- DL manuals
- ABB
- Relays
- REG670
- Technical manual
ABB REG670 Technical manual
Summary of REG670
Page 1
Relion ® 670 series generator protection reg670 2.0 iec technical manual.
Page 3
Document id: 1mrk502052-uen issued: july 2016 revision: b product version: 2.0 © copyright 2014 abb. All rights reserved.
Page 4
Copyright this document and parts thereof must not be reproduced or copied without written permission from abb, and the contents thereof must not be imparted to a third party, nor used for any unauthorized purpose. The software and hardware described in this document is furnished under a license and...
Page 5
Disclaimer the data, examples and diagrams in this manual are included solely for the concept or product description and are not to be deemed as a statement of guaranteed properties. All persons responsible for applying the equipment addressed in this manual must satisfy themselves that each intende...
Page 6
Conformity this product complies with the directive of the council of the european communities on the approximation of the laws of the member states relating to electromagnetic compatibility (emc directive 2004/108/ec) and concerning electrical equipment for use within specified voltage limits (low-...
Page 7
Table of contents section 1 introduction.....................................................................39 this manual...................................................................................... 39 intended audience.........................................................................
Page 8
Identification................................................................................ 77 function block............................................................................. 77 signals.........................................................................................78 basic pa...
Page 9
Settings......................................................................................142 monitored data...........................................................................143 operation principle.................................................................... 143 logic diagram.......
Page 10
Operation principle.................................................................... 180 full scheme measurement................................................... 180 impedance characteristic..................................................... 181 basic operation characteristics...................
Page 11
Filtering.................................................................................237 distance measuring zones................................................... 238 phase-selection element...................................................... 239 directional element............................
Page 12
Functionality.............................................................................. 279 description of input signals........................................................280 description of output signals..................................................... 280 function block..................
Page 13
Under voltage seal-in........................................................... 331 technical data........................................................................... 332 section 8 current protection.........................................................333 instantaneous phase overcurrent ...
Page 14
Internal polarizing................................................................. 363 external polarizing for earth-fault function............................364 directional detection for earth fault function......................... 364 base quantities within the protection.........................
Page 15
Settings......................................................................................402 monitored data...........................................................................403 operation principle.................................................................... 404 technical data......
Page 16
Low pass filtering..................................................................433 calibration of analog inputs..................................................433 technical data........................................................................... 435 negativ sequence time overcurrent pr...
Page 17
Signals.......................................................................................454 settings......................................................................................454 monitored data...........................................................................455 operation p...
Page 18
Functionality.............................................................................. 505 function block........................................................................... 505 signals.......................................................................................505 settings.......
Page 19
Technical data........................................................................... 541 section 10 frequency protection....................................................543 underfrequency protection saptuf ............................................. 543 identification.........................
Page 20
Functionality ............................................................................. 557 function block .......................................................................... 558 signals.......................................................................................558 settings.......
Page 21
Operation principle.................................................................... 604 technical data........................................................................... 606 fuse failure supervision fufspvc................................................606 identification...................
Page 22
Signals..................................................................................648 logic diagram.......................................................................648 interlocking for busbar earthing switch bb_es .........................649 identification.................................
Page 23
Signals..................................................................................695 interlocking for transformer bay ab_trafo ............................697 identification......................................................................... 697 functionality...............................
Page 24
Signals..................................................................................730 settings................................................................................ 731 operation principle............................................................... 731 bay reserve qcrsv.............
Page 25
Settings......................................................................................767 operation principle.................................................................... 767 generic communication function for double point indication dpgapc................................................
Page 26
Functionality.............................................................................. 799 function block........................................................................... 799 signals.......................................................................................799 settings.......
Page 27
Technical data...................................................................... 813 loop delay function block lld.................................................. 813 function block...................................................................... 813 signals..................................
Page 28
Single point input signal attributes converting function block indextspqt............................................................................823 function block...................................................................... 824 signals......................................................
Page 29
Identification.............................................................................. 835 functionality.............................................................................. 835 function block........................................................................... 836 signals.........
Page 30
Function block........................................................................... 849 signals.......................................................................................849 settings......................................................................................849 operation ...
Page 31
Function block........................................................................... 894 signals.......................................................................................894 settings......................................................................................895 operation ...
Page 32
Settings......................................................................................974 operation principle.................................................................... 974 measured value expander block range_xp................................ 975 identification........................
Page 33
Dnp3 protocol................................................................................ 993 iec 61850-8-1 communication protocol......................................... 993 communication interfaces and protocols.................................. 993 settings......................................
Page 34
Identification....................................................................... 1030 function block.................................................................... 1031 signals................................................................................1031 settings........................
Page 35
Functionality....................................................................... 1041 identification....................................................................... 1041 function block.................................................................... 1041 signals...........................
Page 36
Functionality............................................................................ 1061 function block......................................................................... 1062 signals.....................................................................................1062 settings..........
Page 37
Function block......................................................................... 1074 signals.....................................................................................1074 settings....................................................................................1076 operation pri...
Page 38
Signals.....................................................................................1097 settings....................................................................................1097 operation principle ................................................................. 1097 self supervisio...
Page 39
Factory defined settings.......................................................... 1123 signal matrix for binary inputs smbi............................................ 1124 functionality............................................................................ 1124 function block....................
Page 40
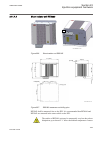
Operation principle.................................................................. 1139 section 21 ied hardware............................................................. 1141 overview.......................................................................................1141 variants of case si...
Page 41
Monitored data................................................................... 1171 technical data.................................................................... 1173 binary input/output module (iom)............................................1174 introduction...................................
Page 42
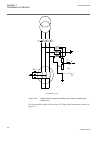
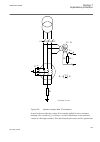
Gps antenna...........................................................................1196 introduction.........................................................................1196 design................................................................................ 1196 technical data................
Page 43
Front view of injection unit, coupling capacitor and shunt resitor unit................................................................................1221 injection unit rex060.........................................................1221 rex060 front panel controls.....................................
Page 44
38.
Page 45
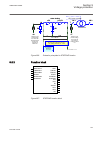
Section 1 introduction 1.1 this manual the technical manual contains application and functionality descriptions and lists function blocks, logic diagrams, input and output signals, setting parameters and technical data, sorted per function. The manual can be used as a technical reference during the ...
Page 46
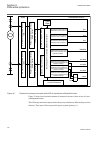
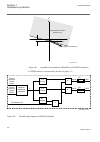
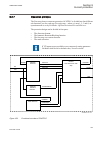
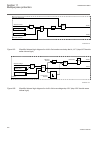
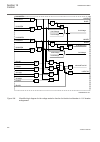
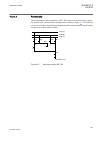
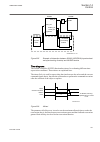
1.3 product documentation 1.3.1 product documentation set iec07000220-4-en.Vsd p la n n in g & p u rc h a se e n gi n e e rin g in st a lli n g c o m m is si o n in g o p e ra tio n m ai n te n a n ce d e co m m is si o n in g d e in st a lli n g & d is p o sa l application manual operation manual i...
Page 47
Well as verifying settings by secondary injection. The manual describes the process of testing an ied in a substation which is not in service. The chapters are organized in the chronological order in which the ied should be commissioned. The relevant procedures may be followed also during the servic...
Page 48
1.3.3 related documents documents related to reg670 identify number application manual 1mrk 502 051-uen commissioning manual 1mrk 502 053-uen product guide 1mrk 502 054-ben technical manual 1mrk 502 052-uen type test certificate 1mrk 502 054-ten 670 series manuals identify number operation manual 1m...
Page 49
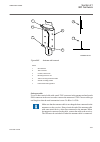
The caution icon indicates important information or warning related to the concept discussed in the text. It might indicate the presence of a hazard which could result in corruption of software or damage to equipment or property. The information icon alerts the reader of important facts and conditio...
Page 50
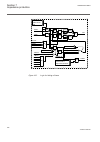
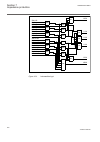
• signals in frames with a shaded area on their right hand side represent setting parameter signals that are only settable via the pst or lhmi. • if an internal signal path cannot be drawn with a continuous line, the suffix -int is added to the signal name to indicate where the signal starts and con...
Page 51
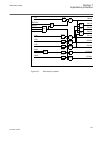
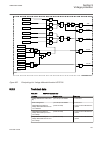
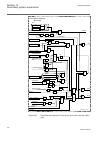
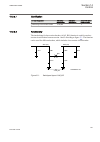
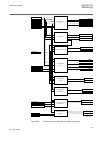
Function block name edition 1 logical nodes edition 2 logical nodes busptrc_b11 busptrc busptrc busptrc_b12 busptrc busptrc busptrc_b13 busptrc busptrc busptrc_b14 busptrc busptrc busptrc_b15 busptrc busptrc busptrc_b16 busptrc busptrc busptrc_b17 busptrc busptrc busptrc_b18 busptrc busptrc busptrc_...
Page 52
Function block name edition 1 logical nodes edition 2 logical nodes cbpgapc cbplln0 cbpmmxu cbpptrc holptov hph1ptov ph3ptuc ph3ptoc rp3pdop cbpmmxu cbpptrc holptov hph1ptov ph3ptoc ph3ptuc rp3pdop ccpdsc ccrpld ccpdsc ccrbrf ccrbrf ccrbrf ccrwrbrf ccrwrbrf ccrwrbrf ccsrbrf ccsrbrf ccsrbrf ccsspvc c...
Page 53
Function block name edition 1 logical nodes edition 2 logical nodes ftaqfvr ftaqfvr ftaqfvr fufspvc sddrfuf fufspvc sddspvc genpdif genpdif gengapc genpdif genphar genptrc goosebinrcv bingrec - goosedprcv dpgrec - gooseintlkrcv intgrec - gooseintrcv intsgrec - goosemvrcv mvgrec - goosesprcv binsgrec...
Page 54
Function block name edition 1 logical nodes edition 2 logical nodes ldrgfc stsggio ldrgfc lexpdis lexpdis lexpdis lexptrc lfpttr lfpttr lfpttr lmbrflo lmbrflo lmbrflo lovptuv lovptuv lovptuv lphd lphd lpttr lpttr lpttr lt3cpdif lt3cpdif lt3cgapc lt3cpdif lt3cphar lt3cptrc lt6cpdif lt6cpdif lt6cgapc ...
Page 55
Function block name edition 1 logical nodes edition 2 logical nodes qcbay qcbay qcrsv qcrsv qcrsv refpdif refpdif refpdif rotiphiz rotiphiz rotiphiz rotiptrc rov2ptov gen2lln0 ph1ptrc rov2ptov ph1ptrc rov2ptov sapfrc sapfrc sapfrc saptof saptof saptof saptuf saptuf saptuf sccvptoc sccvptoc sccvptoc ...
Page 56
Function block name edition 1 logical nodes edition 2 logical nodes tclyltc tclyltc tclyltc tcsltc tcmyltc tcmyltc tcmyltc teigapc teiggio teigapc teiggio teilgapc teilggio teilgapc tmagapc tmaggio tmagapc tppioc tppioc tppioc tr1atcc tr1atcc tr1atcc tr8atcc tr8atcc tr8atcc trpttr trpttr trpttr u2rw...
Page 57
Function block name edition 1 logical nodes edition 2 logical nodes zmfpdis zmflln0 psfpdis zmfpdis zmfptrc zmmmxu psfpdis psfpdis zmfpdis zmfptrc zmmmxu zmhpdis zmhpdis zmhpdis zmmapdis zmmapdis zmmapdis zmmpdis zmmpdis zmmpdis zmqapdis zmqapdis zmqapdis zmqpdis zmqpdis zmqpdis zmrapdis zmrapdis zm...
Page 58
52.
Page 59
Section 2 available functions 2.1 main protection functions 2 = number of basic instances 0-3 = option quantities 3-a03 = optional function included in packages a03 (refer to ordering details) iec 61850 ansi function description generator reg670 reg670 (a20) reg670 (b30) reg670 (c30) differential pr...
Page 60
2.2 back-up protection functions iec 61850 ansi function description generator reg670 reg670 (a20) reg670 (b30) reg670 (c30) current protection phpioc 50 instantaneous phase overcurrent protection 0-4 1 2 2 oc4ptoc 51_67 1) four step phase overcurrent protection 0-6 4 4 4 efpioc 50n instantaneous re...
Page 61
Iec 61850 ansi function description generator reg670 reg670 (a20) reg670 (b30) reg670 (c30) rov2ptov 59n two step residual overvoltage protection 0-3 3 3 3 oexpvph 24 overexcitation protection 0-2 1 1 2 vdcptov 60 voltage differential protection 0-2 2 2 2 stefphiz 59thd 100% stator earth fault prote...
Page 62
Iec 61850 ansi function description generator reg670 reg670 (a20) reg670 (b30) reg670 (c30) locrem handling of lrswitch positions 1+5/apc30 1+5/ apc3 0 1+5/ apc3 0 1+5/ apc3 0 locremctrl lhmi control of psto 1+5/apc30 1+5/ apc3 0 1+5/ apc3 0 1+5/ apc3 0 tcmyltc 84 tap changer control and supervision...
Page 63
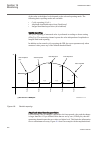
Iec 61850 ansi function description generator reg670 reg670 (a20) reg670 (b30) reg670 (c30) and, or, inv, pulsetimer, gate, timerset, xor, lld, srmemory, rsmemory configurable logic blocks 40-280 40-28 0 40-28 0 40-28 0 andqt, orqt, inverterqt, xorqt, srmemoryqt, rsmemoryqt, timersetqt, pulsetimerqt...
Page 64
Iec 61850 ansi function description generator reg670 reg670 (a20) reg670 (b30) reg670 (c30) drprdre, a1radr, a2radr, a3radr, a4radr, b1rbdr, b2rbdr, b3rbdr, b4rbdr, b5rbdr, b6rbdr disturbance report 1 1 1 1 spgapc generic communication function for single point indication 64 64 64 64 sp16gapc generi...
Page 65
2.4 communication iec 61850 ansi function description generator reg670 reg670 (a20) reg670 (b30) reg670 (c30) station communication lonspa, spa spa communication protocol 1 1 1 1 ade lon communication protocol 1 1 1 1 horzcomm network variables via lon 1 1 1 1 protocol operation selection between sp...
Page 66
Iec 61850 ansi function description generator reg670 reg670 (a20) reg670 (b30) reg670 (c30) multicmdrcv, multicmdsnd multiple command and transmit 60/10 60/10 60/10 60/10 front, lanabi, lanab, lancdi, lancd ethernet configuration of links 1 1 1 1 gateway ethernet configuration of link one 1 1 1 1 op...
Page 67
2.5 basic ied functions table 2: basic ied functions iec 61850 or function name description interrsig self supervision with internal event list selfsupevlst self supervision with internal event list timesynchgen time synchronization module synchbin, synchcan, synchcmpps, synchlon, synchpph, synchpps...
Page 68
Iec 61850 or function name description altrk service tracking activlog activity logging parameters fstaccs field service tool access via spa protocol over ethernet communication pcmaccs ied configuration protocol secalarm component for mapping security events on protocols such as dnp3 and iec103 dnp...
Page 69
Section 3 analog inputs 3.1 introduction analog input channels must be configured and set properly to get correct measurement results and correct protection operations. For power measuring and all directional and differential functions the directions of the input currents must be defined properly. M...
Page 70
3.3 signals table 3: trm_12i output signals name type description status boolean analogue input module status ch1(i) string analogue current input 1 ch2(i) string analogue current input 2 ch3(i) string analogue current input 3 ch4(i) string analogue current input 4 ch5(i) string analogue current inp...
Page 71
Name type description ch3(i) string analogue current input 3 ch4(i) string analogue current input 4 ch5(i) string analogue current input 5 ch6(i) string analogue current input 6 table 6: trm_7i_5u output signals name type description status boolean analogue input module status ch1(i) string analogue...
Page 72
3.4 settings dependent on ordered ied type. Table 8: aisvbas non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description phaseangleref trm40-ch1 - ch12 trm41-ch1 - ch12 mu1-l1i mu1-l2i mu1-l3i mu1-l4i mu1-l1u mu1-l2u mu1-l3u mu1-l4u mu2-l1i mu2-l2i mu2-l3i mu2-l4i mu2-l1u mu2-l2u mu...
Page 73
Name values (range) unit step default description ctstarpoint4 fromobject toobject - - toobject toobject= towards protected object, fromobject= the opposite ctsec4 1 - 10 a 1 1 rated ct secondary current ctprim4 1 - 99999 a 1 3000 rated ct primary current ctstarpoint5 fromobject toobject - - toobjec...
Page 74
Name values (range) unit step default description ctstarpoint2 fromobject toobject - - toobject toobject= towards protected object, fromobject= the opposite ctsec2 1 - 10 a 1 1 rated ct secondary current ctprim2 1 - 99999 a 1 3000 rated ct primary current ctstarpoint3 fromobject toobject - - toobjec...
Page 75
Name values (range) unit step default description ctprim2 1 - 99999 a 1 3000 rated ct primary current ctstarpoint3 fromobject toobject - - toobject toobject= towards protected object, fromobject= the opposite ctsec3 1 - 10 a 1 1 rated ct secondary current ctprim3 1 - 99999 a 1 3000 rated ct primary ...
Page 76
Name values (range) unit step default description ctprim6 1 - 99999 a 1 3000 rated ct primary current ctstarpoint7 fromobject toobject - - toobject toobject= towards protected object, fromobject= the opposite ctsec7 1 - 10 a 1 1 rated ct secondary current ctprim7 1 - 99999 a 1 3000 rated ct primary ...
Page 77
Name values (range) unit step default description ctstarpoint7 fromobject toobject - - toobject toobject= towards protected object, fromobject= the opposite ctsec7 1 - 10 a 1 1 rated ct secondary current ctprim7 1 - 99999 a 1 3000 rated ct primary current ctstarpoint8 fromobject toobject - - toobjec...
Page 78
Table 17: trm_6i monitored data name type values (range) unit description status boolean 0=ok 1=error - analogue input module status table 18: trm_7i_5u monitored data name type values (range) unit description status boolean 0=ok 1=error - analogue input module status table 19: trm_9i_3u monitored d...
Page 79
Protected object line, transformer, etc forward reverse definition of direction for directional functions measured quantity is positive when flowing towards the object e.G. P, q, i reverse forward definition of direction for directional functions e.G. P, q, i measured quantity is positive when flowi...
Page 80
74.
Page 81
Section 4 binary input and output modules 4.1 binary input 4.1.1 binary input debounce filter the debounce filter eliminates bounces and short disturbances on a binary input. A time counter is used for filtering. The time counter is increased once in a millisecond when a binary input is high, or dec...
Page 82
4.1.3.2 setting parameters for binary input/output module table 21: iomin non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description operation off on - - on binary input/output module in operation (on) or not (off) debouncetime 0.001 - 0.020 s 0.001 0.001 debounce time for binary i...
Page 83
Section 5 local human-machine-interface lhmi 5.1 local hmi screen behaviour 5.1.1 identification function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number local hmi screen behaviour screen - - 5.1.2 settings table 22: screen non group settings (basic) name ...
Page 84
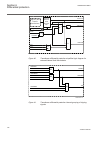
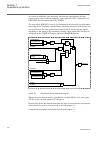
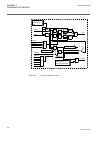
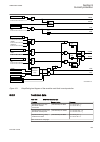
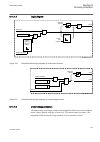
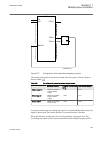
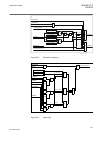
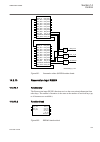
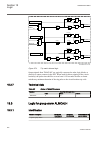
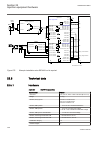
Lhmictrl clrleds hmi-on red-s yellow-s yellow-f clrpulse ledsclrd iec09000320-1-en.Vsd iec09000320 v1 en figure 3: lhmictrl function block 5.2.3 signals table 23: lhmictrl input signals name type default description clrleds boolean 0 input to clear the lcd-hmi leds table 24: lhmictrl output signals ...
Page 85
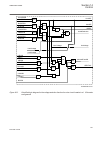
5.3.2 function block ledgen block reset newind ack iec09000321-1-en.Vsd iec09000321 v1 en figure 4: ledgen function block grp1_led1 ^hm1l01r ^hm1l01y ^hm1l01g iec09000322 v1 en figure 5: grp1_led1 function block the grp1_led1 function block is an example. The 15 leds in each of the three groups have...
Page 86
5.3.4 settings table 28: ledgen non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description operation off on - - on operation off/on trestart 0.0 - 100.0 s 0.1 0.0 defines the disturbance length tmax 0.1 - 100.0 s 0.1 1.0 maximum time for the definition of a disturbance table 29: gr...
Page 87
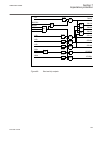
5.4.2 function block fnkeymd1 ^ledctl1 ^fkeyout1 iec09000327 v1 en figure 6: fnkeymd1 function block only the function block for the first button is shown above. There is a similar block for every function key button. 5.4.3 signals table 31: fnkeymd1 input signals name type default description ledct...
Page 88
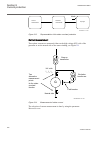
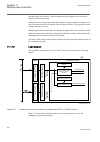
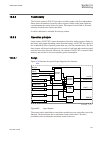
5.5 operation principle 5.5.1 local hmi iec13000239-2-en.Vsd iec13000239 v2 en figure 7: local human-machine interface the lhmi of the ied contains the following elements: • keypad • display (lcd) • led indicators • communication port for pcm600 section 5 1mrk502052-uen b local human-machine-interfa...
Page 89
The lhmi is used for setting, monitoring and controlling. 5.5.1.1 display the lhmi includes a graphical monochrome display with a resolution of 320 x 240 pixels. The character size can vary. The amount of characters and rows fitting the view depends on the character size and the view that is shown. ...
Page 90
• the path shows the current location in the menu structure. If the path is too long to be shown, it is truncated from the beginning, and the truncation is indicated with three dots. • the content area shows the menu content. • the status area shows the current ied time, the user that is currently l...
Page 91
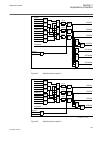
Iec13000281-1-en.Vsd guid-c98d972d-d1d8-4734-b419-161dbc0dc97b v1 en figure 10: function button panel the alarm led panel shows on request the alarm text labels for the alarm leds. Three alarm led pages are available. Iec13000240-1-en.Vsd guid-5157100f-e8c0-4fab-b979-fd4a971475e3 v1 en figure 11: al...
Page 92
There are 15 programmable alarm leds on the front of the lhmi. Each led can indicate three states with the colors: green, yellow and red. The alarm texts related to each three-color led are divided into three pages. 5.5.1.3 keypad the lhmi keypad contains push-buttons which are used to navigate in d...
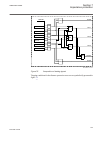
Page 93
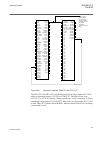
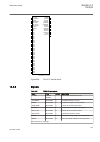
1 18 19 7 6 5 4 3 2 8 20 21 22 17 16 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 23 24 iec15000157-2-en.Vsd iec15000157 v2 en figure 12: lhmi keypad with object control, navigation and command push- buttons and rj-45 communication port 1...5 function button 6 close 7 open 8 escape 9 left 10 down 11 up 12 right 13 key 14 en...
Page 94
19 menu 20 clear 21 help 22 communication port 23 programmable indication leds 24 ied status leds 5.5.2 led 5.5.2.1 functionality the function blocks ledgen and grp1_ledx, grp2_ledx and grp3_ledx (x=1-15) controls and supplies information about the status of the indication leds. The input and output...
Page 95
The yellow and red status leds are configured in the disturbance recorder function, drprdre, by connecting a start or trip signal from the actual function to a bxrbdr binary input function block using the pcm600, and configuring the setting to off, start or trip for that particular signal. 5.5.2.3 i...
Page 96
Function button. The function is positive edge triggered, not level triggered. This means that even if the button is continuously pressed, the acknowledgment/reset only affects indications active at the moment when the button is first pressed. • automatic reset • the automatic reset can only be perf...
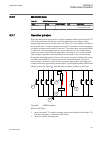
Page 97
= no indication = steady light = flash g = green y = yellow r = red iec09000311.Vsd iec09000311 v1 en figure 13: symbols used in the sequence diagrams sequence 1 (follow-s) this sequence follows the corresponding input signals all the time with a steady light. It does not react on acknowledgment or ...
Page 98
Signal is not present any more. If the signal is still present after acknowledgment it gets a steady light. Activating signal led acknow. En01000231.Vsd iec01000231 v1 en figure 16: operating sequence 3 latchedack-f-s the sequence described below is valid only if the same function block is used for ...
Page 99
Activating signal red led acknow. Iec09000314-1-en.Vsd activating signal yellow g y r r y activating signal green iec09000314 v1 en figure 18: operating sequence 3, three colors involved, alternative 1 if an indication with higher priority appears after acknowledgment of a lower priority indication ...
Page 100
Iec01000235_2_en.Vsd activating signal led reset iec01000235 v2 en figure 20: operating sequence 5 latchedcoll-s that means if an indication with higher priority has reset while an indication with lower priority still is active at the time of reset, the led will change color according to figure 21 ....
Page 101
Iec01000239_2-en.Vsd activating signal 2 led 2 manual reset activating signal 1 automatic reset led 1 disturbance trestart iec01000239 v2 en figure 22: operating sequence 6 (latchedreset-s), two indications within same disturbance figure 23 shows the timing diagram for a new indication after trestar...
Page 102
Figure 24 shows the timing diagram when a new indication appears after the first one has reset but before trestart has elapsed. Iec01000241_2_en.Vsd activating signal 2 led 2 manual reset activating signal 1 automatic reset led 1 disturbance trestart iec01000241 v2 en figure 24: operating sequence 6...
Page 103
Iec01000242_2_en.Vsd activating signal 2 led 2 manual reset activating signal 1 automatic reset led 1 disturbance trestart iec01000242 v2 en figure 25: operating sequence 6 (latchedreset-s), manual reset 5.5.3 function keys 5.5.3.1 functionality local human-machine-interface (lhmi) has five function...
Page 104
Operating sequence the operation mode is set individually for each output, either off, toggle or pulsed. Setting off this mode always sets the outputs to a low value (0). Input value output value iec09000330-2-en.Vsd iec09000330 v2 en figure 26: sequence diagram for setting off setting toggle in thi...
Page 105
500ms 500ms 500ms pulse time pulse time pulse time 500ms iec09000332_2_en.Vsd input value output value iec09000332 v2 en figure 28: sequence diagram for setting pulsed input function all function keys work the same way: when the lhmi is configured so that a certain function button is of type control...
Page 106
100
Page 107
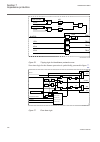
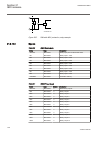
Section 6 differential protection 6.1 transformer differential protection t2wpdif and t3wpdif 6.1.1 identification function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number transformer differential protection, two- winding t2wpdif 3id/i symbol-bb v1 en 87t ...
Page 108
Xx05000050.Vsd iec05000050 v1 en two-winding power transformer with two circuit breakers and two ct-sets on one side xx05000051.Vsd iec05000051 v1 en two-winding power transformer with two circuit breakers and two ct-sets on both sides three-winding applications xx05000052.Vsd iec05000052 v1 en thre...
Page 109
Inrush and ct saturation during external faults. A high set unrestrained differential current protection element is included for a very high speed tripping at high internal fault currents. Included is an sensitive differential protection element based on the theory of negative sequence current compo...
Page 110
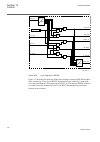
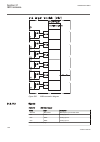
Iec06000250_2_en.Vsd t3wpdif i3pw1ct1* i3pw1ct2* i3pw2ct1* i3pw2ct2* i3pw3ct1* i3pw3ct2* tapoltc1 tapoltc2 oltc1al oltc2al block blkres blkunres blknsunr blknssen trip tripres tripunre trnsunr trnssens start stl1 stl2 stl3 blk2h blk2hl1 blk2hl2 blk2hl3 blk5h blk5hl1 blk5hl2 blk5hl3 blkwav blkwavl1 b...
Page 111
Table 36: t2wpdif output signals name type description trip boolean general, common trip signal tripres boolean trip signal from restrained differential protection tripunre boolean trip signal from unrestrained differential protection trnsunr boolean trip signal from unrestr. Neg. Seq. Diff. Protect...
Page 112
Table 37: t3wpdif input signals name type default description i3pw1ct1 group signal - three phase winding primary ct1 i3pw1ct2 group signal - three phase winding primary ct2 i3pw2ct1 group signal - three phase winding secondary ct1 i3pw2ct2 group signal - three phase winding secondary ct2 i3pw3ct1 g...
Page 113
Name type description blk5hl1 boolean fifth harmonic block signal, phase l1 blk5hl2 boolean fifth harmonic block signal, phase l2 blk5hl3 boolean fifth harmonic block signal, phase l3 blkwav boolean common block signal, waveform criterion, from any phase blkwavl1 boolean block signal, waveform crite...
Page 114
Name values (range) unit step default description crossblocken off on - - on operation off/on for cross-block logic between phases negseqdiffen off on - - on operation off/on for neg. Seq. Differential protections iminnegseq 0.02 - 0.20 ib 0.01 0.04 neg. Seq. Curr. Must be higher than this level to ...
Page 115
Name values (range) unit step default description clocknumberw2 0 [0 deg] 1 [30 deg lag] 2 [60 deg lag] 3 [90 deg lag] 4 [120 deg lag] 5 [150 deg lag] 6 [180 deg] 7 [150 deg lead] 8 [120 deg lead] 9 [90 deg lead] 10 [60 deg lead] 11 [30 deg lead] - - 0 [0 deg] phase displacement between w2 & w1=hv w...
Page 116
Name values (range) unit step default description sotfmode off on - - on operation mode for switch onto fault feature idmin 0.05 - 0.60 ib 0.01 0.30 section1 sensitivity, multi. Of base curr, usually w1 curr. Idunre 1.00 - 100.00 ib 0.01 10.00 unrestr. Prot. Limit, multi. Of base curr. Usually w1 cu...
Page 117
Name values (range) unit step default description connecttypew2 wye (y) delta (d) - - wye (y) connection type of winding 2: y-wye or d- delta connecttypew3 wye (y) delta (d) - - delta (d) connection type of winding 3: y-wye or d- delta clocknumberw2 0 [0 deg] 1 [30 deg lag] 2 [60 deg lag] 3 [90 deg ...
Page 118
Name values (range) unit step default description locationoltc1 not used winding 1 (w1) winding 2 (w2) winding 3 (w3) - - not used transformer winding where oltc1 is located lowtapposoltc1 0 - 10 - 1 1 oltc1 lowest tap position designation (e.G. 1) ratedtapoltc1 1 - 100 - 1 6 oltc1 rated tap/mid-tap...
Page 119
Name type values (range) unit description idl3mag real - a magnitude of fundamental freq. Diff. Current, phase l3 ibias real - a magnitude of the bias current, which is common to all phases idnsmag real - a magnitude of the negative sequence differential current table 46: t3wpdif monitored data name...
Page 120
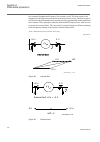
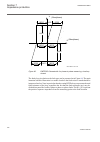
En05000186.Vsd ied i w1 i w2 i w1 i w2 e1 s1 z1 s1 e1 s2 z1 s2 iec05000186 v1 en figure 32: typical ct location and definition of positive current direction even in a healthy power transformer, the currents are generally not equal when they flow through it. This is due to the ratio of the number of ...
Page 121
Proportional bias, which makes the protection operate for a certain percentage differential current related to the current through the transformer. This stabilizes the protection under through fault conditions while still permitting the system to have good basic sensitivity. The following chapters e...
Page 122
1 1_ 1 1_ 2 1_ 3 _ 2 _ 3 2 2 _ 1 2 _ 2 2 _ 3 _ 1 _ 1 3 3 _ 1 3_ 2 3 _ 3 idl il w il w il w un w un w idl a il w b il w c il w un w un w idl il w il w il w é ù é ù é ù é ù ê ú ê ú ê ú ê ú = × + × × + × × ê ú ê ú ê ú ê ú ê ú ê ú ê ú ê ú ë û ë û ë û ë û 1 2 3 4 equation1556 v2 en (equation 2) where: 1....
Page 123
When the end user enters all these parameters, transformer differential function automatically calculates the matrix coefficients. During this calculations the following rules are used: for the phase reference, the first winding with set star (y) connection is always used. For example, if the power ...
Page 124
Table 47: matrices for differential current calculation matrix with zero sequence reduction set to on matrix with zero sequence reduction set to off matrix for reference winding 2 1 1 1 1 2 1 3 1 1 2 - - × - - - - é ù ê ú ê ú ê ú ë û equation1227 v1 en (equation 3) 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 é ù ê ú ê ú ê ú ...
Page 125
Matrix with zero sequence reduction set to on matrix with zero sequence reduction set to off matrix for winding with 120° leading 1 2 1 1 1 1 2 3 2 1 1 - - × - - - - é ù ê ú ê ú ê ú ë û equation1239 v1 en (equation 15) 0 1 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 é ù ê ú ê ú ê ú ë û equation1240 v1 en (equation 16) matrix for...
Page 126
Il1_w1 is the fundamental frequency phase current in phase l1 on the w1 side il2_w1 is the fundamental frequency phase current in phase l2 on the w1 side il3_w1 is the fundamental frequency phase current in phase l3 on the w1 side il1_w2 is the fundamental frequency phase current in phase l1 on the ...
Page 127
Corresponding value for ur_w1 will be calculated and used in the above mentioned equations. By doing this, complete on-line compensation for load tap changer movement is achieved. Differential protection will be ideally balanced for every load tap changer position and no false differential current w...
Page 128
(restrain) current for all three phases. This "maximum principle" makes the differential protection more secure, with less risk to operate for external faults and in the same time brings more meaning to the breakpoint settings of the operate - restrain characteristic. It shall be noted that if the z...
Page 129
Quantities, but zero sequence currents can flow in the earthed star- connected winding. In such cases, an external earth-fault on the star-side causes zero sequence current to flow on the star-side of the power transformer, but not on the other side. This results in false differential currents - con...
Page 130
1. Idmin 2. Endsection1 3. Endsection2 4. Slopesection2 5. Slopesection3 section 1 operate conditionally unrestrainedlimit section 2 section 3 restrain operate unconditionally 5 4 3 2 1 0 0 1 2 3 4 5 idmin endsection1 endsection2 restrain current [ times ibase ] operate current [ times ibase ] slope...
Page 131
Section 1: this is the most sensitive part on the characteristic. In section 1, normal currents flow through the protected circuit and its current transformers, and risk for higher false differential currents is relatively low. An un-compensated on-load tap- changer is a typical reason for existence...
Page 132
2 2 1 _ 2 1 1 _ 1 1 0 1 _ 2 1 _ 2 1 2 _ 1 2 1 _ 1 1 1 0 _ 2 3 _ 1 3 3 _ 1 1 2 _ 1 0 1 1 _ 2 idl ns ins w ins w ur w idl ns a ins w a ins w ur w idl ns a ins w a ins w - - - = - - × + - × - - - × × × × × × × é ù é ù é ù é ù é ù ê ú ê ú ê ú ê ú ê ú ê ú ê ú ê ú ê ú ê ú ê ú ê ú ê ú ê ú ê ú ë û ë û ë û ë...
Page 133
Current from the w2 side compensated for eventual power transformer phase shift and transferred to the power transformer w1 side. These negative sequence current contributions are phasors, which are further used in directional comparisons, to characterize a fault as internal or external. See section...
Page 134
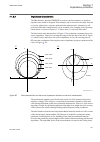
0 deg 180 deg 90 deg 270 deg 120 deg iminnegseq if one or the other of currents is too low, then no measurement is done, and 120 degrees is mapped external fault region internal fault region internal/external fault boundary negseqroa (relay operate angle) en05000188-3-en.Vsd iec05000188 v3 en figure...
Page 135
• if the negative sequence current contributions from the w1 and the w2 sides are in phase, the fault is internal (that is, both phasors are within protected zone) • if the negative sequence currents contributions from w1 and w2 sides are 180 degrees out of phase, the fault is external (that is, w1 ...
Page 136
Different negative sequence source impedance angles on the w1 and w2 sides of the protected power transformer, it may differ somewhat from the ideal zero value. However, during heavy faults, ct saturation might cause the measured phase angle to differ from 180 degrees for an external, and from 0 deg...
Page 137
Because one or more of the fundamental frequency differential currents entered the operate region on the operate - restrain characteristic. So, this protection is not independent of the traditional restrained differential protection - it is activated after the first start signal has been placed. If ...
Page 138
Used for these calculations. The only difference is that the matrix algorithm is fed by instantaneous values of currents, that is, samples. Harmonic and waveform block criteria the two block criteria are the harmonic restrain and the waveform restrain. These two criteria have the power to block a tr...
Page 139
Iec05000343 v1 en figure 37: inrush currents to a transformer as seen by a protective ied. Typical is a high amount of the 2 nd harmonic, and intervals of low current, and low rate-of-change of current within each period. Cross-blocking between phases the basic definition of the cross-blocking is th...
Page 140
Waveblock criterion will temporarily disable the second harmonic blocking feature of the differential protection function. This consequently ensures fast operation of the transformer differential function for a switch onto a fault condition. It shall be noted that this feature is only active during ...
Page 141
If an open ct is detected and the output openct set to 1, then all the differential functions are blocked, except the unrestrained (instantaneous) differential. An alarm signal is also produced after a settable delay (toctalarmdelay) to report to operational personnel for quick remedy actions once t...
Page 142
Adm a /d c on ve rs io n s ca lin g w ith c t ra tio a /d c on ve rs io n s ca lin g w ith c t ra tio p ha so r ca lc ul at io n o f i nd iv id u al ph as e c ur re nt p ha so r ca lc ul at io n o f i nd iv id u al ph as e c ur re nt differential function d er iv e e qu at io n to c al cu la te d if...
Page 143
1. Instantaneous values of currents (samples) from the hv, and lv sides for two- winding power transformers, and from the hv, the first lv, and the second lv side for three-winding power transformers. 2. Currents from all power transformer sides expressed as fundamental frequency phasors with their ...
Page 144
Internal/ external fault discrimin ator t stl1 stl2 stl3 >1 & extfault intfault trnssens trnsunr iec05000167-2-en.Vsd constant ibias a b b>a neg.Seq. Diff current contributions opnegseqdiff=on & iec05000167-tiff v2 en figure 40: transformer differential protection simplified logic diagram for extern...
Page 145
Iec05000279-2-en.Vsd stl1 stl2 stl3 or start blk2hl1 blk2hl2 blk2hl3 or blk2h blkwavl1 blkwavl2 blkwavl3 or blkwav blk5hl1 blk5hl2 blk5hl3 or blk5h iec05000279-tiff v2 en figure 42: transformer differential protection internal grouping of logical signals logic in figures 39 , 40 , 41 and 42 can be s...
Page 146
Blocks with the text inside: 2nd harmonic; wave block and 5th harmonic). If there is less harmonic pollution. Than allowed by the settings i2/i1ratio, and i5/ i1ratio, (then the outputs from the blocks 2nd harmonic and 5th harmonic is 0) then it is assumed that a minor simultaneous internal fault mu...
Page 147
Function range or value accuracy connection type for each of the windings y or d - phase displacement between high voltage winding, w1 and each of the windings, w2 and w3. Hour notation 0–11 - *operate time at 0 to 10 x idmin, restrained function min. = 25 ms max. = 35 ms - *reset time at 10 to 0 x ...
Page 148
Hzpdif can be used to protect generator stator windings, tee-feeders or busbars, reactors, motors, auto-transformers, capacitor banks and so on. One such function block is used for a high-impedance restricted earth fault protection. Three such function blocks are used to form three-phase, phase-segr...
Page 149
6.2.6 monitored data table 52: hzpdif monitored data name type values (range) unit description measvolt real - kv measured rms voltage on ct secondary side 6.2.7 operation principle high impedance protection system is a simple technique which requires that all cts, used in the protection scheme, hav...
Page 150
It is of utmost importance to insure that only one earthing point exists in such protection scheme. 3. Shows the setting (stabilizing) resistor rs. 4. Shows the over-current measuring element. The series connection of stabilizing resistor and over-current element is designated as measuring branch. 5...
Page 151
The voltage waveform is then filtered in order to get its rms value. Note that used filtering is designed in such a way that it ensures complete removal of the dc current component which may be present in the primary fault current. The voltage rms value is then compared with set alarm and trip thres...
Page 152
6.3 generator differential protection genpdif 6.3.1 identification function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number generator differential protection genpdif i d > symbol-nn v1 en 87g 6.3.2 functionality short circuit between the phases of the stat...
Page 153
6.3.3 function block genpdif i3pnct1* i3pnct2* i3ptct1* i3ptct2* block blkres blkunres blknsunr blknssen desensit trip tripres tripunre trnsunr trnssens start stl1 stl2 stl3 blkh openct openctal idl1 idl2 idl3 idnsmag ibias iec11000212-1-en.Vsd iec11000212 v1 en figure 47: genpdif function block 6.3...
Page 154
Table 55: genpdif output signals name type description trip boolean general, common trip signal tripres boolean trip signal from restrained differential protection tripunre boolean trip signal from unrestrained differential protection trnsunr boolean trip signal from unrestr. Neg. Seq. Diff. Protect...
Page 155
Table 57: genpdif group settings (advanced) name values (range) unit step default description endsection1 0.20 - 1.50 ib 0.01 1.25 end of section 1, multiple of generator rated current endsection2 1.00 - 10.00 ib 0.01 3.00 end of section 2, multiple of generator rated current slopesection2 10.0 - 50...
Page 156
6.3.6 monitored data table 59: genpdif monitored data name type values (range) unit description idl1mag real - a fund. Freq. Differential current, phase l1; in primary a idl2mag real - a fund. Freq. Differential current, phase l2; in primary a idl3mag real - a fund. Freq. Differential current, phase...
Page 157
Components than it is to calculate zero-sequence components. Diversity of operation principles integrated in the same protection function enhances the overall performance without a significant increase in cost. A novelty in genpdif, namely the negative-sequence-current-based internal- external fault...
Page 158
One common fundamental frequency bias current is used. The bias current is the magnitude of the highest measured current in the protected circuit. The bias current is not allowed to drop instantaneously, instead, it decays exponentially with a predefined time constant. These principles make the diff...
Page 159
Generator differential protection genpdif function uses two mutually independent characteristics to which magnitudes of the three fundamental frequency rms differential currents are compared at each execution of the differential protection function. These two characteristics divide, each of them ind...
Page 160
Currents in this section can be tolerances of the current transformers used on both sides of the protected generator. Slope in section 1 is always zero percent. Normally, with the protected machine at rated load, the restrain, bias current will be around 1 p.U., that is, equal to the machine rated c...
Page 161
Section 1 operate conditionally unrestrainedlimit section 2 section 3 restrain operate unconditionally 5 4 3 2 1 0 0 1 2 3 4 5 idmin endsection1 endsection2 restrain current [ times ibase ] operate current [ times ibase ] slopesection2 slopesection3 en06000637.Vsd tempidmin iec06000637 v2 en figure ...
Page 162
6.3.7.3 supplementary criteria to relieve the burden of constructing an exact optimal operate-restrain characteristic, two special features supplement the basic stabilized differential protection function, making generator differential protection genpdif a very reliable one. The supplementary criter...
Page 163
If the two negative sequence currents flow in opposite directions, the fault is external. • under external fault condition, the relative angle is theoretically equal to 180°. Under internal fault condition, the angle is ideally 0°, but due to possible different negative-sequence impedance angles on ...
Page 164
Internal fault region 0 deg 180 deg 90 deg 270 deg 120 deg angle could not be measured. One or both currents too small negseqroa (relay operate angle) iminnegseq internal / external fault boundary. Default ± 60 deg external fault region the characteristic is defined by the settings: iminnegseq and n...
Page 165
6.3.7.4 harmonic restrain harmonic restrain is the classical restrain method traditionally used with power transformer differential protections. The goal there was to prevent an unwanted trip command due to magnetizing inrush currents at switching operations, due to magnetizing currents at over-volt...
Page 166
The unwanted trip cannot always be prevented. Still, the information about what was the cause of the open ct secondary circuit, is vital. The principle applied to detect an open ct is a simple pattern recognition method, similar to the waveform check used by the power transformer differential protec...
Page 167
The open ct condition has been detected, it can be reset automatically within the differential function. It is not possible to externally reset an open ct condition. To reset the open ct circuit alarm automatically, the following conditions must be fulfilled: • bias current is for at least one minut...
Page 168
Calculation idiff and ibias calculation instantaneous idiff start and trip logic trip signals start signals block signals intern/ extern fault phasors il1n, il2n,il3n phasors il1t, il2t,il3t samples il1n, il2n,il3n samples iat, ibt,ict magnitude idiff and ibias samples idiff diff.Prot. Characteristi...
Page 169
Idunre idl1mag 2nd and 5th harmonic idl1 and cross block from l2 or l3 opcrossblock=on ibias tripunrel1 stl1 tripresl1 blkhl1 en07000020.Vsd a b b>a and cross block to l2 or l3 and and and blkunres block blkres or 1 intfault iec07000020 v2 en figure 55: generator differential logic diagram 1 interna...
Page 170
En07000022.Vsd stl1 stl2 stl3 or start blkhl1 blkhl2 blkhl3 or blkh iec07000022 v1 en figure 57: generator differential logic diagram 3 en07000023.Vsd tripresl1 tripresl2 tripresl3 or tripres tripunrel1 tripunrel2 tripunrel3 or tripunre or trip trnsunr trnssens iec07000023 v1 en figure 58: generator...
Page 171
Function range or value accuracy reset time at 5 to 0 x idunre unrestrained function min. = 15 ms max. = 30 ms - critical impulse time, unrestrained function 2 ms typically at 0 to 5 x idunre - impulse margin time unrestrained function 10 ms typically - operate time at 0 to 5 x iminnegseq negative s...
Page 172
The most typical application yndx d cb ct ct cb y ied cb cb cb cb autotransformer the most complicated application - autotransformer ct ct ct ct iec05000058-2-en.Vsd iec05000058-2 v1 en figure 59: examples of applications of the refpdif 6.4.3 function block iec06000251_2_en.Vsd refpdif i3p* i3pw1ct1...
Page 173
Table 62: refpdif output signals name type description trip boolean trip by restricted earth fault protection function start boolean start by restricted earth fault protection function dirok boolean directional criteria has operated for internal fault blk2h boolean block due to 2-nd harmonic ires re...
Page 174
6.4.6 monitored data table 66: refpdif monitored data name type values (range) unit description ires real - a magnitude of fund. Freq. Residual current in real - a magnitude of fund. Freq. Neutral current ibias real - a magnitude of the bias current idiff real - a magnitude of fund. Freq. Differenti...
Page 175
Return path via power system l2 l3 l1 l2 l3 i n = - 3izs1 uzs current in the neutral (measured as i n ) serves as a directional reference because it has the same direction for both internal and external faults. Zone of protection i zs1 i zs1 i zs1 ifault roa block i n external fault region l1 zero-s...
Page 176
The abb recommended connection. The differential current becomes zero as both cts ideally measure exactly the same component of the earth- fault current. 2. For an internal fault, the total earth- fault current is composed generally of two zero sequence currents. One zero sequence current (3i zs1 ) ...
Page 177
Refpdif is not sensitive to inrush and overexcitation currents. The only danger is an eventual current transformer saturation. Refpdif has only one operate-bias characteristic, which is described in the table 67 and shown in figure 63 . Table 67: data of the operate-bias characteristic of refpdif de...
Page 178
6.4.7.3 calculation of differential current and bias current the differential current (operate current), as a fundamental frequency phasor, is calculated as (with designations as in figure 61 and figure 62 ): 3 idiff in io = + equation1533 v1 en (equation 29) where: i n is current in the power trans...
