- DL manuals
- Icom
- Transceiver
- D-STAR ID-4100A
- Advanced Manual
Icom D-STAR ID-4100A Advanced Manual
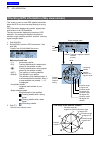
DUAL BAND TRANSCEIVER
ID-4100A
ID-4100E
This manual describes instructions for advanced features and
instructions.
See the Basic manual and the D-STAR guide that come with the
transceiver for precautions, installations, and basic operations.
ADVANCED MANUAL
Summary of D-STAR ID-4100A
Page 1
Dual band transceiver id-4100a id-4100e this manual describes instructions for advanced features and instructions. See the basic manual and the d-star guide that come with the transceiver for precautions, installations, and basic operations. Advanced manual index 13 updating the firmware 12 bluetoot...
Page 2
Introduction i thank you for choosing this icom product. This product is designed and built with icom’ s state of the art technology and craftsmanship. With proper care, this product should provide you with years of trouble-free operation. This product combines traditional analog technologies with t...
Page 3
Introduction ii table of contents by topic controller attaching/installing .................... Basic manual (sec. 1) front panel ................................ Basic manual (sec. 2) display ....................................... Basic manual (sec. 2) power key .................................. ...
Page 4
Introduction iii functions and features of adobe ® acrobat ® reader ® the following functions and features can be used with adobe ® acrobat ® reader ® . • keyword search click “find” (ctrl+f) or “advanced search” (shift+ctrl+f) in the edit menu to open the search screen. This is convenient when sear...
Page 5
Introduction iv controls used for text entry [dial] (rotate) selects [] cancels [ï] sets [mode] moves the cursor to the left [mw] moves the cursor to the right [rx →cs] clears [menu] cancels entering and editing text to change the character type 1. When not selecting text, or an entered text is sel...
Page 6
Introduction v entering and editing text (continued) d usable characters the usable characters and symbols, and the maximum characters differ, depending on the item. See the following list for details. L the usable characters and symbols for each character type are described at the bottom of the pag...
Page 7
Introduction vi entering and editing text (continued) d how to enter (example: entering “calling” as a memory name.) 1. Push [mw]. 2. Rotate [dial] to select “manage memory,” then push [ï]. •displays the manage memory screen. 3. Select “memory ch,” then push [ï]. 4. Select “all,” then push [ï]. •dis...
Page 8: Section
Section 1 memory operation 1-1 general description ................................................................ 1-2 d the number of the memory channel ............................... 1-2 d memory channel content ................................................ 1-2 manage memory screen descriptio...
Page 9: General Description
1 memory operation 1-2 the transceiver has a total of 1000 memory channels (100 channels in each of 26 memory banks, a ~ z) and two call channels (c0/c1) each for the 144 and 430 mhz bands. The memory mode is useful to quickly select often- used frequencies. Memory channels descriptions 000 ~ 999 (t...
Page 10
1 memory operation 1-3 manage memory memory ch call ch all bank a bank z a00 a99 the manage memory screen enables you to easily manage the memory or call channel content. • displays the memory or call channel content. • easy to assign to a bank, and displays the bank content. • easy to add, edit, co...
Page 11: Selecting A Memory Channel
1 memory operation 1-4 in the memory mode, you can select the memory channels by rotating [dial]. 1. Push [v/m] several times until you enter the memory mode. L pushing [v/m] toggles between the vfo and memory modes. 2. Rotate [dial]. •selects a memory channel. L blank channels are not selectable. S...
Page 12: Writing to A Memory Channel
1 memory operation 1-5 after setting a frequency in the vfo mode, you can write it to a selected channel or an automatically selected blank channel. Memory channels 002 to 999 are blank as the default. D writing to the selected channel example: writing 146.030 mhz into memory channel 18. 1. Push [v/...
Page 13
1 memory operation 1-6 d overwriting to the selected channel you can write a frequency into a pre-entered channel. Example: writing 147.030 mhz into memory channel “018.” 1. Push [v/m] several times until you enter the memory mode. 2. Rotate [dial] to select the channel 18. Destination channel 3. Pu...
Page 14
1 memory operation 1-7 you can copy the memory content to another memory channel. Example: copying memory channel “018” to memory channel “019”. Manage memory > memory ch 1. Push [menu]. 2. Rotate [dial] to select “manage memory,” then push [ï]. •displays the manage memory screen. L you can display ...
Page 15: Memory Bank Setting
1 memory operation 1-8 the transceiver has a total of 26 banks (a ~ z). Regular memory channels 0 ~ 999 can be assigned to any bank for easy memory management. Up to 100 channels can be assigned to a bank. D assigning a memory channel to a memory bank example: assigning memory channel “000” to the b...
Page 16
1 memory operation 1-9 d directly writing into a memory bank you can also write the memory content directly into a memory bank channel. This way is a short cut to creating a memory channel, and then assigning it to a bank. In that case, the transceiver automatically selects the lowest blank memory c...
Page 17
1 memory operation 1-10 you can enter an alphanumeric name for each memory, including call channels, and banks. Names can be a maximum of 16 characters. D entering a memory name manage memory > memory ch 1. Push [menu]. 2. Rotate [dial] to select “manage memory,” then push [ï]. •displays the manage ...
Page 18
1 memory operation 1-11 d entering a bank name manage memory > memory ch 1. Push [menu]. 2. Rotate [dial] to select “manage memory,” then push [ï]. •displays the manage memory screen. L you can display the manage memory screen by pushing [mw] on other than the dr screen. 3. Select “memory ch,” then ...
Page 19: Clearing A Memory Channel
1 memory operation 1-12 the transceiver has two memory name display types. 1. Push [v/m] several times until you enter the memory mode. 2. Push [quick]. 3. Rotate [dial] to select “display type,” then push [ï]. 4. Select the display type, then push [ï]. • freq: displays the large font sized frequenc...
Page 20: Section
Section 2 scan operation 2-1 scan ....................................................................................... 2-2 d about the scan function .................................................. 2-2 d vfo scan ........................................................................ 2-2 d mem...
Page 21: Scan
2 scan operation 2-2 scanning is a versatile function that can automatically search for signals. A scan makes it easier to locate stations to contact or listen to, or to skip unwanted channels or frequencies. D about the scan function in the vfo mode the frequencies that are set as “pskip” are skipp...
Page 22
2 scan operation 2-3 d [dial] operation during a scan • rotate [dial] to change the scan direction during a scan. • when the scan is paused, rotate [dial] to resume the scan. D squelch setting for a scan you can change the squelch level to suit your operating needs. Set the squelch level to open the...
Page 23: Vfo Mode Scan
2 scan operation 2-4 1. Push [v/m] several times until you enter the vfo mode. 2. Hold down [scan] for 1 second. •opens the scan type select window. L if you hold down [scan] for 3 seconds, the last selected scan starts. 3. Rotate [dial] to select a scan type, then push [ï]. •the scan starts. L the ...
Page 24
2 scan operation 2-5 d about a scan name when a scan name is assigned, the name is displayed in the scan type select window. (p. 2-4) l the scan name is not displayed during a scan. L see page 2-9 to enter the scan name. When the scan name is assigned scan name when the scan name is not assigned sca...
Page 25: Memory Scan
2 scan operation 2-6 memory scan note: two or more memory channels, which are not set as skip channels, must be entered to start a memory scan. 1. Push [v/m] several times until you enter the memory mode. 2. Hold down [scan] for 1 second. •opens the scan type select window. L if you hold down [scan]...
Page 26: Memory Bank Scan
2 scan operation 2-7 a memory bank scan searches through the memory channels in the selected bank. L two or more memory channels, which are not set as skip channels, must be entered to start a memory bank scan. (p. 1-8) 1. Push [v/m] several times until you enter the memory mode. 2. Push [quick]. 3....
Page 27
2 scan operation 2-8 setting and clearing the skip channel you can set or clear a skip channel setting. The channels that are set as a skip channel are skipped during a scan. 1. Push [v/m] several times until you enter the memory mode. 2. Rotate [dial] to select the memory channel. 3. Push [quick]. ...
Page 28: Entering Scan Edges
2 scan operation 2-9 you can enter the upper and lower frequency edges to the program scan edge ranges for program scans. Each program scan edge range has its own tuning step and the receive mode. The default setting is differ, depending on the transceiver version. You can enter a total of up to 25 ...
Page 29
2 scan operation 2-10 14. Select “mode,” then push [ï]. •displays the selectable mode. 15. Select the receive mode to be used during a scan. L when you select “---,” the receive mode set in the vfo mode is used during a scan. 16. Select “>,” then push [ï]. • the confirmation dialog “write?” is displ...
Page 30: Section
Section 3 priority watch 3-1 priority watch .......................................................................... 3-2 d starting the priority watch ............................................... 3-2 d canceling the priority watch ........................................... 3-2 vfo frequency an...
Page 31: Priority Watch
3 priority watch 3-2 while operating on a vfo frequency, using the dr function or while scanning, priority watch checks for signals on a selected frequency every 5 seconds. Priority watch d starting the priority watch to start the priority watch, select “on” or “bell,” as described below. 1. Push [q...
Page 32
3 priority watch 3-3 step 1. Set the vfo frequency (see basic manual section 3) 1. Push [v/m] several times until you enter the vfo mode. 2. Set the receive frequency and mode you want to monitor. Step 2. Set the priority channel to select a memory channel (p. 1-4) 1. Push [v/m] to enter the memory ...
Page 33
3 priority watch 3-4 step 1. Set the vfo frequency (see basic manual section 3) 1. Push [v/m] several times until you enter the vfo mode. 2. Set the receive frequency and mode you want to monitor. Step 2. Start a memory or bank scan to start a memory scan (p. 2-6) 1. Push [v/m] to enter the memory m...
