- DL manuals
- Kurzweil
- Synthesizer
- PC3
- Musician's Manual
Kurzweil PC3 Musician's Manual
Musician’s Guide
©2008 All rights reserved. Kurzweil ® is a product line of Young Chang Co., Ltd. Young Chang®, Kurzweil ®, V. A. S. T. ®, PC3®, KDFX®,
Pitcher®, and LaserVerb®, KSP8 ™, K2661™, K2600™, K2500™, and K2000™ are trademarks of Young Chang Co., Ltd. All other products
and brand names are trademarks or registered trademarks of their respective companies. Product features and specifications are subject to
change without notice.
You may legally print up to two (2) copies of this document for personal use. Commercial use of any copies of this document
is prohibited. Young Chang Co. retains ownership of all intellectual property represented by this document.
910511 –
V1.0 August 28, 2008
Summary of PC3
Page 1
Musician’s guide ©2008 all rights reserved. Kurzweil ® is a product line of young chang co., ltd. Young chang®, kurzweil ®, v. A. S. T. ®, pc3®, kdfx®, pitcher®, and laserverb®, ksp8 ™, k2661™, k2600™, k2500™, and k2000™ are trademarks of young chang co., ltd. All other products and brand names are ...
Page 2: Save These Instructions
Ii important safety & installation instructions instructions pertaining to the risk of fire, electric shock, or injury to persons warning: when using electric products, basic precautions should always be followed, including the following: 1. Read all of the safety and installation instructions and e...
Page 3
Iii important safety instructions 1) read these instructions 2) keep these instructions. 3) heed all warnings. 4) follow all instructions. 5) do not use this apparatus near water. 6) clean only with dry cloth. 7) do not block any of the ventilation openings. Install in accordance with the manufactur...
Page 4
Iv kurzweil international contacts contact the kurzweil office listed below to locate your local kurzweil representative. Kurzweil music systems 19060 s. Dominguez hills dr. Rancho dominguez california 90220 usa telephone: (310)637-2000 fax: (310)637-2025 http://www.Kurzweilmusicsystems.Com kurzweil ...
Page 5
Toc-i kurzweil international contacts .....................................................................................................................................Iv chapter 1 introduction keeping current...........................................................................................
Page 6
Toc-ii bank buttons.....................................................................................................................................................................3-2 sliders ...........................................................................................................
Page 7
Toc-iii saving and loading files—storage mode...................................................................................................................5-5 special button functions ..................................................................................................................
Page 8
Toc-iv hold through attack (thratt) .............................................................................................................................6-26 hold until decay (tildec)................................................................................................................
Page 9
Toc-v impact.......................................................................................................................................................................6-46 the program fx (progfx) page...........................................................................................
Page 10
Toc-vi veltrk........................................................................................................................................................................6-60 random ..............................................................................................................
Page 11
Toc-vii bend range (semitones) and bend range (cents): up and down .................................................................7-18 aux bend 1 up and aux bend 1 down...............................................................................................................7-19 aux bend 2 ran...
Page 12
Toc-viii local..........................................................................................................................................................................7-48 synczone..........................................................................................................
Page 13
Toc-ix master fx ...................................................................................................................................................................9-7 the chain editor.......................................................................................................
Page 14
Toc-x chapter 10 midi mode the transmit page....................................................................................................................................................10-1 control setup ............................................................................................
Page 15
Toc-xi key action map ...................................................................................................................................................... 11-5 default sequence ............................................................................................................
Page 16
Toc-xii countoff ................................................................................................................................................................12-10 program.................................................................................................................
Page 17
Toc-xiii shift.........................................................................................................................................................................12-25 transpose ........................................................................................................
Page 18
Toc-xiv delays ......................................................................................................................................................................D-14 chorus ..............................................................................................................
Page 19: Chapter 1
Introduction keeping current 1-1 chapter 1 introduction greetings. Your new pc3 offers amazing acoustic, electric, and synthesizer sounds, combined with advanced programming features that will let you create almost any sound you can imagine. The pc3 comes loaded with 64 mb of rom sounds, powered by ...
Page 20: Overview of The Pc3
1-2 introduction overview of the pc3 overview of the pc3 the pc3’s 800+ programs include the orchestral and contemporary sound blocks, general midi (gm), stereo triple strike piano, classic keys for realistic vintage electric piano sounds, and new string sections. Multi-zone performance setups are a...
Page 21: Vast Synthesis
Introduction vast synthesis 1-3 vast synthesis the pc3’s variable architecture synthesis technology (v.A.S.T.) lets you build sounds from realistic instrumental samples and sampled synth waveforms—then modify the nature of those sounds through a wide variety of digital signal-processing (dsp) functi...
Page 22: How to Use This Manual
1-4 introduction how to use this manual how to use this manual this manual describes how to connect and power up your pc3, getting around the front panel, and a brief description of the operating modes. For information on editing and advanced programming features, refer to additional material provid...
Page 23: Options
Introduction options 1-5 options ask your kurzweil dealer about the following pc3 options: sound rom cards the pc3 has sockets for 64 mb and 128 mb rom expansion cards that you can install yourself (the expansion kits come with complete instructions). Pedals the pc3 has jacks for three switch pedals...
Page 24
1-6 introduction options.
Page 25: Chapter 2
Startup make connections 2-1 chapter 2 startup if hooking up new gear is familiar to you, and you just want to get going, here’s a quick description of what you need to get started with your pc3. If you need more information, thorough descriptions of each step follow. Make connections 1. Set the key...
Page 26: Startup—The Details
2-2 startup startup—the details startup—the details this section walks you through the hookup of your pc3. We’ll take a look at the rear panel, then describe the power, audio, and other cable connections. Before you start... Don’t connect anything until you make sure your pc3 is properly and safely ...
Page 27
Startup startup—the details 2-3 digital for digital audio output from the pc3, connect a 75-ohm coaxial cable from the pc3’s rca digital out jack to the aes or s/pdif input of the receiving device. You may need an rca-to- xlr adapter to connect with the receiving device. If the receiving device rece...
Page 28
2-4 startup startup—the details pedals plug your switch or continuous pedals into the corresponding jacks on the pc3’s rear panel. We recommend using the kurzweil pedals described on page 1-2, but you can use almost any switch or continuous pedal, as long as it adheres to the following specifications...
Page 29
Startup startup—the details 2-5 ribbon plug the optional kurzweil ribbon controller into the modular ribbon jack on the rear panel. The ribbon controller itself should rest on a flat surface; it fits nicely between the keys and the buttons and sliders on the front panel. The ribbon is a continuous con...
Page 30
2-6 startup startup—the details xd cards you can use xd memory cards for backing up, archiving, sharing your work, and updating your software (32mb – 256mb will work, type s or no type stated, formatted fat16). The xd card slot is on the back panel of the pc3, but it is easily accessible from the fr...
Page 31: Pc3 Programs
Startup pc3 programs 2-7 pc3 programs the pc3 powers up in program mode, where you can select and play programs (called patches, presets, or voices on other instruments). Programs are preset sounds composed of up to 32 layers of samples or waveforms. If you’ve left program mode, just press the progr...
Page 32
2-8 startup pc3 programs soft buttons on most pc3 screens, the bottom line of the display identifies the function of each of the buttons beneath the display. We call these buttons soft buttons, because they do different things depending on what’s currently showing in the display. In program and quick...
Page 33: Setups
Startup setups 2-9 setups setups are preset combinations of programs. Setups can have up to 16 zones, each of which can be assigned to any range of the keyboard (overlapping or split). Each zone can have its own program, midi channel, and midi control assignments, as well as riff and arpeggiator set...
Page 34: The Other Modes
2-10 startup the other modes the other modes there are five other mode buttons on the front panel. See chapters 3 and 4 for more detailed descriptions of the modes. Effects mode enable/disable effects presets, and set aux overrides. Midi mode configure the pc3 for sending and receiving midi informatio...
Page 35: Chapter 3
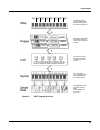
User interface basics mode selection 3-1 chapter 3 user interface basics this chapter will show you how to get around the front panel of your pc3. Your interactions can be divided into three primary operations: mode selection, navigation, and data entry. There is also an assignable control section. ...
Page 36: Mode Buttons
3-2 user interface basics mode buttons song mode use the pc3’s sequencer to record and play back your keyboard performance, play type 0 and type 1 midi sequences, and record multi- timbral sequences received via midi. Storage mode interface with the pc3’s xd card reader or usb port to load and save ...
Page 37: Sliders
User interface basics sliders 3-3 sliders in kb3 mode, the pc3’s nine sliders emulate an organ’s drawbars. For example, slider a emulates an organ’s 16’ drawbar. In other modes, the sliders can be used to send values for different midi controllers. In either case, you may have to move the slider pas...
Page 38: Program and Category Buttons
3-4 user interface basics program and category buttons program and category buttons use the program and category buttons, in conjunction with the bank buttons, to directly select pc3 programs. Each of the 16 categories contains 8 programs. Picking favorites when you select a program within a categor...
Page 39: Pitch Wheel and Mod Wheel
User interface basics pitch wheel and mod wheel 3-5 pitch wheel and mod wheel to the left of the pc3’s keyboard are the pitch wheel and the mod wheel, as well as the sw and arp buttons. Push the pitch wheel away from you to raise the pitch of the note(s) you are playing. Pull it towards you to lower...
Page 40: Navigation
3-6 user interface basics navigation navigation the navigation section of the front panel consists of the display and the buttons surrounding it. These navigation buttons will take you to every one of the pc3’s programming parameters. The display your primary interface with the pc3 is its backlit gr...
Page 41
User interface basics navigation 3-7 the soft buttons the soft buttons are called “soft” because their functions change depending on the currently selected mode and page. Sometimes they perform specific functions, like changing midi channels in program mode. In the program editor and other editors, t...
Page 42
3-8 user interface basics navigation the edit button the edit button activates each of the pc3’s editors, and acts as a shortcut to many pages within the program editor. Pressing the edit button tells the pc3 that you want to change some aspect of the object marked by the cursor. For example, when a...
Page 43: Data Entry
User interface basics data entry 3-9 data entry the data entry section of the front panel includes the alpha wheel, the plus/minus buttons, and the 14-button alphanumeric pad. The alpha wheel the alpha wheel is especially useful because it can quickly enter large or small changes in value. If you tu...
