- DL manuals
- Vacon
- Controller
- 100 HVAC
- Applications Manual
Vacon 100 HVAC Applications Manual
Summary of 100 HVAC
Page 1
Vacon 100 hvac ac drives application manual ®.
Page 3: Preface
Preface document id: dpd01696k date: 11.04.2016 software version: fw0065v032 about this manual this manual is copyright of vacon ltd. All rights reserved. The manual is subject to change without prior notice. In this manual, you can read about the functions of the vacon ® ac drive and how to use the...
Page 4
Chapter 11, fault tracing • the faults and their causes. • resetting the faults. This manual includes a large quantity of parameter tables. These instructions tell you how to read the tables. Index min max unit default id description parameter a i b c d e f g h a. The location of the parameter in th...
Page 5
Functions of the vacon ® ac drive • wizards for startup, pid control, multipump and fire mode to make the commissioning easy. • the funct button for an easy change between the local and the remote control place. The remote control place can be i/o or fieldbus. You can make a selection of the remote ...
Page 6
Vacon · 6 tel. +358 (0)201 2121 · fax +358 (0)201 212 205.
Page 7: Table of Contents
Table of contents preface about this manual 3 functions of the vacon ® ac drive 5 1 quick startup guide 11 1.1 control panel and keypad 11 1.2 the displays 11 1.3 first start-up 12 1.4 description of the applications 13 1.4.1 vacon hvac application 13 2 wizards 20 2.1 pid mini-wizard 20 2.2 multi-pu...
Page 8
5.3 group 3.3: control reference settings 58 5.4 group 3.4: ramp and brakes setup 60 5.5 group 3.5: i/o configuration 61 5.6 group 3.6: fieldbus data mapping 69 5.7 group 3.7: prohibit frequencies 70 5.8 group 3.8: limit supervisions 71 5.9 group 3.9: protections 72 5.10 group 3.10: automatic reset ...
Page 9
10 parameter descriptions 112 10.1 motor settings 112 10.1.1 motor nameplate parameters 112 10.1.2 motor control parameters 113 10.2 start/stop setup 117 10.3 references 124 10.3.1 frequency reference 124 10.3.2 preset frequencies 125 10.3.3 motor potentiometer parameters 127 10.4 ramps and brakes s...
Page 10
11 fault tracing 187 11.1 a fault comes into view 187 11.1.1 resetting with the reset button 187 11.1.2 resetting with a parameter in the graphical display 187 11.1.3 resetting with a parameter in the text display 188 11.2 fault history 189 11.2.1 examining the fault history in the graphical display...
Page 11: Quick Startup Guide
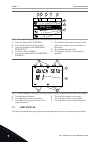
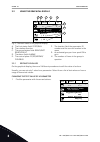
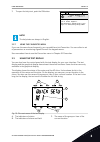
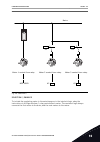
1 quick startup guide 1.1 control panel and keypad the control panel is the interface between the ac drive and the user. With the control panel, you can control the speed of a motor and monitor the status of the ac drive. You can also set the parameters of the ac drive. A b c i h d g f e fig. 1: the...
Page 12
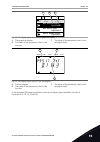
Stop ready i/o main menu a b c d e f h g quick setup ( 17 ) monitor ( 5 ) parameters ( 12 ) m1 id: fig. 2: the graphical display a. The first status field: stop/run b. The rotation direction of the motor c. The second status field: ready/not ready/fault d. The alarm field: alarm/- e. The control pla...
Page 13
1 language selection the selection is different in all the language packages 2 daylight saving* russia us eu off 3 time* hh:mm:ss 4 date* dd.Mm. 5 year* yyyy * if a battery is installed, you see these questions. 6 run startup wizard? Yes no to set the parameter values manually, make the selection no...
Page 14
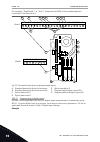
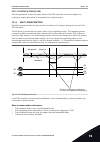
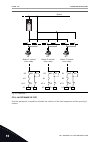
+ - 1 6 2 3 4 5 18 19 30 12 7 13 8 9 10 14 15 16 11 17 a b ma ao1-/gnd +24 v in 24 v out gnd gnd di1 di2 di3 di4 di5 di6 cm cm rs485 rs485 standard i/o board terminal signal description +10 v ref ai1+ ai1- ai2+ ai2- 24 v out reference output 24 v aux. Voltage i/o ground digital input 1 digital input...
Page 15
21 22 23 24 25 26 32 33 run run fault ready relay output 1 relay output 2 relay output 3 from standard i/o board terminal signal default relay board 1 from term. #6 or 12 from term. #13 ro1/1 nc ro1/2 cm ro1/3 no ro2/1 nc ro2/2 cm ro2/3 no ro3/1 cm ro3/2 no fig. 5: the control connection example for...
Page 16
Digital inputs floating connected to gnd (default!) fig. 7: the dip switch vacon · 16 quick startup guide 1 tel. +358 (0)201 2121 · fax +358 (0)201 212 205.
Page 17
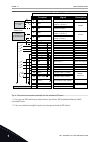
Table 2: quick setup parameter group index parameter min max unit default id description p1.1 motor nominal volt- age varies varies v varies 110 find this value u n on the nameplate of the motor. See p3.1.1.1. P1.2 motor nominal fre- quency 8.0 320.0 hz 50 111 find this value f n on the nameplate of...
Page 18
Table 2: quick setup parameter group index parameter min max unit default id description p1.12 preset frequency 2 p3.3.1 300.00 hz 15.00 106 select with the digital input: preset frequency selection 1 (p3.5.1.16) (default = digital input 5) p1.13 acceleration time 1 0.1 3000.0 s 20.0 103 gives the q...
Page 19
Table 2: quick setup parameter group index parameter min max unit default id description p1.20 startup wizard ** 0 1 0 1171 0 = inactive 1 = activate see chapter 1.3 first start-up. P1.21 fire mode wizard ** 0 1 0 1672 0 = inactive 1 = activate * = the parameter is only visible on the graphical keyp...
Page 20: Wizards
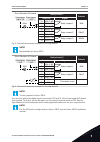
2 wizards 2.1 pid mini-wizard the application wizard helps you to set the basic parameters that are related to the application. To start the pid mini-wizard, set the value activate to parameter p1.17 pid mini-wizard in the quick setup menu. The default settings tell you to use the pid controller in ...
Page 21
9 set the signal range of the analogue input 0 = 0-10v / 0-20ma 1 = 2-10v / 4-20ma see table 15 analogue input settings. 10 set a value for keypad setpoint 1 (p3.12.2.1) and keypad setpoint 2 (p3.12.2.2) depends on the range set in the question 9. 11 using the sleep function 0 = no 1 = yes if you gi...
Page 22
18 set a value for include fc (p3.14.3) 0 = disabled 1 = enabled 19 set a value for autochange interval (p3.14.5) 0.0-3000.0 h 20 set a value for autochange: frequency limit (p3.14.6) 0.00-50.00 hz 21 set a value for bandwidth (p3.14.8) 0-100% 22 set a value for bandwidth delay (p3.14.9) 0-3600 s af...
Page 23
2 set a value for parameter p3.17.3 fire mode fre- quency 8.00 hz...P3.3.1.2 (maxfreqref) 3 activate the signal when the contact opens or when it closes 0 = open contact 1 = closed contact 4 set a value for parameters p3.17.4 fire mode acti- vation on open / p3.17.5 fire mode activation on close mak...
Page 24: User Interfaces
3 user interfaces 3.1 navigation on the keypad the data of the ac drive is in menus and submenus. To move between the menus, use the arrow buttons up and down in the keypad. To go into a group or an item, push the ok button. To go back to the level where you were before, push the back/reset button. ...