Page 34
3 priority watch 3-5 vfo scan and a priority channel checks the selected priority channel every 5 seconds, during a vfo mode scan. Step 1. Set the priority channel to select a memory channel (p. 1-4) 1. Push [v/m] to enter the memory mode. 2. Rotate [dial] to select the memory channel you want to mo...
Page 35
3 priority watch 3-6 vfo scan and a memory/bank scan sequentially checks the memory or bank channels every 5 seconds during a vfo mode scan. A memory scan or bank scan can be selected. Step 1. Start a memory or bank scan to start a memory scan (p. 2-6) 1. Push [v/m] to enter the memory mode. 2. Hold...
Page 36
3 priority watch 3-7 step 1. Set the priority channel to set the vfo frequency (see basic manual section 3) 1. Push [v/m] several times until you enter the vfo mode. 2. Set the receive frequency and mode you want to monitor. To select a memory channel (p. 1-4) 1. Push [v/m] several times until you e...
Page 37
3 priority watch 3-8 checks the selected priority channel every 5 seconds, during a dr scan. Step 1. Set the priority channel to set the vfo frequency (see basic manual section 3) 1. Push [v/m] several times until you enter the vfo mode. 2. Set the receive frequency and mode you want to monitor. To ...
Page 38: Section
Section 4 d-star operation 4-1 “from” (access repeater) setting.......................................... 4-3 d using your transceiver’s repeater list .............................. 4-4 d using the dr scan .......................................................... 4-5 d using the near repeater searc...
Page 39
4-2 skip setting for the dr scan ................................................. 4-40 d individual skip setting .................................................... 4-40 d group skip setting ......................................................... 4-40 entering the repeater group name...............
Page 40
4 d-star operation 4-3 your access repeater must be set in “from” when you make a call on the dr screen. You have five ways to set the access repeater. Search for a repeater using the dr scan (p. 4-5) the normal dr scan searches for output repeater frequencies of nearby repeaters. The scan will stop...
Page 41
4 d-star operation 4-4 d using your transceiver’s repeater list when your access repeater is in your transceiver’s repeater list, you can select it from the list. By only selecting the repeater from the list, the call sign, frequency, duplex and offset frequency settings are automatically set for ea...
Page 42
4 d-star operation 4-5 d using the dr scan the dr scan scans frequencies to find a signal on a repeater or a simplex frequency. You can use two kinds of dr scans, normal scan and near repeater scan. Normal scan to quickly find a repeater, the normal scan skips repeaters that are not specified as an ...
Page 43
4 d-star operation 4-6 d using the near repeater search function step 1: receiving your own position from the gps satellite l when it is difficult to receive signals indoors, even if you are near a window, try going outdoors for better reception. Confirm the gps receiver is receiving your position. ...
Page 44
4 d-star operation 4-7 d using the tx history repeaters you transmitted on before are saved in the tx history. You can select a repeater from the tx history as your access repeater. The tx history saves up to 10 of the latest “from” (access) repeaters. Example: selecting the “hirano” repeater in jap...
Page 45
4 d-star operation 4-8 to make a local area cq call “local cq” setting (p. 4-9) set “cqcqcq” in “to” (destination). To make a call to a specific station “your call sign” setting (p. 4-10) select the station call sign in the your call sign memory. To make a gateway cq call “gateway cq” setting (p. 4-...
Page 46
4 d-star operation 4-9 d using the “local cq” (local area call) when “local cq” is selected on the to select screen, “cqcqcq” is set in “to.” example: making a local area call by accessing the “hirano” repeater. 1. Hold down [dr] for 1 second to display the dr screen. 2. Select “to,” then push [ï]. ...
Page 47
4 d-star operation 4-10 d using “your call sign” the “your call sign” memory saves the “ur” (destination) call signs. When you select an individual station call sign for the “to” (destination) setting using “your call sign,” you can make a gateway call. When you call the destination through a gatewa...
Page 48
4 d-star operation 4-11 d using the tx history the tx history saves the name and/or call sign of up to 20 “to” (destination) settings that were used when you made the calls. Note: until you make a call in the dv mode, you cannot select “to” (destination) from the tx history. Example: selecting the “...
Page 49
4 d-star operation 4-12 d directly entering (rpt) the destination repeater call sign can be directly entered. Example: directly entering the call sign “jp1yiu” 1. Hold down [dr] for 1 second to display the dr screen. 2. Select “to,” then push [ï]. •displays the to select screen. L on the dr screen, ...
Page 50: Connecting to A Reflector
4 d-star operation 4-13 d what is the reflector? A reflector is a special server connected to the internet and running a version of dplus software. If the dplus software is installed on your access repeater, it provides various functions including gateway and reflector linking capabilities (it is kn...
Page 51
4 d-star operation 4-14 using the tx history the tx history saves the up to 5 reflectors that your access repeater linked before. Example: selecting the “ref010bl” in the tx history. 1. Hold down [dr] for 1 second to display the dr screen. 2. Select “to,” then push [ï]. •displays the to select scree...
Page 52
4 d-star operation 4-15 connecting to a reflector (continued) d unlinking a reflector before trying to link to another reflector, be sure to unlink the current connected reflector. 1. Hold down [dr] for 1 second to display the dr screen. 2. Select “to,” then push [ï]. •displays the to select screen....
Page 53
4 d-star operation 4-16 d requesting repeater information when you send the repeater information command, an id message is sent back. 1. Hold down [dr] for 1 second to display the dr screen. 2. Select “to,” then push [ï]. •displays the to select screen. L on the dr screen, pushing [dr] toggles betwe...
Page 54: Message Operation
4 d-star operation 4-17 you can save up to 5 short messages in memory, to transmit in the dv mode. Each message can be up to 20 characters long. D entering a tx message example: entering “japan tom” into message memory number 1. My station > tx message 1. Push [menu]. 2. Rotate [dial] to select “my ...
Page 55
4 d-star operation 4-18 d deleting a tx message you can delete the entered tx message. Example: deleting the entered tx message “japan tom” from message memory number 1. My station > tx message 1. Push [menu]. 2. Rotate [dial] to select “my station,” then push [ï]. 3. Select “tx message,” then push ...
Page 56
4 d-star operation 4-19 1. Push [quick]. 2. Rotate [dial] to select “rx history,” then push [ï]. •displays the rx history screen. 3. Rotate [dial] to select an rx history memory. Information l • the rx history number, the caller’s name (or call sign), destination, rx message, rx date and time, “gw,”...
Page 57
4 d-star operation 4-20 , , displays the position data of the caller station. If a received signal has no data, then no position data is displayed. 6. Push [menu]. • returns to the standby screen. Jg3luk calling to jm1zlk on jp3yhh port a... Jg3luk calling to jm1zlk on jp3yhh port a... Jg3luk callin...
Page 58: Bk Mode Communication
4 d-star operation 4-21 how to use break-in? While using digital call sign squelch, the squelch never opens (no audio is heard) even if a call is received, unless your own call sign is specified. However, when a call including the “bk on” signal (break-in call) is received, the squelch will open and...
Page 59: Emr Communication
4 d-star operation 4-22 4-22 the emr (enhanced monitor request) communication function can be used in only the dv mode. Using the emr function, no call sign setting is necessary. All transceivers that receive an emr signal automatically open their squelch to receive the signal. When an emr signal is...
Page 60: Automatic Dv Detection
4 d-star operation 4-23 if you receive an fm signal while in the dv mode, the “dv” and “fm” icons alternately blink to indicate the received signal is fm. When the dv auto detect function is turned on, the transceiver automatically selects the fm mode to temporarily monitor the signal. (default: off...
Page 61: Automatic Reply Function
4 d-star operation 4-24 when a call addressed to your own call sign is received, the automatic reply function automatically replies with your call sign. (default: off) depending on the setting, a recorded message may be transmitted with the call sign. Note: the automatic reply function temporary set...
Page 62
4 d-star operation 4-25 4-25 d recording an auto reply message you can record the auto reply message and saved on a microsd card to reply to the call with your voice. Tip: be sure a microsd card is in the card slot. Voice memo > dv auto reply 1. Push [menu]. 2. Rotate [dial] to select “voice memo,” ...
Page 63
4 d-star operation 4-26 4-26 d auto position reply function when you receive a call addressed to your own call sign, but are in a situation that makes it difficult to operate the transceiver, this function automatically replies with your own call sign and transmits your position data. After receivin...
Page 64: Data Communication
4 d-star operation 4-27 in addition to digital voice communication, you can send and receive data. And you can use the dv fast data function for data communication. The dv fast data function uses the data and the audio frames to send data approximately 3.5 times faster than the normal speed. So, no ...
Page 65
4 d-star operation 4-28 d dv fast data function to send data using the dv fast data function, do the following. L the dv fast data communication can be made by only the following icom transceivers: id-4100a/e, id-5100a/e*, or id-51a/e (plus, plus2, 50th anniversary model). (as of april 2017) * usabl...
Page 66: Digital Squelch Functions
4 d-star operation 4-29 the digital squelch opens only when you receive a signal addressed to your own call sign, or a signal that includes a matching digital code. You can silently wait for calls from others. You can independently set the digital squelch function in the vfo mode, memory mode, call ...
Page 67
4 d-star operation 4-30 d the digital code squelch setting 1. Push [quick]. 2. Rotate [dial] to select “dsql,” then push [ï]. 3. Select “csqls” or “csql,” then push [ï]. •csqls: turns on the digital code squelch function with the pocket beep. L “csqls” is displayed. •csql: turns on the digital code ...
Page 68: Viewing Call Signs
4 d-star operation 4-31 while in the dv mode, you can display the call sign screen. 1. Push [menu]. 2. Rotate [dial] to select “call sign,” then push [ï]. •displays the call sign screen. 3. Push [menu]. • returns to the standby screen. Destination call sign access repeater call sign gateway repeater...