Page 44
3-10 user interface basics data entry double button presses pressing two or more related buttons simultaneously executes a number of special functions depending on the currently selected mode. Make sure to press them at exactly the same time. In this mode or editor… …pressing these buttons simultane...
Page 45: Intuitive Data Entry
User interface basics intuitive data entry 3-11 intuitive data entry many parameters have values that correspond to standard physical controllers. In many cases, you can select these values “intuitively,” rather than having to scroll through the control source list. Do this by selecting the desired ...
Page 46: Search
3-12 user interface basics search search there’s a convenient way to find any string of characters within the currently selected list, or range of values. Hold the enter button and press any of the numeric buttons. A dialog appears. Type in the string of characters you want to find. For example, if yo...
Page 47: Chapter 4
The operating modes what the modes are 4-1 chapter 4 the operating modes in this chapter we’ll discuss the theory behind the mode concept, and we’ll describe the basic operating features of each mode. What the modes are the modes exist to make the pc3 logical to work with. With as many performance a...
Page 48: Using The Modes
4-2 the operating modes using the modes the following table lists the procedures for moving between modes and editors. Note that the exit button won’t always take you where the table says it will; it often depends on how you got where you are. The table assumes that you’ve entered a given editor via...
Page 49
The operating modes using the modes 4-3 if you’re using a different midi controller, you can make use of setup mode even if your midi controller can transmit on only one midi channel at a time. To do this, go to the receive page in midi mode (by pressing the recv soft button while in midi mode), and...
Page 50
4-4 the operating modes using the modes.
Page 51: Chapter 5
Editing conventions introduction to editing 5-1 chapter 5 editing conventions introduction to editing programming (editing) the pc3 always involves three basic operations: mode selection, navigation, and data entry. First, select the mode that relates to the object you want to edit—a program, a setu...
Page 52: Object Type and Id
5-2 editing conventions object type and id object type and id the pc3 stores its objects in memory using a system of id numbers that are generally organized into banks. Each object is identified by its object type and object id; these make it unique. An object’s type is simply the kind of object it i...
Page 53
Editing conventions saving and naming 5-3 are labeled under each button. If the character that appears is not the one you want, press the button again. Press the +/- button on the alphanumeric pad to switch between upper and lower case characters. Press 0 one or more times to enter the numerals 0 th...
Page 54
5-4 editing conventions saving and naming replace, or change the id and save to an unused id. If you replace a memory object, however, it’s definitely gone! Keyboard naming the keyboard naming feature makes naming objects convenient, by letting you use the keyboard (or your midi controller) to enter ...
Page 55: Deleting Objects
Editing conventions deleting objects 5-5 deleting objects within most editors, there are soft buttons for deleting objects. When you want to delete an object, press the delete soft button, and the pc3 will ask you if you want to delete the object. (at this point in the dialog, you can select another...
Page 56: Special Button Functions
5-6 editing conventions special button functions special button functions the mode buttons and the chan/layer buttons have additional functions, depending on the mode or editor you’re in. The table below describes some of these special button functions. Button mode or editor program editor song mode...
Page 57: Chapter 6
Program mode vast and kb3 programs 6-1 chapter 6 program mode programs are the pc3’s performance-level sound objects. They’re preset sounds equivalent to the patches, presets, voices, or multis that you find on other synths. Program mode is the heart of the pc3, where you select programs for performa...
Page 58: Vast Program Structure
6-2 program mode vast program structure vast program structure you might want to take a look at figure 6-1 on page 6-3, which depicts the hierarchy of a vast program, from individual samples all the way up to setups, which can contain up to 16 programs. Every vast program contains at least one layer...
Page 59
Program mode vast program structure 6-3 figure 6-1 vast program structure zone 1 zone 2 zone 3 zone 4 zone 5 zone 6 zone 7 zone 8 16 keyboard zones— each with independent program, midi channel, and control assignments selected for performance and editing in program mode; up to 32 layers per program ...
Page 60: Kb3 Program Structure
6-4 program mode kb3 program structure kb3 program structure there’s nothing quite like the sound of the classic hammond™ b-3 tone wheel organ, especially when played through a leslie™ rotating speaker system. We’ve done extensive testing and analysis with several tone wheel organs, and created our ...
Page 61
Program mode kb3 program structure 6-5 real-time controls in kb3 mode you have real-time control over many components of kb3 programs directly from the front panel. The sliders emulate the drawbars that are so essential to the tone wheel sound, while the buttons above them (they’re called the mute b...
Page 62
6-6 program mode kb3 program structure in normal operational modes, using the mute buttons to change a program’s kb3 effects doesn’t affect the program; the effects return to their programmed settings the next time you select the program. If, however, you’re in an editor when you change the effects,...
Page 63
Program mode kb3 program structure 6-7 local keyboard channel the local keyboard channel enables the pc3 to receive midi information on a single channel, then rechannelize that information so you can play and control all 16 zones of a setup, even if your midi source transmits on only one channel. Wh...
Page 64
6-8 program mode kb3 program structure you may find it more convenient to use the local keyboard channel. In this case, the pc3 remaps incoming midi to the pc3’s current channel, so in program mode, you’ll always play the program on the pc3’s current channel. Incoming midi also gets sent to the pc3’s...
Page 65: The Program Mode Page
Program mode the program mode page 6-9 the program mode page the top line of the program mode entry-level page shows your mode location, the present midi transposition, the midi bank number and midi program number of the highlighted program, and the current midi channel. The info box at the left of ...
Page 66
6-10 program mode the program mode page if you don’t like the way the physical controllers work in program mode, you can either select a different control setup, or edit the existing one. Any changes you make to the current control setup will also affect the way that setup works in setup mode. There...
Page 67: Editing Vast Programs
Program mode editing vast programs 6-11 editing vast programs the program editor is where you begin to modify the pc3’s resident sounds, and to build your own sounds around sample keymaps and/or waveforms. There’s virtually no limit to the sounds you can create using the tools in the program editor....
Page 68
6-12 program mode editing vast programs two of the soft buttons in the program editor are special cases. They’re the soft buttons that select the editing pages for the first and last dsp functions (pitch and level, respectively) of the current program’s algorithm. One of these soft buttons is labeled...
Page 69: Algorithm Basics
Program mode algorithm basics 6-13 algorithm basics press the alg soft button in the program editor to take you to the algorithm (alg) page. The basic definition: an algorithm is the “wiring” (signal path) of a sample to the audio outputs, through a series of digital signal processing (dsp) functions...
Page 70
6-14 program mode algorithm basics source in the controller list to modulate the function-parameter. The above italicized parameter-types are described in common dsp control parameters on page 6-14. More information on the subpages can be found in the dsp control (dspctl) page on page 6-28 and the d...
Page 71
Program mode algorithm basics 6-15 by adjusting the function-parameter, you can add a fixed amount of adjustment to any dsp function. For the pitch function, adjusting the function-parameter will change the pitch in semitone increments. Use this as a starting point to set the pitch where you want it ...
Page 72
6-16 program mode algorithm basics velocity tracking a positive value for velocity tracking will raise the pitch as you trigger notes with higher attack velocities. This is great for getting a trace of detuning based on your attack velocity, especially in drum programs, where you can make the pitch ...
Page 73
Program mode algorithm basics 6-17 alt input for algorithms (cascade mode) cascade mode is a particularly powerful feature of the pc3 that allows you to create unique algorithms of previously unattainable levels of complexity. The following three figures show the signal path of a program configured us...
Page 74
6-18 program mode algorithm basics the cascade mode algorithms (very much like triple mode on a k2600) start at id 101. Note in the above figures how algorithm 101 looks very similar to algorithm 1. Each cascade mode algorithm corresponds to its non-cascade equivalent, which has the same id number mi...
Page 75: The Keymap Page
Program mode the keymap page 6-19 the output mode parameter determines the number of outputs from the algorithm. With output mode set to normal, the algorithm has one output. With output mode set to sep. L/r, the algorithm has two outputs, each of which is sent to a separate stereo channel. To edit ...
Page 76
6-20 program mode the keymap page key tracking (keytrk) this is one of the six common dsp control parameters. On the keymap page, key tracking affects the interval between notes. The default value of 100 cents (a cent is a hundredth of a semitone) gives you the normal semitone interval between each ...
Page 77
Program mode the keymap page 6-21 once you have the keymaps assigned, go to the output page and set the panning for each sample as desired. Keep in mind that using stereo keymaps reduces the polyphony of the program. For example, if you had a two-layer program with stereo keymaps in each layer, each...
Page 78: The Layer Page
6-22 program mode the layer page as an example, suppose you’re working with a flute keymap and wish to control the amount of chiff heard at the beginning of the sound. On the keymap page in the program editor, set altcontrol to mwheel. Now the mod wheel controls how much of the initial sample attack...
Page 79
Program mode the layer page 6-23 low key (lokey) this sets the lowest active note for the current layer. This parameter’s value cannot be set higher than the value for hikey. The standard midi key range is c 1—g 9 (0-127). Middle c is c 4 (isp). High key (hikey) here you set the highest active note ...
Page 80
6-24 program mode the layer page trigger (trig) set trig to rvrs to have notes triggered on key-up. The initial velocities of notes triggered this way are determined by the release velocities of the keys that trigger them. The default setting is norm . Delay control (dlyctl) here you select, from th...
Page 81
Program mode the layer page 6-25 you could use this parameter to set up a two-layer program that would let you use a midi control to switch between layers, say a guitar sound and a distorted guitar. Both layers would have their enable parameters set to the same control source, say mwheel. One layer ...
Page 82: The Pitch Page
6-26 program mode the pitch page freeze pedal (frzpdl) this parameter activates or deactivates the layer’s response to freeze pedal messages (midi 69). The freeze pedal control causes all notes that are on to sustain without decay until the freeze pedal control goes off. If a note is already decayin...
Page 83: The Algorithm (Alg) Page
Program mode the algorithm (alg) page 6-27 the algorithm (alg) page press the alg soft button to call up the algorithm (alg) page. The top line of the display gives you the usual mode reminder, and tells you which layer you’re looking at, as well as how many layers are in the current program. You ca...
Page 84
6-28 program mode the dsp control (dspctl) page the dsp control (dspctl) page before reading further, be sure to read algorithm basics on page 6-13 and common dsp control parameters on page 6-14. Press the dspctl soft button to call up the dsp control (dspctl) page, which is displayed below: each fie...
