- DL manuals
- Intermec
- Software
- CK30
- Service Manual
Intermec CK30 Service Manual - I/o Control
Chapter 4 — Theory of Operation
POR Reset (Cold Boot)
Power-On Reset circuit VR3 simultaneously asserts the PSC reset input
and the PXA255 nRESET. This ensures that the processor is always in
reset as its power is ramped up.
Soft Reset (Warm Boot)
Warm boot forces code execution to vector to boot code, where the kernel
is restarted without reinitializing the object store. Warm boot is
implemented as in the 700 and 241X products: Pressing and holding the
I key for several seconds:
• The PSC first wakes the system if it is suspended.
• The PSC starts a timer on I key down.
• If the IO key is still down after approximately 5 seconds, the PSC asserts
signal VDD_FAULT* to command a warm boot.
• If the I key is released before the timer expires, the PSC treats it as a
simple Suspend/Resume command and asserts PSC_IRQ to suspend or
resume the system.
The VDD_FAULT* assertion causes the processor to suspend. The PSC
then awakes the system using PSC_IRQ. Code execution starts as it would
on a normal resume but checks the PXA255 power management registers
to determine if the exception was triggered by VDD_FAULT*. If it was,
code execution vectors to the warm boot in the bootloader.
Peripheral Resets
Other functional blocks in the computer have their own resets.
The FPGA generates its own internal reset as part of the download process.
Because it is an SRAM-based device and is not even downloaded until well
after the system reset is release, system reset is not brought out to the
FPGA. After download, functional blocks within the FPGA are reset
through their own memory-mapped control registers.
The audio codec (Proto 0 only) uses the AC97 interface reset (AC_RST).
The Bluetooth module supplies its own power-on reset.
PCI slot reset is provided through the PCI bus reset–PCI-RESET–
generated by the FPGA-based PCI host bridge.
I/O Control
The I key is a simple contact closure to GND on the keypad PCB. The
IO_KEY* signal is debounced in software by the PSC, which then issues a
PSC_IRQ* interrupt to PXA255 GPIO[0] to suspend or resume the
system PXA255. On a resume, the PSC does not issue the interrupt if
BATT_FAULT_IRQ* is asserted (main battery too low to resume).
64
CK30 Handheld Computer Service Manual
Summary of CK30
Page 1
Ck30 handheld computer service manual.
Page 2
Intermec technologies corporation corporate headquarters 6001 36th ave. W. Everett, wa 98203 u.S.A. Www.Intermec.Com the information contained herein is proprietary and is provided solely for the purpose of allowing customers to operate and service intermec-manufactured equipment and is not to be re...
Page 3: Contents
Contents contents before you begin ............................................................................................................. Vii safety summary .................................................................................................. Vii safety icons........................
Page 4
Contents it4000 imager assembly exploded view......................................................................... 35 it4000 imager assembly spare parts list ........................................................................ 35 tethered scan flex assembly exploded view........................
Page 5
Contents display contrast control.................................................................................... 66 temperature compensation................................................................................ 67 backlight.................................................................
Page 6
Contents ac1 4-slot battery charger .............................................................................. 101 ac2 4-bay charging dock ............................................................................... 102 vi ck30 handheld computer service manual.
Page 7: Before You Begin
Before you begin before you begin this section provides you with safety information, technical support information, and sources for additional product information. Safety summary your safety is extremely important. Read and follow all warnings and cautions in this document before handling and operat...
Page 8: Safety Icons
Before you begin safety icons this section explains how to identify and understand dangers, warnings, cautions, and notes that are in this document. You may also see icons that tell you when to follow esd procedures and when to take special precautions for handling optical parts. A warning alerts yo...
Page 9: Global Services and Support
Before you begin global services and support warranty information to understand the warranty for your intermec product, visit the intermec web site at http://www.Intermec.Com, click support, and then click warranty. Disclaimer of warranties: the sample code included in this document is presented for...
Page 10
Before you begin who should read this document? This manual contains all of the information necessary to repair the ck30 handheld computer. It provides an exploded view of the computer, the spare parts lists, procedures that describe how to replace parts, and information about how to test the comput...
Page 11: Troubleshooting
Troubleshooting 1 use this chapter to troubleshoot problems you may encounter while using the ck30. Ck30 handheld computer service manual 1.
