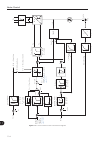
- DL manuals
- WEG
- Power Supply
- CFW-11
- Programming Manual
WEG CFW-11 Programming Manual
Summary of CFW-11
Page 3: Programming Manual
Programming manual series: cfw-11 language: english document number: 10004274148 / 00 software version: 5.8x publication date: 05/2016.
Page 4
Summary of reviews the table below describes all revisions made to this manual. Version review description v5.8x r00 first edition..
Page 5
Summary quick parameter reference, faults and alarms .................... 0-1 1 safety instructions .................................................................. 1-1 1.1 safety warnings in this manual ........................................................ 1-1 1.2 safety warnings on the produc...
Page 6
Summary 10 vvw control ......................................................................... 10-1 10.1 vvw control [25] ............................................................................. 10-3 10.2 motor data [43] ...........................................................................
Page 7
Summary 13 digital and analog inputs and outputs ......................... 13-1 13.1 i/o configuration [07] ..................................................................... 13-1 13.1.1 analog inputs [38] ......................................................................... 13-1 13.1.2 analo...
Page 8
Summary 20 pid regulator [46] .................................................................. 20-1 20.1 description and definitions ........................................................... 20-1 20.2 commissioning ....................................................................................
Page 9
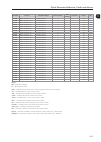
Quick parameter reference, faults and alarms 0-1 0 parameter function adjustable range factory setting user setting properties groups pag. P0000 access to parameters 0 to 9999 0 - - 5-3 p0001 speed reference 0 to 18000 rpm - ro 09 16-1 p0002 motor speed 0 to 18000 rpm - ro 09 16-1 p0003 motor curren...
Page 10
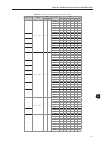
Quick parameter reference, faults and alarms 0-2 0 parameter function adjustable range factory setting user setting properties groups pag. P0030 igbts temperature u -20.0 to 150.0 °c - ro 09, 45 16-6 p0031 igbts temperature v -20.0 to 150.0 °c - ro 09, 45 16-6 p0032 igbts temperature w -20.0 to 150....
Page 11
Quick parameter reference, faults and alarms 0-3 0 parameter function adjustable range factory setting user setting properties groups pag. P0092 speed at last fault 0 to 18000 rpm - ro 08 16-14 p0093 reference last fault 0 to 18000 rpm - ro 08 16-14 p0094 frequency last fault 0.0 to 1020.0 hz - ro 0...
Page 12
Quick parameter reference, faults and alarms 0-4 0 parameter function adjustable range factory setting user setting properties groups pag. P0151 dc regul. Level v/f 339 to 400 v 585 to 800 v 585 to 800 v 585 to 800 v 585 to 800 v 809 to 1000 v 809 to 1000 v 924 to 1200 v 924 to 1200 v 400 v (p0296=0...
Page 13
Quick parameter reference, faults and alarms 0-5 0 parameter function adjustable range factory setting user setting properties groups pag. P0185 dc link regul. Level 339 to 400 v 585 to 800 v 585 to 800 v 585 to 800 v 585 to 800 v 809 to 1000 v 809 to 1000 v 924 to 1200 v 924 to 1200 v 400 v (p0296=...
Page 14
Quick parameter reference, faults and alarms 0-6 0 parameter function adjustable range factory setting user setting properties groups pag. P0205 read parameter sel. 1 0 = not selected 1 = speed refer. # 2 = motor speed # 3 = motorcurrent # 4 = dc link volt # 5 = motor freq. # 6 = motorvoltage # 7 = ...
Page 15
Quick parameter reference, faults and alarms 0-7 0 parameter function adjustable range factory setting user setting properties groups pag. P0220 loc/rem selection src 0 = always loc 1 = always rem 2 = lr key loc 3 = lr key rem 4 = dix 5 = serial/usb loc 6 = serial/usb rem 7 = anybus-cc loc 8 = anybu...
Page 16
Quick parameter reference, faults and alarms 0-8 0 parameter function adjustable range factory setting user setting properties groups pag. P0229 stop mode selection 0 = ramp to stop 1 = coast to stop 2 = fast stop 3 = by ramp with iq* 4 = fast stop with iq* 0 cfg 31, 32, 33, 34 13-31 p0230 dead zone...
Page 17
Quick parameter reference, faults and alarms 0-9 0 parameter function adjustable range factory setting user setting properties groups pag. P0251 ao1 function 0 = speed ref. 1 = total ref. 2 = real speed 3 = torque cur.Ref 4 = torque current 5 = output current 6 = process var. 7 = active current 8 = ...
Page 18
Quick parameter reference, faults and alarms 0-10 0 parameter function adjustable range factory setting user setting properties groups pag. P0257 ao3 function 0 = speed ref. 1 = total ref. 2 = real speed 3 = torque cur.Ref 4 = torque current 5 = output current 6 = process var. 7 = active current 8 =...
Page 19
Quick parameter reference, faults and alarms 0-11 0 parameter function adjustable range factory setting user setting properties groups pag. P0259 ao3 signal type 0 = 0 to 20 ma 1 = 4 to 20 ma 2 = 20 to 0 ma 3 = 20 to 4 ma 4 = 0 to 10 v 5 = 10 to 0 v 6 = -10 to +10 v 4 cfg 39 13-11 p0260 ao4 function...
Page 20
Quick parameter reference, faults and alarms 0-12 0 parameter function adjustable range factory setting user setting properties groups pag. P0266 di4 function 0 = not used 1 = run/stop 2 = general enable 3 = fast stop 4 = fwd run 5 = rev run 6 = start 7 = stop 8 = fwd/rev 9 = loc/rem 10 = jog 11 = i...
Page 21
Quick parameter reference, faults and alarms 0-13 0 parameter function adjustable range factory setting user setting properties groups pag. P0275 do1 function (rl1) 0 = not used 1 = n* > nx 2 = n > nx 3 = n 4 = n = n* 5 = zero speed 6 = is > ix 7 = is 8 = torque > tx 9 = torque 10 = remote 11 = run ...
Page 22
Quick parameter reference, faults and alarms 0-14 0 parameter function adjustable range factory setting user setting properties groups pag. P0276 do2 function (rl2) 0 = not used 1 = n* > nx 2 = n > nx 3 = n 4 = n = n* 5 = zero speed 6 = is > ix 7 = is 8 = torque > tx 9 = torque 10 = remote 11 = run ...
Page 23
Quick parameter reference, faults and alarms 0-15 0 parameter function adjustable range factory setting user setting properties groups pag. P0278 do4 function 0 = not used 1 = n* > nx 2 = n > nx 3 = n 4 = n = n* 5 = zero speed 6 = is > ix 7 = is 8 = torque > tx 9 = torque 10 = remote 11 = run 12 = r...
Page 24
Quick parameter reference, faults and alarms 0-16 0 parameter function adjustable range factory setting user setting properties groups pag. P0295 nd/hd vfd rated curr. 0 = 3.6 a / 3.6 a 1 = 5 a / 5 a 2 = 6 a / 5 a 3 = 7 a / 5.5 a 4 = 7 a / 7 a 5 = 10 a / 8 a 6 = 10 a / 10 a 7 = 13 a / 11 a 8 = 13.5 ...
Page 25
Quick parameter reference, faults and alarms 0-17 0 parameter function adjustable range factory setting user setting properties groups pag. 61 = 8.5 a / 7 a 62 = 10 a / 9 a 63 = 11 a / 9 a 64 = 12 a / 10 a 65 = 15 a / 13 a 66 = 17 a / 17 a 67 = 20 a / 17 a 68 = 22 a / 19 a 69 = 24 a / 21 a 70 = 27 a...
Page 26
Quick parameter reference, faults and alarms 0-18 0 parameter function adjustable range factory setting user setting properties groups pag. P0301 dc-braking speed 0 to 450 rpm 30 rpm v/f, vvw and sless 47 12-22 p0302 dc-braking voltage 0.0 to 10.0 % 2.0 % v/f and vvw 47 12-22 p0303 skip speed 1 0 to...
Page 27
Quick parameter reference, faults and alarms 0-19 0 parameter function adjustable range factory setting user setting properties groups pag. P0323 dc link power back 178 to 282 v 308 to 616 v 308 to 616 v 308 to 616 v 308 to 616 v 425 to 737 v 425 to 737 v 486 to 885 v 486 to 885 v 267 v (p0296=0) 46...
Page 28
Quick parameter reference, faults and alarms 0-20 0 parameter function adjustable range factory setting user setting properties groups pag. P0357 line phase loss time 0 to 60 s 3 s - 45 15-15 p0358 encoder fault config. 0 = off 1 = f067 on 2 = f065, f066 on 3 = all on 3 cfg and encoder 45 15-16 p035...
Page 29
Quick parameter reference, faults and alarms 0-21 0 parameter function adjustable range factory setting user setting properties groups pag. P0403 motor rated frequency 0 to 300 hz 60 (50) hz cfg 05, 43, 94 10-4 p0404 motor rated power 0 = 0.33hp 0.25kw 1 = 0.5hp 0.37kw 2 = 0.75hp 0.55kw 3 = 1hp 0.75...
Page 30
Quick parameter reference, faults and alarms 0-22 0 parameter function adjustable range factory setting user setting properties groups pag. P0408 run self-tuning 0 = no 1 = no rotation 2 = run for i m 3 = run for t m 4 = estimate t m 0 cfg, vvw and vector 05, 43, 94 11-14 p0409 stator resistance 0.0...
Page 31
Quick parameter reference, faults and alarms 0-23 0 parameter function adjustable range factory setting user setting properties groups pag. P0552 trigger condition 0 = p0550* = p0551 1 = p0550* p0551 2 = p0550* > p0551 3 = p0550* 4 = alarm 5 = fault 6 = dix 5 - 52 19-2 p0553 trace sampling period 1 ...
Page 32
Quick parameter reference, faults and alarms 0-24 0 parameter function adjustable range factory setting user setting properties groups pag. P0682 serial/usb control bit 0 = ramp enable bit 1 = general enable bit 2 = run forward bit 3 = jog enable bit 4 = remote bit 5 = 2nd ramp bit 6 = reserved bit ...
Page 33
Quick parameter reference, faults and alarms 0-25 0 parameter function adjustable range factory setting user setting properties groups pag. P0720 dnet master status 0 = run 1 = idle - ro 09, 112 17-2 p0721 canopen comm. Status 0 = disabled 1 = reserved 2 = comm. Enabled 3 = error ctrl.Enab 4 = guard...
Page 34
Quick parameter reference, faults and alarms 0-26 0 parameter function adjustable range factory setting user setting properties groups pag. P0734 anybus write word #3 0 to 1499 0 cfg 114 17-3 p0735 anybus write word #4 0 to 1499 0 cfg 114 17-3 p0736 anybus write word #5 0 to 1499 0 cfg 114 17-3 p073...
Page 35
Quick parameter reference, faults and alarms 0-27 0 parameter function adjustable range factory setting user setting properties groups pag. P0813 temper. V-b5/igbt v5 -20.0 to 150.0 °c - cfw-11m and ro 09, 45 15-18 p0814 temper. W-b5/igbt w5 -20.0 to 150.0 °c - cfw-11m and ro 09, 45 15-18 p0815 curr...
Page 36
Quick parameter reference, faults and alarms 0-28 0 parameter function adjustable range factory setting user setting properties groups pag. P0947 fault number 0 to 65535 ro 09, 115 17-4 p0963 profibus baud rate 0 = 9.6 kbit/s 1 = 19.2 kbit/s 2 = 93.75 kbit/s 3 = 187.5 kbit/s 4 = 500 kbit/s 5 = not d...