Page 85
Program mode the dsp modulation (dspmod) page 6-29 the label of a function-parameter depends on its corresponding function-block in the current layer’s algorithm. The above dspctl page corresponds to the following algorithm: the dsp modulation (dspmod) page before reading further, be sure to read al...
Page 86: The Output Page
6-30 program mode the output page each function-parameter’s subpage contains the programmable parameters of the highlighted function-parameter. By assigning control sources to modulate a function-parameter, you can enable real-time control of your program’s sound and behavior. You can assign src1 to...
Page 87
Program mode the output page 6-31 pan use this parameter to position the current layer’s pre-fx signal. Negative values pan the signal to the left channel, positive values pan to the right, and a value of zero pans to the center. To adjust the post-fx, final-stage gain and panning of the current prog...
Page 88
6-32 program mode the output page output: pan, gain, and mode when the layer fx mode parameter is set to layer-specific fx on the lyr_fx page, three additional parameters appear on the output page: out pan, out gain, and out pan mode. These parameters are analogous to the output parameters on the com...
Page 89: The Common Page
Program mode the common page 6-33 you can remap the keymaps of any program, but you probably won’t want to do this. Drum remapping, say, a piano program (e.G., 1 standard grand) will result in very unpiano-like behavior. Exclusive zone map the exclusive zone map is another parameter that applies pri...
Page 90
6-34 program mode the common page pitch bend range up and down use these parameters to define how much the pitch will change when you move your pitch wheel. For both pitch bend range parameters, positive values will cause the pitch to bend up, while negative values will cause the pitch to bend down. ...
Page 91
Program mode the common page 6-35 there’s a tradeoff here, since many sounds will change in timbre as these single sample roots are pitch-shifted during the portamento. This will be most noticeable for acoustic instrument sounds, and may not be noticeable at all for single-cycle waveforms like sawto...
Page 92: The Lfo Page
6-36 program mode the lfo page output: gain, pan, and pan mode the output parameters on the common page allow you to adjust the final-stage gain and panning of the post-fx signal. Use the outgain parameter to cut or boost the signal. Use the outpan parameter to pan the signal; negative values pan the...
Page 93
Program mode the lfo page 6-37 minimum rate this is the slowest rate at which the lfo runs. When its rate control is set to off, or when the control source assigned to it is at its minimum, the lfo runs at its minimum rate. As previously mentioned, the values 1/4 note, 1/8 note, 1/8 triplet, and 1/1...
Page 94: The Asr Page
6-38 program mode the asr page rate control assign any control source in the list to modulate the lfo’s rate between its minimum and maximum. A continuous control like the mod wheel is a natural choice, enabling you to get just about any rate between minimum and maximum. But you can use a switch con...
Page 95
Program mode the asr page 6-39 trigger this defines the control source that starts the current layer’s asrs. The asr starts when the trigger switches from off to on. If the trigger parameter is set to on, a global asr starts running immediately when you select a program that contains it. A local asr ...
Page 96: The Function (Fun) Page
6-40 program mode the function (fun) page the function (fun) page fun is short for function. The pc3’s four funs greatly extend the flexibility of the control sources. Each fun accepts input from any two control sources, performs a selectable function on the two input signals, and sends the result as...
Page 97
Program mode the amplitude envelope (ampenv) page 6-41 the amplitude envelope (ampenv) page amplitude envelopes have three sections: attack, decay, and release. The attack section determines how long each note takes to reach its assigned amplitude level after you trigger a note on event. The decay s...
Page 98
6-42 program mode the amplitude envelope (ampenv) page because the pc3’s rom samples are stored in a compressed format, applying an altered amplitude envelope can change more than just the amplitude of your sound, since it also changes the rate at which the samples are decompressed for playback. Whe...
Page 99
Program mode the envelope 2 (env2) and envelope 3 (env3) pages 6-43 decay segment the decay section has only one segment. It has values for time and level, just as for the attack section. The decay section begins as soon as the attack section has been completed. It starts at the same amplitude level...
Page 100
6-44 program mode the envelope control (envctl) page another difference is that ampenv always controls the amplitude of the layer, so even if you use it as a control source for other functions, it will still affect the layer’s amplitude. Env2 and env3 affect only those layers that have them assigned...
Page 101
Program mode the envelope control (envctl) page 6-45 this page is a table showing the five envelope control parameters, and their values for each of the three sections of the envelopes. Additionally, the line above the soft buttons lets you make use of the impact feature, which adds an amplitude over...
Page 102: The Program Fx (Progfx) Page
6-46 program mode the program fx (progfx) page velocity tracking use your attack velocity as the control input for the current layer’s attack section (this parameter doesn’t apply to decay or release). When the value of this parameter is greater than 1.000x, attack velocities greater than 64 make th...
Page 103
Program mode the program fx (progfx) page 6-47 on the pc3, a program can have up to 11 insert effects and 2 aux effects using up to 16 dsp “units.” an insert is essentially just an effect that you apply to a program or layer, while aux effects receive signal from all active programs’ aux sends. Note...
Page 104
6-48 program mode the program fx (progfx) page type the type parameter determines how the selected wet aux signal (i.E., with effects applied) is mixed into the final signal. Additionally, it determines the units in which the aux send parameter values are. When type is set to db, the aux send paramet...
Page 105: The Layer Fx (Lyr_Fx) Page
Program mode the layer fx (lyr_fx) page 6-49 the layer fx (lyr_fx) page press the lyr_fx soft button to call up the layer fx (lyr_fx) page. On this page, you can apply layer-specific effects. There are three layer fx modes: use program fx, layer-specific fx , and use another layer’s fx. Use program fx...
Page 106: The Controllers (Ctls) Page
6-50 program mode the controllers (ctls) page the controllers (ctls) page press the ctls soft button to call up the controllers (ctls) page. The controllers page is a list of the controllers on the pc3 you will be most likely to use as control sources and the values of those controllers. The page ap...
Page 107: Function Soft Buttons
Program mode function soft buttons 6-51 function soft buttons the remainder of this chapter describes the soft buttons that perform specific functions, as opposed to selecting programming pages. The descriptions below are arranged in the order in which you would see the soft buttons if you pressed th...
Page 108
6-52 program mode function soft buttons name call up the page that enables you to change the name of the current program. Save start the process of saving the current program. Delete delete the current program from memory. You can also delete any other program from memory by scrolling through the li...
Page 109: Editing Kb3 Programs
Program mode editing kb3 programs 6-53 editing kb3 programs you can edit a wide assortment of any kb3 program’s parameters. You can also create your own kb3 programs, though you must start with an existing kb3 program to do this. A regular pc3 program cannot be turned into a kb3 program. If you’re n...
Page 110
6-54 program mode the tone wheels (tonewl) page upper volume adjust since sample volumes can vary, while the volume of dsp-generated waveforms will remain consistent, you may find it necessary to adjust the level of the sample-based tone wheels. This parameter lets you adjust the amplitude of the upp...
Page 111: The Drawbars (Drawbr) Page
Program mode the drawbars (drawbr) page 6-55 the drawbars (drawbr) page press the drawbr soft button to view the drawbr page. This page lets you edit kb3’s drawbars. Mode when you set mode to preset, the preset drawbar settings on this page will be installed at program selection. The drawbar values ...
Page 112: The Pitch Page
6-56 program mode the pitch page the pitch page the pitch page parameters for kb3 programs is much like the pitch page parameters for vast programs. The only difference is that for kb3 programs, there are no hz, keytrk, or veltrk parameters. For a full description of the pitch-page parameters, see c...
Page 113: The Perc1 Page
Program mode the perc1 page 6-57 the perc1 page percussion is a characteristic feature of tone wheel organs. It’s especially useful while soloing, since percussion adds an extra “plink” (actually an extra tone at a defined harmonic) to the attack. You can reach the percussion parameters by pressing t...
Page 114
6-58 program mode the perc1 page harmonic this parameter switches between high and low harmonic percussion settings. The actual pitch is controlled by the lowharm and highharm parameters. On keyboard models, you can toggle between low and high harmonics by pressing assignable controller button 8 (mu...
Page 115: The Perc2 Page
Program mode the perc2 page 6-59 the perc2 page perclevel, decaytime, orglevel with these parameters you can control the amplitude and decay time of the percussion effect for all combinations of the volume and decay parameters (on the perc1 page). You can also adjust the level of the organ relative ...
Page 116
6-60 program mode the keyclk page keyclick this is where you turn key click on or off. Volume this parameter sets the level of the keyclick; the noise decays from the level you set here. This level is scaled by the drawbar levels, as well as the expression pedal level. Decay sets the basic decay tim...
Page 117: The Misc Page
Program mode the misc page 6-61 the misc page the misc page contains an assortment of control parameters, including leslie speed control and vibrato/chorus selection. Preampresp set this parameter on or off to enable or disable the preamp+expression pedal part of the kb3 model. Turning this on (the ...
Page 118
6-62 program mode the misc page leakmode selects between different leakage models, determining which leakage harmonics are emphasized. Typea provides an overall tone wheel leakage, with all tone wheels leaking a small amount. Typex, typey, and typez emulate different degrees of drawbar leakage, wher...
Page 119: The Eq Page
Program mode the eq page 6-63 lesliepedal set the pedal source to toggle between fast and slow for the leslie™ speaker rotation speed. The eq page the four column headers on this page represent two shelving bands of equalization and two parametric bands. The kb3 eq offered here, though, is not imple...
Page 120: The Program Fx (Progfx) Page
6-64 program mode the program fx (progfx) page the program fx (progfx) page this page is the same as the vast program editor progfx page (see page 6-46) except for one important difference: there is no pre/post insert parameter for the auxiliary sends. The lfo, asr, and fun pages the rest of the pag...
Page 121: Chapter 7
Setup mode 7-1 chapter 7 setup mode in setup mode, the pc3 can take on the identity of 16 distinct instruments and 16 distinct midi transmitters, each of which can use the setup’s physical controller assignments (or any subset of those controller assignments). For example, you can create a setup tha...
Page 122: The Control Setup
7-2 setup mode the control setup the control setup in addition to zone splitting and layering, setup mode is a powerful way to take advantage of the pc3’s programmable sliders, ribbon controllers, and assignable buttons. In order to provide some of the same flexibility for program mode, we created th...
Page 123
Setup mode the control setup 7-3 in summary, physical controller destinations, their curves and states, and the arpeggiator parameters all define controller assignments for programs in program mode. The other parameters have no effect; this keeps program mode relatively simple. Program mode lets you ...
