- DL manuals
- IBM
- Processor
- ThinkPad R30
- Operator's Manual
IBM ThinkPad R30 Operator's Manual - The Operator Panel
2-2
Operator Guide
The Operator Panel
The operator panel is located behind the front bezel door. To access the operator panel,
rotate the top of the front bezel door downward.
The operator panel is controlled by the CPU and a special microprocessor located on the I/O
card, called SystemGuard.
Operator Controls
3.5-Inch
Diskette Drive
Operator Panel Display
Diskette
Eject
Button
Power
Button
Key Mode Switch
Power
Light
3.5-Inch Diskette Drive
In-Use Light
Reset/Scroll Button
Normal
Secure
Service
Power Button
Used to switch the power to the system on or off
Power Light
Green LED: When lit, indicates all voltages in the power supply
are present and within specified limits and all fans are running.
The power-on light is also used to help analyze power and
cooling problems.
Reset/Scroll Button
Used to reset the system unit, depending on the position of the
key mode switch. Also used to scroll the messages on the
Operator Panel Display.
Operator Panel Display
Displays status indication of the system
Key Mode Switch
Is a switch with three positions labeled:
, , and
Summary of ThinkPad R30
Page 1
7015 models r30, r40, and r50 cpu enclosure operator guide.
Page 2: Third Edition (April 1997)
Third edition (april 1997) this edition notice applies to the 7015 model r30, r40, and r50 cpu enclosure operator guide. The following paragraph does not apply to the united kingdom or any country where such provisions are inconsistent with local law: this publication is printed “as is” without warr...
Page 3: Table of Contents
Preface iii table of contents communications statements vii . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Safety notices xi . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . About this book xi...
Page 4
Iv operator guide general information for 4.0gb 4 mm tape drive 2-34 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Recommendations 2-35 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Types of 4 mm tape cartridges 2-35 . . . . . ....
Page 5
Preface v ac rack features 4-2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Ac rack with external device container, cable channel, and rack attachment plate 4-2 power distribution bus 4-3 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ....
Page 6
Vi operator guide running the diagnostic programs from disk or from a server 8-2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Running the diagnostic programs from the network 8-2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Running the diagnostic programs from a tty terminal 8-3 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ...
Page 7
Preface vii display and change diagnostic test list service aid 9-10 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Display or change key modes (display or change electronic mode switch task) 9-11 display previous diagnostic results service aid 9-11 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ....
Page 8
Viii operator guide aix diag command b-4 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Modifying dial-in phone numbers b-5 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Systemguard maintenance menu b-5 . ...
Page 9: Communications Statements
Preface ix communications statements the following statement applies to this product. The statement for other products intended for use with this product appears in their accompanying manuals. Federal communications commission (fcc) statement note: this equipment has been tested and found to comply ...
Page 10
X operator guide for class a equipment were derived for commercial and industrial environments to provide reasonable protection against interference with licensed communication equipment. Attention: this is a class a product. In a domestic environment this product may cause radio interference in whi...
Page 11
Preface xi radio protection for germany dieses gerät ist berechtigt in Übereinstimmung mit dem deutschen emvg vom 9.Nov.92 das eg-konformitätszeichen zu führen. Der aussteller der konformitätserklärung ist die ibm germany. Dieses gerät erfüllt die bedingungen der en 55022 klasse a. Für diese klasse ...
Page 12
Xii operator guide.
Page 13: Safety Notices
Preface xiii safety notices note: for a translation of these notices see the system unit safety information, form number sa23-2652. Definitions of safety notices a danger notice indicates the presence of a hazard that has the potential of causing death or serious personal injury. Danger notices appe...
Page 14: Laser Safety Information
Xiv operator guide laser safety information the optical drive in this system unit is a laser product. The optical drive has a label that identifies its classification. The label, located on the drive, is shown below. Class 1 laser product laser klasse 1 luokan 1 laserlaite appareil a laser de classe...
Page 15: About This Book
Preface xv about this book this book provides information about the operator controls and the devices installed in the 7015 system unit. Definition of machine names and model numbers the models of cpu enclosures referred to in this book are the 7015 model r30, r40, and r50. References to cpu enclosu...
Page 16
Xvi operator guide.
Page 17: Cpu Enclosure
Description 1-1 chapter 1. Cpu enclosure description this chapter contains information about system unit features, parts, and devices on the 7015 model r30, r40, or r50 cpu enclosures. Cpu enclosure the 7015 cpu enclosures are rack-mounted cpus containing a cpu module, i/o module, media module, and ...
Page 18
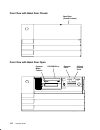
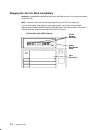
1-2 operator guide front view with bezel door closed bezel door (closed position) front view with bezel door open cd-rom drive optional media position operator panel 3.5-inch diskette drive.
Page 19
Description 1-3 cpu enclosure with connectors (rear view) parallel port serial port 1 serial port 2 adapter locations adapter locations serial port 3 rs485 (out) battery backup unit connector rs485 (in) 0/1 1/1 0/2 0/3 0/4 0/5 0/6 0/7 0/8 1/2 1/3 1/4 1/5 1/6 1/7 1/8.
Page 20
1-4 operator guide.
Page 21
Using the cpu enclosure 2-1 chapter 2. Using the cpu enclosure this chapter contains information about using the cpu enclosure and using devices installed in the cpu enclosure. For information about using a -48 v dc system unit, refer to chapter 6. General information about multiple systems if your ...
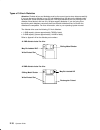
Page 22: The Operator Panel
2-2 operator guide the operator panel the operator panel is located behind the front bezel door. To access the operator panel, rotate the top of the front bezel door downward. The operator panel is controlled by the cpu and a special microprocessor located on the i/o card, called systemguard. Operat...
Page 23
Using the cpu enclosure 2-3 setting the key mode switch the key mode switch has three positions: • – normal • – secure • – service the switch is used to establish the initial program load (ipl) path. The ipl loads the system programs, checks the system hardware, and prepares the system for user oper...
Page 24
2-4 operator guide the following table summarizes the operations possible for each key mode position for the cpu enclosure. Operation key mode switch position normal secure service reset/scroll key enabled disabled enabled systemguard console active enabled enabled enabled systemguard console debug/...
Page 25
Using the cpu enclosure 2-5 • the secure position ( ): the secure position prevents the system from doing an ipl. If the operating system is already loaded, this position does not lock the system console or block system network communication. When loading the operating system with the key mode switc...
Page 26: Electronic Mode Switch
2-6 operator guide electronic mode switch the electronic mode switch (e-key) enables you to remotely change the status of the key mode switch and: • places the system for maintenance or debug purpose from a remote location, from normal to service mode, without a person physically being present near ...
Page 27
Using the cpu enclosure 2-7 reading the operator panel display attention: if you have a flashing 888 in the operator panel display, do not push the reset/scroll button before you carefully read the related documentation. The operator panel display has two 16-position rows. The operator panel display...
Page 28
2-8 operator guide using the reset/scroll button attention: when the key mode switch is in the normal or service position, pressing the reset/scroll button causes the unit to reset and do an initial program load (ipl). Pressing the reset/scroll button while the operating system is running can result...
Page 29
Using the cpu enclosure 2-9 using the 3.5-inch diskette drive the diskette drive is located to the right of the cd-rom drive on the cpu enclosure. The in-use light is on when the system is accessing the drive. Do not stop the system unit or remove a diskette when the in use light is on, or you may l...
Page 30
2-10 operator guide types of 3.5-inch diskettes attention: diskette drives and diskettes must be the correct type to store data successfully. If you use the wrong diskette in your 3.5-inch diskette drive, the data on the diskette could be destroyed. Some computers operate with 720k-byte diskette dri...
Page 31
Using the cpu enclosure 2-11 setting the write-protect tab on 3.5-inch diskettes setting the write-protect tab on a diskette is necessary so that information is not accidentally lost. When the write-protect tab is set (slot open) on a diskette, information can be read from the diskette but cannot be...
Page 32
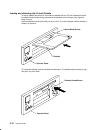
2-12 operator guide loading and unloading the 3.5-inch diskette to load a diskette into the drive, first insert the diskette into the 3.5-inch diskette drive with the labeled metal shutter facing upward and the beveled corner facing to your right and away from you. Push the diskette into the drive u...
Page 33: Using The Cd-Rom Drive
Using the cpu enclosure 2-13 using the cd-rom drive the cd-rom drive position is located in the top media position to the left of the operator panel. Type b bezel (cd-rom and cd-rom2) cd-rom drive note: for a translation of this notice, see system unit safety information. Caution: a class 3 laser is...
Page 34
2-14 operator guide loading the cd-rom disc caddy note: the disc caddy is not compatible with the type c bezel cd-rom drive. The cd-rom media kit contains a cd-rom diagnostic disc and a disc caddy. Open the disc caddy and place the cd-rom disc in the caddy with the printed side up. Disc caddy cd-rom...
