- DL manuals
- Yamaha
- Robotics
- RCX222
- User Manual
Yamaha RCX222 User Manual
Summary of RCX222
Page 1
Rcx 222 eur2153130 e99 ver. 1.30 userʼs manual yamaha 2-axis robot controller.
Page 3: Contents
Contents rcx222 user’s manual t-1 safety instructions 1. Safety information s-1 2. Signal words used in this manual s-2 3. Warning labels s-3 3.1 warning labels s-3 3.1.1 warning label messages on robot and controller s-3 3.1.2 supplied warning labels s-8 3.2 warning symbols s-9 4. Important precaut...
Page 4: Contents
Contents rcx222 user’s manual t-2 t-3 warranty introduction 1 before using the robot controller (be sure to read the following notes) 2 overview of the rcx series 3 chapter 1 using the robot safely 1. Operating environment 1-1 chapter 2 system overview 1. System overview 2-1 1.1 mainsystemconfigurat...
Page 5: Contents
T-2 contents rcx222 user’s manual t-3 4.1 connection example 3-7 4.2 power supply and ground terminals 3-8 4.3 ac power connector wiring 3-9 4.4 considering power capacity and generated heat amount 3-10 4.5 installing an external leakage breaker 3-11 4.6 installing a circuit protector 3-11 4.7 insta...
Page 6: Contents
Contents rcx222 user’s manual t-4 t-5 3.1 part names 4-3 3.2 main functions 4-3 3.3 connection to the robot controller 4-4 3.4 changing the rpb screen settings 4-5 4. Turning power on and off 4-6 5. Operation keys 4-8 5.1 rpb screen 4-8 5.2 operation key layout 4-9 5.3 basic key operation 4-10 5.4 f...
Page 7: Contents
T-4 contents rcx222 user’s manual t-5 9.9 break point 4-47 9.9.1 setting break points 4-48 9.9.2 deleting break points 4-49 9.10 executing a step 4-50 9.11 skipping a step 4-50 9.12 executing the next step 4-51 10. "program" mode 4-52 10.1 scrolling a program listing 4-53 10.2 program editing 4-54 1...
Page 8: Contents
Contents rcx222 user’s manual t-6 t-7 11.2.1 point data input and editing 4-89 11.2.1.1 restoring point data 4-90 11.2.2 point data input by teaching 4-91 11.2.3 point data input by direct teaching 4-93 11.2.4 point jump display 4-94 11.2.5 copying point data 4-95 11.2.6 erasing point data 4-97 11.2...
Page 9: Contents
T-6 contents rcx222 user’s manual t-7 11.10 executing the user function keys 4-154 12. "system" mode 4-155 12.1 parameters 4-157 12.1.1 parameter list 4-159 12.1.2 robot parameters 4-161 12.1.3 axis parameters 4-165 12.1.4 other parameters 4-185 12.1.5 parameters for option boards 4-201 12.1.5.1 opt...
Page 10: Contents
Contents rcx222 user’s manual t-8 t-9 12.6.2.2 saving files 4-269 12.6.2.3 initializing the files 4-270 13. "monitor" mode 4-271 14. "utility" mode 4-274 14.1 canceling emergency stop; motor power and servo on/off 4-276 14.1.1 canceling emergency stop 4-276 14.1.2 motor power and servo on/off 4-277 ...
Page 11: Contents
T-8 contents rcx222 user’s manual t-9 2. Ratings 5-22 3. Precautions 5-23 chapter 6 safety i/o interface 1. Safety i/o interface overview 6-1 1.1 power 6-1 1.2 connector i/o signals 6-2 1.3 connector terminal numbers 6-3 1.4 emergency stop input signal connections 6-4 1.5 dedicated input signal conn...
Page 12: Contents
Contents rcx222 user’s manual t-10 chapter 9 troubleshooting 1. Error messages 9-1 1.1 robot controller error messages 9-1 [ 0] warnings and messages 9-3 [ 1] warnings (error history entry) 9-5 [ 2] robot operating area errors 9-6 [ 3] program file operating errors 9-10 [ 4] data entry and edit erro...
Page 13: Contents
Contents 1. Safety information s-1 2. Signal words used in this manual s-2 3. Warning labels s-3 3.1 warning labels s-3 3.1.1 warning label messages on robot and controller s-3 3.1.2 supplied warning labels s-8 3.2 warning symbols s-9 4. Important precautions for each stage of the robot life cycle s...
Page 15: Safety Instructions
Safety instructions s-1 1. Safety information industrial robots are highly programmable, mechanical devices that provide a large degree of freedom when performing various manipulative tasks. To ensure safe and correct use of yamaha industrial robots and con- trollers*, carefully read and comply with...
Page 16: Safety Instructions
Safety instructions s-2 2. Signal words used in this manual this manual uses the following safety alert symbols and signal words to provide safety instructions that must be observed and to describe handling precautions, prohibited actions, and compulsory actions. Make sure you understand the meaning...
Page 17: Safety Instructions
Safety instructions s-3 3. Warning labels warninglabelsshownbelowareattachedtotherobotbodyandcontrollertoalerttheoperatortopotential hazards. To ensure correct use, read the warning labels and comply with the instructions. 3.1 warning labels w warning if warning labels are removed or difficult to se...
Page 18: Safety Instructions
Safety instructions s-4 warning label 3 (scara robots, cartesian robots, controllers*) ■ * some models w warning improper installation or operation may cause serious injury. Before installing or operating the robot, read the manual and instructions on the warning labels and understand the contents. ...
Page 19: Safety Instructions
Safety instructions s-5 warming label 6 (robot drivers rdv-x/rdv-p) ■ w warning • beforetouchingtheterminalsorconnectorsontheoutsideoftherobotdriver,turnoffthepowerandwaitfor 10 minutes or longer to prevent electrical shock. Otherwise, burn or electrical shock may result. • beforeusingtherobotdriver...
Page 20: Safety Instructions
Safety instructions s-6 warming label 8 (controllers rcx240, controllers rcx340) ■ w warning these are precautions for yamaha and distributors' service personnel. Customers must not attempt to open the covers. W warning wait at least 100 seconds after power-off before opening the covers. Instruction...
Page 21: Safety Instructions
Safety instructions s-7 warning label 11 (controller)* ■ * this label is attached to the front panel. C caution refer to the manual. 取扱説明書参照 read instruction manual instructions on this label thisindicatesimportantinformationthatyoumust knowandisdescribedinthemanual. Beforeusingthecontroller,besuret...
Page 22: Safety Instructions
Safety instructions s-8 3.1.2 supplied warning labels some warning labels are not affixed to robots but included in the packing box. These warning labels should be affixed to an easy-to-see location. Warning label is attached to the robot body. Warning label comes supplied with the robot and should ...
Page 23: Safety Instructions
Safety instructions s-9 3.2 warning symbols warningsymbolsshownbelowareindicatedontherobotsandcontrollerstoalerttheoperatortopotential hazards. To use the yamaha robot safely and correctly always follow the instructions and cautions indicated by the symbols. Electrical shock hazard symbol 1. W warni...
Page 24: Safety Instructions
Safety instructions s-10 4. Important precautions for each stage of the robot life cycle this section describes major precautions that must be observed when using robots and controllers. Be sure to carefully read and comply with all of these precautions even if there is no alert symbol shown. 4.1 pr...
Page 25: Safety Instructions
Safety instructions s-11 4.2 essential precautions for the linear conveyor module the linear conveyor module is a yamaha robot so safety measures must be followed and safety equipment must be installed just as required for other yamaha robots. This section describes essential precautions for handlin...
Page 26: Safety Instructions
Safety instructions s-12 4.3 design 4.3.1 precautions for robots restricting the robot moving speed 1. W warning restriction on the robot moving speed is not a safety-related function. To reduce the risk of collision between the robot and workers, the user must take the necessary protective measures...
Page 27: Safety Instructions
Safety instructions s-13 4.4 moving and installation 4.4.1 precautions for robots installation environment ■ do not use in strong magnetic fields 1. W warning donotusetherobotnearequipmentorinlocationsthatgeneratestrongmagneticfields.Therobotmaybreak down or malfunction if used in such locations. Do...
Page 28: Safety Instructions
Safety instructions s-14 wiring ■ protective measures against electrical shock 1. W warning always ground the robot to prevent electrical shock. Adjustment ■ adjustment that requires removing a cover 1. W warning adjustment by removing a cover require specialized technical knowledge and skills, and ...
Page 29: Safety Instructions
Safety instructions s-15 wiring ■ connection to robot controller 1. The controller parameters are preset at the factory before shipping to match the robot model. Check the specified robot and controller combination, and connect them in the correct combination. Since the software detects abnormal ope...
Page 30: Safety Instructions
Safety instructions s-16 4.5 safety measures 4.5.1 safety measures referring to warning labels and manual 1. W warning • beforestartinginstallationoroperationoftherobot,besuretoreadthewarninglabelsandthismanual,and comply with the instructions. • neverattemptanyrepair,partsreplacementandmodification...
Page 31: Safety Instructions
Safety instructions s-17 w warning • duringstartupormaintenancetasks,displayasign"workinprogress"ontheprogrammingboxand operation panel in order to prevent anyone other than the person for that task from mistakenly operating the start or selector switch. If needed, take other measures such as lockin...
Page 32: Safety Instructions
Safety instructions s-18 4.6 operation when operating a robot, ignoring safety measures and checks may lead to serious accidents. Always take the following safety measures and checks to ensure safe operation. W danger check the following points before starting robot operation. •nooneiswithintherobot...
Page 33: Safety Instructions
Safety instructions s-19 working inside safety enclosures 4. Before starting work within the safety enclosure, always confirm from outside the enclosure that each protective function is operating correctly (see the previous section 2.3). W danger never enter within the movement range while within th...
Page 34: Safety Instructions
Safety instructions s-20 4.6.2 automatic operation checkthefollowingpointswhenoperatingtherobotinautomode.Observetheinstructionsbelowincases where an error occurs during automatic operation. Automatic operation described here includes all operations inautomode. Checkpoints before starting automatic ...
Page 35: Safety Instructions
Safety instructions s-21 use caution when releasing the z-axis (vertical axis) brake 3. W warning theverticalaxiswillslidedownwardwhenthebrakeisreleased,causingahazardoussituation.Takeadequate safety measures in consideration by taking the weight and shape into account. • beforereleasingthebrakeafte...
Page 36: Safety Instructions
Safety instructions s-22 4.7 inspection and maintenance always perform daily and periodic inspections and make a pre-operation check to ensure there are no prob- lems with the robot and related equipment. If a problem or abnormality is found, then promptly repair it or take other measures as necessa...
Page 37: Safety Instructions
Safety instructions s-23 4.7.2 precautions during service work precautions when removing a motor (cartesian robots and vertical mount single-axis robots) 1. W warning theverticalaxiswillslidedownwhenthemotorisremoved,causingahazardoussituation. • turnoffthecontrollerandplaceasupportundertheverticala...
Page 38: Safety Instructions
Safety instructions s-24 4.8 disposal whendisposingofrobotsandrelateditems,handlethemcarefullyasindustrialwastes.Usethecorrect disposal method in compliance with your local regulations, or entrust disposal to a licensed industrial waste disposal company. Disposal of lithium batteries 1. When disposi...
Page 39: Safety Instructions
Safety instructions s-25 5. Emergency action when a person is caught by robot if a person should get caught between the robot and a mechanical part such as the installation base, then release the axis. Emergency action ■ release the axis while referring to the following section in the manual for the...
Page 40: Safety Instructions
Safety instructions s-26 7. Using the robot safely 7.1 movement range when a tool or workpiece is attached to the robot manipulator tip, the actual movement range enlarges from the movement range of the robot itself (figure a) to include the areas taken up by movement of the tool and workpiece attac...
Page 41: Safety Instructions
Safety instructions s-27 7.2 robot protective functions protective functions for yamaha robots are described below. Overload detection 1. This function detects an overload applied to the motor and turns off the servo. If an overload error occurs, take the following measures to avoid such errors: 1. ...
Page 42: Safety Instructions
Safety instructions s-28 7.3 residual risk to ensure safe and correct use of yamaha robots and controllers, system integrators and/or end users imple- ment machinery safety design that conforms to iso12100. Residualrisksforyamaharobotsandcontrollersaredescribedinthedangerorwarninginstructions provid...
Page 44: Safety Instructions
Yamaha motor co., ltd. Im operations all rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced in any form without the permission of yamaha motor co., ltd. Information furnished by yamaha in this manual is believed to be reliable. However, no responsibility is assumed for possible inaccurac...
Page 45: Arranty
W arranty ver.1.01_201209 warranty for information on the warranty period and terms, please contact our distributor where you purchased the product. This warranty does not cover any failure caused by: ■ 1. Installation, wiring, connection to other control devices, operating methods, inspection or ma...
Page 47: Introduction
1 introduction introduction our sincere thanks for your purchase of this yamaha robot controller. This manual explains how to install and operate the yamaha robot controller. Be sure to read this manual carefully as well as related manuals and comply with their instructions for using the yamaha robo...
Page 48
Before using the robot controller (be sure to read the following notes) 2 3 before using the robot controller (be sure to read the following notes) please be sure to perform the following tasks before using the robot controller. Failing to perform these tasks will require absolute reset for setting ...
Page 49: Over
2 3 over view of the rcx series overview of the rcx series the yamaha rcx series robot controllers were developed based on years of yamaha experience and proven achievements in robotics and electronics. These controllers are specifically designed to operate yamaha industrial robots efficiently and a...
Page 50: Memo
4 memo.
Page 51: Chapter 1
Chapter 1 using the robot safely contents 1. Operating environment 1-1.
Page 52: 1-1
1-1.
Page 53: 1-1
1-1 chapter 1 using the robot safel y 1. Operating environment operating temperature operatingtemperature 0°cto40°c the ambient temperature should be maintained within a range of 0 to 40°c in order to guarantee continuous operation of the robot controller that meets the initial specifications. If th...
Page 54: 1-2
1-2 chapter 1 using the robot safel y environments the controller is not designed to meet explosion-proof, dust-proof, and drip-proof specifications, and so do not use it in the following locations. If used in these locations, component corrosion, improper installation, or fire may result. 1)environ...
Page 55: Chapter 2
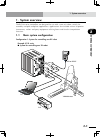
Chapter 2 system overview contents 1. System overview 2-1 1.1 main system configuration 2-1 1.2 rcx22 series axis definition 2-2 2. Part names and functions 2-3 2.1 rcx222 (maximum number of axes: 2) 2-3 2.2 rcx222hp (maximum number of axes: 2) 2-3 3. Control system 2-4 3.1 rcx222/rcx222hp 2-4 4. Op...
Page 56: 2-1
2-1.
Page 57: 2-1
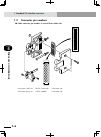
2-1 chapter 2 system over view 1. System overview 1. System overview the rcx22 series controllers are designed for use with a two-axis robot, mainly for assembly and pick-and-place applications. Applications also include various inspection instruments, sealers and spray equipment utilizing linear an...
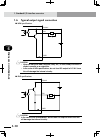
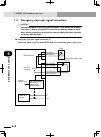
Page 58: 2-2
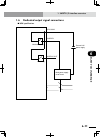
2-2 chapter 2 system over view 2-3 1. System overview configuration 2: system for controlling two single-axis robots example: t9 + t9 ■ system for controlling two single-axis robots xm ym mot or rgen tem p acin n l l1 n1 safet y srv err rpb rob i/o sd/com rdy e-st op b/a bat rcx222 ext.E-st op pin11...
Page 59: 2-2
2-2 2-3 chapter 2 system over view 2. Part names and functions 2. Part names and functions 2.1 rcx222 (maximum number of axes: 2) ■ rcx222 front view xm ym motor rgen temp acin n l l1 n1 safety srv err rpb rob i/o sd/com rdy e-stop b/a bat rcx222 pin11-12 ext.E-stop op.1 op.2 ! 2.2 rcx222hp (maximum...
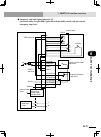
Page 60: 2-4
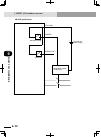
2-4 chapter 2 system over view 2-5 3. Control system 3. Control system the basic block diagram of the control system is shown below. 3.1 rcx222/rcx222hp ■ basic block diagram d.Power board assy cpu board assy driver2 board assy driver2 board assy fan op .Board op.Board cn3 cn4 ac200-230v regenerativ...
Page 61: 2-4
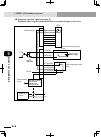
2-4 2-5 chapter 2 system over view 4. Optional devices 4. Optional devices 4.1 rpb programming box the rpb is a hand-held device used to perform all robot operations, including manual operations, program input and editing, teaching and parameter settings. Emergency stop button emergency stop button ...
Page 62: 2-6
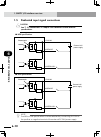
2-6 chapter 2 system over view 5. Basic sequence from installation to operation the basic sequence from installation to actual operation is shown below. Refer to this sequence to use the rcx22 series safely, correctly and effectively. Before beginning the work, read this user's manual thoroughly. In...
Page 63: Chapter 3
Chapter 3 installation contents 1. Unpacking 3-1 1.1 packing box 3-1 1.2 unpacking 3-1 2. Installing the robot controller 3-2 2.1 installation conditions 3-2 2.2 installation methods 3-4 3. Connector names 3-6 4. Connecting to the power 3-7 4.1 connection example 3-7 4.2 power supply and ground term...
Page 64: 3-1
3-1 12.1 wiring methods 3-24 12.2 precautions for installation 3-26 12.3 methods of preventing malfunctions 3-26 13. Checking the robot controller operation 3-27 13.1 cable connection 3-27 13.2 operation check 3-28.
Page 65: 3-1
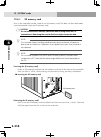
3-1 chapter 3 inst alla tion 1. Unpacking 1.1 packing box the robot controller is high precision equipment and is carefully packed in a cardboard box to avoid shocks and vibrations. If there is any serious damage or dents on the packing box, please notify your yamaha sales dealer without unpacking t...
Page 66: 3-2
3-2 chapter 3 inst alla tion 3-3 2. Installing the robot controller when installing, choose a proper place for your robot controller, taking into account your system layout, accessibility for maintenance, etc. 2.1 installation conditions c caution (1) whencarryingtherobotcontroller,useadollyorsimila...
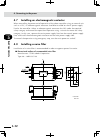
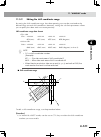
Page 67: 3-2
3-2 3-3 chapter 3 inst alla tion ■ clearance for installing the controller xm ym motor rgen temp acin n l l1 n1 safety srv err rpb rob i/o sd/com rdy e-stop b/a bat rcx222 pin11-12 ext.E-stop op.1 op.2 ! 50mm or more 50mm or more 17mm or more 50mm or more when installing the robot controller, follow...
Page 68: 3-4
3-4 chapter 3 inst alla tion 3-5 2.2 installation methods there are three methods for installing the robot controller as explained below. 1)usingtherubberfeet(attachedasstandardparts) ■ using the rubber feet xm ym mot or rgen tem p acin n l l1 n1 safet y srv err rpb rob i/o sd/com rdy e-st op b/a ba...
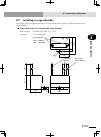
Page 69: 3-4
3-4 3-5 chapter 3 inst alla tion 3)attachingthel-typebrackets(suppliedasstandardaccessories)totherear ■ attaching the l-type brackets to the rear xm ym mot or rgen tem p acin n l l1 n1 safet y srv err rpb rob i/o sd/com rdy e-st op b/a bat rcx222 ext.E-st op pin11-12 op.1 op.2 ! L-type bracket part ...
Page 70: 3-6
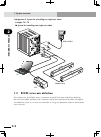
3-6 chapter 3 inst alla tion 3-7 3. Connector names connector names, locations and functions are shown below. ■ rcx connectors xm ym motor rgen temp acin n l l1 n1 safety srv err rpb rob i/o sd/com rdy e-stop b/a bat rcx222 pin11-12 ext.E-stop op.1 op.2 ! T com r rpb e safety q xm q ym y op.1 y op.2...
Page 71: 3-6
3-6 3-7 chapter 3 inst alla tion 4. Connecting to the power attach the power connector to the power cable and insert it into the "ac in" connector on the front panel of the controller as shown below. 4.1 connection example l n l1 n1 leakage breaker noise filter circuit protector circuit protector su...
Page 72: 3-8
3-8 chapter 3 inst alla tion 3-9 4.2 power supply and ground terminals w warning • topreventelectricalshocksormalfunctionscausedbynoise, thegroundterminal(protectiveconductor) must be grounded properly. • topreventelectricalshocks,nevertouchtheacinterminals when power is supplied to the robot contro...
Page 73: 3-8
3-8 3-9 chapter 3 inst alla tion 4.3 ac power connector wiring l length of exposed wire lead strip the wire to expose 8 to 9 mm of bare lead. 8 to 9 mm l wiring insert the wire lead into the opening in the power connector in either of the following methods, and make sure the wire is securely attache...