Page 25
Main menu submenus submenus submenus main menu main menu m2 monitor m1 quick setup m2.1 multimonitor m3.1 motor settings m3.2 start/stop setup m 3.3 r eferences m 3.4 r am ps a nd b ra kes m 3.5 i/o conf igur ation m3.6 fb data mapping m 3.10 a u tomatic r eset m3.11 timer functions m3.18 kwh pulse ...
Page 26
3.2 using the graphical display stop ready i/o main menu a b c d e f h g quick setup ( 17 ) monitor ( 5 ) parameters ( 12 ) m1 id: fig. 9: the main menu of the graphical display a. The first status field: stop/run b. The rotation direction c. The second status field: ready/not ready/fault d. The ala...
Page 27
2 to go to the edit mode, push the ok button 2 times or push the arrow button right. Stop ready i/o rem control place m3.2.1 id: edit help add to favourites 3 to set a new value, push the arrow buttons up and down. Stop ready i/o rem control place m3.2.1 id: fieldbusctrl i/o control 4 to accept the ...
Page 28
3 if the value is numerical, move from digit to digit with the arrow buttons left and right. Change the digits with the arrow buttons up and down. Stop ready i/o minfreqreference p3.3.1.1 id:101 00.00 hz min: 0.00hz max: 50.00hz 4 to accept the change, push the ok button. To ignore the change, go ba...
Page 29
2 to move in the list of values, use the arrow buttons up and down. Stop ready i/o m 3.12.1.3.1 id: days monday tuesday wednesday thursday friday sunday 3 to add a value into your selection, select the box that is next to it with the arrow button right. Stop ready i/o m 3.12.1.3.1 id: days monday tu...
Page 30
Changing the control place 1 anywhere in the menu structure, push the funct button. Stop ready keypad id: m1 main menu monitor ( 12 ) ( 21 ) ( 6 ) parameters diagnostics 2 to make a selection of the local/remote, use the arrow buttons up and down. Push the ok button. Stop ready keypad id:1805 choose...
Page 31
Going into the control page it is easy to monitor the most important values in the control page. 1 anywhere in the menu structure, push the funct button. Stop ready i/o main menu ( 21 ) ( 6 ) parameters ( 12 ) monitor diagnostics m1 id: 2 to make a selection of the control page, push the arrow butto...
Page 32
You can make a selection of the values that show up here (see instructions in chapter 4.1.1 multimonitor). Changing the rotation direction you can change the rotation direction of the motor quickly with the funct button. Note! The command change direction is available in the menu only if the current...
Page 33
4 the rotation direction changes immediately. You can see that the arrow indication in the status field of the display changes. Stop ready i/o id: m1 main menu monitor ( 7 ) parameters ( 15 ) diagnostics ( 6 ) 3.2.4 copying the parameters note! This function is available only in the graphical displa...
Page 34
2 go into the parameter backup submenu. Stop ready keypad id: m6.5 user settings language selection english parameter backup ( 7 ) drive name drive 3 use the arrow buttons up and down to make a selection of a function. Accept the selection with the ok button. Stop ready keypad id: m6.5.1 parameter b...
Page 35
3.2.5 comparing the parameters with this function, you can compare the current parameter set with 1 of these 4 sets. • set 1 (p6.5.4 save to set 1) • set 2 (p6.5.6 save to set 2) • the defaults (p6.5.1 restore factory defaults) • the keypad set (p6.5.2 save to keypad) see more about these parameters...
Page 36
4 examine the comparing between the current values and the values of the other set. Stop ready i/o id:113 active set-set 1 motor nom currnt motor cos phi 0.56a 1.90a 0.68 1.74 a b c d a. The current value b. The value of the other set c. The current value d. The value of the other set 3.2.6 help tex...
Page 37
3 to open the help text, push the ok button. Stop ready i/o id:403 m3.5.1.1 ctrl signal 1 a start signal 1 for control place i/o a. Start signal 1 functionality chosen with i/o a logic in start/stop setup menu. Note! The help texts are always in english. 3.2.7 using the favourites menu if you use th...
Page 38
D. The current location in the menu e. The indicators of the control place f. The indicators of the rotation direction 3.3.1 editing the values changing the text value of a parameter set the value of a parameter with this procedure. 1 find the parameter with the arrow buttons. Ready fault alarm stop...
Page 39
3 move from digit to digit with the arrow buttons left and right. Change the digits with the arrow buttons up and down. 4 accept the change with the ok button. To ignore the change, go back to the level where you were before with the back/reset button. 3.3.2 resetting a fault to reset a fault, you c...
Page 40
2 to make a selection of the local/remote, use the arrow buttons up and down. Push the ok button. Ready fault alarm stop run keypad i/o rev fwd bus 3 to make a selection of local or remote, use the arrow buttons up and down again. To accept the selection, push the ok button. Ready fault alarm stop r...
Page 41
2 to make a selection of the control page, push the arrow buttons up and down. Go in with the ok button. The control page opens. Ready fault alarm stop run keypad i/o rev fwd bus 3 if you use the local control place and the keypad reference, you can set p3.3.6 keypad reference with the ok button. Re...
Page 42
3.4 menu structure menu function quick setup see chapter 1.4.1 vacon hvac application. Monitor multi-monitor * basic timer functions pid controller 1 pid controller 2 multi-pump fieldbus data temperature inputs ** parameters see chapter 5 parameters menu. Diagnostics active faults reset faults fault...
Page 43
Menu function user settings language selections application selection parameter backup * drive name favourites * see chapter 8.2 favourites. User levels see chapter 8.3 user levels. * = the function is not available in the control panel with a text display. ** = the function is only available when t...
Page 44
Note! The multimonitor menu is not available in the text display. Basic the basic monitoring values can include statuses, measurements, and the actual values of parameters and signals. See chapter 4.1.2 basic. Timer functions with this function, you can monitor the timer functions and the real time ...
Page 45
See more on how to use vacon live in the help menu of the program. Fig. 11: the vacon live pc tool user interfaces vacon · 45 24-hour support +358 (0)201 212 575 · email: vacon@vacon.Com 3.
Page 46: Monitoring Menu
4 monitoring menu 4.1 monitor group you can monitor the actual values of the parameters and signals. You can also monitor the statuses and measurements. You can customise some of the values that you can monitor. 4.1.1 multimonitor on the multimonitor page, you can collect 9 items to monitor. Changin...
Page 47
4 to make a selection of a new item in the list, push ok. Stop ready i/o id:1 m2.1.1.1 freqreference 0.00 % motor power output frequency freqreference motor speed motor current motor torque 0.00 hz 10.00 hz 0.00 rpm 0.00 a 0.00 % 4.1.2 basic the basic monitoring values are the actual values of selec...
Page 48
Table 3: items in the monitoring menu index monitoring value unit id description v2.2.1 output frequency hz 1 v2.2.2 frequency reference hz 25 v2.2.3 motor speed rpm 2 v2.2.4 motor current a 3 v2.2.5 motor torque % 4 v2.2.7 motor shaft power % 5 v2.2.8 motor shaft power kw/hp 73 v2.2.9 motor voltage...
Page 49
Table 3: items in the monitoring menu index monitoring value unit id description v2.2.23 appl.Statusword 1 89 b0 = interlock1 b1 = interlock2, b5 = i/o a control act. B6 = i/o b control act. B7 = fieldbus control act. B8 = local control act. B9 = pc control act. B10 = preset frequencies act. B12 = f...
Page 50
Table 4: monitoring of the timer functions index monitoring value unit id description v2.3.1 tc 1, tc 2, tc 3 1441 v2.3.2 interval 1 1442 v2.3.3 interval 2 1443 v2.3.4 interval 3 1444 v2.3.5 interval 4 1445 v2.3.6 interval 5 1446 v2.3.7 timer 1 s 1447 v2.3.8 timer 2 s 1448 v2.3.9 timer 3 s 1449 v2.3...
