- DL manuals
- ABB
- Relays
- rec670
- Applications Manual
ABB rec670 Applications Manual
Summary of rec670
Page 1
Relion® 670 series — bay control rec670 version 2.2 ansi application manual.
Page 3
Document id: 1mrk 511 401-uus issued: october 2017 revision: a product version: 2.2.1 © copyright 2017 abb. All rights reserved.
Page 4
Copyright this document and parts thereof must not be reproduced or copied without written permission from abb, and the contents thereof must not be imparted to a third party, nor used for any unauthorized purpose. The software and hardware described in this document is furnished under a license and...
Page 5
Disclaimer the data, examples and diagrams in this manual are included solely for the concept or product description and are not to be deemed as a statement of guaranteed properties. All persons responsible for applying the equipment addressed in this manual must satisfy themselves that each intende...
Page 6
Conformity this product complies with the directive of the council of the european communities on the approximation of the laws of the member states relating to electromagnetic compatibility (emc directive 2004/108/ec) and concerning electrical equipment for use within specified voltage limits (low-...
Page 7
Table of contents section 1 introduction..........................................................................21 this manual............................................................................................ 21 intended audience..............................................................
Page 8
Examples on how to connect, configure and set ct inputs for most commonly used ct connections.................................... 67 example on how to connect a wye connected three-phase ct set to the ied..........................................................................68 example how to conn...
Page 9
Operation principle.......................................................................... 108 frequency reporting................................................................... 110 reporting filters.......................................................................... 112 scaling factors...
Page 10
Application....................................................................................... 165 setting guidelines............................................................................ 165 directional residual overcurrent protection, four steps ef4ptoc (51n/67n)............................
Page 11
Pole discrepancy protection ccpdsc(52pd)......................................212 identification.................................................................................... 212 application....................................................................................... 212 setting guid...
Page 12
Disconnected equipment detection............................................ 242 power supply quality ..................................................................242 voltage instability mitigation....................................................... 242 backup protection for power system fau...
Page 13
Application....................................................................................... 259 setting guidelines............................................................................ 260 overfrequency protection saptof (81)...............................................260 identificat...
Page 14
Section 13 secondary system supervision..........................................293 current circuit supervision (87).............................................................293 identification.................................................................................... 293 application.......
Page 15
Autorecloser for 1 phase, 2 phase and/or 3 phase operation smbrrec (79).................................................................................... 323 identification.................................................................................... 323 application.............................
Page 16
Reservation function (qcrsv and resin)................................361 interaction between modules...........................................................363 setting guidelines............................................................................ 367 bay control (qcbay).....................
Page 17
Signals in breaker and a half arrangement.................................403 interlocking for double cb bay db (3)............................................. 404 application..................................................................................404 configuration setting....................
Page 18
Section 15 scheme communication.................................................... 465 scheme communication logic for distance or overcurrent protection zcpsch(85)........................................................................465 identification.................................................
Page 19
Setting guidelines............................................................................ 482 current reversal..........................................................................483 weak-end infeed........................................................................ 484 section 16 logi...
Page 20
Application....................................................................................... 498 boolean to integer conversion with logical node representation, 16 bit btigapc......................................................................................... 499 identification..............
Page 21
Application....................................................................................... 524 setting guidelines............................................................................ 524 breaker monitoring sscbr..................................................................525 iden...
Page 22
Setting example...............................................................................559 transformer rated data.............................................................559 setting parameters for insulation loss of life calculation function (lol1)............................................
Page 23
Identification............................................................................... 584 application..................................................................................584 setting guidelines....................................................................... 584 spa communi...
Page 24
Measured value expander block range_xp...................................... 608 identification.................................................................................... 609 application....................................................................................... 609 setting guide...
Page 25
Section 24 requirements....................................................................627 current transformer requirements........................................................ 627 current transformer basic classification and requirements............. 627 conditions..............................
Page 26
20
Page 27
Section 1 introduction 1.1 this manual guid-ab423a30-13c2-46af-b7fe-a73bb425eb5f v18 the application manual contains application descriptions and setting guidelines sorted per function. The manual can be used to find out when and for what purpose a typical protection function can be used. The manual...
Page 28
1.3 product documentation 1.3.1 product documentation set guid-3aa69ea6-f1d8-47c6-a8e6-562f29c67172 v15 iec07000220-4-en.Vsd p la nn in g & p ur ch as e e ng in ee rin g in st al lin g c om m is si on in g o pe ra tio n m ai nt en an ce d ec om m is si on in g d ei ns ta lli ng & d is po sa l applic...
Page 29
The commissioning manual contains instructions on how to commission the ied. The manual can also be used by system engineers and maintenance personnel for assistance during the testing phase. The manual provides procedures for the checking of external circuitry and energizing the ied, parameter sett...
Page 30
1.3.3 related documents guid-94e8a5ca-be1b-45af-81e7-5a41d34ee112 v5 documents related to rec670 document numbers application manual 1mrk 511 401-uus commissioning manual 1mrk 511 403-uus product guide 1mrk 511 404-ben technical manual 1mrk 511 402-uus type test certificate 1mrk 511 404-tus 670 seri...
Page 31
Class 1 laser product. Take adequate measures to protect the eyes and do not view directly with optical instruments. The caution icon indicates important information or warning related to the concept discussed in the text. It might indicate the presence of a hazard which could result in corruption o...
Page 32
• the character ^ in front of an input/output signal name indicates that the signal name may be customized using the pcm600 software. • the character * after an input signal name indicates that the signal must be connected to another function block in the application configuration to achieve a valid...
Page 33
Function block name edition 1 logical nodes edition 2 logical nodes bcztpdif bcztpdif bcztpdif bdcgapc swsggio bbcswi bdcgapc bdzsgapc bbs6lln0 bdzsgapc lln0 bdzsgapc bfptrc_f01 bfptrc bfptrc bfptrc_f02 bfptrc bfptrc bfptrc_f03 bfptrc bfptrc bfptrc_f04 bfptrc bfptrc bfptrc_f05 bfptrc bfptrc bfptrc_f...
Page 34
Function block name edition 1 logical nodes edition 2 logical nodes busptrc_b1 busptrc bbsplln0 busptrc busptrc_b2 busptrc busptrc busptrc_b3 busptrc busptrc busptrc_b4 busptrc busptrc busptrc_b5 busptrc busptrc busptrc_b6 busptrc busptrc busptrc_b7 busptrc busptrc busptrc_b8 busptrc busptrc busptrc...
Page 35
Function block name edition 1 logical nodes edition 2 logical nodes bznpdif_z2 bznpdif bznpdif bznpdif_z3 bznpdif bznpdif bznpdif_z4 bznpdif bznpdif bznpdif_z5 bznpdif bznpdif bznpdif_z6 bznpdif bznpdif bznspdif_a bznspdif bzasgapc bzaspdif bznsgapc bznspdif bznspdif_b bznspdif bzbsgapc bzbspdif bzn...
Page 36
Function block name edition 1 logical nodes edition 2 logical nodes cvmmxn cvmmxn cvmmxn d2ptoc d2lln0 d2ptoc ph1ptrc d2ptoc ph1ptrc dpgapc dpggio dpgapc drprdre drprdre drprdre ecpsch ecpsch ecpsch ecrwpsch ecrwpsch ecrwpsch ef2ptoc ef2lln0 ef2ptrc ef2rdir gen2phar ph1ptoc ef2ptrc ef2rdir gen2phar ...
Page 37
Function block name edition 1 logical nodes edition 2 logical nodes l4cpdif l4clln0 l4cpdif l4cptrc lln0 l4cgapc l4cpdif l4cpsch l4cptrc l4ufcnt l4ufcnt l4ufcnt l6cpdif l6cpdif l6cgapc l6cpdif l6cphar l6cptrc lappgapc lapplln0 lapppdup lapppupf lapppdup lapppupf lccrptrc lccrptrc lccrptrc lcnsptoc l...
Page 38
Function block name edition 1 logical nodes edition 2 logical nodes ns2ptoc ns2lln0 ns2ptoc ns2ptrc ns2ptoc ns2ptrc ns4ptoc ef4lln0 ef4ptrc ef4rdir gen4phar ph1ptoc ef4ptrc ef4rdir ph1ptoc o2rwptov gen2lln0 o2rwptov ph1ptrc o2rwptov ph1ptrc oc4ptoc oc4lln0 gen4phar ph3ptoc ph3ptrc gen4phar ph3ptoc p...
Page 39
Function block name edition 1 logical nodes edition 2 logical nodes schlcch schlcch schlcch scilo scilo scilo scswi scswi scswi sdepsde sdepsde sdepsde sdeptoc sdeptov sdeptrc sesrsyn rsy1lln0 aut1rsyn man1rsyn synrsyn aut1rsyn man1rsyn synrsyn slgapc slggio slgapc smbrrec smbrrec smbrrec smpptrc sm...
Page 40
Function block name edition 1 logical nodes edition 2 logical nodes tr1atcc tr1atcc tr1atcc tr8atcc tr8atcc tr8atcc trpttr trpttr trpttr u2rwptuv gen2lln0 ph1ptrc u2rwptuv ph1ptrc u2rwptuv uv2ptuv gen2lln0 ph1ptrc uv2ptuv ph1ptrc uv2ptuv vdcptov vdcptov vdcptov vdspvc vdrfuf vdspvc vmmxu vmmxu vmmxu...
Page 41
Function block name edition 1 logical nodes edition 2 logical nodes zmmapdis zmmapdis zmmapdis zmmpdis zmmpdis zmmpdis zmqapdis zmqapdis zmqapdis zmqpdis zmqpdis zmqpdis zmrapdis zmrapdis zmrapdis zmrpdis zmrpdis zmrpdis zmrpsb zmrpsb zmrpsb zsmgapc zsmgapc zsmgapc 1mrk 511 401-uus a section 1 intro...
Page 42
36.
Page 43
Section 2 application 2.1 general ied application m13637-3 v13 the intelligent electronic device (ied) is used for the control, protection and monitoring of different types of bays in power networks. The ied is especially suitable for applications in control systems where the iec 61850–8–1 ed 1 or e...
Page 44
Provide a breaker failure function independent from the protection ieds, also for a complete breaker-and-a-half diameter. Disturbance recording and fault locator are available to allow independent post-fault analysis after primary disturbances in case of a failure in the protection system. Duplex co...
Page 45
Iec 61850 or function name ansi function description bay control rec670 (customized) differential protection hzpdif 87 high impedance differential protection, single phase 0-6 2.3 back-up protection functions guid-a8d0852f-807f-4442-8730-e44808e194f0 v13 iec 61850 or function name ansi function desc...
Page 46
Iec 61850 or function name ansi function description rec670 (customized) ov2ptov 59 two step overvoltage protection 0-2 rov2ptov 59n two step residual overvoltage protection 0-2 vdcptov 60 voltage differential protection 0-6 lovptuv 27 loss of voltage check 0-2 frequency protection saptuf 81 underfr...
Page 47
Iec 61850 or function name ansi function description bay control rec670 (customized) locremctrl lhmi control of psto 1 sxcbr circuit breaker 18 tr1atcc 90 automatic voltage control for tap changer, single control 0-4 tr8atcc 90 automatic voltage control for tap changer, parallel control 0-4 tcmyltc ...
Page 48
Iec 61850 or function name ansi function description bay control rec670 (customized) and, gate, inv, lld, or, pulsetimer, rsmemory, srmemory, timerset, xor basic configurable logic blocks (see table 3 ) 40-420 andqt, indcombspqt, indextspqt, invalidqt, inverterqt, orqt, pulsetimerqt, rsmemoryqt, srm...
Page 49
Basic configurable logic block total number of instances pulsetimer 40 rsmemory 40 srmemory 40 timerset 60 xor 40 table 4: number of function instances in apc10 function name function description total number of instances scilo interlocking 10 bb_es 3 a1a2_bs 2 a1a2_dc 3 abc_bc 1 bh_conn 1 bh_line_a...
Page 50
Table 5: number of function instances in apc15 function name function description total number of instances scilo interlocking 15 bb_es 3 a1a2_bs 2 a1a2_dc 3 abc_bc 1 bh_conn 1 bh_line_a 1 bh_line_b 1 db_bus_a 1 db_bus_b 1 db_line 1 abc_line 1 ab_trafo 1 scswi switch controller 15 sxswi circuit swit...
Page 51
Table 6: number of function instances in apc30 function name function description total number of instances scilo interlocking 30 bb_es 6 a1a2_bs 4 a1a2_dc 6 abc_bc 2 bh_conn 2 bh_line_a 2 bh_line_b 2 db_bus_a 3 db_bus_b 3 db_line 3 abc_line 6 ab_trafo 4 scswi switch controller 30 sxswi circuit swit...
Page 52
Configurable logic blocks q/t total number of instances rsmemoryqt 40 srmemoryqt 40 timersetqt 40 xorqt 40 table 8: total number of instances for extended logic package extended configurable logic block total number of instances and 180 gate 49 inv 180 lld 49 or 180 pulsetimer 89 rsmemory 40 slgapc ...
Page 53
Iec 61850 or function name ansi function description bay control rec670 (customized) spgapc generic communication function for single point indication 64 sp16gapc generic communication function for single point indication 16 inputs 24 mvgapc generic communication function for measured values 24 bins...
Page 54
2.5 communication guid-5f144b53-b9a7-4173-80cf-cd4c84579cb5 v15 iec 61850 or function name ansi function description bay control rec670 (customized) station communication lonspa, spa spa communication protocol 1 ade lon communication protocol 1 horzcomm network variables via lon 1 rs485gen rs485 1 d...
Page 55
Iec 61850 or function name ansi function description bay control rec670 (customized) lphd physical device information 1 pcmaccs ied configuration protocol 1 secalarm component for mapping security events on protocols such as dnp3 and iec103 1 fstaccs field service tool access 1 iec 61850-9-2 process...
Page 56
Iec 61850 or function name ansi function description bay control rec670 (customized) ldcmrecbins3_2m receive binary status from remote ldcm, 2mbit 3 scheme communication zcpsch 85 scheme communication logic with delta based blocking scheme signal transmit 0-1 zcrwpsch 85 current reversal and weak-en...
Page 57
2.6 basic ied functions guid-c8f0e5d2-e305-4184-9627-f6b5864216ca v12 table 10: basic ied functions iec 61850 or function name description interrsig self supervision with internal event list timesynchgen time synchronization module bininput, synchcan, synchgps, synchcmpps, synchlon, synchpph, synchp...
Page 58
Table 11: local hmi functions iec 61850 or function name ansi description lhmictrl local hmi signals language local human machine language screen local hmi local human machine screen behavior fnkeyty1–fnkeyty5 fnkeymd1– fnkeymd5 parameter setting function for hmi in pcm600 ledgen general led indicat...
Page 59
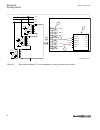
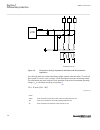
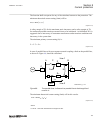
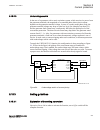
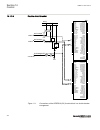
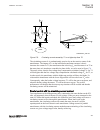
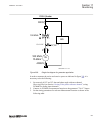
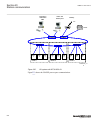
Section 3 configuration 3.1 description of configuration rec670 ip14799-1 v2 3.1.1 introduction ip14800-1 v1 3.1.1.1 description of configuration a30 m15200-3 v7 the configuration of the ied is shown in figure 2 . This configuration is used in single breaker arrangements with single or double busbar...
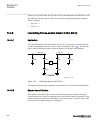
Page 60
Rec670 a30 – double busbar in single breaker arrangement 12ai (6i + 6u) qb1 qa1 qb2 qb9 s cilo 3 control s cswi 3 control s xswi 3 control s cilo 3 control s cswi 3 control s xswi 3 control s cilo 3 control s cswi 3 control s xswi 3 control s cilo 3 control s cswi 3 control s xswi 3 control drp rdre...
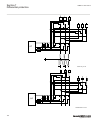
Page 61
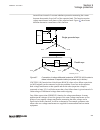
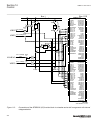
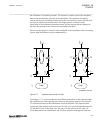
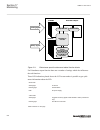
3.1.1.2 description of configuration b30 m15200-12 v5 the configuration of the ied is shown in figure 3 . This configuration is used in double breaker arrangements. Control, measuring and interlocking is fully configured, including communication with other bays such as other lines and the bus couple...
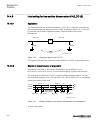
Page 62
Rec670 b30 - double breaker arrangement 12ai (6i + 6u) qb1 qa1 qb61 qb2 qa2 qb62 qb9 s cilo 3 control s cswi 3 control s xcbr 3 control etp mmtr met w/varh brc ptoc 46 iub> cc psdc 52pd pd other functions available from the function library lov ptuv 27 3u vdc ptov 60 ud> ccs spvc 87 ind/i tcl yltc 8...
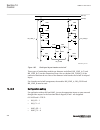
Page 63
3.1.1.3 description of configuration c30 m15200-24 v5 the configuration of the ied is shown on figure 4 . This configuration is used in breaker-and-a-half arrangements for a full diameter. The configuration can also be used for a section of the diameter with utilization of a part of the apparatuses ...
Page 64
S cilo 3 control s cswi 3 control s xswi 3 control s cilo 3 control s cswi 3 control s xswi 3 control s cilo 3 control s cswi 3 control s xswi 3 control s cilo 3 control s cswi 3 control s xswi 3 control s cilo 3 control s cswi 3 control s xswi 3 control s cilo 3 control s cswi 3 control s xswi 3 co...
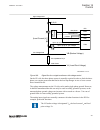
Page 65
3.1.1.4 description of configuration d30 guid-15d86a4c-4d37-432e-8dc2-518814830097 v1 rec670 d30 – double busbar in single breaker arrangement with pmu functionality 12ai (6i + 6u) qb1 qa1 qb2 qb9 s cilo 3 control s cswi 3 control s xswi 3 control s cilo 3 control s cswi 3 control s xswi 3 control s...
Page 66
• single breaker (double or single bus) arrangement (a30) • double breaker arrangement (b30) • breaker-and-a-half arrangement for a complete diameter (c30) • single breaker (double bus) arrangement with pmu functionality (d30) optional functions are available in pcm600 application configuration tool...
Page 67
Section 4 analog inputs 4.1 introduction semod55003-5 v11 analog input channels must be configured and set properly in order to get correct measurement results and correct protection operations. For power measuring, all directional and differential functions, the directions of the input currents mus...
Page 68
4.2.1.1 example semod55055-11 v5 usually the a phase-to-ground voltage connected to the first vt channel number of the transformer input module (trm) is selected as the phase reference. The first vt channel number depends on the type of transformer input module. For a trm with 6 current and 6 voltag...
Page 69
4.2.2.1 example 1 semod55055-23 v6 two ieds used for protection of two objects. Transformer protection transformer line line setting of current input: set parameter ct_wyepoint with transformer as reference object. Correct setting is "toobject" forward reverse definition of direction for directional...
Page 70
4.2.2.3 example 3 semod55055-35 v7 one ied used to protect two objects. Transformer and line protection transformer line setting of current input: set parameter ct_wyepoint with transformer as reference object. Correct setting is "toobject" reverse forward definition of direction for directional lin...
Page 71
Direction for the current channels to the line protection is set with the line as reference object and the directional functions of the line protection shall be set to forward to protect the line. Transformer and line protection transformer line setting of current input for transformer functions: se...
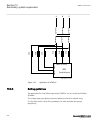
Page 72
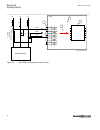
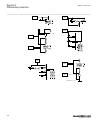
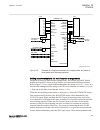
Busbar protection busbar 1 2 2 1 en06000196_ansi.Vsd ansi06000196 v1 en-us figure 11: example how to set ct_wyepoint parameters in the ied for busbar protection, it is possible to set the ct_wyepoint parameters in two ways. The first solution will be to use busbar as a reference object. In that case...
Page 73
Regardless which one of the above two options is selected, busbar differential protection will behave correctly. The main ct ratios must also be set. This is done by setting the two parameters ctsec and ctprim for each current channel. For a 1000/5 a ct, the following settings shall be used: • ctpri...
Page 74
It shall be noted that depending on national standard and utility practices, the rated secondary current of a ct has typically one of the following values: • 1a • 5a however, in some cases, the following rated secondary currents are used as well: • 2a • 10a the ied fully supports all of these rated ...
Page 75
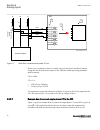
Protected object ct 600/5 wye connected ied ansi13000002-3-en.Vsd 1 2 3 4 smai_20 a i_ a i_ b i_ c b c i_a i_b i_c ansi13000002 v3 en-us figure 13: wye connected three-phase ct set with wye point towards the protected object where: 1) the drawing shows how to connect three individual phase currents ...
Page 76
3) these three connections are the links between the three current inputs and the three input channels of the preprocessing function block 4). Depending on the type of functions, which need this current information, more than one preprocessing block might be connected in parallel to the same three p...
Page 77
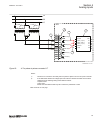
Protected object ct 800/1 wye connected ied ansi11000026-5-en-.Vsd 4 1 2 3 a ia ib ic b c ia ib ic smai_20_2 block revrot ^grp2_a ^grp2_b ^grp2_c ^grp2n ai3p ai1 ai2 ai3 ai4 ain 5 ansi11000026 v5 en-us figure 14: wye connected three-phase ct set with its wye point away from the protected object in t...
Page 78
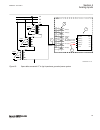
7 8 9 10 11 12 1 2 3 4 5 6 a ia ib ic b c protected object ct 800/1 wye connected ia ib ic ai 01 (i) ai 02 (i) ai 03 (i) ai 04 (i) ai 05 (i) ai 06 (i) in ied 1 3 4 2 5 ansi06000644-2-en.Vsd 6 smai2 block ai3p ai1 ai2 ai3 ai4 ain ^grp2_b ^grp2_a ^grp2_c ^grp2n type ansi06000644 v2 en-us figure 15: wy...
Page 79
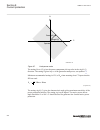
5) is a connection made in the signal matrix tool (smt) and application configuration tool (act), which connects the residual/neutral current input to the fourth input channel of the preprocessing function block 6). Note that this connection in smt shall not be done if the residual/neutral current i...
Page 80
A ia ib ic b c protected object ied c t 6 0 0/ 5 in d e lta d a b c o nn ec te d ia-ib ib-ic ic-ia 1 2 3 4 ansi11000027-2-en.Vsd smai_20 ansi11000027 v2 en-us figure 16: delta dab connected three-phase ct set section 4 1mrk 511 401-uus a analog inputs 74 bay control rec670 2.2 ansi application manua...
Page 81
Where: 1) shows how to connect three individual phase currents from a delta connected three-phase ct set to three ct inputs of the ied. 2) is the trm where these current inputs are located. It shall be noted that for all these current inputs the following setting values shall be entered. Ct prim =60...