Page 12: Troubleshooting The Ck30
Chapter 1 — troubleshooting troubleshooting the ck30 use this table to find common problems users may experience with their ck30 and possible solutions. Problem solution you press ito turn on the ck30 and nothing happens. Try these possible solutions in order: • make sure you have a charged battery ...
Page 13
Chapter 1 — troubleshooting troubleshooting the ck30 (continued) problem solution nothing is displayed on the screen. Try these possible solutions in order: • the contrast may be set too light or too dark. Press b and then e repeatedly until you reach the desired contrast level. • if you have a ck30...
Page 14
Chapter 1 — troubleshooting troubleshooting the ck30 (continued) problem solution the ck30 will not communicate in a serial network. Try these possible solutions in order: • the ck30 may not be properly configured for serial communications. Make sure the serial communications parameters are properly...
Page 15
Chapter 1 — troubleshooting troubleshooting the ck30 (continued) problem solution the ck30 will not communicate in a wireless network. Try these possible solutions in order: • make sure that the radio is configured properly for the network. If the radio is properly configured, there may be a problem...
Page 16
Chapter 1 — troubleshooting troubleshooting the ck30 (continued) problem solution the ck30 cold boots or loses settings after the main battery is replaced. Try these possible solutions in order: • make sure the main battery is fully charged. • the bridge battery or the power circuitry on the main pc...
Page 17: Replacing Parts
Replacing parts 2 use this chapter to learn how to open, replace parts in, and close the ck30 handheld computer. It also provides preliminary cautions to follow when servicing the ck30. Ck30 handheld computer service manual 7.
Page 18: Cautions
Chapter 2 — replacing parts cautions note: opening this product can result in voiding the warranty. The internal workings of this product can only be accessed by intermec service personnel. Integrated circuits on the printed circuit board (pcb) in the computer are very sensitive to damage by electro...
Page 19: Replacing Parts
Chapter 2 — replacing parts replacing parts this section describes how to open, replace parts in, and close the ck30 handheld computer. Each procedure also lists the tools and parts that you will need. Opening the ck30 to replace the internal parts of the ck30, you need to open it. To open the compu...
Page 20
Chapter 2 — replacing parts 5 remove the scanner or imager flex cable from the main pcb. 6 disconnect the trigger reed switch cable from j4 on the main pcb. The top and bottom covers are now separated. Trigger reed switch cable scanner or imager flex cable j4 7 lay both covers down so that the exter...
Page 21
Chapter 2 — replacing parts screw (2 places) screw (2 places) screw (2 places) antenna antenna ground plane bottom cover retainer clips mini pci shield assembly mini pci radio assembly 4 use the antenna cable remover tool to carefully lift the antenna off of the mini pci radio assembly. Insert the p...
Page 22: Replacing The Ethernet Card
Chapter 2 — replacing parts replacing the ethernet card to replace the ethernet card, you may need the following tools and parts: • t10 torx screwdriver • small phillips screwdriver • ethernet card assembly (p/n 073867-001) • ethernet cable assembly (p/n 073096-001) • 2-56 x 3/16 stainless steel scr...
Page 23
Chapter 2 — replacing parts 6 replace the mini pci shield assembly by threading the ethernet cable through the opening in the shield and replacing the four phillips screws. 7 connect the ethernet cable to j12 on the main pcb. 8 close the ck30. For help, see “closing the ck30” on page 27. Replacing t...
Page 24
Chapter 2 — replacing parts flip main pcb over to access bluetooth radio screw (1 place) display flex cable keypad flex cable bluetooth radio module bluetooth radio retaining clip screw (2 places) 6 lift up on the bluetooth radio module and remove it from the main pcb. 7 replace the bluetooth radio ...
Page 25: Replacing The Main Pcb
Chapter 2 — replacing parts replacing the main pcb to replace the main pcb, you need the following tools: • t10 torx screwdriver • small phillips screwdriver you also need one of the following parts depending on the ck30 configuration: • ck30 64m/64m main pcb assembly (p/n 072291s-007) • ck30 32m/32...
Page 26
Chapter 2 — replacing parts screw (2 places) display flex cable keypad flex cable 6 remove the bluetooth radio (if necessary). For help, see “replacing the bluetooth radio” on page 13. 7 attach the new lcd support bar to the new main pcb. Lcd support bar 8 (if necessary) replace the bluetooth radio....
Page 27: Replacing The Bezel Assembly
Chapter 2 — replacing parts replacing the bezel assembly to replace the bezel assembly, you need one of the following parts depending on the ck30 configuration: • ck30 programmable 42-key bezel assembly (p/n 073297-001) • ck30 international 42-key bezel assembly (p/n 073298-001) • ck30 3270/5250 42-...
