopped due to emergency stop input). Programs other than the one commanding actua...
Page 431
Appendi x intelli gent a c tuat or 407 description action parameter setting manipulation/operation want to output signal when the actuator enters a specified area (zone). A desired actuator zone can be set for each axis. A desired output port to turn on when the axis enters the zone can be set for e...
Page 432
Appendi x intelli gent a c tuat or 408 ~ combination table of x-sel linear/rotary control parameters permitted encoder processing method axis-specific parameter no. 1, axis operation type axis-specific parameter no. 68, mode selection for linear movement axis axis-specific parameter no. 66, mode sel...
Page 433
Appendi x intelli gent a c tuat or 409 ~ error level control program run (application only) error level system error assignment source error no. (hex) display (7- segment display, etc.) error list (application only) error led output (main only) other parameter no. 4 = 0 other parameter no. 4 = 1 err...
Page 434
Appendi x intelli gent a c tuat or 410 program run (application only) error level system error assignment source error no. (hex) display (7- segment display, etc.) error list (application only) error led output (main only) other parameter no. 4 = 0 other parameter no. 4 = 1 error reset (application ...
Page 435
Appendi x intelli gent a c tuat or 411 ~ error list (main application) (in the panel window, the three digits after “e” indicate an error number.) error no. Error name description, action, etc. 200 encoder parameter data version mismatch warning the version of encoder parameter data is not supported...
Page 436
Appendi x intelli gent a c tuat or 412 (in the panel window, the three digits after “e” indicate an error number.) error no. Error name description, action, etc. 400 mounted-sio unopen error (s) an attempt was made to use a channel that is not open. 401 mounted-sio in-use error an attempt was made t...
Page 437
Appendi x intelli gent a c tuat or 413 (in the panel window, the three digits after “e” indicate an error number.) error no. Error name description, action, etc. 601 emg logic error a broken pin in the controller is suspected 602 enb logic error a broken pin in the controller is suspected 603 drive-...
Page 438
Appendi x intelli gent a c tuat or 414 (in the panel window, the three digits after “e” indicate an error number.) error no. Error name description, action, etc. 622 mounted-sio undefined control command receive error an undefined control command was received from the mounted-sio. 623 driver error d...
Page 439
Appendi x intelli gent a c tuat or 415 (in the panel window, the three digits after “e” indicate an error number.) error no. Error name description, action, etc. 63e abz encoder magnetic-pole sensor signal logic error check if the encoder cable is connected. 63f encoder control constant error the en...
Page 440
Appendi x intelli gent a c tuat or 416 (in the panel window, the three digits after “e” indicate an error number.) error no. Error name description, action, etc. 65a unsupported encoder id error the encoder is not supported. No encoder control constant record is available that corresponds to the enc...
Page 441
Appendi x intelli gent a c tuat or 417 (in the panel window, the three digits after “e” indicate an error number.) error no. Error name description, action, etc. 667 invalid driver initialization communication line specification error at specification of valid axis initialization communication line ...
Page 442
Appendi x intelli gent a c tuat or 418 (in the panel window, the three digits after “e” indicate an error number.) error no. Error name description, action, etc. 801 scif overrun status (iai protocol reception) communication failure. Check for noise, connected equipment and communication setting. 80...
Page 443
Appendi x intelli gent a c tuat or 419 (in the panel window, the three digits after “e” indicate an error number.) error no. Error name description, action, etc. 81a mounted-sio overrun status (sel reception) communication failure. Check for noise, connected equipment and communication setting. 81b ...
Page 444
Appendi x intelli gent a c tuat or 420 (in the panel window, the three digits after “e” indicate an error number.) error no. Error name description, action, etc. 900 blank step shortage error there are not enough blank steps to save step data. Provide enough blank steps needed to save step data. 901...
Page 445
Appendi x intelli gent a c tuat or 421 (in the panel window, the three digits after “e” indicate an error number.) error no. Error name description, action, etc. A0b flash-rom verify error error erasing/writing the flash rom a0c flash-rom ack timeout error erasing/writing the flash rom a0d head sect...
Page 446
Appendi x intelli gent a c tuat or 422 (in the panel window, the three digits after “e” indicate an error number.) error no. Error name description, action, etc. A23 absolute-data backup battery voltage-low warning (main analysis) the voltage of the absolute-data backup battery is low. Check the bat...
Page 447
Appendi x intelli gent a c tuat or 423 (in the panel window, the three digits after “e” indicate an error number.) error no. Error name description, action, etc. A40 data change refusal error during flash rom write data cannot be changed while the flash rom is being written. A41 duplicate flash-rom ...