Page 179
1 current[4] = max (i3pw2ct2) ctfactorsec2 × equation1529 v1 en (equation 33) current[5] = in equation1530 v1 en (equation 34) the bias current is thus generally equal to none of the input currents. If all primary ratings of the cts were equal to ibase, then the bias current would be equal to the hi...
Page 180
(refpdif) must remain stable during an external fault, and immediately after the fault has been cleared by some other protection. For an external earth faults with no ct saturation, the residual current in the lines (3i o ) and the neutral current (i n in figure 61 ) are theoretically equal in magni...
Page 181
6.4.7.5 algorithm of the restricted earth-fault protection 1. Check if current in the neutral ineutral (in) is less than 50% of the base sensitivity idmin. If yes, only service values are calculated, then refpdif algorithm is not used. 2. If current in the ineutral (in) is more than 50% of idmin, th...
Page 182
Function range or value accuracy directional characteristic fixed 180 degrees or ± 60 to ± 90 degrees ± 2.0 degrees operate time, trip at 0 to 10 x idmin min = 15 ms max = 30 ms - reset time, trip at 10 to 0 x idmin min = 15 ms max = 30 ms - second harmonic blocking 60.0% of fundamental (hidden sett...
Page 183
Section 7 impedance protection 7.1 full-scheme distance measuring, mho characteristic zmhpdis 7.1.1 identification function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number full-scheme distance protection, mho characteristic zmhpdis s00346 v1 en 21 7.1.2 fu...
Page 184
7.1.3 function block zmhpdis i3p* u3p* curr_inp* volt_inp* pol_volt* block blkz blkzmtd blkhsir blktrip blkpe blkpp extnst intrnst dircnd stcnd* ldcnd trip trl1 trl2 trl3 trpe trpp start stl1 stl2 stl3 stpe stpp sttimer iec06000423-2-en.Vsd iec06000423 v3 en figure 64: zmhpdis function block 7.1.4 s...
Page 185
Table 70: zmhpdis output signals name type description trip boolean trip general trl1 boolean trip phase l1 trl2 boolean trip phase l2 trl3 boolean trip phase l3 trpe boolean trip phase-to-earth trpp boolean trip phase-to-phase start boolean start general stl1 boolean start phase l1 stl2 boolean sta...
Page 186
Name values (range) unit step default description zrevpe 0.005 - 3000.000 ohm/p 0.001 30.000 reverse reach of the phase to earth loop(magnitude) tpe 0.000 - 60.000 s 0.001 0.000 delay time for operation of phase to earth elements iminoppe 10 - 30 %ib 1 20 minimum operation phase to earth current opm...
Page 187
7.1.6.2 impedance characteristic the mho distance function zmhpdis is present with four instances so that four separate zones could be designed. Each instance can be selected to be either forward or reverse with positive sequence polarized mho characteristic; alternatively self polarized offset mho ...
Page 188
Identification with load encroachment for mho function fmpspdis, where also the relevant settings can be found. Information about the load encroachment from fmpspdis to the zone measurement is given in binary format to the input signal ldcnd. 7.1.6.3 basic operation characteristics each impedance zo...
Page 189
Compensation for earth -return path for faults involving earth is done by setting the parameter kn and knang where kn is the magnitude of the earth -return path and knang is the argument of the earth-return path. 0 1 1 3 z z kn z - = × iecequation14023 v1 en (equation 35) ( ) 0 1 arg 3 1 z z knang z...
Page 190
The function can be blocked in the following ways: • activating of input block blocks the whole function • activating of the input blkz (fuse failure) blocks all output signals • activating of the input blkzmtd blocks the delta based time domain algorithm • activating of the input blkhsir blocks the...
Page 191
Where u l1l2 equation1790 v2 en is the voltage vector difference between phases l1 and l2 i l1l2 equation1791 v2 en is the current vector difference between phases l1 and l2 zpp is the positive sequence impedance setting for phase-to-phase fault u pol is the polarizing voltage the polarized voltage ...
Page 192
The condition for operation at phase-to-phase fault is that the angle β between the two compensated voltages ucomp1 and ucomp2 is greater than or equal to 90° (figure 67 ). The angle will be 90° for fault location on the boundary of the circle. The angle β for l1-to-l2 fault can be defined according...
Page 193
Voltage and the current must lie between the blinders in second quadrant and fourth quadrant. See figure 68 . Operation occurs if 90≤β≤270 and argdir≤φ≤argnegres. Where argdir is the setting parameter for directional line in fourth quadrant in the directional element, zdmrdir. Argnegres is the setti...
Page 194
X r argdir argnegres zpp zrevpp ul1l2 ϕ il1l2 en06000469.Eps iec06000469 v1 en figure 69: operation characteristic for reverse phase l1-to-l2 fault phase-to-earth fault mho the measuring of earth faults uses earth-return compensation applied in a conventional way. The compensation voltage is derived...
Page 195
1 l loop pol ucomp u i z = - × equation1793 v1 en (equation 39) where u pol is the polarizing voltage (memorized ul1 for phase l1-to- earth fault) z loop is the loop impedance, which in general terms can be expressed as ( ) 1 1 z +zn 1 z kn = × + where z 1 is the positive sequence impedance of the l...
Page 196
Comp u ß i l1· x i l1 ·r i l1 ·zpe il1·zn loop l1 z • i f upol il1 (ref) en06000472_2.Vsd iec06000472 v2 en figure 70: simplified offset mho characteristic and vector diagram for phase l1- to-earth fault operation occurs if 90≤β≤270. Offset mho the characteristic for offset mho at earth fault is a c...
Page 197
Zpe i 1 l • zpe • l1 i - u = u l1 comp1 ß jx i l1l2 r vpe re z • i - l1 u l1 ) l1 = zrevpe • (-i - 1 l 2 comp u u en 06000465.Vsd 2 i 1 l l • • iec06000465 v1 en figure 71: simplified offset mho characteristic and voltage vector for phase l1- to-earth fault operation occurs if 90≤β≤270. Offset mho, ...
Page 198
I l1 jx u l1 f argdir i l1 argnegres il1·r en 06000466.Vsd iec06000466 v1 en figure 72: simplified characteristic for offset mho in forward direction for l1-to- earth fault offset mho, reverse direction in the same way as for offset in forward direction, the selection of offset mho in reverse direct...
Page 199
X r argdir argnegres zpe zrevpe ul1 ϕ il 1 en06000470.Eps iec06000470 v1 en figure 73: simplified characteristic for offset mho in reverse direction for l1-to- earth fault 7.1.6.5 simplified logic diagrams distance protection zones the design of the distance protection zones are presented for all me...
Page 200
Are converted within the zone measuring function into corresponding boolean expressions for each condition separately. Input signal stcnd is connected from fmpspdis function output signal stcndphs. The input signal dircnd is used to give condition for directionality for the distance measuring zones....
Page 201
Iec11000217-1-en.Vsd and and and and and and stpe or release or or or or stl1 stl2 stl3 stpp start or stl1n stl2n stl3n stl1l2 stl2l3 stl3l1 iec11000217 v1 en figure 75: composition of starting signals tripping conditions for the distance protection zone one are symbolically presented in figure 76 ....
Page 202
Iec11000218-1-en.Vsd 15ms or t tpp blktrip t and and and stl1 stl2 stl3 trip trl1 trl2 trl3 and timer tpp=on stpp and timer tpe=on stpe and t tpe iec11000218 v1 en figure 76: tripping logic for the distance protection zone zone timer logic for the distance protection is symbolically presented in fig...
Page 203
7.1.7 technical data table 74: zmhpdis technical data function range or value accuracy number of zones, ph-e max 4 with selectable direction - minimum operate current (10–30)% of ibase - positive sequence impedance, ph-e loop (0.005–3000.000) w/phase ± 2.0% static accuracy conditions: voltage range:...
Page 204
7.2.3 function block iec06000422_2_en.Vsd zdmrdir i3p* u3p* dir_curr dir_volt dir_pol stfw strv stdircnd iec06000422 v2 en figure 78: zdmrdir function block 7.2.4 signals table 75: zdmrdir input signals name type default description i3p group signal - group signal for current input u3p group signal ...
Page 205
Table 78: zdardir output signals name type description stfwpe boolean forward start signal from phase-to-ground directional element strvpe boolean reverse start signal from phase-to-ground directional element direfcnd integer start direction binary coded 7.2.5 settings table 79: zdmrdir group settin...
Page 206
Table 82: zdardir group settings (advanced) name values (range) unit step default description angleop 90 - 180 deg 1 160 operation sector angle kmag 0.50 - 3000.00 ohm 0.01 40.00 boost-factor in -u0comp and -u2comp polarization table 83: zdardir non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit st...
Page 207
L1l2 l1l2m l1l2 0.85 u1 0.15 u1 argdir arg argneg re s i × + × - equation1619 v1 en (equation 43) where: argdir setting for the lower boundary of the forward directional characteristic, by default set to 15 (= -15 degrees) argnegres setting for the upper boundary of the forward directional character...
Page 208
X r -argdir argnegres zset reach point -zs en06000416.Vsd iec06000416 v1 en figure 79: setting angles for discrimination of forward fault the reverse directional characteristic is equal to the forward characteristic rotated by 180 degrees. The code built up for release of the measuring fault loops i...
Page 209
The directional impedance element for mho characteristic (zdmrdir) function has the following output signals: the stdircnd output provides an integer signal that depends on the evaluation and is derived from a binary coded signal as follows: bit 11 (2048) bit 10 (1024) bit 9 (512) bit 8 (256) bit 7 ...
Page 210
The zmfpdis function is a six zone full scheme protection with three fault loops for phase-to-phase faults and three fault loops for phase-to-earth faults for each of the independent zones, which makes the function suitable in applications with single- phase autoreclosing. The zones can operate inde...
Page 211
7.3.3 function block zmfpdis i3p* u3p* block vtsz blkz1 blkz2 blkz3 blkz4 blkz5 blkzrv blktrz1 blktrz2 blktrz3 blktrz4 blktrz5 blktrzrv tripz1 trl1z1 trl2z1 trl3z1 tripz2 trl1z2 trl2z2 trl3z2 tripz3 tripz4 tripz5 tripzrv startz1 stndz1 startz2 stl1z2 stl2z2 stl3z2 stndz2 startz3 stndz3 startz4 stndz...
Page 212
Name type default description blkz1 boolean 0 resets all outputs and internal timers of zone 1 blkz2 boolean 0 resets all outputs and internal timers of zone 2 blkz3 boolean 0 resets all outputs and internal timers of zone 3 blkz4 boolean 0 resets all outputs and internal timers of zone 4 blkz5 bool...
Page 213
Name type description stl3z2 boolean start in phase l3 from zone 2 - forward direction stndz2 boolean start in any phase or phases from zone 2 - any direction startz3 boolean start in any phase or phases from zone 3 - zone direction stndz3 boolean start in any phase or phases from zone 3 - any direc...
Page 214
7.3.5 settings table 87: zmfpdis group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description operation off on - - off operation mode off / on rldfw 0.01 - 5000.00 ohm/p 0.01 60.00 resistance determining the load impedance area - forward rldrv 0.01 - 5000.00 ohm/p 0.01 60.00 resistance d...
Page 215
Name values (range) unit step default description rfppz2 0.01 - 9000.00 ohm/l 0.01 30.00 fault resistance reach, ph-ph, zone 2 rfpez2 0.01 - 9000.00 ohm/l 0.01 100.00 fault resistance reach, ph-e, zone 2 tppz2 0.000 - 60.000 s 0.001 0.400 time delay to trip, phase-phase, zone 2 tpez2 0.000 - 60.000 ...
Page 216
Name values (range) unit step default description iminoppez4 5 - 6000 %ib 1 10 minimum operate phase current for phase-earth loops, zone 4 opmodez5 disable-zone enable ph-e enable phph enable ph-e phph - - enable ph-e phph on/off setting for ph-ph and ph-e loops, zone 5 dirmodez5 non-directional for...
Page 217
Table 88: zmfpdis group settings (advanced) name values (range) unit step default description zonelinkstart phase selection 1st starting zone - - phase selection select. Of start source for all zonelinked trip delay timers inreleasepe 5 - 400 %iph 1 400 3i0 limit for releasing phase-to-earth measuri...
Page 218
Table 89: zmfpdis non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description globalbasesel 1 - 12 - 1 1 selection of one of the global base value groups 7.3.6 monitored data table 90: zmfpdis monitored data name type values (range) unit description l1dir integer 1=forward 2=reverse...
Page 219
The phasor filter is frequency adaptive in the sense that its coefficients are changed based on the estimated power system frequency. A half cycle filter will not be able to reject both even and odd harmonics. So, while odd harmonics will be completely attenuated, accuracy will be affected by even h...
Page 220
Impact on operate times. However, this will be evident primarily at higher source impedance ratios (sirs), sir 5 and above, or close to the reach limit. The iec 60044-5 transient classification is of little or no use in this connection. It is not primarily the damping of transients that is important...
Page 221
Phase-earth fault and the function will eventually use phase-to-phase zone measurements also here. In cases where the fault current infeed is more or less completely of zero sequence nature (all phase currents in phase), the measurement will be performed in the phase- to-earth loops only for a phase...
Page 222
However, if the ‘seriescomp’ option is chosen (only available in zmfcpdis) the value is changed to 0.95. 7.3.7.5 fuse failure the zmfpdis function has to be blocked by an additional function like the fuse failure supervision (fufspvc) or an equivalent external device. Typically, the binary input vts...
Page 223
Rfpe x1pe+xn x1pe+xn rfpe r1pe+rn rfpe rfpe rfpe rfpe r r1pe+rn (ohm/loop) iec11000415-1-en.Vsd x0pe-x1pe xn 3 = r0pe-r1pe rn 3 = j n j n x (ohm/loop) iec11000415 v1 en figure 82: zmfpdis characteristic for phase-to-earth measuring, ohm/loop domain 1mrk502052-uen b section 7 impedance protection 217...
Page 224
J r1pp rfpp x1pp x1pp rfpp r1pp rfpp rfpp rfpp rfpp r x (ohm/phase) (ohm/phase) iec11000416-1-en.Vsd j 0 1 3 x pe x rvpe xnrv - = 0 1 3 x pe x fwpe xnfw - = 0 1 3 x pg x fwpg xnfw - = 0 1 3 x pg x rvpg xnrv - = 0 1 3 x pe x rvpe xnrv - = 0 1 3 x pe x fwpe xnfw - = 2 2 2 2 2 2 iec11000416 v1 en figur...
Page 225
Ul1 r1 + j x1 il1 rfpe phase-to-earth fault in phase l1 phase-to-phase fault in phase l1-l2 three-phase fault or phase-to- phase-earth fault (arc + tower resistance) 0 (r0-r1)/3 + j (x0-x1)/3 ) in ul1 r1 + j x1 il1 ul2 r1 + j x1 il2 rfpp ul1 r1 + j x1 il1 ul3 r1 + j x1 il3 0.5·rfpp 0.5·rfpp (arc res...
Page 226
Encroachment. Separate resistive blinder setting is available in forward and reverse direction. The use of the load encroachment feature is essential for long heavily loaded lines, where there might be a conflict between the necessary emergency load transfer and necessary sensitivity of the distance...
Page 227
Dirmodez3-5 non-directional forward reverse dir(ln & lmln)z3-5 true (1) fw(ln & lmln) rv(ln & lmln) fw(ln & lmln) dir(ln & lmln)z1 fw(ln & lmln) dir(ln & lmln)z2 rv(ln & lmln) dir(ln & lmln)zrv iec12000137-2-en.Vsd iec12000137 v2 en figure 86: connection of directional signals to zones zml1zx ndzx p...
Page 228
Tzx t tppzx t tpezx block ppzx pezx timerlinkszx looplink (tpp-tpe) looplink & zonelink no links lnkz1 false (0) timerlinkszx = looplink & zonelink lnkzrv lnkz2 lnkzx or lnkz3 lnkz4 lnkz5 zonelinkstart stphs phase selection 1st starting zone vtsz blkzx blktrzx or or or or or and and or and and and t...
Page 229
T 15 ms stl1zx t 15 ms tripzx and and and and trl1zx trl2zx trl3zx t 15 ms t 15 ms startzx stl2zx stl3zx and and and tzx block vtsz blkzx blktrzx t 15 ms and t 15 ms and stndzx or or l1zx l2zx l3zx ppzx ndzx or pezx iec12000138-1-en.Vsd iec12000138 v1 en figure 89: start and trip outputs 1mrk502052-...
Page 230
Phsl1 phsl2 phsl3 phsl1l2 phsl2l3 phsl3l1 block vtsz or t 15 ms and or or or or t 15 ms and t 15 ms and startnd or or t 15 ms and stphs t 15 ms and stpp stpe iec12000133-1-en.Vsd iec12000133 v1 en figure 90: additional start outputs 1 section 7 1mrk502052-uen b impedance protection 224 technical man...
Page 231
Phsl1 phsl2 phsl3 phsl1l2 phsl2l3 phsl3l1 stfwl1 stfwl2 stfwl3 fwl1 fwl2 fwl1l2 fwl3 fwl2l3 fwl3l1 block vtsz or t 15 ms and and and and and and and or or or or in present t 15 ms and t 15 ms and stfwpe and =1 =2 =3 stfw1ph stfw2ph stfw3ph iec12000134-1-en.Vsd iec12000134 v1 en figure 91: additional...
Page 232
7.3.8 technical data table 91: zmfpdis, zmfcpdis technical data function range or value accuracy number of zones 3 selectable directions, 3 fixed directions - minimum operate current, ph-ph and ph-e (5-6000)% of ibase ±1.0% of i r positive sequence reactance reach, ph-e and ph-ph loop (0.01 - 3000.0...
Page 233
Faults generating heavily distorted signals. These faults are handled with outmost security and dependability, although sometimes with reduced operating speed. High speed distance protection zmfcpdis is fundamentally the same function as zmfpdis but provides more flexibility in zone settings to suit...
Page 234
7.4.3 function block zmfcpdis i3p* u3p* block vtsz blkz1 blkz2 blkz3 blkz4 blkz5 blkzrv blktrz1 blktrz2 blktrz3 blktrz4 blktrz5 blktrzrv tripz tripz1 trl1z1 trl2z1 trl3z1 tripz2 trl1z2 trl2z2 trl3z2 tripz3 tripz4 tripz5 tripzrv startz startz1 stndz1 startz2 stl1z2 stl2z2 stl3z2 stndz2 startz3 stndz3...
Page 235
7.4.4 signals table 92: zmfcpdis input signals name type default description i3p group signal - group signal for current input u3p group signal - group signal for voltage input block boolean 0 resets all outputs and internal timers of entire function vtsz boolean 0 resets all outputs and internal ti...
Page 236
Name type description tripz5 boolean trip in any phase or phases from zone 5 - zone direction tripzrv boolean trip in any phase or phases from zone rv - reverse dir. Startz1 boolean start in any phase or phases from zone 1 - forward direction stndz1 boolean start in any phase or phases from zone 1 -...
Page 237
Name type description strvl3 boolean fault detected in phase l3 - reverse direction strvpe boolean fault with earth connection detected - reverse direction stfw1ph boolean single-phase fault detected - forward direction stfw2ph boolean two-phase fault detected - forward direction stfw3ph boolean thr...
Page 238
Name values (range) unit step default description r0fwpez1 0.00 - 3000.00 ohm/p 0.01 15.00 zero seq. Resistive reach, ph-e, zone 1, forward direction rfpez1 0.01 - 9000.00 ohm/l 0.01 100.00 fault resistance reach, ph-e, zone 1, forw & rev dir. X1rvpez1 0.01 - 3000.00 ohm/p 0.01 30.00 pos. Seq. React...
Page 239
Name values (range) unit step default description x1fwppz3 0.01 - 3000.00 ohm/p 0.01 40.00 positive seq. Reactance reach, ph-ph, zone 3, zone direction r1fwppz3 0.00 - 1000.00 ohm/p 0.01 5.00 positive seq. Resistive reach, ph-ph, zone 3, zone direction rffwppz3 0.01 - 9000.00 ohm/l 0.01 30.00 fault ...
Page 240
Name values (range) unit step default description r1fwpez4 0.00 - 1000.00 ohm/p 0.01 5.00 positive seq. Resistive reach, ph-e, zone 4, zone direction x0fwpez4 0.01 - 9000.00 ohm/p 0.01 120.00 zero seq. Reactance reach, ph-e, zone 4, zone direction r0fwpez4 0.00 - 3000.00 ohm/p 0.01 15.00 zero seq. R...
Page 241
Name values (range) unit step default description tppz5 0.000 - 60.000 s 0.001 1.600 time delay to trip, phase-phase, zone 5 tpez5 0.000 - 60.000 s 0.001 1.600 time delay to trip, phase-earth, zone 5 iminopppz5 5 - 6000 %ib 1 10 minimum operate ph-ph current for phase-phase loops, zone 5 iminoppez5 ...
Page 242
Name values (range) unit step default description timerlinksz1 looplink (tpp-tpe) looplink & zonelink no links - - looplink (tpp- tpe) how start of trip delay timers should be linked for zone 1 timermodez2 disable all enable ph-e enable phph enable ph-e phph - - enable ph-e phph on/off setting for p...
Page 243
7.4.6 monitored data table 97: zmfcpdis monitored data name type values (range) unit description l1dir integer 1=forward 2=reverse 0=no direction - direction in phase l1 l2dir integer 1=forward 2=reverse 0=no direction - direction in phase l2 l3dir integer 1=forward 2=reverse 0=no direction - direct...
Page 244
There will be a slightly variable underreach, on average in the same order as the magnitude ratio between the harmonic and the fundamental component. 7.4.7.2 distance measuring zones the execution of the different fault loops within the ied are of full scheme type, which means that earth fault loop ...
Page 245
It is the frequency content of the transients that is decisive, i.E. How difficult it is to filter out the specific frequency. So, even if two cvts, one passive and the other active type, comply with the same transient class, the active type requires more extensive filtering in order to avoid transi...
Page 246
In cases where the fault current infeed is more or less completely lack of zero sequence nature (all phase currents in phase), the measurement will be performed in the phase- to-earth loops only for a phase-to-phase-earth fault. However, should it be desirable to use phase-to-earth (and only phase-t...
Page 247
However, if the seriescomp option is chosen (only available in zmfcpdis) the value is changed to 0.95. 7.4.7.5 fuse failure the zmfcpdis function has to be blocked by an additional function like the fuse failure supervision (fufspvc) or an equivalent external device. Typically, the binary input vtsz...
Page 248
R1pe+rnfw rffwpe x1fwpe+xnfw x1rvpe+xnrv rffwpe rfrvpe rffwpe rfrvpe rfrvpe r x (ohm/loop) (ohm/loop) iec11000417-1-en.Vsd j n 0 1 3 x pe x rvpe xnrv - = 0 1 3 x pe x fwpe xnfw - = 0 1 3 x pg x fwpg xnfw - = 0 1 3 x pg x rvpg xnrv - = 0 1 3 x pe x fwpe xnfw - = 0 1 3 r pe r pe rnfw - = j n j n 1 1 x...
Page 249
J r1pp rffwpp x1fwpp x1rvpp rffwpp rfrvpp rffwpp rfrvpp rfrvpp r x (ohm/phase) (ohm/phase) iec11000418-1-en.Vsd j 0 1 3 x pe x rvpe xnrv - = 0 1 3 x pe x fwpe xnfw - = 0 1 3 x pg x fwpg xnfw - = 0 1 3 x pg x rvpg xnrv - = 0 1 3 x pe x rvpe xnrv - = 0 1 3 x pe x fwpe xnfw - = 2 2 2 2 2 2 j n n j iec1...
Page 250
Ul1 r1 + j x1 il1 rfpe phase-to-earth fault in phase l1 phase-to-phase fault in phase l1-l2 three-phase fault or phase-to- phase-earth fault (arc + tower resistance) 0 (r0-r1)/3 + j (x0-x1)/3 ) in ul1 r1 + j x1 il1 ul2 r1 + j x1 il2 rfpp ul1 r1 + j x1 il1 ul3 r1 + j x1 il3 0.5·rfpp 0.5·rfpp (arc res...
Page 251
Phsl1 phsl2 phsl3 phsl1l2 phsl2l3 phsl3l1 block vtsz or t 15 ms and or or or or t 15 ms and t 15 ms and startnd or or t 15 ms and stphs t 15 ms and stpp stpe iec12000133-1-en.Vsd iec12000133 v1 en figure 98: additional start outputs 1 1mrk502052-uen b section 7 impedance protection 245 technical man...
Page 252
Phsl1 phsl2 phsl3 phsl1l2 phsl2l3 phsl3l1 stfwl1 stfwl2 stfwl3 fwl1 fwl2 fwl1l2 fwl3 fwl2l3 fwl3l1 block vtsz or t 15 ms and and and and and and and or or or or in present t 15 ms and t 15 ms and stfwpe and =1 =2 =3 stfw1ph stfw2ph stfw3ph iec12000134-1-en.Vsd iec12000134 v1 en figure 99: additional...
Page 253
T 15 ms stl1zx t 15 ms tripzx and and and and trl1zx trl2zx trl3zx t 15 ms t 15 ms startzx stl2zx stl3zx and and and tzx block vtsz blkzx blktrzx t 15 ms and t 15 ms and stndzx or or l1zx l2zx l3zx ppzx ndzx or pezx iec12000138-1-en.Vsd iec12000138 v1 en figure 101: start and trip outputs 1mrk502052...
Page 254
Tzx t tppzx t tpezx block ppzx pezx timerlinkszx looplink (tpp-tpe) looplink & zonelink no links lnkz1 false (0) timerlinkszx = looplink & zonelink lnkzrv lnkz2 lnkzx or lnkz3 lnkz4 lnkz5 zonelinkstart stphs phase selection 1st starting zone vtsz blkzx blktrzx or or or or or and and or and and and t...
Page 255
Phsl1 phsl2 phsl3 phsl1l2 phsl2l3 phsl3l1 strvl1 strvl2 strvl3 rvl1 rvl2 rvl1l2 rvl3 rvl2l3 rvl3l1 block vtsz or t 15 ms and and and and and and and or or or or in present t 15 ms and t 15 ms and strvpe and iec12000141-1-en.Vsd iec12000141 v1 en figure 103: additional start outputs 3 1mrk502052-uen ...
Page 256
Zml1zx ndzx phsl1 and or zml2zx phsl2 and zml3zx phsl3 and zml1l2zx phsl1l2 and zml2l3zx phsl2l3 and zml3l1zx phsl3l1 and or dirl1zx and dirl2zx and and or and and and dirl3zx dirl1l2zx dirl2l3zx dirl3l1zx l1zx pezx l2zx l3zx ppzx or or or iec12000140-1-en.Vsd iec12000140 v1 en figure 104: intermedi...
Page 257
7.4.8 technical data table 98: zmfcpdis technical data function range or value accuracy number of zones 3 selectable directions, 3 fixed directions - minimum operate current, ph-ph and ph-e (5 - 6000)% of ibase ±1.0% of i n positive sequence reactance reach, ph-e and ph-ph loop (30 - 3000) Ω/phase "...
Page 258
Centre of pole slip en07000003.Vsd angle = 90° angle = -90° iec07000003 v1 en figure 105: the centre of pole slip the centre of the pole slip can occur in the generator itself or somewhere in the power system. When a pole slip occurs within the generator it is essential to trip the generator. If the...
Page 259
First action should be to split the network into two parts, after line protection action. If this fails there should be operation of the generator pspppam in zone 2, to prevent further damages to the generator, shaft and turbine. 7.5.3 function block iec10000045-1-en.Vsd pspppam i3p* u3p* block blkg...
Page 260
Name type description sfreq real slip frequency slipzohm real slip impedance in ohms slipzper real slip impedance in percent of zbase ucos real ucosphi voltage ucosper real ucosphi voltage in percent of ubase 7.5.5 settings table 101: pspppam group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step defa...
Page 261
7.5.6 monitored data table 104: pspppam monitored data name type values (range) unit description sfreq real - hz slip frequency slipzohm real - ohm slip impedance in ohms slipzper real - % slip impedance in percent of zbase ucos real - kv ucosphi voltage ucosper real - % ucosphi voltage in percent o...
Page 262
Iec06000437_2_en.Vsd ied b a e b e a x’ d x t x s zone 1 zone 2 jx r x’ d x t x s b a d apparent generator impedance pole slip impedance movement iec06000437 v2 en figure 107: movements in the impedance plain where: x' d = transient reactance of the generator x t = short-circuit reactance of the ste...
Page 263
En07000004.Vsd iec07000004 v1 en figure 108: different generator quantities as function of the angle between the equivalent generators an alarm is given when movement of the rotor is detected and the rotor angle exceeds the angle set for 'warnangle'. Slipping is detected when: • a change of rotor an...
Page 264
The trip1 tripping command and signal are generated after n1 slips in zone 1, providing the rotor angle is less than tripangle. The trip2 signal is generated after n2 slips in zone 2, providing the rotor angle is less than tripangle. All signals are reset if: • the direction of movement reverses • t...
Page 265
7.5.8 technical data table 105: pspppam technical data function range or value accuracy impedance reach (0.00 - 1000.00)% of zbase ±2.0% of u r /i r zone 1 and zone 2 trip counters (1 - 20) - 7.6 out-of-step protection oosppam 7.6.1 identification function description iec 61850 identification iec 60...
Page 266
7.6.3 function block oosppam i3p1* i3p2* u3p* block blkgen blkmot extz1 trip tripz1 tripz2 start genmode motmode r x slipfreq rotorang ucosphi iec12000188-3-en.Vsd iec12000188 v3 en figure 110: oosppam function block 7.6.4 signals table 106: oosppam input signals name type default description i3p1 g...
Page 267
Name type description slipfreq real slip frequency in hz rotorang real rotor angle as estimated by the out-of-step function ucosphi real estimated ucos(phi) voltage during pole slip, in v 7.6.5 settings table 108: oosppam group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description opera...
Page 268
Table 111: oosppam non group settings (advanced) name values (range) unit step default description startangle 90.0 - 130.0 deg 0.1 110.0 angle between two rotors to get the start signal, in deg tripangle 15.0 - 90.0 deg 0.1 60.0 maximum rotor angle to allow trip signals, in deg 7.6.6 monitored data ...
Page 269
-1.5 -1 -0.5 0 0.5 1 1.5 -1 -0.5 0 0.5 1 1.5 --------- ------- ------ ------ ------ ------ ------- ----- --- --- -- --- --- --- --- ---- ---- ---- ---- ---- ---- ---- ---- ----- ----- ------ real part (r) of z in ohms im ag ina ry pa rt (x ) o f z in o hm s ^ ^ ^ ^ ^ ^ ^ ^ ^ ^ ^ ^ ^ ^ ^ ^ ^ ^ -- -- ...
Page 270
Degrees. It can be observed in figure 112 that the angle reaches 180 degrees when the complex impedance z(r, x) crosses the impedance line se – re. It then changes the sign, and continues from -180 degrees to 0 degrees, and so on. Figure 112 shows the rotor (power) angle and the magnitude of z(r, x)...
Page 271
-1 -0.5 0 0.5 1 1.5 -1 -0.8 -0.6 -0.4 -0.2 0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1 ------ ------ ----- ---- ---- ---- ----- ----- ----- ---- --- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- --- --- --- --- --- --- --- --- --- --- --- --- ---- ---- ---- --- real part (r) of z in ohms → im ag ina ry pa rt (x ) o f z in o hm s → ^ ^ ^ ^ ^ ...
Page 272
-0.8 -0.6 -0.4 -0.2 0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1 -0.6 -0.4 -0.2 0 0.2 0.4 0.6 ----- ---- ---- ---- --- --- --- --- --- --- --- --- ---- --- -- -- -- -- -- - - - -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- --- --- --- --- ---- - real part (r) of z in ohms im ag ina ry pa rt (x ) o f z in o ...
Page 273
Voltage and nominal current. The impedances from the position of the out-of-step protection in the direction of the normal load flow can be taken as forward. The out-of-step relay, as in figure 115 looks into the system and the impedances in that direction are forward impedances: • forwardx = xtr + ...
Page 274
The direction from the right to the left, and exits the lens on the opposite side. When the complex impedance exits the lens on the side opposite to its entrance, the 1st pole-slip has already occurred and more pole-slips can be expected if the generator is not disconnected. Figure 111 shows two pol...
Page 275
Not already disconnected after the first pole-slip. The measured value of slipspersecond (slipfreq) is equal to the average slip-frequency of the machine between the last two successive pole-slips. 7.6.7.4 taking care of the circuit breaker although out-of-step events are relatively rare, the out-of...
Page 276
-0.6 -0.4 -0.2 0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 -0.4 -0.2 0 0.2 0.4 0.6 real part (r) of z in ohms → im ag ina ry pa rt (x ) o f z in o hm s → r[ohm] no trip region loci of z(r, x) no trip region rotor angle = ±180° x[ohm] re - receiving end (infinite bus) ← this circle is loci of the rotor angle = 90° 2 relay se ...
Page 277
7.6.7.5 design at every execution of the function the following is calculated: active power p, reactive power q, rotor angle rotorang, quantity ucosphi, the positive-sequence current current and voltage voltage. All other quantities, that can as well be read as outputs, are only calculated if the z(...
Page 278
7.6.8 technical data table 113: oosppam technical data function range or value accuracy impedance reach (0.00 - 1000.00)% of zbase ±2.0% of u r /(√3 ⋅ i r ) rotor start angle (90.0 - 130.0) degrees ±5.0 degrees rotor trip angle (15.0 - 90.0) degrees ±5.0 degrees zone 1 and zone 2 trip counters (1 - ...
Page 279
7.7.3 function block iec07000031_2_en.Vsd lexpdis i3p* u3p* block blktrz1 blktrz2 trip trz1 trz2 start stz1 stz2 xohm xpercent rohm rpercent iec07000031 v2 en figure 119: lexpdis function block 7.7.4 signals table 114: lexpdis input signals name type default description i3p group signal - current gr...
Page 280
7.7.5 settings table 116: lexpdis group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description operation off on - - off operation off / on operationz1 off on - - on operation off/on zone z1 xoffsetz1 -1000.00 - 1000.00 % 0.01 -10.00 offset of z1 circle top point along x axis in % of zbas...
Page 281
7.7.6 monitored data table 120: lexpdis monitored data name type values (range) unit description xohm real - ohm reactance in primary ohms xpercent real - % reactance in percent of zbase rohm real - ohm resistance in primary ohms rpercent real - % resistance in percent of zbase 7.7.7 operation princ...
Page 282
• offset mho circle for z1 • offset mho circle for z2 • directional blinder r x underexcitation protection restrain area z1, fast zone z2, slow zone iec06000455-2-en.Vsd underexitation protection restrain area directional blinder r iec06000455 v2 en figure 120: three characteristics in lexpdis prote...
Page 283
R offset z1 or z2 xoffsetz1 z1diameter z (apparent impedance) z1 = z - (xoffsetz1 + z1diameter/2) en06000456-2.Vsd iec06000456 v2 en figure 121: zone measurement in lexpdis protection function the impedance z1 is constructed from the measured apparent impedance z and the impedance corresponding to t...
Page 284
R x underexcitation protection restrain area dirangle xoffsetdirline z (apparent impedance) en06000457.Vsd iec06000457 v1 en figure 122: impedance constructed as xoffsetdirline in lexpdis protection lexpdis function is schematically described in figure 123 . En06000458-2.Vsd apparent impedance calcu...
Page 285
7.7.8 technical data table 121: lexpdis technical data function range or value accuracy x offset of mho top point for zone 1 and zone 2 (–1000.00–1000.00)% of z base ±5.0% of u r /i r diameter of mho circle for zone 1 and zone 2 (0.0–3000.00)% of z base ±5.0% of u r /i r independent time delay for z...
Page 286
The protection function can detect earth faults in the entire rotor winding and associated connections. Requires injection unit rex060 and a coupling capacitor unit rex061 for correct operation. 7.8.3 description of input signals the inputs to the sensitive rotor earth-fault protection function bloc...
Page 287
Output signal description frequ measured frequency of the injected voltage rfault estimated fault resistance in Ω zref selected reference impedance number zrefre the real part (resistance) of the used reference impedance zrefim the imaginary part (reactance) of the used reference impedance urmsstat ...
Page 288
The injection equipment provides calculation of the fault resistance: • if the fault resistance is equal or below 10 kΩ, rfault is displayed in Ω • if the fault resistance is above 10 kΩ, rfault is initially displayed as -1000 until the fault resistance has reached a stable value and then displayed ...
Page 289
Name type description start boolean start (common ac and dc side of exciter) startdc boolean start for dc side of exciter startac boolean start for ac side of exciter alarm boolean alarm error boolean error errstat integer error indication rave real measured resistance to earth in ohm at inj freq xa...
Page 290
Table 129: rotiphiz non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description k1real -10000000000.000 - 10000000000.000 - 0.001 10000.000 multiplication factor k1 for calibration, real part k1imag -10000000000.000 - 10000000000.000 - 0.001 0.000 multiplication factor k1 for calibr...
Page 291
7.8.9 operation principle the protection principle is based on injection of voltage to the exciter point of the field circuit. Uinj rshunt ~ step-up transformer r o t o r e f rex060/rim module reg670 4 5 6 3 1 7 i u generator r n 2 rex061 generator protection panel r c iec11000014-4-en.Vsd u> 8 iec1...
Page 292
7.8.9.1 the injection unit rex060 in je ct io n r ot o r p s m backplane front-plate back view front view power connector ied and injection connectors p o w er s ta to r r o to r in je ct io n s ta to r top view hmi with logic 1 1 1 18 18 5 x11 x61 x81 injection switch 1 5 1 5 x62 x82 keylock led in...
Page 293
7.8.9.2 rotor earth fault protection function the injection to the rotor is schematically shown in figure 127 . Dc ac rex 061 c rot r f + u inj - i inj c rot rotor reference impedance r f + u inj - i inj iec11000065-1-en.Vsd iec11000065 v1 en figure 127: equivalent diagram for sensitive rotor earth ...
Page 294
The injection unit rex060 is connected to the generator and to ied as shown in figure 125 . 7.8.9.3 general measurement of earth fault impedance from the rex060 the injected voltage and current are delivered as ac voltages to ied. The injected voltage and current is measured and analyzed in the prot...
Page 295
Other factors to achieve impedance values related to the primary system. The factor k2 [Ω] will compensate for the series impedance z series the healthy impedance measured at non-faulted conditions is referred to as the reference impedance in further text. In ied the measured impedance is compared t...
Page 296
7.8.9.4 simplified logic diagram uinj rshunt rotiphiz rex060 reg670 1 i u u_i_ref u_u_ref x s k1 k2 compare & evaluate zref1 zref2 3 2 4 5 6 7 iec10000327-2-en.Vsd bare z measured z inj i inj u ¸ r f iec10000327 v1 en figure 129: simplified logic diagram for sensitive rotor earth fault protection, i...
Page 297
Iec10000326-3.Vsd r f trip alarm or tripdelay adaptive iec10000326 v2 en figure 130: rotiphiz alarm and trip logic if the fault resistance r f is smaller than r alarm and longer than alarm delay (using delay-on), output alarm is set. If the fault resistance r f is smaller than r trip , using interna...
Page 298
Trip time fault resistance r trip r alarm iec11000002-1-en.Vsd 10 filterlength × 2 filterlength × iec11000002 v1 en figure 131: trip time characteristic as function of fault resistance a third high level step for the detection of excitation system earth faults on the ac side of the excitation rectif...
Page 299
Function range or value accuracy alarm limit of fault resistance (100 - 1000000)Ω 5% of 1 kΩ at r f ≤ 1 kΩ 5% of 10 kΩ at 1 kΩ f ≤ 20 kΩ 10% of set value at 20 kΩ f ≤ 200 kΩ operate time, start at r f ~ 0 Ω and filter length = 1 s 1.00 s typically - operate time, trip at r f ~ 0 Ω and filter length ...
Page 300
Operating mode and is fully functional even with the generator at standstill. It is still required to have a standard 95% stator earth-fault protection, based on the neutral point fundamental frequency displacement voltage, operating in parallel with the 100% stator earth-fault protection function. ...
Page 301
Output signal description rfault estimated fault resistance in Ω zref selected reference impedance number zrefre the real part (resistance) of the used reference impedance zrefim the imaginary part (reactance) of the used reference impedance urmsstat this signal is set true, if the measured rms volt...
Page 302
The injection equipment provides calculation of the fault resistance: • if the fault resistance is equal or below 10 kΩ, rfault is displayed in Ω • if the fault resistance is above 10 kΩ, rfault is initially displayed as -1000 until the fault resistance has reached a stable value and then displayed ...
Page 303
Name type description rave real measured resistance to earth in ohm at inj freq xave real measured reactance to earth in ohm at inj freq frequ real measured frequency of injected voltage into stator rfault real estimated fault resistance in ohm zref integer selected reference impedance number zrefre...
Page 304
Name values (range) unit step default description refx2 -1000000.000 - 1000000.000 ohm 0.001 2000.000 reference reactance x2 in ohm refr3 0.001 - 1000000000.000 ohm 0.001 1000.000 reference resistance r3 in ohm refx3 -1000000.000 - 1000000.000 ohm 0.001 2000.000 reference reactance x3 in ohm refr4 0...
Page 305
7.9.9 operation principle the protection function is based on signal injection into a stator winding. These square wave signals are generated in a separate injection unit rex060. The injection signals are connected to the stator winding via: • secondary winding of a voltage transformer (vt) located ...
Page 306
Uinj rshunt ~ step-up transformer 95 % sef 10 0 % s e f rex060/sim module reg670 5 6 8 3 1 7 9 i u generator r n 2 generator protection panel iec11000067-2-en.Vsd u> 4 10 iec11000067 v1 en figure 133: example installation for stator injection 1 generator unit consisting of a synchronous generator an...
Page 307
The injection unit rex060 in je ct io n r ot o r p s m backplane front-plate back view front view power connector ied and injection connectors p o w er s ta to r r o to r in je ct io n s ta to r top view hmi with logic 1 1 1 18 18 5 x11 x61 x81 injection switch 1 5 1 5 x62 x82 keylock led injection ...
Page 308
Refer to the hardware section in this manual for a detailed description of rex060. 7.9.9.2 generator system earthing methods there are several principles for system earthing of synchronous generators. The choice of earthing method depends on different factors: • limitation of earth fault current at ...
Page 309
These earthing alternatives are characterized by the following properties: a: high-resistance earthing with a neutral point resistor this earthing method utilizes a high resistance in the primary circuit by inserting resistor r n between the generator neutral and the ground. The actual resistance va...
Page 310
Resistance value r n is generally extremely small (i.E. Typically imposed ohmic value to the primary circuit becomes quite high (i.E. In the order of kΩ). The equivalent resistance in the primary circuit can be calculated as follows: 2 1 2 eq n r u r u = æ ö × ç ÷ è ø equation2517 v1 en where: u1/u2...
Page 311
Quite high (i.E. In the order of kΩ). The equivalent resistance in the primary circuit can be calculated as follows: 2 1 3 2 eq n r u r u = æ ö × ç ÷ × è ø equation2519 v1 en where: u1/u2 is the turn (i.E. Rated voltage) ratio of one phase of the power transformer, e.G. 8 3 500 3 kv v equation2521 v...
Page 312
For all the alternatives the 100% stator earth fault protection can be applied. 7.9.9.3 100% stator earth fault protection function the injection to the stator is schematically shown in figure 136 . It should be observed that in this figure injection equivalent circuit is also shown with all impedan...
Page 313
+ u inj - r n c stat i inj a b iec11000009-2-en.Vsd iec11000009 v1 en figure 137: effective high-resistance generator earthing via a distribution transformer another alternative is shown in figure 138 (high-resistance earthing via a delta, grounded-wye transformer). In this case the transformer must...
Page 314
C stat r n + u inj - i inj a b iec11000010-3-en.Vsd iec11000010 v1 en figure 138: high-resistance generator earthing via a delta, grounded-wye transformer it is also possible to make the injection via vt open delta connection, as shown in figure 139 . Section 7 1mrk502052-uen b impedance protection ...
Page 315
U 1 / u 2 y c stat r n + u inj - i inj r d a b n d r u u r × ÷ ÷ ø ö ç ç è æ >> 2 2 1 iec11000011-3-en.Vsd y y iec11000011 v1 en figure 139: injection via open delta vt connection it must be observed that the resistor r d is normally applied for ferro-resonance damping. The resistance r d is will ha...
Page 316
With various generator system earthing methods. It is therefore recommended to make the injection via the open delta vt on the terminal side in most applications. Accuracy for sttiphiz is installation dependent and it mainly depends on the characteristic of grounding or voltage transformer used to i...
Page 317
+ u inj - i inj z shunt r f z series iec11000003-2-en.Vsd z bare z measured iec11000003 v1 en figure 140: equivalent of the impedance measurement in non-faulted operation r f is very large. A “healthy” impedance is calculated as: 1 2 measured bare z k z k = × + equation2501 v1 en for definition of k...
Page 318
Opencircuitlimit open circuit hysteresis 0 no open-circuit open- circuit open- circuit characteristics iec11000073-1-en.Vsd z measured { } re iec11000073 v1 en figure 141: open circuit characteristics blocking: the output opcirc is blocked during an error occurring and during initialization of funct...
Page 319
• the influence from the impedance z mt will be different when the generator is stand-still and when it is in operation • the capacitance to earth will vary if the generator breaker is open or closed • the capacitance will vary if the generator is energized or not depending on stator end winding cor...
Page 320
And the real part gives the fault conductance: 1 1 1 re f ref r z z æ ö = - ç ÷ ç ÷ è ø equation2421 v1 en in the settings there are given two resistance levels: • ralarm given in Ω. If f alarm r r equation2524 v1 en an alarm signal alarm is given after a set delay talarm. • rtrip given in Ω. If f t...
Page 321
Trip time fault resistance r trip r alarm iec11000002-1-en.Vsd 10 filterlength × 2 filterlength × iec11000002 v1 en figure 142: trip time characteristic as function of fault resistance during run-up and shut down of the generator, i.E. When the rotational speed of the generator changes, there will o...
Page 322
• generator voltage impedance 1 • generator voltage > set value and generator circuit breaker open: reference impedance 2 • generator voltage > set value and generator circuit breaker closed: reference impedance 3 the monitoring, enabled in ict, will give indication if several reference impedance va...
Page 323
7.9.9.6 simplified logic diagram uinj rshunt 95% stator earth fault protection sttiphiz rex060 reg670 1 i u u_i_sef u_u_sef x s a>b a b k1 k2 u un> = 5% t ton=0.5s 95% trip un compare & evaluate zref2 zref3 zref4 zref5 select reference 3 8 2 4 5 6 7 9 iec10000325-2-en.Vsd measured z bare z inj i inj...
Page 324
Iec10000326-3.Vsd r f trip alarm or tripdelay adaptive iec10000326 v2 en figure 144: sttiphiz alarm and trip logic if the fault resistance r f is smaller than r alarm and last longer than set alarm delay, output alarm is set. If the fault resistance r f is smaller than r trip , output signal trip is...
Page 325
7.10 under impedance protection for generators and transformers zgvpdis 7.10.1 identification function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ ieeeidentification under impedance function for generators and transformers zgvpdis s00346 v1 en 21g 7.10.2 functionality the und...
Page 326
7.10.4 signals table 144: zgvpdis input signals name type default description i3p group signal - connection for current sample signals u3p group signal - connection for voltage sample signals block boolean 0 block of the function blkz boolean 0 block due to fuse failure blkuv boolean 0 block of the ...
Page 327
Name values (range) unit step default description opmodez2 off pp loops enhancedreach - - enhancedreach operation mode of zone 2: off/ph-ph/ enhancedreach z2fwd 3.0 - 200.0 % zb 0.1 15.0 zone 2 forward reach in % of rated impedance, 100%=full load z2rev 3.0 - 200.0 % zb 0.1 8.0 zone 2 reverse reach ...
Page 328
7.10.6 monitored data table 149: zgvpdis monitored data name type values (range) unit description ul1 real - kv voltage in phase l1 ul2 real - kv voltage in phase l2 ul3 real - kv voltage in phase l3 il1 real - a current in phase l1 il2 real - a current in phase l2 il3 real - a current in phase l3 7...