Page 51
4.1.5 pid2 controller monitoring table 6: monitoring of the values of the pid2 controller index monitoring value unit id description v2.5.1 pid2 setpoint varies 83 v2.5.2 pid2 feedback varies 84 v2.5.3 pid2 error value varies 85 v2.5.4 pid2 output % 86 v2.5.5 pid2 status 87 0=stopped 1=running 2=in ...
Page 52
4.1.7 fieldbus process data monitoring table 8: fieldbus data monitoring index monitoring value unit id description v2.8.1 fb control word 874 v2.8.2 fb speed reference 875 v2.8.3 fb data in 1 876 v2.8.4 fb data in 2 877 v2.8.5 fb data in 3 878 v2.8.6 fb data in 4 879 v2.8.7 fb data in 5 880 v2.8.8 ...
Page 53: Parameters Menu
5 parameters menu the hvac application has the following parameter groups: menu and parameter group description group 3.1: motor settings basic and advanced motor settings. Group 3.2: start/stop setup start and stop functions. Group 3.3: control reference settings frequency reference setup. Group 3....
Page 54
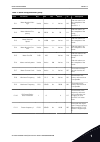
Table 9: motor nameplate parameters index parameter min max unit default id description p3.1.1.1 motor nominal volt- age varies varies v varies 110 p3.1.1.2 motor nominal fre- quency 8.00 320.00 hz 50 / 60 111 p3.1.1.3 motor nominal speed 24 19200 rpm varies 112 p3.1.1.4 motor nominal cur- rent vari...
Page 55
Table 10: motor control settings index parameter min max unit default id description p3.1.2.1 switching frequency 1.5 varies khz varies 601 p3.1.2.2 motor switch 0 1 0 653 0 = disabled 1 = enabled p3.1.2.4 zero frequency volt- age 0.00 40.00 % varies 606 p3.1.2.5 motor preheat func- tion 0 3 0 1225 ...
Page 56
5.2 group 3.2: start/stop setup table 11: start/stop setup menu index parameter min max unit default id description p3.2.1 remote control place 0 1 0 172 0 = i/o control 1 = fieldbus control p3.2.2 local/remote 0 1 0 211 0 = remote 1 = local p3.2.3 keypad stop button 0 1 0 114 0 = no (always ena- bl...
Page 57
Table 11: start/stop setup menu index parameter min max unit default id description p3.2.8 fieldbus start logic 0 1 0 889 0 = a rising edge is necessary 1 = state p3.2.9 start delay 0.00 60.00 s 0.00 524 parameters menu vacon · 57 24-hour support +358 (0)201 212 575 · email: vacon@vacon.Com 5.
Page 58
5.3 group 3.3: control reference settings table 12: control reference settings index parameter min max unit default id description p3.3.1 minimum frequency 0.00 p3.3.2 hz 0.00 101 p3.3.2 maximum frequency p3.3.1 320.00 hz 0.00 102 p3.3.3 i/o control refer- ence a selection 1 11 6 117 1 = preset freq...
Page 59
Table 12: control reference settings index parameter min max unit default id description p3.3.11 preset frequency 0 p3.3.1 p3.3.2 hz 5.00 180 p3.3.12 preset frequency 1 p3.3.1 p3.3.1 hz 10.00 105 p3.3.13 preset frequency 2 p3.3.1 p3.3.1 hz 15.00 106 p3.3.14 preset frequency 3 p3.3.1 p3.3.1 hz 20.00 ...
Page 60
5.4 group 3.4: ramp and brakes setup table 13: ramp and brakes setup index parameter min max unit default id description p3.4.1 ramp 1 shape 0.0 10.0 s 0.0 500 p3.4.2 acceleration time 1 0.1 3000.0 s 5.0 103 p3.4.3 deceleration time 1 0.1 3000.0 s 5.0 104 p3.4.4 ramp 2 shape 0.0 10.0 s 0.0 501 p3.4....
Page 61
5.5 group 3.5: i/o configuration table 14: digital input settings index parameter default id description p3.5.1.1 control signal 1 a digin slota.1 403 p3.5.1.2 control signal 2 a digin slota.2 404 p3.5.1.3 control signal 1 b digin slot0.1 423 p3.5.1.4 control signal 2 b digin slot0.1 424 p3.5.1.5 i/...
Page 62
Table 14: digital input settings index parameter default id description p3.5.1.23 pid1 select setpoint digin slot0.1 1047 open = setpoint 1 closed = setpoint 2 p3.5.1.24 pid2 start signal digin slot0.2 1049 open = pid2 in stop mode closed = pid2 regulating p3.5.1.25 pid2 select setpoint digin slot0....
Page 63
Table 14: digital input settings index parameter default id description p3.5.1.44 fire mode preset frequency selection 0 digin slot0.1 15531 p3.5.1.45 fire mode preset frequency selection 1 digin slot0.1 15532 p3.5.1.46 param. Set 1/2 sel. Digin slot0.1 496 open = parameter set 1 closed = parameter ...
Page 64
Table 15: analogue input settings index parameter min max unit default id description p3.5.2.1 ai1 signal selection anin slota.1 377 p3.5.2.2 ai1 filter time 0.0 300.0 s 1.0 378 p3.5.2.3 ai1 signal range 0 1 0 379 0 = 0–10v / 0–20ma 1 = 2–10v / 4–20ma p3.5.2.4 ai1 custom. Min -160.00 160.00 % 0.00 3...
Page 65
Table 15: analogue input settings index parameter min max unit default id description p3.5.2.25 ai5 signal selection anin slot0.1 188 see p3.5.2.1 p3.5.2.26 ai5 filter time 0.0 300.0 s 1.0 189 see p3.5.2.2 p3.5.2.27 ai5 signal range 0 1 0 190 see p3.5.2.3 p3.5.2.28 ai5 custom. Min -160.00 160.00 % 0...
Page 66
Table 16: digital output settings on standard i/o board index parameter min max unit default id description p3.5.3.2.1 basic ro1 function 0 41 2 11001 the function selection for basic r01 0 = none 1 = ready 2 = run 3 = fault 4 = faultinvert 5 = alarm 6 = reverse 7 = at speed 8 = motor regulator acti...
Page 67
Table 16: digital output settings on standard i/o board index parameter min max unit default id description p3.5.3.2.1 basic ro1 function 0 41 2 11001 29 = motor 3 control 30 = motor 4 control 31 = motor 5 control 32 = reserved 33 = reserved 34 = maintenance alarm 35 = maintenance fault 36 = thermis...
Page 68
Table 17: standard i/o board analogue output settings index parameter min max unit default id description p3.5.4.1.1 ao1 function 0 pid feed- back 2 10050 0 = test 0% (not used) 1 = test 100% 2 = output freq (0 - fmax) 3 = freq reference (0 - fmax) 4 = motor speed (0 - motor nominal speed) 5 = outpu...
Page 69
Table 17: standard i/o board analogue output settings index parameter min max unit default id description p3.5.4.1.5 ao1 maximum scale varies varies varies 0.0 10054 slot c, d and e analogue outputs shows only parameters for existing outputs in slot c/d/e. The selections are the same as in basic a01...
Page 70
Table 19: the default values for process data out in fieldbus data default value scale process data out 1 output frequency 0.01 hz process data out 2 motor speed 1 rpm process data out 3 motor current 0.1 a process data out 4 motor torque 0.1% process data out 5 motor power 0.1% process data out 6 m...
Page 71
5.8 group 3.8: limit supervisions table 21: limits supervision settings index parameter min max unit default id description p3.8.1 supervision #1 item selection 0 7 0 1431 0 = output frequency 1 = frequency reference 2 = motor current 3 = motor torque 4 = motor power 5 = dc-link voltage 6 = analogue...