Page 37
Quick parameter reference, faults and alarms 0-29 0 parameter function adjustable range factory setting user setting properties groups pag. P1028 softplc parameter 19 -32768 to 32767 0 - 50 18-1 p1029 softplc parameter 20 -32768 to 32767 0 - 50 18-1 p1030 softplc parameter 21 -32768 to 32767 0 - 50 ...
Page 38
Quick parameter reference, faults and alarms 0-30 0 fault/alarm description possible causes f006 (1) imbalance or input phase loss mains voltage imbalance too high or phase missing in the input power supply. Note: - if the motor is unloaded or operating with reduced load this fault may not occur. - ...
Page 39
Quick parameter reference, faults and alarms 0-31 0 fault/alarm description possible causes a050 (1) igbt high temperature u a high temperature alarm was detected by the ntc temperature sensors located on the igbts. Note: it may be disabled by setting p0353 = 2 or 3. Surrounding air temperature is t...
Page 40
Quick parameter reference, faults and alarms 0-32 0 fault/alarm description possible causes f076 motor current imbalance fault of motor current unbalance. Note: it may be disabled by setting p0342 = 0. Loose connection or broken wiring between the motor and inverter connection. Vector control with w...
Page 41
Quick parameter reference, faults and alarms 0-33 0 fault/alarm description possible causes a138 (5) profibus dp interface in clear mode it indicates that the inverter received a command from the profibus dp network master to enter the clear mode. Verify the network master status, making sure it is ...
Page 42
Quick parameter reference, faults and alarms 0-34 0 fault/alarm description possible causes f183 igbt overload + temperature overtemperature related to the igbts overload protection. Surrounding air temperature too high. Operation with frequencies f185 (8) pre-charge contac fault it indicates fault ...
Page 43
Quick parameter reference, faults and alarms 0-35 0 fault/alarm description possible causes f238 (5) profibus dp interface in clear mode refer to the profibus dp communication manual. F239 (5) offline profibus dp interface f240 (5) profibus dp module access error a300 (10) high temperature at igbt u...
Page 44
Quick parameter reference, faults and alarms 0-36 0 fault/alarm description possible causes f322 (10) overtemperature at igbt v b3 overtemperature fault measured with the temperature sensor (ntc) of the book 3 v phase igbt. High ambient temperature (*) and high output current. Blocked or defective f...
Page 45
Quick parameter reference, faults and alarms 0-37 0 fault/alarm description possible causes a357 (10) high load at igbt v b2 overload alarm at book 2 v phase igbt. High current at the inverter output (see figure 8.1 of the cfw-11m user's manual). F358 (10) overload at igbt v b2 overload fault at boo...
Page 46
Quick parameter reference, faults and alarms 0-38 0 fault/alarm description possible causes a391 (10) current unbalance at phase v b1 phase v book 1current unbalance alarm. It indicates a 20 % unbalance in the current distribution between this phase and the smallest current of the same phase in othe...
Page 47
Quick parameter reference, faults and alarms 0-39 0 fault/alarm description possible causes a402 (10) current unbalance at phase u b5 phase u book 5 current unbalance alarm. It indicates a 20 % unbalance in the current distribution between this phase and the smallest current of the same phase in oth...
Page 48
Quick parameter reference, faults and alarms 0-40 0 models where they can occur: (1) all the models from frame size a to g. (2) cfw110086t2, cfw110105t2, cfw110045t4, cfw110058t4, cfw110070t4 and cfw110088t4. (3) all the models of frame sizes d and e. (4) all the models of frame sizes a, b and c. (5...
Page 49
Safety instructions 1-1 1 1 safety instructions this manual contains the information necessary for the correct use of the cfw-11 frequency inverter. It has been developed to be used by qualified personnel with suitable training or technical qualification for operating this type of equipment. 1.1 saf...
Page 50
Safety instructions 1-2 1 1.3 preliminary recommendations danger! Only qualified personnel familiar with the cfw-11 frequency inverter and associated equipment should plan or implement the installation, start-up and subsequent maintenance of this equipment. These personnel must follow all the safety...
Page 51
General information 2-1 2 2 general information 2.1 about this manual this manual presents the necessary information for the configuration of all of the functions and parameters of the cfw-11 frequency inverter. This manual must be used together with the cfw-11 user's manual. The text intents to sup...
Page 52
2-2 2 general information ntc: it’s a resistor whose resistance value in ohms decreases proportionally to the temperature increase; it is used as a temperature sensor in power modules. Keypad (hmi): human-machine interface; it is the device that allows the control of the motor, the visualization and...
Page 53
General information 2-3 2 khz: kilohertz = 1000 hz. Ma: milliamp = 0.001 amp. Min: minute. Ms: millisecond = 0.001 second. Nm: newton meter; torque measurement unit. Rms: "root mean square"; effective value. Rpm: revolutions per minute: speed measurement unit. S: second. V: volt. Ω: ohm. 2.2.2 numer...
Page 54
2-4 2 general information.
Page 55
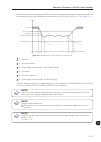
About the cfw-11 3-1 3 3 about the cfw-11 3.1 about the cfw-11 the cfw-11 is a high performance frequency inverter that makes it possible the control of speed and torque of three-phase ac induction motors. The principal characteristic of this product is the "vectrue" technology, which presents the f...
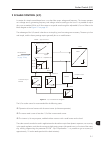
Page 56
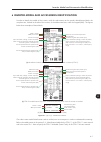
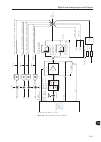
About the cfw-11 3 3-2 analog inputs (ai1 and ai2) flash memory module (slot 5) digital inputs (di1 to di6) power supplies for electronics and for interface between power and control usb pc power control three-phase rectifier motor igbt inverter power supply = dc link connection = dynamic braking ...
Page 57
About the cfw-11 3-3 3 a – mounting supports (for surface mounting) b – heatsink c – top cover d – fan with fixing support e – comm 2 module (anybus) f – accessory board module g – flash memory module h – front cover i – keypad (hmi) figure 3.2 - cfw-11 main components usb connector usb led off: wit...
Page 58
About the cfw-11 3 3-4.
Page 59
Keypad (hmi) 4-1 4 4 keypad (hmi) 4.1 keypad (hmi) through the keypad (hmi) it is possible to command the inverter, visualize and adjust all the parameters. It presents a navigation manner similar to the one used in cell phones, with options to access the parameters sequentially or by means of group...
Page 60
Keypad (hmi) 4-2 4 1 2 3 cover cover for battery access press the cover and rotate it counterclockwise remove the cover 4 5 6 remove the battery with the help of a screwdriver positioned in the right side hmi without the battery install the new battery positioning it first at the left side 7 8 press...
Page 61
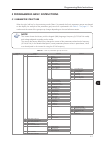
Programming basic instructions 5-1 5 5 programming basic instructions 5.1 parameter structure when the right "soft key" in the monitoring mode ("menu") is pressed, the first 4 parameter groups are showed on the display. An example of the parameter group structure is presented in the table 5.1 on pag...
Page 62
Programming basic instructions 5-2 5 5.2 groups accessed in the option menu in the monitoring mode in the monitoring mode access the groups of the option "menu" by pressing the right "soft key". Table 5.2 - parameter groups accessed in the option menu of the monitoring mode group contained parameter...
Page 63
Programming basic instructions 5-3 5 5.3 password setting in p0000 p0000 – access to parameters adjustable range: 0 to 9999 factory setting: 0 properties: access groups via hmi: 00 all parameters in order to be able to change the content of the parameters, it is necessary to set correctly the passwo...
Page 64
Programming basic instructions 5-4 5 5.4 hmi [30] in the group "30 hmi" are the parameters related to the presentation of information on the keypad (hmi) display. See next the detailed description of the possible settings for those parameters. P0193 – day of the week adjustable range: 0 = sunday 1 =...
Page 65
Programming basic instructions 5-5 5 description: those parameters set the date and time of the cfw-11 real time clock. It is important to configure them with the correct date and time so that the fault and alarm record occurs with actual date and time information. P0200 – password adjustable range:...
Page 66
Programming basic instructions 5-6 5 p0205 – reading parameter selection 1 p0206 – reading parameter selection 2 p0207 – reading parameter selection 3 adjustable range: 0 = not selected 1 = speed reference # 2 = motor speed # 3 = motor current # 4 = dc link voltage # 5 = motor frequency # 6 = motor ...
Page 67
Programming basic instructions 5-7 5 p0208 – reference scale factor adjustable range: 1 to 18000 factory setting: 1800 (1500) p0212 – reference decimal point adjustable range: 0 = wxyz 1 = wxy.Z 2 = wx.Yz 3 = w.Xyz factory setting: 0 properties: access groups via hmi: 01 parameter groups 30 hmi desc...
Page 68
Programming basic instructions 5-8 5 p0209 – reference engineering unit 1 p0210 – reference engineering unit 2 p0211 – reference engineering unit 3 adjustable range: 32 to 127 factory setting: p0209 = 114 (r) p0210 = 112 (p) p0211 = 109 (m) properties: access groups via hmi: 01 parameter groups 30 h...
Page 69
Programming basic instructions 5-9 5 p0216 – hmi display contrast adjustable range: 0 to 37 factory setting: 27 properties: access groups via hmi: 01 parameter groups 30 hmi description: it allows setting the keypad (hmi) display contrast level. Higher values configure a higher contrast level. 5.5 d...
Page 70
Programming basic instructions 5-10 5 5.6 display indications in the monitoring mode settings every time the inverter is powered the display goes to the monitoring mode. In order to make it easier the reading of the motor main parameters, the keypad (hmi) display can be configured to show them in 3 ...
Page 71
Programming basic instructions 5-11 5 seq. Action/result display indication 1 - monitoring mode. - press "menu" (right "soft key"). Ready loc 0rpm 16:10 menu 0 rpm 0.0 a 0.0 hz 2 - the group "00 all parameters" is already selected . Ready loc 0rpm return 16:10 select 00 all parameters 01 parameter g...
Page 72
Programming basic instructions 5-12 5 5.7 incompatibility between parameters if any of the combinations listed below occur, the cfw-11 goes to the "config" state. 1) two or more dix (p0263...P0270) programmed for (4 = fwd run). 2) two or more dix (p0263...P0270) programmed for (5 = rev run). 3) two ...
Page 73
Inverter model and accessories identification 5-13 6 25) [p0221 or p0222 programmed for (7 = e.P.)] and [without dix (p0263...P0270) programmed for (11 = increase e.P.) or without dix (p0263...P0270) programmed for (12 = decrease e.P.)]. 26) [p0221 and p0222 not programmed for (7 = e.P.)] and [with ...
Page 74
Inverter model and accessories identification 5-14 6.
Page 75
Inverter model and accessories identification 6-1 6 6 inverter model and accessories identification in order to identify the model of the inverter, verify the code existent on the product identification labels: the complete one, located at the side of the inverter, or the abbreviated one, under the ...
Page 76
Inverter model and accessories identification 6-2 6 6.1 inverter data [42] in this group are the parameters related to the inverter information and characteristics, such as inverter model, accessories identified by the control circuit, software version, switching frequency, etc. P0023 – software ver...
Page 77
Inverter model and accessories identification 6-3 6 table 6.1 - cfw-11 accessory identification codes name description slot identification code p0027 p0028 ioa-01 module with 2 14-bit analog inputs, 2 digital inputs, 2 14-bit analog outputs in voltage or current, 2 open collector digital outputs 1 f...