Page 329
R jx impedanceang offset mho, zone3 offset mho, zone2 offset mho, zone1 iec11000294-2-en.Vsd iec11000294 v2 en figure 146: offset mho characteristics of three zones the complete functionality is shown in figure 147 . 1mrk502052-uen b section 7 impedance protection 323 technical manual.
Page 330
Zone 1 zone 2 opmodez3 z3fwd z3rev tz3 loadenchmodz3 zone 3 opmodeu u tu uvsealin ³ ³ u3p i3p blkz block blckuv truv trz3 stz3 operate trz2 stz2 start trz1 stz1 opmodez2 z2fwd z2rev tz2 loadenchmodz2 opmodez1 z1fwd z1rev tz1 loadench rld argld stuv 1 1 iec11000295-3-en.Vsd ³1 iec11000295 v2 en figur...
Page 331
Trz1 iec11000297-3-en.Vsd block blkz u3p i3p stz1 opmodez1 z1fwd z1rev comparator zl1l2 opmodez1 z1fwd z1rev comparator zl2l3 comparator zl3l1 opmodez1 z1fwd z1rev 1 ³ impedanceang impedanceang impedanceang t tz1 iec11000297 v3 en figure 148: block diagram of zone 1 the functionality included in zon...
Page 332
Iec11000296-2-en.Vsd jx l l i · 2 1 ß fwd z l l i l l u ucomp 1 2 1 2 1 1 · - = rev z l l i l l u ucomp 1 2 1 2 1 2 · + = fwd z l l i 1 2 1 · rev z l l i 1 2 1 · - r l l i · 2 1 iec11000296 v2 en figure 149: simplified offset mho characteristics for l1-l2 fault in zone 1 criteria: operation occurs i...
Page 333
Block 1 & loadenchmodz2 t f 1 measuring loop enhancedreach opmodez2 z2fwd z2rev impedanceang zero sequence voltage compensation load encroachment rld argld u3p i3p blkz stz2 trz2 iec11000298-3-en.Vsd measuring loop phase-to-phase (zl1l2 opmodez2 z2fwd z2rev impedanceang tz2 t iec11000298 v3 en figur...
Page 334
I1mag i2mag i3mag a==b a b a==b a b a==b a b max & & a b c startph1 startph2 startph3 & & & start ³1 iec11000307_1_en.Vsd 1 ³ iec11000307 v1 en figure 151: logic diagram for the selection of the maximum current loop the phase-to-earth voltage is compensated with zero sequence voltage in order to avo...
Page 335
ß iec11000300-2-en.Vsd 1 1 2 1 2 2 ucomp ul l il l z fwd 2 1 2 1 2 2 ucomp ul l il l z rev 1 2 il l r 1 2 2 il l z rev 1 2 il l jx 1 2 2 il l z fwd iec11000300 v2 en figure 153: simplified offset mho characteristics for l1-to-l2 fault in zone 2 operation occurs if 90° ≤ β ≤ 270°. Impedance defined i...
Page 336
Sl.No measuring loop voltage phasor current phasor 1 il1 1 0 ul e u - 1 il 2 il2 2 0 ul e u - 2 il 3 il3 3 0 ul e u - 3 il operate time the operate time delay for zone 2 can be provided using the setting tz2. Zone 2 is provided load encroachment detection feature based on positive sequence component...
Page 337
Load encroachment characteristic argld argld argld argld rld -rld jx r iec11000304_1_en iec11000304 v1 en figure 154: load encroachment characteristics 7.10.7.5 under voltage seal-in the under voltage seal-in logic ensures the trip under fault condition, where as under impedance function will reset ...
Page 338
Iec11000306-3-en.Vsd opmodeu a a b up1p2 u a a b up2p3 u a a b up3p1 u 1 zone 3 start & & 1 b0 b1 int zone 2 start 10 ms 1 & tu tpulse = 1sec truv q -1 stuv drop-off timer 0 = off 1 = z2start 2 = z3start 1 blkuv block t t q -1 iec11000306 v3 en figure 155: under voltage seal-in for zone 2 and zone 3...
Page 339
Section 8 current protection 8.1 instantaneous phase overcurrent protection 3-phase output phpioc 8.1.1 identification function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number instantaneous phase overcurrent protection 3-phase output phpioc 3i>> symbol-z v...
Page 340
Table 152: phpioc output signals name type description trip boolean trip signal from any phase trl1 boolean trip signal from phase l1 trl2 boolean trip signal from phase l2 trl3 boolean trip signal from phase l3 8.1.5 settings table 153: phpioc group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step de...
Page 341
Output function phpioc. In a comparator the rms values are compared to the set operation current value of the function (ip>>). If a phase current is larger than the set operation current a signal from the comparator for this phase is set to true. This signal will, without delay, activate the output ...
Page 342
8.2.1 identification function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number four step phase overcurrent protection 3-phase output oc4ptoc toc-reva v2 en 51/67 8.2.2 functionality the four step three-phase overcurrent protection function oc4ptoc has an in...
Page 343
8.2.3 function block iec06000187-3-en.Vsd oc4ptoc i3p* u3p* block blktr blkst1 blkst2 blkst3 blkst4 enmult1 enmult2 enmult3 enmult4 trip tr1 tr2 tr3 tr4 trl1 trl2 trl3 tr1l1 tr1l2 tr1l3 tr2l1 tr2l2 tr2l3 tr3l1 tr3l2 tr3l3 tr4l1 tr4l2 tr4l3 start st1 st2 st3 st4 stl1 stl2 stl3 st1l1 st1l2 st1l3 st2l1...
Page 344
Name type default description blkst3 boolean 0 block of step3 blkst4 boolean 0 block of step4 enmult1 boolean 0 when activated, the current multiplier is in use for step1 enmult2 boolean 0 when activated, the current multiplier is in use for step2 enmult3 boolean 0 when activated, the current multip...
Page 345
Name type description stl3 boolean start signal from phase l3 st1l1 boolean start signal from step1 phase l1 st1l2 boolean start signal from step1 phase l2 st1l3 boolean start signal from step1 phase l3 st2l1 boolean start signal from step2 phase l1 st2l2 boolean start signal from step2 phase l2 st2...
Page 346
Name values (range) unit step default description characterist1 ansi ext. Inv. Ansi very inv. Ansi norm. Inv. Ansi mod. Inv. Ansi def. Time l.T.E. Inv. L.T.V. Inv. L.T. Inv. Iec norm. Inv. Iec very inv. Iec inv. Iec ext. Inv. Iec s.T. Inv. Iec l.T. Inv. Iec def. Time reserved programmable ri type rd...
Page 347
Name values (range) unit step default description k2 0.05 - 999.00 - 0.01 0.05 time multiplier for the inverse time delay for step 2 imin2 1 - 10000 %ib 1 50 minimum operate current for step2 in % of ibase t2min 0.000 - 60.000 s 0.001 0.000 minimum operate time for inverse curves for step 2 i2mult 1...
Page 348
Name values (range) unit step default description characterist4 ansi ext. Inv. Ansi very inv. Ansi norm. Inv. Ansi def. Time l.T.E. Inv. L.T.V. Inv. L.T. Inv. Iec norm. Inv. Iec very inv. Iec inv. Iec ext. Inv. Iec s.T. Inv. Iec l.T. Inv. Iec def. Time reserved programmable ri type rd type - - ansi ...
Page 349
Name values (range) unit step default description ttrcrv1 0.005 - 100.000 - 0.001 13.500 parameter tr for customer programmable curve for step 1 tcrcrv1 0.1 - 10.0 - 0.1 1.0 parameter cr for customer programmable curve for step 1 harmblock1 off on - - off enable block of step 1 from harmonic restrai...
Page 350
Name values (range) unit step default description treset4 0.000 - 60.000 s 0.001 0.020 constant reset time for step 4 tpcrv4 0.005 - 3.000 - 0.001 1.000 parameter p for customer programmable curve for step 4 tacrv4 0.005 - 200.000 - 0.001 13.500 parameter a for customer programmable curve for step 4...
Page 351
8.2.7 operation principle the four step phase overcurrent protection oc4ptoc is divided into four different sub-functions, one for each step. For each step x , where x is step 1, 2, 3 and 4, an operation mode is set by dirmodex: off/non-directional/forward/reverse. The protection design can be divid...
Page 352
A common setting for all steps, startphsel, is used to specify the number of phase currents to be high to enable operation. The settings can be chosen: 1 out of 3, 2 out of 3 or 3 out of 3. The sampled analogue phase currents are processed in a pre-processing function block. Using a parameter settin...
Page 353
Phase-phase short circuit: 1 2 1 2 1 2 1 2 = - = - refl l l l dirl l l l u u u i i i equation1449 v1 en (equation 57) 2 3 2 3 2 3 2 3 = - = - refl l l l dirl l l l u u u i i i equation1450 v1 en (equation 58) 3 1 3 1 3 1 3 1 = - = - refl l l l dirl l l l u u u i i i equation1451 v1 en (equation 59) ...
Page 354
U ref i dir rca roa forward reverse roa en05000745.Vsd iec05000745 v1 en figure 159: directional characteristic of the phase overcurrent protection the default value of anglerca is –65°. The parameters angleroa gives the angle sector from anglerca for directional borders. A minimum current for direc...
Page 356
A b a>b block and i op extract second harmonic current component extract fundamental current component x 2ndharmstab a b a>b a b a>b 0.07*ibase iec13000014-2-en.Vsd 2ndh_block_int iec13000014 v2 en figure 161: second harmonic blocking 8.2.9 technical data table 164: oc4ptoc technical data function s...
Page 357
8.3 instantaneous residual overcurrent protection efpioc 8.3.1 identification function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number instantaneous residual overcurrent protection efpioc in>> ief v1 en 50n 8.3.2 functionality the instantaneous residual ov...
Page 358
Table 166: efpioc output signals name type description trip boolean trip signal 8.3.5 settings table 167: efpioc group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description operation off on - - off operation off / on in>> 5 - 2500 %ib 1 200 operate residual current level in % of ibase t...
Page 359
There is also a possibility to activate a preset change of the set operation current via a binary input (enable multiplier multen). In some applications the operation value needs to be changed, for example due to transformer inrush currents. Efpioc function can be blocked from the binary input block...
Page 360
8.4.2 functionality the four step residual overcurrent protection ef4ptoc has an inverse or definite time delay independent for each step. All iec and ansi time-delayed characteristics are available together with an optional user defined characteristic. Ef4ptoc can be set directional or non-directio...
Page 361
Table 172: ef4ptoc input signals name type default description i3p group signal - group connection for operate current u3p group signal - group connection for polarizing voltage i3ppol group signal - group connection for polarizing current i3pdir group signal - group connection for directional curre...
Page 362
Name type description stfw boolean start signal forward direction strv boolean start signal reverse direction 2ndharmd boolean 2nd harmonic block signal 8.4.5 settings table 174: ef4ptoc group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description operation off on - - off operation off /...
Page 363
Name values (range) unit step default description actundertime cb position cb command - - cb position select signal to activate under time (cb pos / cb command) tundertime 0.000 - 60.000 s 0.001 0.300 time delay for under time dirmode1 off non-directional forward reverse - - non-directional directio...
Page 364
Name values (range) unit step default description characterist2 ansi ext. Inv. Ansi very inv. Ansi norm. Inv. Ansi mod. Inv. Ansi def. Time l.T.E. Inv. L.T.V. Inv. L.T. Inv. Iec norm. Inv. Iec very inv. Iec inv. Iec ext. Inv. Iec s.T. Inv. Iec l.T. Inv. Iec def. Time reserved programmable ri type rd...
Page 365
Name values (range) unit step default description t3 0.000 - 60.000 s 0.001 0.800 time delay of step 3 when definite time char. Is selected k3 0.05 - 999.00 - 0.01 0.05 time multiplier for the step 3 selected time characteristic imin3 1.00 - 10000.00 %ib 1.00 33 minimum operate residual current for ...
Page 366
Table 175: ef4ptoc group settings (advanced) name values (range) unit step default description resettypecrv1 instantaneous iec reset ansi reset - - instantaneous reset curve type for step1 (instantaneous / iec / ansi) treset1 0.000 - 60.000 s 0.001 0.020 reset time delay for step 1 tpcrv1 0.005 - 3....
Page 367
Name values (range) unit step default description tprcrv3 0.005 - 3.000 - 0.001 0.500 param pr for customized inverse reset time curve for step 3 ttrcrv3 0.005 - 100.000 - 0.001 13.500 param tr for customized inverse reset time curve for step 3 tcrcrv3 0.1 - 10.0 - 0.1 1.0 param cr for customized in...
Page 368
8.4.7 operation principle this function has the following three “analog inputs” on its function block in the configuration tool: 1. I3p, input used for “operating quantity”. Supply the zero-sequence magnitude measuring functionality. 2. U3p, input used for “voltage polarizing quantity”. Supply eithe...
Page 369
Where: il1, il2 and il3 are fundamental frequency phasors of three individual phase currents. The residual current is pre-processed by a discrete fourier filter. Thus the phasor of the fundamental frequency component of the residual current is derived. The phasor magnitude is used within the ef4ptoc...
Page 370
The residual current is pre-processed by a discrete fourier filter. Thus the phasor of the fundamental frequency component of the polarizing current is derived. This phasor is then multiplied with pre-set equivalent zero-sequence source impedance in order to calculate equivalent polarizing voltage u...
Page 371
8.4.7.5 base quantities within the protection the base quantities are entered as global settings for all functions in the ied. Base current (ibase) shall be entered as rated phase current of the protected object in primary amperes. Base voltage (ubase) shall be entered as rated phase-to-phase voltag...
Page 372
• time delay related settings. By these parameter settings the properties like definite time delay, minimum operating time for inverse curves, reset time delay and parameters to define user programmable inverse curve are defined. • supervision by second harmonic blocking feature (on/off). By this pa...
Page 373
Directional supervision element and the integrated directional comparison function. The protection has integrated directional feature. As the operating quantity current lop is always used. The polarizing method is determined by the parameter setting polmethod. The polarizing quantity will be selecte...
Page 374
• directional element will be internally enabled to operate as soon as iop is bigger than 40% of i>dir and directional condition is fulfilled in set direction. • relay characteristic angle anglerca, which defines the position of forward and reverse areas in the operating characteristic. Directional ...
Page 375
X a a>b b i>dir polmethod=voltage polmethod=dual or forward_int reverse_int block stage1_dir_int 0.6 x 0.4 and stage3_dir_int stage4_dir_int stage2_dir_int or strv upolmin ipolmin anglerca t f 0.0 x t f rnpol xnpol 0.0 d ir e ct io n al c h ar a ct e ri st ic fwd rvs and and and stfw forward_int rev...
Page 376
1. Current fundamental frequency component > iminopharmblk 2. Current second harmonic component > iminopharmblk 3. Ratio of the 2nd harmoinc component in relation to the fundamental frequency component in the residual current exceeds the preset level defined parameter 2ndharmstab setting if all the ...
Page 377
A b a>b block and i op extract second harmonic current component extract fundamental current component x 2ndharmstab a b a>b a b a>b 0.07*ibase iec13000015-3-en.Vsd usestartvalue in1> in2> in3> in4> a b a>b t t=70ms or and blkpartransf=on q -1 or 2ndh_block_int q -1 = unit delay iec13000015 v3 en fi...
Page 378
Step 2 or 3 (dependent on setting) the function will give a trip after a set delay tsotf. This delay is normally set to a short time (default 200 ms). The under-time logic always uses the start signal from the step 4. The under-time logic will normally be set to operate for a lower current level tha...
Page 379
Directio n elemen t 4 step over current elemen t one ele me nt fo r ea ch step harmonic restrain t mode sele ction earthfaultdir ection harmrestrb lock ena bledir ena blestep1-4 directio nalmode1-4 trip elemen t ena bledir ang levalid directio nal che ck ope ratin gcurrent switcho nto fa ult star t ...
Page 380
Function range or value accuracy real part of source z used for current polarization (0.50-1000.00) w/phase - imaginary part of source z used for current polarization (0.50–3000.00) w/phase - operate time, start function at 0 to 2 x i set min 18 ms max 28 ms - reset time, start function at 2 to 0 x ...
Page 381
Directional operation can be combined together with corresponding communication logic in permissive or blocking teleprotection scheme. The same logic as for directional zero sequence current can be used. Current reversal and weak-end infeed functionality are available. 8.5.3 function block ns4ptoc i...
Page 382
Table 180: ns4ptoc output signals name type description trip boolean general trip signal tr1 boolean trip signal from step 1 tr2 boolean trip signal from step 2 tr3 boolean trip signal from step 3 tr4 boolean trip signal from step 4 start boolean general start signal st1 boolean start signal step 1 ...
Page 383
Name values (range) unit step default description characterist1 ansi ext. Inv. Ansi very inv. Ansi norm. Inv. Ansi mod. Inv. Ansi def. Time l.T.E. Inv. L.T.V. Inv. L.T. Inv. Iec norm. Inv. Iec very inv. Iec inv. Iec ext. Inv. Iec s.T. Inv. Iec l.T. Inv. Iec def. Time reserved programmable ri type rd...
Page 384
Name values (range) unit step default description k2 0.05 - 999.00 - 0.01 0.05 time multiplier for the step 2 selected time characteristic imin2 1.00 - 10000.00 %ib 1.00 50 minimum current for step 2 t2min 0.000 - 60.000 s 0.001 0.000 minimum operate time for inverse time characteristic step 2 i2mul...
Page 385
Name values (range) unit step default description characterist4 ansi ext. Inv. Ansi very inv. Ansi norm. Inv. Ansi mod. Inv. Ansi def. Time l.T.E. Inv. L.T.V. Inv. L.T. Inv. Iec norm. Inv. Iec very inv. Iec inv. Iec ext. Inv. Iec s.T. Inv. Iec l.T. Inv. Iec def. Time reserved programmable ri type rd...
Page 386
Name values (range) unit step default description resettypecrv2 instantaneous iec reset ansi reset - - instantaneous reset curve type for step2 (instantaneous / iec / ansi) treset2 0.000 - 60.000 s 0.001 0.020 reset time delay for step 2 tpcrv2 0.005 - 3.000 - 0.001 1.000 param p for customized inve...
Page 387
Name values (range) unit step default description tprcrv4 0.005 - 3.000 - 0.001 0.500 param pr for customized inverse reset time curve for step 4 ttrcrv4 0.005 - 100.000 - 0.001 13.500 param tr for customized inverse reset time curve for step 4 tcrcrv4 0.1 - 10.0 - 0.1 1.0 param cr for customized in...
Page 388
( ) 2 1 2 1 2 3 3 i il a il a il = × + × + × equation2266 v2 en (equation 68) where: il1, il2 and il3 are fundamental frequency phasors of three individual phase currents. A is so called operator which gives a phase shift of 120 deg, that is, a = 1∠120 deg a 2 similarly gives a phase shift of 240 de...
Page 389
The magnitude of polarizing voltage must be bigger than a minimum level defined by setting upolmin. Note that –u2 is used to determine the location of the fault. This ensures the required inversion of the polarizing voltage within the function. 8.5.7.3 external polarizing for negative sequence funct...
Page 390
• type of reset characteristic (instantaneous / iec reset /ansi reset).By this parameter setting it is possible to select the reset characteristic of the stage. For the complete list of available reset curves, refer to chapter "" • time delay related settings. By these parameter settings the propert...
Page 391
Supervision element and the integrated directional comparison function. The operating and polarizing quantity are then used inside the directional element, as shown in figure 165 , to determine the direction of the fault. Anglerca forward area iop = i2 upol=-u2 reverse area iec10000031-1-en.Vsd iec1...
Page 392
1. Stfw=1 when tip of i2 phasor (operating quantity magnitude) is in forward area, see fig 165 (operating quantity magnitude is bigger than setting i>dir) 2. Strv=1 when tip of i2 phasor (operating quantity magnitude) is in the reverse area, see fig 165 . (operating quantity magnitude is bigger than...
Page 393
8.5.8 technical data table 185: ns4ptoc technical data function range or value accuracy operate value, negative sequence current, step 1-4 (1-2500)% of lbase ± 1.0% of i r at i £ i r ± 1.0% of i at i > i r reset ratio > 95% at (10-2500)% of ibase - independent time delay for step 1, 2, 3, and 4 at 0...
Page 394
8.6.2 functionality in networks with high impedance earthing, the phase-to-earth fault current is significantly smaller than the short circuit currents. Another difficulty for earth fault protection is that the magnitude of the phase-to-earth fault current is almost independent of the fault location...
Page 395
Time characteristic gives better time-selectivity in case of high zero-resistive fault currents. Phase currents phase- ground voltages in un iec13000013-1-en.Vsd iec13000013 v1 en figure 174: connection of sdepsde to analog preprocessing function block overcurrent functionality uses true 3i0, i.E. S...
Page 396
8.6.4 signals table 186: sdepsde input signals name type default description i3p group signal - group signal for current u3p group signal - group signal for voltage block boolean 0 blocks all the outputs of the function blktr boolean 0 blocks the trip outputs of the function blktrdir boolean 0 block...
Page 397
8.6.5 settings table 188: sdepsde group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description operation off on - - off operation off / on opmode 3i0cosfi 3i03u0cosfi 3i0 and fi - - 3i0cosfi selection of operation mode for protection dirmode forward reverse - - forward direction of opera...
Page 398
Name values (range) unit step default description tmin 0.000 - 60.000 s 0.001 0.040 minimum operate time for iec idmt curves, in sec kin 0.05 - 2.00 - 0.01 1.00 idmt time mult for non-dir res over current protection opun> off on - - off operation of non-directional residual overvoltage protection un...
Page 399
8.6.6 monitored data table 192: sdepsde monitored data name type values (range) unit description incosphi real - a magnitude of residual current along the polarizing quantity 3i0cos(fi-rca) in real - a measured magnitude of the residual current 3i0 un real - kv measured magnitude of the residual vol...
Page 400
= = o o 0 , 90 rcadir roadir 0 3i j = - 0 ref ang(3i ) ang(3u ) - = 0 ref 3u u 0 3i cos × j iec06000648-4-en.Vsd iec06000648 v4 en figure 176: rcadir set to 0° iec06000649_3_en.Vsd ref u = − = 90 , 90 rcadir roadir 0 3i 0 3 ⋅ ϕ i cos ϕ = − 0 (3 ) ( ) ref ang i ang u − 0 3u iec06000649 v3 en figure 1...
Page 401
Roadir is relay operating angle. Roadir is identifying a window around the reference direction in order to detect directionality. Figure 178 shows the restrictions made by the roadir. Operate area roadir iec06000650_2_en.Vsd = o 0 rcadir 0 3i j 0 3 × j i cos - = 0 3 ref u u iec06000650 v2 en figure ...
Page 402
-3u 0 =u ref operate area instrument transformer angle error 3i 0 (prim) 3i 0 (to prot) characteristic after angle compensation rcacomp iec06000651-3-en.Vsd rcadir = 0º iec06000651 v3 en figure 179: explanation of rcacomp directional residual power protection measuring 3i 0 · 3u 0 · cos φ φ is defin...
Page 403
This variant has the possibility of choice between definite time delay and inverse time delay. The inverse time delay is defined as: 0 0 inv 0 0 ksn (3i 3u cos (reference)) t 3i 3u cos (measured) × × × j = × × j equation1942 v2 en (equation 69) directional residual current protection measuring 3i 0 ...
Page 404
This variant has definite time delay. Directional functions for all the directional functions there are directional start signals stfw: fault in the forward direction, and strv: fault in the reverse direction. Even if the directional function is set to operate for faults in the forward direction, a ...
Page 405
Opinnondir> = on & opun> = on & t tun opmode = 3i0cosfi & opmode = 3i0 and fi & opmode = 3i03u0cosfi & rcadir rcacomp roadir & dirmode = forward dirmode = reverse ³ 1 & & & ³ 1 t tdef t tdef ³ 1 stdirin trdirin stndin trndin stun trun stfw strv t s n timechar innondir> & direction detection logic t ...
Page 406
Function range or value accuracy operate level for non- directional overcurrent (1.00-400.00)% of lbase ±1.0% of i r at i £ i r ± 1.0% of i at i > i r operate level for non- directional residual overvoltage (1.00-200.00)% of ubase ± 0.5% of u r at u £ u r ± 0.5% of u at u > u r residual release curr...
Page 407
8.7.1 identification function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number thermal overload protection, two time constants trpttr symbol-a v1 en 49 8.7.2 functionality if a power transformer reaches very high temperatures the equipment might be damaged....
Page 408
8.7.4 signals table 194: trpttr input signals name type default description i3p group signal - group signal for current input block boolean 0 block of function cooling boolean 0 cooling input off / on. Changes ib setting and time constant enmult boolean 0 enable multiplier for currentreference setti...
Page 409
Name values (range) unit step default description tau1low 5 - 2000 %tc1 1 100 multiplier in % to tc1 when current is ilow-tc1 ihightau2 30.0 - 250.0 %ib2 1.0 100.0 current set, in % of ibase2 for rescaling tc2 by tc2-ihigh tau2high 5 - 2000 %tc2 1 100 multiplier in % to tc2 when current is >ihigh-tc...
Page 410
Name type values (range) unit description treslo integer - - estimated time to reset of the function (in min) ttripcal integer 0=not active 1=long time 2=active - calculated time status to trip: not active/long time/ active trescal integer 0=not active 1=long time 2=active - calculated time status t...
Page 411
( ) 1 t n final final n e t d - - q = q - q - q × equation1175 v1 en (equation 74) where: q n is the calculated present temperature q n-1 is the calculated temperature at the previous time step q final is the calculated final (steady state) temperature with the actual current d t is the time step be...
Page 412
When the current is so high that it has given a start signal start, the estimated time to trip is continuously calculated and given as analogue output ttrip. If this calculated time get less than the setting time warning, set in minutes, the output warning is activated. In case of trip a pulse with ...
Page 413
8.7.8 technical data table 199: trpttr technical data function range or value accuracy base current 1 and 2 (30–250)% of ibase ±1.0% of i r operate time: 2 2 2 2 p ref i i t ln i i t æ ö - ç ÷ = × ç ÷ - è ø equation1356 v2 en (equation 77) i = actual measured current ip = load current before overloa...
Page 414
Ccrbrf can be single- or three-phase initiated to allow use with single phase tripping applications. For the three-phase version of ccrbrf the current criteria can be set to operate only if two out of four for example, two phases or one phase plus the residual current start. This gives a higher secu...
Page 415
Table 201: ccrbrf output signals name type description trbu boolean back-up trip by breaker failure protection function trbu2 boolean second back-up trip by breaker failure protection function trret boolean retrip by breaker failure protection function trretl1 boolean retrip by breaker failure prote...
Page 416
Table 204: ccrbrf non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description globalbasesel 1 - 12 - 1 1 selection of one of the global base value groups 8.8.6 monitored data table 205: ccrbrf monitored data name type values (range) unit description il1 real - a measured current in ...
Page 417
Where it is sufficient to detect failure to open (high current) in one pole or high residual current and 2 out of 4 where at least two current (phase current and/or residual current) shall be high for breaker failure detection. • the current detection level for the residual current can be set differ...
Page 418
T t1 tpulse and and or or or trretl3 trretl2 bfp started l1 retrip time out l1 cb closed l1 trret trretl1 cbflt cb pos check no cbpos check and or from other phases iec09000978-3-en.Vsd retripmode 1 iec09000978 v3 en figure 187: simplified logic scheme of the retrip logic function iec09000979-3-en.V...
Page 419
8.8.8 technical data table 206: ccrbrf technical data function range or value accuracy operate phase current (5-200)% of lbase ±1.0% of i r at i £ i r ±1.0% of i at i > i r reset ratio, phase current > 95% - operate residual current (2-200)% of lbase ±1.0% of i r at i £ i r ±1.0% of i at i > i r res...
Page 420
8.9.2 functionality an open phase can cause negative and zero sequence currents which cause thermal stress on rotating machines and can cause unwanted operation of zero sequence or negative sequence current functions. Normally the own breaker is tripped to correct such a situation. If the situation ...
Page 421
Table 208: ccpdsc output signals name type description trip boolean trip signal to cb start boolean trip condition true, waiting for time delay 8.9.5 settings table 209: ccpdsc group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description operation off on - - off operation off / on ttrip ...
Page 422
Pole discordance signal from circuit breaker + circuit breaker en05000287.Vsd iec05000287 v2 en figure 190: pole discordance external detection logic this binary signal is connected to a binary input of the ied. The appearance of this signal will start a timer that will give a trip signal after the ...
Page 423
The function also has a binary input that can be configured from the autoreclosing function, so that the pole discordance function can be blocked during sequences with a single pole open if single pole autoreclosing is used. The simplified block diagram of the current and contact based pole discorda...
Page 424
If the pole discordance protection is enabled, then two different criteria can generate a trip signal trip: • pole discordance signaling from the circuit breaker. • unsymmetrical current detection. 8.9.7.1 pole discordance signaling from circuit breaker if one or two poles of the circuit breaker hav...
Page 425
8.10 directional underpower protection guppdup 8.10.1 identification function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number directional underpower protection guppdup p 2 symbol-ll v2 en 37 8.10.2 functionality the task of a generator in a power plant is ...
Page 426
Underpower ied overpower ied q q p p operating point without turbine torque margin margin operate line operate line operating point without turbine torque iec06000315-2-en.Vsd iec06000315 v2 en figure 193: protection with underpower ied and overpower ied 8.10.3 function block iec07000027-2-en.Vsd gu...
Page 427
Table 214: guppdup output signals name type description trip boolean common trip signal trip1 boolean trip of stage 1 trip2 boolean trip of stage 2 start boolean common start start1 boolean start of stage 1 start2 boolean start of stage 2 p real active power in mw ppercent real active power in % of ...
Page 428
Name values (range) unit step default description iampcomp30 -10.000 - 10.000 % 0.001 0.000 amplitude correction compensates current error at 30% of ir iampcomp100 -10.000 - 10.000 % 0.001 0.000 amplitude correction compensates current error at 100% of ir uampcomp5 -10.000 - 10.000 % 0.001 0.000 amp...
Page 429
Iec09000018-2-en.Vsd chosen current phasors chosen voltage phasors complex power calculation p derivation of s(composant) in char angle s(angle) s(angle) power1 t trip1 start1 q p = powre q = powim s(angle) power2 t trip2 start2 iec09000018 v2 en figure 195: simplified logic diagram of the power pro...
Page 430
Set value: mode formula used for complex power calculation l1 * 1 1 3 l l s u i = × × equation1703 v1 en (equation 84) l2 * 2 2 3 l l s u i = × × equation1704 v1 en (equation 85) l3 * 3 3 3 l l s u i = × × equation1705 v1 en (equation 86) the active and reactive power is available from the function ...
Page 431
( ) old calculated s k s 1 k s = × + - × equation1959 v1 en (equation 87) where s is a new measured value to be used for the protection function s old is the measured value given from the function in previous execution cycle s calculated is the new calculated value in the present execution cycle k t...
Page 432
Iec05000652 v2 en figure 196: calibration curves the first current and voltage phase in the group signals will be used as reference and the amplitude and angle compensation will be used for related input signals. Analog outputs (monitored data) from the function can be used for service values or in ...
Page 433
8.11 directional overpower protection goppdop 8.11.1 identification function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number directional overpower protection goppdop p > 2 document172362-img158942 v2 en 32 8.11.2 functionality the task of a generator in a ...
Page 434
Underpower ied overpower ied q q p p operating point without turbine torque margin margin operate line operate line operating point without turbine torque iec06000315-2-en.Vsd iec06000315 v2 en figure 197: reverse power protection with underpower ied and overpower ied 8.11.3 function block iec070000...
Page 435
Table 222: goppdop output signals name type description trip boolean common trip signal trip1 boolean trip of stage 1 trip2 boolean trip of stage 2 start boolean common start start1 boolean start of stage 1 start2 boolean start of stage 2 p real active power p in mw ppercent real active power p in %...
Page 436
Table 224: goppdop group settings (advanced) name values (range) unit step default description k 0.000 - 0.999 - 0.001 0.000 low pass filter coefficient for power measurement, p and q hysteresis1 0.2 - 5.0 %sb 0.1 0.5 absolute hysteresis of stage 1 in % of sbase hysteresis2 0.2 - 5.0 %sb 0.1 0.5 abs...
Page 437
8.11.6 monitored data table 226: goppdop monitored data name type values (range) unit description p real - mw active power p in mw ppercent real - % active power p in % of sbase q real - mvar reactive power q in mvar qpercent real - % reactive power q in % of sbase 8.11.7 operation principle a simpl...
Page 438
Table 227: complex power calculation set value: mode formula used for complex power calculation l1, l2, l3 * * * 1 1 2 2 3 3 l l l l l l s u i u i u i = × + × + × equation1697 v1 en (equation 88) arone * * 1 2 1 2 3 3 l l l l l l s u i u i = × - × equation1698 v1 en (equation 89) posseq * 3 posseq p...
Page 439
Value. The drop-power value of stage1 can be calculated with the power1(2), hysteresis1(2): drop-power1(2) = power1(2) – hysteresis1(2) for small power1 values the hysteresis1 may not be too big, because the drop- power1(2) would be too small. In such cases, the hysteresis1 greater than (0.5 · power...
Page 440
Iec05000652 v2 en figure 200: calibration curves the first current and voltage phase in the group signals will be used as reference and the amplitude and angle compensation will be used for related input signals. Analog outputs from the function can be used for service values or in the disturbance r...
Page 441
8.11.8 technical data table 228: goppdop technical data function range or value accuracy power level for step 1 and step 2 (0.0–500.0)% of sbase when measuring transformer inputs are used, the following accuracy can be obtained for low pickup settings which are typical for reverse power protection a...
Page 442
• unbalanced loads • line to line faults • line to earth faults • broken conductors • malfunction of one or more poles of a circuit breaker or a disconnector ns2ptoc can also be used as a backup protection, that is, to protect the generator in case line protections or circuit breakers fail to clear ...
Page 443
8.12.4 signals table 229: ns2ptoc input signals name type default description i3p group signal - group connection for neg seq. Block boolean 0 block of function blkst1 boolean 0 block of step 1 blkst2 boolean 0 block of step 2 blktr boolean 0 block of trip signals table 230: ns2ptoc output signals n...
Page 444
Name values (range) unit step default description t1max 0.00 - 6000.00 s 0.01 1000.00 maximum trip delay for step 1, in sec resetmultip1 0.01 - 20.00 - 0.01 1.00 reset multiplier for k1, defines reset time of inverse curve opstep2 off on - - on enable execution of step 2 i2-2> 3 - 500 %ib 1 10 negat...
Page 445
Step 1 of ns2ptoc can operate in the definite time (dt) or inverse time (idmt) mode depending on the selected value for the curvetype1 parameter. If curvetype1= definite, ns2ptoc operates with a definite time delay characteristic and if curvetype1 = inverse, ns2ptoc operates with an inverse time del...
Page 446
Current i2-1> operate time t1min t1max (default= 1000 s) (default= 5 s) k1 iec09000691-2-en.Vsd iec09000691 v2 en figure 202: inverse time characteristic with t1min and t1max for a detailed description of inverse time characteristic, see chapter "inverse characteristics" . The reset time is exponent...
Page 447
After start, a certain hysteresis is used before resetting start levels. For both steps the reset ratio is 0.97. 8.12.7.2 alarm function the alarm function is operated by start signal and used to warn the operator for an abnormal situation, for example, when generator continuous negative sequence cu...
Page 448
8.12.8 technical data table 234: ns2ptoc technical data function range or value accuracy operate current, step 1 - 2 (3-500)% of ibase ±1.0% of i r at i ≤ i r ±1.0% of i at i > i r reset ratio >95% - operate time, start at 0 to 2 x i set min. = 15 ms max. = 30 ms - reset time, start at 2 to 0 x i se...
Page 449
8.13.1.1 functionality inadvertent or accidental energizing of off-line generators has occurred often enough due to operating errors, breaker head flashovers, control circuit malfunctions, or a combination of these causes. Inadvertently energized generator operates as induction motor drawing a large...
Page 450
8.13.1.4 settings table 237: aegpvoc group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description operation off on - - off operation off / on i> 5 - 900 %ib 1 120 operate phase current level in % of ibase toc 0.000 - 60.000 s 0.001 0.030 trip time delay for over current level armu 2 - 15...
Page 451
When the maximum phase-to-phase voltage is larger than disarmu> for the period tdisarm, it is ensured generator is on line. During this state, undervoltage operation is disarmed, blocking the overcurrent operation and thus the function becomes inoperative. Block input can be used to block aegpvoc . ...
Page 452
Function range or value accuracy impulse margin time, undervoltage 15 ms typically - operate value, overvoltage (2-200)% of ubase ±0.5% of u r at u ≤ u r ±0.5% of u at u > u r definite time delay, overcurrent, at 0 to 2 x i set (0.000-60.000) s ±0.2% or ±35 ms whichever is greater definite time dela...
Page 453
8.14.3 function block vrpvoc i3p* u3p* block blkoc blkuv trip troc truv start stoc stuv iec12000184-1-en.Vsd iec12000184 v1 en figure 207: vrpvoc function block 8.14.4 signals table 241: vrpvoc input signals name type default description i3p group signal - three phase group signal for current inputs...
Page 454
8.14.5 settings table 243: vrpvoc group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description operation off on - - off operation off / on startcurr 2.0 - 5000.0 %ib 1.0 120.0 start current level in % of ibase characterist ansi ext. Inv. Ansi very inv. Ansi norm. Inv. Ansi mod. Inv. Ansi...
Page 455
8.14.6 monitored data table 246: vrpvoc monitored data name type values (range) unit description imax real - a maximum phase current magnitude uumin real - kv minimum ph-to-ph voltage magnitude 8.14.7 operation principle 8.14.7.1 measured quantities the voltage-restrained time overcurrent protection...
Page 456
Vdepfact *startcurr/100*ibase) and (uhighlimit/100*ubase; startcurr/ 100*ibase). In the first point the factor 0.25 that multiply ubase cannot be changed. Ubase start level of the current startcurr vdepfact * startcurr uhighlimit 0,25 iec10000123-2-en.Vsd iec10000123 v2 en figure 208: example for st...
Page 457
8.14.7.4 logic diagram iec10000214-1-en.Vsd startcurr x a b a>b voltage control or restraint feature inverse def time selected inverse time selected or stoc troc minph-phvoltage maxphcurr iec10000214 v1 en figure 210: simplified internal logic diagram for overcurrent function operation_uv=on startvo...
Page 458
The start signal starts a definite time delay. If the value of the start signal is logical true for longer than the set time delay, the undervoltage step sets its trip signal to logical true. This undervoltage functionality together with additional act logic can be used to provide functionality for ...
Page 459
Function range or value accuracy independent time delay to operate, undervoltage at 2 to 0 x u set (0.00 - 6000.00) s ±0.2% or ±35 ms whichever is greater internal low voltage blocking (0.0 - 5.0)% of ubase ±0.25% of u r overcurrent: critical impulse time impulse margin time 10 ms typically at 0 to ...
Page 460
8.15.3 function block iec12000027-1-en.Vsd gspttr i3p* block setlkout reset ibase trip start lockout blkrecl iec12000027 v1 en figure 212: gspttr function block 8.15.4 signals table 248: gspttr input signals name type default description i3p group signal - current group connection block boolean 0 bl...
Page 461
Name values (range) unit step default description tmin 1.0 - 120.0 s 0.1 10.0 minimum time, used in operate characteristic tmax 100.0 - 2000.0 s 0.1 300.0 maximum time, used in operate characteristic tcutoff 10.0 - 2000.0 s 0.1 120.0 cut-off time, used in operate characteristic treset 10.0 - 2000.0 ...
Page 462
Current measurement overload characteristic trip logic block iec12000013-1-en.Vsd iec12000013 v1 en figure 213: representation of the stator overload protection current measurement three phase currents are measured either on the high voltage (hv) side of the generator or on the neutral side of the s...
Page 463
• when measurcurrent = rms (default); the maximum true rms current value from the three-phase input currents is used as the measured quantity for the stator overload protection. • when measurcurrent = posseqnegseq; the weighted sum of positive and negative sequence stator currents in primary amperes...
Page 464
1 2 1 op k t i ibase = æ ö - ç ÷ è ø guid-e050ab5e-b2a4-4838-9e0f-c8133a63df54 v1 en (equation 100) where: t op is operate time in seconds k1 is a multiplier (it shall have default value of 41.4 in order to get the operating points as prescribed by the standard, see table 254 ) i is measured current...
Page 465
Tmin tcutoff tmax i> ibase t (s) i (a) - ÷ ø ö ç è æ = 1 2 1 ibase i k op t iec12000009-1-en.Vsd iec12000009 v1 en t_mintripdelay tcutoff t_maxtripdelay ipickup ibase t(s) i(a) 1 2 ibase i td1 tr t ansi12000009-1-en.Vsd ansi12000009 v1 en figure 215: operating characteristic for overload function as...
Page 466
Addition to this it is also possible to specify the cut-off time below which the idmt curve defined by the above equation will be used. Note that tcutoff shall be always set to the smaller value than tmax. The operate time of the stator overload function is calculated by using the integration princi...
Page 467
Imeasured ibase * i> pickup hysteresis theta 100 start trip reclslevtheta treset t t t iec12000014-1-en.Vsd iec12000014 v1 en figure 216: operating principles of the stator overload function 1mrk502052-uen b section 8 current protection 461 technical manual.
Page 468
Tripping logic this tripping logic provides some additional features regarding blocking and tripping options available within the function. The list below describes functionality of every binary input and output from the function which influence the trip logic. Available binary inputs: block prevent...
Page 469
8.15.8 technical data table 255: gspttr technical data function range or value accuracy current start level for overload protection (105.0–900.0)% of ibase ±1.0% of i r at i ≤ i r ±1.0% of i at i > i r reset ratio >95% start time at 0 to 2 x i set min. = 50 ms max. = 170 ms thermal time characterist...
Page 470
Current is default (i.E. Recommended) measurement for generators with static excitation system. When the dc current is used, the function can provide a dc current ripple alarm, due to possible problem with the static excitation equipment. The rotor dc current can be also sent to the plant supervisor...
Page 471
Name type description blkrecl boolean block machine closing command alripple boolean ripple alarm, is set (with delay-on 20ms) if instripplealarm is active longer than talarmripple imeas real measured current, used for calculation of operate time 8.16.5 settings table 258: grpttr group settings (bas...
Page 472
Table 259: grpttr non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description measurcurrent rms dc - - dc measured current quantity (rms or calculated dc) ct_location lv_winding hv_winding - - lv_winding excitation transformer winding where used ct is located globalbasesel 1 - 12 - ...
Page 473
Current measurement overload characteristic trip logic alarm ripple detection block block undercurrent protection for rotor winding block iec12000016-1-en.Vsd iec12000016 v1 en figure 219: representation of the rotor overload protection each of these five sub-blocks will be described in the followin...
Page 474
Step-up transformer g field breaker excitation transformer i l1 i l2 i l3 u a u a pri-side (hv) sec-side (lv) iec12000019-1-en.Vsd two alternative measurement points for the rotor overload function l1 i l2 i l3 i iec12000019 v1 en figure 220: measurement of rotor currents the selection of current me...
Page 475
Where i l1 , i l2 and i l3 are instantaneous sampled values of the three-phase currents from lv side of the excitation transformer. Note that this calculation is done twenty times per power system cycle. After that the average dc current value i dc is calculated over one power system cycle by using ...
Page 476
In order to obtain such operating characteristic the rotor overload function utilizes the following formula in order to calculate the operate time: 1 2 1 op k t i ibase = æ ö - ç ÷ è ø guid-e050ab5e-b2a4-4838-9e0f-c8133a63df54 v1 en (equation 103) where: t op is operate time in seconds k1 is a multi...
Page 477
As shown in figure 221 it is possible to define the maximum (tmax) and minimum (tmin) operate time for the function regardless of the level of the measured current. In addition to this it is also possible to specify the cut-off time below which the idmt curve defined by the above equation will be us...
Page 478
Imeasured ibase * i> pickup hysteresis theta 100 start trip reclslevtheta treset t t t iec12000015-1-en.Vsd iec12000015 v1 en figure 222: operating principles of the rotor overload function section 8 1mrk502052-uen b current protection 472 technical manual.
Page 479
Under current protection of rotor winding one undercurrent protection level with definite time delay is available within the function. It can be used to either alarm or trip for low-excitation/loss-of-excitation condition of the machine. This built-in feature monitors the level of the measured curre...
Page 480
Tripuc, operation of the undercurrent feature start, current bigger than i> level startuc, current smaller than i level lockout, sealed-in trip output signal from the function. Note that lockout feature is only enabled by setting autolockout = “on” blkrecl, output signal active as long as theta > re...
Page 481
8.16.8 technical data table 262: grpttr technical data function range or value accuracy overcurrent start level for overload protection (105.0–900.0)% of ibase ±1.0% of i r at i ≤ i r ±1.0% of i at i > i r reset ratio, overcurrent >95% — start time, overcurrent at 0 to 2 x i set min = 50 ms — max = ...
Page 482
476.
Page 483
Section 9 voltage protection 9.1 two step undervoltage protection uv2ptuv 9.1.1 identification function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number two step undervoltage protection uv2ptuv 3u symbol-r-2u-greater-than v2 en 27 9.1.2 functionality underv...
Page 484
9.1.3 function block iec06000276-2-en.Vsd uv2ptuv u3p* block blktr1 blkst1 blktr2 blkst2 trip tr1 tr1l1 tr1l2 tr1l3 tr2 tr2l1 tr2l2 tr2l3 start st1 st1l1 st1l2 st1l3 st2 st2l1 st2l2 st2l3 iec06000276 v2 en figure 225: uv2ptuv function block 9.1.4 signals table 263: uv2ptuv input signals name type de...
Page 485
Name type description st1 boolean common start signal from step1 st1l1 boolean start signal from step1 phase l1 st1l2 boolean start signal from step1 phase l2 st1l3 boolean start signal from step1 phase l3 st2 boolean common start signal from step2 st2l1 boolean start signal from step2 phase l1 st2l...
Page 486
Name values (range) unit step default description opmode2 1 out of 3 2 out of 3 3 out of 3 - - 1 out of 3 number of phases required for op (1 of 3, 2 of 3, 3 of 3) from step 2 u2 1.0 - 100.0 %ub 0.1 50.0 voltage setting/start val (dt & idmt) in % of ubase, step 2 t2 0.000 - 60.000 s 0.001 5.000 defi...
Page 487
Name values (range) unit step default description bcrv2 0.50 - 100.00 - 0.01 1.00 parameter b for customer programmable curve for step 2 ccrv2 0.0 - 1.0 - 0.1 0.0 parameter c for customer programmable curve for step 2 dcrv2 0.000 - 60.000 - 0.001 0.000 parameter d for customer programmable curve for...
Page 488
Uv2ptuv can be set to measure phase-to-earth fundamental value, phase-to-phase fundamental value, phase-to-earth true rms value or phase-to-phase true rms value. The choice of the measuring is done by the parameter conntype. The voltage related settings are made in percent of base voltage which is s...
Page 489
Where: un set value for step 1 and step 2 u measured voltage the type b curve is described as: n n k t u u u 2.0 480 0.055 32 0.5 × = + æ ö × - ç ÷ è ø equation1432 v2 en (equation 107) the customer programmable curve can be created as: p n n k a t d u u b c u é ù ê ú ê ú × = + ê ú æ ö ê ú × - ç ÷ ê...
Page 490
Voltage idmt voltage time ul1 ul2 ul3 iec12000186-1-en.Vsd iec12000186 v1 en figure 226: voltage used for the inverse time characteristic integration trip signal issuing requires that the undervoltage condition continues for at least the user set time delay. This time delay is set by the parameter t...
Page 491
Voltage time hystabs1 start trip u1 start trip t tireset1 time time integrator t frozen timer linearly decreased instantaneous measured voltage tireset1 iec05000010-4-en.Vsd iec05000010 v4 en figure 227: voltage profile not causing a reset of the start signal for step 1, and inverse time delay at di...
Page 492
Voltage time hystabs1 start trip start u1 start trip t tireset1 time time integrator t frozen timer linearly decreased instantaneous measured voltage tireset1 iec05000011-en-3.Vsd iec05000011 v3 en figure 228: voltage profile causing a reset of the start signal for step 1, and inverse time delay at ...