Page 72
5.9 group 3.9: protections table 22: protections settings index parameter min max unit default id description p3.9.1 response to ana- logue input low fault 0 4 0 700 0 = no action 1 = alarm 2 = alarm, set the pre- set fault frequency (p3.3.19) 3 = fault (stop accord- ing to stop mode) 4 = fault (sto...
Page 73
Table 22: protections settings index parameter min max unit default id description p3.9.15 underload fault (broken belt/dry pump) 0 3 0 713 see p3.9.2. P3.9.16 underload protec- tion: field weaken- ing area load 10.0 150.0 % 50.0 714 p3.9.17 underload protec- tion: zero frequency load 5.0 150.0 % 10...
Page 74
*) this parameter is not visible if the drive does not have support for safety torque off functionality. 5.10 group 3.10: automatic reset table 23: autoreset settings index parameter min max unit default id description p3.10.1 automatic reset 0 1 1 731 0 = disabled 1 = enabled p3.10.2 restart functi...
Page 75
5.11 group 3.11: timer functions table 24: 3.11.1 interval 1 index parameter min max unit default id description p3.11.1.1 on time 00:00:00 23:59:59 hh:mm: ss 00:00:00 1464 p3.11.1.2 off time 00:00:00 23:59:59 hh:mm: ss 00:00:00 1465 p3.11.1.3 from day 0 6 0 1466 0 = sunday 1 = monday 2 = tuesday 3 ...
Page 76
Table 26: 3.11.3 interval 3 index parameter min max unit default id description p3.11.3.1 on time 00:00:00 23:59:59 hh:mm: ss 00:00:00 1474 see interval 1. P3.11.3.2 off time 00:00:00 23:59:59 hh:mm: ss 00:00:00 1475 see interval 1. P3.11.3.3 from day 0 6 0 1476 see interval 1. P3.11.3.4 to day 0 6 ...
Page 77
Table 29: 3.11.6 timer 1 index parameter min max unit default id description p3.11.6.1 duration 0 72000 s 0 1489 p3.11.6.2 assign to channel 0 3 0 1490 a checkbox selec- tion 0 = not used 1 = time channel 1 2 = time channel 2 3 = time channel 3 p3.11.6.3 mode toff ton toff 15527 table 30: 3.11.7 tim...
Page 78
5.12 group 3.12: pid-controller 1 table 32: pid controller 1 basic settings index parameter min max unit default id description p3.12.1.1 pid gain 0.00 1000.00 % 100.00 118 p3.12.1.2 pid integration time 0.00 600.00 s 1.00 119 p3.12.1.3 pid derivation time 0.00 100.00 s 0.00 132 p3.12.1.4 process un...
Page 79
Table 33: setpoint settings index parameter min max unit default id description p3.12.2.1 keypad setpoint 1 varies varies varies 0 167 p3.12.2.2 keypad setpoint 2 varies varies varies 0 168 p3.12.2.3 setpoint ramp time 0.00 300.0 s 0.00 1068 p3.12.2.4 setpoint source 1 selection 0 19 1 332 0 = not u...
Page 80
Table 33: setpoint settings index parameter min max unit default id description p3.12.2.16 sleep delay 2 0 3000 s 0 1076 see p3.12.2.8. P3.12.2.17 wake-up level 2 -214748. 36 214748. 36 varies 0.0000 1077 see p3.12.2.8. P3.12.2.18 setpoint 2 wake-up mode 0 1 0 15540 0 = absolute level 1 = relative s...
Page 81
Table 34: feedback settings index parameter min max unit default id description p3.12.3.1 feedback function 1 9 1 333 1 = only source1 in use 2 = sqrt(source1); (flow=constant x sqrt(pressure)) 3 = sqrt(source1- source 2) 4 = sqrt(source 1) + sqrt (source 2) 5 = source 1 + source 2 6 = source 1 - so...
Page 82
Table 35: feedforward settings index parameter min max unit default id description p3.12.4.1 feedforward func- tion 1 9 1 1059 see p3.12.3.1 p3.12.4.2 feedforward func- tion gain -1000 1000 % 100.0 1060 see p3.12.3.2 p3.12.4.3 feedforward 1 source selection 0 14 0 1061 see p3.12.3.3 p3.12.4.4 feedfo...
Page 83
5.13 group 3.13: pid-controller 2 table 38: basic settings index parameter min max unit default id description p3.13.1.1 enable pid 0 1 0 1630 0 = disabled 1 = enabled p3.13.1.2 output in stop 0.0 100.0 % 0.0 1100 p3.13.1.3 pid gain 0.00 1000.00 % 100.00 1631 see p3.12.1.1. P3.13.1.4 pid integration...
Page 84
Table 39: setpoints index parameter min max unit default id description p3.13.2.1 keypad setpoint 1 0.00 100.00 varies 0.00 1640 p3.13.2.2 keypad setpoint 2 0.00 100.00 varies 0.00 1641 p3.13.2.3 setpoint ramp time 0.00 300.00 s 0.00 1642 p3.13.2.4 setpoint source 1 selection 0 19 1 1643 0 = not use...
Page 85
Table 40: feedbacks index parameter min max unit default id description p3.13.3.1 feedback function 1 9 1 1650 see p3.12.3.1. P3.13.3.2 feedback function gain -1000.0 1000.0 % 100.0 1651 see p3.12.3.2. P3.13.3.3 feedback 1 source selection 0 14 1 1652 see p3.12.3.3. P3.13.3.4 feedback 1 minimum -200...
Page 86
5.14 group 3.14: multipump table 42: multipump parameters index parameter min max unit default id description p3.14.1 number of motors 1 5 1 1001 p3.14.2 interlock function 0 1 1 1032 0 = not used 1 = enabled p3.14.3 include fc 0 1 1 1028 0 = disabled 1 = enabled p3.14.4 autochange 0 1 1 1027 0 = di...
Page 87
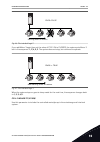
5.15 group 3.16: fire mode table 43: fire mode parameters index parameter min max unit default id description p3.16.1 fire mode password 0 9999 0 1599 1002 = enabled 1234 = test mode p3.16.2 fire mode activ. Open digin slot0.2 1596 open = fire mode active closed = no action p3.16.3 fire mode activ. ...
Page 88
5.16 group 3.17: application settings table 44: application settings index parameter min max unit default id description p3.17.1 password 0 9999 0 1806 p3.17.2 °c / °f selection °c 1197 p3.17.3 kw/hp selection kw 1198 p3.17.4 functbuttonconfig 0 7 7 1195 b0 = local/remote b1 = control page b2 = chan...
Page 89: Diagnostics Menu
6 diagnostics menu 6.1 active faults when there is a fault or many faults, the display shows the name of the fault and blinks. Push ok to go back to the diagnostics menu. The submenu active faults shows the number of faults. To see the fault-time data, make a selection of a fault and push ok. The fa...
Page 90
6.4 total counters table 46: the total counter parameters in the diagnostics menu index parameter min max unit default id description v4.4.1 energy counter varies 2291 the quantity of energy taken from the supply network. You cannot reset the counter. In the text display: the highest energy unit tha...
Page 91
Table 46: the total counter parameters in the diagnostics menu index parameter min max unit default id description v4.4.14 power on time (text keypad) hh:min: ss the power on time in hours, minutes and seconds. V4.4.15 start command counter 2295 the number of times that the power unit has been start...
Page 92
6.6 software info table 48: the software info parameters in the diagnostics menu index parameter min max unit default id description v4.6.1 software package (graphical keypad) 2524 the code for the soft- ware identification v4.6.2 software package id (text keypad) v4.6.3 software package version (te...