Page 69: Repeater List
4 d-star operation 4-32 you can save repeater information for quick and simple communication in up to 1500 repeater memory channels (repeater list) in up to 50 groups. Entering data into the repeater list is required to use the dr function. You can enter four types of frequencies into the repeater l...
Page 70
4 d-star operation 4-33 d required items for the communication cases repeater list contents used as an access repeater used as a destination repeater used for dv simplex used as an fm repeater used for fm simplex type dv repeater dv repeater dv simplex fm repeater fm simplex name sub name call sign ...
Page 71
4 d-star operation 4-34 d entering new information into the repeater list step 1. Selecting the repeater group dv memory > repeater list 1. Push [menu]. 2. Rotate [dial] to select “dv memory,” then push [ï]. 3. Select “repeater list,” then push [ï]. 4. Select a repeater group to add a repeater to, t...
Page 72
4 d-star operation 4-35 step 7. Changing the repeater group l the repeater group that is selected in ‘step 1. Selecting the repeater group’ is displayed. You can skip this setting and go to the next item. To change the group, follow the steps, described below. 1. Select “group,” then push [ï]. •ente...
Page 73
4 d-star operation 4-36 step 15. Selecting the position data accuracy level l when the near repeater search function is not used, or the distance between your position and a repeater is not displayed, select “off,” and go to ‘step 18. Setting the utc offset.’ 1. Select “position,” then push [ï]. 2. ...
Page 74: Editing A Repeater List
4 d-star operation 4-37 this function edits a repeater’s data. This is useful when already-entered data is incorrect, has changed, or some data needs to be added to the list. Dv memory > repeater list 1. Push [menu]. 2. Rotate [dial] to select “dv memory,” then push [ï]. 3. Select “repeater list,” t...
Page 75
4 d-star operation 4-38 you can move the entered repeaters to rearrange their display order in the selected repeater group. The entered repeater cannot be moved out of their assigned repeater group. Example: moving "hamacho" above “inage.” dv memory > repeater list 1. Push [menu]. 2. Rotate [dial] t...
Page 76
4 d-star operation 4-39 this section describes how to add new repeater information to the repeater list using the rx history. 1. Push [quick]. 2. Rotate [dial] to select “rx history,” then push [ï]. • displays the rx history screen. 3. Rotate [dial] to display the repeater you want to add to the rep...
Page 77: Skip Setting For The Dr Scan
4 d-star operation 4-40 you can set repeaters as scan skip repeaters. The selected repeaters are skipped for faster scanning. You can set the skip setting to all repeaters in the selected repeater group, or to individual repeaters. L when a repeater is specified as a skip repeater, its “use (from)” ...
Page 78
4 d-star operation 4-41 dv memory > repeater list > repeater group 1. Push [menu]. 2. Rotate [dial] to select “dv memory,” then push [ï]. 3. Select “repeater list,” then push [ï]. 4. Select a repeater group that you edit the name. (example: 22:) 5. Push [quick]. 6. Select “edit name,” then push [ï]....
Page 79: Repeater Detail Screen
4 d-star operation 4-42 according to the content, such as position data, utc offset, and so on, the distance between your position and the repeater or the repeater time can be displayed on the repeater detail screen. The detail screen can also be entered from the from select screen. Example: display...
Page 80
4 d-star operation 4-43 you can manually enter a your (destination) call sign. When a your (destination) call sign is set to “to,” you can make a call to a station, even if you do not know where the station is currently located. Up to 300 your call signs can be entered. Example: entering “station 1/...
Page 81
4 d-star operation 4-44 you can delete your (destination) call signs from the your call sign memory. Dv memory > your call sign 1. Push [menu]. 2. Rotate [dial] to select “dv memory,” then push [ï]. 3. Select “your call sign,” then push [ï]. 4. Push [quick]. 5. Select “delete,” then push [ï]. •the c...
Page 82
4 d-star operation 4-45 you can move your call signs to rearrange their display order. It is easy to find stations that you often communicate with if the stations are moved to the top of the list. Example: moving “station 1” above “station 3.” dv memory > your call sign 1. Push [menu]. 2. Rotate [di...
Page 83: Your Setting Is Correct?
4 d-star operation 4-46 if you make a local area call with a gateway setting still selected in “to,” the destination repeater will be busy while you transmit. So the stations that use that repeater as their access repeater cannot access it, as shown below. Be sure to set cqcqcq in “to” when you inte...
Page 84: Section
5-1 section 5 gps operation 5-1 gps operation ........................................................................ 5-2 d confirming the gps signal receiving .............................. 5-2 d when a received signal contains position data ............... 5-2 checking your location ................
Page 85: Gps Operation
5 gps operation 5-2 connection gps operation note: the built-in gps receiver cannot calculate its position data if it cannot receive signals from the gps satellites. The transceiver has a built-in internal gps receiver. The gps receiver’s position data can be received in any mode. Also, a nmea forma...
Page 86: Checking Your Location
5 gps operation 5-3 you can check your current location. This section is described using received position data. D displaying position data 1. Push [quick]. 2. Select “gps position,” then push [ï]. •displays the gps position screen. 3. Rotate [dial] to select the screen. • my screen (my), the receiv...
Page 87
5 gps operation 5-4 gps position data has two transmit modes, d-prs and nmea. Moreover, with the d-prs mode data, five position formats, position (mobile station/base station), object, item and weather, are selectable. Nmea d-prs position (mobile) item position (base) object weather •d-prs: d-prs is...
Page 88
5 gps operation 5-5 d displayed items depending on the caller’s transmit mode or transmit format, the displayed items differ. D-prs position object item nmea mobile base data extension: off data extension: course/speed data extension: power/height/gain/directivity data extension: off data extension:...
Page 89
5 gps operation 5-6 d tx format: d-prs position (mobile) displays the following items when the caller’s tx format is d-prs position (mobile). Compass displays the caller’s direction from your location latitude displays the caller’s latitude longitude displays the caller’s longitude gl displays the g...
Page 90
5 gps operation 5-7 d tx format: d-prs object displays the following items when the caller’s tx format is d-prs object. Compass displays the object’s direction from your location latitude displays the object’s latitude longitude displays the object’s longitude gl displays the grid locator based on t...
Page 91
5 gps operation 5-8 d tx format: d-prs weather displays the following items when the caller’s tx format is d-prs weather. Compass displays the caller’s direction from your location latitude displays the caller’s latitude longitude displays the caller’s longitude gl displays the grid locator based on...
Page 92: Pm74So
5 gps operation 5-9 d changing the gps memory or alarm you can change the gps memory or gps alarm in the gps position screen. 1. Push [quick]. 2. Rotate [dial] to select “gps position,” then push [ï]. •displays the gps position screen. 3. Rotate [dial] to display the mem screen or alm screen. 4. Pus...
Page 93
5 gps operation 5-10 d changing the compass direction you can change the compass direction between heading up, north up, and south up. Checking your location (continued) heading up north up south up 1. Push [quick]. 2. Rotate [dial] to select “gps position,” then push [ï]. •displays the gps position...
Page 94
5 gps operation 5-11 this screen is used to view gps satellite information when the gps icon does not stop blinking for a long time. Gps information displays the quantity, signal power and location of the gps satellites. The sky view screen displays the location of gps satellites. The screen also di...
Page 95
5 gps operation 5-12 d type of position data gps position data has two types of tx mode, d-prs and nmea. Moreover, in the d-prs mode, you can select a tx format from position (mobile station/base station), object, item and weather. Type of position data for transmission nmea (p. 5-25) d-prs (p. 5-13...
Page 96: Transmitting D-Prs Data
5 gps operation 5-13 when d-prs is selected as gps tx mode, you can transmit d-prs data. When operating in the d-prs mode, the following codes are transmitted to the pc. D-prs code is based on aprs ® code. (aprs ® : automatic packet reporting system). D d-prs d-prs is a mode that simultaneously send...
Page 97
5 gps operation 5-14 d displayed items depending on the tx format, the setting items and displayed order of the items differ. D-prs position object item mobile base data extension: off data extension: course/speed data extension: power/height/gain/directivity data extension: off data extension: cour...
Page 98
5 gps operation 5-15 d setting d-prs position (mobile/base) set to transmit as a d-prs position. 1. Setting the gps tx mode to d-prs gps > gps tx mode 1. Push [menu]. 2. Rotate [dial] to select “gps,” then push [ï]. 3. Select “gps tx mode,” then push [ï]. 4. Select “d-prs,” then push [ï]. Tip: if th...
Page 99
5 gps operation 5-16 d setting d-prs position (mobile/base) (continued) 6. Entering a comment enter a comment, and transmit it with the d-prs position data. The number of characters you can enter differs, depending on the data extension and altitude settings. (see to the right.) data extension altit...
Page 100
5 gps operation 5-17 d setting d-prs position (mobile/base) (continued) 12. Setting the antenna gain l this item is displayed when “9. Setting data extension” is set to “power/height/gain/directivity.” select the gain of the base station’s antenna, to transmit along with the position data. 1. Select...
Page 101
5 gps operation 5-18 d setting d-prs object/item (continued) 5. Setting data type set the object or item’s status. 1. Select “data type,” then push [ï]. 2. Select the option, then push [ï]. (for an object) •live object: the object is valid. •killed object: the object is invalid. (for an item) •live ...
Page 102
5 gps operation 5-19 d setting d-prs object/item 8. Setting the position (continued) entering the altitude 14. Select “altitude,” then push [ï]. •displays the altitude screen. 15. Rotate [dial] to select between plus and minus. 16. Push [mw] to move the cursor forwards, or push [mode] to move the cu...
Page 103
5 gps operation 5-20 d setting d-prs object/item (continued) 15. Setting the antenna directivity l this item is displayed when “9. Setting data extension” is set to “power/height/gain/directivity.” select the direction the base object or item’s antenna was pointing. 1. Select “directivity,” then pus...