Page 82
A ia ib ic b c protected object ied c t 8 0 0 /1 in d e lta d c a c o n ne ct ed ic-ib ib-ia ia-ic 2 3 4 ansi11000028-2-en.Vsd smai_20 ansi11000028 v2 en-us figure 17: delta dac connected three-phase ct set in this case, everything is done in a similar way as in the above described example, except t...
Page 83
For correct terminal designations, see the connection diagrams valid for the delivered ied. Protected object a b c ied in p 2 4 ansi11000029-3-en.Vsd 3 c t 1 0 0 0 /1 a) b) ins ins (+) (+) (-) (-) (+) (-) 1 smai_20_2 block revrot ^grp2_a ^grp2_b ^grp2_c ^grp2_n ai3p ai1 ai2 ai3 ai4 ain ansi11000029 ...
Page 84
4.2.3 relationships between setting parameter base current, ct rated primary current and minimum pickup of a protection ied guid-8eb19363-9178-4f04-a6ac-af0c2f99c5ab v1 note that for all line protection applications (e.G. Distance protection or line differential protection) the parameter base curren...
Page 85
4.2.4.1 example semod55055-47 v3 consider a vt with the following data: 132kv 120v 3 3 equation1937 v1 en-us (equation 1) the following setting should be used: vtprim=132 (value in kv) vtsec=120 (value in v) 4.2.4.2 examples how to connect, configure and set vt inputs for most commonly used vt conne...
Page 86
• 100 v • 110 v • 115 v • 120 v • 230 v the ied fully supports all of these values and most of them will be shown in the following examples. 4.2.4.3 examples on how to connect a three phase-to-ground connected vt to the ied semod55055-87 v9 figure 20 gives an example on how to connect the three phas...
Page 87
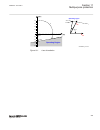
19 20 21 22 23 24 13 14 15 16 17 18 a ai 07 (i) ai 08 (v) ai 09 (v) ai 10 (v) ai 11 (v) ai 12 (v) ied b c 66 3 110 3 kv v 1 3 2 66 3 110 3 kv v 66 3 110 3 kv v #not used 5 ansi06000599-2-en.Vsd smai2 block ^grp2_a type ai3p ai1 ai2 ai3 ai4 ain ^grp2_b ^grp2_c ^grp2n 4 ansi06000599 v2 en-us figure 20...
Page 88
Where: 1) shows how to connect three secondary phase-to-ground voltages to three vt inputs on the ied 2) is the trm where these three voltage inputs are located. For these three voltage inputs, the following setting values shall be entered: vtprim = 132 kv vtsec = 110 v inside the ied, only the rati...
Page 89
19 20 21 22 23 24 13 14 15 16 17 18 a ai 07(i) ai08 (v) ai09 (v) ai10(v) ai11(v) ai12(v) ied b c 13.8 120 kv v 1 2 3 #not used 13.8 120 kv v 5 ansi06000600-3-en.Vsd smai2 block ^grp2_a (a-b) ^grp2_b (b-c) ^grp2_c (c-a) ^grp2n type ai3p ai1 ai2 ai3 ai4 ain 4 ansi06000600 v3 en-us figure 22: a two pha...
Page 90
3) are three connections made in the signal matrix tool (smt), application configuration tool (act), which connects these three voltage inputs to first three input channels of the preprocessing function block 5). Depending on the type of functions, which need this voltage information, more than one ...
Page 91
19 20 21 22 23 24 13 14 15 16 17 18 a ai 07 (i) ai 08 (v) ai 09 (v) ai 10 (v) ai 11 (v) ai 12 (v) ied b c 6.6 3 110 3 kv v +3vo 6.6 3 110 3 kv v 6.6 3 110 3 kv v 1 2 4 3 # not used 5 ansi06000601-2-en.Vsd # not used # not used smai2 block ^grp2_a ^grp2_b ^grp2_c ^grp2n type ai3p ai1 ai2 ai3 ai4 ain ...
Page 92
Where: 1) shows how to connect the secondary side of the open delta vt to one vt input on the ied. +3vo shall be connected to the ied 2) is the trm where this voltage input is located. It shall be noted that for this voltage input the following setting values shall be entered: 3 6.6 11.43 vtprim kv ...
Page 93
4.2.4.6 example how to connect the open delta vt to the ied for low impedance grounded or solidly grounded power systems semod55055-199 v6 figure 24 gives an example about the connection of an open delta vt to the ied for low impedance grounded or solidly grounded power systems. It shall be noted th...
Page 94
19 20 21 22 23 24 13 14 15 16 17 18 a ai07 (i) ai08 (v) ai09 (v) ai10 (v) ai11 (v) ai12 (v) ied b c 138 3 115 3 kv v +3vo 138 3 115 3 kv v 138 3 115 3 kv v 1 2 4 3 ansi06000602-2-en.Vsd 5 # not used # not used # not used smai2 block ^grp2_a ^grp2_b ^grp2_c ^grp2n type ai3p ai1 ai2 ai3 ai4 ain ansi06...
Page 95
Where: 1) shows how to connect the secondary side of open delta vt to one vt input in the ied. +3vo shall be connected to the ied. 2) is trm where this voltage input is located. It shall be noted that for this voltage input the following setting values shall be entered: 138 3 138 3 vtprim kv = × = e...
Page 96
90
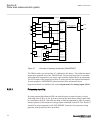
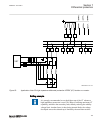
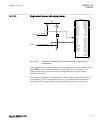
Page 97
Section 5 local hmi amu0600442 v14 ansi13000239-2-en.Vsd ansi13000239 v2 en-us figure 25: local human-machine interface the lhmi of the ied contains the following elements: 1mrk 511 401-uus a section 5 local hmi bay control rec670 2.2 ansi 91 application manual.
Page 98
• keypad • display (lcd) • led indicators • communication port for pcm600 the lhmi is used for setting, monitoring and controlling. 5.1 display guid-55739d4f-1da5-4112-b5c7-217aaf360ea5 v11 the lhmi includes a graphical monochrome liquid crystal display (lcd) with a resolution of 320 x 240 pixels. T...
Page 99
Iec15000270-1-en.Vsdx iec15000270 v1 en-us figure 26: display layout 1 path 2 content 3 status 4 scroll bar (appears when needed) the function key button panel shows on request what actions are possible with the function buttons. Each function button has a led indication that can be used as a feedba...
Page 100
Iec13000281-1-en.Vsd guid-c98d972d-d1d8-4734-b419-161dbc0dc97b v1 en-us figure 27: function button panel the indication led panel shows on request the alarm text labels for the indication leds. Three indication led pages are available. Iec13000240-1-en.Vsd guid-5157100f-e8c0-4fab-b979-fd4a971475e3 v...
Page 101
5.2 leds amu0600427 v13 the lhmi includes three protection status leds above the display: normal, pickup and trip. There are 15 programmable indication leds on the front of the lhmi. Each led can indicate three states with the colors: green, yellow and red. The texts related to each three-color led ...
Page 102
Iec16000076-1-en.Vsd iec16000076 v1 en-us figure 29: openclose_led connected to sxcbr 5.3 keypad amu0600428 v17 the lhmi keypad contains push-buttons which are used to navigate in different views or menus. The push-buttons are also used to acknowledge alarms, reset indications, provide help and swit...
Page 103
Ansi15000157-1-en.Vsdx 1 18 19 7 6 5 4 3 2 8 20 21 22 17 16 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 23 24 ansi15000157 v1 en-us figure 30: lhmi keypad with object control, navigation and command push- buttons and rj-45 communication port 1...5 function button 6 close 7 open 8 escape 9 left 10 down 11 up 12 right 13 key...
Page 104
19 menu 20 clear 21 help 22 communication port 23 programmable indication leds 24 ied status leds 5.4 local hmi functionality 5.4.1 protection and alarm indication guid-09ccb9f1-9b27-4c12-b253-fbe95ea537f5 v15 protection indicators the protection indicator leds are normal, pickup and trip. Table 12:...
Page 105
Table 14: trip led (red) led state description off normal operation. On a protection function has tripped. An indication message is displayed if the auto-indication feature is enabled in the local hmi. The trip indication is latching and must be reset via communication, lhmi or binary input on the l...
Page 106
Numerical values are presented either in integer or in decimal format with minimum and maximum values. Character strings can be edited character by character. Enumerated values have a predefined set of selectable values. 5.4.3 front communication guid-fd72a445-c8c1-4bfe-90e3-0ac78ae17c45 v11 the rj-...
Page 107
Section 6 wide area measurement system 6.1 c37.118 phasor measurement data streaming protocol configuration pmuconf guid-747c6ad7-e6a1-466e-92d1-68865681f92f v1 6.1.1 identification guid-1e140ea0-d198-443a-b445-47cefd2e6134 v1 function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification an...
Page 108
Corresponding pmu id for that pmureport instance. Whereas, for udp clients, the pmureport instance for each udp channel is defined by the user in the pmu and the client has to know the pmu id corresponding to that instance in order to be able to communicate. More information is available in the sect...
Page 109
As can be seen, there are two separate parameters in the ied for selecting port numbers for tcp connections; one for ieee1344 protocol (1344tcpport) and another one for c37.118 protocol (c37.118 tcpport). Client can communicate with the ied over ieee1344 protocol using the selected tcp port defined ...
Page 110
1. Senddataudp[x] – enable / disable udp data stream 2. Protocolonudp[x] – send ieee1344 or c37.118 on udp 3. Pmureportudp[x] – instance number of pmureport function block that must send data on this udp stream (udp client group[x]) 4. Udpdestaddres[x] – udp destination address for udp client group[...
Page 111
The data streams in the ied can be sent as unicast or as multicast. The user-defined ip address set in the parameter udpdestaddress[x] for each udp stream defines if it is a unicast or multicast. The address range 224.0.0.0 to 239.255.255.255 (class d ip addresses) is treated as multicast. Any other...
Page 112
6.2.2 application guid-8df29209-252a-4e51-9f4a-b14b669e71ab v4 the phasor measurement reporting block moves the phasor calculations into an ieee c37.118 and/or ieee 1344 synchrophasor frame format. The pmureport block contains parameters for pmu performance class and reporting rate, the idcode and g...
Page 113
Iec140000118-2-en.Vsd iec140000118 v2 en-us figure 33: multiple instances of pmureport function block figure 34 shows both instances of the phasorreport function blocks. The instance number is visible in the bottom of each function block. For each instance, there are four separate phasorreport block...
Page 114
Iec140000120-2-en.Vsd iec140000120 v2 en-us figure 35: multiple instances of analogreport blocks figure 36 shows both instances of binaryreport function blocks. The instance number is visible in the bottom of each function block. For each instance, there are three separate binaryreport blocks capabl...
Page 115
• to measure the power system related ac quantities (voltage, current) and to calculate the phasor representation of these quantities. • to synchronize the calculated phasors with the utc by time-tagging, in order to make synchrophasors (time is reference). • to publish all phasor-related data by me...
Page 116
Iec140000146-1-en.Vsd phasor1 phasor2 phasor32 analog1 analog2 analog24 freqtrig dfdttrig maghightrig maglowtrig binary1 binary2 binary24 pmureport1 smai smmi meas. Trm mu trm mim protection op up oc uv or num ieeec37.118 / 1344 messages u/i samples bim gps / irig-b pps time data u i u i i/p 8 tcp 6...
Page 117
This adaptive filtering is ensured by proper configuration and settings of all relevant pre-processing blocks, see signal matrix for analog inputs in the application manual. Note that in all preconfigured ieds such configuration and settings are already made and the three-phase voltage are used as m...
Page 118
Name type values (range) unit description freqrefchsel integer - - frequency reference channel number selected freqrefcherr boolean 0=freq ref not available 1=freq ref error 2=freq ref available - frequency reference channel error freqtrig boolean - - frequency trigger dfdttrig boolean - - rate of c...
Page 119
6.2.3.3 scaling factors for analogreport channels guid-0ddaf6a9-8643-4fdd-97cf-9e35ef40af7e v2 the internal calculation of analog values in the ied is based on 32 bit floating point. Therefore, if the user selects to report the analog data (analogdatatype) as integer, there will be a down-conversion...
Page 120
3277.0 analogxrange = iecequation2446 v1 en-us the scale factor is calculated as follows: (3277.0 2.0) 0.1 and 0.0 65535.0 scalefactor offset ´ = = = iecequation2447 v1 en-us the scale factor will be sent as 1 on configuration frame 2, and 0.1 on configuration frame 3. The range of analog values tha...
Page 121
6.2.3.4 pmu report function blocks connection rules in pcm600 application configuration tool (act) guid-66667179-f3e1-455b-8b99-6d73f37e949b v3 there are 3 important general rules which have to be considered in pcm600 act for the connection of preprocessor blocks (smai) and 3phsum blocks to phasorre...
Page 122
The phasorreport filtering window is designed to receive updated input every 0.9 ms and therefore the application will fail. Rule 2: the same smai or 3phsum block can be connected to more than one phasorreport block only if all the connected phasorreport blocks have similar instance number or only i...
Page 123
Iec140000127-2-en.Vsd iec140000127 v2 en-us figure 41: an example of correct connection of smai and phasorreport blocks in act figure 42 shows an example of wrong connection of smai and phasorreport blocks in act where the same smai block is connected to different phasorreport blocks with different ...
Page 124
Iec140000128-2-en.Vsd iec140000128 v2 en-us figure 42: an example of wrong connection of smai and phasorreport blocks in act rule 3: this rule is only related to the connection of 3phsum block to the phasorreport block. If 3phsum block is configured to use external dft reference (from smai reference...
Page 125
Iec140000129-2-en.Vsd iec140000129 v2 en-us figure 43: an example of correct connection of 3phsum and phasorreport blocks in act iec140000130-1-en.Vsd iec140000130 v1 en-us figure 44: smai1 setting parameters example-showing that smai3 is selected as the dft reference (dftrefgrp3) 1mrk 511 401-uus a...
Page 126
Iec140000131-1-en iec140000131 v1 en-us figure 45: 3phsum setting parameters example-showing that 3phsum is using the external dft reference coming indirectly from smai3 figure 46 shows an example of wrong connection of 3phsum and phasorreport blocks in act where smai3 is configured as the reference...
Page 127
Is adapted according to the performance class (svcclass) and reporting rate of the connected instance of phasorreport function block. On the other hand, when 3phsum uses external dft reference, it also adapts its filtering according to the smai reference block. Therefore, in order to avoid two diffe...
Page 128
1. Pmureport 2. Phasorreport 3. Analogreport 4. Binaryreport each category has its corresponding parameter settings except for binaryreport function block which does not have any specific parameters and settings. 1. Pmureport is the main function block which controls the operation of other pmu repor...
Page 129
Synchrophasors. The options are rectangular or polar format. Rectangular format represents the synchrophasor as real and imaginary values, real value first (a + bj) while the polar format represents the synchrophasor as magnitude and angle, magnitude first (a e jα ). • phasordatatype: it refers to t...
Page 130
The frequency-deviation and rate-of-change-of-frequency data are sent via the freq and dfreq fields of data frame organization of ieee c37.118.2 message format. Depends on the selected data type, the size of each field can be 2 (integer) or 4 (float) bytes per ieee c37.118.2 message. The data sent v...
Page 131
Power system signal at the time it is applied to the pmu input. All of these estimates must be compensated for pmu processing delays including analog input filtering, sampling, and estimation group delay. If the sample time tags are compensated for all input delays, the time tag of the sample in the...
Page 132
This setting is only important if the analogdatatype setting is selected as integer. More information is available under the section scaling factors for analogreport channels . • analogxunittype: unit type for analog signal x. It refers to the 4-byte anunit field of the configuration frames 1, 2 org...
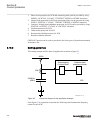
Page 133
Section 7 differential protection 7.1 high impedance differential protection, single phase hzpdif (87) ip14239-1 v4 7.1.1 identification m14813-1 v4 function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number high impedance differential protection, single pha...
Page 134
Ansi05000163-1-en.Vsd 3·87 87n 3·87t g 3·87g 3·87b 3·87t 3·87 3·87 3·87b ansi05000163 v2 en-us section 7 1mrk 511 401-uus a differential protection 128 bay control rec670 2.2 ansi application manual.
Page 135
Ansi05000738-2-en.Vsd 3·87 21 3·87 21 52 52 52 ansi05000738 v2 en-us figure 47: different applications of a 1ph high impedance differential protection hzpdif (87) function 7.1.2.1 the basics of the high impedance principle semod54734-153 v9 the high impedance differential protection principle has be...
Page 136
87n en05000164_ansi.Vsd ansi05000164 v1 en-us figure 48: example for the high impedance restricted earth fault protection application for a through fault one current transformer might saturate when the other cts still will feed current. For such a case a voltage will be developed across the measurin...
Page 137
The minimum operating voltage has to be calculated (all loops) and the ied function is set higher than the highest achieved value (setting trippickup). As the loop resistance is the value to the connection point from each ct, it is advisable to do all the ct core summations in the switchgear to have...
Page 138
Table 17: 1 a channels: input with minimum operating down to 40 ma operating voltage trippickup stabilizing resistor r ohms operating current level 1 a stabilizing resistor r ohms operating current level 1 a 20 v 500 0.040 a -- -- 40 v 1000 0.040 a -- -- 60 v 1500 0.040 a 600 0.100 a 80 v 2000 0.040...
Page 139
Ir ied pickup current (u>trip/seriesresistor) ires is the current through the voltage limiter and Σimag is the sum of the magnetizing currents from all cts in the circuit (for example, 4 for restricted earth fault protection, 2 for reactor differential protection, 3-5 for autotransformer differentia...
Page 140
Ansi05000427-2-en.Vsd i> r rres rl rct rct rl vr a) through load situation b) through fault situation vr vr c) internal faults vr protected object ansi05000427 v2 en-us figure 49: the high impedance principle for one phase with two current transformer inputs section 7 1mrk 511 401-uus a differential...
Page 141
7.1.3 connection examples for high impedance differential protection guid-8c58a73d-7c2e-4be5-ab87-b4c93fb7d62b v5 warning! Use extreme caution! Dangerously high voltages might be present on this equipment, especially on the plate with resistors. De-energize the primary object protected with this equ...
Page 142
Pos description 1 scheme grounding point it is important to insure that only one grounding point exist in this scheme. 2 three-phase plate with setting resistors and metrosils. Protective ground is a separate 4 mm screw terminal on the plate. 3 necessary connection for three-phase metrosil set. 4 po...
Page 143
L1 (a) l2 (b) l3 (c) protected object ct 1500/5 star/wye connected 7 8 9 10 11 12 1 2 3 4 5 6 ai01 (i) ai02 (i) ai03 (i) ai04 (i) ai05 (i) ai06 (i) 6 ied x1 r 1 1 2 4 5 v r 2 1 3 4 2 1 2 3 n 1-ph plate with metrosil and resistor 2 3 5 4 n l1 (a) l2 (b) l3 (c) c t 1 5 0 0 /5 1 ansi09000170-5-en.Vsdx ...
Page 144
7.1.4.1 configuration m13076-5 v4 the configuration is done in the application configuration tool. 7.1.4.2 settings of protection function m13076-10 v6 operation: the operation of the high impedance differential function can be switched enabled or disabled. Alarmpickup: set the alarm level. The sens...
Page 145
Transformers in the feeder circuit (for example, in the transformer bushings). It is often required to separate the protection zones that the feeder is protected with one scheme while the t-zone is protected with a separate differential protection scheme. The 1ph high impedance differential hzpdif (...
Page 146
87 en05000165_ansi.Vsd ansi05000165 v1 en-us 3·87 ansi05000739-2-en.Vsd ansi05000739 v2 en-us section 7 1mrk 511 401-uus a differential protection 140 bay control rec670 2.2 ansi application manual.
Page 147
Figure 52: the protection scheme utilizing the high impedance function for the t- feeder normally this scheme is set to achieve a sensitivity of around 20 percent of the used ct primary rating so that a low ohmic value can be used for the series resistor. It is strongly recommended to use the highes...
Page 148
( ) 3 2000 200 0 3 50 60 10 .100 5 ip approx a - = ° + × - ° × £ equation1887-ansi v1 en-us (equation 17) where 100 ma is the current drawn by the ied circuit and 10 ma is the current drawn by each ct just at pickup 20 ma is current drawn by metrosil at pickup the magnetizing current is taken from t...
Page 149
Ansi05000176-2-en.Vsd 3·87 ansi05000176 v2 en-us figure 53: application of the1ph high impedance differential protection hzpdif (87) function on a reactor setting example it is strongly recommended to use the highest tap of the ct whenever high impedance protection is used. This helps in utilizing m...
Page 150
But in the unused taps, owing to auto-transformer action, voltages much higher than design limits might be induced. Basic data: current transformer ratio: 100/5 a (note: must be the same at all locations) ct class: c200 secondary resistance: 0.1 ohms (at 100/5 tap) cable loop resistance: ct) to be l...
Page 151
Where 200ma is the current drawn by the ied circuit and 50ma is the current drawn by each ct just at pickup. The magnetizing current is taken from the magnetizing curve of the current transformer cores, which should be available. The current value at trippickup is taken. 7.1.4.5 alarm level operatio...
Page 152
Iec05000749 v1 en-us figure 54: current voltage characteristics for the non-linear resistors, in the range 10-200 v, the average range of current is: 0.01–10 ma section 7 1mrk 511 401-uus a differential protection 146 bay control rec670 2.2 ansi application manual.
Page 153
Section 8 current protection 8.1 instantaneous phase overcurrent protection phpioc (50) ip14506-1 v6 8.1.1 identification m14880-1 v5 function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number instantaneous phase overcurrent protection phpioc 3i>> symbol-z v...
Page 154
Must operate very quickly for faults very close to the generation (and relay) point, for which very high fault currents are characteristic. The instantaneous phase overcurrent protection phpioc (50) can operate in 10 ms for faults characterized by very high currents. 8.1.3 setting guidelines ip14979...
Page 155
Multpu: the set operate current can be changed by activation of the binary input multpu to the set factor multpu. 8.1.3.1 meshed network without parallel line m12915-9 v8 the following fault calculations have to be done for three-phase, single-phase-to- ground and two-phase-to-ground faults. With re...
Page 156
Ansi09000023-1-en.Vsd ~ ~ z a z b z l a b ied i fa fault ansi09000023 v1 en-us figure 56: through fault current from b to a: i fa the ied must not trip for any of the two through-fault currents. Hence the minimum theoretical current setting (imin) will be: imin max i fa i fb , ( ) ³ equation78 v1 en...
Page 157
Ansi09000024-1-en.Vsd ~ ~ z a z b z l a b i f fault ied ansi09000024 v1 en-us figure 57: fault current: i f the ied setting value pickup is given in percentage of the primary base current value, ibase. The value for pickup is given from this formula: 100 is pickup ibase = × ansiequation1147 v1 en-us...
Page 158
~ ~ z a z b z l1 a b i m fault ied z l2 m c line 1 line 2 ansi09000025_2_en.Vsd ansi09000025 v2 en-us figure 58: two parallel lines. Influence from parallel line to the through fault current: i m the minimum theoretical current setting for the overcurrent protection function (imin) will be: imin max...
