- DL manuals
- ABB
- Protection Device
- Relion RES670
- Technical Manual
ABB Relion RES670 Technical Manual
Summary of Relion RES670
Page 1
Relion® 670 series — phasor measurement unit res670 version 2.2 ansi technical manual.
Page 3
Document id: 1mrk 511 408-uus issued: october 2017 revision: a product version: 2.2.1 © copyright 2017 abb. All rights reserved.
Page 4
Copyright this document and parts thereof must not be reproduced or copied without written permission from abb, and the contents thereof must not be imparted to a third party, nor used for any unauthorized purpose. The software and hardware described in this document is furnished under a license and...
Page 5
Disclaimer the data, examples and diagrams in this manual are included solely for the concept or product description and are not to be deemed as a statement of guaranteed properties. All persons responsible for applying the equipment addressed in this manual must satisfy themselves that each intende...
Page 6
Conformity this product complies with the directive of the council of the european communities on the approximation of the laws of the member states relating to electromagnetic compatibility (emc directive 2004/108/ec) and concerning electrical equipment for use within specified voltage limits (low-...
Page 7
Table of contents section 1 introduction..........................................................................31 this manual............................................................................................ 31 presumptions for technical data................................................
Page 8
Section 5 local human-machine-interface lhmi ...............................75 local hmi screen behaviour...................................................................75 identification...................................................................................... 75 settings................
Page 9
Settings............................................................................................108 protocol reporting via ieee 1344 and c37.118 pmureport............110 identification.................................................................................... 110 functionality.............
Page 10
Design........................................................................................ 167 technical data................................................................................. 168 section 8 current protection..............................................................169 directi...
Page 11
Settings............................................................................................216 monitored data.................................................................................221 operation principle.......................................................................... 221...
Page 12
Low pass filtering........................................................................258 calibration of analog inputs........................................................258 technical data................................................................................. 260 directional overpo...
Page 13
Design........................................................................................ 297 technical data................................................................................. 299 section 10 frequency protection.........................................................301 underfreq...
Page 14
Technical data................................................................................. 318 frequency time accumulation protection function ftaqfvr (81a).....318 identification.................................................................................... 318 functionality ................
Page 15
Function block................................................................................. 363 signals.............................................................................................364 settings...........................................................................................
Page 16
Functionality.................................................................................... 389 function block................................................................................. 389 signals..............................................................................................
Page 17
Function block................................................................................. 411 signals.............................................................................................412 settings...........................................................................................
Page 18
Technical data............................................................................ 432 controllable gate function block gate............................................433 function block............................................................................ 433 signals.....................
Page 19
Signals........................................................................................443 technical data............................................................................ 443 configurable logic blocks q/t...............................................................443 andqt func...
Page 20
Function block............................................................................ 456 signals........................................................................................456 settings.......................................................................................457 technic...
Page 21
Integer to boolean 16 conversion ib16.................................................468 identification.................................................................................... 468 functionality.................................................................................... 469 funct...
Page 22
Function block................................................................................. 483 signals.............................................................................................483 settings...........................................................................................
Page 23
Breaker monitoring sscbr..................................................................532 identification.................................................................................... 532 functionality.................................................................................... 533 f...
Page 24
Measured value expander block range_xp...................................... 583 identification.................................................................................... 583 functionality.................................................................................... 583 function block...
Page 25
Identification.................................................................................... 599 functionality.................................................................................... 600 function block....................................................................................
Page 26
Generic communication function for single point indication spgapc, sp16gapc.....................................................................628 functionality............................................................................... 628 function block............................................
Page 27
Identification............................................................................... 641 functionality............................................................................... 641 function block............................................................................ 641 signals......
Page 28
Measurands user defined signals for iec 60870-5-103 i103measusr................................................................................687 functionality............................................................................... 687 identification.............................................
Page 29
Identification............................................................................... 697 function block............................................................................ 697 signals........................................................................................697 settings...
Page 30
Function block............................................................................ 707 signals........................................................................................708 settings.......................................................................................708 operati...
Page 31
Authorization with central account management enabled ied..747 authority management authman.......................................................749 identification.................................................................................... 749 authman...........................................
Page 32
Real-time clock (rtc) operation................................................ 768 synchronization alternatives.......................................................770 process bus iec/uca 61850-9-2le synchronization................ 771 precision time protocol (ptp) ..................................
Page 33
Functionality.................................................................................... 786 function block................................................................................. 786 signals..............................................................................................
Page 34
Analog digital conversion module (adm)........................................ 811 introduction.................................................................................811 design........................................................................................ 811 binary input module (...
Page 35
Design........................................................................................ 845 technical data............................................................................ 846 optical ethernet module.................................................................. 847 introduction...
Page 36
Mounting procedure for side-by-side rack mounting.................. 867 ied mounted with a rhgs6 case.............................................. 867 side-by-side flush mounting............................................................ 868 overview...................................................
Page 37
Section 1 introduction 1.1 this manual guid-ab423a30-13c2-46af-b7fe-a73bb425eb5f v18 the technical manual contains operation principle descriptions, and lists function blocks, logic diagrams, input and output signals, setting parameters and technical data, sorted per function. The manual can be used...
Page 38
• rated secondary phase current i r is either 1 a or 5 a depending on selected trm. • rated secondary phase-to-phase voltage u r is within the range from 100 v to 120 v. • rated secondary power for three-phase system s r = √3 × u r × i r 8. For operate and reset time testing, the default setting val...
Page 39
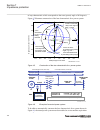
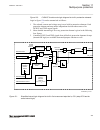
1.3 product documentation 1.3.1 product documentation set guid-3aa69ea6-f1d8-47c6-a8e6-562f29c67172 v15 iec07000220-4-en.Vsd p la nn in g & p ur ch as e e ng in ee rin g in st al lin g c om m is si on in g o pe ra tio n m ai nt en an ce d ec om m is si on in g d ei ns ta lli ng & d is po sa l applic...
Page 40
The commissioning manual contains instructions on how to commission the ied. The manual can also be used by system engineers and maintenance personnel for assistance during the testing phase. The manual provides procedures for the checking of external circuitry and energizing the ied, parameter sett...
Page 41
1.3.3 related documents guid-94e8a5ca-be1b-45af-81e7-5a41d34ee112 v5 documents related to res670 document numbers application manual 1mrk 511 407-uus commissioning manual 1mrk 511 409-uus product guide 1mrk 511 410-ben technical manual 1mrk 511 408-uus type test certificate 1mrk 511 410-tus 670 seri...
Page 42
Class 1 laser product. Take adequate measures to protect the eyes and do not view directly with optical instruments. The caution icon indicates important information or warning related to the concept discussed in the text. It might indicate the presence of a hazard which could result in corruption o...
Page 43
• the character ^ in front of an input/output signal name indicates that the signal name may be customized using the pcm600 software. • the character * after an input signal name indicates that the signal must be connected to another function block in the application configuration to achieve a valid...
Page 44
Function block name edition 1 logical nodes edition 2 logical nodes bcztpdif bcztpdif bcztpdif bdcgapc swsggio bbcswi bdcgapc bdzsgapc bbs6lln0 bdzsgapc lln0 bdzsgapc bfptrc_f01 bfptrc bfptrc bfptrc_f02 bfptrc bfptrc bfptrc_f03 bfptrc bfptrc bfptrc_f04 bfptrc bfptrc bfptrc_f05 bfptrc bfptrc bfptrc_f...
Page 45
Function block name edition 1 logical nodes edition 2 logical nodes busptrc_b1 busptrc bbsplln0 busptrc busptrc_b2 busptrc busptrc busptrc_b3 busptrc busptrc busptrc_b4 busptrc busptrc busptrc_b5 busptrc busptrc busptrc_b6 busptrc busptrc busptrc_b7 busptrc busptrc busptrc_b8 busptrc busptrc busptrc...
Page 46
Function block name edition 1 logical nodes edition 2 logical nodes bznpdif_z2 bznpdif bznpdif bznpdif_z3 bznpdif bznpdif bznpdif_z4 bznpdif bznpdif bznpdif_z5 bznpdif bznpdif bznpdif_z6 bznpdif bznpdif bznspdif_a bznspdif bzasgapc bzaspdif bznsgapc bznspdif bznspdif_b bznspdif bzbsgapc bzbspdif bzn...
Page 47
Function block name edition 1 logical nodes edition 2 logical nodes cvmmxn cvmmxn cvmmxn d2ptoc d2lln0 d2ptoc ph1ptrc d2ptoc ph1ptrc dpgapc dpggio dpgapc drprdre drprdre drprdre ecpsch ecpsch ecpsch ecrwpsch ecrwpsch ecrwpsch ef2ptoc ef2lln0 ef2ptrc ef2rdir gen2phar ph1ptoc ef2ptrc ef2rdir gen2phar ...
Page 48
Function block name edition 1 logical nodes edition 2 logical nodes l4cpdif l4clln0 l4cpdif l4cptrc lln0 l4cgapc l4cpdif l4cpsch l4cptrc l4ufcnt l4ufcnt l4ufcnt l6cpdif l6cpdif l6cgapc l6cpdif l6cphar l6cptrc lappgapc lapplln0 lapppdup lapppupf lapppdup lapppupf lccrptrc lccrptrc lccrptrc lcnsptoc l...
Page 49
Function block name edition 1 logical nodes edition 2 logical nodes ns2ptoc ns2lln0 ns2ptoc ns2ptrc ns2ptoc ns2ptrc ns4ptoc ef4lln0 ef4ptrc ef4rdir gen4phar ph1ptoc ef4ptrc ef4rdir ph1ptoc o2rwptov gen2lln0 o2rwptov ph1ptrc o2rwptov ph1ptrc oc4ptoc oc4lln0 gen4phar ph3ptoc ph3ptrc gen4phar ph3ptoc p...
Page 50
Function block name edition 1 logical nodes edition 2 logical nodes schlcch schlcch schlcch scilo scilo scilo scswi scswi scswi sdepsde sdepsde sdepsde sdeptoc sdeptov sdeptrc sesrsyn rsy1lln0 aut1rsyn man1rsyn synrsyn aut1rsyn man1rsyn synrsyn slgapc slggio slgapc smbrrec smbrrec smbrrec smpptrc sm...
Page 51
Function block name edition 1 logical nodes edition 2 logical nodes tr1atcc tr1atcc tr1atcc tr8atcc tr8atcc tr8atcc trpttr trpttr trpttr u2rwptuv gen2lln0 ph1ptrc u2rwptuv ph1ptrc u2rwptuv uv2ptuv gen2lln0 ph1ptrc uv2ptuv ph1ptrc uv2ptuv vdcptov vdcptov vdcptov vdspvc vdrfuf vdspvc vmmxu vmmxu vmmxu...
Page 52
Function block name edition 1 logical nodes edition 2 logical nodes zmmapdis zmmapdis zmmapdis zmmpdis zmmpdis zmmpdis zmqapdis zmqapdis zmqapdis zmqpdis zmqpdis zmqpdis zmrapdis zmrapdis zmrapdis zmrpdis zmrpdis zmrpdis zmrpsb zmrpsb zmrpsb zsmgapc zsmgapc zsmgapc section 1 1mrk 511 408-uus a intro...
Page 53
Section 2 available functions guid-f5776dd1-bd04-4872-bb89-a0412b4b5cc3 v1 the following tables list all the functions available in the ied. Those functions that are not exposed to the user or do not need to be configured are not described in this manual. 2.1 wide area measurement functions guid-8a1...
Page 54
2.2 back-up protection functions guid-a8d0852f-807f-4442-8730-e44808e194f0 v13 iec 61850 or function name ansi function description res670 (customized) impedance protection zmrpsb 68 power swing detection 0-1 oosppam 78 out-of-step protection 0-2 current protection oc4ptoc 51_67 1) directional phase...
Page 55
2.3 control and monitoring functions guid-e3777f16-0b76-4157-a3bf-0b6b978863de v15 iec 61850 or function name ansi function description phasor measurement unit res670 (customized) control qcbay bay control 1 locrem handling of lr-switch positions 1 locremctrl lhmi control of psto 1 sxcbr circuit bre...
Page 56
Iec 61850 or function name ansi function description phasor measurement unit res670 (customized) indcalh logic for group indication 5 and, gate, inv, lld, or, pulsetimer, rsmemory, srmemory, timerset, xor basic configurable logic blocks (see table 2 ) 40-420 andqt, indcombspqt, indextspqt, invalidqt...
Page 57
Basic configurable logic block total number of instances lld 40 or 298 pulsetimer 40 rsmemory 40 srmemory 40 timerset 60 xor 40 table 3: total number of instances for configurable logic blocks q/t configurable logic blocks q/t total number of instances andqt 120 indcombspqt 20 indextspqt 20 invalidq...
Page 58
Iec 61850 or function name ansi function description phasor measurement unit res670 (customized) monitoring cvmmxn power system measurement 6 cmmxu current measurement 10 vmmxu voltage measurement phase-phase 6 cmsqi current sequence measurement 6 vmsqi voltage sequence measurement 6 vnmmxu voltage ...
Page 59
2.4 communication guid-5f144b53-b9a7-4173-80cf-cd4c84579cb5 v15 iec 61850 or function name ansi function description phasor measurement unit res670 (customized) station communication lonspa, spa spa communication protocol 1 ade lon communication protocol 1 horzcomm network variables via lon 1 rs485g...
Page 60
Iec 61850 or function name ansi function description phasor measurement unit res670 (customized) pcmaccs ied configuration protocol 1 secalarm component for mapping security events on protocols such as dnp3 and iec103 1 fstaccs field service tool access 1 iec 61850-9-2 process bus communication, 8 m...
Page 61
2.5 basic ied functions guid-c8f0e5d2-e305-4184-9627-f6b5864216ca v12 table 5: basic ied functions iec 61850 or function name description interrsig self supervision with internal event list timesynchgen time synchronization module synchcan, synchcmpps, synchpps, synchcmpps time synchronization timez...
Page 62
Table 6: local hmi functions iec 61850 or function name ansi description lhmictrl local hmi signals language local human machine language screen local hmi local human machine screen behavior fnkeyty1–fnkeyty5 fnkeymd1– fnkeymd5 parameter setting function for hmi in pcm600 ledgen general led indicati...
Page 63
Section 3 analog inputs semod55010-1 v3 3.1 introduction semod55003-5 v11 analog input channels must be configured and set properly in order to get correct measurement results and correct protection operations. For power measuring, all directional and differential functions, the directions of the in...
Page 64
Desired virtual input (smai) of the ied and used internally in the configuration. 3.3 signals pid-3920-outputsignals v6 table 7: trm_12i output signals name type description status boolean analog input module status ch1(i) string analogue current input 1 ch2(i) string analog current input 2 ch3(i) s...
Page 65
Name type description ch10(v) string analog voltage input 10 ch 11(v) string analog voltage input 11 ch12(v) string analog voltage input 12 pid-3922-outputsignals v6 table 9: trm_6i output signals name type description status boolean analog input module status ch1(i) string analogue current input 1 ...
Page 66
Pid-3924-outputsignals v7 table 11: trm_9i_3u output signals name type description status boolean analog input module status ch1(i) string analogue current input 1 ch2(i) string analog current input 2 ch3(i) string analog current input 3 ch4(i) string analog current input 4 ch5(i) string analog curr...
Page 67
3.4 settings semod129840-4 v2 dependent on ordered ied type. Pid-4153-settings v7 table 13: aisvbas non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description phaseangleref trm40-ch1 - ch12 trm41-ch1 - ch12 mu1-ia mu1-ib mu1-ic mu1-i0 mu1- va mu1- vb mu1-vc mu1-v0 mu2-ia mu2-ib mu2...
Page 68
Pid-3920-settings v7 table 14: trm_12i non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description ct_wyepoint1 fromobject toobject - - toobject toobject= towards protected object, fromobject= the opposite ctsec1 1 - 10 a 1 1 rated ct secondary current ctprim1 1 - 99999 a 1 3000 rat...
Page 69
Name values (range) unit step default description ctsec10 1 - 10 a 1 1 rated ct secondary current ctprim10 1 - 99999 a 1 3000 rated ct primary current ct_wyepoint11 fromobject toobject - - toobject toobject= towards protected object, fromobject= the opposite ctsec11 1 - 10 a 1 1 rated ct secondary c...
Page 70
Name values (range) unit step default description vtprim7 0.05 - 2000.00 kv 0.05 400.00 rated vt primary voltage vtsec8 0.001 - 999.999 v 0.001 110.000 rated vt secondary voltage vtprim8 0.05 - 2000.00 kv 0.05 400.00 rated vt primary voltage vtsec9 0.001 - 999.999 v 0.001 110.000 rated vt secondary ...
Page 71
Pid-3923-settings v7 table 17: trm_7i_5u non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description ct_wyepoint1 fromobject toobject - - toobject toobject= towards protected object, fromobject= the opposite ctsec1 1 - 10 a 1 1 rated ct secondary current ctprim1 1 - 99999 a 1 3000 r...
Page 72
Pid-3924-settings v7 table 18: trm_9i_3u non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description ct_wyepoint1 fromobject toobject - - toobject toobject= towards protected object, fromobject= the opposite ctsec1 1 - 10 a 1 1 rated ct secondary current ctprim1 1 - 99999 a 1 3000 r...
Page 73
Name values (range) unit step default description vtsec11 0.001 - 999.999 v 0.001 110.000 rated vt secondary voltage vtprim11 0.05 - 2000.00 kv 0.05 400.00 rated vt primary voltage vtsec12 0.001 - 999.999 v 0.001 110.000 rated vt secondary voltage vtprim12 0.05 - 2000.00 kv 0.05 400.00 rated vt prim...
Page 74
Name values (range) unit step default description ctprim8 1 - 99999 a 1 3000 rated ct primary current ct_wyepoint9 fromobject toobject - - toobject toobject= towards protected object, fromobject= the opposite ctsec9 1 - 10 a 1 1 rated ct secondary current ctprim9 1 - 99999 a 1 3000 rated ct primary ...
Page 75
Pid-3922-monitoreddata v6 table 23: trm_6i monitored data name type values (range) unit description status boolean 0=ok 1=error - analog input module status pid-3923-monitoreddata v6 table 24: trm_7i_5u monitored data name type values (range) unit description status boolean 0=ok 1=error - analog inp...
Page 76
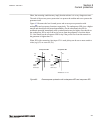
For directional functions the directional conventions are defined as follows (see figure 2 ) • forward means the direction is into the object. • reverse means the direction is out from the object. Protected object line, transformer, etc forward reverse definition of direction for directional functio...
Page 77
3.7 technical data semod55412-1 v1 m16988-1 v11 table 27: trm - energizing quantities, rated values and limits for protection transformer description value frequency rated frequency f r 50/60 hz operating range f r ± 10% current inputs rated current i r 1 or 5 a operating range (0-100) x i r thermal...
Page 78
Description value thermal withstand 80 × i r for 1 s 25 × i r for 10 s 10 × i r for 1 min 1.8 × i r for 30 min 1.1 × i r continuously 65 × i r for 1 s 20 × i r for 10 s 8 × i r for 1 min 1.6 × i r for 30 min 1.1 × i r continuously burden r r voltage inputs *) rated voltage u r 110 or 220 v operating...
Page 79
Section 4 binary input and output modules 4.1 binary input 4.1.1 binary input debounce filter guid-ae43976c-e966-484c-af39-89b2b12f56dc v5 the debounce filter eliminates bounces and short disturbances on a binary input. A time counter is used for filtering. The time counter is increased once in a mi...
Page 80
4.1.3.1 setting parameters for binary input modules pid-3473-settings v2 table 30: bim non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description operation disabled enabled - - enabled operation disabled/enabled debouncetime 0.001 - 0.020 s 0.001 0.001 debounce time for binary inpu...
Page 81
Section 5 local human-machine-interface lhmi 5.1 local hmi screen behaviour 5.1.1 identification guid-84392eff-4d3f-4a67-a6ed-34c6e98574d6 v1 function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number local hmi screen behaviour screen - - 5.1.2 settings pid-...
Page 82
5.2 local hmi signals 5.2.1 identification guid-03ab7aee-87d3-4f3c-b6b9-b1eb1b538e38 v1 function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number local hmi signals lhmictrl - - 5.2.2 function block guid-a8ac51e9-5bd7-4a80-9576-4816f14dd08d v2 lhmictrl clrle...
Page 83
5.3 basic part for led indication module 5.3.1 identification guid-6e36c0bc-f284-4c88-a4a8-9535d3be8b14 v2 function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number basic part for led indication module ledgen - - basic part for led indication hw module grp1...
Page 84
Pid-4114-outputsignals v5 table 36: ledgen output signals name type description newind boolean new indication signal if any led indication input is set ack boolean a pulse is provided when the leds are acknowledged pid-1697-inputsignals v18 table 37: grp1_led1 input signals name type default descrip...
Page 85
5.4 lcd part for hmi function keys control module guid-eecae7fa-7078-472c-a429-f7607db884eb v2 5.4.1 identification guid-e6611022-5ea3-420d-adcd-9d1e7604efeb v1 function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number lcd part for hmi function keys control...
Page 86
5.4.4 settings pid-1657-settings v19 table 42: fnkeymd1 non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description mode disabled toggle pulsed - - disabled output operation mode pulsetime 0.001 - 60.000 s 0.001 0.200 pulse time for output controlled by lcdfn1 labelon 0 - 18 - 1 lcd...
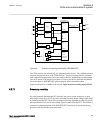
Page 87
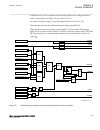
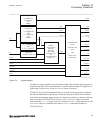
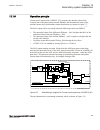
5.5 operation principle 5.5.1 local hmi amu0600442 v14 ansi13000239-2-en.Vsd ansi13000239 v2 en-us figure 7: local human-machine interface the lhmi of the ied contains the following elements: 1mrk 511 408-uus a section 5 local human-machine-interface lhmi phasor measurement unit res670 2.2 ansi 81 t...
Page 88
• keypad • display (lcd) • led indicators • communication port for pcm600 the lhmi is used for setting, monitoring and controlling. 5.5.1.1 keypad amu0600428 v17 the lhmi keypad contains push-buttons which are used to navigate in different views or menus. The push-buttons are also used to acknowledg...
Page 89
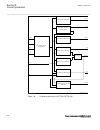
Ansi15000157-1-en.Vsdx 1 18 19 7 6 5 4 3 2 8 20 21 22 17 16 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 23 24 ansi15000157 v1 en-us figure 8: lhmi keypad with object control, navigation and command push- buttons and rj-45 communication port 1...5 function button 6 close 7 open 8 escape 9 left 10 down 11 up 12 right 13 key ...
Page 90
19 menu 20 clear 21 help 22 communication port 23 programmable indication leds 24 ied status leds 5.5.1.2 display guid-55739d4f-1da5-4112-b5c7-217aaf360ea5 v11 the lhmi includes a graphical monochrome liquid crystal display (lcd) with a resolution of 320 x 240 pixels. The character size can vary. Th...
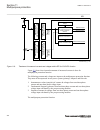
Page 91
Iec15000270-1-en.Vsdx iec15000270 v1 en-us figure 9: display layout 1 path 2 content 3 status 4 scroll bar (appears when needed) • the path shows the current location in the menu structure. If the path is too long to be shown, it is truncated from the beginning, and the truncation is indicated with ...
Page 92
Iec15000138-1-en.Vsdx iec15000138 v1 en-us figure 10: truncated path the number after : (colon sign) at the end of the function instance, for example, 1 in smai1:1, indicates the number of that function instance. The function key button panel shows on request what actions are possible with the funct...
Page 93
Iec13000281-1-en.Vsd guid-c98d972d-d1d8-4734-b419-161dbc0dc97b v1 en-us figure 11: function button panel the indication led panel shows on request the alarm text labels for the indication leds. Three indication led pages are available. Iec13000240-1-en.Vsd guid-5157100f-e8c0-4fab-b979-fd4a971475e3 v...
Page 94
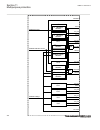
5.5.1.3 leds amu0600427 v13 the lhmi includes three protection status leds above the display: normal, pickup and trip. There are 15 programmable indication leds on the front of the lhmi. Each led can indicate three states with the colors: green, yellow and red. The texts related to each three-color ...
Page 95
Iec16000076-1-en.Vsd iec16000076 v1 en-us figure 13: openclose_led connected to sxcbr 5.5.2 led configuration alternatives 5.5.2.1 functionality guid-1a03e0ef-c10f-4797-9d9f-5cca86ca29eb v5 the function blocks ledgen and grp1_ledx, grp2_ledx and grp3_ledx (x=1-15) controls and supplies information a...
Page 96
• green led: unlit > no power; blinking > startup or abnormal situation (ied is not in service); steady > ied is in service • yellow led: unlit > no attention required; blinking > ied is in testmode (ied is not in normal service); steady > at least one of the signals configured to turn the yellow le...
Page 97
Acknowledgment/reset guid-e6727e8f-c28b-4295-ae21-bc5643363805 v3 • from local hmi • the active led indications can be acknowledged/reset manually. Manual acknowledgment and manual reset have the same meaning and is a common signal for all the operating sequences and leds. The function is positive e...
Page 98
Only working in collecting (coll) mode. Sequence 5 is working according to latched type and collecting mode while sequence 6 is working according to latched type and re-starting (reset) mode. The letters s and f in the sequence names have the meaning s = steady and f = flash. At the activation of th...
Page 99
Activating signal green led iec09000312_1_en.Vsd g r g g activating signal red iec09000312 v1 en-us figure 16: operating sequence 1, two colors sequence 2 (follow-f) semod56072-47 v2 this sequence is the same as sequence 1, follow-s, but the leds are flashing instead of showing steady light. Sequenc...
Page 100
Acknowledgment has been performed on a higher priority signal. The low priority signal will be shown as acknowledged when the high priority signal resets. Activating signal red led acknow iec09000313_1_en.Vsd activating signal green r r g iec09000313 v1 en-us figure 18: operating sequence 3 (latched...
Page 101
Activating signal red led acknow. Iec09000315-1-en.Vsd activating signal yellow g g r r y activating signal green iec09000315 v1 en-us figure 20: operating sequence 3, three colors involved, alternative 2 sequence 4 (latchedack-s-f) semod56072-64 v1 this sequence has the same functionality as sequen...
Page 102
Activating signal red led reset iec09000316_1_en.Vsd activating signal green r g iec09000316 v1 en-us figure 22: operating sequence 5, two colors sequence 6 latchedreset-s semod56072-75 v4 in this mode all activated leds, which are set to sequence 6 (latchedreset-s), are automatically reset at a new...
Page 103
Iec01000239_2-en.Vsd activating signal 2 led 2 manual reset activating signal 1 automatic reset led 1 disturbance trestart iec01000239 v2 en-us figure 23: operating sequence 6 (latchedreset-s), two indications within same disturbance figure 24 shows the timing diagram for a new indication after tres...
Page 104
Iec01000240_2_en.Vsd activating signal 2 led 2 manual reset activating signal 1 automatic reset led 1 disturbance trestart disturbance trestart iec01000240 v2 en-us figure 24: operating sequence 6 (latchedreset-s), two different disturbances figure 25 shows the timing diagram when a new indication a...
Page 105
Iec01000241_2_en.Vsd activating signal 2 led 2 manual reset activating signal 1 automatic reset led 1 disturbance trestart iec01000241 v2 en-us figure 25: operating sequence 6 (latchedreset-s), two indications within same disturbance but with reset of activating signal between figure 26 shows the ti...
Page 106
Iec01000242_2_en.Vsd activating signal 2 led 2 manual reset activating signal 1 automatic reset led 1 disturbance trestart iec01000242 v2 en-us figure 26: operating sequence 6 (latchedreset-s), manual reset 5.5.3 function keys 5.5.3.1 functionality guid-bed38e9a-c90d-4b7f-aa20-42821c4f6a1c v3 local ...