Page 78
Inverter model and accessories identification 6-4 6 table 6.4 - example of the two first characters of the code showed in p0028 for profibus dp-05 and flash memory module 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 0 0 5 0 p0029 – power hardware configuration adjustable range: bit 0 to 5 = rated current bit 6 and 7...
Page 79
Inverter model and accessories identification 6-5 6 table 6.6 - current codification for the parameter p0029 frame size voltage bits current bits 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 a 200... 240 v 0 0 2 a* 0 0 0 0 0 0 6 a* 0 0 0 0 0 1 7 a* 0 0 0 0 1 0 10 a 0 0 0 0 1 1 7 a 0 0 0 1 0 0 10 a 0 0 0 1 0 1 13 a 0 0 0 1 1 0 1...
Page 80
Inverter model and accessories identification 6-6 6 frame size voltage bits current bits 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 e 53 a 1 1 0 0 0 1 63 a 1 1 0 0 1 0 80 a 1 1 0 0 1 1 107 a 0 1 0 0 1 1 125 a 0 1 0 1 0 0 150 a 0 1 0 1 0 1 f 170 a 0 1 0 1 1 0 216 a 0 1 0 1 1 1 289 a 0 1 1 0 0 0 g 315 a 0 1 1 0 0 1 365 a 0 1 1 ...
Page 81
Inverter model and accessories identification 6-7 6 p0295 – nd/hd vfd rated current adjustable range: 0 = 3.6 a / 3.6 a 1 = 5 a / 5 a 2 = 6 a / 5 a 3 = 7 a / 5.5 a 4 = 7 a / 7 a 5 = 10 a / 8 a 6 = 10 a / 10 a 7 = 13 a / 11 a 8 = 13.5 a / 11 a 9 = 16 a / 13 a 10 = 17 a / 13.5 a 11 = 24 a / 19 a 12 = ...
Page 82
Inverter model and accessories identification 6-8 6 63 = 11 a / 9 a 64 = 12 a / 10 a 65 = 15 a / 13 a 66 = 17 a / 17 a 67 = 20 a / 17 a 68 = 22 a / 19 a 69 = 24 a / 21 a 70 = 27 a / 22 a 71 = 30 a / 24 a 72 = 32 a / 27 a 73 = 35 a / 30 a 74 = 44 a / 36 a 75 = 46 a / 39 a 76 = 53 a / 44 a 77 = 54 a /...
Page 83
Inverter model and accessories identification 6-9 6 description: this parameter presents the inverter rated current for the normal overload regimen (nd) and for the heavy overload regimen (hd). The inverter operation mode, if it is nd or hd, is defined by the content of p0298. P0296 – line rated vol...
Page 84
Inverter model and accessories identification 6-10 6 p0297 – switching frequency adjustable range: 0 = 1.25 khz 1 = 2.5 khz 2 = 5.0 khz 3 = 10.0 khz 4 = 2.0 khz factory setting: according to inverter model properties: cfg access groups via hmi: 01 parameter groups 42 inverter data description: refer...
Page 85
Inverter model and accessories identification 6-11 6 description: set the content of this parameter according to the application. The normal duty regimen (nd) defines the maximum current for continuous operation (i nom-nd ) and an overload of 110 % during 1 minute. It must be used for driving motors...
Page 86
Inverter model and accessories identification 6-12 6.
Page 87
Starting-up and settings 7-1 7 7 starting-up and settings in order to start-up in the several types of controls, beginning from the factory settings, consult the following sections: - section 9.5 energy saving function on page 9-13 . - section 10.3 vvw control mode start-up on page 10-4 . - section ...
Page 88
Starting-up and settings 7-2 7 table 7.1 - parameter p0204 options p0204 action 0, 1 not used: no action 2 reset p0045: resets the enabled fan hour counter 3 reset p0043: resets the enabled hours counter 4 reset p0044: resets the kwh counter 5 load 60 hz: loads the 60 hz factory settings into the in...
Page 89
Starting-up and settings 7-3 7 p0317 - oriented start-up adjustable range: 0 = no 1 = yes factory setting: 0 properties: cfg access groups via hmi: 02 oriented start-up description: when this parameter is changed to “1”, the oriented start-up routine starts. The cfw11 goes into the “conf” state, whi...
Page 90
Starting-up and settings 7-4 7 note! Valid for p0318 = 1. When the inverter is powered and the memory module is present, the current parameter contents are compared with the contents of the parameters saved in the mmf and, in case they are different, the keypad (hmi) will exhibit the message "flash ...
Page 91
Starting-up and settings 7-5 7 example: version v1.60 → (x = 1, y = 6 and z = 0) previously stored in the keypad (hmi) inverter version: v1.75 → (x’ = 1, y’ = 7 and z’ = 5) p0319 = 2 → f082 [(y = 6) → (y’ = 7)] inverter version: v1.62 → (x’ = 1, y’ = 6 and z’ = 2) p0319 = 2 → normal copy [(y = 6) = ...
Page 92
Starting-up and settings 7-6 7 8. In order to copy the contents of the inverter a parameters to other inverters, repeat the same procedures 5 to 7 described previously. Inverter a parameters eeprom hmi inv → hmi hmi → inv eeprom hmi inverter b parameters figure 7.2 - parameter copy from "inverter a"...
Page 93
8-1 8 available control types 8 available control types 8.1 control types the inverter feeds the motor with variable voltage, current and frequency, by means of whose the control of the motor speed is obtained. The values applied to the motor follow a control strategy, which depends on the selected ...
Page 94
Available control types 8-2 8.
Page 95
9-1 9 scalar control (v/f) 9 scalar control (v/f) it consists of a simple control based on a curve that links output voltage and frequency. The inverter operates as a voltage source, generating frequency and voltage values according to that curve. It is possible to adjust this curve to standard 50 h...
Page 96
Scalar control (v/f) 9-2 9 9.1 v/f control [23] p0136 – manual torque boost adjustable range: 0 to 9 factory setting: according to inverter model properties: v/f access groups via hmi: 01 parameter groups 23 v/f control description: it acts at low speeds, increasing the inverter output voltage in or...
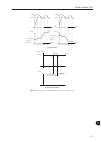
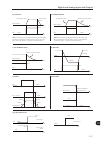
Page 97
9-3 9 scalar control (v/f) p0136 i x r p0137 automatic i x r voltage applied to the motor p0007 p0139 active output current speed reference figure 9.3 - torque boost block diagram output voltage nominal 1/2 nominal compensation zone n nom/2 n nom speed figure 9.4 - effect of p0137 on the v/f curve (...
Page 98
Scalar control (v/f) 9-4 9 speed total reference (refer to figure 9.1 on page 9-1 ) slip compensation ∆ f output active current p0139 p0138 figure 9.5 - slip compensation block diagram output voltage (function of the motor load) speed n nom v nom ∆v ∆f figure 9.6 - v/f curve with slip compensation f...
Page 99
9-5 9 scalar control (v/f) p0140 – dwell time at start adjustable range: 0.0 to 10.0 s factory setting: 0.0 s p0141 – dwell speed at start adjustable range: 0 to 300 rpm factory setting: 90 rpm properties: v/f and vvw access groups via hmi: 01 parameter groups 23 v/f control description: p0140 sets ...
Page 100
Scalar control (v/f) 9-6 9 description: in order to get an overview of the control types, as well as orientation to choose the most suitable type for the application, refer to the chapter 8 available control types on page 8-1 . For the v/f mode, select p0202 = 0, 1 or 2: parameter p0202 setting for ...
Page 101
9-7 9 scalar control (v/f) the factory setting of p0144 (8.0 %) is adequate for standard motors with rated frequency of 60 hz. When using a motor with rated frequency (adjusted in p0403) different from 60 hz, the default value for p0144 may become inadequate, being able to cause difficulties in the ...
Page 102
Scalar control (v/f) 9-8 9 description: it is the current limitation for the v/f control with actuation mode defined by p0344 (refer to the table 9.1 on page 9-8 ) and the current limit defined by p0135. Table 9.1 - current limitation configuration p0344 function description 0 = hold - fl on current...
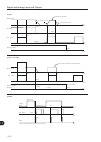
Page 103
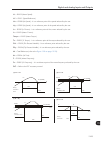
9-9 9 scalar control (v/f) motor current p0135 p0135 speed speed acceleration via ramp (p0100) deceleration via ramp (p0101) during acceleration during deceleration time time time motor current time (a) "ramp hold" motor current p0135 time time time decelerates via ramp p0101 speed (b) "ramp deceler...
Page 104
Scalar control (v/f) 9-10 9 9.4 v/f dc voltage limitation [27] there are two functions in the inverter for limiting the dc link voltage during the motor braking. They act limiting the braking torque and power, avoiding therefore the tripping of the inverter by overvoltage (f022). The overvoltage on ...
Page 105
9-11 9 scalar control (v/f) dc link voltage (p0004) f022 – overvoltage time dc link regulation output speed time p0151 nominal u d figure 9.11 - example of the dc link voltage limitation working with the ramp hold function 2 - ramp acceleration: it is effective in any situation, regardless of the mo...
Page 106
Scalar control (v/f) 9-12 9 dc link voltage (p0004) f022-overvoltage time dc link regulation output speed time p0151 nominal u d figure 9.13 - example of the dc link voltage limitation working with the ramp acceleration function p0150 – dc regulator type (v/f) adjustable range: 0 = ramp hold 1 = ram...
Page 107
9-13 9 scalar control (v/f) description: it is the actuation level of the dc link voltage limitation function for the v/f mode. Setting of p0151 value: a) the p0151 factory setting leaves inactive the dc link voltage limitation function for the v/f mode. In order to activate it, one must reduce the ...
Page 108
Scalar control (v/f) 9-14 9 the energy saving function reduces the motor losses when it is running with loads significantly below the rated load. The efficiency is increased by reducing the motor flux, which is kept saturated for any load value. The function is active when the applied load is smalle...
Page 109
9-15 9 scalar control (v/f) p0589 – level of minimum applied voltage adjustable range: 40 to 80 % factory setting: 40 % properties: cfg, v/f access groups via hmi: description: this parameter defines the minimum voltage value that will be applied to the motor when the energy saving function is activ...
Page 110
Scalar control (v/f) 9-16 9 c) adjust the password p0000 = 5: according to the section 5.3 password setting in p0000 on page 5-3 , of this manual. D) adjust the inverter to operate with the application line and motor: execute the oriented start-up routine according to the item 5.2.2 - oriented start...
Page 111
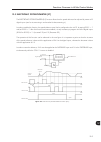
10-1 10 vvw control 10 vvw control the vvw (voltage vector weg) control mode uses a control method with intermediate performance between v/f and sensorless vector. Refer to the figure 10.1 on page 10-2 block diagram. The main advantage compared to the v/f control is the better speed regulation with ...
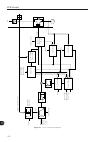
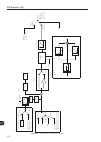
Page 112
Vvw control 10-2 10 p0202=5 (vvw control) u d p0151 u d dc v oltage regulation hold p0100-p0104 t filter + + reference (r efer to figure 13.9 on page 13-34 ) p0134 p0133 p0403 f slip f slip calculation f o t l /t r , s r f o l a l o m torque estimation p0404, p0399, p0401, p0409, p0402, p0403 u d l ...
Page 113
10-3 10 vvw control 10.1 vvw control [25] the parameter group [25] – vvw control – contains only 5 parameters related to that function: p0139, p0140, p0141, p0202 and p0397. However, since the parameters p0139, p0140, p0141 and p0202 were already presented in the section 9.1 v/f control [23] on page...
Page 114
Vvw control 10-4 10 p0400 – motor rated voltage p0401 – motor rated current p0402 – motor rated speed p0403 – motor rated frequency p0404 – motor rated power p0406 – motor ventilation refer to the section 11.7 motor data [43] on page 11-10 , for more information. P0407 – motor rated power factor adj...