Page 35
Using the cpu enclosure 2-15 type c bezel cd-rom drive note: for a translation of this notice, see system unit safety information. Caution: a class 3 laser is contained in the device. Do not attempt to operate the device while it is disassembled. Do not attempt to open the covers of the device, as i...
Page 36
2-16 operator guide loading the cd-rom drive notes: the disc caddy is not compatible with the type c bezel cd-rom drive. Always handle discs by the edges to avoid leaving fingerprints. Discs can be wiped with a soft, lint-free cloth or lens tissue. Always wipe in a straight line from the inner hub t...
Page 37
Using the cpu enclosure 2-17 unloading the cd-rom drive note: always handle discs by the edges to avoid leaving fingerprints. Discs can be wiped with a soft, lint-free cloth or lens tissue. Always wipe in a straight line from the inner hub to the outer rim. 1. Push and hold the unload button until t...
Page 38
2-18 operator guide emergency eject note: execute the following procedure only when the disc drawer does not eject after the unload button is pressed. 1. Power-off the cd-rom drive. 2. Insert a straight metal small-diameter rod such as a straightened paper clip into the emergency eject hole as shown...
Page 39
2-19 using the cpu-media enclosure using the 1/4-inch internal tape drive the 1.2 g-byte or the 150 mb 1/4-inch tape drive, if present, is an optional device in the cpu enclosure and is located in the bottom media position to the left of the operator panel. Blue unload button status light front pane...
Page 40
2-20 operator guide setting the write-protect tab on 1/4-inch tape cartridges setting the write-protect tab on a tape cartridge is necessary so that information is not accidentally lost. When the write-protect tab of a tape cartridge is set (pointing to safe), information can be read from the tape b...
Page 41: The 1/4-Inch Tape
2-21 using the cpu-media enclosure loading the 1/4-inch tape cartridge a diagram inside the drive opening shows how to load a tape. To load a tape cartridge, push the unload button. When the button is pushed, the front panel of the drive partially opens toward the front of the system unit. Unload bu...
Page 42
2-22 operator guide unloading the 1/4-inch tape cartridge to unload the cartridge, use the same procedure you used for loading except pullthe cartridge from the drive opening. 1. Push the unload button. 2. Pull the front panel open (flat). 3. Pull the tape cartridge out of the drive. 4. Push the fro...
Page 43
2-23 using the cpu-media enclosure retensioning the tape drive works best when it is operated as a streaming tape. If the tape cartridge has been operated in the streaming mode, it is not necessary to re-tension the tape. If the tape is used in a non-streaming mode (many start and stop operations), ...
Page 44
2-24 operator guide tape cartridge data efficiency note: for maximum efficiency, operate the 1/4-inch tape drive in the streaming mode whenever possible. The 1/4-inch tape cartridge efficiency is defined as the amount of data that can be stored on the cartridge and the data rate at which the data ca...
Page 45
2-25 using the cpu-media enclosure general information for 5.0gb 8 mm tape drive note: the 5.0gb 8 mm tape drive, if present, is an optional device in the cpu enclosure and is located in the bottom media position to the left of the operator panel. Recommendations • use only data grade 8 mm tape cart...
Page 46
2-26 operator guide tape cartridge compatibility the 8 mm tape drive is compatible with existing 8-mm tape subsystems that comply with the american national standard (ansi) x3b5/89–136, helical-scan digital computer tape cartridge, 8 mm for information exchange. Data compression effectively increase...
Page 47
2-27 using the cpu-media enclosure operating in harsh environments the 8-mm tape drive is ideally suited to streaming operations, as opposed to tape movement operations involving multiple stop/starts and random searches. When the tape is used for frequent stop and start operations, streaming movemen...
Page 48
2-28 operator guide 5.0 0.0 2.0 8 mm media capacity vs file size average data file size 4.0 3.0 1.0 short filemark long filemark 5.0gb mode 1g 100m 10m 1m 100k 10k 1k (one filemark per data file) media capacity (t imes 10e9).
Page 49
2-29 using the cpu-media enclosure using the 5.0gb 8 mm tape drive the 5.0gb 8 mm tape drive, if present, is an optional device in the cpu enclosure and is located in the bottom media position to the left of the operator panel. Status lights the 5.0gb 8 mm tape drive has two green status lights and ...
Page 50
2-30 operator guide status light states the following table explains the meaning of the green and amber status lights. • the post has completed successfully, but no tape cartridge has been inserted. Status lights on the 5.0gb 8 mm tape drive status lights state status disturbance ready busy on off f...
Page 51: The 8 Mm Tape
2-31 using the cpu-media enclosure loading the 8 mm tape cartridge before loading the tape cartridge, make sure the power is on and the write-protect switch on the tape cartridge is properly set. Refer to “setting the write-protect tab” on page 2-26. The tape drive loads the tape from the cartridge ...
Page 52
2-32 operator guide unloading the 8 mm tape cartridge before performing the unload operation, make sure the power to the 8 mm tape drive is on. To unload and eject the tape cartridge, press the unload button. The 8 mm tape drive rewinds the tape and then ejects the tape cartridge from the tape drive...
Page 53
2-33 using the cpu-media enclosure cleaning the tape path on the 5.0gb 8 mm tape drive attention: do not use video cleaning cartridges in the 8 mm tape drive. Video cleaning cartridges can damage the 8-mm tape drive. Some video cleaning cartridges are extremely abrasive. A 5.0gb 8 mm tape drive may ...
Page 54
2-34 operator guide general information for 4.0gb 4 mm tape drive the 4.0gb 4 mm tape drive, if present, is an optional device in the cpu enclosure and is located in the bottom media position to the left of the operator panel. The 4.0gb 4 mm tape drive is an internal streaming tape drive that is use...
Page 55
2-35 using the cpu-media enclosure recommendations attention: tape cartridges that do not carry the proper dds symbol cannot be written to and their use will cause the 4 mm tape drive to report an error. • use only 4 mm digital data storage (dds) cartridges. Attention: use of other than recommended ...
Page 56
2-36 operator guide tape cartridge compatibility the 4 mm tape drive is compatible with existing 4 mm tape subsystems that are designed to operate with digital data storage approved media, which meet the following standards: • for dds llll – american national standard (ansi) standard, x3.203-191, he...
Page 57
2-37 using the cpu-media enclosure increased if 4 mm tape cartridges are operated, stored, or shipped outside the temperature or humidity ranges shown in the following table. Before using a cartridge, always let it adjust (acclimate) to the operating environment. Do this by placing the cartridge wit...
Page 58
2-38 operator guide using the 4.0gb 4 mm tape drive the 4.0gb 4 mm tape drive, if present, is an optional device in the cpu enclosure and is located in the bottom media position to the left of the operator panel. Status lights the 4.0gb 4 mm tape drive has two green status lights and one amber statu...
Page 59
2-39 using the cpu-media enclosure off • the power is off. • the post has completed successfully, but no tape cartridge has been loaded. Status lights on the 4.0gb 4 mm tape drive status the power-on self-test (post) is running or the diagnostic cartridge is running. Led test. Disturbance (amber) re...
Page 60: The 4 Mm Tape
2-40 operator guide loading the 4 mm tape cartridge before loading the tape cartridge, make sure the power is on and the write-protect switch on the tape cartridge is properly set. Refer to “setting the write-protect tab on 4 mm tape cartridges” on page 2-36. The tape drive loads the tape from the c...
Page 61
2-41 using the cpu-media enclosure unloading the 4 mm tape cartridge before performing the unload operation, make sure the power to the 4 mm tape drive is on. To unload and eject the tape cartridge, press the unload button. The 4 mm tape drive rewinds the tape and then ejects the tape cartridge from...
Page 62
2-42 operator guide cleaning the tape path on the 4.0gb 4 mm tape drive the 4 mm tape path should be cleaned either approximately every 30 hours of tape motion or once a month, whichever occurs first. The 4 mm tape drive monitors the recording quality of the tape cartridge and indicates that the tap...
Page 63: Introduction
Using systemguard 3-1 chapter 3. Using systemguard this chapter introduces the systemguard service processor which is included in all symmetric multiprocessor models. Introduction smp servers include a service processor, called systemguard, as a standard feature. Systemguard continually monitors the...
Page 64: Systemguard Power
3-2 operator guide systemguard power systemguard has its own dc power boundary. This means that even if the system power is off (power button of the system in the off position), systemguard is still powered on, as long as the cpu enclosure still still has power. This allows control of the system eve...
Page 65: The Operator Panel
Using systemguard 3-3 the operator panel the operator panel is the first level of user interface to systemguard. The operator panel has the following features: power button it should generally stay pushed in all the time if you want to be able to power on or off the system remotely. Reset button it ...
Page 66: Systemguard Consoles
3-4 operator guide systemguard consoles systemguard works with two types of consoles: • the bump console, which is an ascii terminal attached to the s1 serial port. This console provides the normal input to the bump. It can be local or remote. The line speed for the bump console must be set to 9600 ...