Page 159
8.2 directional phase overcurrent protection, four steps oc4ptoc(51_67) semod129998-1 v8 8.2.1 identification m14885-1 v6 function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number directional phase overcurrent protection, four steps oc4ptoc toc-reva v2 en-u...
Page 160
Delay characteristics. The selectivity between different overcurrent protections is normally enabled by co-ordination between the function time delays of the different protections. To enable optimal co-ordination between all overcurrent protections, they should have the same time delay characteristi...
Page 161
The parameters for the directional phase overcurrent protection, four steps oc4ptoc (51/67) are set via the local hmi or pcm600. The following settings can be done for oc4ptoc (51/67). Common base ied values for primary current (ibase), primary voltage (ubase) and primary power (sbase) are set in th...
Page 162
V ref i dir ansi09000636-1-en.Vsd 1 2 2 3 4 ansi09000636 v1 en-us figure 59: directional function characteristic 1. Rca = relay characteristic angle 2. Roa = relay operating angle 3. Reverse 4. Forward 8.2.3.1 settings for each step m12982-19 v10 x means step 1, 2, 3 and 4. Dirmodeselx: the directio...
Page 163
Characteristx: selection of time characteristic for step x. Definite time delay and different types of inverse time characteristics are available according to table 19 . Table 19: inverse time characteristics curve name ansi extremely inverse ansi very inverse ansi normal inverse ansi moderately inv...
Page 164
Iminx: minimum pickup current for step x in % of ibase. Set iminx below pickupx for every step to achieve ansi reset characteristic according to standard. If iminx is set above pickupx for any step the ansi reset works as if current is zero when current drops below iminx. Txmin: minimum trip time fo...
Page 165
Table 20: reset possibilities curve name curve index no. Instantaneous 1 iec reset (constant time) 2 ansi reset (inverse time) 3 the delay characteristics are described in technical manual. There are some restrictions regarding the choice of the reset delay. For the definite time delay characteristi...
Page 166
8.2.3.2 setting example guid-20729467-24ab-42f0-9fd1-d2959028732e v1 directional phase overcurrent protection, four steps can be used in different ways, depending on the application where the protection is used. A general description is given below. The pickup current setting of the inverse time pro...
Page 167
Im ax ipu 1.2 k ³ × equation1262 v2 en-us (equation 28) where: 1.2 is a safety factor k is the reset ratio of the protection imax is the maximum load current the load current up to the present situation can be found from operation statistics. The current setting must remain valid for several years. ...
Page 168
Protected zone). A fault current calculation gives the largest current of faults, iscmax, at the most remote part of the primary protected zone. The risk of transient overreach must be considered, due to a possible dc component of the short circuit current. The lowest current setting of the fastest ...
Page 169
Time-current curves fault current 10 10 0.01 10000 en05000204.Ai str tfunc1 n n tfunc2 trip time n iec05000204 v2 en-us figure 62: fault time with maintained selectivity the operation time can be set individually for each overcurrent protection. To assure selectivity between different protection fun...
Page 170
Example for time coordination assume two substations a and b directly connected to each other via one line, as shown in the figure 63 . Consider a fault located at another line from the station b. The fault current to the overcurrent protection of ied b1 has a magnitude so that the overcurrent prote...
Page 171
40 100 40 40 220 t ms ms ms ms ms d ³ + + + = equation1266 v1 en-us (equation 32) where it is considered that: the operate time of overcurrent protection b1 is 40 ms the breaker open time is 100 ms the resetting time of protection a1 is 40 ms and the additional margin is 40 ms 8.3 instantaneous resi...
Page 172
M12762-6 v8 common base ied values for primary current (ibase), primary voltage (vbase) and primary power (sbase) are set in the global base values for settings function gbasval. Globalbasesel: this is used to select gbasval function for reference of base values. The basic requirement is to assure s...
Page 173
The function shall not operate for any of the calculated currents to the protection. The minimum theoretical current setting (imin) will be: im , fa fb in max i i equation284 v2 en-us (equation 33) a safety margin of 5% for the maximum static inaccuracy and a safety margin of 5% for maximum possible...
Page 174
Considering the safety margins mentioned previously, the minimum setting (is) is: i s = 1.3 × i min equation288 v3 en-us (equation 36) the ied setting value in>> is given in percent of the primary base current value, ibase. The value for in>> is given by the formula: ( ) 100 s in i ibase iecequation...
Page 175
8.4.2 application m12509-12 v10 the directional residual overcurrent protection, four steps ef4ptoc (51n_67n) is used in several applications in the power system. Some applications are: • ground-fault protection of feeders in effectively grounded distribution and subtransmission systems. Normally th...
Page 176
Table 21: time characteristics curve name ansi extremely inverse ansi very inverse ansi normal inverse ansi moderately inverse ansi/ieee definite time ansi long time extremely inverse ansi long time very inverse ansi long time inverse iec normal inverse iec very inverse iec inverse iec extremely inv...
Page 177
8.4.3 setting guidelines ip14988-1 v1 m15282-3 v11 when inverse time overcurrent characteristic is selected, the trip time of the stage will be the sum of the inverse time delay and the set definite time delay. Thus, if only the inverse time delay is required, it is important to set the definite tim...
Page 178
V pol = 3v 0 or v 2 rca operation idirpu en 05000135-4- ansi.Vsd ansi05000135 v3 en-us figure 67: relay characteristic angle given in degree in a normal transmission network a normal value of rca is about 65°. The setting range is -180° to +180°. Polmethod: defines if the directional polarization is...
Page 179
Calculate the value of zn as v/(√3 · 3i 0 ) typically, the minimum znpol (3 · zero sequence source) is set. The setting is in primary ohms. When the dual polarizing method is used, it is important that the setting pickupx or the product 3i 0 · znpol is not greater than 3v 0 . If so, there is a risk ...
Page 180
Residual fundamental current will however be significant. The inrush current of the transformer in service before the parallel transformer energizing, will be a little delayed compared to the first transformer. Therefore, we will have high 2 nd harmonic current initially. After a short period this c...
Page 181
The function is divided into two parts. The sotf function will give operation from step 2 or 3 during a set time after change in the position of the circuit breaker. The sotf function has a set time delay. The under time function, which has 2 nd harmonic restrain blocking, will give operation from s...
Page 182
To assure selectivity between different protections, in the radial network, there has to be a minimum time difference dt between the time delays of two protections. To determine the shortest possible time difference, the operation time of protections, breaker opening time and protection resetting ti...
Page 183
Ansi10000058-1-en.Vsdx trip time pickup current tx txmin ansi10000058 v1 en-us figure 69: minimum pickup current and trip time for inverse time characteristics in order to fully comply with the curves definition, the setting parameter txmin shall be set to the value which is equal to the operate tim...
Page 184
[ ] p a t s b td i c ipickup = + × - æ ö ç ÷ ç ÷ ç ÷ æ ö ç ÷ ç ÷ è ø è ø equation1722 v1 en-us (equation 38) further description can be found in the technical reference manual. Tprcrvx, ttrcrvx, tcrcrvx: parameters for user programmable of inverse reset time characteristic curve. Further description...
Page 185
Xx05000149_ansi.Vsd 67n ansi05000149 v1 en-us figure 70: connection of polarizing voltage from an open (ansi-broken) delta the different steps can be described as follows. Step 1 m15282-123 v6 this step has directional instantaneous function. The requirement is that overreaching of the protected lin...
Page 186
The residual current out on the line is calculated at a fault on the remote busbar (one- or two-phase-to-ground fault). To assure selectivity it is required that step 1 shall not give a trip at this fault. The requirement can be formulated according to equation 39 . Step1 0 i 1.2 3i (remote busbar) ...
Page 187
Ansi05000152_2_en.Vsd one phase-to-ground fault 67n 0 3i ansi05000152 v2 en-us figure 73: step 1, third calculation in this case the residual current out on the line can be larger than in the case of ground fault on the remote busbar. Step1 0 i 1.2 3i ³ × equation1201 v3 en-us (equation 41) the curr...
Page 188
The residual current, out on the line, is calculated at an operational case with minimal ground-fault current. The requirement that the whole line shall be covered by step 2 can be formulated according to equation 42 . Step2 0 i 0.7 3i (at remote busbar) ³ × equation1202 v4 en-us (equation 42) to as...
Page 189
En05000156_ansi.Vsd 67n one phase ground fault 3i0 67n 3i0 x ansi05000156 v1 en-us figure 76: step 3, selectivity calculation 1 0 step3 step2 02 3i i .2 i 3i ³ × × equation1204 v4 en-us (equation 44) where: i step2 is the chosen current setting for step 2 on the faulted line. Step 4 m15282-177 v4 th...
Page 190
8.5.1 identification guid-e1720ada-7f80-4f2c-82a1-ef2c9ef6a4b4 v1 function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number four step negative sequence overcurrent protection ns4ptoc i2 4 4 alt iec10000053 v1 en-us 46i2 8.5.2 application guid-343023f8-afe3-...
Page 191
Choice of time characteristics: there are several types of time characteristics available such as definite time delay and different types of inverse time characteristics. The selectivity between different overcurrent protections is normally enabled by co- ordination between the operating time of the...
Page 192
8.5.3 setting guidelines guid-460d6c58-598c-421e-aa9e-fd240210a6cc v2 the parameters for four step negative sequence overcurrent protection ns4ptoc (46i2) are set via the local hmi or protection and control manager (pcm600). The following settings can be done for the four step negative sequence over...
Page 193
Curve name iec normal inverse iec very inverse iec inverse iec extremely inverse iec short time inverse iec long time inverse iec definite time user programmable asea ri rxidg (logarithmic) the different characteristics are described in the technical reference manual (trm). Pickupx: operation negati...
Page 194
Iminx operate time current tx txmin iec10000058 iec10000058 v2 en-us figure 77: minimum operate current and operation time for inverse time characteristics resettypecrvx: the reset of the delay timer can be made in different ways. By choosing setting there are the following possibilities: curve name...
Page 195
Tpcrvx, tacrvx, tbcrvx, tccrvx: parameters for programmable inverse time characteristic curve. The time characteristic equation is according to equation 45 : [ ] p a t s b td i c ipickup = + × - æ ö ç ÷ ç ÷ ç ÷ æ ö ç ÷ ç ÷ è ø è ø equation1722 v1 en-us (equation 45) further description can be found ...
Page 196
Anglerca forward area iop = i2 vpol=-v2 reverse area ansi10000031-1-en.Vsd ansi10000031 v1 en-us figure 78: relay characteristic angle given in degree in a transmission network a normal value of rca is about 80°. Vpolmin: minimum polarization (reference) voltage % of vbase. I>dir: operate residual c...
Page 197
8.6.1 identification semod172025-2 v4 function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number sensitive directional residual over current and power protection sdepsde - 67n 8.6.2 application semod171959-4 v12 in networks with high impedance grounding, the...
Page 198
When should the sensitive directional residual overcurrent protection be used and when should the sensitive directional residual power protection be used? Consider the following: • sensitive directional residual overcurrent protection gives possibility for better sensitivity. The setting possibiliti...
Page 199
8.6.3 setting guidelines semod171961-4 v10 the sensitive ground-fault protection is intended to be used in high impedance grounded systems, or in systems with resistive grounding where the neutral point resistor gives an ground-fault current larger than what normal high impedance gives but smaller t...
Page 200
Where i j is the capacitive ground fault current at a non-resistive phase-to-ground fault x c is the capacitive reactance to ground in a system with a neutral point resistor (resistance grounded system) the impedance z 0 can be calculated as: c n 0 c n jx 3r z jx 3r - × = - + equation1946 v1 en-us (...
Page 201
Substation a substation b z lineab,1 (pos. Seq) z lineab,0 (zero seq) z linebc,1 (pos. Seq) z linebc,0 (zero seq) v 0a v 0b 3i 0 phase to ground fault r n z t,1 (pos. Seq) z t,0 (zero seq) source impedance z sc (pos. Seq) en06000654_ansi.Vsd ansi06000654 v1 en-us figure 80: equivalent of power syste...
Page 202
0a 0 t,0 n v 3i (z 3r ) = × + equation2024-ansi v1 en-us (equation 52) ob 0 t ,0 n lineab,0 v 3i (z 3r z ) = × + + equation2025-ansi v1 en-us (equation 53) the residual power, measured by the sensitive ground fault protections in a and b will be: 0a 0a 0 s 3v 3i = × equation2026-ansi v1 en-us (equat...
Page 203
Globalbasesel: it is used to select a gbasval function for reference of base values. Rotresu: it is a setting for rotating the polarizing quantity (3v 0 ) by 0 or 180 degrees. This parameter is set to 180 degrees by default in order to inverse the residual voltage (3v 0 ) to calculate the reference ...
Page 204
-3v 0 3i 0 rca = -90 °, roa = 90° = ang(3i 0 ) – ang(v ref ) 3i 0 cos v ref en06000649_ansi.Vsd ansi06000649 v1 en-us figure 82: characteristic for rcadir equal to -90° when opmodesel is set to 3i03v0cosfi the apparent residual power component in the direction is measured. When opmodesel is set to 3...
Page 205
V ref =-3v 0 operate area 3i 0 rca = 0º roa = 80º ansi06000652-2-en.Vsd ansi06000652 v2 en-us figure 83: characteristic for rcadir = 0° and roadir = 80° dirmode is set forward or reverse to set the direction of the operation for the directional function selected by the opmodesel. All the directional...
Page 206
Roadir is relay operating angle. Roadir is identifying a window around the reference direction in order to detect directionality. Roadir is set in degrees. For angles differing more than roadir from rcadir the function is blocked. The setting can be used to prevent unwanted operation for non-faulted...
Page 207
Table 24: inverse time characteristics curve name ansi extremely inverse ansi very inverse ansi normal inverse ansi moderately inverse ansi/ieee definite time ansi long time extremely inverse ansi long time very inverse ansi long time inverse iec normal inverse iec very inverse iec inverse iec extre...
Page 208
Tvn is the definite time delay for the trip function of the residual voltage protection, given in s. 8.7 thermal overload protection, one time constant fahrenheit/celsius lfpttr/lcpttr (26) ip14512-1 v7 8.7.1 identification 8.8 thermal overload protection, two time constants trpttr (49) ip14513-1 v4...
Page 209
Overload protection provides information and makes temporary overloading of transformers possible. The permissible load level of a power transformer is highly dependent on the cooling system of the transformer. There are two main principles: • oa: the air is naturally circulated to the coolers witho...
Page 210
Globalbasesel: selects the global base value group used by the function to define (ibase), (ubase) and (sbase). Iref: reference level of the current given in % of ibase. When the current is equal to iref the final (steady state) heat content is equal to 1. It is suggested to give a setting correspon...
Page 211
If the transformer has forced cooling (foa) the measurement should be made both with and without the forced cooling in operation, giving tau2 and tau1. The time constants can be changed if the current is higher than a set value or lower than a set value. If the current is high it is assumed that the...
Page 212
Thetainit: heat content before activation of the function. This setting can be set a little below the alarm level. If the transformer is loaded before the activation of the protection function, its temperature can be higher than the ambient temperature. The start point given in the setting will prev...
Page 213
8.9.3 setting guidelines m11546-4 v9 the parameters for breaker failure protection 3-phase activation and output ccrbrf (50bf) are set via the local hmi or pcm600. The following settings can be done for the breaker failure protection. Globalbasesel: selects the global base value group used by the fu...
Page 214
Retripmode functionmode description no cbpos check current re-trip is done without check of current level contact re-trip is done without check of auxiliary contact position current/contact re-trip is done without check of current level or auxiliary contact position butripmode: back-up trip mode is ...
Page 215
T2: time delay of the back-up trip. The choice of this setting is made as short as possible at the same time as unwanted operation must be avoided. Typical setting is 90 – 200ms (also dependent of re-trip timer). The minimum time delay for the re-trip can be estimated as: _ 2 1 ³ + + + cbopen bfp re...
Page 216
T2mph: time delay of the back-up trip at multi-phase initiate. The critical fault clearance time is often shorter in case of multi-phase faults, compared to single phase- to-ground faults. Therefore there is a possibility to reduce the back-up trip delay for multi-phase faults. Typical setting is 90...
Page 217
Stub protection stbptoc (50stb) is a simple phase overcurrent protection, fed from the two current transformer groups feeding the object taken out of service. The stub protection is only activated when the disconnector of the object is open. Stbptoc (50stb) enables fast fault clearance of faults at ...
Page 218
Settingcontinuous the function is activated independent of presence of any external release signal. Ipickup: current level for the stub protection, set in % of ibase. This parameter should be set so that all faults on the stub can be detected. The setting should thus be based on fault calculations. ...
Page 219
Also be realized within the protection itself, by using opened and close signals for each circuit breaker pole, connected to the protection. • each phase current through the circuit breaker is measured. If the difference between the phase currents is larger than a currunsympu this is an indication o...
Page 220
8.12 directional underpower protection guppdup (37) semod156693-1 v4 8.12.1 identification semod158941-2 v4 function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number directional underpower protection guppdup p 2 symbol-ll v2 en-us 37 8.12.2 application semo...
Page 221
When the steam ceases to flow through a turbine, the cooling of the turbine blades will disappear. Now, it is not possible to remove all heat generated by the windage losses. Instead, the heat will increase the temperature in the steam turbine and especially of the blades. When a steam turbine rotat...
Page 222
Protection (reference angle set to 0) to trip if the active power from the generator is less than about 2%. One should set the overpower protection (reference angle set to 180) to trip if the power flow from the network to the generator is higher than 1%. Underpower protection overpower protection q...
Page 223
Set value mode formula used for complex power calculation bc * * ( ) bc b c s v i i = × - equation2059-ansi v1 en-us (equation 68) ca * * ( ) ca c a s v i i = × - equation2060-ansi v1 en-us (equation 69) a * 3 a a s v i = × × equation2061-ansi v1 en-us (equation 70) b * 3 b b s v i = × × equation206...
Page 224
Operate angle1(2) power1(2) p q en06000441.Vsd iec06000441 v1 en-us figure 87: underpower mode the setting power1(2) gives the power component pick up value in the angle1(2) direction. The setting is given in p.U. Of the generator rated power, see equation 73 . Minimum recommended setting is 0.2% of...
Page 225
Operate angle1(2) = 0 ° power1(2) p q en06000556.Vsd iec06000556 v1 en-us figure 88: for low forward power the set angle should be 0° in the underpower function tripdelay1(2) is set in seconds to give the time delay for trip of the stage after pick up. Hysteresis1(2) is given in p.U. Of generator ra...
Page 226
The value of k=0.92 is recommended in generator applications as the trip delay is normally quite long. The calibration factors for current and voltage measurement errors are set % of rated current/voltage: imagcomp5, imagcomp30, imagcomp100 vmagcomp5, vmagcomp30, vmagcomp100 imagcomp5, imagcomp30, i...
Page 227
Often, the motoring condition may imply that the turbine is in a very dangerous state. The task of the reverse power protection is to protect the turbine and not to protect the generator itself. Steam turbines easily become overheated if the steam flow becomes too low or if the steam ceases to flow ...
Page 228
May cause cavitations. The risk for damages to hydro turbines can justify reverse power protection in unattended plants. A hydro turbine that rotates in water with closed wicket gates will draw electric power from the rest of the power system. This power will be about 10% of the rated power. If ther...
Page 229
Mode: the voltage and current used for the power measurement. The setting possibilities are shown in table 27 . Table 27: complex power calculation set value mode formula used for complex power calculation a,b,c * * * a b c a b c s v i v i v i = × + × + × equation2038 v1 en-us (equation 77) arone * ...
Page 230
Operate angle1(2) power1(2) p q en06000440.Vsd iec06000440 v1 en-us figure 90: overpower mode the setting power1(2) gives the power component pick up value in the angle1(2) direction. The setting is given in p.U. Of the generator rated power, see equation 86 . Minimum recommended setting is 0.2% of ...
Page 231
Operate angle1(2 ) = 180 o power1(2) p q iec06000557-2-en.Vsd iec06000557 v2 en-us figure 91: for reverse power the set angle should be 180° in the overpower function tripdelay1(2) is set in seconds to give the time delay for trip of the stage after pick up. Hysteresis1(2) is given in p.U. Of genera...
Page 232
S td s td s old calculated = ⋅ + − ( ) ⋅ 1 equation1893-ansi v1 en-us (equation 88) where s is a new measured value to be used for the protection function s old is the measured value given from the function in previous execution cycle s calculated is the new calculated value in the present execution...
Page 233
8.14.2 application semod171858-5 v3 conventional protection functions can not detect the broken conductor condition. Broken conductor check (brcptoc, 46) function, consisting of continuous current unsymmetrical check on the line where the ied connected will give alarm or trip at detecting broken con...
Page 234
8.15.2 application guid-5ec8baec-9118-49ec-970c-43d6c416640a v1 guid-bacae67b-e64b-4963-b323-ecb0b69031b9 v2 shunt capacitor banks (scbs) are somewhat specific and different from other power system elements. These specific features of scb are briefly summarized in this section. A capacitor unit is t...
Page 235
Capacitor unit (can) rack iec09000753_1_en.Vsd iec09000753 v1 en-us figure 92: replacement of a faulty capacitor unit within scb there are four types of the capacitor unit fusing designs which are used for construction of scbs: externally fused where an individual fuse, externally mounted, protects ...
Page 236
Which type of fusing is used may depend on can manufacturer or utility preference and previous experience. Because the scbs are built from the individual capacitor units the overall connections may vary. Typically used scb configurations are: 1. Delta-connected banks (generally used only at distribu...
Page 237
In addition, to fault conditions scb can be exposed to different types of abnormal operating conditions. In accordance with iec and ansi standards capacitors shall be capable of continuous operation under contingency system and bank conditions, provided the following limitations are not exceeded: 1....
Page 238
1. Short circuit protection for scb and connecting leads (can be provided by using phpioc, oc4ptoc, cvgapc, t2wpdif/t3wpdif or hzpdif functions) 2. Ground-fault protection for scb and connecting leads (can be provided by using efpioc, ef4ptoc, cvgapc, t2wpdif/t3wpdif or hzpdif functions) 3. Current ...
Page 239
1000 200[ ] 289 3 400[ ] r mvar i a kv × = = × iec09000755 v1 en-us (equation 89) or on the secondary ct side: _ ec 289 0.578 500 1 r s a i a = = iec09000756 v1 en-us (equation 90) note that the scb rated current on the secondary ct side is important for secondary injection of the function. The para...
Page 240
Pu_37 =70% (of ibase); current level for undercurrent pickup tuc =5s; time delay for undercurrent trip undercurrent feature is blocked by operation of reconnection inhibit feature. Reactive power overload feature: operation qol =enabled; to enable this feature up_qol =130% (of scb mvar rating); reac...
Page 241
In simple words this means that the cb is not breaking the current at the first zero crossing after separation of the cb contacts. Instead current is re-ignited and only braked at consecutive current zero crossings. This condition is manifested as high current pulses at the moment of current re-igni...
Page 242
Current and three-phase voltage input in the configuration tool, but it will always measure the maximum phase current and the minimum phase-to-phase voltage. Vrpvoc (51v) function module has two independent protection each consisting of: • one overcurrent step with the following built-in features: •...