Page 28
Chapter 2 — replacing parts 4 once a corner of the bezel is loose, gently pull up on the bezel to remove it. 5 remove the adhesive residue left on the top cover from the bezel assembly. 6 separate the adhesive strip from the back of your new bezel assembly. 7 insert the keypad bezel end of the assem...
Page 29
Chapter 2 — replacing parts screw (2 places) display flex cable keypad flex cable 5 lift the display assembly away from the top cover. 6 remove the power indicator/good read light pipe assembly and the speaker pcb assembly. (if necessary) remove and replace the user indicator light pipe assembly. 7 ...
Page 30
Chapter 2 — replacing parts 8 insert the new display assembly into the top cover. 9 attach the display flex cable and the keypad flex cable to the main pcb. 10 replace the main pcb and secure it with the two phillips screws removed in step 3. 11 connect the power indicator/good read light pipe assem...
Page 31: Replacing The Se1200 Scanner
Chapter 2 — replacing parts keypad assembly keypad flex cable 4 remove the adhesive residue left by the keypad assembly on the top cover. 5 remove the adhesive backing from the new keypad assembly. Keypad assembly adhesive backing 6 connect the keypad flex cable to the keypad assembly and firmly att...
Page 32
Chapter 2 — replacing parts to replace the se1200 scanner 1 open the ck30. For help, see “opening the ck30” on page 9. 2 from the bottom cover, remove the four phillips screws that attach the scan engine assembly. 3 lift the scan engine assembly away from the bottom cover. Screw (4 places) se1200 sc...
Page 33: Replacing The Ev10 Scanner
Chapter 2 — replacing parts visor large scan mount bracket shield se1200 scan flex engine screw (2 places) 7 insert the scan engine in the scan mount bracket and attach it with the two phillips screws removed in step 4. 8 insert the scan engine assembly into the bottom cover and attach with the four...
Page 34
Chapter 2 — replacing parts 4 turn the scan engine assembly over and remove the two phillips screws that attach the scan engine and ground spring to the small scan mount bracket. 5 disconnect the scan flex cable from the scan engine assembly. Screw (3 places) screw (2 places) ev10 scan flex cable en...
Page 35: Replacing The It4000 Imager
Chapter 2 — replacing parts replacing the it4000 imager to replace the it4000 imager, you need the following tools and parts: • t10 torx screwdriver • small phillips screwdriver • it4000 imager assembly (p/n 073416s-001) • phillips 4-20 x .250 thread-form screw (p/n 525023) to replace the it4000 ima...
Page 36
Chapter 2 — replacing parts you also need one or more of the following parts depending on what you need to replace: • tethered scan flex assembly (p/n 072786-004) • tethered scanner door (p/n 073366-001) • tethered scanner cover (p/n 073179-001) • phillips 2-56 x 3/16 steel screw (p/n 591884-001) • ...
Page 37: Closing The Ck30
Chapter 2 — replacing parts tethered scanner door b insert a new tethered scanner door and snap it in place. 6 insert a new tethered scan flex assembly into the mounting bracket and attach it with the two screws removed in step 4. 7 insert the tethered scan flex assembly into the bottom cover and at...
Page 38
Chapter 2 — replacing parts 4 replace the six torx screws (four self-tapping and two machine) and tighten to 9 in-lb. 5 replace the four phillips screws and tighten to 2 to 3 in-lb. Screw (4 places) screw (2 places) screw (2 places) screw (2 places) 6 while holding the ck30 in one hand, insert the t...
Page 39: Views
Spare parts list and exploded views 3 this chapter provides the exploded views and spare parts list for the ck30a, ck30b, and ck30c handheld computers. Ck30 handheld computer service manual 29.
Page 40: Ck30 Exploded View
Chapter 3 — spare parts list and exploded views ck30 exploded view this exploded view contains parts for the 802.11b/g radio version of the ck30. To identify a part, find the part in the exploded view and locate its callout in the following spare parts list. See “ethernet card assembly exploded view...
Page 41: Ck30 Spare Parts List
Chapter 3 — spare parts list and exploded views ck30 spare parts list to identify a part, find the callout in this list and locate the part in the previous exploded view. Callout description part number 1 speaker pcb assembly 073146-002 2 power indicator/good read light pipe assembly 073030-002 3 di...