Page 107
Fnkeymd1 - fnkeymd5 function block also has a number of settings and parameters that control the behavior of the function block. These settings and parameters are normally set using the pst. Operating sequence guid-84ca7c61-4f83-4f86-a07f-bf9ec4e309bf v5 the operation mode is set individually for ea...
Page 108
Note that the third positive edge on the input attribute does not cause a pulse, since the edge was applied during pulse output. A new pulse can only begin when the output is zero; else the trigger edge is lost. 500ms 500ms 500ms pulse time pulse time pulse time 500ms iec09000332_2_en.Vsd input valu...
Page 109
Section 6 wide area measurement system 6.1 c37.118 phasor measurement data streaming protocol configuration pmuconf guid-747c6ad7-e6a1-466e-92d1-68865681f92f v1 6.1.1 identification guid-1e140ea0-d198-443a-b445-47cefd2e6134 v1 function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification an...
Page 110
Corresponding pmu id for that pmureport instance. Whereas, for udp clients, the pmureport instance for each udp channel is defined by the user in the pmu and the client has to know the pmu id corresponding to that instance in order to be able to communicate. More information is available in the sect...
Page 111
There is a default header file, named "ieee1344header.Txt", located in the "tools" folder in the ied. The user is allowed to access and update this text file and write it back to the ied using a ftp client (e.G. Filezilla). If the user-defined (updated) header file is larger than 1400 bytes, then it...
Page 112
Respectively. It is up to the tcp client to decide which pmureport function block shall communicate with that client. Upon successful reception of the first command by the ied, the pmu id will be extracted out of the command; if there is a pmureport instance configured in the ied with matching pmu i...
Page 113
However, such a remote control to stop the streams from the client is only possible when the parameter senddataudp[x] is set to setbyprotocol. The command rtdoff/rtdon sent by the client is stored in the ied, i.E. If the ied is rebooted for some reason, the state of the stream will remain the same. ...
Page 114
The pmu clients receiving the udp frames can also connect to the ied to request (command frame) config frame 1, config frame 2, config frame 3, or header frame, and to disable/enable real time data. This can be done by connecting to the tcp port selected in tcpportudpdatactrl[x] for each udp group. ...
Page 115
Name values (range) unit step default description protocolonudp2 ieee1344 c37.118 - - c37.118 select protocol for udp client group2 pmureportudp2 1 - 2 - 1 1 pmureport instance used for udp client group2 udpdestaddres2 0 - 16 ip address 1 234.5.6.8 udp destination address for udp client group2 udpde...
Page 116
Name values (range) unit step default description pmureportudp5 1 - 2 - 1 1 pmureport instance used for udp client group5 udpdestaddres5 0 - 16 ip address 1 234.5.6.11 udp destination address for udp client group5 udpdestport5 1024 - 65534 - 1 8914 udp destination port for udp client group5 sendcfgo...
Page 117
The message generated by the pmureport function block is set in accordance with the ieee c37.118 and/or ieee 1344 standards. There are settings for phasor type (positive sequence, negative sequence or zero sequence in case of 3-phase phasor and a, b or c in case of single phase phasor), pmu's servic...
Page 118
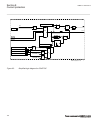
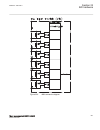
There are four separate phasorreport blocks including 32 configurable phasor channels (8 phasor channels in each phasorreport block). Each phasor channel can be configured as a 3-phase (symmetrical components positive/negative/zero) or single-phase phasor (a/b/c). Iec140000119-2-en.Vsd iec140000119 ...
Page 119
Three separate binaryreport blocks capable of reporting up to 24 binary signals (8 binary signals in each binaryreport block). These binary signals can be for example dis-connector or breaker position indications or internal/external protection alarm signals. Iec140000121-2-en.Vsd iec140000121 v2 en...
Page 120
Ansi14000304.Vsd analogreport3 ^analog17 ^analog18 ^analog19 ^analog20 ^analog21 ^analog22 ^analog23 ^analog24 ansi14000304 v1 en-us ansi14000305.Vsd binaryreport1 ^binary1 ^binary2 ^binary3 ^binary4 ^binary5 ^binary6 ^binary7 ^binary8 ansi14000305 v1 en-us ansi14000306.Vsd binaryreport2 ^binary9 ^b...
Page 121
Ansi14000309.Vsd phasorreport2 ^phasor9 ^phasor10 ^phasor11 ^phasor12 ^phasor13 ^phasor14 ^phasor15 ^phasor16 ansi14000309 v1 en-us ansi14000310.Vsd phasorreport3 ^phasor17 ^phasor18 ^phasor19 ^phasor20 ^phasor21 ^phasor22 ^phasor23 ^phasor24 ansi14000310 v1 en-us ansi14000311.Vsd phasorreport4 ^pha...
Page 122
Pid-6238-inputsignals v2 table 47: analogreport1 input signals name type default description analog1 real 0.0 analog input channel 1 analog2 real 0.0 analog input channel 2 analog3 real 0.0 analog input channel 3 analog4 real 0.0 analog input channel 4 analog5 real 0.0 analog input channel 5 analog6...
Page 123
Pid-6241-inputsignals v3 table 50: binaryreport1 input signals name type default description binary1 boolean 0 binary input channel 1 binary2 boolean 0 binary input channel 2 binary3 boolean 0 binary input channel 3 binary4 boolean 0 binary input for channel 4 binary5 boolean 0 binary input channel ...
Page 124
Pid-6252-inputsignals v3 table 53: phasorreport1 input signals name type default description phasor1 group signal - group signal input for phasor1 phasor2 group signal - group signal input for phasor2 phasor3 group signal - group signal input for phasor3 phasor4 group signal - group signal input for...
Page 125
Pid-6254-inputsignals v2 table 55: phasorreport3 input signals name type default description phasor17 group signal - group signal input for phasor17 phasor18 group signal - group signal input for phasor18 phasor19 group signal - group signal input for phasor19 phasor20 group signal - group signal in...
Page 126
6.2.5 settings semod119927-1 v2 pid-6244-settings v2 table 57: pmureport non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description operation disabled enabled - - enabled operation mode off/on svcclass p class m class - - p class service class global_pmu_id 0 - 16 - 1 0 global pmu ...
Page 127
Pid-6238-settings v2 table 58: analogreport1 non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description analog1range 3277.0 - 10000000000.0 - 0.1 3277.0 (+/-) range for scaling analog 1 in integer format analog1unittype single point-on- wave rms of analog input peak of analog input...
Page 128
Name values (range) unit step default description analog7range 3277.0 - 10000000000.0 - 0.1 3277.0 (+/-) range for scaling analog 7 in integer format analog7unittype single point-on- wave rms of analog input peak of analog input - - rms of analog input unit type for analog 7 analog8range 3277.0 - 10...
Page 129
Name values (range) unit step default description analog12unittype single point-on- wave rms of analog input peak of analog input - - rms of analog input unit type for analog 12 analog13range 3277.0 - 10000000000.0 - 0.1 3277.0 (+/-) range for scaling analog 13 in integer format analog13unittype sin...
Page 130
Pid-6240-settings v2 table 60: analogreport3 non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description analog17range 3277.0 - 10000000000.0 - 0.1 3277.0 (+/-) range for scaling analog 17 in integer format analog17unittype single point-on- wave rms of analog input peak of analog in...
Page 131
Name values (range) unit step default description analog23range 3277.0 - 10000000000.0 - 0.1 3277.0 (+/-) range for scaling analog 23 in integer format analog23unittype single point-on- wave rms of analog input peak of analog input - - rms of analog input unit type for analog 23 analog24range 3277.0...
Page 132
Name values (range) unit step default description phasor7 posseq negseq zeroseq a b c - - posseq group selector for phasor7 phasor8 a b c posseq negseq zeroseq - - posseq group selector for phasor8 phasor1report disabled enabled - - enabled reporting phasor 1 phasor1usefreqsrc disabled enabled - - e...
Page 133
Name values (range) unit step default description phasor8report disabled enabled - - enabled reporting phasor 8 phasor8usefreqsrc disabled enabled - - enabled include phasor 8 for automatic frequency source selection phasor1 posseq negseq zeroseq a b c - - posseq group selector for phasor1 pid-6253-...
Page 134
Name values (range) unit step default description phasor15 posseq negseq zeroseq a b c - - posseq group selector for phasor15 phasor16 posseq negseq zeroseq a b c - - posseq group selector for phasor16 phasor9report disabled enabled - - enabled reporting phasor 9 phasor9usefreqsrc disabled enabled -...
Page 135
Pid-6254-settings v2 table 63: phasorreport3 non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description phasor17 posseq negseq zeroseq a b c - - posseq group selector for phasor17 phasor18 posseq negseq zeroseq a b c - - posseq group selector for phasor18 phasor19 posseq negseq zer...
Page 136
Name values (range) unit step default description phasor17usefreqsrc disabled enabled - - enabled include phasor 17 for automatic frequency source selection phasor18report disabled enabled - - enabled reporting phasor 18 phasor18usefreqsrc disabled enabled - - enabled include phasor 18 for automatic...
Page 137
Pid-6255-settings v2 table 64: phasorreport4 non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description phasor25 posseq negseq zeroseq a b c - - posseq group selector for phasor25 phasor26 posseq negseq zeroseq a b c - - posseq group selector for phasor26 phasor27 posseq negseq zer...
Page 138
Name values (range) unit step default description phasor25usefreqsrc disabled enabled - - enabled include phasor 25 for automatic frequency source selection phasor26report disabled enabled - - enabled reporting phasor 26 phasor26usefreqsrc disabled enabled - - enabled include phasor 26 for automatic...
Page 139
Name type values (range) unit description freqrefcherr boolean 0=freq ref not available 1=freq ref error 2=freq ref available - frequency reference channel error freqtrig boolean - - frequency trigger dfdttrig boolean - - rate of change of frequency trigger maghightrig boolean - - magnitude high tri...
Page 140
Pid-6240-monitoreddata v2 table 68: analogreport3 monitored data name type values (range) unit description analog17 real - - analog input channel 17 analog18 real - - analog input channel 18 analog19 real - - analog input channel 19 analog20 real - - analog input channel 20 analog21 real - - analog ...
Page 141
Pid-6243-monitoreddata v2 table 71: binaryreport3 monitored data name type values (range) unit description binary17 boolean - - binary input channel 17 binary18 boolean - - binary input channel 18 binary19 boolean - - binary input channel 19 binary20 boolean - - binary input channel 20 binary21 bool...
Page 142
Pid-6253-monitoreddata v2 table 73: phasorreport2 monitored data name type values (range) unit description phasor9 real - - phasor 9 amplitude phasor9 real - deg phasor 9 angle phasor10 real - - phasor 10 amplitude phasor10 real - deg phasor 10 angle phasor11 real - - phasor 11 amplitude phasor11 re...
Page 143
Name type values (range) unit description phasor23 real - deg phasor 23 angle phasor24 real - - phasor 24 amplitude phasor24 real - deg phasor 24 angle pid-6255-monitoreddata v2 table 75: phasorreport4 monitored data name type values (range) unit description phasor25 real - - phasor 25 amplitude pha...
Page 144
Requirements with a specific attention to the total vector error (tve) requirement. The tve is calculated using the following equation: 2 2 2 2 r r i i r i ( x ( n ) x ) ( x ( n ) x ) tve x x - + - = + guid-80d9b1ea-a770-4f50-9530-61644b4debbe v1 en-us (equation 1) where, x r (n) and x i (n) are the...
Page 145
Iec140000146-1-en.Vsd phasor1 phasor2 phasor32 analog1 analog2 analog24 freqtrig dfdttrig maghightrig maglowtrig binary1 binary2 binary24 pmureport1 smai smmi meas. Trm mu trm mim protection op up oc uv or num ieeec37.118 / 1344 messages u/i samples bim gps / irig-b pps time data u i u i i/p 8 tcp 6...
Page 146
This adaptive filtering is ensured by proper configuration and settings of all relevant pre-processing blocks, see signal matrix for analog inputs in the application manual. Note that in all preconfigured ieds such configuration and settings are already made and the three-phase voltage are used as m...
Page 147
Name type values (range) unit description freqrefchsel integer - - frequency reference channel number selected freqrefcherr boolean 0=freq ref not available 1=freq ref error 2=freq ref available - frequency reference channel error freqtrig boolean - - frequency trigger dfdttrig boolean - - rate of c...
Page 148
6.2.7.3 scaling factors for analogreport channels guid-0ddaf6a9-8643-4fdd-97cf-9e35ef40af7e v2 the internal calculation of analog values in the ied is based on 32 bit floating point. Therefore, if the user selects to report the analog data (analogdatatype) as integer, there will be a down-conversion...
Page 149
3277.0 analogxrange = iecequation2446 v1 en-us the scale factor is calculated as follows: (3277.0 2.0) 0.1 and 0.0 65535.0 scalefactor offset ´ = = = iecequation2447 v1 en-us the scale factor will be sent as 1 on configuration frame 2, and 0.1 on configuration frame 3. The range of analog values tha...
Page 150
6.2.8 technical data semod172233-1 v1 guid-f0baebd8-e361-4d50-9737-7df8b043d66a v4 the ied is compliant with the synchrophasor measurement requirements of ieee c37.118.1-2011, including the amendment (ieee c37.118.1a-2014) for both p and m performance classes. The ied is also compliant with synchrop...
Page 151
Section 7 impedance protection 7.1 power swing detection zmrpsb (68) ip14499-1 v3 7.1.1 identification m14853-1 v3 function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number power swing detection zmrpsb zpsb symbol-ee v1 en-us 68 7.1.2 functionality m13873-3...
Page 152
7.1.4 signals pid-3663-inputsignals v6 table 77: zmrpsb (68) input signals name type default description i3p group signal - group signal for current input v3p group signal - group signal for voltage input block boolean 0 block of function blk_ss boolean 0 block inhibit of start output for slow swing...
Page 153
Name values (range) unit step default description r1finfw 0.01 - 1000.00 ohm/l 0.01 30.00 fault resistance coverage to inner resistive line, forward x1inrv 0.01 - 3000.00 ohm/p 0.01 30.00 inner reactive boundary, reverse r1finrv 0.01 - 1000.00 ohm/l 0.01 30.00 fault resistance line to inner resistiv...
Page 154
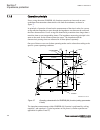
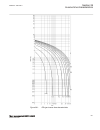
7.1.6 operation principle m13877-4 v4 power swing detection (zmrpsb ,68) function comprises an inner and an outer quadrilateral measurement characteristic with load encroachment, as shown in figure 37 . Its principle of operation is based on the measurement of the time it takes for a power swing tra...
Page 155
Re a a v rset i æ ö £ ç ÷ è ø equation1557 v1 en-us (equation 3) im a a v xset i æ ö £ ç ÷ è ø equation1558 v1 en-us (equation 4) the r set and x set are r and x boundaries. 7.1.6.1 resistive reach in forward direction m13877-6 v3 to avoid load encroachment, the resistive reach is limited in forward...
Page 156
7.1.6.2 resistive reach in reverse direction m13877-15 v3 to avoid load encroachment in reverse direction, the resistive reach is limited by setting the parameter rldoutrv for the outer boundary of the load encroachment zone. The distance to the inner resistive load boundary rldinrv is determined by...
Page 157
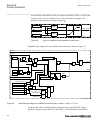
7.1.6.4 basic detection logic m13877-24 v7 the operation of the power swing detection zmrpsb (68) is only released if the magnitude of the current is above the setting of the min operating current, iminpupg. Zmrpsb (68) function can operate in two operating modes: • the 1 out of 3 operating mode is ...
Page 158
Ansi01000057-2-en.Vsd det-a det-b det-c det1of3 - int. Det2of3 - int. And and and or or ansi01000057 v2 en-us figure 39: detection of power swing for 1-of-3 and 2-of-3 operating mode en05000114-1-ansi.Vsd trsp i0check and blk_i0 and blk_ss block inhibit zout_c zout_b zout_a det1of3 - int. Rel1ph blk...
Page 159
7.1.6.5 operating and inhibit conditions m13877-38 v4 figure 40 presents a simplified logic diagram for the power swing detection function zmrpsb (68). The internal signals det1of3 and det2of3 relate to the detailed logic diagrams in figure 38 and figure 39 respectively. Selection of the operating m...
Page 160
7.1.7 technical data m16036-1 v10 table 82: zmrpsb (68) technical data function range or value accuracy reactive reach (0.10-3000.00) w/phase ±2.0% static accuracy conditions: voltage range: (0.1-1.1) x v n current range: (0.5-30) x i n angle: at 0 degrees and 85 degrees resistive reach (0.10–1000.0...
Page 161
There are several out-of-step relays in the power system, then the one which finds the center of oscillation in its zone 1 should operate first. Two current channels i3p1 and i3p2 are available in oosppam function to allow the direct connection of two groups of three-phase currents; that may be need...
Page 162
Pid-3539-outputsignals v10 table 84: oosppam (78) output signals name type description trip boolean common trip, issued when either zone 1 or zone 2 trip tripz1 boolean zone 1 trip tripz2 boolean zone 2 trip pickup boolean set when measured impedance enters lens characteristic genmode boolean genera...
Page 163
Table 86: oosppam (78) group settings (advanced) name values (range) unit step default description noofslipsz1 1 - 20 - 1 1 number of pole-slips in zone 1 required for zone 1 trip noofslipsz2 1 - 60 - 1 3 number of pole-slips in zone 2 required for zone 2 trip treset 1.000 - 60.000 s 0.001 6.000 tim...
Page 164
7.2.6 monitored data pid-3539-monitoreddata v8 table 89: oosppam (78) monitored data name type values (range) unit description current real - a magnitude of the measured positive-sequence current, in a voltage real - kv magnitude of the measured positive-sequence voltage, in v r real - % real part o...
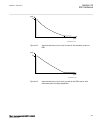
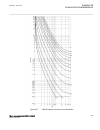
Page 165
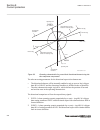
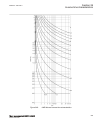
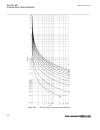
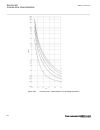
-1.5 -1 -0.5 0 0.5 1 1.5 -1 -0.5 0 0.5 1 1.5 ------- ------ ------ ----- ----- ----- ----- ----- --- -- --- - -- -- - -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- --- --- --- --- --- --- --- --- ---- ---- ---- ---- ------ real part (r) of z in ohms im a g in a ry p a rt ( x ) o f z in o h m s ^ ^ ^ ^ ^ ^ ^ ^ ^ ^ ^ ^ ^ ^...
Page 166
Rotor (power) angle δ can be thought of as the angle between the two lines, connecting point 0 in figure 42 , that is, z(r, x) under normal load, with the points se and re, respectively. These two lines are not shown in figure 42 . Normal values of the power angle, that is, under stable, steady-stat...
Page 167
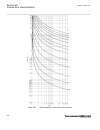
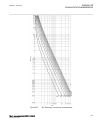
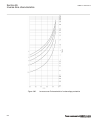
-1 -0.5 0 0.5 1 1.5 -1 -0.8 -0.6 -0.4 -0.2 0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1 ------ ------ ----- ---- ---- ---- ----- ----- ----- ---- --- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- --- --- --- --- --- --- --- --- --- --- --- --- ---- ---- ---- --- real part (r) of z in ohms → im ag ina ry pa rt (x ) o f z in o hm s → ^ ^ ^ ^ ^ ...
Page 168
Of-step characteristic which corresponds to the rotor (power) angle of 90 degrees). Figure 45 illustrates construction of the lens characteristic for a power system. -0.8 -0.6 -0.4 -0.2 0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1 -0.6 -0.4 -0.2 0 0.2 0.4 0.6 ---- --- --- --- --- --- --- -- -- -- -- -- --- -- --- --- -- - -...
Page 169
System, or as a single machine – infinite bus equivalent system, the following information is necessary: zgen(rgen, xgen), ztr(rtr, xtr), zline(rline, xline), zeq(req, xeq), and the setting pickupangle, for example 120 degrees. All impedances must be referred to the voltage level where the out-of-st...
Page 170
Right to left in case of a generator and in the opposite direction in case of a motor. Another requirement is that the travel across the lens takes no less than a specific minimum traverse time, typically 40...60 milliseconds. The above timing is used to discriminate a fault from an out-of-step cond...
Page 171
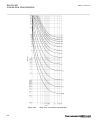
Pickupangle = 120° → fsmax = 25 × 0.333 = 8.333 hz pickupangle = 130° → fsmax = 25 × 0.277 = 6.944 hz the minimum value of fsmax is 6.994 hz. When pickupangle = 110 degrees, fsmax = 7.777 hz. This implies, that the default pickupangle = 110 degrees covers 90% of cases as, the typical final slip freq...
Page 172
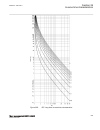
The second method this method is more exact. If the break-time of the circuit breaker is known, (and specified as the setting tbreaker) than it is possible to initiate a trip (break) command almost exactly tbreaker milliseconds before the rotor (power) angle reaches 0 degrees, where the currents are...
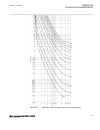
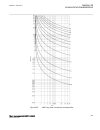
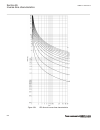
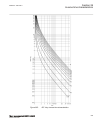
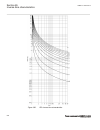
Page 173
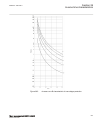
0 200 400 600 800 1000 1200 -5 0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 c urr en t i n ka , t rip c om m and to c b , r ot or ang le in ra d → time in milliseconds → pos. Seq. Current in ka trip command to cb rotor angle in radian fault occurs ← normal load current ← min. Current very high currents due to out-of-step ...
Page 174
Iec10000116-3-en.Vsd genmode calculation of r and x parts of the complex positive- sequence impedance z(r, x) upsre upsim upsmag r ipsre ipsim z(r,x) z(r,x) within limit of reach? X no return yes z(r,x) within lens characteristic? No yes z(r,x) entered lens from? Function alert right left z(r,x) exi...
Page 175
Section 8 current protection 8.1 directional phase overcurrent protection, four steps oc4ptoc(51_67) semod129998-1 v8 8.1.1 identification m14885-1 v6 function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number directional phase overcurrent protection, four s...
Page 176
8.1.3 function block m12609-3 v8 =ansi06000187=4=en=original.Vsdx oc4ptoc (51_67) i3p* v3p* block blktr blk1 blk2 blk3 blk4 multpu1 multpu2 multpu3 multpu4 trip trst1 trst2 trst3 trst4 tr_a tr_b tr_c trst1_a trst1_b trst1_c trst2_a trst2_b trst2_c trst3_a trst3_b trst3_c trst4_a trst4_b trst4_c pick...
Page 177
8.1.4 signals pid-6973-inputsignals v3 table 91: oc4ptoc (51_67) input signals name type default description i3p group signal - group signal for current input v3p group signal - group signal for voltage input block boolean 0 block of function blktr boolean 0 block of trip blk1 boolean 0 block of ste...
Page 178
Name type description trst2_c boolean trip signal from step2 phase c trst3_a boolean trip signal from step3 phase a trst3_b boolean trip signal from step3 phase b trst3_c boolean trip signal from step3 phase c trst4_a boolean trip signal from step4 phase a trst4_b boolean trip signal from step4 phas...
Page 179
8.1.5 settings pid-6973-settings v3 table 93: oc4ptoc (51_67) group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description operation disabled enabled - - disabled operation disabled/enabled anglerca 40 - 65 deg 1 55 relay characteristic angle (rca) angleroa 40 - 89 deg 1 80 relay operati...
Page 180
Name values (range) unit step default description characterist2 ansi ext. Inv. Ansi very inv. Ansi norm. Inv. Ansi mod. Inv. Ansi def. Time l.T.E. Inv. L.T.V. Inv. L.T. Inv. Iec norm. Inv. Iec very inv. Iec inv. Iec ext. Inv. Iec s.T. Inv. Iec l.T. Inv. Iec def. Time reserved programmable ri type rd...
Page 181
Name values (range) unit step default description pickup3 5 - 2500 %ib 1 250 operating phase current level for step 3 in % of ibase t3 0.000 - 60.000 s 0.001 0.800 def time delay or add time delay for inverse char of step 3 td3 0.05 - 999.00 - 0.01 0.05 time multiplier for the inverse time delay for...
Page 182
Table 94: oc4ptoc (51_67) group settings (advanced) name values (range) unit step default description puminopphsel 1 - 100 %ib 1 7 minimum current for phase selection in % of ibase 2ndharmstab 5 - 100 % 1 20 operate level of 2nd harmonic curr in % of fundamental curr i1>min 5 - 2500 %ib 1 5 minimum ...
Page 183
Name values (range) unit step default description tbcrv2 0.00 - 20.00 - 0.01 0.00 parameter b for customer programmable curve for step 2 tccrv2 0.1 - 10.0 - 0.1 1.0 parameter c for customer programmable curve for step 2 tprcrv2 0.005 - 3.000 - 0.001 0.500 parameter pr for customer programmable curve...
Page 184
Name values (range) unit step default description resettypecrv4 instantaneous iec reset ansi reset - - instantaneous selection of reset curve type for step 4 treset4 0.000 - 60.000 s 0.001 0.020 constant reset time for step 4 tpcrv4 0.005 - 3.000 - 0.001 1.000 parameter p for customer programmable c...
Page 185
Name type values (range) unit description ia real - a current in phase a ib real - a current in phase b ic real - a current in phase c 8.1.7 operation principle m12883-3 v10 directional phase overcurrent protection, four steps oc4ptoc (51_67) is divided into four different sub-functions. For each st...
Page 186
Ansi05000740-3-en.Vsdx direction element 4 step overcurrent element one element for each step harmonic restraint mode selection dirphaflt dirphbflt dirphcflt harmrestrblock enabledir enablestep1-4 directionalmode1-4 faultstate element faultstate i3p v3p pickup trip ansi05000740 v3 en-us figure 51: f...
Page 187
Measured value (dft or rms) do not influence the operation of directional part of oc4ptoc. Service values for individually measured phase currents are available on the local hmi for oc4ptoc (51/67) function, which simplifies testing, commissioning and in service operational checking of the function....
Page 188
For close-in three-phase faults, the v1 am memory voltage, based on the same positive sequence voltage, ensures correct directional discrimination. The memory voltage is used for 100 ms or until the positive sequence voltage is restored. After 100 ms, the following occurs: • if the current is still ...
Page 189
V ref i dir rca roa forward reverse roa en05000745_ansi.Vsd ansi05000745 v1 en-us figure 52: directional characteristic of the phase overcurrent protection the default value of anglerca is –55°. The parameter angleroa gives the angular distance from anglerca to define the directional borders. A mini...
Page 191
Greater comparator directional element i3p v3p directional release block dfwdlx dfwdlxx drevlx drevlxx stlx forward_int reverse_int x- means three phases 1,2 and 3 xx – means phase to phase 12,23,31 anglerca angleroa puminopphsel ansi15000266-2-en.Vsdx ansi15000266 v2 en-us figure 54: oc4 directiona...
Page 192
Hi u lo y min max ix>_used ix>max ix> ix>min iec17000018-1-en.Vsdx iec17000018 v1 en-us figure 55: logic for limitation of used operation current value the stdircnd output provides an integer signal that depends on the start and directional evaluation and is derived from a binary coded signal as des...
Page 193
Restraint feature is active, the oc4ptoc 51_67 function output signal st2ndhrm will be set to the logical value one. A b a>b block and i op extract second harmonic current component extract fundamental current component x 2ndharmstab a b a>b a b a>b 0.07*ibase iec13000014-2-en.Vsd 2ndh_block_int iec...
Page 194
Function setting range accuracy operate time, start non-directional at 0 to 10 x i set min. = 5 ms max. = 20 ms - reset time, start non-directional at 10 x i set to 0 min. = 20 ms max. = 35 ms - critical impulse time 10 ms typically at 0 to 2 x i set - impulse margin time 15 ms typically - 8.2 direc...