Page 115
10-5 10 vvw control b) prepare the inverter and apply power: according to the section 5.1 - prepare for start-up, of the cfw-11 user's manual. C) adjust the password p0000 = 5: according to the section 5.3 password setting in p0000 on page 5-3 , of this manual. D) adjust the inverter to operate with...
Page 116
Vvw control 10-6 10 seq. Action/result display indication 1 - monitoring mode. - press "menu" (right "soft key"). Ready loc 0rpm 13:48 menu 0 rpm 0.0 a 0.0 hz 2 - the group "00 all parameters" is already selected. Ready loc 0rpm return 13:48 select 00 all parameters 01 parameter groups 02 oriented s...
Page 117
10-7 10 vvw control seq. Action/result display indication 14 - if necessary, change the content of p0400 according to the motor rated voltage. Therefore press "select". This change corrects the output voltage by the factor x = p0400/p0296. Config loc 0rpm reset 13:48 select motor rated eff. P0399: 6...
Page 118
Vvw control 10-8 10
Page 119
11-1 11 vector control 11 vector control it consists in the control type based on the separation of the motor current into two components: flux producing current i d (oriented with the motor electromagnetic flux). Torque producing current i q (perpendicular to the motor flux vector). The i d current...
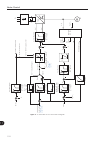
Page 120
Vector control 11-2 11 speed r egulator dc link r egulator flux r egulator maximum output voltage r egulator total r eference (refer to the figure 13.8 on page 13-33 ) gp = p0161 gi = p0162 gp = p0167 gi = p0168 us d * flux current aix = 2 – max . T orque current p0185alue p0185=default v alue m i t...
Page 121
11-3 11 vector control the vector control with encoder presents the same advantages of the sensorless control previously described, with the following additional benefits: torque and speed control down to 0 (zero) rpm. Speed control accuracy of 0.01 % (if the 14-bit analog speed reference via option...
Page 122
Vector control 11-4 11 dc link r egulator maximum output voltage r egulator aix = 2 – max. T orque current p0185alue p0185 = default v alue gp = p0186 gi = p0187 u d p0185 speed r egulator flux r egulator maximum output voltage regulator (r efer to the figure 13.8 on page 13-33 ) gp = p0161 gi = p01...
Page 123
11-5 11 vector control 11.2 i/f mode (sensorless) note! It is activated automatically at low speeds if p0182 > 3 and when the control mode is sensorless vector (p0202 = 3). The operation at the low speed region may present instability. In this region the motor operation voltage is also very low, bei...
Page 124
Vector control 11-6 11 note! Every time that p0408 = 1 or 2 the parameter p0413 (mechanic time constant – t m ) will be adjusted for a value close to the motor rotor mechanic time constant. Therefore, the motor rotor inertia (table data valid for weg motors), the inverter rated voltage and current, ...
Page 125
11-7 11 vector control note! (*) weg motors that can be used with the optimal flux function: nema premium efficiency, nema high efficiency, iec premium efficiency, iec top premium efficiency and "alto rendimento plus". When this function is activating, the motor flux is controlled in a way to reduce...
Page 126
Vector control 11-8 11 note! For torque control in the sensorless vector mode (p0202 = 3), observe: - the torque limits (p0169/p0170) must be higher than 30 % to assure the motor starting. After the start and with the motor rotating above 3 hz, they can be reduced, if necessary, to values below 30 %...
Page 127
11-9 11 vector control the optimal braking makes it possible braking the motor with a higher torque than the one obtained with traditional methods, as for instance, the braking by the injection of direct current (dc braking). In the dc braking case, only the losses in the motor rotor are used to dis...
Page 128
Vector control 11-10 11 examples: 1 hp/0.75 kw, iv poles: η = 0.76 resulting in tb1 = 0.32. 20 hp/15.0 kw, iv poles: η = 0.86 resulting in tb1 = 0.16. T t nom n n nom tb1 1.0 0 0 0.2 1.0 2.0 (c) (b) (a) figure 11.3 - t x n curve for optimal braking with a typical 10 hp/7.5 kw motor, driven by an inv...
Page 129
11-11 11 vector control p0398 – motor service factor adjustable range: 1.00 to 1.50 factory setting: 1.00 properties: cfg access groups via hmi: 01 parameter groups 43 motor data description: it is the continuous overload capability, i.E., a reserve of power that gives the motor the capability to wi...
Page 130
Vector control 11-12 11 description: set it according to the used motor nameplate data, taking into consideration the motor voltage. In the guided start-up routine the value adjusted in p0401 automatically modifies the parameters related to the motor overload protection, according to the table 11.2 ...
Page 131
11-13 11 vector control table 11.1 - p0404 (motor rated power) setting p0404 motor rated power (hp) p0404 motor rated power (hp) 0 0.33 31 300.0 1 0.50 32 350.0 2 0.75 33 380.0 3 1.0 34 400.0 4 1.5 35 430.0 5 2.0 36 440.0 6 3.0 37 450.0 7 4.0 38 475.0 8 5.0 39 500.0 9 5.5 40 540.0 10 6.0 41 600.0 11...
Page 132
Vector control 11-14 11 p0406 – motor ventilation adjustable range: 0 = self-ventilated 1 = separate ventilation 2 = optimal flux 3 = extended protection factory setting: 0 properties: cfg access groups via hmi: 01 parameter groups 43 motor data description: during the oriented start-up routine, the...
Page 133
11-15 11 vector control 11.7.1 adjustment of the parameters p0409 to p0412 based on the motor data sheet being in the possession of the motor equivalent circuit data, it is possible to calculate the value to be programmed in the parameters from p0409 to p0412, instead of using the self-tuning to obt...
Page 134
Vector control 11-16 11 when, on the data sheet, it is considered connection in yy or ∆∆ and the motor is connected in ∆: p409 = 4 x r s 3 p411 = 4 x σls 3 when, on the data sheet, it is considered connection in ∆ and the motor is connected in yy: p409 = r s 4 p411 = σls 4 when, on the data sheet, i...
Page 135
11-17 11 vector control p0161 – speed regulator proportional gain adjustable range: 0.0 to 63.9 factory setting: 7.0 p0162 – speed regulator integral gain adjustable range: 0.000 to 9.999 factory setting: 0.005 properties: pm and vector access groups via hmi: 01 parameter groups 29 vector control 90...
Page 136
Vector control 11-18 11 7. Adjust p0161 and p0162 according to the response type presented in the figure 11.4 on page 11-17 . A) reduce the proportional gain (p0161) and/or increase the integral gain (p0162). B) speed regulator is optimized. C) increase the proportional gain and/or reduce the integr...
Page 137
11-19 11 vector control p0166 – speed regulator differential gain adjustable range: 0.00 to 7.99 factory setting: 0.00 properties: pm and vector access groups via hmi: 01 parameter groups 29 vector control 90 speed regulator description: the differential action helps minimize the motor speed variati...
Page 138
Vector control 11-20 11 11.8.3 flux regulator [92] the parameters related to the cfw-11 flux regulator are presented next. P0175 – flux regulator proportional gain adjustable range: 0.0 to 31.9 factory setting: 2.0 p0176 – flux regulator integral gain adjustable range: 0.000 to 9.999 factory setting...
Page 139
11-21 11 vector control p0181 – magnetization mode adjustable range: 0 = general enable 1 = run/stop factory setting: 0 properties: cfg and encoder access groups via hmi: 01 parameter groups 29 vector control 92 flux regulator description: table 11.4 - magnetization mode p0181 action 0 = general ena...
Page 140
Vector control 11-22 11 description: this parameter defines the value of the maximum output voltage. Its standard value is defined in the condition of the nominal supply voltage. The voltage reference used in the regulator "maximum output voltage" (see the figure 11.1 on page 11-2 or figure 11.2 on ...
Page 141
11-23 11 vector control p0183 – current in the i/f mode adjustable range: 0 to 9 factory setting: 1 properties: sless access groups via hmi: 01 parameter groups 29 vector control 93 i/f control description: it defines the current to be applied to the motor when the inverter is operating in the i/f m...
Page 142
Vector control 11-24 11 description: by changing from the factory setting to one of the 4 available options, it is possible to estimate the value of the parameters related to the motor being used. Refer to the next description for more details on each option. Table 11.6 - self-tuning options p0408 s...
Page 143
11-25 11 vector control note! Every time that p0408 = 1 or 2: the parameter p0413 (mechanic time constant – tm) will be adjusted to a value close to the motor mechanic time constant. Therefore, the motor rotor inertia (table data valid for weg motors), the inverter rated voltage and current are take...
Page 144
Vector control 11-26 11 description: it is the motor magnetizing current value, which is automatically adjusted by the self-tuning ( section 11.3 self- tuning on page 11-5 ). Its value can also be obtained on the motor data sheet ( item 11.7.1 adjustment of the parameters p0409 to p0412 based on the...
Page 145
11-27 11 vector control description: this parameter is automatically adjusted during the self-tuning. This parameter can also be calculated from the motor data sheet ( item 11.7.1 adjustment of the parameters p0409 to p0412 based on the motor data sheet on page 11-15 ). The p0412 setting determines ...
Page 146
Vector control 11-28 11 description: this parameter is automatically adjusted during the self-tuning. The p0413 setting determines the speed regulator gains (p0161 and p0162). When p0408 = 1 or 2, it must be observed: if p0413 = 0, the time constant t m will be obtained in function of the inertia of...
Page 147
11-29 11 vector control description: these parameters limit the motor current component that produces "+" (p0169) or "-" (p0170) torque. The adjustment is expressed as a percentage of the motor nominal torque current. The positive torque occurs when the motor drives the load in the clockwise directi...
Page 148
Vector control 11-30 11 p0172 – maximum "-" torque current at maximum speed adjustable range: 0.0 to 350.0 % factory setting: 125.0 % properties: vector access groups via hmi: 01 parameter groups 29 vector control 95 torque curr.Limit description: torque current limitation in function of the speed: ...
Page 149
11-31 11 vector control p0184 – dc link regulation mode adjustable range: 0 = with losses 1 = without losses 2 = enable/disable dix factory setting: 1 properties: cfg, pm and vector access groups via hmi: 01 parameter groups 29 vector control 96 dc link regulator description: it enables or disables ...
Page 150
Vector control 11-32 11 description: this parameter defines the dc link voltage regulation level during the braking. During the braking, the time of the deceleration ramp is automatically extended, thus avoiding an overvoltage fault (f022). The setting of the dc link regulation can be done in two ma...
Page 151
11-33 11 vector control 11.8.8 droop function [90] the droop function is used in applications of load distribution, where two or more inverter/motor sets run a load that mechanically couples the motors, and in which little speed variations between the motors are acceptable. For the application of th...
Page 152
Vector control 11-34 11 description: the response time of the droop function is adjusted using p0334, which defines the constant time applied to the filter used in the torque current. The droop value in rpm can be obtained by means of the following equations: x 0.1 [rpm] iqf x p0333 x p0295 p0401 dr...
Page 153
11-35 11 vector control c) adjust the password p0000 = 5: according to the section 5.3 password setting in p0000 on page 5-3 , of this manual. D) adjust the inverter to operate with the application line and motor: by means of the "oriented start-up" menu access p0317 and change its content to 1, whi...
Page 154
Vector control 11-36 11 seq. Action/result display indication 1 - monitoring mode. - press "menu" (right "soft key"). Ready loc 0rpm 13:48 menu 0 rpm 0.0 a 0.0 hz 2 - the group "00 all parameters" is already selected. Ready loc 0rpm return 13:48 select 00 all parameters 01 parameter groups 02 orient...