Page 42
Chapter 3 — spare parts list and exploded views ethernet card assembly exploded view this illustration shows an exploded view of the ethernet card assembly. To identify a part, find the part in the exploded view and locate its callout in the following spare parts list. The ethernet card is only avai...
Page 43
Chapter 3 — spare parts list and exploded views se1200 scan engine assembly exploded view this illustration shows the se1200 scan engine assembly in relation to the bottom cover. To identify a part, find the part in the exploded view and locate its callout in the following spare parts list. Screw (4...
Page 44
Chapter 3 — spare parts list and exploded views ev10 scan engine assembly exploded view this illustration shows the ev10 scan engine assembly in relation to the bottom cover. To identify a part, find the part in the exploded view and locate its callout in the following spare parts list. Screw (3 pla...
Page 45
Chapter 3 — spare parts list and exploded views it4000 imager assembly exploded view this illustration shows the it4000 imager assembly in relation to the bottom cover. To identify a part, find the part in the exploded view and locate its callout in the following spare parts list. Screw (3 places) 1...
Page 46
Chapter 3 — spare parts list and exploded views tethered scan flex assembly exploded view this illustration shows the tethered scan flex assembly in relation to the bottom cover. To identify a part, find the part in the exploded view and locate its callout in the following spare parts list. 1 2 3 4 ...
Page 47: Safety Labels Exploded View
Chapter 3 — spare parts list and exploded views safety labels exploded view this illustration shows the location of the safety labels. To identify a part, find the part in the exploded view and locate its callout in the following spare parts list. 1 2 3 4 5 safety labels spare parts list to identify...
Page 48
Chapter 3 — spare parts list and exploded views 38 ck30 handheld computer service manual.
Page 49: Theory of Operation
Theory of operation 4 this chapter provides the theory of operation for the ck30 handheld computers and its supporting accessories. Ck30 handheld computer service manual 39.
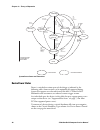
Page 50: System Architecture
Chapter 4 — theory of operation system architecture the ck30 platform is a 32-bit 3.3v system, with the processor and fpga cores running at 1.3v and 2.5v, respectively. The design is contained on a single main pcb, except for the following modules: • the keypad is a separate, replaceable module that...
Page 51: Processor Core
Chapter 4 — theory of operation processor core processor the ck30 platform is built around the intel pxa255 “cotulla” xscale processor (u1). The low-end configurations of the ck30 (ck30aa and ck30ba) use a 200mhz version of the pxa250 for cost reasons. The high-end configuration (ck30ca) uses a 400m...
Page 52: Memory
Chapter 4 — theory of operation fpga_clk 49.77mhz. Enabled immediately before fpga download. Fpga_clk serves both the scanner interface and mini pci bridge resident in the fpga. Audio codec sampling in computers equipped with audio is based on the audio codec local 24.576mhz oscillator. Memory ram u...
Page 53: I/o Signals
Chapter 4 — theory of operation i/o signals platform-specific peripheral control input and output signals are implemented through pxa255 gpio pins, fpga (u8) i/o pins, and through hcr registers u11 and u16. In general, signals are assigned among these devices according to these criteria: pxa255 outp...
Page 54
Chapter 4 — theory of operation pxa255 gpio signal descriptions (continued) pxa255 gpio function signal description usage gp2 bt_wakeup* system resume interrupt from bluetooth module. This is a maskable resume source (see note 1). Enabled when you select system wakeup from bluetooth wakeup event. Px...
Page 55
Chapter 4 — theory of operation pxa255 gpio signal descriptions (continued) pxa255 gpio function signal description usage gp32 -sdmmc_wp sd slot write protect 0 = write protect 1 = writes enabled gp38 -hcr_oe hcr registers output enable. This signal floats high on cold boot so that hcr register outp...
Page 56
Chapter 4 — theory of operation hcr output signal descriptions (continued) hcr bit function signal description usage u16 20 cf_reset compact flash slot 0 reset (unused in ck30). 0 = idle 1 = reset u16 21 usb_en enables pull-up on usb bus to acknowledge host and start communications. This can be used...
Page 57: I2C Bus
Chapter 4 — theory of operation fpga io signal descriptions function signal description usage vol0 vol1 vol2 beep volume control 000 = lowest volume 111 = highest volume scan_led scanner good read led 0 = led off 1 = led on scan_led_high good read led intensity control 0 = low intensity 1 = high int...