Page 74: 3-10
3-10 chapter 3 inst alla tion 3-11 4.4 considering power capacity and generated heat amount the required power capacity and generated heat amount depend on the robot model and the number of axes to be controlled. C caution the power supply voltage for the robot controller must always be regulated wi...
Page 75: 3-10
3-10 3-11 chapter 3 inst alla tion 4.5 installing an external leakage breaker since the robot controller drives the motors by pwm control of igbt, leakage current flows at high frequencies. This might cause the external leakage breaker to malfunction. When installing an external leakage current brea...
Page 76: 3-12
3-12 chapter 3 inst alla tion 3-13 4.7 installing an electromagnetic contactor when controlling the power on/off operation of the robot controller using an external unit suchasaplc,anelectromagneticcontactorshouldbeinstalledontheacpowersupply line for the controller. Select an electromagnetic contac...
Page 77: 3-12
3-12 3-13 chapter 3 inst alla tion 4.9 installing a surge absorber userswhowishtoimproveimmunitytosurgenoisefromlightningstrikesshouldinstalla surge absorber. ■ dimensional outlines of recommended surge absorber manufacturer :soshinelectricco.,ltd. Typeno. :lt-c12g801ws status indicator φ4.3 +0.3 -0...
Page 78: 3-14
3-14 chapter 3 inst alla tion 3-15 5. Robot connections 5.1 connecting the robot cables connect the robot cables to the "xm", "ym" and "rob i/o" connectors on the front panel of the controller as shown below. The robot cable specifications depend on the robot model, so refer to each robot user's man...
Page 79: 3-14
3-14 3-15 chapter 3 inst alla tion 5. Robot connections 5.2 noise countermeasures the robot cables which are connected to the controller's xm and ym connectors are motor power cables, and these cables emit switching noise which occurs during motor control. This noise could cause malfunctions in sens...
Page 80: 3-16
3-16 chapter 3 inst alla tion 3-17 6. Connecting the rpb programming box as shown in the figure below, the rpb should be connected to the rpb connector on the front panel of the robot controller. If not connecting the rpb, plug a terminator (supplied as an accessory) into the rpb connector. C cautio...
Page 81: 3-16
3-16 3-17 chapter 3 inst alla tion 7. I/o connections the various input/output (i/o) signals from peripheral equipment can be connected to the robotcontroller.Eachi/oissetwithanumber,andthei/oconnectortobeuseddepends on that number. For more detailed information on inputs and outputs, see chapter 5,...
Page 82: 3-18
3-18 chapter 3 inst alla tion 3-19 8. Connecting a host computer as a standard feature, the robot controller has an rs-232c interface port for data communication with a host computer. Most computer models having an rs-232c port can be interfaced to the robot controller, by connecting the com connect...
Page 83: 3-18
3-18 3-19 chapter 3 inst alla tion 9. Connecting the absolute battery the absolute batteries shipped with the controller are unused, and the battery connectors are left disconnected to prevent discharge. After installing the controller, always be sure to connect the absolute batteries before connect...
Page 84: 3-20
3-20 chapter 3 inst alla tion 3-21 w warning • whenreplacingtheabsolutebatterywiththepowerturnedon,put the robot in the emergency stop status. • performtheworkaftercheckingthatthereisnoelectrical shockhazardintheperipheralunitsofthecontroller. • theabsolutebatteryreplacementintheservoonstatusis haza...
Page 85: 3-20
3-20 3-21 chapter 3 inst alla tion 10. Replacing the absolute battery the absolute battery will wear down and must be replaced as needed. For example, when problems with backing up data occur, replace the battery since the battery has reached the end of the service life. Though battery wear depends ...
Page 86: 3-22
3-22 chapter 3 inst alla tion 3-23 11. Connecting a regenerative unit whenaregenerativeunitisrequired,connectittothergenandtempconnectorson the front panel of the controller. The regenerative unit is attached to the right side of the controller prior to shipping. N note • thercx222mayrequirearegener...
Page 87: 3-22
3-22 3-23 chapter 3 inst alla tion ■ regenerative unit block diagram rcx222 rgen temp regenerative unit standard cable length: 300mm thermal sensor (normally closed) c caution (1) thegenerativeunitbecomeshotduringoperation.Donottouchitto avoid burns. Also do not install the generative unit near an o...
Page 88: 3-24
3-24 chapter 3 inst alla tion 3-25 12. Precautions for cable routing and installation 12.1 wiring methods various cables are used to connect the robot controller to peripheral devices. Follow the precautions below when making cable routing and connections to avoid malfunctions due to noise. C cautio...
Page 89: 3-24
3-24 3-25 chapter 3 inst alla tion refer to the drawing below when making the cable connections. ■ cable connection xm ym motor rgen temp acin n l l1 n1 safety srv err rpb rob i/o sd/com rdy e-stop b/a bat rcx222 pin11-12 ext.E-stop op.1 op.2 ! Dio cable safety cable power cable robot cable communic...
Page 90: 3-26
3-26 chapter 3 inst alla tion 3-27 12.2 precautions for installation this robot controller is not designed with an explosion-proof, dust-proof or drip-proof structure. Do not install it in the following locations or environments (1) where exposed to flammable gases or liquids. (2) where conductive d...
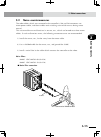
Page 91: 3-26
3-26 3-27 chapter 3 inst alla tion 13. Checking the robot controller operation this section explains how to check the controller operation using a special connector that comes with the controller and an applicable robot. Before beginning this check, finish making connections to the following items. ...
Page 92: 3-28
3-28 chapter 3 inst alla tion 13.2 operation check after connecting the robot and special connector (supplied) to the controller, turn on the power to the controller and check the following points. Normal operation •the"rdy"and"srv"ledlampsonthefrontpanelofthecontrollerlightup.The "err"ledlampisoff....
Page 93: Chapter 4
Chapter 4 operation contents 1. Operation overview 4-1 2. The rcx robot controller 4-2 2.1 part names 4-2 2.2 main functions 4-2 3. Rpbprogrammingbox 4-3 3.1 part names 4-3 3.2 main functions 4-3 3.3 connection to the robot controller 4-4 3.4 changing the rpb screen settings 4-5 4. Turning power on ...
Page 94
9. "auto" mode 4-30 9.1 automatic operation 4-33 9.2 stopping the program 4-34 9.3 resetting the program 4-35 9.4 switching task display 4-37 9.5 switching the program 4-38 9.6 changing the automatic movement speed 4-39 9.7 executing the point trace 4-40 9.7.1 ptp motion mode 4-42 9.7.2 arch motion ...
Page 95
10.3.4 copying a program 4-69 10.3.5 erasing a program 4-70 10.3.6 renaming a program 4-71 10.3.7 changing the program attribute 4-72 10.3.8 displaying object program information 4-73 10.3.9 creating a sample program automatically 4-74 10.4 compiling 4-76 10.5 line jump and character string search 4...
Page 96
11.5.2 editing the shift coordinate range 4-121 11.5.2.1 restoring a shift coordinate range 4-123 11.5.3 shift coordinate setting method 1 4-124 11.5.4 shift coordinate setting method 2 4-127 11.6 displaying, editing and setting hand definitions 4-130 11.6.1 editing hand definitions 4-133 11.6.1.1 r...
Page 97
12.5 self diagnosis 4-251 12.5.1 controller check 4-252 12.5.2 error history display 4-253 12.5.3 displaying the absolute battery condition 4-254 12.5.4 displaying the total operation time 4-255 12.5.5 system error details display 4-256 12.6 backup processes 4-257 12.6.1 sd memory card 4-258 12.6.1....
Page 98: 4-1
4-1.
Page 99: 4-1
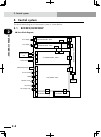
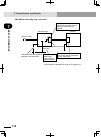
4-1 chapter 4 opera tion 1. Operation overview the controller configuration and main functions are shown below. Set up the equipment as needed according to the operation to be performed. C caution theexternalcircuitconnectedtotherobotcontrollershouldbepreparedby the user. N note • refertochapter5for...
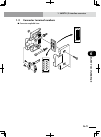
Page 100: 4-2
4-2 chapter 4 opera tion 4-3 2. The rcx robot controller 2.1 part names controller front panel ■ part names and layout xm ym motor rgen temp acin n l l1 n1 safety srv err rpb rob i/o sd/com rdy e-stop b/a bat rcx222 pin11-12 ext.E-stop op.1 op.2 ! Q ac in terminal y rpb connector u sd/com connector ...
Page 101: 4-2
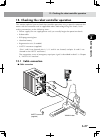
4-2 4-3 chapter 4 opera tion 3. Rpb programming box the rpb programming box connects to the robot controller and is used to edit and execute robot programs. 3.1 part names ■ programming box y enable switch (rpb-e only) rear view t selector switch (rpb-e only) q display (liquid crystal screen) e emer...
Page 102: 4-4
4-4 chapter 4 opera tion 4-5 t selector switch (rpb-e only) thisswitchcanbeusedasneededbywiringtothesafetyconnectorbytheuser. The switch on/off function is disabled if not wired correctly. Y 3-position enable switch (rpb-e only) this switch is provided for safety. Pressing it to mid-position only al...
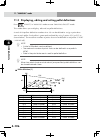
Page 103: 4-4
4-4 4-5 chapter 4 opera tion 3.4 changing the rpb screen settings the rpb screen contrast can be adjusted, and the key-press volume can be changed as needed. 1) turn on the power while holding down on the rpb. Therpbsettingscreen("adjust"mode)appears. ■ "adjust" mode for changing rpb screen settings...
Page 104: 4-6
4-6 chapter 4 opera tion 4-7 4. Turning power on and off this section explains how to turn power on and off, assuming that the external emergency stop circuit and other necessary units are connected according to the instructions in chapter 3, "installation", and also that the robot controller operat...
Page 105: 4-6
4-6 4-7 chapter 4 opera tion 4) if return-to-origin is incomplete, eliminate the problem and perform absolute reset. Then start the robot operation. Refer to "11.8 absolute reset" in this chapter for how to perform absolute reset. ■ "manual" mode screen manual –––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––...
Page 106: 4-8
4-8 chapter 4 opera tion 4-9 5. Operation keys 5.1 rpb screen the rpb screen display is composed of 4 areas as shown below. ■ rpb screen example program >edit '***** test1 program ***** 2 ' 3 do2(0)=0 4 wait di3(4,3,2)=3 5 move p,p0 select copy cut paste bs 1st line 2nd line 3rd line 4th line 5th li...
Page 107: 4-8
4-8 4-9 chapter 4 opera tion 5.2 operation key layout the operation keys are covered with a plastic sheet to prevent dust. There are 3 main kinds of keys. 1) function keys 2) control keys 3) data keys ■ sheet key layout function key data key control key 5. Operation keys.
Page 108: 4-10
4-10 chapter 4 opera tion 4-11 5.3 basic key operation 1)eachoperationkeyhas3differentfunctionsasshownbelow. Use or as needed to enable various functions. ■ key configuration shift 1 shift 2 shift 3 2) there are 3 ways (shift 1 to shift 3) to use each operation key. Shift example of key input input ...
Page 109: 4-10
4-10 4-11 chapter 4 opera tion 5.4 function keys to operate the rpb, select the menus by pressing the function keys. Therelationofthefunctionkeystotheirmenusin"manual"modeisshownbelow. Function key selected menu (f1) point (f2) pallet (f4) vel+ (f5) vel- + (f6) shift + (f7) hand + (f8) unitchg + (f9...
Page 110: 4-12
4-12 chapter 4 opera tion 4-13 relation of function keys to menus ■ function keys and menus manual 50%[mg][s0h0j] current position point pallet vel+ vel- ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ [f1] [f2] [f3] [f4] [f5] ∧ shift hand unitchg vel++ vel— ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ [f6] [f7] [f8] [f9] [f10] ...Upper ∨ abs.Rst coordi ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ [f11] [...
Page 111: 4-12
4-12 4-13 chapter 4 opera tion 5.5 control keys thereare6kindsofcontrolkeys:(1)modeselectionkeys,(2)extendedfunctionkeys, (3)cursorkeys,(4)pagekeys,(5)editkeys,(6)jogkeys. The functions of each key are explained below. (1) mode selection keys : displays the mode menu (highest hierarchy). : selects t...
Page 112: 4-14
4-14 chapter 4 opera tion 4-15 (5) edit keys these keys are enabled when the editing cursor is displayed. : toggles between "insert" and "overwrite" modes. The cursor "_" appears in "overwrite" mode and " ■ " appears in "insert" mode. : deletes one character at the cursor position. : inserts one lin...
Page 113: 4-14
4-14 4-15 chapter 4 opera tion 5.6 data keys the data keys are used for data input, programming and data editing. There are 2 kinds of data keys. (1) alphanumeric keys to :entersnumbers. To :entersalphabeticcharacters. : inserts spaces. (2) symbol keys 5.7 other keys (1) enter key : pressingthiskeye...
Page 114: 4-16
4-16 chapter 4 opera tion 4-17 6. Emergency stop if for some reason you want to stop the robot immediately during operation, press the emergency stop button on the rpb. Pressing the emergency stop button cuts off power to the robot to stop operation. A message appears on the rpb screen as shown belo...
Page 115: 4-16
4-16 4-17 chapter 4 opera tion 6.1 emergency stop reset to return to normal operation after emergency stop, emergency stop must be reset. N note • emergency stop can also be triggered by an emergency stop input from thesafetyi/ointerface.Tocancelthisemergencystop,refertochapter6. • originpositionsar...
Page 116: 4-18
4-18 chapter 4 opera tion 4-19 4) press (motor). The following screen appears. ■ "utility>motor" mode (1) utility>motor motor power: off d1=m1: brake d5=m5: no axis d2=m2: brake d6=m6: no axis d3=m3: no axis d4=m4: no axis on off 5) press (on) to turn on the motor power. At the same time, the servom...
Page 117: 4-18
4-18 4-19 chapter 4 opera tion 6. Emergency stop 6.2 overload error reset in order to restore (enable) robot operation following a "17.4: overload" error occurrence, the overload cause must be identified and corrected, and then the error status must be reset. N notes • anemergencystopstatusisestabli...
Page 118: 4-20
4-20 chapter 4 opera tion 4-21 6. Emergency stop press the key at this time to return to the original mode with the motor power off. Continue with the following steps to turn the motor power on. 4) press the (motor) key. The following screen is then displayed. ■ motor power on (1) utility>motor moto...
Page 119: 4-20
4-20 4-21 chapter 4 opera tion 7. Mode configuration the robot operation mode consists of the following modes. “service” mode basic operation modes “auto” mode “manual” mode “program” mode “system” mode “di/do monitor” mode “utility” mode "service"modecanbeusedonlywhen"safe"modeisenabled. 7.1 basic ...
Page 120: 4-22
4-22 chapter 4 opera tion 4-23 c caution the"system"modeisusedtoselectthe"service"modefunctions.(referto '12.3.2settingthe"service"mode'inthischapter.) (2) "auto" mode select this mode to execute robot programs. Robot programs can be executed only in this mode. Operable tasks in this mode differ dep...
Page 121: 4-22
4-22 4-23 chapter 4 opera tion 7.3 mode hierarchy robot operation is mainly performed by pressing the function keys to select the desired mode from the menu. (refer to the "mode hierarchy diagram" described later.) whenthecontrolleristurnedon,the"manual"modemenufirstappearsonthescreen. Pressing disp...
Page 122: 4-24
4-24 chapter 4 opera tion 4-25 functions are switched with the and shift keys. The menu display changes while this shift key is pressed. ■ shift keys ■ function switching reset task dir vel+ vel- ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ [f1] ↓ [f2] [f3] [f4] [f5] ∧ point direct break vel++ vel-- ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ [f6] [f7] [f8] [f9] [f10] ...
Page 123: 4-24
4-24 4-25 chapter 4 opera tion n note • whenthedataisbeingeditedsuchasin"edit"mode, is inoperative. After pressing to return the mode hierarchy, press . • fromhereinthisuser'smanualthemodehierarchystatusisstatedinthe order as shown below. First(highest)hierarchy>secondhierarchy>thirdhierarchy>fourth...
Page 124: 4-26
4-26 chapter 4 opera tion 4-27 ■ mode hierarchy diagram f1 auto f1 edit f2 teach f3 jump f4 vel+ f5 vel- f6 copy f7 erase f8 unitchg f9 vel++ f10 vel-- f11 find f12 find+ f13 find- f1 undo f3 jump f1 point f1 edit f2 teach f3 jump f4 vel+ f5 vel- f6 copy f7 erase f8 unitchg f9 vel++ f10 vel-- f11 tr...
Page 125: 4-26
4-26 4-27 chapter 4 opera tion f1 edit f4 vel+ f5 vel- f6 method1 f8 unitchg f9 vel++ f10 vel-- f1 m1 f2 m2 (f3 m3) (f4 m4) (f5 m5) (f6 m6) f11 all f1 4points f2 3points f5 simple f4 vel+ f5 vel- f8 unitchg f9 vel++ f10 vel-- f4 vel+ f5 vel- f8 unitchg f9 vel++ f10 vel-- f4 vel+ f5 vel- f8 unitchg f...
Page 126: 4-28
4-28 chapter 4 opera tion 4-29 8. "service" mode 8. "service" mode "service"modecanbeusedonlywhen"safe"modeisenabled. Use"service"modetoperformsafemaintenanceworkwiththerpbwhilewithinthe safetyenclosureoftherobotsystem.Thismodecanbeselectedbyturningdi02("service" mode input) off. C caution • use"sys...
Page 127: 4-28
4-28 4-29 chapter 4 opera tion 8. "service" mode 8.4 limits on robot moving speed robot operation from within the safety enclosure of the robot system is mainly for teaching and maintenance for the robot. Therefore,robotmovingspeedinservicemodeislimitedto3%ofthemaximumspeed so that the robot will mo...
Page 128: 4-30
4-30 chapter 4 opera tion 4-31 9. "auto" mode 9. "auto" mode "auto"modeexecutesrobotlanguageprogramsandrelatedtasks. Theinitial"auto"modescreenisshownbelow. ■ "auto" mode auto [t1] 100% s@ ————————————————————————————————————— 1 ’***** test1 program ***** 2 start *subtask,t2 3 do2(0)=0 4 wait di3(4,...
Page 129: 4-30
4-30 4-31 chapter 4 opera tion 9. "auto" mode i pointer display the program line number to be executed next is shown highlighted in the program listing. O guideline the contents assigned to function keys are shown highlighted. A message on what to do next also appears here in some operation steps. U...
Page 130: 4-32
4-32 chapter 4 opera tion 4-33 9. "auto" mode validkeysandsubmenudescriptionsin"auto"modeareshownbelow. Valid keys menu function cursorkey ( ↑/↓) scrollstheprogramlisting. Pagekey ( 〈〈 / 〈〈 ) switchestootherscreens. F1 reset resetstheprogram. F2 task changestheprogramlistingaccordingtoeachtask. F3 d...
Page 131: 4-32
4-32 4-33 chapter 4 opera tion 9. "auto" mode 9.1 automatic operation program commands are executed continuously during automatic operation. Before starting automatic operation, make sure that return-to-origin, program debugging, i/o signal connections and point data teaching have already been compl...
Page 132: 4-34
4-34 chapter 4 opera tion 4-35 9. "auto" mode the following keys are enabled during automatic operation. Valid keys menu function f9 vel++ increasesautomaticmovementspeedfortheselected robotgroupin5%increments. F10 vel-- decreasesautomaticmovementspeedfortheselected robotgroupin5%decrements. Robot (...
Page 133: 4-34
4-34 4-35 chapter 4 opera tion 9. "auto" mode 9.3 resetting the program to restart a program stopped with from the beginning, reset the program. N note the output is also reset when the program is reset. However, the output will not be reset in the following cases: 1. “do cond. On pgm reset / rescdo...
Page 134: 4-36
4-36 chapter 4 opera tion 4-37 9. "auto" mode • when the program "_select" exists: 1) press (reset)in"auto"mode. Thefollowingmessageappearsontheguidelinewhen"_select"existsamong the programs. Press (yes)toresettheselectedprogrambyswitchingitto "_select",orpress (no) to just reset the current program...
Page 135: 4-36
4-36 4-37 chapter 4 opera tion 9. "auto" mode 9.4 switching task display when a program executing multiple tasks is stopped, the program listing for each task can be displayed. [procedure] 1) press during program execution to stop the program. 2) press to display the program listing. The pointer ind...
Page 136: 4-38
4-38 chapter 4 opera tion 4-39 9. "auto" mode 9.5 switching the program if the program displayed on the screen is not the one you want to execute, it can be switched to another program. N note the output is reset when the program is switched. However, the output will not be reset in the following ca...