Page 448
Appendi x intelli gent a c tuat or 424 (in the panel window, the three digits after “e” indicate an error number.) error no. Error name description, action, etc. A5e i/o-port/flag count specification error the specified number of i/o ports/flags is invalid. A5f fieldbus error (lerror-on) a lerror-on...
Page 449
Appendi x intelli gent a c tuat or 425 (in the panel window, the three digits after “e” indicate an error number.) error no. Error name description, action, etc. B00 scha setting error the setting of scha command is invalid. B01 tpcd setting error the setting of tpcd command is invalid. B02 slen set...
Page 450
Appendi x intelli gent a c tuat or 426 (in the panel window, the three digits after “e” indicate an error number.) error no. Error name description, action, etc. B1d ethernet non-open error an attempt was made to use a channel not opened by own task. B1e ethernet multiple writ execution error writ c...
Page 451
Appendi x intelli gent a c tuat or 427 (in the panel window, the three digits after “e” indicate an error number.) error no. Error name description, action, etc. C07 subroutine non-definition error the subroutine specified for call is not defined. C08 subroutine duplicate-definition error the same s...
Page 452
Appendi x intelli gent a c tuat or 428 (in the panel window, the three digits after “e” indicate an error number.) error no. Error name description, action, etc. C1f input-condition cnd shortage error the necessary input condition is not found when an expansion condition is used. C21 input-condition...
Page 453
Appendi x intelli gent a c tuat or 429 (in the panel window, the three digits after “e” indicate an error number.) error no. Error name description, action, etc. C40 string-variable delimiter non-detection error delimiter cannot be detected in the string variable. C41 string-variable copy size over ...
Page 454
Appendi x intelli gent a c tuat or 430 (in the panel window, the three digits after “e” indicate an error number.) error no. Error name description, action, etc. C5b timing limit over error (flash rom write) error writing the flash rom c5c flash-rom verify error (flash rom write) error writing the f...
Page 455
Appendi x intelli gent a c tuat or 431 (in the panel window, the three digits after “e” indicate an error number.) error no. Error name description, action, etc. C71 synchro slave-axis command error a command was issued to the synchro slave axis. C72 overrun error the overrun sensor was actuated. C7...
Page 456
Appendi x intelli gent a c tuat or 432 (in the panel window, the three digits after “e” indicate an error number.) error no. Error name description, action, etc. C89 acceleration/deceleration specification error the specified acceleration/deceleration is invalid. C8b circle/arc calculation logic err...
Page 457
Appendi x intelli gent a c tuat or 433 (in the panel window, the three digits after “e” indicate an error number.) error no. Error name description, action, etc. Ca5 stop deviation overflow error movement may have occurred during stopping due to external force or operation may have been restricted d...
Page 458
Appendi x intelli gent a c tuat or 434 (in the panel window, the three digits after “e” indicate an error number.) error no. Error name description, action, etc. Cbb reference-point/px-axis end-point duplication error at palletizing angle acquisition angle cannot be calculated because the reference ...
Page 459
Appendi x intelli gent a c tuat or 435 (in the panel window, the three digits after “e” indicate an error number.) error no. Error name description, action, etc. D01 encoder eeprom-write timeout error the encoder is faulty or failure occurred in the encoder communication. D02 encoder eeprom-read tim...
Page 460
Appendi x intelli gent a c tuat or 436 (in the panel window, the three digits after “e” indicate an error number.) error no. Error name description, action, etc. D20 driver error (refer to error no. Ca1.) d22 encoder rotation reset error the encoder is faulty or has turned. D23 encoder alarm reset e...
Page 461
Appendi x intelli gent a c tuat or 437 (in the panel window, the three digits after “e” indicate an error number.) error no. Error name description, action, etc. D58 fieldbus error (init timeout) an init timeout was detected. Check the statuses of monitor leds on the front panel of the board by refe...
Page 462
Appendi x intelli gent a c tuat or 438 (in the panel window, the three digits after “e” indicate an error number.) error no. Error name description, action, etc. D68 no remote-mode control support board error hardware supporting remote-mode control is not installed, although remote- mode control (au...
Page 463
Appendi x intelli gent a c tuat or 439 (in the panel window, the three digits after “e” indicate an error number.) error no. Error name description, action, etc. E14 sci receive-data-register full wait timeout error communication failure. Check for noise, shorting, circuit failure and slave card. E1...
Page 464
Appendi x intelli gent a c tuat or 440 (in the panel window, the three digits after “e” indicate an error number.) error no. Error name description, action, etc. E2d receive-data checksum error when sending eeprom information acquisition command the checksum of receive data is invalid when a slave-e...