Page 67
Using systemguard 3-5 init phase init phase is entered when the power button on the operator panel is pressed on or when the power-on command is entered on the bump console or service console. If the system key is in normal mode, the bump runs the built-in or resident power-on (pon)-tests on the cpu...
Page 68
3-6 operator guide phase change (stand-by to init) the phase change from stand-by to init is called crossing the power boundary. This is achieved by pushing the power button on the operator panel or by typing the keyword power at the stand-by prompt (>). Note that if you type power while the power b...
Page 69
Using systemguard 3-7 power-on (pon) tests pon tests are run by systemguard whenever the system power comes on. There are two types of tests: • a comprehensive set of tests are performed on the processors, cache, memory and related hardware when the fast-ipl flag is disabled. • a minimum core set of...
Page 70
3-8 operator guide there are other resident pon tests to check other system resources. These tests are a subset of the systemguard maintenance offline tests, and reside within the flash eprom. These tests are divided into the following groups: bump quick i/o test group these tests check the accessib...
Page 71
Using systemguard 3-9 phase change (init to maint) the maintenance phase is entered from the init phase if the system key is in service mode. If the bump console present flag is set, the maintenance menu is displayed on the bump console, and the system waits for an operator action. The maintenance m...
Page 72
3-10 operator guide working with systemguard you can change systemguard parameters and flags from different locations they can be changed from the systemguard stand-by menu, the systemguard maintenance menu, the diagnostics interface, and also from aix. When the key signal is received, systemguard c...
Page 73
Using systemguard 3-11 when the system is in stand-by mode and the system key (physical or electronic key) is in service mode, the stand-by menu can be accessed and systemguard executed. If you turn the system unit power on from stand-by mode with the system key in the normal position, the system bo...
Page 74
3-12 operator guide stand-by menu the stand-by menu can only be entered when the system is in stand-by mode (the word stand-by must be displayed on the lcd display). Perform the following steps to bring up the stand-by menu. 1. With stand-by displayed on the lcd display press the enter key on the bu...
Page 75
Using systemguard 3-13 how to display the system configuration the system configuration can be displayed through the stand-by menu or through the maintenance menu. Displaying configuration through the stand-by menu this option displays the system configuration table. This configuration can be viewed...
Page 76
3-14 operator guide display configuration sib14 ps04 sib24 sib15 ps05 sib25 sib16 ps06 sib26 fc8e000000000000 sib17 ps07 sib27 mp d78605 19h0464 mpe d78605 mca 01 c fc8e000000000000 mcae 01 c e1ff000000000000 mca 02 c f48e000000000000 mcae 02 c 708f000000000000 mca 03 c fc8e000000000000 mcae 03 c ec...
Page 77
Using systemguard 3-15 • cpux ec+s: the agent status information of the cpu cards and the vpd information is given. • mcx ec+s: this field gives the memory card vpd values. • mcax loc. Code+status: this parameter contains the location code and the status information of the micro channel adapters (mc...
Page 78
3-16 operator guide and parameters (set during manufacturing), see the table in “default parameter values” on page b–1 of the service guide for your system. The following flags can be managed: • remote authorization: only the local operator can enable this flag to enable remote maintenance to be per...
Page 79
Using systemguard 3-17 set configuration this menu option enables you to configure or unconfigure units and devices. 1. Enter 3 in the main menu to select this option. 2. You should then see a first-level screen similar to the following. It displays the units and devices that can be configured, alon...
Page 80
3-18 operator guide ssbus maintenance this option is used to investigate and check devices on the ssbus and is meant only for trained service personnel. Use this option to investigate and check devices on the ssbus. 1. Enter 4 in the main menu to select this option. Systemguard displays the followin...
Page 81
Using systemguard 3-19 i 2 c maintenance use this option to do maintenance operations on the i 2 c buses of a selected unit, in order to investigate and check the connected devices. When exiting this menu, the previous status of the op and sib microcontrollers are restored (except for voltage margin...
Page 82
3-20 operator guide set voltage margins note: this option can be only used for error analysis or factory test and must be used only by trained service personnel. Restore nominal voltage values before restarting other operations. Any data written on the disk in marginal mode must be removed before re...
Page 83
Using systemguard 3-21 maintenance menu the maintenance menu also enables you to display the configuration of the system in a non-cryptic, easily understandable way, to perform various tests, to continue ipl either from network, a specific scsi device or from the boot list, and to set flags concerni...
Page 84
3-22 operator guide display configuration use this option to view the system hardware configuration. This option provides different screens with the following levels of information: • system-level information • unit-level information • device-level information. Enter 0 in the maintenance menu to sel...
Page 85
Using systemguard 3-23 • voltage margins for cpus, asics, and other components. • device status information. • options to select various types of devices. Display configuration – main unit margins value: +5 volt –> normal cpu (3.65 volt) –> normal asic (3.6 volt) –> normal scsi devices: present –> #...
Page 86
3-24 operator guide 1. To see device-level information, enter the corresponding command number for the device. The device-level screen is displayed. 2. Enter x to return to the system-level configuration display screen. Display configuration – device level this screen is shown when you select one of...
Page 87
Using systemguard 3-25 display bump error log use this option to view the bump firmware error log. 1. Enter 1 in the maintenance menu to select this option. The contents of the logging buffer are displayed as shown in the following screen: display bump error log event # 1: 40140100000000000000000000...
Page 88
3-26 operator guide system boot this command enables you to begin boot activity. Enter 6 in the main menu to select this option. The following screen is displayed: system boot 0> boot from list 1> boot from network 2> boot from scsi device select [x:exit]: the menu enables you to boot in three diffe...
Page 90
3-28 operator guide off-line tests attention: these menus are only to be used when directed by service support personnel. Some of the tests described require test equipment or resources not available on your system. This option under the maintenance menu enables you to run the off-line tests in a co...
Page 91
Using systemguard 3-29 0 displays the build test menu, which enables you to specify the test list (see “build test list” below). 1 displays and enables modification of the tests in the build list (see page 3-31). 2 deletes the tests in the build list, after operator confirmation. Attempting to delet...
Page 92
3-30 operator guide 3. Once you have selected the test groups, you can specify individual tests within a group. For example, the following screen enables you to specify individual bump quick io tests: build test list group 01 bump quick io test description test description 01 debug line 02 s1 asl (b...
Page 93
Using systemguard 3-31 modify/display test list once the test list is built, you can use this option to view or modify it. Each test is identified by a number xxyy, where xx is the group number and yy is the test number. 1. Enter 2 in the off-line tests menu to view or modify the test list. The foll...
Page 94
3-32 operator guide execute test list this command enables you to run the test list once it is built (and possibly modified). All the tests in the test list are run one at a time with the selected execution options. • enter 3 in the off-line tests main menu to run the selected tests. The following s...
Page 95
Using systemguard 3-33 power-on command parameters during the standby idle phase, the system power can be turned on (and the ipl started) by entering a bump console power-on string through line s1 or a service console power-on string through line s2 (see “working with systemguard” on page 3-10 for a...
Page 96
3-34 operator guide set configuration this command is used to configure electronic boards like i/o cards or micro channel adapter (mca) devices. 1. Enter 2 in the set parameters menu to display the set configuration menu as shown below: set configuration 0> cpu card 1> memory card 2> basic mca adapt...
Page 97
Using systemguard 3-35 1. Enter 3 in the set parameters menu to display the phone numbers menu shown here: phone numbers 0> service center dial–out (1) –> 1> service center dial–out (2) –> 2> customer hub dial–out (1) –> 3> customer hub dial–out (2) –> 4> system dial–in –> 5> system operator voice –...
Page 98
3-36 operator guide • enter 4 in the set parameters menu to display the miscellaneous parameters menu. The value set for all the flags, except fast ipl, is permanent until a new change is made. Miscellaneous parameters 0> bump console –> present 1> autoservice ipl –> disabled 2> dial_out authorizati...
Page 99
Using systemguard 3-37 2. The new flag status (opposite of the previous state) is displayed. Boot multiuser aix in service flag enables multiuser aix boots to proceed even if the mode switch is in the service position (when booting by selecting option 6 in the maintenance menu). When the flag is ena...
Page 100
3-38 operator guide set national language use this option in the main menu to set the national language used for “systemguard”. Once selected, the effect is immediate and all the console messages are presented in the selected language. 1. Enter 9 in the maintenance menu to select this option. The fo...
Page 101
Using systemguard 3-39 some common systemguard tasks the following tasks are done through the stand-by and maintenance menus that are part of systemguard. Note that these tasks can also be carried out from aix diagnostics. How to set the electronic key the key can be set electronically, making it ea...
Page 102
3-40 operator guide the configuration display is a good picture of the systemguard configuration on one screen. Here is an example: display configuration machine type/model: 7013j30 45067 firmware release: standby –> 1600 backup eprom –> 0701 flash eprom –> 0704 service contract: last update (yymmdd...