Page 93: I/o and Hardware Menu
7 i/o and hardware menu in this menu, there are different settings that are related to the options. 7.1 basic i/o in the basic i/o menu, you can monitor the statuses of the inputs and the outputs. I/o and hardware menu vacon · 93 24-hour support +358 (0)201 212 575 · email: vacon@vacon.Com 7.
Page 94
Table 49: the basic i/o parameters in the i/o and hardware menu index parameter min max unit default id description v5.1.1 digital input 1 0 1 0 2502 status of the digital input signal v5.1.2 digital input 2 0 1 0 2503 status of the digital input signal v5.1.3 digital input 3 0 1 0 2504 status of th...
Page 95
Table 49: the basic i/o parameters in the i/o and hardware menu index parameter min max unit default id description v5.1.11 analogue output 1 mode 1 3 1 2512 shows the mode that is set for the analogue input signal. The selec- tion is made with a dip switch on the control board. 1 = 0...20ma 3 = 0.....
Page 96
7.3 real time clock table 51: the real time clock parameters in the i/o and hardware menu index parameter min max unit default id description v5.5.1 battery state 1 3 2205 status of the battery. 1 = not installed 2 = installed 3 = replace the battery p5.5.2 time hh:mm: ss 2201 the current time of th...
Page 97
Table 52: power unit settings, fan index parameter min max unit default id description p5.5.1.1 fan control mode 0 1 1 2377 0 = always on 1 = optimised v5.6.1.5 fan lifetime n/a n/a h 849 fan lifetime p5.6.1.6 fan lifetime alarm limit 0 200 000 h 50 000 824 fan lifetime alarm limit p5.6.1.7 fan life...
Page 98
7.5 keypad table 54: the keypad parameters in the i/o and hardware menu index parameter min max unit default id description p5.7.1 timeout time 0 60 min 0 804 the time after which the display goes back to the page that is set with parameter p5.7.2. 0 = not used p5.7.2 default page 0 4 0 2318 0 = non...
Page 99: Menus
8 user settings, favourites and user level menus 8.1 user settings table 55: general settings in the user settings menu index parameter min max unit default id description p6.1 language selection varies varies varies 802 the selection is differ- ent in all the language packages m6.5 parameter backup...
Page 100
8.1.1 parameter backup table 56: the parameter backup parameters in the user settings menu index parameter min max unit default id description p6.5.1 restore factory defaults 831 restores the default parameter values and starts the startup wiz- ard. P6.5.2 save to keypad * 2487 saves the parameter v...
Page 101
Table 57: the parameter compare index parameter min max unit default id description p6.6.1 active set-set 1 2493 starts to compare parameters to the selected set. P6.6.2 active set-set 2 2494 starts to compare parameters to the selected set. P6.6.3 active set-defaults 2495 starts to compare paramete...
Page 102
2 make a selection of add to favourites and push the ok button. Stop ready i/o motor nom freq edit help add to favourites 3 the steps are now completed. To continue, read the instructions on the display. Stop ready i/o motor nom freq was added to favourites. Press ok to continue. Removing an item fr...
Page 103
8.3 user levels use the user level parameters to keep the personnel who are not approved from making changes in the parameters. You can also prevent accidental changes in the parameters. When you make a selection of a user level, the user cannot see all the parameters on the display of the control p...
Page 104
3 to change the digits of the access code, use all the arrow buttons. Stop ready alarm i/o id:2362 p8.2 access code min:0 max:9 00000 4 accept the change with the ok button. Vacon · 104 user settings, favourites and user level menus 8 tel. +358 (0)201 2121 · fax +358 (0)201 212 205.
Page 105
9 monitoring value descriptions this chapter gives you the basic descriptions of all monitoring values. 9.1 basic v2.2.1 output frequency (id 1) this monitoring value shows the actual output frequency to the motor. V2.2.2 frequency reference (id 25) this monitoring value shows the actual frequency r...
Page 106
V2.2.12 motor temperature (id 9) this monitoring value shows the calculated motor temperature in percentage of the nominal working temperature. When the value rises above 105%, motor thermal protection fault occurs. V2.2.13 analogue input 1 (id 59) this monitoring value shows the value of the analog...
Page 107
V2.2.23 appl. Status word 1 (id 89) this monitoring value shows the bit coded statuses of the application. V2.2.24 appl. Status word 2 (id 90) this monitoring value shows the bit-coded statuses of the application. V2.2.25 kwh trip counter low (id 1054) this monitoring value shows the actual value of...
Page 108
V2.3.2 interval 1 (id 1442) this monitoring value shows the status of the interval function. V2.3.3 interval 2 (id 1443) this monitoring value shows the status of the interval function. V2.3.4 interval 3 (id 1444) this monitoring value shows the status of the interval function. V2.3.5 interval 4 (id...
Page 109
V2.4.4 pid1 output (id 23) this monitoring value shows the output of the pid controller as a percentage (0-100%). V2.4.5 pid1 status (id 24) this monitoring value shows the state of the pid controller. 9.4 pid2 controller v2.5.1 pid2 setpoint (id 83) this monitoring value shows the value of the pid ...
Page 110
9.6 fieldbus data v2.8.1 fb control word (id 874) this monitoring value shows the status of the fieldbus control word that the application uses in bypass mode. Depending on the fieldbus type or profile, the data that is received from the fieldbus can be modified before it is sent to the application....
Page 111
V2.8.11 fb status word (id 864) this monitoring value shows the status of the fieldbus status word that the application uses in bypass mode. Depending on the fieldbus type or profile, the data can be modified before it is sent to the fieldbus. V2.8.12 fb speed actual (id 865) this monitoring value s...
Page 112: Parameter Descriptions
10 parameter descriptions in this chapter, you can find data on the most special parameters of the application. For most parameters of the vacon 100 application, a basic description is sufficient. You can find these basic descriptions in the parameter tables of chapter 5 parameters menu. If other da...
Page 113
Select the type of the motor. You can select for example, asynchronous induction motor (im) or synchronous permanent magnet motor (pm). 10.1.2 motor control parameters p3.1.2.1 switching frequency (id 601) use this parameter to set the switching frequency of the ac drive. If you increase the switchi...
Page 114
P3.1.2.6 motor preheat function (id 1226) use this parameter to set the temperature limit of the motor preheat function. When the heatsink temperature or the measured motor temperature goes below this level, motor preheat becomes active. P3.1.2.7 motor preheat current (id 1227) use this parameter to...
Page 115
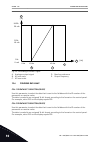
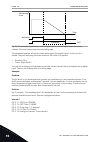
Un u[v] f[hz] nominal voltage of the motor linear squared field weakening point nominal frequency of the motor fig. 13: linear and squared change of the motor voltage p3.1.2.15 overvoltage control (id 607) use this parameter to set the overvoltage controller out of operation. See the description in ...
Page 116
This is done to prevent the operation of the pm motor in the field weakening area. The nominal voltage of the pm motor is much lower than the full output voltage of the drive. The nominal voltage of the pm motor agrees to the back-emf voltage of the motor at nominal frequency. But in a different mot...
Page 117
The bit b0 controls the search direction. When you set the bit to 0, the shaft frequency is searched in 2 directions, the positive and the negative. When you set the bit to 1, the shaft frequency is searched only in the frequency reference direction. This prevents the shaft movements for the other d...
Page 118
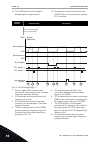
Selection number selection name description 0 yes the keypad stop button is always enabled. 1 no limited function of the keypad stop button. P3.2.4 start function (id 505) use this parameter to select the type of the start function. Selection number selection name description 0 ramping the drive dri...
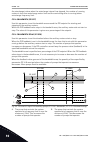
Page 119
Before you can start the motor, you must open the start/stop contact. In all the examples of the next pages, the stop mode is coasting. Cs = control signal. Selection number selection name description 0 cs1 = forward cs2 = backward the functions activate when the contacts are closed. T output freque...