Page 493
A a b u1 u tr1 st1 iec09000785-3-en.Vsd t t1 treset1 r t and iec09000785 v3 en figure 229: detailed logic diagram for step 1, dt operation u1 st1 tr1 treset1 t1 iec10000039-3-en.Vsd iec10000039 v3 en figure 230: example for definite time delay stage1 reset 1mrk502052-uen b section 9 voltage protecti...
Page 494
U1 st1 tr1 treset1 t1 iec10000040-3-en.Vsd iec10000040 v3 en figure 231: example for definite time delay stage1 operation 9.1.7.3 blocking it is possible to block two step undervoltage protection uv2ptuv partially or completely, by binary input signals or by parameter settings, where: block: blocks ...
Page 495
Time u normal voltage u1 u2 intblkstval1 intblkstval2 disconnection tblkuv1 t1,t1min tblkuv2 t2,t2min block step 1 block step 2 en05000466.Vsd iec05000466 v1 en figure 232: blocking function 9.1.7.4 design the voltage measuring elements continuously measure the three phase-to-neutral voltages or the...
Page 496
Start st1l1 st1l2 st1l3 tr1l1 tr1l2 tr1l3 st1 tr1 start st2l1 st2l2 st2l3 tr2l1 tr2l2 tr2l3 st2 tr2 trip comparator ul1 comparator ul2 comparator ul3 minvoltselector comparator ul1 comparator ul2 ul3 minvoltselector start t1 & trip output logic step 1 start t2 & trip output logic step 2 phase 3 phas...
Page 497
9.1.8 technical data table 269: uv2ptuv technical data function range or value accuracy operate voltage, low and high step (1.0–100.0)% of ubase ±0.5% of u r absolute hysteresis (0.0–50.0)% of ubase ±0.5% of u r internal blocking level, step 1 and step 2 (1–50)% of ubase ±0.5% of u r inverse time ch...
Page 498
9.2.2 functionality overvoltages may occur in the power system during abnormal conditions such as sudden power loss, tap changer regulating failures, and open line ends on long lines. Ov2ptov has two voltage steps, each of them with inverse or definite time delayed. Ov2ptov has a high reset ratio to...
Page 499
Name type description tr1l2 boolean trip signal from step1 phase l2 tr1l3 boolean trip signal from step1 phase l3 tr2 boolean common trip signal from step2 tr2l1 boolean trip signal from step2 phase l1 tr2l2 boolean trip signal from step2 phase l2 tr2l3 boolean trip signal from step2 phase l3 start ...
Page 500
Name values (range) unit step default description characterist2 definite time inverse curve a inverse curve b inverse curve c prog. Inv. Curve - - definite time selection of time delay curve type for step 2 opmode2 1 out of 3 2 out of 3 3 out of 3 - - 1 out of 3 number of phases required for op (1 o...
Page 501
Name values (range) unit step default description ccrv2 0.0 - 1.0 - 0.1 0.0 parameter c for customer programmable curve for step 2 dcrv2 0.000 - 60.000 - 0.001 0.000 parameter d for customer programmable curve for step 2 pcrv2 0.000 - 3.000 - 0.001 1.000 parameter p for customer programmable curve f...
Page 502
The setting of the analog inputs are given as primary phase-to-earth or phase-to-phase voltage. Ov2ptov will operate if the voltage gets higher than the set percentage of the set base voltage ubase. This means operation for phase-to-earth voltage over: (%) ( ) 3 u ubase kv > × equation1434 v1 en (eq...
Page 503
Where: un> set value for step 1 and step 2 u measured voltage the type b curve is described as: 2.0 480 0.035 32 0.5 n n k t u u u iecequation2423 v2 en (equation 113) the type c curve is described as: 3.0 480 0.035 32 0.5 n n k t u u u × = + æ ö - > × - ç ÷ > è ø iecequation2425 v1 en (equation 114...
Page 504
Iec05000016-2-en.Vsd voltage idmt voltage time ul1 ul2 ul3 iec05000016 v2 en figure 235: voltage used for the inverse time characteristic integration operation of the trip signal requires that the overvoltage condition continues for at least the user set time delay. This time delay is set by the par...
Page 505
Trip u1> trip t time time integrator t frozen timer instantaneous voltage voltage time hystabs1 start start tireset1 measured tireset1 linearly decreased iec09000055-2-en.Vsd iec09000055 v2 en figure 236: voltage profile not causing a reset of the start signal for step 1, and inverse time delay at d...
Page 506
Time integrator voltage time start trip start u1> start trip t tireset1 time t frozen timer linearly decreased instantaneous measured voltage tireset1 iec05000020-3-en.Vsd hystabs1 iec05000020 v3 en figure 237: voltage profile causing a reset of the start signal for step 1, and inverse time delay at...
Page 507
U1> u a>b a b t treset1 t t1 and tr1 st1 off delay on delay iec10000100-2-en.Vsd iec10000100 v2 en figure 238: detailed logic diagram for step 1, definite time delay, dt operation treset1 u1> start trip t1 iec10000037-2-en.Vsd iec10000037 v2 en figure 239: example for step 1, definite time delay sta...
Page 508
Treset1 u1> start trip t1 iec10000038-2-en.Vsd iec10000038 v2 en figure 240: example for definite time delay stage 1 operation 9.2.7.3 blocking it is possible to block two step overvoltage protection ov2ptov partially or completely, by binary input signals where: block: blocks all outputs blktr1: bl...
Page 509
Start st1l1 st1l2 st1l3 tr1l1 tr1l2 tr1l3 st1 tr1 start st2l1 st2l2 st2l3 tr2l1 tr2l2 tr2l3 st2 tr2 start trip comparator ul1 > u1> comparator ul2 > u1> comparator ul3 > u1> maxvoltselect comparator ul1 > u2> comparator ul2 > u2> comparator ul3 > u2> maxvoltselect start t1 t1reset & trip output logi...
Page 510
9.2.8 technical data table 276: ov2ptov technical data function range or value accuracy operate voltage, step 1 and 2 (1.0-200.0)% of ubase ±0.5% of u r at u ≤ u r ±0.5% of u at u > u r absolute hysteresis (0.0–50.0)% of ubase ±0.5% of u r at u ≤ u r ±0.5% of u at u > u r inverse time characteristic...
Page 511
9.3 two step residual overvoltage protection rov2ptov 9.3.1 identification function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number two step residual overvoltage protection rov2ptov 3u0 trv v1 en 59n 9.3.2 functionality residual voltages may occur in the p...
Page 512
Name type default description blkst1 boolean 0 block of step 1 blktr2 boolean 0 block of operate signal, step 2 blkst2 boolean 0 block of step 2 table 278: rov2ptov output signals name type description trip boolean trip tr1 boolean common trip signal from step1 tr2 boolean common trip signal from st...
Page 513
Name values (range) unit step default description t2min 0.000 - 60.000 s 0.001 5.000 minimum operate time for inverse curves for step 2 k2 0.05 - 1.10 - 0.01 0.05 time multiplier for the inverse time delay for step 2 hystabs2 0.0 - 50.0 %ub 0.1 0.5 absolute hysteresis in % of ubase, step 2 table 280...
Page 514
Table 281: rov2ptov non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description globalbasesel 1 - 12 - 1 1 selection of one of the global base value groups 9.3.6 monitored data table 282: rov2ptov monitored data name type values (range) unit description ulevel real - kv magnitude of...
Page 515
• inverse curve a • inverse curve b • inverse curve c • customer programmable inverse curve the type a curve is described as: n n k t u u u = æ ö - > ç ÷ > è ø iecequation2422 v1 en (equation 117) where: un> set value for step 1 and step 2 u measured voltage the type b curve is described as: 2.0 480...
Page 516
0 100 crvsatn b c × - > equation1440 v1 en (equation 121) the details of the different inverse time characteristics are shown in section "inverse characteristics" . Trip signal issuing requires that the residual overvoltage condition continues for at least the user set time delay. This time delay is...
Page 517
Trip u1> trip t time time integrator t frozen timer instantaneous voltage voltage time hystabs1 start start tireset1 measured tireset1 linearly decreased iec09000055-2-en.Vsd iec09000055 v2 en figure 243: voltage profile not causing a reset of the start signal for step 1, and inverse time delay 1mrk...
Page 518
Time integrator voltage time start trip start u1> start trip t tireset1 time t frozen timer linearly decreased instantaneous measured voltage tireset1 iec05000020-3-en.Vsd hystabs1 iec05000020 v3 en figure 244: voltage profile causing a reset of the start signal for step 1, and inverse time delay de...
Page 519
U1> u a>b a b t treset1 t t1 and tr1 st1 off delay on delay iec10000100-2-en.Vsd iec10000100 v2 en figure 245: detailed logic diagram for step 1, definite time delay, dt operation u1 st1 tr1 treset1 t1 iec10000039-3-en.Vsd iec10000039 v3 en figure 246: example for definite time delay stage 1 reset 1...
Page 520
U1 st1 tr1 treset1 t1 iec10000040-3-en.Vsd iec10000040 v3 en figure 247: example for definite time delay stage 1 operation 9.3.7.3 blocking it is possible to block two step residual overvoltage protection rov2ptov partially or completely, by binary input signals where: block: blocks all outputs blkt...
Page 521
Iec05000748_2_en.Vsd un st1 tr1 st2 tr2 start trip comparator un > u1> start t2 treset2 & trip output logic step 2 phase 1 phase 1 time integrator tireset2 resettypecrv2 start start t1 treset1 & trip output logic step 1 time integrator tireset1 resettypecrv1 comparator un > u2> start trip trip or or...
Page 522
Function range or value accuracy minimum operate time (0.000-60.000) s ± 0.2% or ± 45 ms whichever is greater operate time, start at 0 to 2 x u set min. = 15 ms max. = 30 ms - reset time, start at 2 to 0 x u set min. = 15 ms max. = 30 ms - operate time, start at 0 to 1.2 x u set min. = 20 ms max. = ...
Page 523
9.4.4 signals table 284: oexpvph input signals name type default description i3p group signal - current connection u3p group signal - voltage connection block boolean 0 block of function reset boolean 0 reset operation table 285: oexpvph output signals name type description trip boolean trip from ov...
Page 524
Table 287: oexpvph group settings (advanced) name values (range) unit step default description t1tailor 0.00 - 9000.00 s 0.01 7200.00 time delay t1 (longest) for tailor made curve, in sec t2tailor 0.00 - 9000.00 s 0.01 3600.00 time delay t2 for tailor made curve, in sec t3tailor 0.00 - 9000.00 s 0.0...
Page 525
Unless corrective action is taken. Transformer manufacturers recommend an overexcitation protection as a part of the transformer protection system. Overexcitation results from excessive applied voltage, possibly in combination with below-normal frequency. Such conditions may occur when a transformer...
Page 526
Ratio of the actual generator terminal voltage to the actual frequency should not exceed 1.1 times the ratio of transformer rated voltage to the rated frequency on a sustained basis, see equation 124 . E f ---- 1.1 £ ur fr ------ × equation900 v1 en (equation 124) or equivalently, with 1.1 · ur = v/...
Page 527
Between the primary and the secondary winding: xleak = xleak1 = xleak2 = xsc / 2 = 0.075 pu. Oexpvph calculates the internal induced voltage e if xleak (meaning the leakage reactance of the winding where oexpvph is connected) is known to the user. The assumption taken for two-winding power transform...
Page 528
• oexpvph can be connected to any power transformer side, independent from the power flow. • the side with a possible load tap changer must not be used. 9.4.7.2 operate time of the overexcitation protection the operate time of oexpvph is a function of the relative overexcitation. Basically there are...
Page 529
( ) ( ) op t 2 0 m t v hz 0.18 dt k - > ³ × ò iecequation2300 v1 en (equation 129) a digital, numerical relay will instead look for the lowest j (that is, j = n) where it becomes true that: dt m(j) v/hz> – ( ) 2 j k = n å × 0.18 k × ³ equation906 v1 en (equation 130) where: d t is the time interval ...
Page 530
A definite minimum time, tmin, can be used to limit the operate time at high degrees of overexcitation. In case the inverse delay is shorter than tmin, oexpvph function trips after tmin seconds. The inverse delay law is not valid for values exceeding mmax. The delay will be tmin, irrespective of the...
Page 531
The tailor-made law allows a user to design an arbitrary delay characteristic. In this case the interval between m = v/hz>, and m = mmax is automatically divided into five equal subintervals, with six delays. (settings t1, t2, t3, t4, t5 and t6) as shown in figure 252 . These times should be set so ...
Page 532
( ) e f m p.U. = ur fr iecequation2299 v1 en (equation 132) if vperhz value is less than setting v/hz> (in %), the power transformer is underexcited. If vperhz is equal to v/hz> (in %), the excitation is exactly equal to the power transformer continuous capability. If vperhz is higher than v/hz>, th...
Page 533
9.4.7.6 logic diagram iec05000162-3-en.Vsd t ³1 & & block xleak ei m= (ei / f) (ur / fr) m = relative v/hz as service value v/hz>> m>v/hz>> v/hz> m>v/hz> ieee law tailor-made law tmax calculation of internal induced voltage ei k m m talarm alarm trip alarmlevel u3p i3p t t tmin & iec05000162 v3 en f...
Page 534
9.5 voltage differential protection vdcptov 9.5.1 identification function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number voltage differential protection vdcptov - 60 9.5.2 functionality a voltage differential monitoring function is available. It compares ...
Page 535
Name type description u2low boolean loss of u2 voltage ul1diff real differential voltage phase l1 ul2diff real differential voltage phase l2 ul3diff real differential voltage phase l3 9.5.5 settings table 293: vdcptov group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description operation...
Page 536
9.5.6 monitored data table 296: vdcptov monitored data name type values (range) unit description ul1diff real - kv differential voltage phase l1 ul2diff real - kv differential voltage phase l2 ul3diff real - kv differential voltage phase l3 9.5.7 operation principle the voltage differential protecti...
Page 537
Udtripl1> u1 and o r udalarml1> udtripl2> udalarml2> udtripl3> udalarml3> and and and and and t treset t talarm o r t ttrip trip start alarm u1 u1 u2 u2 u2 and t talarm t t1 or and and and block and and u1low u2low en06000382-2.Vsd blkdiffatulow and and iec06000382 v3 en figure 255: principle logic ...
Page 538
9.6 100% stator earth fault protection, 3rd harmonic based stefphiz 9.6.1 identification function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number 100% stator earth fault protection, 3rd harmonic based stefphiz - 59thd 9.6.2 functionality stator earth fault...
Page 539
X e3 rf t cb 2 (1- x) e3 over- voltage protection 10% – 100% differential 0% – 30% cb 1 may not exist rn n cb 1 stator winding ut un x e3 rf transformer t cb 2 (1- x) e3 x neutral point fundamental frequency over-voltage protection 5% - 100% 3rd harmonic differential 0% - 30% cb 1 may not exist 1 or...
Page 540
9.6.4 signals table 298: stefphiz input signals name type default description u3pneut group signal - voltage connection neutral side u3pterm group signal - open-delta connection on terminal side cbclosed boolean 1 true means breaker between gen. & trafo is closed block boolean 0 complete block of th...
Page 541
9.6.5 settings table 300: stefphiz group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description operation off on - - off operation off / on beta 0.50 - 10.00 - 0.01 3.00 portion of voltn3rdharmonic used as bias cbexists no yes - - no defines if generator cb exists (between gen & transfor...
Page 542
Name type values (range) unit description angle real - deg angle between 3rd harmonic votage phasors, radians du3 real - kv diff. Between 3rd harm. Volt. At both sides of gen., volts bu3 real - kv bias voltage, a part of voltn3rdharmonic, primary volts un real - kv fund. Frequency voltage at generat...
Page 543
En06000448.Vsd u 3n u 3t - du 3 + - u 3 + - u 3n + + u 3t,l1 - + u 3t,l2 - + u 3t,l3 - iec06000448 v2 en figure 258: generator 3 rd harmonic voltage characteristic at normal operation the generator is modeled as parts of a winding where a 3 rd harmonic voltage is induced along the winding, represent...
Page 544
3t 3n 3n u u u beta + ³ equation1712 v2 en (equation 134) u 3n , and u 3t are third harmonic phasors with real and imaginary parts. The factor beta must be set not to risk operation under non-faulted conditions. The voltage u 3n is measured via a voltage transformer between the generator neutral poi...
Page 545
En06000449.Vsd samples: generator terminal voltage 3rd harmonic fourier filtering giving ut3 complex ut3 samples: generator neutral point voltage 3rd harmonic fourier filtering giving un3 complex un3 stator earth fault detection 3rd harmonic based start start and trip logic trip trip3h tripun start3...
Page 546
Iec07000186 v1 en figure 260: simplified start and trip logical diagram of the 100% stator earth fault protection, 3rd harmonic based stefphiz protection there are two different cases of generator block configuration; with or without generator circuit breaker. If there is no generator breaker the ca...
Page 547
Will be reduced compared to the normal operating condition. Therefore, there is a possibility to reduce the sensitivity of the protection when the generator circuit breaker is open. With the setting cbexists change of the sensitivity is enabled. If the binary input signal cbclosed is activated the s...
Page 548
542.
Page 549
Section 10 frequency protection 10.1 underfrequency protection saptuf 10.1.1 identification function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number underfrequency protection saptuf f symbol-p v1 en 81 10.1.2 functionality underfrequency occurs as a result...
Page 550
10.1.4 signals table 304: saptuf input signals name type default description u3p group signal - three phase group signal for voltage inputs block boolean 0 block of function blktrip boolean 0 blocking operate output blkrest boolean 0 blocking restore output table 305: saptuf output signals name type...
Page 551
Table 307: saptuf non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description globalbasesel 1 - 12 - 1 1 selection of one of the global base value groups 10.1.6 monitored data table 308: saptuf monitored data name type values (range) unit description ulevel real - kv level of measur...
Page 552
Voltage level causes a short time delay. For the definite time delay, the setting tdelay sets the time delay. For the voltage dependent time delay the measured voltage level and the settings unom, umin, exponent, tmax and tmin set the time delay according to figure 263 and equation 135 . The setting...
Page 553
Umin = 90% unom = 100% tmax = 1.0 s tmin = 0.0 s exponent = 0, 1, 2, 3 and 4 90 95 100 0 0.5 1 en05000075.Vsd t im ed ly o pe ra te [s ] u [% of ubase] exponenent 0 1 2 3 4 iec05000075 v1 en figure 263: voltage dependent inverse time characteristics for underfrequency protection saptuf. The time del...
Page 554
Restorefreq, the restore output is issued after the time delay trestore. The design of underfrequency protection saptuf is schematically described in figure 264 . Frequency comparator f voltage start start trip comparator minvalfreqmeas block comparator f > restorefreq block or time integrator timer...
Page 555
10.2.2 functionality overfrequency protection function saptof is applicable in all situations, where reliable detection of high fundamental power system frequency is needed. Overfrequency occurs because of sudden load drops or shunt faults in the power network. Close to the generating plant, generat...
Page 556
10.2.5 settings table 311: saptof group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description operation off on - - off operation off / on startfrequency 35.00 - 90.00 hz 0.01 51.20 frequency set value tdelay 0.000 - 60.000 s 0.001 0.000 operate time delay treset 0.000 - 60.000 s 0.001 0...
Page 557
Should be set as a phase-phase voltage in kv. To avoid oscillations of the output start signal, a hysteresis has been included. 10.2.7.2 time delay the time delay for overfrequency protection saptof is a settable definite time delay, specified by the setting tdelay. Trip signal issuing requires that...
Page 558
Voltage start start trip start & trip output logic time integrator definite time delay tdelay treset comparator minvalfreqmeas block iec05000735-2-en.Vsdx frequency comparator f > startfrequency trip blkdmagn block or blktrip iec05000735 v2 en figure 266: simplified logic diagram for saptof 10.2.8 t...
Page 559
10.3 rate-of-change frequency protection sapfrc 10.3.1 identification function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number rate-of-change frequency protection sapfrc df/dt > symbol-n v1 en 81 10.3.2 functionality the rate-of-change frequency protection...
Page 560
Table 316: sapfrc output signals name type description trip boolean operate/trip signal for frequency gradient start boolean start/pick-up signal for frequency gradient restore boolean restore signal for load restoring purposes blkdmagn boolean blocking indication due to low amplitude 10.3.5 setting...
Page 561
10.3.7.1 measurement principle the rate-of-change of the fundamental frequency of the selected voltage is measured continuously, and compared with the set value, startfreqgrad. Rate-of-change frequency protection sapfrc is also dependent on the voltage magnitude. If the voltage magnitude decreases b...
Page 562
If the measured voltage level decreases below the setting of minvalfreqmeas in the preprocessing function, both the start and the trip outputs are blocked. 10.3.7.4 design rate-of-change frequency protection (sapfrc) measuring element continuously measures the frequency of the selected voltage and c...
Page 563
10.3.8 technical data table 319: sapfrc technical data function range or value accuracy operate value, start function (-10.00-10.00) hz/s ±10.0 mhz/s operate value, restore enable frequency (45.00-65.00) hz ±2.0 mhz definite restore time delay (0.000-60.000) s ±0.2% or ±100 ms whichever is greater d...
Page 564
10.4.3 function block guid-e27e0bc3-cb61-4e9e-9117-6ab8906f8362 v1 en figure 269: ftaqfvr function block 10.4.4 signals table 320: ftaqfvr input signals name type default description i3p group signal - group signal for three phase current u3p group signal - group signal for three phase voltage block...
Page 565
Name type description strorhld boolean activated when function starts or holdacc input is active freqok boolean indicates the system frequency within the frequency band limits voltok boolean indicates the system voltage within the voltage band limits 10.4.5 settings table 322: ftaqfvr group settings...
Page 566
10.4.6 monitored data table 324: ftaqfvr monitored data name type values (range) unit description freq real - hz measured frequency value acctime real - s accumulated time for frequency band limits lastevtd real - - accumulation time for last event of frequency within band 10.4.7 operation principle...
Page 567
Voltage band limit check will be ignored for the start output if the enavoltcheck setting is disabled. The voltage band limits are set with the settings uhighlimit and ulowlimit. The output voltok is activated only if the system positive-sequence voltage falls within the voltage band limits and the ...
Page 568
Comparator if f and f > freqlowlimit then start comparator i start signal routing based on generator start or stop detection logic and voltage band limit check logic u3p i3p cbopen cbclose comparator if freqhighlimit freqlowlimit then error block loadinit resetacc holdtime start error tripacc tripco...
Page 569
Table 325: ftaqfvr technical data function range or value accuracy operate value, frequency high limit level at symmetrical three phase voltage (35.00 – 90.00) hz ±2.0 mhz operatevalue, frequency low limit level at symmetrical three phase voltage (30.00 – 85.00) hz ±2.0 mhz operate value, voltage hi...
Page 570
564.
Page 571
Section 11 multipurpose protection 11.1 general current and voltage protection cvgapc 11.1.1 identification function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number general current and voltage protection cvgapc 2(i>/u - 11.1.2 functionality the protection ...
Page 572
To prevent damages on the generator or turbine, it is essential that high speed tripping is provided in case of inadvertent energization of the generator. This tripping should be almost instantaneous ( there is a risk that the current into the generator at inadvertent energization will be limited so...
Page 573
Name type default description blkoc2 boolean 0 block of over current function oc2 blkoc2tr boolean 0 block of trip for over current function oc2 enmltoc2 boolean 0 when activated, the current multiplier is in use for oc2 blkuc1 boolean 0 block of under current function uc1 blkuc1tr boolean 0 block o...
Page 574
Name type description diroc2 integer directional mode of oc2 (nondir, forward,reverse) udirlow boolean low voltage for directional polarization current real measured current value icosfi real measured current multiplied with cos (phi) voltage real measured voltage value uiangle real angle between vo...
Page 575
Name values (range) unit step default description restrcurrinput posseq negseq 3*zeroseq max - - posseq select current signal which will be used for curr restrain restrcurrcoeff 0.00 - 5.00 - 0.01 0.00 restraining current coefficient rcadir -180 - 180 deg 1 -75 relay characteristic angle roadir 1 - ...
Page 576
Name values (range) unit step default description dirprinc_oc1 i&u icosphi&u - - i&u measuring on iandu or icosphiandu for oc1 actlowvolt1_vm non-directional block memory - - non-directional low voltage level action for dir_oc1 (nodir, blk, mem) operation_oc2 off on - - off operation oc2 off / on st...
Page 577
Name values (range) unit step default description actlowvolt2_vm non-directional block memory - - non-directional low voltage level action for dir_oc2 (nodir, blk, mem) operation_uc1 off on - - off operation uc1 off / on enblklowi_uc1 off on - - off enable internal low current level blocking for uc1...
Page 578
Name values (range) unit step default description curvetype_ov2 definite time inverse curve a inverse curve b inverse curve c prog. Inv. Curve - - definite time selection of time delay curve type for ov2 tdef_ov2 0.00 - 6000.00 s 0.01 1.00 operate time delay in sec for definite time use of ov2 tmin_...
Page 579
Table 329: cvgapc group settings (advanced) name values (range) unit step default description currmult_oc1 1.0 - 10.0 - 0.1 2.0 multiplier for scaling the current setting value for oc1 rescrvtype_oc1 instantaneous iec reset ansi reset - - instantaneous selection of reset curve type for oc1 tresetdef...
Page 580
Name values (range) unit step default description tresetdef_ov1 0.00 - 6000.00 s 0.01 0.00 reset time delay in sec for definite time use of ov1 tresetidmt_ov1 0.00 - 6000.00 s 0.01 0.00 reset time delay in sec for idmt curves for ov1 a_ov1 0.005 - 999.000 - 0.001 0.140 parameter a for customer progr...
Page 581
Name values (range) unit step default description rescrvtype_uv2 instantaneous frozen timer linearly decreased - - instantaneous selection of reset curve type for uv2 tresetdef_uv2 0.00 - 6000.00 s 0.01 0.00 reset time delay in sec for definite time use of uv2 tresetidmt_uv2 0.00 - 6000.00 s 0.01 0....
Page 582
11.1.7 operation principle 11.1.7.1 measured quantities within cvgapc general current and voltage protection (cvgapc) function is always connected to three-phase current and three-phase voltage input in the configuration tool, but it will always measure only one current and one voltage quantity sele...
Page 583
The user can select to measure one of the voltage quantities shown in table 333 : table 333: voltage selection for cvgapc function set value for the parameter voltageinput comment 1 phase1 cvgapc function will measure the phase l1 voltage phasor 2 phase2 cvgapc function will measure the phase l2 vol...
Page 584
Connection is entered as a setting parameter for the pre-processing block, which will then take automatic care about it. The user can select one of the current quantities shown in table 334 for built-in current restraint feature: table 334: restraint current selection for cvgapc function set value f...
Page 585
Not cause the overcurrent step start signal. Start signal will only come if all of the enabled built-in features in the overcurrent step are fulfilled at the same time. Second harmonic feature the overcurrent protection step can be restrained by a second harmonic component in the measured current qu...
Page 586
Set value for the parameter currentinput set value for the parameter voltageinput comment phase1 phase2-phase3 directional overcurrent function for the first phase is obtained. Typical setting for rcadir is +30° or +45° phase2 phase3-phase1 directional overcurrent function for the second phase is ob...
Page 587
U=-3u0 operate region rcadir roadir ipickup i=3io mta line f en05000253.Vsd iec05000253 v1 en figure 273: cvgapc, icosphi&u directional operating principle where: rcadir is -75° roadir is 50° note that it is possible to decide by a parameter setting how the directional feature shall behave when the ...
Page 588
Selected voltage magnitude oc1 stage pickup level startcurr_oc1 vdepfact_oc1 * startcurr_oc1 uhighlimit_oc1 ulowlimit_oc1 en05000324.Vsd iec05000324 v1 en figure 274: example for oc1 step current pickup level variation as function of measured voltage magnitude in slope mode of operation • voltage co...
Page 589
Current restraint feature the overcurrent protection step operation can be made dependent of a restraining current quantity (see table 334 ). Practically then the pickup level of the overcurrent step is not constant but instead increases with the increase in the magnitude of the restraining current....
Page 590
11.1.7.5 built-in overvoltage protection steps two overvoltage protection steps are available. They are absolutely identical and therefore only one will be explained here. Overvoltage step simply compares the magnitude of the measured voltage quantity (see table 333 ) with the set pickup level. The ...
Page 591
En08000288.Vsd 3ip 3up blkoc1 trov1 troc1 cvgapc truv1 s r q q iec08000288 v1 en figure 277: configuration of the inadvertent energizing function the setting of the general current and voltage function (typical values) is done as shown in table 336 . Table 336: the setting of the general current and...
Page 592
Activated after the set delay. At this moment the block signal to the overcurrent function will be deactivated. It the generator is energized at stand still conditions, that is, when the voltage is zero, the overcurrent function will operate after the short set delay if the generator current is larg...
Page 593
The following currents and voltages are inputs to the multipurpose protection function. They must all be expressed in true power system (primary) amperes and kilovolts. 1. Instantaneous values (samples) of currents & voltages from one three-phase current and one three-phase voltage input. 2. Fundame...
Page 594
Uc2 uc1 current truc1 stuc2 truc2 stoc1 blk2nd stoc2 troc2 ov1 stov1 trov1 ov2 stov2 trov2 uv1 stuv1 truv1 uv2 stuv2 truv2 selected current selected restraint current en05000170.Vsd selected voltage ³1 ³1 udirlow troc1 oc1 2 nd harmonic restraint current restraint directionality voltage control / re...
Page 595
Logic in figure 279 can be summarized as follows: 1. The selected currents and voltage are given to built-in protection elements. Each protection element and step makes independent decision about status of its start and trip output signals. 2. More detailed internal logic for every protection elemen...
Page 596
A b b>a selected current startcurr_uc1 operation_uc1=on bin input: blkuc1 stuc1 en05000750.Vsd truc1 bin input: blkuc1tr def and and iec05000750 v1 en figure 281: simplified internal logic diagram for built-in first undercurrent step that is, uc1 (step uc2 has the same internal logic) a b a>b select...
Page 597
And a b b>a selected voltage startvolt_uv1 operation_uv1=on blkuv1 inverse time selected en05000752.Vsd inverse def def time selected or stuv1 truv1 and blktruv 1 iec05000752 v1 en figure 283: simplified internal logic diagram for built-in first undervoltage step uv1 (step uv2 has the same internal ...
Page 598
Function range or value accuracy start time at 0 to 10 x i set min. = 5 ms max. = 20 ms - reset time at 10 to 0 x i set min. = 20 ms max. = 35 ms - undercurrent: start time at 2 to 0 x i set min. = 15 ms max. = 30 ms - reset time at 0 to 2 x i set min. = 15 ms max. = 30 ms - overcurrent: inverse tim...
Page 599
Function range or value accuracy inverse time characteristics, see table 971 3 curve types see table 971 high and low voltage limit, voltage dependent operation, step 1 - 2 (1.0 - 200.0)% of ubase ±1.0% of u r at u ≤ u r ±1.0% of u at u > u r directional function settable: nondir, forward and revers...
Page 600
594.
Page 601
Section 12 system protection and control 12.1 multipurpose filter smaihpac 12.1.1 identification function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number multipurpose filter smaihpac - - 12.1.2 functionality the multi-purpose filter function block, smaihpa...
Page 602
Table 339: smaihpac output signals name type description ai3p group signal analog input 3-phase group ai1 group signal analog input 1 ai2 group signal analog input 2 ai3 group signal analog input 3 ai4 group signal analog input 4 12.1.5 settings table 340: smaihpac non group settings (basic) name va...
Page 603
Any signal (e.G. 37,2hz) present in the waveforms of the connected cts and/or vts. The magnitude and the phase angle of this phasor are calculated with very high precision. For example the magnitude and phase angle of the phasor can be estimated even if it has magnitude of one per mille (i.E. 1‰ ) i...
Page 604
The filter output can also be connected to the measurement function blocks such as cvmmxn (measurements), cmmxu (phase current measurement), vmmxu (phase-phase voltage measurement), etc. The filter has as well additional capability to report the exact frequency of the extracted signal. Thus the user...
Page 605
Second feature which is determined by the selected value for parameter filterlength is the capability of the filter to separate the desired signal from the other disturbing signals which may have similar frequency value. Note that the filter output will be the phasor with the highest magnitude withi...
Page 606
Some examples how this parameter influence the calculation rate for the extracted phasor: • when overlap=0% the new phasor value is calculated only once per filterlength • when overlap=50% the new phasor value is calculated two times per filterlength • when overlap=75% the new phasor value is calcul...
Page 607
The data shown in the figure comes from the comtrade file captured by the ied. The following traces are presented in this figure. A) waveforms of the stator three-phase currents given in primary ka. B) rms value of the sub-synchronous resonance current extracted by the filter in primary amperes. C) ...
Page 608
602.
Page 609
Section 13 secondary system supervision 13.1 current circuit supervision ccsspvc 13.1.1 identification function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number current circuit supervision ccsspvc - 87 13.1.2 functionality open or short circuited current tr...
Page 610
13.1.4 signals table 343: ccsspvc input signals name type default description i3p group signal - group signal for three phase current input iref group signal - residual reference current input block boolean 0 block of function table 344: ccsspvc output signals name type description fail boolean dete...
Page 613
13.2.2 functionality the aim of the fuse failure supervision function fufspvc is to block voltage measuring functions at failures in the secondary circuits between the voltage transformer and the ied in order to avoid inadvertent operations that otherwise might occur. The fuse failure supervision fu...
Page 614
13.2.4 signals table 349: fufspvc input signals name type default description i3p group signal - current connection u3p group signal - voltage connection block boolean 0 block of function cbclosed boolean 0 active when circuit breaker is closed mcbop boolean 0 active when external mcb opens protecte...
Page 615
13.2.5 settings table 351: fufspvc group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description operation off on - - off operation off / on opmode off unsins uzsizs uzsizs or unsins uzsizs and unsins optimzsns - - uzsizs operating mode selection 3u0> 1 - 100 %ub 1 30 operate level of res...
Page 616
13.2.6 monitored data table 353: fufspvc monitored data name type values (range) unit description 3i0 real - a magnitude of zero sequence current 3i2 real - a magnitude of negative sequence current 3u0 real - kv magnitude of zero sequence voltage 3u2 real - kv magnitude of negative sequence voltage ...
Page 617
Il1 il2 il3 zero sequence filter negative sequence filter ul1 ul2 ul3 zero sequence filter negative sequence filter currzeroseq currnegseq a b a>b a b a>b a b a>b a b a>b 3i2 t 100 ms t 100 ms voltzeroseq voltnegseq and and fusefaildetzeroseq fusefaildetnegseq sequence detection 3u0> 3u2> 3i0 3i2 3u...
Page 618
Opening of the breaker, which might cause unbalance conditions for which the fuse failure might operate. The output signal blkz will also be blocked if the internal dead line detection is activated. The dead line detection signal has a 200 ms drop-out time delay. The input signal mcbop is supposed t...
Page 619
In addition to the above conditions, at least one of the following conditions shall be fulfilled in order to activate the internal fusefaildetdudi signal: • the magnitude of the phase currents in three phases are higher than the setting iph> • the circuit breaker is closed (cbclosed = true) the firs...
Page 620
Di ul1 du> a b a>b t 20 ms t 1.5 cycle and dudi detection phase 1 uph> dudi detection phase 2 same logic as for phase 1 il1 dudi detection phase 3 same logic as for phase 1 ul3 a b a ul1 il1 a b a>b iph> and and cbclosed or or and a b a ul2 il2 a b a>b and and or or and a b a ul3 il3 a b a>b and and...
Page 621
Deltail1 deltaul1 deltail2 deltaul2 deltail3 deltaul3 stdil1 stdil2 stdil3 stdi stdu stdul1 stdul2 stdul3 iec12000165-1-en.Vsd intblock or or 20 ms 20 ms or t 20 ms t 20 ms t 20 ms and and and and and and and and t 20 ms t 20 ms t 20 ms t 20 ms t t iec12000165 v1 en figure 291: internal signals delt...
Page 622
Il1 il2 il3 a b a a b a a b a idld ul1 ul2 ul3 a b a a b a a b a udld or and and and and and and and allcurrlow deadlinedet1ph dld3ph dld1ph intblock dead line detection iec10000035-1-en.Vsd iec10000035 v2 en figure 292: simplified logic diagram for dead line detection part 13.2.7.4 main logic a sim...
Page 623
As soon as any fuse failure situation is detected, signals fusefaildetzeroseq, fusefaildetnegseq or fusefaildetdudi, and the specific functionality is released, the function will activate the output signal blku. The output signal blkz will be activated as well if the internal dead phase detection, d...
Page 624
Sealin = on all ul usealin any ul usealin t 5 s and 3ph mcbop all ul > usealin t 60 s cbclosed block and test test active and blocfuse = yes opmode and t 200 ms and or discpos blku blkz and and fusefaildetzeroseq uzsizs or unsins uzsizs and unsins uzsizs unsins optimzsns and fusefaildetnegseq or and...
Page 625
13.2.8 technical data table 354: fufspvctechnical data function range or value accuracy operate voltage, zero sequence (1-100)% of ubase ± 0.5% of u r operate current, zero sequence (1–100)% of ibase ± 0.5% of i r operate voltage, negative sequence (1-100)% of ubase 0.5% of u r operate current, nega...
Page 626
Vdspvc is designed to detect fuse failures or faults in voltage measurement circuit, based on phase wise comparison of voltages of main and pilot fused circuits. Vdspvc blocking output can be configured to block functions that need to be blocked in case of faults in the voltage circuit. 13.3.3 funct...
Page 627
13.3.5 settings table 357: vdspvc group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description operation off on - - off operation mode off / on ud>mainblock 10.0 - 80.0 %ub 0.1 20.0 blocking picked up voltage level in % of ubase when main fuse fails ud>pilotalarm 10.0 - 80.0 %ub 0.1 30.0...
Page 628
13.3.7 operation principle vdspvc requires six voltage inputs, which are the three phase voltages on main and pilot fuse groups. The initial voltage difference between the two groups is theoretical zero in the healthy condition. Any subsequent voltage difference will be due to a fuse failure. If the...
Page 629
13.3.8 technical data table 361: vdspvc technical data function range or value accuracy operate value, block of main fuse failure (10.0-80.0)% of ubase ±0.5% of ur reset ratio operate time, block of main fuse failure at 1 to 0 x u r min. = 5 ms – max. = 15 ms reset time, block of main fuse failure a...
Page 630
624.
Page 631
Section 14 control 14.1 synchrocheck, energizing check, and synchronizing sesrsyn 14.1.1 identification function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number synchrocheck, energizing check, and synchronizing sesrsyn sc/vc symbol-m v1 en 25 14.1.2 functi...
Page 632
14.1.3 function block sesrsyn u3pbb1* u3pbb2* u3pln1* u3pln2* block blksynch blksc blkenerg b1qopen b1qcld b2qopen b2qcld ln1qopen ln1qcld ln2qopen ln2qcld ub1ok ub1ff ub2ok ub2ff uln1ok uln1ff uln2ok uln2ff startsyn tstsynch tstsc tstenerg aenmode menmode synok autosyok autoenok mansyok manenok tst...
Page 633
Name type default description b1qopen boolean 0 open status for cb or disconnector connected to bus1 b1qcld boolean 0 close status for cb or disconnector connected to bus1 b2qopen boolean 0 open status for cb or disconnector connected to bus2 b2qcld boolean 0 close status for cb or disconnector conn...
Page 634
Name type description uselfail boolean selected voltage transformer fuse failed b1sel boolean bus1 selected b2sel boolean bus2 selected ln1sel boolean line1 selected ln2sel boolean line2 selected synprogr boolean synchronizing in progress synfail boolean synchronizing failed uoksyn boolean voltage a...
Page 635
Name values (range) unit step default description uhighlinesynch 50.0 - 120.0 %ubl 1.0 80.0 voltage high limit line for synchronizing in % of ubaseline udiffsynch 0.02 - 0.50 pu 0.01 0.10 voltage difference limit for synchronizing in p.U of set voltage base value freqdiffmin 0.003 - 0.250 hz 0.001 0...
Page 636
Name values (range) unit step default description ulowbusenerg 10.0 - 80.0 %ubb 1.0 40.0 voltage low limit bus for energizing check in % of ubasebus ulowlineenerg 10.0 - 80.0 %ubl 1.0 40.0 voltage low limit line for energizing check in % of ubaseline umaxenerg 50.0 - 180.0 %ub 1.0 115.0 maximum volt...
Page 637
Table 366: sesrsyn non group settings (advanced) name values (range) unit step default description phaseshift -180 - 180 deg 1 0 additional phase angle for selected line voltage 14.1.6 monitored data table 367: sesrsyn monitored data name type values (range) unit description udiffme real - - calcula...
Page 638
The internal logic for each function block as well as, the input and outputs, and the setting parameters with default setting and setting ranges is described in this document. For application related information, please refer to the application manual. 14.1.7.2 logic diagrams logic diagrams the logi...
Page 639
A number of outputs are available as information about fulfilled checking conditions. Uoksc shows that the voltages are high, udiffsc, frdiffa, frdiffm, phdiffa, phdiffm shows when the voltage difference, frequency difference and phase angle difference conditions are out of limits. Output inadvcls, ...
Page 640
The function will compare the values for the bus and line voltage with the set values for uhighbussynch and uhighlinesynch, which is a supervision that the voltages are both live. Also the voltage difference is checked to be smaller than the set value for udiffsynch, which is a p.U value of set volt...
Page 641
Or and s r udiffsynch uhighbussynch uhighlinesynch freqdiffmax freqdiffmin freqratechange and t 50 ms and and and and tclose pulse and startsyn blksynch synprogr synok synfail tmax synch tstsynok iec06000636-4-en.Vsd fbus&fline ± 5hz phase diff phasediff=closing angle tbreaker freqdiff close pulse i...
Page 642
Be 1=off, 2=dllb, 3=dbll and 4= both. Not connected input will mean that the setting is done from parameter setting tool. The active position can be read on outputs modeaen resp modemen. The modes are 0=off, 1=dllb, 2=dbll and 3=both. The inputs block and blkenerg are available for total block of th...
Page 643
Fbus and fline ±5 hz autoenerg uhighbusenerg ulowlineenerg and ulowbusenerg uhighlineenerg and or and or t tautoenerg and and umaxenerg autoenok tstenok selectedfuseok or block blkenerg tstenerg dllb dbll iec14000030-1-en.Vsd both iec14000030 v1 en figure 300: automatic energizing manenerg cbconfig ...
Page 644
Fuse failure supervision external fuse failure signals or signals from a tripped fuse switch/mcb are connected to binary inputs that are configured to the inputs of sesrsyn function in the ied. Alternatively, the internal signals from fuse failure supervision can be used when available. There are tw...
Page 645
The function checks the fuse-failure signals for bus 1, bus 2 and line voltage transformers. Inputs ub1ok-ub1ff supervise the mcb for bus 1 and ub2ok- ub2ff supervises the mcb for bus 2. Uln1ok and uln1ff supervises the mcb for the line voltage transformer. The inputs fail (ff) or healthy (ok) can a...
Page 646
This voltage selection function uses the binary inputs from the disconnectors and circuit breakers auxiliary contacts to select the right voltage for the sesrsyn function. For the bus circuit breaker one side of the circuit breaker is connected to the busbar and the other side is connected either to...
Page 647
And and or or uln1ff uln1ok ub1ff ub1ok ub2ff ub2ok b1qcld b1qopen ln1qcld ln1qopen block ln1sel and and uselfail uln2ff uln2ok or and and b2qcld b2qopen ln2qcld ln2qopen and and ln2sel or and b2sel and and and en05000780-2.Vsd or or line2voltage bus2voltage line1voltage invalidselection linevoltage...
Page 648
And and or or uln1ff uln1ok ub1ff ub1ok ub2ff ub2ok b1qcld b1qopen ln1qcld ln1qopen block line1voltage ln1sel and and uselfail uln2ff uln2ok or and and and and and 1 b1sel bus1voltage and and and b2qcld b2qopen ln2qcld ln2qopen bus2voltage ln2sel and and 1 b2sel line2voltage or en05000781-2.Vsd or o...
Page 649
14.1.8 technical data table 368: sesrsyn technical data function range or value accuracy phase shift, j line - j bus (-180 to 180) degrees - voltage high limit for synchronizing and synchrocheck (50.0-120.0)% of ubase ± 0.5% of u r at u ≤ u r ± 0.5% of u at u > u r reset ratio, synchrocheck > 95% - ...
Page 650
Function range or value accuracy time delay for energizing check when voltage jumps from 0 to 90% of urated (0.000-60.000) s ± 0.2% or ± 100 ms whichever is greater operate time for synchrocheck function when angle difference between bus and line jumps from “phasediff” + 2 degrees to “phasediff” - 2...
Page 651
The open or closed positions of the hv apparatuses are inputs to software modules distributed in the control ieds. Each module contains the interlocking logic for a bay. The interlocking logic in a module is different, depending on the bay function and the switchyard arrangements, that is, double-br...
Page 652
Disc qb1 and qb2 closed wa1 not earthed wa2 not earthed wa1 and wa2 interconn disc qb1 and qb2 closed wa1 not earthed wa2 not earthed wa1 and wa2 interconn . . . . . Station bus qb1 wa1 wa2 bay 1 bay n bus coupler wa1 unearthed wa1 unearthed wa1 and wa2 interconn wa1 and wa2 interconn in other bay q...
Page 653
Switch on the other side of the transformer, if there is no disconnector between cb and transformer. • circuit breaker opening is only interlocked in a bus-coupler bay, if a bus bar transfer is in progress. To make the implementation of the interlocking function easier, a number of standardized and ...
Page 654
14.2.3.3 function block iec05000359-2-en.Vsd scilo posopen posclose open_en close_en en_open en_close iec05000359 v2 en figure 307: scilo function block 14.2.3.4 signals table 369: scilo input signals name type default description posopen boolean 0 open position of switch device posclose boolean 0 c...
Page 655
Open_en posopen posclose 1 en_open en_close close_en scilo =1 & >1 >1 & & & en04000525.Vsd iec04000525 v1 en figure 308: scilo function logic diagram 14.2.4 interlocking for busbar earthing switch bb_es 14.2.4.1 identification function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification an...
Page 656
14.2.4.3 function block iec05000347-2-en.Vsd bb_es qc_op qc_cl bb_dc_op vp_bb_dc exdu_bb qcrel qcitl bbesoptr bbescltr iec05000347 v2 en figure 310: bb_es function block 14.2.4.4 logic diagram exdu_bb en04000546.Vsd vp_bb_dc bb_dc_op 1 qcrel qcitl & bbesoptr bbescltr qc_op qc_cl bb_es iec04000546 v1...
Page 657
14.2.5.1 identification function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number interlocking for bus-section breaker a1a2_bs - 3 14.2.5.2 functionality the interlocking for bus-section breaker (a1a2_bs) function is used for one bus- section circuit breake...
Page 658
14.2.5.3 function block iec05000348-2-en.Vsd a1a2_bs qa1_op qa1_cl qb1_op qb1_cl qb2_op qb2_cl qc3_op qc3_cl qc4_op qc4_cl s1qc1_op s1qc1_cl s2qc2_op s2qc2_cl bbtr_op vp_bbtr exdu_12 exdu_es qa1o_ex1 qa1o_ex2 qa1o_ex3 qb1_ex1 qb1_ex2 qb2_ex1 qb2_ex2 qa1oprel qa1opitl qa1clrel qa1clitl qb1rel qb1itl ...
Page 659
14.2.5.4 logic diagram qa1_op qb1_op qa1_cl qb1_cl qb2_cl qb2_op qc3_op qc4_cl s2qc2_cl qc4_op s2qc2_op s1qc1_cl s1qc1_op 1 qa1opitl qa1oprel en04000542.Vsd =1 =1 =1 =1 =1 =1 =1 qc3_cl vps2qc2 vps1qc1 vpqc4 vpqc3 vpqb2 vpqb1 vpqa1 a1a2_bs & >1 & & vpqb1 qb1_op qa1o_ex1 vpqb2 qb2_op qa1o_ex2 vp_bbtr ...