Page 103
Using systemguard 3-41 setting fast ipl through the maintenance menu 1. Enter the maintenance menu. 2. Enter 8 to select the set parameters menu. 3. Enter 4 from the set parameters menu to select the miscellaneous parameters menu. 4. Option 3 in this menu should show the current status of the fast i...
Page 104
3-42 operator guide how to set the service line speed by default, the service line speed is 1200 baud or 2400 baud depending on the level of systemguard. This speed can be changed through the systemguard maintenance menu. In order to use the service console properly, the terminal connected to the s2...
Page 105
Using systemguard 3-43 setting line speed through aix 1. With aix up and running, log in as user root. 2. Type the following command to view current settings: mpcfg –dm the following is the output of the command: index name value 1 modem parameters file name 2 service line speed 3 protocol inter dat...
Page 106
3-44 operator guide how to set up console mirroring console mirroring concepts console mirroring is a way to provide the customer a view of what the person working remotely from the service console is doing on the system. When mirroring is active, the service console and the bump console are logical...
Page 107
Using systemguard 3-45 setting up console mirroring in order to setup console mirroring, you need first to authorize the service console, and set up the right line speed. Refer to previous chapters on how to set up the service line speed and how to authorize the service console. Then do the followin...
Page 108
3-46 operator guide how to enable surveillance surveillance is implemented by the survd daemon. This daemon, when started, establishes a heartbeat between aix and systemguard. In case of an aix hang, systemguard detects it and reboots the system. To implement the surveillance, do the following: 1. E...
Page 109
Using systemguard 3-47 modem configuration the modem on line s2 must be configured using an ascii modem configuration file which describes various parameters using a specific syntax. Aix uses this file directly. The bump uses the same information (in condensed form) stored in non-volatile memory (nv...
Page 110
3-48 operator guide how to reboot aix from the remote service console it is possible for the remote personnel connected via the service console to reboot aix from the remote site. Prerequisites the following procedure must be carried out from the bump console in order to allow aix to boot remotely f...
Page 111
Using systemguard 3-49 rebooting to single-user and then to multi-user this allows the remote support personnel connected to the system via a modem to the s2 port to shut down and reboot the system in diagnostics mode for hardware diagnostics purposes. After running diagnostics, the remote personnel...
Page 112
3-50 operator guide 3. From this menu, enter 4 . To select the miscellaneous parameters menu, which is similar to the following: miscellaneous parameters 0> bump console –> present 1> autoservice ipl –> disabled 2> dial_out authorization –> disabled 3> fast ipl –> enabled 4> set mode to normal when ...
Page 113
Using systemguard 3-51 10.At this point, a boot from scsi device screen appears. This displays the present device location code. If it is not the device you want to boot from, go through each option and change it to the desired bus, slot, scsi id, and lun id. Option 4 allows you to change all these ...
Page 114
3-52 operator guide how to boot from the network the system can be booted from the network through the maintenance menu. Network boot allows a system to be reinstalled via the network and also allows various maintenance tasks to be carried out on the local machine. Use the following procedure to boo...
Page 115
Using systemguard 3-53 5. The select boot (startup) device menu appears, which is similar to the following: select boot (startup) device select the device to boot (startup) this machine. Warning: if you are using token–ring, selection of an incorrect data rate can result in total disruption of the t...
Page 116
3-54 operator guide 7. Enter the appropriate ip addresses, and enter 99 to return to the main menu. A screen similar to the following appears: main menu 1. Select boot (startup) device 2. Select language for these menus 3. Send test transmission (ping) 4. Exit main menu and start system (boot) type ...
Page 117
Using systemguard 3-55 how to disable and enable processors in the smp servers, it is possible to disable/enable processors. A suspected faulty processor can be disabled so that the system can run without it. The processors can be disabled/enabled through the stand-by menu, maintenance menu, diagnos...
Page 119
Using systemguard 3-57 5. The cpu card screen appears and looks similar to the following: cpu card – (cpu1) present conditions: pr #0 –> valid & enabled pr #1 –> valid & enabled commands: 0> enable 1> disable 2> temporary disable select [x:exit]: 6. From this screen, you can disable or enable a part...
Page 120
3-58 operator guide customizing systemguard for your needs systemguard is controlled by several flags. The flags consist of contract flags, operational flags, remote maintenance flags, and test flags. Remote service flag this flag is disabled at the factory and must be enabled for remote service ope...
Page 121
Using systemguard 3-59 phone numbers if remote maintenance is used, systemguard requires several phone numbers to be entered. Additional information is provided in “phone numbers” on page 3-34. Service line speed parameters if remote maintenance is used, systemguard requires that the line speed be c...
Page 122
3-60 operator guide reloading the flash eeprom follow this procedure to load a new version of systemguard into the flash eeprom. Only system administrators should perform this procedure. Prerequisites to install a new version of the eeprom firmware, you need either a firmware diskette containing a b...
Page 123: Ac Rack
Ac rack description 4-1 chapter 4. Ac rack description this chapter contains information about the ac 7015 model r00 rack features and parts. For information about using the ac 7015 model r00 rack, refer to chapter 5. For information about the dc 7015 model r00 rack, refer to chapters 6 and 7. Ac ra...
Page 124: Ac Rack Features
4-2 operator guide ac rack features the ac 7015 rack can contain the following alternate rack features: • external device container • cable channel • rack attachment plate ac rack with external device container, cable channel, and rack attachment plate external device container cable channel rack at...
Page 125
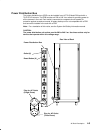
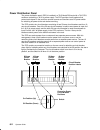
Ac rack description 4-3 power distribution bus the power distribution bus (pdb) can be installed in an ac 7015 model r00 rack with a 7015 cpu enclosure. The pdb contains six 200 to 240 v ac outlets for providing power to all the drawers in the rack. Each outlet is connected to a separate circuit bre...
Page 126
4-4 operator guide cluster power control the cluster power controller (cpc) provides: • connectivity between the remote support facility and multiple cpus through the modem • connectivity from any attached cpu to any attached disk drive drawer • central power-on and power-off through the tty. The cp...
Page 127
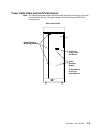
Ac rack description 4-5 uninterruptible power source the uninterruptible power source (ups) can be installed in a 7015 model r00 rack. The ups contains one power plug (in) and one power outlet (out) for connecting to the power distribuion bus (pdb)..
Page 128
4-6 operator guide power distribution unit (supported) the power distribution unit supplies 200 to 240 v ac from each of the six ac power outlets. These outlets provide power to all the drawers in the rack. The optional battery backup unit attaches to the power distribution unit and can provide 300 ...
Page 129
Ac rack description 4-7 battery backup unit (supported) note: the battery backup unit (bbu) can only be installed in the rack with a power distribution unit. The bbu cannot be installed in a rack with a power distribution bus. In addition to supporting other types of drawers in a rack, the bbu can s...
Page 130: System Unit Devices
4-8 operator guide system unit devices for more information about system unit devices, refer to the site and hardware planning information. Scsi-2 drawer (supported) note: compartment d of the scsi drawer can contain a 5.0 gb 8 mm tape drive, a 4.0 gb 4 mm tape drive, 1/4-inch tape drive, or a disk ...
Page 131
Ac rack description 4-9 disk drive there are no operator controls on the disk drive. Because data can become unusable if a disk drive problem occurs, you should back up the data stored on the disks. See your operating system documentation for information about using diskettes or tape drives to back ...
Page 132
4-10 operator guide ac rack cables and the cpu enclosure connectors cpu enclosure.
Page 133
Ac rack description 4-11 notes: 1. It is recommended that a trained service representative connect or disconnect any cables attached to the cpu enclosure. However, if you choose to connect or disconnect cables attached to the system unit, observe the following safety notices. 2. For a translation of...
Page 134
4-12 operator guide cable path note: it is recommended that a trained service representative connect or disconnect any cables attached to the cpu enclosure. However, if you choose to connect or disconnect cables attached to the system unit, observe the following information. Use the cable restraint ...
Page 135
Ac rack description 4-13 location codes and identification labels note: the scsi drawer is optional in a rack with a cpu enclosure. Several types of labels identify the locations of adapters and devices within the system unit. Numbers on these labels correspond to the location codes that are display...
Page 136
4-14 operator guide scsi drawer id label this label contains a two-digit number that identifies the slot in the cpu enclosure where the scsi adapter is located (drawer id). The number on this label corresponds to the characters cd in the location code. One label is located in the lower-right corner ...
Page 137
Ac rack description 4-15 scsi device address label this label contains a one-digit number that identifies the address of the device. The number on this label corresponds to the character g in the location code. One label is located in the upper-right corner of each device (behind the cover). A secon...