Page 243
8.16.2.3 undervoltage seal-in guid-13be02d3-1322-4075-859b-617cff608657 v7 in the case of a generator with a static excitation system, which receives its power from the generator terminals, the magnitude of a sustained phase short-circuit current depends on the generator terminal voltage. In case of...
Page 244
Pickup_curr: operation phase current level given in % of ibase. Characterist: selection of time characteristic: definite time delay and different types of inverse time characteristics are available; see technical manual for details. Tdef_oc: definite time delay. It is used if definite time character...
Page 245
8.16.3.2 voltage-restrained overcurrent protection for generator and step-up transformer guid-263b960b-2280-461c-b455-f17b7d278f60 v8 an example of how to use vrpvoc (51v) function to provide voltage restrained overcurrent protection for a generator is given below. Let us assume that the time coordi...
Page 246
• pickup current of the overcurrent stage: 150% of generator rated current at rated generator voltage; • pickup voltage of the undervoltage stage: 70% of generator rated voltage; • trip time: 3.0 s. The overcurrent stage and the undervoltage stage shall be set in the following way: 1. Set operation ...
Page 247
Section 9 voltage protection 9.1 two step undervoltage protection uv2ptuv (27) ip14544-1 v3 9.1.1 identification m16876-1 v7 function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number two step undervoltage protection uv2ptuv 3u symbol-r-2u-greater-than v2 en...
Page 248
The function has a high measuring accuracy and a settable hysteresis to allow applications to control reactive load. In many cases, uv2ptuv (27) is a useful function in circuits for local or remote automation processes in the power system. 9.1.3 setting guidelines m13851-3 v9 all the voltage conditi...
Page 249
9.1.3.5 backup protection for power system faults m13851-62 v3 the setting must be below the lowest occurring "normal" voltage and above the highest occurring voltage during the fault conditions under consideration. 9.1.3.6 settings for two step undervoltage protection m13851-65 v14 the following se...
Page 250
There is a short circuit or ground faults in the system. The time delay must be coordinated to the other short circuit protections. Tresetn: reset time for step n if definite time delay is used, given in s. The default value is 25 ms. Tnmin: minimum operation time for inverse time characteristic for...
Page 251
9.2.1 identification m17002-1 v8 function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number two step overvoltage protection ov2ptov 3u> symbol-c-2u-smaller-than v2 en-us 59 9.2.2 application m13799-3 v9 two step overvoltage protection ov2ptov (59) is applica...
Page 252
Expectancy. In many cases, it is a useful function in circuits for local or remote automation processes in the power system. 9.2.3 setting guidelines m13852-4 v10 the parameters for two step overvoltage protection (ov2ptov ,59) are set via the local hmi or pcm600. All the voltage conditions in the s...
Page 253
9.2.3.3 power supply quality m13852-16 v1 the setting has to be well above the highest occurring "normal" voltage and below the highest acceptable voltage, due to regulation, good practice or other agreements. 9.2.3.4 high impedance grounded systems m13852-19 v6 in high impedance grounded systems, g...
Page 254
Characteristicn: this parameter gives the type of time delay to be used. The setting can be definite time, inverse curve a, inverse curve b, inverse curve c or i/prog. Inv. Curve. The choice is highly dependent of the protection application. Opmoden: this parameter describes how many of the three me...
Page 255
Therefore a tuning parameter crvsatn is set to compensate for this phenomenon. In the voltage interval pickup> up to pickup> · (1.0 + crvsatn/100) the used voltage will be: pickup> · (1.0 + crvsatn/100). If the programmable curve is used, this parameter must be calculated so that: 0 100 crvsatn b c ...
Page 256
Does not provide any guidance in finding the faulted component. Therefore, rov2ptov (59n) is often used as a backup protection or as a release signal for the feeder ground fault protection. 9.3.3 setting guidelines m13853-3 v8 all the voltage conditions in the system where rov2ptov (59n) performs it...
Page 257
9.3.3.3 power supply quality m13853-15 v3 the setting must be above the highest occurring "normal" residual voltage and below the highest acceptable residual voltage, due to regulation, good practice or other agreements. 9.3.3.4 high impedance grounded systems m13853-18 v10 in high impedance grounde...
Page 258
9.3.3.5 direct grounded system guid-ea622f55-7978-4d1c-9af7-2bab5628070a v8 in direct grounded systems, an ground fault on one phase is indicated by voltage collapse in that phase. The other healthy phase will still have normal phase-to-ground voltage. The residual sum will have the same value as th...
Page 259
Rov2ptov (59n) will measure the residual voltage corresponding to the nominal phase-to-ground voltage for a high-impedance grounded system. The measurement will be based on the neutral voltage displacement. The setting parameters described below are identical for the two steps (n = step 1 and 2). Th...
Page 260
Tdn: time multiplier for inverse time characteristic. This parameter is used for co- ordination between different inverse time delayed undervoltage protections. Acrvn, bcrvn, ccrvn, dcrvn, pcrvn: parameters for step n, to set to create programmable undervoltage inverse time characteristic. Descripti...
Page 261
Internal fuses instead of a current unbalance protection measuring the current between the neutrals of two half’s of the capacitor bank. The function requires voltage transformers in all phases of the capacitor bank. Figure 97 shows some different alternative connections of this function. Vd>l1 ph b...
Page 262
The application to supervise the voltage on two voltage transformers in the generator circuit is shown in figure 98 . Vd> v1 v2 to protection to excitation gen en06000389_ansi.Vsd ansi06000389 v1 en-us figure 98: supervision of fuses on generator circuit voltage transformers 9.4.3 setting guidelines...
Page 263
Factor is defined as v2 · rflx and shall be equal to the v1 voltage. Each phase has its own ratio factor. Vdtrip: the voltage differential level required for tripping is set with this parameter. For application on capacitor banks the setting will depend of the capacitor bank voltage and the number o...
Page 264
9.5 loss of voltage check lovptuv (27) semod171868-1 v2 9.5.1 identification semod171954-2 v2 function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number loss of voltage check lovptuv - 27 9.5.2 application semod171876-4 v3 the trip of the circuit breaker at ...
Page 265
Section 10 frequency protection 10.1 underfrequency protection saptuf (81) ip15746-1 v3 10.1.1 identification m14865-1 v5 function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number underfrequency protection saptuf f symbol-p v1 en-us 81 10.1.2 application m1...
Page 266
10.1.3 setting guidelines m13355-3 v8 all the frequency and voltage magnitude conditions in the system where saptuf (81) performs its functions should be considered. The same also applies to the associated equipment, its frequency and time characteristic. There are two specific application areas for...
Page 267
10.2.1 identification m14866-1 v4 function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number overfrequency protection saptof f > symbol-o v1 en-us 81 10.2.2 application m14952-3 v4 overfrequency protection function saptof (81) is applicable in all situations...
Page 268
Equipment protection, such as for motors and generators the setting has to be well above the highest occurring "normal" frequency and well below the highest acceptable frequency for the equipment. Power system protection, by generator shedding the setting must be above the highest occurring "normal"...
Page 269
10.3.3 setting guidelines m14971-3 v7 the parameters for rate-of-change frequency protection sapfrc (81) are set via the local hmi or or through the protection and control manager (pcm600). All the frequency and voltage magnitude conditions in the system where sapfrc (81) performs its functions shou...
Page 270
10.4 frequency time accumulation protection function ftaqfvr (81a) guid-124a1f91-44c0-4db6-8603-cc8ca19ae2a6 v3 10.4.1 identification guid-87605da0-eaa6-4a6c-bf03-7fdb187e1b29 v2 function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ ieeeidentification frequency time accumulati...
Page 271
1.0 - + frequency or resonant frequency ratio s tr e ss m ag ni fic ati on f ac to r iec12000611-2-en.Vsd 50 100 150 200 250 300 iec12000611 v2 en-us figure 99: typical stress magnification factor curve according ansi/ieee c37.106-2003 standard each turbine manufactured for different design of blade...
Page 272
56 0.01 0.1 1 10 100 1000 58 frequency (hz) time (minutes) time (minutes) time (minutes) time (minutes) iec13000258-1-en.Ai continuous operation prohibited operation 60 62 56 0.01 0.1 1 10 100 1000 58 frequency (hz) continuous operation 60 62 56 0.01 0.1 1 10 100 1000 58 frequency (hz) 60 62 continu...
Page 273
Setting procedure on the ied the parameters for the frequency time accumulation protection ftaqfvr (81a) are set using the local hmi or through the dedicated software tool in protection and control manager (pcm600). Common base ied values for primary current ibase and primary voltage vbase are set i...
Page 274
268.
Page 275
Section 11 multipurpose protection 11.1 general current and voltage protection cvgapc ip14552-1 v2 11.1.1 identification m14886-2 v3 function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number general current and voltage protection cvgapc 2(i>/u - 11.1.2 appl...
Page 276
• definite time delay or inverse time overcurrent toc/idmt delay for both steps • second harmonic supervision is available in order to only allow operation of the overcurrent stage(s) if the content of the second harmonic in the measured current is lower than pre-set level • directional supervision ...
Page 277
The user can select, by a setting parameter currentinput, to measure one of the following current quantities shown in table 28 . Table 28: available selection for current quantity within cvgapc function set value for parameter "currentinput” comment 1 phasea cvgapc function will measure the phase a ...
Page 278
Table 29: available selection for voltage quantity within cvgapc function set value for parameter "voltageinput" comment 1 phasea cvgapc function will measure the phase a voltage phasor 2 phaseb cvgapc function will measure the phase b voltage phasor 3 phasec cvgapc function will measure the phase c...
Page 279
Phase-to-phase voltages vab, vbc and vca. This information about actual vt connection is entered as a setting parameter for the pre-processing block, which will then take automatically care about it. 11.1.2.2 base quantities for cvgapc function semod53443-112 v3 the parameter settings for the base q...
Page 280
• 80-95% stator earth fault protection (measured or calculated 3vo) (59gn) • rotor earth fault protection (with external combiflex rxtte4 injection unit) (64f) • underimpedance protection (21) • voltage controlled/restrained overcurrent protection (51c, 51v) • turn-to-turn & differential backup prot...
Page 281
There is a risk that the current into the generator at inadvertent energization will be limited so that the “normal” overcurrent or underimpedance protection will not detect the dangerous situation. The delay of these protection functions might be too long. The reverse power protection might detect ...
Page 282
Practically constant. It shall be noted that directional negative sequence oc element offers protection against all unbalance faults (phase-to-phase faults as well). Care shall be taken that the minimum pickup of such protection function shall be set above natural system unbalance level. An example ...
Page 283
If required, this cvgapc function can be used in directional comparison protection scheme for the power line protection if communication channels to the remote end of this power line are available. In that case typically two negseq overcurrent steps are required. One for forward and one for reverse ...
Page 284
Op 2 ns r td t i i = æ ö ç ÷ è ø equation1740-ansi v1 en-us (equation 96) where: t op is the operating time in seconds of the negative sequence overcurrent ied td is the generator capability constant in seconds i ns is the measured negative sequence current i r is the generator rated current by defi...
Page 285
Op p t td a b m c = × æ ö + ç ÷ - è ø equation1742-ansi v1 en-us (equation 99) where: t op is the operating time in seconds of the inverse time overcurrent toc/idmt algorithm td is time multiplier (parameter setting) m is ratio between measured current magnitude and set pickup current level a, b, c ...
Page 286
11.1.3.3 generator stator overload protection in accordance with iec or ansi standards m13088-81 v3 example will be given how to use one cvgapc function to provide generator stator overload protection in accordance with iec or ansi standard if minimum-operating current shall be set to 116% of genera...
Page 287
In order to achieve such protection functionality with one cvgapc functions the following must be done: 1. Connect three-phase generator currents to one cvgapc instance (for example, gf01) 2. Set parameter currentinput to value posseq 3. Set base current value to the rated generator current in prima...
Page 288
Proper timing of cvgapc function made in this way can easily be verified by secondary injection. All other settings can be left at the default values. If required delayed time reset for oc1 step can be set in order to insure proper function operation in case of repetitive overload conditions. Furthe...
Page 289
11.1.3.5 voltage restrained overcurrent protection for generator and step-up transformer m13088-158 v4 example will be given how to use one cvgapc function to provide voltage restrained overcurrent protection for a generator. Let us assume that the time coordination study gives the following require...
Page 290
Generator can be achieved. Let us assume that from rated generator data the following values are calculated: • maximum generator capability to contentiously absorb reactive power at zero active loading 38% of the generator mva rating • generator pull-out angle 84 degrees this functionality can be ac...
Page 291
0.2 0.4 0.6 -0.2 0.6 0.8 0.8 1 d ilowset b a c 0.4 0.2 0 1.2 1.4 -0.4 -0.6 -0.8 -rca operating region q [pu] p [pu] rca v ps i ps ilowset operating region en05000535_ansi.Vsd ansi05000535 v1 en-us figure 101: loss of excitation 1mrk 511 401-uus a section 11 multipurpose protection bay control rec670...
Page 292
286.
Page 293
Section 12 system protection and control 12.1 multipurpose filter smaihpac guid-6b541154-d56b-452f-b143-4c2a1b2d3a1f v1 12.1.1 identification guid-8224b870-3daa-44bf-b790-6600f2ad7c5d v1 function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number multipurpose...
Page 294
• sub-synchronous resonance protection for turbo generators • sub-synchronous protection for wind turbines/wind farms • detection of sub-synchronous oscillation between hvdc links and synchronous generators • super-synchronous protection • detection of presence of the geo-magnetic induced currents •...
Page 295
12.1.3 setting guidelines 12.1.3.1 setting example guid-5a3f67bd-7d48-4734-948c-01daf9470ef8 v2 a relay type used for generator subsynchronous resonance overcurrent protection shall be replaced. The relay had inverse time operating characteristic as given with the following formula: 01 op s k t t i ...
Page 296
Freqbandwidth 0.0 filterlength 1.0 s overlap 75 operation on now the settings for the multi-purpose overcurrent stage one shall be derived in order to emulate the existing relay operating characteristic. To achieve exactly the same inverse time characteristic the programmable idmt characteristic is ...
Page 297
Then exact replica of the existing relay will be achieved. The following table summarizes all required settings for the multi-purpose function: setting group1 operation on currentinput maxph ibase 1000 voltageinput maxph ubase 20.50 operharmrestr off i_2ndi_fund 20.0 blklevel2nd 5000 enrestraincurr ...
Page 298
292.
Page 299
Section 13 secondary system supervision 13.1 current circuit supervision (87) ip14555-1 v5 13.1.1 identification m14870-1 v5 function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number current circuit supervision ccsspvc - 87 13.1.2 application m12395-13 v9 o...
Page 300
13.1.3 setting guidelines m12397-17 v8 globalbasesel: selects the global base value group used by the function to define ibase, vbase and sbase as applicable. Current circuit supervision ccsspvc (87) compares the residual current from a three- phase set of current transformer cores with the neutral ...
Page 301
To the voltage instrument transformers, and shall be equipped with auxiliary contacts that are wired to the ieds. Separate fuse-failure monitoring ieds or elements within the protection and monitoring devices are another possibilities. These solutions are combined to get the best possible effect in ...
Page 302
13.2.3.2 setting of common parameters m13683-9 v9 set the operation mode selector operation to enabled to release the fuse failure function. The voltage threshold vppu is used to identify low voltage condition in the system. Set vppu below the minimum operating voltage that might occur during emerge...
Page 303
100 3 2 2 3 vbase v pu v equation1757-ansi v4 en-us (equation 108) where: v2pu is the maximal negative sequence voltage during normal operation conditions, plus a margin of 10...20% vbase is the base voltage for the function according to the setting globalbasesel the setting of the current limit 3i2...
Page 304
3 0 3 0 100 = × i i pu ibase equation2293-ansi v2 en-us (equation 111) where: 3i0pu is the maximal zero sequence current during normal operating conditions, plus a margin of 10...20% ibase is the base current for the function according to the setting globalbasesel 13.2.3.5 delta v and delta i guid-0...
Page 305
Set the idldpu with a sufficient margin below the minimum expected load current. A safety margin of at least 15-20% is recommended. The operate value must however exceed the maximum charging current of an overhead line, when only one phase is disconnected (mutual coupling to the other phases). Set t...
Page 306
Fusefailsupvn ied a b c v 2a v 2b v 2 c v 1 a v 1 b v 1 c ansi12000143-1-en.Vsd main vt circuit p ilo t v t c ir cu it ansi12000143 v1 en-us figure 103: application of vdspvc 13.3.3 setting guidelines guid-0d5a517c-1f92-46b9-ac2d-f41ed4e7c39e v1 guid-52bf4e8e-0b0c-4f75-99c4-0bcb22cdd166 v2 the param...
Page 307
The connection type for the main and the pilot fuse groups must be consistent. The settings vdif main block, vdif pilot alarm and vsealin are in percentage of the base voltage, vbase. Set vbase to the primary rated phase-to-phase voltage of the potential voltage transformer. Vbase is available in th...
Page 308
302.
Page 309
Section 14 control 14.1 synchronism check, energizing check, and synchronizing sesrsyn (25) ip14558-1 v4 14.1.1 identification m14889-1 v4 function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number synchrocheck, energizing check, and synchronizing sesrsyn sc...
Page 310
• the voltages v-line and v-bus are higher than the set values for vhighbussynch and vhighlinesynch of the respective base voltages gblbaseselbus and gblbaseselline. • the difference in the voltage is smaller than the set value of vdiffsynch. • the difference in frequency is less than the set value ...
Page 311
The reference voltage can be phase-neutral a, b, c or phase-phase a-b, b-c, c-a or positive sequence (require a three phase voltage, that is va, vb and vc) . By setting the phases used for sesrsyn, with the settings selphasebus1, selphasebus2, selphaseline2 and selphaseline2, a compensation is made ...
Page 312
• live line and live bus. • voltage level difference. • frequency difference (slip). The bus and line frequency must also be within a range of ±5 hz from rated frequency. • phase angle difference. A time delay is available to ensure that the conditions are fulfilled for a minimum period of time. In ...
Page 313
Fuse fail fuse fail line voltage line bus voltage line reference voltage bus voltage 52 ansi10000079-2-en.Vsd synchrocheck vhighbussc > 50 – 120% of gblbaseselbus vhighlinesc >50 – 120% of gblbaseselline vdiffsc phasediffm phasediffa freqdiffm freqdiffa ansi10000079 v2 en-us figure 105: principle fo...
Page 314
1 2 a b energizingcheck line voltage bus voltage ansi10000078-4-en.Vsd vlivebusenerg > 50 - 120 % of gblbaseselbus vlivelineenerg > 50 - 120 % of gblbaseselline vdeadbusenerg vdeadlineenerg vmaxenerg gblbaseselline ansi10000078 v4 en-us figure 106: principle for the energizing check function the ene...
Page 315
Depends on the status of the breakers and/or disconnectors. By checking the status of the disconnectors auxiliary contacts, the right voltages for the synchronism check and energizing check functions can be selected. Available voltage selection types are for single circuit breaker with double busbar...
Page 316
Ansi09000171_1_en.Vsd sesrsyn (25) menmode intone psto swposn name1 name2 off dl db dlb slggio name3 name4 ansi09000171 v1 en-us figure 107: selection of the energizing direction from a local hmi symbol through a selector switch function block. 14.1.3 application examples m12323-3 v7 the synchronism...
Page 317
14.1.3.1 single circuit breaker with single busbar m12324-3 v12 linevoltage/1/2/3 bus 1voltage bus 1 189 line v ref 1 fuse vt fuse vt 152 ansi0000093-1-en.Vsd va/vb/vc sesrsyn (25) v3pb1* v3pb2* v3pl1* v3pl2* block blksynch blksc blkenerg bus1_op bus1_cl bus2_op bus2_cl line1_op line1_cl line2_op li...
Page 318
14.1.3.2 single circuit breaker with double busbar, external voltage selection m12325-3 v8 line voltag e 1/2/3 bus voltage bus 1 bus 2 189 289 line fuse vt fuse vt fuse vt 152 ansi10000094-1-en.Vsd vref1 va/vb/ v c sesrsyn (25) v3pb1* v3pb2* v3pl1* v3pl2* block blksynch blksc blkenerg bus1_op bus1_c...
Page 319
14.1.3.3 single circuit breaker with double busbar, internal voltage selection m12326-3 v7 linevoltage/1/2/3 bus1voltage bus2voltage bus 1 bus 2 189 289 line vref1 vref2 va/vb/vc fuse vt fuse vt fuse vt 152 ansi10000095-1-en.Vsd sesrsyn (25) v3pb1* v3pb2* v3pl1* v3pl2* block blksynch blksc blkenerg ...
Page 320
14.1.3.4 double circuit breaker m12329-3 v7 linevoltage/1/2/3 bus 1 voltage bus 2 voltage bus 1 bus 2 line 252 fuse vt fuse vt fuse vt 152 252 152 ansi10000096-1-en.Vsd vref1 vref2 va/vb/vc sesrsyn (25) v3pb1* v3pb2* v3pl1* v3pl2* block blksynch blksc blkenerg bus1_op bus1_cl bus2_op bus2_cl line1_o...
Page 321
A double breaker arrangement requires two function blocks, one for breaker wa1_qa1 and one for breaker wa2_qa1. No voltage selection is necessary, because the voltage from busbar 1 vt is connected to v3pb1 on sesrsyn for wa1_qa1 and the voltage from busbar 2 vt is connected tov3pb1 on sesrsyn for wa...
Page 322
Tie cb bus 1 cb ansi10000097-1-en.Vsd vref1 vref2 bus1 voltage bus 2voltage line 1 voltage 1/2/3 line 2 voltage 989 989 line 1 line 2 vref3 bus 1 bus 2 289 189 152 289 189 152 fuse vt fuse vt 6189 6289 152 fuse vt fuse vt va/vb/vc sesrsyn (25) v3pb1* v3pb2* v3pl1* v3pl2* block blksynch blksc blkener...
Page 323
The connections are similar in all sesrsyn functions, apart from the breaker position indications. The physical analog connections of voltages and the connection to the ied and sesrsyn (25) function blocks must be carefully checked in pcm600. In all sesrsyn functions the connections and configuratio...
Page 324
14.1.4 setting guidelines m12550-3 v14 the setting parameters for the synchronizing, synchronism check and energizing check function sesrsyn (25) are set via the local hmi (lhmi) or pcm600. This setting guidelines describes the settings of the sesrsyn (25) function via the lhmi. Common base ied valu...
Page 325
• no voltage selection, no voltage sel. • single circuit breaker with double bus, double bus • breaker-and-a-half arrangement with the breaker connected to busbar 1, 1 1/2 bus cb • breaker-and-a-half arrangement with the breaker connected to busbar 2, 1 1/2 bus alt. Cb • breaker-and-a-half arrangeme...
Page 326
Are provided, and it is better to let the synchronizing function close, as it will close at exactly the right instance if the networks run with a frequency difference. To avoid overlapping of the synchronizing function and the synchrocheck function the setting freqdiffmin must be set to a higher val...
Page 327
Expected to be outside the limits from the start, a margin needs to be added. A typical setting is 600 seconds. Tminsynch the setting tminsynch is set to limit the minimum time at which the synchronizing closing attempt is given. The synchronizing function will not give a closing command within this...