Page 660
Vpqa1 vpqc4 vpqc3 vps2qc2 qc3_op qa1_op qc4_op exdu_es vps2qc2 s2qc2_op qb2_ex1 vpqc4 s2qc2_cl qc4_cl qb1_op qb2_op qb1_op qa1_op qb2_cl vpqb2 qb2_op vpqb1 qb1_cl qb1_op vpqb2 vpqb1 vpqa1 1 qb2itl qb2rel en04000543.Vsd exdu_es qb2_ex2 vpqb1 vpqb2 1 qc3rel qc3itl qb2_op >1 1 s1s2cltr qb2optr & & 1 qc...
Page 661
Name type default description exdu_12 boolean 0 no transm error from any bay connected to busbar 1 and 2 exdu_es boolean 0 no transm error from bays containing earth. Sw. Qc1 or qc2 qa1o_ex1 boolean 0 external open condition for apparatus qa1 qa1o_ex2 boolean 0 external open condition for apparatus ...
Page 662
14.2.6.1 identification function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number interlocking for bus-section disconnector a1a2_dc - 3 14.2.6.2 functionality the interlocking for bus-section disconnector (a1a2_dc) function is used for one bus-section disco...
Page 663
14.2.6.4 logic diagram qb_op qb_cl s1qc1_cl en04000544.Vsd =1 =1 =1 vpqb vpdctr dcoptr dccltr s1qc1_op s2qc2_op s2qc2_cl vps1qc1 vps2qc2 & >1 & & 1 qbopitl qboprel vps1qc1 vps2qc2 vps1_dc s1qc1_op s2qc2_op s1dc_op exdu_es exdu_bb qbop_ex1 vps1qc1 vps2qc2 vps2_dc s1qc1_op s2qc2_op s2dc_op exdu_es exd...
Page 664
Name type default description s2qc2_op boolean 0 qc2 on bus section 2 is in open position s2qc2_cl boolean 0 qc2 on bus section 2 is in closed position s1dc_op boolean 0 all disconnectors on bus section 1 are in open position s2dc_op boolean 0 all disconnectors on bus section 2 are in open position ...
Page 665
14.2.7.2 functionality the interlocking for bus-coupler bay (abc_bc) function is used for a bus-coupler bay connected to a double busbar arrangement according to figure 315 . The function can also be used for a single busbar arrangement with transfer busbar or double busbar arrangement without trans...
Page 666
14.2.7.3 function block iec05000350-2-en.Vsd abc_bc qa1_op qa1_cl qb1_op qb1_cl qb2_op qb2_cl qb7_op qb7_cl qb20_op qb20_cl qc1_op qc1_cl qc2_op qc2_cl qc11_op qc11_cl qc21_op qc21_cl qc71_op qc71_cl bbtr_op bc_12_cl vp_bbtr vp_bc_12 exdu_es exdu_12 exdu_bc qa1o_ex1 qa1o_ex2 qa1o_ex3 qb1_ex1 qb1_ex2...
Page 667
14.2.7.4 logic diagram qa1_op qb1_op qa1_cl qb1_cl qb20_cl qb20_op qb7_op qb2_cl qc11_op qc2_cl qb2_op qc2_op qc1_cl qc1_op qc11_cl qc71_op vpqb1 qc71_cl qb1_op qc21_cl qc21_op qa1o_ex1 vpqb2 vpqb1 qa1o_ex3 exdu_12 bbtr_op vp_bbtr qa1o_ex2 qb20_op vpqb20 vpqb7 vpqb20 1 qa1opitl qa1oprel qa1clrel 1 q...
Page 668
Vpqa1 vpqc1 vpqb1 vpqc2 qa1_op vpqc21 qb1_op qc2_op vpqb1 qb2_ex1 qc1_op exdu_es qc21_op vp_bc_12 exdu_bc vpqc1 qb2_ex2 vpqc21 bc_12_cl qb1_cl qc1_cl qb2_ex3 exdu_es qc21_cl 1 qb2itl en04000535.Vsd & & >1 & qb2rel iec04000535 v1 en vpqa1 vpqc1 vpqb20 vpqc2 qa1_op vpqc71 qb20_op qc2_op vpqc2 qb7_ex1 ...
Page 669
Vpqb1 vpqb7 vpqb20 vpqb2 qb20_op qb1_op qb7_op qb1_op qb2_op qb2_op vpqb1 qb1_cl qb20_op vpqb2 vpqb20 vpqb1 vpqa1 qb7_op vpqb1 qa1_op qb1_op vpqb1 vpqa1 qb20_op qb1_op qa1_op qb2_op vpqb7 vpqa1 qb7_op vpqb2 qa1_op vpqb7 1 1 qc1itl qc1rel qc2rel qc2itl bc27optr 1 en04000537.Vsd & & & qb220otr 1 qb220...
Page 670
Name type default description qc11_cl boolean 0 earthing switch qc11 on busbar wa1 is in closed position qc21_op boolean 0 earthing switch qc21 on busbar wa2 is in open position qc21_cl boolean 0 earthing switch qc21 on busbar wa2 is in closed position qc71_op boolean 0 earthing switch qc71 on busba...
Page 671
Name type description qb1rel boolean switching of qb1 is allowed qb1itl boolean switching of qb1 is forbidden qb2rel boolean switching of qb2 is allowed qb2itl boolean switching of qb2 is forbidden qb7rel boolean switching of qb7 is allowed qb7itl boolean switching of qb7 is forbidden qb20rel boolea...
Page 672
14.2.8 interlocking for 1 1/2 cb bh 14.2.8.1 identification function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number interlocking for 1 1/2 breaker diameter bh_conn - 3 interlocking for 1 1/2 breaker diameter bh_line_a - 3 interlocking for 1 1/2 breaker di...
Page 673
14.2.8.3 function blocks bh_line_a qa1_op qa1_cl qb6_op qb6_cl qb1_op qb1_cl qc1_op qc1_cl qc2_op qc2_cl qc3_op qc3_cl qb9_op qb9_cl qc9_op qc9_cl cqa1_op cqa1_cl cqb61_op cqb61_cl cqc1_op cqc1_cl cqc2_op cqc2_cl qc11_op qc11_cl volt_off volt_on exdu_es qb6_ex1 qb6_ex2 qb1_ex1 qb1_ex2 qb9_ex1 qb9_ex...
Page 674
Iec05000353-2-en.Vsd bh_line_b qa1_op qa1_cl qb6_op qb6_cl qb2_op qb2_cl qc1_op qc1_cl qc2_op qc2_cl qc3_op qc3_cl qb9_op qb9_cl qc9_op qc9_cl cqa1_op cqa1_cl cqb62_op cqb62_cl cqc1_op cqc1_cl cqc2_op cqc2_cl qc21_op qc21_cl volt_off volt_on exdu_es qb6_ex1 qb6_ex2 qb2_ex1 qb2_ex2 qb9_ex1 qb9_ex2 qb...
Page 675
14.2.8.4 logic diagrams qa1_op qb61_op qa1_cl qb61_cl qb62_cl qb62_op qc1_op qc2_cl 2qc3_cl qc2_op 2qc3_op 1qc3_cl 1qc3_op en04000560.Vsd =1 =1 =1 =1 =1 =1 =1 qc1_cl vp2qc3 vp1qc3 vpqc2 vpqc1 vpqb62 vpqb61 vpqa1 bh_conn vpqb61 1 qa1clitl & 1 qb62itl qb62rel vpqa1 vpqc1 vpqc2 vp2qc3 qa1_op qc1_op qc2...
Page 676
Qa1_op qb1_op qa1_cl qb1_cl qb6_cl qb6_op qc9_op qb9_cl qc3_op qc2_cl qb9_op qc2_op qc1_cl qc1_op qc3_cl cqc1_op cqc1_cl cqa1_cl cqa1_op 1 qb6itl qb6rel en04000554.Vsd =1 =1 =1 =1 =1 =1 =1 =1 =1 =1 qc9_cl vpcqc1 vpcqa1 vpqc3 vpqc2 vpqc1 vpqb9 vpqc9 vpqb6 vpqb1 vpqa1 bh_line_a =1 =1 cqc2_op cqc2_cl c...
Page 677
Vpqa1 vpqb6 vpqc9 qb9_ex2 qb6_op qb9_ex1 vpcqc2 vpcqc1 vpcqb61 vpqc3 vpqc2 vpqc1 qa1_op 1 qb9itl qb9rel en04000555.Vsd & vpcqa1 >1 & & >1 & 1 qb1itl qb1rel 1 qc1itl qc1rel & 1 qc2itl qc2rel & 1 qc3itl qc3rel >1 qc1_op qc2_op qb9_ex3 vpqa1 vpqc1 vpqc2 vpqc11 qa1_op qc1_op qc2_op qc11_op exdu_es qb1_e...
Page 678
Qa1_op qb2_op qa1_cl qb2_cl qb6_cl qb6_op qc9_op qb9_cl qc3_op qc2_cl qb9_op qc2_op qc1_cl qc1_op qc3_cl cqc1_op cqc1_cl cqa1_cl cqa1_op 1 qb6itl qb6rel en04000557.Vsd =1 =1 =1 =1 =1 =1 =1 =1 =1 =1 qc9_cl vpcqc1 vpcqa1 vpqc3 vpqc2 vpqc1 vpqb9 vpqc9 vpqb6 vpqb2 vpqa1 bh_line_b =1 =1 cqc2_op cqc2_cl c...
Page 679
Vpqa1 vpqb6 vpqc9 qb9_ex2 qb6_op qb9_ex1 vpcqc2 vpcqc1 vpcqb62 vpqc3 vpqc2 vpqc1 qa1_op 1 qb9itl qb9rel en04000558.Vsd & vpcqa1 >1 & & >1 & 1 qb2itl qb2rel 1 qc1itl qc1rel & 1 qc2itl qc2rel & 1 qc3itl qc3rel >1 qc1_op qc2_op qb9_ex3 vpqa1 vpqc1 vpqc2 vpqc21 qa1_op qc1_op qc2_op qc21_op exdu_es qb2_e...
Page 680
14.2.8.5 signals table 379: bh_line_a input signals name type default description qa1_op boolean 0 qa1 is in open position qa1_cl boolean 0 qa1 is in closed position qb6_op boolean 0 qb6 is in open position qb6_cl boolean 0 qb6 is in close position qb1_op boolean 0 qb1 is in open position qb1_cl boo...
Page 681
Name type default description qb9_ex2 boolean 0 external condition for apparatus qb9 qb9_ex3 boolean 0 external condition for apparatus qb9 qb9_ex4 boolean 0 external condition for apparatus qb9 qb9_ex5 boolean 0 external condition for apparatus qb9 qb9_ex6 boolean 0 external condition for apparatus...
Page 682
Name type default description qc1_cl boolean 0 qc1 is in closed position qc2_op boolean 0 qc2 is in open position qc2_cl boolean 0 qc2 is in closed position qc3_op boolean 0 qc3 is in open position qc3_cl boolean 0 qc3 is in closed position qb9_op boolean 0 qb9 is in open position qb9_cl boolean 0 q...
Page 683
Table 382: bh_line_b output signals name type description qa1clrel boolean closing of qa1 is allowed qa1clitl boolean closing of qa1 is forbidden qb6rel boolean switching of qb6 is allowed qb6itl boolean switching of qb6 is forbidden qb2rel boolean switching of qb2 is allowed qb2itl boolean switchin...
Page 684
Name type default description qb61_ex2 boolean 0 external condition for apparatus qb61 qb62_ex1 boolean 0 external condition for apparatus qb62 qb62_ex2 boolean 0 external condition for apparatus qb62 table 384: bh_conn output signals name type description qa1clrel boolean closing of qa1 is allowed ...
Page 685
Wa1 (a) wa2 (b) qb1 qc1 qa1 qc2 qc9 qb61 qb9 qb2 qc4 qa2 qc5 qc3 qb62 db_bus_b db_line db_bus_a en04000518.Vsd iec04000518 v1 en figure 321: switchyard layout double circuit breaker three types of interlocking modules per double circuit breaker bay are defined. Db_bus_a handles the circuit breaker q...
Page 686
14.2.9.3 logic diagrams qa1_op qb61_op qa1_cl qb61_cl qb1_cl qb1_op qc1_op qc2_cl qc11_cl qc2_op qc11_op qc3_cl qc3_op en04000547.Vsd =1 =1 =1 =1 =1 =1 =1 qc1_cl vpqc11 vpqc3 vpqc2 vpqc1 vpqb1 vpqb61 vpqa1 db_bus_a vpqb61 1 qa1clitl & & >1 & 1 qb1itl qb1rel vpqa1 vpqc1 vpqc2 vpqc11 qa1_op qc1_op qc2...
Page 687
Qa2_op qb62_op qa2_cl qb62_cl qb2_cl qb2_op qc4_op qc5_cl qc21_cl qc5_op qc21_op qc3_cl qc3_op en04000552.Vsd =1 =1 =1 =1 =1 =1 =1 qc4_cl vpqc21 vpqc3 vpqc5 vpqc4 vpqb2 vpqb62 vpqa2 db_bus_b vpqb62 1 qa2clitl & & >1 & 1 qb2itl qb2rel vpqa2 vpqc4 vpqc5 vpqc21 qa2_op qc4_op qc5_op qc21_op vpqc4 vpqc21...
Page 688
Qa1_op qa2_op qa1_cl qa2_cl qb61_cl qb61_op qc1_op qc2_cl qc5_op qc4_cl qc2_op qc4_op qb62_cl qb62_op qc5_cl qc3_op qc3_cl qb9_cl qb9_op 1 qb9itl qb9rel en04000549.Vsd =1 =1 =1 =1 =1 =1 =1 =1 =1 =1 qc1_cl vpqc3 vpqb9 vpqc5 vpqc4 vpqb62 vpqc2 vpqc1 vpqb61 vpqa2 vpqa1 db_line =1 =1 qc9_op qc9_cl volt_...
Page 689
1 qc3itl qc3rel en04000551.Vsd vpqb62 vpqb9 qb61_op qb62_op qb9_op vpqb9 vpvolt qb9_op volt_off & & vpqb61 1 qc9itl qc9rel iec04000551 v1 en 14.2.9.4 function block iec05000354-2-en.Vsd db_bus_a qa1_op qa1_cl qb1_op qb1_cl qb61_op qb61_cl qc1_op qc1_cl qc2_op qc2_cl qc3_op qc3_cl qc11_op qc11_cl exd...
Page 690
Iec05000356-2-en.Vsd db_line qa1_op qa1_cl qa2_op qa2_cl qb61_op qb61_cl qc1_op qc1_cl qc2_op qc2_cl qb62_op qb62_cl qc4_op qc4_cl qc5_op qc5_cl qb9_op qb9_cl qc3_op qc3_cl qc9_op qc9_cl volt_off volt_on qb9_ex1 qb9_ex2 qb9_ex3 qb9_ex4 qb9_ex5 qb9rel qb9itl qc3rel qc3itl qc9rel qc9itl iec05000356 v2...
Page 691
14.2.9.5 signals table 385: db_bus_a input signals name type default description qa1_op boolean 0 qa1 is in open position qa1_cl boolean 0 qa1 is in closed position qb1_op boolean 0 qb1 is in open position qb1_cl boolean 0 qb1 is in closed position qb61_op boolean 0 qb61 is in open position qb61_cl ...
Page 692
Table 387: db_bus_b input signals name type default description qa2_op boolean 0 qa2 is in open position qa2_cl boolean 0 qa2 is in closed position qb2_op boolean 0 qb2 is in open position qb2_cl boolean 0 qb2 is in closed position qb62_op boolean 0 qb62 is in open position qb62_cl boolean 0 qb62 is...
Page 693
Table 389: db_line input signals name type default description qa1_op boolean 0 qa1 is in open position qa1_cl boolean 0 qa1 is in closed position qa2_op boolean 0 qa2 is in open position qa2_cl boolean 0 qa2 is in closed position qb61_op boolean 0 qb61 is in open position qb61_cl boolean 0 qb61 is ...
Page 694
14.2.10 interlocking for line bay abc_line 14.2.10.1 identification function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number interlocking for line bay abc_line - 3 14.2.10.2 functionality the interlocking for line bay (abc_line) function is used for a line...
Page 695
14.2.10.3 function block iec05000357-2-en.Vsd abc_line qa1_op qa1_cl qb9_op qb9_cl qb1_op qb1_cl qb2_op qb2_cl qb7_op qb7_cl qc1_op qc1_cl qc2_op qc2_cl qc9_op qc9_cl qc11_op qc11_cl qc21_op qc21_cl qc71_op qc71_cl bb7_d_op bc_12_cl bc_17_op bc_17_cl bc_27_op bc_27_cl volt_off volt_on vp_bb7_d vp_bc...
Page 696
14.2.10.4 logic diagram qa1_op qb9_op qa1_cl qb9_cl qb1_cl qb1_op qb2_op qb7_cl qc9_op qc2_cl qb7_op qc2_op qc1_cl qc1_op qc9_cl qc21_op qc21_cl qc11_cl qc11_op 1 qb9itl qb9rel en04000527.Vsd =1 =1 =1 =1 =1 =1 =1 =1 =1 =1 qb2_cl vpqc21 vpqc11 vpqc9 vpqc2 vpqc1 vpqb7 vpqb2 vpqb1 vpqb9 vpqa1 abc_line ...
Page 697
& & & ³1 qb1rel qb1itl vpqa1 vpqb2 vpqc1 vpqc2 vpqc11 qa1_op qb2_op qc1_op qc2_op qc11_op exdu_es qb1_ex1 vpqb2 vp_bc_12 qb2_cl bc_12_cl exdu_bc qb1_ex2 vpqc1 vpqc11 qc1_cl qc11_cl exdu_es qb1ex3 en04000528.Vsd 1 iec04000528 v1 en 1mrk502052-uen b section 14 control 691 technical manual.
Page 698
& & & ³1 1 qb2rel qb2itl vpqa1 vpqb1 vpqc1 vpqc2 vpqc21 qa1_op qb1_op qc1_op qc2_op qc21_op exdu_es qb2_ex1 vpqb1 vp_bc_12 qb1_cl bc_12_cl exdu_bc qb2_ex2 vpqc1 vpqc21 qc1_cl qc21_cl exdu_es qb2_ex3 en04000529.Vsd iec04000529 v1 en section 14 1mrk502052-uen b control 692 technical manual.
Page 699
& & >1 1 vpqc9 vpqc71 vp_bb7_d vp_bc_17 vp_bc_27 qc9_op qc71_op exdu_es bb7_d_op exdu_bpb bc_17_op bc_27_op exdu_bc qb7_ex1 vpqa1 vpqb1 vpqc9 vpqb9 vpqc71 vp_bb7_d vp_bc_17 qa1_cl qb1_cl qc9_op qb9_cl qc71_op exdu_es bb7_d_op exdu_bpb bc_17_cl exdu_bc qb7_ex2 qb7rel qb7itl iec04000530 v1 en 1mrk5020...
Page 700
Vpqa1 vpqc9 vpqb2 vpqb9 vp_bb7_d vpqc71 vp_bc_27 qb2_cl exdu_es qa1_cl qc71_op qb9_cl qc9_op bb7_d_op bc_27_cl qb7_ex3 exdu_bc vpqc9 exdu_bpb vpqc71 qb2_op qb1_op vpqb9 vpqb2 vpqb1 qb7_ex4 exdu_es qc71_cl qc9_cl qb9_op vpqb7 qb9_op qb7_op vpvolt vpqb9 volt_off & & & & >1 1 1 qc1itl qc1rel qc2rel qc2...
Page 701
Vpqb2 vpqb1 qb2_op qb1_op 1 qb12cltr qb12optr en04000532.Vsd >1 & vpqb12tr qb7optr qb7cltr vpqb7tr qb7_op qb7_cl vpqb7 vpqb2 qb2_cl qb2_op qb2optr qb2cltr vpqb2tr qb1optr qb1cltr vpqb1tr qb1_op qb1_cl vpqb1 iec04000532 v1 en 14.2.10.5 signals table 391: abc_line input signals name type default descr...
Page 702
Name type default description qc21_cl boolean 0 earthing switch qc21 on busbar wa2 is in closed position qc71_op boolean 0 earthing switch qc71 on busbar wa7 is in open position qc71_cl boolean 0 earthing switch qc71 on busbar wa7 is in closed position bb7_d_op boolean 0 disconnectors on busbar wa7 ...
Page 703
Table 392: abc_line output signals name type description qa1clrel boolean closing of qa1 is allowed qa1clitl boolean closing of qa1 is forbidden qb9rel boolean switching of qb9 is allowed qb9itl boolean switching of qb9 is forbidden qb1rel boolean switching of qb1 is allowed qb1itl boolean switching...
Page 704
14.2.11.2 functionality the interlocking for transformer bay (ab_trafo) function is used for a transformer bay connected to a double busbar arrangement according to figure 327 . The function is used when there is no disconnector between circuit breaker and transformer. Otherwise, the interlocking fo...
Page 705
14.2.11.3 function block iec05000358-2-en.Vsd ab_trafo qa1_op qa1_cl qb1_op qb1_cl qb2_op qb2_cl qc1_op qc1_cl qc2_op qc2_cl qb3_op qb3_cl qb4_op qb4_cl qc3_op qc3_cl qc11_op qc11_cl qc21_op qc21_cl bc_12_cl vp_bc_12 exdu_es exdu_bc qa1_ex1 qa1_ex2 qa1_ex3 qb1_ex1 qb1_ex2 qb1_ex3 qb2_ex1 qb2_ex2 qb2...
Page 706
14.2.11.4 logic diagram qa1_op qb1_op qa1_cl qb1_cl qb2_cl qb2_op qc1_op qc2_cl qc3_op qb4_cl qc2_op qb4_op qb3_cl qb3_op qc3_cl qc21_op vpqb1 qc21_cl vpqb2 qc11_cl qc11_op vpqc1 qc3_cl qc2_cl qc1_cl qa1_ex3 qc3_op qa1_ex2 vpqb4 vpqb3 vpqc2 qa1_ex1 1 qa1clitl qa1clrel en04000538.Vsd =1 =1 =1 =1 =1 =...
Page 707
Vpqa1 vpqc1 vpqb1 vpqc2 vpqc21 vpqc3 qa1_op qc1_op exdu_es qb1_op qc21_op qc3_op qc2_op qb2_ex1 vp_bc_12 bc_12_cl qc3_op qb1_cl exdu_bc vpqc3 vpqb1 vpqc3 vpqc2 vpqc1 qb2_ex2 1 qb2itl en04000540.Vsd & & >1 & qb2rel vpqc21 qc1_cl qc2_cl qc3_cl qc21_cl exdu_es qb2_ex3 iec04000540 v1 en vpqb1 vpqb3 vpqb...
Page 708
Name type default description qc2_op boolean 0 qc2 is in open position qc2_cl boolean 0 qc2 is in closed position qb3_op boolean 0 qb3 is in open position qb3_cl boolean 0 qb3 is in closed position qb4_op boolean 0 qb4 is in open position qb4_cl boolean 0 qb4 is in closed position qc3_op boolean 0 q...
Page 709
Name type description qc2itl boolean switching of qc2 is forbidden qb1optr boolean qb1 is in open position qb1cltr boolean qb1 is in closed position qb2optr boolean qb2 is in open position qb2cltr boolean qb2 is in closed position qb12optr boolean qb1 or qb2 or both are in open position qb12cltr boo...
Page 710
14.2.12.4 logic diagram pos_eval position openpos closepos iec08000469-1-en.Vsd position including quality open/close position of switch device iec08000469-1-en v1 en only the value, open/close, and status is used in this function. Time information is not used. Input position (value) signal quality ...
Page 711
• select-execute principle to give high reliability • selection function to prevent simultaneous operation • selection and supervision of operator place • command supervision • block/deblock of operation • block/deblock of updating of position indications • substitution of position and quality indic...
Page 712
Four types of function blocks are available to cover most of the control and supervision within the bay. These function blocks are interconnected to form a control function reflecting the switchyard configuration. The total number used depends on the switchyard configuration. These four types are: •...
Page 713
Cause number name description supported 9 blocked-by-process control action is blocked due to some external event at process level that prevents a successful operation, for example blocking indication (eehealth in xcbr or xswi) x 10 blocked-by- interlocking control action is blocked due to interlock...
Page 714
Cause number name description supported -32 persistantintermedi atestate switch stopped in intermediate state x -33 switchreturnedtoin itpos switch returned to the initial position x -34 switchinbadstate switch is in a bad position state x -35 notexpectedfinalpo sition switch did not reach the expec...
Page 715
Internal cause number addcause in iec61850-8-1 name ed 2 ed 1 -24 24 -24 blocked_for_open_cmd -25 24 -25 blocked_for_close_cmd -30 24 -30 longoperationtime -31 16 -31 switchnotstartmoving -32 16 -32 persistantintermediatestate -33 22 -33 switchreturnedtoinitpos -34 4 -34 switchinbadstate -35 22 -35 ...
Page 716
Table 400: qcbay output signals name type description psto integer value for the operator place allocation upd_blkd boolean update of position is blocked cmd_blkd boolean function is blocked for commands loc boolean local operation allowed sta boolean station operation allowed rem boolean remote ope...
Page 717
To adapt the signals from the local hmi or from an external local/remote switch, the function blocks locrem and locremctrl are needed and connected to qcbay. Permitted source to operate (psto) the actual state of the operator place is presented by the value of the permitted source to operate, psto s...
Page 718
• blocking of position indications, bl_upd. This input will block all inputs related to apparatus positions for all configured functions within the bay. • blocking of commands, bl_cmd. This input will block all commands for all configured functions within the bay. • blocking of function, block. If t...
Page 719
14.3.5.2 signals table 403: locrem input signals name type default description ctrloff boolean 0 disable control locctrl boolean 0 local in control remctrl boolean 0 remote in control lhmictrl integer 0 lhmi control table 404: locrem output signals name type description off boolean control is disabl...
Page 720
Name type description hmictr7 integer bitmask output 7 to local remote lhmi input hmictr8 integer bitmask output 8 to local remote lhmi input hmictr9 integer bitmask output 9 to local remote lhmi input hmictr10 integer bitmask output 10 to local remote lhmi input hmictr11 integer bitmask output 11 t...
Page 721
Qcbay lr_ off lr_ loc lr_ rem lr_ valid bl_ upd bl_ cmd psto upd_ blkd cmd_ blkd locrem ctrloff locctrl remctrl lhmictrl off local remote valid locremctrl psto1 psto2 psto3 psto4 psto5 psto6 psto7 psto8 psto9 psto 10 psto 11 psto 12 hmictr1 hmictr2 hmictr3 hmictr4 hmictr5 hmictr6 hmictr7 hmictr8 hmi...
Page 722
14.3.6.1 functionality the switch controller (scswi) initializes and supervises all functions to properly select and operate switching primary apparatuses. The switch controller may handle and operate on one three-phase device or up to three one-phase devices. 14.3.6.2 function block block exe_op ps...
Page 723
Name type default description xposl1 group signal - group signal from xcbr/xswi per phase xposl2 group signal - group signal from xcbr/xswi per phase xposl3 group signal - group signal from xcbr/xswi per phase table 409: scswi output signals name type description exe_op boolean execute command for o...
Page 724
The l_sel input must be set before l_open or l_close is operated, if the control model is select before operate. 14.3.6.4 settings table 410: scswi non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description ctlmodel dir norm sbo enh - - sbo enh specifies control model type posdepen...
Page 725
Command sequence is finished. If an error occurs in one of the steps in the command sequence, the sequence is terminated. The last error (l_cause) can be read from the function block and used for example at commissioning. There is no relation between the command direction and the actual position. Fo...
Page 726
Blocking principles the blocking signals are normally coming from the bay control function (qcbay) and via the iec 61850 communication from the operator place. The different blocking possibilities are: • block/deblock of command. It is used to block command for operation of position. • blocking of f...
Page 727
Iec09000209-2-en.Vsd synchro check or scswi sxcbr close sync_ok exe_cl synchronizing function sy_inpro start_sy closecb sesrsyn canc_sy iec09000209 v2 en figure 335: example of interaction between scswi, sesrsyn (synchrocheck and synchronizing function) and sxcbr function time diagrams the switch co...
Page 728
Select tresresponse timer reservation granted res_grt t1>tresresponse, then 1- of-n-control in 'cause' is set t1 reservation request res_rq iec05000093-2-en.Vsd iec05000093 v2 en figure 337: tresresponse the timer texecutionfb supervises the time between the execute command and the command terminati...
Page 729
The parameter tsynchronizing is used to define the maximum allowed time between the start signal for synchronizing and the confirmation that synchronizing is in progress. Execute command sy_inpro sync_ok t2>tsynchronizing, then blocked-by-synchrocheck in 'cause' is set tsynchrocheck t1 start_sy tsyn...
Page 730
14.3.7.3 signals table 411: sxcbr input signals name type default description block boolean 0 block of function lr_swi boolean 0 local/remote switch indication from switchyard open boolean 0 pulsed signal used to immediately open the switch close boolean 0 pulsed signal used to immediately close the...
Page 731
14.3.7.4 settings table 413: sxcbr non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description tstartmove 0.000 - 60.000 s 0.001 0.100 supervision time for the apparatus to move after a command tintermediate 0.000 - 60.000 s 0.001 0.150 allowed time for intermediate position adaptiv...
Page 732
From i/o switchlr tru e fals e local= operation at switch yard level remote= operation at ied or higher level en05000096.Vsd iec05000096 v1 en figure 341: local/remote switch blocking principles sxcbr includes several blocking principles. The basic principle for all blocking signals is that they wil...
Page 733
When the position of the sxcbr is substituted, its iec 61850-8-1 data object is marked as “substituted", in addition to the substituted quality, but the position quality of the connected scswi is not dependent on the substitution indication in the quality, so it does not show that it is derived from...
Page 734
Exe_cl closepos exe_cl openpos adaptivepulse=false tclosepulse tclosepulse adaptivepulse=true en05000098.Vsd iec05000098 v1 en figure 343: execute output pulse if the pulse is set to be adaptive, it is not possible for the pulse to exceed topenpulse or tclosepulse. The execute output pulses are rese...
Page 735
Exe_op closepos exe_op openpos adaptivepulse=false topenpulse topenpulse adaptivepulse=true tstartmove timer en05000099.Vsd iec05000099 v1 en figure 344: open command with open position indication 14.3.8 circuit switch sxswi 14.3.8.1 functionality the purpose of circuit switch (sxswi) function is to...
Page 736
14.3.8.3 signals table 414: sxswi input signals name type default description block boolean 0 block of function lr_swi boolean 0 local/remote switch indication from switchyard open boolean 0 pulsed signal used to immediately open the switch close boolean 0 pulsed signal used to immediately close the...
Page 737
14.3.8.4 settings table 416: sxswi non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description tstartmove 0.000 - 60.000 s 0.001 3.000 supervision time for the apparatus to move after a command tintermediate 0.000 - 60.000 s 0.001 15.000 allowed time for intermediate position adapti...
Page 738
From i/o switchlr tru e fals e local= operation at switch yard level remote= operation at ied or higher level en05000096.Vsd iec05000096 v1 en figure 346: local/remote switch blocking principles sxswi includes several blocking principles. The basic principle for all blocking signals is that they wil...
Page 739
When the position of the sxswi is substituted, its iec 61850-8-1 data object is marked as “substituted", in addition to the substituted quality, but the position quality of the connected scswi is not dependent on the substitution indication in the quality, so it does not show that it is derived from...
Page 740
Exe_cl closepos exe_cl openpos adaptivepulse=false tclosepulse tclosepulse adaptivepulse=true en05000098.Vsd iec05000098 v1 en figure 348: execute output pulse if the pulse is set to be adaptive, it is not possible for the pulse to exceed topenpulse or tclosepulse. The execute output pulses are rese...
Page 741
Exe_op closepos exe_op openpos adaptivepulse=false topenpulse topenpulse adaptivepulse=true tstartmove timer en05000099.Vsd iec05000099 v1 en figure 349: open command with open position indication 14.3.9 bay reserve qcrsv 14.3.9.1 functionality the purpose of the reservation function is primarily to...
Page 742
14.3.9.3 signals table 417: qcrsv input signals name type default description exch_in integer 0 used for exchange signals between different bayres blocks res_rq1 boolean 0 signal for app. 1 that requests to do a reservation res_rq2 boolean 0 signal for app. 2 that requests to do a reservation res_rq...
Page 743
14.3.9.4 settings table 419: qcrsv non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description tcancelres 0.000 - 60.000 s 0.001 10.000 supervision time for canceling the reservation paramrequest1 other bays res. Only own bay res. - - only own bay res. Reservation of the own bay onl...
Page 744
Controller scswi. If the bay already is reserved the command sequence will be reset and the scswi will set the attribute "1-of-n-control" in the "cause" signal. Reservation of other bays when the function qcrsv receives a request from an apparatus in the own bay that requires other bays to be reserv...
Page 745
Qcrsv exch_in res_rq1 res_rq2 res_rq3 res_rq4 res_rq5 res_rq6 res_rq7 res_rq8 blk_res override res_data res_grt1 res_grt2 res_grt3 res_grt4 res_grt5 res_grt6 res_grt7 res_grt8 res_bays ack_to_b reserved exch_out qcrsv exch_in res_rq1 res_rq2 res_rq3 res_rq4 res_rq5 res_rq6 res_rq7 res_rq8 blk_res ov...
Page 746
Resin2 exch_in bay_ack bay_val bay_res ack_f_b any_ack valid_tx re_rq_b v_re_rq exch_out iec09000807_1_en.Vsd iec09000807 v1 en figure 353: resin2 function block 14.3.10.3 signals table 420: resin1 input signals name type default description bay_ack boolean 0 another bay has acknow. The reservation ...
Page 747
Table 423: resin2 output signals name type description ack_f_b boolean all other bays have acknow. The reserv. Req. From this bay any_ack boolean any other bay has acknow. The reserv. Req. From this bay valid_tx boolean the reserv. And acknow. Signals from other bays are valid re_rq_b boolean reques...
Page 748
En05000089.Vsd & ³1 ³1 & ³1 ³1 & ³1 futureuse ack_f_b any_ack valid_tx re_rq_b v _re_rq bay_val bay_res exch_in int bin bin int exch_out bay_ack iec05000089 v1 en figure 354: logic diagram for resin figure 355 describes the principle of the data exchange between all resin modules in the current bay....
Page 749
Bay 1 bay 2 bay n qcrsv res_data resin exch_in bay_ack bay_val bay_res ack_f_b any_ack valid_tx re_rq_b v_re_rq exch_out resin bay_ack bay_val bay_res ack_f_b any_ack valid_tx re_rq_b v_re_rq exch_out resin exch_in bay_ack bay_val bay_res ack_f_b any_ack valid_tx re_rq_b v_re_rq exch_out en05000090....
Page 750
Methods are available, the master-follower method, the circulating current method and the reverse reactance method. The first two methods require exchange of information between the parallel transformers and this is provided for within iec 61850-8-1. Voltage control includes many extra features such...
Page 751
Via coded binary (binary), binary coded decimal (bcd) signals or gray coded binary signals the tap changer control and supervision, (tcmyltc or tclyltc) decodes binary data from up to six binary inputs to an integer value. The input pattern may be decoded either as bin, bcd or gray format depending ...
Page 752
Table 426: binary, bcd and gray conversion iec06000522 v1 en the gray code conversion above is not complete and therefore the conversion from decimal numbers to gray code is given below. Section 14 1mrk502052-uen b control 746 technical manual.
Page 753
Table 427: gray code conversion iec06000523 v1 en via a ma input signal any of the six inputs on the ma card (mim) can be used for the purpose of tap changer position reading connected to the tap changer control and supervision, 6 binary inputs tcmyltc or 32 binary inputs tclyltc. 1mrk502052-uen b s...
Page 754
The measurement of the tap changer position via mim module is based on the principle that the specified ma input signal range (usually 4-20 ma) is divided into n intervals corresponding to the number of positions available on the tap changer. All ma values within one interval are then associated wit...
Page 755
Atccout man auto iblk pgtfwd pltrev qgtfwd qltrev revacblk uhigh ulow i3p1 i3p2 u3p2 block manctrl autoctrl psto ublk hourhunt dayhunt mferr follower master autoblk totblk adapt homing parallel single hunting t1pg vtalarm trfdisc icirc commerr outofpos horiz3 lva1 t1incld deblkaut horiz2 lva4 q2on s...
Page 756
Table 428: binary signals: atccout / yltcin signal description raisevolt order to tcmyltc or tclyltc to make a raise command lowervolt order to tcmyltc or tclyltc to make a lower command automaticctrl the regulation is in automatic control extraiseblock block raise commands extlowerblock block lower...
Page 757
Signal description termisforcedmaster activated when the transformer is selected master in the master-follower parallel control mode termismaster activated for the transformer that is master in the master-follower parallel control mode termreadyformsf activated when the transformer is ready for mast...
Page 758
Table 434: integer signals: yltcout / atccin signal description tapposition actual tap position as reported from the load tap changer numberofoperations accumulated number of tap changer operations tappositionmaxvolt tap position for highest voltage tappositionminvolt tap position for lowest voltage...
Page 759
Iec07000037_2_en.Vsd tclyltc yltcin* tcinprog inerr reseterr outerr rs_clcnt rs_opcnt parity bierr b1 b2 b3 b4 b5 b6 b7 b8 b9 b10 b11 b12 b13 b14 b15 b16 b17 b18 b19 b20 b21 b22 b23 b24 b25 b26 b27 b28 b29 b30 b31 b32 ma uraise ulower hiposal loposal poserral cmderral tcerral posout converr newpos h...
Page 760
Name type default description b1 boolean 0 bit 1 from tap changer for the tap position b2 boolean 0 bit 2 from tap changer for the tap position b3 boolean 0 bit 3 from tap changer for the tap position b4 boolean 0 bit 4 from tap changer for the tap position b5 boolean 0 bit 5 from tap changer for th...
Page 761
Name type default description bierr boolean 0 error bit from tap changer for the tap position b1 boolean 0 bit 1 from tap changer for the tap position b2 boolean 0 bit 2 from tap changer for the tap position b3 boolean 0 bit 3 from tap changer for the tap position b4 boolean 0 bit 4 from tap changer...
Page 762
Table 438: tclyltc output signals name type description uraise boolean raise voltage command to tap changer ulower boolean lower voltage command to tap changer hiposal boolean alarm for tap in highest volt position loposal boolean alarm for tap in lowest volt position poserral boolean alarm that ind...
Page 763
Table 442: tcmyltc non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description lowvolttap 1 - 63 - 1 1 tap position for lowest voltage highvolttap 1 - 63 - 1 33 tap position for highest voltage malow 0.000 - 25.000 ma 0.001 4.000 ma for lowest voltage tap position mahigh 0.000 - 25....
Page 764
Name values (range) unit step default description clfactor 1.0 - 3.0 - 0.1 2.0 adjustable factor for contact life function initclcounter 0 - 9999999 s 1 250000 cl counter start value enabtapcmd off on - - on enable commands to tap changer globalbasesel 1 - 12 - 1 1 selection of one of the global bas...
Page 765
Avoid unnecessary operation during shorter voltage deviations from the target value, and in order to coordinate with other automatic voltage controllers in the system. Tcmyltc and tclyltc are an interface between tr1atcc and tr8atcc and the transformer load tap changer. More specifically this means ...
Page 766
Function range or value accuracy level for number of counted raise/lower within 24 hours (0–100) operations/day - time window for hunting alarm (1–120) minutes - hunting detection alarm, max operations/window (3–30) operations/window - alarm level of active power in forward and reverse direction at ...
Page 767
Operating on pre-set values. Hardware switches are however sources for maintenance issues, lower system reliability and an extended purchase portfolio. The selector switch function eliminates all these problems. 14.5.3 function block slgapc block psto up down ^p01 ^p02 ^p03 ^p04 ^p05 ^p06 ^p07 ^p08 ...
Page 768
Table 449: slgapc output signals name type description p01 boolean selector switch position 1 p02 boolean selector switch position 2 p03 boolean selector switch position 3 p04 boolean selector switch position 4 p05 boolean selector switch position 5 p06 boolean selector switch position 6 p07 boolean...
Page 769
14.5.5 settings table 450: slgapc non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description operation off on - - off operation off/on nrpos 2 - 32 - 1 32 number of positions in the switch outtype pulsed steady - - steady output type, steady or pulse tpulse 0.000 - 60.000 s 0.001 0...
Page 770
And the block names are fully settable by the user. These names will appear in the menu, so the user can see the position names instead of a number. 14.5.7.1 graphical display there are two possibilities for slgapc • if it is used just for the monitoring, the switches will be listed with their actua...
Page 771
From the graphical display: iec06000421-2-en.Vsd i ../control/sld/switch smbrrec control wfm pilot setup off damage control dal ../control/sld/switch smbrrec control wfm pilot setup off p: disc n: disc fe ok cancel ../control/sld/switch smbrrec control wfm pilot setup off damage control dfw change t...
Page 772
14.6.2 functionality the selector mini switch vsgapc function block is a multipurpose function used for a variety of applications, as a general purpose switch. Vsgapc can be controlled from the menu or from a symbol on the single line diagram (sld) on the local hmi. 14.6.3 function block vsgapc bloc...
Page 773
14.6.5 settings table 454: vsgapc non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description operation off on - - off operation off / on ctlmodel dir norm sbo enh - - dir norm specifies the type for control model according to iec 61850 mode steady pulsed - - pulsed operation mode t...
Page 774
Ipos1 ipos2 name of displayed string default string value 0 0 posundefined p00 1 0 position1 p01 0 1 position2 p10 1 1 posbadstate p11 14.7 generic communication function for double point indication dpgapc 14.7.1 identification function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification a...
Page 775
Table 456: dpgapc output signals name type description position integer double point indication 14.7.5 settings the function does not have any parameters available in the local hmi or pcm600. 14.7.6 operation principle when receiving the input signals, dpgapc sends the signals over iec 61850-8-1 to ...
Page 776
14.8.3 function block spc8gapc block psto ^out1 ^out2 ^out3 ^out4 ^out5 ^out6 ^out7 ^out8 iec07000143-3-en.Vsd iec07000143 v3 en figure 363: spc8gapc function block 14.8.4 signals table 457: spc8gapc input signals name type default description block boolean 0 blocks the function operation psto integ...
Page 777
Name values (range) unit step default description pulsemode3 pulsed latched - - pulsed setting for pulsed/latched mode for output 3 tpulse3 0.01 - 6000.00 s 0.01 0.10 pulse time output 3 pulsemode4 pulsed latched - - pulsed setting for pulsed/latched mode for output 4 tpulse4 0.01 - 6000.00 s 0.01 0...
Page 778
14.9.2 functionality automationbits function for dnp3 (autobits) is used within pcm600 to get into the configuration of the commands coming through the dnp3 protocol. The autobits function plays the same role as functions goosebinrcv (for iec 61850) and multicmdrcv (for lon). 14.9.3 function block i...
Page 779
Table 461: autobits output signals name type description cmdbit1 boolean command out bit 1 cmdbit2 boolean command out bit 2 cmdbit3 boolean command out bit 3 cmdbit4 boolean command out bit 4 cmdbit5 boolean command out bit 5 cmdbit6 boolean command out bit 6 cmdbit7 boolean command out bit 7 cmdbi...
Page 780
Table 463: dnpgen non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description operation off on - - off operation mode off / on table 464: chserrs485 non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description baudrate 300 bd 600 bd 1200 bd 2400 bd 4800 bd 9600 bd 19...
Page 781
Table 466: ch1tcp non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description operation off tcp/ip udp-only - - off operation mode tcpiplisport 1 - 65535 - 1 20000 tcp/ip listen port udpportaccdata 1 - 65535 - 1 20000 udp port to accept udp datagrams from master udpportinitnul 1 - 6...
Page 782
Table 470: ch3tcp non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description operation off tcp/ip udp-only - - off operation mode tcpiplisport 1 - 65535 - 1 20000 tcp/ip listen port udpportaccdata 1 - 65535 - 1 20000 udp port to accept udp datagrams from master udpportinitnul 1 - 6...
Page 783
Name values (range) unit step default description masteraddres 0 - 65519 - 1 1 master address obj1defvar 1:bisinglebit 2:biwithstatus - - 1:bisinglebit object 1, default variation obj2defvar 1:bichwithouttim e 2:bichwithtime 3:bichwithreltim e - - 3:bichwithreltim e object 2, default variation obj3d...
Page 784
Name values (range) unit step default description confmultfrag no yes - - yes confirm each multiple fragment urenable no yes - - yes unsolicited response enabled urevclassmask off class 1 class 2 class 1 and 2 class 3 class 1 and 3 class 2 and 3 class 1, 2 and 3 - - off unsolicited response, event c...
Page 785
Table 476: mst1tcp non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description operation off on - - off operation off / on slaveaddress 0 - 65519 - 1 1 slave address masteraddres 0 - 65519 - 1 1 master address valmasteraddr no yes - - yes validate source (master) address masterip-ad...
Page 786
Table 477: mst1tcp non group settings (advanced) name values (range) unit step default description addrqueryenbl no yes - - yes address query enable tapplconftout 0.00 - 300.00 s 0.01 10.00 application layer confim timeout applmultfrgres no yes - - yes enable application for multiple fragment respon...
Page 787
Name values (range) unit step default description tselecttimeout 1.0 - 60.0 s 0.1 30.0 select timeout tbrokencontout 0 - 3600 s 1 0 broken connection timeout tkeepalivet 0 - 3600 s 1 10 keep-alive timer table 478: mst2tcp non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description o...
Page 788
Name values (range) unit step default description obj22defvar 1:bincnt32evwout t 2:bincnt16evwout t 5:bincnt32evwith t 6:bincnt16evwith t - - 1:bincnt32evwou tt object 22, default variation obj30defvar 1:ai32int 2:ai16int 3:ai32intwithoutf 4:ai16intwithoutf 5:ai32fltwithf 6:ai64fltwithf - - 3:ai32in...
Page 789
Name values (range) unit step default description turevbuftout2 0.00 - 60.00 s 0.01 5.00 unsolicited response class 2 event buffer timeout urevcntthold3 1 - 100 - 1 5 unsolicited response class 3 event count report treshold turevbuftout3 0.00 - 60.00 s 0.01 5.00 unsolicited response class 3 event bu...
Page 790
Name values (range) unit step default description obj4defvar 1:dichwithouttim e 2:dichwithtime 3:dichwithreltim e - - 3:dichwithreltim e object 4, default variation obj10defvar 1:bo 2:bostatus - - 2:bostatus object 10, default variation obj20defvar 1:bincnt32 2:bincnt16 5:bincnt32woutf 6:bincnt16wou...
Page 791
Name values (range) unit step default description urofflineretry 0 - 10 - 1 5 unsolicited response retries before off- line retry mode turretrydelay 0.00 - 60.00 s 0.01 5.00 unsolicited response retry delay in s turofflrtrydel 0.00 - 60.00 s 0.01 30.00 unsolicited response off-line retry delay in s ...
Page 792
Name values (range) unit step default description masteripnetmsk 0 - 18 ip address 1 255.255.255.255 master ip net mask obj1defvar 1:bisinglebit 2:biwithstatus - - 1:bisinglebit object 1, default variation obj2defvar 1:bichwithouttim e 2:bichwithtime 3:bichwithreltim e - - 3:bichwithreltim e object ...
Page 793
Name values (range) unit step default description confmultfrag no yes - - yes confirm each multiple fragment urenable no yes - - yes unsolicited response enabled urevclassmask off class 1 class 2 class 1 and 2 class 3 class 1 and 3 class 2 and 3 class 1, 2 and 3 - - off unsolicited response, event c...
Page 794
14.9.6 operation principle automationbits function (autobits) has 32 individual outputs which each can be mapped as a binary output point in dnp3. The output is operated by a "object 12" in dnp3. This object contains parameters for control-code, count, on-time and off-time. To operate an autobits ou...
Page 795
14.10.3 function block iec05000698-2-en.Vsd singlecmd block ^out1 ^out2 ^out3 ^out4 ^out5 ^out6 ^out7 ^out8 ^out9 ^out10 ^out11 ^out12 ^out13 ^out14 ^out15 ^out16 iec05000698 v3 en figure 365: singlecmd function block 14.10.4 signals table 484: singlecmd input signals name type default description b...