Page 465
Appendi x intelli gent a c tuat or 441 (in the panel window, the three digits after “e” indicate an error number.) error no. Error name description, action, etc. E50 driver special command ack-timeout error ack cannot be detected for the driver special command. E51 drive unit error (drvesr) error no...
Page 466
Appendi x intelli gent a c tuat or 442 (in the panel window, the three digits after “e” indicate an error number.) error no. Error name description, action, etc. E6d drive-source cutoff relay error the drive-source cutoff relay may have been melted. When turning on the power to a q type controller, ...
Page 467
Appendi x intelli gent a c tuat or 443 (in the panel window, the three digits after “e” indicate an error number.) error no. Error name description, action, etc. E83 i/o slot card error the i/o slot card is invalid. E84 resolution parameter error check axis-specific parameter nos. 47, 50, 51, 44, 42...
Page 468
Appendi x intelli gent a c tuat or 444 (in the panel window, the three digits after “e” indicate an error number.) error no. Error name description, action, etc. Ff0 ~ f00 shutdown error (hi_sysdwn () definition) a shutdown error (hi_sysdwn () definition) was detected. F03 ~ f58 shutdown error (os c...
Page 469
Appendi x intelli gent a c tuat or 445 ~ error list (main core) (in the panel window, the three digits after “e” indicate an error number.) error no. Error name description, action, etc. A70 scif overrun error communication error. Check for noise, connected equipment and communication setting. (when...
Page 470
Appendi x intelli gent a c tuat or 446 (in the panel window, the three digits after “e” indicate an error number.) error no. Error name description, action, etc. A85 from write request error before erase is complete when updating, a flash-rom write command was received before a flash-rom erase comma...
Page 471
Appendi x intelli gent a c tuat or 447 (in the panel window, the three digits after “e” indicate an error number.) error no. Error name description, action, etc. E90 core code flash-rom status error the core program is invalid. Contact the manufacturer. E91 application code flash-rom status error th...
Page 472
Appendi x intelli gent a c tuat or 448 (in the panel window, the three digits after “e” indicate an error number.) error no. Error name description, action, etc. Eac servo control underrun error a servo control underrun error was detected. Ead boot error a fpga boot watchdog was detected. The core p...
Page 474
448 appendix intelligent actuator ~ troubleshooting of x-sel controller the x-sel controller has a panel window on its front face. Error numbers will be displayed in this panel window. When the power is turned on, normally “rdy” or “ardy” will be displayed. “p01” or other code will be displayed whil...
Page 475
Appendi x intelli gent a c tuat or 449 troubleshooting (causes and countermeasures for key errors) error no. Error name cause countermeasure acf ac power cutoff momentary power failure has occurred or the voltage has dropped. 100 v is input while the controller’s voltage specification is 200 v. Chec...
Page 476
Appendi x intelli gent a c tuat or 450 error no. Error name cause countermeasure 914 ca2 abnormal absolute-data backup battery voltage the pg cable was disconnected from the controller. Absolute reset has not been executed after the initial setup. The voltage of the absolute-data backup battery has ...
Page 477
Appendi x intelli gent a c tuat or 451 error no. Error name cause countermeasure d18 speed loop underrun error the driver cpu board was damaged due to noise in the encoder cable. Replace the board and implement noise control measures. 807 shutdown relay er status the transistor on the power-supply b...
Page 478
452 appendix intelligent actuator servo gain adjustment since the servo has been adjusted at the factory in accordance with the standard specification of the actuator, the servo gain need not be changed in normal conditions of use. However, vibration or noise may occur depending on how the actuator ...
Page 479
453 appendix intelligent actuator.
Page 480
454 appendix intelligent actuator z speed loop integral time constant (parameter list 1) driver card parameter number unit input range default (reference) 44 - 1 ~ 1000 30 this parameter determines the level of response with respect to a speed control loop. Increasing the setting too much results in...
Page 481
455 appendix intelligent actuator trouble report sheet trouble report sheet date: company name department reported by tel (ext) fax iai agent purchase date serial number manufacture date [1] number of axes axis(es) 1 = 2 = type 3 = 4 = 5 = 6 = 7 = 8 = [2] type of problem 1. Disabled operation 2. P...
Page 482
Catalog no.: xsel pq type-mj0148-4a oct.2007 head office: 2690 w. 237th street, torrance, ca 90505 tel (310) 891-6015 fax (310) 891-0815 chicago office: 1261 hamilton parkway, itasca, il 60143 tel (630) 467-9900 fax (630) 467-9912 atlanta office: 1220-e kenneston circle, marrietta, ga 30066 tel (678...