Page 328
Phasediffa setting. Fluctuations occurring at high speed autoreclosing limit phasediffa setting. Tscm and tsca the purpose of the timer delay settings, tscm and tsca, is to ensure that the synchrocheck conditions remains constant and that the situation is not due to a temporary interference. Should ...
Page 329
The threshold voltages vdeadbusenerg and vdeadlineenerg, have to be set to a value greater than the value where the network is considered not to be energized. A typical value can be 40% of the base voltages. A disconnected line can have a considerable potential due to, for instance, induction from a...
Page 330
14.2.2 application m12391-3 v8 automatic reclosing is a well-established method for the restoration of service in a power system after a transient line fault. The majority of line faults are flashovers, which are transient by nature. When the power line is switched off by the operation of line prote...
Page 331
Single-pole tripping and single-phase automatic reclosing is a way of limiting the effect of a single-phase line fault on power system operation. Especially at higher voltage levels, the majority of faults are of single-phase type (around 90%). To maintain system stability in power systems with limi...
Page 332
Cb, reclosing of the second cb is cancelled and thus the stress on the power system is limited. The auto recloser can be selected to perform single-phase and/or three-phase automatic reclosing from several single-shot to multiple-shot reclosing programs. The three-phase auto reclosing dead time can ...
Page 333
When single and/or three phase auto reclosing is considered, there are a number of cases where the tripping shall be three phase anyway. For example: • evolving fault where the fault during the dead-time spreads to another phase. The other two phases must then be tripped and a three phase dead-time ...
Page 334
14.2.2.2 initiate auto reclosing and conditions for start of a reclosing cycle m12391-94 v5 the usual way to start an auto reclosing cycle, or sequence, is to start it at selective tripping by line protection by applying a signal to the ri input. Starting signals can be either, general trip signals ...
Page 335
• tripping from delayed distance protection zones • tripping from back-up protection functions • tripping from breaker failure function • intertrip received from remote end circuit breaker failure function • busbar protection tripping depending of the starting principle (general trip or only instant...
Page 336
14.2.2.7 maximum number of reclosing shots m12391-120 v7 the maximum number of auto reclosing shots in an auto reclosing cycle is selected by the setting noofshots. A maximum of five shots can be done. The type of auto reclosing used at the first auto reclosing shot is set by the setting armode. The...
Page 337
When a circuit breaker closing command is issued, the prepare three-pole output trip is set. When issuing a circuit breaker closing command the treclaim timer is started. If no tripping takes place during that time, the auto recloser resets to the “ready” state and the active output resets. If the f...
Page 338
Table 32: type of reclosing shots at different settings of armode or integer inputs to modeint modeint (integer) armode type of fault 1st shot 2nd-5th shot 1 3ph 1ph 3ph 3ph 2ph 3ph 3ph 3ph 3ph 3ph 2 1/2/3ph 1ph 1ph 3ph 2ph 2ph 3ph 3ph 3ph 3ph 3 1/2ph 1ph 1ph 3ph 2ph 2ph 3ph 3ph ..... ..... 4 1ph + ...
Page 339
Ansi09000168_1_en.Vsd smbrrec (79) modeint psto swposn name1 name2 3 1/3 intone slggio ansi09000168 v1 en-us figure 114: selection of the auto-reclose mode from a hardware functional key in front of the ied 14.2.2.15 auto reclosing reset timer m12391-202 v4 the treset timer defines the time it takes...
Page 340
May be made or the auto reclosing sequence is ended. After reclaim timer time-out the auto recloser resets, but the circuit breaker remains open. The circuit breaker closed information through the cbclosed input is missing. Thus, the auto recloser is not ready for a new auto reclosing cycle. Normall...
Page 341
Lock-out rxmd1 11 12 21 main zak close close command smbo or smbrrec (79) or ccrbrf (50bf) bj-trip zcvpsof-trip inhibit unsuccl trbu ansi05000315_2_en.Vsd set reset electrical reset relay ansi05000315 v2 en-us figure 115: lock-out arranged with an external lock-out relay close command or smbrrec (79...
Page 342
Then be stopped, and instead the timer, t1 3ph, for three-pole auto reclosing will be started from zero. The sequence will continue as a three-pole auto reclosing sequence, if it is a selected alternative reclosing mode. The second fault which can be single- phase is tripped three-pole because the t...
Page 343
Blkoff used to unblock the auto recloser when it has been blocked due to activating blkon input or by an unsuccessful auto reclosing attempt if the blockbyunsuccl setting is set to on. Blkon used to block the auto recloser, for example, when certain special service conditions arise. When used, block...
Page 344
Plclost this is intended for line protection permissive signal channel lost (fail) for example, plc= power line carrier failure. It can be connected, when it is required to prolong the auto reclosing dead time when communication is not working, that is, one line end might trip with a zone2 delay. If...
Page 345
The signal is required for three-phase shots 1-5 to proceed (note! Not the high-speed step). Tholhold signal “thermal overload protection holding back auto reclosing”. It can be connected to a thermal overload protection trip signal which resets only when the thermal content has fallen to an accepta...
Page 346
1pt1 and 2pt1 indicates that single-pole or two-pole auto reclosing is in progress. It is used to temporarily block an ground-fault and/or pole disagreement function during the single- pole or two-pole open interval. 3pt1, 3pt2, 3pt3, 3pt4 and 3pt5 indicates that three-pole auto reclosing shots one ...
Page 347
Mode when a valid integer is connected to the modeint input, the selected armode setting will be invalid and the modeint input value will be used instead. The selected mode is reported as an integer on the mode output. The six possible modes are described in table 32 with their corresponding modeint...
Page 348
Connection and setting examples figure 117 is showing an example of how to connect the auto recloser when used for three-pole auto reclosing and figure 118 is showing an example of how to connect the auto recloser when used for single-pole, two-pole or three-pole auto reclosing. Ansi04000135-3-en.Vs...
Page 349
Ansi04000136-3-en.Vsd on off blkon blkoff inhibit blocked seton inprogr active unsuccl succl closecb permit1p 3pt1 wfmaster reset 1pt1 2pt1 trsotf tr2p tr3p sync input xx xx xx xx xx xx xx xx xx xx or or output xx or protection xxxx-trip zcvpsof-trip zmqpdis (21)-trip trip-tr2p trip-tr3p sesrsyn (25...
Page 350
For tslavedeadtime is 0.1sec because both master and slave should not send the breaker closing command at the same time. The slave should take the duration of the breaker closing time of the master into consideration before sending the breaker closing command. A setting twaitformaster sets a maximum...
Page 351
Ansi04000137-3-en.Vsd active unsuccl ready 3pt2 3pt3 wait cbready trsotf reset blkoff blkon off on blocked seton inprogr 3pt4 sync inhibit terminal ‘‘ master ” priority = high smbrrec (79) wait terminal ‘‘ slave ” priority = low cb1 cb2 wfmaster wfmaster *) other input/output signals as in previous ...
Page 352
General settings operation: the operation of the auto recloser can be switched enabled or disabled. Externalctrl: this setting makes it possible to switch the auto recloser on or off using an external switch via io or communication ports. Armode: there are six different possibilities in the selectio...
Page 353
Zoneseqcoord: the zonestep input is used when coordination between local auto reclosers and down stream auto reclosers is needed. When this input is activated the auto recloser increases its actual shot number by one and enters “reset time” status. If a start is received during this reclaim time the...
Page 354
Pulse setting may facilitate dynamic indication at testing, for example, in debug mode of the application configuration tool (act) in pcm600. In circuit breakers without anti-pumping relays, the setting cutpulse = enabled can be used to avoid repeated closing operations when reclosing onto a fault. ...
Page 355
Single-phase auto reclosing dead time: a typical setting is t1 1ph = 800ms. Due to the influence of energized phases the arc extinction may not be instantaneous. In long lines with high voltage the use of shunt reactors in the form of a star with a neutral reactor improves the arc extinction. Three-...
Page 356
Auto reclosing operation. When the wait input is reset at the time of a successful reclosing of the first circuit breaker, the slave is released to continue the auto reclosing sequence after the set tslavedeadtime. The reason for shortening the time, for the normal dead timers with the value of tsla...
Page 357
Station hmi gw cc station bus breakers disconnectors grounding switches ansi08000227.Vsd apparatus control ied close/open local hmi apparatus control ied apparatus control ied local hmi local hmi close/open close/open ansi08000227 v1 en-us figure 120: overview of the apparatus control functions feat...
Page 358
• reservation input resin • local remote locrem • local remote control locremctrl the signal flow between the function blocks is shown in figure 121 . To realize the reservation function, the function blocks reservation input (resin) and bay reserve (qcrsv) also are included in the apparatus control...
Page 359
En05000116_ansi.Vsd sxcbr scswi scilo sxcbr sxcbr scswi scilo sxswi 189 989 iec 61850 qcbay 152 ansi05000116 v1 en-us figure 121: signal flow between apparatus control function blocks when all functions are situated within the ied 1mrk 511 401-uus a section 14 control bay control rec670 2.2 ansi 353...
Page 360
Merging unit bay level ied xcbr xcbr xcbr scswi iec 61850 on station bus xswi qcbay scilo scswi goosexlnrcv scilo xlnproxy goosexlnrcv xlnproxy -qa1 -qb1 -qb9 goose over process bus iec16000070-1-en.Vsdx iec16000070 v1 en-us figure 122: signal flow between apparatus control functions with xcbr and x...
Page 361
Control operation can be performed from the local ied hmi. If users are defined in the ied, then the local/remote switch is under authority control, otherwise the default user can perform control operations from the local ied hmi without logging in. The default position of the local/remote switch is...
Page 362
14.3.1.1 bay control qcbay m16595-3 v9 the bay control (qcbay) is used to handle the selection of the operator place per bay. The function gives permission to operate from two main types of locations either from remote (for example, control centre or station hmi) or from local (local hmi on the ied)...
Page 363
14.3.1.2 switch controller scswi m16596-3 v5 scswi may handle and operate on one three-phase device or three one-phase switching devices. After the selection of an apparatus and before the execution, the switch controller performs the following checks and actions: • a request initiates to reserve ot...
Page 364
The purpose of these functions is to provide the actual status of positions and to perform the control operations, that is, pass all the commands to the primary apparatus via output boards and to supervise the switching operation and position. Switches have the following functionalities: • local/rem...
Page 365
Iec16000071 v1 en-us figure 124: configuration with xlnproxy and goosexlnrcv where all the iec 61850 modelled data is used, including selection 1mrk 511 401-uus a section 14 control bay control rec670 2.2 ansi 359 application manual.
Page 366
Iec16000072 v1 en-us figure 125: configuration with xlnproxy and goosexlnrcv where only the mandatory data in the iec 61850 modelling is used all the information from the xlnproxy to the scswi about command following status, causes for failed command and selection status is transferred in the output...
Page 367
Table 35: possible cause values from xlnproxy cause no cause description conditions 8 blocked-by-mode the beh input is 5. 2 blocked-by-switching-hierarchy the loc input indicates that only local commands are allowed for the breaker ied function. -24 blocked-for-open-cmd the blkopn is active indicati...
Page 368
Wants the reservation sends a reservation request to other bays and then waits for a reservation granted signal from the other bays. Actual position indications from these bays are then transferred over the station bus for evaluation in the ied. After the evaluation the operation can be executed wit...
Page 369
En 05000118_ansi.Vsd scswi selected res_ ext + ied bi bo ied bi bo or other scswi in the bay ansi05000118 v2 en-us figure 127: application principles for reservation with external wiring the solution in figure 127 can also be realized over the station bus according to the application example in figu...
Page 370
• the switch controller (scswi) initializes all operations for one apparatus. It is the command interface of the apparatus. It includes the position reporting as well as the control of the position • the circuit breaker (sxcbr) is the process interface to the circuit breaker for the apparatus contro...
Page 371
Sxcbr (circuit breaker) interlocking function block (not a ln) scswi (switching control) qcbay (bay control) smbrrec (auto- reclosure) i/o trip close rel. Res. Req. Start a r close cb position res. Granted operator place selection scswi (switching control) sxswi (disconnector) open cmd close cmd pos...
Page 372
Ansi05000120-2-en.Vsd zmqpdis (distance) sxcbr (circuit breaker) interlocking function block (not a ln) scswi (switching control) qcbay (bay control) smbrrec (auto- reclosure) i/o trip close rel. Res. Req. In iti at e a r close cb position res. Granted operator place selection scswi (switching contr...
Page 373
14.3.3 setting guidelines m16669-3 v4 the setting parameters for the apparatus control function are set via the local hmi or pcm600. 14.3.3.1 bay control (qcbay) m16670-3 v7 if the parameter allpstovalid is set to no priority, all originators from local and remote are accepted without any priority. ...
Page 374
The time parameter tresresponse is the allowed time from reservation request to the feedback reservation granted from all bays involved in the reservation function. When the time has expired, the control function is reset, and a cause-code is given. Tsynchrocheck is the allowed time for the synchron...
Page 375
Command output pulse remains active until the timer topenpulsetclosepulse has elapsed. Topenpulse is the output pulse length for an open command. If adaptivepulse is set to adaptive, it is the maximum length of the output pulse for an open command. The default length is set to 200 ms for a circuit b...
Page 376
14.3.3.5 bay reserve (qcrsv) m16677-3 v3 the timer tcancelres defines the supervision time for canceling the reservation, when this cannot be done by requesting bay due to for example communication failure. When the parameter paramrequestx (x=1-8) is set to only own bay res. Individually for each ap...
Page 377
Example 100a) after grounding of a line. Circuit breakers are usually not interlocked. Closing is only interlocked against running disconnectors in the same bay, and the bus-coupler opening is interlocked during a busbar transfer. The positions of all switching devices in a bay and from some other b...
Page 378
When they are set to 0=false. 14.4.2 interlocking for line bay abc_line (3) ip14139-1 v2 14.4.2.1 application m13561-3 v8 the interlocking for line bay (abc_line, 3) function is used for a line connected to a double busbar arrangement with a transfer busbar according to figure 130 . The function can...
Page 379
These signals from each line bay (abc_line, 3) except that of the own bay are needed: signal 789optr 789 is open vp789tr the switch status for 789 is valid. Exdu_bpb no transmission error from the bay that contains the above information. For bay n, these conditions are valid: and bb7_d_op vp_bb7_d e...
Page 380
Section 1 section 2 a1a2_dc(bs) b1b2_dc(bs) abc_line abc_bc abc_line abc_bc (wa1)a1 (wa2)b1 (wa7)c c b2 a2 en04000479_ansi.Vsd ansi04000479 v1 en-us figure 132: busbars divided by bus-section disconnectors (circuit breakers) to derive the signals: signal bc_12_cl a bus-coupler connection exists betw...
Page 381
These signals from each bus-section disconnector bay (a1a2_dc) are also needed. For b1b2_dc, corresponding signals from busbar b are used. The same type of module (a1a2_dc) is used for different busbars, that is, for both bus-section disconnector a1a2_dc and b1b2_dc. Signal dcoptr the bus-section di...
Page 382
Bc12cltr (sect.1) dccltr (a1a2) dccltr (b1b2) or and bc12cltr (sect.2) vpbc12tr (sect.1) vpdctr (a1a2) vpdctr (b1b2) vpbc12tr (sect.2) or bc17optr (sect.1) dcoptr (a1a2) bc17optr (sect.2) bc17cltr (sect.1) dccltr (a1a2) bc17cltr (sect.2) vpbc17tr (sect.1) vpdctr (a1a2) vpbc17tr (sect.2) bc27optr (se...
Page 383
14.4.2.4 configuration setting m13560-108 v4 if there is no bypass busbar and therefore no 789 disconnector, then the interlocking for 789 is not used. The states for 789, 7189g, bb7_d, bc_17, bc_27 are set to open by setting the appropriate module inputs as follows. In the functional block diagram,...
Page 384
14.4.3 interlocking for bus-coupler bay abc_bc (3) ip14144-1 v2 14.4.3.1 application m13555-3 v8 the interlocking for bus-coupler bay (abc_bc, 3) function is used for a bus-coupler bay connected to a double busbar arrangement according to figure 134 . The function can also be used for a single busba...
Page 385
Signal q1289optr 189 or 289 or both are open. Vp1289tr the switch status of 189 and 289 are valid. Exdu_12 no transmission error from the bay that contains the above information. For bus-coupler bay n, these conditions are valid: 1289optr (bay 1) 1289optr (bay 2) . . . . . . 1289optr (bay n-1) and b...
Page 386
The following signals from each bus-section disconnector bay (a1a2_dc) are needed. For b1b2_dc, corresponding signals from busbar b are used. The same type of module (a1a2_dc) is used for different busbars, that is, for both bus-section disconnector a1a2_dc and b1b2_dc. Signal dcoptr the bus-section...
Page 387
14.4.3.4 signals from bus-coupler m13553-58 v5 if the busbar is divided by bus-section disconnectors into bus-sections, the signals bc_12 from the busbar coupler of the other busbar section must be transmitted to the own busbar coupler if both disconnectors are closed. En04000484_ansi.Vsd section 1 ...
Page 388
If the busbar is divided by bus-section circuit breakers, the signals from the bus-section coupler bay (a1a2_bs), rather than the bus-section disconnector bay (a1a2_dc), must be used. For b1b2_bs, corresponding signals from busbar b are used. The same type of module (a1a2_bs) is used for different b...
Page 389
• 7189g_op = 1 • 7189g_cl = 0 if there is no second busbar b and therefore no 289 and 2089 disconnectors, then the interlocking for 289 and 2089 are not used. The states for 289, 2089, 2189g, bc_12, bbtr are set to open by setting the appropriate module inputs as follows. In the functional block dia...
Page 390
189 289 189g 289g wa1 (a) wa2 (b) 389g 489g 489 389 252 and 489g are not used in this interlocking ab_trafo en04000515_ansi.Vsd 252 152 ansi04000515 v1 en-us figure 140: switchyard layout ab_trafo (3) m13566-4 v4 the signals from other bays connected to the module ab_trafo are described below. 14.4....
Page 391
En04000487_ansi.Vsd section 1 section 2 a1a2_dc(bs) b1b2_dc(bs) ab_trafo abc_bc ab_trafo abc_bc (wa1)a1 (wa2)b1 (wa7)c c b2 a2 ansi04000487 v1 en-us figure 141: busbars divided by bus-section disconnectors (circuit breakers) the project-specific logic for input signals concerning bus-coupler are the...
Page 392
If there is no second busbar b at the other side of the transformer and therefore no 489 disconnector, then the state for 489 is set to open by setting the appropriate module inputs as follows: • 489_op = 1 • 489_cl = 0 14.4.5 interlocking for bus-section breaker a1a2_bs (3) ip14154-1 v2 14.4.5.1 ap...
Page 393
En04000489_ansi.Vsd section 1 section 2 a1a2_bs b1b2_bs abc_line abc_bc abc_line abc_bc (wa1)a1 (wa2)b1 (wa7)c c b2 a2 ab_trafo ab_trafo ansi04000489 v1 en-us figure 143: busbars divided by bus-section circuit breakers to derive the signals: signal bbtr_op no busbar transfer is in progress concernin...
Page 394
Signal s1s2optr no bus-section coupler connection between bus-sections 1 and 2. Vps1s2tr the switch status of bus-section coupler bs is valid. Exdu_bs no transmission error from the bay that contains the above information. For a bus-section circuit breaker between a1 and a2 section busbars, these co...
Page 395
For a bus-section circuit breaker between b1 and b2 section busbars, these conditions are valid: en04000491_ansi.Vsd s1s2optr (a1a2) bc12optr (sect.1) 1289optr (bay 1/sect.2) 1289optr (bay n/sect.2) s1s2optr (a1a2) bc12optr (sect.2) 1289optr (bay 1/sect.1) 1289optr (bay n /sect.1) bbtr_op vp_bbtr ex...
Page 396
14.4.6 interlocking for bus-section disconnector a1a2_dc (3) ip14159-1 v2 14.4.6.1 application m13544-3 v7 the interlocking for bus-section disconnector (a1a2_dc, 3) function is used for one bus-section disconnector between section 1 and 2 according to figure 146 . A1a2_dc (3) function can be used f...
Page 397
Signal s1dc_op all disconnectors on bus-section 1 are open. S2dc_op all disconnectors on bus-section 2 are open. Vps1_dc the switch status of disconnectors on bus-section 1 is valid. Vps2_dc the switch status of disconnectors on bus-section 2 is valid. Exdu_bb no transmission error from any bay that...
Page 398
For a bus-section disconnector, these conditions from the a1 busbar section are valid: 189optr (bay 1/sect.A1) s1dc_op vps1_dc exdu_bb en04000494_ansi.Vsd and 189optr (bay n/sect.A1) . . . . . . . . . Vp189tr (bay 1/sect.A1) vp189tr (bay n/sect.A1) exdu_bb (bay 1/sect.A1) exdu_bb (bay n/sect.A1) . ....
Page 399
En04000496_ansi.Vsd 289optr (22089otr)(bay 1/sect.B1) s1dc_op vps1_dc exdu_bb 289optr (22089otr)(bay n/sect.B1) . . . . . . . . . Vp289tr (v22089tr)(bay 1/sect.B1) vp289tr (v22089tr)(bay n/sect.B1) exdu_bb (bay 1/sect.B1) exdu_bb (bay n/sect.B1) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . And and and ansi04...
Page 400
The same type of module (a1a2_dc) is used for different busbars, that is, for both bus-section disconnector a1a2_dc and b1b2_dc. But for b1b2_dc, corresponding signals from busbar b are used. En04000498_ansi.Vsd section 1 section 2 a1a2_dc(bs) b1b2_dc(bs) db_bus db_bus db_bus db_bus (wa1)a1 (wa2)b1 ...
Page 401
En04000499_ansi.Vsd 189optr (bay 1/sect.A1) s1dc_op vps1_dc exdu_bb and 189optr (bay n/sect.A1) . . . . . . . . . Vp189tr (bay 1/sect.A1) vp189tr (bay n/sect.A1) exdu_db (bay 1/sect.A1) exdu_db (bay n/sect.A1) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . And and ansi04000499 v1 en-us figure 153: signals from...
Page 402
En04000501_ansi.Vsd 289optr (bay 1/sect.B1) s1dc_op vps1_dc exdu_bb and 289optr (bay n/sect.B1) . . . . . . . . . Vp289tr (bay 1/sect.B1) vp289tr (bay n/sect.B1) exdu_db (bay 1/sect.B1) exdu_db (bay n/sect.B1) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . And and ansi04000501 v1 en-us figure 155: signals from...
Page 403
En04000503_ansi.Vsd section 1 section 2 a1a2_dc(bs) b1b2_dc(bs) bh_line (wa1)a1 (wa2)b1 b2 a2 bh_line bh_line bh_line ansi04000503 v1 en-us figure 157: busbars divided by bus-section disconnectors (circuit breakers) the project-specific logic is the same as for the logic for the double-breaker confi...