Page 137: 4-38
4-38 4-39 chapter 4 opera tion 9. "auto" mode 9.6 changing the automatic movement speed automatic movement speed for the selected robot group can be set within the range of 1 to 100%. N note automatic movement speeds once set here are stored in the internal memory even when the power is turned off. ...
Page 138: 4-40
4-40 chapter 4 opera tion 4-41 9. "auto" mode 9.7 executing the point trace point data positions can be checked by actually moving the robot arm in the following modes. •ptpmotionmode •archmotionmode •linearinterpolationmotionmode(linearinterpolationmotionatthesubrobotis not supported in controller ...
Page 139: 4-40
4-40 4-41 chapter 4 opera tion 9. "auto" mode validkeysandsubmenudescriptionsin"auto>point"modeareshownbelow. Valid keys menu function cursorkey ( ↑/↓) switchesthepointnumberandscrollsthescreen. Pagekey ( 〈〈 / 〈〈 ) switchestootherscreens. F1 ptp/ arch/ linear switchesthetracemovementmode. F2 a.Pos s...
Page 140: 4-42
4-42 chapter 4 opera tion 4-43 9. "auto" mode 9.7.1 ptp motion mode [procedure] 1) press in"auto>point"modetodisplayascreenlikethatshownbelow,then press (ptp) to select the ptp motion mode. ■ point trace screen in ptp motion mode (1) auto >point 100% [mg][s0h0j] ————————————x———————y———————z———————r...
Page 141: 4-42
4-42 4-43 chapter 4 opera tion 9. "auto" mode 9.7.2 arch motion mode [procedure] 1) press in"auto>point"modetodisplayascreenlikethatshownbelow,then press (arch). ■ point trace screen in arch motion mode (1) auto >point 100% [mg][s0h0j] ————————————x———————y———————z———————r——— p3 = 150.50 64.53 p4 = ...
Page 142: 4-44
4-44 chapter 4 opera tion 4-45 9. "auto" mode n note enterthenumberofpulsesforthey-axis. 4)usethecursor( ↑/↓) keys to select the point number to be checked. 5) press to move the robot by arch motion to the specified point position. The trace speed is one fifth of the automatic movement speed. To sto...
Page 143: 4-44
4-44 4-45 chapter 4 opera tion 9. "auto" mode 9.7.3 linear interpolation motion mode [procedure] 1) press in"auto>point"modetodisplayascreenlikethatshownbelow,then press (linear). ■ point trace screen in linear interpolation motion mode (1) auto >point 100% [mg][s0h0j] ————————————x———————y———————z—...
Page 144: 4-46
4-46 chapter 4 opera tion 4-47 9. "auto" mode 9.8 direct command execution in"auto>direct"mode,onelineofthecommandstatementcanbeexecutedjustafter you have entered it. [procedure] 1) press (direct)in"auto"mode. Thescreenswitchesto"auto>direct"modeandthecursorappearsonthescreen. The prompt (>) also ap...
Page 145: 4-46
4-46 4-47 chapter 4 opera tion 9. "auto" mode 9.9 break point an ongoing program can be stopped if a break point is set in the program. This is useful when debugging the program. The program execution pauses on the line just prior to a break point. The program execution will restart from the break p...
Page 146: 4-48
4-48 chapter 4 opera tion 4-49 9. "auto" mode 9.9.1 setting break points to make program debugging easy, the program execution can be stopped on the line where a break point is set. [procedure] 1) press (break)in"auto"modetoswitchto"auto>break"mode. 2)usethecursorkeystoselectthelinenumberonwhichabre...
Page 147: 4-48
4-48 4-49 chapter 4 opera tion 9. "auto" mode 9.9.2 deleting break points break points can be deleted. Press (search)asneededtofindabreakpointthat was set. [procedure] 1)usethecursor( ↑/↓) keys to select the line number where the break point is set. 2) press (cancel). The " b " mark disappears and t...
Page 148: 4-50
4-50 chapter 4 opera tion 4-51 9. "auto" mode 9.10 executing a step w warning the robot may begin to move when step is executed. To avoid danger, do not enter the robot movement range. [procedure] 1) press (step)in"auto"mode. 2)eachtimethiskeyispressed,thecommandstatementofthehighlightedlinenumber i...
Page 149: 4-50
4-50 4-51 chapter 4 opera tion 9. "auto" mode 9.12 executing the next step w warning the robot may begin to move when next is executed. To avoid danger, do not enter the robot movement range. [procedure] 1) press (next)in"auto"mode. 2)eachtimethiskeyispressed,thecommandstatementofthehighlightedlinen...
Page 150: 4-52
4-52 chapter 4 opera tion 4-53 10. "program" mode 10. "program" mode robot language programs can be edited, deleted and managed in "program" mode. The initial "program" mode screen is shown below. When "program" mode is entered, the currently selected program appears on the screen. ■ "program" mode ...
Page 151: 4-52
4-52 4-53 chapter 4 opera tion 10. "program" mode valid keys and submenu descriptions in "program" mode are shown below. Valid keys menu function cursorkey ( ↑/↓) selectstheprogramandscrollsthescreen. Pagekey ( 〈〈 / 〈〈 ) switchesthepagedisplay. F1 edit editstheprogram. F3 dir displaystheprogramdata....
Page 152: 4-54
4-54 chapter 4 opera tion 4-55 10. "program" mode 10.2 program editing [procedure] 1) press (edit)in"program"mode. A cursor appears on the top line of a program listing as shown below, allowing program editing. 2)usethecursorkeystomovethecursortothepositiontobeeditedandentera program command with th...
Page 153: 4-54
4-54 4-55 chapter 4 opera tion 10. "program" mode validkeysandsubmenudescriptionsin"program>edit"modeareshownbelow. Valid keys menu function cursorkey ( ↑/↓) movesthecursorandscrollsthescreen. Pagekey ( 〈〈 / 〈〈 ) switchesthepagedisplay. Ins switchesbetweeninsertandovertypemodes. L.Ins insertsoneblan...
Page 154: 4-56
4-56 chapter 4 opera tion 4-57 10. "program" mode 10.2.1 cursor movement [procedure] 1) pressing the cursor ( ↑/↓)keysin"program>edit"modemovesthecursorupor down one line at a time. Pressing the cursor ( ←/→) keys moves the cursor right or left one character at a time. 2) pressing the page ( , , , )...
Page 155: 4-56
4-56 4-57 chapter 4 opera tion 10. "program" mode 10.2.2 insert/overwrite mode switching [procedure] 1) press in"program>edit"mode. The cursor changes to underline ( _ ) form, and the screen switches to insert mode. In insert mode, the input character is inserted just previous to the cursor position...
Page 156: 4-58
4-58 chapter 4 opera tion 4-59 10. "program" mode 10.2.3 inserting a line [procedure] pressing ( = + )in"program>edit"modeinsertsablanklineatthe line previous to the cursor position. ■ inserting a line program >edit 3 do2(0)=0 4 wait di3(4,3,2)=3 5 _ 6 move p,p0 ’origin 7 move p,p1 select copy cut p...
Page 157: 4-58
4-58 4-59 chapter 4 opera tion 10. "program" mode 10.2.6 user function key display userfunctionkeysmakeiteasiertoenterprograms. N note when using this function, it is necessary to make a program named "function" and then write command statements for registering functions. For information on how to r...
Page 158: 4-60
4-60 chapter 4 opera tion 4-61 10. "program" mode 10.2.7 quitting program editing press toquitprogrameditingin"program>edit"mode. 10.2.8 specifying the copy/cut lines [procedure] 1)in"program>edit"mode,movethecursortothelineyouwanttocopyorcut. 2) press (select)toselecttheline. 3)usethecursor( ↓) key...
Page 159: 4-60
4-60 4-61 chapter 4 opera tion 10. "program" mode 10.2.9 copying the selected lines [procedure] after selecting the lines in "10.2.8", press (copy). The data on the selected lines are copied into the buffer. The " c " marks then disappear. ■ copying the selected lines program >edit 1 ’***** test2 pr...
Page 160: 4-62
4-62 chapter 4 opera tion 4-63 10. "program" mode 10.2.11 pasting the data [procedure] when (paste)ispressedin"program>edit"mode,thedatastoredintothe buffer by copy/cut operation is inserted just before the cursor line. ■ pasting the data program >edit 1 ’***** test2 program ***** 2 ’ 3 do2(0)=0 4 w...
Page 161: 4-62
4-62 4-63 chapter 4 opera tion 10. "program" mode 10.2.13 line jump [procedure] 1)in"program>edit"mode,press (jump)toenter"program>edit>jump" mode. Themessage"enterlineno.>"appearsontheguideline. ■ line jump program >edit 1 ’***** test2 program ***** 2 goto *_’ 3 do2(0)=0 4 wait di3(4,3,2)=3 5 move ...
Page 162: 4-64
4-64 chapter 4 opera tion 4-65 10. "program" mode 10.2.14 searching a character string [procedure] 1)in"program>edit"mode,press (find)toenter"program>edit>find" mode. The message "character string >" appears on the guideline. 2)enterthecharacterstringyouwanttosearchforandpress . A maximum of 20 char...
Page 163: 4-64
4-64 4-65 chapter 4 opera tion 10. "program" mode 10.3 directory when (dir) is pressed in "program" mode, information on each program appears as shown below. N note a maximum of 100 programs can be stored. ■ program information (1) program >dir > no. 1 test1 55 952 rw 2 * test2 50 907 rw 3 parts100 ...
Page 164: 4-66
4-66 chapter 4 opera tion 4-67 10. "program" mode contents of each item are shown below. Item description no. Indicatestheserialnumberoftheprogram.Thenumber oftheprogramwhichiscurrentlyselectedishighlighted (reversedbackground). Name indicatestheprogramname. The"*"mark(reversedbackground)showsthis p...
Page 165: 4-66
4-66 4-67 chapter 4 opera tion 10. "program" mode 10.3.1 cursor movement [procedure] to select the program, use the cursor ( ↑/↓) keys in "program>dir" mode. The pointer cursor moves to the selected program number. The program name is displayed at the right end on the system line (1st line). 10.3.2 ...
Page 166: 4-68
4-68 chapter 4 opera tion 4-69 10. "program" mode 10.3.3 directory information display [procedure] in "program>dir" mode, press (info) to enter "program>dir>info" mode. The following information on the selected program appears. ■ program information program >dir>info > source(use/sum) = 1316/364580 ...
Page 167: 4-68
4-68 4-69 chapter 4 opera tion 10. "program" mode 10.3.4 copying a program a program in the directory can be copied under a different name. N note program names can be up to 8 characters and consist of a combination of alphanumeric characters (0 to 9, a to z) and underscores ( _ ). [procedure] 1) in...
Page 168: 4-70
4-70 chapter 4 opera tion 4-71 10. "program" mode 10.3.5 erasing a program unnecessaryprogramsinthedirectorycanbeerased. C caution • programswithan"ro(readonly)"attributecannotbeerased.When these programs must be erased, change the attribute. • tochangetheprogramattribute,referto"10.3.7changingthepr...
Page 169: 4-70
4-70 4-71 chapter 4 opera tion 10. "program" mode 10.3.6 renaming a program to change the names of programs in the directory, proceed as follows. [procedure] 1) in "program>dir" mode, use the cursor ( ↑/↓) keys to select the program to be renamed. 2) press (rename)toenter"program>dir>rename"mode. Th...
Page 170: 4-72
4-72 chapter 4 opera tion 4-73 10. "program" mode 10.3.7 changing the program attribute editinganderasingtheprogramscanbeprohibitedbyspecifyingtheprogramattribute. Therearetwoprogramattributes:rwandro.Eachtimeachangeismadeaprogram attribute is alternately switched. 1. Rw (read or write) program cont...
Page 171: 4-72
4-72 4-73 chapter 4 opera tion 10. "program" mode 10.3.8 displaying object program information to display information on an executable object program, proceed as follows. [procedure] 1) press (object)toenter"program>dir>object"mode. 2) object information appears as shown below. ■ object program info...
Page 172: 4-74
4-74 chapter 4 opera tion 4-75 10. "program" mode 10.3.9 creating a sample program automatically this section explains the procedure of automatically creating a sample program for defininguserfunctionkeyswhichcanbeusedin"manual"and"program"modes. N note use caution when creating a sample program aut...
Page 173: 4-74
4-74 4-75 chapter 4 opera tion 10. "program" mode [sample program listing] ***sampleprogram **** '*you can change any statements * '*as you like. * '*willhelpyouin * '*manualandprogrammode. * '********************************************************* *m_f1:'do(20)alternate do(20)=~do(20) *m_f2:'do(2...
Page 174: 4-76
4-76 chapter 4 opera tion 4-77 10. "program" mode 10.4 compiling to compile the program and create an executable object program, follow the procedure below. The object program allows you to check input errors or bugs after program editing. N note even if the specified program is yet not compiled, it...
Page 175: 4-76
4-76 4-77 chapter 4 opera tion 10. "program" mode 10.5 line jump and character string search the (jump), (find), (find+) and (find-) keys can be used inthesamewayasin"program>edit"mode. Referto"10.2.13linejump"and"10.2.14searchingacharacterstring"earlierinthis chapter.) 10.6 registering user functio...
Page 176: 4-78
4-78 chapter 4 opera tion 4-79 10. "program" mode ■ registering "function" program (2) program >dir no. Rw/ro 1 test1 55 952 rw 2 *test2 50 907 rw 3 parts100 38 843 rw 4 function 1 1 rw new info name line byte 5) press (edit)toenter"program>edit"mode. A cursor appears on the first line. 6)enteracomm...
Page 177: 4-78
4-78 4-79 chapter 4 opera tion 10. "program" mode when registering function keys for i/o commands in "manual" mode n note • inone"function"program,functionsforprogrameditandi/ofunctions in "manual" mode can be used together and defined. • besidestheabovemethod,userfunctionscanalsobedefinedbythe next...
Page 178: 4-80
4-80 chapter 4 opera tion 4-81 10. "program" mode example) *m_f2:’moment .. Characterstring"moment"isassignedto . Do (20) =1 .......... Do (20) is turned on when is pressed. Do (20) =0 ........... Do (20) is turned off when is released. *m_f14:’alter ..... Characterstring"alter"isassignedto . Do (20...
Page 179: 4-80
4-80 4-81 chapter 4 opera tion 10. "program" mode 10.7 resetting an error in the selected program if an error "9.1 program destroyed" occurs in the selected program data, this function resets the error and allows you to continue editing. C caution this function resets an error, but does not restore ...
Page 180: 4-82
4-82 chapter 4 opera tion 4-83 11. "manual" mode 11. "manual" mode pointdataandshiftdatacoordinatescanbedefinedandeditedin"manual"mode. Theinitial"manual"modescreenisshownbelow. ■ "manual" mode o guideline manual 50%[mg][s0h0x] s@ ————————————————————————————————————— current position *mx= 0.00 *my=...
Page 181: 4-82
4-82 4-83 chapter 4 opera tion 11. "manual" mode i current position this shows the current position of the robot. When an "m" letter is followed by a number it indicates the position in "pulse" units (integer display) and when an "x" to "a" letter follows, it indicates "mm" units (decimal point disp...
Page 182: 4-84
4-84 chapter 4 opera tion 4-85 11. "manual" mode 11.1 manual movement in"manual"mode,youcanmanuallymovetherobotwiththejogkeysasexplained below. W warning therobotstartstomovewhenajogkeyispressed.Toavoid danger, do not enter the robot movement range. N note • fordetailsonthesoftlimits,referto"12.1.3a...
Page 183: 4-84
4-84 4-85 chapter 4 opera tion 11. "manual" mode if robot movement beyond the +/- soft limits is attempted with the jog keys, the error message "2.1: over soft limit" appears and the robot does not move. (2) when the current position is displayed in "mm" units: a letter "x" is displayed on the upper...
Page 184: 4-86
4-86 chapter 4 opera tion 4-87 11. "manual" mode 2. When return-to-origin is not complete c caution if return-to-origin is incomplete, the soft limits do not work correctly. N note if return-to-origin is incomplete, the current position always appears as "pulse" units when the controller is turned o...
Page 185: 4-86
4-86 4-87 chapter 4 opera tion 11. "manual" mode 11.2 displaying and editing point data press (point)in"manual"modetoenter"manual>point"mode.Thismode allows you to display and edit the point data. One point is made up of data from 6 axes (x, y, z, r, a, b). The rcx22 series uses only two axes (x, y)...
Page 186: 4-88
4-88 chapter 4 opera tion 4-89 11. "manual" mode validkeysandsubmenudescriptionsin"manual>point"modeareshownbelow. Valid keys menu function cursorkey ( ↑/↓) specifiesthepointdataandscrollsthescreen. Pagekey ( 〈〈 / 〈〈 ) switchestootherscreens. F1 edit enterspointdatawithkeys. F2 teach enterspointdata...
Page 187: 4-88
4-88 4-89 chapter 4 opera tion 11. "manual" mode 11.2.1 point data input and editing [procedure] 1)in"manual>point"mode,usethecursor( ↑/↓) keys to select the point to edit. 2) press (edit)toenter"manual>point>edit"mode. An edit cursor appears at the left end of the point line data that was selected....
Page 188: 4-90
4-90 chapter 4 opera tion 4-91 11. "manual" mode 4) press , cursor up/down ( ↑/↓) keys or page up/down ( , ) keys to finish the point data input. Press if you want to cancel the point data input. Validkeysandsubmenudescriptionsin"manual>point>edit"modeareshownbelow. Valid keys menu function cursorke...
Page 189: 4-90
4-90 4-91 chapter 4 opera tion 11. "manual" mode 11.2.2 point data input by teaching the current position of the robot can be obtained as point data by teaching. N note point data teaching cannot be performed when return-to-origin is incomplete. Perform point teaching after performing absolute reset...
Page 190: 4-92
4-92 chapter 4 opera tion 4-93 11. "manual" mode ■ point data teaching (2) manual >point 50% [mg][s0h0x] ————————————x———————y———————z———————r——— p7 = 100.00 250.00 p8 = 50.00 100.00 p9 = 122.62 -24.54 edit teach jump vel+ vel- comnt : [ ] [pos] 50.00 100.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 4...
Page 191: 4-92
4-92 4-93 chapter 4 opera tion 11. "manual" mode 11.2.3 point data input by direct teaching point data can also be obtained by direct teaching (moving the robot by hand to the target point while the robot servo is off). W warning whenyouperformdirectteaching,makesurethattheemergency stop button is p...
Page 192: 4-94
4-94 chapter 4 opera tion 4-95 11. "manual" mode 11.2.4 point jump display [procedure] 1) press (jump)in"manual>point"mode. Themessage"enterpointno.>"appearsontheguideline. ■ point jump (1) manual >point 50%[mg][s0h0x] ————————————x———————y———————z———————r——— p7 = 100.00 250.00 p8 = 50.00 100.00 p9 ...
Page 193: 4-94
4-94 4-95 chapter 4 opera tion 11. "manual" mode 11.2.5 copying point data point data can be copied under another point number. N note if a hand system flag is set in the point data, the hand system flag will also be copied. [procedure] 1) press (copy)in"manual>point"mode. The message "copy(####-###...
Page 194: 4-96
4-96 chapter 4 opera tion 4-97 11. "manual" mode ■ copying point data (2) manual >point 50% [mg][s0h0x] ————————————x———————y———————z———————r——— p30 = 100.00 250.00 p31 = 50.00 100.00 p32 = 122.62 -24.54 (30-34,50)copy ok? Yes no comnt : [ ] [pos] 50.00 100.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00...
Page 195: 4-96
4-96 4-97 chapter 4 opera tion 11. "manual" mode 11.2.6 erasing point data [procedure] 1) press (erase)in"manual>point"mode. Themessage"erase(####-####)>"appearsontheguideline. ■ erasing point data (1) manual >point 50% [mg][s0h0x] ————————————x———————y———————z———————r——— p30 = 100.00 250.00 p31 = 5...
Page 196: 4-98
4-98 chapter 4 opera tion 4-99 11. "manual" mode 11.2.7 point data trace point data positions can be checked by actually moving the robot. Referto"9.7executingthepointtrace"earlierinthischapterfordetails. N note • in"auto>point"mode,pressing (modify)returnsto "manual>point"modethatwasactivebeforetra...
Page 197: 4-98
4-98 4-99 chapter 4 opera tion 11. "manual" mode validkeysandsubmenudescriptionsin"manual>point"commentmodeareshown below. Valid keys menu function cursorkey ( ↑/↓) specifiespointdataorscrollsthescreenvertically. Pagekey ( 〈〈 / 〈〈 ) switchestootherscreens. F1 edit editspointcomments. F2 teach enters...
Page 198: 4-100
4-100 chapter 4 opera tion 4-101 11. "manual" mode 11.2.8.1 point comment input and editing n note • forpointcomments,itisadvisabletoenteracharacterstringthatiseasy to understand. • apointcommentcanbeupto15characters. [procedure] 1)in"manual>point>comment"mode,usethecursor( ↑/↓) keys to select the p...