Page 124: The Setup Editor
7-4 setup mode the setup editor table 7-2 gives you a quick visual reminder of how zones behave depending on their status. Remember that any changes you make to zone status in setup mode are temporary; as soon as you select another setup, that setup’s programmed zone status takes over. To change a s...
Page 125
Setup mode the channel/program (ch/prog) page 7-5 the channel/program (ch/prog) page this is the first page you see when you enter the setup editor. Here, you can select programs, midi channels, and midi bank numbers for each of the setup’s 16 zones. You can also solo or mute each zone, and assign zo...
Page 126
7-6 setup mode the channel/program (ch/prog) page channel the channel parameter defines the midi transmit channel for the currently selected zone. You can set it to any of the 16 midi channels. Normally, you will want each zone on a separate midi channel. This is necessary if you want to combine diff...
Page 127
Setup mode the channel/program (ch/prog) page 7-7 when you change the value of the program parameter, the value of midiprog automatically changes correspondingly. If you want to transmit a midi program change number different from the one corresponding to the local program, select the local program ...
Page 128
7-8 setup mode the channel/program (ch/prog) page bankmode for each zone to suit the instrument that is receiving data from it. The default setting, which works with the largest number of other instruments, is ctl 0/32. A bankmode value of k2600 is intended for use with the k2000, k2500, or k2600. T...
Page 129
Setup mode the key/velocity (key/vel) page 7-9 the key/velocity (key/vel) page the key/velocity page allows you to set key range, velocity range, transposition, and note maps for each zone. Parameter range of values default low key c -1 to g9 c -1 high key c -1 to g9 g9 transpose -128 to +127 semito...
Page 130
7-10 setup mode the key/velocity (key/vel) page low key (lokey), high key (hikey) the lokey and hikey parameters define the note range of the currently selected zone. The easiest way to change these values is to press the enter button and press the key of the note you wish to enter.You can set these ...
Page 131
Setup mode the key/velocity (key/vel) page 7-11 velocity scale (velscale) this lets you amplify or diminish velocity response. Normal response is 100%. Higher values make the keyboard more sensitive (you don’t need to play as hard to get higher midi velocities) while lower values make it less sensit...
Page 132
7-12 setup mode the key/velocity (key/vel) page velocity offset veloffset also changes the response, but in a more direct way, by adding or subtracting a constant to the key velocity. For example, if this is set to 25 (assuming a scale of 100%), then 25 is added to the velocity of every keystroke, u...
Page 133
Setup mode the key/velocity (key/vel) page 7-13 offset and scale work together. If scaling takes the velocity out of the ballpark — for example, you want to set it to 300% but that puts all of your notes at maximum velocity — using a negative offset, say around -60, can make it possible to still pla...
Page 134
7-14 setup mode the key/velocity (key/vel) page velocity curve (velcurve) velcurve lets you taper the velocity response. The default setting is linear, which means that the output velocity changes directly proportionally to the played velocity. Expand produces a curve that is less steep than the lin...
Page 135
Setup mode the key/velocity (key/vel) page 7-15 crossfade is designed to be used in tandem with the reverse crossfade curve, enabling you to perform smooth crossfades between different programs. Bump tapers velocity response to resemble a bell curve, so that notes are loudest when your keystrike vel...
Page 136
7-16 setup mode the key/velocity (key/vel) page low velocity (lovel), highvelocity (hivel) lovel and hivel set the minimum and maximum velocity limits that the current zone transmits. A keystroke in the current zone whose velocity — after it has been scaled and offset — is below the minimum does not...
Page 137
Setup mode the pan/volume (pan/vol) page 7-17 the pan/volume (pan/vol) page by changing the parameters on this page, you can define how each zone sends midi volume and pan messages. Entry volume, exit volume entry volume enables you to control the initial midi volume setting for each zone of the curr...
Page 138: The Bend Page
7-18 setup mode the bend page most programs respond to pan messages on the next keystrike. This means that if you hold a note and change the pan, the current note will stay at its current position until you strike it again. However, a pc3 program that uses the panner algorithm will respond to real-t...
Page 139: Controllers
Setup mode controllers 7-19 pitchdwn ). Any physical controller that uses the control destination list can be assigned to pitchup or pitchdwn. To keep things simple though, you will normally want to use bendup as a pitch wheel destination and use auxbend 1 and auxbend 2 for other controllers, such a...
Page 140
7-20 setup mode controllers the pc3’s physical controllers include the following: • the nine sliders (a, b, c, d, e, f, g, h, i) in the assignable controllers section • the two continuous control pedal jacks (cc pedal 1 and cc pedal 2) • the optional ribbon controller, which you can define as a one- ...
Page 141
Setup mode controllers 7-21 switch controllers the controller destination list the table below contains the available values for the destination parameter for each controller, in scrolling order. Note that the pc3 has destinations with controller numbers greater than 127—there are 127 midi controlle...
Page 142
7-22 setup mode controllers 7 volume midi volume 8 balance midi balance 9 midi 09 10 pan midi pan—programs which use the panner algorithm will respond to real-time pan adjustments; all other programs will respond on the next note start 11 express midi expression—an attenuator for fading in and out. ...
Page 143
Setup mode controllers 7-23 92–95 midi 92–95 midi controllers 92–95 96 note st note state—sends 0 for off and 127 for on 97 key st key state—sends 0 for off and 127 for on 98 keynum key number—sends key number of the pressed key 99 bkeynum bipolar key number—sends the key number for the pressed key ...
Page 144
7-24 setup mode controllers 126 rel state release state—sends a value of 127 during the release portion of the amplitude envelope, and sends a value of 0 otherwise 127 on 128 pitch pitch—values above and below 64 bend the pitch up and down, respectively 129 pitchrev pitch—values above and below 64 b...
Page 145
Setup mode controllers 7-25 155 arpvel arpeggiator velocity (see the arpeggiator (arpzon) page on page 7-38) 156 arpdur arpeggiator duration (see the arpeggiator (arpzon) page on page 7-38) 157 latch arpeggiator latch (see the arpeggiator (arpzon) page on page 7-38) 158 latch2 arpeggiator latch 2 (s...
Page 146
7-26 setup mode controllers continuous controller parameters the continuous (physical) controllers are those that have a range of values: the two wheels, the optional ribbon controller, the nine sliders, the two continuous control pedals, the optional breath controller (the jack of which is connecte...
Page 147
Setup mode controllers 7-27 entry (ent) and exit values entry value allows you to specify an initial value for a controller in a setup that will be sent whenever you select that setup. For example, if you want to make sure that all of the modulation in a zone is turned off when you select a setup, a...
Page 148
7-28 setup mode controllers on control (oncontrol) oncontrol determines what midi controller or other message will be sent when the switch is on—that is, either pressed and held or toggled from the off position. The list of available controllers on page 7-21 is the same as for the continuous control...
Page 149: The Wheel Page
Setup mode the wheel page 7-29 the wheel page the two wheels are typical of what is found on many keyboards. The left one is normally used for pitch bend and springs back to center, while the right wheel is normally used as a standard mod wheel. On the wheel page in the setup editor, the pitch wheel...
Page 150: The Slider and Slid2 Pages
7-30 setup mode the slider and slid2 pages the slider and slid2 pages you can assign each of the pc3’s nine programmable sliders to a destination on each of the 16 zones. Or, you can assign any combination of sliders to the same zone, allowing you tremendous flexibility. For example, you can assign s...
Page 151
Setup mode the continuous control pedal (cpedal) page 7-31 the continuous control pedal (cpedal) page if you look at the back of the instrument, you will see that there are two jacks for plugging in two cc (continuous control) pedals and a jack labeled breath controller. Like the nine programmable s...
Page 152: The Pressure (Press) Page
7-32 setup mode the pressure (press) page the pressure (press) page the pc3 features mono pressure, commonly called aftertouch on other keyboards. A word about pressure: key range in a zone does not define which notes will generate pressure in that zone. If pressure is enabled in a zone, playing with...
Page 153
Setup mode the footswitch pages (ft sw1, ft sw2, ft sw3) 7-33 the footswitch pages (ft sw1, ft sw2, ft sw3) on the back of the instrument, there are three jacks for footswitch pedals. All the foot switches in the default control setup are set to a switch type that doesn’t generate a note, and conseq...
Page 154
7-34 setup mode the arpeggiator switch (arp sw) page the arpeggiator switch (arp sw) page the pc3 keyboard offers two panel switches, located above the pitch and mod wheels. The left switch is the arp (short for “arpeggiator”) button. By default, the arp switch functions as the arpeggiator switch, a...
Page 155: The Switch Page
Setup mode the switch page 7-35 the switch page the right panel switch is the sw button, located above the modwheel. By default, this switch is assigned to midi29, but you can assign this switch to any midi controller. The switch page parameters are described in switch controllers on page 7-21. Para...
Page 156: The Ribbon Page
7-36 setup mode the ribbon page the ribbon page the ribbon page lets you define the controller assignment for the pc3’s ribbon controller. The optional ribbon controller senses movement when you press on it and move your finger left or right; this creates numerous possibilities for controlling pitch, ...
Page 157
Setup mode the ribbon configuration (ribcfg) page 7-37 the ribbon configuration (ribcfg) page once you’ve selected a destination for the optional ribbon controller, you can use the parameters on the ribcfg page to define how the ribbons respond to finger position and pressure. Ribbon configuration you ca...
Page 158
7-38 setup mode the arpeggiator (arpzon) page absolute means that the zero point for the ribbon is always at exactly the same physical location on the ribbon. By default this is the center of the ribbon, although you can use the center parameter to put the zero point elsewhere. In absolute mode, jus...
Page 159
Setup mode the arpeggiator (arpzon) page 7-39 active the first parameter on the arpeggiator menu isactive, which specifies whether or not the arpeggiator is on for the current zone. This parameter can be switched from the arpzon page, or for real-time control, it can be switched on using controller nu...
Page 160
7-40 setup mode the arpeggiator (arpzon) page latch latch determines how the arpeggiator responds to notes when they are triggered. Keys means that the arpeggiator plays only while you are holding one or more keys down (or note triggers on). As you play different notes, they get added to the arpeggi...
Page 161
Setup mode the arpeggiator (arpzon) page 7-41 random plays the currently latched notes in completely random order. Shuffle plays them at random, but keeps track of the notes so that no note repeats until all of the others have played. Walk is a “random walk” order: each successive note is either the ...