Page 404
14.4.7.2 signals in single breaker arrangement m15053-6 v5 the busbar grounding switch is only allowed to operate if all disconnectors of the bus- section are open. En04000505_ansi.Vsd section 1 section 2 a1a2_dc(bs) b1b2_dc(bs) ab_trafo abc_line bb_es abc_line (wa1)a1 (wa2)b1 (wa7)c c b2 a2 bb_es a...
Page 405
Signal dcoptr the bus-section disconnector is open. Vpdctr the switch status of bus-section disconnector dc is valid. Exdu_dc no transmission error from the bay that contains the above information. If no bus-section disconnector exists, the signal dcoptr, vpdctr and exdu_dc are set to 1 (true). If t...
Page 406
189optr (bay 1/sect.A2) bb_dc_op vp_bb_dc exdu_bb en04000507_ansi.Vsd 189optr (bay n/sect.A2) . . . . . . . . . Vp189tr (bay 1/sect.A2) vp189tr (bay n/sect.A2) vpdctr (a1/a2) exdu_bb (bay n/sect.A2) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . And dcoptr (a1/a2) exdu_bb (bay 1/sect.A2) exdu_dc (a1/a2) and an...
Page 407
289optr(22089otr)(bay 1/sect.B1) bb_dc_op vp_bb_dc exdu_bb en04000508_ansi.Vsd 289ptr (22089otr)(bay n/sect.B1) . . . . . . . . . Vp289tr(v22089tr) (bay 1/sect.B1) vp289tr(v22089tr) (bay n/sect.B1) vpdctr (b1/b2) exdu_bb (bay n/sect.B1) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . And and and dcoptr (b1/b2) ...
Page 408
For a busbar grounding switch on bypass busbar c, these conditions are valid: 789optr (bay 1) bb_dc_op vp_bb_dc exdu_bb en04000510_ansi.Vsd and and and 789optr (bay n) . . . . . . . . . Vp789tr (bay 1) vp789tr (bay n) exdu_bb (bay 1) exdu_bb (bay n) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Ansi04000510 v...
Page 409
Signal 189optr 189 is open. 289optr 289 is open. Vp189tr the switch status of 189 is valid. Vp289tr the switch status of 289 is valid. Exdu_db no transmission error from the bay that contains the above information. These signals from each bus-section disconnector bay (a1a2_dc) are also needed. For b...
Page 410
14.4.8 interlocking for double cb bay db (3) ip14167-1 v2 14.4.8.1 application m13585-3 v10 the interlocking for a double busbar double circuit breaker bay including db_bus_a (3), db_bus_b (3) and db_line (3) functions are used for a line connected to a double busbar arrangement according to figure ...
Page 411
• 989_op = 1 • 989_cl = 0 • 989g_op = 1 • 989g_cl = 0 if, in this case, line voltage supervision is added, then rather than setting 989 to open state, specify the state of the voltage supervision: • 989_op = volt_off • 989_cl = volt_on if there is no voltage supervision, then set the corresponding i...
Page 412
Wa1 (a) wa2 (b) 189 189g 289g 989g 689 989 289 189g 289g 389g 689 389g 6289 6189 189g 289g 989g 989 bh_line_a bh_line_b bh_conn en04000513_ansi.Vsd 152 152 152 ansi04000513 v1 en-us figure 168: switchyard layout breaker-and-a-half m13570-7 v4 three types of interlocking modules per diameter are defi...
Page 413
If, in this case, line voltage supervision is added, then rather than setting 989 to open state, specify the state of the voltage supervision: • 989_op = volt_off • 989_cl = volt_on if there is no voltage supervision, then set the corresponding inputs as follows: • volt_off = 1 • volt_on = 0 14.5 vo...
Page 414
Secondary side of the power transformer. The control method is based on a step-by-step principle which means that a control pulse, one at a time, will be issued to the tap changer mechanism to move it one position up or down. The length of the control pulse can be set within a wide range to accommod...
Page 415
Time delay (inverse or definite time) is set to avoid unnecessary operation during shorter voltage deviations from the target value, and in order to coordinate with other automatic voltage controllers in the system. Tcmyltc and tclyltc (84)are an interface between the automatic voltage control for t...
Page 416
Analog quantities are fed to the ied via the transformer input module, the analog to digital converter and thereafter a pre-processing block. In the pre-processing block, a great number of quantities for example, phase-to-phase analog values, sequence values, max value in a three phase group etc., a...
Page 417
Ansi10000044-1-en.Vsd l oa d t ap c h an g e r raise,lower signals/alarms position mim bom ied trm 3ph or ph-ph or 1ph currents high voltage side low voltage side line impedance r+jx load center 3ph or ph-ph or 1ph voltages i a ,i b ,i c (load current) i l vl (load point voltage) vb (busbar voltage)...
Page 418
Automatic voltage control for a single transformer semod159053-73 v6 automatic voltage control for tap changer, single control tr1atcc (90) measures the magnitude of the busbar voltage v b . If no other additional features are enabled (line voltage drop compensation), this voltage is further used fo...
Page 419
When v b falls below setting vblock, or alternatively, falls below setting vmin but still above vblock, or rises above vmax, actions will be taken in accordance with settings for blocking conditions (refer to table 40 ). If the busbar voltage rises above vmax, tr1atcc (90) can initiate one or more f...
Page 420
T 1 tmin d = equation1848 v2 en-us (equation 117) where: da absolute voltage deviation from the set point d relative voltage deviation in respect to set deadband value for the last equation, the condition t1 > tmin shall also be fulfilled. This practically means that tmin will be equal to the set t1...
Page 421
Line voltage drop semod159053-105 v6 the purpose with the line voltage drop compensation is to control the voltage, not at the power transformer low voltage side, but at a point closer to the load point. Figure 172 shows the vector diagram for a line modelled as a series impedance with the voltage v...
Page 422
~ l o a d r l x l v b v l v b r l i l jx l i l re ansi06000487-2-en.Vsd ansi06000487 v2 en-us figure 172: vector diagram for line voltage drop compensation the calculated load voltage v l is shown on the local hmi as value uload under main menu/test/function status/control/transformervoltagecontrol(...
Page 423
With these factors, tr1atcc (90) or tr8atcc (90) adjusts the value of the set voltage vset according to the following formula: 2 l a ci i vsetadjust vset s s i base = + × + equation1978-ansi v2 en-us (equation 118) v set, adjust adjusted set voltage in per unit vset original set voltage: base qualit...
Page 424
Assuming for instance that they start out on the same tap position and that the lv busbar voltage v b is within vset ± dv, then a gradual increase or decrease in the load would at some stage make v b fall outside vset ± dv and a raise or lower command would be initiated. However, the rate of change ...
Page 425
Two inputs are pulse activated, and the most recent activation is valid that is, an activation of any of these two inputs overrides previous activations. If none of these inputs has been activated, the default is that the transformer acts as a follower (given of course that the settings are parallel...
Page 426
Figure 175 , shows a vector diagram where the principle of reverse reactance has been introduced for the transformers in figure 174 . The transformers are here supposed to be on the same tap position, and the busbar voltage is supposed to give a calculated compensated value v l that coincides with t...
Page 427
En06000491_ansi.Vsd load t1 i l t2 i cc....T2 i cc....T1 v b v l i t1 i t2 v b v l1 ri t1 jx l i t 1 i cc -i cc (i t1 +i t2 )/2 i t1 i t2 v l2 r l i t2 jx l i t2 ansi06000491 v1 en-us figure 176: circulating current caused by t1 on a higher tap than t2. The circulating current i cc is predominantly ...
Page 428
1. That the busbar or load voltage is regulated to a preset target value 2. That the load is shared between parallel transformers in proportion to their ohmic short circuit reactance if the transformers have equal percentage impedance given in the respective transformer mva base, the load will be di...
Page 429
Di i cc _ i i v c i x = × × equation1979-ansi v1 en-us (equation 119) where x i is the short-circuit reactance for transformer i and c i , is a setting parameter named comp which serves the purpose of alternatively increasing or decreasing the impact of the circulating current in tr8atcc control cal...
Page 430
Line voltage drop compensation for parallel control semod159053-186 v3 the line voltage drop compensation for a single transformer is described in section "line voltage drop" . The same principle is used for parallel control with the circulating current method and with the master – follower method, ...
Page 431
Hv side, but open on the lv side (hot stand-by), to follow the voltage regulation of loaded parallel transformers, and thus be on a proper tap position when the lv circuit breaker closes. For this function, it is needed to have the lv vts for each transformer on the cable (tail) side (not the busbar...
Page 432
Tr8atcc (90) in adapt mode will continue the calculation of v di , but instead of adding v di to the measured busbar voltage, it will compare it with the deadband dv. The following control rules are used: 1. If v di is positive and its modulus is greater than dv, then initiate an vlower command. Tap...
Page 433
The calculation of circulating currents. The capacitive current is part of the imaginary load current and therefore essential in the calculation. The calculated circulating current and the real circulating currents will in this case not be the same, and they will not reach a minimum at the same time...
Page 434
For t2 and t1. This in turn would be misinterpreted as a circulating current, and would upset a correct calculation of i cc . Thus, if the actual connection is as in the left figure the capacitive current i c needs to be compensated for regardless of the operating conditions and in atcc this is made...
Page 435
Atcc ied hv-side pforward lv-side ansi06000536-2-en.Vsd qforward (inductive) ansi06000536 v2 en-us figure 178: power direction references with the four outputs in the function block available, it is possible to do more than just supervise a level of power flow in one direction. By combining the outp...
Page 436
T1 t2 t3 99000952.Vsd v 1 v 2 v 3 z 1 z 2 z 3 i 1 i 2 i 3 =0 i l =i 1 +i 2 ansi99000952 v1 en-us figure 179: disconnection of one transformer in a parallel group when the busbar arrangement is more complicated with more buses and bus couplers/bus sections, it is necessary to engineer a specific stat...
Page 437
Tcmyltc or tclyltc (84) function block for the same transformer as tr8atcc (90) block belongs to. There are 10 binary signals and 6 analog signals in the data set that is transmitted from one tr8atcc (90) block to the other tr8atcc (90) blocks in the same parallel group: table 37: binary signals sig...
Page 438
• setv • vctrstatus • x2 the transformers controlled in parallel with the circulating current method or the master-follower method must be assigned unique identities. These identities are entered as a setting in each tr8atcc (90), and they are predefined as t1, t2, t3,..., t8 (transformers 1 to 8). ...
Page 439
For the automatic voltage control for tap changer function, tr1atcc (90) for single control and tr8atcc (90) for parallel control, three types of blocking are used: partial block: prevents operation of the tap changer only in one direction (only vraise or vlower command is blocked) in manual and aut...
Page 440
Setting values (range) description revactpartbk(auto matically reset) alarm auto block the risk of voltage instability increases as transmission lines become more heavily loaded in an attempt to maximize the efficient use of existing generation and transmission facilities. In the same time lack of r...
Page 441
Setting values (range) description tapchgbk (manually reset alarm auto block auto&man block if the input tcinprog of tcmyltc or tclyltc (84) function block is connected to the tap changer mechanism, then this blocking condition will be active if the tcinprog input has not reset when the ttctimeout t...
Page 442
Setting values (range) description tapposbk (automatically reset/manually reset) alarm auto block auto&man block this blocking/alarm is activated by either: 1. The tap changer reaching an end position i.E. One of the extreme positions according to the setting parameters lowvolttap and highvolttap . ...
Page 443
Setting values (range) description mfposdiffbk (manually reset) alarm auto block in the master-follower mode, if the tap difference between a follower and the master is greater than the set value (setting parameter mfposdifflim ) then this blocking condition is fulfilled and the outputs outofpos and...
Page 444
Blockings activated by the operating conditions, without setting or separate external activation possibilities, are listed in table 43 . Table 43: blockings without setting possibilities activation type of blocking description disconnected transformer (automatically reset) auto block automatic contr...
Page 445
Block is received from any of the group members, automatic operation is blocked in the receiving tr8atccs (90) that is, all units of the parallel group. The following conditions in any one of tr8atccs (90) in the group will cause mutual blocking when the circulating current method is used: • over-cu...
Page 446
Example, iblk for over-current blocking. The other tr8atccs (90) that receive a mutual block signal will only set its autoblk output. The mutual blocking remains until tr8atcc (90) that dispatched the mutual block signal is de-blocked. Another way to release the mutual blocking is to force tr8atcc (...
Page 447
Usually the tap changer mechanism can give a signal, “tap change in progress”, during the time that it is carrying through an operation. This signal from the tap changer mechanism can be connected via a bim module to tcmyltc (84) or tclyltc (84) input tcinprog, and it can then be used by tcmyltc (84...
Page 448
The second use is to detect a jammed tap changer. If the timer ttctimeout times out before the tcinprog signal is set back to zero, the output signal tcerral is set high and tr1atcc (90) or tr8atcc (90) function is blocked. The third use is to check the proper operation of the tap changer mechanism....
Page 449
Wearing of the tap changer contacts semod159053-376 v4 two counters, contactlife and noofoperations are available within the tap changer control and supervision function, 6 binary inputs tcmyltc or 32 binary inputs tclyltc (84). They can be used as a guide for maintenance of the tap changer mechanis...
Page 450
Tautomsf: time delay set in a follower for execution of a raise or lower command given from a master. This feature can be used when a parallel group is controlled in the master-follower mode, follow tap, and it is individually set for each follower, which means that different time delays can be used...
Page 451
I1base: base current in primary ampere for the hv-side of the transformer. I2base: base current in primary ampere for the lv-side of the transformer. Vbase: base voltage in primary kv for the lv-side of the transformer. Measmode: selection of single phase, or phase-phase, or positive sequence quanti...
Page 452
Equal to dv in . The setting shall be smaller than vdeadband. Typically the inner deadband can be set to 25-70% of the vdeadband value. Vmax: this setting gives the upper limit of permitted busbar voltage (see section "automatic voltage control for a single transformer" , figure 170 ). It is set in ...
Page 453
Rline and xline: for line voltage drop compensation, these settings give the line resistance and reactance from the station busbar to the load point. The settings for rline and xline are given in primary system ohms. If more than one line is connected to the lv busbar, equivalent rline and xline val...
Page 454
Assume that we want to achieve that j 2 = -90°, then: 0 1 1 ( ) 90 0 1 0 1 90 90 j j j j j j j j + - d = ´ ß d = ´ = ß - = + ß = - - j j j j v z i ve ze ie zie equation1983-ansi v1 en-us (equation 124) if for example cos j = 0.8 then j = arcos 0.8 = 37°. With the references in figure 181 , j will be...
Page 455
V b ji t *xline v l xline rline zline i t i t *rline j=30 0 j 1 j 2 dv j 1 =11 0 -90 0 =-79 0 en06000630_ansi.Vsd ansi06000630 v1 en-us figure 182: transformer with reverse reactance regulation poorly adjusted to the power factor as can be seen in figure 182 , the change of power factor has resulted...
Page 456
A combination of line voltage drop compensation and parallel control with the negative reactance method is possible to do simply by adding the required rline values and the required xline values separately to get the combined impedance. However, the line drop impedance has a tendency to drive the ta...
Page 457
Twindowhunt: setting of the time window for the window hunting function. This function is activated when the number of contradictory commands to the tap changer exceeds the specified number given by noopwindow within the time twindowhunt. Noopwindow: setting of the number of contradictory tap change...
Page 458
Q>: when the reactive power exceeds the value given by this setting, the output qgtfwd will be activated after the time delay tpower. It shall be noticed that the setting is given with sign, which effectively means that the function picks up for all values of reactive power greater than the set valu...
Page 459
• a is a safety margin that shall cover component tolerances and other non-linear measurements at different tap positions (for example, transformer reactances changes from rated value at the ends of the regulation range). In most cases a value of a = 1.25 serves well. This calculation gives a settin...
Page 460
14.5.3.3 tcmyltc and tclyltc (84) general settings semod171501-150 v6 lowvolttap: this gives the tap position for the lowest lv-voltage. Highvolttap: this gives the tap position for the highest lv-voltage. Malow: the ma value that corresponds to the lowest tap position. Applicable when reading of th...
Page 461
14.6 logic rotating switch for function selection and lhmi presentation slgapc semod114936-1 v4 14.6.1 identification semod167845-2 v3 function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number logic rotating switch for function selection and lhmi presentati...
Page 462
Nrpos: sets the number of positions in the switch (max. 32). Outtype: steady or pulsed. Tpulse: in case of a pulsed output, it gives the length of the pulse (in seconds). Tdelay: the delay between the up or down activation signal positive front and the output activation. Stopatextremes: sets the beh...
Page 463
Ansi07000112-3-en.Vsd psto cmdpos12 ipos1 nam_pos1 nam_pos2 ipos2 cmdpos21 disabled enabled vsgapc smbrrec_79 on off seton intone inv out input ansi07000112 v3 en-us figure 185: control of autorecloser from local hmi through selector mini switch vsgapc is also provided with iec 61850 communication s...
Page 464
It is especially intended to be used in the interlocking station-wide logics. To be able to get the signals into other systems, equipment or functions, one must use other tools, described in the engineering manual, and define which function block in which systems, equipment or functions should recei...
Page 465
14.9.1 identification semod176456-2 v3 function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number single point generic control 8 signals spc8gapc - - 14.9.2 application semod176511-4 v6 the single point generic control 8 signals (spc8gapc) function block is ...
Page 466
14.10.1 identification guid-c3bb63f5-f0e7-4b00-af0f-917ecf87b016 v4 function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number automationbits, command function for dnp3 autobits - - 14.10.2 application semod158637-5 v4 automation bits, command function for d...
Page 467
14.11.2 application m12445-3 v3 single command, 16 signals (singlecmd) is a common function and always included in the ied. The ieds may be provided with a function to receive commands either from a substation automation system or from the local hmi. That receiving function block has outputs that ca...
Page 468
Single command function singlecmd cmdouty outy function n en04000207.Vsd function n iec04000207 v2 en-us figure 187: application example showing a logic diagram for control of built-in functions single command function singlesmd cmdouty outy device 1 user- defined conditions configuration logic circ...
Page 469
Parameters to be set are mode, common for the whole block, and cmdouty which includes the user defined name for each output signal. The mode input sets the outputs to be one of the types disabled, steady, or pulse. • disabled, sets all outputs to 0, independent of the values sent from the station le...
Page 470
464.
Page 471
Section 15 scheme communication 15.1 scheme communication logic for distance or overcurrent protection zcpsch(85) ip15749-1 v3 15.1.1 identification m14854-1 v4 function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number scheme communication logic for distanc...
Page 472
A permissive scheme is inherently faster and has better security against false tripping than a blocking scheme. On the other hand, a permissive scheme depend on a received cr signal for a fast trip, so its dependability is lower than that of a blocking scheme. 15.1.2.1 blocking schemes m16866-24 v5 ...
Page 473
A b or b z rev a z rev a cs a trip b = or b + tcoord+ cr iec09000015_2_en.Vsd iec09000015 v2 en-us figure 189: principle of blocking scheme or: overreaching cr: communication signal received cs: communication signal send z rev a : reverse zone 15.1.2.2 delta blocking scheme guid-d699d2d8-6479-4b40-8...
Page 474
Since the blocking signal is initiated by the delta based detection which is very fast the time delay tcoord can be set to zero seconds, except in cases where the transmission channel is slow. The timer tsendmin for prolonging the send signal is proposed to set to zero. A b or b deltabaseddetection ...
Page 475
Permissive underreaching scheme m16866-53 v4 permissive underreaching scheme is not suitable to use on short line length due to difficulties for distance protection measurement in general to distinguish between internal and external faults in those applications. The underreaching zones at the local ...
Page 476
A b or a or b ur b cs b ur a cs a trip: ur or or+cr iec09000013-2-en.Vsd iec09000013 v2 en-us figure 191: principle of permissive underreaching scheme ur: underreaching or: overreaching cr: communication signal received cs: communication signal send permissive overreaching scheme m16866-41 v4 in a p...
Page 477
The send signal (cs) might be issued in parallel both from an overreaching zone and an underreaching, independent tripping zone. The cs signal from the overreaching zone must not be prolonged while the cs signal from zone 1 can be prolonged. To secure correct operations of current reversal logic in ...
Page 478
15.1.2.4 intertrip scheme m16866-71 v4 in some power system applications, there is a need to trip the remote end breaker immediately from local protections. This applies for instance when transformers or reactors are connected to the system without circuit-breakers or for remote tripping following o...
Page 479
15.1.3.2 delta blocking scheme guid-f4359690-f433-46cb-a173-8c14559e3fcf v1 set operation = enabled set schemetype = deltablocking set tcoord = 0 s set tsendmin = 0 s set unblock = disabled (set to norestart if unblocking scheme with no alarm for loss of guard is to be used. Set to restart if unbloc...
Page 480
15.1.3.6 intertrip scheme m13869-62 v5 set operation = enabled set schemetype = intertrip set tcoord = 50 ms (10 ms + maximal transmission time) set tsendmin = 0.1 s (0 s in parallel line applications) set unblock = disabled set tsecurity = 0.015 s 15.2 current reversal and weak-end infeed logic for...
Page 481
En99000043_ansi.Vsd strong source line 1 line 2 a:1 a:2 b:1 b:2 a b weak source fault closed closed closed closed ansi99000043 v1 en-us figure 193: current distribution for a fault close to b side when all breakers are closed when the breaker b1 opens for clearing the fault, the fault current throug...
Page 482
When zone 1 is not available, weak-end infeed tripping logic is used. The weak end infeed function only works together with permissive overreach communication schemes as the carrier send signal must cover the complete line length. The wei function sends back (echoes) the received signal under the co...
Page 483
Set tdelayrev timer at the maximum reset time for the communication equipment that gives the carrier receive (crl) signal plus 30 ms. A minimum setting of 40 ms is recommended, typical 60 ms. A long tdelayrev setting increases security against unwanted tripping, but delay the fault clearing in case ...
Page 484
This logic enables fast fault clearing during certain conditions, but naturally, it can not fully replace a teleprotection scheme. The logic can be controlled either by the autorecloser (zone extension) or by the loss- of-load current (loss-of-load acceleration). The loss-of-load acceleration gives ...
Page 485
The setting of the minimum current detector, mincurr, should be set higher than the unsymmetrical current that might flow on the non faulty line, when the breaker at remote end has opened (three-phase). At the same time it should be set below the minimum load current transfer during normal operation...
Page 486
The communication logic module enables blocking as well as permissive under/ overreaching schemes. The logic can also be supported by additional logic for weak- end infeed and current reversal, included in the current reversal and weak-end infeed logic for residual overcurrent protection (ecrwpsch, ...
Page 487
15.5 current reversal and weak-end infeed logic for residual overcurrent protection ecrwpsch (85) ip14365-1 v4 15.5.1 identification m14883-1 v2 function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number current reversal and weak-end infeed logic for residua...
Page 488
En99000044_ansi.Vsd strong source line 1 line 2 a:1 a:2 b:1 b:2 a b weak source closed closed open closed fault ansi99000044 v1 en-us figure 196: current distribution for a fault close to b side when breaker at b1 is opened when the breaker on the parallel line operates, the fault current on the hea...
Page 489
Common base ied values for primary current (ibase), primary voltage (vbase) and primary power (sbase) are set in a global base values for settings function gbasval. Globalbasesel: it is used to select a gbasval function for reference of base values. 15.5.3.1 current reversal m13933-6 v5 the current ...