Page 155
11-37 11 vector control seq. Action/result display indication 10 - if necessary, change the content of p0296 according to the used line voltage. Therefore press "select". This change will affect p0151, p0153, p0185, p0190, p0321, p0322, p0323 and p0400. Config loc 0rpm reset 13:48 select type of con...
Page 156
Vector control 11-38 11 seq. Action/result display indication 20 at this point, the keypad (hmi) presents the option to run the "self-tuning". Whenever possible the self- tuning must be carried out. - thus, press "select" to access p0408 and then to select the desired option. Refer to the item 11.8....
Page 157
12-1 12 functions common to all the control modes 12 functions common to all the control modes this section describes the functions that are common to all the cfw-11 inverter control modes (v/f, vvw, sensorless, and encoder). 12.1 ramps [20] the inverter ramps functions allow the motor to accelerate...
Page 158
Functions common to all the control modes 12-2 12 open open 24v time 24v time p0102 p0100 dix - run/stop 2 nd ramp dix motor speed p0103 p0101 time figure 12.1 - second ramp actuation in this example, the commutation to the 2nd ramp (p0102 or p0103) is done by means of one of the digital inputs from...
Page 159
12-3 12 functions common to all the control modes p0105 – 1st/2nd ramp selection adjustable range: 0 = 1 st ramp 1 = 2 nd ramp 2 = dix 3 = serial/usb 4 = anybus-cc 5 = canopen/devicenet/profibus dp 6 = softplc 7 = plc11 factory setting: 2 properties: cfg access groups via hmi: 01 parameter groups 20...
Page 160
Functions common to all the control modes 12-4 12 p0121 – keypad reference adjustable range: 0 to 18000 rpm factory setting: 90 rpm properties: access groups via hmi: 01 parameter groups 21 speed references description: when the and hmi keys are active (p0221 or p0222 = 0), this parameter sets the v...
Page 161
12-5 12 functions common to all the control modes p0122 – jog + speed reference p0123 – jog - speed reference adjustable range: 0 to 18000 rpm factory setting: 150 rpm (125 rpm) properties: pm and vector access groups via hmi: 01 parameter groups 21 speed references description: the jog+ or jog- com...
Page 162
Functions common to all the control modes 12-6 12 p0133 – minimum speed reference limit adjustable range: 0 to 18000 rpm factory setting: 90 rpm (75 rpm) p0134 – maximum speed reference limit adjustable range: 0 to 18000 rpm factory setting: 1800 rpm (1500 rpm) properties: access groups via hmi: 01 ...
Page 163
12-7 12 functions common to all the control modes 12.4 multispeed [36] the multispeed function is used when one wishes to have up to 8 predefined fixed speeds, which are commanded through the digital inputs (di4, di5 and di6). P0124 – multispeed reference 1 adjustable range: 0 to 18000 rpm factory s...
Page 164
Functions common to all the control modes 12-8 12 description: the multispeed brings as advantages the stability of the predefined fixed references, and the immunity against electric noises (isolated digital inputs dix). In order to activate the multispeed function one must configure the parameter p...
Page 165
12-9 12 functions common to all the control modes 12.5 electronic potentiometer [37] the electronic potentiometer (e.P.) function allows that the speed reference be adjusted by means of 2 digital inputs (one for incrementing it and another for decrementing it). In order to enable this function, the ...
Page 166
Functions common to all the control modes 12-10 12 12.6 zero speed logic [35] this function allows the configuration of a speed in which the inverter will enter a stop condition (disable itself). It is recommended to use this function when the commands run/stop, direction of rotation, loc/rem and jo...
Page 167
12-11 12 functions common to all the control modes when the pid regulator is active (p0203 = 1) and in automatic mode, for the inverter to leave the disable condition, besides the condition programmed in p0218, it is also necessary that the pid error (the difference between the setpoint and the proc...
Page 168
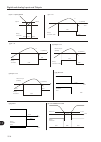
Functions common to all the control modes 12-12 12 12.7.1 v/f flying start and vvw in the v/f and vvw mode, the inverter imposes a fixed frequency at the start, defined by the speed reference, and applies a voltage ramp defined at the parameter p0331. The flying start function will be activated afte...
Page 169
12-13 12 functions common to all the control modes p0327 – f.S. Current ramp i/f adjustable range: 0.000 to 1.000 s factory setting: 0.070 s description: it defines the time for the i/f current to change from 0 to (0.9 x p0401) at the beginning of the frequency scan (f), in order to minimize the gen...
Page 170
Functions common to all the control modes 12-14 12 h. Geral (c/ g/p=on) ou g/p( c/ hg=on) + 24 v tempo (c) (a) (d) 4xp412 1s p134 n* n p0329xp0412 tempo - p134 (b) 4xp412 1s 2xp412 p329xp412 n* n p001 tempo p003 p327 tempo p134 i/f vetorial i/f i = 0.9 x p0401 vetorial n n p0001 p0134 p0134 n p0327 ...
Page 171
12-15 12 functions common to all the control modes 12.7.2.2 p0202 = 4 during the time period when the motor is being magnetized, the identification of the motor speed occurs. Once the magnetization is finished, the motor will be operated starting from that speed until reaching the speed reference in...
Page 172
Functions common to all the control modes 12-16 12 p0331 – voltage ramp adjustable range: 0.2 to 60.0 s factory setting: 2.0 s properties: v/f and vvw access groups via hmi: 01 parameter groups 44 flystart/ridethru description: this parameter sets the necessary time for the output voltage to reach t...
Page 173
12-17 12 functions common to all the control modes back" (t4) level, defined at the parameter p0323. The motor will reaccelerate, following the adjusted ramp, from the actual speed value to the value defined by the speed reference (p0001) (refer to the figure 12.8 on page 12-17 ). F021 t0 t1 t2 t3 t...
Page 174
Functions common to all the control modes 12-18 12 p0321 – dc link power loss adjustable range: 178 to 282 v 308 to 616 v 308 to 616 v 308 to 616 v 308 to 616 v 425 to 737 v 425 to 737 v 486 to 885 v 486 to 885 v factory setting: 252 v (p0296 = 0) 436 v (p0296 = 1) 459 v (p0296 = 2) 505 v (p0296 = 3...
Page 175
12-19 12 functions common to all the control modes p0326 – ride-through integral gain adjustable range: 0.000 to 9.999 factory setting: 0.128 properties: vector access groups via hmi: 01 parameter groups 44 flystart/ridethru description: these parameters configure the vector mode ride-through pi con...
Page 176
Functions common to all the control modes 12-20 12 p0299 - dc-braking start time adjustable range: 0.0 to 15.0 s factory setting: 0.0 s properties: v/f, vvw and sless access groups via hmi: 01 parameter groups 47 dc braking description: this parameter sets the dc braking time at starting. Injection ...
Page 177
12-21 12 functions common to all the control modes (a) v/f scalar p0300 motor speed p0301 dead time open time dix – run/stop +24 v (b) vvw and sensorless vector p0300 open dix – run/stop dc current injection time +24 v p0301 motor speed figure 12.11 - (a) and (b) - dc braking operation at the ramp d...
Page 178
Functions common to all the control modes 12-22 12 during the braking process, if the inverter is enabled, the braking is interrupted and the inverter will operate normally again. Attention! The dc braking may continue active after the motor has already stopped. Be careful with the motor thermal siz...
Page 179
12-23 12 functions common to all the control modes description: this parameter adjusts the current level (dc braking torque) applied to the motor during the braking. The programmed current level is a percentage of the inverter rated current. This parameter works only in the sensorless vector control...
Page 180
Functions common to all the control modes 12-24 12 description: this actuation of these parameters occurs as presented in the figure 12.13 on page 12-24 next. The passage through the avoided speed range (2 x p0306) takes place by means of the acceleration/deceleration ramps. The function does not op...
Page 181
12-25 12 functions common to all the control modes p0192 – status encoder zero search adjustable range: 0 = off 1 = finished factory setting: properties: ro v/f, vvw and vector access groups via hmi: 00 all parameters description: on the inverter initialization, this parameter starts on zero. When t...
Page 182
Functions common to all the control modes 12-26 12.
Page 183
13-1 13 digital and analog inputs and outputs 13 digital and analog inputs and outputs this section presents the parameters for the configuration of the cfw-11 inputs and outputs, as well as the parameters for the command of the inverter in the local or remote situations. 13.1 i/o configuration [07]...
Page 184
Digital and analog inputs and outputs 13-2 13 p0230 – analog input dead zone adjustable range: 0 = off 1 = on factory setting: 0 properties: access groups via hmi: 07 i/o configuration or 01 parameter groups 38 analog inputs 38 analog inputs description: this parameter acts only for the analog input...
Page 185
13-3 13 digital and analog inputs and outputs p0231 – ai1 signal function p0236 – ai2 signal function p0241 – ai3 signal function adjustable range: 0 = speed reference 1 = n* without ramp 2 = maximum torque current 3 = process variable 4 = ptc 5 = not used 6 = not used 7 = plc use factory setting: 0...
Page 186
Digital and analog inputs and outputs 13-4 13 in order that the expressions which determine the total current and the maximum torque developed by the motor ( section 11.5 torque control on page 11-7 and item 11.8.6 torque current limitation [95] on page 11-28 ) remain valid, replace p0169, p0170 by ...
Page 187
13-5 13 digital and analog inputs and outputs p0235 – ai1 filter p0240 – ai2 filter p0245 – ai3 filter p0250 – ai4 filter adjustable range: 0.00 to 16.00 s factory setting: 0.00 s properties: access groups via hmi: 07 i/o configuration or 01 parameter groups 38 analog inputs 38 analog inputs descrip...
Page 188
Digital and analog inputs and outputs 13-6 13 the aix’ internal value is the result of the following equation: alx' = alx + offset x 10 v x gain 100 for instance: aix=5 v, offset=-70 % and gain=1.000: alx' = 5 + (-70) x 10 v x1 = –2 v 100 aix’=-2 v means that the motor will rotate in the reverse dir...
Page 189
13-7 13 digital and analog inputs and outputs table 13.2 - configuration of the analog input signals p0233, p0243 p0238, p0248 input signal switch position 0 0 (0 to 10) v / (0 to 20) ma off/on 1 1 (4 to 20) ma on 2 2 (10 to 0) v / (20 to 0) ma off/on 3 3 (20 to 4) ma on – 4 (-10 to +10) v off when ...
Page 190
Digital and analog inputs and outputs 13-8 13 p0251 – ao1 function p0254 – ao2 function adjustable range: 0 = speed reference 1 = total reference 2 = real speed 3 = torque current reference 4 = torque current 5 = output current 6 = process variable 7 = active current 8 = output power 9 = pid setpoin...
Page 191
13-9 13 digital and analog inputs and outputs description: these parameters set the functions of the analog outputs, according to the table 13.3 on page 13-9 . Table 13.3 - analog output functions functions p0251 (ao1) p0254 (ao2) p0257 (ao3) p0260 (ao4) speed reference 0 0 0 0 total reference 1 1 1...
Page 192
Digital and analog inputs and outputs 13-10 13 function ao1 - p0251 ao2 - p0254 ao3 - p0257 ao4 - p0260 aox output power active current output current torque current torque current reference real speed total reference speed reference process variable (pid) pid setpoint torque current > 0 motor torqu...
Page 193
13-11 13 digital and analog inputs and outputs table 13.4 - full scale scale of the analog output indications variable full scale (*) speed reference p0134 total reference real speed encoder speed torque current reference 2.0 x i nomhd torque current torque current > 0 motor torque 2.0 x i nom outpu...