Page 162
7-42 setup mode the arpeggiator (arpzon) page unipolar means that after playing up to the shift limit, the arpeggiator begins shifting notes in the opposite direction, until it reaches the original pitch, where it reverses again. To determine the next note when it reaches the shift limit, the arpegg...
Page 163
Setup mode the arpeggiator (arpzon) page 7-43 the arpeggiator can be a lot of fun, even if you don’t always understand exactly what it’s doing. Keep in mind that the stranger the algorithm you set up, the more unlikely the notes will stay close to one key, so if you want to create something that’s g...
Page 164: The Common Page
7-44 setup mode the common page the common page the common page contains parameters that effect every zone in the current setup. Tempo when clock source is set to internal, the tempo parameter sets the pc3 system’s tempo. The tempo parameter values are in units of bpm (beats per minute). Clock sourc...
Page 165
Setup mode the common page 7-45 arpeggiator global (arpglobal) with the arpglobal parameter, you can set each zone’s arpeggiator to act as if they all have the same parameters on the arpzon page. In addition to off, there are as many arpglobal setting as there are zones in the current setup. For exa...
Page 166: Riffs
7-46 setup mode riffs kb3 channel with this parameter, you can specify the kb3 channel in the current setup. Note that if you assign a kb3 program to a zone not assigned to the kb3 channel, the pc3 will notify you on the ch/prg page. For setups with kb3 and vast programs, you can program a switch to...
Page 167
Setup mode the riff1 page 7-47 riff setting the riff parameter to on will enable the riff feature for the current zone in setup mode. Setting this parameter to off will disable the riff for this zone. Song select the song you wish to use in the song parameter by using the alpha wheel, -/+ buttons, o...
Page 168
7-48 setup mode the riff1 page so, if you use the settings described above and in trigger, you setup’s riff will start when you press a#0, and it will stop when you press and release a0. Note: the lokey and hikey values on the keyvel page do affect the riff. If your riff's trigger and release notes ...
Page 169: The Riff2 Page
Setup mode the riff2 page 7-49 zone or to the first available zone). If another riff is already running, downbeatwait behaves just like downbeat. With this synctype to anybeatwait, the riff will wait for the next beat to start. The difference from anybeat is that if there is no riff to sync to, this ...
Page 170
7-50 setup mode the riff2 page link the link parameter allows you to have a riff play only while a key is pressed. Set the trigger and release ranges, and any key that is pressed and held within this range will play the selected riff. Release the key and the riff will stop. Playing any other key in ...
Page 171
Setup mode the riff2 page 7-51 start use the start parameter to specify the riff start point. The time format is bar : beat : tick. Beat can be set from 1 to 4. Tick can be set from 0 to 959. Since there are 960 possible start points within a beat, you can specify your riff to start on any common be...
Page 172: The Utility Soft Buttons
7-52 setup mode the fx pages: fx, auxfx1, auxfx2, and mastfx velocity this parameter allows you scale the value of the velocities that were recorded in the sequence by values from 0% to 255%. The fx pages: fx, auxfx1, auxfx2, and mastfx the four setup mode fx pages—fx, auxfx1, auxfx2, and mastfx—wor...
Page 173
Setup mode the utility soft buttons 7-53 save pressing save calls up the standard save dialog. Simultaneously pressing the plus and minus data entry buttons toggles between saving the setup to the first available empty location, or replacing a currently existing setup. Delete this erases a setup from...
Page 174
7-54 setup mode the utility soft buttons.
Page 175: Chapter 8
Quick access mode 8-1 chapter 8 quick access mode in quick access mode, you can select programs or setups with a single press of an alphanumeric button (or with other data entry methods). The pc3 offers a number of ways to quickly make selections while performing, but only quick access mode lets you...
Page 176: Making Your Own Qa Banks
8-2 quick access mode making your own qa banks each bank contains ten memory slots, or entries, where you can store programs or setups in any combination. Any program or setup in the currently selected bank can be selected with the numeric buttons 0 through 9. If the highlighted entry contains a pro...
Page 177
Quick access mode making your own qa banks 8-3 the qa editor the only way to edit a locked qa bank without unlocking it is through the qa editor. Though you can use the qa editor to edit both locked and unlocked banks. To enter the qa editor, press either the edit button or the edit soft button, and...
Page 178
8-4 quick access mode making your own qa banks.
Page 179: Chapter 9
Effects basic overview 9-1 chapter 9 effects the pc3 boasts a powerful effects processor that puts the power of an entire studio at your fingertips. This chapter contains everything you’ll need to know to use the pc3’s effects and chain editor to their fullest potentials. This chapter begins with a f...
Page 180
9-2 effects basic overview note that when an aux effect is applied post-insert, the wet aux signal has a series of effects applied to it—i.E., cascaded effects. When an aux effect is applied pre-insert, the wet aux signal has no insert effect applied to it, and the final output has parallel effects—i...
Page 181
Effects basic overview 9-3 the chanfx page in effects mode—or the fx page in either setup or song mode—provides per-channel control over effects allocation. The channel with a box around its channel number is the current channel in program mode, or the specified aux effect channel in setup and song m...
Page 182
9-4 effects basic overview master effects there are two master effects that are applied at the final stage of the signal path: an eq and a compressor. These are global effects, and apply to all signals routed to the pc3’s primary outputs. Neither the eq nor the compressor use up any dsp units, so you...
Page 183: Effects Mode
Effects effects mode 9-5 effects mode press the effect mode select button to enter effects mode. As stated previously, the configurations in effect mode apply in every mode except for setup mode and song mode— these modes have their own effects page (almost identical to those in effects mode) whose c...
Page 184
9-6 effects the auxfx1 and auxfx2 pages if override is set to no, the top line of the page displays the aux 1 chain that is loaded for the current program, as well as the current channel. In the case of the screenshot below, the aux 1 chain of the current program is 906 medium hall2, and the current...
Page 185: The Master Page
Effects the master page 9-7 the master page note: in setup mode and song mode, this page corresponds in appearance and function to the mastfx page, though the mastfx page works on a per setup/song basis. Pressing the master soft button calls up the master page. The master page contains the settings ...
Page 186: The Chain Editor
9-8 effects the chain editor the chain editor pressing the edit button while a chain (other than 0 none) is highlighted—on any of the various effects pages—will call up the chain editor. From the program editor, the program’s insert and aux chains can be edited from the progfx and lyrfx pages. In se...
Page 187: The Mod Pages
Effects the mod pages 9-9 editing effect-blocks to edit the parameters of an effect, select its effect-box on the main page and press the edit button. For each effect, there are one or more pages of parameters that are specific to that effect. Any parameter controlled by an effect mod will display a ...
Page 188: Effects Parameters
9-10 effects fxlfo, fxasr, and fxfun pages fxlfo, fxasr, and fxfun pages the fxlfo, fxasr, and fxfun pages are the pages from which you edit the effects-only control sources. These are control sources that can be used by the effects mods in the current chain. The parameters on these pages work exact...
Page 189
Effects general parameters 9-11 value is context-sensitive—in this example, the choices would be “rvb->cmp” and “cmp->rvb”. A/dry->b is also found in many combination algorithms, and controls the amount of signal that will pass dry (unprocessed) through the first component into the second component. ...
Page 190: Delays
9-12 effects delays wet bal (wet balance). Some reverb algorithms are actually two stereo reverbs in one, with each one receiving a different mono signal. This balances the outputs of the two reverbs—0% means they are being mixed equally. Delays there are two types of taps in the multitap delays: th...
Page 191: Equalizers (Eq)
Effects equalizers (eq) 9-13 diff amt adjusts the diffuser intensity. Range is 0 to 100%. C fdbk n dly adjusts the delay length of the c channel’s nth feedback tap, fed back to the c channel’s delay input. Range is 0 to 2600 ms. Spectral multitap delays these 4- and 6-tap delays have their feedback ...
Page 192
9-14 effects compressors, expanders, and gates midn freq sets the center frequency for parametric band n, with a range of 16 to 25088 hz, in increments of a semitone. Midn width set the bandwidth of the filter on band n, with a range of 0.01 to 5 octaves. Enhancers enhancers modify the spectral conte...
Page 193
Effects compressors, expanders, and gates 9-15 smoothtime smooths the output of the expander’s envelope detector by putting a lowpass filter in the control signal path. Smoothing will affect the attack or release times only when this parameter is longer than one of the other times. The range is 0.0 t...
Page 194: Chorus
9-16 effects chorus gate time is the time that the gate will stay open after the sidechain signal reaches the threshold. Its range is 0 to 3000ms. Ducking reverses the action of the gate. Normally this if set to “off”, and the gate opens when the input signal rises above the threshold. But when this...
Page 195: Flanger
Effects flanger 9-17 l/r phase or lfon lrphs adjusts the relative phases of the lfos for the left and right channels in the stereo choruses. Flanger flanging is the process of adding or subtracting a signal with a time-displaced replica of itself, which results in a series of notches in the frequenc...
Page 196: Filters
9-18 effects filters dly fine adjusts the delay with a resolution down to 0.2 ms. Range is -20.0 to 20.0 ms. Spacing determines the starting pitch of the descending buzz and how fast it descends, by setting the initial separation of impulses and the subsequent rate of increasing impulse separation. ...
Page 197: Distortion
Effects distortion 9-19 max freq is the resonant frequency of the filter at the peak of the internal envelope. It can be set lower than min freq (above), in which case the filter will sweep downwards, then back up. Range is 16 to 8372 hz. Trigger is the input-signal threshold at which the envelope det...
Page 198: Rotating Speakers
9-20 effects rotating speakers cab preset selects from eight cabinet simulations which have been created based on measurements of real guitar amplifier cabinets. The presets are: basic, lead 12, 2x12, open 12, open 10, 4x12, hot 2x12, and hot 12. Cab bypass switches on and off the cabinet-simulation ...
Page 199
Effects rotating speakers 9-21 lo size and hi size are the effective sizes (radius of rotation) of the rotating speakers in millimeters. This affects the amount of doppler shift or vibrato of the low frequency signal. The range is 0 to 250 mm. Lo trem and hi trem control the depth of tremolo (amplit...
Page 200: Tremolo and Autopan
9-22 effects tremolo and autopan vibrato/chorus the vibrato/chorus algorithm (and also the kb3 effects algorithm) simulates the vibrato and chorus effects on a tone wheel organ, and is used in conjunction with the rotary speaker. It has several unique parameters: vibchinout is an in/out switch for t...