Page 490
Protection function protection function tele- protection equipment tele- protection equipment tele- communication system cs from the protection function, operate and reset time cs initiation to the communication system, operate and reset time cs propagation, propagation cr selection and decision, op...
Page 491
Section 16 logic 16.1 tripping logic smpptrc (94) ip14576-1 v4 16.1.1 identification semod56226-2 v7 function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number tripping logic smpptrc 1 -> 0 iec15000314 v1 en-us 94 16.1.2 application m12252-3 v10 all trip sig...
Page 492
Tripping and autoreclosing is used on the line, both breakers are normally set up for 1/3-pole tripping and 1/3-phase autoreclosing. Alternatively, the breaker chosen as master can have single-pole tripping, while the slave breaker could have three-pole tripping and autoreclosing. In the case of a p...
Page 493
16.1.2.2 single- and/or three-pole tripping m14828-11 v6 the single-/three-pole tripping operation mode will give single-pole tripping for single-phase faults and three-pole tripping for multi-phase fault. This operating mode is always used together with a single-phase autoreclosing scheme. The sing...
Page 494
Other back-up functions are connected to the input trinp_3p as described above for three-pole tripping. A typical connection for a single-pole tripping scheme is shown in figure 200 . Block blklkout trinp_3p trinp_a trinp_b trinp_c ps_a ps_b ps_c 1ptrz 1ptrgf p3ptr setlkout rstlkout cnd trip smpptrc...
Page 495
16.1.2.4 lock-out m14828-18 v5 the smpptrc function block is provided with possibilities to initiate lock-out. The lock-out can be set to only activate the block closing output cllkout or initiate the block closing output and also maintain the trip signal output tr3p (latched trip). The lock-out can...
Page 496
Cnd smagapc bfi_3p fw rev protection 1 bfi_a fw_a rev_a bfi_b fw_b rev_b bfi_c fw_c rev_c protection 2 cnd protection 4 - - - stn fwn revn protection 3 block pu_dir1 pu_dir2 pu_dir3 pu_dir4 pu_dir5 pu_dir6 pu_dir7 pu_dir8 pu_dir9 pu_dir10 pu_dir11 pu_dir12 pu_dir13 pu_dir14 pu_dir15 pu_dir16 cnd sta...
Page 497
The trip function (smpptrc) splits up the directional data as general output data for bfi_3p, bfi_a, bfi_b, bfi_c, stn, fw and rev. All start and directional outputs are mapped to the logical node data model of the trip function and provided via the iec 61850 attributes dirgeneral, dirl1, dirl2, dir...
Page 498
16.2.1 identification semod167882-2 v3 function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number trip matrix logic tmagapc - - 16.2.2 application m15321-3 v12 the trip matrix logic tmagapc function is used to route trip signals and other logical output sign...
Page 499
16.3.2 application guid-70b268a9-b248-422d-9896-89fecff80b75 v1 group alarm logic function almcalh is used to route alarm signals to different leds and/or output contacts on the ied. Almcalh output signal and the physical outputs allows the user to adapt the alarm signal to physical tripping outputs...
Page 500
16.5.1.1 application guid-9bad30fb-4b75-4e14-82a8-6a59b09fa6ea v1 group indication logic function indcalh is used to route indication signals to different leds and/or output contacts on the ied. Indcalh output signal ind and the physical outputs allows the user to adapt the indication signal to phys...
Page 501
For controllable gates, settable timers and sr flip-flops with memory, the setting parameters are accessible via the local hmi or via the pst tool. 16.6.2.1 configuration guid-d93e383c-1655-46a3-a540-657141f77cf0 v4 logic is configured using the act configuration tool in pcm600. Execution of functio...
Page 502
Always be careful when connecting function blocks with a fast cycle time to function blocks with a slow cycle time. Remember to design the logic circuits carefully and always check the execution sequence for different functions. In other cases, additional time delays must be introduced into the logi...
Page 503
I3pw1ct1 i3pw2ct1 i3p refpdif (87n) ansi11000083_1_en.Vsd ansi11000083 v1 en-us figure 204: refpdif (87n) function inputs for autotransformer application for normal transformers only one winding and the neutral point is available. This means that only two inputs are used. Since all group connections...
Page 504
16.8.2 application semod175832-4 v4 boolean 16 to integer conversion function b16i is used to transform a set of 16 binary (logical) signals into an integer. It can be used – for example, to connect logical output signals from a function (like distance protection) to integer inputs from another func...
Page 505
The sum of the numbers in column “value when activated” when all inx (where 1≤x≤16) are active that is=1; is 65535. 65535 is the highest boolean value that can be converted to an integer by the b16i function block. 16.9 boolean to integer conversion with logical node representation, 16 bit btigapc s...
Page 506
Name of input type default description value when activated value when deactivated in4 boolean 0 input 4 8 0 in5 boolean 0 input 5 16 0 in6 boolean 0 input 6 32 0 in7 boolean 0 input 7 64 0 in8 boolean 0 input 8 128 0 in9 boolean 0 input 9 256 0 in10 boolean 0 input 10 512 0 in11 boolean 0 input 11 ...
Page 507
According to the table below from 0 to 32768. This follows the general formula: inx = 2 x-1 where 1≤x≤16. The sum of all the values on the activated inx will be available on the output out as a sum of the values of all the inputs inx that are activated. Out is an integer. When all inx where 1≤x≤16 a...
Page 508
16.11.1 identification semod167944-2 v4 function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number integer to boolean 16 conversion with logic node representation itbgapc - - 16.11.2 application semod158512-5 v7 integer to boolean 16 conversion with logic no...
Page 509
Name of outx type description value when activated value when deactivated out14 boolean output 14 8192 0 out15 boolean output 15 16384 0 out16 boolean output 16 32768 0 the sum of the numbers in column “value when activated” when all outx (1≤x≤16) are active equals 65535. This is the highest integer...
Page 510
If the values are above this range, the resolution becomes lower due to the 32 bit float representation 99 999.99 seconds talarm ≤ 999 999.0 seconds 99 999.99 seconds twarning ≤ 999 999.0 seconds note that talarm and twarning are independent settings, that is, there is no check if talarm > twarning....
Page 511
Refsource: this setting is used to select the reference source between input and setting for comparison. • input ref: the function will take reference value from input ref • set value: the function will take reference value from setting setvalue setvalue: this setting is used to set the reference va...
Page 512
16.14 comparator for real inputs - realcomp 16.14.1 identification guid-0d68e846-5a15-4c2c-91a2-f81a74034e81 v1 function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number comparator for real inputs realcomp real 16.14.2 application guid-5f7b1683-9799-4d27-b3...
Page 513
Equalbandlow: this setting is used to set the equal condition low band limit in % of reference value. This low band limit will act as reset limit for inlow output when inlow. 16.14.4 setting example guid-e7070cf6-b44b-4799-be18-5c75b9fe2a87 v2 let us consider a comparison is to be done between curre...
Page 514
508.
Page 515
Section 17 monitoring 17.1 measurement guid-9d2d47a0-fe62-4fe3-82ee-034bed82682a v1 17.1.1 identification semod56123-2 v8 function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number power system measurements cvmmxn p, q, s, i, u, f symbol-rr v1 en-us - phase ...
Page 516
17.1.2 application semod54488-4 v12 measurement functions are used for power system measurement, supervision and reporting to the local hmi, monitoring tool within pcm600 or to station level for example, via iec 61850. The possibility to continuously monitor measured values of active power, reactive...
Page 517
• i: phase currents (magnitude and angle) (cmmxu) • v: voltages (phase-to-ground and phase-to-phase voltage, magnitude and angle) (vmmxu, vnmmxu) the cvmmxn function calculates three-phase power quantities by using fundamental frequency phasors (dft values) of the measured current and voltage signal...
Page 518
U system mean voltage, calculated according to selected mode i system mean current, calculated according to selected mode f frequency relevant settings and their values on the local hmi under main menu/settings/ied settings/monitoring/servicevalues(p_q)/cvmmxn(p_q): • when system voltage falls below...
Page 519
Vgenzerodb: minimum level of voltage in % of vbase, used as indication of zero voltage (zero point clamping). If measured value is below vgenzerodb calculated s, p, q and pf will be zero. Igenzerodb: minimum level of current in % of ibase, used as indication of zero current (zero point clamping). If...
Page 520
Observe the related zero point clamping settings in setting group n for cvmmxn (vgenzerodb and igenzerodb). If measured value is below vgenzerodb and/or igenzerodb calculated s, p, q and pf will be zero and these settings will override xzerodb. Xreptyp: reporting type. Cyclic (cyclic), magnitude dea...
Page 521
100 30 5 imagcomp5 imagcomp30 imagcomp100 -10 +10 magnitude compensation % of in measured current % of in 0-5%: constant 5-30-100%: linear >100%: constant 100 30 5 iangcomp5 iangcomp30 iangcomp100 -10 +10 angle compensation degrees measured current % of in ansi05000652_3_en.Vsd ansi05000652 v3 en-us...
Page 522
Measurement function application for a 380kv ohl semod54481-12 v11 single line diagram for this application is given in figure 207 : 380kv busbar 380kv ohl p q 800/5 a ansi09000039-1-en.Vsd 380kv 120v / 3 3 kv ied ansi09000039 v1 en-us figure 207: single line diagram for 380kv ohl application in ord...
Page 523
Table 46: general settings parameters for the measurement function setting short description selected value comments operation operation off/on on function must be on powampfact amplitude factor to scale power calculations 1.000 it can be used during commissioning to achieve higher measurement accur...
Page 524
Setting short description selected value comments phihilim high high limit (physical value), % of sbase 60 high alarm limit that is, extreme overload alarm, hence it will be 415 mw. Philim high limit (physical value), in % of sbase 50 high warning limit that is, overload warning, hence it will be 37...
Page 525
132kv busbar 200/5 33kv busbar 500/5 p q 31.5 mva ansi09000040-1-en.Vsd 33kv 120v / 3 3 v ab ied ansi09000040 v1 en-us figure 208: single line diagram for transformer application in order to measure the active and reactive power as indicated in figure 208 , it is necessary to do the following: 1. Se...
Page 526
Table 49: general settings parameters for the measurement function setting short description selected value comment operation operation disabled / enabled enabled function must be enabled powampfact magnitude factor to scale power calculations 1.000 typically no scaling is required powangcomp angle ...
Page 527
230kv busbar 300/5 4000/5 100 mva g p q 100 mva 15.65kv ansi09000041-1-en.Vsd 15/0.12kv v ab , v bc , ied ansi09000041 v1 en-us figure 209: single line diagram for generator application in order to measure the active and reactive power as indicated in figure 209 , it is necessary to do the following...
Page 528
Table 50: general settings parameters for the measurement function setting short description selected value comment operation operation off/on on function must be on powampfact amplitude factor to scale power calculations 1.000 typically no scaling is required powangcomp angle compensation for phase...
Page 529
17.2.3 setting guidelines guid-df6bec98-f806-41ce-8c29-bee9c88fc1fd v2 the parameters for gas medium supervision ssimg can be set via local hmi or protection and control manager pcm600. Operation: this is used to disable/enable the operation of gas medium supervision i.E. Off/on. Presalmlimit: this ...
Page 530
17.3 liquid medium supervision ssiml (71) guid-37669e94-4830-4c96-8a67-09600f847f23 v3 17.3.1 identification guid-4ce96ef6-42c6-4f2e-a190-d288abf766f6 v3 function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number insulation liquid monitoring function ssiml -...
Page 531
Ttempalarm: this is used to set the time delay for a temperature alarm indication, given in s. Ttemplockout: this is used to set the time delay for a temperature lockout indication, given in s. Tresetlevelalm: this is used for the level alarm indication to reset after a set time delay in s. Tresetle...
Page 532
Circuit breaker status monitoring the breaker status ensures proper functioning of the features within the protection relay such as breaker control, breaker failure and autoreclosing. The breaker status is monitored using breaker auxiliary contacts. The breaker status is indicated by the binary outp...
Page 533
N u m b e r o f m a ke -b re a k op e ra tio n s ( n ) interrupted current (ka) p1 p2 100000 50000 20000 10000 2000 5000 1000 100 200 500 10 20 50 0.1 0.2 0.5 1 2 5 10 20 50 100 iec12000623_1_en.Vsd iec12000623 v1 en-us figure 210: an example for estimating the remaining life of a circuit breaker ca...
Page 534
Rated current. The remaining life of the cb would be (10000 – 10) = 9989 at the rated operating current after one operation at 10 ka. • breaker interrupts at and above rated fault current, that is, 50 ka, one operation at 50 ka is equivalent to 10000/50 = 200 operations at the rated operating curren...
Page 535
17.4.3 setting guidelines guid-ab93ad9b-e6f8-4f1a-b353-aa1008c15679 v2 the breaker monitoring function is used to monitor different parameters of the circuit breaker. The breaker requires maintenance when the number of operations has reached a predefined value. For proper functioning of the circuit ...
Page 536
Spchalmtime: time delay for spring charging time alarm. Tdgaspresalm: time delay for gas pressure alarm. Tdgaspreslo: time delay for gas pressure lockout. Dircoef: directional coefficient for circuit breaker life calculation. Ratedopercurr: rated operating current of the circuit breaker. Ratedfltcur...
Page 537
17.5.3 setting guidelines ip14841-1 v1 m12811-3 v3 the input parameters for the event function (event) can be set individually via the local hmi (main menu/settings / ied settings / monitoring / event function) or via the parameter setting tool (pst). Eventmask (ch_1 - 16) m12811-5 v3 the inputs can...
Page 538
17.6.1 identification m16055-1 v8 function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number disturbance report drprdre - - disturbance report a1radr - a4radr - - disturbance report b1rbdr - b22rbdr - - 17.6.2 application m12152-3 v9 to get fast, complete an...
Page 539
The pcm600 using the disturbance handling tool, for report reading or further analysis (using wavewin, that can be found on the pcm600 installation cd). The user can also upload disturbance report files using ftp or mms (over 61850–8–1) clients. If the ied is connected to a station bus (iec 61850-8-...
Page 540
Trip value rec fault locator sequential of events event recorder indications disturbance recorder disturbance report binary signals analog signals drprdre fl ansi09000336-2-en.Vsdx axradr bxrbdr ansi09000336 v2 en-us figure 211: disturbance report functions and related function blocks for disturbanc...
Page 541
Red led: steady light triggered on binary signal n with setledx = trip (or start and trip) flashing the ied is in configuration mode operation m12179-82 v6 the operation of disturbance report function drprdre has to be set enabled or disabled. If disabled is selected, note that no disturbance report...
Page 542
17.6.3.1 recording times m12179-88 v5 prefault recording time (prefaultrect) is the recording time before the starting point of the disturbance. The setting should be at least 0.1 s to ensure enough samples for the estimation of pre-fault values in the trip value recorder (tvr) function. Postfault r...
Page 543
For each of the 352 signals, it is also possible to select if the signal is to be used as a trigger for the start of the disturbance report and if the trigger should be activated on positive (1) or negative (0) slope. Trigdrn: disturbance report may trig for binary input n (enabled) or not (disabled...
Page 544
17.6.3.4 sub-function parameters m12179-389 v3 all functions are in operation as long as disturbance report is in operation. Indications m12179-448 v4 indicationman: indication mask for binary input n. If set (show), a status change of that particular input, will be fetched and shown in the disturba...
Page 545
Handled if the recording functions do not have proper settings. The goal is to optimize the settings in each ied to be able to capture just valuable disturbances and to maximize the number that is possible to save in the ied. The recording time should not be longer than necessary (postfaultrect and ...
Page 546
17.7.2 application guid-f9d225b1-68f7-4d15-aa89-c9211b450d19 v3 the logical signal status report (binstatrep) function makes it possible to poll signals from various other function blocks. Binstatrep has 16 inputs and 16 outputs. The output status follows the inputs and can be read from the local hm...
Page 547
Distance to fault is very important for those involved in operation and maintenance. Reliable information on the fault location greatly decreases the downtime of the protected lines and increases the total availability of a power system. The fault locator is started with the input calcdist to which ...
Page 548
In the observed bay (no parallel line expected since chosen input is set to zero). Use the parameter setting tool within pcm600 for changing analog configuration. The measured phase voltages can be fine tuned with the parameters vagain, vbgain and vcgain to further increase the accuracy of the fault...
Page 549
En07000113_1_ansi.V sd a b c 1 2 3 4 5 6 9 10 1 2 3 4 5 6 9 10 i1 i2 i3 i5 i1 i2 i3 i5 ansi07000113 v2 en-us figure 214: example of connection of parallel line in for fault locator lmbrflo 17.9 limit counter l4ufcnt guid-22e141db-38b3-462c-b031-73f7466dd135 v1 17.9.1 identification guid-f3fb7b33-b18...
Page 550
17.9.2 application guid-41b13135-5069-4a5a-86ce-b7dbe9cfef38 v2 limit counter (l4ufcnt) is intended for applications where positive and/or negative sides on a binary signal need to be counted. The limit counter provides four independent limits to be checked against the accumulated counted value. The...
Page 551
17.10.3 setting guidelines guid-d3bed56a-ba80-486f-b2a8-e47f7ac63468 v1 the settings talarm and twarning are user settable limits defined in hours. The achievable resolution of the settings is 0.1 hours (6 minutes). Talarm and twarning are independent settings, that is, there is no check if talarm >...
Page 552
Transformer mva rating is based on maximum allowable temperature of the insulation. Design standards express temperature limits for transformers exceeds ambient temperature. Use of ambient temperature as a base ensures that a transformer has adequate thermal capacity and independent of daily environ...
Page 553
Empirical formulae given by relevant standards. The hot spot temperature shall be monitored continuously so that it will not exceed the transformer oil flashover value. Figure 215 shows the complex transformer temperature distribution. The assumptions made are: • oil temperature increases linearly f...
Page 554
Temperature without separately considering the effects of oil flow blockage and malfunction of cooler groups. Normal life expected of the transformer is a conventional reference based on the designed operating condition and ambient temperature. If the transformer load exceeds its rated condition, ag...
Page 555
Planned loading beyond nameplate rating hours of the day 12 2 4 6 8 12 10 2 4 6 8 10 12 2 4 6 8 12 10 2 4 6 8 10 12 2 4 6 8 12 10 2 4 6 8 10 12 2 4 6 8 12 10 2 4 6 8 10 hours of the day hours of the day hours of the day 80°c 90°c 100°c 110°c 120°c 130°c 140°c 80°c 90°c 100°c 110°c 120°c 130°c 140°c ...
Page 556
Insulation aging or deterioration is a time function of temperature, moisture content, and oxygen content. With modern oil preservation systems, the moisture and oxygen contributions to insulation deterioration can be minimized, leaving insulation temperature as the controlling parameter. Temperatur...
Page 557
• three phase trafo: the function considers the given transformer as three phase transformer. • single phase trafo: the function considers the given transformer as single phase transformer. Based on the settings traforating and trafotype, transformer parameters are selected for temperature calculati...
Page 558
• iec: transformer parameters like constants, winding and oil exponents will be taken from iec 60076-7 standard for temperature calculations. • ieee: transformer parameters like constants, winding and oil exponents will be taken from ieee c57.96-1995 standard for temperature calculations. Currselect...
Page 559
• winding 1&3: only winding 1 and winding 3 cts are available. This option can be selected when three winding transformer is considered. • winding 2&3: only winding 2 and winding 3 cts are available. This option can be selected when three winding transformer is considered. • all windings: all windin...
Page 560
Tankmass: this setting is used to set the transformer tank mass. This mass is only the tank and fittings that are in contact with heated oil. Loadloss: this setting is used to set the transformer load loss at rated condition. Ttloadloss: this setting is used to set the transformer load loss arrived ...
Page 561
Guid-5832e7af-0a4f-4b50-8045-94bf9433a1bf v1 winding to oil temperature gradient differs from winding to winding depending on current density in the winding, physical dimensions, cooling system etc., this value can be between 10 to 20 ̊ c for both distribution and power transformers. For low current...
Page 562
Lowvolttap: this setting is used to set the position number of tap changer at possible minimum voltage. Guid-e9ec48cc-08d6-498e-bfb7-6f40ad9436a7 v1 the following settings are required to perform the calculation of top oil temperature using monthly model of ambient temperature when ambvalid is low: ...
Page 563
Hptmprisew3: this setting is used to set the hot spot temperature rise of winding 3 above ambient temperature in k (kelvin). Topoiltmprise: this setting is used to set the top oil temperature rise above ambient temperature in k (kelvin). The above setting values (hptmprisewx and topoiltmprise) shoul...
Page 564
Expectedlife: the transformer expected insulation life in hours can be set by this setting. As per ieee c57.91-1995 the normal life expectancy at a continuous hot spot temperature of 110 ̊ c is 180,000 hours. Ageingratemeth: this setting is used to select the method to be used for transformer insula...
Page 565
• top oil temperature = 120°c • hot spot winding temperature = 200°c • short-time loading (1/2 h or less) = 300% • for power transformer with 65°c hot spot temperature rise: • top oil temperature = 110°c • hot spot winding temperature = 180°c • maximum loading = 200% settings related to warning and ...
Page 566
Parameter value note ct ratio winding 1 1000/1 a ct ratio winding 2 2000/1 a ct ratio winding 3 1000/1 a 17.11.3.2 setting parameters for insulation loss of life calculation function (lol1) guid-6869a06a-4ddc-4fb5-ac56-5463f3709862 v1 table 54: setting parameters for insulation loss of life calculat...
Page 567
Setting short description selected value avgoiltmprise set the transformer average oil temperature rise for the calculation of oil time constant 45° c coilcoremass set the transformer coil and core assembly mass for the calculation of oil time constant 65.0 t oilmass set the transformer oil mass for...
Page 568
Setting short description selected value wdgtooilgrad3 set the transformer winding to oil temperature gradient for the winding 3 when the winding time constant mode is selected as calculated 20° c culossw1 set the transformer winding loss for the winding 1 when the winding time constant mode is sele...
Page 569
Setting short description selected value marchambtmp set the march month average ambient temperature for the calculation of top oil temperature when ambient temperature sensor failure/absence 30° c aprilambtmp set the april month average ambient temperature for the calculation of top oil temperature...
Page 570
Setting short description selected value topoiltmprise set the top oil temperature rise for the calculation of hot spot to top oil temperature gradient 55° c ratedcurrw1 set the rated current of the winding 1 696.0 a ratedcurrw2 set the rated current of the winding 2 1255.0 a ratedcurrw3 set the rat...
Page 571
Section 18 metering 18.1 pulse-counter logic pcfcnt ip14600-1 v3 18.1.1 identification m14879-1 v4 function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number pulse-counter logic pcfcnt s00947 v1 en-us - 18.1.2 application m13395-3 v6 pulse-counter logic (pcf...
Page 572
Configuration of inputs and outputs of pcfcnt is made via pcm600. On the binary input module (bim), the debounce filter default time is set to 1 ms, that is, the counter suppresses pulses with a pulse length less than 1 ms. The input oscillation blocking frequency is preset to 40 hz meaning that the...