Page 796
14.10.5 settings table 486: singlecmd non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description operation off steady pulsed - - off operation off / on 14.10.6 operation principle single command, 16 signals (singlecmd) function has 16 binary output signals. The outputs can be indiv...
Page 797
Section 15 logic 15.1 tripping logic common 3-phase output smpptrc 15.1.1 identification function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number tripping logic common 3-phase output smpptrc i->o symbol-k v1 en 94 15.1.2 functionality a function block for ...
Page 798
15.1.4 signals table 487: smpptrc input signals name type default description block boolean 0 block of function blklkout boolean 0 blocks circuit breaker lockout output (cllkout) trin boolean 0 trip all phases trinl1 boolean 0 trip phase 1 trinl2 boolean 0 trip phase 2 trinl3 boolean 0 trip phase 3 ...
Page 799
15.1.5 settings table 489: smpptrc group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description operation off on - - off operation off / on program 3 phase 1ph/3ph 1ph/2ph/3ph - - 1ph/3ph three ph; single or three ph; single, two or three ph trip ttripmin 0.000 - 60.000 s 0.001 0.150 min...
Page 800
Inputs enable single- phase and two-phase tripping for those functions which do not have their own phase selection capability, and therefore which have just a single trip output and not phase segregated trip outputs for routing through the phase segregated trip inputs of the expanded smpptrc functio...
Page 801
Trinl1 psl1 trinl2 psl2 trinl3 psl3 - loop -loop trin l1trip or or or and and and or or or and or and or and and t twaitforphs l2trip l3trip iec10000056-3-en.Vsd 1 ptref 1 ptrz iec10000056 v3 en figure 369: phase segregated front logic 1mrk502052-uen b section 15 logic 795 technical manual.
Page 802
Iec10000268-2-en.Vsd l1trip l2trip l3trip p3ptr -loop rtrip strip ttrip 150 ms t or t 2000 ms or and or or 150 ms t or t 2000 ms or and or or and or 150 ms t t 2000 ms or and or or and and and block iec10000268 v2 en figure 370: additional logic for the 1ph/3ph operating mode section 15 1mrk502052-u...
Page 803
Iec05000520-4-en.Vsdx block ttripmin tevolvingfault ttripmin ttripmin tevolvingfault tevolvingfault iec05000520-wmf v4 en figure 371: additional logic for the 1ph/2ph/3ph operating mode 1mrk502052-uen b section 15 logic 797 technical manual.
Page 804
Iec05000521-3.Vsd iec05000521-wmf v3 en figure 372: final tripping circuits 15.1.7 technical data table 491: smpptrc technical data function range or value accuracy trip action 3-ph, 1/3-ph, 1/2/3-ph - minimum trip pulse length (0.000-60.000) s ± 0.2% or ± 30 ms whichever is greater 3-pole trip dela...
Page 805
15.2.2 functionality trip matrix logic tmagapc function is used to route trip signals and other logical output signals to different output contacts on the ied. The trip matrix logic function has 3 output signals and these outputs can be connected to physical tripping outputs according to the specifi...
Page 806
Name type default description blk3 boolean 0 block of output 3 input1 boolean 0 binary input 1 input2 boolean 0 binary input 2 input3 boolean 0 binary input 3 input4 boolean 0 binary input 4 input5 boolean 0 binary input 5 input6 boolean 0 binary input 6 input7 boolean 0 binary input 7 input8 boolea...
Page 807
15.2.5 settings table 494: tmagapc group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description operation off on - - off operation off / on pulsetime 0.050 - 60.000 s 0.001 0.150 output pulse time ondelay 0.000 - 60.000 s 0.001 0.000 output on delay time offdelay 0.000 - 60.000 s 0.001 0...
Page 808
Pulsetime ondelay output 1 pulsetime ondelay output 2 pulsetime ondelay output 3 input 17 input 32 input 1 input 16 iec09000612-3-en.Vsd ³1 ³1 ³1 ³1 & & & & & & ³1 ³1 t t t offdelay t t t t offdelay t offdelay t modeoutput1=pulsed modeoutput2=pulsed modeoutput3=pulsed iec09000612 v3 en figure 374: t...
Page 809
15.3.2 functionality the group alarm logic function almcalh is used to route several alarm signals to a common indication, led and/or contact, in the ied. 15.3.3 function block almcalh block input1 input2 input3 input4 input5 input6 input7 input8 input9 input10 input11 input12 input13 input14 input1...
Page 810
Table 497: almcalh output signals name type description alarm boolean or function betweeen inputs 1 to 16 15.3.5 settings table 498: almcalh group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description operation off on - - off operation off / on 15.3.6 operation principle the logic for g...
Page 811
15.4 logic for group warning wrncalh 15.4.1 identification function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number logic for group warning wrncalh - - 15.4.2 functionality the group warning logic function wrncalh is used to route several warning signals t...
Page 812
Name type default description input9 boolean 0 binary input 9 input10 boolean 0 binary input 10 input11 boolean 0 binary input 11 input12 boolean 0 binary input 12 input13 boolean 0 binary input 13 input14 boolean 0 binary input 14 input15 boolean 0 binary input 15 input16 boolean 0 binary input 16 ...
Page 813
15.4.7 technical data table 503: number of wrncalh instances function quantity with cycle time 3 ms 8 ms 100 ms wrncalh - - 5 15.5 logic for group indication indcalh 15.5.1 identification function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number logic for g...
Page 814
15.5.4 signals table 504: indcalh input signals name type default description block boolean 0 block of function input1 boolean 0 binary input 1 input2 boolean 0 binary input 2 input3 boolean 0 binary input 3 input4 boolean 0 binary input 4 input5 boolean 0 binary input 5 input6 boolean 0 binary inpu...
Page 815
When any one of 16 input signals (input1 to input16) has logical value 1, the ind output signal will get logical value 1. The function has a drop-off delay of 200 ms when all inputs are reset to provide a steady signal. Ind ³1 200 ms t iec13000193-1-en.Vsd input1 input16 iec13000193 v1 en 15.5.7 tec...
Page 816
• or function block. Each block has up to six inputs and two outputs where one is inverted. • pulsetimer function block can be used, for example, for pulse extensions or limiting of operation of outputs, settable pulse time. • rsmemory function block is a flip-flop that can reset or set an output fr...
Page 817
15.6.1.2 signals table 508: and input signals name type default description input1 boolean 1 input signal 1 input2 boolean 1 input signal 2 input3 boolean 1 input signal 3 input4 boolean 1 input signal 4 table 509: and output signals name type description out boolean output signal nout boolean inver...
Page 818
Table 512: gate output signals name type description out boolean output from gate 15.6.2.3 settings table 513: gate group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description operation off on - - off operation off/on 15.6.2.4 technical data table 514: number of gate instances logic blo...
Page 819
15.6.3.3 technical data table 517: number of inv instances logic block quantity with cycle time 3 ms 8 ms 100 ms inv 90 90 240 15.6.4 loop delay function block lld the logic loop delay function block (lld) function is used to delay the output signal one execution cycle, that is, the cycle time of th...
Page 820
15.6.5.1 function block iec04000405_2_en.Vsd or input1 input2 input3 input4 input5 input6 out nout iec04000405 v2 en figure 380: or function block 15.6.5.2 signals table 521: or input signals name type default description input1 boolean 0 input 1 to or gate input2 boolean 0 input 2 to or gate input3...
Page 821
15.6.6.1 function block pulsetimer input out iec04000407-3-en.Vsd iec04000407 v3 en figure 381: pulsetimer function block 15.6.6.2 signals table 524: pulsetimer input signals name type default description input boolean 0 input to pulse timer table 525: pulsetimer output signals name type description...
Page 822
Table 528: truth table for rsmemory function block reset set out nout 0 0 last value inverted last value 0 1 1 0 1 0 0 1 1 1 0 1 15.6.7.1 function block rsmemory set reset out nout iec09000294-1-en.Vsd iec09000294 v1 en figure 382: rsmemory function block 15.6.7.2 signals table 529: rsmemory input s...
Page 823
15.6.8 set-reset with memory function block srmemory the set-reset with memory function block (srmemory) is a flip-flop with memory that can set or reset an output from two inputs respectively. Each srmemory function block has two outputs, where one is inverted. The memory setting controls if, after...
Page 824
15.6.8.4 technical data table 537: number of srmemory instances logic block quantity with cycle time 3 ms 8 ms 100 ms srmemory 10 10 20 15.6.9 settable timer function block timerset the settable timer function block (timerset) timer has two outputs for the delay of the input signal at drop-out and a...
Page 825
Table 539: timerset output signals name type description on boolean output from timer, pick-up delayed off boolean output from timer, drop-out delayed 15.6.9.3 settings table 540: timerset group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description operation off on - - off operation off...
Page 826
15.6.10.2 signals table 543: xor input signals name type default description input1 boolean 0 input 1 to xor gate input2 boolean 0 input 2 to xor gate table 544: xor output signals name type description out boolean output from xor gate nout boolean inverted output from xor gate 15.6.10.3 technical d...
Page 827
• invalidqt function which sets quality invalid of outputs according to a "valid" input. Inputs are copied to outputs. If input valid is 0, or if its quality invalid bit is set, all outputs invalid quality bit will be set to invalid. The time stamp of an output will be set to the latest time stamp o...
Page 828
15.7.1.1 function block andqt input1 input2 input3 input4 out nout iec09000297-1-en.Vsd iec09000297 v1 en figure 387: andqt function block 15.7.1.2 signals table 546: andqt input signals name type default description input1 boolean 1 input signal 1 input2 boolean 1 input signal 2 input3 boolean 1 in...
Page 829
15.7.2.1 function block indcombspqt sp_in* time* blocked* subst* invalid* test* sp_out iec15000146.Vsd iec15000146 v1 en figure 388: indcombspqt function block 15.7.2.2 signals table 549: indcombspqt input signals name type default description sp_in boolean 0 single point indication time group signa...
Page 830
Indextspqt can propagate the quality, the value and the time stamps of the signals via iec 61850. 15.7.3.1 function block indextspqt si_in* si_out time blocked subst invalid test iec14000067-1-en.Vsd iec14000067 v1 en figure 389: indextspqt function block 15.7.3.2 signals table 552: indextspqt input...
Page 831
All outputs outputx (where 1 stamp of any output outputx (where 1 any input and the input valid. Invalidqt can propagate the quality, the value and the time stamps of the signals via iec 61850. 15.7.4.1 function block invalidqt input1 input2 input3 input4 input5 input6 input7 input8 input9 input10 i...
Page 832
Name type default description input14 boolean 0 indication input 14 input15 boolean 0 indication input 15 input16 boolean 0 indication input 16 valid boolean 1 inputs are valid or not table 556: invalidqt output signals name type description output1 boolean indication output 1 output2 boolean indica...
Page 833
15.7.5.1 function block inverterqt input out iec09000299-1-en.Vsd iec09000299 v1 en figure 391: inverterqt function block 15.7.5.2 signals table 558: inverterqt input signals name type default description input boolean 0 input signal table 559: inverterqt output signals name type description out boo...
Page 834
15.7.6.1 function block orqt input1 input2 input3 input4 input5 input6 out nout iec09000298-1-en.Vsd iec09000298 v1 en figure 392: orqt function block 15.7.6.2 signals table 561: orqt input signals name type default description input1 boolean 0 input signal 1 input2 boolean 0 input signal 2 input3 b...
Page 835
When the input goes to 1, the output will be 1 for the time set by the time delay parameter t. Then it returns to 0. When the output changes value, the time stamp of the output signal is updated. The supported “quality” state bits are propagated from the input to the output at each execution cycle. ...
Page 836
15.7.8 reset/set function block rsmemoryqt the reset-set function (rsmemoryqt) is a flip-flop with memory that can reset or set an output from two inputs respectively. Each rsmemoryqt function block has two outputs, where one is inverted. The memory setting controls if, after a power interruption, t...
Page 837
15.7.8.3 settings table 571: rsmemoryqt group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description memory off on - - on operating mode of the memory function 15.7.8.4 technical data table 572: number of rsmemoryqt instances logic block quantity with cycle time 3 ms 8 ms 100 ms rsmemory...
Page 838
15.7.9.2 signals table 574: srmemoryqt input signals name type default description set boolean 0 input signal to set reset boolean 0 input signal to reset table 575: srmemoryqt output signals name type description out boolean output signal nout boolean inverted output signal 15.7.9.3 settings table ...
Page 839
15.7.10.1 function block timersetqt input on off iec14000068-1-en.Vsd iec14000068 v1 en figure 396: timersetqt function 15.7.10.2 signals table 578: timersetqt input signals name type default description input boolean 0 input signal table 579: timersetqt output signals name type description on boole...
Page 840
One of the outputs is inverted. The output signal out is 1 if the input signals are different and 0 if they are equal. Table 582: truth table for xorqt function block input1 input2 out nout 0 0 0 1 0 1 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 1 0 1 xorqt can propagate the quality, value and time stamps of the signals via iec ...
Page 841
15.8 extension logic package when extra configurable logic blocks are required, an additional package can be ordered. Table 586: number of instances in the extension logic package logic block quantity with cycle time 3 ms 8 ms 100 ms and 40 40 100 gate - - 49 inv 40 40 100 lld - - 49 or 40 40 100 pu...
Page 842
15.9.3 function block fxdsign off on intzero intone intalone realzero strnull zerosmpl grp_off iec05000445-3-en.Vsd iec05000445 v3 en figure 398: fxdsign function block 15.9.4 signals table 587: fxdsign output signals name type description off boolean boolean signal fixed off on boolean boolean sign...
Page 843
• strnull is a string, fixed to an empty string (null) value • zerosmpl is a channel index, fixed to 0 value • grp_off is a group signal, fixed to 0 value 15.10 boolean 16 to integer conversion b16i 15.10.1 identification function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ie...
Page 844
Name type default description in5 boolean 0 input 5 in6 boolean 0 input 6 in7 boolean 0 input 7 in8 boolean 0 input 8 in9 boolean 0 input 9 in10 boolean 0 input 10 in11 boolean 0 input 11 in12 boolean 0 input 12 in13 boolean 0 input 13 in14 boolean 0 input 14 in15 boolean 0 input 15 in16 boolean 0 i...
Page 845
The sum of the value on each inx corresponds to the integer presented on the output out on the function block b16i name of input type default description value when activated value when deactivated in1 boolean 0 input 1 1 0 in2 boolean 0 input 2 2 0 in3 boolean 0 input 3 4 0 in4 boolean 0 input 4 8 ...
Page 846
15.11.2 functionality boolean 16 to integer conversion with logic node representation function btigapc is used to transform a set of 16 binary (logical) signals into an integer. The block input will freeze the output at the last value. Btigapc can receive remote values via iec 61850 depending on the...
Page 847
Name type default description in13 boolean 0 input 13 in14 boolean 0 input 14 in15 boolean 0 input 15 in16 boolean 0 input 16 table 593: btigapc output signals name type description out integer output value 15.11.5 settings the function does not have any parameters available in the local hmi or pcm6...
Page 848
Name of input type default description value when activated value when deactivated in4 boolean 0 input 4 8 0 in5 boolean 0 input 5 16 0 in6 boolean 0 input 6 32 0 in7 boolean 0 input 7 64 0 in8 boolean 0 input 8 128 0 in9 boolean 0 input 9 256 0 in10 boolean 0 input 10 512 0 in11 boolean 0 input 11 ...
Page 849
15.12.3 function block ib16 block inp out1 out2 out3 out4 out5 out6 out7 out8 out9 out10 out11 out12 out13 out14 out15 out16 iec06000501-3-en.Vsdx iec06000501 v3 en figure 401: ib16 function block 15.12.4 signals table 596: ib16 input signals name type default description block boolean 0 block of fu...
Page 850
15.12.5 setting parameters the function does not have any parameters available in local hmi or protection and control ied manager (pcm600) 15.12.6 operation principle with integer 15 on the input inp the out1 = out2 = out3= out4 =1 and the remaining outx = 0 for (5≤x≤16). Outx represents a value whe...
Page 851
Name of outx type description value when activated value when deactivated out11 boolean output 11 1024 0 out12 boolean output 12 2048 0 out13 boolean output 13 4096 0 out14 boolean output 14 8192 0 out15 boolean output 15 16384 0 out16 boolean output 16 32768 0 the sum of the numbers in column “valu...
Page 852
Input block will freeze the output at the last received value and blocks new integer values to be received and converted to binary coded outputs. 15.13.3 function block itbgapc block psto out1 out2 out3 out4 out5 out6 out7 out8 out9 out10 out11 out12 out13 out14 out15 out16 iec14000012-1-en.Vsd iec1...
Page 853
Name type description out14 boolean output 14 out15 boolean output 15 out16 boolean output 16 15.13.5 settings this function does not have any setting parameters. 15.13.6 operation principle an example is used to explain the principle of operation: with integer 15 sent to and received by the itbgapc...
Page 854
Name of outx type description value when activated value when deactivated out8 boolean output 8 128 0 out9 boolean output 9 256 0 out10 boolean output 10 512 0 out11 boolean output 11 1024 0 out12 boolean output 12 2048 0 out13 boolean output 13 4096 0 out14 boolean output 14 8192 0 out15 boolean ou...
Page 855
15.14.3 function block tigapc in out tigapc in out iec14000013-1-en.Vsd iec14000013 v1 en figure 403: tigapc function block 15.14.4 signals table 603: tigapc input signals name type default description in boolean 0 input to integrator table 604: tigapc output signals name type description out boolea...
Page 856
Integration 0 0 0 t t t 1 t reset in t int t delay out iec13000175-2-en.Vsd iec13000175 v2 en figure 404: in pulse length sufficient for integration to reach the set t delay , out is set until the t reset time has elapsed, which resets t delay and out 0 0 0 t t t in integration 1 t int t delay trese...
Page 857
0 0 0 t t t 1 in integration t int t delay out treset treset treset iec13000177-2-en.Vsd iec13000177 v2 en figure 407: the next in pulse is received before t reset has elapsed. Sufficient time during the pulses is accumulated to reach t delay . When t delay is reached, out is set until t reset time ...
Page 858
15.15.2 functionality elapsed time integrator (teigapc) function is a function that accumulates the elapsed time when a given binary signal has been high, see also figure 408 . Time integration with retain block acctime reset in twarning talarm overflow warning alarm q -1 a>b a b a>b a b a>b a b and...
Page 859
15.15.4 signals table 608: teigapc input signals name type default description block boolean 0 freeze the integration and block the other outputs in boolean 0 the input signal that is used to measure the elapsed time, when its value is high reset boolean 0 reset the integration time table 609: teiga...
Page 860
Time integration transgression supervision plus retain block acctime reset in talarm overflow warning alarm iec12000195-4-en.Vsd loop delay loop delay twarning iec12000195 v4 en figure 410: teigapc simplified logic teigapc main functionalities • integration of the elapsed time when in has been high ...
Page 861
Talarm and twarning are possible to be defined with a resolution of 10 ms, depending on the level of the defined values for the parameters. The limit for the overflow supervision is fixed at 999999.9 seconds. The outputs freeze if an overflow occurs. 15.15.6.1 operation accuracy the accuracy of teig...
Page 862
856.
Page 863
Section 16 monitoring 16.1 measurements 16.1.1 identification function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number measurements cvmmxn p, q, s, i, u, f symbol-rr v1 en - phase current measurement cmmxu i symbol-ss v1 en - phase-phase voltage measuremen...
Page 864
For efficient production, transmission and distribution of electrical energy. It provides to the system operator fast and easy overview of the present status of the power system. Additionally, it can be used during testing and commissioning of protection and control ieds in order to verify proper op...
Page 865
It is possible to calibrate the measuring function above to get better then class 0.5 presentation. This is accomplished by angle and amplitude compensation at 5, 30 and 100% of rated current and at 100% of rated voltage. The power system quantities provided, depends on the actual hardware, (trm) an...
Page 866
Iec05000701-2-en.Vsd vmmxu u3p* ul12 ul12rang ul12angl ul23 ul23rang ul23angl ul31 ul31rang ul31angl iec05000701 v2 en figure 413: vmmxu function block iec05000703-2-en.Vsd cmsqi i3p* 3i0 3i0rang 3i0angl i1 i1rang i1angl i2 i2rang i2angl iec05000703 v2 en figure 414: cmsqi function block iec05000704...
Page 867
16.1.4 signals table 613: cvmmxn input signals name type default description i3p group signal - group signal for current input u3p group signal - group signal for voltage input table 614: cvmmxn output signals name type description s real apparent power magnitude of deadband value s_range integer ap...
Page 868
Name type description il2 real il2 amplitude, magnitude of reported value il2rang integer il2 amplitude range il2angl real il2 angle, magnitude of reported value il3 real il3 amplitude, magnitude of reported value il3rang integer il3 amplitude range il3angl real il3 angle, magnitude of reported valu...
Page 869
Name type description i2 real i2 amplitude, magnitude of reported value i2rang integer i2 amplitude range i2angl real i2 angle, magnitude of reported value table 621: vmsqi input signals name type default description u3p group signal - group connection abstract block 4 table 622: vmsqi output signal...
Page 870
16.1.5 settings the available setting parameters of the measurement function (mmxu, msqi) are depending on the actual hardware (trm) and the logic configuration made in pcm600. These six functions are not handled as a group, so parameter settings are only available in the first setting group. The fo...
Page 871
Name values (range) unit step default description ureptyp cyclic dead band int deadband - - cyclic reporting type imin 0.0 - 500.0 %ib 0.1 5.0 minimum value in % of ibase imax 0.0 - 500.0 %ib 0.1 200.0 maximum value in % of ibase ireptyp cyclic dead band int deadband - - cyclic reporting type frmin ...
Page 872
Name values (range) unit step default description plowlim -2000.0 - 2000.0 %sb 0.1 -120.0 low limit in % of sbase plowlowlim -2000.0 - 2000.0 %sb 0.1 -150.0 low low limit in % of sbase plimhyst 0.000 - 100.000 % 0.001 5.000 hysteresis value in % of range (common for all limits) qdbrepint 1 - 300 typ...
Page 873
Name values (range) unit step default description frhihilim 0.000 - 100.000 hz 0.001 65.000 high high limit (physical value) frhilim 0.000 - 100.000 hz 0.001 63.000 high limit (physical value) frlowlim 0.000 - 100.000 hz 0.001 47.000 low limit (physical value) frlowlowlim 0.000 - 100.000 hz 0.001 45...
Page 874
Name values (range) unit step default description il2angdbrepint 1 - 300 type 1 10 cycl: report interval (s), db: in % of range, int db: in %s il3dbrepint 1 - 300 type 1 10 cycl: report interval (s), db: in % of range, int db: in %s il3max 0.0 - 500.0 %ib 0.1 200.0 maximum value in % of ibase il3rep...
Page 875
Name values (range) unit step default description il3lowlowlim 0.0 - 500.0 %ib 0.1 60.0 low low limit in % of ibase il3min 0.0 - 500.0 %ib 0.1 50.0 minimum value in % of ibase il3limhys 0.000 - 100.000 % 0.001 5.000 hysteresis value in % of range and is common for all limits table 629: vmmxu non gro...
Page 876
Name values (range) unit step default description ul12lowlowlim 0.0 - 200.0 %ub 0.1 60.0 low low limit in % of ubase uampcomp100 -10.000 - 10.000 % 0.001 0.000 amplitude factor to calibrate voltage at 100% of ur ul12min 0.0 - 200.0 %ub 0.1 50.0 minimum value in in % of ubase ul12limhys 0.000 - 100.0...
Page 877
Name values (range) unit step default description i1dbrepint 1 - 300 type 1 10 cycl: report interval (s), db: in % of range, int db: in %s i1zerodb 0 - 100000 m% 1 1 zero point clamping i1min 0.0 - 500.0 %ib 0.1 50.0 minimum value in % of ibase i1max 0.0 - 500.0 %ib 0.1 200.0 maximum value in % of i...
Page 878
Name values (range) unit step default description i1angzerodb 0 - 100000 m% 1 0 zero point clamping in 0,001% of range i1angmin -180.000 - 180.000 deg 0.001 -180.000 minimum value i2hihilim 0.0 - 500.0 %ib 0.1 150.0 high high limit in % of ibase i2hilim 0.0 - 500.0 %ib 0.1 120.0 high limit in % of i...
Page 879
Name values (range) unit step default description u1angdbrepint 1 - 300 type 1 10 cycl: report interval (s), db: in % of range, int db: in %s u2dbrepint 1 - 300 type 1 10 cycl: report interval (s), db: in % of range, int db: in %s u2zerodb 0 - 100000 m% 1 1 zero point clamping u2min 0.0 - 200.0 %ub ...
Page 880
Name values (range) unit step default description u2lowlim 0.0 - 200.0 %ub 0.1 80.0 low limit in % of ubase u2lowlowlim 0.0 - 200.0 %ub 0.1 60.0 low low limit in % of ubase u2angzerodb 0 - 100000 m% 1 0 zero point clamping in 0,001% of range table 635: vnmmxu non group settings (basic) name values (...
Page 881
Table 636: vnmmxu non group settings (advanced) name values (range) unit step default description ul1hihilim 0.0 - 200.0 %ub 0.1 150.0 high high limit in % of ubase ul1hilim 0.0 - 200.0 %ub 0.1 120.0 high limit in % of ubase ul1lowlim 0.0 - 200.0 %ub 0.1 80.0 low limit in % of ubase ul1lowlowlim 0.0...
Page 882
Table 638: cmmxu monitored data name type values (range) unit description il1 real - a il1 amplitude, magnitude of reported value il1angl real - deg il1 angle, magnitude of reported value il2 real - a il2 amplitude, magnitude of reported value il2angl real - deg il2 angle, magnitude of reported valu...
Page 883
Name type values (range) unit description i1imag real - - i1 amplitude, magnitude of instantaneous value i1 real - a i1 amplitude, magnitude of reported value i1angim real - - i1 angle, magnitude of instantaneous value i1angl real - deg i1 angle, magnitude of reported value i2imag real - - i2 amplit...
Page 884
Table 642: vnmmxu monitored data name type values (range) unit description ul1 real - kv ul1 amplitude, magnitude of reported value ul1angl real - deg ul1 angle, magnitude of reported value ul2 real - kv ul2 amplitude, magnitude of reported value ul2angl real - deg ul2 angle, magnitude of reported v...
Page 885
Continuous monitoring of the measured quantity users can continuously monitor the measured quantity available in each function block by means of four defined operating thresholds, see figure 417 . The monitoring has two different modes of operating: • overfunction, when the measured current exceeds ...
Page 886
Of the value to the higher levels depends on the selected reporting mode. The following basic reporting modes are available: • cyclic reporting (cyclic) • amplitude dead-band supervision (dead band) • integral dead-band supervision (int deadband) cyclic reporting the cyclic reporting of measured val...
Page 887
Band supervision. The picture is simplified: the process is not continuous but the values are evaluated with a time interval of one execution cycle from each other. Iec99000529-2-en.Vsdx y t value reported (1st) value reported value reported y1 y2 y3 y y y y y y value reported iec99000529 v2 en figu...
Page 888
Iec99000530-2-en.Vsdx y t value reported (1st) y1 value reported a1 y2 value reported y3 y4 a value reported a2 y5 a3 a4 a5 a7 a6 value reported a2 >= pre-set value a1 >= pre-set value a >= pre-set value a3 + a4 + a5 + a6 + a7 >= pre-set value iec99000530 v2 en figure 420: reporting with integral de...
Page 889
Set value for parameter “mode” formula used for complex, three- phase power calculation formula used for voltage and current magnitude calculation comment 1 l1, l2, l3 * * * 1 1 2 2 3 3 = × + × + × l l l l l l s u i u i u i equation1385 v1 en 1 2 3 1 2 3 ( ) / 3 ( ) / 3 = + + = + + l l l l l l u u u...
Page 890
It shall be noted that only in the first two operating modes that is, 1 & 2 the measurement function calculates exact three-phase power. In other operating modes that is, from 3 to 9 it calculates the three-phase power under assumption that the power system is fully symmetrical. Once the complex app...
Page 891
Iec05000652 v2 en figure 421: calibration curves the first current and voltage phase in the group signals will be used as reference and the amplitude and angle compensation will be used for related input signals. Low pass filtering in order to minimize the influence of the noise signal on the measur...
Page 892
Default value for parameter k is 0.00. With this value the new calculated value is immediately given out without any filtering (that is, without any additional delay). When k is set to value bigger than 0, the filtering is enabled. Appropriate value of k shall be determined separately for every appl...
Page 893
Busbar protected object p q iec09000038-1-en.Vsd ied iec09000038-1-en v1 en figure 422: internal ied directionality convention for p & q measurements practically, it means that active and reactive power will have positive values when they flow from the busbar towards the protected object and they wi...
Page 894
Compensation at 5, 30 and 100% of rated current. The compensation below 5% and above 100% is constant and linear in between, see figure 421 . Phase currents (amplitude and angle) are available on the outputs and each amplitude output has a corresponding supervision level output (ilx_rang). The super...
Page 895
Function range or value accuracy active power, p 0.1 x u r r 0.2 x i r r ± 1.0% of s r at s ≤ s r ± 1.0% of s at s > s r conditions: 0.8 x u r r 0.2 x i r r reactive power, q 0.1 x u r r 0.2 x i r r apparent power, s 0.1 x u r r 0.2 x i r r power factor, cos (φ) 0.1 x u r r 0.2 x i r r ± 0.02 table ...
Page 896
Table 647: vmsqi technical data function range or value accuracy voltage positive sequence, u1 (10 to 300) v ± 0.5% of u at u ≤ 50 v ± 0.2% of u at u > 50 v voltage zero sequence, 3u0 (10 to 300) v ± 0.5% of u at u ≤ 50 v ± 0.2% of u at u > 50 v voltage negative sequence, u2 (10 to 300) v ± 0.5% of ...
Page 897
16.2.3 function block ssimg block blk_alm pressure temp pres_alm pres_lo set_p_lo set_t_lo reset_lo pressure pres_alm pres_lo temp temp_alm temp_lo iec09000129-1-en.Vsd iec09000129 v1 en figure 423: ssimg function block 16.2.4 signals table 649: ssimg input signals name type default description bloc...
Page 898
16.2.5 settings table 651: ssimg group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description operation off on - - off operation off / on pressalmlimit 1.00 - 100.00 - 0.01 5.00 alarm setting for pressure presslolimit 1.00 - 100.00 - 0.01 3.00 pressure lockout setting tempalarmlimit -40....
Page 899
When temperature input temp is greater than tempalarmlimit, then temperature alarm temp_alm will be initiated. Similarly, if temperature input temp is greater than templolimit, then temp_lo will be initiated. There may be sudden change in temperature of the medium for a very small time, for which th...
Page 900
16.3.2 functionality liquid medium supervision ssiml is used for monitoring the circuit breaker condition. Binary information based on the oil level in the circuit breaker is used as input signals to the function. In addition, the function generates alarms based on received information. 16.3.3 funct...
Page 901
16.3.5 settings table 655: ssiml group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description operation off on - - off operation off / on levelalmlimit 1.00 - 100.00 - 0.01 5.00 alarm setting for level levellolimit 1.00 - 100.00 - 0.01 3.00 level lockout setting tempalarmlimit -40.00 - 2...
Page 902
When temperature input temp is greater than tempalarmlimit, then temperature alarm temp_alm will be initiated. Similarly, if temperature input temp is greater than templolimit, then temp_lo will be initiated. There may be sudden change in temperature of the medium for a very small time, for which th...
Page 903
16.4.2 functionality the breaker monitoring function sscbr is used to monitor different parameters of the breaker condition. The breaker requires maintenance when the number of operations reaches a predefined value. For a proper functioning of the circuit breaker, it is essential to monitor the circ...
Page 904
Table 658: sscbr output signals name type description openpos boolean cb is in open position closepos boolean cb is in closed position invdpos boolean cb is in invalid position trcmd boolean open command issued to cb trvtopal boolean cb open travel time exceeded set value trvtclal boolean cb close t...
Page 905
Name values (range) unit step default description currexponent 0.50 - 3.00 - 0.01 2.00 current exponent value used for energy calculation accstopcurr 5.00 - 100.00 %ib 0.01 10.00 rms current level below which energy accumulation stops almacccurrpwr 0.00 - 20000.00 - 0.01 2500.00 alarm level for accu...
Page 906
16.4.6 monitored data table 661: sscbr monitored data name type values (range) unit description ttrvop real - ms travel time of the cb during opening operation ttrvcl real - ms travel time of the cb during closing operation nooper integer - - number of cb operation cycle cblifeph integer - - cb rema...
Page 907
I3p-ilrmsph posclose posopen block blkalm cb contact travel time ttrvop trvtopal trvtclal rsttrvt operalm cb gas pressure indication sprchrst sprchrd cblifeph ttrvcl nooper cblifeal i3p-il ipowph trind openpos closepos invdpos cb status cb operation monitoring cb operation cycles accumulated energy ...
Page 908
16.4.7.1 circuit breaker contact travel time the circuit breaker contact travel time subfunction calculates the breaker contact travel time for opening and closing operations. The operation of the breaker contact travel time measurement is described in figure 427 . Contact travel time calculation po...
Page 909
Time is calculated by adding the value set with the closetimecorr (t3+t4) setting to the measured closing time. The last measured opening travel time (ttrvop) and the closing travel time (ttrvcl) are given as service values. The values can be reset using the clear menu on the lhmi or by activation t...
Page 910
Have the same value or if the auxiliary input contact posclose is low and the posopen input is high but the current is above the setting accstopcurr. The status of the breaker is indicated with the binary outputs openpos, closepos and invdpos for open, closed and error position respectively. 16.4.7....
Page 911
The old circuit breaker operation counter value can be used by adding the value to the initcbremlife parameter. The value can be reset using the clear menu from lhmi or by activating the input rstcbwr. 16.4.7.4 accumulated energy the accumulated energy subfunction calculates the accumulated energy (...
Page 912
Main contact close open posclose 1 0 energy accumulation starts conttrcorr (negative) main contact close posclose energy accumulation starts conttrcorr (positive) 1 0 open iec12000618_1_en.Vsd iec12000618 v1 en figure 432: significance of correction factor setting the conttrcorr setting is used to d...
Page 913
Posclose posopen rstcbwr block blkalm operation counter alarm limit check nooper operalm operlo iec12000617 v2 en figure 433: functional module diagram for circuit breaker operation cycles operation counter the operation counter counts the number of operations based on the state of change of the aux...
Page 914
Inactive timer the inactive timer module calculates the number of days the circuit breaker has remained in the same open or closed state. The value is calculated by monitoring the states of the posopen and posclose auxiliary contacts. The number of inactive days inadays is available as a service val...
Page 915
16.4.7.8 circuit breaker gas pressure indication the circuit breaker gas pressure indication subfunction monitors the gas pressure inside the arc chamber. The operation is described in figure 436 . Preslo block blkalm presalm gpresalm gpreslo t tdgaspresalm t tdgaspreslo and and iec12000622 v3 en fi...
Page 916
16.5 event function event 16.5.1 identification function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number event function event s00946 v1 en - 16.5.2 functionality when using a substation automation system with lon or spa communication, time-tagged events ca...
Page 917
16.5.4 signals table 663: event input signals name type default description block boolean 0 block of function input1 group signal 0 input 1 input2 group signal 0 input 2 input3 group signal 0 input 3 input4 group signal 0 input 4 input5 group signal 0 input 5 input6 group signal 0 input 6 input7 gro...
Page 918
16.5.5 settings table 664: event non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description spachannelmask off channel 1-8 channel 9-16 channel 1-16 - - off spa channel mask lonchannelmask off channel 1-8 channel 9-16 channel 1-16 - - off lon channel mask eventmask1 noevents onset ...
Page 919
Name values (range) unit step default description eventmask10 noevents onset onreset onchange autodetect - - autodetect reporting criteria for input 10 eventmask11 noevents onset onreset onchange autodetect - - autodetect reporting criteria for input 11 eventmask12 noevents onset onreset onchange au...
Page 920
16.5.6 operation principle the main purpose of the event function (event) is to generate events when the state or value of any of the connected input signals is in a state, or is undergoing a state transition, for which event generation is enabled. Each event function has 16 inputs input1 - input16....
Page 921
To protect the sa system from signals with a high change rate that can easily saturate the event function or the communication subsystems behind it, a quota limiter is implemented. If an input creates events at a rate that completely consume the granted quota then further events from the channel wil...
Page 922
• event list • indications • event recorder • trip value recorder • disturbance recorder the disturbance report function is characterized by great flexibility regarding configuration, starting conditions, recording times, and large storage capacity. A disturbance is defined as an activation of an in...
Page 923
Iec05000431-3-en.Vsd a4radr ^input31 ^input32 ^input33 ^input34 ^input35 ^input36 ^input37 ^input38 ^input39 ^input40 iec05000431 v3 en figure 440: a4radr function block, derived analog inputs iec05000432-3-en.Vsd b1rbdr ^input1 ^input2 ^input3 ^input4 ^input5 ^input6 ^input7 ^input8 ^input9 ^input1...
Page 924
Table 666: a1radr input signals name type default description grpinput1 group signal - group signal for input 1 grpinput2 group signal - group signal for input 2 grpinput3 group signal - group signal for input 3 grpinput4 group signal - group signal for input 4 grpinput5 group signal - group signal ...
Page 925
Table 668: a3radr input signals name type default description grpinput21 group signal - group signal for input 21 grpinput22 group signal - group signal for input 22 grpinput23 group signal - group signal for input 23 grpinput24 group signal - group signal for input 24 grpinput25 group signal - grou...
Page 926
Name type default description input6 boolean 0 binary channel 6 input7 boolean 0 binary channel 7 input8 boolean 0 binary channel 8 input9 boolean 0 binary channel 9 input10 boolean 0 binary channel 10 input11 boolean 0 binary channel 11 input12 boolean 0 binary channel 12 input13 boolean 0 binary c...
Page 927
Name type default description input38 boolean 0 binary channel 38 input39 boolean 0 binary channel 39 input40 boolean 0 binary channel 40 input41 boolean 0 binary channel 41 input42 boolean 0 binary channel 42 input43 boolean 0 binary channel 43 input44 boolean 0 binary channel 44 input45 boolean 0 ...
Page 928
Name type default description input70 boolean 0 binary channel 70 input71 boolean 0 binary channel 71 input72 boolean 0 binary channel 72 input73 boolean 0 binary channel 73 input74 boolean 0 binary channel 74 input75 boolean 0 binary channel 75 input76 boolean 0 binary channel 76 input77 boolean 0 ...
Page 929
Name values (range) unit step default description timelimit 0.5 - 10.0 s 0.1 1.0 fault recording time limit postretrig off on - - off post-fault retrig enabled (on) or not (off) maxnostorerec 10 - 100 - 1 100 maximum number of stored disturbances zeroangleref 1 - 30 ch 1 1 trip value recorder, phaso...
Page 930
Name values (range) unit step default description undertrigop02 off on - - off use under level trigger for analog channel 2 (on) or not (off) undertrigle02 0 - 200 % 1 50 under trigger level for analog channel 2 in % of signal overtrigop02 off on - - off use over level trigger for analog channel 2 (...
Page 931
Name values (range) unit step default description undertrigle07 0 - 200 % 1 50 under trigger level for analog channel 7 in % of signal overtrigop07 off on - - off use over level trigger for analog channel 7 (on) or not (off) overtrigle07 0 - 5000 % 1 200 over trigger level for analog channel 7 in % ...
Page 932
Name values (range) unit step default description operation16 off on - - off operation on/off operation17 off on - - off operation on/off operation18 off on - - off operation on/off operation19 off on - - off operation on/off operation20 off on - - off operation on/off table 680: a2radr non group se...
Page 933
Name values (range) unit step default description overtrigle14 0 - 5000 % 1 200 over trigger level for analog channel 14 in % of signal nomvalue15 0.0 - 999999.9 - 0.1 0.0 nominal value for analog channel 15 undertrigop15 off on - - off use under level trigger for analog channel 15 (on) or not (off)...
Page 934
Name values (range) unit step default description undertrigop20 off on - - off use under level trigger for analog channel 20 (on) or not (off) undertrigle20 0 - 200 % 1 50 under trigger level for analog channel 20 in % of signal overtrigop20 off on - - off use over level trigger for analog channel 2...
Page 935
Name values (range) unit step default description undertrigle22 0 - 200 % 1 50 under trigger level for analog channel 22 in % of signal overtrigop22 off on - - off use over level trigger for analog channel 22 (on) or not (off) overtrigle22 0 - 5000 % 1 200 over trigger level for analog channel 22 in...
Page 936
Name values (range) unit step default description overtrigop27 off on - - off use over level trigger for analog channel 27 (on) or not (off) overtrigle27 0 - 5000 % 1 200 over trigger level for analog channel 27 in % of signal nomvalue28 0.0 - 999999.9 - 0.1 0.0 nominal value for analog channel 28 u...
Page 937
Name values (range) unit step default description operation37 off on - - off operation on/off operation38 off on - - off operation on/off operation39 off on - - off operation on/off operation40 off on - - off operation on/off table 684: a4radr non group settings (advanced) name values (range) unit s...
Page 938
Name values (range) unit step default description nomvalue35 0.0 - 999999.9 - 0.1 0.0 nominal value for analog channel 35 undertrigop35 off on - - off use under level trigger for analog channel 35 (on) or not (off) undertrigle35 0 - 200 % 1 50 under trigger level for analog channel 35 in % of signal...
Page 939
Name values (range) unit step default description undertrigle40 0 - 200 % 1 50 under trigger level for analog channel 40 in % of signal overtrigop40 off on - - off use over level trigger for analog channel 40 (on) or not (off) overtrigle40 0 - 5000 % 1 200 over trigger level for analog channel 40 in...
Page 940
Name values (range) unit step default description trigdr08 off on - - off trigger operation on/off setled08 off start trip start and trip - - off set led on hmi for binary channel 8 trigdr09 off on - - off trigger operation on/off setled09 off start trip start and trip - - off set led on hmi for bin...
Page 941
Name values (range) unit step default description setled16 off start trip start and trip - - off set led on hmi for binary channel 16 funtype1 0 - 255 - 1 0 function type for binary channel 1 (iec -60870-5-103) infno1 0 - 255 - 1 0 information number for binary channel 1 (iec -60870-5-103) funtype2 ...
Page 942
Name values (range) unit step default description infno12 0 - 255 - 1 0 information number for binary channel 12 (iec -60870-5-103) funtype13 0 - 255 - 1 0 function type for binary channel 13 (iec -60870-5-103) infno13 0 - 255 - 1 0 information number for binary channel 13 (iec -60870-5-103) funtype...
Page 943
Name values (range) unit step default description indicationma07 hide show - - show indication mask for binary channel 7 triglevel08 trig on 0 trig on 1 - - trig on 1 trigger on positive (1) or negative (0) slope for binary input 8 indicationma08 hide show - - show indication mask for binary channel...
Page 944
Table 687: b2rbdr non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description trigdr17 off on - - off trigger operation on/off setled17 off start trip start and trip - - off set led on hmi for binary channel 17 trigdr18 off on - - off trigger operation on/off setled18 off start trip...
Page 945
Name values (range) unit step default description setled25 off start trip start and trip - - off set led on hmi for binary channel 25 trigdr26 off on - - off trigger operation on/off setled26 off start trip start and trip - - off set led on hmi for binary channel 26 trigdr27 off on - - off trigger o...
Page 946
Name values (range) unit step default description infno18 0 - 255 - 1 0 information number for binary channel 18 (iec -60870-5-103) funtype19 0 - 255 - 1 0 function type for binary channel 19 (iec -60870-5-103) infno19 0 - 255 - 1 0 information number for binary channel 19 (iec -60870-5-103) funtype...
Page 947
Name values (range) unit step default description infno30 0 - 255 - 1 0 information number for binary channel 30 (iec -60870-5-103) funtype31 0 - 255 - 1 0 function type for binary channel 31 (iec -60870-5-103) infno31 0 - 255 - 1 0 information number for binary channel 31 (iec -60870-5-103) funtype...
Page 948
Name values (range) unit step default description indicationma25 hide show - - show indication mask for binary channel 25 triglevel26 trig on 0 trig on 1 - - trig on 1 trigger on positive (1) or negative (0) slope for binary input 26 indicationma26 hide show - - show indication mask for binary chann...
Page 949
Name values (range) unit step default description setled35 off start trip start and trip - - off set led on hmi for binary channel 35 trigdr36 off on - - off trigger operation on/off setled36 off start trip start and trip - - off set led on hmi for binary channel 36 trigdr37 off on - - off trigger o...
Page 950
Name values (range) unit step default description trigdr44 off on - - off trigger operation on/off setled44 off start trip start and trip - - off set led on hmi for binary channel 44 trigdr45 off on - - off trigger operation on/off setled45 off start trip start and trip - - off set led on hmi for bi...
Page 951
Name values (range) unit step default description infno38 0 - 255 - 1 0 information number for binary channel 38 (iec -60870-5-103) funtype39 0 - 255 - 1 0 function type for binary channel 39 (iec -60870-5-103) infno39 0 - 255 - 1 0 information number for binary channel 39 (iec -60870-5-103) funtype...
Page 952
Table 690: b3rbdr non group settings (advanced) name values (range) unit step default description triglevel33 trig on 0 trig on 1 - - trig on 1 trigger on positive (1) or negative (0) slope for binary input 33 indicationma33 hide show - - show indication mask for binary channel 33 triglevel34 trig o...
Page 953
Name values (range) unit step default description triglevel45 trig on 0 trig on 1 - - trig on 1 trigger on positive (1) or negative (0) slope for binary input 45 indicationma45 hide show - - show indication mask for binary channel 45 triglevel46 trig on 0 trig on 1 - - trig on 1 trigger on positive ...
Page 954
Name values (range) unit step default description trigdr54 off on - - off trigger operation on/off setled54 off start trip start and trip - - off set led on hmi for binary channel 54 trigdr55 off on - - off trigger operation on/off setled55 off start trip start and trip - - off set led on hmi for bi...
Page 955
Name values (range) unit step default description setled62 off start trip start and trip - - off set led on hmi for binary channel 62 trigdr63 off on - - off trigger operation on/off setled63 off start trip start and trip - - off set led on hmi for binary channel 63 trigdr64 off on - - off trigger o...
Page 956
Name values (range) unit step default description infno57 0 - 255 - 1 0 information number for binary channel 57 (iec -60870-5-103) funtype58 0 - 255 - 1 0 function type for binary channel 58 (iec -60870-5-103) infno58 0 - 255 - 1 0 information number for binary channel 58 (iec -60870-5-103) funtype...
Page 957
Name values (range) unit step default description indicationma52 hide show - - show indication mask for binary channel 52 triglevel53 trig on 0 trig on 1 - - trig on 1 trigger on positive (1) or negative (0) slope for binary input 53 indicationma53 hide show - - show indication mask for binary chann...
Page 958
Table 693: b5rbdr non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description trigdr65 off on - - off trigger operation on/off setled65 off start trip start and trip - - off set led on hmi for binary channel 65 trigdr66 off on - - off trigger operation on/off setled66 off start trip...
Page 959
Name values (range) unit step default description setled73 off start trip start and trip - - off set led on hmi for binary channel 73 trigdr74 off on - - off trigger operation on/off setled74 off start trip start and trip - - off set led on hmi for binary channel 74 trigdr75 off on - - off trigger o...
Page 960
Name values (range) unit step default description infno66 0 - 255 - 1 0 information number for binary channel 66 (iec -60870-5-103) funtype67 0 - 255 - 1 0 function type for binary channel 67 (iec -60870-5-103) infno67 0 - 255 - 1 0 information number for binary channel 67 (iec -60870-5-103) funtype...
Page 961
Name values (range) unit step default description infno78 0 - 255 - 1 0 information number for binary channel 78 (iec -60870-5-103) funtype79 0 - 255 - 1 0 function type for binary channel 79 (iec -60870-5-103) infno79 0 - 255 - 1 0 information number for binary channel 79 (iec -60870-5-103) funtype...