Page 199: 4-100
4-100 4-101 chapter 4 opera tion 11. "manual" mode 11.2.8.3 jump to a point comment n note valid point numbers are from 0 to 9999. [procedure] 1) press (jump)in"manual>point>comment"mode. Themessage"enterpointno.>"appearsontheguideline. ■ jumping to a point comment display (1) manual >point>comment ...
Page 200: 4-102
4-102 chapter 4 opera tion 4-103 11. "manual" mode 2)use to , and to enter the point number range for the copy source and the point number for the copy destination in the following format, and press . "(copy start number) – (copy end number), (copy destination number)" for example, to copy the point...
Page 201: 4-102
4-102 4-103 chapter 4 opera tion 11. "manual" mode 11.2.8.5 erasing point comments point comments already entered can be deleted. N note valid point numbers are from 0 to 9999. [procedure] 1) press (erase)in"manual>point>comment"mode. Themessage"erase(####-####)>"appearsontheguideline. 2) use to and...
Page 202: 4-104
4-104 chapter 4 opera tion 4-105 11. "manual" mode 11.2.8.6 point comment search point comments already entered can be located. N note a point comment can be up to 15 characters. [procedure] 1) press (find)in"manual>point>comment"mode. The message "character string >" appears on the guideline. 2)ent...
Page 203: 4-104
4-104 4-105 chapter 4 opera tion 11. "manual" mode 11.2.9 point data error reset if an error "9.2 point data destroyed" occurs in the point data, this function resets the error and allows you to continue editing. C caution this function resets an error, but does not restore the point data. A problem...
Page 204: 4-106
4-106 chapter 4 opera tion 4-107 11. "manual" mode 11.3 displaying, editing and setting pallet definitions press (pallet)in"manual"modetoenter"manual>pallet"mode. This mode allows you to display, edit and set pallet definitions. A total of 20 pallets (definition numbers 0 to 19) can be defined to as...
Page 205: 4-106
4-106 4-107 chapter 4 opera tion 11. "manual" mode ■ pallet definition (2) manual >pallet 50%[mg][s0h0x] pl0 =set pl1 = pl2 =set pl3 = [pos] 400.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 edit method vel+ vel- palletdefinitionnumbersmarked"set"meanthattheyhavealreadybeendefined. Validkeysandsubmenudescriptionsin"manual>pall...
Page 206: 4-108
4-108 chapter 4 opera tion 4-109 11. "manual" mode 11.3.1 editing pallet definitions n note themaximumnumberofpointsperpalletis32767(=nx*ny*nz). [procedure] 1)in"manual>pallet"mode,selectthepalletnumberwiththecursor( ↑/↓) keys. 2) press (edit)toenter"manual>pallet>edit"mode. 3)usethecursor( ↑/↓) key...
Page 207: 4-108
4-108 4-109 chapter 4 opera tion 11. "manual" mode 11.3.1.1 point setting in pallet definition in"manual>pallet>edit"mode,ascreenlikethatshownbelowisdisplayed. N note • eachpalletisgeneratedwith5pointsforpalletdefinition. • these5pointsshouldbedefinedinorderfromp[1]top[5].See"11.3 displaying, editin...
Page 208: 4-110
4-110 chapter 4 opera tion 4-111 11. "manual" mode 11.3.1.1.1 editing the point in pallet definition n note • eachpalletisgenerated(outlined)with5points,soalwaysspecifythese 5 points for pallet definition. • pointdatainthepalletdefinitionmustbeenteredin"mm"units. • the5pointsshouldbedefinedinorderfr...
Page 209: 4-110
4-110 4-111 chapter 4 opera tion 11. "manual" mode 11.3.2 pallet definition by teaching n note pallets cannot be defined by teaching if return-to-origin is incomplete. Perform teaching after performing absolute reset. [procedure] 1)selectthepalletnumberin"manual>pallet"modewiththecursor( ↑/↓) keys. ...
Page 210: 4-112
4-112 chapter 4 opera tion 4-113 11. "manual" mode ■ pallet definition by teaching (2) manual >pallet>method 50%[mg][s0h0x] pallet no.=pl0 [xy] move arm to p[1] and press enter key vel+ vel– [pos] 50.00 100.00 0.00 0.00 5) perform teaching at p[2], p[3], p[4] and p[5] (only when "3-d" is selected) a...
Page 211: 4-112
4-112 4-113 chapter 4 opera tion 11. "manual" mode n note • eachpalletisgeneratedwith5pointsforpalletdefinition. • the5pointsshouldbedefinedinorderfromp[1]top[5].See"11.3 displaying, editing and setting pallet definitions". Validkeysandsubmenudescriptionsin"manual>pallet>method"modeareshown below. V...
Page 212: 4-114
4-114 chapter 4 opera tion 4-115 11. "manual" mode 11.3.3 copying a pallet definition n note • validpalletnumbersarefrom0to19. • palletdefinitioncannotbecopiedifthecurrentlyselectedpalletis undefined. [procedure] 1)selectthepalletnumberin"manual>pallet"withthecursor( ↑/↓) keys. 2) press (copy) and t...
Page 213: 4-114
4-114 4-115 chapter 4 opera tion 11. "manual" mode 11.3.4 deleting a pallet definition n note pallet definition cannot be deleted if the currently selected pallet is undefined. [procedure] 1)selectthepalletnumberin"manual>pallet"modewiththecursor( ↑/↓) keys. 2) press (erase). A confirmation message ...
Page 214: 4-116
4-116 chapter 4 opera tion 4-117 11. "manual" mode 11.4 changing the manual movement speed manual movement speed of the selected robot group can be set anywhere within the range from1to100%.Movementspeedin"manual"modeissetseparatelyfromthe"auto" modemovementspeed.One-fifthofthemaximumspeedin"auto"mo...
Page 215: 4-116
4-116 4-117 chapter 4 opera tion 11. "manual" mode 11.5 displaying, editing and setting shift coordinates press (shift)in"manual"modetoenter"manual>shift"mode. This mode allows you to display, edit and set shift coordinates. Shiftcoordinatescannotbeusedwithmultityperobots. N note shift coordinates c...
Page 216: 4-118
4-118 chapter 4 opera tion 4-119 11. "manual" mode when"manual>shift"modeisentered,ascreenlikethatshownbelowappears. The currently selected shift coordinate number is highlighted. ■ "manual>shift" mode manual >shift 50% [mg][s1h0x] ————————————x———————y———————z———————r——— s0 = 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 s1...
Page 217: 4-118
4-118 4-119 chapter 4 opera tion 11. "manual" mode 11.5.1 editing shift coordinates [procedure] 1)inthe"manual>shift"mode,selectashiftcoordinatenumberwiththecursor( ↑/↓) keys. 2) press (edit)toenter"manual>shift>edit"mode. 3)usethecursor( ←/→) key to move the cursor to the position you want to chang...
Page 218: 4-120
4-120 chapter 4 opera tion 4-121 11. "manual" mode 7) press toquiteditingandreturnto"manual>shift"mode. N note the shift coordinate data on which the cursor was positioned when returning to"manual>shift"modeisusedastheshiftcoordinatesforthecurrently selected robot group. Validkeysandsubmenudescripti...
Page 219: 4-120
4-120 4-121 chapter 4 opera tion 11. "manual" mode 11.5.2 editing the shift coordinate range by setting the shift coordinate range, the robot operating area can be restricted to the desired range on each shift coordinate. Moreover, setting the soft limit parameters allows you to specify the robot wo...
Page 220: 4-122
4-122 chapter 4 opera tion 4-123 11. "manual" mode 2) press (range)toenterthe"manual>shift>range"mode. A cursor for editing the shift coordinate range appears. ■ editing shift coordinate range (1) manual >shift>range 50% [mg][s1h0x] ————————————x———————y———————z———————r——— range of shift coorinate [...
Page 221: 4-122
4-122 4-123 chapter 4 opera tion 11. "manual" mode 6) to continue editing the shift coordinate range on the minus side, repeat steps 3) to 5). 7) press toquiteditingandreturnto"manual>shift"mode. N note theshiftcoordinatenumberselectedwhenreturningto"manual>shift" mode is used as the shift coordinat...
Page 222: 4-124
4-124 chapter 4 opera tion 4-125 11. "manual" mode 11.5.3 shift coordinate setting method 1 this method sets the shift coordinate data by performing teaching at two points and then entering the plus/minus direction of those two points. The first teach point 1 (1st p) becomes the shift coordinate ori...
Page 223: 4-124
4-124 4-125 chapter 4 opera tion 11. "manual" mode n note perform teaching carefully to obtain accurate points. Precise shift coordinates cannot be set if a point is inaccurate. 4) press , and the current position is then obtained as "1st p". (this value becomes the shift coordinate origin.) ■ shift...
Page 224: 4-126
4-126 chapter 4 opera tion 4-127 11. "manual" mode validkeysandsubmenudescriptionsin"manual>shift>method1"modeareshown below. Valid keys menu function f4 vel+ increasesmanualmovementspeedfortheselected robotgroupinsteps.(1 →5→20→50→100%) f5 vel- decreasesmanualmovementspeedfortheselected robotgroupi...
Page 225: 4-126
4-126 4-127 chapter 4 opera tion 11. "manual" mode 11.5.4 shift coordinate setting method 2 this method sets the shift coordinate data by performing teaching at two points and then entering the coordinate values of those two points. ■ shift coordinate setting method 2 (1) x x’ y y’ p1 p2 [procedure]...
Page 226: 4-128
4-128 chapter 4 opera tion 4-129 11. "manual" mode n note perform teaching carefully to obtain accurate points. Precise shift coordinates cannot be set if a point is inaccurate. 4) press to obtain the current position as "1st p". An edit cursor appears at the head of the "1st p" line. ■ shift coordi...
Page 227: 4-128
4-128 4-129 chapter 4 opera tion 11. "manual" mode 6) determine the teach point 2 with the same procedure as for point 1. N note the z-direction shift value is automatically obtained when point 1 is determined, so the z-axis data at point 2 is ignored. 7) when point 2 has been entered, the shift coo...
Page 228: 4-130
4-130 chapter 4 opera tion 4-131 11. "manual" mode 11.6 displaying, editing and setting hand definitions press (hand)in"manual"modetoenter"manual>hand"mode.Thismode allows you to display, edit and set hand definitions. However, the standard coordinates must be set when a scara robot is used. Refer t...
Page 229: 4-130
4-130 4-131 chapter 4 opera tion 11. "manual" mode when"manual>hand"modeisentered,ascreenlikethatshownbelowappears. The currently selected hand definition number is highlighted. ■ hand definition screen manual >hand 50% [mg][s0h1x] ————————————1———————2———————3———————4——— h0 = 0 0.00 0.00 h1 = 0.00 ...
Page 230: 4-132
4-132 chapter 4 opera tion 4-133 11. "manual" mode movement of each robot type and the parameter contents are shown below. Setting units for each parameter are shown in parentheses. Cartesian robots 1) hand attached to 2nd arm a. Robot movement •hand"n"movestoaspecifiedpoint. B. Parameter descriptio...
Page 231: 4-132
4-132 4-133 chapter 4 opera tion 11. "manual" mode 11.6.1 editing hand definitions [procedure] 1) press (edit)in"manual>hand"mode. 2)usethecursor( ↑/↓) keys to select the hand definition you want to edit. An edit cursor appears at the left end of the selected hand definition line. ■ hand editing scr...
Page 232: 4-134
4-134 chapter 4 opera tion 4-135 11. "manual" mode 7) press toquiteditingandreturnto"manual>hand"mode. N note the hand definition data with which the cursor was positioned when returningto"manual>hand"modeisusedasthecurrenthanddefinition. Validkeysandsubmenudescriptionsin"manual>hand>edit"modearesho...
Page 233: 4-134
4-134 4-135 chapter 4 opera tion 11. "manual" mode 11.6.2 hand definition setting method 1 by using this method, a hand attached to the 2nd arm can be set to the current hand definition. N note hand definition data is set by teaching the identical points that are used for hand working points and non...
Page 234: 4-136
4-136 chapter 4 opera tion 4-137 11. "manual" mode 5)usethejogkeystomovetherobotworkingpointtopoint2.(positionitaccurately.) 6) press to enter the teaching value. Thehanddefinitionsettingendsandthescreenreturnsto"manual>hand"mode. Validkeysandsubmenudescriptionsin"manual>hand>method1"modeareshown be...
Page 235: 4-136
4-136 4-137 chapter 4 opera tion 11. "manual" mode 11.7 changing the display units the units used to indicate the current position on the rpb screen can be switched to either "pulses" and "mm". If hand data for the r-axis is selected (hand definition is made), then "tool coordinate" mode can also be...
Page 236: 4-138
4-138 chapter 4 opera tion 4-139 11. "manual" mode 11.8 absolute reset absolute reset is an operation to find the origin position, when the position detector in the motor cannot identify the origin position (called "origin incomplete" from now on). Movement commands in robot language cannot be execu...
Page 237: 4-138
4-138 4-139 chapter 4 opera tion 11. "manual" mode 11.8.1 checking absolute reset check the status of absolute reset on each axis of the robot controller. [procedure] 1) press (rst.Abs)in"manual"modetoenter"manual>rst.Abs"mode. ■ checking absolute reset this screen shows the following information. M...
Page 238: 4-140
4-140 chapter 4 opera tion 4-141 11. "manual" mode 11.8.2 absolute reset on each axis this section explains how to perform absolute reset of each axis using the robot controller. The absolute reset method differs depending on the following settings for the "origin detection method" parameter. 1. Mar...
Page 239: 4-140
4-140 4-141 chapter 4 opera tion 11. "manual" mode key operations to move to a position where absolute reset is possible for instance, when the current axis position is q (machine reference: 82%): press (adj. +), and the axis moves to w and the machine reference will change to around 50%. (absolute ...
Page 240: 4-142
4-142 chapter 4 opera tion 4-143 11. "manual" mode [procedure] ■ absolute reset of each axis (mark method) (1) manual >rst.Abs 50% [mg] [sohoj] –––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––– press f.Key to get axis for absrst m1 = ng / mark m5= no axis m2 = ok / mark m6= no axis m3 = no axis no axis m4 = ...
Page 241: 4-142
4-142 4-143 chapter 4 opera tion 11. "manual" mode 2) in servo-on usethejogkeysor (adj.+) and (adj.-) to move the selected axis to a position where absolute reset is possible. Set so that the machine reference is within a range of 44 to 56%. W warning therobotstartstomovewhenajogkeyormovementkeyis p...
Page 242: 4-144
4-144 chapter 4 opera tion 4-145 11. "manual" mode ■ absolute reset of each axis (mark method) (4) manual >rst.Abs>m1 50% [mg] [sohoj] –––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––– align axes with mark,& press enter m1 = ng / 54% m5= no axis m2 = / m6= no axis m3 = m4 = ok 72% adj.+ adj.- vel+ vel- no ax...
Page 243: 4-144
4-144 4-145 chapter 4 opera tion 11. "manual" mode 2. When the stroke end or sensor method is used as the origin detection method when the selected axis uses the stroke end or sensor method, the servo must be turned on to perform return-to-origin. W warning the robot starts to move when absolute res...
Page 244: 4-146
4-146 chapter 4 opera tion 4-147 11. "manual" mode 2) after return-to-origin is complete, the machine reference of the selected axis is displayed. ■ absolute reset of each axis (stroke end / sensor method) (2) manual 50% [mg] [sohoj] –––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––– machine reference (%) m2 ...
Page 245: 4-146
4-146 4-147 chapter 4 opera tion 11. "manual" mode 11.8.3 absolute reset on all axes this section explains how to perform absolute reset on all axes of the robot controller. The sequence for performing absolute reset of the axes is given below. 1. First, perform absolute reset at the current positio...
Page 246: 4-148
4-148 chapter 4 opera tion 4-149 11. "manual" mode absolute reset position and "0" pulse position when absolute reset is performed at position a, the position b (machine reference 38%) is reset as the "0" pulse position. This means that the robot will move to the "0" pulse position after performing ...
Page 247: 4-148
4-148 4-149 chapter 4 opera tion 11. "manual" mode 1) press (all)in"manual>rst.Abs"modetoenter"absreset"modeforall axes. ■ absolute reset of all axes (mark method) (2) this screen shows the following information. Manual >rst.Abs>all 50% [mg] [sohoj] –––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––– align axe...
Page 248: 4-150
4-150 chapter 4 opera tion 4-151 11. "manual" mode ■ absolute reset of all axes (mark method) (3) manual >rst.Abs>all 50% [mg] [sohoj] –––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––– align axes with mark,& press enter m1 = ng / 50% m5= no axis m2 = m6= no axis no axis no axis m3 = m4 = ok / 72% adj.+ adj.-...
Page 249: 4-150
4-150 4-151 chapter 4 opera tion 11. "manual" mode 5) when absolute reset ends correctly on all axes using the mark method, a confirmation message appears on the guideline if axes using the stroke end or sensor methods are present. Press (yes)toperformabsoluteresetonaxesusingthestrokeendorsensor met...
Page 250: 4-152
4-152 chapter 4 opera tion 4-153 11. "manual" mode 7) when absolute reset of all axes ends correctly, the dashed line (- - - -) on the message line changes to a solid line (––––), and return-to-origin is now complete. Next press an axis movement key and the rpb screen will display the current positi...
Page 251: 4-152
4-152 4-153 chapter 4 opera tion 11. "manual" mode 11.9 setting the standard coordinates the standard coordinates set for scara robots are treated as cartesian coordinates using the x-axis rotating center as the coordinate origin. The following operations and functions are enabled on scara robots by...
Page 252: 4-154
4-154 chapter 4 opera tion 11. "manual" mode 11.10 executing the user function keys userfunctionkeysallowyoutoperformvarioustaskseasilywhenneeded.Forexample, assigning operation of an air-driven unit connected to an output port to a function key will proveusefulwhenperformingpointteachingin"manual"m...
Page 253: 4-155
4-155 chapter 4 opera tion 12. "system" mode 12. "system" mode the"system"modecontrolsallkindsofoperatingconditionsfortheoverallrobotsystem. Theinitial"system"modescreenisshownbelow. ■ "system" mode screen q mode hierarchy e message line w version display t robot model name r online command executio...
Page 254: 4-156
4-156 chapter 4 opera tion 4-157 12. "system" mode i other expanded configurations when expansion boards are installed into the option slot of the controller, the board type and mode setting appear here. Display meaning dio_n(m/n..) anoptionaldiowithnpnspecificationsisinstalled.Thenumberin parenthes...
Page 255: 4-156
4-156 4-157 chapter 4 opera tion 12. "system" mode 12.1 parameters this section explains various parameters relating to the controller setting and robot operation. There are 4 types of parameters: robot parameters and axis parameters for robot operation, controller setting parameters and option boar...
Page 256: 4-158
4-158 chapter 4 opera tion 4-159 12. "system" mode 5)edittheselectedparameter. There are two ways to edit parameters. The first is by entering data with the numeric keys, and the second is by selecting items with the function keys. When entering data with the numeric keys, values entered outside the...
Page 257: 4-158
4-158 4-159 chapter 4 opera tion 12. "system" mode 12.1.1 parameter list ■ robot parameters refer to "12.1.2 robot parameters" in this chapter for details on parameters. No. Name displayed name identifier setting range default setting unit 1 tipweight*2 tipweight[kg] weight 0to200 robottype kg 2 ret...
Page 258: 4-160
4-160 chapter 4 opera tion 4-161 12. "system" mode whenrobottypeis"multixy" •itisnecessarytosetthetipweightparameterforeachaxis.(setthex-axistipweight andy-axistipweight.) •setthe"axistipweight"axisparameter. •accelerationwillnotchangeevenifthe"tipweight"robotparameterischanged. Whenrobottypeis"comp...
Page 259: 4-160
4-160 4-161 chapter 4 opera tion 12. "system" mode 12.1.2 robot parameters on the rpb screen each robot parameter appears in the following format. Main group parameters sub group parameters mg= sg= main robot parameters sub robot parameters mr= sr= n note a description and method for setting robot p...
Page 260: 4-162
4-162 chapter 4 opera tion 4-163 12. "system" mode 1. Tip weight [kg] /weight this parameter sets the tip weight of robot (workpiece weight + tool weight) in kg units. The maximum value is set when the parameters are initialized. The maximum allowable value is determined automatically according to t...
Page 261: 4-162
4-162 4-163 chapter 4 opera tion 12. "system" mode 2. Origin sequence /origin this parameter sets a sequence for performing absolute reset and return-to-origin on each axis of the robot. The numbers 3 1 2 4 5 6 are set automatically when the parameters are initialized. Enteraxisnumbersoftherobotinth...