Page 138
4-16 operator guide creating cover labels note: either a 5.0gb 8 mm tape drive or a 4.0gb 4 mm tape drive can be installed in the right media position. Use the following steps and the sheet of peel-off numbers supplied with your system to create cover labels for scsi drawers. 1. Remove the cover fro...
Page 139
Ac rack description 4-17 4. Look at the scsi device address label on the bracket for each device. These numbers are the third digits of the cover labels..
Page 140
4-18 operator guide location code format for non-scsi devices the following example is for non-scsi devices. These include planars, memory cards, adapters, and async distribution boxes. Use the example to determine the physical location of a device. Note: the g and h fields each can contain one, two...
Page 141
Ac rack description 4-19 location code table for scsi and non-scsi devices use the following table to determine the physical location of a device or unit. Note: the location code format for 9333 devices is described on the previous page and in 9333 documentation. Use the following example to identif...
Page 142
4-20 operator guide pair description value s1 s2 s3 serial port 1 connector. Serial port 2 connector. Serial port 3 connector. 11 12 13 14 21 22 23 24 remote async node 1 on line 1. Remote async node 2 on line 1. Remote async node 3 on line 1. Remote async node 4 on line 1. Remote async node 1 on li...
Page 143: Starting The Ac Rack
Using the ac rack 5-1 chapter 5. Using the ac rack this chapter contains information about using, starting, and stopping the ac 7015 model r00 rack containing a 7015 cpu enclosure. For information about using the dc 7015 model r00 rack, refer to chapters 6 and 7. Starting the ac rack powering on the...
Page 144
5-2 operator guide manually starting by reloading the flash eeprom follow this procedure to load a new version of systemguard into the flash eeprom. Prerequisites if the system is not yet booted, you need a firmware diskette containing the new version of the firmware to be loaded. If the system is a...
Page 145
Using the ac rack 5-3 manually powering on the ac rack containing a pdu 1. Set the key mode switch to the service position. Key mode switch normal secure service operator panel note: for a translation of this notice, see the system unit safety information manual. Caution: this product is equipped wi...
Page 146
5-4 operator guide 5. Close the rear door of the rack. 6. Plug all external device power cords into the electrical outlets. 7. Switch on power to all external devices attached to the rack (including rack expansion drawers). Note: before setting the power button to on, wait for the operator panel dis...
Page 147
Using the ac rack 5-5 manually powering on the ac rack with a pdb note: ensure that the key mode switch is set to the service position to prevent system unit power from being switched on unexpectedly. 1. Set the key mode switch to the service position. Key mode switch normal secure service operator ...
Page 148
5-6 operator guide 3. Plug all drawer power cords into the outlets on the pdb. 4. Close the rear door of the rack. 5. Switch on power to all drawers connected to the pdb. 6. Set the key mode switch to the normal position. Note: before setting the power button to on, wait for the operator panel displ...
Page 149: Stopping The Ac Rack
Using the ac rack 5-7 stopping the ac rack note: the system unit can contain either a power distribution unit (pdu) or a power distribution bus (pdb). The following methods can be used to stop (switch off power to) the rack containing either a pdu or a pdb: • under ordinary conditions power is switc...
Page 150
5-8 operator guide attention: this unit may have more than one power supply cord. To completely remove power, you must disconnect all power supply cords. 3. Switch off power to all external devices attached to the system unit, and then unplug the device power cords from the electrical outlets. Note:...
Page 151
Using the ac rack 5-9 stopping the ac rack containing a pdb – under ordinary conditions notes: before turning the power off the drawers or external devices, ask the customer about their system high availability requirements. Other drawers in this system unit may be provided power from a pdb in an at...
Page 152
5-10 operator guide immediately stopping the ac rack containing a pdb attention: unpredictable results can occur that affect your data files if you use this method to stop the system unit. If drawers in an attached system unit are receiving power from the pdb of this system unit, the drawers in the ...
Page 153: -48 V Dc Rack
Description – -48 v dc rack 6-1 chapter 6. Description – -48 v dc rack this chapter contains information about a -48 v dc rack containing a 7015 cpu enclosure. For a description of an ac rack, refer to chapter 4. -48 v dc rack the dc 7015 model r00 rack contains a 7015 cpu enclosure with a -48 v dc ...
Page 154
6-2 operator guide power distribution panel the power distribution panel (pdp) is installed in a 7015 model r00 rack with a 7015 cpu enclosure containing a -48 v dc power supply. The pdp provides circuit breakers that protect each drawer in the rack from excess currents and functions as a dc power s...
Page 155
Description – -48 v dc rack 6-3 power cable paths and the cpu enclosure note: the following illustration shows the power cable path going from the top of the rack to the bottom of the rack. The power cables can be connected to the pdp from above the rack. Cable restraint straps rear view of rack a -...
Page 156
6-4.
Page 157: Setting The Key Mode Switch
Using the -48 v dc rack 7-1 chapter 7. Using the -48 v dc rack this chapter contains information about using the -48 v dc rack. For information about using an ac rack and the devices installed in an ac rack, refer to chapter 3. Some devices installed in an ac system with a cpu enclosure containing a...
Page 158
7-2 operator guide methods of starting the -48 v dc rack the four methods of starting the 7015 cpu enclosure installed in a dc rack are as follows: • manually. The power is switched on manually, and the rack does a normal or a service ipl. • remotely. The power is switched on from another location, ...
Page 159: Stopping The -48 V Dc Rack
Using the -48 v dc rack 7-3 stopping the -48 v dc rack the following methods can be used to stop (switch off power to) the rack: • under ordinary conditions. Power is switched off to the cpu enclosure and to other drawers if they are connected using the power control cables. • immediately. All power...
Page 160
7-4 operator guide stopping the -48 v dc rack immediately attention: unpredictable results that affect your data files can occur if you use this method to stop the rack. Note: drawers in this rack may be receiving power from a pdp in another rack. If you need to switch off all power to the system qu...
Page 161
Using the diagnostics 8-1 chapter 8. Using the diagnostics this chapter describes how to run the diagnostics from the network server. Diagnostic programs operating considerations the following items identify some things to consider before using the diagnostic programs. Note: when possible, run the o...
Page 162
8-2 operator guide running diagnostic programs from tape drives to load and execute diagnostics from a tape drive perform the following: 1. Power-on the tape drive if it is an externally attached device. 2. Set the key mode switch to the service position, and then power-on the system unit. 3. Remove...
Page 163
Using the diagnostics 8-3 running the diagnostic programs from a tty terminal consider the following when you run diagnostic programs using a tty-type terminal as the console display: • see the operator manual for your type of tty terminal to find the key sequences you need to respond to the diagnos...
Page 164
8-4 operator guide general attributes always required the following general attributes are the default settings for the diagnostic programs. Be sure your terminal is set to these attributes. Note: these attributes should be set before the diagnostic programs are loaded. Refer to the following table....
Page 165
Using the diagnostics 8-5 general setup attributes description 3161/3164 settings 3151 /51/61 settings 3151 /11/31/41 settings tab field field field the column tab stops are ignored, and the tab operation depends on the field attribute character positions. Trace all both inbound data (data to the sy...
Page 166
8-6 operator guide additional keyboard attributes the following keyboard attributes are for the keyboard attached to the 3151, 3161, and 3164 terminals. Keyboard setup attributes 3151/11/ 31 /41 settings 3151 /51/61) settings 3161 /3164 settings description enter return return return the enter key f...
Page 167
Using the diagnostics 8-7 diagnostic modes of operation the diagnostics can be run in three modes: • maintenance mode allows checking of most system resources • concurrent mode allows the normal system functions to continue while selected resources are being checked. • standalone mode allows checkin...
Page 168
8-8 operator guide concurrent mode concurrent mode provides a way to run diagnostics on some of the system resources while the system is running normal system activity. Because the system is running in normal operation, some of the resources cannot be tested in concurrent mode. The following resourc...
Page 169
Using the diagnostics 8-9 standalone mode standalone mode provides the most complete checkout of the system resources. This mode also requires that no other programs be running on the system. Standalone mode can be loaded in three ways: • from removable media. This method is the only method availabl...
Page 170
8-10 operator guide 11. If you loaded the diagnostics from the disk, press the f3 key (from a defined terminal) or press 99 (for an undefined terminal) to shutdown the diagnostics before turning off the system unit. Note: pressing the f3 key (from a defined terminal) produces a “confirm exit” popup ...
Page 171
Using the diagnostics 8-11 when the system exerciser is running, most built-in error recovery procedures are turned off. This can cause occasional errors to be reported that normally have no effect on system operation. Parts should only be replaced when the following occurs: • a high number of error...
Page 172: Reading A Flashing
8-12 operator guide reading a flashing 888 message on a multi-line operator panel display an 888 flashing in the first line of the operator panel display indicates that a hardware or software error has been detected and that an error message is being displayed. For additional information about flash...
Page 173
Using the diagnostics 8-13 is the second line of the operator panel display blank? No the message has a type 103 or 105 message included in it. Press the reset button once, then go to step 3. Read out the srn and fru information for these message types. Yes this completes the readout of this message...