Page 104
5 gps operation 5-21 d setting d-prs weather set to transmit as a d-prs weather station. 1. Setting the gps tx mode to d-prs gps > gps tx mode 1. Push [menu]. 2. Rotate [dial] to select “gps,” then push [ï]. •displays the gps screen. 3. Select “gps tx mode,” then push [ï]. 4. Select “d-prs,” then pu...
Page 105
5 gps operation 5-22 d setting d-prs weather (continued) 7. Entering a comment enter a comment to transmit as a d-prs weather station. 1. Select “comment,” then push [ï]. 2. Push [quick]. 3. Select “edit,” then push [ï]. •displays the “comment” screen. 4. Enter a comment of up to 43 characters. Sele...
Page 106
5 gps operation 5-23 d weather station transmission when you transmit as a weather station, you should set the weather station’s settings, and input the weather data to the [data] terminal. You can input the weather data from a third party’s weather device by converting it to the aprs weather format...
Page 107
5 gps operation 5-24 d-prs data content d-prs data content are shown below. Dposition (mobile) (e.G.) (e.G.) dposition (base) (e.G.) dobject (e.G.) ditem (e.G.) dweather q w e r o i u o !1 !3 !4 !0 !0 ja3yua-a>api410,dstar*:/002338h3437.38n/13534.29e>090/002/a=000012id-4100 op.Satoh q w e r o i i u ...
Page 108: Transmitting Nmea Data
5 gps operation 5-25 set a gps sentence to transmit gps data in the dv mode. D setting the gps data sentence gps > gps tx mode > nmea > gps sentence 1. Push [menu]. 2. Rotate [dial] to select “gps,” then push [ï]. 3. Select “gps tx mode,” then push [ï]. 4. Select “nmea,” then push [ï]. 5. Select “gp...
Page 109
5 gps operation 5-26 d entering a gps message enter a gps message to be transmitted with the position data. Example: entering “japan tom” gps > gps tx mode > nmea > gps message 1. Push [menu]. 2. Rotate [dial] to select “gps,” then push [ï]. •displays the gps screen. 3. Select “gps tx mode,” then pu...
Page 110: Adding Or Editing Gps Memory
5 gps operation 5-27 d add a gps memory example: add "home" into (no group) 1. Adding gps memory and entering the edit mode gps > gps memory 1. Push [menu]. 2. Rotate [dial] to select “gps,” then push [ï]. 3. Select “gps memory,” then push [ï]. • the previously added gps memories are displayed on th...
Page 111
5 gps operation 5-28 d add a gps memory (continued) 3. Entering the gps memory date 1. Select “date,” then push [ï]. •enters the date entry mode. 2. Push [mw] to move the cursor forwards, or push [mode] to move the cursor backwards to select a digit to enter. 3. Rotate [dial] to enter the date. • ra...
Page 112
5 gps operation 5-29 to cancel the entered data: to cancel the entered data, push [] to display the confirmation dialog, as shown below. Select to cancel entering and the display returns to the gps memory group screen. To view the entered content: to view the entered content, select the gps memory ...
Page 113
5 gps operation 5-30 d entering the gps memory group name you can enter a name for each gps memory group. Gps > gps memory 1. Push [menu]. 2. Rotate [dial] to select “gps,” then push [ï]. 3. Select “gps memory,” then push [ï]. •displays the gps memory screen. 4. Select the group that the name to be ...
Page 114
5 gps operation 5-31 you can move the entered gps memories to rearrange their display order in the selected gps memory group. In order to move the gps memory out of their assigned memory group, edit and move, and then save. Gps > gps memory 1. Push [menu]. 2. Rotate [dial] to select “gps,” then push...
Page 115
5 gps operation 5-32 d setting the gps alarm a gps alarm can sound when a target location comes into the alarm area. This function can be set to the caller station, all gps memory channels, a specified memory group or a specified memory channel. 0.25’ 0.25’ 0.25’ 0.25’ n your location your location ...
Page 116
5 gps operation 5-33 d setting the gps alarm (continued) example: set the alarm setting to rx (rx/memory). Gps > gps alarm 1. Push [menu]. 2. Rotate [dial] to select “gps,” then push [ï]. 3. Select “gps alarm,” then push [ï]. •displays the gps alarm screen. 4. Select “alarm select,” then push [ï]. 5...
Page 117: Gps Logger Function
5 gps operation 5-34 the gps logger function enables you to save the position data from a gps receiver into a microsd card as a log. The gps logger saves latitude, longitude, altitude, positioning state, course, speed and date. If you use this gps logger while driving, you can check your driving his...
Page 118
5 gps operation 5-35 d setting the gps record sentence select the gps sentence for the gps logger function. The function records only the selected sentence, so the data volume will be reduced. See the contents table shown below before selecting. Gps > gps logger > record sentence 1. Push [menu]. 2. ...
Page 119
5 gps operation 5-36 d viewing the log data on a pc map if you want to display the your log data, copy the log file to your pc. L windows 10 is used for these instructions. 1. Turn off the transceiver, then remove the microsd card from the transceiver. L to removing the card while the transceiver po...
Page 120
5 gps operation 5-37 q gga protocol header ( $gpgga) w utc of position (16:12:29.487) e latitude (north 37º 23.2475′) n=north, s=south r longitude (west 121º 58.3416′) e=east, w=west t gps quality indicator (1) 0=fix not available or invalid, 1=sps mode 2=dgps (sps), 6=estimated (dead reckoning) mod...
Page 121
5 gps operation 5-38 in the dv mode, this function automatically transmits the gps receiver’s current position data at a selected interval, and should only be used in the simplex mode. L your own call sign must be entered to activate the gps automatic transmission. L when “gps tx mode” is set to “nm...
Page 122: Section
Section 6 using a microsd card 6-1 saving data onto a microsd card ........................................... 6-2 saving the setting data onto a microsd card ......................... 6-3 saving with a different file name ............................................. 6-4 loading the saved data file...
Page 123
6 using a microsd card 6-2 you can save the following data onto the card: • data settings of the transceiver memory channel contents, repeater lists, your (ur) memory and gps memories that are saved in the transceiver. • communication contents communication audio. • communication log the communicati...
Page 124
6 using a microsd card 6-3 you can save the memory channels, menu screen item settings, and repeater lists on a microsd card. Saving data settings on a card enables you to easily restore the transceiver to its previous settings, even if you perform an all reset. You can save the setting data as a ne...
Page 125
6 using a microsd card 6-4 sd card > save setting 1. Push [menu]. 2. Rotate [dial] to select “sd card,” then push [ï]. 3. Select “save setting,” then push [ï]. 4. Select “>,” then push [ï]. •displays the file name screen. 5. Push [rx→cs]. •deletes the entered characters. L if [rx→cs] is continuously...
Page 126
6 using a microsd card 6-5 memory channels, menu screen item settings, and repeater lists can be copied to the transceiver. This function is convenient when copying saved data, such as memory channels, or repeater lists, to another id-4100a/e, and then operating with the same data. Tip: saving the c...
Page 127
6 using a microsd card 6-6 a backup file enables easy restoration, even if the data on the microsd card is accidentally deleted. L if your pc does not have a microsd card slot, connect a memory card reader (user supplied) to use the microsd card. D about the microsd card’s folder contents the folder...
Page 128
6 using a microsd card 6-7 d making a backup file on your pc windows ® 10 is used for these instructions. 1. Insert the microsd card into the microsd card drive or a memory card reader* on your pc. *user supplied. 2. Click the “open folder to view files” option to access the card. Click •displays th...
Page 129
6 using a microsd card 6-8 please read this section before importing or exporting a comma separated values (csv) format file from the microsd card. You can import or export the following data: • your call sign memory • repeater list • gps memory importing or exporting a csv format file d importing n...
Page 130
6 using a microsd card 6-9 d exporting you can export your call sign memory, repeater list and gps memory. To save as a new file example: exporting the your call sign memory. Sd card > import/export > export 1. Push [menu]. 2. Rotate [dial] to select “sd card,” then push [ï]. 3. Select “import/expor...
Page 131: Section
Section 7 voice memory 7-1 recording a qso audio ......................................................... 7-2 playing back the recorded audio ............................................ 7-3 changing the qso recorder settings ..................................... 7-4 deleting the audio folder/file ...
Page 132: Recording A Qso Audio
7 voice memory 7-2 to stop recording 1. Push [quick]. 2. Rotate [dial] to select “>,” then push [ï]. Tip: when the ptt automatic recording function is set to on, the recording automatically starts when “>” is selected. In that case, recording continues even while no signal is received. See page 7-4 ...
Page 133
7 voice memory 7-3 voice memo > qso recorder > play files 1. Push [menu]. 2. Rotate [dial] to select “voice memo,” then push [ï]. 3. Select “qso recorder,” then push [ï]. 4. Select “play files,” then push [ï]. •displays the recorded file folders. 5. Select the folder that contains the audio file to ...
Page 134
7 voice memory 7-4 you can change the recording setting on the menu screen. See page 9-21 for details. Record only the received audio voice memo > qso recorder > recorder set > rec mode l the default setting is “tx&rx” (both transmitted and received audio are recorded). Continue to record even while...
Page 135
7 voice memory 7-5 note: a deleted audio file can not be recovered. D delete an audio folder note: all audio files in the folder are deleted. Voice memo > qso recorder > play files 1. Push [menu]. 2. Rotate [dial] to select “voice memo,” then push [ï]. 3. Select “qso recorder,” then push [ï]. 4. Sel...
Page 136: Viewing The File Information
7 voice memory 7-6 tip: to view the folder information push [quick] in step 5, and then select “folder information” to view the folder information. Created date folder name total files (total size) file information examples l depending on the recording status, some data may not be displayed. L the f...