Page 120
12. The stop button on the keypad is pushed again to stop the drive. 13. The attempt to start the drive with the start button is not successful, because cs1 is inactive. Selection number selection name description 1 cs1 = forward (edge) cs2 = inverted stop 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 9 8 set frequency 0 hz keypad...
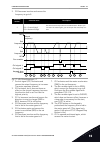
Page 121
9. Cs2 becomes inactive and causes the frequency to go to 0. Selection number selection name description 2 cs1 = forward (edge) cs2 = backward (edge) use this function to prevent an accidental start. Before you can start the motor again, you must open the start/stop con- tact. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 1...
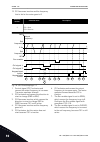
Page 122
12. Cs1 becomes inactive and the frequency that is fed to the motor goes to 0. Selection number selection name description 3 cs1 = start cs2 = reverse 1 2 3 4 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 5 t output frequency fwd rev ctrl signal 2 ctrl signal 1 run enable set frequency set frequency 0 hz keypad stop button keyp...
Page 123
9. The stop button on the keypad is pushed and the frequency that is fed to the motor goes to 0. (this signal only works if the value of p3.2.3 keypad stop button is yes.) 10. The drive starts because the start button on the keypad was pushed. 11. The drive is stopped again with the stop button on t...
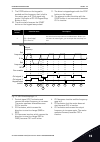
Page 124
7. The run enable signal is set to open, which causes the frequency to go to 0. Configure the run enable signal with parameter p3.5.1.10. 8. Before the drive can start, you must open and close cs1 again. 9. The stop button on the keypad is pushed and the frequency that is fed to the motor goes to 0....
Page 125
P3.3.5 keypad control reference selection (id 121) use this parameter to select the reference source when the control place is keypad. P3.3.6 keypad reference (id 184) use this parameter to adjust the frequency reference on the keypad. This parameter gives the frequency reference of the drive when t...
Page 126
P3.3.11 preset frequency 0 (id 180) use this parameter to set the preset frequency reference when the preset frequencies function is used. Select the preset frequencies with the digital input signals. P3.3.12 preset frequency 1 (id 105) use this parameter to set the preset frequency reference when t...
Page 127
To make a selection of a preset frequency between 1 and 7, give digital inputs to p3.5.1.15 (preset frequency selection 0), p3.5.1.16 (preset frequency selection 1), and/or p3.5.1.17 (preset frequency selection 2). The different sets of active digital inputs determine the preset frequency. You can f...
Page 128
This parameter defines when the reference of the motor potentiometer is set to 0. There are 3 selections in the reset function: no reset, reset when the drive stops, or reset when the drive is powered down. Selection number selection name description 0 no reset the last motor potentiometer frequency...
Page 129
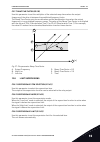
[t] [hz] id103, id104 id500 id500 fig. 20: the acceleration/deceleration curve (s-shaped) p3.4.2 acceleration time 1 (id 103) use this parameter to set the time that is necessary for the output frequency to increase from zero frequency to maximum frequency. P3.4.3 deceleration time 1 (id 104) use th...
Page 130
[t] [hz] id103, id104 id500 id500 fig. 21: the acceleration/deceleration curve (s-shaped) p3.4.5 acceleration time 2 (id 502) use this parameter to set the time that is necessary for the output frequency to increase from zero frequency to maximum frequency. P3.4.6 deceleration time 2 (id 503) use th...
Page 131
P3.4.11 frequency to start dc braking at ramp stop (id 515) use this parameter to set the output frequency at which the dc braking starts. P3.4.12 flux braking (id 520) use this parameter to enable the flux braking function. You can use flux braking as an alternative to dc braking. Flux braking incr...
Page 132
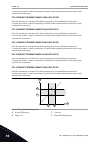
For example, "digin slota.1" or "di a.1" shows that the din1 on the standard board is connected in the board slot a. 2 1 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 30 a b 21 22 23 24 25 26 33 34 slot a slot b c a b d e a.1 g f a.2 a.1 a.2 a.3 a.4 a.5 a.6 fig. 22: the option board slots and programm...
Page 133
Stop ready i/o id:405 p3.5.1.7 digital inputs b a c diginslota.3 diginslot0.2 diginslota.6 fault reset close ext fault open ext fault close fig. 23: the digital inputs menu in the graphical display a. The graphical display b. The name of the parameter, that is, the function c. The value of the param...
Page 134
Input type (graphi- cal display) input type (text dis- play) slot input # explanation digin di a 1 digital input #1 (terminal 8) on a board in slot a (standard i/o board). Digin di a 2 digital input #2 (terminal 9) on a board in slot a (standard i/o board). Digin di a 3 digital input #3 (terminal 10...
Page 135
2 in the edit mode, the slot value digin slota is underlined and blinks. If you have more digital inputs available in your i/o, for example, because of option boards in slots c, d or e, make a selection of them. Stop ready i/o ext fault close p3.5.1.7 id:405 min: max: digin slota.3 3 to activate the...
Page 136
Programming in the text display 1 make a selection of a parameter. To go into the edit mode, push the ok button. Ready fault alarm stop run keypad 1/o rev fwd bus 2 in the edit mode, the letter d blinks. If you have more digital inputs available in your i/o, for example, because of option boards in ...
Page 137
5 if the digital input di6 was already used for some other function, a message scrolls on the display. Change one of these selections. Ready fault alarm stop run keypad 1/o rev fwd bus after the steps, a digital signal to the digital input di6 controls the function external fault close. The value of...
Page 138
P3.5.1.1 control signal 1 a (id 403) use this parameter to select the digital input signal (control signal 1) that starts and stops the drive when the control place is i/o a (fwd). P3.5.1.2 control signal 2 a (id 404) use this parameter to select the digital input signal (control signal 2) that star...
Page 139
When the contact is open, the start of the motor is disabled. When the contact is closed, the start of the motor is enabled. To stop, the drive obeys the value of p3.2.5 stop function. Note! The state of the drive remains in 'not ready' if the state of this signal is 'opened'. P3.5.1.12 run interloc...
Page 140
P3.5.1.19 timer 2 (id 448) use this parameter to select the digital input signal that starts the timer. The timer starts when this signal is deactivated (falling edge). The output is deactivated when the time defined in the duration parameter has elapsed. P3.5.1.20 timer 3 (id 449) use this paramete...
Page 141
P3.5.1.29 motor 4 interlock (id 429) use this parameter to select the digital input signal that is used as interlock signal for the multi-pump system. P3.5.1.30 motor 5 interlock (id 430) use this parameter to select the digital input signal that is used as interlock signal for the multi-pump system...
Page 142
P3.5.1.46 parameter set 1/2 selection (id 496) use this parameter to set the digital input that selects the parameter set to be used. The parameter gives the digital input which is used to select parameter set 1 or set 2. The function is enabled if other slots than digin slot0 are selected to this p...
Page 143
10.5.4 digital outputs p3.5.3.2.1 basic ro1 function (id 11001) use this parameter to select a function or a signal that is connected to the relay output. Parameter descriptions vacon · 143 24-hour support +358 (0)201 212 575 · email: vacon@vacon.Com 10
Page 144
Table 60: the output signals through ro1 selection number selection name description 0 not used the output is not used. 1 ready the ac drive is ready to operate. 2 run the ac drive operates (the motor runs). 3 general fault a fault trip occurred. 4 general fault inverted a fault trip did not occur. ...
Page 145
Table 60: the output signals through ro1 selection number selection name description 24 reserved 25 pid1 supervision limits the feedback value of the pid1 controller is not in the super- vision limits. 26 pid2 supervision limits the feedback value of the pid2 controller is not in the super- vision l...