Page 201: Pitcher
Effects pitcher 9-23 50% weight is the relative amount of attenuation added when the lfo is at the -6db point. This causes the lfo shape to bow up (positive values) or down (negative values). Range is -16 to 3 db. L/r phase sets the phase relationship of the channels. “in” flips the left channel’s lf...
Page 202: Stereo Simulation
9-24 effects stereo simulation stereo simulation the mono to stereo algorithm converts a monaural input to simulated stereo output. In select selects the input signal to be “stereo-ized”. It can be left, right, or both: (l+r)/2. Centergain is the level of the summed left and right channels. Range is...
Page 203: Fxmod Diagnostic
Effects fxmod diagnostic 9-25 fxmod diagnostic this algorithm allows you to view the current levels of any data sliders, midi controls, switches, or internally generated vast lfos, asrs, funs, etc. Which are available as modulation sources. It has no effect on any signal being routed through it. Up ...
Page 204
9-26 effects mono algorithms.
Page 205: Chapter 10
Midi mode the transmit page 10-1 chapter 10 midi mode the pc3 sends and receives midi on traditional 5-pin din connectors and through usb. Midi can be sent and received on all ports at once. Press the midi mode button to enter midi mode. There are three pages in midi mode: • transmit (xmit soft butt...
Page 206
10-2 midi mode the transmit page control setup this is where you select the current control setup, zone 1 of which sets the physical controller assignments for all programs while you’re in program mode. Refer to chapters 6 and 7 for more information on the control setup. Destination the destination ...
Page 207: The Receive Page
Midi mode the receive page 10-3 pressure map this is like the velocity map, but it controls the aftertouch values sent by the pc3 to its midi out port. Use this exclusively to adjust the response of midi devices connected to the pc3’s midi out port. Changing the pressure map on this page does not af...
Page 208
10-4 midi mode the receive page basic channel the basic channel determines which channel will always be available to receive midi information. Depending on the midi receive mode (below), the basic channel may be the only receiving channel, or one of several. Midi receive mode (midi mode) the midi mo...
Page 209: The Channels Page
Midi mode the channels page 10-5 instrument has a different sysexid. Then you can direct sysex messages to the appropriate pc3 with the sysexid byte that’s included with every sysex message. A value of 127 specifies “omni receive.” that is, at this value, a pc3 responds to a sysex message regardless ...
Page 210
10-6 midi mode the channels page enable use this parameter to turn the currently selected channel on or off. When on, the channel will receive midi information, and the settings of the parameters on the midi channels page will be in effect. When off, the channel will ignore all midi information. Pro...
Page 211: Program Change Formats
Midi mode program change formats 10-7 program change formats the pc3 can store more programs than the midi program change specification can handle (midi lets you send program change numbers from 0 to 127 or 1 to 128 only). So we’ve designed a system that makes program selection more flexible. This is ...
Page 212
10-8 midi mode program change formats if your pc3 is already in the memory bank you want to use, you can send it single pchs from 0 to 127, to select programs within that memory bank. The pc3’s response depends on the setting for the bank/select parameter on the midimode recv page. If you want to ch...
Page 213
Midi mode program change formats 10-9 memory bank. You’ll know which memory bank is selected by looking at the id of the currently selected quick access bank in the top line of the quick access mode page. Qaccess and midi transmission if you’re in quick access mode and you’re using the qaccess forma...
Page 214
10-10 midi mode the soft buttons in midi mode the soft buttons in midi mode the first three soft buttons select the three midi mode pages. The prgchg soft button lets you send a program change command on any midi channel. The rsetch soft button lets you return all channel parameters to their default ...
Page 215: Chapter 11
Master mode master mode page 1 11-1 chapter 11 master mode press the master mode button to enter master mode, which contains parameters affecting the pc3’s overall performance. When you exit master mode it saves a master table (unless mastertablelock is on — more on this later) which is basically th...
Page 216
11-2 master mode master mode page 1 tune adjusting the value of this parameter tunes every program in the pc3 by the amount you specify. Tuning can be adjusted up or down 100 cents (one semitone) in one-cent increments. This parameter is useful for getting in tune with recordings and acoustic instru...
Page 217
Master mode master mode page 1 11-3 digital output this digital output parameter specifies the pc3's digital output sample rate. Internally clocked sample rates go from 44.1k up to 192k. Externally synced sample rates cover 20-220khz in 3 ranges. Be sure the external clock frequency is within the ran...
Page 218: Master Mode Page 2
11-4 master mode master mode page 2 master mode page 2 velocity map the velocity map determines the way the pc3 generates midi velocity information. Different maps generate different velocity values for the same attack velocity. If you change the setting of the velocity map parameter, remember that ...
Page 219
Master mode master mode page 2 11-5 scroll through the list of intonation tables, and listen for the differences between semitones. Some of the intervals between semitones may be quite different from equal intonation, but you’ll notice that all notes are precisely tuned with notes that are an octave...
Page 220
11-6 master mode master mode page 2 demo button the demo button parameter determines whether or not pressing the play/pause button plays a demo song for the current program. Numeric entry global means that any entry you make from the alphanumeric keypad will select the object indicated, regardless o...
Page 221
Master mode the soft buttons in master mode (page 1 and page 2) 11-7 the soft buttons in master mode (page 1 and page 2) save pressing the save soft button saves the current configuration of the master pages (both 1 and 2). About pressing the about soft button calls up the general info page for the p...
Page 222
11-8 master mode the soft buttons in master mode (page 1 and page 2) delete the delete objects utility is very useful for reclaiming unused ram in your pc3. This utility allows you to select any arbitrary group of objects for deleting. This can be a convenient way to delete individual or selected gr...
Page 223
Master mode the soft buttons in master mode (page 1 and page 2) 11-9 utils pressing the utils soft button calls up the utility page, which gives you access to two analytic and diagnostic tool. Additionally, pressing the two right-most soft buttons will call up the utility page from any mode or edito...
Page 224
11-10 master mode the soft buttons in master mode (page 1 and page 2) loader pressing the loader soft button calls up the boot loader. See appendix b. Reset press the reset soft button if you want to return your pc3’s memory to the state it was in when you bought it. Caution: resetting the pc3 syste...
Page 225: Chapter 12
Song mode and the song editor getting started with the sequencer 12-1 chapter 12 song mode and the song editor getting started with the sequencer the pc3’s sequencer is a powerful and versatile tool for songwriters, composers, and anyone else who wants to record and play back songs. As with any tool...
Page 226
12-2 song mode and the song editor song mode: the main page the events field on the top line displays the free ram available for events in the selected song. The song status,also on the top line of the display, is always one of the following: stopped the default sequencer status; also appears when yo...
Page 227
Song mode and the song editor song mode: the main page 12-3 recording track (rectrk) the rectrk parameter determines which track is record enabled. Set the record enabled track to mult to record more than one channel simultaneously. When rectrk is set to a single track (1–16), record (r) is displaye...
Page 228
12-4 song mode and the song editor song mode: the main page pan you can set an initial pan position (the balance between the left and right audio channels) for the playback and recording of each track as a value between 0 and 127. A value of 64 is center. If the channel of the rectrk or the control ...
Page 229
Song mode and the song editor song mode: the main page 12-5 the track selected as the rectrk will display an (r), designating it as the recording track. If the rectrk is set to mult, initially all empty tracks will have record (r) as a track status indicator, any of which can be switched back to emp...
Page 230: Save Changes
12-6 song mode and the song editor song mode: the main page the load, save, and export soft buttons the load soft button calls up a scrolling list from which you can quickly locate and load a sequence. You can select a sequence using either the alpha wheel or -/+ buttons, or you can enter a sequence...
Page 231: Song Mode: The Big Page
Song mode and the song editor song mode: the big page 12-7 song mode: the big page on the big page, the pc3 displays—in a large font, thus the page’s name—the current time/ location of the “playhead” of the sequencer in a bar : beat : tick format (like the riff time/ location display). Also displaye...
Page 232: Song Mode: The Fx Pages
12-8 song mode and the song editor song mode: the fx pages when recording beyond your initially specified song end point, you’ll notice that the song end location automatically moves and rounds to the next bar, so as to always be ahead of the playhead. It is possible to move the song end point to a l...
Page 233: Song Mode: The Mixer Page
Song mode and the song editor song mode: the mixer page 12-9 song mode: the mixer page the mixer page shows the initial settings for the program number, panning, and volume of each track (in groups of 8). The bottom part of the screen displays information about the currently selected track. To chang...
Page 234: Done
12-10 song mode and the song editor song mode: the metro page the done soft button if no changes were made in the mixer page, pressing the done soft button calls up the main page. If changes were made, pressing the done soft button calls up the “save changes” dialogue. Song mode: the metro page all ...
Page 235: Rec
Song mode and the song editor song mode: the metro page 12-11 channel this parameter determines the midi channel to which the metronome program and events are sent. Strong note this parameter determines the midi number of the note played by the metronome for the downbeats (the “1” of each measure). ...
Page 236
12-12 song mode and the song editor song mode: the filter pages (recflt and plyflt) song mode: the filter pages (recflt and plyflt) on the recflt and plyflt pages you can specify what event are ignored during, respectively, recording and playback. Both pages have the same parameters with the same ra...
Page 237: Rec
Song mode and the song editor song mode: the filter pages (recflt and plyflt) 12-13 lovel lovel determines the lowest note on/off velocity that is recorded/played back when notes is set to on. Hi the hi to the right of lovel determines the highest note on/off velocity that is recorded/played back wh...
Page 238: Done
12-14 song mode and the song editor song mode: the misc page the done soft button if no changes were made in the recflt/plyflt page, pressing the done soft button calls up the main page. If changes were made, pressing the done soft button calls up the “save changes” dialogue. Song mode: the misc pag...
Page 239: Song Mode: The Stats Page
Song mode and the song editor song mode: the stats page 12-15 grid the grid parameter determines the resolution of quantization and the position of the grid points. Swing the swing parameter determines the amount (in units of percent) of “swing” applied during quantization. Release the release param...
Page 240: The Song Editor
12-16 song mode and the song editor the song editor the song editor in general, you’ll get to the song editor pages by pressing the edit button any time you’re in song mode. There’s one exception: if the program parameter is currently highlighted on the display, you’ll enter the program editor when ...
Page 241
Song mode and the song editor song editor: the common page 12-17 timesig affects the click, playback looping, and locate function as well as some editing operations. Does not change the recorded data, though it does change the way data is displayed on the screen. Fx track the pc3 uses the channel of...