Page 137
7 voice memory 7-7 you can check the microsd card memory capacity and available recording time. Sd card > sd card info 1. Push [menu]. 2. Rotate [dial] to select “sd card,” then push [ï]. 3. Select “sd card info,” then push [ï]. • displays the remaining capacity and available recording time. 4. Push...
Page 138
7 voice memory 7-8 you can play back the recorded qso audio on your pc. L operation data is not displayed. Windows 10 is used for these instructions. Example: playing back the audio file on the microsd card on the pc, through the memory card reader (user supplied). 1. Insert the microsd card into a ...
Page 139: Section
Section 8 repeater and duplex operations 8-1 fm repeater operation........................................................... 8-2 d checking the repeater input signal ................................. 8-3 d 1750 hz tone burst ......................................................... 8-3 duplex opera...
Page 140: Fm Repeater Operation
8 repeater and duplex operations 8-2 a repeater receives signals and on one frequency, and then retransmits them on a different frequency. When using a repeater, the transmit frequency is shifted from the receive frequency by a frequency offset. A repeater can be accessed using the duplex function b...
Page 141
8 repeater and duplex operations 8-3 d checking the repeater input signal you can check whether another station’s transmit signal can be received directly or not, by listening to the repeater input frequency. 1. Push [moni] to listen on the repeater input frequency. • while monitoring, “busy” blinks...
Page 142: Duplex Operation
8 repeater and duplex operations 8-4 the duplex operation shifts the transmit frequency up or down from the receive frequency by an offset amount. D setting the frequency offset note: the frequency offset cannot be changed when using the dr function. Dup/tone... > offset freq 1. Push [menu]. 2. Rota...
Page 143: Off Band Indication
8 repeater and duplex operations 8-5 if the transmit frequency is out of the amateur band, the off band indication, “off band,” is displayed on the display when [ptt] is pushed. Check the frequency offset or duplex direction in this case. (p. 8-2) off band indication displayed when the operating fre...
Page 144: Section
9-1 section 9 menu screen selecting a menu item ............................................................ 9-2 d menu screen operation ................................................. 9-2 menu items and default settings ............................................ 9-3 dup/tone items ................
Page 145: Selecting A Menu Item
9 menu screen 9-2 you can use the menu screen to set infrequently changed values or function settings. In addition to this page, see pages 9-3 through 9-15 for details of each item’s options and their default value. Selecting a menu item tip: the menu screen is constructed in a tree structure. You m...
Page 146
9 menu screen 9-3 note: the default settings shown in bold letters below are for the usa version. The default settings may differ, depending on your transceiver version. Dup/tone... Settings to access repeaters. Offset freq 0.000~ 0.600.00* 1 ~59.995 mhz sets the frequency offset for duplex (repeate...
Page 147
9 menu screen 9-4 voice memo set the tx/rx voice recording options. Qso recorder set qso recorder options. >* starts recording the received signal audio. L while recording, > is displayed. Play files* plays the recorded audio. Recorder set rec mode tx&rx or rx only selects whether or not to record t...
Page 148
9 menu screen 9-5 gps tx mode set the gps tx mode. Off turns off the gps tx function. D-prs unproto address api410,dstar* enters an unproto address, or keeps the default. Tx format position symbol 1:car, 2:van, 3:truck, or 4:house qth (vhf) selects a d-prs symbol to transmit. Ssid - - -, (-0), -1~-1...
Page 149
9 menu screen 9-6 directivity omni, 45°ne, 90°e, 135°se, 180°s, 225°sw, 270°w, 315°nw, or 360°n selects an object’s antenna directivity information to transmit. Ssid - - -, (-0), -1~-15, or -a~-z selects the aprs ® call sign ssid for the object. Time stamp dhm or hms selects a format to transmit the...
Page 150
9 menu screen 9-7 gps alarm alarm select off, rx, group, or memory select the target for the gps alarm function. Alarm area (group) 0.08’ ~ 0.25’ ~ 59.99’* 1 enter the gps alarm active range. Alarm area (rx/memory) limited, extended, or both select the gps alarm active range. Gps logger* 2 gps logge...
Page 151
9 menu screen 9-8 tx bass cut, normal, or boost sets the dv mode transmit audio bass filter level to cut, normal or boost. Tx treble cut, normal, or boost sets the dv mode transmit audio treble filter level to cut, normal or boost. Auto reply off, on, voice, or position selects the automatic reply f...
Page 152
9 menu screen 9-9 speech sets the speech functions. Rx call sign speech off, on (kerchunk), or on (all) selects the rx call sign speech function option while on, or turns it off. Rx>cs speech off or on turns the rx>cs speech function on or off. Dial speech off or on turn the dial speech function on ...
Page 153
9 menu screen 9-10 remote mic key selects the key function for [f-1] or [f-2] on the supplied remote-control microphone. During rx/standby [f-1]:mode [f-2]:monitor selects the key function to be used while receiving or in the standby mode. During tx [f-1]:t-call [f-2]:--- selects the key function to...
Page 154
9 menu screen 9-11 backlight night time setting night time setting off or on selects whether or not to turn down the backlight brightness for nighttime operation. Brightness 1~ 2~4 selects the backlight brightness level for nighttime operation. Night time start 0:00~ 18:00~23:59 sets the start time ...
Page 155
9 menu screen 9-12 menu items and default settings (continued) display unit latitude/longitude ddd°mm.Mm' or ddd°mm'ss" selects position format to display the position. Altitude/distance m or ft/ml* selects the units to display the distance and altitude. Speed km/h, mph*, or knots selects the units ...
Page 156
9 menu screen 9-13 menu items and default settings (continued) sd card* 1 sets the microsd card options. Load setting file selection all, except my station, or repeater list only loads the settings file to the transceiver. Save setting > saves the settings as a new file. File selection saves the set...
Page 157
9 menu screen 9-14 menu items and default settings (continued) note: the default settings shown in bold letters below are for the usa version. The default settings may differ, depending on your transceiver version. Headset set af output headset only or headset & speaker selects the af output option ...
Page 158
9 menu screen 9-15 menu items and default settings (continued) note: the default settings shown in bold letters below are for the usa version. The default settings may differ, depending on your transceiver version. Others set other options. Information voltage displays the power source voltage. Vers...
Page 159: Dup/tone Items
9 menu screen 9-16 offset frequency (default: 0.600.00*) dup/tone... > offset freq set the frequency offset for duplex (repeater) operation to between 0.000.00 and 59.99500 mhz. L the duplex shift direction (dup–/dup+) is set in the duplex setting window. L when the dr function is on, editing is res...
Page 160: Manage Memory Items
9 menu screen 9-17 memory ch manage memory > memory ch you can delete, copy and edit your memory data. Up to 1000 memory channels can be saved. Also, 26 memory banks, a to z, can be used to save groups of operating channels, and so on. Up to 100 channels can be assigned to a bank. • all: all memory ...
Page 161: Scan Items
9 menu screen 9-18 pause timer (default: 10sec) scan > pause timer select the scan pause time. When receiving a signal, the scan pauses for the scan pause timer time. • 2sec ~ 20sec : when a signal is received, the scan pauses for 2 ~ 20 seconds (set in 2 second steps). • hold : the scan pauses on a...
Page 162
9 menu screen 9-19 program link (default: refer to the table below) scan > program link this item sets the link function for two or more program scan edge ranges to be sequentially scanned during the program link scan. The link function scans all frequencies in the scan range. Default settings of th...
Page 163
9 menu screen 9-20 editing a program scan link name 1. Select a program link number between 0 and 9, then push [quick]. 2. Select “edit name,” then push [ï]. •enters the program link name edit mode. 3. Enter a program scan link name of up to 16 characters. ( example: japan) selectable characters and...
Page 164
9 menu screen 9-21 > voice memo > qso recorder > > after selecting “>,” push [ï] to start voice recording. •“recording started.” is displayed. Information l •be sure a microsd card is in the card slot. • while recording, “>” is displayed on the qso recorder screen. To stop recording, select “ stop>>...
Page 165
9 menu screen 9-22 ptt auto rec (default: off) voice memo > qso recorder > recorder set > ptt auto rec turn the ptt automatic recording function on or off. L transmitting from a bluetooth vox device, or sending a ci-v command also starts recording. L when "rec mode" is set to "rx only," the transmit...
Page 166: Voice Tx Items
9 menu screen 9-23 record voice tx > record up to one minute of audio can be recorded onto a microsd card for voice transmission. (p. 10-5) four independent voice audios can be memorized into each memory t1 ~ t4. While recording a qso voice audio, this function is disabled. Tip: be sure a microsd ca...
Page 167: Gps Items
9 menu screen 9-24 gps select (default: internal gps) gps > gps set > gps select select either the internal or external gps receiver that the transceiver receives its position data from, or to manually enter your current position data. • off: a gps receiver is not used. • internal gps: position data...
Page 168
9 menu screen 9-25 symbol list gps items (continued) previous view.
Page 169
9 menu screen 9-26 ssid (default: ---) gps > gps tx mode > d-prs > tx format > position > ssid select an ssid based on aprs ® to add to your call sign, to show your operating style to other stations. The addition methods of the ssid may differ, depending on whether the call sign includes a space or ...
Page 170
9 menu screen 9-27 altitude (default: off) gps > gps tx mode > d-prs > tx format > position > altitude select whether or not to transmit altitude data along with the position data in the d-prs mode. • off: no altitude data is transmitted. • on: transmits altitude data along with the position data. T...
Page 171
9 menu screen 9-28 object name gps > gps tx mode > d-prs > tx format > object > object name enter an object name of up to 9 characters. Data type (default: live object) gps > gps tx mode > d-prs > tx format > object > data type set the object’s status. •live object: the object is valid. •killed obje...