Page 962
Name values (range) unit step default description indicationma73 hide show - - show indication mask for binary channel 73 triglevel74 trig on 0 trig on 1 - - trig on 1 trigger on positive (1) or negative (0) slope for binary input 74 indicationma74 hide show - - show indication mask for binary chann...
Page 963
Name values (range) unit step default description setled83 off start trip start and trip - - off set led on hmi for binary channel 83 trigdr84 off on - - off trigger operation on/off setled84 off start trip start and trip - - off set led on hmi for binary channel 84 trigdr85 off on - - off trigger o...
Page 964
Name values (range) unit step default description trigdr92 off on - - off trigger operation on/off setled92 off start trip start and trip - - off set led on hmi for binary channel 92 trigdr93 off on - - off trigger operation on/off setled93 off start trip start and trip - - off set led on hmi for bi...
Page 965
Name values (range) unit step default description infno86 0 - 255 - 1 0 information number for binary channel 86 (iec -60870-5-103) funtype87 0 - 255 - 1 0 function type for binary channel 87 (iec -60870-5-103) infno87 0 - 255 - 1 0 information number for binary channel 87 (iec -60870-5-103) funtype...
Page 966
Table 696: b6rbdr non group settings (advanced) name values (range) unit step default description triglevel81 trig on 0 trig on 1 - - trig on 1 trigger on positive (1) or negative (0) slope for binary input 81 indicationma81 hide show - - show indication mask for binary channel 81 triglevel82 trig o...
Page 967
Name values (range) unit step default description triglevel93 trig on 0 trig on 1 - - trig on 1 trigger on positive (1) or negative (0) slope for binary input 93 indicationma93 hide show - - show indication mask for binary channel 93 triglevel94 trig on 0 trig on 1 - - trig on 1 trigger on positive ...
Page 968
Name type values (range) unit description untrigstatch7 boolean - - under level trig for analog channel 7 activated ovtrigstatch7 boolean - - over level trig for analog channel 7 activated untrigstatch8 boolean - - under level trig for analog channel 8 activated ovtrigstatch8 boolean - - over level ...
Page 969
Name type values (range) unit description untrigstatch19 boolean - - under level trig for analog channel 19 activated ovtrigstatch19 boolean - - over level trig for analog channel 19 activated untrigstatch20 boolean - - under level trig for analog channel 20 activated ovtrigstatch20 boolean - - over...
Page 970
Name type values (range) unit description untrigstatch31 boolean - - under level trig for analog channel 31 activated ovtrigstatch31 boolean - - over level trig for analog channel 31 activated untrigstatch32 boolean - - under level trig for analog channel 32 activated ovtrigstatch32 boolean - - over...
Page 971
The functions included in the disturbance report are: • event list (el) • indications (ind) • event recorder (er) • trip value recorder(tvr) • disturbance recorder (dr) figure 442 shows the relations between disturbance report, included functions and function blocks. Event list (el), event recorder ...
Page 972
En05000161.Vsd disturbance report record no. N record no. N+1 record no. N+100 general dist. Information indications trip values event recordings disturbance recording event list iec05000161 v1 en figure 443: disturbance report structure up to 100 disturbance reports can be stored. If a new disturba...
Page 973
The maximum number of recordings depend on each recordings total recording time. Long recording time will reduce the number of recordings to less than 100. The ied flash disk should not be used to store any user files. This might cause disturbance recordings to be deleted due to lack of disk space. ...
Page 974
Disturbance recorder (dr), event recorder (er) and indication function register disturbance data and events during trecording, the total recording time. The total recording time, trecording, of a recorded disturbance is: trecording = prefaultrect + tfault + postfaultrect or prefaultrect + timelimit ...
Page 975
Iec10000029-1-en.Vsd a3radr a2radr a1radr smai ai1 ai2 ai3 ai4 ai3p ^grp2l1 ^grp2l2 ^grp2l3 block ^grp2n input1 input2 input3 input4 input5 input6 ... A4radr input31 input32 input33 input34 input35 input36 ... Input40 internal analogue signals external analogue signals ain type iec10000029 v1 en fig...
Page 976
If operation = off, no waveform (samples) will be recorded and reported in graph. However, trip value, pre-fault and fault value will be recorded and reported. The input channel can still be used to trig the disturbance recorder. If operation = on, waveform (samples) will also be recorded and report...
Page 977
From a logic zero, the selected signal will not be listed in the indications list of the disturbance report. Analog-signal trigger all analog signals are available for trigger purposes, no matter if they are recorded in the disturbance recorder or not. The settings are overtrigop, undertrigop, overt...
Page 978
Function range or value accuracy maximum number of recordings 100, first in - first out - time tagging resolution 1 ms see table 844 maximum number of analog inputs 30 + 10 (external + internally derived) - maximum number of binary inputs 96 - maximum number of phasors in the trip value recorder per...
Page 979
16.7.3 function block binstatrep block ^input1 ^input2 ^input3 ^input4 ^input5 ^input6 ^input7 ^input8 ^input9 ^input10 ^input11 ^input12 ^input13 ^input14 ^input15 ^input16 output1 output2 output3 output4 output5 output6 output7 output8 output9 output10 output11 output12 output13 output14 output15 ...
Page 980
Table 700: binstatrep output signals name type description output1 boolean logical status report output 1 output2 boolean logical status report output 2 output3 boolean logical status report output 3 output4 boolean logical status report output 4 output5 boolean logical status report output 5 output...
Page 981
T t inputn outputn iec09000732-1-en.Vsd iec09000732 v1 en figure 448: binstatrep logical diagram 16.8 measured value expander block range_xp 16.8.1 identification function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number measured value expander block range_...
Page 982
16.8.4 signals table 702: range_xp input signals name type default description range integer 0 measured value range table 703: range_xp output signals name type description highhigh boolean measured value is above high-high limit high boolean measured value is between high and high-high limit normal...
Page 983
16.9.2 functionality the 30 limit counter l4ufcnt provides a settable counter with four independent limits where the number of positive and/or negative flanks on the input signal are counted against the setting values for limits. The output for each limit is activated when the counted value reaches ...
Page 984
• stops counting and activates a steady overflow indication for the next count • rolls over to zero and activates a steady overflow indication for the next count • rolls over to zero and activates a pulsed overflow indication for the next count the pulsed overflow output lasts up to the first count ...
Page 985
16.9.4 function block l4ufcnt block input reset error overflow limit1 limit2 limit3 limit4 value iec12000029-1-en.Vsd iec12000029 v1 en figure 452: l4ufcnt function block 16.9.5 signals table 705: l4ufcnt input signals name type default description block boolean 0 block of function input boolean 0 i...
Page 986
16.9.6 settings table 707: l4ufcnt group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description operation off on - - off operation off / on counttype positive edge negative edge both edges - - positive edge select counting on positive and/or negative flanks counterlimit1 1 - 65535 - 1 10...
Page 987
Section 17 metering 17.1 pulse-counter logic pcfcnt 17.1.1 identification function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number pulse-counter logic pcfcnt s00947 v1 en - 17.1.2 functionality pulse-counter logic (pcfcnt) function counts externally genera...
Page 988
17.1.4 signals table 710: pcfcnt input signals name type default description block boolean 0 block of function read_val boolean 0 initiates an additional pulse counter reading bi_pulse boolean 0 connect binary input channel for metering rs_cnt boolean 0 resets pulse counter value table 711: pcfcnt o...
Page 989
17.1.6 monitored data table 713: pcfcnt monitored data name type values (range) unit description cnt_val integer - - actual pulse counter value scal_val real - - scaled value with time and status information 17.1.7 operation principle the registration of pulses is done for positive transitions (0- >...
Page 990
En05000744.Vsd pulsecounter block read_val bi_pulse pulse input out database pulse counter value: 0...2147483647 sms settings 1.Operation = off/on 2.Treporting = 0s...60min 3.Event mask = no events/report events singlecmdfunc outx singlecmdfunc outx i/o-module pulse length >1s invalid restart blocke...
Page 991
The new_val signal is a pulse signal. The signal is set if the counter value was updated since last report. Note, the pulse is short, one cycle. The scal_val signal consists of scaled value (according to parameter scale), time and status information. 17.1.8 technical data table 714: pcfcnt technical...
Page 992
Energy values are available as output signals and also as pulse outputs. Integration of energy values can be controlled by inputs (startacc and stopacc) and enaacc setting and it can be reset to initial values with rstacc input. The maximum demand for active and reactive powers are calculated for th...
Page 993
Name type description erfpulse boolean accumulated forward reactive energy pulse errpulse boolean accumulated reverse reactive energy pulse eafalm boolean alarm for active forward energy exceed limit in set interval earalm boolean alarm for active reverse energy exceed limit in set interval erfalm b...
Page 994
Name values (range) unit step default description earaccplsqty 0.001 - 10000.000 mwh 0.001 100.000 pulse quantity for active reverse accumulated energy value erfaccplsqty 0.001 - 10000.000 mvarh 0.001 100.000 pulse quantity for reactive forward accumulated energy value erraccplsqty 0.001 - 10000.000...
Page 995
Name type values (range) unit description maxpafd real - mw maximum forward active power demand value for set interval maxpard real - mw maximum reverse active power demand value for set interval maxprfd real - mvar maximum forward reactive power demand value for set interval maxprrd real - mvar max...
Page 996
T f startacc accinprg rstacc ³1 q -1 stopacc & false & enaacc iec13000186-4-en.Vsd q -1 = unit delay iec13000186 v4 en figure 457: accinprg logic diagram the accumulated energy values (in mwh and mvarh) are available as service values and also as pulsed output depending on the exxaccplsqty setting, ...
Page 997
Pulses can be reset to zero by activating rstacc input or by using the local hmi reset menu. The pulse on and off time duration is set by the settings tenergyonpls and tenergyoffpls. Figure 459 shows the logic for pulse output generation for the integrated energy in the active forward direction. Sim...
Page 998
Average power calculation x a>b a b q -1 t f 0.0 tenergy ealim p (active forward) rstmaxd eafalm maxpafd max iec13000189-4-en.Vsd q -1 = unit delay iec13000189 v4 en figure 460: logic for maximum power demand calculation and energy alarm 17.2.8 technical data 17.2.8.1 technical data table 720: funct...
Page 999
Section 18 station communication 18.1 670 series protocols each ied is provided with a communication interface, enabling it to connect to one or many substation level systems or equipment, either on the substation automation (sa) bus or substation monitoring (sm) bus. Following communication protoco...
Page 1000
138.227.102.10 with subnet mask 255.255.255.0 and port 2 has ip- address 138.227.103.10 with subnet mask 255.255.255.0 18.3.2 settings table 722: iec61850-8-1 non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description operation off on - - off operation off/on portselgoose front lan...
Page 1001
18.3.4.1 functionality generic communication function for single point indication spgapc is used to send one single logical signal to other systems or equipment in the substation. 18.3.4.2 function block spgapc block ^in iec14000021-1-en.Vsd iec14000021 v1 en figure 461: spgapc function block sp16ga...
Page 1002
Name type default description in6 boolean 0 input 6 status in7 boolean 0 input 7 status in8 boolean 0 input 8 status in9 boolean 0 input 9 status in10 boolean 0 input 10 status in11 boolean 0 input 11 status in12 boolean 0 input 12 status in13 boolean 0 input 13 status in14 boolean 0 input 14 status...
Page 1003
Name type values (range) unit description out10 group signal - - output 10 status out11 group signal - - output 11 status out12 group signal - - output 12 status out13 group signal - - output 13 status out14 group signal - - output 14 status out15 group signal - - output 15 status out16 group signal...
Page 1004
18.3.5.3 signals table 728: mvgapc input signals name type default description block boolean 0 block of function in real 0 analog input value table 729: mvgapc output signals name type description value real magnitude of deadband value range integer range 18.3.5.4 settings table 730: mvgapc non grou...
Page 1005
18.3.5.5 monitored data table 731: mvgapc monitored data name type values (range) unit description value real - - magnitude of deadband value range integer 1=high 2=low 3=high-high 4=low-low 0=normal - range 18.3.5.6 operation principle upon receiving an analog signal at its input, generic communica...
Page 1006
18.3.6.3 signals table 732: prpstatus output signals name type description prp-a link boolean prp-a link status prp-a valid boolean prp-a link valid prp-b link boolean prp-b link status prp-b valid boolean prp-b link valid 18.3.6.4 settings table 733: prp non group settings (basic) name values (rang...
Page 1007
Same, the last package is discarded. The prp communication is based on the so called duo driver concept. The prpstatus function block supervise the redundant communication on the two channels. If no data package has been received on one (or both) channels within the last 10 s, the output prp-a link ...
Page 1008
18.4 lon communication protocol 18.4.1 functionality an optical network can be used within the substation automation system. This enables communication with the ied through the lon bus from the operator’s workplace, from the control center and also from other terminals. Lon communication protocol is...
Page 1009
And node number are identifying the nodes (max. 255 subnets, 127 nodes per one subnet). The lon bus links the different parts of the protection and control system. The measured values, status information, and event information are spontaneously sent to the higher-level devices. The higher-level devi...
Page 1010
Vertical communication vertical communication describes communication between the monitoring devices and protection and control ieds. This communication includes sending of changed process data to monitoring devices as events and transfer of commands, parameter data and disturbance recorder files. T...
Page 1011
Function block first lon address in function block event:9 1152 event:10 1168 event:11 1184 event:12 1200 event:13 1216 event:14 1232 event:15 1248 event:16 1264 event:17 1280 event:18 1296 event:19 1312 event:20 1328 event masks event mask for each input can be set individually from parameter setti...
Page 1012
Analog value all analog values are reported cyclic. The reporting interval is taken from the connected function if there is a limit supervised signal. Otherwise it is taken from the event function block. Command handling commands are transferred using transparent spa-bus messages. The transparent sp...
Page 1013
Multicmdsnd: 7 bay e1 multicmdsnd: 9 bay e3 lon bay e4 multicmdsnd: 9 en05000718.Vsd iec05000718 v2 en figure 466: examples connections between multicmdsnd and multicmdrcv function blocks in three ieds the network variable connections are done from the nv connection window. From lnt window select co...
Page 1014
En05000720.Vsd iec05000720 v1 en figure 468: the download configuration window in lnt communication ports the serial communication module (slm) is a mezzanine module placed on the main processing module (num) and is used for lon, spa, iec 60870-5-103 and dnp communication. There are two types of io ...
Page 1015
Name function block spa address description bl_cmd scswi06 1 i 5234 spa parameters for block command bl_cmd scswi07 1 i 5258 spa parameters for block command bl_cmd scswi08 1 i 5283 spa parameters for block command bl_cmd scswi09 1 i 5307 spa parameters for block command bl_cmd scswi10 1 i 5331 spa ...
Page 1016
Name function block spa address description bl_cmd scswi30 1 i 5811 spa parameters for block command bl_cmd scswi31 1 i 5835 spa parameters for block command bl_cmd scswi32 1 i 5859 spa parameters for block command cancel scswi01 1 i 5107 spa parameters for cancel command cancel scswi02 1 i 5131 spa...
Page 1017
Name function block spa address description cancel scswi22 1 i 5611 spa parameters for cancel command cancel scswi23 1 i 5635 spa parameters for cancel command cancel scswi24 1 i 5659 spa parameters for cancel command cancel scswi25 1 i 5683 spa parameters for cancel command cancel scswi26 1 i 5707 ...
Page 1018
Name function block spa address description selectopen=00, selectclose=01, so on. Scswi12 1 i 5369 spa parameters for select (open/ close) command selectopen=00, selectclose=01, so on. Scswi13 1 i 5393 spa parameters for select (open/ close) command selectopen=00, selectclose=01, so on. Scswi14 1 i ...
Page 1019
Name function block spa address description excopen=00, excclose=01, so on. Scswi02 1 i 5130 spa parameters for operate (open/ close) command excopen=00, excclose=01, so on. Scswi02 1 i 5152 spa parameters for operate (open/ close) command excopen=00, excclose=01, so on. Scswi04 1 i 5177 spa paramet...
Page 1020
Name function block spa address description excopen=00, excclose=01, so on. Scswi26 1 i 5706 spa parameters for operate (open/ close) command excopen=00, excclose=01, so on. Scswi27 1 i 5730 spa parameters for operate (open/ close) command excopen=00, excclose=01, so on. Scswi28 1 i 5754 spa paramet...
Page 1021
Name function block spa address description sub value sxcbr18 3 i 179 spa parameter for position to be substituted sub value sxswi01 3 i 196 spa parameter for position to be substituted sub value sxswi02 3 i 216 spa parameter for position to be substituted sub value sxswi03 3 i 235 spa parameter for...
Page 1022
Name function block spa address description sub value sxswi24 3 i 625 spa parameter for position to be substituted sub value sxswi25 3 i 644 spa parameter for position to be substituted sub value sxswi26 3 i 663 spa parameter for position to be substituted sub value sxswi27 3 i 682 spa parameter for...
Page 1023
Name function block spa address description sub enable sxswi01 3 i 197 spa parameter for substitute enable command sub enable sxswi02 3 i 215 spa parameter for substitute enable command sub enable sxswi03 3 i 234 spa parameter for substitute enable command sub enable sxswi04 3 i 252 spa parameter fo...
Page 1024
Name function block spa address description sub enable sxswi25 3 i 645 spa parameter for substitute enable command sub enable sxswi26 3 i 664 spa parameter for substitute enable command sub enable sxswi27 3 i 683 spa parameter for substitute enable command sub enable sxswi28 3 i 702 spa parameter fo...
Page 1025
Name function block spa address description update block sxswi03 3 i 236 spa parameter for update block command update block sxswi04 3 i 253 spa parameter for update block command update block sxswi05 3 i 273 spa parameter for update block command update block sxswi06 3 i 291 spa parameter for updat...
Page 1026
Name function block spa address description update block sxswi26 3 i 662 spa parameter for update block command update block sxswi27 3 i 681 spa parameter for update block command update block sxswi28 3 i 700 spa parameter for update block command 18.4.4 technical data table 739: lon communication p...
Page 1027
18.5.3 settings table 740: spa non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description slaveaddress 1 - 899 - 1 30 slave address baudrate 300 bd 1200 bd 2400 bd 4800 bd 9600 bd 19200 bd 38400 bd - - 9600 bd baudrate on serial line table 741: lonspa non group settings (basic) nam...
Page 1028
Table 742: spa addresses for the mim function function block spa address mim3-ch1 4-o-6508 mim3-ch2 4-o-6511 mim3-ch3 4-o-6512 mim3-ch4 4-o-6515 mim3-ch5 4-o-6516 mim3-ch6 4-o-6519 mim4-ch1 4-o-6527 mim4-ch2 4-o-6530 mim4-ch3 4-o-6531 mim4-ch4 4-o-6534 mim4-ch5 4-o-6535 mim4-ch6 4-o-6538 mim5-ch1 4-...
Page 1029
Function block spa address mim9-ch3 4-o-6626 mim9-ch4 4-o-6629 mim9-ch5 4-o-6630 mim9-ch6 4-o-6633 mim10-ch1 4-o-6641 mim10-ch2 4-o-6644 mim10-ch3 4-o-6645 mim10-ch4 4-o-6648 mim10-ch5 4-o-6649 mim10-ch6 4-o-6652 mim11-ch1 4-o-6660 mim11-ch2 4-o-6663 mim11-ch3 4-o-6664 mim11-ch4 4-o-6667 mim11-ch5 4...
Page 1030
Function block spa address mim15-ch6 4-o-6747 mim16-ch1 4-o-6755 mim16-ch2 4-o-6758 mim16-ch3 4-o-6759 mim16-ch4 4-o-6762 mim16-ch5 4-o-6763 mim16-ch6 4-o-6766 the spa addresses for the pulse counter values pcfcnt:1 to pcfcnt:16 are found in table 743 . Table 743: spa addresses for the pcfcnt functi...
Page 1031
Single command, 16 signals function consists of three function blocks; singlecmd:1 to singlecmd:3 for 16 binary output signals each. The signals can be individually controlled from the operator station, remote-control gateway, or from the local hmi on the ied. For single command, 3 signals function ...
Page 1032
Function block spa address cmd input spa address cmd output singlecmd2-cmd14 4-s-4685 5-o-540 singlecmd2-cmd15 4-s-4686 5-o-541 singlecmd2-cmd16 4-s-4687 5-o-542 singlecmd3-cmd1 4-s-4705 5-o-543 singlecmd3-cmd2 4-s-4706 5-o-544 singlecmd3-cmd3 4-s-4707 5-o-545 singlecmd3-cmd4 4-s-4708 5-o-546 single...
Page 1033
The mode input defines if the output signals from singlecmd:1 is off, steady or setable pulse length signals. This is set in parameter setting tool (pst) under: main menu/settings / ied settings / control / commands / single command or via parameter setting tool (pst). Event function event the event...
Page 1034
Table 745: status and event codes single indication 1) double indication event block status set event reset event intermedi ate 00 closed 10 open 01 undefined 11 event:1 input 1 input 2 input 3 input 4 input 5 input 6 input 7 input 8 input 9 input 10 input 11 input 12 input 13 input 14 input 15 inpu...
Page 1035
Event block ^input1 ^input2 ^input3 ^input4 ^input5 ^input6 ^input7 ^input8 ^input9 ^input10 ^input11 ^input12 ^input13 ^input14 ^input15 ^input16 block ilrang psto ul12rang ul31rang ul23rang 3i0rang 3u0rang false iec07000065-2-en.Vsd iec07000065 v2 en figure 470: connection of protection signals fo...
Page 1036
18.6 iec 60870-5-103 communication protocol 18.6.1 introduction iec 60870-5-103 communication protocol is mainly used when a protection ied communicates with a third party control or monitoring system. This system must have software that can interpret the iec 60870-5-103 communication messages. 18.6...
Page 1037
18.6.2.3 function block iec10000287-1-en.Vsd i103meas block il1 il2 il3 in ul1 ul2 ul3 ul1l2 un p q f iec10000287 v1 en figure 471: i103meas function block 18.6.2.4 signals table 747: i103meas input signals name type default description block boolean 0 block of service value reporting il1 real 0.0 s...
Page 1038
Name values (range) unit step default description maxul1 0.05 - 2000.00 kv 0.05 230.00 maximum voltage for phase l1 maxul2 0.05 - 2000.00 kv 0.05 230.00 maximum voltage for phase l2 maxul3 0.05 - 2000.00 kv 0.05 230.00 maximum voltage for phase l3 maxul1-ul2 0.05 - 2000.00 kv 0.05 400.00 maximum vol...
Page 1039
18.6.3.4 signals table 749: i103measusr input signals name type default description block boolean 0 block of service value reporting input1 real 0.0 service value for measurement on input 1 input2 real 0.0 service value for measurement on input 2 input3 real 0.0 service value for measurement on inpu...
Page 1040
18.6.4 function status auto-recloser for iec 60870-5-103 i103ar 18.6.4.1 functionality i103ar is a function block with defined functions for autorecloser indications in monitor direction. This block includes the functiontype parameter, and the information number parameter is defined for each output ...
Page 1041
18.6.5 function status earth-fault for iec 60870-5-103 i103ef 18.6.5.1 functionality i103ef is a function block with defined functions for earth fault indications in monitor direction. This block includes the functiontype parameter, and the information number parameter is defined for each output sig...
Page 1042
18.6.6 function status fault protection for iec 60870-5-103 i103fltprot 18.6.6.1 functionality i103fltprot is used for fault indications in monitor direction. Each input on the function block is specific for a certain fault type and therefore must be connected to a correspondent signal present in th...
Page 1043
18.6.6.3 function block iec10000291-1-en.Vsd i103fltprot block 64_stl1 65_stl2 66_stl3 67_stin 68_trgen 69_trl1 70_trl2 71_trl3 72_trbkup 73_scl 74_fw 75_rev 76_trans 77_recev 78_zone1 79_zone2 80_zone3 81_zone4 82_zone5 84_stgen 85_bfp 86_mtrl1 87_mtrl2 88_mtrl3 89_mtrn 90_ioc 91_ioc 92_ief 93_ief ...
Page 1044
Name type default description 76_trans boolean 0 information number 76, signal transmitted 77_recev boolean 0 information number 77, signal received 78_zone1 boolean 0 information number 78, zone 1 79_zone2 boolean 0 information number 79, zone 2 80_zone3 boolean 0 information number 80, zone 3 81_z...
Page 1045
18.6.7.2 identification function description function block name iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number ied status for iec 60870-5-103 i103ied - - 18.6.7.3 function block i103ied block 19_ledrs 21_testm 22_setch 23_grp1 24_grp2 25_grp3 26_grp4 iec10000292-2-en.Vsd iec10000292 v2 en f...
Page 1046
18.6.8 supervison status for iec 60870-5-103 i103superv 18.6.8.1 functionality i103superv is a function block with defined functions for supervision indications in monitor direction. This block includes the functiontype parameter, and the information number parameter is defined for each output signa...
Page 1047
18.6.9 status for user defined signals for iec 60870-5-103 i103usrdef 18.6.9.1 functionality i103usrdef is a function block with user defined input signals in monitor direction. Each instance is associated with a function type (fun) and each input signal with an information number (inf). Additionall...
Page 1048
Name type default description input4 boolean 0 binary signal input 4 input5 boolean 0 binary signal input 5 input6 boolean 0 binary signal input 6 input7 boolean 0 binary signal input 7 input8 boolean 0 binary signal input 8 rt_start boolean 0 trig to set base of relative time rt_start registers the...
Page 1049
Name values (range) unit step default description typno7 absolute relative - - absolute type identification (typ) typno8 absolute relative - - absolute type identification (typ) gino1 excluded included - - included response and status change (gi) gino2 excluded included - - included response and sta...
Page 1050
18.6.10.2 identification function description function block name iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number function commands for iec 60870-5-103 i103cmd - - 18.6.10.3 function block iec10000282-1-en.Vsd i103cmd block 16-ar 17-diff 18-prot iec10000282 v1 en figure 479: i103cmd function ...
Page 1051
18.6.11.2 identification function description function block name iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number ied commands for iec 60870-5-103 i103iedcmd - - 18.6.11.3 function block iec10000283-1-en.Vsd i103iedcmd block 19-ledrs 23-grp1 24-grp2 25-grp3 26-grp4 iec10000283 v1 en figure 48...
Page 1052
18.6.12 function commands user defined for iec 60870-5-103 i103usrcmd 18.6.12.1 functionality i103usrcmd is a command block in control direction with user defined output signals. These function blocks include the functiontype parameter for each block in the private range, and the information number ...
Page 1053
Name type description output6 boolean command output 6 output7 boolean command output 7 output8 boolean command output 8 18.6.12.5 settings table 771: i103usrcmd non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description functiontype 1 - 255 - 1 1 function type (1-255) pulsemode st...
Page 1054
18.6.13.3 function block iec10000285-1-en.Vsd i103gencmd block ^cmd_off ^cmd_on iec10000285 v1 en figure 482: i103gencmd function block 18.6.13.4 signals table 772: i103gencmd input signals name type default description block boolean 0 block of command table 773: i103gencmd output signals name type ...
Page 1055
Setting the report intermediate position = off. See the settings for rs485 and optical serial communication for more information. Input select is a single-indication signal, and it is also gi enabled. State transitions to on and off are reported spontaneously. When input block is on, the function wi...
Page 1056
18.6.15 operation principle 18.6.15.1 general iec 60870-5-103 is an unbalanced (master-slave) protocol for coded-bit serial communication exchanging information with a control system, and with a data transfer rate up to 38400 bit/s. In iec terminology, a primary station is a master and a secondary s...
Page 1057
Function type is selected with parameter functiontype. Information number is defined for each output signals. Table 777: i103iedcmd supported indications inf description 19 led reset 23 activate setting group 1 24 activate setting group 2 25 activate setting group 3 26 activate setting group 4 funct...
Page 1058
Inf 1) description 6 output signal 06 7 output signal 07 8 output signal 08 1) user defined information number status terminal status indications in monitor direction, i103ied indication block for status in monitor direction with defined ied functions. Number of instances: 1 function type is selecte...
Page 1059
Inf description gi typ cot 6* input signal 06 x/- 1/2 1,7,(9) 7* input signal 07 x/- 1/2 1,7,(9) 8* input signal 08 x/- 1/2 1,7,(9) 1) * user defined information number supervision indications in monitor direction, i103superv indication block for supervision in monitor direction with defined functio...
Page 1060
Information number is defined for each input signal. Number of instances: 1 info. No. Message supported 64 start l1 yes 65 start l2 yes 66 start l3 yes 67 start in yes 84 general start yes 69 trip l1 yes 70 trip l2 yes 71 trip l3 yes 68 general trip yes 74 fault forward/line yes 75 fault reverse/bus...
Page 1061
Info. No. Message supported 70 trip l2 yes 71 trip l3 yes 68 general trip yes 74 fault forward/line yes 75 fault reverse/busbar yes 85 breaker failure yes 86 trip measuring system l1 yes 87 trip measuring system l2 yes 88 trip measuring system l3 yes 89 trip measuring system n yes 90 over current tr...
Page 1062
The upper limit is the maximum value that can be encoded into the asdu (application service data unit). Any value higher than this value will be tagged as overflow. The factors 1.2 and 2.4 are taken from the 103 standard and require that a rated value to use as base exists, and then use 1.2 or 2.4 t...
Page 1063
Table 786: i103measusr supported indications inf fun gi typ cot description * 1) * 2) no, polled with cl2 * 3) 2,7 meas1 * * no, polled with cl2 * 2,7 meas2 * * no, polled with cl2 * 2,7 meas3 * * no, polled with cl2 * 2,7 meas4 * * no, polled with cl2 * 2,7 meas5 * * no, polled with cl2 * 2,7 meas6...
Page 1064
Channel number used for the remaining 32 analog signals are numbers in the private range 64 to 95. Binary signals, 128-channels: for each channel the user can specify a function type and an information number. Disturbance upload all analog and binary signals that are recorded with disturbance record...
Page 1065
Another information element in asdu23 is the fan (fault number). According to the standard this is a number that is incremented when a protection function takes action. Fan is equal to disturbance number, which is incremented for each disturbance. Asdu26 / asdu31 when a disturbance has been selected...
Page 1066
Supported 10 generic data no 11 generic identification no 23 list of recorded disturbances yes 26 ready for transm. Of disturbance data yes 27 ready for transm. Of a channel yes 28 ready for transm of tags yes 29 transmission of tags yes 30 transmission fo disturbance data yes 31 end of transmission...
Page 1067
18.6.16 technical data table 787: iec 60870-5-103 communication protocol function value protocol iec 60870-5-103 communication speed 9600, 19200 bd 18.7 horizontal communication via goose for interlocking gooseintlkrcv 18.7.1 functionality goose communication can be used for exchanging information b...
Page 1068
18.7.2 function block iec07000048.Vsd gooseintlkrcv block ^resreq ^resgrant ^app1_op ^app1_cl app1val ^app2_op ^app2_cl app2val ^app3_op ^app3_cl app3val ^app4_op ^app4_cl app4val ^app5_op ^app5_cl app5val ^app6_op ^app6_cl app6val ^app7_op ^app7_cl app7val ^app8_op ^app8_cl app8val ^app9_op ^app9_c...
Page 1069
Table 789: gooseintlkrcv output signals name type description resreq boolean reservation request resgrant boolean reservation granted app1_op boolean apparatus 1 position is open app1_cl boolean apparatus 1 position is closed app1val boolean apparatus 1 position is valid app2_op boolean apparatus 2 ...
Page 1070
Name type description app13_op boolean apparatus 13 position is open app13_cl boolean apparatus 13 position is closed app13val boolean apparatus 13 position is valid app14_op boolean apparatus 14 position is open app14_cl boolean apparatus 14 position is closed app14val boolean apparatus 14 position...
Page 1071
18.8 goose binary receive goosebinrcv 18.8.1 function block goosebinrcv block ^out1 dvalid1 ^out2 dvalid2 ^out3 dvalid3 ^out4 dvalid4 ^out5 dvalid5 ^out6 dvalid6 ^out7 dvalid7 ^out8 dvalid8 ^out9 dvalid9 ^out10 dvalid10 ^out11 dvalid11 ^out12 dvalid12 ^out13 dvalid13 ^out14 dvalid14 ^out15 dvalid15 ...
Page 1072
Name type description out4 boolean binary output 4 dvalid4 boolean valid data on binary output 4 out5 boolean binary output 5 dvalid5 boolean valid data on binary output 5 out6 boolean binary output 6 dvalid6 boolean valid data on binary output 6 out7 boolean binary output 7 dvalid7 boolean valid da...
Page 1073
18.9 goose function block to receive a double point value goosedprcv 18.9.1 identification function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number goose function block to receive a double point value goosedprcv - - 18.9.2 functionality goosedprcv is used ...
Page 1074
18.9.5 settings table 796: goosedprcv non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description operation off on - - off operation off/on 18.9.6 operation principle the datavalid output will be high if the incoming message is with valid data. The commvalid output will become low w...
Page 1075
18.10.3 function block iec10000250-1-en.Vsd gooseintrcv block ^intout datavalid commvalid test iec10000250 v1 en figure 487: gooseintrcv function block 18.10.4 signals table 797: gooseintrcv input signals name type default description block boolean 0 block of function table 798: gooseintrcv output s...
Page 1076
The implementation for iec 61850 quality data handling is restricted to a simple level. If quality data validity is good then the datavalid output will be high. If quality data validity is invalid, questionable, overflow, failure or old data then the datavalid output will be low. 18.11 goose functio...
Page 1077
Table 801: goosemvrcv output signals name type description mvout real measurand value output datavalid boolean data valid for measurand value output commvalid boolean communication valid for measurand value output test boolean test output 18.11.5 settings table 802: goosemvrcv non group settings (ba...
Page 1078
18.12.2 functionality goosesprcv is used to receive a single point value using iec 61850 protocol via goose. 18.12.3 function block goosesprcv block ^spout datavalid commvalid test iec10000248-1-en.Vsd iec10000248 v1 en figure 489: goosesprcv function block 18.12.4 signals table 803: goosesprcv inpu...
Page 1079
The input of this goose block must be linked in smt by means of a cross to receive the binary single point values. The implementation for iec 61850 quality data handling is restricted to a simple level. If quality data validity is good then the datavalid output will be high. If quality data validity...
Page 1080
18.13.3 function block iec06000007-2-en.Vsd multicmdrcv block error newdata output1 output2 output3 output4 output5 output6 output7 output8 output9 output10 output11 output12 output13 output14 output15 output16 valid iec06000007 v2 en figure 490: multicmdrcv function block iec06000008-2-en.Vsd multi...
Page 1081
Table 807: multicmdsnd input signals name type default description block boolean 0 block of function input1 boolean 0 input 1 input2 boolean 0 input 2 input3 boolean 0 input 3 input4 boolean 0 input 4 input5 boolean 0 input 5 input6 boolean 0 input 6 input7 boolean 0 input 7 input8 boolean 0 input 8...
Page 1082
Table 809: multicmdsnd output signals name type description error boolean multisend error 18.13.5 settings table 810: multicmdrcv non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description tmaxcycletime 0.050 - 200.000 s 0.001 11.000 maximum cycle time between receptions of input d...
Page 1083
18.14 security events on protocols secalarm 18.14.1 security alarm secalarm 18.14.1.1 signals table 812: secalarm output signals name type description eventid integer eventid of the generated security event seqnumber integer sequence number of the generated security event 18.14.1.2 settings table 81...
Page 1084
Name values (range) unit step default description extlogsrv2port 1 - 65535 - 1 514 external log server 2 port number extlogsrv2ip 0 - 18 ip address 1 127.0.0.1 external log server 2 ip-address extlogsrv3type off syslog udp/ip syslog tcp/ip cef tcp/ip - - off external log server 3 type extlogsrv3port...
Page 1085
Section 19 remote communication 19.1 binary signal transfer 19.1.1 identification function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number binary signal transfer binsignreceive - - binary signal transfer binsigntransm - - 19.1.2 functionality the remote en...
Page 1086
19.1.3 function block iec07000043-2-en.Vsd ldcmrecbinstat1 comfail ybit nocarr nomess addrerr lngtherr crcerror remcomf lowlevel iec07000043 v2 en iec07000044-2-en.Vsd ldcmrecbinstat2 comfail ybit nocarr nomess addrerr lngtherr crcerror trdelerr syncerr remcomf remgpser substitu lowlevel iec07000044...
Page 1087
Name type description nomess boolean no start and stop flags identified for the incoming message addrerr boolean incoming message from non-valid address lngtherr boolean wrong length of the incoming message crcerror boolean identified error by crc check in incoming message remcomf boolean remote ter...
Page 1088
Name type description ybit boolean detected error in remote end with incoming message nocarr boolean no carrier is detected in the incoming message nomess boolean no start and stop flags identified for the incoming message addrerr boolean incoming message from non-valid address lngtherr boolean wron...
Page 1089
Table 819: ldcmrecbinstat2 non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description channelmode blocked normal outofservice - - normal channel mode of ldcm, 0=off, 1=on, 2=outofservice terminalno 0 - 255 - 1 0 terminal number used for line differential communication remotetermno ...
Page 1090
Table 820: ldcmrecbinstat3 non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description channelmode blocked normal outofservice - - normal channel mode of ldcm, 0=off, 1=on, 2=outofservice terminalno 0 - 255 - 1 0 terminal number used for line differential communication remotetermno ...
Page 1091
19.1.6 monitored data table 821: ldcmrecbinstat1 monitored data name type values (range) unit description commstatus boolean 0=ok 1=syncerr 2=no rxd 3=localgpserr 4=remgpserr 5=locandremg pserr 6=localaderr 7=remaderr 8=locandrema derr 9=addresserr 10=freqconferr 11=latencyconf err - status of commu...
Page 1092
19.1.7 operation principle the communication is made on standard itu (ccitt) pcm digital 64 kbit/s channels. It is a two-way communication where telegrams are sent every 5 ms (same in 50 hz and 60 hz), exchanging information between two ieds. The format used is c37.94 and one telegram consists of st...
Page 1093
19.2 transmission of analog data from ldcm ldcmtransmit 19.2.1 function block ldcmtrn ^ct1l1 ^ct1l2 ^ct1l3 ^ct1n ^ct2l1 ^ct2l2 ^ct2l3 ^ct2n iec10000017-1-en.Vsd iec10000017 v1 en figure 495: ldcmtransmit function block the function blocks are not represented in the application configuration tool exc...
Page 1094
1088.
Page 1095
Section 20 basic ied functions 20.1 authority check athchck 20.1.1 identification function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number authority check athchck - - 20.1.2 functionality to safeguard the interests of our customers, both the ied and the to...
Page 1096
Iec12000202-2-en.Vsd iec12000202 v2 en figure 496: pcm600 user management tool 20.1.3 operation principle there are different levels (or types) of users that can access or operate different areas of the ied and tools functionality. The pre-defined user types are given in table 825 . Ensure that the ...
Page 1097
Table 825: pre-defined user types access rights guest super user spa guest system operator protection engineer design engineer user administrator basic setting possibilities (change setting group, control settings, limit supervision) r r/w r r/w r/w r/w r advanced setting possibilities (for example ...
Page 1098
The maximum of characters in a password is 18. At least one user must be included in the useradministrator group to be able to write users, created in pcm600, to ied. At delivery the default user is the superuser. No log on is required to operate the ied until a user has been created with the ied us...
Page 1099
At delivery, the ied user has full access as superuser when using the lhmi and as administrator when using ftp or pcm600 until central account management is activated. Table 826: default users user name user rights superuser full rights, only presented in lhmi. Lhmi is logged on by default until oth...
Page 1100
Management of user credentials and roles is handled on the central account management server e.G. Sdm600 the ied employs two strategies to ensure availability of the authentication system even if there is a problem with the network or authentication server: • a substation can be equipped with two re...
Page 1101
20.2 authority management authman 20.2.1 identification function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number authority management authman - - 20.2.2 authman this function enables/disables the maintenance menu. It also controls the maintenance menu log ...
Page 1102
If normal ftp is required to read out disturbance recordings, create a specific account for this purpose with rights only to do file transfer. The password of this user will be exposed in clear text on the wire. 20.3.3 settings table 830: ftpaccs non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit s...
Page 1103
20.4.4 signals table 831: athstat output signals name type description usrblked boolean at least one user is blocked by invalid password loggedon boolean at least one user is logged on the output signal usrblked is not valid if the ied is centralized account management enabled. 20.4.5 settings the f...
Page 1104
Interrsig fail warning tsyn cerr rtcerr stupblk iec09000787-2-en.Vsdx iec09000787 v2 en figure 498: interrsig function block 20.5.3 signals table 832: interrsig output signals name type description fail boolean internal fail warning boolean internal warning tsyncerr boolean time synchronization erro...
Page 1105
Output relay is an or-function between the int-fail signal see figure 500 and a couple of more severe faults that can occur in the ied, see figure 499 iec04000520 v1 en figure 499: hardware self-supervision, potential-free alarm contact timesyncherror e.G. Bim 1 error io fail io stopped io started o...
Page 1106
Some signals are available from the interrsig function block. The signals from this function block are sent as events to the station level of the control system. The signals from the interrsig function block can also be connected to binary outputs for signalization via output relays or they can be u...
Page 1107
Name of signal description displayed on local hmi as reasons for activation lmderror lon/mip device error status slm301 lon network interface, mip/dps, is in an unrecoverable error state. Apperror runtime applicatio n error status runtime app error this signal will be active if one or more of the ap...
Page 1108
Card name of signal description displayed on local hmi as reasons for activation adm adm-error a/d module error status adm32 activated if the module has a hardware error. Oem oem-error optical ethernet module error status oem3nn activated if the module has a hardware error. N = slot number ldcm ldcm...
Page 1109
20.6 time synchronization timesynchgen 20.6.1 functionality the time synchronization function is used to select a common source of absolute time for the synchronization of the ied when it is a part of a protection system. This makes it possible to compare events and disturbance data between all ieds...
Page 1110
Table 836: timesynchgen non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description coarsesyncsrc off spa lon sntp dnp iec103 - - off coarse time synchronization source finesyncsource off spa lon bin gps gps+spa gps+lon gps+bin sntp gps+sntp irig-b gps+irig-b pps - - off fine time s...
Page 1111
Table 839: dstenable non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description dst enable off on - - on enables or disables the use of daylight saving time table 840: dstbegin non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description monthinyear january february...
Page 1112
Table 841: dstend non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description monthinyear january february march april may june july august september october november december - - october month in year when daylight time ends dayinweek sunday monday tuesday wednesday thursday friday...
Page 1113
Table 842: timezone non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description timezone -12:00 -11:00 -10:00 -9:30 -9:00 -8:00 -7:00 -6:00 -5:00 -4:30 -4:00 -3:30 -3:00 -2:00 -1:00 0:00 1:00 2:00 3:00 3:30 4:00 4:30 5:00 5:30 5:45 6:00 6:30 7:00 8:00 8:45 9:00 9:30 10:00 10:30 11:0...
Page 1114
20.6.3 operation principle 20.6.3.1 general concepts time definitions the error of a clock is the difference between the actual time of the clock, and the time the clock is intended to have. Clock accuracy indicates the increase in error, that is, the time gained or lost by the clock. A disciplined ...
Page 1115
Sw time time regulator (fast or slow) time tagging and general synchronization time regulator (setting: see technical manual) commu- nication events synchronization for differential protection (echo mode) diff. Commu- nication *iec 61850-9-2 iec16000002-2-en.Vsdx external synchronization sources tra...
Page 1116
New start-up is also required, for example, after maintenance of the auxiliary voltage system. When the time difference is >16μs, the differential function is blocked and the time regulator for the hardware clock automatically uses a fast mode to synchronize the clock systems. The time adjustment is...
Page 1117
20.6.3.2 real-time clock (rtc) operation the ied has a built-in real-time clock (rtc) with a resolution of one second. The clock has a built-in calendar that handles leap years through 2038. Real-time clock at power off during power off, the system time in the ied is kept by a capacitor-backed real-...
Page 1118
Such that one message can be lost without getting a tsyncerr, but if more than one message is lost, a tsyncerr is given. 20.6.3.3 synchronization alternatives four main alternatives of external synchronization sources are available. The synchronization message is applied: • via any of the communicat...
Page 1119
Synchronization via built-in-gps the built-in gps clock modules receive and decode time information from the global positioning system. The modules are located on the gps time synchronization module (gtm). Synchronization via binary input the ied accepts minute pulses to a binary input. These minute...
Page 1120
A b c en05000251.Vsd iec05000251 v1 en figure 504: binary minute pulses the default time-out-time for a minute pulse is two minutes, and if no valid minute pulse is received within two minutes a syncerr will be given. If contact bounce occurs, only the first pulse will be detected as a minute pulse....
Page 1121
To receive irig-b there are two connectors in the irig-b module, one galvanic bnc connector and one optical st connector. Irig-b 12x messages can be supplied via the galvanic interface, and irig-b 00x messages can be supplied via either the galvanic interface or the optical interface, where x (in 00...
Page 1122
20.7.2 function block actvgrp actgrp1 actgrp2 actgrp3 actgrp4 actgrp5 actgrp6 grp1 grp2 grp3 grp4 grp5 grp6 setchgd remseten iec05000433-3-en.Vsd iec05000433 v3 en figure 505: activegroup function block 20.7.3 signals table 845: actvgrp input signals name type default description actgrp1 boolean 0 s...
Page 1123
20.7.4 settings table 847: setgrps non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description activesetgrp settinggroup1 settinggroup2 settinggroup3 settinggroup4 settinggroup5 settinggroup6 - - settinggroup1 active setting group maxnosetgrp 1 - 6 - 1 1 max number of setting groups...
Page 1124
Iec05000119-3-en.Vsd iox-bly1 iox-bly2 iox-bly3 iox-bly4 +rl2 Æ Æ Æ Æ activate group 4 activate group 3 activate group 2 activate group 1 iox-bly5 iox-bly6 Æ Æ activate group 5 activate group 6 actvgrp actgrp1 actgrp2 actgrp3 actgrp4 actgrp5 actgrp6 grp1 grp2 grp3 grp4 grp5 grp6 setchgd remseten iec...
Page 1125
20.8.2 function block iec09000946.Vsd chnglck lock* active override iec09000946 v2 en figure 507: chnglck function block 20.8.3 signals table 848: chnglck input signals name type default description lock boolean 0 activate change lock table 849: chnglck output signals name type description active bo...
Page 1126
Binary input function 1 activated 0 deactivated 20.9 test mode functionality testmode 20.9.1 functionality when the test mode functionality testmode is activated, all the functions in the ied are automatically blocked. Activated testmode is indicating by a flashing yellow led on the local hmi. It is...
Page 1127
Table 851: testmode output signals name type description test boolean in test via ied test or via ld0 mode ied_test boolean ied test mode is active block boolean active when ld0 is blocked or test blocked noevent boolean event disabled during test mode input boolean ied test input is active setting ...
Page 1128
If the ied is restarted while set to ied testmode by a binary input all functions will be temporarily unblocked during startup, which might cause unwanted operations. The testmode function block might be used to automatically block functions when a test handle is inserted in a test switch. A contact...
Page 1129
20.11 product information prodinf 20.11.1 functionality the product identifiers function contains constant data (i.E. Not possible to change) that uniquely identifies the ied: • productver • productdef • firmwarever • serialno • orderingno • productiondate • iedprodtype the settings are visible on t...
Page 1130
2 is the minor version of the manufactured product this means, new functions or new hardware added to the product 3 is the major revision of the manufactured product this means, functions or hardware is either changed or enhanced in the product • iedmainfuntype • main function type code according to...
Page 1131
Name type default description bi4 boolean 0 smt connect input bi5 boolean 0 smt connect input bi6 boolean 0 smt connect input bi7 boolean 0 smt connect input bi8 boolean 0 smt connect input bi9 boolean 0 smt connect input bi10 boolean 0 smt connect input table 855: smbi output signals name type desc...
Page 1132
The application manual to get information about how binary inputs are sent from one ied configuration. 20.13.2 function block iec05000439-2-en.Vsd smbo bo1 bo2 bo3 bo4 bo5 bo6 bo7 bo8 bo9 bo10 ^bo1 ^bo2 ^bo3 ^bo4 ^bo5 ^bo6 ^bo7 ^bo8 ^bo9 ^bo10 iec05000439 v2 en figure 510: smbo function block 20.13....