Page 194
Digital and analog inputs and outputs 13-12 13 table 13.5 - dip switches related to the analog outputs parameter output switch location p0253 ao1 s1.1 control board p0256 ao2 s1.2 p0259 ao3 s2.1 ioa p0262 ao4 s2.2 table 13.6 - configuration of the analog outputs ao1 and ao2 signals p0253, p0256 outp...
Page 195
13-13 13 digital and analog inputs and outputs the indication is done by means of the numbers 1 and 0, representing respectively the "active" and "inactive" states of the inputs. The state of each input is considered as one digit in the sequence where di1 represents the least significant digit. Exam...
Page 196
Digital and analog inputs and outputs 13-14 13 table 13.9 - digital input functions functions p0263 (di1) p0264 (di2) p0265 (di3) p0266 (di4) p0267 (di5) p0268 (di6) p0269 (di7) p0270 (di8) not used 0, 13 and 23 0, 13 and 23 0*, 13 and 23 0* and 23 0 and 23 0 and 23 0*, 13 and 23 0*, 13 and 23 run/s...
Page 197
13-15 13 digital and analog inputs and outputs when torque is selected, the speed regulator parameters p0161 and p0162 become inactive (*). Thus, the total reference becomes the input of the torque current regulator. Refer to the figure 11.1 on page 11-2 and figure 11.2 on page 11-4 . (*) the pid-ty...
Page 198
Digital and analog inputs and outputs 13-16 13 - programming off: when this function is programmed and the digital input is with +24 v, parameter changes will not be allowed, regardless of the values set at p0000 and p0200. When the dix input is with 0 v, the parameter changes will be conditioned to...
Page 199
13-17 13 digital and analog inputs and outputs dix 24 v motor speed deceleration ramp dix open time motor speed motor runs free (coasts) time time time 24 v open 24 v time time dix open 24 v time time motor speed dix forward open open 24 v time time 24 v time p0102 p0100 dix - run/stop dix – ramp 2 ...
Page 200
Digital and analog inputs and outputs 13-18 13 time motor speed 24 v 24 v run/stop jog speed (p0122) deceleration ramp 24 v dix - jog general enable open open acceleration ramp (h) jog with fault 24 v general enable run/stop time 24 v time time 24 v without fault reset dix - reset open motor speed i...
Page 201
13-19 13 digital and analog inputs and outputs time time 24 v motor speed open time 24 v time time 24 v open dix - reverse dix - forward motor speed forward figure 13.6 - (a) to (m) - details on the operation of the digital input functions time motor speed 24 v open 24 v dix - run/stop acceleration ...
Page 202
Digital and analog inputs and outputs 13-20 13 13.1.4 digital outputs / relays [41] the cfw-11 has 3 relay digital outputs as standard on its control board, and 2 more digital outputs of the open collector type that can be added with the accessories ioa-01 or iob-01. The next parameters configure th...
Page 203
13-21 13 digital and analog inputs and outputs table 13.11 - digital output functions functions p0275 (do1) p0276 (do2) p0277 (do3) p0278 (do4) p0279 (do5) not used 0 and 29 0 0 0, 29, 37, 38, 39, 40, 41 and 42 0, 29, 37, 38, 39, 40, 41 and 42 n* > nx 1 1 1* 1 1 n > nx 2 2* 2 2 2 n 3 3 3 3 3 n = n* ...
Page 204
Digital and analog inputs and outputs 13-22 13 - no f070: it means that the inverter is not disabled by the f070 fault (overcurrent or short-circuit). - no f071: it means that the inverter is not disabled by the f071 fault (output overcurrent). - no f006+f021+f022: it means that the inverter is not ...
Page 205
13-23 13 digital and analog inputs and outputs n = p0002 (motor speed). N* = p0001 (speed reference). Nx = p0288 (nx speed) – it is a reference point of the speed selected by the user. Ny = p0289 (ny speed) – it is a reference point of the speed selected by the user. Ix = p0290 (ix current) – it is ...
Page 206
Digital and analog inputs and outputs 13-24 13 on relay/ transistor off is off time (f) is > ix ix (p0290) (g) is is relay/ transistor on off on ix (p0290) time on off off relay/ transistor motor torque (p0009) tx (p0293) time (h) torque > tx p0291 relay/ transistor off off on speed (e) n = 0 (zero)...
Page 207
13-25 13 digital and analog inputs and outputs (m) process variable time off on on vpy (p0534) relay/ transistor process variable (l) process variable > pvx on off time vpx (p0533) process variable relay/ transistor off relay/ transistor on on off time pre-charge level dc link (n) pre-charge ok enab...
Page 208
Digital and analog inputs and outputs 13-26 13 p0281 – fx frequency adjustable range: 0.0 to 300.0 hz factory setting: 4.0 hz properties: access groups via hmi: 07 i/o configuration or 01 parameter groups 41 digital outputs 41 digital outputs description: it is used in the digital output and relay f...
Page 209
13-27 13 digital and analog inputs and outputs p0287 – hysteresis for nx and ny adjustable range: 0 to 900 rpm factory setting: 18 rpm (15 rpm) properties: access groups via hmi: 07 i/o configuration or 01 parameter groups 41 digital outputs 41 digital outputs description: it is used in the n > nx a...
Page 210
Digital and analog inputs and outputs 13-28 13 description: it specifies the value in rpm, ± 1 % of the motor rated speed (hysteresis), below which the actual speed will be considered null for the zero speed disable function. This parameter is also used by the functions of the digital and relay outp...
Page 211
13-29 13 digital and analog inputs and outputs 13.2 local and remote command in those parameter groups one can configure the origin of the main inverter commands when in the local or in the remote situation, as the speed reference, speed direction, run/stop and jog. P0220 – local/remote selection so...
Page 212
Digital and analog inputs and outputs 13-30 13 description: they define the origin of the speed reference in the local situation and in the remote situation. Some notes about the options for those parameters: the aix’ designation refers to the analog signal obtained after the addition of the aix inp...
Page 213
13-31 13 digital and analog inputs and outputs p0224 – run/stop selection – local situation p0227 – run/stop selection - remote situation adjustable range: 0 = keys , 1 = dix 2 = serial/usb 3 = anybus-cc 4 = canopen/devicenet/profibus dp 5 = softplc 6 = plc11 factory setting: p0224 = 0 p0227 = 1 pro...
Page 214
Digital and analog inputs and outputs 13-32 13 description: it defines the motor stop mode when the inverter receives the "stop" command. The table 13.12 on page 13-32 describes the options of this parameter. Table 13.12 - stop mode selection p0229 description 0 = ramp to stop the inverter will appl...
Page 215
13-33 13 digital and analog inputs and outputs { command via digital inputs (dix) p0333 p0122 p0334 p0123 iq iqf droop ai2 ai3 ai4 ai1 p0239 p0234 p0244 p0249 p0237 p0232 p0242 p0247 p0019 p0020 p0021 p0018 p0236 = 1 r ef . After r amp (p0236 = no r amp r eference) (*) p0231 = 1 - r ef . After r amp...
Page 216
Digital and analog inputs and outputs 13-34 13 local reference (p0221) local reference remote reference local commands remote commands (p0220) local/remote selection reference commands commands reference forward/reverse (p0223) jog (p0225) run/stop (p0224) remote reference (p0222) forward/reverse (p...
Page 217
14-1 14 dynamic braking 14 dynamic braking the braking torque that can be obtained through the application of frequency inverters without dynamic braking resistors varies from 10 % to 35 % of the motor rated torque. In order to obtain higher braking torques, resistors for dynamic braking are used. I...
Page 218
Dynamic braking 14-2 14 the next table presents the overvoltage trip level. Table 14.1 - overvoltage (f022) trip levels inverter v nom p0296 f022 220/230 v 0 > 400 v 380 v 1 > 800 v 400/415 v 2 440/460 v 3 480 v 4 500/525 v 5 > 1000 v 550/575 v 6 600 v 7 660/690 v 8 > 1200 v f022 - overvoltage dynam...
Page 219
14-3 14 dynamic braking p0155 – dynamic braking resistor power adjustable range: 0.02 to 650.00 kw factory setting: 2.60 kw properties: access groups via hmi: 01 parameter groups 28 dynamic braking description: this parameter adjusts the trip level of the braking resistor overload protection. It mus...
Page 220
Dynamic braking 14-4 14.
Page 221
15-1 15 faults and alarms 15 faults and alarms the troubleshooting structure of the inverter is based on the indication of faults and alarms. In a fault event the igbts firing pulses are disabled and the motor coasts to stop. The alarm works as a warning to the user that critical operation condition...
Page 222
Faults and alarms 15-2 15 note! In order to assure the conformity of the cfw-11 motor overload protection with the ul508c standard, observe the following: the "trip" current is equal to 1.25 times the motor nominal current (p0401) adjust in the "oriented start-up" menu. The maximum allowed value for...
Page 223
15-3 15 faults and alarms ptc xc1: 2 3 8 7 ai1 ao1 cc11 program p0231 = 4. Set s1.4 = off (0 to 10 v). Program p0251 = 13. Set s1.1 = off (4 to 20 ma, 0 to 20 ma). Program p0236 = 4. Set s1.3 = off (0 to ± 10 v) program p0254 = 13. Set s1.2 = off (4 to 20 ma, 0 to 20 ma). Ptc 5 6 10 9 ai2 ao2 progra...
Page 224
Faults and alarms 15-4 15 15.3 protections [45] the parameters related to motor and inverter protections are found in this group. P0030 – u arm igbt temperature p0031 – v arm igbt temperature p0032 – w arm igbt temperature p0033 – rectifier temperature p0034 – internal air temperature adjustable ran...
Page 225
15-5 15 faults and alarms description: these parameters are used for the motor overload protection (i x t – f072). The motor overload current (p0156, p0157 and p0158) is the value from which the inverter starts considering that the motor is operating with overload. The bigger the difference between ...
Page 226
Faults and alarms 15-6 15 p0159 – motor thermal class adjustable range: 0 = class 5 1 = class 10 2 = class 15 3 = class 20 4 = class 25 5 = class 30 6 = class 35 7 = class 40 8 = class 45 factory setting: 1 properties: cfg, v/f, vvw and vector access groups via hmi: 01 parameter groups 45 protection...
Page 227
15-7 15 faults and alarms example: for a motor with the following characteristics, i n = 10.8 a t br = 4 s (hot motor blocked rotor time) i p / i n = 7.8 ⇒ i p = 7.8 x 10.8 a= 84.2 a sf = 1.15 one gets, overload current = i p = 84.2 x 100 = 678 % i n x sf 10.8 x 1.15 overload time = t br = 4 s after...
Page 228
Faults and alarms 15-8 15 overload time class 45 class 40 class 35 class 30 class 25 class 20 class 15 class 10 class 5 0 1 1x 0,1 1 100 10 1000 10000 100000 2x 3x 4x 5x 6x 7x 8x 9x 10x 2 3 4 5 6 7 9 10 8 current x in for f.S. = 1.15 current x in for f.S. = 1.00 (b) - hot motor overload curves for l...
Page 229
15-9 15 faults and alarms note! The faults f051, f078, f156, f301, f304, f307, f310, f313, f316, f319, f322, f325, f328, f331, f334, f337, f340 and f343 allow a conditional reset, i.E., the reset will only occur if the temperature gets back to the normal operation range. If after auto-reset, the sam...
Page 230
Faults and alarms 15-10 15 p0348 – motor overload protection adjustable range: 0 = off 1 = fault/alarm 2 = fault 3 = alarm factory setting: 1 properties: cfg access groups via hmi: 01 parameter groups 45 protections description: this parameter allows the desired protection level for the motor overlo...