Page 172
9 menu screen 9-29 position gps > gps tx mode > d-prs > tx format > object > position displays the position information of the object. Push [quick] to open the window shown below. Tip: when you select “capture from gps” or “set from gps memory,” you can capture the position from the gps, or set the ...
Page 173
9 menu screen 9-30 power (default: 0w) gps > gps tx mode > d-prs > tx format > object > power select the tx power level of the object, to transmit along with the position data. Options: set to between 0, 1, 4, 9, 16, 25, 36, 49, 64, and 81w. L this item is displayed when “data extension” is set to “...
Page 174
9 menu screen 9-31 item name gps > gps tx mode > d-prs > tx format > item > item name enter an item name of up to 9 characters. Data type (default: live item) gps > gps tx mode > d-prs > tx format > item > data type set the item’s status. •live item: the item is valid. •killed item: the item is inva...
Page 175
9 menu screen 9-32 position gps > gps tx mode > d-prs > tx format > item > position displays the position information of the item. Push [quick] to open the window shown below. Tip: when you select “capture from gps” or “set from gps memory,” you can capture the position from the gps, or set the item...
Page 176
9 menu screen 9-33 power (default: 0w) gps > gps tx mode > d-prs > tx format > item > power select the tx power level of the item, to transmit along with the position data. Options: set to between 0, 1, 4, 9, 16, 25, 36, 49, 64, and 81w. L this item is displayed when “data extension” is set to “powe...
Page 177
9 menu screen 9-34 symbol (default: wx station) gps > gps tx mode > d-prs > tx format > weather > symbol the symbol is an icon which represents weather station’s means of transportation or location. The saved symbol is transmitted along with the position data while in the d-prs mode. See page 9-25 f...
Page 178
9 menu screen 9-35 gps sentence (default: gga) gps > gps tx mode > nmea > gps sentence select sentences to be transmitted in the gps mode to transmit position data. Options: set to between rmc, gga, gll, vtg, gsa and gsv. Information l • a maximum of four gps sentences can be set at a time. •display...
Page 179
9 menu screen 9-36 gps information gps > gps information displays the gps satellite direction, altitude, satellite number and receiving status. (p. 5-11) (example: tracking 4 satellites) untracking satellite regular characters (example: 01) tracking satellites (weak signal) reversed characters (exam...
Page 180
9 menu screen 9-37 (base station)> compass* displays the caller’s direction from your position latitude displays the caller’s latitude longitude displays the caller’s longitude gl displays the grid locator based on the latitude and longitude of the caller’s position. Alt displays the caller’s altitu...
Page 181
9 menu screen 9-38 alm screen (gps alarm position) compass* displays gps alarm area’s direction from your position latitude displays gps alarm area’s latitude longitude displays gps alarm area’s longitude gl displays the grid locator based on the latitude and longitude of gps alarm area’s. Dst displ...
Page 182
9 menu screen 9-39 alarm select (default: off) gps > gps alarm> alarm select select the target position(s) for the gps alarm function. •off: turns off the function. •rx: the gps alarm sounds when a target (the last received position) enters in your active alarm range, . •group: the gps alarm sounds ...
Page 183
9 menu screen 9-40 gps items (continued) gps logger (default: off) gps > gps logger > gps logger turn the gps logger function on or off. This function logs the position, altitude, course, speed and number of satellites being used. •off: turns off the function. •on: the transceiver automatically logs...
Page 184: Call Sign Items
9 menu screen 9-41 call sign call sign sets or views the “ur,” “r1,” “r2,” and “my” call signs to use in the dv mode. When not using the dr function, sets the call signs on this screen. For simplex operation (dv mode) you can set the “ur” and “my” call signs. For duplex (repeater) operation (dv mode...
Page 185: Rx History Items
9 menu screen 9-42 rx history rx history when a call is received in the dv mode, the call information such as the caller station’s call sign, the repeater’s call sign, and so on, are saved on this screen. Up to 50 records can be saved. L even if the transceiver is off, the saved records are not dele...
Page 186
9 menu screen 9-43 (mobile station)> compass* displays the caller’s direction from your position latitude displays the caller’s latitude longitude displays the caller’s longitude gl displays the grid locator based on the caller’s latitude and longitude alt displays the caller’s altitude dist* displa...
Page 187
9 menu screen 9-44 compass* displays the caller’s direction from your position latitude displays the caller’s latitude longitude displays the caller’s longitude gl displays the grid locator based on the caller’s latitude and longitude dist* displays the caller’s distance from your position temp disp...
Page 188: Dv Memory Items
9 menu screen 9-45 your call sign dv memory > your call sign the transceiver has a total of 300 memories to save an individual station call sign. The saved call sign and name are displayed on the your call sign or rx history screen. L you can enter the your (ur) call sign into the memory using the r...
Page 189
9 menu screen 9-46 type fm repeater name fm repeater name of up to 16 alphanumeric characters sub name fm repeater sub name of up to 8 alphanumeric characters call sign fm repeater call sign group repeater group where the repeater is assigned use(from) select whether or not to use the fm repeater as...
Page 190: My Station Items
9 menu screen 9-47 my call sign my station > my call sign the transceiver has a total of 6 memories to save your own call signs. You can enter a call sign of up to 8 digits. Also, a note of up to 4 characters, for operating radio type, area, and so on, can be entered. L see the d-star guide for my c...
Page 191: Dv Set Items
9 menu screen 9-48 rx bass (default: normal) dv set > tone control > rx bass set the received audio bass filter level to cut, normal or boost. •cut: reduces the low frequencies •normal: normal tone balance •boost: increases the low frequencies rx treble (default: normal) dv set > tone control > rx t...
Page 192
9 menu screen 9-49 fast data (default: off) dv set > dv fast data > fast data select whether or not to use the dv fast data function for data communication in the dv mode. The dv fast data function uses the data and the audio frames to send data approximately 3.5 times faster than the normal speed. ...
Page 193
9 menu screen 9-50 bk (default: off) dv set > bk the break-in (bk) function enables you to break into a conversation, where the two other stations are communicating with call sign squelch enabled. • off: turns off the function. • on: turns on the function. L the bk function is automatically turned o...
Page 194: Speech Items
9 menu screen 9-51 rx call sign speech (default: on (kerchunk)) speech > rx call sign speech turn the rx call sign speech function on or off for calls received in the dv mode. • off: the caller station’s call sign is not announced, even when a call is received. • on (kerchunk): the caller station’s ...
Page 195
9 menu screen 9-52 speech speed (default: fast) speech > speech speed set the speech speed to slow or fast. Speech level (default: 7) speech > speech level adjust the voice synthesizer volume level to between 0 (off), 1 (minimum) and 9 (maximum). The voice synthesizer audio output level is linked wi...
Page 196: Dtmf Items
9 menu screen 9-53 you can set the dtmf tone code and dtmf memory channel for dtmf tone operation. See pages 10-8 ~ 10-10 for details. Dtmf memory (default: d0) dtmf > dtmf memory shows a list of the dtmf memory channels. • d0 to d#: dtmf memory channel list dtmf speed (default: 100ms) dtmf > dtmf s...
Page 197: Qso/rx Log Items
9 menu screen 9-54 qso log (default: off) qso/rx log > qso log select whether or not to make a communication log on a microsd card. The communication log is made on a microsd card, and saved in the “csv” format. L this function requires a microsd card (user supplied). • off: the qso log function is ...
Page 198
9 menu screen 9-55 the call log contents are shown below: contents example descriptions tx/rx tx rx transmission and reception date 4/1/2017 13:51:48 4/1/2017 13:51:48 date and time the call was started. Frequency 438.010000 438.010000 operating frequencies ( when duplex is set, the rx frequency is ...
Page 199
9 menu screen 9-56 the rx log contents are shown below: contents example descriptions frequency 438.010000 rx frequency mode dv operating mode (dv mode is fixed) caller ja3yua a call sign of the caller station (up to 8 characters) / 4100 note after the call sign (up to 4 characters) called cqcqcq ca...
Page 200: Function Items
9 menu screen 9-57 squelch/att select (default: s-meter squelch) function > squelch/att select select the function that varies according to the [sql] control position. • off: both the s-meter squelch and attenuator are disabled. • s-meter squelch: the s-meter squelch activates and adjusts the squelc...
Page 201
9 menu screen 9-58 • during rx/standby: ● : default setting : available n/a: not available function description remote mic key up/down mic key [f-1] [f-2] [up] [dn] --- no function up push to increase the frequency, memory channel, repeater or station call sign. N/a n/a ● down push to decrease the ...
Page 202
9 menu screen 9-59 function description remote mic key up/down mic key [f-1] [f-2] [up] [dn] tone/dsql push to select between tone types. > fm/fm-n tone: repeater tone tsqls: pocket beep with tone squelch tsql: (tone squelch) dtcss: pocket beep with dtcs code squelch dtcs: dtcs code squelch tsql-r: ...
Page 203
9 menu screen 9-60 one-touch ptt (remote mic) (default: off) function > one-touch ptt (remote mic) set the on-touch ptt function for the hm-207s. The function enables you to transmit without sequentially holding down the [ptt] button. • off: push [ptt] to transmit and release to receive. • on: push ...
Page 204
9 menu screen 9-61 ci-v transceive (default: off) function > ci-v > ci-v transceive turn the ci-v transceive function on or off. • off: turns off the function. • on: when you change a setting on one transceiver, the same settings is automatically changed on other connected transceivers or receivers....
Page 205: Display Items
9 menu screen 9-62 lcd backlight brightness (default: 4) display > lcd backlight brightness set the lcd backlight brightness level to between 1 (dark) and 4 (bright). Lcd backlight color (default: white) display > lcd backlight color set the lcd backlight color to between white, amber, green, and bl...
Page 206
9 menu screen 9-63 lcd contrast (default: 8) display > lcd contrast set the lcd contrast level to between 1 (lowest contrast) and 16 (highest contrast). Rx call sign (default: normal) display > rx call sign select whether or not to display the call sign and the message of the caller station, when a ...