Page 174: Step 4. Other Numbers
8-14 operator guide step 3. Reading the type 103 and 105 message a type 103 and 105 message is generated when a hardware error is detected. Use the following steps and information to record srn and fru location code information. 1. Record all characters following the first 103 or 105 in the first li...
Page 175: Tasks
Using the service aids 9-1 chapter 9. Introduction to tasks and service aids beginning with version 4.2 there are two top level menus seen by the user – tasks and resources. Once a task has been selected, then a list of resources will be displayed for selection to run the task on. Or after selecting...
Page 176
9-2 operator guide run diagnostics task the run diagnostics task invokes the resource selection list menu. When the commit key is pressed, diagnostics are run on all selected resources. The procedures for running the diagnostics depends on the states of the diagnostics run time options. The run time...
Page 177
Using the service aids 9-3 • run tests multiple times this option allows the user to select if the diagnostic should be run in loop mode or not (the default is no). Note: this option is only displayed when running online diagnostics in service mode. Process supplemental media task this prompts for e...
Page 178: Aix Shell Prompt Service Aid
9-4 operator guide periodic diagnostics service aid 9-13 product topology service aid 9-13 scsi bus service aid and scsi bus analyzer task 9-13 scsi tape utilities service aid 9-14 service aids for use with ethernet 9-14 service hints service aid 9-15 ssa service aid 9-15 trace service aid 9-15 7318...
Page 179
Using the service aids 9-5 • save or restore diagnostics modes and remote support phone number this function allows the diagnostics modes and remote support phone number to be saved and restored. The location of the save area is to be defined. • flash eprom download this function updates the flash e...
Page 180: Based Diagnostic Task
9-6 operator guide disk based diagnostic update service aid and update disk based diagnostic task this service aid allows fixes (apars) to be applied. Disk based diagnostic update service aid before version 4.2 prior to version 4.2 this service aid is used to update the diagnostics on the disk drive...
Page 181: Disk Media Service Aids
Using the service aids 9-7 to prevent problems that may occur when running this service aid from disk, it is suggested that this service aid be run from the diagnostics that are loaded from removable media when possible. Display/alter sector service aid note: to access this service aid refer to the ...
Page 182
9-8 operator guide 2. Do a format without certify. 3. Run a second pass of the erase service aid. For a newly installed drive, you can insure that all blocks on the drive are overwritten with your pattern if you use the following procedure: 1. Format the drive. 2. Check the defect map by running the...
Page 183: Diskette Media Service Aid
Using the service aids 9-9 indicates that the disk needs to be backed up and replaced. Formatting the disk does not improve the availability of spare sectors. Diskette media service aid this service aid provides a way to verify the data written on a diskette. When this service aid is selected, a men...
Page 184
9-10 operator guide display software product data beginning with version 4.2 this service aid displays information about the installed software and provides the following functions: • list installed software • list applied but not committed software updates • show software installation history • sho...
Page 185: Mode Switch Task)
Using the service aids 9-11 diagnostic test list menu lists all resources that can be deleted from the diagnostic test list. Note: only resources that were previously detected by the diagnostics and have not been deleted from the diagnostic test list is listed. If no resources are available to be de...
Page 186: Log Task
9-12 operator guide hardware error report service aid and display hardware error log task this service aid provides a tool for viewing the hardware error log and performing error log analysis. It uses the errpt command to do this. The display error summary and display error detail selection provide ...
Page 187: Product Topology Service Aid
Using the service aids 9-13 periodic diagnostics service aid this service aid provides a tool for configuring periodic diagnostics and automatic error log analysis. A hardware resource can be chosen to be tested once a day, at a user specified time. If the resource cannot be tested because it is bus...
Page 188
9-14 operator guide when the scsi bus service aid is entered a description of the service aid is displayed. Pressing the enter key will display the adapter selection menu. This menu allows the user to enter which address to transmit the scsi inquiry command. When the adapter is selected the scsi bus...
Page 189: Service Hints Service Aid
Using the service aids 9-15 when the ethernet service aid is executed, one of the following messages is returned: • no errors occurred. • an adapter error occurred. • a transmit time–out occurred. • a transmit error occurred. • a receive time–out occurred. • a receive error occurred. • a system erro...
Page 190
9-16 operator guide 7318 serial communications network server service aid this service aid provides a tool for diagnosing terminal server problems..
Page 191
Using the system verification procedure 10-1 chapter 10. Using the system verification procedure the system verification procedure is used to check the system for correct operation. This chapter contains information about pre-procedure considerations and running the system verification. Step 1. Cons...
Page 192
10-2 operator guide step 2. Loading the diagnostic programs 1. Stop all application programs running on the operating system. 2. Stop the operating system. (if help is needed, call your 800 support number.) 3. Turn off the system. 4. Set the mode switch to the service position. 5. If you want to run...
Page 193
Using the system verification procedure 10-3 step 4. Additional system verification the checkout programs end with either the testing complete menu and a message stating no trouble was found or the a problem was detected on (time stamp) menu with an srn. 1. Press enter to return to the diagnostic se...
Page 194
10-4 operator guide.
Page 195
Hardware problem determination 11-1 chapter 11. Hardware problem determination if you have an error or failure on your system, this chapter contains steps for obtaining a service request number (srn). You report the srn to the service organization. The service organization uses the srn to determine ...
Page 196: Step 2
11-2 operator guide step 2 (from step 1) the aix operating system contains the diagnostic programs. Other operating systems may not contain diagnostic programs. Is aix operating system used on this system? No go to step 21. Yes go to step 3. Step 3 (from step 2) determine if the aix operating system...
Page 197: Step 5
Hardware problem determination 11-3 step 5 (from step 4) this step loads concurrent diagnostics. 1. Log on as root or as superuser . 2. Enter the diag command. 3. Wait until the words diagnostic operating instructions are displayed, or wait for three minutes. Are the diagnostic operating instruction...
Page 198: Step 6
11-4 operator guide step 6 (from steps 3, 4, 5, 7) this step loads the diagnostics. 1. Set the mode switch to the service position. 2. Be sure the power switches of the attached devices are set to on. 3. Set the power switch on the system unit to on. 4. If c31 is displayed, follow the displayed inst...
Page 199
Hardware problem determination 11-5 6. Starting at the top of the following table, find your symptom and follow the instructions given in the action column. Symptom action the system stops with a blank operator panel display and the words diagnostic operating instructions are displayed with no obvio...
Page 200: Step 7
11-6 operator guide step 7 (from step 6, 18) the following steps analyze a steady (not flashing) number displayed in the operator panel display while attempting to load the diagnostics. Operator panel display number action 200 be sure the key mode switch is set to the service position. If the key mo...
Page 201: Step 9
Hardware problem determination 11-7 step 9 (from steps 6, 18, 20) the following steps analyze a console display problem. Find your type of console display in the following table; then, follow the instructions given in the action column. Console display action display device go to the your display do...
Page 202: Step 11
11-8 operator guide step 11 (from steps 10, 20) there is a problem with the keyboard. Find the type of keyboard you are using in the following table; then follow the instructions given in the action column. Keyboard type action tty-terminal keyboard. This applies to all attached terminals. Go to the...
Page 203
Hardware problem determination 11-9 system response action the diagnostic mode selection menu is displayed. Select problem determination , and then go to step 13. The missing resource menu is displayed. Follow the displayed instructions until either the diagnostic selection menu or an srn is display...
Page 204: Step 13
11-10 operator guide step 13 (from step 12) the system checkout option checks all of the resources (available in standalone mode only). Select and run the diagnostic tests on the resources you are having problems with or run system checkout to check all of the configured resources. Find the response...
Page 205: Step 15
Hardware problem determination 11-11 step 15 (from steps 12, 13) the diagnostic programs produced an srn for this problem. 1. Record the srn and any other numbers. 2. Report the srn to the service organization. 3. Stop. You have completed these procedures. Step 16 (from step 6) the system stopped wi...
Page 206: Step 18
11-12 operator guide step 18 (from step 17) the following steps analyze a failure to load the diagnostic programs from a disk, or a failure to determine whether the diagnostic programs are on a disk. 1. Set the power switch on the system unit to off. 2. Set the key mode switch to the service positio...
Page 207: Step 19
Hardware problem determination 11-13 7. Starting at the top of the following table, find your symptom; then perform the specific action. Symptom action the system stops with a blank operator panel display, and the words diagnostic operating instructions are displayed with no obvious problem on the c...
Page 208: Step 21
11-14 operator guide step 21 (from steps 2 and 7) an english-only version of diagnostics are provided on cd-rom disc. Do you want to run diagnostics from cd-rom disc? No if you have a problem, call for service, and report the problem. Yes go to step 17. Step 22 (from step 16) an english-only version...
Page 209
Systemguard test groups a-1 appendix a. Systemguard test groups systemguard test groups table the following diagram shows the various test groups and their associated tests. To modify the test list, the tests have to be selected in the xxyy format, where xx is the group number and yy is the test num...