Page 195
Directional operation can be combined together with the corresponding communication logic in permissive or blocking teleprotection scheme. The current reversal and weak- end infeed functionality are available as well. The residual current can be calculated by summing the three-phase currents or taki...
Page 196
Name type default description blk4 boolean 0 block of step 4 (pickup and trip) multpu1 boolean 0 when activated, the pickup multiplier is in use for step1 multpu2 boolean 0 when activated, the pickup multiplier is in use for step2 multpu3 boolean 0 when activated, the pickup multiplier is in use for...
Page 197
Pid-6967-settings v3 table 101: ef4ptoc (51n_67n) group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description operation disabled enabled - - disabled operation disabled/enabled endir disable enable - - enable enabling the directional calculation anglerca -180 - 180 deg 1 65 relay charac...
Page 198
Name values (range) unit step default description dirmodesel1 disabled non-directional forward reverse - - non-directional directional mode of step 1 (off, non-dir, forward, reverse) characterist1 ansi ext. Inv. Ansi very inv. Ansi norm. Inv. Ansi mod. Inv. Ansi def. Time l.T.E. Inv. L.T.V. Inv. L.T...
Page 199
Name values (range) unit step default description characterist2 ansi ext. Inv. Ansi very inv. Ansi norm. Inv. Ansi mod. Inv. Ansi def. Time l.T.E. Inv. L.T.V. Inv. L.T. Inv. Iec norm. Inv. Iec very inv. Iec inv. Iec ext. Inv. Iec s.T. Inv. Iec l.T. Inv. Iec def. Time reserved programmable ri type rd...
Page 200
Name values (range) unit step default description characterist3 ansi ext. Inv. Ansi very inv. Ansi norm. Inv. Ansi mod. Inv. Ansi def. Time l.T.E. Inv. L.T.V. Inv. L.T. Inv. Iec norm. Inv. Iec very inv. Iec inv. Iec ext. Inv. Iec s.T. Inv. Iec l.T. Inv. Iec def. Time reserved programmable ri type rd...
Page 201
Name values (range) unit step default description characterist4 ansi ext. Inv. Ansi very inv. Ansi norm. Inv. Ansi mod. Inv. Ansi def. Time l.T.E. Inv. L.T.V. Inv. L.T. Inv. Iec norm. Inv. Iec very inv. Iec inv. Iec ext. Inv. Iec s.T. Inv. Iec l.T. Inv. Iec def. Time reserved programmable ri type rd...
Page 202
Name values (range) unit step default description tacrv1 0.005 - 200.000 - 0.001 13.500 param a for customized inverse trip time curve for step 1 tbcrv1 0.00 - 20.00 - 0.01 0.00 param b for customized inverse trip time curve for step 1 tccrv1 0.1 - 10.0 - 0.1 1.0 param c for customized inverse trip ...
Page 203
Name values (range) unit step default description tpcrv3 0.005 - 3.000 - 0.001 1.000 param p for customized inverse trip time curve for step 3 tacrv3 0.005 - 200.000 - 0.001 13.500 param a for customized inverse trip time curve for step 3 tbcrv3 0.00 - 20.00 - 0.01 0.00 param b for customized invers...
Page 204
Table 103: ef4ptoc (51n_67n) non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description globalbasesel 1 - 12 - 1 1 selection of one of the global base value groups seqtypeidir zero seq neg seq - - zero seq choice of measurand for directional current seqtypeipol zero seq neg seq - -...
Page 205
8.2.7.1 operating quantity within the function m13941-58 v9 the function always uses residual current (3i 0 ) for its operating quantity. The residual current can be: 1. Directly measured (when a dedicated ct input of the ied is connected in pcm600 to the fourth analog input of the pre-processing bl...
Page 206
8.2.7.2 internal polarizing m13941-82 v11 a polarizing quantity is used within the protection in order to determine the direction to the ground fault (forward/reverse). The function can be set to use voltage polarizing, current polarizing or dual polarizing. Voltage polarizing when voltage polarizin...
Page 207
It shall be noted that residual voltage (-3v 0 ) or negative sequence voltage (-3v 2 ) is used to determine the location of the ground fault. This ensures the required inversion of the polarizing voltage within the ground-fault function. Current polarizing when current polarizing is selected, the fu...
Page 208
In order to enable current polarizing, the magnitude of the polarizing current shall be bigger than a minimum level defined by setting parameter ipolmin. Dual polarizing when dual polarizing is selected, the function will use the vectorial sum of the voltage based and current based polarizing in acc...
Page 209
8.2.7.6 internal ground-fault protection structure m13941-157 v5 the protection is internally divided into the following parts: 1. Four residual overcurrent steps. 2. Directional supervision element for residual overcurrent steps with integrated directional comparison step for communication based gr...
Page 210
Set outside inx>max and inx>min, the closest of the limits to inx> is used by the function. If inx>max is smaller then inx>min, the limits are swapped. The principle of the limitation is shown in figure 58 . Hi u lo y min max inx>_used inx>max inx> inx>min iec17000017-1-en.Vsdx iec17000017 v1 en-us ...
Page 211
Input blkx. The trip signals from the function can be blocked from the binary input blktr. 8.2.7.8 directional supervision element with integrated directional comparison function m13941-179 v11 at least one of the four residual overcurrent steps shall be set as directional in order to enable executi...
Page 212
Purev 0.6 * indirpu pufw -rca -85 deg 40% of indirpu indirpu rca 65° vpol = -3v 0 i = 3i op 0 rca +85 deg rca -85 deg characteristic for purev characteristic for pufw characteristic for reverse release of measuring steps characteristic for forward release of measuring steps -rca +85 deg ansi11000243...
Page 213
These signals shall be used for communication based ground-fault teleprotection communication schemes (permissive or blocking). Simplified logic diagram for directional supervision element with integrated directional comparison step is shown in figure 61 : x a a>b b idirpu polmethod=voltage polmetho...
Page 214
2ndharmstab), output signal 2ndharmd is set to logical value one and the harmonic restraining feature to the function block will be applicable. Blocking from the 2nd harmonic element activates if all of three criteria are satisfied: 1. The fundamental frequency component of the current > 1% of ibase...
Page 216
The sotf logic uses the pickup signal from step 2 or step 3 for its operation, selected by setting parameter stepforsotf. The setting parameter sotfsel can be set for activation of cb position open change, cb position closed change or cb close command. In case of a residual current pickup from step ...
Page 217
Undertime enharmrestsotf actundrtimesel t4u and t tundertime or open closed close command sotfsel t4u stepforsotf pust2 pust3 and t tsotf and block 2nd harmonic and open close close command pust4 sotf undertime trip disabled or undertime sotf sotf ansi06000643-5-en.Vsdx ansi06000643 v5 en-us figure ...
Page 218
En 06000376_ansi. Vsd direction element 4 step over current element one element for each step harmonic restraint mode selection ground faultdirection harmrestrblock enabledir enablestep1-4 directionalmode1-4 trip element enabledir anglevalid directional check operatingcurrent switchontofault pickup ...
Page 219
Function range or value accuracy inverse time characteristics, see table 687 , table 688 and table 689 16 curve types see table 687 , table 688 and table 689 second harmonic blocking (5–100)% of fundamental ±2.0% of i n minimum polarizing voltage (1–100)% of vbase ±0.5% of v n minimum polarizing cur...
Page 220
All iec and ansi time delayed characteristics are available together with an optional user defined characteristic. The directional function is voltage polarized. Ns4ptoc (4612) can be set directional or non-directional independently for each of the steps. Ns4ptoc (4612) can be used as main protectio...
Page 221
8.3.4 signals pid-4151-inputsignals v4 table 106: ns4ptoc (46i2) input signals name type default description i3p group signal - group connection for operate current i3pdir group signal - group connection for directional current v3p group signal - group connection for polarizing voltage block boolean...
Page 222
8.3.5 settings pid-4151-settings v4 table 108: ns4ptoc (46i2) group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description operation disabled enabled - - disabled operation disabled/enabled endir disable enable - - enable enabling the directional calculation anglerca -180 - 180 deg 1 65 ...
Page 223
Name values (range) unit step default description dirmodesel2 disabled non-directional forward reverse - - non-directional directional mode of step 2 (disabled, nondir, forward, reverse) characterist2 ansi ext. Inv. Ansi very inv. Ansi norm. Inv. Ansi mod. Inv. Ansi def. Time l.T.E. Inv. L.T.V. Inv....
Page 224
Name values (range) unit step default description characterist3 ansi ext. Inv. Ansi very inv. Ansi norm. Inv. Ansi mod. Inv. Ansi def. Time l.T.E. Inv. L.T.V. Inv. L.T. Inv. Iec norm. Inv. Iec very inv. Iec inv. Iec ext. Inv. Iec s.T. Inv. Iec l.T. Inv. Iec def. Time reserved programmable ri type rd...
Page 225
Name values (range) unit step default description i2-4> 1 - 2500 %ib 1 17 negative sequence current op level for step 4 in % of ibase t4 0.000 - 60.000 s 0.001 1.200 time delay of step 4 when definite time char. Is selected td4 0.05 - 999.00 - 0.01 0.05 time multiplier for the step 4 selected time c...
Page 226
Name values (range) unit step default description tccrv2 0.1 - 10.0 - 0.1 1.0 param c for customized inverse trip time curve for step 2 tprcrv2 0.005 - 3.000 - 0.001 0.500 param pr for customized inverse reset time curve for step 2 ttrcrv2 0.005 - 100.000 - 0.001 13.500 param tr for customized inver...
Page 227
Table 110: ns4ptoc (46i2) non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description globalbasesel 1 - 12 - 1 1 selection of one of the global base value groups 8.3.6 monitored data pid-4151-monitoreddata v4 table 111: ns4ptoc (46i2) monitored data name type values (range) unit des...
Page 228
Where: ia, ib, ic are fundamental frequency phasors of three individual phase currents. A is so called operator which gives a phase shift of 120 deg, that is, a = 1∠120 deg a 2 similarly gives a phase shift of 240 deg, that is, a 2 = 1∠240 deg the phasor magnitude is used within the ns4ptoc (4612) p...
Page 229
Magnitude of polarizing voltage must be bigger than a minimum level defined by setting vpolmin. Note that –v2 is used to determine the location of the fault. This ensures the required inversion of the polarizing voltage within the function. 8.3.7.3 external polarizing for negative sequence function ...
Page 230
Are available. For the complete list of available inverse curves, refer to chapter "inverse characteristics" • type of reset characteristic (instantaneous / iec reset /ansi reset).By this parameter setting it is possible to select the reset characteristic of the stage. For the complete list of avail...
Page 231
8.3.7.6 directional supervision element with integrated directional comparison function guid-f54e21f7-7c99-41d6-bec6-2d6ec6d2b2a3 v3 at least one of the four negative sequence overcurrent steps must be set as directional in order to enable execution of the directional supervision element and the int...
Page 232
Directional comparison step, built-in within directional supervision element, set ns4ptoc (4612) output binary signals: 1. Pufw=1 when tip of i2 phasor (operating quantity magnitude) is in forward area, see fig 67 (operating quantity magnitude is bigger than setting indirpu) 2. Purev=1 when tip of i...
Page 233
X a a>b b idirpu polmethod=voltage polmethod=dual or forward_int reverse_int block stage1_dir_int 0.6 x 0.4 and stage3_dir_int stage4_dir_int stage2_dir_int or purev vpolmin ipolmin anglerca t f 0.0 x t f rnpol xnpol 0.0 d ire ct io na l c ha ra ct eri st ic fwd rvs and and and pufw forward_int reve...
Page 234
Function range or value accuracy minimum operate time for inverse curves, step 1 - 4 (0.000 - 60.000) s ±0.2% or ±35 ms whichever is greater inverse time characteristics, see table 687 , table 688 and table 689 16 curve types see table 687 , table 688 and table 689 minimum trip current, step 1 - 4 (...
Page 235
8.4.2 functionality semod171959-4 v12 in networks with high impedance grounding, the phase-to-ground fault current is significantly smaller than the short circuit currents. Another difficulty for ground fault protection is that the magnitude of the phase-to-ground fault current is almost independent...
Page 236
With large capacitive ground fault currents. In such networks, the active fault current would be small and by using sensitive directional residual power protection, the operating quantity is elevated. Therefore, better possibility to detect ground faults. In addition, in low impedance grounded netwo...
Page 237
8.4.3 function block semod172780-4 v6 ansi07000032-2-en.Vsd sdepsde (67n) i3p* v3p* block blktr blktrdir blkndn blkvn trip trdirin trndin trvn pickup pudirin pundin puvn pufw purev cnd vnrel ansi07000032 v2 en-us figure 70: sdepsde (67n) function block 8.4.4 signals pid-3892-inputsignals v7 table 11...
Page 238
Name type description pufw boolean pickup of directional function for a fault in forward direction purev boolean pickup of directional function for a fault in reverse direction cnd integer direction of fault. A general signal common to all three mode of residual over current protection vnrel boolean...
Page 239
Name values (range) unit step default description timechar ansi ext. Inv. Ansi very inv. Ansi norm. Inv. Ansi mod. Inv. Ansi def. Time l.T.E. Inv. L.T.V. Inv. L.T. Inv. Iec norm. Inv. Iec very inv. Iec inv. Iec ext. Inv. Iec s.T. Inv. Iec l.T. Inv. Iec def. Time reserved programmable ri type rd type...
Page 240
Table 117: sdepsde (67n) non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description globalbasesel 1 - 12 - 1 1 global base selection for function groups table 118: sdepsde (67n) non group settings (advanced) name values (range) unit step default description rotresv 0 deg 180 deg - ...
Page 241
Used for directionality and is defined as vref = -3v 0 e —jrcadir , that is -3v 0 inversely rotated by the set characteristic angle rcadir. Rcadir is normally set equal to 0 in a high impedance grounded network with a neutral point resistor as the active current component is appearing out on the fau...
Page 242
-3v 0 3i 0 rca = -90 °, roa = 90° = ang(3i 0 ) – ang(v ref ) 3i 0 cos v ref en06000649_ansi.Vsd ansi06000649 v1 en-us figure 72: rcadir set to -90° for trip, the operating quantity 3i 0 cos φ, the residual current 3i 0 , and the residual voltage 3v 0 must be larger than the set levels : incosphipu, ...
Page 243
Trip area roadir ansi06000650-3-en.Vsd 0 rcadir 0 3i 0 3 i cos 0 3 ref v v ansi06000650 v3 en-us figure 73: characteristic with roadir restriction the function indicates forward/reverse direction to the fault. Reverse direction is defined as 3i 0 ·cos (φ + 180°) ≥ the set value. It is also possible ...
Page 244
-3v 0 =v ref trip area instrument transformer angle error 3i 0 (prim) 3i 0 (to prot) characteristic after angle compensation rcacomp ansi06000651-2-en.Vsd rcadir = 0º ansi06000651 v2 en-us figure 74: explanation of rcacomp directional residual power protection measuring 3i 0 · 3v 0 · cos φ semod1719...
Page 245
Tdef or after the inverse time delay (setting tdsn) the binary output signals trip and trdirin get activated. The function shall indicate forward/reverse direction to the fault. Reverse direction is defined as 3i 0 · 3v 0 ·cos (φ + 180°) ³ the set value. This variant has the possibility of choice be...
Page 246
Trip from this function can be blocked from the binary input blktrdir. When the function picks up, binary output signals pickup and pudirin are activated. If the output signals pickup and pudirin remain active for the set delay tdef the binary output signals trip and trdirin get activated. The funct...
Page 247
In addition, there is also a separate non-directional residual over voltage protection, with its own definite time delay tvn and set level vn_pu. For trip, the residual voltage 3v 0 shall be larger than the set level (vn_pu). Trip from this function can be blocked from the binary input blkvn. When t...
Page 248
8.4.8 technical data semod173352-1 v1 semod173350-2 v16 table 120: sdepsde (67n) technical data function range or value accuracy trip level for 3i 0 ·cosj directional residual overcurrent (0.25-200.00)% of ibase ±1.0% of i n at i £ i n ±1.0% of i at i > i n trip level for 3i0·3v 0 ·cosj directional ...
Page 249
8.5 thermal overload protection, one time constant fahrenheit/celsius lfpttr/lcpttr (26) ip14512-1 v7 8.5.1 identification m17106-1 v7 function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number thermal overload protection, one time constant, fahrenheit lfptt...
Page 250
8.5.3 function block m12627-3 v8 lcpttr (26) i3p* block blktr multpu ambtemp sensflt reset trip bfi_3p alarm lockout ansi14000052-1-en.Vsd ansi13000199 v2 en-us lfpttr (26) i3p* block blktr multpu ambtemp sensflt reset trip bfi_3p alarm lockout ansi14000054-1-en.Vsd ansi13000301 v2 en-us figure 77: ...
Page 251
Name type default description multpu boolean 0 current multiplyer used when thol is for two or more lines ambtemp real 0 ambient temperature from external temperature sensor sensflt boolean 0 validity status of ambient temperature sensor reset boolean 0 reset of internal thermal load counter pid-390...
Page 252
Name values (range) unit step default description triptemp 0 - 300 deg c 1 90 temperature level for trip recltemp 0 - 300 deg c 1 75 temperature for reset of lockout after trip tpulse 0.05 - 0.30 s 0.01 0.10 operate pulse length. Minimum one execution cycle ambisens disabled enabled - - disabled ext...
Page 253
Table 128: lfpttr (26) non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description globalbasesel 1 - 12 - 1 1 selection of one of the global base value groups 8.5.6 monitored data pid-3908-monitoreddata v7 table 129: lcpttr (26) monitored data name type values (range) unit descripti...
Page 254
From the largest of the three-phase currents a final temperature is calculated according to the expression: 2 final ref ref i t i æ ö q = × ç ÷ ç ÷ è ø equation1167 v1 en-us (equation 23) where: i is the largest phase current, i ref is a given reference current and t ref is steady state temperature ...
Page 255
When the component temperature reaches the set alarm level alarmtemp the output signal alarm is set. When the component temperature reaches the set trip level triptemp the output signal trip is set. There is also a calculation of the present time to trip with the present current. This calculation is...
Page 256
Calculation of final temperature final temp > trip temp actual temp > alarm temp actual temp > trip temp actual temp calculation of time to trip calculation of time to reset of lockout calculation of actual temperature lockout logic ambtemp pickup temp trip lockout ttrip tenrecl i3p enmult sensflt a...
Page 257
8.5.8 technical data m12352-1 v14 table 131: lfpttr/lcpttr (26)technical data function range or value accuracy reference current (2-400)% of ibase ±1.0% of i n reference temperature (0-600)°f, 0 - 300)°c ± 2.0°f, ±2.0°c trip time: 2 2 2 2 2 ln p trip amb p ref ref i i t t t i i i t t - = - - - × é ù...
Page 258
8.6.2 functionality semod155787-4 v6 the task of a generator in a power plant is to convert mechanical energy available as a torque on a rotating shaft to electric energy. Sometimes, the mechanical power from a prime mover may decrease so much that it does not cover bearing losses and ventilation lo...
Page 259
8.6.3 function block semod172623-4 v4 ansi07000027-2-en.Vsd guppdup (37) i3p* v3p* block block1 block2 trip trip1 trip2 pickup pickup1 pickup2 p ppercent q qpercent ansi07000027 v2 en-us figure 80: guppdup (37) function block 8.6.4 signals pid-3709-inputsignals v6 table 132: guppdup (37) input signa...
Page 260
8.6.5 settings pid-3709-settings v6 table 134: guppdup (37) group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description operation disabled enabled - - disabled operation disabled/enabled opmode1 disabled underpower - - underpower operation mode for stage 1 off / on power1 0.0 - 500.0 %s...
Page 261
Name values (range) unit step default description iangcomp5 -10.000 - 10.000 deg 0.001 0.000 corr of error betw current and voltage angles at 5% of ir iangcomp30 -10.000 - 10.000 deg 0.001 0.000 corr of error betw current and voltage angles at 30% of ir iangcomp100 -10.000 - 10.000 deg 0.001 0.000 c...
Page 262
Chosen current phasors chosen voltage phasors complex power calculation p derivation of s( composant) in char angle s( angle) s( angle) power1 t trip 1 pickup1 q p = powre q = powim s( angle) power2 trip2 pickup2 0 t 0 ansi06000438-2-en.Vsd ansi06000438 v2 en-us figure 81: simplified logic diagram o...
Page 263
Set value: mode formula used for complex power calculation ca * * ( ) ca c a s v i i = × - equation2060-ansi v1 en-us (equation 33) a * 3 a a s v i = × × equation2061-ansi v1 en-us (equation 34) b * 3 b b s v i = × × equation2062-ansi v1 en-us (equation 35) c * 3 c c s v i = × × equation2063-ansi v1...
Page 264
If the measured power drops under the drop-power1(2) value, the function will reset after a set time dropdelay1(2). The reset means that the pickup signal will drop out and that the timer of the stage will reset. 8.6.7.1 low pass filtering semod172136-39 v3 in order to minimize the influence of the ...
Page 265
100 30 5 imagcomp5 imagcomp30 imagcomp100 -10 +10 magnitude compensation % of in measured current % of in 0-5%: constant 5-30-100%: linear >100%: constant 100 30 5 iangcomp5 iangcomp30 iangcomp100 -10 +10 angle compensation degrees measured current % of in ansi05000652_3_en.Vsd ansi05000652 v3 en-us...
Page 266
8.6.8 technical data semod175153-1 v1 semod175152-2 v11 table 139: guppdup (37) technical data function range or value accuracy power level for step 1 and step 2 (0.0–500.0)% of sbase ±1.0% of s n at s ≤ s n ±1.0% of s at s > s n where s r = 1,732*v n *i n characteristic angle for step 1 and step 2 ...
Page 267
Often, the motoring condition may imply that the turbine is in a very dangerous state. The task of the reverse power protection is to protect the turbine and not to protect the generator itself. Figure 83 illustrates the low forward power and reverse power protection with underpower and overpower fu...
Page 268
8.7.3 function block semod172667-4 v4 ansi07000028-2-en.Vsd goppdop (32) i3p* v3p* block block1 block2 trip trip1 trip2 pickup pickup1 pickup2 p ppercent q qpercent ansi07000028 v2 en-us figure 84: goppdop (32) function block 8.7.4 signals pid-3710-inputsignals v7 table 140: goppdop (32) input signa...
Page 269
8.7.5 settings pid-3710-settings v7 table 142: goppdop (32) group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description operation disabled enabled - - disabled operation disabled/enabled opmode1 disabled overpower - - overpower operation mode for stage 1 off / on power1 0.0 - 500.0 %sb ...
Page 270
Name values (range) unit step default description iangcomp5 -10.000 - 10.000 deg 0.001 0.000 corr of error betw current and voltage angles at 5% of ir iangcomp30 -10.000 - 10.000 deg 0.001 0.000 corr of error betw current and voltage angles at 30% of ir iangcomp100 -10.000 - 10.000 deg 0.001 0.000 c...
Page 271
Ansi06000567-2-en.Vsd chosen current phasors chosen voltage phasors complex power calculation p derivation of s(composant) in char angle s(angle) s(angle) > power1 t trip1 pickup1 q p = powre q = powim s(angle) > power2 t trip2 pickup2 ansi06000567 v2 en-us figure 85: simplified logic diagram of the...
Page 272
Set value: mode formula used for complex power calculation c,a * c a ca * s v (i i ) = × - equation2043 v1 en-us (equation 43) a * a a s 3 v i = × × equation2044 v1 en-us (equation 44) b * b b s 3 v i = × × equation2045 v1 en-us (equation 45) c * c c s 3 v i = × × equation2046 v1 en-us (equation 46)...
Page 273
8.7.7.1 low pass filtering semod172154-37 v4 in order to minimize the influence of the noise signal on the measurement it is possible to introduce the recursive, low pass filtering of the measured values for s (p, q). This will make slower measurement response to the step changes in the measured qua...
Page 274
100 30 5 imagcomp5 imagcomp30 imagcomp100 -10 +10 magnitude compensation % of in measured current % of in 0-5%: constant 5-30-100%: linear >100%: constant 100 30 5 iangcomp5 iangcomp30 iangcomp100 -10 +10 angle compensation degrees measured current % of in ansi05000652_3_en.Vsd ansi05000652 v3 en-us...
Page 275
8.7.8 technical data semod175160-1 v1 semod175159-2 v9 table 147: goppdop (32) technical data function range or value accuracy power level for step 1 and step 2 (0.0–500.0)% of sbase ±1.0% of s n at s ≤ s n ±1.0% of s at s > s n characteristic angle for step 1 and step 2 (-180.0–180.0) degrees ±2.0 ...
Page 276
270
Page 277
Section 9 voltage protection 9.1 two step undervoltage protection uv2ptuv (27) ip14544-1 v3 9.1.1 identification m16876-1 v7 function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number two step undervoltage protection uv2ptuv 3u symbol-r-2u-greater-than v2 en...
Page 278
9.1.3 function block m13794-3 v6 ansi06000276-2-en.Vsd uv2ptuv (27) v3p* block blktr1 blk1 blktr2 blk2 trip trst1 trst1_a trst1_b trst1_c trst2 trst2_a trst2_b trst2_c pickup pu_st1 pu_st1_a pu_st1_b pu_st1_c pu_st2 pu_st2_a pu_st2_b pu_st2_c ansi06000276 v2 en-us figure 87: uv2ptuv (27) function bl...
Page 279
Name type description trst2_a boolean trip signal from step2 phase a trst2_b boolean trip signal from step2 phase b trst2_c boolean trip signal from step2 phase c pickup boolean common pickup signal pu_st1 boolean common pickup signal from step1 pu_st1_a boolean pickup signal from step1 phase a pu_s...
Page 280
Name values (range) unit step default description tblkuv1 0.000 - 60.000 s 0.001 0.000 time delay of internal (low level) blocking for step 1 hystabs1 0.0 - 50.0 %vb 0.1 0.5 absolute hysteresis in % of vbase, step 1 operationstep2 disabled enabled - - enabled enable execution of step 2 characterist2...
Page 281
Name values (range) unit step default description pcrv1 0.000 - 3.000 - 0.001 1.000 parameter p for customer programmable curve for step 1 crvsat1 0 - 100 % 1 0 tuning param for prog. Under voltage inverse-time curve, step 1 treset2 0.000 - 60.000 s 0.001 0.025 reset time delay used in iec definite ...
Page 282
9.1.7 operation principle m15326-3 v9 two-step undervoltage protection (uv2ptuv ,27) is used to detect low power system voltage. If one, two or three phase voltages decrease below the set value, a corresponding start signal is generated. The parameters opmode1 and opmode2 influence the requirements ...
Page 283
9.1.7.2 time delay m15326-10 v11 the time delay for the two steps can be either definite time delay (dt) or inverse time undervoltage (tuv). For the inverse time delay three different modes are available: • inverse curve a • inverse curve b • customer programmable inverse curve the type a curve is d...
Page 284
Vpickup · (1.0 – crvsatn/100) the used voltage will be: vpickup · (1.0 – crvsatn/ 100). If the programmable curve is used this parameter must be calculated so that: 0 100 crvsatn b c × - > equation1435 v1 en-us (equation 53) the lowest voltage is always used for the inverse time delay integration. T...
Page 285
Voltage time hystabs1 pickup trip pickup1 pickup trip t tireset1 time time integrator t frozen timer linearly decreased instantaneous measured voltage tireset1 ansi05000010-3-en.Vsd ansi05000010 v3 en-us figure 89: voltage profile not causing a reset of the pickup signal for step 1, and inverse time...
Page 286
Voltage time hystabs1 pickup trip pickup pickup 1 pickup trip t tireset1 time time integrator t frozen timer linearly decreased instantaneous measured voltage tireset1 ansi05000011-2-en.Vsd ansi05000011 v2 en-us figure 90: voltage profile causing a reset of the pickup signal for step 1, and inverse ...
Page 287
When definite time delay is selected the function will trip as shown in figure 91 . Detailed information about individual stage reset/operation behavior is shown in figure 92 and figure 93 respectively. Note that by setting tresetn = 0.0s, instantaneous reset of the definite time delayed stage is en...