Page 262: 4-164
4-164 chapter 4 opera tion 4-165 12. "system" mode 3. R-axis orientation /rorien on scara robots, this parameter sets whether or not to maintain the r-axis direction (orientation) when moving manually across the xy axes. The r direction (orientation) is automatically set when the parameters are init...
Page 263: 4-164
4-164 4-165 chapter 4 opera tion 12. "system" mode 12.1.3 axis parameters eachaxisparameterisdisplayedinthefollowingformatontherpbscreen. Main robot axis setting sub robot axis setting m?= s?= main auxiliary axis setting sub auxiliary axis setting m?= s?= n note a description and method for setting ...
Page 264: 4-166
4-166 chapter 4 opera tion 4-167 12. "system" mode 1. Accel coefficient [%] /accel thisparametersetsaccelerationin"auto"modeinarangefrom1to100%during movement by robot movement command. This is automatically set to 100% when the parameters are initialized. If the tip weight (workpiece weight + tool ...
Page 265: 4-166
4-166 4-167 chapter 4 opera tion 12. "system" mode 2. Decel. Rate [%]/decrat this parameter sets the deceleration rate in a range from 1 to 100% during movement by robot movement command. This parameter value is a rate to the acceleration. A deceleration rate inherent to each axis is automatically s...
Page 266: 4-168
4-168 chapter 4 opera tion 4-169 12. "system" mode 3. +soft limit [pulse] /plmt+ 4. -soft limit [pulse] /plmt- these parameters set the plus (+) soft limits and minus (-) soft limits that determine the range the robot can move. Soft limits inherent to each axis are automatically set when the paramet...
Page 267: 4-168
4-168 4-169 chapter 4 opera tion 12. "system" mode 5) repeat the above steps 3) and 4) if necessary. 6) press to quit the edit mode. 5. Tolerance [pulse] /tole this parameter sets the tolerance range of the target position where robot movement ends. This is set to a value unique to each axis when in...
Page 268: 4-170
4-170 chapter 4 opera tion 4-171 12. "system" mode 4)enterthevaluewith to , and and then press . If the value you input was a real number (number containing a decimal point), then the tolerance range is converted into "pulse" units. 5) repeat the above steps 3) and 4) if necessary. 6) press to quit ...
Page 269: 4-170
4-170 4-171 chapter 4 opera tion 12. "system" mode 6. Out position [pulse] /outpos during ptp movement in a program, the next command can be executed when the robot enters the range specified by the out position for the target position. This parameter sets the out position range. When initialized, t...
Page 270: 4-172
4-172 chapter 4 opera tion 4-173 12. "system" mode 4)enterthevaluewith to , and and then press . If the value you input was a real number (number containing a decimal point), then it is converted into pulse units. 5) repeat the above steps 3) and 4) if necessary. 6) press to quit the edit mode..
Page 271: 4-172
4-172 4-173 chapter 4 opera tion 12. "system" mode 7. Arch position [pulse] /arch when an arch motion command (optional ptp operation) is executed, arch movement begins when the robot enters the arch position range set by this parameter for the target position. This parameter is set to a value uniqu...
Page 272: 4-174
4-174 chapter 4 opera tion 4-175 12. "system" mode 3) select the axis with cursor ( ↑/↓) keys. ■ setting the "arch position [pulse]" system >param>axis v9.00 7.Arch position[pulse] ( 0. 56mm) m1= 2000 m2= 2000 [1-6144000] enter >_ 2000 4)enterthevaluewith to , and and then press . If the value you i...
Page 273: 4-174
4-174 4-175 chapter 4 opera tion 12. "system" mode 8. Origin speed [pulse/ms] /orgspd this parameter sets the return-to-origin movement speed in pulses per millisecond. This speed is set to a value unique to each axis when initialized. C caution themaximumreturn-to-originspeedisdeterminedbythemotor....
Page 274: 4-176
4-176 chapter 4 opera tion 4-177 12. "system" mode 9. Manual accel [%] /manacc this parameter sets the acceleration in a range from 1 to 100% during robot manual movement. The manual acceleration is automatically set to 100 when the parameters are initialized. If the tip weight (workpiece weight + t...
Page 275: 4-176
4-176 4-177 chapter 4 opera tion 12. "system" mode 10. Origin shift [pulse] /shift this parameter is used to correct the origin position error when the motor has been replaced for some reason or the robot origin position has shifted due to mechanical shocks. This parameter is set to 0 when initializ...
Page 276: 4-178
4-178 chapter 4 opera tion 4-179 12. "system" mode 11. Arm length [mm] /armlen this parameter sets the x, y axis arm length on scara robots. This is automatically determined according to the current robot type when initialized. The arm length is also determined automatically when standard coordinate...
Page 277: 4-178
4-178 4-179 chapter 4 opera tion 12. "system" mode 12. Offset pulse /offset on scara robots, this parameter sets the offset pulses when the x, y, r axes are at 0 pulses. When initialized, this is set to a value unique to each robot type that is currently set. •x-axisoffsetpulses ... Angle formed by ...
Page 278: 4-180
4-180 chapter 4 opera tion 4-181 12. "system" mode 13. Axis tip weight [kg] /axstip this parameter sets the weight of each axis tip (workpiece weight + tool weight) in kilogramunitsonmultityperobots.Amaximumvalueissetwhentheparameters are initialized. The maximum weight is automatically determined a...
Page 279: 4-180
4-180 4-181 chapter 4 opera tion 12. "system" mode 14. Origin method /orgsns this parameter selects the method for performing return-to-origin on the robot. When initialized, this is automatically set according to the current robot model. Three methods are available as follows: "sensor" ...... Origi...
Page 280: 4-182
4-182 chapter 4 opera tion 4-183 12. "system" mode 15. Origin direction /orgdir this parameter specifies the direction for return-to-origin. When initialized, this is automatically set according to the current robot model. "---" ...... Axis returns to origin in the manual movement minus (-) directio...
Page 281: 4-182
4-182 4-183 chapter 4 opera tion 12. "system" mode 16. Motor direction /motdir this parameter specifies the robot movement direction. When initialized, this is set automatically according to the current robot model. "---" ...... Motor minus (-) direction is set as the - direction. "+++" .... Motor m...
Page 282: 4-184
4-184 chapter 4 opera tion 12. "system" mode 17. Limitless motion / nolmt this parameter specifies the axis that is allowed to perform the limitless motion. When the parameter is initialized, all axes become invalid. Invalid ...........Makes the limitless motion of the set axis invalid. The movement...
Page 283: 4-185
4-185 chapter 4 opera tion 12. "system" mode 12.1.4 other parameters when changing other parameters on the rpb, use the descriptions in this section. ■ editing other parameters system >param>others v9.08 1.Display language(jpn/eng) english 2.Data display length 6char 3.Parameter display unit pulse 4...
Page 284: 4-186
4-186 chapter 4 opera tion 4-187 12. "system" mode 1. Display language / dsplng this parameter sets the language for displaying messages on the rpb. N note this parameter will not change even if parameter initialization is performed. [procedure] 1)select"1.Displaylanguage(jpn/eng)"in"system>param>ot...
Page 285: 4-186
4-186 4-187 chapter 4 opera tion 12. "system" mode 2. Data display length/datlen this parameter sets the number of digits to display such as for point data. This is automatically set to "6char" (6 digits) when the parameters are initialized. [procedure] 1)select"2.Datadisplaylength"in"system>param>o...
Page 286: 4-188
4-188 chapter 4 opera tion 4-189 12. "system" mode 3. Parameter display unit/pdunit this parameter sets the units for showing axis parameters. This is automatically set to "pulses" when the parameters are initialized. [procedure] 1)select"3.Parameterdisplayunits"in"system>param>others"mode. 2) press...
Page 287: 4-188
4-188 4-189 chapter 4 opera tion 12. "system" mode 4. Do cond. On emg /emgcdo thisparametersetswhetherornottoholdoutputofthedo/mo/lo/to/soports when an emergency stop signal is input to the controller. This is automatically set to "hold"whentheparametersareinitialized. C caution this parameter is in...
Page 288: 4-190
4-190 chapter 4 opera tion 4-191 12. "system" mode 5. Incremental mode /incmod this parameter sets whether to have origin incomplete status every time power to this controller is turned on. This is automatically set invalid when the parameters are initialized. N note • whenthisparameterisvalid(enabl...
Page 289: 4-190
4-190 4-191 chapter 4 opera tion 12. "system" mode 6. Di noise filter/scanmd this parameter sets whether to cancel external input signals (dedicated input signals, general-purpose input signals) that might appear like noise in the form of short pulses. Whenthisparameterissetto"valid",theonandoffperi...
Page 290: 4-192
4-192 chapter 4 opera tion 4-193 12. "system" mode 7. True condition / expcfg this parameter selects the operation when the conditional expression, which is used forthestoponoptioninanif(includingelseif),whiletowend,wait,move, ordrivestatement,isanumericexpression. This parameter is set to "-1" when...
Page 291: 4-192
4-192 4-193 chapter 4 opera tion 12. "system" mode 8. Unit select / ptunit this parameter selects the point data unit system to be used when the controller is started. For incremental specification robots and semi-absolute specification robots, the current position is displayed in "pulse" units at c...
Page 292: 4-194
4-194 chapter 4 opera tion 4-195 12. "system" mode 9. Error output (do & so) / erport this parameter selects the port used for error output. This parameter is set to "off" when the parameters are initialized. The following ports can be used as error output ports: do20 to do27, so20 to so27. N note •...
Page 293: 4-194
4-194 4-195 chapter 4 opera tion 12. "system" mode 10. Movei/drivei start position /movimd this parameter setting is used when a relative motion operation is stopped by an interlock or emergency stop, etc., and specifies whether motion is to occur to the original target position, or to a new target ...
Page 294: 4-196
4-196 chapter 4 opera tion 4-197 12. "system" mode 11. Servo on when power on / srvoon usethisparametertoselectwhethertostartthecontrollerwithservo-onorservo-off when the controller power is turned on. Whenrobotnumbersaresetbygeneration,thisparameterisresetto"yes". Setting meaning yes whensafemodese...
Page 295: 4-196
4-196 4-197 chapter 4 opera tion 12. "system" mode 12. Manual move mode /movmod when an axis movement key is held down, inching movement switches to continuous movement.Usethisparametertoshortenthetimetakentoswitchtothecontinuous movement. This parameter can also be used for the online command @jog ...
Page 296: 4-198
4-198 chapter 4 opera tion 4-199 12. "system" mode 13. Do cond. On pgm reset / rescdo usethisparametertoselectwhethertoresetthedo/mo/lo/to/soportoutputs whenaprogramisresetorahaltstatementisexecuted.Wheninitialized,this parameterissetto"reset". N note this parameter is enabled from controllers with ...
Page 297: 4-198
4-198 4-199 chapter 4 opera tion 12. "system" mode setting meaning hold outputsarenot reset. Thedo/mo/lo/to/soportoutputsarenotreseteven whenanyofthefollowingsareexecuted. Theoutputsarenotreseteven: ■ whencompileendedsuccessfullyin"program" mode. ■ whenaprogramwascompiledin"auto"modeand thecompileen...
Page 298: 4-200
4-200 chapter 4 opera tion 4-201 12. "system" mode 15. Skip undefined parameters there are cases where new parameters are added according to the software upgrading for robot controllers. If you attempt to load the parameter file containing these newparametersintoacontrollerofanearlierversion,anerror...
Page 299: 4-200
4-200 4-201 chapter 4 opera tion 12. "system" mode 12.1.5 parameters for option boards this section explains how to set parameters for option boards from the rpb. Option boards are roughly divided into three types: option dio boards, serial i/o boards and network board. For option dio boards, there ...
Page 300: 4-202
4-202 chapter 4 opera tion 4-203 12. "system" mode option boards installed into the option slots are displayed on the rpb screen. Type display meaning optiondio dio_n(n) anoptiondioboardofnpnspecificationsis installed.Thenumberinparenthesesisanid number. Dio_p(n) anoptiondioboardofpnpspecificationsi...
Page 301: 4-202
4-202 4-203 chapter 4 opera tion 12. "system" mode 12.1.5.1 option dio setting make the dio option board setting as explained below. Parameter meaning 1 dc24vwatching setswhethertoissueanerror"12.31:didc24v disconnected"whenthe24vpowersupplyisnot connected. Whensetto"invalid",noerrorwillbeissuedeven...
Page 302: 4-204
4-204 chapter 4 opera tion 4-205 12. "system" mode 12.1.5.2 serial io setting make the serial io option board setting as explained below. N note • emergencystopreadysignal(di00),interlockinput(di11)andservice modeinput(di02)onthesafetyconnectorareenabledevenwhenthe serial io is enabled. • fordetaile...
Page 303: 4-204
4-204 4-205 chapter 4 opera tion 12. "system" mode 1. Serial io [procedure] 1)in"system>param>op.Brd"mode,selecttheseriali/ooptionboardandpress (select). 2) select the "1. Serial io" parameter with the cursor ( ↑/↓) keys. 3) press (edit). ■ "serial io" setting system >param>op.Brd v9.08 1.Serial io ...
Page 304: 4-206
4-206 chapter 4 opera tion 4-207 12. "system" mode 2. Remote cmd/io cmd (si05) [procedure] 1)in"system>param>op.Brd"mode,selecttheseriali/ooptionboardandpress (select). 2) select the "2. Remote cmd / io cmd (si05)" parameter with the cursor ( ↑/↓) keys. 3) press (edit). ■ "remote cmd / io cmd (si05)...
Page 305: 4-206
4-206 4-207 chapter 4 opera tion 12. "system" mode 3. Output msg to sow(1) [procedure] 1)in"system>param>op.Brd"mode,selecttheseriali/ooptionboardandpress (select). 2) select the "3. Output msg to sow(1)" parameter with the cursor ( ↑/↓) keys. 3) press (edit). ■ "output msg to sow(1)" setting system...
Page 306: 4-208
4-208 chapter 4 opera tion 4-209 12. "system" mode 4. Io size (devicenet only) n note this parameter is supported by controllers with a devicenet board installed and from ver. 9.08 onwards. Earlier version controllers do not have this "4. Io size" parameter, so the number of occupied channels is the...
Page 307: 4-208
4-208 4-209 chapter 4 opera tion 12. "system" mode 12.1.5.3 setting the network parameters whenusingethernet,yousetfiveparametersincludingtheparametertoenableordisable theethernetboard. C caution when making the ethernet settings to use telnet, you will need to set any other parameters than those sh...
Page 308: 4-210
4-210 chapter 4 opera tion 4-211 12. "system" mode ■ network setting (2) system >param>op.Brd>select v9.00 1.Board condition valid 2.Ip address 3.Subnet mask 4.Gateway 5.Port no 192.168. 0. 2 255.255.255. 0 192.168. 0. 1 23 edit jump 2) select the parameter with the cursor ( ↑/↓) keys. C caution cha...
Page 309: 4-210
4-210 4-211 chapter 4 opera tion 12. "system" mode 12.2 communication parameters set the following parameters for communication procedures when using the rs-232c interface. There are 8 kinds of communication parameters. 1. Communication mode 2. Data bit 3. Baud rate 4. Stop bit 5. Parity 6. Terminat...
Page 310: 4-212
4-212 chapter 4 opera tion 4-213 12. "system" mode 4) set the parameter with the function keys. The selectable values or items appear as function key menus on the guideline. 5) press to quit the setting. To continue selecting other items, use the cursor ( ↑/↓) keys. Validkeysandsubmenudescriptionsin...
Page 311: 4-212
4-212 4-213 chapter 4 opera tion 12. "system" mode 1. Cmu (communication) mode this parameter sets the communication mode on the computer. N note • onlinecommandscanbeexecutedonlyin"online"mode. • thecmu(communication)modecanbechangedwitheitheronlineor offline statements in robot language. [procedur...
Page 312: 4-214
4-214 chapter 4 opera tion 4-215 12. "system" mode 2. Data bits this parameter sets the data bit length. N note katakana letters (japanese phonetic) cannot be sent if data bit length was set to 7 bits. [procedure] 1)select"2.Databits"in"system>cmu"mode. 2) press (edit). The function key menu changes...
Page 313: 4-214
4-214 4-215 chapter 4 opera tion 12. "system" mode 3. Baud rate this parameter sets the communication speed. N note communication errors are more prone to occur at high communication speeds. If communication errors frequently occur, set a lower communication speed. [procedure] 1)select"3.Baudrate"in...
Page 314: 4-216
4-216 chapter 4 opera tion 4-217 12. "system" mode 4. Stop bit this parameter sets the stop bit length. N note set to 2 bits if communication errors frequently occur. [procedure] 1)select"4.Stopbit"in"system>cmu"mode. 2) press (edit). The function key menu changes. ■ setting the "stop bit" system >c...
Page 315: 4-216
4-216 4-217 chapter 4 opera tion 12. "system" mode 5. Parity this parameter sets the parity check. N note use the parity check as often as possible. [procedure] 1)select"5.Parity"in"system>cmu"mode. 2) press (edit). The function key menu changes. ■ setting the "parity" system >cmu v9.00 1.Cmu mode o...
Page 316: 4-218
4-218 chapter 4 opera tion 4-219 12. "system" mode 6. Termination code this parameter sets the line feed code. [procedure] 1)select"6.Terminationcode"in"system>cmu"mode. 2) press (edit). The function key menu changes. ■ setting the "termination code" system >cmu v9.00 3.Baud rate 9600 4.Stop bit 1 5...
Page 317: 4-218
4-218 4-219 chapter 4 opera tion 12. "system" mode 7. Flow control this parameter sets communication flow control. N note communication data omissions may occur if flow control is set to "no". [procedure] 1)select"7.Flowcontrol"in"system>cmu"mode. 2) press (edit). ■ flow control setting system >cmu ...
Page 318: 4-220
4-220 chapter 4 opera tion 4-221 12. "system" mode 12.3 option parameters the option parameters are used to set expanded controller functions. These parameters consistof4types:parametersforareacheckoutput,parametersrelatingtosafemode, parameters relating to the serial i/o, and parameters relating to...
Page 319: 4-220
4-220 4-221 chapter 4 opera tion 12. "system" mode 12.3.1 setting the area check output this function checks whether the current robot position is within an area specified by the area check output parameter’s point data, and outputs the result to the specified port. A maximum of 4 areas can be check...
Page 320: 4-222
4-222 chapter 4 opera tion 4-223 12. "system" mode n note • iftheportusedforareacheckoutputisthesameastheoutputportused by the program, then the output data might be changed. So do not use the same output port. • ifthesameportisdesignatedforadifferentareacheckoutput,orwill be output. • oncontrollers...
Page 321: 4-222
4-222 4-223 chapter 4 opera tion 12. "system" mode when the comparison points are set as shown below, and the robot axis tip is moved between the marks, the output is off at and the output is on at . (when "5. Criterion selection for area check output" is set so that the area check output turns on w...
Page 322: 4-224
4-224 chapter 4 opera tion 4-225 12. "system" mode 3) select the parameter items with the cursor ( ↑/↓) keys. ■ selecting the area check output parameters system >option>pos.Out v9.08 1.Output of area1 no 2.Output por1(do & so) 20 3.Compare point number11 p0 4.Compare point number12 p0 5.Condition i...
Page 323: 4-224
4-224 4-225 chapter 4 opera tion 12. "system" mode 3) select the robot for the area check with (no), (main) or (sub). Robot details no theareacheckoutputisnotexecuted. Main theareacheckoutputisexecutedforthemainrobot. Sub theareacheckoutputisexecutedforthesubrobot. 4) press to quit the setting. To c...
Page 324: 4-226
4-226 chapter 4 opera tion 4-227 12. "system" mode 2) press (edit). The function key menu changes. ■ selecting the area check output port (controllers prior to ver. 9.22) system >option>pos.Out>select v9.08 1.Output of area1 main 2.Output por1(do & so) 20 3.Compare point number11 p0 4.Compare point ...
Page 325: 4-226
4-226 4-227 chapter 4 opera tion 12. "system" mode 3. Comparison point no. 1 4. Comparison point no. 2 set the point numbers for determining the area to perform area check. Point numbers from p0 to p4000 can be used to specify an area for controllers prior to ver. 9.39 while point numbers from p0 to...
Page 326: 4-228
4-228 chapter 4 opera tion 4-229 12. "system" mode 3)enterthepointnumberwith to and press . 4) select "4. Compare point number n2" with the cursor ( ↑/↓) keys and enter point number as in step 3). 5) press to quit the setting. To continue selecting other items, use the cursor ( ↑/↓) keys. Example:wh...
Page 327: 4-228
4-228 4-229 chapter 4 opera tion 12. "system" mode 5. Condition for area check output selects the condition that allows the area check output to turn on, from either when the robot is within a specified area or when outside it. N note • thisparameterissupportedbycontrollersofver.9.08onwards.Onearlie...