Page 210
Operator guide a-2 group no test test no group 05 dcb and memory test group 01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 50 mm data lines test mm address lines test mm board dec. Test mm basic acc. Test mm components test ecc component test ecc mechanism test refresh mech. Test ecc data lines access. Test mm full tes...
Page 211
Systemguard test groups a-3 systemguard test group descriptions the following is a description of the different test groups and the tests available under them. All of these tests are performed automatically at power-on with default parameters. They can also be performed selectively (selection of tes...
Page 212
Operator guide a-4 bump, remote, and special asynchronus lines test these tests are meant to check the asynchronus lines of the standard i/o and the asynchronus lines controller in the super i/o. These tests contain sub-tests, which are described as follows. Each sub-test saves and restores the line...
Page 213
Systemguard test groups a-5 nvram test this test checks the accessibility of nvram bytes. It contains the following sub-tests: nvram data lines access test this test saves the first nvram byte. Then a read / write operation is done word by word. It restores the first nvram byte. Nvram address lines ...
Page 214
Operator guide a-6 dtr register test this test writes, reads and compares a 1 among 0 bits in dtr registers. Ctr register test this test writes, reads and compares a 1 among 0 bits in ctr registers. It saves and restores the ctr register value. Miscellaneous registers test this test checks accessibi...
Page 215
Systemguard test groups a-7 entry parameters parameters name definition possible values default value parameter 1 sub test # subtest number 0 or 1 0 = all tests linked parameter 2 proc # processor number 8 8 = bump check–sum test it checks the crc value for all present vpds; it checks the crc value ...
Page 216
Operator guide a-8 bpp external loopback test (bpp ext l–b test ) note: this test can only be performed by field or manufacturing people. This test checks the accessibility of the super–io chip. It saves and restores used registers. This test is not performed at power on. Entry parameters parameters...
Page 217
Systemguard test groups a-9 ionian-ssga registers test this test is performed by all the processors and it checks the accessibility from the processor to the ionian and ssga chips. Following h/w parts are checked. 1. Dcb asic 2. Ionian asic 3. Ssga asic the following sub-tests are included under the...
Page 218
Operator guide a-10 walking 0 address test this test detects the address lines which are cut. Super i/o and uart access test this test checks the accessibility of the super i/o chip from the processors. They don’t check the functional aspects of the super i/o chip (this is done by the bump directly)...
Page 219
Systemguard test groups a-11 initial values test this test checks the initial values of the ionian and ssga asics. It is only run at pon time. Ssga interrupt registers test this test writes and reads specific values from each of the interrupt registers. The values are then compared. Values are saved...
Page 220
Operator guide a-12 in memory and in cache. Then it reads the second mb from cache and first mb from the memory. Level 2 cache data test this test checks the validity of the static memory rams forming the level 2 cache. It calculates the memory address available and then validates the level 2 cache ...
Page 221
Systemguard test groups a-13 walking 1 data test this test basically identifies if any data lines are stuck at level 0 or to any other data line. This test writes “1s among 0s” pattern on the cache line. Then it is read and compared. Walking 0 data test this test isolates the open lines among the da...
Page 222
Operator guide a-14 2. Connection of high order address lines between cpu cards and system planar asics 3. Connection of high order address lines between system planar asics and memory chips. This test consists of two sub-tests. Words manipulated / used are not restored at the end of the test. This ...
Page 223
Systemguard test groups a-15 basic main memory test this test is performed by all the processors and it checks the capability to access the main memory in all kinds of data formats. This test applies to one main memory location and the words used during the test are not restored. This test partially...
Page 224
Operator guide a-16 main memory components test this test is performed by all the processors to check all the main memory locations. From the h/w point of view, this test checks the memory chips mounted on the main memory cards. This test can be launched in two modes, as follows: 1. Bit map elaborat...
Page 225
Systemguard test groups a-17 ecc data lines accessibility test this test checks the accessiblity for all the data lines to the ecc memory banks, through smc asics. The following h/w parts are checked by running this test. • dcb asics • smc asics • connection of data lines between cpu daughter boards...
Page 226
Operator guide a-18 ecc memory component test this test is identical to the main memory components test but it is applied to the ecc memory components. Error correction mechanism test this test checks the hardware mechanisms enabling the detection of and the correction of single bit errors when work...
Page 227
Systemguard test groups a-19 interrupt tests group these tests are performed by the bump as well as the processors. They are launched at power on and under control of off line test monitor. They collectively check the interrupt system. The following tests are available under this group. Bump to cpu ...
Page 228
Operator guide a-20 cpu multiprocessor test group these tests are launched at power-on and are also available under the control of the off line tests monitor. These tests check the multi-processor mechanisms, atomic instructions, cache coherency, main memory sharing, and multi-resources sharing. The...
Page 229
Systemguard test groups a-21 instruction. This is issued by processor 0 which is set to global copy back mode. Caching is inhibited for processor 1. Paradox detection: dcbst not from line owner here, processor 1 is set to local copy back mode. Memory coherency is enabled for processor 0. This test v...
Page 230
Operator guide a-22 main memory sharing test this test is launched by the bump and performed by all configured processors. It has a sub-test to check the capability of all the processors to access the main memory. The following h/w parts are checked during the process: 1. Dcb asics 2. Ionian asics 3...
Page 231: Default Parameter Values
Modifying systemguard parameters b-1 appendix b. Modifying systemguard parameters many systemguard parameters can be modified in several ways. Some can be modified using the systemguard stand-by menu, others using the systemguard maintenance menu, and others using the aix diag or mpcfg commands or d...
Page 232
B-2 operator guide flag, parameter and keyword default values name default value bump console power-on command string power service console power-on command string blank (not set) bump console power-on command flag enabled service console power-on command flag disabled remote authorization flag disa...
Page 233
Modifying systemguard parameters b-3 changing flags and parameters under aix service aids the service aids are recommended to change the flags. The service aids can be entered using the diag command or by booting diagnostics in service mode. They display or change flag values using 0 (zero) for disa...
Page 234
B-4 operator guide systemguard maintenance menu starting from the main maintenance menu: • enter 2 to enable the flag. Or • enter 3 to disable the flag. Aix diag command starting from the service aids selection menu: 1. Select the bump service aids option. 2. Select the display or change flags and c...
Page 235
Modifying systemguard parameters b-5 modifying dial-in phone numbers these parameters can be changed under systemguard using the maintenance menu, or under aix using the diag command. Systemguard maintenance menu starting from the main maintenance menu: 1. Enter 8 to set parameters. 2. Enter 3 for p...
Page 236
B-6 operator guide modifying the electronic mode switch from service line flag this flag can be changed under systemguard using the maintenance menu, or under aix using the diag command. Systemguard maintenance menu starting from the main maintenance menu: 1. Enter 8 to set parameters. 2. Enter 4 fo...
Page 237: Reloading The Flash Eeprom
Modifying systemguard parameters b-7 reloading the flash eeprom follow this procedure to load a new version of systemguard into the flash eeprom, which may be necessary when you install a new version of aix for example. Only system administrators should perform this procedure. Prerequisites if the s...
Page 238
B-8 operator guide.
Page 239: Configuration
Systemguard remote operation configuration c-1 appendix c. Systemguard remote operation configuration to use the remote operation capabilities of systemguard and also allow console mirroring, you must have flags, parameters and tty configurations properly enabled. Below, are tty0 and tty1 settings, ...
Page 240
Operator guide c-2 the configuration of the tty1 for the s2 port looks similar to the following: [top] [entry fields] tty tty1 tty type tty tty interface rs232 description asynchronous terminal status available location 00–00–s2–00 parent adapter sa1 port number [s2] enable login disable baud rate [...
Page 241
Systemguard remote operation configuration c-3 the modem parameters file name value should be set to the file name of your modem configuration file. The service line speed should be set to your modem and tty capabilities (9600 is recommended). • service flags: mpcfg –ds index name value 1 remote ser...
Page 242: Modem Configuration Files
Operator guide c-4 modem configuration files if you want to attach a modem to the s2 port to enable automatic problem reporting from systemguard or dial-in access from a remote location, you have to provide a configuration file for the modem are using. This file is also necessary to use the mirrorin...
Page 243
Systemguard remote operation configuration c-5 disconnect: send ”+++ath0\r” delay 2 send ”atq1v0e0\r” delay 2 done condin: send ”at&f1e0v0q0s0=2\r” expect ”0\r” or ”ok\r” send ”atq1&w0\r” # (there can be no reply) done condwait: send ”at&f1v0e0q0s0=2&w0\r” expect ”0\r” or ”ok\r” done waitcall: i...
Page 245: Appendix D: Supplies
Supplies d-1 appendix d: supplies this appendix contains a list of supplies and the part numbers needed to order them. Part number description 21f8593 8-mm cleaning tape cartridge 21f8595 8-mm data tape cartridge (5-pack) 21f8763 4-mm data tape cartridge (5-pack) 21f8758 4-mm dds iiii data tape cart...