Page 231
15-11 15 faults and alarms p0350 – inverter overload protection (igbts) adjustable range: 0 = fault is active, with switching frequency reduction 1 = fault and alarm are active, with switching frequency reduction 2 = fault is active, without switching frequency reduction 3 = fault and alarm are acti...
Page 232
Faults and alarms 15-12 15 description: this parameter is useful when the motor is equipped with ptc type temperature sensors, allowing the configuration of the protection level for the motor overtemperature function. The details on the actuation of the available options are in the table 15.4 on pag...
Page 233
15-13 15 faults and alarms description: the cfw-11 is equipped with two fans: an internal fan and a heatsink fan, and the activation of both will be controlled via software by means of the inverter programming. The options available for the setting of this parameter are the following: table 15.5 - o...
Page 234
Faults and alarms 15-14 15 description: the overtemperature protection is carried out by means of the measurement of the temperature with the igbts and power board internal air ntcs, being able to generate alarms and faults. In order to configure the desired protection, set p0353 according to the ta...
Page 235
15-15 15 faults and alarms description: this parameter allows disabling the actuation of f185 fault – fault in the preload contactor. If p0355 = 0, the fault in the preload contactor will remain deactivated. F185 fault will not be generated. When the inverter is a frame size e with dc power supply i...
Page 236
Faults and alarms 15-16 15 p0358 – encoder fault configuration adjustable range: 0 = off 1 = f067 on 2 = f065, f066 active 3 = all active factory setting: 3 properties: cfg and encoder access groups via hmi: 01 parameter groups 45 protections description: this parameter allows disabling the fault de...
Page 237
15-17 15 faults and alarms p0360 – temperature imbalance configuration adjustable range: 0 = fault/alarm 1 = fault factory setting: 0 properties: frame h and cfg access groups via hmi: 01 parameter groups 45 protections description: this parameter allows choosing whether showing or not the alarm of ...
Page 238
Faults and alarms 15-18 15 p0810 – temperature v-b4/igbt v4 p0811 – temperature w-b4/igbt w4 p0812 – temperature u-b5/igbt u5 p0813 – temperature v-b5/igbt v5 p0814 – temperature w-b5/igbt w5 adjustable range: -20.0 °c to 150.0 °c factory setting: properties: ro access groups via hmi: 01 parameter g...
Page 239
15-19 15 faults and alarms p0834 - dim1 and dim2 status adjustable range: bit 0 = dim1 bit 1 = dim2 factory setting: properties: cfw-11m and ro access groups via hmi: 01 parameter groups or 09 read only parameters 40 digital inputs description: through this parameter it is possible to visualize the ...
Page 240
Faults and alarms 15-20 15 description: these parameters allow selecting the type of desired action, temperature fault, temperature alarm or broken cable alarm. The rupture of the cable that connects the sensor to the ioe-0x module may cause any of those actions, depending on the selected option. Th...
Page 241
15-21 15 faults and alarms 15.4.2 pt100 or kty84 temperature sensor type the parameters described in this section will be shown on the hmi when the ioe-02 or ioe 03 optional module is connected into the slot 1 (xc41 connector). Refer to the figure 3.1 on page 3-2 . P0375 - sensor 1 fault/alarm tempe...
Page 242
Faults and alarms 15-22 15 description: this parameter indicates, in celsius degrees, the highest temperature among the pt100 or kty84 used sensors. Note! If any of the temperature fault/alarm configuration parameters, p0374, p0377, p0380, p0383 and/or p0386, is programmed with the "inactive" option...
Page 243
16-1 16 read only parameters [09] 16 read only parameters [09] in order to facilitate the visualization of the main reading variables of the inverter, the group [09] - "read only parameters" can be accessed directly. It is important to point out that all the parameters of that group can only be visu...
Page 244
Read only parameters [09] 16-2 16 p0003 – motor current adjustable range: 0.0 to 4500.0 a factory setting: properties: ro access groups via hmi: 09 read only parameters description: it indicates the inverter output current in amps (a), by means of 1.0 second filter. P0004 – dc link voltage (u d ) ad...
Page 245
16-3 16 read only parameters [09] description: it indicates one of the 8 possible inverter states. The description of each state is presented in the next table. In order to facilitate the visualization, the inverter status is also showed on the top left corner of the keypad (hmi) ( figure 5.3 on pag...
Page 246
Read only parameters [09] 16-4 16 p0009 = t m x 100 x y i tm 1) p0202 ≠ 3: i tm = p0401 2 - p0410 x p0178 2 0.5 100 in v/f or vvw the adjusts are: p0178 = 100 % and p0190 = 0.95 x p0400 2) p0202 = 3: i tm = p0401 2 - id* x p0178 2 0.5 100 y = 1 for n ≤ p0190 x n sinc p0400 y = n sinc x p0190 for n >...
Page 247
16-5 16 read only parameters [09] p0011 – cos phi of the output adjustable range: 0.00 to 1.00 factory setting: properties: ro access groups via hmi: 09 read only parameters description: this parameter indicates the value of the cosine of the angle between the voltage and output current. The electri...
Page 248
Read only parameters [09] 16-6 16 p0030 – temperature igbts u p0031 – temperature igbts v p0032 – temperature igbts w p0033 – temperature of the rectifier adjustable range: -20.0 to 150.0°c factory setting: 0 properties: cfg access groups via hmi: 01 parameter groups 45 protections 09 read only desc...
Page 249
16-7 16 read only parameters [09] p0036 – heatsink fan speed adjustable range: 0 to 15000 rpm factory setting: properties: ro access groups via hmi: 09 read only parameters description: it indicates the heatsink fan actual speed, in revolutions per minute (rpm). Note! This parameter has no function ...
Page 250
Read only parameters [09] 16-8 16 description: this parameter shows the counting of the pulses of the encoder. The counting can be increased from 0 to 40000 (hourly turn) or decreased from 40000 to 0 (rotate counterclockwise). This parameter can be visualized in the analogical exits when p0257 = 49 ...
Page 251
16-9 16 read only parameters [09] p0044 – kwh counter adjustable range: 0 to 65535 kwh factory setting: properties: ro access groups via hmi: 09 read only parameters description: it indicates the energy consumed by the motor. It indicates up to 65535 kwh, and then it gets back to zero. By setting p0...
Page 252
Read only parameters [09] 16-10 16 description: they indicate the alarm (p0048) or fault (p0049) number that occasionally be present at the inverter. In order to understand the meaning of the codes used for faults and alarms, refer to the chapter 15 faults and alarms on page 15-1 in this manual and ...
Page 253
16-11 16 read only parameters [09] p0050 – last fault p0054 – second fault p0058 – third fault p0062 – fourth fault p0066 – fifth fault p0070 – sixth fault p0074 – seventh fault p0078 – eighth fault p0082 – ninth fault p0086 – tenth fault adjustable range: 0 to 999 factory setting: properties: ro ac...
Page 254
Read only parameters [09] 16-12 16 p0083 – ninth fault day/month p0087 – tenth fault day/month adjustable range: 00/00 to 31/12 factory setting: properties: ro access groups via hmi: 08 fault history description: they indicate the day and the month of the last to the tenth fault occurrence. P0052 – ...
Page 255
16-13 16 read only parameters [09] p0065 – fourth fault time p0069 – fifth fault time p0073 – sixth fault time p0077 – seventh fault time p0081 – eighth fault time p0085 – ninth fault time p0089 – tenth fault time adjustable range: 00:00 to 23:59 factory setting: properties: ro access groups via hmi...
Page 256
Read only parameters [09] 16-14 16 p0092 – speed at the moment of the last fault adjustable range: 0 to 18000 rpm factory setting: properties: ro access groups via hmi: 08 fault history description: it is the record of the motor speed at the moment of the last fault occurrence. P0093 – reference at ...
Page 257
16-15 16 read only parameters [09] p0096 – dix status at the moment of the last fault adjustable range: bit 0 = di1 bit 1 = di2 bit 2 = di3 bit 3 = di4 bit 4 = di5 bit 5 = di6 bit 6 = di7 bit 7 = di8 factory setting: properties: ro access groups via hmi: 08 fault history description: it indicates th...
Page 258
Read only parameters [09] 16-16 16 p0800 – temperature u-b1/igbt u1 p0801 – temperature v-b1/igbt v1 p0802 – temperature w-b1/igbt w1 p0803 – temperature u-b2/igbt u2 p0804 – temperature v-b2/igbt v2 p0805 – temperature w-b2/igbt w2 p0806 – temperature u -b3/igbt u3 p0807 – temperature v-b3/igbt v3 ...
Page 259
16-17 16 read only parameters [09] p0817 – current w-b1/igbt w1 p0818 – current u-b2/igbt u2 p0819 – current v-b2/igbt v2 p0820 – current w-b2/igbt w2 p0821 – current u-b3/igbt u3 p0822 – current v-b3/igbt v3 p0823 – current w-b3/igbt w3 p0824 – current u-b4/igbt u4 p0825 – current v-b4/igbt v4 p082...
Page 260
Read only parameters [09] 16-18 16 description: this reading parameter indicates the current (a) of the igbts of each phase. In a modular drive, this information is shown for each book, and for frame h it is shown for each igbt module. P0834 – dim1 and dim2 status p0835 – ret. Temperature fase r p08...
Page 261
17-1 17 communication [49] 17 communication [49] for the exchange of information through communication networks, the cfw-11 has several standardized communication protocols, like modbus, canopen, devicenet, and ethernet/ip. For more details regarding the inverter configuration for operating with tho...
Page 262
Communication [49] 17-2 17 p0711 – devicenet reading word #3 p0712 – devicenet reading word #4 p0713 – devicenet reading word #5 p0714 – devicenet reading word #6 p0715 – devicenet writing word #3 p0716 – devicenet writing word #4 p0717 – devicenet writing word #5 p0718 – devicenet writing word #6 p...
Page 263
17-3 17 communication [49] p0733 – anybus reading word #8 p0734 – anybus writing word #3 p0735 – anybus writing word #4 p0736 – anybus writing word #5 p0737 –anybus writing word #6 p0738 – anybus writing word #7 p0739 – anybus writing word #8 those are parameters for the configuration and operation ...
Page 264
Communication [49] 17-4 17 p0757 – profibus writing word #10 p0918 – profibus address p0922 – profibus telegram selection p0944 – fault counter p0947 – fault number p0963 – profibus baud rate p0964 – drive identification p0965– profile identification p0967 – control word 1 p0968 – status word 1 thos...
Page 265
18-1 18 softplc [50] 18 softplc [50] 18.1 softplc the softplc function allows the frequency inverter to assume plc (programmable logical controller) functions. For more details regarding the programming of those functions in the cfw-11, refer to the cfw-11 softplc manual. The parameters related to t...
Page 266
Softplc [50] 18-2 18 description: by means of this parameter, it is possible to visualize the status of the 8 digital inputs (di9 to di16) of the ioc-01, ioc-02 or ioc-03 module. The indication is done by means of the numbers 1 and 0, representing respectively the "active" and "inactive" states of t...
Page 267
19-1 19 trace function [52] 19 trace function [52] 19.1 trace function the trace function is used to record variables of interest from the cfw-11 (as current, voltage, speed) when a particular event occurs in the system (e.G.: alarm/fault, high current, etc.). This system event, for starting the dat...
Page 268
Trace function [52] 19-2 19 description: it defines the value for comparison with the variable selected in p0550. The full range of the variables selectable as trigger is presented in the next table. Table 19.1 - full scale of the variables selectable as trigger variable full scale speed reference 1...