Page 328: 4-230
4-230 chapter 4 opera tion 4-231 12. "system" mode 12.3.2 setting the "service" mode thesesettingsspecifythe"service"modelevelandparametersforrpbcontrolled operations which are performed within the robot system's safety enclosure area. Parameter settings made here are only valid until the controller...
Page 329: 4-230
4-230 4-231 chapter 4 opera tion 12. "system" mode 2. Operating speed limits in "service" mode specify the maximum robot operating speed. Description * setsrobotoperationwithin3%ofmaximumoperating speed. Setsnolimitonrobotoperatingspeed. *:thesearedefaultsettings. W warning restriction on the robot ...
Page 330: 4-232
4-232 chapter 4 opera tion 4-233 12. "system" mode [procedure] 1) press (service)in"system>option"mode. Themessage,"enterpassword"appearsontheguideline. Enter"saf"hereandpress . ■ entering the "service" mode setting password system >option v9.00 enter password >_ 2) the following screen appears when...
Page 331: 4-232
4-232 4-233 chapter 4 opera tion 12. "system" mode 1. "service" mode level set the service mode level by referring to the table below. N note the settings made here are only valid until the controller power is turned off. Save these settings if you want to use them again after power is turned off. W...
Page 332: 4-234
4-234 chapter 4 opera tion 4-235 12. "system" mode 2. Operating speed limits in "service" mode specify the maximum robot operating speed. N note the settings made here are only valid until the controller power is turned off. Save these settings if you want to use them again after power is turned off...
Page 333: 4-234
4-234 4-235 chapter 4 opera tion 12. "system" mode 3. Operating device in "service" mode specify the operating device to use. N note the settings made here are only valid until the controller power is turned off. Save these settings if you want to use them again after power is turned off. W warning ...
Page 334: 4-236
4-236 chapter 4 opera tion 4-237 12. "system" mode 12.3.2.1 saving the "service" mode parameters tosavetheparametersettingsfor"service"mode,followtheprocedurebelow. The parameter settings made here are only valid until the controller power is turned off, unless you save those settings. W warning alt...
Page 335: 4-236
4-236 4-237 chapter 4 opera tion 12. "system" mode 12.3.2.2 help display in "service" mode todisplaythehelpmessagesfor"service"modeparameters,proceedasfollows. [procedure] 1) press (help)in"system>option>service"mode. ■ help display in "service" mode system >option>service>help v9.00 security level ...
Page 336: 4-238
4-238 chapter 4 opera tion 4-239 12. "system" mode 12.3.3 sio settings theseriali/ounitallowsthemasterstationsequencer(plc)tosendandreceiveparallel port on/off data in the robot controller i/o unit, regardless of the robot program. This function allows using i/o devices such as sensors and relays as...
Page 337: 4-238
4-238 4-239 chapter 4 opera tion 12. "system" mode valid keys and submenu descriptions in this mode are shown below. Valid keys menu function cursorkey ( ↑/↓) selectsthesioparameter. F1 edit changesthesioparameter. F2 jump movesthecursortothedesignatedsioparameter. 1. Direct connection from si n ( )...
Page 338: 4-240
4-240 chapter 4 opera tion 4-241 12. "system" mode 2. Direct connection from di n ( ) to so n ( ) parallel port input can be directly connected to serial port output. The relation between serial and parallel ports that can be set is as follows. N note output results might be incorrect if the sio spe...
Page 339: 4-240
4-240 4-241 chapter 4 opera tion 12. "system" mode 12.3.4 double-carrier setting this controller has a function to prevent two carriers (sliders) from colliding with each other, when the two carriers are installed on the same axis of double-carrier type robots. C caution the anti-collision function ...
Page 340: 4-242
4-242 chapter 4 opera tion 4-243 12. "system" mode 12.3.4.2 setting the double-carrier parameters [procedure] 1) press the (w.Carrier)in"system>option"mode. ■ double-carrier parameter setting (1) system >option>w.Carrier v9.00 1.Stroke[mm] 0.00 2.Carrier1 m1 3.Carrier2 m2 4.Control mode off edit jum...
Page 341: 4-242
4-242 4-243 chapter 4 opera tion 12. "system" mode 2)enterthestrokein"mm"unitsandpress .Upto2decimalplacesare allowed. Refer to the drawing below to determine the stroke. ■ stroke setting origin position origin position point where one carrier is closest to the other stroke 2. Carrier 1 setting 3. C...
Page 342: 4-244
4-244 chapter 4 opera tion 4-245 12. "system" mode 4. Control mode setting select the double-carrier functions. [procedure] 1) select "4. Control mode" and press (edit). ■ double-carrier parameter setting (4) system >option>w.Carrier>edit v9.00 1.Stroke[mm] 650.00 2.Carrier1 m1 3.Carrier2 m2 4.Contr...
Page 343: 4-244
4-244 4-245 chapter 4 opera tion 12. "system" mode 12.4 initialization when initializing the parameter data you entered, follow the descriptions in this section. [procedure] 1) press (init)in"system"mode. The initialization screen appears. ■ initialization screen system >init v9.00 param memory cmu ...
Page 344: 4-246
4-246 chapter 4 opera tion 4-247 12. "system" mode 12.4.1 initializing the parameters to initialize the "robot" parameters, "axis" parameters and "other" parameters, follow the procedure below. The"displaylanguage(jpn/eng)"settingamong"other"parametersisnotchangedby initialization. N note • entirepa...
Page 345: 4-246
4-246 4-247 chapter 4 opera tion 12. "system" mode 12.4.2 initializing the memory this initializes the program, point data, shift coordinates, hand definitions and pallet definitions. Before initializing, make sure that the currently input data is no longer needed. N note • externaldatamustbeinputto...
Page 346: 4-248
4-248 chapter 4 opera tion 4-249 12. "system" mode validkeysandsubmenudescriptionsin"system>init>memory"modeareshown below. Valid keys menu function f1 program deletestheprogramdata. F2 point deletesthepointdata. F3 shift initializestheshiftcoordinatedata. F4 hand initializesthehanddefinitiondata. F...
Page 347: 4-248
4-248 4-249 chapter 4 opera tion 12. "system" mode 12.4.4 clock setting a clock function is provided in the controller for setting the date and time. C caution the clock used in the controller might differ from the correct time. If this happens, set the correct time. [procedure] 1) press (clock)in"s...
Page 348: 4-250
4-250 chapter 4 opera tion 4-251 12. "system" mode 12.4.5 system generation in system generation in the robot controller, the specifications for the robot being connected and the axis configurations are set prior to shipment. The user does not normally need to set the system generation with (generat...
Page 349: 4-250
4-250 4-251 chapter 4 opera tion 12. "system" mode 12.5 self diagnosis this function makes a check of the controller and displays the error history and battery voltages. [procedure] 1)in"system"mode,press (diagnos)toenter"system>diagnos"mode ■ self diagnosis system >diagnos v9.00 check histry batter...
Page 350: 4-252
4-252 chapter 4 opera tion 4-253 12. "system" mode 12.5.1 controller check this makes a self-diagnosis check of the controller. N note • anerrormessagewillalwaysappearifdc24visnotsuppliedtostd.Dio. • anerrormessagewillalwaysappearifdc24visnotsuppliedtothe option dio. [procedure] 1) press (check)toen...
Page 351: 4-252
4-252 4-253 chapter 4 opera tion 12. "system" mode 12.5.2 error history display to display past errors that occurred, follow the procedure below. A maximum of 500 items may be stored in the error history. C caution • errorsarenotrecordedwhenidenticaltoaprecedingerrorthatjust occurred. • theerrorcate...
Page 352: 4-254
4-254 chapter 4 opera tion 4-255 12. "system" mode 12.5.3 displaying the absolute battery condition usethefollowingproceduretocheckwhetherthebatteryforretainingabsolutedatais low or not. [procedure] 1) press (battery). ■ displaying the absolute battery condition system >diagnos>battery v9.00 absolut...
Page 353: 4-254
4-254 4-255 chapter 4 opera tion 12. "system" mode 12.5.4 displaying the total operation time usethefollowingproceduretocheckthetotalcontrolleroperationtime. [procedure] 1) press (total). ■ displaying the total operation time system >diagnos>total v9.00 total operation time (06/07/01, 12:05) year da...
Page 354: 4-256
4-256 chapter 4 opera tion 4-257 12. "system" mode 12.5.5 system error details display details of important software errors that have occurred in the past can be displayed. N note all error information will be initialized when the error history is initialized. [procedure] 1) press (sys. Chk). ■ erro...
Page 355: 4-256
4-256 4-257 chapter 4 opera tion 12. "system" mode 12.6 backup processes the various data in the controller's internal memory can be backed up in the internal flash rom or the sd memory card. [procedure] 1) press (backup)inthe"system"mode. ■ backup system >backup v9.00 sd card from validkeysandsubme...
Page 356: 4-258
4-258 chapter 4 opera tion 4-259 12. "system" mode 12.6.1 sd memory card data in the controller can be saved on an sd memory card. The data can then be loaded into the controller from the sd memory card. C caution do not remove the sd memory card while data is being saved on it or loaded from it. Re...
Page 357: 4-258
4-258 4-259 chapter 4 opera tion 12. "system" mode [procedure] 1) press (sdcard)in"system>backup"mode. When the sd memory card is inserted in the slot, information on files stored on the sd memory card is displayed. If no sd memory card is inserted, a "15.21: cannot find media" error occurs. ■ sd me...
Page 358: 4-260
4-260 chapter 4 opera tion 4-261 12. "system" mode 12.6.1.1 loading files data stored on an sd memory card can be loaded back into the controller's internal memory. C caution do not remove the sd memory card while data is being loaded from it. N note with a subdirectory selected, pressing (load) wil...
Page 359: 4-260
4-260 4-261 chapter 4 opera tion 12. "system" mode file types that can be loaded the following file formats can be loaded. If an attempt was made to load a file with another format, then a "15.5 illegal file type" error occurs. File name file type *.All allfile *.Pgm programfile *.Pnt pointdatafile ...
Page 360: 4-262
4-262 chapter 4 opera tion 4-263 12. "system" mode 12.6.1.2 saving files data in the controller's internal memory can be saved on an sd memory card. N note file names can be up to 8 characters consisting of a combination of alphanumeric characters (0 to 9, a to z) and underscores ( _ ). C caution do...
Page 361: 4-262
4-262 4-263 chapter 4 opera tion 12. "system" mode 3)enterthefilename. ■ saving a file (2) sd:\ file1 .All 102520 06/04/07 13:30 file2 .Pgm 8528 06/04/12 17:07 subdir . 06/03/27 15:21 file3 .Pnt 1741 06/04/21 10:45 enter file name >abc system >backup>sdcard>save v9.00 .All 4) press . A confirmation ...
Page 362: 4-264
4-264 chapter 4 opera tion 4-265 12. "system" mode 12.6.1.3 deleting files the data stored on an sd memory card can be deleted if needed. N note subdirectories cannot be deleted. C caution do not remove the sd memory card while a file is being deleted from it. [procedure] 1)in"system>backup>sdcard"m...
Page 363: 4-264
4-264 4-265 chapter 4 opera tion 12. "system" mode 12.6.1.4 previewing files the beginning of a file stored on an sd memory card can be previewed on the screen. N note the preview shows a maximum 512-bytes of information from the beginning of a file. [procedure] 1)in"system>backup>sdcard"mode,select...
Page 364: 4-266
4-266 chapter 4 opera tion 4-267 12. "system" mode 12.6.2 internal flash rom various data can be backed up in the controller's internal flash rom. The data backed up in the flash rom can then be loaded back into the controller's internal memory. N note if the data in the internal memory is destroyed...
Page 365: 4-266
4-266 4-267 chapter 4 opera tion 12. "system" mode 12.6.2.1 loading files the various data backed up in the controller's internal flash rom can be loaded back into the controller's internal memory. N note if the data in the internal memory is destroyed for any reason, it can be restored by loading t...
Page 366: 4-268
4-268 chapter 4 opera tion 4-269 12. "system" mode validkeysandsubmenudescriptionsin"system>backup>from>load"modeare shown below. Valid keys menu function f1 .All filesareloadedasallfiles. F2 .Pgm onlyprogramfilesareloaded. F3 .Pnt onlypointfilesareloaded. F4 .Sft onlyshiftfilesareloaded. F5 .Hnd on...
Page 367: 4-268
4-268 4-269 chapter 4 opera tion 12. "system" mode 12.6.2.2 saving files thedatainthecontroller'sinternalmemoryaresavedasallfilesontheflashrom.The data cannot be saved separately. If data is already saved, the new data cannot be saved until the files are initialized. N note if the data in the intern...
Page 368: 4-270
4-270 chapter 4 opera tion 12. "system" mode 12.6.2.3 initializing the files the data saved on the controller's flash rom can be initialized. N note if the data in the internal memory is destroyed for any reason, it can be restored by loading the backup data from the internal flash rom. We rec- omme...
Page 369: 4-271
4-271 chapter 4 opera tion 13. "monitor" mode 13. "monitor" mode the "monitor" mode displays the i/o status regardless of the current mode and level. The "monitor" mode display is overlapped onto the screen during normal operation. So the robot controller can still be operated even with the monitor ...
Page 370: 4-272
4-272 chapter 4 opera tion 4-273 13. "monitor" mode 3) press again to display other monitor screens. Pressing shifts the monitor screen in the following sequence. Di monitor → do monitor → mo monitor →lo/tomonitor→ si monitor → so monitor → siw monitor → sow monitor → variable monitor → task monitor...
Page 371: 4-272
4-272 4-273 chapter 4 opera tion 13. "monitor" mode ■ example of task information display manual >point 50% [mg][s0h0j] task monitor:line(status),pri t1 = 6(run),32 t5 = t2 = 10(sus),32 t6 = t3 = t7 = t4 = t8 = 12(run),35 edit teach jump vel+ vel- ________________ x ________ y ________ z _________ r...
Page 372: 4-274
4-274 chapter 4 opera tion 4-275 14. "utility" mode 14. "utility" mode the"utility"modecanbeenteredfromanyothermoderegardlessofthemodelevel. N note the current internal controller temperature is displayed on the right end of the 3rd line. [procedure] 1) press ( + ). The"utility"modescreenisdisplayed...
Page 373: 4-274
4-274 4-275 chapter 4 opera tion 14. "utility" mode validkeysandsubmenudescriptionsin"utility"modeareshownbelow. Valid keys menu function f1 motor turnsthemotorpowerandservoonandoff. F2 sequenc prohibitsorpermitsexecutingthesequenceprogram. F3 armtype setsthearmhandtype.(validonlyonscararobots) f5 r...
Page 374: 4-276
4-276 chapter 4 opera tion 4-277 14. "utility" mode 14.1 canceling emergency stop; motor power and servo on/off 14.1.1 canceling emergency stop emergencystopmustbecancelledtoturntheservoonandoperatetherobotagaininthe following cases. (1) when the emergency stop button was released after pressing the...
Page 375: 4-276
4-276 4-277 chapter 4 opera tion 14. "utility" mode 14.1.2 motor power and servo on/off this is usually used with the motor power turned on. This operation is performed after emergency stop has been cancelled or when turning the servo on/off temporarily in order to perform direct teaching. C caution...
Page 376: 4-278
4-278 chapter 4 opera tion 4-279 14. "utility" mode 4) to set the servo of each axis to "on", "off" or "free", select the axis with the cursor ( ↑/↓) keys. When setting the servo to "on", the servo power for the axis must be turned on beforehand by the operation in step 2. ■ setting the servo of eac...
Page 377: 4-278
4-278 4-279 chapter 4 opera tion 14. "utility" mode 14.2 overload error reset and motor and servo power on/off 14.2.1 emergency stop reset an emergency stop status is established when an overload error occurs. The procedure for resetting an emergency stop status is given in section "14.1.1 canceling...
Page 378: 4-280
4-280 chapter 4 opera tion 4-281 14. "utility" mode 14.3 enabling/disabling the sequence execution flag to enable or disable execution of sequence programs, proceed as follows. N note the following conditions must be satisfied before executing a sequence program. 1. An object program must be made fo...
Page 379: 4-280
4-280 4-281 chapter 4 opera tion 14. "utility" mode 14.4 resetting the output ports thisresetsthegeneral-purposeoutputportsdo2()todo27()/mo2()tomo27()/lo0()/ to0()/so2() to so27()/sow(2) to sow(15). [procedure] 1) press (rst.Do)in"utility"mode. A confirmation message appears on the guideline. ■ rese...
Page 380: 4-282
4-282 chapter 4 opera tion 4-283 14. "utility" mode 14.5 changing the execution level program execution levels can be set as shown in the table below. However, the following commands are usable only when return-to-origin is complete. Movementcommands : move,move2,movei,movei2,drive,drive2, drivei,dr...
Page 381: 4-282
4-282 4-283 chapter 4 opera tion 14. "utility" mode 14.5.1 changing the execution level to change the execution level, proceed as follows. [procedure] 1) press ( + )twicetoenter"utility"mode,thenpress (execute). ■ changing the execution level (1) utility date,time : 06/06/01,12:36:37 (36 °c) execut ...
Page 382: 4-284
4-284 chapter 4 opera tion 4-285 14. "utility" mode 14.5.2 displaying the help message see the help message as needed. [procedure] 1) press (help). The first page of the help screen appears. Press (nextp.)orcursor( ↓) key to refer to the next page or press (prev. P.) or cursor ( ↑) key to refer to t...
Page 383: 4-284
4-284 4-285 chapter 4 opera tion 14. "utility" mode 14.6 changing the access level (operation level) once the robot system is installed, anyone can change its program and point data. However, unauthorized changing of such data can be a source of trouble. To prevent such problems, the robot controlle...
Page 384: 4-286
4-286 chapter 4 opera tion 4-287 14. "utility" mode 14.6.1 entering the password the password must be entered in order to change the access level. [procedure] 1) press (access)in"utility"mode. Amessage"enterpassword"appearsontheguideline.Enterwith"lvl"hereandpress . ■ setting the access level (1) ut...
Page 385: 4-286
4-286 4-287 chapter 4 opera tion 14. "utility" mode 14.6.2 changing the access level change the access level as needed. [procedure] 1) set the access level with (level0)to (level3). ■ setting the access level (3) utility >access access level: level2 level0 level1 level2 level3 help.
Page 386: 4-288
4-288 chapter 4 opera tion 14. "utility" mode 14.6.3 displaying the help message see the help message as needed. [procedure] 1) press (help). The first page of the help screen appears. Press (nextp.)orcursor( ↓) key to refer to the next page or press (prev. P.) or cursor ( ↑) key to refer to the pre...
Page 387: Chapter 5
Chapter 5 parallel i/o interface contents 1. Standard i/o interface overview 5-1 1.1 id setting 5-2 1.2 connector i/o signals 5-3 1.3 connector pin numbers 5-6 1.4 connecting the power supply 5-7 1.4.1 npn/pnp power connector wiring 5-8 1.5 typical input signal connection 5-9 1.6 typical output sign...
Page 388: 5-1
5-1.
Page 389: 5-1
5-1 chapter 5 parallel i/o interf ace 1. Standard i/o interface overview toconnectthercxcontrollertoanexternaldevicesuchasaplc,signalinput/output diooptionboardsareavailable.Uptotwodiooptionboardscanbeinstalledineach unit of the rcx22 series. There are two types of dio option boards: npn and pnp spe...
Page 390: 5-2
5-2 chapter 5 parallel i/o interf ace 5-3 1.1 id setting usethedipswitchonthediooptionboardtosettheboardid(1to4).Thisid determines the correspondence between the i/o connector pins and the controller i/o signals. C caution when using two or more dio option boards, set different ids so that they do n...
Page 391: 5-2
5-2 5-3 chapter 5 parallel i/o interf ace 1.2 connector i/o signals ■ i/o signals when id = 1 pin i/o signal remarks 1 di01 servoon dedicatedinput 2 di10 sequenceprogramcontrol dedicatedinput 3 di03 steprun dedicatedinput 4 chk1 checkinput1 shortedtochk2 5 di05 i/ocommandrun dedicatedinput 6 di06 sp...
Page 392: 5-4
5-4 chapter 5 parallel i/o interf ace 5-5 ■ i/o signals when id = 2, 3 or 4 pin id signal 2 3 4 1 --- spare 2 di40 di70 di120 general-purposeinput 3 --- spare 4 di41 di71 di121 general-purposeinput 5 --- spare 6 --- spare 7 --- spare 8 di50 di100 di130 general-purposeinput 9 di51 di101 di131 general...
Page 393: 5-4
5-4 5-5 chapter 5 parallel i/o interf ace ■ pinout tables std.Io 1 di01 servoon 26 di12 run 2 di10 seqcontrol 27 di13 auto 3 di03 step-r 28 di14 origin 4 chk1 checkinput1 29 di15 reset 5 di05 iocommand 30 di16 manual 6 di06 (spare) 31 di17 abs(absolute) reset 7 di07 (spare) 32 di30 general-purpose i...