Page 207
9 menu screen 9-64 opening message (default: on) display > opening message select whether or not to display the opening message at power on. • off: opening message is not displayed. • on: icom logo, my call sign, the product model (“id-4100a” or “id-4100e”)* are displayed. *depending on the version....
Page 208
9 menu screen 9-65 choose your language carefully when the system language of the transceiver is set to japanese, the transceiver has the capability to display both english and japanese characters. However, if you select japanese as the display language, all menu items throughout the transceiver sys...
Page 209: Sounds Items
9 menu screen 9-66 beep level (default: 9) sounds > beep level set the beep audio output level to between 0 (off), 1 (minimum) and 9 (maximum). Key-touch beep (default: on) sounds > key-touch beep turn the confirmation beep tones on or off. • off: no beep sounds. • on: a beep sounds when you push a ...
Page 210: Time Set Items
9 menu screen 9-67 date time set > date/time > date manually set the date to between 2000/01/01 and 2099/12/31. Time time set > date/time > time manually set the time that is displayed at the top of the screen to between 0:00 and 23:59. The time is displayed in the 24 hour format. L when “gps time c...
Page 211: Sd Card Items
9 menu screen 9-68 load setting sd card > load setting select from the list when you load the setting file. Save setting sd card > save setting save the setting file. Import sd card > import/export > import import the ur call sign, repeater list or gps memory data in the csv format file. Export sd c...
Page 212: Bluetooth
9 menu screen 9-69 the optional ut-137 bluetooth unit is required. Bluetooth (default: off) bluetooth set > bluetooth turns the bluetooth function on or off. L to use the bluetooth function, the optional ut-137 bluetooth unit is required. • off: turns off the function. • on: turns on the function. A...
Page 213
9 menu screen 9-70 vox (default: off) bluetooth set > headset set > vox > vox the voice operated transmission (vox) function starts transmitting without pushing [ptt] when you speak into the microphone, then automatically returns to receive when you stop speaking. L to use the vox function, the opti...
Page 214
9 menu screen 9-71 custom key (default: [play]: ---, [fwd]: up, [rwd]: down) bluetooth set > headset set > icom headset > custom key assigns the following key functions to the custom key ([play]/[fwd]/[rwd]) on the optional vs-3 headset. Function description --- no function up push to increase the f...
Page 215
9 menu screen 9-72 bluetooth ® set items (continued) function description voice tx (t1) • push to transmit the voice audio recorded on the microsd card once. • hold down for 1 second to repeatedly transmit the voice audio. L this key function can also be used on the dr screen. L if the voice audio i...
Page 216: Others Items
9 menu screen 9-73 voltage others > information > voltage displays the voltage of the external power supply. Version others > information > version displays the transceiver firmware’s version number. L when the optional ut-137 bluetooth unit is installed, the unit’s version number is also displayed....
Page 217: Section
Section 10 other functions 10-1 selecting a squelch delay .................................................... 10-2 transmit power levels and rf meter .................................... 10-2 attenuator function ............................................................... 10-3 d operating the at...
Page 218: Selecting A Squelch Delay
10 other functions 10-2 you can select a squelch delay in the menu screen to prevent repeated opening and closing of the squelch while receiving the same signal. Function > squelch delay 1. Push [menu]. 2. Rotate [dial] to select “function,” then push [ï]. 3. Select “squelch delay,” then push [ï]. 4...
Page 219: Attenuator Function
10 other functions 10-3 the transceiver has an rf attenuator related to the squelch control setting. You can add up to approximately 20 db of attenuation at its maximum setting. You can set the attenuator to [sql] in the menu screen. Function > squelch/att select 1. Push [menu]. 2. Rotate [dial] to ...
Page 220: Band Scope Function
10 other functions 10-4 use the band scope function to visually search for a specified frequency range around the displayed frequency. You can use this function to search for a signal, and see the received signal strength level. The band scope function has two sweep types, single sweep and continuou...
Page 221: Voice Tx Function
10 other functions 10-5 the voice tx function transmits the audio that is on the microsd card, one time or repeatedly, for up to 10 minutes at the specified interval. Up to 4 memories can be used for repeatedly calling cq or for other events. When the key function [voice tx (t1)] is assigned to a mi...
Page 222
10 other functions 10-6 d transmitting the recorded voice audio note: be sure to insert a microsd card into the transceiver. Voice tx > > 1. Push [menu]. 2. Rotate [dial] to select “voice tx,” then push [ï]. 3. Select “>,” then push [ï]. 4. Select the memory number, “t1” ~ “t4,” then push [ï]. •the ...
Page 223: Home Channel Function
10 other functions 10-7 d home channel setting 1. Select a mode (vfo or memory) or the dr screen in which you want to set the home channel. 2. Select a frequency to be set as the home channel. L on the dr screen, select “from.” 3. Push [quick]. 4. Rotate [dial] to select “home ch set,” then push [ï]...
Page 224: Using The Dtmf Memory
10 other functions 10-8 the transceiver can save up to 16 memories of 24-digit dtmf code. D entering dtmf code dtmf > dtmf memory 1. Push [menu]. 2. Rotate [dial] to select “dtmf,” then push [ï]. 3. Select “dtmf memory,” then push [ï]. •displays the dtmf memory list (d0 to d#). 4. Select the dtmf me...
Page 225
10 other functions 10-9 d transmitting dtmf code 1. Push [quick]. 2. Rotate [dial] to select “dtmf tx,” then push [ï]. 3. Select the dtmf memory channel to transmit, then push [ï]. •transmits the selected dtmf code. L the dtmf code scrolls during transmission. D transmitting dtmf code (direct input)...
Page 226
10 other functions 10-10 d selecting the dtmf transmit speed you can select the dtmf transmit speed. Dtmf > dtmf speed 1. Push [menu]. 2. Rotate [dial] to select “dtmf,” then push [ï]. 3. Select “dtmf speed,” then push [ï]. 4. Select a transmit speed. •100ms: transmits the dtmf tones at about 100 mi...
Page 227: Tone Squelch Operation
10 other functions 10-11 step 1. Setting the tone squelch frequency dup/tone... > tsql freq 1. Push [v/m] several times until you enter the vfo mode. 2. Push [mode] several times until you select the fm or fm-n (fm narrow) mode. 3. Rotate [dial] to set an operating frequency. 4. Push [menu]. 5. Rota...
Page 228: Dtcs Squelch Operation
10 other functions 10-12 the tone squelch opens only when you receive a signal containing a matching dtcs code in the fm or fm narrow mode. You can silently wait for calls from others using the same tone. Also, a reversed tone squelch function will mute the squelch when you receive a signal containi...
Page 229
10 other functions 10-13 there are 10 weather channels for monitoring the national oceanographic and atmospheric administration (noaa) weather broadcasts. D selecting a weather channel 1. Push [quick]. 2. Rotate [dial] to select “weather ch,” then push [ï]. • enters the weather channel mode. 3. Rota...
Page 230: Cloning Function
10 other functions 10-14 transceiver-to-transceiver cloning using a microsd card (p. 10-15) master sub cloning from a pc using a microsd card (p. 10-17, cs-4100 instruction manual) to the memory card reader to the memory card slot l if your pc does not have a microsd card slot, connect a memory card...
Page 231
10 other functions 10-15 step 2. Remove the microsd card from the master transceiver, then insert it into the sub transceiver. 1. Hold down the master transceiver’s [ ] to turn off the power. 2. Remove the microsd card from the master transceiver. 3. Insert the microsd card into the sub transceiver,...
Page 232
10 other functions 10-16 d transceiver-to-transceiver cloning using a microsd card (continued) cloning function step 3. Loading the setting data into the sub transceiver. Sd card > load setting 1. Push [menu]. 2. Rotate [dial] to select “sd card,” then push [ï]. 3. Select “load setting,” then push [...
Page 233
10 other functions 10-17 d cloning from a pc using a microsd card you can clone transceivers from a pc using a microsd card. Set memory content, menu item settings and repeater list in the cs-4100 cloning software , and save them in an “icf” file format. Copy the “icf” file to the “setting” folder i...
Page 234: Resetting The Cpu
10 other functions 10-18 occasionally, erroneous information will be displayed when, for example, first applying power. This may be caused externally by static electricity or by other factors. If this problem occurs, turn off the transceiver. After waiting a few seconds, turn on the transceiver agai...
Page 235
10 other functions 10-19 d ci-v connection example the transceiver's operating frequency, mode, vfo and memory selection, can be remotely controlled using a pc. The icom communications interface v (ci-v) is used for remote control. D preparing to control the transceiver, first set its address, data ...
Page 236
10 other functions 10-20 d command table cmd. Sub cmd. Data description 00 see p. 10-21 send operating frequency for transceive 01 see p. 10-21 send operating mode for transceive 03 see p. 10-21 read operating frequency 04 see p. 10-21 read operating mode 05 see p. 10-21 send operating frequency 06 ...
Page 237
10 other functions 10-21 cmd. Sub cmd. Data description 22 00 see p. 10-26 send/read dv tx data (up to 30 byte) 01 00 00 send/read auto dv rx data output off 01 send/read auto dv rx data output on 01 see p. 10-26 send/read dv rx data (up to 30 byte) 02 00, 01 send/read dv data tx setting (00=ptt, 01...
Page 238
10 other functions 10-22 remote jack (ci-v) information (continued) vox gain setting command: 14 16 off 1 2 3 4 0000 ~ 0022 0023 ~ 0046 0047 ~ 0069 0070 ~ 0092 0093 ~ 0115 5 6 7 8 9 0016 ~ 0139 0140 ~ 0162 0163 ~ 0185 0186 ~ 0208 0209 ~ 0232 10 0233 ~ 0255 repeater tone/tone squelch frequency settin...