Page 288
Pickup1 pu_st1 trst1 treset1 t1 ansi10000040-3-en.Vsd ansi10000040 v3 en-us figure 93: example for definite time delay stage1 operation 9.1.7.3 blocking m15326-20 v8 it is possible to block two step undervoltage protection uv2ptuv (27) partially or completely, by binary input signals or by parameter...
Page 289
Time v normal voltage pickup1 pickup2 intblkstval1 intblkstval2 disconnection tblkuv1 t1,t1min tblkuv2 t2,t2min block step 1 block step 2 en05000466_ansi.Vsd ansi05000466 v1 en-us figure 94: blocking function 9.1.7.4 design m15326-35 v9 the voltage measuring elements continuously measure the three p...
Page 290
Pickup pu_st1_a pu_st1_b pu_st1_c trst1_a trst1_b trst1_c pu_st1 trst1 pickup pu_st2_a pu_st2_b pu_st2_c trst2_a trst2_b trst2_c pu_st2 trst2 trip comparator va comparator vb comparator vc minvoltselector comparator va comparator vb comparator vc minvoltselector pickup & trip output logic step 1 pic...
Page 291
9.1.8 technical data ip13001-1 v1 m13290-1 v15 table 154: uv2ptuv (27) technical data function range or value accuracy trip voltage, low and high step (1.0–100.0)% of vbase ±0.5% of v n absolute hysteresis (0.0–50.0)% of vbase ±0.5% of v n internal blocking level, step 1 and step 2 (1.0–50.0)% of vb...
Page 292
9.2.2 functionality ov2ptov m13798-3 v15 overvoltages may occur in the power system during abnormal conditions such as sudden power loss, tap changer regulating failures, and open line ends on long lines. Two step overvoltage protection (ov2ptov, 59) function can be used to detect open line ends, no...
Page 293
Name type default description blk1 boolean 0 block of step 1 blktr2 boolean 0 block of trip signal, step 2 blk2 boolean 0 block of step 2 pid-3535-outputsignals v7 table 156: ov2ptov (59) output signals name type description trip boolean trip trst1 boolean common trip signal from step1 trst1_a boole...
Page 294
9.2.5 settings pid-3535-settings v7 table 157: ov2ptov (59) group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description operation disabled enabled - - disabled operation disabled/enabled operationstep1 disabled enabled - - enabled enable execution of step 1 characterist1 definite time i...
Page 295
Table 158: ov2ptov (59) group settings (advanced) name values (range) unit step default description treset1 0.000 - 60.000 s 0.001 0.025 reset time delay used in iec definite time curve step 1 resettypecrv1 instantaneous frozen timer linearly decreased - - instantaneous selection of used idmt reset ...
Page 296
Table 159: ov2ptov (59) non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description conntype phn dft phph dft phn rms phph rms - - phn dft group selector for connection type globalbasesel 1 - 12 - 1 1 selection of one of the global base value groups 9.2.6 monitored data pid-3535-mon...
Page 297
Vpickup vbase kv > ⋅ (%) ( ) / 3 equation1610 v2 en-us (equation 54) and operation for phase-to-phase voltage over: vpickup (%) vbase(kv) > × equation1992 v1 en-us (equation 55) when phase-to-ground voltage measurement is selected the function automatically introduces division of the base value by t...
Page 298
Where: vpickup > set value for step 1 and step 2 v measured voltage the type b curve is described as: t td v vpickup vpickup = ⋅ ⋅ − > > − + 480 32 0 5 0 035 . . Ansiequation2287 v3 en-us (equation 57) the type c curve is described as: t td v vpickup vpickup = ⋅ ⋅ − > > − + 480 32 0 5 0 035 . . Ansi...
Page 299
Ansi05000016-2-en.Vsd voltage idmt voltage time va vb vc ansi05000016 v2 en-us figure 97: voltage used for the inverse time characteristic integration operation of the trip signal requires that the overvoltage condition continues for at least the user set time delay. This time delay is set by the pa...
Page 300
Ansi05000019-3-en.Vsd voltage time hystabs1 pickup trip pu_overvolt1 pickup trip t tireset1 time time integrator t frozen timer linearly decreased instantaneous measured voltage tireset1 ansi05000019 v3 en-us figure 98: voltage profile not causing a reset of the pickup signal for step 1, and inverse...
Page 301
Voltage time hystabs1 pickup trip pickup pickup1 pickup trip t tireset1 time time integrator t frozen timer linearly decreased instantaneous measured voltage tireset1 ansi05000020-2-en.Vsd ansi05000020 v2 en-us figure 99: voltage profile causing a reset of the pickup signal for step 1, and inverse t...
Page 302
Either 1 or 2 respectively), instantaneous reset of the definite time delayed stage is ensured. A>b a b vpickup> v t treset1 t t1 and trst1 pu_st1 off delay on delay ansi10000100-2-en.Vsd ansi10000100 v2 en-us figure 100: logic diagram for step 1, definite time delay, dt operation pickup1 pickup tri...
Page 303
Pickup1 pickup trip treset1 t1 ansi10000038-2-en.Vsd ansi10000038 v2 en-us figure 102: example for definite time delay stage 1 operation 9.2.7.3 blocking m15330-20 v8 it is possible to block two step overvoltage protection ov2ptov, (59) partially or completely, by binary input signals where: block: ...
Page 304
Pickup pu_st1_a pu_st1_b pu_st1_c trst1-a trst1_b trst1_c pu_st1 trst1 pickup pu_st2_a pu_st2_b pu_st2_c trst2-a trst2-c pu_st2 trst2 trip _ . Comparator va > pickup 1 comparator vb > comparator vc > maxvoltselect comparator va > comparator vb > comparator vc > maxvoltselect pickup & trip output log...
Page 305
9.2.8 technical data ip13013-1 v1 m13304-1 v14 table 161: ov2ptov (59) technical data function range or value accuracy trip voltage, step 1 and 2 (1.0-200.0)% of vbase ±0.5% of v n at v ≤ v n ±0.5% of v at v > v n absolute hysteresis (0.0–50.0)% of vbase ±0.5% of v n at v ≤ v n ±0.5% of v at v > v n...
Page 306
300
Page 307
Section 10 frequency protection 10.1 underfrequency protection saptuf (81) ip15746-1 v3 10.1.1 identification m14865-1 v5 function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number underfrequency protection saptuf f symbol-p v1 en-us 81 10.1.2 functionality ...
Page 308
10.1.4 signals pid-6752-inputsignals v2 table 162: saptuf (81l) input signals name type default description v3p group signal - three phase group signal for voltage inputs block boolean 0 block of function blktrip boolean 0 blocking operate output blkrest boolean 0 blocking restore output pid-6752-ou...
Page 309
Name values (range) unit step default description exponent 0.0 - 5.0 - 0.1 1.0 for calculation of the curve form for voltage based timer t_maxtripdelay 0.010 - 60.000 s 0.001 1.000 maximum time operation limit for voltage based timer t_mintripdelay 0.010 - 60.000 s 0.001 1.000 minimum time operation...
Page 310
Voltage level causes a short time delay. For the definite time delay, the setting tdelay sets the time delay. For the voltage dependent time delay the measured voltage level and the settings vnom, vmin, exponent, t_maxtripdelay and t_mintripdelay set the time delay according to figure 105 and equati...
Page 311
( ) _ _ _ exponent v vmin t t maxtripdelay t mintripdelay t mintripdelay vnom vmin - = × - + - é ù ê ú ë û equation1559 v1 en-us (equation 61) where: t is the voltage dependent time delay (at constant voltage), v is the measured voltage exponent is a setting, vmin, vnom are voltage settings correspo...
Page 312
10.1.6.4 blocking m13354-50 v7 it is possible to block underfrequency protection saptuf (81) partially or completely, by binary input signals or by parameter settings, where: block: blocks the start, trip and restore outputs blktrip: blocks the trip output blkrest: blocks the restore output if the m...
Page 313
Frequency f voltage pickup trip v block f > restorefreq block or definite timer or voltage based timer treset tdelay trestore restore ansi16000041-1-en.Vsdx trip pickup blktrip and pickup & trip output logic blkrest and blkdmagn ansi16000041 v1 en-us figure 106: simplified logic diagram for saptuf (...
Page 314
Function range or value accuracy reset time, definite time function at f set - 0.02 hz to f set + 0.02 hz (0.000-60.000)s ±0.2% or ±120 ms whichever is greater voltage dependent time delay settings: vnom=(50-150)% of v base vmin=(50-150)% of v base exponent=0.0-5.0 t_maxtripdelay=(0.010– 60.000)s t_...
Page 315
Saptof (81) is provided with an undervoltage blocking. The operation is based on positive sequence voltage measurement and requires two phase-phase or three phase-neutral voltages to be connected. For information about how to connect analog inputs, refer to application manual/ied application/analog ...
Page 316
10.2.5 settings pid-6751-settings v2 table 169: saptof (81h) group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description operation disabled enabled - - disabled operation disabled/enabled pufrequency 35.00 - 90.00 hz 0.01 51.20 frequency set value intblocklevel 0.0 - 100.0 %vb 1.0 50.0 ...
Page 317
10.2.6.2 time delay m14958-9 v8 the time delay for overfrequency protection saptof (81) is a settable definite time delay, specified by the setting tdelay. Trip signal issuing requires that the overfrequency condition continues for at least the user set time delay, tdelay. If the pickup condition, w...
Page 318
Frequency f > startfrequency voltage pickup trip v block block or definite timer treset tdelay ansi16000042-1-en.Vsdx trip pickup blkdmagn blktrip and pickup & trip output logic ansi16000042 v1 en-us figure 108: simplified logic diagram for saptof (81) 10.2.7 technical data m14964-1 v12 table 171: s...
Page 319
10.3.1 identification m14868-1 v4 function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number rate-of-change of frequency protection sapfrc df/dt > symbol-n v1 en-us 81 10.3.2 functionality m14965-3 v13 the rate-of-change of frequency protection function (sap...
Page 320
Pid-6754-outputsignals v2 table 173: sapfrc (81r) output signals name type description trip boolean trip signal pickup boolean pickup signal restore boolean restore signal for load restoring purposes blkdmagn boolean blocking indication due to low magnitude 10.3.5 settings pid-6754-settings v2 table...
Page 321
No pickup or trip signal is issued. If the frequency recovers, after a frequency decrease, a restore signal is issued. 10.3.6.1 measurement principle m14970-6 v8 the rate-of-change of the fundamental frequency of the selected voltage is measured continuously, and compared with the set value, pufreqg...
Page 322
Block: blocks the start and trip outputs blktrip: blocks the trip output blkrest: blocks the restore output if the measured voltage level decreases below the setting of intblocklevel, both the pickup and the trip outputs are blocked. 10.3.6.4 design m14970-34 v7 rate-of-change frequency protection (...
Page 323
Ansi16000040-1-en.Vsdx restore voltage pickup pickup trip block if [startfreqgrad and df/dt or [startfreqgrad>0 and df/dt > startfreqgrad] then pickup v blkdmagn rate-of-change of frequency block or blkrest > f > restorefreq trestore restore and blktrip trip and pickup pickup & trip output logic def...
Page 324
10.3.7 technical data m14976-1 v9 table 176: sapfrc (81) technical data function range or value accuracy trip value, pickup function (-10.00-10.00) hz/s ±10.0 mhz/s trip value, restore enable frequency (45.00-65.00) hz ±2.0 mhz definite restore time delay (0.000-60.000) s ±0.2% or ±100 ms whichever ...
Page 325
It is possible to create functionality with more than one frequency band limit by using multiple instances of the function. This can be achieved by a proper configuration based on the turbine manufacturer specification. 10.4.3 function block guid-e3d2093b-8a97-4037-aafe-5483489bf350 v2 ftaqfvr (81a)...
Page 326
Name type description tripcont boolean trip signal when continuous time is exceeded the set limit bfi_3p boolean pickup signal of the function accalarm boolean alarm signal for reaching the frequency time accumulation value strorhld boolean activated when function starts or holdacc input is active f...
Page 327
10.4.6 monitored data pid-6515-monitoreddata v4 table 181: ftaqfvr (81a) monitored data name type values (range) unit description freq real - hz measured frequency value acctime real - s accumulated time for frequency band limits 10.4.7 operation principle guid-db8a3411-2fa6-47b1-bc75-9892bd224dc0 v...
Page 328
Voltage band limit check will be ignored for the bfi_3p output if the enavoltcheck setting is disabled. The voltage band limits are set with the settings vhighlimit and vlowlimit. The output voltok is activated only if the system positive-sequence voltage falls within the voltage band limits and the...
Page 329
Ansi12000609-1-en.Vsd comparator if f and f > freqlowlimit then pickup comparator i pickup signal routing based on generator start or stop detection logic and voltage band limit check logic v3p i3p cbopen cbclose comparator if freqhighlimit freqlowlimit then error block loadinit resetacc holdtime bf...
Page 330
Guid-e8d0ee7c-d7b8-46c3-9c0d-363ffc75de93 v5 table 182: ftaqfvr (81a) technical data function range or value accuracy trip value, frequency high limit level at symmetrical three phase voltage (35.00 – 90.00) hz ±2.0 mhz trip value, frequency low limit level at symmetrical three phase voltage (30.00 ...
Page 331
Section 11 multipurpose protection 11.1 general current and voltage protection cvgapc ip14552-1 v2 11.1.1 identification m14886-2 v3 function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number general current and voltage protection cvgapc 2(i>/u - 11.1.2 func...
Page 332
11.1.3 signals pid-3857-inputsignals v8 table 183: cvgapc input signals name type default description i3p group signal - group signal for current input v3p group signal - group signal for voltage input block boolean 0 block of function blkoc1 boolean 0 block of over current function oc1 blkoc1tr boo...
Page 333
Name type description trov2 boolean trip signal from overvoltage function ov2 truv1 boolean trip signal from undervoltage function uv1 truv2 boolean trip signal from undervoltage function uv2 pickup boolean common pickup signal pu_oc1 boolean pickup signal from overcurrent function oc1 pu_oc2 boolea...
Page 334
11.1.4 settings pid-3857-settings v9 table 185: cvgapc group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description operation disabled enabled - - disabled operation disabled/enabled currentinput phase a phase b phase c posseq negseq 3*zeroseq maxph minph unbalanceph phase ab phase bc ph...
Page 335
Name values (range) unit step default description lowvolt_vm 0.0 - 5.0 %vb 0.1 0.5 below this level in % of vbase setting actlowvolt takes over operation_oc1 disabled enabled - - disabled disable/enable operation of oc1 pickupcurr_oc1 2.0 - 5000.0 %ib 1.0 120.0 operate current level for oc1 in % of ...
Page 336
Name values (range) unit step default description operation_oc2 disabled enabled - - disabled disable/enable operation od oc2 pickupcurr_oc2 2.0 - 5000.0 %ib 1.0 120.0 operate current level for oc2 in % of ibase curvetype_oc2 ansi ext. Inv. Ansi very inv. Ansi norm. Inv. Ansi mod. Inv. Ansi def. Tim...
Page 337
Name values (range) unit step default description enblklowi_uc1 disabled enabled - - disabled enable internal low current level blocking for uc1 blklowcurr_uc1 0 - 150 %ib 1 20 internal low current blocking level for uc1 in % of ibase pickupcurr_uc1 2.0 - 150.0 %ib 1.0 70.0 operate undercurrent leve...
Page 338
Name values (range) unit step default description tmin_ov2 0.00 - 6000.00 s 0.01 0.05 minimum operate time for inverse-time curves for ov2 td_ov2 0.05 - 999.00 - 0.01 0.30 time multiplier for the dependent time delay for ov2 operation_uv1 disabled enabled - - disabled disable/enable operation of uv1...
Page 339
Table 186: cvgapc group settings (advanced) name values (range) unit step default description multpu_oc1 1.0 - 10.0 - 0.1 2.0 multiplier for scaling the current setting value for oc1 rescrvtype_oc1 instantaneous iec reset ansi reset - - instantaneous selection of reset curve type for oc1 tresetdef_o...
Page 340
Name values (range) unit step default description rescrvtype_ov1 instantaneous frozen timer linearly decreased - - instantaneous selection of reset curve type for ov1 tresetdef_ov1 0.00 - 6000.00 s 0.01 0.00 reset time delay in sec for definite time use of ov1 tresetidmt_ov1 0.00 - 6000.00 s 0.01 0....
Page 341
Name values (range) unit step default description c_uv1 0.000 - 1.000 - 0.001 1.000 parameter c for customer programmable curve for uv1 d_uv1 0.000 - 10.000 - 0.001 0.000 parameter d for customer programmable curve for uv1 p_uv1 0.001 - 10.000 - 0.001 0.020 parameter p for customer programmable curv...
Page 342
Name type values (range) unit description icosfi real - a measured current multiplied with cos (phi) voltage real - kv measured voltage value viangle real - deg angle between voltage and current 11.1.6 operation principle 11.1.6.1 measured quantities within cvgapc m13751-3 v3 general current and vol...
Page 343
Set value for the parameter currentinput comment 11 phaseb-phasec cvgapc function will measure the current phasor internally calculated as the vector difference between the phase b current phasor and phase c current phasor (i b -i c ) 12 phasec-phasea cvgapc function will measure the current phasor ...
Page 344
Set value for the parameter voltageinput comment 10 phasea-phaseb cvgapc function will measure the voltage phasor internally calculated as the vector difference between the phase a voltage phasor and phase b voltage phasor (v a -v b ) 11 phaseb-phasec cvgapc function will measure the voltage phasor ...
Page 345
11.1.6.2 base quantities for cvgapc function m13751-133 v3 the parameter settings for the base quantities, which represent the base (100%) for pickup levels of all measuring stages, shall be entered as setting parameters for every cvgapc function. Base current shall be entered as: 1. Rated phase cur...
Page 346
This feature will simple prevent overcurrent step pickup if the second-to-first harmonic ratio in the measured current exceeds the set level. Directional feature m13751-263 v5 the overcurrent protection step operation can be made dependent on the relevant phase angle between measured current phasor ...
Page 347
Two types of directional measurement principles are available, i & v and icosphi&v. The first principle, referred to as "i & v" in the parameter setting tool, checks that: • the magnitude of the measured current is bigger than the set pick-up level • the phasor of the measured current is within the ...
Page 348
V=-3v0 operate region rcadir roadir ipickup i=3io mta line f en05000253_ansi.Vsd ansi05000253 v1 en-us figure 115: cvgapc, icosphi&v directional operating principle where: rcadir is 75° roadir is 50° note that it is possible to decide by a parameter setting how the directional feature shall behave w...
Page 349
Selected voltage magnitude oc1 stage pickup level pickupcurr_oc1 vdepfact_oc1 * pickupcurr_oc1 vhighlimit_oc1 vlowlimit_oc1 en05000324_ansi.Vsd ansi05000324 v1 en-us figure 116: example for oc1 step current pickup level variation as function of measured voltage magnitude in slope mode of operation •...
Page 350
Current restraint feature m13751-338 v3 the overcurrent protection step operation can be made dependent of a restraining current quantity (see table 191 ). Practically then the pickup level of the overcurrent step is not constant but instead increases with the increase in the magnitude of the restra...
Page 351
Time than the set time delay the undercurrent step will set its trip signal to one. Reset of the pickup and trip signal can be instantaneous or time delay in accordance with the setting. 11.1.6.5 built-in overvoltage protection steps m13751-234 v3 two overvoltage protection steps are available. They...
Page 352
Adm a /d c o nv er si o n s ca lin g w ith c t r a tio a /d c o nv e rs io n sc al in g w ith c t r a tio p ha so r ca lc u la tio n o f in d iv id ua l c ur re nt s p ha so r ca lc u la tio n o f in d iv id u a l v ol ta g e s cvgapc function ied p h as or s & sa m pl es p h as or s & sa m pl es cu...
Page 353
1. Selects one current from the three-phase input system (see table 189 ) for internally measured current. 2. Selects one voltage from the three-phase input system (see table 190 ) for internally measured voltage. 3. Selects one current from the three-phase input system (see table 191 ) for internal...
Page 354
Uc2 uc1 current truc1 pu_uc2 truc2 pu_oc1 blk2nd pu_oc2 troc2 ov1 pu_ov1 trov1 ov2 pu_ov2 trov2 uv1 pu_uv1 truv1 uv2 pu_uv2 truv2 selected current selected restraint current en05000170_ansi.Vsd selected voltage vdirlow troc1 oc1 2 nd harmonic restraint current restraint directionality voltage contro...
Page 355
Ansi05000170 v1 en-us figure 120: cvgapc function main logic diagram for built-in protection elements logic in figure 120 can be summarized as follows: 1. The selected currents and voltage are given to built-in protection elements. Each protection element and step makes independent decision about st...
Page 356
A b b>a selected current pickupcurr_uc1 operation_uc1=on bin input: blkuc1 pu_uc1 en05000750_ansi.Vsd truc1 bin input: blkuc1tr 0-def and and 0 ansi05000750 v1 en-us figure 122: simplified internal logic diagram for built-in first undercurrent step that is, uc1 (step uc2 has the same internal logic)...
Page 357
And a b b>a selected voltage pickupvolt_uv1 operation_uv1=on blkuv1 inverse time selected en05000752_ansi.Vsd inverse 0-def def time selected or pu_uv1 truv1 and blktruv1 0 ansi05000752 v1 en-us figure 124: simplified internal logic diagram for built-in first undervoltage step uv1 (step uv2 has the ...
Page 358
Function range or value accuracy pickup time at 0 to 2 x i set min. = 15 ms max. = 30 ms - reset time at 2 x i set to 0 min. = 15 ms max. = 30 ms - pickup time at 0 to 10 x i set min. = 5 ms max. = 20 ms - reset time at 10 x i set to 0 min. = 20 ms max. = 35 ms - undercurrent: pickup time at 2 x i s...
Page 359
Function range or value accuracy inverse time characteristics, see table 696 3 curve types see table 696 high and low voltage limit, voltage dependent operation, step 1 - 2 (1.0 - 200.0)% of vbase ±1.0% of v n at v ≤ v n ±1.0% of v at v > v n directional function settable: nondir, forward and revers...
Page 360
354.
Page 361
Section 12 system protection and control 12.1 multipurpose filter smaihpac guid-6b541154-d56b-452f-b143-4c2a1b2d3a1f v1 12.1.1 identification guid-8224b870-3daa-44bf-b790-6600f2ad7c5d v1 function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number multipurpose...
Page 362
Pid-6733-outputsignals v1 table 195: smaihpac output signals name type description ai3p group signal analog input 3-phase group ai1 group signal analog input 1 ai2 group signal analog input 2 ai3 group signal analog input 3 ai4 group signal analog input 4 12.1.5 settings guid-5ea398ad-66e2-4240-8918...
Page 363
Note that the special filtering algorithm is used to extract these phasors. This algorithm is different from the standard one-cycle digital fourier filter typically used by the numerical ieds. This filter provides extremely good accuracy of measurement and excellent noise rejection, but at the same ...
Page 364
• presence of special railway frequencies (e.G. 16.7hz or 25hz) in the three-phase power system • sensitive reverse power protection • stator or rotor ground fault protection for special injection frequencies (e.G. 25hz) • etc. The filter output can also be connected to the measurement function bloc...
Page 365
Be used to extract low frequency signals. For example if 16,7 hz signal shall be extracted the minimum filter length in milliseconds shall be: 1000 3 180 16.7 ms × = equation000028 v1 en-us (equation 63) thus based on the data from table 197 the minimum acceptable value for this parameter would be “...
Page 366
If for any reason this natural frequency band shall be extended (e.G. To get accurate but wider filter) it is possible to increase the pass band by entering the value different from zero for parameter freqbandwidth. In such case the total filter pass band can be defined as: ± (value given in table 1...
Page 367
Iec13000178-2-en.Vsd a b c iec13000178 v3 en-us figure 125: example of filter calculation the data shown in the figure comes from the comtrade file captured by the ied. The following traces are presented in this figure. A) waveforms of the stator three-phase currents given in primary ka. B) rms valu...
Page 368
With above given settings the sub-synchronous current magnitude and frequency are calculated approximately four times per second (that is, correct value is four times per 1024 ms). Section 12 1mrk 511 408-uus a system protection and control 362 phasor measurement unit res670 2.2 ansi technical manua...
Page 369
Section 13 secondary system supervision 13.1 current circuit supervision (87) ip14555-1 v5 13.1.1 identification m14870-1 v5 function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number current circuit supervision ccsspvc - 87 13.1.2 functionality m12444-3 v10...
Page 370
13.1.4 signals pid-6806-inputsignals v2 table 199: ccsspvc (87) input signals name type default description i3p group signal - group signal for three phase current input iref group signal - residual reference current input block boolean 0 block of function pid-6806-outputsignals v2 table 200: ccsspv...
Page 373
13.2.1 identification m14869-1 v4 function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number fuse failure supervision fufspvc - - 13.2.2 functionality semod113820-4 v12 the aim of the fuse failure supervision function (fufspvc) is to block voltage measuring ...
Page 374
13.2.3 function block m13678-3 v9 fufspvc i3p* v3p* block 52a mcbop 89b blktrip blkz blkv 3ph dld1ph dld3ph pu_di pu_di_a pu_di_b pu_di_c pu_dv pu_dv_a pu_dv_b pu_dv_c ansi14000065-1-en.Vsd ansi14000065 v1 en-us figure 129: fufspvc function block 13.2.4 signals pid-3492-inputsignals v9 table 205: fu...
Page 375
Name type description pu_di_b boolean start signal of sudden change in current, phase b pu_di_c boolean start signal of sudden change in current, phase c pu_dv boolean common start signal of sudden change in voltage pu_dv_a boolean start signal of sudden change in voltage, phase a pu_dv_b boolean st...
Page 376
Table 208: fufspvc non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description globalbasesel 1 - 12 - 1 1 selection of one of the global base value groups 13.2.6 monitored data pid-3492-monitoreddata v8 table 209: fufspvc monitored data name type values (range) unit description 3i0 ...
Page 377
A drop out delay of 100 ms for the measured zero-sequence and negative sequence current will prevent a false fuse failure detection at un-equal breaker opening at the two line ends. Ia ib ic zero sequence filter negative sequence filter va vb vc zero sequence filter negative sequence filter currzero...
Page 378
Internal functions of the ied itself in order to receive a block command from internal functions. Through or gate it can be connected to both binary inputs and internal function outputs. The input blktrip is intended to be connected to the trip output from any of the protection functions included in...
Page 379
• the change in voltage dv • the change in current di the internal fusefaildetdvdi signal is activated if the following conditions are fulfilled: • the magnitude of the phase-ground voltage has been above vppu for more than 1.5 cycles (i.E. 30 ms in a 50 hz system) • the magnitude of dv in three pha...
Page 380
The delta function (except the sudden change of voltage and current detection) is deactivated by setting the parameter opdvdi to disabled. Section 13 1mrk 511 408-uus a secondary system supervision 374 phasor measurement unit res670 2.2 ansi technical manual.
Page 381
Ia va a b a>b t 1.5 cycle and dvdi detection phase 1 vppu dvdi detection phase 2 same logic as for phase 1 ia vb dvdi detection phase 3 same logic as for phase 1 ia vc a b a va ia a b a>b 50p and and 52a or or and a b a vb ib a b a>b and and or or and a b a vc ic a b a>b and and or or and and fusefa...
Page 382
Deltaia deltava deltaib deltavb deltaic deltavc pu_di_a pu_di_b pu_di_c pu_di pu_dv pu_dv_a pu_dv_b pu_dv_b ansi12000165-2-en.Vsd intblock and and and and and and and or or and or 20 ms 0 20 ms 0 20 ms 0 20 ms 0 20 ms 0 20 ms 0 ansi12000165 v2 en-us figure 132: internal signals deltav or deltai and ...