Page 58: Fpga Download
Chapter 4 — theory of operation addr decode, rd/wr ctl pci irq ctl sd31..0 sa25..0 scan_irq ad31..0 hcr_wr2* hcr_wr5* sdbuf_d7..0 scan_dreq host cpu i/f scanner i/f mini-pci slot gpio logicore pci core par perr# serr# frame# irdy# trdy# stop# devsel# rst# pci_clk req#, gnt# c/be#3..0 bus arbiter ini...
Page 59: Fpga Power Management
Chapter 4 — theory of operation the loader then writes byte values to the fpga, with write strobe pwe* serving as the cclk download clock. The fpga io is nominally hi-z during download. When the download is complete, the fpga enables its outputs. When its internal dlls have locked, it raises its don...
Page 60: Fpga Bus Interface
Chapter 4 — theory of operation software is responsible for shutting off fpga core power in a critical battery situation. If fpga power is still on when the system suspends, it will be shut off in hardware by the “type 2” interlock mechanism described in “device power control” on page 58. Fpga bus i...
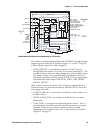
Page 61: Power System
Chapter 4 — theory of operation power system architecture, power supplies power supply controller i2c bus scan + 5 volts + 3.3 volt backup regulator fpga power enable aquila (cx1) power supply block diagram (6/26/02) voltage limit detector pll_vcc ldo manual reset 3.3v reset supercap voltage referen...
Page 62: Main Battery
Chapter 4 — theory of operation power supplies and capacities load vdc capacity regulator cpu core supply 1.30v .5a u45 buck switcher from 3.3 vdc vccn and vcckp 3.3v .2a system 3.3v (u39 from main battery, or u44 from supercap) pll_vcc 1.3v .03a filtered cpu core supply core logic, memory io, and a...
Page 63: Supercap
Chapter 4 — theory of operation the charging current is applied through the contacts on the base of the battery; the 26-pin dock connector is not used for charging. See “ad1 charging” on page 99 for details on the charging circuit in the dock. Supercap a 10-farad 2.5v supercap (c89) provides backup ...
Page 64
Chapter 4 — theory of operation power management architecture memory-mapped registers gpio i2c driver batt_fault pxa250-based system intermec battery manager wince power manager power supplies main battery super cap power supply controller low batt detect battery, supercap, temperature monitoring lo...
Page 65
Chapter 4 — theory of operation system hardware power states power consumption system power states os power states processor power states (typical at 8v) (maximum at 8v) notes, conditions off n/a n/a n/a n/a main battery out, supercap fully depleted. Suspend suspend sleep 2ma supercap fully charged....
Page 66: Device Power States
Chapter 4 — theory of operation running normal suspending suspended suspend successful resuming resume succeeded i/o key or main battery low dead warm-booting cold-booting suspending, hcrs off main battery critically low or removed i/o key down 5 sec warm boot done cold boot done limbo suspend succe...
Page 67
Chapter 4 — theory of operation device power states device computer awake (system on) computer suspended, main battery in computer suspended, main battery out critical shutdown type comments power supply controller on on on - cpu core supply on off off - vccn and vcckp on on on - pll_vcc on off off ...
Page 68
Chapter 4 — theory of operation device power control peripheral devices both internal and external to the pxa255 are enabled and disabled under software control. External devices also have hardware shutdown features to cut their power quickly in a critically-low battery situation (low-battery hardwa...
Page 69
Chapter 4 — theory of operation the output, batt_fault* then gates off the load enable lines through gates u17, u25, and u26. Flip-flop u15 latches the state of batt_fault* so that these loads do not come back on again when power is restored. Battery state system state device power ok not important ...
Page 70: Battery Status Monitoring
Chapter 4 — theory of operation where [ack] = ack from pxa255, [nak] = nak from pxa255 hex command return data 0x10 setlowbatled 0x10 0x11 clearlowbatled 0x11 0x12 pscsoftwarever 0x12 + psc firmware version byte 0x30 readmainbatvoltage 0x30 + main battery voltage byte 0x40 readsupercapvoltage 0x40 +...
Page 71: Low-Battery Handling
Chapter 4 — theory of operation power management software on the pxa255 uses the battery voltage and temperature data for temperature-compensated fuel gauging and low- battery detection. Three levels of battery status are indicated through an icon in the status bar: percentage of charge remaining ic...