Page 1133
20.14 signal matrix for ma inputs smmi 20.14.1 functionality the signal matrix for ma inputs (smmi) function is used within the application configuration tool (act) in direct relation with the signal matrix tool (smt). See the application manual for information about how milliamp (ma) inputs from ex...
Page 1134
20.14.4 operation principle the signal matrix for ma inputs (smmi) function, see figure 511 , receives its inputs from the real (hardware) ma inputs (the mim boards) via the signal matrix tool (smt), and makes them available to the rest of the configuration via its analog outputs, named ai1 to ai6. ...
Page 1135
• n=2 and m=12 in task group 1 • n=14 and m=24 in task group 2 • n=26 and m=36 in task group 3 the task time defines the execution repetition rate, and is 3, 8 or 1 ms respectively for the three task time groups. 20.15.3 signals table 859: smai1 input signals name type default description block bool...
Page 1136
Name type default description grp2l2 string - second analog input used for phase l2 or l2-l3 quantity grp2l3 string - third analog input used for phase l3 or l3-l1 quantity grp2n string - fourth analog input used for residual or neutral quantity table 862: smai2 output signals name type description ...
Page 1137
Table 863: smai1 non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description globalbasesel 1 - 12 - 1 1 selection of one of the global base value groups dftrefextout internaldftref dftrefgrp1 dftrefgrp2 dftrefgrp3 dftrefgrp4 dftrefgrp5 dftrefgrp6 dftrefgrp7 dftrefgrp8 dftrefgrp9 dft...
Page 1138
Table 865: smai2 non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description globalbasesel 1 - 12 - 1 1 selection of one of the global base value groups dftreference internaldftref dftrefgrp1 dftrefgrp2 dftrefgrp3 dftrefgrp4 dftrefgrp5 dftrefgrp6 dftrefgrp7 dftrefgrp8 dftrefgrp9 dft...
Page 1139
The smai function will always calculate the residual sum of current/voltage if the input grpxn is not connected in smt. Applications with a few exceptions shall always be connected to ai3p. 20.15.5.1 frequency values the smai function includes a functionality based on the level of positive sequence ...
Page 1140
The outputs from the above configured smai block shall only be used for overfrequency protection (saptof), underfrequency protection (saptuf) and rate-of-change frequency protection (sapfrc) due to that all other information except frequency and positive sequence voltage might be wrongly calculated....
Page 1141
20.17 primary system values primval 20.17.1 identification function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number primary system values primval - - 20.17.2 functionality the rated system frequency and phase rotation direction are set under main menu/ con...
Page 1142
20.18.2 function block 3phsum block revrot ^g1ai3p* ^g2ai3p* ai3p ai1 ai2 ai3 ai4 iec05000441-3-en.Vsdx iec05000441 v3 en figure 515: 3phsum function block 20.18.3 signals table 869: 3phsum input signals name type default description block boolean 0 block blkgr1 boolean 0 block input for group 1 blk...
Page 1143
20.18.4 settings settings dftrefextout and dftreference shall be set to default value internaldftref if no vt inputs are available. Table 871: 3phsum non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description globalbasesel 1 - 12 - 1 1 selection of one of the global base value grou...
Page 1144
20.19.2 function blocks dosfrnt linkup warning alarm iec09000749-1-en.Vsd iec09000749 v1 en figure 516: dosfrnt function block linkup warning alarm doslanab iec13000308-1-en.Vsd iec13000308 v1 en figure 517: doslanab function block linkup warning alarm doslancd iec13000309-1-en.Vsd iec13000309 v1 en...
Page 1145
20.19.4 settings the function does not have any parameters available in the local hmi or pcm600. 20.19.5 monitored data table 876: dosfrnt monitored data name type values (range) unit description state integer 0=off 1=normal 2=throttle 3=discardlow 4=discardall 5=stoppoll - frame rate control state ...
Page 1146
• linkup indicates the ethernet link status • warning indicates that communication (frame rate) is higher than normal • alarm indicates that the ied limits communication section 20 1mrk502052-uen b basic ied functions 1140 technical manual.
Page 1147
Section 21 ied hardware 21.1 overview 21.1.1 variants of case size with local hmi display iec04000458-2-en.Psd iec04000458 v2 en figure 519: 1/2 19” case with local hmi display. 1mrk502052-uen b section 21 ied hardware 1141 technical manual.
Page 1148
Iec05000762-2-en.Psd iec05000762 v2 en figure 520: 3/4 19” case with local hmi display. Iec04000460-2-en.Psd iec04000460 v2 en figure 521: 1/1 19” case with local hmi display. Section 21 1mrk502052-uen b ied hardware 1142 technical manual.
Page 1149
21.1.2 case from the rear side table 879: designations for 1/2 x 19” casing with 1 trm slot 1mrk002801-ac-2-670-1.2-pg v.3 en 1mrk002801-ac-2-670-1.2-pg v3 en module rear positions psm x11 bim, bom, som, iom or mim x31 and x32 etc. To x51 and x52 slm x301:a, b, c, d ldcm, irig-b or rs485 x302 ldcm o...
Page 1150
Table 880: designations for 3/4 x 19” casing with 1 trm slot 1mrk002801-ac-3-670-1.2-pg v.3 en 1mrk002801-ac-3-670-1.2-pg v3 en module rear positions psm x11 bim, bom, som, iom or mim x31 and x32 etc. To x101 and x102 slm x301:a, b, c, d ldcm, irig-b or rs485 x302 ldcm or rs485 x303 oem x311:a, b, c...
Page 1151
Table 881: designations for 3/4 x 19” casing with 2 trm slot 1mrk002801-ac-4-670-1.2-pg v.3 en 1mrk002801-ac-4-670-1.2-pg v3 en module rear positions psm x11 bim, bom, som, iom or mim x31 and x32 etc. To x71 and x72 slm x301:a, b, c, d ldcm, irig-b or rs485 x302 ldcm or rs485 x303 oem x311:a, b, c, ...
Page 1152
Table 882: designations for 1/1 x 19” casing with 1 trm slot 1mrk002801-ac-5-670-1.2-pg v.3 en 1mrk002801-ac-5-670-1.2-pg v3 en module rear positions psm x11 bim, bom, som, iom or mim x31 and x32 etc. To x161 and x162 slm x301:a, b, c, d ldcm, irig-b or rs485 x302 ldcm or rs485 x303 oem x311:a, b, c...
Page 1153
Table 883: designations for 1/1 x 19” casing with 2 trm slots 1mrk002801-ac-6-670-1.2-pg v.3 en 1mrk002801-ac-6-670-1.2-pg v3 en module rear positions psm x11 bim, bom, som, iom or mim x31 and x32 etc. To x131 and x132 slm x301:a, b, c, d ldcm, irig-b or rs485 x302 ldcm or rs485 x303 oem x311:a, b, ...
Page 1154
21.2 hardware modules 21.2.1 overview table 884: basic modules module description power supply module (psm) including a regulated dc/dc converter that supplies auxiliary voltage to all static circuits. • an internal fail alarm output is available. Numerical module (num) module for overall applicatio...
Page 1155
21.2.2 numeric processing module (num) 21.2.2.1 introduction the numeric processing module (num), is a cpu-module that handles all protection functions and logic. For communication with high speed modules, e.G. Analog input modules and high speed serial interfaces, the num is equipped with a compact...
Page 1156
21.2.2.3 block diagram en04000473.Vsd logic compact flash north bridge cpu memory pc-mip pmc connector u b m co n n e ct or ethernet b ac kp la n e co nn ec to r pci-pci- bridge iec04000473 v1 en figure 522: numeric processing module block diagram 21.2.3 power supply module (psm) 21.2.3.1 introducti...
Page 1157
Regulated dc/dc converter that provides full isolation between the terminal and the external battery system. Connection diagram iec08000476 v2 en figure 523: psm connection diagram. 21.2.3.3 technical data table 886: psm - power supply module quantity rated value nominal range auxiliary dc voltage, ...
Page 1158
21.2.5.2 design the transformer module has 12 input transformers. There are several versions of the module, each with a different combination of voltage and current input transformers. Basic versions: • 6 current channels and 6 voltage channels • 7 current channels and 5 voltage channels • 9 current...
Page 1159
Iec08000479 v2 en figure 524: trm connection diagram 21.2.5.3 technical data table 887: trm - energizing quantities, rated values and limits for protection transformer modules quantity rated value nominal range current i r = 1 or 5 a (0.2-40) × i r operative range (0-100) x i r permissive overload 4...
Page 1160
Table 888: trm - energizing quantities, rated values and limits for measuring transformer modules quantity rated value nominal range current i r = 1 or 5 a (0-1.8) × i r at i r = 1 a (0-1.6) × i r at i r = 5 a permissive overload 1.1 × i r cont. 1.8 × i r for 30 min at i r = 1 a 1.6 × i r for 30 min...
Page 1161
Input signals are sampled with a sampling freqency of 5 khz at 50 hz system frequency and 6 khz at 60 hz system frequency. The a\d converted signals goes through a filter with a cut off frequency of 500 hz and are reported to the numerical module (num) with 1 khz at 50 hz system frequency and 1,2 kh...
Page 1162
21.2.7 binary input module (bim) 21.2.7.1 introduction the binary input module has 16 optically isolated inputs and is available in two versions, one standard and one with enhanced pulse counting capabilities on the inputs to be used with the pulse counter function. The binary inputs are freely prog...
Page 1163
300 176 144 88 72 38 32 19 17 24/30v 48/60v 110/125v 220/250v [v] xx06000391-2-en.Vsd iec06000391 v2 en figure 526: voltage dependence for the binary inputs iec99000517-abc v1 en operation operation uncertain no operation this binary input module communicates with the numerical module (num). The des...
Page 1164
En07000104-3.Vsd 50 55 [ms] [ma] iec07000104 v3 en figure 527: approximate binary input inrush current for the standard version of bim. En07000105-1.Vsd 50 5.5 [ms] [ma] iec07000105 v2 en figure 528: approximate binary input inrush current for the bim version with enhanced pulse counting capabilitie...
Page 1165
Iec99000503 v3 en figure 529: connection diagram 21.2.7.3 signals table 890: bim output signals name type description status boolean binary input module status bi1 boolean binary input 1 value bi2 boolean binary input 2 value bi3 boolean binary input 3 value bi4 boolean binary input 4 value bi5 bool...
Page 1166
Name type description bi8 boolean binary input 8 value bi9 boolean binary input 9 value bi10 boolean binary input 10 value bi11 boolean binary input 11 value bi12 boolean binary input 12 value bi13 boolean binary input 13 value bi14 boolean binary input 14 value bi15 boolean binary input 15 value bi...
Page 1167
Quantity rated value nominal range counter input frequency 10 pulses/s max - oscillating signal discriminator blocking settable 1–40 hz release settable 1–30 hz debounce filter settable 1–20 ms maximum 176 binary input channels may be activated simultaneously with influencing factors within nominal ...
Page 1168
The high closing and carrying current capability allows connection directly to breaker trip and closing coils. If breaking capability is required to manage fail of the breaker auxiliary contacts normally breaking the trip coil current, a parallel reinforcement is required. For configuration of the o...
Page 1169
Iec99000505 v3 en figure 531: connection diagram 21.2.8.3 signals table 895: bom input signals name type default description block boolean 0 block binary outputs bo1 boolean 0 binary output 1 bo2 boolean 0 binary output 2 bo3 boolean 0 binary output 3 bo4 boolean 0 binary output 4 bo5 boolean 0 bina...
Page 1170
Name type default description bo13 boolean 0 binary output 13 bo14 boolean 0 binary output 14 bo15 boolean 0 binary output 15 bo16 boolean 0 binary output 16 bo17 boolean 0 binary output 17 bo18 boolean 0 binary output 18 bo19 boolean 0 binary output 19 bo20 boolean 0 binary output 20 bo21 boolean 0...
Page 1171
Name type values (range) unit description bo2 boolean 0=normal 1=forced 2=blocked - binary output 2 status bo3value boolean 1=1 0=0 - binary output 3 value bo3force boolean 0=normal 1=forced - binary output 3 force bo3 boolean 0=normal 1=forced 2=blocked - binary output 3 status bo4value boolean 1=1...
Page 1172
Name type values (range) unit description bo9 boolean 0=normal 1=forced 2=blocked - binary output 9 status bo10value boolean 1=1 0=0 - binary output 10 value bo10force boolean 0=normal 1=forced - binary output 10 force bo10 boolean 0=normal 1=forced 2=blocked - binary output 10 status bo11value bool...
Page 1173
Name type values (range) unit description bo16 boolean 0=normal 1=forced 2=blocked - binary output 16 status bo17value boolean 1=1 0=0 - binary output 17 value b017force boolean 0=normal 1=forced - binary output 17 force bo17 boolean 0=normal 1=forced 2=blocked - binary output 17 status bo18value bo...
Page 1174
Name type values (range) unit description bo23 boolean 0=normal 1=forced 2=blocked - binary output 23 status bo24value boolean 1=1 0=0 - binary output 24 value bo24force boolean 0=normal 1=forced - nary output 24 force bo24 boolean 0=normal 1=forced 2=blocked - binary output 24 status 21.2.8.6 techn...
Page 1175
21.2.9 static binary output module (som) 21.2.9.1 introduction the static binary output module has six fast static outputs and six change over output relays for use in applications with high speed requirements. 21.2.9.2 design the static output module (som) have 6 normally open (no) static outputs a...
Page 1176
Iec09000975 v1 en figure 533: connection diagram of the static output module 21.2.9.3 signals table 900: som input signals name type default description block boolean 0 block binary outputs bo1 boolean 0 binary output 1 bo2 boolean 0 binary output 2 bo3 boolean 0 binary output 3 bo4 boolean 0 binary...
Page 1177
21.2.9.4 settings table 902: som non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description operation off on - - on operation off/on 21.2.9.5 monitored data table 903: som monitored data name type values (range) unit description status boolean 0=ok 1=error - static binary output mo...
Page 1178
Name type values (range) unit description bo6value boolean 1=1 0=0 - binary output 6 value bo6force boolean 0=normal 1=forced - binary output 6 force bo6 boolean 0=normal 1=forced 2=blocked - binary output 6 status bo7value boolean 1=1 0=0 - binary output 7 value bo7force boolean 0=normal 1=forced -...
Page 1179
21.2.9.6 technical data table 904: som - static output module (reference standard: iec 61810-2): static binary outputs function of quantity static binary output trip rated voltage 48-60 vdc 110-250 vdc number of outputs 6 6 impedance open state ~300 kΩ ~810 kΩ test voltage across open contact, 1 min...
Page 1180
Maximum 72 outputs may be activated simultaneously with influencing factors within nominal range. After 6 ms an additional 24 outputs may be activated. The activation time for the 96 outputs must not exceed 200 ms. 48 outputs can be activated during 1 s. Continued activation is possible with respect...
Page 1181
The making capacity of the reed relays are limited. Iec1mrk002801-aa11-utan-ram v2 en figure 534: binary in/out module (iom), input contacts named xa corresponds to rear position x31, x41, and so on, and output contacts named xb to rear position x32, x42, and so on the binary input/output module ver...
Page 1182
Xx04000069.Vsd iec04000069 v1 en figure 535: iom with mov protection, relay example 21.2.10.3 signals table 906: iomin output signals name type description status boolean binary input part of iom module status bi1 boolean binary input 1 value bi2 boolean binary input 2 value bi3 boolean binary input...
Page 1183
21.2.10.4 settings table 908: iomin non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description operation off on - - on binary input/output module in operation (on) or not (off) debouncetime 0.001 - 0.020 s 0.001 0.001 debounce time for binary inputs oscblock 1 - 40 hz 1 40 oscillat...
Page 1184
Name type values (range) unit description bo5value boolean 1=1 0=0 - binary output 5 value bo5force boolean 0=normal 1=forced - binary output 5 force bo5 boolean 0=normal 1=forced 2=blocked - binary output 5 status bo6value boolean 1=1 0=0 - binary output 6 value bo6force boolean 0=normal 1=forced -...
Page 1185
Name type values (range) unit description bo12value boolean 1=1 0=0 - binary output 12 value bo12force boolean 0=normal 1=forced - binary output 12 force bo12 boolean 0=normal 1=forced 2=blocked - binary output 12 status 21.2.10.6 technical data table 911: iom - binary input/output module quantity r...
Page 1186
Function or quantity trip and signal relays fast signal relays (parallel reed relay) making capacity at inductive load with l/r>10 ms 0.2 s 1.0 s 30 a 10 a 0.4 a 0.4 a making capacity at resistive load 0.2 s 1.0 s 30 a 10 a 220–250 v/0.4 a 110–125 v/0.4 a 48–60 v/0.2 a 24–30 v/0.1 a breaking capacit...
Page 1187
Breaking capacity for ac, cos j >0.4 250 v/8.0 a 250 v/8.0 a breaking capacity for dc with l/r 48 v/1 a 110 v/0.4 a 220 v/0.2 a 250 v/0.15 a 48 v/1 a 110 v/0.4 a 220 v/0.2 a 250 v/0.15 a maximum capacitive load - 10 nf maximum 72 outputs may be activated simultaneously. After 6 ms an additional 24 o...
Page 1188
Iec99000504 v2 en figure 536: mim connection diagram 21.2.11.3 signals table 914: mim output signals name type description status boolean milliampere input module status ch1 real analog input 1 ch2 real analog input 2 ch3 real analog input 3 table continues on next page section 21 1mrk502052-uen b i...
Page 1189
Name type description ch4 real analog input 4 ch5 real analog input 5 ch6 real analog input 6 21.2.11.4 settings table 915: mim non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description operation off on - - on operation off/on maxreportt 0 - 3600 s 1 1 maximum time between reports...
Page 1190
Name values (range) unit step default description valueminch4 -10000000000.000 - 10000000000.000 - 0.001 4.000 min primary value corr. To iminch4 valuemaxch4 -10000000000.000 - 10000000000.000 - 0.001 20.000 max primary value corr. To imaxch4 endeadbandch5 off on - - off enable amplitude deadband re...
Page 1191
Name type values (range) unit description ch4 real - a service value analog input 4 ch5 real - a service value analog input 5 ch6 real - a service value analog input 6 21.2.11.6 technical data table 917: mim - ma input module quantity: rated value: nominal range: input resistance r in = 194 ohm - in...
Page 1192
Iec05000760 v2 en figure 537: the slm variants, component side view 1 receiver, lon 2 transmitter, lon 3 receiver, spa/iec 60870-5-103/dnp3 4 transmitter, spa/iec 60870-5-103/dnp3 a snap in connector for plastic fiber b st connector for glass fiber observe that when the slm connectors are viewed fro...
Page 1193
Table 919: slm – spa/iec 60870-5-103/dnp3 port quantity range or value optical connector glass fiber: type st plastic fiber: type hfbr snap-in fiber, optical budget glass fiber: 11 db (1000m/3000ft m typically *) plastic fiber: 7 db (25m/80ft m typically *) fiber diameter glass fiber: 62.5/125 mm pl...
Page 1194
Screw terminal x3 1 2 1 2 3 4 5 6 screw terminal x1 backplane angle bracket rs485 pwb iec06000517 v1 en figure 538: rs485 connector • 2-wire: connect pin 1 to pin 6 and pin 2 to pin 5 • termination (2-wire): connect pin 1 to pin 3 • termination (4-wire): connect pin 1 to pin 3 and pin 4 to pin 6 sof...
Page 1195
21.2.14 optical ethernet module (oem) 21.2.14.1 introduction the optical fast-ethernet module is used for fast and interference-free communication of synchrophasor data over ieee c37.118 and/or ieee 1344 protocols. It is also used to connect an ied to the communication buses (like the station bus) t...
Page 1196
21.2.14.4 technical data table 922: oem - optical ethernet module quantity rated value number of channels 1 or 2 standard ieee 802.3u 100base-fx type of fiber 62.5/125 mm multimode fibre wave length 1300 nm optical connector type st communication speed fast ethernet 100 mbit/s 21.2.15 line data comm...
Page 1197
St st io -c o n n e c to r iec07000087=1=en=original.Vsd iec07000087 v2 en figure 540: the sr-ldcm layout. Pcmip type ii single width format with two pci connectors and one i/o st type connector c iec06000393=1=en=original.Vsd iec06000393 v2 en figure 541: the mr-ldcm and lr-ldcm layout. Pcmip type ...
Page 1198
Table 923: line data communication module characteristic range or value type of ldcm short range (sr) medium range (mr) long range (lr) type of fiber graded-index multimode 62.5/125 µm singlemode 9/125 µm singlemode 9/125 µm peak emission wave length nominal maximum minimum 820 nm 865 nm 792 nm 1310...
Page 1199
21.2.16.2 design the galvanic x.21 line data communication module uses a abb specific pc*mip type ii format. C en07000196.Vsd iec07000196 v1 en figure 542: overview of the x.21 ldcm module 1 2 3 4 en07000239.Wmf 1 8 9 15 iec07000239 v1 en figure 543: the x.21 ldcm module external connectors 1. Earth...
Page 1200
I/o 100k w 100nf soft ground en07000242.Vsd iec07000242 v1 en figure 544: schematic view of soft earth earthing three different kinds of earthing principles can be set (used for fault tracing): 1. Direct earth - the normal earthing is direct earth, connect terminal 2 directly to the chassis. 2. No e...
Page 1201
A maximum of 100 meter of cable is allowed to ensure the quality of the data (deviation from x.21 standard cable length). Synchronization the x.21 ldcm works like a dte (data terminal equipment) and is normally expecting synchronization from the dce (data circuit equipment). The transmission is norm...
Page 1202
All communication between the gcm and the num is via the pci-bus. Pps time data is sent from the gcm to the rest of the time system to provide 1μs accuracy at sampling level. An optical transmitter for pps output is available for time synchronization of another relay with an optical pps input. The p...
Page 1203
Xx04000155.Vsd 1 2 4 3 5 6 7 iec04000155 v2 en figure 545: antenna with console where: 1 gps antenna 2 tnc connector 3 console, 78x150 mm 4 mounting holes 5.5 mm 5 tab for securing of antenna cable 6 vertical mounting position 7 horizontal mounting position antenna cable use a 50 ohm coaxial cable w...
Page 1204
21.2.18.3 technical data table 928: gps – antenna and cable function value max antenna cable attenuation 26 db @ 1.6 ghz antenna cable impedance 50 ohm lightning protection must be provided externally antenna cable connector sma in receiver end tnc in antenna end accuracy +/-1μs 21.2.19 irig-b time ...
Page 1205
St y2 t a1 iec06000304=1=en=original.Ai iec06000304 v2 en figure 546: irig-b pc-mip board with top left st connector for optical irig-b 00x 820 nm multimode fibre optic signal input and lower left bnc connector for irig-b signal input 21.2.19.3 settings table 929: irig-b non group settings (basic) n...
Page 1206
Quantity rated value supported formats irig-b 00x, irig-b 12x accuracy +/-10μs for irig-b 00x and +/-100μs for irig-b 12x input impedance 100 k ohm optical connector: optical connector irig-b type st type of fibre 62.5/125 μm multimode fibre supported formats irig-b 00x accuracy +/- 1μs 21.3 dimensi...
Page 1207
Xx08000166.Vsd j g f k h iec08000166 v1 en figure 548: case without rear cover with 19” rack mounting kit case size (mm) a b c d e f g h j k 6u, 1/2 x 19” 265.9 223.7 201.1 252.9 205.7 190.5 203.7 465.1 187.6 482.6 6u, 3/4 x 19” 265.9 336.0 201.1 252.9 318.0 190.5 316.0 465.1 187.6 482.6 6u, 1/1 x 1...
Page 1208
21.3.2 flush mounting dimensions c a b e d iec08000162-2-en.Vsd iec08000162 v2 en figure 549: flush mounting case size tolerance cut-out dimensions (mm) a +/-1 b +/-1 c d 6u, 1/2 x 19" 210.1 254.3 4.0-10.0 12.5 6u, 3/4 x 19" 322.4 254.3 4.0-10.0 12.5 6u, 1/1 x 19" 434.7 254.3 4.0-10.0 12.5 e = 188.6...
Page 1209
21.3.3 side-by-side flush mounting dimensions iec06000182-2-en.Vsd iec06000182 v2 en figure 550: a 1/2 x 19” size ied side-by-side with rhgs6 xx05000505.Vsd b a c g d e f iec05000505 v1 en figure 551: panel-cut out dimensions for side-by-side flush mounting case size (mm) tolerance a ±1 b ±1 c ±1 d ...
Page 1210
21.3.4 wall mounting dimensions iec04000471-2-en.Vsd iec04000471 v2 en figure 552: wall mounting case size (mm) a b c d e 6u, 1/2 x 19” 292.0 267.1 272.8 390.0 243.0 6u, 3/4 x 19” 404.3 379.4 272.8 390.0 243.0 6u, 1/1 x 19” 516.0 491.1 272.8 390.0 243.0 21.3.5 external resistor unit for high impedan...
Page 1211
Xx06000232.Eps dimension mm [inches] [18.98] [18.31] [0.33] [6 .9 7 ] [4 .0 2 ] [1 .4 8 ] [0.79] [7.68] iec06000232 v2 en figure 553: dimension drawing of a one phase impedance resistor unit en06000234.Eps [inches] [18.98] [18.31] [0.33] [7 .5 0 ] [1 0 .4 7 ] [7.68] [0.79] [1 .5 0 ] iec06000234 v2 e...
Page 1212
21.3.6 external current transformer unit 5 7 [2 .2 4 ] 89 [3 .5 ] xx06000233.Vsd 482.6 [19] dimension mm [inches] iec06000233 v1 en figure 555: dimension drawing of summation current transformers 21.4 mounting alternatives 21.4.1 flush mounting 21.4.1.1 overview the flush mounting kit can be used fo...
Page 1213
21.4.1.2 mounting procedure for flush mounting 1 3 5 4 2 6 iec08000161-2-en.Vsd iec08000161 v2 en figure 556: flush mounting details. Posno description quantity type 1 sealing strip, used to obtain ip54 class. The sealing strip is factory mounted between the case and front plate. - - 2 fastener 4 - ...
Page 1214
21.4.2 19” panel rack mounting 21.4.2.1 overview all ied sizes can be mounted in a standard 19” cubicle rack by using the for each size suited mounting kit which consists of two mounting angles, fastening screws and washers for the angles. The mounting angles are reversible which enables mounting of...
Page 1215
21.4.2.2 mounting procedure for 19” panel rack mounting 1a iec08000160-3-en.Vsdx 1a 2 3 iec08000160 v3 en figure 557: 19” panel rack mounting details the required torque for the screws is 3.5 nm. Pos description quantity type 1a mounting angles, which can be mounted, either to the left or right side...
Page 1216
21.4.3 wall mounting 21.4.3.1 overview all case sizes, 1/2 x 19”, 3/4 x 19”,1/1 x 19”, can be wall mounted. It is also possible to mount the ied on a panel or in a cubicle. Use only the screws included in the mounting kit when mounting the plates and the angles on the ied. Screws with wrong dimensio...
Page 1217
Posno description quantity type 1 bushing 4 - 2 screw 8 m4x10 3 screw 4 m6x12 or corresponding 4 mounting bar 2 - 5 screw 6 m5x8 6 side plate 2 - 21.4.3.3 how to reach the rear side of the ied the ied can be equipped with a rear protection cover recommended to be used with this type of mounting. See...
Page 1218
21.4.4 side-by-side 19” rack mounting 21.4.4.1 overview ied case size 1/2 x 19” or 3/4 x 19” and rhgs cases can be mounted side-by-side up to a maximum size of 19”. For side-by-side rack mounting, the side-by-side mounting kit together with the 19” rack panel mounting kit must be used. The mounting ...
Page 1219
21.4.4.3 ied in the 670 series mounted with a rhgs6 case an 1/2 x 19” or 3/4 x 19” size ied can be mounted with a rhgs (6 or 12 depending on ied size) case. The rhgs case can be used for mounting a test switch of type rtxp 24. It also has enough space for a terminal base of rx 2 type for mounting of...
Page 1220
Use only the screws included in the mounting kit when mounting the plates and the angles on the ied. Screws with wrong dimension may damage the pcbs inside the ied. Please contact factory for special add on plates for mounting ft switches on the side (for 1/2 19" case) or bottom of the relay. 21.4.5...
Page 1221
21.5 technical data 21.5.1 enclosure table 931: case material steel sheet front plate steel sheet profile with cut-out for hmi surface treatment aluzink preplated steel finish light grey (ral 7035) table 932: water and dust protection level according to iec 60529 front ip40 (ip54 with sealing strip)...
Page 1222
Table 936: auxiliary power supply and binary i/o connectors connector type rated voltage maximum conductor area screw compression type 250 v ac 2.5 mm 2 (awg14) 2 × 1 mm 2 (2 x awg18) terminal blocks suitable for ring lug terminals 300 v ac 3 mm 2 (awg14) because of limitations of space, when ring l...
Page 1223
Table 939: frequency influence (reference standard: iec 60255–1) dependence on within nominal range influence frequency dependence, operate value f r ±2.5 hz for 50 hz f r ±3.0 hz for 60 hz ±1.0% / hz frequency dependence for distance protection operate value f r ±2.5 hz for 50 hz f r ±3.0 hz for 60...
Page 1224
Test type test values reference standards pulse magnetic field immunity test 1000 a/m iec 61000–4–9, class v damped oscillatory magnetic field test 100 a/m iec 61000-4-10, class v radiated electromagnetic field disturbance 20 v/m, 80-1000 mhz 1.4-2.7 ghz iec 60255-26 radiated electromagnetic field d...
Page 1225
Table 944: mechanical tests test type test values reference standards vibration response test class ii iec 60255-21-1 vibration endurance test class i iec 60255-21-1 shock response test class i iec 60255-21-2 shock withstand test class i iec 60255-21-2 bump test class i iec 60255-21-2 seismic test c...
Page 1226
1220
Page 1227
Section 22 injection equipment hardware this chapter describes the hardware equipment used for sensitive rotor earth fault protection and 100% stator earth fault protection by injection. The descriptions includes diagrams from different elevations indicating the location of connection terminals and ...
Page 1228
22.1.1.2 rex060 front panel controls iec11000053-1-en.Vsd iec11000053 v1 en figure 563: rex060 front panel section 22 1mrk502052-uen b injection equipment hardware 1222 technical manual.
Page 1229
Table 945: hmi keys on the front of the injection unit rex060 key function the injection switch enables injection at rotor and stator 2 s after switching on. A led indicates that the injection switch is set to enable injection. The injection switch can be padlocked in off position in order to cut-of...
Page 1230
217 [8,54] 25 5 [1 0] 23 5 [9 ,2 5 ] 84 [3,3] 84 [3,3] Ø 5,5 [0,22] 22 3 [8 ,7 8] 2 [0,079] 155 [6,1] 19 9 [7 ,8 3] 38 [1 ,5 ] iec11000037-2-en.Vsd iec11000037 v2 en figure 565: measure and drilling plan rex061 shall be mounted close to the generator in order to limit the exposure of the field circu...
Page 1231
22.1.1.4 shunt resistor unit rex062 x1 iec11000038-1-en.Vsd iec11000038 v1 en figure 566: shunt resistor unit rex062 217 [8,54] 25 5 [1 0 ] 2 35 [9 ,2 5] 84 [3,3] 84 [3,3] Ø 5,5 [0,22] 22 3 [8 ,7 8] 2 [0,079] 155 [6,1] 19 9 [7 ,8 3] 38 [1 ,5 ] iec11000039-2-en.Vsd iec11000039 v2 en figure 567: rex06...
Page 1232
Be installed to get a open air convection and prevent contact with combustible material to the surface. 22.1.2 injection unit rex060 from rear side 22.1.2.1 injection unit rex060 r ot o r in je ct io n p ow e r s up pl y backplane front-plate back view front view power connector ied and injection co...
Page 1233
In figure 569 below the content of display is shown for a rex060 with one sim and one rim module. Row 1 contains mains frequency information. Row 2-3 contains stator information and row 4-5 rotor. Column 1 (empty) gives status, column 2 and 3 are informative and column 4 contains variables, settable...
Page 1234
Table 946: status symbols and their description status symbol description of the status priority iec10000329 v1 en over voltage occurred, injection is blocked. This can occur on both x61/62 and x81/82 (stator & rotor) simultaneously or on either of them. The symbol is displayed in the status column ...
Page 1235
Saturation when the voltage or current amplifiers in an injection module saturates due to high voltage level, it is indicated with a warning symbol in the status column in the rex060 display . Besides this a binary out for the specific module is set active to indicate to the ied that the signal may ...
Page 1236
22.3 coupling capacitor unit rex061 22.3.1 introduction rex061 isolates the injection circuit from the rotor exciter voltage. The rex061 coupling capacitor unit grounding point and grounding brush of the rotor shaft should be properly interconnected. 22.3.2 design measure points are added to the cap...
Page 1237
22.4 shunt resistor unit rex062 22.4.1 introduction rex062 is typically used when injection is done via a grounding transformer. 22.4.2 design rex062 for stator protection is used when either injection via a grounding transformer (i.E. Not via a vt) is used or when maximum voltage posed on injection...
Page 1238
Bi ai (u), current measure ai (u), voltage measure bi rl+ rl+ bi bi rl+ bi (bi) reg670 pe el + - x61:14; i a sense x61:15; i b sense x61:12; u a sense x61:13; u b sense u a out; x61:8 u b out; x61:9 i a out; x61:10 i b out; x61:11 u a out; x81:8 u b out; x81:9 i a out; x81:10 i b out; x81:11 block 2...
Page 1239
Table 948: rex060 power supply technical data quantity rated value nominal range auxiliary dc voltage, el (input) el = (24 – 60) v el = (90 – 250) v el ±20% el ±20% power consumption 30 w – auxiliary dc power in-rush – table 949: rex061 technical data function range or values accuracy for machines w...
Page 1240
Table 951: degree of protection description values rex060 front panel mounted, front rear, sides, top, bottom and connection terminals ip40 ip54 ip20 rex061 and rex062 top front, rear, sides and bottom ip41 ip20 22.5.2 type tests according to standards table 952: electromagnetic compatibility tests ...
Page 1241
Table 953: insulation tests, rex060, rex062 and reg670 test type test values reference standard dielectric test 2.0 kv ac, 1 min iec 60255-27 impulse voltage test 5.0 kv, 1.2/50 µs, 0.5 j iec 60255-27 insulation resistance >100 mΩ at 500v dc iec 60255-27 table 954: insulation tests, rex061 test type...
Page 1242
Table 956: environmental tests test type test value reference standard cold test operation storage 16 h at -25°c 16 h at -40°c iec 60068-2-1 dry heat test operation storage 16 h at +70°c 16 h at +85°c iec 60068-2-2 damp heat test steady state cyclic 240 h at +40ºc humidity 93% 6 cycles at +25 to +55...
Page 1243
Section 23 labels 23.1 labels on ied front view of ied ie c15000506-1-en.V sd 1 4 2 3 5 6 7 8 9 10 iec15000506 v1 en 1mrk502052-uen b section 23 labels 1237 technical manual.
Page 1244
10 9 8 7 6 7 6 5 1 2 3 4 iec15000504-1-en.Vsdx iec15000504 v1 en figure 573: example of ied label 1 qr-code containing the complete ordering code 2 power supply module (psm) 3 ma input module (mim) 4 ordering and serial number 5 manufacturer 6 transformer designations 7 transformer input module, rat...
Page 1245
1 warning label 2 caution label 3 class 1 laser product label iec06000575 v1 en 4 warning label 23.2 labels on injection equipment front view of injection unit rex060 iec11000226 v1 en 1mrk502052-uen b section 23 labels 1239 technical manual.
Page 1246
1a 1b 1c 1d iec11000233-1-en.Vsd iec11000233 v1 en 1a product type, description and serial number 1b order number and dc supply voltage 1c stator and rotor input module designations 1d manufacturer 2 iec11000234-1-en.Vsd iec11000234 v1 en 2 ordering and serial number rear view of injection unit rex0...
Page 1247
Front view of coupling capacitor unit rex061 iec11000229 v1 en 1 warning label (hot surface) 2 ordering number rear view of coupling capacitor unit rex061 iec11000228 v1 en 1 warning label 2 caution label 3 esd label 4 warning label 1mrk502052-uen b section 23 labels 1241 technical manual.
Page 1248
Front view of shunt resistor unit rex062 iec11000231 v1 en 1 warning label (hot surface) 2 ordering number rear view of shunt resistor unit rex062 iec11000230 v1 en 1 warning label 2 caution label 3 esd label 4 warning label section 23 1mrk502052-uen b labels 1242 technical manual.
Page 1249
Section 24 connection diagrams the connection diagrams are delivered on the ied connectivity package dvd as part of the product delivery. The latest versions of the connection diagrams can be downloaded from http://www.Abb.Com/substationautomation . Connection diagrams for customized products connec...
Page 1250
1244.
Page 1251
Section 25 inverse time characteristics 25.1 application in order to assure time selectivity between different overcurrent protections at different points in the network different time delays for the different protections are normally used. The simplest way to do this is to use definite time-lag. In...
Page 1252
En05000131.Vsd time fault point position iec05000131 v1 en figure 576: inverse time overcurrent characteristics with inst. Function the inverse time characteristic makes it possible to minimize the fault clearance time and still assure the selectivity between protections. To assure selectivity betwe...
Page 1253
En05000132.Vsd i> i> a1 b1 feeder time axis t=0 t=t 1 t=t 2 t=t 3 iec05000132 v1 en figure 577: selectivity steps for a fault on feeder b1 where: t=0 is the fault occurs t=t 1 is protection b1 trips t=t 2 is breaker at b1 opens t=t 3 is protection a1 resets in the case protection b1 shall operate wi...
Page 1254
25.2 principle of operation 25.2.1 mode of operation the function can operate in a definite time-lag mode or in a current definite inverse time mode. For the inverse time characteristic both ansi and iec based standard curves are available. Also programmable curve types are supported via the compone...
Page 1255
( ) - × × - = × > æ ö æ ö ç ÷ ç ÷ è ø è ø p op i t b k c a k in equation1190 v1 en (equation 159) where: t op is the operating time of the protection the time elapsed to the moment of trip is reached when the integral fulfils according to equation 160 , in addition to the constant time delay: 0 - × ...
Page 1256
Iec05000133-3-en.Vsd tmin current operate time imin iec05000133 v2 en figure 578: minimum time-lag operation for the iec curves in order to fully comply with iec curves definition setting parameter tmin shall be set to the value which is equal to the operating time of the selected iec inverse time c...
Page 1257
The rd inverse curve gives a logarithmic delay, as used in the combiflex protection rxidg. The curve enables a high degree of selectivity required for sensitive residual earth-fault current protection, with ability to detect high-resistive earth faults. The curve is described by equation 163 : [ ] 5...
Page 1258
[ ] 2 1 r t t s k i in = × - > æ ö ç ÷ ç ÷ ç ÷ æ ö ç ÷ ç ÷ è ø è ø equation1197 v2 en (equation 165) where: the set value t r is the reset time in case of zero current after fault clearance. The possibility of choice of reset characteristics is to some extent dependent of the choice of time delay ch...
Page 1259
In version 2.0, a typical starting time delay of 24ms is subtracted from the set trip time delay, so that the resulting trip time will take the internal ied start time into consideration. 25.3 inverse characteristics table 959: ansi inverse time characteristics function range or value accuracy opera...
Page 1260
Table 960: iec inverse time characteristics function range or value accuracy operating characteristic: ( ) 1 = × - æ ö ç ÷ ç ÷ è ø p a t k i equation1251-small v1 en i = i measured /i set k = (0.05-2.00) in steps of 0.01 iec 60255-151, ± 2.0% or ± 40 ms whichever is greater iec normal inverse a=0.14...
Page 1261
Table 962: ansi inverse time characteristics for line differential protection function range or value accuracy operating characteristic: ( ) 1 p a t b k tdef i æ ö ç ÷ = + × + ç ÷ ç - ÷ è ø equation1249-small v2 en reset characteristic: ( ) 2 1 = × - tr t k i equation1250-small v1 en i = i measured ...
Page 1262
Table 963: iec inverse time characteristics for line differential protection function range or value accuracy operating characteristic: ( ) 1 = × - æ ö ç ÷ ç ÷ è ø p a t k i equation1251-small v1 en i = i measured /i set k = (0.05-2.00) in steps of 0.01 iec 60255-151, ± 5.0% or ± 40 ms whichever is ...
Page 1263
Table 964: ri and rd type inverse time characteristics for line differential protection function range or value accuracy ri type inverse characteristic 1 0.236 0.339 = × - t k i equation1137-small v1 en i = i measured /i set k = (0.05-2.00) in steps of 0.01 iec 60255-151, ± 5.0% or ± 40 ms whichever...
Page 1264
Table 966: iec inverse time characteristics for sensitive directional residual overcurrent and power protection function range or value accuracy operating characteristic: ( ) 1 = × - æ ö ç ÷ ç ÷ è ø p a t k i equation1251-small v1 en i = i measured /i set 0.10 ≤ k ≤ 2.00 1.5 x i set ≤ i ≤ 20 x i set...
Page 1265
Table 967: ri and rd type inverse time characteristics for sensitive directional residual overcurrent and power protection function range or value accuracy ri type inverse characteristic 1 0.236 0.339 = × - t k i equation1137-small v1 en i = i measured /i set 0.10 ≤ k ≤ 2.00 1.5 x i set ≤ i ≤ 20 x i...
Page 1266
Table 969: iec inverse time characteristics for voltage restrained time overcurrent protection function range or value accuracy operating characteristic: ( ) 1 = × - æ ö ç ÷ ç ÷ è ø p a t k i equation1251-small v1 en i = i measured /i set 0.10 ≤ k ≤ 3.00 iec 60255-151, ±5.0% or ±40 ms whichever is g...
Page 1267
Table 971: inverse time characteristics for undervoltage protection function range or value accuracy type a curve: = æ ö ç ÷ è ø k t u u u equation1431-small v1 en u set u = u measured k = (0.05-1.10) in steps of 0.01 ±5.0% or ±45 ms whichever is greater type b curve: 2.0 480 0.055 32 0.5 × = + × - ...
Page 1268
Table 972: inverse time characteristics for residual overvoltage protection function range or value accuracy type a curve: = - > > æ ö ç ÷ è ø t k u u u equation1436-small v1 en u> = u set u = u measured k = (0.05-1.10) in steps of 0.01 ±5.0% or ±45 ms whichever is greater type b curve: 2.0 480 32 0...
Page 1269
A070750 v2 en figure 579: ansi extremely inverse time characteristics 1mrk502052-uen b section 25 inverse time characteristics 1263 technical manual.
Page 1270
A070751 v2 en figure 580: ansi very inverse time characteristics section 25 1mrk502052-uen b inverse time characteristics 1264 technical manual.
Page 1271
A070752 v2 en figure 581: ansi normal inverse time characteristics 1mrk502052-uen b section 25 inverse time characteristics 1265 technical manual.
Page 1272
A070753 v2 en figure 582: ansi moderately inverse time characteristics section 25 1mrk502052-uen b inverse time characteristics 1266 technical manual.
Page 1273
A070817 v2 en figure 583: ansi long time extremely inverse time characteristics 1mrk502052-uen b section 25 inverse time characteristics 1267 technical manual.
Page 1274
A070818 v2 en figure 584: ansi long time very inverse time characteristics section 25 1mrk502052-uen b inverse time characteristics 1268 technical manual.
Page 1275
A070819 v2 en figure 585: ansi long time inverse time characteristics 1mrk502052-uen b section 25 inverse time characteristics 1269 technical manual.
Page 1276
A070820 v2 en figure 586: iec normal inverse time characteristics section 25 1mrk502052-uen b inverse time characteristics 1270 technical manual.
Page 1277
A070821 v2 en figure 587: iec very inverse time characteristics 1mrk502052-uen b section 25 inverse time characteristics 1271 technical manual.
Page 1278
A070822 v2 en figure 588: iec inverse time characteristics section 25 1mrk502052-uen b inverse time characteristics 1272 technical manual.
Page 1279
A070823 v2 en figure 589: iec extremely inverse time characteristics 1mrk502052-uen b section 25 inverse time characteristics 1273 technical manual.
Page 1280
A070824 v2 en figure 590: iec short time inverse time characteristics section 25 1mrk502052-uen b inverse time characteristics 1274 technical manual.
Page 1281
A070825 v2 en figure 591: iec long time inverse time characteristics 1mrk502052-uen b section 25 inverse time characteristics 1275 technical manual.
Page 1282
A070826 v2 en figure 592: ri-type inverse time characteristics section 25 1mrk502052-uen b inverse time characteristics 1276 technical manual.
Page 1283
A070827 v2 en figure 593: rd-type inverse time characteristics 1mrk502052-uen b section 25 inverse time characteristics 1277 technical manual.
Page 1284
Guid-acf4044c-052e-4cbd-8247-c6abe3796fa6 v1 en figure 594: inverse curve a characteristic of overvoltage protection section 25 1mrk502052-uen b inverse time characteristics 1278 technical manual.
Page 1285
Guid-f5e0e1c2-48c8-4dc7-a84b-174544c09142 v1 en figure 595: inverse curve b characteristic of overvoltage protection 1mrk502052-uen b section 25 inverse time characteristics 1279 technical manual.
Page 1286
Guid-a9898db7-90a3-47f2-aef9-45ff148cb679 v1 en figure 596: inverse curve c characteristic of overvoltage protection section 25 1mrk502052-uen b inverse time characteristics 1280 technical manual.
Page 1287
Guid-35f40c3b-b483-40e6-9767-69c1536e3cbc v1 en figure 597: inverse curve a characteristic of undervoltage protection 1mrk502052-uen b section 25 inverse time characteristics 1281 technical manual.
Page 1288
Guid-b55d0f5f-9265-4d9a-a7c0-e274aa3a6bb1 v1 en figure 598: inverse curve b characteristic of undervoltage protection section 25 1mrk502052-uen b inverse time characteristics 1282 technical manual.
Page 1289
Section 26 glossary 26.1 glossary ac alternating current acc actual channel act application configuration tool within pcm600 a/d converter analog-to-digital converter adbs amplitude deadband supervision adm analog digital conversion module, with time synchronization ai analog input ansi american nat...
Page 1290
Cb circuit breaker cbm combined backplane module ccitt consultative committee for international telegraph and telephony. A united nations-sponsored standards body within the international telecommunications union. Ccm can carrier module ccvt capacitive coupled voltage transformer class c protection ...
Page 1291
Dfc data flow control dft discrete fourier transform dhcp dynamic host configuration protocol dip-switch small switch mounted on a printed circuit board di digital input dllb dead line live bus dnp distributed network protocol as per ieee std 1815-2012 dr disturbance recorder dram dynamic random acc...
Page 1292
Gde graphical display editor within pcm600 gi general interrogation command gis gas-insulated switchgear goose generic object-oriented substation event gps global positioning system gsal generic security application gse generic substation event hdlc protocol high-level data link control, protocol ba...
Page 1293
Instance when several occurrences of the same function are available in the ied, they are referred to as instances of that function. One instance of a function is identical to another of the same kind but has a different number in the ied user interfaces. The word "instance" is sometimes defined as ...
Page 1294
Num numerical module oco cycle open-close-open cycle ocp overcurrent protection oem optical ethernet module oltc on-load tap changer otev disturbance data recording initiated by other event than start/pick-up ov overvoltage overreach a term used to describe how the relay behaves during a fault condi...
Page 1295
Sbo select-before-operate sc switch or push button to close scl short circuit location scs station control system scada supervision, control and data acquisition sct system configuration tool according to standard iec 61850 sdu service data unit slm serial communication module. Sma connector submini...
Page 1296
Tm transmit (disturbance data) tnc connector threaded neill-concelman, a threaded constant impedance version of a bnc connector tp trip (recorded fault) tpz, tpy, tpx, tps current transformer class according to iec trm transformer module. This module transforms currents and voltages taken from the p...
Page 1297
1291.
Page 1298
Contact us for more information please contact: abb ab substation automation products se-721 59 västerås, sweden phone +46 (0) 21 32 50 00 www.Abb.Com/substationautomation note: we reserve the right to make technical changes or modify the contents of this document without prior notice. Abb ab does n...