Page 383
Ia ib ic a b a a b a a b a idldpu va vb vc a b a a b a a b a vdldpu or and and and and and and and allcurrlow deadlinedet1ph dld3ph dld1ph intblock dead line detection ansi0000035-1-en.Vsd ansi0000035 v1 en-us figure 133: simplified logic diagram for dead line detection part 13.2.7.4 main logic guid...
Page 384
The delta function can be activated by setting the parameter opdvdi to enabled. When selected it operates in parallel with the sequence based algorithms. As soon as any fuse failure situation is detected, signals fusefaildetzeroseq, fusefaildetnegseq or fusefaildetdvdi, and the specific functionalit...
Page 385
Sealin = enabled all vl sealinpu any vl ealinpu t 5 s and 3ph mcbop all vl > vsealinpu t 60 s 52a block and test test active and blocfuse = yes opmodesel and t 200 ms and or 89b blkv blkz and and fusefaildetzeroseq v0i0 or v2i2 v0i0 and v2i2 v0i0 v2i2 optimzsns and fusefaildetnegseq or and and currz...
Page 386
Figure 134: simplified logic diagram for fuse failure supervision function, main logic 13.2.8 technical data m16069-1 v12 table 210: fufspvctechnical data function range or value accuracy trip voltage, zero sequence (1-100)% of vbase ±0.5% of v n trip current, zero sequence (1–100)% of ibase ±0.5% o...
Page 387
Section 14 control 14.1 logic rotating switch for function selection and lhmi presentation slgapc semod114936-1 v4 14.1.1 identification semod167845-2 v3 function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number logic rotating switch for function selection ...
Page 388
14.1.3 function block semod114954-4 v6 slgapc block psto up down ^p01 ^p02 ^p03 ^p04 ^p05 ^p06 ^p07 ^p08 ^p09 ^p10 ^p11 ^p12 ^p13 ^p14 ^p15 ^p16 ^p17 ^p18 ^p19 ^p20 ^p21 ^p22 ^p23 ^p24 ^p25 ^p26 ^p27 ^p28 ^p29 ^p30 ^p31 ^p32 swposn iec14000005-1-en.Vsd iec14000005 v1 en-us figure 135: slgapc functio...
Page 389
Pid-6641-outputsignals v3 table 212: slgapc output signals name type description p01 boolean selector switch position 1 p02 boolean selector switch position 2 p03 boolean selector switch position 3 p04 boolean selector switch position 4 p05 boolean selector switch position 5 p06 boolean selector swi...
Page 390
14.1.5 settings pid-6641-settings v3 table 213: slgapc non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description operation disabled enabled - - disabled operation disabled/enabled nrpos 2 - 32 - 1 32 number of positions in the switch outtype pulsed steady - - steady output type, s...
Page 391
Kept and further operation will be blocked. The operator place (local or remote) is specified through the psto input. If any operation is allowed the signal intone from the fixed signal function block can be connected. Slgapc function block has also an integer value output, that generates the actual...
Page 392
Ansi06000421-2-en.Vsd ../control/sld/switch smbrrec control wfm pilot setup off damage control dal ../control/sld/switch smbrrec control wfm pilot setup off p: disc n: disc fe ok cancel ../control/sld/switch smbrrec control wfm pilot setup off damage control dfw change to the "switches" page of the ...
Page 393
14.2.2 functionality semod158756-5 v9 the selector mini switch (vsgapc) function block is a multipurpose function used for a variety of applications, as a general purpose switch. Vsgapc can be controlled from the menu, from a symbol on the single line diagram (sld) on the local hmi or from binary in...
Page 394
14.2.5 settings pid-6504-settings v6 table 217: vsgapc non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description operation disabled enabled - - disabled operation disabled/enabled ctlmodel dir norm sbo enh - - dir norm specifies the type for control model according to iec 61850 mo...
Page 395
The following table shows the relationship between ipos1/ipos2 inputs and the name of the string that is shown on the sld. The value of the strings are set in pst. Ipos1 ipos2 name of displayed string default string value 0 0 posundefined p00 1 0 position1 p01 0 1 position2 p10 1 1 posbadstate p11 1...
Page 396
14.3.4 signals semod55883-1 v2 pid-4139-inputsignals v12 table 218: dpgapc input signals name type default description open boolean 0 open indication close boolean 0 close indication valid boolean 0 valid indication pid-4139-outputsignals v11 table 219: dpgapc output signals name type description po...
Page 397
Refer to table 220 for the description of the input-output relationship in terms of the value and the quality attributes. Table 220: description of the input-output relationship valid open close position value description 0 - - 0 intermediate 1 0 0 0 intermediate 1 1 0 1 open 1 0 1 2 closed 1 1 1 3 ...
Page 398
14.4.3 function block semod176479-4 v5 spc8gapc block psto ^out1 ^out2 ^out3 ^out4 ^out5 ^out6 ^out7 ^out8 ansi07000143-3-en.Vsd ansi07000143 v1 en-us figure 139: spc8gapc function block 14.4.4 signals pid-3575-inputsignals v8 table 221: spc8gapc input signals name type default description block boo...
Page 399
14.4.5 settings pid-3575-settings v8 table 223: spc8gapc non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description operation disabled enabled - - disabled operation disabled/enabled pulsemode1 pulsed latched - - pulsed setting for pulsed/latched mode for output 1 tpulse1 0.01 - 60...
Page 400
Psto is the universal operator place selector for all control functions. Although, psto can be configured to use local or all operator places, only remote operator place is used in spc8gapc function. 14.5 automationbits, command function for dnp3.0 autobits semod158589-1 v3 14.5.1 identification gui...
Page 401
14.5.3 function block semod158603-4 v3 iec09000925-1-en.Vsd autobits block psto ^cmdbit1 ^cmdbit2 ^cmdbit3 ^cmdbit4 ^cmdbit5 ^cmdbit6 ^cmdbit7 ^cmdbit8 ^cmdbit9 ^cmdbit10 ^cmdbit11 ^cmdbit12 ^cmdbit13 ^cmdbit14 ^cmdbit15 ^cmdbit16 ^cmdbit17 ^cmdbit18 ^cmdbit19 ^cmdbit20 ^cmdbit21 ^cmdbit22 ^cmdbit23...
Page 402
Name type description cmdbit5 boolean command out bit 5 cmdbit6 boolean command out bit 6 cmdbit7 boolean command out bit 7 cmdbit8 boolean command out bit 8 cmdbit9 boolean command out bit 9 cmdbit10 boolean command out bit 10 cmdbit11 boolean command out bit 11 cmdbit12 boolean command out bit 12 ...
Page 403
14.5.6 operation principle semod158597-4 v5 automationbits function (autobits) has 32 individual outputs which each can be mapped as a binary output point in dnp3. The output is operated by a "object 12" in dnp3. This object contains parameters for control-code, count, on-time and off-time. To opera...
Page 404
14.6.3 function block semod116040-4 v2 iec05000698-2-en.Vsd singlecmd block ^out1 ^out2 ^out3 ^out4 ^out5 ^out6 ^out7 ^out8 ^out9 ^out10 ^out11 ^out12 ^out13 ^out14 ^out15 ^out16 iec05000698 v3 en-us figure 141: singlecmd function block 14.6.4 signals pid-6189-inputsignals v6 table 227: singlecmd in...
Page 405
Name type description out14 boolean single command output 14 out15 boolean single command output 15 out16 boolean single command output 16 14.6.5 settings pid-6189-settings v6 table 229: singlecmd non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description operation disabled steady ...
Page 406
400
Page 407
Section 15 logic 15.1 tripping logic smpptrc (94) ip14576-1 v4 15.1.1 identification semod56226-2 v7 function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number tripping logic smpptrc 1 -> 0 iec15000314 v1 en-us 94 15.1.2 functionality m12275-3 v12 a function...
Page 408
15.1.3 function block m12638-3 v7 smpptrc (94) block blklkout trinp_3p trinp_a trinp_b trinp_c ps_a ps_b ps_c 1ptrz 1ptrgf p3ptr setlkout rstlkout cnd trip tr_a tr_b tr_c tr1p tr2p tr3p cllkou t bfi_3p bfi_a bfi_b bfi_c stn fw rev ansi05000707-4-en.Vsdx ansi05000707 v4 en-us figure 142: smpptrc (94)...
Page 409
Guid-d6b3dfe3-f7df-4602-b57e-764dc9eb0d4a v1 table 231: smpptrc output signals name type description trip boolean general trip output signal trl1 boolean trip signal from phase l1 trl2 boolean trip signal from phase l2 trl3 boolean trip signal from phase l3 tr1p boolean trip single-pole tr2p boolean...
Page 410
15.1.6 operation principle m12255-3 v12 the duration of the trip output signal is settable (ttripmin). The pulse length should be long enough to secure the opening of the circuit breaker. There is a single input (trinp_3p) through which all trip output signals from the protection functions within th...
Page 411
Blklkout tripall tripl1 tripl2 tripl3 setlkout rstlkout trip final tripping circuits tr_a tr_b tr_c tr1p tr2p tr3p cllkout simplified logic where setting program = 3 phase block blklkout trinp_3p trinp_a trinp_b trinp_c 1ptrz 1ptrgf setlkout rstlkout trip tr_a tr_b tr_c tr3p cllkout block trinp_3p t...
Page 412
The inputs 1ptrz and 1ptrgf enable single-pole and two-pole tripping for those functions which do not have their own pole selection capability (i.E. Which have just a single trip output). An example of such a protection function is the residual overcurrent protection. The smpptrc (94) function has t...
Page 413
Cndx =[ b0, b1, b2, b3, b4, b5, b6, b7, b8, b9, b10, b11, b12, b13, b14 ] b0= bfi_3p (general pickup) b1= fw (forward) b2= rev (reverse) b3= bfi_a (pickup a) b4= fw_a (forward a) b5= rev_a (reverse a) b6= bfi_b (pickup b) b7= fw_b (forward b) b8= rev_b (reverse b) b9= bfi_c (pickup c) b10= fw_c (for...
Page 414
15.1.6.1 logic diagram m12258-7 v6 ansi05000517=4=en=original.Vsd tripall block and trinp_a t ttripmin or trinp_b trinp_c trinp_3p 1ptrgf 1ptrz or ansi05000517 v4 en-us figure 144: three-phase front logic — simplified logic diagram ansi10000056=4=en=original.Vsd l1trip trinp_3p or 1ptrgf t twaitforp...
Page 415
Tripl1 block and l1trip t tevolvingfault t ttripmin l2trip l3trip p3ptr or or or and trip iec17000065-2-en.Vsdx iec17000065 v2 en-us figure 146: simplified additional logic per phase, program = 1p/3p or 1p/2p/3p ansi17000066=1=en=original.Vsd tr_a t 3ms blklkout or or tripl1 and tripl3 tripl2 tripal...
Page 416
Ansi16000179=1=en=original.Vsdx bfi_3p bfi_a and fw and rev fw_a rev_a bfi_3p fw bfi_a dirl1 bfi_b bfi_c cnd xor and and fw_b rev_b xor and and fw_c rev_c xor bfi_b b0 b1 out bitstoint b0 b1 out bitstoint dirl2 b0 b1 out bitstoint dirl3 b0 b1 out bitstoint rev dir dirgeneral (61850 standard) 0 = unk...
Page 417
15.2 general start matrix block smagapc 15.2.1 identification guid-c6d3de50-03d2-4f27-82ff-623e81d019f4 v1 function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number generat start matrix block smagapc - - 15.2.2 functionality guid-ba516165-96de-4cd9-979b-294...
Page 418
15.2.4 signals pid-6906-inputsignals v2 table 235: smagapc input signals name type default description block boolean 0 block of function pu_dir1 integer 0 pick up direction input 1 pu_dir2 integer 0 pick up direction input 2 pu_dir3 integer 0 pick up direction input 3 pu_dir4 integer 0 pick up direc...
Page 419
15.2.6 operation principle guid-02403756-5715-4d6b-9308-540d72979bd0 v2 start matrix the start matrix function requires that a protection function delivers the directional output signals in a fixed order to start matrix. A directional input signal stdirx of the start matrix is of type word. Each inp...
Page 420
Start criteria pu_dirx cndout direction criteria cndin cnd start criteria cndout start criteria pu_dirx cndout start criteria pu_dirx cndout start criteria pu_dirx cndout start criteria pu_dirx cndout start criteria pu_dirx cndout start criteria pu_dirx cndout start criteria pu_dirx cndout start cri...
Page 421
Bfi_3p (in) bfi_a (in) bfi_c (in) and fw (in) and rev (in) and fw_a (in) and rev_a (in) and fw_b (in) and rev_b (in) and fw_c (in) and rev_c (in) bfi_3p (out) fw (out) rev (out) bfi_a (out) fw_a (out) rev_a (out) bfi_b (out) fw_b (out) rev_b (out) bfi_c (out) fw_c (out) rev_c (out) cndout bfi_b (in)...
Page 422
Startcomb to make it possible to provide the directional information from a protection function, a startcomb block is used in between the application function and the start matrix function. The startcomb function has one block input and 14 boolean inputs that convert the 14 boolean inputs into a wor...
Page 423
Protection functions some protection functions are provided with start and directional outputs, for example: • protection 1: general start, fw and rev • protection 2: phase-wise stlx, fwlx and revlx (where x = 1, 2 and 3) • protection 3: stn, fwn and revn • protection 4: stdir connection example in ...
Page 424
Bfi_3p fw rev protection 1 bfi_a fw_a rev_a bfi_b fw_b rev_b bfi_c fw_c rev_c protection 2 cnd protection 4 - - - stn fwn revn protection 3 startcomb block bfi_3p fw rev bfi_a fw_a rev_a bfi_b fw_b rev_b bfi_c fw_c rev_c stn fwn revn cnd startcomb block bfi_3p fw rev bfi_a fw_a rev_a bfi_b fw_b rev_...
Page 425
15.3.1 identification semod167882-2 v3 function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number trip matrix logic tmagapc - - 15.3.2 functionality m15321-3 v12 the trip matrix logic tmagapc function is used to route trip signals and other logical output si...
Page 426
15.3.4 signals pid-6513-inputsignals v4 table 238: tmagapc input signals name type default description block boolean 0 block of function blk1 boolean 0 block of output 1 blk2 boolean 0 block of output 2 blk3 boolean 0 block of output 3 input1 boolean 0 binary input 1 input2 boolean 0 binary input 2 ...
Page 427
Name type default description input30 boolean 0 binary input 30 input31 boolean 0 binary input 31 input32 boolean 0 binary input 32 pid-6513-outputsignals v4 table 239: tmagapc output signals name type description output1 boolean or function betweeen inputs 1 to 16 output2 boolean or function betwee...
Page 428
1. When any one of first 16 inputs signals (input1 to input16) has logical value 1 the first output signal (output1) will get logical value 1. 2. When any one of second 16 inputs signals (input17 to input32) has logical value 1 the second output signal (output2) will get logical value 1. 3. When any...
Page 429
Breaker(s) the pulse time shall be set to at least 0.150 seconds in order to obtain satisfactory minimum duration of the trip pulse to the circuit breaker trip coils. 15.3.7 technical data guid-3ab1ee95-51bf-4cc4-99bd-f4ecdaacb75a v1 table 241: number of tmagapc instances function quantity with cycl...
Page 430
15.4.4 signals pid-6510-inputsignals v5 table 242: almcalh input signals name type default description block boolean 0 block of function input1 boolean 0 binary input 1 input2 boolean 0 binary input 2 input3 boolean 0 binary input 3 input4 boolean 0 binary input 4 input5 boolean 0 binary input 5 inp...
Page 431
15.4.6 operation principle guid-0405bb7b-7ef7-4546-92cd-f703aa0dd9f4 v2 the logic for group alarm almcalh block is provided with 16 input signals and one alarm output signal. The function block incorporates internal logic or gate in order to provide grouping of connected input signals to the output ...
Page 432
15.5.2 functionality guid-f7d9a012-3ad4-4d86-be97-df2a99be5383 v4 the group warning logic function (wrncalh) is used to route several warning signals to a common indication, led and/or contact, in the ied. 15.5.3 function block guid-c909e4fb-3f7a-47f7-8988-36b159e2c7b2 v1 wrncalh block input1 input2...
Page 433
Name type default description input14 boolean 0 binary input 14 input15 boolean 0 binary input 15 input16 boolean 0 binary input 16 pid-4127-outputsignals v3 table 247: wrncalh output signals name type description warning boolean or function betweeen inputs 1 to 16 15.5.5 settings pid-4127-settings ...
Page 434
15.5.7 technical data guid-70b7357d-f467-4cf5-9f73-641a82d334f5 v1 table 249: number of wrncalh instances function quantity with cycle time 3 ms 8 ms 100 ms wrncalh - - 5 15.6 logic for group indication indcalh 15.6.1 identification guid-3b5d4371-420d-4249-b6a4-5a168920d635 v4 function description i...
Page 435
15.6.4 signals pid-4128-inputsignals v4 table 250: indcalh input signals name type default description block boolean 0 block of function input1 boolean 0 binary input 1 input2 boolean 0 binary input 2 input3 boolean 0 binary input 3 input4 boolean 0 binary input 4 input5 boolean 0 binary input 5 inp...
Page 436
15.6.6 operation principle guid-72b1b4e8-bc6c-4af7-8b41-058241b944f8 v2 the logic for group indication indcalh block is provided with 16 input signals and 1 ind output signal. The function block incorporates internal logic or gate in order to provide grouping of connected input signals to the output...
Page 437
• and function block. The and function is used to form general combinatory expressions with boolean variables. The and function block has up to four inputs and two outputs. One of the outputs is inverted. • gate function block is used for whether or not a signal should be able to pass from the input...
Page 438
15.7.1 and function block and ip11013-1 v2 m11453-3 v4 the and function is used to form general combinatory expressions with boolean variables. The and function block has up to four inputs and two outputs. One of the outputs is inverted. 15.7.1.1 function block m11452-3 v2 and input1 input2 input3 i...
Page 439
15.7.2 controllable gate function block gate ip11021-1 v2 m11489-3 v2 the controllable gate function block (gate) is used for controlling if a signal should be able to pass from the input to the output or not depending on a setting. 15.7.2.1 function block m11490-3 v2 iec04000410-2-en.Vsd gate input...
Page 440
15.7.3 inverter function block inv ip11011-1 v2 15.7.3.1 function block m11445-3 v1 iec04000404_2_en.Vsd inv input out iec04000404 v2 en-us figure 160: inv function block 15.7.3.2 signals pid-3803-inputsignals v5 table 261: inv input signals name type default description input boolean 0 input pid-38...
Page 441
15.7.4.1 function block guid-ee44cfdf-c8f7-4870-bd1c-98d9cd91fd97 v4 lld input out iec15000144.Vsd iec15000144 v1 en-us figure 161: lld function block 15.7.4.2 signals pid-3805-inputsignals v5 table 264: lld input signals name type default description input boolean 0 input signal pid-3805-outputsign...
Page 442
15.7.5.1 function block m11448-3 v1 iec04000405_2_en.Vsd or input1 input2 input3 input4 input5 input6 out nout iec04000405 v2 en-us figure 162: or function block 15.7.5.2 signals pid-3806-inputsignals v5 table 267: or input signals name type default description input1 boolean 0 input 1 to or gate in...
Page 443
15.7.6 pulse timer function block pulsetimer ip11016-1 v2 m11466-3 v3 the pulse (pulsetimer) function can be used, for example, for pulse extensions or limiting the operation time of outputs. The pulsetimer has a settable length. When the input is 1, the output will be 1 for the time set by the time...
Page 444
15.7.6.4 technical data guid-e05e5fb1-23e7-4816-84f2-1fbffdff2b43 v1 table 273: number of pulsetimer instances logic block quantity with cycle time range or value accuracy 3 ms 8 ms 100 ms pulsetimer 10 10 20 (0.000–90000.000) s ±0.5% ±10 ms 15.7.7 reset-set with memory function block rsmemory guid-...
Page 445
Pid-3811-outputsignals v5 table 276: rsmemory output signals name type description out boolean output signal nout boolean inverted output signal 15.7.7.3 settings pid-3811-settings v5 table 277: rsmemory group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description memory disabled enabled...
Page 446
15.7.8.1 function block m11484-3 v2 srmemory set reset out nout iec04000408_2_en.Vsd iec04000408 v2 en-us figure 165: srmemory function block 15.7.8.2 signals pid-3813-inputsignals v5 table 280: srmemory input signals name type default description set boolean 0 input signal to set reset boolean 0 in...
Page 447
15.7.9 settable timer function block timerset ip11022-1 v2 m11494-3 v3 the settable timer function block (timerset) timer has two outputs for the delay of the input signal at drop-out and at pick-up. The timer has a settable time delay. It also has an operation setting enabled and disabled that cont...
Page 448
Pid-6976-outputsignals v1 table 285: timerset output signals name type description on boolean output from timer, pickup delay off boolean output from timer, dropout delay 15.7.9.3 settings pid-6976-settings v1 table 286: timerset group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default descripti...
Page 449
15.7.10.1 function block m11476-3 v1 iec04000409-2-en.Vsd xor input1 input2 out nout iec04000409 v2 en-us figure 168: xor function block 15.7.10.2 signals pid-3817-inputsignals v2 table 289: xor input signals name type default description input1 boolean 0 input 1 to xor gate input2 boolean 0 input 2...
Page 450
• andqt and function block. The function also propagates the time stamp and the quality of input signals. Each block has four inputs and two outputs where one is inverted. • indcombspqt combines single input signals to group signal. Single position input is copied to value part of sp_out output. Tim...
Page 451
• timersetqt function has pick-up and drop-out delayed outputs related to the input signal. The timer has a settable time delay. The function also propagates the time stamp and the quality of the input signal. • xorqt xor function block. The function also propagates the time stamp and the quality of...
Page 452
15.8.1.3 technical data guid-23d4121a-4c9a-4072-bbe3-6db076edab79 v1 table 294: number of andqt instances logic block quantity with cycle time 3 ms 8 ms 100 ms andqt - 20 100 15.8.2 single point indication related signals combining function block indcombspqt guid-13c9325d-d3a0-480f-9f3b-738a13e0ecf8...
Page 453
Pid-3792-outputsignals v2 table 296: indcombspqt output signals name type description sp_out boolean single point indication 15.8.2.3 technical data guid-27df23c0-a0b2-4bb0-80b5-fc7b7f7fe448 v1 table 297: number of indcombspqt instances logic block quantity with cycle time 3 ms 8 ms 100 ms indcombsp...
Page 454
Pid-3821-outputsignals v2 table 299: indextspqt output signals name type description si_out boolean single indication time group signal timestamp of input blocked boolean blocked for update subst boolean substituted invalid boolean invalid value test boolean testmode 15.8.3.3 technical data guid-c1e...
Page 455
15.8.4.1 function block guid-0bd84306-0965-4702-8d5c-9570a70168ea v1 invalidqt input1 input2 input3 input4 input5 input6 input7 input8 input9 input10 input11 input12 input13 input14 input15 input16 valid output1 output2 output3 output4 output5 output6 output7 output8 output9 output10 output11 output...
Page 456
Name type default description input15 boolean 0 indication input 15 input16 boolean 0 indication input 16 valid boolean 1 inputs are valid or invalid pid-3822-outputsignals v5 table 302: invalidqt output signals name type description output1 boolean indication output 1 output2 boolean indication out...
Page 457
15.8.5.1 function block guid-06c5c594-e00b-4fd5-8b0f-4ed05db348b6 v2 inverterqt input out iec09000299-1-en.Vsd iec09000299 v1 en-us figure 173: inverterqt function block 15.8.5.2 signals guid-4543c4c9-fae2-4328-8de2-4a5756a020e9 v1 pid-3804-inputsignals v5 table 304: inverterqt input signals name ty...
Page 458
15.8.6.1 function block guid-bcdfd5f0-4f30-4012-ba49-2e5c2115912e v2 orqt input1 input2 input3 input4 input5 input6 out nout iec09000298-1-en.Vsd iec09000298 v1 en-us figure 174: orqt function block 15.8.6.2 signals guid-4543c4c9-fae2-4328-8de2-4a5756a020e9 v1 pid-3807-inputsignals v5 table 307: orq...
Page 459
15.8.7 pulse timer function block pulsetimerqt guid-5cb71bd1-58a0-4a06-9207-6dae389b5288 v2 guid-d930e5a7-c564-4464-b97f-c72b4801c917 v4 the pulse timer function block (pulsetimerqt) can be used, for example, for pulse extensions or for limiting the operation time of the outputs. Pulsetimerqt has a ...
Page 460
15.8.7.3 settings pid-3810-settings v5 table 312: pulsetimerqt non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description t 0.000 - 90000.000 s 0.001 0.010 pulse time length 15.8.7.4 technical data guid-61263951-53a8-4113-82b5-3db3bf0d9449 v1 table 313: number of pulsetimerqt insta...
Page 461
15.8.8.1 function block guid-bdbfd8ba-9253-4277-96d8-0ff7ee93b56e v1 rsmemoryqt set reset out nout iec14000069-1-en.Vsd iec14000069 v1 en-us figure 176: rsmemoryqt function block 15.8.8.2 signals guid-4543c4c9-fae2-4328-8de2-4a5756a020e9 v1 pid-3812-inputsignals v5 table 315: rsmemoryqt input signal...
Page 462
15.8.9 set/reset function block srmemoryqt guid-d910ba2d-07fa-44c5-a820-e0413ad7fd91 v2 guid-39060d4b-9aa7-4505-9487-88b2cbc534f0 v5 the set-reset function (srmemoryqt) is a flip-flop with memory that can set or reset an output from two inputs respectively. Each srmemoryqt function block has two out...
Page 463
Pid-3814-outputsignals v5 table 321: srmemoryqt output signals name type description out boolean output signal nout boolean inverted output signal 15.8.9.3 settings pid-3814-settings v5 table 322: srmemoryqt group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description memory disabled ena...
Page 464
15.8.10.1 function block guid-13589bae-38ae-46a1-8e9f-94bcd1cbcbf1 v1 timersetqt input on off iec14000068-1-en.Vsd iec14000068 v1 en-us figure 178: timersetqt function 15.8.10.2 signals guid-4543c4c9-fae2-4328-8de2-4a5756a020e9 v1 pid-3816-inputsignals v5 table 324: timersetqt input signals name typ...
Page 465
15.8.11 exclusive or function block xorqt guid-76adacc1-a273-4100-be62-99bcdabfeb7a v2 guid-62986d87-1690-499e-b8d3-1f51d2da191e v4 the exclusive or function (xorqt) function is used to generate combinatory expressions with boolean variables. Xorqt function has two inputs and two outputs. One of the...
Page 466
15.8.11.3 technical data guid-1c381e02-6b9e-44dc-828f-8b3ea7edaa54 v1 table 331: number of xorqt instances logic block quantity with cycle time 3 ms 8 ms 100 ms xorqt - 10 30 15.9 extension logic package ip11362-1 v2 when extra configurable logic blocks are required, an additional package can be ord...
Page 467
15.10.2 functionality m15322-3 v12 the fixed signals function (fxdsign) has nine pre-set (fixed) signals that can be used in the configuration of an ied, either for forcing the unused inputs in other function blocks to a certain level/value, or for creating certain logic. Boolean, integer, floating ...
Page 468
15.10.6 operation principle semod54827-5 v6 there are nine outputs from fxdsign function block: • off is a boolean signal, fixed to off (boolean 0) value • on is a boolean signal, fixed to on (boolean 1) value • intzero is an integer number, fixed to integer value 0 • intone is an integer number, fi...
Page 469
15.11.3 function block semod175798-5 v4 iec07000128-2-en.Vsd b16i block in1 in2 in3 in4 in5 in6 in7 in8 in9 in10 in11 in12 in13 in14 in15 in16 out iec07000128 v2 en-us figure 181: b16i function block 15.11.4 signals pid-3606-inputsignals v4 table 334: b16i input signals name type default description...