Page 72: Battery Status Led
Chapter 4 — theory of operation software low-battery thresholds the first low-battery thresholds are defined in software as part of the power management driver running on the pxa255. Temperature- compensated battery level sampled through psc u38 (see “battery status monitoring” on page 60) is averag...
Page 73: Reset Control
Chapter 4 — theory of operation red led states power state indication comments no battery red led off. Low battery the red ck30 led turns on continuously while ck30 is running once battery voltage falls below the software low-battery threshold. This continues until suspend – either by the i key or w...
Page 74: I/o Control
Chapter 4 — theory of operation por reset (cold boot) power-on reset circuit vr3 simultaneously asserts the psc reset input and the pxa255 nreset. This ensures that the processor is always in reset as its power is ramped up. Soft reset (warm boot) warm boot forces code execution to vector to boot co...
Page 75: Resume Events
Chapter 4 — theory of operation resume events in addition to the i key, the ck30 is designed to optionally wake from the following sources. Source wakes after battery replaced* implementation i key (suspend/resume) yes rtc alarm no not supported in current software tethered scanner trigger (“trigger...
Page 76: Suspend Events
Chapter 4 — theory of operation suspend events source conditions i key (suspend/resume) none os auto-suspend timer none application-program-initiated suspend none suspend through reader command none hardware critically low battery threshold (includes battery removal) instantaneous battery level fall...
Page 77: Temperature Compensation
Chapter 4 — theory of operation boots. The factory-set default is restored if the registry is lost or “restore defaults” is selected from the configuration menu. Temperature compensation temperature compensation is implemented in the software display driver, using temperature information read throug...
Page 78: Wakeup Keys
Chapter 4 — theory of operation while the keypad is idle, software drives all eight-column lines low and waits for an interrupt indicating a key press or release. Software then checks key_ret7:0 to identify the row in which a key changed state and debounces the key change for approximately 8 ms. If ...
Page 79: I/o Key
Chapter 4 — theory of operation since key_ret0 can toggle pxa255 gpio1, which is always enabled as a system wakeup pin, any key located in keypad row 0 functions as a wakeup key if its column line is driven low during suspend. In the first three keypad styles, the 1, 2, 3, scan button (where present...
Page 80
Chapter 4 — theory of operation addr decode, rd/wr ctl pci irq ctl sd31..0 sa25..0 scan_irq ad31..0 hcr_wr2* hcr_wr5* sdbuf_d7..0 scan_dreq host cpu i/f scanner i/f mini-pci slot o gpio logicore pci core par perr# serr# frame# irdy# trdy# stop# devsel# rst# pci_clk req#, gnt# c/be#3..0 bus arbiter i...
Page 81
Chapter 4 — theory of operation sdram controller when the pci card initiates a pci transaction to read data from system sdram or write data to it, the pci bridge raises the sa_breq signal to request the system bus from pxa255. When the pxa255 has completed any pending operations, it raises sa_bgnt t...
Page 82
Chapter 4 — theory of operation sdram densities the sdram controller in the current version of the fpga code supports 64mbit, 128mbit and 256mbit sdram densities. The current ck30 configurations use 128mbit and 256mbit parts, but the main board is designed to support up to 128mb (using 512mbit parts...
Page 83
Chapter 4 — theory of operation mini pci 3.3vaux is supported, though none of the currently supported cards makes use of it. It is currently jumpered to pci_3.3v (which goes away if the slot is powered down) but can be changed to system 3.3v (always backed up) through r165. The bridge also supports ...
Page 84: 802.11B/g Radio
Chapter 4 — theory of operation 802.11b/g radio 802.11b and 802.11g are supported through an actiontec 802mig2 type 3a mini pci card based on the intersil prism gt chipset. The 802mig2 is a “flashless” card: it has a small eeprom for parameters like mac address, but there is no flash holding a firmw...
Page 85
Chapter 4 — theory of operation supported scanners device interface type support status dbp supported in se900 compatibility mode. Ev10 1d imager mds mds mode to be added in a future release. Dbp supported in architecture, but not implemented. E1022/e1025 decoded rsttl supported in architecture, but...
Page 86: Scanner Interface
Chapter 4 — theory of operation scanner interface scanners are interfaced through two scanner ports on the ck30 main pcb: • 22-pin vertical zif connector j2 supports the i2 and it4000 2d imagers and may later be used on the el10 micro-mirror laser. The signal set is as defined by hhp for the it4000 ...