Page 394: 5-6
5-6 chapter 5 parallel i/o interf ace 5-7 1.3 connector pin numbers ■ cable connector pin numbers as viewed from solder side 26 28 30 32 34 36 38 40 42 44 46 48 50 27 29 31 33 35 37 39 41 43 45 47 49 24 22 20 18 16 14 10 8 6 4 2 1 3 5 7 9 11 12 13 15 17 19 21 23 25 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 1...
Page 395: 5-6
5-6 5-7 chapter 5 parallel i/o interf ace 1.4 connecting the power supply connect a 24v dc power supply to the power connector on the dio option board. Usetheconnectorthatcomeswiththediooptionboardtomakethewiring. ■ power connector (viewed from cable insertion side) 2 1 connector type no. 734-102 wa...
Page 396: 5-8
5-8 chapter 5 parallel i/o interf ace 5-9 1.4.1 npn/pnp power connector wiring l length of exposed wire lead strip the wire to expose 7 mm of bare lead. 7mm l wiring terminate the wiring as shown in the following photos. ■ when using the lever to make the connection (1) using your finger, press down...
Page 397: 5-8
5-8 5-9 chapter 5 parallel i/o interf ace 1.5 typical input signal connection ■ npn specifications dc24v di di gnd ■ pnp specifications dc24v di di gnd 1. Standard i/o interface overview.
Page 398: 5-10
5-10 chapter 5 parallel i/o interf ace 5-11 1.6 typical output signal connection ■ npn specifications dc24v do gnd c caution • whenaninductiveload(solenoid,relay,etc.)isused,alwaysconnecta diode in parallel as a surge killer. • inthecaseofnpnspecifications,donotshortdooutputtodc24vsince this will da...
Page 399: 5-10
5-10 5-11 chapter 5 parallel i/o interf ace 1.7 dedicated i/o signals these signals are used to control the robot controller from an external device. 1.7.1 dedicated input signals these input signals are used to control the robot controller from an external device. The input status can be checked fr...
Page 400: 5-12
5-12 chapter 5 parallel i/o interf ace 5-13 di10 sequence permit allows or prohibits the execution of a sequence program. In"auto"or"manual"mode,asequenceprogramisexecutedwhilethissignalis on. However, no sequence program is executed unless a sequence object (complied sequenceprogram)existsand"seque...
Page 401: 5-12
5-12 5-13 chapter 5 parallel i/o interf ace di17 abs (absolute) reset performs absolute reset on the absolute specification axes. Inmanualmode,attherisingedgeofthissignal,absoluteresetisperformed on each axis in the return-to-origin order specified by parameter. If no absolute specification axis exi...
Page 402: 5-14
5-14 chapter 5 parallel i/o interf ace 5-15 do10 "auto" mode thissignalisonwhilethecontrollerisin"auto"mode. Do11 return-to-origin complete this signal is on when return-to-origin has been completed on all incremental axes and semi-absolute axes and absolute reset has been performed on all absolute ...
Page 403: 5-14
5-14 5-15 chapter 5 parallel i/o interf ace 1.8 general-purpose i/o signals these general-purpose i/o signals are available to the user and can be connected to externaldevicessuchassensors,valvesandplc.Thei/ostatuscanbecheckedfromthe robot program or sequence program. Any desired value can be output...
Page 404: 5-16
5-16 chapter 5 parallel i/o interf ace 5-17 ■ the swi command was executed by (direct)in"auto"mode. (reset (off) does not occur if the swi statement was executed in the program.) ■ theonlinecommands@reset,@initpgm,@initmem,@initall, or @swi were executed. ■ thehaltstatementwasexecutedintheprogram. 1...
Page 405: 5-16
5-16 5-17 chapter 5 parallel i/o interf ace ■ turning the power on (while emergency stop input is off) di00 (in safety connector) do00 mprdy (in safety connector) do01 do02 do03 approx. 3 sec. Control power emergency stop ready signal emergency stop contact monitor main power on ready main power cpu...
Page 406: 5-18
5-18 chapter 5 parallel i/o interf ace 5-19 1.9.2 emergency stop and servo on ■ emergency stop and servo on di00 (in safety connector) emergency stop ready signal do00 emergency stop contact monitor mprdy (in safety connector) main power on ready main power do02 servo-on state do03 alarm di01 servo ...
Page 407: 5-18
5-18 5-19 chapter 5 parallel i/o interf ace 1.9.3 abs (absolute) reset ■ absolute reset conditions:manualmodeandservoon di00 (in safety connector) emergency stop ready signal do00 emergency stop contact monitor do02 servo-on state do03 alarm do10 auto mode di11 (in safety connector) interlock input ...
Page 408: 5-20
5-20 chapter 5 parallel i/o interf ace 5-21 1.9.4 mode switching ■ mode switching di13 auto mode switching di16 manual mode switching do10 auto mode •"auto"and"manual"modescanbeswitchedindependentofdi00(emergency stop ready signal) and di11 (interlock input) status. •afterswitchingto"auto"mode,makes...
Page 409: 5-20
5-20 5-21 chapter 5 parallel i/o interf ace 1.9.5 automatic operation ■ automatic operation di00 (in safety connector) emergency stop ready signal do00 emergency stop contact monitor do02 servo-on state do03 alarm do10 auto mode di11 (in safety connector) interlock input di12 auto operation start do...
Page 410: 5-22
5-22 chapter 5 parallel i/o interf ace 5-23 2. Ratings c caution see "7. I/o connections" in chapter 3 for a definition of npn and pnp specifications. 1. Input ■ npn specifications method dcinput(positivecommontype) photocouplerinsulationmethod input power dc24v±10%,7ma/point load offvoltage:20.0vmi...
Page 411: 5-22
5-22 5-23 chapter 5 parallel i/o interf ace 3. Precautions 1.Whenusingadual-leadproximitysensorasaninputsignal,checkwhetherornotit iswithininputsignalspecifications. Ifthesensorhasahighresidualvoltageduringonandoff,thismightcause malfunctions. 2.Takenoisepreventivemeasureswhenusinganinductiveloadsuc...
Page 412: 5-24
5-24 memo.
Page 413: Chapter 6
Chapter 6 safety i/o interface contents 1. Safety i/o interface overview 6-1 1.1 power 6-1 1.2 connector i/o signals 6-2 1.3 connector terminal numbers 6-3 1.4 emergency stop input signal connections 6-4 1.5 dedicated input signal connections 6-10 1.6 dedicated output signal connections 6-11 1.7 inp...
Page 414: 6-1
6-1.
Page 415: 6-1
6-1 chapter 6 safety i/o interf ace 1. Safety i/o interface overview therobotcontrollerisprovidedwithsafetyi/ointerfacesforcompatibilitywiththe system used by the customer. A description of the i/o terminals and connection methods are explained below. Connect the i/o terminals correctly for effectiv...
Page 416: 6-2
6-2 chapter 6 safety i/o interf ace 6-3 1.2 connector i/o signals pin i/o symbol name remarks 1 di.Com dedicatedinputcommon 2 interlock(di11) interlockinput photocouplerinputdc24v,7ma 3 service(di02) servicemodeinput photocouplerinputdc24v,7ma 4 do.Com dedicatedoutputcommon 5 mprdy mainpowersupplyre...
Page 417: 6-2
6-2 6-3 chapter 6 safety i/o interf ace 1.3 connector terminal numbers ■ connector exploded view 20 18 16 14 10 8 6 4 2 1 3 5 7 9 11 12 13 15 17 19 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 1. Safety i/o interface overview.
Page 418: 6-4
6-4 chapter 6 safety i/o interf ace 6-5 1.4 emergency stop input signal connections c caution externalemergencystopandtherpbemergencystopbuttonaredisabled when pins 11 and 12 on the safety connector are directly shorted to each other. Make connections to ensure the system including the robot control...
Page 419: 6-4
6-4 6-5 chapter 6 safety i/o interf ace ■ emergency stop input signal connection (2) connection when using the rpb-e (provided with an enable switch) with an external emergency stop circuit selector 13 14 rpb connector safety connector 13 e-stopin1 11 e-stop24v 12 e-stoprdy rpb-e external emergency ...
Page 420: 6-6
6-6 chapter 6 safety i/o interf ace 6-7 ■ emergency stop input signal connection (3) connection when using the standard rpb with an external emergency stop circuit 13 14 rpb connector safety connector 13 e-stopin1 11 e-stop24v 12 e-stoprdy rpb external emergency stop circuit dc24v main power supply ...
Page 421: 6-6
6-6 6-7 chapter 6 safety i/o interf ace operation description: •therpbemergencystopswitchandexternalemergencystopswitchareconnected in series. A.Innormaloperation,e-stop24visconnectedtoe-stoprdyviatherpb emergencystopswitchandsafetyconnector,andthecontrollerinternalmotor power relay turns on. B.When...
Page 422: 6-8
6-8 chapter 6 safety i/o interf ace 6-9 c caution externalemergencystopandtherpbemergencystopbuttonaredisabled when pins 11 and 12 on the safety connector are directly shorted to each other. Make connections to ensure the system including the robot controller will always operate safely. ■ connection...
Page 423: 6-8
6-8 6-9 chapter 6 safety i/o interf ace operation description: •therpb-eemergencystopswitchandexternalemergencystopswitchare connectedinseries.Theenableswitchisalsoconnectedinseriestotherpb-e emergency stop switch, but can be bypassed with the service key switch. 1. When the service key switch conta...
Page 424: 6-10
6-10 chapter 6 safety i/o interf ace 6-11 1.5 dedicated input signal connections c caution see "7. I/o connections" in chapter 3 for a definition of npn and pnp specifications. ■ npn specifications + 1 di.Com 3 service 2 interlock photocoupler external 24v power supply ■ pnp specifications + 1 di.Co...
Page 425: 6-10
6-10 6-11 chapter 6 safety i/o interf ace 1.6 dedicated output signal connections ■ npn specifications 4 do.Com 5 mprdy 6 servo out main power supply on/off circuit l n + mechanical relay photorelay external 24v power supply 1. Safety i/o interface overview.
Page 426: 6-12
6-12 chapter 6 safety i/o interf ace 6-13 ■ pnp specifications 4 do.Com 5 mprdy 6 servo out mechanical relay photorelay main power supply on/off circuit l n external 24v power supply + 1. Safety i/o interface overview.
Page 427: 6-12
6-12 6-13 chapter 6 safety i/o interf ace 1.7 input signal description c caution see "7. I/o connections" in chapter 3 for a definition of npn and pnp specifications. N note • npnandpnpspecificationsaredeterminedbythedi.Comand do.Com inputs. • a7mainputcurrentisrequired. 1. Di02 service mode input (...
Page 428: 6-14
6-14 chapter 6 safety i/o interf ace 3. Di00 emergency stop inputs (e-stop24v, e-stoprdy: di00, e-stopin1, 2, 3, 4) emergencystopsignalinputsareusedwhenmakingtheinterlockcircuittoensure the system including the robot controller will operate safely. Contacts must be closed for the system to function ...
Page 429: Chapter 7
Chapter 7 rs-232c interface contents 1. Communication overview 7-1 2. Communication function overview 7-2 3. Communication specifications 7-3 3.1 connector 7-3 3.2 transmission mode and communication parameters 7-5 3.3 communication flow control 7-6 3.3.1 flow control during transmit 7-6 3.3.2 flow ...
Page 430: 7-1
7-1.
Page 431: 7-1
7-1 chapter 7 rs-232c interf ace 1. Communication overview the robot controller can communicate with external devices in the following two modes using the rs-232c interface. These modes can be used individually or jointly in a variety of applications using the rs- 232c interface. (1)datacommunicatio...
Page 432: 7-2
7-2 chapter 7 rs-232c interf ace 7-3 2. Communication function overview therearetwotypesofrobotcontrollercommunicationmodes,"online"and"offline". (1) "offline" mode in"offline"mode,thecommunicationbetweentherobotandexternalunitis executedwithsendcommandsintheprogram. •sendcommand(robot →externalunit...
Page 433: 7-2
7-2 7-3 chapter 7 rs-232c interf ace 3. Communication specifications 3.1 connector the rs-232c interface connector is located on the front panel of the robot controller as shown below. ■ rs-232c interface xm ym motor rgen temp acin n l l1 n1 safety srv err rpb rob i/o sd/com rdy e-stop b/a bat rcx22...
Page 434: 7-4
7-4 chapter 7 rs-232c interf ace 7-5 3. Connection cable examples a. Cable capable of hardware busy control nc rxd txd nc gnd nc rts cts nc 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 controller dcd rxd txd dtr gnd dsr rts cts external device b. Cable not using control wire nc rxd txd nc gnd nc rts cts nc 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 c...
Page 435: 7-4
7-4 7-5 chapter 7 rs-232c interf ace 3.2 transmission mode and communication parameters transmission mode fullduplex synchronous system start-stopsynchronization baud rate [bps] 4800,[9600],19200,38400,57600 character length [bit] [8],7 stop bit [bit] [1],2 parity [odd],even,none termination code [c...
Page 436: 7-6
7-6 chapter 7 rs-232c interf ace 7-7 3.3 communication flow control software flow control (xon/xoff) and hardware flow control (rts/cts) methods can be selected by specifying the communication parameters. N note when flow control is set to "xon/xoff" or "none", cts status does not affect transmissio...
Page 437: 7-6
7-6 7-7 chapter 7 rs-232c interf ace 3.4 other caution items 1) the controller allows receiving data as long as the receive buffer has a free area. The receive buffer is cleared in the following cases. •whenthepowerwasturnedoffandturnedbackon. •whentheprogramwasreset. •whenanonlinestatementoroffline...
Page 438: 7-8
7-8 chapter 7 rs-232c interf ace 7-9 ■ problems caused by poor connections external device * rcx222 connector metal parts fg potential ground wire was not at ground potential or not connected. Improper ground wire connection might cause electrical shock if connector metal parts are touched. Malfunct...
Page 439: 7-8
7-8 7-9 chapter 7 rs-232c interf ace 3.5 character code table hex. 0- 1- 2- 3- 4- 5- 6- 7- 8- 9- a- b- c- d- e- f- -0 sp 0 @ p p ー タ ミ -1 xon ! 1 a q a q 。 ア チ ム -2 " 2 b r b r 「 イ ツ メ -3 stop xoff # 3 c s c s 」 ウ テ モ -4 $ 4 d t d t 、 エ ト ヤ -5 % 5 e u e u . オ ナ ユ -6 & 6 f v f v ヲ カ ニ ヨ -7 ' 7 g w g ...
Page 440: 7-10
7-10 chapter 7 rs-232c interf ace 3.6 connecting to a pc the following are examples of connecting to a pc using the yamaha communication cable. 1) using the pc's com port ■ com port pc rcx222 25 pins 25 pins or 9 pins 9 pins 9 pins 9 pins com port communication cable w communication cable q * commun...
Page 441: Chapter 8
Chapter 8 specifications contents 1. Controller basic specifications 8-1 2. Controller basic functions 8-3 3. Controllerexternalview 8-4 3.1 rcx222 external view 8-4 3.2 rcx222hp external view 8-5 4. Rpbbasicspecificationsandexternalview 8-6.
Page 442: 8-1
8-1.
Page 443: 8-1
8-1 chapter 8 specifica tions 1. Controller basic specifications item rcx222 rcx222 hp basic specifications applicablerobots yamahasingle-axisrobots,cartesianrobots,p&probots connectablemotor capacity lessthan800w(2axestotal) 800to1200w(2axestotal) powercapacity 1700va 2400va dimensions w130×h210×d1...
Page 444: 8-2
8-2 chapter 8 specifica tions 8-3 item rcx222 rcx222 hp externali/o std.Dio input dedicated10points,general-purpose16points output dedicated12points,general-purpose8points safety input emergencystopinput servicemodeinput interlockinput enableswitchinput(enabledonlywhenrpb-eisused) output servoonstat...
Page 445: 8-2
8-2 8-3 chapter 8 specifica tions 2. Controller basic functions function description operationmodes automode(majorfunctions:programexecution,stepexecution,etc.) programmode(majorfunctions:programcreationandediting,etc.) manualmode(majorfunctions:jogmovement,pointdatateaching,etc.) systemmode(majorfu...
Page 446: 8-4
8-4 chapter 8 specifica tions 8-5 3. Controller external view 3.1 rcx222 external view ■ standard rcx222 bottom view xm ym motor rgen temp acin n l l1 n1 safety srv err rpb rob i/o sd/com rdy e-stop b/a bat rcx222 pin11-12 ext.E-stop op.1 op.2 ! 16 16 50 50 130 100 250 210 225 (22) 158 210 6-m3 5.5 ...
Page 447: 8-4
8-4 8-5 chapter 8 specifica tions 3.2 rcx222hp external view ■ rcx222hp (high power version) bottom view xm ym motor rgen temp acin n l l1 n1 safety srv err rpb rob i/o sd/com rdy e-stop b/a bat rcx222 pin11-12 ext.E-stop op.1 op.2 ! 16 16 50 50 126 210 158 (22) 130 158 100 250 210 28 225 6-m3 5.5 1...
Page 448: 8-6
8-6 chapter 8 specifica tions 8-7 4. Rpb basic specifications and external view ■ rpb basic specifications item rpb rpb-e displayscreen liquidcrystaldisplay(40characters×15lines) *effectivenumberoflinesforrcx222:8lines emergencystopbutton normally-closedcontract(withlockfunction) enableswitch notpro...
Page 449: 8-6
8-6 8-7 chapter 8 specifica tions ■ rpb-e external view 136 180 250 50.2 140 selector switch enable switch unit: mm 4. Rpb basic specifications and external view.
Page 450: 8-8
8-8 memo.
Page 451: Chapter 9
Chapter 9 troubleshooting contents 1. Error messages 9-1 1.1 robot controller error messages 9-1 [0]warningsandmessages 9-3 [1]warnings(errorhistoryentry) 9-5 [2]robotoperatingareaerrors 9-6 [3]programfileoperatingerrors 9-10 [4]dataentryandediterrors 9-12 [5]robotlanguagesyntax(compiling)errors 9-1...
Page 452: 9-1
9-1.
Page 453: 9-1
9-1 chapter 9 troubleshooting 1. Error messages 1.1 robot controller error messages when an error occurs, an error message appears on the message line (second line) of the rpb screen. Errormessagescomprisethefollowingelements. 12.1: emg.Stop on message error classification no. Error no. Error group ...
Page 454: 9-2
9-2 chapter 9 troubleshooting 9-3 [format] errorno. : [,]errormessage ... Displays the error message on screen. Code : ... Displays the error code in hexadecimal numbers. Meaning/cause : ... Displays the meaning and cause of the error. Action : ... Displays a message explaining action needed to elim...
Page 455: 9-2
9-2 9-3 chapter 9 troubleshooting [ 0] warnings and messages 0.0 : undefined error code : &h0000 meaning/cause :undefinedsystemerror. Action : contact our company. 0.1 : origin incomplete * if the cause of the origin incomplete error can be pinpointed, an error code will be attached in parentheses a...
Page 456: 9-4
9-4 chapter 9 troubleshooting 9-5 0.5 : busy code : &h0005 meaning/cause : data is being saved on a memory card or internal rom. Action : --- 0.6 : program suspended by "hold" code : &h0006 meaning/cause :programexecutionwasinterruptedbyaholdcommand. Action : press to cancel hold condition and start...
Page 457: 9-4
9-4 9-5 chapter 9 troubleshooting 0.14 : stop executed code :&h000e meaning/cause : stop was commanded while executing a direct command so operation was stopped. Action : --- 0.15 : can't execute while servo on code : &h000f meaning/cause :writingin"all"or"prm"fileswasattemptedduringservo-on. "all"o...
Page 458: 9-6
9-6 chapter 9 troubleshooting 9-7 1.34 abs.Backup fin code : &h0122 meaning/cause : finished making backup of robot position data during power cutoff. Action : --- [ 2] robot operating area errors 2.1 : over soft limit code : &h0201 meaning/cause : soft limit value preset in the parameter for operat...
Page 459: 9-6
9-6 9-7 chapter 9 troubleshooting 2.8 : movable range cal. Failed code : &h0208 meaning/cause : a. Calculation of movement path failed. B. Current position is not within movement range. Action : 1. Change to a correct movement point. 2. Change current position to within movement range. 2.9 : overlap...
Page 460: 9-8
9-8 chapter 9 troubleshooting 9-9 2.19 : lefty now selected code : &h0213 meaning/cause : on scara type robots, arm will now use the left-handed system for starting cartesian movement. Action : --- 2.20 : illegal hand type code : &h0214 meaning/cause : an r-axis hand definition was attempted on a ro...