Page 470
Pid-3606-outputsignals v3 table 335: b16i output signals name type description out integer output value 15.11.5 monitored data pid-3606-monitoreddata v4 table 336: b16i monitored data name type values (range) unit description out integer - - output value 15.11.6 settings abbd8e283673 v3 the function...
Page 471
Name of input type default description value when activated value when deactivated in7 boolean 0 input 7 64 0 in8 boolean 0 input 8 128 0 in9 boolean 0 input 9 256 0 in10 boolean 0 input 10 512 0 in11 boolean 0 input 11 1024 0 in12 boolean 0 input 12 2048 0 in13 boolean 0 input 13 4096 0 in14 boolea...
Page 472
15.12.2 functionality semod175781-4 v8 boolean to integer conversion with logical node representation, 16 bit (btigapc) is used to transform a set of 16 boolean (logical) signals into an integer. The block input will freeze the output at the last value. 15.12.3 function block semod175801-5 v4 btigap...
Page 473
Name type default description in12 boolean 0 input 12 in13 boolean 0 input 13 in14 boolean 0 input 14 in15 boolean 0 input 15 in16 boolean 0 input 16 pid-6944-outputsignals v2 table 339: btigapc output signals name type description out integer output value 15.12.5 settings abbd8e283673 v3 the functi...
Page 474
Name of input type default description value when activated value when deactivated in1 boolean 0 input 1 1 0 in2 boolean 0 input 2 2 0 in3 boolean 0 input 3 4 0 in4 boolean 0 input 4 8 0 in5 boolean 0 input 5 16 0 in6 boolean 0 input 6 32 0 in7 boolean 0 input 7 64 0 in8 boolean 0 input 8 128 0 in9 ...
Page 475
15.13.2 functionality semod158373-5 v6 integer to boolean 16 conversion function (ib16) is used to transform an integer into a set of 16 boolean (logical) signals. 15.13.3 function block semod158389-4 v4 ansi06000501-1-en.Vsd ib16 block inp out1 out2 out3 out4 out5 out6 out7 out8 out9 out10 out11 ou...
Page 476
Name type description out8 boolean output 8 out9 boolean output 9 out10 boolean output 10 out11 boolean output 11 out12 boolean output 12 out13 boolean output 13 out14 boolean output 14 out15 boolean output 15 out16 boolean output 16 15.13.5 setting parameters abbd8e242451 v3 the function does not h...
Page 477
The sum of the value on each inx corresponds to the integer presented on the output out on the function block ib16. Name of outx type description value when activated value when deactivated out1 boolean output 1 1 0 out2 boolean output 2 2 0 out3 boolean output 3 4 0 out4 boolean output 4 8 0 out5 b...
Page 478
15.14.1 identification semod167944-2 v4 function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number integer to boolean 16 conversion with logic node representation itbgapc - - 15.14.2 functionality semod158421-5 v9 integer to boolean conversion with logic nod...
Page 479
15.14.4 signals pid-3627-inputsignals v7 table 345: itbgapc input signals name type default description block boolean 0 block of function psto integer 1 operator place selection pid-3627-outputsignals v7 table 346: itbgapc output signals name type description out1 boolean output 1 out2 boolean outpu...
Page 480
Outputs out1 = 1; and out2 = 2; and out3= 4; and out4 = 8. The sum of these outx (1≤x≤4) is equal to the integer 15 received via the iec 61850 network. The remaining outx = 0 for (5≤x≤16). Outx represents a value when activated. The value of each of the outx is in accordance with the table 347 . Whe...
Page 481
The sum of the numbers in column “value when activated” when all outx (1≤x≤16) are active equals 65535. This is the highest integer that can be converted to boolean by the itbgapc function block. The operator position input (psto) determines the operator place. The integer number that is communicate...
Page 482
Time integration with retain block acctime reset in twarning talarm overflow warning alarm q -1 a>b a b a>b a b a>b a b and and and q -1 = unit delay iec13000290-2-en.Vsd 999 999 s iec13000290 v2 en-us figure 185: teigapc logics the main features of teigapc • applicable to long time integration up t...
Page 483
15.15.4 signals pid-6836-inputsignals v2 table 349: teigapc input signals name type default description block boolean 0 freeze the integration and block the other outputs in boolean 0 the input signal that is used to measure the elapsed time, when its value is high reset boolean 0 reset the integrat...
Page 484
Figure 187 describes the simplified logic of the function where the block “time integration“ covers the logics for the first two items listed above while the block “transgression supervision plus retain“ contains the logics for the last two. Time integration transgression supervision plus retain blo...
Page 485
• overflow if output acctime >999999.9 seconds • alarm if acctime > talarm • warning if acctime > twarning the acctime output represents the integrated time in seconds while toverflow, talarm and twarning are the time limit parameters in seconds. Talarm and twarning are user settable limits. They ar...
Page 486
Table 353: number of teigapc instances function quantity with cycle time 3 ms 8 ms 100 ms teigapc 4 4 4 15.16 comparator for integer inputs intcomp 15.16.1 identification guid-5992b0f2-fc1b-4838-9bab-2d2542bb264d v1 function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37...
Page 487
Pid-6928-outputsignals v2 table 355: intcomp output signals name type description inequal boolean input value is equal to the reference value inhigh boolean input value is higher than the reference value inlow boolean input value is lower than the reference value 15.16.5 settings pid-6928-settings v...
Page 488
From second input signal (ref). If refsource is selected as set value then the reference value for comparison is taken from setting (setvalue). The comparison can be done either between absolute values or signed values and it depends on the setting enaabs. If enaabs is selected as absolute then both...
Page 489
15.17 comparator for real inputs realcomp 15.17.1 identification guid-0d68e846-5a15-4c2c-91a2-f81a74034e81 v1 function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number comparator for real inputs realcomp real 15.17.2 functionality guid-e17a88d7-d095-4f36-9c...
Page 490
15.17.5 settings pid-6897-settings v2 table 361: realcomp group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description enaabs signed absolute - - signed selection for absolute or signed comparison refsource set value input ref - - set value selection for reference value either input or s...
Page 491
High comparator low comparator xor abs input ref inhigh inequal inlow t f abs equalbandhigh enaabs equalbandlow refsource setvalue setvalprefix iec15000130-2-en.Vsdx t f t f iec15000130 v2 en-us figure 189: logic diagram for realcomp this function has two settings equalbandhigh and equalbandlow to p...
Page 492
When enaabs is set as absolute comparison and setvalue is set less than 0.2% of the set unit then inlow output will never pickups. During the above mentioned condition, due to marginal value for avoiding oscillations of function outputs, the inlow output will never set. 15.17.7 technical data guid-6...
Page 493
Section 16 monitoring 16.1 measurements ip14593-1 v3 16.1.1 identification semod56123-2 v8 function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number power system measurements cvmmxn p, q, s, i, u, f symbol-rr v1 en-us - phase current measurement cmmxu i sym...
Page 494
16.1.2 functionality semod54488-4 v12 measurement functions are used for power system measurement, supervision and reporting to the local hmi, monitoring tool within pcm600 or to station level for example, via iec 61850. The possibility to continuously monitor measured values of active power, reacti...
Page 495
• i: phase currents (magnitude and angle) (cmmxu) • v: voltages (phase-to-ground and phase-to-phase voltage, magnitude and angle) (vmmxu, vnmmxu) the cvmmxn function calculates three-phase power quantities by using fundamental frequency phasors (dft values) of the measured current and voltage signal...
Page 496
Cvmmxn i3p* v3p* s s_range p_inst p p_range q_inst q q_range pf pf_range ilag ilead v v_range i i_range f f_range ansi10000016-1-en.Vsd ansi10000016 v1 en-us figure 191: cvmmxn function block ansi05000699-2-en.Vsd cmmxu i3p* i_a ia_range ia_angl i_b ib_range ib_angl i_c ic_range ic_angl ansi05000699...
Page 497
Iec05000703-2-en.Vsd cmsqi i3p* 3i0 3i0rang 3i0angl i1 i1rang i1angl i2 i2rang i2angl iec05000703 v2 en-us figure 194: cmsqi function block ansi05000704-2-en.Vsd vmsqi v3p* 3v0 3v0rang 3v0angl v1 v1rang v1angl v2 v2rang v2angl ansi05000704 v2 en-us figure 195: vmsqi function block ansi09000850-1-en....
Page 498
Pid-6713-outputsignals v3 table 364: cvmmxn output signals name type description s real apparent power magnitude of deadband value s_range integer apparent power range p_inst real active power p real active power magnitude of deadband value p_range integer active power range q_inst real reactive pow...
Page 499
Name type description ic real phase c current magnitude of reported value ic_range integer phase c current magnitude range ic_angl real phase c current magnitude angle pid-6738-inputsignals v2 table 367: vmmxu input signals name type default description v3p group signal - group signal for voltage in...
Page 500
Name type description i1rang integer i1 magnitude range i1angl real i1 angle, magnitude of reported value i2 real i2 magnitude of reported value i2rang integer i2 magnitude range i2angl real i2 angle, magnitude of reported value pid-6739-inputsignals v2 table 371: vmsqi input signals name type defau...
Page 501
Pid-6737-outputsignals v2 table 374: vnmmxu output signals name type description va real va amplitude, magnitude of reported value va_range integer vaamplitude range va_angl real va angle, magnitude of reported value vb real vb amplitude, magnitude of reported value vb_range integer vb amplitude ran...
Page 502
Name values (range) unit step default description sreptyp cyclic deadband int deadband db & cyclic 5s db & cyclic 30s db & cyclic 1min - - cyclic reporting type pmin -2000.0 - 2000.0 %sb 0.1 -200.0 minimum value in % of sbase pmax -2000.0 - 2000.0 %sb 0.1 200.0 maximum value in % of sbase preptyp cy...
Page 503
Name values (range) unit step default description frreptyp cyclic deadband int deadband db & cyclic 5s db & cyclic 30s db & cyclic 1min - - cyclic reporting type operation disabled enabled - - disabled operation disabled/enabled globalbasesel 1 - 12 - 1 1 selection of one of the global base value gr...
Page 504
Name values (range) unit step default description qdbrepint 1 - 100000 type 1 10 cycl: report interval (s), db: in 0,001% of range, int db: in 0,001%s qzerodb 0 - 100000 m% 500 1000 magnitude zero point clamping in 0,001% of range qhihilim -2000.0 - 2000.0 %sb 0.1 150.0 high high limit in % of sbase...
Page 505
Name values (range) unit step default description frdbrepint 1 - 100000 type 1 10 cycl: report interval (s), db: in 0,001% of range, int db: in 0,001%s frzerodb 0 - 100000 m% 10 100 magnitude zero point clamping in 0,001% of range frhihilim 0.000 - 100.000 hz 0.001 65.000 high high limit (physical v...
Page 506
Name values (range) unit step default description ia_reptyp cyclic deadband int deadband db & cyclic 5s db & cyclic 30s db & cyclic 1min - - cyclic reporting type ia_angdbrepint 1 - 100000 s 1 10 cyclic report interval (s) ib_dbrepint 1 - 100000 type 1 10 cycl: report interval (s), db: in 0,001% of ...
Page 507
Name values (range) unit step default description iangcomp5 -10.000 - 10.000 deg 0.001 0.000 angle calibration for current at 5% of in iangcomp30 -10.000 - 10.000 deg 0.001 0.000 angle calibration for current at 30% of in iangcomp100 -10.000 - 10.000 deg 0.001 0.000 angle calibration for current at ...
Page 508
Name values (range) unit step default description vabangdbrepint 1 - 100000 s 1 10 cyclic report interval (s) vbc_dbrepint 1 - 100000 type 1 10 cycl: report interval (s), db: in 0,001% of range, int db: in 0,001%s vbc_zerodb 0 - 100000 m% 500 1000 magnitude zero point clamping in 0,001% of range vbc...
Page 509
Name values (range) unit step default description vbc_limhys 0.000 - 100.000 % 0.001 5.000 hysteresis value in % of range, common for all limits vca_hihilim 0.0 - 200.0 %vb 0.1 150.0 high high limit in % of ubase vca_hilim 0.0 - 200.0 %vb 0.1 120.0 high limit in % of vbase vca_lowlim 0.0 - 200.0 %vb...
Page 510
Name values (range) unit step default description i1angdbrepint 1 - 100000 s 1 10 cyclic report interval (s) i2dbrepint 1 - 100000 type 1 10 cycl: report interval (s), db: in 0,001% of range, int db: in 0,001%s i2zerodb 0 - 100000 m% 500 1000 magnitude zero point clamping in 0,001% of range i2min 0....
Page 511
Pid-6739-settings v2 table 383: vmsqi non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description 3v0dbrepint 1 - 100000 type 1 10 cycl: report interval (s), db: in 0,001% of range, int db: in 0,001%s 3v0zerodb 0 - 100000 m% 500 1000 magnitude zero point clamping in 0,001% of range ...
Page 512
Name values (range) unit step default description v2reptyp cyclic deadband int deadband db & cyclic 5s db & cyclic 30s db & cyclic 1min - - cyclic reporting type v2limhys 0.000 - 100.000 % 0.001 5.000 hysteresis value in % of range, common for all limits v2angdbrepint 1 - 100000 s 1 10 cyclic report...
Page 513
Name values (range) unit step default description va_min 0.0 - 200.0 %vb 0.1 50.0 minimum value in % of vbase va_max 0.0 - 200.0 %vb 0.1 200.0 maximum value in % of vbase globalbasesel 1 - 12 - 1 1 selection of one of the global base value groups va_reptyp cyclic deadband int deadband db & cyclic 5s...
Page 514
Table 386: vnmmxu non group settings (advanced) name values (range) unit step default description va_hihilim 0.0 - 200.0 %vb 0.1 150.0 high high limit in % of ubase va_hilim 0.0 - 200.0 %vb 0.1 120.0 high limit in % of vbase va_lowlim 0.0 - 200.0 %vb 0.1 80.0 low limit in % of vbase va_lowlowlim 0.0...
Page 515
Pid-6735-monitoreddata v3 table 388: cmmxu monitored data name type values (range) unit description ia real - a phase a current magnitude of reported value ia_angl real - deg phase a current magnitude angle ib real - a phase b current magnitude of reported value ib_angl real - deg phase b current ma...
Page 516
Name type values (range) unit description i1angl real - deg i1 angle, magnitude of reported value i2 real - a i2 magnitude of reported value i2angl real - deg i2 angle, magnitude of reported value pid-6739-monitoreddata v2 table 391: vmsqi monitored data name type values (range) unit description 3v0...
Page 517
The number of processed alternate measuring quantities depends on the type of ied and built-in options. The information on measured quantities is available for the user at different locations: • locally by means of the local hmi • remotely using the monitoring tool within pcm600 or over the station ...
Page 518
Iec05000657-3-en.Vsdx x_range= 1 x_range = 3 x_range=0 hysteresis high-high limit high limit low limit low-low limit x_range=2 x_range=4 y t x_range=0 y = magnitude of the measured quantity iec05000657 v3 en-us figure 197: presentation of operating limits each analog output has one corresponding sup...
Page 519
Cyclic reporting semod54417-158 v3 the cyclic reporting of measured value is performed according to chosen setting (xreptyp). The measuring channel reports the value independent of magnitude or integral dead-band reporting. In addition to the normal cyclic reporting the ied also report spontaneously...
Page 520
Iec99000529-2-en.Vsdx y t value reported (1st) value reported value reported y1 y2 y3 y y y y y y value reported iec99000529 v2 en-us figure 199: magnitude dead-band supervision reporting after the new value is reported, the ±Δy limits for dead-band are automatically set around it. The new value is ...
Page 521
Iec99000530-2-en.Vsdx y t value reported (1st) y1 value reported a1 y2 value reported y3 y4 a value reported a2 y5 a3 a4 a5 a7 a6 value reported a2 >= pre-set value a1 >= pre-set value a >= pre-set value a3 + a4 + a5 + a6 + a7 >= pre-set value iec99000530 v2 en-us figure 200: reporting with integral...
Page 522
Iec16000109-1-en.Vsdx y1...Y7 : cyclic reported values, depending upon time Δt. Y’ and y” : deadband reported value, change is greater than setting Δt Δt Δt Δt Δt Δt y1 y2 y3 y4 y5 y6 y7 +Δy -Δy value time y’ y” value reported iec16000109 v1 en-us figure 201: example of value reporting in mode dead ...
Page 523
Which one of the nine available measuring modes shall be used within the function. Available options are summarized in the following table: set value for parameter “mode” formula used for complex, three- phase power calculation formula used for voltage and current magnitude calculation comment 1 a, ...
Page 524
Set value for parameter “mode” formula used for complex, three- phase power calculation formula used for voltage and current magnitude calculation comment 8 b * 3 b b s v i = × × equation1575 v1 en-us (equation 78) 3 b b v v i i = × = equation1576 v1 en-us (equation 79) used when only v b phase-to- ...
Page 525
Each analog output has a corresponding supervision level output (x_range). The output signal is an integer in the interval 0-4, see section "measurement supervision" . Calibration of analog inputs semod54417-293 v5 measured currents and voltages used in the cvmmxn function can be calibrated to get 0...
Page 526
The measured quantity. Filtering is performed in accordance with the following recursive formula: (1 ) old calculated x k x k x = × + - × equation1407 v1 en-us (equation 86) where: x is a new measured value (that is p, q, s, v, i or pf) to be given out from the function x old is the measured value g...
Page 527
Directionality semod54417-256 v7 if ct grounding parameter is set as described in section "analog inputs" , active and reactive power will be always measured towards the protected object. This is shown in the following figure 203 . Busbar protected object p q ansi05000373_2_en.Vsd 52 ied ansi0500037...
Page 528
Outputs and iec 61850. This is achieved by magnitude and angle compensation at 5, 30 and 100% of rated current. The compensation below 5% and above 100% is constant and linear in between, see figure 202 . Phase currents (magnitude and angle) are available on the outputs and each magnitude output has...
Page 529
Function range or value accuracy active power, p (10 to 300) v (0.1-4.0) x i n ± 0.5% of s n at s ≤0.5 x s n ± 0.5% of s at s > 0.5 x s n (100 to 220) v (0.5-2.0) x i n cos φ ± 0.2% of p reactive power, q (10 to 300) v (0.1-4.0) x i n ± 0.5% of s n at s ≤0.5 x s n ± 0.5% of s at s > 0.5 x s n (100 t...
Page 530
Guid-9b8a7fa5-9c98-4cbd-a162-7112869cf030 v5 table 396: cmsqi technical data function range or value accuracy current positive sequence, i1 three phase settings (0.1–4.0) × i n ± 0.3% of i n at i ≤ 0.5 × i n ± 0.3% of i at i > 0.5 × i n current zero sequence, 3i0 three phase settings (0.1–1.0) × i n...
Page 531
16.2.2 functionality guid-0692cd0d-f33e-4370-ac91-b216caaafc28 v6 insulation supervision for gas medium (ssimg (63)) is used for monitoring the circuit breaker condition. Binary information based on the gas pressure in the circuit breaker is used as input signals to the function. In addition, the fu...
Page 532
Pid-6950-outputsignals v6 table 400: ssimg output signals name type description lockout boolean pressure below lockout level or temperature above lockout level preslo boolean pressure below lockout level templo boolean temperature above lockout level alarm boolean pressure below alarm level or tempe...
Page 533
16.2.6 monitored data pid-6950-monitoreddata v5 table 402: ssimg monitored data name type values (range) unit description pressure real - - pressure service value temp real - deg temperature of the insulation medium 16.2.7 operation principle guid-359458ea-ffaa-4a44-a8e8-9469ca069c80 v7 gas medium s...
Page 534
The output alarm goes high if the pressure alarm condition or the temperature alarm condition exists inside the circuit breaker. The output alarm can be blocked by activating block or blkalm inputs. The output lockout goes high if the pressure lockout condition or the temperature lockout condition e...
Page 535
16.3.2 functionality guid-3b1a665f-60a5-4343-85f4-ad9c066cbe8d v6 insulation supervision for liquid medium (ssiml (71)) is used for monitoring the transformer condition. Binary information based on the oil level in the transformer is used as input signals to the function. In addition, the function g...
Page 536
Pid-6951-outputsignals v7 table 405: ssiml output signals name type description lockout boolean level below lockout level or temperature above lockout level lvllo boolean level below lockout level templo boolean temperature above lockout level alarm boolean level below alarm level or temperature abo...
Page 537
16.3.6 monitored data pid-6951-monitoreddata v5 table 407: ssiml monitored data name type values (range) unit description level real - - level service value temp real - deg temperature of the insulation medium 16.3.7 operation principle guid-f4340b59-90d0-4ea7-9fd8-f21d425c884a v7 liquid medium supe...
Page 538
Can be used for blocking the alarms, and the block input can block both alarm and the lockout indications. The output alarm goes high if the level alarm condition or the temperature alarm condition exists in the transformer. The output alarm can be blocked by activating block or blkalm inputs. The o...
Page 539
16.4.2 functionality guid-e1fd74c3-b9b6-4e11-aa1b-7e7f822fb4dd v11 the circuit breaker condition monitoring function (sscbr) is used to monitor different parameters of the breaker condition. The breaker requires maintenance when the number of operations reaches a predefined value. For a proper funct...
Page 540
Name type default description rstcbwr boolean 0 reset of cb remaining life and operation counter rsttrvt boolean 0 reset of cb closing and opening travel times rstipow boolean 0 reset of accumulated i^currexponent rstspcht boolean 0 reset of cb spring charging time pid-3267-outputsignals v10 table 4...
Page 541
Name values (range) unit step default description ratedopercurr 100.00 - 5000.00 a 0.01 1000.00 rated operating current of the breaker opernorated 1 - 99999 - 1 10000 number of operations possible at rated current ratedfltcurr 500.00 - 99999.99 a 0.01 5000.00 rated fault current of the breaker opern...
Page 542
Name values (range) unit step default description initacccurrpwr 0.00 - 9999.99 - 0.01 0.00 initial value for accum i^currexponent integr over cb open travel time value initinactdays 0 - 9999 day 1 0 initial value for inactive days inactivealhrs 0 - 23 hour 1 0 alarm time for inactive days counter i...
Page 543
I3p-ilrmsph posclose posopen block blkalm cb contact travel time ttrvop trvtopal trvtclal rsttrvt operalm cb gas pressure indication sprchrst sprchrd cblifeph ttrvcl nooper cblifeal i3p-il ipowph trind openpos closepos invdpos cb status cb operation monitoring cb operation cycles accumulated energy ...
Page 544
Iec12000624 v3 en-us figure 207: functional module diagram of breaker monitoring 16.4.7.1 circuit breaker contact travel time guid-3af0ee8d-aa8e-4f83-9916-61b5d0d6b05b v12 the circuit breaker contact travel time subfunction calculates the breaker contact travel time for opening and closing operation...
Page 545
Topen t1 t2 t3 tclose t4 main contact posclose posopen 0 1 0 1 1 0 ttravelopen = topen + t1 + t2 ttravelclose = tclose + t3 + t4 iec12000616_2_en.Vsd iec12000616 v2 en-us figure 209: travel time calculation there is a time difference t1 between the pickup of the main contact opening and the opening ...
Page 546
16.4.7.2 circuit breaker status guid-390a1250-b258-4023-9a7d-0d7e19e13a6c v12 the circuit breaker status subfunction monitors the position of the circuit breaker, that is, whether the breaker is in the open, closed or error position. The operation is described in figure 210 . Phase current check con...
Page 547
Posclose block blkalm cb remaining life estimation alarm limit check i3p-ilrmsph rstcbwr cblifeph cblifeal iec12000620-3-en.Vsd iec12000620 v3 en-us figure 211: functional module diagram for estimating the life of the circuit breaker circuit breaker remaining life estimation if the interrupted curre...
Page 548
Posclose block blkalm accumulated energy calculation alarm limit check i3p-ilrmsph lrstipow trind ipowph ipowalph ipowloph i3p-il trcmd iec12000619-3-en.Vsd iec12000619 v3 en-us figure 212: functional module diagram for estimating accumulated energy accumulated energy calculation accumulated energy ...
Page 549
The trip initiation and the opening of the main contact is introduced by the setting opertimedelay. The accumulated energy output ipowph is provided as a service value. The value can be reset by enabling rstipow through lhmi or by activating the input rstipow. Alarm limit check the ipowalph alarm is...
Page 550
Alarm limit check operalm is generated when the number of operations exceeds the set value of the operalmlevel threshold setting. If the number of operations increases and exceeds the limit value set with the operlolevel setting, the operlo output is activated. The binary outputs operalm and operalo...
Page 551
Sprchrd block blkalm spring charging time measurement alarm limit check sprchrst rstspcht spcht spchalm iec12000621 v2 en-us figure 216: functional module diagram for circuit breaker spring charge indication spring charging time measurement spring charging time calculation will be initiated as soon ...
Page 552
Preslo block blkalm presalm gpresalm gpreslo and and 0 tdgaspresalm 0 tdgaspreslo ansi12000622 v1 en-us figure 217: functional module diagram for circuit breaker gas pressure indication when the presalm binary input is activated, the gpresalm output is activated after a time delay set with the tdgas...
Page 553
16.5 event function event semod120002-1 v2 16.5.1 identification semod167950-2 v2 function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number event function event s00946 v1 en-us - 16.5.2 functionality m12805-6 v11 when using a substation automation system wi...
Page 554
16.5.4 signals ip11335-1 v2 pid-4145-inputsignals v6 table 415: event input signals name type default description block boolean 0 block of function input1 group signal 0 input 1 input2 group signal 0 input 2 input3 group signal 0 input 3 input4 group signal 0 input 4 input5 group signal 0 input 5 in...
Page 555
16.5.5 settings ip11336-1 v2 pid-4145-settings v6 table 416: event non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description spachannelmask disabled channel 1-8 channel 9-16 channel 1-16 - - disabled spa channel mask lonchannelmask disabled channel 1-8 channel 9-16 channel 1-16 - ...
Page 556
Name values (range) unit step default description eventmask8 noevents onset onreset onchange autodetect - - autodetect reporting criteria for input 8 eventmask9 noevents onset onreset onchange autodetect - - autodetect reporting criteria for input 9 eventmask10 noevents onset onreset onchange autode...
Page 557
Name values (range) unit step default description minrepintval6 0 - 3600 s 1 2 minimum reporting interval input 6 minrepintval7 0 - 3600 s 1 2 minimum reporting interval input 7 minrepintval8 0 - 3600 s 1 2 minimum reporting interval input 8 minrepintval9 0 - 3600 s 1 2 minimum reporting interval in...
Page 558
Events are produced according to set event masks. The event masks are treated commonly for both the lon and spa communication. An eventmask can be set individually for each input channel. These settings are available: • noevents • onset • onreset • onchange • autodetect it is possible to define whic...
Page 559
16.6.2 functionality m12153-3 v13 complete and reliable information about disturbances in the primary and/or in the secondary system together with continuous event-logging is accomplished by the disturbance report functionality. Disturbance report (drprdre), always included in the ied, acquires samp...
Page 560
Semod54837-4 v4 iec05000430-4-en.Vsdx a1radr ^grp input1 ^grp input2 ^grp input3 ^grp input4 ^grp input5 ^grp input6 ^grp input7 ^grp input8 ^grp input9 ^grp input10 iec05000430 v4 en-us figure 220: a1radr function block example for a1radr-a3radr semod54843-4 v3 iec05000431-3-en.Vsd a4radr ^input31 ...
Page 561
16.6.4 signals pid-3949-outputsignals v2 table 417: drprdre output signals name type description drpoff boolean disturbance report function turned off recstart boolean disturbance recording started recmade boolean disturbance recording made cleared boolean all disturbances in the disturbance report ...
Page 562
A4radr block is used to record the calculated analog values of any type, not related to hardware devices (e.G. Difference currents, power factors etc.). Pid-4017-inputsignals v6 table 419: a4radr input signals name type default description input31 real 0 analog channel 31 input32 real 0 analog chann...