Page 246: Ordering Keys
D-2 operator guide ordering keys for protection against unauthorized key duplication, the key mode switch is equipped with a medeco high-security lock. Keys for this lock are a factory restricted series, and duplicate keys are not available through normal commercial channels. The metal code tag supp...
Page 247: Key Reorder Form
Supplies d-3 key reorder form this form, when accompanied by the metal code tag supplied with the original keys, represents an authorized order for additional factory keys. Please indicate the quantity required and enclose a check or money order for the appropriate amount. Number of keys required___...
Page 248
D-4 operator guide.
Page 249
Operator panel display numbers e-1 appendix e. Operator panel display numbers this appendix contains lists of the various numbers and characters that may be displayed in the three-digit display. The numbers and characters are divided into two broad categories. The first grouping is those that track ...
Page 250
E-2 operator guide 185 a checkstop condition occurred during the pon. 186 system logic-generated checkstop (model 250 only). 187 graphics-generated checkstop (model 250). 195 pon logout completed. 888 pon did not start..
Page 251
Operator panel display numbers e-3 power-on self-test (post) indicators 20c l2 cache post error. (the display shows a solid 20c for 5 seconds.) 21c l2 cache is not detected. (the display shows a solid 21c for 2 seconds.) 22c attempting a normal mode ipl from fddi specified in nvram ipl device list. ...
Page 252
E-4 operator guide 230 attempting a normal mode ipl from adapter feature rom specified in ipl rom device list. 231 attempting a normal mode ipl from ethernet specified in ipl rom device list. 232 attempting a normal mode ipl from standard i/o planar-attached devices specified in rom default device l...
Page 253
Operator panel display numbers e-5 260 information is being displayed on the display console. 261 no supported local system display adapter was found. 262 keyboard not detected as being connected to the system’s keyboard port. 263 attempting a normal mode ipl from adapter feature rom specified in th...
Page 254
E-6 operator guide 312 flash utility rom ram post memory configuration error or no memory found (irrecoverable). 313 flash utility rom ram post failure (irrecoverable). 314 flash utility rom power status register failed (irrecoverable). 315 flash utility rom detected a low voltage condition. 318 fla...
Page 255
Operator panel display numbers e-7 529 the configuration manager is unable to update odm data (irrecoverable error). 530 the program savebase returned an error. 531 the configuration manager is unable to access the pdat object class (irrecoverable error). 532 there is not enough memory to continue (...
Page 256
E-8 operator guide 597 ocs software being configured. 598 ocs hosts being configured during system reboot. 599 configuring fddi data link control. 600 starting network boot portion of /sbin/rc.Boot 602 configuring network parent devices. 603 /usr/lib/methods/defsys, /usr/lib/methods/cfgsys, or /usr/...
Page 257
Operator panel display numbers e-9 722 unknown disk being identified or configured. 723 unknown cd-rom being identified or configured. 724 unknown tape drive being identified or configured. 725 unknown display adapter being identified or configured. 726 unknown input device being identified or confi...
Page 258
E-10 operator guide 854 3270 host connection program/6000 connection being identified or configured. 855 portmaster adapter/a being identified or configured. 857 fsla adapter being identified or configured. 858 5085/5086/5088 adapter being identified or configured. 859 fddi adapter being identified ...
Page 259
Operator panel display numbers e-11 925 three-button mouse being identified or configured. 926 5083 tablet being identified or configured. 927 5083 tablet being identified or configured. 928 standard speaker being identified or configured. 929 dials being identified or configured. 930 lighted progra...
Page 260
E-12 operator guide diagnostic load progress indicators the following dump progress indicators, or dump status codes, are part of a type 102 message. Note: when a lowercase c is listed, it displays in the lower half of the seven-segment character position. The leftmost position is blank on the follo...
Page 261: Power States
System power states f-1 appendix f. System power states the state of the system is dependant on the condition of four variable conditions that effect how the system ipls or shutsdown. The four conditions are: • the position of the power-on button this button has two positions. It can be pressed in t...
Page 262
F-2 operator guide if the command sbb is entered on the bump console, and the system key is in the normal position, the system goes to the sbb_ecmd state. • if the power-on button is pressed and changes from the on position to the off position, the system sets the was_shutdown status to false. • if ...
Page 263
System power states f-3 • if the power_fault status is false, the system attempts to power on. If the system then detects a power fault, the power_fault status is set to true. The system displays an operator panel lcd error message, and the system goes to the main_standby status. If no power fault i...
Page 264
F-4 operator guide if the system power does not turn on, the power-on button may be in the off position. Go to the system unit and press the power-on button (only press the button once), if the system power still does not turn on there may be an earlier fault condition. Remove main power from the sy...
Page 265
Glossary x-1 glossary: special terms used in systemguard bp (back plane). A panel located in the system unit and used to interconnect boards and devices. Bist (built in self-test). Tests performed during the standby phase of the ipl process. The bist phase comes ahead of the post phase. Bump (bring-...
Page 266
X-2 operator guide which can be removed without turning the power off to the entire system). Ros (read-only storage). Storage which does not support writing. Scsi (small computer system interface). A standard bus interface used to connect peripherals such as disk drives or tape drives. Sib (system i...
Page 267: Index
Index x-3 index symbols -48 v dc rack containing cpu enclosure, 6-1 description, 6-1 power distribution panel, 6-2 power distribution panel, 6-2 -48 v dc system unit, power cables, 6-3 numbers 1/4-inch tape cartridge compatibility, 2-23 efficiency, 2-24–2-29 environment considerations, operating ran...
Page 268
X-4 operator guide tape cartridge setting the write-protect tab, 2-26 types, 2-25 using, 5.0gb drive, 2-29 a about this book, xv ac rack, 4-1 cable path, 4-12 containing a pdb stopping immediately, 5-10 stopping under ordinary conditions, 5-9 containing a pdu stopping immediately, 5-8 stopping under...
Page 269
Index x-5 emergency eject hole, 2-15 headphone jack, 2-15 loading the disc, 2-16 status light, 2-15 unload button, 2-15 unloading, 2-17 volume control, 2-15 cd-rom drive, using, 2-13 change configuration or vital product data service aid, 9-9 circuit breakers 10 amp, 6-2 50 amp, 6-2 cleaning 1/4-tap...
Page 270
X-6 operator guide disk based diagnostic update service aid, 9-6 disk drive, location, 4-8 disk maintenance service aid, 9-6 disk media service aid, 9-7 disk to disk copy service aid, 9-6 diskette 1mb, 2-10 2mb, 2-10 3.5-inch, setting the write-protect tab, 2-11 handling, 2-9 loading and unloading, ...
Page 271
Index x-7 erasure, 4 mm data cartridge, 2-37 erasure, 8 mm data cartridge, 2-27 external device container, 4-2 f fastipl flag, 3-36 flash eeprom, reloading, b-7 flashing 888, multi-line display, 888 numbers, 8-12 front bezel, 1-2 g general information 4.0gb 4 mm tape drive, 2-34 5.0gb 8 mm tape driv...
Page 272
X-8 operator guide location code table, scsi and non-scsi devices, 4-19 location identification labels, 4-13 locations adapters, 1-3 bezel door, opened, 1-2 front view with bezel door closed, 1-2 operator panel, 2-2 parallel ports, 1-3 rs485 ports, 1-3 serial ports, 1-3 m maintenance password, 3-37 ...
Page 273
Index x-9 sbb_gateway, f-1 sbb_menu, f-2 sbb_pcmd, f-2 wait_power_on, f-2 wait_rebuilding, f-3 power states, system, f-1 power-on from bump console, f-3 power-on test indicators, e-1 power-on using the power-on button, f-4 powering on the ac rack containing a pdb, manual, 5-5 containing a pdu, manua...
Page 274
X-10 operator guide display and change diagnostic test list service aid, 9-10 display diagnostic run time options task, 9-2 display or change configuration or vital product data, 9-9 display or change key modes, 9-11 display previous diagnostic results, 9-11 display test patterns, 9-11 display/alter...
Page 275
Index x-11 set up console mirroring, 3-44 set up dial-out feature, 3-46 components, 3-2 console mirroring, 3-44 consoles, 3-4 dial-in phone numbers, modifying, b-5 dial-out authorization flag, modifying, b-4 dial-out phone numbers, modifying, b-5 electronic key, 3-4 electronic mode switch, modifying...
Page 276
X-12 operator guide 4 mm 4.0 gigabyte, 2-38 general information, 2-34 8 mm, 5.0gb drive, 2-29 tape drive, 4.0gb 4 mm, general information, 2-34 tape drive, 4gb 4 mm, recommendations, 2-35 tape drive, 5.0gb 8 mm, general information, 2-25 tasks, 9-1 display hardware error log, 9-12 display or change ...