Page 573
Cvmmxn p_ inst q_ inst etpmmtr p q rstacc rstdmd startacc stopacc iec130 00190-2-en.Vsdx iec13000190 v2 en-us figure 217: connection of energy calculation and demand handling function etpmmtr to the measurements function (cvmmxn) the energy values can be read through communication in mwh and mvarh i...
Page 574
Operation: disabled/enabled enaacc: disabled/enabled is used to switch the accumulation of energy on and off. Tenergy: time interval when energy is measured. Tenergyonpls: gives the pulse length on time of the pulse. It should be at least 100 ms when connected to the pulse counter function block. Ty...
Page 575
Section 19 ethernet-based communication 19.1 access point 19.1.1 application guid-2942df07-9bc1-4f49-9611-a5691d2c925c v1 the access points are used to connect the ied to the communication buses (like the station bus) that use communication protocols. The access point can be used for single and redu...
Page 576
When saving the ect configuration after selecting a subnetwork, ect creates the access point in the scl model. Unselecting the subnetwork removes the access point from the scl model. This column is editable for iec61850 ed2 ieds and not editable for iec61850 ed1 ieds because in iec61850 ed1 only one...
Page 577
19.2 redundant communication 19.2.1 identification guid-b7ae0374-0336-42b8-90af-3ae1c79a4116 v1 function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number iec 62439-3 parallel redundancy protocol prp - - iec 62439-3 high-availability seamless redundancy hsr ...
Page 578
Iec09000758-4-en.Vsd switch a ap1 phyportb phyporta ap1 phyporta phyportb ap1 phyportb phyporta ap1 phyporta phyportb switch b device 1 device 2 device 3 device 4 iec09000758 v4 en-us figure 218: parallel redundancy protocol (prp) section 19 1mrk 511 401-uus a ethernet-based communication 572 bay co...
Page 579
Iec16000038-1-en.Vsdx ap1 phyportb phyporta ap1 phyporta phyportb ap1 phyporta phyportb ap1 phyportb phyporta device 1 device 2 device 3 device 4 iec16000038 v1 en-us figure 219: high-availability seamless redundancy (hsr) 19.2.3 setting guidelines guid-887b0ae2-0f2e-414d-96fd-7ec935c5d2d8 v1 redund...
Page 580
Iec16000039-1-en.Vsdx iec16000039 v1 en-us figure 220: ect screen with redundancy set to prp-1 on access point 1 and hsr access point 3 19.3 merging unit 19.3.1 application guid-e630c16f-edb8-40ae-a8a2-94189982d15f v1 the iec/uca 61850-9-2le process bus communication protocol enables an ied to commu...
Page 581
Iec17000044-1-en.Vsdx iec17000044 v1 en-us figure 221: merging unit 19.3.2 setting guidelines guid-3449ab24-8c9d-4d9a-bd46-5ddf59a0f8e3 v1 for information on the merging unit setting guidelines, see section iec/uca 61850-9-2le communication protocol . 19.4 routes 19.4.1 application guid-19616ac4-0ff...
Page 582
Destination specifies the destination. Destination subnet mask specifies the subnetwork mask of the destination. Section 19 1mrk 511 401-uus a ethernet-based communication 576 bay control rec670 2.2 ansi application manual.
Page 583
Section 20 station communication 20.1 communication protocols m14815-3 v13 each ied is provided with several communication interfaces enabling it to connect to one or many substation level systems or equipment, either on the substation automation (sa) bus or substation monitoring (sm) bus. Available...
Page 584
Kiosk 2 kiosk 3 station hsi base system engineering workstation sms gateway printer cc iec09000135_en.V sd kiosk 1 ied 1 ied 2 ied 3 ied 1 ied 2 ied 3 ied 1 ied 2 ied 3 iec09000135 v1 en-us figure 222: sa system with iec 61850–8–1 m16925-3 v4 figure 223 shows the goose peer-to-peer communication. Se...
Page 585
Control protection control protection control and protection goose en05000734.Vsd station hsi microscada gateway ied a ied a ied a ied a ied a iec05000734 v1 en-us figure 223: example of a broadcasted goose message 20.2.2 setting guidelines semod55317-5 v7 there are two settings related to the iec 6...
Page 586
Application semod55350-5 v8 generic communication function for single point value (spgapc) function is used to send one single logical output to other systems or equipment in the substation. Sp16gapc can be used to send up to 16 single point values from the application functions running in the same ...
Page 587
Function block type data type goosesprcv single point goosevctrrcv vctr signals parallel mode goosexlnrcv switch status application guid-808177b7-02ca-40df-b41b-8b580e38478b v1 the goose receive function blocks are used to receive subscribed data from the goose protocol. The validity of the data val...
Page 588
20.3 lon communication protocol ip14420-1 v1 20.3.1 application ip14863-1 v1 m14804-3 v5 control center ied ied ied gateway star coupler rer 111 station hsi microscada iec05000663-1-en.Vsd iec05000663 v2 en-us figure 225: example of lon communication structure for a substation automation system an o...
Page 589
Glass fibre plastic fibre wavelength 820-900 nm 660 nm transmitted power -13 dbm (hfbr-1414) -13 dbm (hfbr-1521) receiver sensitivity -24 dbm (hfbr-2412) -20 dbm (hfbr-2521) the lon protocol m14804-32 v2 the lon protocol is specified in the lontalkprotocol specification version 3 from echelon corpor...
Page 590
The node address is transferred to lnt via the local hmi by setting the parameter servicepinmsg = yes. The node address is sent to lnt via the lon bus, or lnt can scan the network for new nodes. The communication speed of the lon bus is set to the default of 1.25 mbit/s. This can be changed by lnt. ...
Page 591
When communicating with a pc connected to the utility substation lan via wan and the utility office lan (see figure 226 ), and when using the rear optical ethernet port, the only hardware required for a station monitoring system is: • optical fibres from the ied to the utility substation lan • pc co...
Page 592
20.4.2 setting guidelines m11876-3 v6 spa, iec 60870-5-103 and dnp3 use the same rear communication port. This port can be set for spa use on the local hmi under main menu /configuration / communication /station communication/port configuration/slm optical serial port/protocol:1. When the communicat...
Page 593
20.5 iec 60870-5-103 communication protocol ip14615-1 v2 20.5.1 application ip14864-1 v1 m17109-3 v6 tcp/ip control center ied ied ied gateway star coupler station hsi ansi05000660-4-en.Vsd ansi05000660 v4 en-us figure 227: example of iec 60870-5-103 communication structure for a substation automati...
Page 594
The iec 60870-5-103 communication messages. For detailed information about iec 60870-5-103, refer to iec 60870 standard part 5: transmission protocols, and to the section 103, companion standard for the informative interface of protection equipment. 20.5.1.2 design m17109-41 v1 general m17109-43 v2 ...
Page 595
Function block with pre-defined functions in control direction, i103cmd. This block includes the function type parameter, and the information number parameter is defined for each output signal. • function commands in control direction function block with user defined functions in control direction, ...
Page 596
Connected to the disturbance function blocks a1radr to a4radr. The eight first ones belong to the public range and the remaining ones to the private range. 20.5.2 settings m17109-116 v1 20.5.2.1 settings for rs485 and optical serial communication m17109-118 v12 general settings spa, dnp and iec 6087...
Page 597
Guid-cd4eb23c-65e7-4ed5-afb1-a9d5e9ee7ca8 v3 en guid-cd4eb23c-65e7-4ed5-afb1-a9d5e9ee7ca8 v3 en-us figure 228: settings for iec 60870-5-103 communication the general settings for iec 60870-5-103 communication are the following: • slaveaddress and baudrate: settings for slave number and communication...
Page 598
In addition there is a setting on each event block for function type. Refer to description of the main function type set on the local hmi. Commands m17109-138 v2 as for the commands defined in the protocol there is a dedicated function block with eight output signals. Use pcm600 to configure these s...
Page 599
Dra#-input acc iec103 meaning 15 70 private range 16 71 private range 17 72 private range 18 73 private range 19 74 private range 20 75 private range 21 76 private range 22 77 private range 23 78 private range 24 79 private range 25 80 private range 26 81 private range 27 82 private range 28 83 priv...
Page 600
Reb 207 private range reg 150 private range req 245 private range rer 152 private range res 118 private range refer to the tables in the technical reference manual /station communication, specifying the information types supported by the communication protocol iec 60870-5-103. To support the informa...
Page 601
Section 21 remote communication 21.1 binary signal transfer ip12423-1 v2 21.1.1 identification m14849-1 v3 function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number binary signal transfer, receive binsignrec1_1 binsignrec1_2 binsignreceive2 - - binary signa...
Page 602
Where the differential current is evaluated. If the evaluation results in a trip, the trip signal will be sent over the two communication links. Ied-a ied-b ied-c iec16000077-1-en.Vsd 3-end differential protection with two communication links ldcm312 ldcm312 ldcm313 ldcm312 iec16000077 v1 en-us figu...
Page 603
Ld cm ld cm ld cm ld cm ld cm ld cm ld cm ld cm ld cm ld cm ld cm ld cm ld cm ld cm ld cm ld cm en06000519-2.Vsd iec06000519 v2 en-us figure 230: direct fibre optical connection between two ieds with ldcm the ldcm can also be used together with an external optical to galvanic g.703 converter as show...
Page 604
Channelmode defines how an ied discards the ldcm information when one of the ieds in the system is out of service: it can either be done on the ied out of service by setting all local ldcms to channel mode outofservice or at the remote end by setting the corresponding ldcm to channel mode blocked. I...
Page 605
The same is applicable for slot 312-313 and slot 322-323. Diffsync defines the method of time synchronization for the line differential function: echo or gps. Using echo in this case is safe only if there is no risk of varying transmission asymmetry. Gpssyncerr: when gps synchronization is lost, syn...
Page 606
Maxtransmdelay indicates maximum transmission delay. Data for maximum 40 ms transmission delay can be buffered up. Delay times in the range of some ms are common. If data arrive in wrong order, the oldest data is disregarded. Maxtdifflevel indicates the maximum time difference allowed between intern...
Page 607
Linkforwarded is used to configure the ldcm to merge the inter-trip and block signals from another ldcm-receiver. This is used when the analog signals for the ldcm-transmitter is connected to the receiver of another ldcm. 1mrk 511 401-uus a section 21 remote communication bay control rec670 2.2 ansi...
Page 608
602.
Page 609
Section 22 security 22.1 authority status athstat semod158575-1 v2 22.1.1 application semod158527-5 v3 authority status (athstat) function is an indication function block, which informs about two events related to the ied and the user authorization: • the fact that at least one user has tried to log...
Page 610
• built-in real time clock (in operation/out of order). • external time synchronization (in operation/out of order). Events are also generated: • whenever any setting in the ied is changed. The internal events are time tagged with a resolution of 1 ms and stored in a list. The list can store up to 4...
Page 611
The binary input controlling the function is defined in act or smt. The chnglck function is configured using act. Lock binary input signal that will activate/deactivate the function, defined in act or smt. Guid-8c333bc0-aa7a-4ed1-a772-18c22e8eee62 v5 when chnglck has a logical one on its input, then...
Page 612
• linksts indicates the ethernet link status for the rear ports (single communication) • chalists and chblists indicates the ethernet link status for the rear ports channel a and b (redundant communication) • linkstatus indicates the ethernet link status for the front port 22.4.2 setting guidelines ...
Page 613
Section 23 basic ied functions 23.1 ied identifiers terminalid ip15060-1 v2 23.1.1 application m15324-3 v6 ied identifiers (terminalid) function allows the user to identify the individual ied in the system, not only in the substation, but in a whole region or a country. Use only characters a-z, a-z ...
Page 614
23.2.2 factory defined settings m11789-39 v10 the factory defined settings are very useful for identifying a specific version and very helpful in the case of maintenance, repair, interchanging ieds between different substation automation systems and upgrading. The factory made settings can not be ch...
Page 615
23.3.1 identification semod113212-2 v3 function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number measured value expander block range_xp - - 23.3.2 application semod52434-4 v5 the current and voltage measurements functions (cvmmxn, cmmxu, vmmxu and vnmmxu), ...
Page 616
Parameters are available in the ied. Any of them can be activated through the different programmable binary inputs by means of external or internal control signals. A function block, setgrps, defines how many setting groups are used. Setting is done with parameter maxsetgr and shall be set to the re...
Page 617
23.6 summation block 3 phase 3phsum semod55968-1 v2 23.6.1 application semod56004-4 v3 the analog summation block 3phsum function block is used in order to get the sum of two sets of 3 phase analog signals (of the same type) for those ied functions that might need it. 23.6.2 setting guidelines semod...
Page 618
23.7.2 application guid-d58eca9a-9771-443d-bf84-8ef582a346bf v4 global base values function (gbasval) is used to provide global values, common for all applicable functions within the ied. One set of global values consists of values for current, voltage and apparent power and it is possible to have t...
Page 619
23.9 signal matrix for binary outputs smbo semod55215-1 v2 23.9.1 application semod55213-5 v4 the signal matrix for binary outputs function smbo is used within the application configuration tool in direct relation with the signal matrix tool. Smbo represents the way binary outputs are sent from one ...
Page 620
23.11.1 application semod55744-4 v10 signal matrix for analog inputs (smai), also known as the preprocessor function block, analyses the connected four analog signals (three phases and neutral) and calculates all relevant information from them like the phasor magnitude, phase angle, frequency, true ...
Page 621
The above described scenario does not work if smai setting connectiontype is ph-n. If only one phase-ground voltage is available, the same type of connection can be used but the smai connectiontype setting must still be ph-ph and this has to be accounted for when setting minvalfreqmeas. If smai sett...
Page 622
The setting connectiontype: connection type for that specific instance (n) of the smai (if it is ph-n or ph-ph). Depending on connection type setting the not connected ph-n or ph-ph outputs will be calculated as long as they are possible to calculate. E.G. At ph-ph connection a, b and c will be calc...
Page 623
Iec07000197.Vsd smai instance 3 phase group smai1:1 1 smai2:2 2 smai3:3 3 smai4:4 4 smai5:5 5 smai6:6 6 smai7:7 7 smai8:8 8 smai9:9 9 smai10:10 10 smai11:11 11 smai12:12 12 task time group 1 smai instance 3 phase group smai1:13 1 smai2:14 2 smai3:15 3 smai4:16 4 smai5:17 5 smai6:18 6 smai7:19 7 smai...
Page 624
Shout-down of the machine. In other application the usual setting of the parameter dftreference of smai is internaldftref. Example 1 ansi07000198.Vsd smai1:1 block dftspfc ^grp1_a ^grp1_b ^grp1_c ^grp1_n type spfcout ai3p ai1 ai2 ai3 ai4 ain smai1:13 block dftspfc ^grp1_a ^grp1_b ^grp1_c ^grp1_n typ...
Page 625
Example 2 ansi07000198.Vsd smai1:13 block dftspfc ^grp1_a ^grp1_b ^grp1_c ^grp1_n type spfcout ai3p ai1 ai2 ai3 ai4 ain smai1:1 block dftspfc ^grp1_a ^grp1_b ^grp1_c ^grp1_n type spfcout ai3p ai1 ai2 ai3 ai4 ain smai1:25 block dftspfc ^grp1_a ^grp1_b ^grp1_c ^grp1_n type spfcout ai3p ai1 ai2 ai3 ai4...
Page 626
23.12 test mode functionality testmode ip1647-1 v3 23.12.1 application m11407-3 v8 the protection and control ieds may have a complex configuration with many included functions. To make the testing procedure easier, the ieds include the feature that allows individual blocking of a single-, several-,...
Page 627
Or lhmi. If a function of an ied is set to off, the related beh is set to off as well. The related mod keeps its current state. When the setting operation is set to off, the behavior is set to off and it is not possible to override it. When a behavior of a function is offthe function will not execut...
Page 628
23.13 time synchronization timesynchgen ip1750-1 v2 23.13.1 application m11345-3 v10 use time synchronization to achieve a common time base for the ieds in a protection and control system. This makes it possible to compare events and disturbance data between all ieds in the system. If a global commo...
Page 629
• coarse time messages are sent every minute and contain complete date and time, that is year, month, day, hour, minute, second and millisecond. • fine time messages are sent every second and comprise only seconds and milliseconds. The selection of the time source is done via the corresponding setti...
Page 630
Hmi is main menu/configuration/time/synchronization. The parameters are categorized as time synchronization (timesynchgen) and irig-b settings (irig- b:1) in case that irig-b is used as the external time synchronization source. Timesynch m11348-167 v15 when the source of the time synchronization is ...
Page 631
• disabled • sntp -server set the course time synchronizing source (coarsesyncsrc) to disabled when gps time synchronization of line differential function is used. Set the fine time synchronization source (finesyncsource) to gps. The gps will thus provide the complete time synchronization. Gps alone...
Page 632
Setting example 9-2 rec ptp ptp station bus gps sam600-ts sam600-ct sam600-vt ptp ptp 9-2 ptp rel mu gtm pps iec16000167-1-en.Vsdx 9-2 9-2 9-2 process bus iec16000167 v1 en-us figure 237: example system figure 237 describes an example system. The rec and rel are both using the 9-2 stream from the sa...
Page 633
Section 24 requirements 24.1 current transformer requirements ip15171-1 v2 m11609-3 v2 the performance of a protection function will depend on the quality of the measured current signal. Saturation of the current transformers (cts) will cause distortion of the current signals and can result in a fai...
Page 634
Flux is 90 % of the saturation flux (Ψ sat ). As the present ct standards have no limitation of the level of remanent flux, these cts are also classified as for example, class tpx, p and px according to iec. The iec tr 61869-100, edition 1.0 2017-01, instrument transformers – guidance for applicatio...
Page 635
With small airgaps and therefore will be cts of lr type (for example, class pr, tpy or pxr). Very high remanence level in a protection core ct can cause the following problems for protection ieds: 1. Unwanted operation of differential (i.E. Unit) protections for external faults 2. Unacceptably delay...
Page 636
Acceptable at all maximum remanence has been considered for fault cases critical for the security, for example, faults in reverse direction and external faults. Because of the almost negligible risk of additional time delays and the non-existent risk of failure to operate the remanence have not been...
Page 637
Resistance, the resistance of a single secondary wire, may normally be used in the calculation for three-phase faults. As the burden can be considerable different for three-phase faults and phase-to-ground faults it is important to consider both cases. Even in a case where the phase-to-ground fault ...
Page 638
24.1.6.1 breaker failure protection m11621-3 v5 the cts must have a rated equivalent limiting secondary e.M.F. E al that is larger than or equal to the required rated equivalent limiting secondary e.M.F. E alreq below: s n r a l a lre q ct l 2 pn n op i s e e 5 i r r i i ³ = × × + + æ ö × ç ÷ è ø eq...
Page 639
S n r a l a lre q ct l 2 pn n op i s e e 1.5 i r r i i ³ = × × + + æ ö × ç ÷ è ø equation1678 v1 en-us (equation 129) where: i op the primary operate value (a) i pr the rated primary ct current (a) i sr the rated secondary ct current (a) i n the nominal current of the protection ied (a) r ct the sec...
Page 640
R ct the secondary resistance of the ct (w) r l the resistance of the secondary cable and additional load (w). The loop resistance containing the phase and neutral wires, must be used for faults in solidly grounded systems. The resistance of a single secondary wire should be used for faults in high ...
Page 641
24.1.7 current transformer requirements for cts according to other standards semod53771-1 v1 m11623-4 v3 all kinds of conventional magnetic core cts are possible to use with the ieds if they fulfill the requirements corresponding to the above specified expressed as the rated equivalent limiting seco...
Page 642
24.1.7.3 current transformers according to ansi/ieee m11623-22 v6 current transformers according to ansi/ieee are partly specified in different ways. A rated secondary terminal voltage v ansi is specified for a ct of class c. V ansi is the secondary terminal voltage the ct will deliver to a standard...
Page 643
24.2 voltage transformer requirements m11608-3 v5 the performance of a protection function will depend on the quality of the measured input signal. Transients caused by capacitive coupled voltage transformers (ccvts) can affect some protection functions. Magnetic or capacitive voltage transformers c...
Page 644
24.5 sample specification of communication requirements for the protection and control terminals in digital telecommunication networks guid-0a9f36af-3802-42fe-8970-4662798c19d1 v2 the communication requirements are based on echo timing. Bit error rate (ber) according to itu-t g.821, g.826 and g.828 ...
Page 645
• format: transparent • maximum channel delay • loop time ied with echo synchronization of differential clock (without gps clock) • both channels must have the same route with maximum asymmetry of 0,2-0,5 ms, depending on set sensitivity of the differential protection. • a fixed asymmetry can be com...
Page 646
640
Page 647
Section 25 glossary m14893-1 v16 ac alternating current acc actual channel act application configuration tool within pcm600 a/d converter analog-to-digital converter adbs amplitude deadband supervision adm analog digital conversion module, with time synchronization ai analog input ansi american nati...
Page 648
Cb circuit breaker cbm combined backplane module ccitt consultative committee for international telegraph and telephony. A united nations-sponsored standards body within the international telecommunications union. Ccm can carrier module ccvt capacitive coupled voltage transformer class c protection ...
Page 649
Dbll dead bus live line dc direct current dfc data flow control dft discrete fourier transform dhcp dynamic host configuration protocol dip-switch small switch mounted on a printed circuit board di digital input dllb dead line live bus dnp distributed network protocol as per ieee std 1815-2012 dr di...
Page 650
Ftp file transfer protocol fun function type g.703 electrical and functional description for digital lines used by local telephone companies. Can be transported over balanced and unbalanced lines gcm communication interface module with carrier of gps receiver module gde graphical display editor with...
Page 651
Ieee p1386.1 pci mezzanine card (pmc) standard for local bus modules. References the cmc (ieee p1386, also known as common mezzanine card) standard for the mechanics and the pci specifications from the pci sig (special interest group) for the electrical emf (electromotive force). Ieee 1686 standard ...
Page 652
Lib 520 high-voltage software module lcd liquid crystal display ldcm line data communication module ldd local detection device led light-emitting diode lnt lon network tool lon local operating network mcb miniature circuit breaker mcm mezzanine carrier module mim milli-ampere module mpm main process...
Page 653
Pmc pci mezzanine card por permissive overreach pott permissive overreach transfer trip process bus bus or lan used at the process level, that is, in near proximity to the measured and/or controlled components prp parallel redundancy protocol psm power supply module pst parameter setting tool within...
Page 654
Sma connector subminiature version a, a threaded connector with constant impedance. Smt signal matrix tool within pcm600 sms station monitoring system sntp simple network time protocol – is used to synchronize computer clocks on local area networks. This reduces the requirement to have accurate hard...
Page 655
Trm transformer module. This module transforms currents and voltages taken from the process into levels suitable for further signal processing. Typ type identification umt user management tool underreach a term used to describe how the relay behaves during a fault condition. For example, a distance ...
Page 656
650
Page 657
651.
Page 658
— abb ab grid automation products 721 59 västerås, sweden phone: +46 (0) 21 32 50 00 abb.Com/protection-control © copyright 2017 abb. All rights reserved. Specifications subject to change without notice. 1mrk 511 401-uus.