Page 146
Selection number selection name description 0 test 0% (not used) the analogue output is set to 0% or 20% so that it agrees with parameter p3.5.4.1.3. 1 test 100% the analogue output is set to 100% of the signal (10v / 20ma). 2 output frequency the actual output frequency from 0 to maximum frequency ...
Page 147
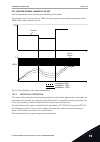
The filtering function is disabled when the filtering time is 0. P3.5.4.1.3 ao1 minimum (id 10052) use this parameter to change the range of the analogue output signal. For example, if '4ma' is selected, the range of analogue output signal is 4..20ma. Select the signal type (current/voltage) with th...
Page 148
0% 100% 50% c b a d e 0 ma 20 ma 10 ma [hz] [%] 10 hz 40 hz 0 hz fig. 25: the scaling of the ao1 signal a. Analogue output signal b. Ao min scale c. Ao max scale d. Max freq reference e. Output frequency 10.6 fieldbus data map p3.6.1 fb dataout 1 selection (id 852) use this parameter to select the d...
Page 149
P3.6.3 fb dataout 3 selection (id 854) use this parameter to select the data that is sent to the fieldbus with the id number of the parameter or monitor value. The data is scaled to an unsigned 16-bit format according to the format on the control panel. For example, value 25.5 on the display equals ...
Page 150
In some processes it can be necessary to avoid some frequencies because they cause mechanical resonance. P3.7.2 prohibit frequency range 1 high limit (id 510) use this parameter to prevent the drive operating on the prohibited frequencies. In some processes it can be necessary to avoid some frequenc...
Page 151
P3.7.7 ramp time factor (id 518) use this parameter to set the multiplier of the selected ramp times when the output frequency of the drive is between the prohibited frequency limits. The ramp time factor sets the acceleration and the deceleration time when the output frequency is in a prohibited fr...
Page 152
P3.8.4 supervision #1 limit hysteresis (id 1434) use this parameter to set the supervision limit hysteresis for the selected item. The unit shows automatically. P3.8.5 supervision #2 item selection (id 1435) use this parameter to select the supervision item. The output of the supervision function ca...
Page 153
P3.9.5 response to output phase fault (id 702) use this parameter to select the response of the drive to an 'output phase' fault. If the measurement of the motor current detects that there is no current in 1 motor phase, an output phase fault occurs. See p3.9.2 for more information. 10.9.1 motor the...
Page 154
The default value is set for conditions where there is no external fan. If you use an external fan, you can set the value higher than without the fan, for example at 90%. If you change parameter p3.1.1.4 (motor nominal current), parameter p3.9.2.3 is automatically set to its default value. Although ...
Page 155
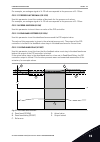
P3.9.10 motor thermal loadability (id 708) use this parameter to set the thermal loadability of the motor. For example, if you set the value to 130%, the motor goes to the nominal temperature with 130% of the motor nominal current. I/it t t t current fault/ alarm loadability 80% loadability 100% loa...
Page 156
Note! If you use long motor cables (max. 100 m) with small drives (≤1.5 kw), the motor current that the drive measures can be much higher than the actual motor current. It is because there are capacitive currents in the motor cable. P3.9.11 motor stall fault (id 709) use this parameter to select the...
Page 157
Note! For a stall state to occur, the output frequency must be below this limit for a certain time. 10.9.3 underload (dry pump) protection the motor underload protection makes sure that there is a load on the motor when the drive operates. If the motor loses the load, a problem can occur in the proc...
Page 158
Id714 id715 f 5 hz underload area torque field weakening point fig. 31: setting of the minimum load p3.9.17 underload protection: zero frequency load (id 715) use this parameter to set the minimum torque that the motor needs when the output frequency of the drive is 0. P3.9.18 underload protection: ...
Page 159
P3.9.19 response to fieldbus communication fault (id 733) use this parameter to select the response of the drive to a 'fieldbus timeout' fault. If the data connection between the master and the fieldbus board is defective, a fieldbus fault occurs. P3.9.20 slot communication fault (id 734) use this p...
Page 160
P3.9.29 response to safe torque off (sto) fault (id 775) use this parameter to select the response of the drive to a 'sto fault'. This parameter defines the response for f30 – safe torque off (fault id: 530). This parameter defines drive operation when safe torque off (sto) function is activated (e....
Page 161
With parameter p3.10.5, you can set the maximum number of automatic reset trials during the trial time set in p3.10.4. The fault type does not have an effect on the maximum number. Fault trigger autoreset trial time wait time wait time wait time id717 reset 1 reset 2 trial time id718 fault active al...
Page 162
P3.10.12 autoreset: external fault (id 726) use this parameter to enable the automatic reset after an external fault. P3.10.13 autoreset: underload fault (id 738) use this parameter to enable the automatic reset after an underload fault. P3.10.14 autoreset: pid supervision fault (id 15538) use this ...
Page 163
P assigntochannel interval 1 interval 2 interval 3 interval 4 timer 1 timer 2 timer 3 interval 5 timechannel 1 timechannel 2 timechannel 3 fig. 34: assigning intervals and timers to time channels is flexible. Every interval and timer has a parameter with which you can assign them to a time channel. ...
Page 164
Duration remaining time activation time out fig. 35: the activation signal comes from a digital input or a virtual digital input, like a time channel. The timer counts down from the falling edge. The parameters below will set the timer active when the digital input 1 on the slot a is closed. They wi...
Page 165
Interval 2 p3.11.2.1: on time: 09:00:00 p3.11.2.2: off time: 13:00:00 p3.11.2.3: from day: saturday p3.11.2.4: to day: sunday p3.11.2.5: assign to channel: time channel 1 timer 1 you can start the motor with the digital input 1 on slot a during other times than those specified with the intervals. In...
Page 166
P3.11.6.1 duration (id 1489) use this parameter to set the duration that the timer runs when the activation signal is removed (off-delay). P3.11.6.2 assign to channel (id 1490) use this parameter to select the time channel where the output of the timer function is assigned. You can use the time chan...
Page 167
For example, an analogue signal of 4...20 ma corresponds to the pressure of 0...10 bar. P3.12.1.7 process unit decimals (id 1035) use this parameter to set the number of decimals for the process unit values. For example, an analogue signal of 4...20 ma corresponds to the pressure of 0...10 bar. P3.1...
Page 168
10.12.2 setpoints p3.12.2.1 keypad setpoint 1 (id 167) use this parameter to set the setpoint value of the pid controller when the setpoint source is 'keypad sp'. The value of this parameter is given in the selected process unit. P3.12.2.2 keypad setpoint 2 (id 168) use this parameter to set the set...
Page 169
P3.12.2.10 sp1 wake-up mode (id 15539) use this parameter to select the operation for the wake up level parameter. With these parameters, you can set when the drive wakes up from the sleep mode. The drive wakes up from the sleep mode when the value of pid feedback goes below the wake-up level. This ...
Page 170
P3.12.3.2 feedback function gain (id 1058) use this parameter to adjust the gain of the feedback signal. This parameter is used, for example, with the value 2 in feedback function. P3.12.3.3 feedback 1 source selection (id 334) use this parameter to select the source of the pid feedback signal. The ...
Page 171
Pid + + lt ft ffw level ref level control outflow control fig. 40: the feedforward control p3.12.4.2 feedforward gain (id 1060) use this parameter to adjust the gain of the feedforward signal. P3.12.4.3 feedforward 1 source selection (id 1061) use this parameter to select the source of the pid feedf...
Page 172
P3.12.5.1 enable process supervision (id 735) regulating mode upper limit (id736) lower limit (id758) actual value delay (id737) alarm or fault reference fig. 41: the feedback supervision function use this parameter to enable the feedback supervision function. Set the upper limit and the lower limit...