Page 269
19-3 19 trace function [52] - if p0552≠6 and any di is configured for "trace function", the trigger will never occur as a result of the di activation. - these three programming options do not prevent the inverter from being enabled. P0553 – trace sampling period adjustable range: 1 to 65535 factory ...
Page 270
Trace function [52] 19-4 19 p0560 – trace available memory adjustable range: 0 to 100 % factory setting: properties: ro access groups via hmi: 01 parameter groups 52 trace function description: it shows the amount of memory available for storing trace function points. The range from 0 to 100 % indic...
Page 271
19-5 19 trace function [52] description: they select the signals that will be recorded at the channels 1 to 4 of the trace function. The options are the same that are available at p0550. By selecting the "not selected" option, the total memory available for the trace function is distributed between ...
Page 272
Trace function [52] 19-6 19 description: p0572 to p0575 record the date and hour of the trigger occurrence. These parameters and the points acquired by the trace function are not saved when the inverter is powered off. There are two possibilities for p0572 to p0575 being null: - no acquisition was p...
Page 273
20-1 20 pid regulator [46] 20 pid regulator [46] 20.1 description and definitions the cfw-11 has the special function pid regulator, which can be used to control a closed loop process. This function places a proportional, integral and derivative regulator, superposed to the normal cfw-11 speed contr...
Page 274
Pid regulator [46] 20-2 20 setpoint definition (reference of the process variable) p0525 setpoint r eference (r efer to the figure 13.8 on page 13-33 ) p0221 / p0222=0 enable feedback p0524 (r efer to the figure 13.1 on page 13-2 and figure 13.2 on page 13-5 ) p0040 p0528 p0041 + - academic pid p013...
Page 275
20-3 20 pid regulator [46] 20.2 commissioning before doing a detailed description of the parameters related to this function, a step by step guide for putting the pid into operation will be presented. Note! In order that the pid function works properly, it is fundamental to verify if the inverter is...
Page 276
Pid regulator [46] 20-4 20 (a) direct (b) reverse process variable process variable set point set point ed = p0041 - p0040 (%) er = p0040 - p0041 (%) direct pid (p0527 = 0) reverse pid (p0527 = 1) p0040 p0040 p0041 p0041 p0535 p0535 ai2 ai2 t t t (c) sleep mode motor speed being: ed or er the percen...
Page 277
20-5 20 pid regulator [46] example: - full scale of the transducer (maximum output value) = 25 bar (fs = 25); - operation range (range of interest) = 0 to 15 bar (or = 15). Opting to maintain p0237 = 1.000 and p0239 = 0 (factory setting), which is the most common for most of the applications: - p052...
Page 278
Pid regulator [46] 20-6 20 example: given a pressure transducer with a 4 to 20 ma output and a full scale of 25 bar (i.E., 4 ma = 0 bar and 20 ma = 25 bar) and p0237=2.000. If it is wished to control 10 bar, the following setpoint must be entered: setpoint (%) = 10 x 2 x 100 % = 80 % 25 in case the ...
Page 279
20-7 20 pid regulator [46] as a summary of this guide, a schematic of the connections of the cfw-11 for the pid regulator application, as well as the setting of the parameters used in this example, are presented next. Off on 1 2 s1 3 4 15 17 18 12 13 11 1 2 3 4 5 6 di1 di3 di4 com 24vcc dgnd +ref ai...
Page 280
Pid regulator [46] 20-8 20 20.3 sleep mode the sleep mode is a useful resource for saving energy when using the pid regulator. Refer to the figure 20.2 on page 20-4 . In many pid applications energy is wasted by keeping the motor turning at the minimum speed when, for instance, the pressure or the t...
Page 281
20-9 20 pid regulator [46] 20.5 connection of a 2-wire transducer in the 2-wire configuration the transducer signal and its supply share the same wires. The figure 20.5 on page 20-9 illustrates this type of connection. Off on 1 2 s1 3 4 15 17 18 12 13 11 1 2 3 4 5 6 di1 di3 di4 com 24vcc dgnd +ref a...
Page 282
Pid regulator [46] 20-10 20 p0203 – special function selection adjustable range: 0 = none 1 = pid regulator factory setting: 0 properties: cfg access groups via hmi: 01 parameter groups 46 regulador pid description: it enables the use of the pid regulator special function, when set to 1. When p0203 ...
Page 283
20-11 20 pid regulator [46] table 20.3 - suggestions for pid regulator gain settings quantity gains proportional p0520 integral p0521 differential p0522 pneumatic system pressure 1 0.043 0.000 pneumatic system flow 1 0.037 0.000 hydraulic system pressure 1 0.043 0.000 hydraulic system flow 1 0.037 0...
Page 284
Pid regulator [46] 20-12 20 description: it selects the regulator feedback input (process variable). After choosing the feedback input, the function of the selected input must be programmed at p0231 (for ai1), p0236 (for ai2), p0241 (for ai3) or p0246 (for ai4). P0525 – keypad pid setpoint adjustabl...
Page 285
20-13 20 pid regulator [46] p0528 – process variable scale factor adjustable range: 1 to 9999 factory setting: 1000 p0529 – process variable decimal point adjustable range: 0 = wxyz 1 = wxy.Z 2 = wx.Yz 3 = w.Xyz factory setting: 1 properties: access groups via hmi: 01 parameter groups 46 pid regulat...
Page 286
Pid regulator [46] 20-14 20 p0530 – process variable engineering unit 1 p0531 – process variable engineering unit 2 p0532 – process variable engineering unit 3 adjustable range: 32 to 127 factory setting: p0530 = 37 p0531 = 32 p0532 = 32 properties: access groups via hmi: 01 parameter groups 46 pid ...
Page 287
20-15 20 pid regulator [46] p0535 – wake up band adjustable range: 0 to 100 % factory setting: 0 % properties: access groups via hmi: 01 parameter groups 46 pid regulator description: the parameter p0535 works together with the parameter p0218 (condition to leave the zero speed disable), giving the ...
Page 288
Pid regulator [46] 20-16 20 20.7 academic pid the controller implemented in the cfw-11 is of the academic type. The equations that characterize the academic pid, which is the base of this function algorithm, are presented next. The transfer function in the academic pid regulator frequency dominion i...
Page 289
21-1 21 pm vector control 21 pm vector control 21.1 permanent magnet synchronous motors (pmsm) permanent magnet synchronous motors are alternating current motors with three-phase stator winding, similar to the induction motor, and permanent magnet rotor. Pmsm for industrial applications have sinusoi...
Page 290
Pm vector control 21-2 21 21.2.1 sensorless pm - p0202 = 7 the sensorless pm control uses two rotor position estimation methods, the method for low speed injects a signal with a frequency of ±1 khz, which causes an increase in the acoustic noise, and the method for higher speeds is based on the outp...
Page 291
21-3 21 pm vector control 21.2.2 pm with encoder - p0202 = 6 the pm with encoder control presents the advantages described for the sensorless control, plus a speed control accuracy of 0.01 % (by using the 14-bit analog reference via ioa-01, or by digital references via hmi, profibus dp, devicenet). ...
Page 292
Pm vector control 21-4 21 21.2.3 modified functions almost all the functions presented in this manual remain active when the options 6 or 7 are programmed in p0202. The functions no longer active or that suffered any modification are described in the section 21.3 programming basic instructions – inc...
Page 293
21-5 21 pm vector control torque control range: 10 % to 180 %. Accuracy: ± 5 % of the rated torque. When the speed regulator is positively or negatively saturated, then p0169 and p0170 limit the torque current, respectively. The torque, in percentage, at the motor shaft (showed at p0009) is given by...
Page 294
Pm vector control 21-6 21 p0401 – motor rated current p0402 – motor rated speed adjustable range: 0 to 18000 rpm factory setting: 1750 rpm (1458 rpm) properties: cfg access groups via hmi: 01 parameter groups 43 motor data description: adjust it according to the used motor nameplate data. For pm mot...
Page 295
21-7 21 pm vector control description: value obtained from the motor data sheet. If this information is not available, use the factory setting. P0430 – pm type adjustable range: 0 = factory setting 1 = cooling tower factory setting: 0 properties: cfg and pm access groups via hmi: 01 parameter groups...
Page 296
Pm vector control 21-8 21 p0442 – inductance lq - ct p0443 – inductance lq - ct adjustable range: 0.0 to 400.0 mh factory setting: 0.0 mh properties: cfg and pm access groups via hmi: 01 parameter groups 43 motor data description: adjust them according to the motor nameplate data. If these pieces of...
Page 297
21-9 21 pm vector control description: values obtained from the motor nameplate data. The view of parameters p0435 and p0444 will depend on the value set in p0430. Note! If this information is not available, it can be obtained using the following procedure: 1. Drive the motor with no load, setting p...
Page 298
Pm vector control 21-10 21 p0439 – iq current regulator integral gain p0441 – id current regulator integral gain adjustable range: 0 to 1.999 factory setting: 0.005 properties: pm access groups via hmi: 01 parameter groups 29 vector control 92 flux regulator description: parameters p0438, p0439, p04...
Page 299
21-11 21 pm vector control 21.7.4 torque current limitation [95] p0169 – maximum "+" torque current p0170 – maximum "-" torque current adjustable range: 0.0 to 350.0 % factory setting: 125.0 % properties: pm and vector access groups via hmi: 01 parameter groups 29 vector control 95 torque curr. Limi...
Page 300
Pm vector control 21-12 21 description: it enables or disables the without losses function of the dc link regulator, according to the next table. Table 21.1 - dc link regulation modes p0184 action 0 = with losses (optical braking) inactive. If it is used, f022 (overvoltage) may occur during the spee...
Page 301
21-13 21 pm vector control description: these parameters configure the vector mode ride-through pi controller, which is responsible for keeping the dc link voltage at the level set in p0322. Figure 21.1 on page 21-2 and figure 21.2 on page 21-3 regulator r.T. Figure 21.3 - ride-through pi controller...
Page 302
Pm vector control 21-14 21 parameters related to the motor: program the parameters p0398, p0400 ... P0435 directly with the motor nameplate data. E) adjust specific parameters and functions, digital and analog inputs and outputs, hmi keys, according to the application needs. For applications: - that...
Page 303
21-15 21 pm vector control - motor vibration (it generally occurs when p0202 = 7) 1. Decrease the id proportional gain (p0440) in steps of 0.05 down to the minimum of 0.2. 2. Decrease reduce the iq proportional gain (p0438) in steps of 0.05 down to the minimum of 0.5. 3. Decrease the speed proportio...
Page 304
Pm vector control 21-16 21 seq. Action/result display indication 1 - monitoring mode. - press "menu" (right "soft key"). Ready loc 0rpm 13:48 menu 0 rpm 0.0 a 0.0 hz 2 - the group "00 all parameters" is already selected. Ready loc 0rpm return 13:48 select 00 all parameters 01 parameter groups 02 ori...
Page 305
21-17 21 pm vector control seq. Action/result display indication 14 - if necessary, change the content of p0401 according to the rated motor current. Therefore press "selec.". This change will affect p0156, p0157 and p0158. Config loc 0rpm reset 13:48 select motor rated voltage p0400: 440v motor rat...
Page 306
Pm vector control 21-18 21 21.9 faults and alarms when the control mode is pm with encoder (p0202 = 6), fault reset will only be accepted with stopped motor. Except for the f079 (encoder fault) reset, which could occur with the motor shaft in movement; however, the motor must be stopped in order to ...
Page 307
Weg drives & controls - automação ltda. Jaraguá do sul - sc - brazil phone 55 (47) 3276-4000 - fax 55 (47) 3276-4020 são paulo - sp - brazil phone 55 (11) 5053-2300 - fax 55 (11) 5052-4212 automacao@weg.Net www.Weg.Net.