Page 87
Chapter 4 — theory of operation using the scanner interface signal set - part 1 (continued) signal name source/ destination 2d imager usage dbp scanner usage tethered undecoded scanner usage (10-pin only) imager_pixclk fpga io pixel clock from scanner data valid on rising edge beep/scanner present 0...
Page 88: 1D Dbp Scanner Interface
Chapter 4 — theory of operation using the scanner interface signal set – part 2 (continued) signal name source/ destination spi scanner usage el10 usage tethered decoded scanner usage ( 10-pin only ) decoded scanner ( e1025 ) usage speed/range/ gdrd fpga out speed select 0 = 200 scans/ sec (ev10) 0 ...
Page 89
Chapter 4 — theory of operation image capture state machine addr decode, rd/wr ctl dma buffer ctl regs fifo sd31..0 sa25..0 scan_irq hcr_wr2* hcr_wr5* sdbuf_d7..0 scan_dreq host cpu i/f scanner i/f gpio req#, gnt# bus arbiter dbp count logic dqm3..0 noe npwe rdy rd/wr fpga_cs dbp_hsync sos_vsync ill...
Page 90: Wands and Wand Emulation
Chapter 4 — theory of operation • speed/range/goodread is set high or low depending on the scanner. This is a general-purpose control line used for spotter beam control, scan speed selection, goodread indication on tethered scanner, or serial txd to decoded-output scanners, depending on the installe...
Page 91
Chapter 4 — theory of operation image capture state machine addr decode, rd/wr ctl dma buffer ctl regs fifo sd31..0 sa25..0 scan_irq hcr_wr2* hcr_wr5* sdbuf_d7..0 scan_dreq host cpu i/f scanner i/f gpio req#, gnt# bus arbiter dbp count logic dqm3..0 noe npwe rdy rd/wr fpga_cs dbp_hsync sos_vsync ill...
Page 92: 1D Mds Scanner Interface
Chapter 4 — theory of operation horizontal (dbp_hsync) and vertical (sos_vsync) sync pulses from the scanner mark the start of lines and frames, respectively. The 8-bit pixel data is collected in a 32-deep fifo, which in turn feeds a 16-deep 32-bit-wide dma buffer. When the dma buffer is half full, ...
Page 93: Scanner Power
Chapter 4 — theory of operation standard asynchronous serial signals txd, rxd, rts and cts are multiplexed onto the 10-pin scanner connector as shown in the “tethered scanner signal descriptions” table on page 84, and routed through the fpga. Scan_rts and scan_cts are accessed by software through me...
Page 94
Chapter 4 — theory of operation tethered scanner signal descriptions pin signal name scanner signal description 1 vext +5v in switched scanner power: selectable (flex option) as either: • 5 vdc ± 5% @ 250ma maximum continuous (default) • switched off when the ck30 suspends, and on low-battery. Can b...
Page 95
Chapter 4 — theory of operation pin 1 10-pin stewart 937-sp-301010r-k2 (view looking into connector) tethered scanner connector tethered scanner auto-detect the 072786 tethered scan flex assembly incorporates a max471 current sensor (u1) to detect when a tethered scanner is plugged in. This is inten...
Page 96
Chapter 4 — theory of operation this is specifically not a ck30 requirement, but is expected to be a requirement for future products, which will all use the same docking connector. • undecoded scanners use the fpga count gathering logic (see “1d dbp scanner interface” on page 78). When an undecoded ...
Page 97: Trigger and Scanner Control
Chapter 4 — theory of operation the teth_sos pin on 26-pin docking connector j13 is used in conjunction with teth_present to indicate when a decoded tethered scanner is plugged into the docking connector: teth_present teth_sos description 0 x teth_sos functions as the tethered scanner sos input into...
Page 98
Chapter 4 — theory of operation dock interface signal descriptions pin signal name description signal characteristics 3 txd serial data output to dock (pxa255 ff uart) rs-232 levels 6 rxd serial data input from dock (pxa255 ff uart) rs-232 levels, 5k pull-down 4 rts serial handshake output to dock (...
Page 99: Usb Port
Chapter 4 — theory of operation dock interface signal descriptions (continued) pin signal name description signal characteristics 12 teth_pre sent scanner interlock to mux internal and external undecoded scanners. 0 = undecoded scanner present 1 = no undecoded scanner present 3.3v cmos 22 tx+ ethern...