Page 173
10.12.6 pressure loss compensation when you pressurise a long pipe that has many outlets, the best position for the sensor is in the middle of the pipe (the position 2 in the figure). You can also put the sensor directly after the pump. This gives the right pressure directly after the pump, but fart...
Page 174
With flow and compensation position 1 position 2 pressure no flow pipe length setpoint max freq and flow min freq and flow setpoint + max compensation setpoint pt pt fig. 43: enable setpoint 1 for pressure loss compensation 10.13 pid controller 2 10.13.1 basic settings p3.13.1.1 enable pid (id 1630)...
Page 175
P3.13.1.2 output in stop (id 1100) use this parameter to set the output value of the pid controller as a percentage of its maximum output value when it is stopped from a digital output. 10.14 multi-pump function the multi-pump function lets you control a maximum of 4 motors, pumps or fans with the p...
Page 176
When to disconnect and/or remove motors: • the feedback value is not in the bandwidth area. • the regulating motor operates at a close to minimum frequency (+2 hz). • the conditions above are true for longer than the bandwidth delay. • there are more motors that operate than the regulating one. P3.1...
Page 177
Starting order of motors id428 =false m1 m2 m3 m4 m5 fig. 46: the interlock logic 2 if you add motor 3 again (you set the value of p3.5.1.36 to closed), the system puts motor 3 last in the sequence: 1, 2, 4, 5, 3. The system does not stop, but continues to operate. New starting order of motors id428...
Page 178
Selection number selection name description 0 disabled the drive is always connected to motor 1. The interlocks do not have an effect on motor 1. Motor 1 is not included in the autochange logic. 1 enabled it is possible to connect the drive to any of the motors in the system. The interlocks have an ...
Page 179
K2 k3 k2 k3 m1 motor 1 control from relay motor 2 control from relay motor 3 control from relay not used mains m2 m3 fig. 48: selection 0 selection 1, enabled to include the regulating motor in the autochange or in the interlock logic, obey the instructions in the figure below. 1 relay controls each...
Page 180
K1 k1.1 k2 k2.1 k3 k3.1 k1 k1.1 k2 k2.1 k3 k3.1 k1.1 k1 k2 k3 k2 k3 k3 k1 k3 k1 k2 k1 k2.1 k2 k1 k3.1 k3 k2 mains m1 m2 m3 from relay motor 2 control motor 1 control from relay motor 3 control from relay fig. 49: selection 1 p3.14.4 autochange (id 1027) use this parameter to enable or disable the ro...
Page 181
Selection number selection name description 0 disabled in normal operation, the sequence of the motors is always 1, 2, 3, 4, 5. The sequence can change during the operation if you add or remove interlocks. After the drive stops, the sequence always changes back. 1 enabled the system changes the sequ...
Page 182
An autochange is done when the autochange interval has elapsed, the number of running motors is less than autochange motor limit and the controlling drive is running below autochange frequency limit. P3.14.8 bandwidth (id 1097) use this parameter to set the bandwith area around the pid setpoint for ...
Page 183
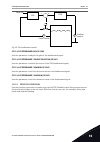
C. The number pumps that operate increases or decreases, if the pid controller cannot keep the process value feedback in the specified bandwidth around the setpoint. D. The specified bandwidth around the setpoint. 10.15 fire mode when fire mode is active, the drive resets all faults that occur and c...
Page 184
It is possible to try the fire mode with the password that activates the test mode. Then the warranty stays valid. Note! If fire mode is enabled, and you give the correct password to the parameter fire mode password, all the fire mode parameters become locked. To change the fire mode parameters, cha...
Page 185
P3.16.6 fire mode reverse (id 1618) use this parameter to select the digital input signal that gives a command for reverse rotation direction during the fire mode. The parameter does not have an effect in normal operation. If it is necessary for the motor to operate always forward or always reverse ...
Page 186
10.16 application settings p3.17.1 password (id 1806) use this parameter to set the administrator password. P3.17.2 c/f selection (id 1197) use this parameter to set the temperature measuring unit. The system shows all the temperature-related parameters and monitoring values in the set unit. P3.17.3...
Page 187: Fault Tracing
11 fault tracing when the control diagnostics of the ac drive find an unusual condition in the operation of the drive, the drive shows a notification about it. You can see the notification on the display of the control panel. The display shows the code, the name and a short description of the fault ...
Page 188
2 go to the submenu reset faults. Stop ready i/o id: m4.1 diagnostics ( 39 ) reset faults ( 0 ) active faults fault history 3 make a selection of the parameter reset faults. Stop ready i/o id: m4.2 reset faults help reset faults resetting with a parameter in the text display 1 go to the diagnostics ...
Page 189
3 make a selection of the value yes and push ok. Ready fault alarm stop run keypad i/o rev fwd bus 11.2 fault history in the fault history, you can find more data on the faults. There is a maximum number of 40 faults in the fault history. Examining the fault history in the graphical display 1 to see...
Page 190
3 you see the data in a list. Stop ready i/o code 39 source 3 source 1 id 380 state info old date 7.12.2009 time 04:46:33 operating time 862537s source 2 fault history m4.3.3.2 id: examining the fault history in the text display 1 push ok to go to fault history. Ready fault alarm stop run keypad 1/o...
Page 191
3 use the arrow button down to examine all the data. Ready fault alarm stop run keypad 1/o rev fwd bus ready fault alarm stop run keypad 1/o rev fwd bus ready fault alarm stop run keypad 1/o rev fwd bus fault tracing vacon · 191 24-hour support +358 (0)201 212 575 · email: vacon@vacon.Com 11.
Page 192
11.3 fault codes table 61: fault codes fault code fault id fault name possible cause how to correct the fault 1 1 overcurrent (hard- ware fault) there is too high a current (>4*i h) in the motor cable. Its cause can be 1 of these. • a sudden heavy load increase • a short circuit in the motor cables ...
Page 193
Table 61: fault codes fault code fault id fault name possible cause how to correct the fault 8 600 system fault there is no communication between the control board and the power. Reset the fault and restart the drive. If the fault occurs again, ask instructions from the distributor near to you. 602 ...
Page 194
Table 61: fault codes fault code fault id fault name possible cause how to correct the fault 9 80 undervoltage (fault) the dc-link voltage is lower than the limits. • too low a supply volt- age • ac drive internal fault • a defective input fuse • the external charge switch is not closed note! This f...
Page 195
Table 61: fault codes fault code fault id fault name possible cause how to correct the fault 19 180 power overload (short-time supervi- sion) the power of the drive is too high. Decrease the load. 181 power overload (long-time supervi- sion) 25 motor control fault a malfunction in the start angle id...
Page 196
Table 61: fault codes fault code fault id fault name possible cause how to correct the fault 30 520 safety diagnostics the sto inputs have a dif- ferent status. Do a check of the external safety switch. Do a check of the input connection and cable of the safety switch. Reset the drive and restart. I...
Page 197
Table 61: fault codes fault code fault id fault name possible cause how to correct the fault 33 fire mode enabled the fire mode of the drive is enabled. The protections of the drive are not used. 37 360 device changed (same type) the option board was replaced by a new one that you have used before i...
Page 198
Table 61: fault codes fault code fault id fault name possible cause how to correct the fault 50 1050 ai low fault 1 or more of the available analogue input signals is below 50% of the minimum signal range. A control cable is defective or loose. A mal- function in a signal source. Replace the defecti...
Page 199
Table 61: fault codes fault code fault id fault name possible cause how to correct the fault 101 1101 process supervision fault (pid1) the pid controller: the feed- back value is not in the supervision limits and the delay, if you set the delay. 105 1105 process supervision fault (pid2) the pid cont...
Page 201
Document id: rev. K sales code: doc-app100hvac+dluk vacon ltd member of the danfoss group runsorintie 7 65380 vaasa finland www.Danfoss.Com.