Page 461: 9-8
9-8 9-9 chapter 9 troubleshooting 2.26 : collision in w. Carrier code : &h021a meaning/cause : failed to move the double-carrier axis, because one carrier will interfere with the other carrier. Action :ifthiserroroccurredduringmanualmode: 1. Move the other carrier to a position where the two carrier...
Page 462: 9-10
9-10 chapter 9 troubleshooting 9-11 [ 3] program file operating errors 3.1 : too many programs code : &h0301 meaning/cause : making of a new program was attempted after number of programs exceeded 100. Action : make a new program after deleting an unnecessary program. (make a backup if necessary.) 3...
Page 463: 9-10
9-10 9-11 chapter 9 troubleshooting 3.10 : object program doesn't exist code : &h030a meaning/cause : the object program name is not registered. Action : make an object program. 3.11 : cannot use function code : &h030b meaning/cause :unabletoexecuteorunneededhierarchywasselected. Action : --- 3.12 :...
Page 464: 9-12
9-12 chapter 9 troubleshooting 9-13 3.17 : cannot erase current program code : &h0311 meaning/cause : currently selected program cannot be deleted. Action : 1. Cancel deletion of program. 2. Change the specified program. 3.18 : duplicated breakpoint code : &h0312 meaning/cause : setting of breakpoin...
Page 465: 9-12
9-12 9-13 chapter 9 troubleshooting [ 5] robot language syntax (compiling) errors 5.1 : syntax error code : &h0501 meaning/cause : syntax error found in program. Action : change to the correct syntax. 5.2 : data error code : &h0502 meaning/cause : data entered in wrong format. Action : input the dat...
Page 466: 9-14
9-14 chapter 9 troubleshooting 9-15 5.7 : illegal axis name code : &h0507 meaning/cause : robot axis name is wrong. Action : change to the correct axis name. 5.8 : illegal order code : &h0508 meaning/cause : wrong bit specified for input/output port. Action : change to ascending order starting from ...
Page 467: 9-14
9-14 9-15 chapter 9 troubleshooting 5.16 : wend without while code : &h0510 meaning/cause :thereisnowhilestatementcorrespondingtothewend statement. Action :1.Deletethewendstatement. 2.Addawhilestatementcorrespondingtothewend statement. 5.17 : while without wend code : &h0511 meaning/cause :thereisno...
Page 468: 9-16
9-16 chapter 9 troubleshooting 9-17 5.22 : if without endif code : &h0516 meaning/cause :thereisnoendifstatementcorrespondingtoifstatement. Action : 1. Delete the if statement. 2.Addanendifstatementcorrespondingtotheifstatement. 5.23 : else without endif code : &h0517 meaning/cause :thereisnoendifst...
Page 469: 9-16
9-16 9-17 chapter 9 troubleshooting 5.29 : undefined array code : &h051d meaning/cause : assignment/reference was made for undefined array. Action : define the undefined array. 5.30 : undefined identifier code :&h051e meaning/cause : an undefined identifier was used. Action : define an identifier fo...
Page 470: 9-18
9-18 chapter 9 troubleshooting 9-19 5.37 : specification mismatch code : &h0525 meaning/cause : cannot execute command under present robot specifications. Action : change command for execution. 5.38 : illegal option code : &h0526 meaning/cause :errorispresentincommandoption. Action : change to a cor...
Page 471: 9-18
9-18 9-19 chapter 9 troubleshooting 5.44 : cannot use external label code : &h052c meaning/cause : command cannot use an external label. Action : 1. Change to an internal label. 2. Change execution command. 5.45 : illegal program name code : &h052d meaning/cause :a.Whentransmittingaprogramfilebysend...
Page 472: 9-20
9-20 chapter 9 troubleshooting 9-21 5.49 : select without end select code : &h0531 meaning/cause :thereisnoendselectstatementcorrespondingtoselect statement. Action :1.Deletetheselectstatement. 2.Addanendselectstatementcorrespondingtotheselect statement. 5.50 : case without end select code : &h0532 ...
Page 473: 9-20
9-20 9-21 chapter 9 troubleshooting 5.55 : elseif without endif code : &h0537 meaning/cause :thereisnoendifstatementcorrespondingtoelseif statement. Action :1.Deletetheelseifstatement. 2.Addanendifstatementcorrespondingtotheelseif statement. [ 6] robot language execution errors 6.1 : illegal command...
Page 474: 9-22
9-22 chapter 9 troubleshooting 9-23 6.6 : subscript out of range code : &h0606 meaning/cause : a subscript of an array variable has exceeded the range defined in dim statement. Action : change the subscript of array variable to within the defined range. 6.7 : return without gosub code : &h0607 meani...
Page 475: 9-22
9-22 9-23 chapter 9 troubleshooting 6.13 : restart without suspend code : &h060d meaning/cause :restartcommandwasexecutedforatasknotexecutedby suspendcommand. Action :confirmexecutionofsuspendcommand. 6.14 : task number error code :&h060e meaning/cause : a. Task number is outside the range 2 to 8. B...
Page 476: 9-24
9-24 chapter 9 troubleshooting 9-25 6.19 : sub without call code : &h0613 meaning/cause :subcommandwasexecutedwithoutexecutingcall command. Action :confirmexecutionofcallcommand. 6.20 : not execute call code : &h0614 meaning/cause :callcommandwasnotexecuted. Action :confirmexecutionofcallcommand. 6....
Page 477: 9-24
9-24 9-25 chapter 9 troubleshooting 6.26 : no sufficient memory for out code : &h061a meaning/cause :failedtorunanoutcommandduetoinsufficientmemory causedbymultipleoutcommandsthatwererunin succession. Action :checkthenumberofoutcommands.Themaximumnumber ofoutcommandsthatcanberuninparallelis16. 6.27 ...
Page 478: 9-26
9-26 chapter 9 troubleshooting 9-27 6.32 : path execute error code : &h0620 meaning/cause : cannot execute path motion. A. Acceleration zone distance is too short. B. Speed is too high in the position where the direction changes. Action : 1. Reduce the speed setting. 2.Lengthenthestraightlineorcircu...
Page 479: 9-26
9-26 9-27 chapter 9 troubleshooting 9.3 : memory destroyed code : &h0903 meaning/cause :errorormalfunctionoccurredinthememory. Action : initialize memory. 9.4 : parameter destroyed code : &h0904 meaning/cause : part or all of the parameter data has been destroyed. Action : initialize the parameter d...
Page 480: 9-28
9-28 chapter 9 troubleshooting 9-29 9.33 : sys. Generation destroyed code : &h0921 meaning/cause : part or all of the system generation data has been destroyed. Action : remake the system generation data correctly. 9.34 : sys. Generation mismatch code : &h0922 meaning/cause : mistake made in specify...
Page 481: 9-28
9-28 9-29 chapter 9 troubleshooting 9.41 : local variable memory full code : &h0929 meaning/cause : number of local variables defined within subroutine has exceeded upper limit. Action : 1. Reduce number of local variables defined in the subroutine. 2.Usetheglobalvariable. [10] system setting or har...
Page 482: 9-30
9-30 chapter 9 troubleshooting 9-31 10.9 : cannot set no axis code : &h0a09 meaning/cause : a no-axis setting was attempted on an axis which cannot accept it. The following axes cannot be set to no-axis. • xandyaxesexceptonmultityperobots action : 1. Do not make a no-axis setting. 2. Change the axis...
Page 483: 9-30
9-30 9-31 chapter 9 troubleshooting [12] i/o and option board errors 12.1 : emg.Stop on code : &h0c01 meaning/cause :a.Emergencystopbuttonwaspressed. B.Emergencystopterminalsonsafetyconnectorareopen (emergency stop status). C. Rpb or terminator are not connected to rpb connector. D.Safetyconnectoris...
Page 484: 9-32
9-32 chapter 9 troubleshooting 9-33 12.11 : cc-link communication error code : &h0c0b meaning/cause :a.Errorincableforcc-linksystem. B.Wrongcommunicationsettingforcc-linksystem. C. Master station sequencer power is turned off, has stopped operating or is damaged. D.Breakdownincc-linkcompatibleunit. ...
Page 485: 9-32
9-32 9-33 chapter 9 troubleshooting 12.18 : incorrect devicenet setting code : &h0c12 meaning/cause : a. The macid or communication speed setting is incorrect. Action : 1. Check the macid and communication speed settings. 12.19 : devicenet link error(explicit) code : &h0c13 meaning/cause :a.Thedevic...
Page 486: 9-34
9-34 chapter 9 troubleshooting 9-35 12.34 : pos.Out point not exist code : &h0c22 meaning/cause : comparison point data does not exist. Action : set comparison point data correctly. 12.35 : pos.Out point unit error code : &h0c23 meaning/cause : comparison points 1 and 2 do not use the same unit syst...
Page 487: 9-34
9-34 9-35 chapter 9 troubleshooting 12.75 : illegal remote command code : &h0c4b meaning/cause : a. The remote command or command data is incorrect. Action : 1. Check the remote command or command data. [13] rpb errors 13.1 : rpb communication error code : &h0d01 meaning/cause :erroroccurredincommun...
Page 488: 9-36
9-36 chapter 9 troubleshooting 9-37 [14] rs-232c communication errors 14.1 : communication error code :&h0e01 meaning/cause : a. During external communication via the rs-232c, an error occurred. B. An overrun error or framing error occurred via the rs-232c. C. Power supply for external device turned...
Page 489: 9-36
9-36 9-37 chapter 9 troubleshooting 14.21 : no return code (c/r) code :&h0e15 meaning/cause : 1. Character string in 1 line exceeded 75 letters. 2. Cr code (0dh) was not added at end of line. Action :1.Limitnumberofcharactersin1lineto75letters. 2. Add a cr code at the end of a single line. 14.22 : n...
Page 490: 9-38
9-38 chapter 9 troubleshooting 9-39 [15] memory card errors 15.1 : invalid file attribute code : &h0f01 meaning/cause : a. Directory was accessed. B. Read/write protected file was accessed. Action : 1. Change to a file which can be accessed. 2. Change to a file allowing read/write. 15.2 : read only ...
Page 491: 9-38
9-38 9-39 chapter 9 troubleshooting 15.11 : directory full code : &h0f0b meaning/cause : the file storage capacity was exceeded. Action :1.Useanewmemorycard. 2. Change the directory to save. 3. Delete unnecessary files. 15.12 : disk full code : &h0f0c meaning/cause : write failed. No space is availa...
Page 492: 9-40
9-40 chapter 9 troubleshooting 9-41 15.23 : aborted code : &h0f17 meaning/cause : the key was pressed during reading/writing from or into memory card, and the operation halted. Action : --- 15.24 : media hardware error code : &h0f18 meaning/cause : a. Memory card is defective b.Erroroccurredincontro...
Page 493: 9-40
9-40 9-41 chapter 9 troubleshooting 17.2 : watchdog error (driver) code : &h1102 meaning/cause : a. Malfunction occurred in driver unit due to external noise. B. Controller is defective. Action : 1. Turn the power on again. 2. Replace the controller. Dedicated output : *2 17.3 : over current code : ...
Page 494: 9-42
9-42 chapter 9 troubleshooting 9-43 17.5 : over heat code : &h1105 meaning/cause : temperature in power module of driver unit exceeded 80。c. Action : 1. Improve the equipment environment. 2. Check that cooling fan is working correctly. 3.Lowertherobotdutycycleanddecreasetheamountofheat generated. 4....
Page 495: 9-42
9-42 9-43 chapter 9 troubleshooting 17.11 : feedback error 2 code : &h110b meaning/cause : motor cable is broken. Action : replace the motor cable or encoder cable. Dedicated output : *2 17.16 : over velocity 1 code : &h1110 meaning/cause : axis movement speed exceeded the limit during linear interp...
Page 496: 9-44
9-44 chapter 9 troubleshooting 9-45 17.21 : bad origin sensor code : &h1115 meaning/cause : a. Origin sensor is defective. B. Origin sensor wiring is broken. Action : 1. Replace the origin sensor. 2. Replace the rob i/o cable. 17.22 : bad pz code : &h1116 meaning/cause : a. Motor is defective. B. Re...
Page 497: 9-44
9-44 9-45 chapter 9 troubleshooting 17.31 : servo off code : &h111f meaning/cause : movement command was attempted in servo off state. Action : change status to servo on. 17.33 : busy now code : &h1121 meaning/cause : a. Servo-off command was attempted while the driver was stopped. B. Return-to-orig...
Page 498: 9-46
9-46 chapter 9 troubleshooting 9-47 17.42 : cannot reset position code : &h112a meaning/cause : absinit or absinit2 statement was executed at a position where the current position cannot be reset. Action : move to a position where the current position can be reset, and then execute the absinit or ab...
Page 499: 9-46
9-46 9-47 chapter 9 troubleshooting 17.85: backup position data error 2 code : &h1155 meaning/cause : failed to read out the robot position data during start-up of the controller. Action : perform absolute reset. 17.90 : drive2 module type error code : &h115a meaning/cause : motor specifications do ...
Page 500: 9-48
9-48 chapter 9 troubleshooting 9-49 17.94 : abs. Battery low voltage code :&h115e meaning/cause : battery for retaining absolute data is low or not installed. Action : 1. Replace battery. 2. Install battery. Dedicated output : do15 (battery alarm output) turns on when absolute battery is low. 17.112...
Page 501: 9-48
9-48 9-49 chapter 9 troubleshooting 19.2 : over current code : &h1302 meaning/cause : a. Short-circuit, earth fault or wire breakage occurred in motor cable. B. Motor failure. C. Controller board is defective. D. Robot number setting is incorrect. Action : 1. Replace the motor cable. 2. Replace the ...
Page 502: 9-50
9-50 chapter 9 troubleshooting 9-51 19.7 : p.E. Counter over code : &h1307 meaning/cause : deviation counter error. Action : −−− 19.11 : system fault code : &h130b meaning/cause : a. Driver was not recognized correctly at power-on. B.Externalnoisehasdisruptedsoftwareprogram. C. Rs-232c receiving buf...
Page 503: 9-50
9-50 9-51 chapter 9 troubleshooting 19.16 : abnormal voltage code : &h1310 meaning/cause : a. Ac power line voltage is too high. B. Regenerative unit (rg1) connection is incorrect. C. Temperature of regenerative absorption resistance is too high (above 120°c). D.Rgencablefailed. E. Regenerative unit...
Page 504: 9-52
9-52 chapter 9 troubleshooting 9-53 19.23 : abs.Bat.L-voltage code : &h1317 meaning/cause : absolute battery voltage is less than 3.1v. Action : replace the absolute battery. 19.24 : abs.Data error code : &h1318 meaning/cause : absolute search for "semi-absolute" ended abnormally. Action : register ...
Page 505: 9-52
9-52 9-53 chapter 9 troubleshooting 19.28 : coord.Val. Error code : &h131c meaning/cause : a. Poor connection of communication cable b. Open-circuit fault of communication cable c. Data destruction due to external noise action : 1. Connect the communication cable correctly. 2. Replace the communicat...
Page 506: 9-54
9-54 chapter 9 troubleshooting 9-55 19.40 : abs.Os error code : &h1328 meaning/cause : −−− action : −−− 19.41 : abs.Ro error code : &h1329 meaning/cause : rob i/o cable broke during power-off. Action : −−− 19.42 : abs.Re error code : &h132a meaning/cause : rob i/o cable broke during power-on. Action...
Page 507: 9-54
9-54 9-55 chapter 9 troubleshooting 21.3 : system error (taskid) code : &h1503 meaning/cause : software error occurred. Action : contact our company with details of this problem. 21.4 : system error (drcom) code : &h1504 meaning/cause : software error occurred. Action : contact our company with deta...
Page 508: 9-56
9-56 chapter 9 troubleshooting 9-57 21.14 : dpram error (ptp data) code :&h150e meaning/cause : 1. Failed to write ptp command data into driver. Action : 1. Replace the driver. 2. Replace the controller. 21.41 : system error (exception) code : &h1529 meaning/cause : a. Software error occurred. Actio...
Page 509: 9-56
9-56 9-57 chapter 9 troubleshooting 22.9 : abnormal over voltage code : &h1609 meaning/cause : a. Output voltage for motor power supply exceeded 420 volts. B. Regenerative unit not connected to controller. C. Regenerative unit safety device triggered due to temperature rise (120 °c or more) in regen...
Page 510: 9-58
9-58 chapter 9 troubleshooting 9-59 22.13 : bus interface overtime code : &h160d meaning/cause : could not acquire access rights to dual port ram. Action : replace the controller. Dedicated output : *1 22.14 : abnormal driver unit error code :&h160e meaning/cause :erroroccurredinhardware. Action : c...
Page 511: 9-58
9-58 9-59 chapter 9 troubleshooting 22.41 : opt.1 interface overtime code : &h1629 meaning/cause : 1. Failed to acquire access privilege for interface with option board connected to option slot 1. Action : 1. Replace the option board connected to option slot 1. : 2. Replace the controller. Dedicated...
Page 512: 9-60
9-60 chapter 9 troubleshooting 9-61 22.50 : yc-link disconnect code : &h1632 meaning/cause : the secondary station connection test failed at primary station startup. A. The secondary station power is off. B. The yc-link communication cable and terminal resistor are disconnected. C. The secondary sta...
Page 513: 9-60
9-60 9-61 chapter 9 troubleshooting 22.54 : yc-link parameter error code : &h1636 meaning/cause : mismatch between the secondary station parameter and the setting. A. The secondary station parameter setting was changed, or the controller was replaced. Action : 1. Verify that the correct sr1 is conne...
Page 514: 9-62
9-62 chapter 9 troubleshooting 9-63 1.2 rpb error messages when a hardware error or a software error occurs in the rpb, the following messages are highlighted (shown with reversed background) on the guideline of the lowest line of the screen. Rpb trap!! Contents :undefinedoperationcodewasexecuted. C...
Page 515: 9-62
9-62 9-63 chapter 9 troubleshooting rpb transmit error!! (time out error) contents : transmitting to controller is impossible. Cause : a. The cable is broken or disconnected. B.Noresponsefromcontrollerduetoproblemincpuunit. Action : 1. Replace rpb cable. 2. Replace the rpb. 3. Replace the controller...
Page 516: 9-64
9-64 chapter 9 troubleshooting 9-65 2. Troubleshooting 2.1 when trouble occurs please contact our company with details of the problem that occurs. Report the following items in as much detail as possible. Item description what happened •controllermodelnameandserialno. Example:rcx222+regenerativeunit...
Page 517: 9-64
9-64 9-65 chapter 9 troubleshooting 2.2 acquiring error information errorhistory(log)informationisstoredinsidetherobotcontroller.Thefollowingtwo methods are available for checking this information. 2.2.1 acquiring information from the rpb [procedure] 1) press (diagnos)in"system"mode. 2) to check con...
Page 518: 9-66
9-66 chapter 9 troubleshooting 9-67 2.3 troubleshooting checkpoints 1. Installation and power supply symptom possible cause check items corrective action 1 controllerwon't turnonevenwith powersupplied. • powernotsupplied. • problemincontroller internalpower. • checkpowerinput terminalconnection (l/n...
Page 519: 9-66
9-66 9-67 chapter 9 troubleshooting 2. Robot operation symptom possible cause check items corrective action 1 controllerturns onbutcan't executeprogram andmanual movement. • interlocksignal. • checktheinterlock signalofthe safetyi/o interfaceconnector andalsocheckthe 24vpowersupply forconnection. • ...
Page 520: 9-68
9-68 chapter 9 troubleshooting 9-69 symptom possible cause check items corrective action 3 positiondeviation occurred. • thereare2 maintypesof position deviation. 1.Electrical position deviation 2.Mechanical position deviation incase1,if position deviation occurs,youcan perform absolutereset andretu...
Page 521: 9-68
9-68 9-69 chapter 9 troubleshooting 3. I/o operation symptom possible cause check items corrective action 1 won'toperate evenwhen dedicatedinput signalis supplied. • nodc24vsupply. • checkthatdc24v issuppliedfromi/o interfaceconnector (std.Dio). • supplydc24v. • probleminsignal connection. • checkwi...
Page 522: User'S Manual
All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced in any form without the permission of yamaha motor co., ltd. Information furnished by yamaha in this manual is believed to be reliable. However, no responsibility is assumed for possible inaccuracies or omissions. If you find any par...
Page 523: Im Operations
Http://global.Yamaha-motor.Com/business/robot/ robot manuals can be downloaded from our company website. Please use the following for more detailed information. Yamaha motor co., ltd. Im operations 882 soude, nakaku, hamamatsu, shizuoka, 435-0054, japan tel. 81-53-460-6103 fax. 81-53-460-6811.
Page 524: Im Operations
Http://global.Yamaha-motor.Com/business/robot/ robot manuals can be downloaded from our company website. Please use the following for more detailed information. Yamaha motor co., ltd. Im operations 882 soude, nakaku, hamamatsu, shizuoka, 435-0054, japan tel. 81-53-460-6103 fax. 81-53-460-6811.