Page 100: Scanner Interface
Chapter 4 — theory of operation full handshaking is supported, except for ri (ring indicate). This was left out in anticipation of some db9 cables supplying +5v, instead of ri, on dsub pin 9. U23 and its charge pumps are left on while the ck30 is on, but it draws very little current with no rs-232 d...
Page 101: Storage Card (Sd Card)
Chapter 4 — theory of operation the module is interfaced through a 4-wire serial connection to the pxa255’s “bt” uart. This uart, and its counterpart in the bluetooth module, are capable of high-speed operation (up to 921.6kbps), but in the current software are run at 115.2kbps. The operating system...
Page 102: Beeper
Chapter 4 — theory of operation connector j17 is modified with a retainer clip (to hold the card in place during a drop) and a “debounce plate” assembly that increases the contact force on the card to minimize contact bounce during drop. Unfortunately, the added contact force tends to defeat the slo...
Page 103: Debug Support
Chapter 4 — theory of operation • hardware tone duration control in the fpga: this was a contingency against concerns about windowsce interrupt latencies leading to noticeably sloppy software-controlled tone durations. In that event, pxa255 pwm1 would continue to generate the tones, but a timer buil...
Page 104: Debug Board
Chapter 4 — theory of operation cpu jtag tm s tdi td o tc k g n d 3.3 v 5 1 10 6 15 11 fpga jtag tm s tdi td o tc k g n d 3.3 v reset 1 2 19 20 g n d g n d g n d g n d g n d g n d n c cp u jt ag n c n c rs t td o nc tc k tm s td i m r* 3.3 v g n d g n d g n d i2c sd a sc k g n d target system flex p...
Page 105: Firmware Upgrade
Chapter 4 — theory of operation a custom debug board supporting ethernet, logic analyzer connectors, hexadecimal debug leds, and test and reset switches connects to these connectors through a buffered “pod board” and flex and ribbon cable assembly: 073274 pcb assy,debug,cx1 073418 flex circuit,j34,t...
Page 106: Accessories
Chapter 4 — theory of operation in-system programmability of programmable devices fpga the sram-based fpga supports two programming models. In normal operation, the fpga is downloaded at boot time and on every resume by the fpga download driver running on the pxa255 processor. See “fpga download” on...
Page 107
Chapter 4 — theory of operation 8-pin rj45 ethernet connector pin no. Signal name i/o to terminal description 1 tx+ o ethernet tpetxp 2 tx- o ethernet tpetxn 3 rx+ i ethernet tperxp 4 n/c 5 n/c 6 rx- i ethernet tperxn 7 n/c 8 n/c type-b usb connector pin no. Signal name i/o to terminal description 1...
Page 108
Chapter 4 — theory of operation 26-pin jae interface connector pin no. Signal name i/o to terminal description 1 gnd ground 2 vcc_ext (5v) o external 5v @ 500 ma maximum output 3 txd* o rs-232 txd 4 rts* o rs-232 rts 5 dtr* o rs-232 dtr 6 rxd* i rs-232 rxd 7 cd i rs-232 dcd (activesync wakeup) 8 cts...
Page 109
Chapter 4 — theory of operation ad1 1-bay communications dock the ad1 charges a single ck30 battery while on the unit. It also provides a db9 male connector for serial communications, an 8-pin rj45 connector for 10/100 ethernet communications, a type-b usb connector for usb communications and a 26-p...
Page 110
Chapter 4 — theory of operation ad1 input power requirements the ad1 requires 12 vdc at 4a. The 073573 power supply is qualified for use with the ad1. Ad2 4-bay communications dock the ad2 can charge four ck30 units at the same time. It also provides four db9 male connectors for serial communication...
Page 111: Ac1 4-Slot Battery Charger
Chapter 4 — theory of operation during this phase the bq2954 slowly ramps down the charge current until the designed trip point (imax/20) is reached. At this point charge current is terminated and the charge cycle is complete. The bq2954 uses the current mirror (u3) to measure the charge current. Th...
Page 112: Ac2 4-Bay Charging Dock
Chapter 4 — theory of operation temperature monitoring is done using a voltage divider formed by r1, r17 and a ntc thermistor (rt1). If the battery voltage is at a value that the bq2954 identifies as being below the reference voltage, and the ambient temperature is within acceptable limits then a ch...
Page 113
Corporate headquarters 6001 36th avenue west everett, washington 98203 u.S.A. Tel 425.348.2600 fax 425.355.9551 www.Intermec.Com ck30 handheld computer service manual *073967-001* p/n 073967-001.