Page 242
12-18 song mode and the song editor song editor: the track page soft buttons on the common page track – calls up the track page. This page accesses useful track based edit functions. There is a selectable edit function that can be applied to the selected track or all tracks in your song. The track p...
Page 243
Song mode and the song editor song editor: the track page 12-19 since these parameters are common to most track functions, we will define them first. Then we’ll describe the individual functions along with the parameters specific to each, which are normally found on the left side of the page. The funct...
Page 244
12-20 song mode and the song editor song editor: the track page lovel an attack velocity range can be specified as criteria for selecting note events for editing. The lovel parameter sets the lowest velocity a note needs to have in order to be edited. Notes on the selected track(s) with a attack velo...
Page 245
Song mode and the song editor song editor: track functions 12-21 song editor: track functions erase this function erases specified events from a region of time, but it doesn’t delete the region of time. The result is like erasing a section of recording tape. If you want to completely remove a segment...
Page 246
12-22 song mode and the song editor song editor: track functions specify a bar, beat, and tick location in the destination track where the copied data will be placed with the location parameter. If the length of the copied region extends from the location point beyond the song’s existing end point, ...
Page 247
Song mode and the song editor song editor: track functions 12-23 insert the insert function is used to add blank time to the current song, modifying the song’s end point appropriately. The insert function will affect all tracks. This is similar to splicing a piece of blank tape to an existing segmen...
Page 248
12-24 song mode and the song editor song editor: track functions quantize use the quantize function to adjust the timing of note events. Keep in mind that only note events are quantized; other types of events, such as controllers, are not quantized. Quant : off/1 to 100% the quantize parameter deter...
Page 249
Song mode and the song editor song editor: track functions 12-25 shift the shift function allows you to offset the existing midi events forward or backward in time any number of ticks (1/480th of a beat) and beats. This function only affects the end point if any of the shifted events are after the e...
Page 250
12-26 song mode and the song editor song editor: track functions grab grab is similar to the copy function, except that the grab function allows you to copy selected data from tracks that exist in other songs in memory. Srcsong : song list the source song parameter is set to the id and name of the s...
Page 251
Song mode and the song editor song editor: track functions 12-27 change the change function is used to modify attack velocities, release velocities, or the values of any existing controller data on the current track. A static change of values can be made as well as having the change take place over ...
Page 252: Song Editor: The Event Page
12-28 song mode and the song editor song editor: the event page remap use the remap function to apply the values of any one type of controller data, already recorded on a track, to another controller type. The effect the real time changes of the “old” controller had will be replaced by the effect th...
Page 253
Song mode and the song editor song editor: the event page 12-29 to scroll through the events, make sure the location (bar and beat, in the first column) is highlighted. Use the alpha wheel, the up and down cursor buttons, or the plus/minus buttons. As you scroll through the events, each event is exec...
Page 254
12-30 song mode and the song editor song editor: the event page event type and value the event type and value region displays the midi event type (and related information) at each event-list location in the song. Different event types display different kinds of information, and have different editab...
Page 255: Chapter 13
Storage mode storage mode page 13-1 chapter 13 storage mode storage mode lets you use xd memory cards to load, save, back up, and copy files between the pc3 and the outside world. Storage mode in the pc3 allows flexibility to organize files and their contents. Its features can save you time by allowing...
Page 256: Directories
13-2 storage mode directories using xd cards you can use xd cards for all your backup and storage requirements. Xd cards are sold in a variety of sizes; the pc3 will work with any size, so long as it’s 32mb – 256mb, type s or no type stated, and formatted as fat16. The xd card slot is on the back pa...
Page 257: Common Dialogues
Storage mode common dialogues 13-3 the root directory is displayed as a backslash: path:\ if you press the load button and load a file from a subdirectory called sounds, the path field will appear as path:\sounds\ the backslash character is a directory separator, as in the following path: path: ewtu...
Page 258: The Store Page
13-4 storage mode the store page the file name/new directory/rename dialogue when you create a new file in storage mode, create a new directory, or rename a file or directory, the pc3 prompts you to enter the object’s name. This file name dialogue appears as shown below, although both the new director...
Page 259
Storage mode the store page 13-5 at the top right of the page, the display shows how much memory is available in the current storage device. Along the bottom of the page are the store page’s six soft buttons. Below is a description of the function of each soft button: select select the highlighted o...
Page 260: The Load Page
13-6 storage mode the load page there are five soft buttons on the store advanced page: select select the highlighted object. An asterix (*) appears between the id and object type of selected objects. Next scroll to next entry. Same function as pressing the down or + buttons, or turning the alpha whe...
Page 261
Storage mode the load page 13-7 the objects in the list are usually grouped by type (program, setup, etc.). The list can be scrolled using the alpha wheel or the up or down cursors. Each line in the scrollable list represents one object, and displays the object’s type, id, and name. The id numbers a...
Page 262
13-8 storage mode the load page loading methods once you have pressed ok to decide on what bank to use, you will see this dialog: the soft buttons control the mode for loading and renumbering of objects from the file. Here’s how they work: ovfill first deletes all ram objects in the selected bank, an...
Page 263
Storage mode the load page 13-9 number 69 (its bank-specific id in the 385...512 bank) when deciding upon a new object id. If the 129...256 bank was previously empty, and the load mode is append, then the program will end up with id 197 (128 + 69). For loading as “everything,” the id number for an ob...
Page 264: The Utilities (Utils) Page
13-10 storage mode the utilities (utils) page the utilities (utils) page pressing the utils soft button calls up the utilities page, where the pc3 displays the contents of the current directory, in an alphabetized scrolling list. If the current directory cannot be located (for example, if you’ve cha...
Page 265: Appendix A
Midi implementation chart a-1 appendix a midi implementation chart model: pc3 manufacturer: date: 12/01/07 young chang version 1.0 digital synthesizers mode 1: omni on, poly mode 2: omni on, mono o = yes mode 3: omni off, poly mode 4: omni off, mono x =no function transmitted recognized remarks basi...
Page 266
A-2 midi implementation chart.
Page 267: Appendix B
B--1 appendix b pc3 bootloader the bootloader is the program that runs when the pc3 is first turned on. Its job is to check that hardware is functional, initialize the digital systems, and load the main synthesizer program. Under normal circumstances you might not even notice that the bootloader is t...
Page 268
B--2 updating pc3 software and objects the most common use of the bootloader menu is to update your pc3 using new versions of software and objects supplied by kurzweil. New versions will be made periodically as we add new features or improve performance; download these free upgrades from our website...
Page 269
B--3 pc3 diagnostics this program runs specific hardware checks on pc3 systems. Most of the time you won’t need to run the diagnostics, but if you’re having some problems with the instrument it may be helpful to perform these interactive tests when contacting kurzweil support. To exit the diagnostic ...
Page 270
B--4 restoring the pc3 file system it is possible (though not likely) that the pc3 file system can become corrupted due to hardware failure or power outage during certain operations. This will result in the bootloader being unable to bring up the synthesizer system correctly. In such a circumstance, ...
Page 271: Appendix C
C--1 appendix c changing pc3 voltage in most cases, you will not need to change the voltage on your pc3. However, since different countries use different standard voltage settings, there may be times when you need to make the change. The pc3’s fuse holder (where the power cable plugs in) is where yo...
Page 272
C--2 pull up gently to open the fuse holder cover. The cover is hinged next to the power cord connection. Pry out the fuse holder..
Page 273
C--3 if there is only one fuse in the fuse holder, you must remove the metal clip on the empty side. The clip just pulls off:.
Page 274
C--4 the clip removed from the fuse holder: remove the fuse. Install two 250 ma fast blow fuses for 230v or two 500 ma fast blow fuses for 115v, one on each side of the fuse holder. The fuse holder will accept either 1.25" x 0.25" size or 5 mm x 20 mm size fuses. If using 5 mm x 20 mm size fuses, in...
Page 275: Appendix D
Pc3 objects (v 1.20) programs d-1 appendix d pc3 objects (v 1.20) programs press the info soft button for controller information. Id program id program id program 1 standard grand 27 supertramp wurly 53 lord’s b3 mwheel 2 studio grand 28 flyddarkside/wah 54 ole time gospel 3 rubensteinswcomp 29 what...
Page 276
D-2 pc3 objects (v 1.20) programs 79 airy pad 112 levin/gabrlfrtls 145 xfadbelltonerhds 80 cathedral vox 113 nyc kits 146 extreme hardstrk 81 classic comp 114 la kits 147 fagen phaser 82 fitty-fitty lead 115 rock kits 148 royalscam rhds 83 big old jupiter 116 roots/indie kit 149 austnctylmtswrly 84 ...
Page 277
Pc3 objects (v 1.20) programs d-3 178 whiter shade b3 211 arp2500 brass 244 drypumpin'drums 179 doors vox 212 synbell morph 245 60s rock&soul 180 indagardenoveden 213 perc>morph>bass 246 headhunters kit 181 animals vox 214 eviloctavewheel 247 frantichousedrms 182 magic wolf 215 tranceriff 248 dance/...
Page 278
D-4 pc3 objects (v 1.20) programs 277 downwardspiralmw 310 mono trekkies 343 organmode pn/hrp 278 va1dstpulsewheel 311 disco divebomb 344 dr.John's rmi 279 neworderpulses 312 mutrontweetyperc 345 phase sw organ 280 va1 detunedpulse 313 disgusting bass 346 spaced out bach 281 va1 detuned saws 314 va1...
Page 279
Pc3 objects (v 1.20) programs d-5 376 breakestra kit 409 reeds & bells 442 woodwind section 377 cosmic sus pedal 410 perc atk strings 443 ensemble wwinds 378 digitalmoonscape 411 william tell a 444 bassclar/clar/fl 379 falgor'slament 412 william tell b 445 solo fr horn 380 bpm bionicstrngs 413 orch ...
Page 280
D-6 pc3 objects (v 1.20) programs 475 solo viola slow 508 chimes/glock 541 pizzbass/arcolead 476 solo cello fast 509 bells across 542 lead & adagio 477 solo cello slow 510 celesteglockharp 543 adagio split 478 solo basso 1 511 chime bell 544 adagio bs/vln i 479 solo basso 2 slo 512 carillon 545 trip...