Page 239
10 other functions 10-23 dv rx message command: 20 0101, 20 0102 x x x x x x x x @1 ~ @8 @9 ~ #2 • • • x x • • • x x q ~ @0 q ~ @0: message (20 characters) @1 ~ @8: call sign of the caller station (8 characters) @9 ~ #2: note of the caller station (4 characters) l ff: when no call sign is received s...
Page 240
10 other functions 10-24 q ~ o: call sign/ssid *9 ascii characters (a–z, 0–9, /, -, space) !0 , !1: symbol *2 ascii characters (00h–efh) !2 ~ !6: latitude (ddºmm.Mmm format) !7 ~ @2: longitude (dddºmm.Mmm format) @3 ~ @6: altitude (0.1 meter steps) @7 , @8: course (1 degree steps) @9 ~ #1: speed (0....
Page 241
10 other functions 10-25 q ~ o: call sign/ssid *9 ascii characters (a–z, 0–9, /, -, space) !0 , !1: symbol *2 ascii characters (00h–efh) !2 ~ !6: latitude (ddºmm.Mmm format) !7 ~ @2: longitude (dddºmm.Mmm format) @3 ~ @6: altitude (0.1 meter steps) @7 , @8: course (1 degree steps) @9 ~ #1: speed (0....
Page 242
10 other functions 10-26 manually entered position data command: 23 02 x x x x y ~ !1 • • • x x x x !2 ~ !5 • • • x x • • • x x q ~ t q ~ t: latitude (ddºmm.Mmm format) y ~ !1: longitude (dddºmm.Mmm format) !2 ~ !5: altitude (0.1 meter steps) q ~ t: latitude (ddºmm.Mmm format) y ~ !1: longitude (ddd...
Page 243: Section
Section 11 options 11-1 options ..................................................................................11-2 previous view.
Page 244: Options
11 options 11-2 options microphone/speaker hm-154 hand microphone hm-207s hand microphone ( remote - control ) hm-209 noise canceling microphone hm-232 hand microphone ( simple ) opc-440 mic extension cable : 5 m (16.4 ft)* opc-647 mic extension cable : 2.5 m (8.2 ft)* sp-30 external speaker : 2.8 m...
Page 245: Section
Section 12 bluetooth ® operation 12-1 bluetooth ® operations ........................................................... 12-2 turning on the bluetooth ® function ..................................... 12-2 connecting to a bluetooth ® headset..................................... 12-3 vox function .......
Page 246: Bluetooth
12 bluetooth ® operation 12-2 if you install the optional ut-137 bluetooth ® unit in the transceiver, you can connect to other bluetooth devices. In this section, the id-4100a/e with the ut-137 is described as simply the “transceiver.” you can connect other devices to the transceiver. Icom headset w...
Page 247: Connecting to A Bluetooth
12 bluetooth ® operation 12-3 you can connect the optional bluetooth headset to the transceiver. Step 1. Selecting the pairing mode of the headset. See the instruction manual of the headset to select the pairing mode. Step 2. Searching for the headset (transceiver) bluetooth set > pairing/connect 1....
Page 248: Vox Function
12 bluetooth ® operation 12-4 the voice operated exchange (vox) function toggles the transceiver between transmit and receive by your voice. This function provides hands-free operation. You can use the vox function with the optional vs-3 or a third party’s bluetooth headset. Depending on the headset...
Page 249
12 bluetooth ® operation 12-5 d vox-related settings you can set the “vox delay” and “vox time-out timer” on the menu screen. Vox delay bluetooth set > headset set > vox > vox delay the vox delay is the amount of time the transmitter stays on after you stop speaking. It enables for normal pauses in ...
Page 250
12 bluetooth ® operation 12-6 d af output select the af output device if “af output” is set to “headset & speaker,” you can hear audio from both a connected bluetooth headset and the transceiver’s speaker. Bluetooth set > headset set > af output 1. Push [menu]. 2. Rotate [dial] to select “bluetooth ...
Page 251
12 bluetooth ® operation 12-7 other settings of the headset (continued) d about the icom headset (vs-3) you can set the detailed settings of the optional vs-3 bluetooth headset . Also, you can assign a key function to [play], [fwd], and [rwd] on the vs-3’s “custom key” screen. Power save screen the ...
Page 252
12 bluetooth ® operation 12-8 the rs-ms1a is a freeware application for android devices. With the rs-ms1a, you can use the extended d-star functions to exchange pictures or messages, or display the received d-prs station data on a map application. To use the rs-ms1a, download it from the google™ pla...
Page 253
12 bluetooth ® operation 12-9 the rs-ms1i is a freeware application for ios devices. With the rs-ms1i, you can use the extended d-star functions to exchange pictures or messages, or display the received d-prs station data on a map application. To use the rs-ms1i, download it from the apple app store...
Page 254
12 bluetooth ® operation 12-10 before connecting to an android™ device, you must pair with it. •how to pair (see below) •how to connect (p. 12-11) d pairing with an android™ device this section describes how to pair with an android device. Note: depending on the device, you may not be able to pair w...
Page 255
12 bluetooth ® operation 12-11 d connection this section describes how to connect to the transceiver from an android device. Step 1. Preparing for the connection (transceiver) function > ci-v > ci-v transceive set “ci-v transceive” to on to control the transceiver and the rs-ms1a with ci-v commands....
Page 256
12 bluetooth ® operation 12-12 before connecting to an ios device, you must pair with it. •how to pair (see below) l see page 12-13 to connect to the paired device. D pairing with an ios™ device note: depending on the device, you may not be able to pair with the bluetooth device. Step 1. Starting th...
Page 257
12 bluetooth ® operation 12-13 d connection this section describes how to connect to the paired transceiver from an ios device. 1. Tap the rs-ms1i icon to start. Rs-ms1i icon 2. Tap “other.” 3. Tap “bluetooth connection.” 4. Tap the displayed ut-137’s name to connect. • the ios device starts to conn...
Page 258: Device
12 bluetooth ® operation 12-14 there are 3 ways to disconnect from a bluetooth device (headset device or data device). •turn off a headset •turn off the bluetooth on a data device l see the instruction manual of the headset or a data device for details. Or, you can disconnect from a bluetooth device...
Page 259: Deleting A Bluetooth
12 bluetooth ® operation 12-15 you can delete a bluetooth device from the pairing list. Before deleting a connected bluetooth device, disconnect it. Bluetooth set > pairing/connect 1. Push [menu]. 2. Rotate [dial] to select “bluetooth set,” then push [ï]. 3. Select “pairing/connect,” then push [ï]. ...
Page 260: Unit Name
12 bluetooth ® operation 12-16 you can edit the bluetooth unit name. After initializing the unit, the edited name remains. Bluetooth set > bluetooth device information 1. Push [menu]. 2. Rotate [dial] to select “bluetooth set,” then push [ï]. 3. Select “bluetooth device information,” then push [ï]. ...
Page 261: Unit
12 bluetooth ® operation 12-17 you can initialize the installed ut-137 bluetooth ® unit . You should initialize the unit if you have trouble during bluetooth operation. When you do a partial reset or all reset, the bluetooth settings returns to their factory defaults. However, the device name and pa...
Page 262
12 bluetooth ® operation 12-18 displays the paired bluetooth device you can pair 3 types of the bluetooth devices: headset, data device, and low energy device. Up to 7 bluetooth devices can be paired with the ut- 137. However, you cannot pair with 7 headsets only, 7 data devices only, or 7 low energ...
Page 263: Section
Section 13 updating the firmware 13-1 general ................................................................................. 13-2 d about updating the firmware ......................................... 13-2 d cautions ........................................................................ 13-2 d...
Page 264: General
13 updating the firmware 13-2 d about updating the firmware you can update the id-4100a/e’s firmware using a microsd card. Updating the firmware can add new functions or improve performance parameters. You can download the latest firmware from the icom website. Http://www.Icom.Co.Jp/world/index.Html...
Page 265: Updating The Firmware
13 updating the firmware 13-3 these instructions are based on microsoft ® windows ® 10. Step 1. Downloading the firmware file 1. Access the following url. Http://www.Icom.Co.Jp/world/index.Html 2. Click . Click 3. Click the “firmware updates/software downloads” link. Click 4. Click the firmware file...
Page 266
13 updating the firmware 13-4 step 3. Copy the downloaded firmware data 1. Double-click the created folder. (example: 4100e101). 2. Copy the downloaded firmware data into the id-4100 folder on a microsd card. (example: 4100e101.Dat). Click step 4: removing the microsd card turn off the transceiver, ...
Page 267
13 updating the firmware 13-5 6. Carefully read all the displayed precautions. After you read and agree with all them, select , then push [ï]. •the updating starts. Information l •to cancel the updating, select . • the transceiver reads the firmware file from the microsd card and writes it to the ma...
Page 268: Index
Index i number 1750 hz tone burst ..................................................8-3 a access point mode ................................................9-67 active band ............................................................9-60 af output .......................................................
Page 269
Index ii d (continued) dtcs dtcs code .........................................................9-16 dtcs polarity .....................................................9-16 dtcs squelch operation ...................................10-12 dtmf memory ............................................. 9-53, ...
Page 270
Index iii m manage memory screen ..........................................1-3 memory bank ..........................................................1-8 assigning a memory channel .................................1-8 bank name, entering ..........................................1-11 selecting the me...
Page 271
Index iv r (continued) rf meter ................................................................10-2 rs-ms1a ...............................................................12-8 rs-ms1i ................................................................12-9 rx bass..........................................
Page 272
Index v v (continued) voice tx function ...................................................10-5 changing the voice tx settings ..........................10-6 recording ............................................................10-5 transmitting .........................................................
Page 273
1-1-32 kamiminami, hirano-ku, osaka 547-0003, japan a-7367-3ex © 2017 icom inc..