Page 563
Guid-d3a8067f-80f8-4174-bd2d-4c43f4b99020 v3 b2rbdr to b22rbdr functions have the same input signal specifications as b1rbdr but with different numbering: • b2rbdr: input17 to input32 (binary channels 17 to 32) • b3rbdr: input33 to input48 (binary channels 33 to 48) • b4rbdr: input49 to input64 (bin...
Page 564
Pid-4014-settings v7 table 422: a1radr non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description operation01 disabled enabled - - disabled operation on/off operation02 disabled enabled - - disabled operation on/off operation03 disabled enabled - - disabled operation on/off operati...
Page 565
Name values (range) unit step default description nomvalue03 0.0 - 999999.9 - 0.1 0.0 nominal value for analog channel 3 undertrigop03 disabled enabled - - disabled use under level trigger for analog channel 3 (on) or not (off) undertrigle03 0 - 200 % 1 50 under trigger level for analog channel 3 in...
Page 566
Name values (range) unit step default description overtrigle07 0 - 5000 % 1 200 over trigger level for analog channel 7 in % of signal nomvalue08 0.0 - 999999.9 - 0.1 0.0 nominal value for analog channel 8 undertrigop08 disabled enabled - - disabled use under level trigger for analog channel 8 (on) ...
Page 567
Pid-3798-settings v6 table 424: b1rbdr non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description trigdr01 disabled enabled - - disabled trigger operation on/off setled01 disabled pickup trip pickup and trip - - disabled set led on hmi for binary channel 1 trigdr02 disabled enabled...
Page 568
Name values (range) unit step default description setled08 disabled pickup trip pickup and trip - - disabled set led on hmi for binary channel 8 trigdr09 disabled enabled - - disabled trigger operation on/off setled09 disabled pickup trip pickup and trip - - disabled set led on hmi for binary channe...
Page 569
Name values (range) unit step default description setled16 disabled pickup trip pickup and trip - - disabled set led on hmi for binary channel 16 funtype1 0 - 255 - 1 0 function type for binary channel 1 (iec -60870-5-103) infno1 0 - 255 - 1 0 information number for binary channel 1 (iec -60870-5-10...
Page 570
Name values (range) unit step default description infno11 0 - 255 - 1 0 information number for binary channel 11 (iec -60870-5-103) funtype12 0 - 255 - 1 0 function type for binary channel 12 (iec -60870-5-103) infno12 0 - 255 - 1 0 information number for binary channel 12 (iec -60870-5-103) funtype...
Page 571
Name values (range) unit step default description indicationma05 hide show - - show indication mask for binary channel 5 triglevel06 trig on 0 trig on 1 - - trig on 1 trigger on positive (1) or negative (0) slope for binary input 6 indicationma06 hide show - - show indication mask for binary channel...
Page 572
Guid-8702c5b9-05a3-4e61-8952-c66483ffdfe2 v3 b2rbdr to b22rbdr functions have the same non group settings (basic) as b1rbdr but with different numbering (examples given in brackets): • b2rbdr: 17 to 32 (setled17, set led on hmi for binary channel 17) • b3rbdr: 33 to 48 (setled33, set led on hmi for ...
Page 573
• b18rbdr: 273 to 288 (indicationma273, indication mask for binary channel 273) • b19rbdr: 289 to 304 (indicationma289, indication mask for binary channel 289) • b20rbdr: 305 to 320 (indicationma305, indication mask for binary channel 305) • b21rbdr: 321 to 336 (indicationma321, indication mask for ...
Page 574
Name type values (range) unit description untrigstatch9 boolean - - under level trig for analog channel 9 activated ovtrigstatch9 boolean - - over level trig for analog channel 9 activated untrigstatch10 boolean - - under level trig for analog channel 10 activated ovtrigstatch10 boolean - - over lev...
Page 575
Name type values (range) unit description untrigstatch20 boolean - - under level trig for analog channel 20 activated ovtrigstatch20 boolean - - over level trig for analog channel 20 activated untrigstatch21 boolean - - under level trig for analog channel 21 activated ovtrigstatch21 boolean - - over...
Page 576
Name type values (range) unit description untrigstatch31 boolean - - under level trig for analog channel 31 activated ovtrigstatch31 boolean - - over level trig for analog channel 31 activated untrigstatch32 boolean - - under level trig for analog channel 32 activated ovtrigstatch32 boolean - - over...
Page 577
16.6.7 operation principle m12155-6 v10 disturbance report drprdre is a common name for several functions to supply the operator, analysis engineer, and so on, with sufficient information about events in the system. The functions included in the disturbance report are: • sequential of events (soe) •...
Page 578
Trip value rec sequential of events event recorder indications disturbance recorder axradr bxrbdr disturbance report binary signals analog signals drprdre ansi09000337-2-en.Vsd ansi09000337 v2 en-us figure 223: disturbance report functions and related function blocks the whole disturbance report can...
Page 579
Disturbance report record no. N record no. N+1 record no. N+100 general dist. Information & setting infotrmation indications trip values event recordings disturbance recording event list (soe) ansi05000161-2-en.Vsdx ansi05000161 v2 en-us figure 224: disturbance report structure up to 100 disturbance...
Page 580
The maximum number of recordings depend on each recordings total recording time. Long recording time will reduce the number of recordings to less than 100. The ied flash disk should not be used to store any user files. This might cause disturbance recordings to be deleted due to lack of disk space. ...
Page 581
During post processing of the disturbance record, the header file is updated with a section called settings . Settings has complete setting values of the configured components that are read during the trigger time. The setting values, runtime status and the behavior of each component are compared be...
Page 582
Prefaultrect timelimit postfaultrect en05000487.Vsd 1 2 3 trig point iec05000487 v1 en-us figure 226: the recording times definition prefaultrect, 1 pre-fault or pre-trigger recording time. The time before the fault including the trip time of the trigger. Use the setting prefaultrect to set this tim...
Page 583
Ansi10000029-1-en.Vsd a3radr a2radr a1radr smai ai1 ai2 ai3 ai4 ai3p ^grp2_a ^grp2_b ^grp2_c block ^grp2_n input1 input2 input3 input4 input5 input6 ... A4radr input31 input32 input33 input34 input35 input36 ... Input40 internal analog signals external analog signals ain type ansi10000029 v1 en-us f...
Page 584
For each of the analog signals, operation = enabled means that it is recorded by the disturbance recorder. The trigger is independent of the setting of operation, and triggers even if operation is set to disabled. Both undervoltage and overvoltage can be used as trigger conditions. The same applies ...
Page 585
Manual trigger m12155-167 v4 a disturbance report can be manually triggered from the local hmi, pcm600 or via station bus (iec 61850). When the trigger is activated, the manual trigger signal is generated. This feature is especially useful for testing. Refer to the operator's manual for procedure. B...
Page 586
Function range or value accuracy maximum number of binary inputs 352 - maximum number of phasors in the trip value recorder per recording 30 - maximum number of indications in a disturbance report 352 - maximum number of events in the event recording per recording 150 - maximum number of events in t...
Page 587
16.7.3 function block guid-ba0a5bc3-493b-4fe3-b4a9-14f60a88a22f v2 binstatrep block ^input1 ^input2 ^input3 ^input4 ^input5 ^input6 ^input7 ^input8 ^input9 ^input10 ^input11 ^input12 ^input13 ^input14 ^input15 ^input16 output1 output2 output3 output4 output5 output6 output7 output8 output9 output10 ...
Page 588
Pid-4144-outputsignals v6 table 429: binstatrep output signals name type description output1 boolean logical status report output 1 output2 boolean logical status report output 2 output3 boolean logical status report output 3 output4 boolean logical status report output 4 output5 boolean logical sta...
Page 589
T t inputn outputn iec09000732-1-en.Vsd iec09000732 v1 en-us figure 229: binstatrep logical diagram 16.8 measured value expander block range_xp semod52451-1 v2 16.8.1 identification semod113212-2 v3 function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number ...
Page 590
16.8.3 function block semod54336-4 v3 iec05000346-2-en.Vsd range_xp range* highhigh high normal low lowlow iec05000346 v2 en-us figure 230: range_xp function block 16.8.4 signals semod53803-1 v2 pid-3819-inputsignals v5 table 431: range_xp input signals name type default description range integer 0 ...
Page 591
Table 433: input integer value converted to binary output signals measured supervised value is: below low-low limit between low‐ low and low limit between low and high limit between high- high and high limit above high-high limit output: lowlow high low high normal high high high highhigh high 16.9 ...
Page 592
16.9.3.1 design guid-b643c994-d0ba-4be9-bacb-adea0197cae4 v1 figure 231 illustrates the general logic diagram of the function. Block counttype input reset error overflow limit1 … 4 counterlimit1...4 maxvalue onmaxvalue initialvalue value operation counter overflow detection limit check error detecti...
Page 593
Iec12000626_1_en.Vsd max value +3 ® max value -1 ® max value ® max value +1 ® max value +2 ® max value -1 ® max value ® 0 ® 1 2 ... ... ... ... Overflow indication actual value counted value iec12000626 v1 en-us figure 232: overflow indication when onmaxvalue is set to rollover pulsed the error outp...
Page 594
16.9.5 signals pid-6966-inputsignals v2 table 434: l4ufcnt input signals name type default description block boolean 0 block of function input boolean 0 input for counter reset boolean 0 reset of function pid-6966-outputsignals v2 table 435: l4ufcnt output signals name type description error boolean...
Page 595
16.9.7 monitored data pid-6966-monitoreddata v2 table 437: l4ufcnt monitored data name type values (range) unit description value integer - - counted value 16.9.8 technical data guid-c43b8654-60fe-4e20-8328-754c238f4ad0 v3 table 438: l4ufcnt technical data function range or value accuracy counter va...
Page 596
Time accumulation with retain block acc_hour reset in twarning talarm overflow warning alarm q -1 a>b a b a>b a b a>b a b & & & q -1 = unit delay iec15000321-1-en.Vsd acc_day 99 999.9 h taddtotime addtime iec15000321 v1 en-us figure 234: teilgapc logics the main features of teilgapc are: • applicabl...
Page 597
16.10.4 signals pid-6998-inputsignals v1 table 439: teilgapc input signals name type default description block boolean 0 freeze the accumulation and block the outputs in boolean 0 the input signal that is used to measure the elapsed time, when its value is high addtime boolean 0 add time to the accu...
Page 598
Time accumulation transgression supervision plus retain block acc_hour reset in talarm overflow warning alarm iec15000322.Vsd loop delay loop delay twarning acc_day addtime taddtotime iec15000322 v1 en-us figure 236: teilgapc simplified logic teilgapc main functionalities • in: accumulation of the e...
Page 599
• the amount of time to be added is defined by a setting taddtotime • time is added through activation of input addtime or from lhmi or with iec 61850 command • block: freeze the accumulation and block/reset the other outputs • independent of the input in value • block request overrides resetrequest...
Page 600
Consequently in case of a power failure, there is a risk of losing the difference in time between actual time and last time stored in the non-volatile memory. 16.10.7 technical data guid-f5e124e3-0b85-41ac-9830-a2362fd289f2 v1 table 442: teilgapc technical data function range or value accuracy time ...
Page 601
Section 17 metering 17.1 pulse-counter logic pcfcnt ip14600-1 v3 17.1.1 identification m14879-1 v4 function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number pulse-counter logic pcfcnt s00947 v1 en-us - 17.1.2 functionality m13394-3 v7 pulse-counter logic (p...
Page 602
17.1.4 signals pid-6509-inputsignals v4 table 443: pcfcnt input signals name type default description bi_pulse boolean 0 connect binary input channel for metering block boolean 0 block of function read_val boolean 0 initiates an additional pulse counter reading rs_cnt boolean 0 resets pulse counter ...
Page 603
17.1.6 monitored data pid-6509-monitoreddata v4 table 446: pcfcnt monitored data name type values (range) unit description scal_val real - - scaled value with time and status information 17.1.7 operation principle ip14087-1 v2 m13397-3 v5 the registration of pulses is done for positive transitions (...
Page 604
M13399-3 v9 figure 238 shows the pulse-counter logic function block with connections of the inputs and outputs. En05000744_ansi.Vsd pulsecounter block read_val bi_pulse pulse input out database pulse counter value: 0...2147483647 sms settings 1.Operation = off/on 2.Treporting = 0s...60min 3.Event ma...
Page 605
The blocked signal is a steady signal and is set when the counter is blocked. There are two reasons why the counter is blocked: • the block input is set, or • the binary input module, where the counter input is situated, is inoperative. The new_val signal is a pulse signal. The signal is set if the ...
Page 606
17.2.2 functionality guid-6898e29b-da70-421c-837c-1bbed8c63a7a v3 power system measurement (cvmmxn) can be used to measure active as well as reactive power values. Function for energy calculation and demand handling (etpmmtr) uses measured active and reactive power as input and calculates the accumu...
Page 607
17.2.4 signals pid-6872-inputsignals v3 table 448: etpmmtr input signals name type default description p real 0 measured active power q real 0 measured reactive power startacc boolean 0 start to accumulate energy values stopacc boolean 0 stop accumulating energy values rstacc boolean 0 reset of accu...
Page 608
17.2.5 settings pid-6872-settings v3 table 450: etpmmtr non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description operation disabled enabled - - disabled operation disabled/enabled enaacc disabled enabled - - disabled activate the accumulation of energy values tenergy 1 minute 5 m...
Page 609
Name values (range) unit step default description earprestval 0.000 - 100000000.000 mwh 0.001 0.000 preset initial value for reverse active energy erfpresetval 0.000 - 100000000.000 mvarh 0.001 0.000 preset initial value for forward reactive energy errpresetval 0.000 - 100000000.000 mvarh 0.001 0.00...
Page 610
Zero clamping detection p q maximum power demand calculation energy accumulation calculation startacc stopacc rstdmd maxpafd maxpard maxprfd maxprrd eafalm earalm erfalm erralm eafacc earacc erfacc erracc accinprg eafpulse earpulse erfpulse errpulse rstacc iec13000185-2-en.Vsd iec13000185 v2 en-us f...
Page 611
Forward direction. Similarly, the integration of energy in active reverse, reactive forward and reactive reverse is done. T f t f t f x 60.0 q -1 0.0 q -1 & rstacc eafprestval accinprg p* (active forward) eafacc a>b a b 1000 gwh q -1 = unit delay iec13000187-5-en.Vsdx iec13000187 v5 en-us figure 242...
Page 612
A>b a b counter rst cu cv x q -1 ÷ ÷ r i r i a>b a b 0 counter rst cu cv q -1 eafpulse rstacc eafacc t f t toff tp 0 q -1 tenergyoffpls 1000 gwh eafaccplsqty tenergyonpls q -1 = unit delay iec13000188-5-en.Vsdx iec13000188 v5 en-us figure 243: logic for pulse generation of integrated active forward ...
Page 613
17.2.8 technical data 17.2.8.1 technical data guid-da0a8ab5-755d-4f35-8c69-ffaa951fe374 v1 table 453: function range or value accuracy energy metering mwh export/import, mvarh export/import input from mmxu. No extra error at steady load 1mrk 511 408-uus a section 17 metering phasor measurement unit ...
Page 614
608.
Page 615
Section 18 ethernet 18.1 access point 18.1.1 introduction guid-6e5d2696-a8ee-43e7-a94b-69c3d0612127 v1 an access point is an ethernet communication interface for single or redundant station communication. Each access point is allocated with one physical ethernet port, two physical ethernet ports are...
Page 616
Name values (range) unit step default description description 1 - 18 - 1 station bus user editable access point description [1-18 char] ptp disabled enabled slave only - - disabled precision time protocol pcm600access disabled enabled - - enabled pcm600 access ftp disabled on - - on ftp and ftps acc...
Page 617
Pid-6637-settings v3 table 455: ap_front non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description ipaddress 0 - 18 ip address 1 10.1.150.3 ip address of the access point subnetmask 0 - 18 ip address 1 255.255.255.0 subnet mask of the access point description 1 - 18 - 1 frontport ...
Page 618
18.2 access point diagnostics 18.2.1 functionality guid-20f64a6d-aa8c-47d7-aa7d-4810996b2ff2 v1 the access point diagnostics function blocks (rchlcch, schlcch and frontstatus) supervise communication. Schlcch is used for communication over the rear ethernet ports, rchlcch is used for redundant commu...
Page 619
Pid-6819-outputsignals v2 table 458: rchlcch output signals name type description redlinka boolean channel a redundancy status redlinkb boolean channel b redundancy status dosalarm boolean denial of service alarm (a + b) pid-6813-outputsignals v3 table 459: frontstatus output signals name type descr...
Page 620
18.3 redundant communication 18.3.1 identification guid-b7ae0374-0336-42b8-90af-3ae1c79a4116 v1 function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number iec 62439-3 parallel redundancy protocol prp - - iec 62439-3 high-availability seamless redundancy hsr ...
Page 621
Iec09000758-4-en.Vsd switch a ap1 phyportb phyporta ap1 phyporta phyportb ap1 phyportb phyporta ap1 phyporta phyportb switch b device 1 device 2 device 3 device 4 iec09000758 v4 en-us figure 249: redundant station bus iec 62439-3 high-availabillity seamless redundancy (hsr) hsr applies the principle...
Page 622
Iec16000038-1-en.Vsdx ap1 phyportb phyporta ap1 phyporta phyportb ap1 phyporta phyportb ap1 phyportb phyporta device 1 device 2 device 3 device 4 iec16000038 v1 en-us figure 250: hsr ring 18.4 merging unit 18.4.1 introduction guid-e630c16f-edb8-40ae-a8a2-94189982d15f v1 the iec/uca 61850-9-2le proce...
Page 623
18.4.2 settings pid-6770-settings v2 table 463: mu1 non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description samplevalueid 0 - 34 - 1 abb_mu0101 sample value id (svid) for the merging unit [0-34 char] apconnection none ap1 ap2 ap3 ap4 - - none access point connection for the merg...
Page 624
Name type values (range) unit description testmode boolean 1=yes 0=no - quality of one or more subscribed analogue channels is test simmode boolean 1=yes 0=no - mu delivers simulated data accepted by ied badreference boolean 1=yes 0=no - badreference indication output for i1 derived boolean 1=yes 0=...
Page 625
Name type values (range) unit description operatorblocked boolean 1=yes 0=no - operatorblocked indication output for i2 oscillatory boolean 1=yes 0=no - oscillatory indication output for i2 outofrange boolean 1=yes 0=no - outofrange indication output for i2 overflow boolean 1=yes 0=no - overflow ind...
Page 626
Name type values (range) unit description derived boolean 1=yes 0=no - derived indication output for i4 failure boolean 1=yes 0=no - failure indication output for i4 inaccurate boolean 1=yes 0=no - inaccurate indication output for i4 inconsistent boolean 1=yes 0=no - inconsistent indication output f...
Page 627
Name type values (range) unit description source boolean 0=process 1=substituted - source indication output for va test boolean 1=yes 0=no - test indication output for va validity integer 0=good 2=reserved 1=invalid 3=questionable - validity indication output va badreference boolean 1=yes 0=no - bad...
Page 628
Name type values (range) unit description olddata boolean 1=yes 0=no - olddata indication output for vc operatorblocked boolean 1=yes 0=no - operatorblocked indication output for vc oscillatory boolean 1=yes 0=no - oscillatory indication output for vc outofrange boolean 1=yes 0=no - outofrange indic...
Page 629
18.5 routes 18.5.1 introduction guid-95f9c7ba-92f8-489f-ad0a-047410b5e66f v1 a route is a specified path for data to travel between the source device in a subnetwork to the destination device in a different subnetwork. A route consists of a destination address and the address of the gateway to be us...
Page 630
18.5.3 monitored data pid-6761-monitoreddata v2 table 467: route_1 monitored data name type values (range) unit description routeconfig integer 0=ok 1=error -1=off - route configuration status section 18 1mrk 511 408-uus a ethernet 624 phasor measurement unit res670 2.2 ansi technical manual.
Page 631
Section 19 station communication 19.1 communication protocols m14815-3 v13 each ied is provided with several communication interfaces enabling it to connect to one or many substation level systems or equipment, either on the substation automation (sa) bus or substation monitoring (sm) bus. Available...
Page 632
Iec15000400-1-en.Vsd iec15000400 v1 en-us figure 252: protocol diagnostic screen in lhmi 19.3 dnp3 protocol guid-54a54716-23bd-4e7c-8245-de2b4c75e8dc v1 dnp3 (distributed network protocol) is a set of communications protocols used to communicate data between components in process automation systems....
Page 633
Communication over mms are supported. Disturbance recording file (comtrade) uploading can be done over mms or ftp. The front port is only intended for pcm600 communication, maintenance, training and test purposes due to risk of interference during normal operation. 19.4.2 communication interfaces an...
Page 634
Name values (range) unit step default description remmodcontrol disabled maintenance all levels - - disabled remote mode control allowsimulation no yes - - no allow simulated goose values or simulated sampled measured values remsetcontroled2 disabled enabled - - disabled changing settings over 61850...
Page 635
19.4.5.2 function block semod54714-4 v4 spgapc block ^in iec14000021-1-en.Vsd iec14000021 v1 en-us figure 253: spgapc function block sp16gapc block ^in1 ^in2 ^in3 ^in4 ^in5 ^in6 ^in7 ^in8 ^in9 ^in10 ^in11 ^in12 ^in13 ^in14 ^in15 ^in16 iec14000020-1-en.Vsd iec14000020 v1 en-us figure 254: sp16gapc fu...
Page 636
Name type default description in6 boolean 0 input 6 status in7 boolean 0 input 7 status in8 boolean 0 input 8 status in9 boolean 0 input 9 status in10 boolean 0 input 10 status in11 boolean 0 input 11 status in12 boolean 0 input 12 status in13 boolean 0 input 13 status in14 boolean 0 input 14 status...
Page 637
Name type values (range) unit description out7 group signal - - output 7 status out8 group signal - - output 8 status out9 group signal - - output 9 status out10 group signal - - output 10 status out11 group signal - - output 11 status out12 group signal - - output 12 status out13 group signal - - o...
Page 638
19.4.6.2 function block semod54712-4 v4 mvgapc block ^in ^value range iec14000022-1-en.Vsd iec14000022 v1 en-us figure 255: mvgapc function block 19.4.6.3 signals semod55948-1 v2 pid-6753-inputsignals v1 table 475: mvgapc input signals name type default description block boolean 0 block of function ...
Page 639
Name values (range) unit step default description mv llim -5000.00 - 5000.00 xbase 0.01 -800.00 low limit multiplied with the base prefix (multiplication factor) mv lllim -5000.00 - 5000.00 xbase 0.01 -900.00 low low limit multiplied with the base prefix (multiplication factor) mv min -5000.00 - 500...
Page 640
19.4.7 goose function block to receive a double point value goosedprcv 19.4.7.1 identification guid-8c11db9a-7844-4e1f-a6bb-d97ece350fc1 v1 function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number goose function block to receive a double point value goosed...
Page 641
Pid-6828-outputsignals v3 table 480: goosedprcv output signals name type description dpout integer double point output datavalid boolean data valid for double point output commvalid boolean communication valid for double point output test boolean test output 19.4.7.5 settings pid-6828-settings v3 ta...
Page 642
The input of this goose block must be linked either in smt by means of a cross or in act by means of a goose connection (if easy goose engineering is enabled) to receive the double point values. The implementation for iec 61850 quality data handling is restricted to a simple level. If quality data v...
Page 643
Visible and possible to make only if easy goose engineering is enabled. For instructions on how to enable easy goose engineering in pcm600, refer to the engineering manual. Pid-6829-inputsignals v3 table 482: gooseintrcv input signals name type default description block boolean 0 block of function s...
Page 644
Data value data valid comm valid test incoming data with q=test+olddata freeze 0 1 1 receiver in block freeze 0 1 0 receiver in block and communication error freeze 0 0 0 receiver in test mode and incoming data with q= normal updated 1 1 0 receiver in test mode and incoming data with q= test updated...
Page 645
19.4.9.3 function block guid-a0b333cc-aef4-40ea-b152-364648ab78d3 v1 iec10000251-2-en.Vsd goosemvrcv block ^srcmvout ^mvout datavalid commvalid test iec10000251 v2 en-us figure 258: goosemvrcv function block 19.4.9.4 signals guid-2dc54788-86af-4b4b-8e57-a89e30f0c433 v1 except for the block input, th...
Page 646
19.4.9.6 operation principle guid-7b24a6d3-2e5f-4961-a0a6-86436373809e v5 the datavalid output will be high if the incoming message is with valid data. The commvalid output will become low when the sending ied is under total failure condition and the goose transmission from the sending ied does not ...
Page 647
19.4.10 goose function block to receive a single point value goosesprcv 19.4.10.1 identification guid-f2b30a70-842e-435e-8fab-b1e58b9c0164 v1 function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number goose function block to receive a single point value goos...
Page 648
Pid-6832-outputsignals v3 table 489: goosesprcv output signals name type description spout boolean single point output datavalid boolean data valid for single point output commvalid boolean communication valid for single point output test boolean test output 19.4.10.5 settings pid-6832-settings v3 t...
Page 649
The input of this goose block must be linked either in smt by means of a cross or in act by means of a goose connection (if easy goose engineering is enabled) to receive the binary single point values. The implementation for iec 61850 quality data handling is restricted to a simple level. If quality...
Page 650
19.4.11.2 function block semod173210-4 v5 iec07000048-4-en.Vsd gooseintlkrcv block ^srcresreq ^srcresgr ^srcapp1 ^srcapp2 ^srcapp3 ^srcapp4 ^srcapp5 ^srcapp6 ^srcapp7 ^srcapp8 ^srcapp9 ^srcapp10 ^srcapp11 ^srcapp12 ^srcapp13 ^srcapp14 ^srcapp15 ^resreq ^resgrant ^app1_op ^app1_cl app1val ^app2_op ^a...
Page 651
Enabled. For instructions on how to enable easy goose engineering in pcm600, refer to the engineering manual. Pid-6831-inputsignals v3 table 491: gooseintlkrcv input signals name type default description block boolean 0 block of output signals srcresreq boolean 0 source to reservation request srcres...
Page 652
Name type description app3val boolean apparatus 3 position is valid app4_op boolean apparatus 4 position is open app4_cl boolean apparatus 4 position is closed app4val boolean apparatus 4 position is valid app5_op boolean apparatus 5 position is open app5_cl boolean apparatus 5 position is closed ap...
Page 653
Name type description app15val boolean apparatus 15 position is valid commvalid boolean communication valid test boolean test output 19.4.11.4 settings semod173168-1 v2 pid-6831-settings v3 table 493: gooseintlkrcv non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description operatio...
Page 654
(if easy goose engineering is enabled) to receive any data. Only those outputs whose source input is linked/connected will be updated. The implementation for iec 61850 quality data handling is restricted to a simple level. If quality data validity is good then the appxval output will be high. If qua...
Page 655
19.4.12.2 signals semod173166-1 v2 guid-2dc54788-86af-4b4b-8e57-a89e30f0c433 v1 except for the block input, the rest of the inputs of this goose function block are used for goose connections. These connections are visible and possible to make only if easy goose engineering is enabled. For instructio...
Page 656
Name type description dvalid3 boolean valid data on binary output 3 out4 boolean binary output 4 dvalid4 boolean valid data on binary output 4 out5 boolean binary output 5 dvalid5 boolean valid data on binary output 5 out6 boolean binary output 6 dvalid6 boolean valid data on binary output 6 out7 bo...
Page 657
19.4.12.4 operation principle guid-950f2501-9183-43c0-a193-7d15124f6cce v1 the dvalidx output will be high if the incoming message is with valid data. The commvalid output will become low when the sending ied is under total failure condition and the goose transmission from the sending ied does not h...
Page 658
19.5 iec/uca 61850-9-2le communication protocol guid-6814f62b-8d99-4679-a11e-68048d1ac424 v2 19.5.1 introduction guid-fe2ac08a-2e04-4e73-8ca4-905522b1026a v2 the iec/uca 61850-9-2le process bus communication protocol enables an ied to communicate with devices providing measured values in digital for...