Page 281
Pc3 objects (v 1.20) programs d-7 574 verysloverythick 607 fast bassi div 640 adagio magic 575 touch thick mix 608 fast tremolo 897 ezra’s burner 576 more viola 609 legato violins i 898 hottubegospel 577 slostr prs swell 610 legato violins ii 899 b3 midrange 578 rite of strings 611 legato violin div...
Page 282
D-8 pc3 objects (v 1.20) programs 929 all out 960 vast1-3ch/perc2 1020 va1nakedpwmmono 930 j’s comper 961 fisher’s vast b3 1021 va1nakedsawpoly 931 brother jack 991 hotmalletmwheel 1022 va1nakedsqrpoly 932 model one 992 screaminwhlbass 1023 va1nakedsqrmono 933 thick gospel 993 syncwheellead 1024 va1...
Page 283: Setups
Pc3 objects (v 1.20) setups d-9 setups id setup id setup id setup 1 teknoriff sw 1-8 32 latin danzhall 63 grandpad & magic 2 bluesjam in g 33 metal 64 tinklysweepyspcy 3 techno substance 34 growth pad 65 pulsing anthem 4 acoustic split 35 morricone's fall 66 pedhold pnosolo 5 slap/ep split 36 string...
Page 284
D-10 pc3 objects (v 1.20) effect presets with algorithms effect presets with algorithms how to use these tables each effect preset in the pc3 is based on an effect algorithm from the kurzweil ksp8 effects processor. To make the fullest use of the pc3’s effects, you will need to download a copy of th...
Page 285
Pc3 objects (v 1.20) effect presets with algorithms d-11 24 real big room alg 5 classic verb 2u 25 the comfy club alg 9 diffuse verb 3u 26 spitty drum room alg 7 tq verb 3u 27 stall one alg 7 tq verb 3u 28 green room alg 7 tq verb 3u 29 tabla room alg 12 panaural room 3u 30 large room alg 7 tq verb ...
Page 286
D-12 pc3 objects (v 1.20) effect presets with algorithms 59 spacious hall alg 5 classic verb 2u 60 classic chapel alg 5 classic verb 2u 61 semisweet hall alg 5 classic verb 2u 62 pipes hall alg 404 chorusreverb 2u 63 reflective hall alg 5 classic verb 2u 64 smoooth hall alg 5 classic verb 2u 65 empty...
Page 287
Pc3 objects (v 1.20) effect presets with algorithms d-13 92 medm warm plate alg 7 tq verb 3u 93 bloom plate alg 9 diffuse verb 3u 94 clean plate alg 9 diffuse verb 3u 95 plate mail alg 11 omniverb 3u 96 realsmoothplate alg 9 diffuse verb 3u 97 classic plate alg 5 classic verb 2u 98 weighty platey al...
Page 288
D-14 pc3 objects (v 1.20) effect presets with algorithms delays 125 drum latch 2 alg 10 omniplace 3u 126 diffuse gate alg 9 diffuse verb 3u 127 acid trip room alg 10 omniplace 3u 128 ringy drum plate alg 104 gated laserverb 3u 129 oil tank alg 104 gated laserverb 3u 130 wobbly plate alg 104 gated la...
Page 289
Pc3 objects (v 1.20) effect presets with algorithms d-15 154 medslapback 76ms alg 190 moving delay 1u 155 longishslap 95ms alg 151 4-tap delay 1u 156 wide slapbk 76ms alg 191 dual movdelay 1u 157 titeslapamb 50ms alg 191 dual movdelay 1u 158 33ms ambience alg 191 dual movdelay 1u 159 17ms ambience a...
Page 290
D-16 pc3 objects (v 1.20) effect presets with algorithms chorus 191 furbelows alg 9 diffuse verb 3u 192 festoons alg 9 diffuse verb 3u 193 ducked delay alg 174 gated delay 2u 194 drum+bass zapper alg 174 gated delay 2u 195 3banddly drums=! Alg 173 3 band delay 2u 196 warped echoes alg 191 dual movde...
Page 291
Pc3 objects (v 1.20) effect presets with algorithms d-17 flange phaser flange 225 big slow flange alg 225 flanger 1 1u 226 squeeze flange alg 225 flanger 1 1u 227 sweet flange alg 225 flanger 1 1u 228 throaty flange alg 225 flanger 1 1u 229 pseudoanagtrflng alg 225 flanger 1 1u 230 flanger double al...
Page 292
D-18 pc3 objects (v 1.20) effect presets with algorithms trem / panner / spatial rotary 256 fast&slow phaser alg 250 lfo phaser 1u 257 wawawawawawawawa alg 253 singlelfo phaser 1u 258 slow swish phase alg 253 singlelfo phaser 1u 259 slippery slope alg 385 frequency offset 2u 260 static phaser 1 alg ...
Page 293
Pc3 objects (v 1.20) effect presets with algorithms d-19 distortion 288 dirtyrotors fast alg 292 vc+dist+hilorotr 2u 289 dirtyrotors slow alg 292 vc+dist+hilorotr 2u 290 moredistrotor f alg 293 vc+dist+1rotor 2 2u 291 moredistrotor s alg 293 vc+dist+1rotor 2 2u 292 heavydistrotor f alg 294 vc+dist+h...
Page 294
D-20 pc3 objects (v 1.20) effect presets with algorithms dynamics eq / filters 322 shaper->flange alg 321 flangeshaper 2u 323 shaper->reverb alg 322 shaperreverb 2u 329 aliaser alg 308 quantize+alias 1u dynamics 330 hkcompressor 3:1 alg 330 hardkneecompress 1u 331 hkcompressor 5:1 alg 330 hardkneeco...
Page 295
Pc3 objects (v 1.20) effect presets with algorithms d-21 357 phunk env filter alg 360 env follow filt 2u 358 synth env filter alg 360 env follow filt 2u 359 bass env filter alg 360 env follow filt 2u 360 epno env filter alg 360 env follow filt 2u 362 lfo sweep filter alg 362 lfo sweep filter 2u 363 ...
Page 296
D-22 pc3 objects (v 1.20) effect presets with algorithms chorus / combi 395 contact alg 387 wackedpitchlfo 3u 396 drum frightener alg 387 wackedpitchlfo 3u 397 mad hatter alg 387 wackedpitchlfo 3u 398 fallout alg 387 wackedpitchlfo 3u 399 ascension alg 387 wackedpitchlfo 3u chorus 400 basicchorusdel...
Page 297
Pc3 objects (v 1.20) effect presets with algorithms d-23 flange / combi 428 speechorusdeep alg 400 chorus+delay 1u 429 chorus room alg 404 chorusreverb 2u 430 chorus smallhall alg 404 chorusreverb 2u 431 chorus med hall alg 404 chorusreverb 2u 432 chorus big hall alg 404 chorusreverb 2u 433 chorus e...
Page 298
D-24 pc3 objects (v 1.20) effect presets with algorithms 462 flange hall alg 454 2u 463 flangedlybighall alg 453 flan+dly+reverb 2u 464 flange theatre alg 454 2u 465 flangetap synth alg 452 flange4tap 2u 466 flange room alg 453 flan+dly+reverb 2u 467 flange echo alg 452 flange4tap 2u 468 flange 4 ta...
Page 299: Index
Index-i index numerics 50% weight 9-23 a a/dry->b parameter 9-11 a->b cfg parameter 9-10 adding layers 6-51 additional sounds 1-5 adjust parameter (envctl) 6-45 algorithms d-10 editing 6-18 all controllers off 10-4 all notes off 10-4 alpha wheel 2-7, 3-9 alphabetic entry 3-9, 5-3 alphanumeric pad 3-...
Page 300
Index-ii contour 9-18 contrast 2-5 control setup 6-9 setup editor 7-2 control sources configuring 6-9 funs 6-40 key tracking 6-15 source 1 and source 2 6-16 velocity tracking 6-16 controllers entry values in program mode 6-10 controlling lfo rate 6-38 conventions for editing objects 5-1 copy song edi...
Page 301
Index-iii envelope control 6-44 envelope control parameters 6-45 envelope filter 9-18 envelopes 6-41, 6-43 eq morpher 9-14 eq page (program editor) 6-63 eqs 9-13 equalizers 9-13 erase song mode track page 12-21 event page song mode 12-28 everything loading objects as 13-9 exit button 3-8 exit values...
Page 302
Index-iv polyphony 6-54 kb3 channel 6-4 kb3 programs 2-8, 6-4 key tracking 6-15 key tracking parameter (envctl) 6-45 key tracking parameter (keymap) 6-20 key/velocity (key/vel) page 7-9 keyboard naming 5-4 keyclk page (program editor) 6-59 keymap page (program editor) 6-19 keymap parameter (keymap) ...
Page 303
Index-v minimum rate parameter (lfo) 6-37 misc page (program editor) 6-61 mod mode 9-23 mod wheel 3-5 mode buttons 3-2 mode parameter (asr) 6-39 mode selection 3-1, 4-1 modes 4-1 program 6-1 modes, using 4-2 modulator ring modulation 9-23 momentary switch type 7-27 mono sound systems 2-2 monophonic ...
Page 304
Index-vi phase parameter (lfo) 6-38 pitch 9-23 pitch bend mode parameter (layer) 6-23 pitch bend range parameter (common) 6-34 pitch page (program editor: kb3) 6-56 pitch wheel 3-5 play/pause button with easy audition 2-7 playback loops 6-21 playback mode parameter (keymap) 6-21 plus/minus buttons 3...
Page 305
Index-vii ribbon page setup mode 7-37 ribbons center 7-38 large ribbon configuration 7-37 position mode (posmode) 7-37 ribbon configuration (ribcfg) page 7-37 spring 7-38 riffs setup mode 7-46 ring modulation 9-23 rms settle 9-24 rom objects 5-3 rom objects, saving 5-2 room type 9-11 rotating speakers...
Page 306
Index-viii smooth rate 9-18 smoothtime 9-15 smth rate 9-19 soft buttons 3-7 master mode 11-7 midi mode 10-10 in program editor 6-11 in program mode 6-10 setup editor 7-52 special functions 6-51 software upgrades 2-10 soloing a zone 7-4 song button 5-6 song editor 12-16 track page 12-18 song mode 12-...
Page 307
Index-ix x xcouple parameter 9-10 xcrs fin 9-17 xcurs crs 9-17 xd memory cards 1-4, 2-6 xfer 9-14 xmit page 10-1 xover 9-20 xpose 2-8, 6-10 z zone status leds 7-3 zones soloing 7-4.
Page 308
Index-x.