Page 659
Name type description smpllost boolean fatal error or recovery state after fatal error. High if any subscribed channel has bad quality or test while ied not in test mode. Musynch boolean mu not synced or mu clock not synced to same clock as ied testmode boolean quality of one or more subscribed anal...
Page 660
19.5.5 monitored data pid-6850-monitoreddata v3 table 499: mu1_hw monitored data name type values (range) unit description mudata boolean 0=ok 1=error - fatal error, data not received, transmission errors, time- sync issues or inconsistent sample rate synch boolean 0=ok 1=error - operational mode on...
Page 661
Name type values (range) unit description test boolean 1=yes 0=no - test indication output for i1 validity integer 0=good 2=reserved 1=invalid 3=questionable - validity indication output i1 badreference boolean 1=yes 0=no - badreference indication output for i2 derived boolean 1=yes 0=no - derived i...
Page 662
Name type values (range) unit description operatorblocked boolean 1=yes 0=no - operatorblocked indication output for i3 oscillatory boolean 1=yes 0=no - oscillatory indication output for i3 outofrange boolean 1=yes 0=no - outofrange indication output for i3 overflow boolean 1=yes 0=no - overflow ind...
Page 663
Name type values (range) unit description derived boolean 1=yes 0=no - derived indication output for va failure boolean 1=yes 0=no - failure indication output for va inaccurate boolean 1=yes 0=no - inaccurate indication output for va inconsistent boolean 1=yes 0=no - inconsistent indication output f...
Page 664
Name type values (range) unit description source boolean 0=process 1=substituted - source indication output for vb test boolean 1=yes 0=no - test indication output for vb validity integer 0=good 2=reserved 1=invalid 3=questionable - validity indication output vb badreference boolean 1=yes 0=no - bad...
Page 665
Name type values (range) unit description olddata boolean 1=yes 0=no - olddata indication output for 3v0 operatorblocked boolean 1=yes 0=no - operatorblocked indication output for 3v0 oscillatory boolean 1=yes 0=no - oscillatory indication output for 3v0 outofrange boolean 1=yes 0=no - outofrange in...
Page 666
Ct ct combi sensor merging unit merging unit ethernet switch combi sensor conventional vt iec/uca 61850-9-2le iec/uca 61850-9-2le iec/uca 61850-9-2le splitter electrical-to- optical converter 1pps 1pps 1pps 110 v 1 a station wide gps clock iec080000723enoriginal.Vsd preprocessing blocks smai applica...
Page 667
• ok[0] indicates that the merging unit samples are received from the merging unit and are accepted. • error[1] indicates that the merging unit samples are generated by internal substitution. • synch: • ok[0] indicates • when synclostmode = block, and the time quality of the hardware is within the s...
Page 668
Unspecified] [or] merging unit is not time synchronized [smpsynch flag in datastream is equal to 0] • when synclostmode = noblock, the merging unit samples are not received • testmode: • no[0] indicates that no merging unit analog channels are in testmode • yes[1] indicates that one/more subscribed ...
Page 669
Synclostmode is not required to set as block/blockonlostutc when differential protection based on echo mode. A missing pps however will lead to a drift between mu and ied. Therefore protection functions in this case will be blocked. Guid-37c7609a-d9cd-435f-bbee-7518b88beedf v1 functions can be block...
Page 670
19.6 lon communication protocol ip14420-1 v1 19.6.1 functionality m11924-3 v6 an optical network can be used within the substation automation system. This enables communication with the ied through the lon bus from the operator’s workplace, from the control center and also from other terminals. Lon ...
Page 671
19.6.3 operation principle ip14439-1 v2 m15083-3 v2 the speed of the network depends on the medium and transceiver design. With protection and control devices, fibre optic media is used, which enables the use of the maximum speed of 1.25 mbits/s. The protocol is a peer-to-peer protocol where all the...
Page 672
Add lon device types lnt m15083-19 v3 a new device is added to lon network tool from the device menu or by installing the device from the abb lon device types package for lnt 505 using sldt package version 1p2 r04. Lon net address m15083-22 v3 to establish a lon connection, the ied has to be given a...
Page 673
The first lon address in every event function block is found in table 503 . The formula for calculating the lon address is: lon address = (evblknr-1)×16 + signalnr +1023 for instance, the first pin at event block number 2 has the address: (2-1)×16 +1 +1023 = 1040 table 503: lon adresses for event fu...
Page 674
• no events • onset, at pick-up of the signal • onreset, at drop-out of the signal • onchange, at both pick-up and drop-out of the signal • autodetect, the event function makes the reporting decision (reporting criteria for integers has no semantic, prefer to be set by the user) single indication m1...
Page 675
Table 504: spa addresses for commands from the operator workplace to the ied for apparatus control name function block spa address description bl_cmd scswi01 1 i 5115 spa parameters for block command bl_cmd scswi02 1 i 5139 spa parameters for block command bl_cmd scswi02 1 i 5161 spa parameters for ...
Page 676
Name function block spa address description bl_cmd scswi22 1 i 5619 spa parameters for block command bl_cmd scswi23 1 i 5643 spa parameters for block command bl_cmd scswi24 1 i 5667 spa parameters for block command bl_cmd scswi25 1 i 5691 spa parameters for block command bl_cmd scswi26 1 i 5715 spa ...
Page 677
Name function block spa address description cancel scswi12 1 i 5371 spa parameters for cancel command cancel scswi13 1 i 5395 spa parameters for cancel command cancel scswi14 1 i 5419 spa parameters for cancel command cancel scswi15 1 i 5443 spa parameters for cancel command cancel scswi16 1 i 5467 ...
Page 678
Name function block spa address description selectopen=00, selectclose=01, selopen+ilo=10, selclose+ilo=11, selopen+sco=20, selclose+sco=21, selopen+ilo+sco=30, selclose+ilo+sco=31 scswi01 1 i 5105 spa parameters for select (open/ close) command note: send select command before operate command selec...
Page 679
Name function block spa address description selectopen=00, selectclose=01, so on. Scswi21 1 i 5584 spa parameters for select (open/ close) command selectopen=00, selectclose=01, so on. Scswi22 1 i 5609 spa parameters for select (open/ close) command selectopen=00, selectclose=01, so on. Scswi23 1 i ...
Page 680
Name function block spa address description excopen=00, excclose=01, so on. Scswi09 1 i 5298 spa parameters for operate (open/close) command excopen=00, excclose=01, so on. Scswi10 1 i 5322 spa parameters for operate (open/close) command excopen=00, excclose=01, so on. Scswi11 1 i 5346 spa parameter...
Page 681
Name function block spa address description excopen=00, excclose=01, so on. Scswi31 1 i 5826 spa parameters for operate (open/close) command excopen=00, excclose=01, so on. Scswi32 1 i 5850 spa parameters for operate (open/close) command sub value sxcbr01 2 i 7854 spa parameter for position to be su...
Page 682
Name function block spa address description sub value sxswi02 3 i 216 spa parameter for position to be substituted sub value sxswi03 3 i 235 spa parameter for position to be substituted sub value sxswi04 3 i 254 spa parameter for position to be substituted sub value sxswi05 3 i 272 spa parameter for...
Page 683
Name function block spa address description sub value sxswi24 3 i 625 spa parameter for position to be substituted sub value sxswi25 3 i 644 spa parameter for position to be substituted sub value sxswi26 3 i 663 spa parameter for position to be substituted sub value sxswi27 3 i 682 spa parameter for...
Page 684
Name function block spa address description sub enable sxcbr17 3 i 159 spa parameter for substitute enable command sub enable sxcbr18 3 i 178 spa parameter for substitute enable command sub enable sxswi01 3 i 197 spa parameter for substitute enable command sub enable sxswi02 3 i 215 spa parameter fo...
Page 685
Name function block spa address description sub enable sxswi21 3 i 569 spa parameter for substitute enable command sub enable sxswi22 3 i 588 spa parameter for substitute enable command sub enable sxswi23 3 i 607 spa parameter for substitute enable command sub enable sxswi24 3 i 626 spa parameter fo...
Page 686
Name function block spa address description update block sxcbr15 3 i 122 spa parameter for update block command update block sxcbr16 3 i 131 spa parameter for update block command update block sxcbr17 3 i 160 spa parameter for update block command update block sxcbr18 3 i 177 spa parameter for updat...
Page 687
Name function block spa address description update block sxswi19 3 i 529 spa parameter for update block command update block sxswi20 3 i 548 spa parameter for update block command update block sxswi21 3 i 567 spa parameter for update block command update block sxswi22 3 i 586 spa parameter for updat...
Page 688
Multicmdsnd: 7 bay e1 multicmdsnd: 9 bay e3 lon bay e4 multicmdsnd: 9 en05000718.Vsd iec05000718 v2 en-us figure 264: examples connections between multicmdsnd and multicmdrcv function blocks in three ieds the network variable connections are done from the nv connection window. From lnt window select...
Page 689
There are two ways of downloading nv connections. Either the users can use the drag- and-drop method where they can select all nodes in the device window, drag them to the download area in the bottom of the program window and drop them there; or, they can perform it by selecting the traditional menu...
Page 690
Iec16000079-1-en.Vsd iec16000079 v1 en-us figure 267: rear view of 1/2 x 19” casing with 1 trm slot there are two types of io connectors: snap-in connectors for plastic fibre cables and st/bayonet connectors for glass fibre cables. The slm can be equipped with either type of connector or a combinati...
Page 691
19.7.2 measurands for iec 60870-5-103 i103meas 19.7.2.1 functionality guid-557fb587-9127-4d99-b2c6-16445e06f220 v3 103meas is a function block that reports all valid measuring types depending on connected signals. The set of connected input will control which asdus (application service data units) a...
Page 692
19.7.2.3 function block guid-ec5f1c83-0f47-4548-86e3-ffe056571241 v2 ansi10000287-1-en.Vsd i103meas block i_a i_b i_c in v_a v_b v_c v_ab v_n p q f ansi10000287 v1 en-us figure 268: i103meas function block 19.7.2.4 signals pid-6625-inputsignals v4 table 505: i103meas input signals name type default ...
Page 693
19.7.2.5 settings pid-6625-settings v4 table 506: i103meas non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description functiontype 1 - 255 - 1 1 function type (1-255) maxia 1 - 99999 a 1 3000 maximum current phase a maxib 1 - 99999 a 1 3000 maximum current phase b maxic 1 - 99999 a...
Page 694
19.7.3.3 function block guid-c234101e-f9b9-4db0-874c-c51bb50588cb v1 iec10000288-1-en.Vsd i103measusr block ^input1 ^input2 ^input3 ^input4 ^input5 ^input6 ^input7 ^input8 ^input9 iec10000288 v1 en-us figure 269: i103measusr function block 19.7.3.4 signals pid-3791-inputsignals v5 table 507: i103mea...
Page 695
Name values (range) unit step default description maxmeasur3 0.05 - 10000000000.00 - 0.05 1000.00 maximum value for measurement on input 3 maxmeasur4 0.05 - 10000000000.00 - 0.05 1000.00 maximum value for measurement on input 4 maxmeasur5 0.05 - 10000000000.00 - 0.05 1000.00 maximum value for measur...
Page 696
19.7.4.4 signals pid-3973-inputsignals v5 table 509: i103ar input signals name type default description block boolean 0 block of status reporting 16_aract boolean 0 information number 16, auto-recloser active 128_cbon boolean 0 information number 128, circuit breaker on by auto- recloser 130_blkd bo...
Page 697
19.7.5.3 function block guid-25b47484-2976-4063-bd81-ae02d03b08b0 v1 iec10000290-1-en.Vsd i103ef block 51_effw 52_efrev iec10000290 v1 en-us figure 271: i103ef function block 19.7.5.4 signals pid-3974-inputsignals v5 table 511: i103ef input signals name type default description block boolean 0 block...
Page 698
19.7.6.2 identification guid-55593ec4-7aed-47a0-8311-db22d013a193 v1 function description function block name iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number function status fault protection for iec 60870-5-103 i103fltprot - - 19.7.6.3 function block guid-f0ed13b8-6b82-4ca7-8f22-c200c33ebb7e ...
Page 699
19.7.6.4 signals pid-6864-inputsignals v1 table 513: i103fltprot input signals name type default description block boolean 0 block of status reporting. 64_pu_a boolean 0 information number 64, pickup phase a 65_pu_b boolean 0 information number 64, pickup phase b 66_pu_c boolean 0 information number...
Page 700
Name type default description 93_ief boolean 0 information number 93, ground-fault trip, stage high arinprog boolean 0 autorecloser in progress (smbrrec- inprogr) fltloc boolean 0 faultlocator faultlocation valid (lmbrflo- calcmade) 19.7.6.5 settings pid-6864-settings v1 table 514: i103fltprot non g...
Page 701
19.7.7.4 signals pid-3975-inputsignals v5 table 515: i103ied input signals name type default description block boolean 0 block of status reporting 19_ledrs boolean 0 information number 19, reset leds 21_testm boolean 0 information number 21, test mode is active 22_setch boolean 0 information number ...
Page 702
19.7.8.3 function block guid-69c2c974-2d64-4174-9f9a-15383c09050d v1 iec10000293-1-en.Vsd i103superv block 32_measi 33_measu 37_ibkup 38_vtff 46_grwa 47_gral iec10000293 v1 en-us figure 274: i103superv function block 19.7.8.4 signals pid-3976-inputsignals v5 table 517: i103superv input signals name ...
Page 703
Information number (inf). Additionally, all input signals may be defined to use relative time and how to respond to a gi request. The user is responsible for assigning a proper fun value and proper inf values to all connected inputs. See settings for details. 19.7.9.2 identification guid-474fdf39-ce...
Page 704
Name type default description input7 boolean 0 binary signal input 7 input8 boolean 0 binary signal input 8 rt_start boolean 0 trig to set base of relative time guid-9e29de39-ea74-4d62-a2ba-f8e31a3d8757 v2 rt_start registers the positive transition (0->1) of a pulse and sets the time from which rela...
Page 705
Name values (range) unit step default description gino1 excluded included - - included response and status change (gi) gino2 excluded included - - included response and status change (gi) gino3 excluded included - - included response and status change (gi) gino4 excluded included - - included respon...
Page 706
19.7.10.2 identification guid-cfd43980-0791-40d1-9136-cf4ccc35549a v1 function description function block name iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number function commands for iec 60870-5-103 i103cmd - - 19.7.10.3 function block guid-c0680812-c488-4546-aa65-f590955dbf0c v1 iec10000282-1-...
Page 707
19.7.11 ied commands for iec 60870-5-103 i103iedcmd 19.7.11.1 functionality guid-19ad44b2-21d6-4db0-ad74-1578da30c100 v5 i103iedcmd is a command block in control direction with defined ied functions. All outputs are pulsed and they are not stored. Pulse length is fixed to 400ms. 19.7.11.2 identifica...
Page 708
19.7.11.5 settings pid-3788-settings v5 table 526: i103iedcmd non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description functiontype 1 - 255 - 1 255 function type (1-255) 19.7.12 function commands user defined for iec 60870-5-103 i103usrcmd 19.7.12.1 functionality guid-2989eac8-20...
Page 709
Pid-3790-outputsignals v5 table 528: i103usrcmd output signals name type description output1 boolean command output 1 output2 boolean command output 2 output3 boolean command output 3 output4 boolean command output 4 output5 boolean command output 5 output6 boolean command output 6 output7 boolean c...
Page 710
The i103gencmd component can be configured as either 2 pulsed on/off or 2 steady on/off outputs. The on output is pulsed with a command with value 2, while the off output is pulsed with a command value 1. If in steady mode is on asserted and off deasserted with command 2 and vice versa with command ...
Page 711
19.7.13.5 settings pid-3970-settings v5 table 532: i103gencmd non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description functiontype 1 - 255 - 1 1 function type (1-255) pulselength 0.000 - 60.000 s 0.001 0.400 pulse length infno 1 - 255 - 1 1 information number for command output ...
Page 712
19.7.14.2 identification guid-abf81c27-4605-4a15-9cf5-77ff82de8747 v1 function description function block name iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number ied commands with position and select for iec 60870-5-103 i103poscmd - - 19.7.14.3 function block guid-3a31c1f2-1fb5-4db0-a698-ad3f557...
Page 713
19.7.15 ied commands with position for iec 60870-5-103 i103poscmdv 19.7.15.1 functionality guid-cf04d9ac-40be-46a3-a418-77204d2b0f27 v2 i103poscmdv is a transceiver function that monitors activity on its input signals and interprets any state transition into commands sent over an established iec 608...
Page 714
19.7.15.4 signals pid-6578-inputsignals v5 table 535: i103poscmdv input signals name type default description block boolean 0 block of command position integer 0 position of controllable object 19.7.15.5 settings pid-6578-settings v6 table 536: i103poscmdv non group settings (basic) name values (ran...
Page 715
• autorecloser on/off • teleprotection on/off • protection on/off • led reset • characteristics 1 - 4 (setting groups) • file transfer (disturbance files) • time synchronization for detailed information about iec 60870-5-103, refer to the iec 60870 standard part 5: transmission protocols, and to the...
Page 716
Function command block in control direction with defined output signals. Number of instances: 1 function type is selected with parameter functiontype. Information number is defined for each output signals. Table 538: pre-defined i103cmd supported indications inf description 16 auto-recloser on/off 1...
Page 717
Function type is selected with parameter functiontype. Information number is defined for each input signals. Table 540: i103ied supported functions inf description 19 led reset 21 testmode 22 local parameter setting 23 setting group 1 active 24 setting group 2 active 25 setting group 3 active 26 set...
Page 718
Information number is defined for output signals. Table 542: i103superv supported functions info. No. Message typ gi cot 32 measurand supervision i 1 y 1,7,9 33 measurand supervision v 1 y 1,7,9 37 i>>back-up operation 1 y 1,7,9 38 vt fuse failure 1 y 1,7,9 46 group warning 1 y 1,7,9 47 group alarm ...
Page 719
Number of instances: 1 function type is selected with parameter functiontype. Information number is defined for each input signal. Table 545: inf description typ gi cot 64 pickup phase a 2 y 1,7,9 65 pickup phase b 2 y 1,7,9 66 pickup phase c 2 y 1,7,9 67 pickup residual current in 2 y 1,7,9 68 trip...
Page 720
Measurands m11874-382 v2 function blocks in monitor direction for input measurands. Typically connected to monitoring function, for example to power measurement cvmmxn. Measurands in public range, i103meas m11874-385 v8 number of instances: 1 the ied reports all valid measuring types depending on co...
Page 721
Measurands in private range, i103measusr m11874-431 v5 number of instances: 3 function type parameter for each block in private range. Information number must be selected for measurands. Table 547: i103measusr supported indications inf fun gi typ cot description * 1) * 2) no, polled with cl2 * 3) 2,...
Page 722
• i a connected to channel 1 on disturbance function block a1radr • i b connected to channel 2 on disturbance function block a1radr • i c connected to channel 3 on disturbance function block a1radr • i n connected to channel 4 on disturbance function block a1radr • v ae connected to channel 5 on dis...
Page 723
• bit tp: the protection equipment has tripped during the fault • bit tm: the disturbance data are currently being transmitted • bit test: the disturbance data have been recorded during normal operation or test mode. • bit otev: the disturbance data recording has been initiated by another event than...
Page 724
Supported connectors connector f-sma no connector bfoc/2.5 yes interoperability, application layer m11874-524 v3 supported selection of standard asdus in monitoring direction asdu yes 1 time-tagged message yes 2 time-tagged message with rel. Time yes 3 measurands i yes 4 time-tagged message with rel...
Page 725
Supported test mode no blocking of monitoring direction yes disturbance data yes private data yes generic services no 19.7.16.2 communication ports m11874-626 v3 the serial communication module (slm) is used for spa/iec 60870-5-103/dnp and lon communication. This module is a mezzanine module, and is...
Page 726
19.8.2 design semod119958-1 v1 19.8.2.1 general m14792-3 v3 the common behavior for all 16 outputs of the multicmdrcv is set to either of two modes: steady or pulse. • 1 = steady: this mode simply forwards the received signals to the binary outputs. • 2 = pulse: when a received signal transitions fr...
Page 727
Semod120009-4 v2 iec06000008-2-en.Vsd multicmdsnd block input1 input2 input3 input4 input5 input6 input7 input8 input9 input10 input11 input12 input13 input14 input15 input16 error iec06000008 v2 en-us figure 283: multicmdsnd function block 19.8.4 signals semod119963-1 v2 pid-400-inputsignals v10 ta...
Page 728
Name type default description input13 boolean 0 input 13 input14 boolean 0 input 14 input15 boolean 0 input 15 input16 boolean 0 input 16 pid-400-outputsignals v10 table 550: multicmdrcv output signals name type description error boolean multireceive error newdata boolean new data is received output...
Page 729
19.8.5 settings semod119927-1 v2 pid-400-settings v10 table 552: multicmdrcv non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description tmaxcycletime 0.050 - 200.000 s 0.001 11.000 maximum cycle time between receptions of input data tmincycletime 0.000 - 200.000 s 0.001 0.000 minim...
Page 730
19.9 security events on protocols secalarm 19.9.1 security alarm secalarm guid-205b0024-da06-4369-8707-5e1d2d035995 v2 19.9.1.1 signals pid-3430-outputsignals v6 table 554: secalarm output signals name type description eventid integer eventid of the generated security event seqnumber integer sequenc...
Page 731
19.10.2 settings pid-6908-settings v2 table 556: activlog non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description extlogsrv1type disabled extlogsrv1type syslog tcp/ip cef tcp/ip - - disabled external log server 1 type extlogsrv1port 1 - 65535 - 1 514 external log server 1 port n...
Page 732
726.
Page 733
Section 20 remote communication 20.1 binary signal transfer ip12423-1 v2 20.1.1 identification m14849-1 v3 function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number binary signal transfer, receive binsignrec1_1 binsignrec1_2 binsignreceive2 - - binary signa...
Page 734
20.1.3 signals guid-0918c53d-f755-4fa1-bb3c-f672afc6a7d2 v1 signals are available in the signal matrix tool (smt) and as hardware channels in the application configuration tool (act). Pid-6471-outputsignals v2 table 557: ldcmrecbinstat1 output signals name type description comfail boolean detected e...
Page 735
Name type description gpserror boolean problem with gps synchronization in remote or local end nocarr boolean no carrier is detected in the incoming message nomess boolean no start and stop flags identified for the incoming message lngtherr boolean wrong length of the incoming message ybit boolean d...
Page 736
Pid-6474-outputsignals v2 table 560: ldcmrecbins2_2m output signals name type description comfail boolean detected error in the differential communication comalm boolean delayed alarm signal for communication failure blkdiff boolean link error, values are substituted, diff protection is blocked addr...
Page 737
Pid-6475-outputsignals v2 table 561: ldcmrecbins3_2m output signals name type description comfail boolean detected error in the differential communication comalm boolean delayed alarm signal for communication failure blkdiff boolean link error, values are substituted, diff protection is blocked addr...
Page 738
20.1.4 settings pid-6471-settings v2 table 562: ldcmrecbinstat1 non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description channelmode blocked normal outofservice - - normal channel mode of ldcm terminalno 0 - 255 - 1 0 terminal number used for line differential communication remot...
Page 739
Name values (range) unit step default description comalrmresdel 5 - 10000 ms 5 100 reset delay before communication alarm signal is reset redchswtime 0 - 500 ms 5 0 time delay before switching in redundant channel redchrturntime 5 - 500 ms 5 100 time delay before switching back from redundant channe...
Page 740
Name values (range) unit step default description comalrmresdel 5 - 10000 ms 5 100 reset delay before communication alarm signal is reset redchswtime 0 - 500 ms 5 0 time delay before switching in redundant channel redchrturntime 5 - 500 ms 5 100 time delay before switching back from redundant channe...
Page 741
Name values (range) unit step default description redchrturntime 5 - 500 ms 5 100 time delay before switching back from redundant channel asymdelay -20.00 - 20.00 ms 0.01 0.00 asymmetric delay when communication use echo synch. Maxtransmdelay 0 - 40 ms 1 20 max allowed transmission delay maxtdifflev...
Page 742
Name values (range) unit step default description deadbandtdiff 200 - 1000 us 1 300 deadband for t diff linkforwarded disabled ldcm305 ldcm306 ldcm312 ldcm313 ldcm322 ldcm323 - - disabled link forwarded from other ldcm redundantch disabled enabled - - disabled redundant channel enabled 20.1.5 monito...
Page 743
Pid-6473-monitoreddata v2 table 569: ldcmrecbinstat3 monitored data name type values (range) unit description commstatus boolean 0=ok 1=syncerr 2=no rxd 3=localgpserr 4=remgpserr 5=locandremg pserr 6=localaderr 7=remaderr 8=locandrema derr 9=addresserr 10=freqconferr 11=latencyconf err - status of c...
Page 744
Pid-6475-monitoreddata v2 table 571: ldcmrecbins3_2m monitored data name type values (range) unit description commstatus boolean 0=ok 1=syncerr 2=no rxd 3=localgpserr 4=remgpserr 5=locandremg pserr 6=localaderr 7=remaderr 8=locandrema derr 9=addresserr 10=freqconferr 11=latencyconf err - status of c...
Page 745
If communication is used for line differential purposes, transmitted data consists of three currents, clock information, trip, block and alarm signals and eight binary signals which can be used for any purpose. The three currents are represented as sampled values. If communication is used exclusivel...
Page 746
20.2.2 function block semod171559-1 v1 guid-05808cf6-34d6-4c76-a7a2-a26e5a96ec44 v2 ldcmtrn ^ct1l1 ^ct1l2 ^ct1l3 ^ct1n ^ct2l1 ^ct2l2 ^ct2l3 ^ct2n iec10000017-1-en.Vsd iec10000017 v1 en-us figure 285: ldcmtrn function block guid-893e3ded-5c51-4b78-8585-1c4e1f573b34 v1 ldcmtrn_2m ^ch1 ^ch2 ^ch3 ^ch4 ^...
Page 747
Name type default description ct2l2 string 0 input to be used for transmit ct-group2 line l2 to remote end ct2l3 string 0 input to be used for transmit ct-group2 line l3 to remote end ct2n string 0 input to be used for transmit ct-group2 neutral n to remote end pid-6449-inputsignals v2 table 573: ld...
Page 748
742.
Page 749
Section 21 security 21.1 authority check athchck 21.1.1 identification guid-fbef319b-94e6-41fb-bb9f-d870e0425128 v2 function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number authority check athchck - - 21.1.2 functionality semod117051-23 v6 to safeguard the...
Page 750
Iec12000202-2-en.Vsd iec12000202 v2 en-us figure 287: pcm600 user management tool 21.1.3 operation principle guid-b555edd0-baf1-4f0e-9162-bdb3a3468cf2 v8 there are different levels (or types) of users that can access or operate different areas of the ied and tools functionality. The pre-defined user...
Page 751
Table 574: pre-defined user types access rights guest super user spa guest system operator protection engineer design engineer user administrator basic setting possibilities (change setting group, control settings, limit supervision) r r/w r r/w r/w r/w r advanced setting possibilities (for example ...
Page 752
Only characters a - z, a - z and 0 - 9 should be used in user names and passwords. The maximum of characters in a password is 18. At least one user must be included in the useradministrator group to be able to write users, created in pcm600, to ied. Semod176296-5 v9 at delivery the default user is t...
Page 753
21.1.3.1 authorization with central account management enabled ied guid-1a836989-5d89-4f3d-b3a2-3babcdffb440 v1 the users, their roles and rights are created, deleted and edited only in the central account management server (sdm600). However, the user rights can be edited in the ied by using the pcm...
Page 754
Changes in user management settings do not cause an ied reboot. The pcm600 tool caches the login credentials after successful login for 15 minutes. During that time no more login will be necessary. The successfully activation of central account management will disable built-in users or remove all lo...
Page 755
Table 577: authority-related ied functions function description authority status athstat this function is an indication function block for user logon activity. User denied attempt to logon and user successful logon are reported. Authority check athchck to safeguard the interests of our customers, bo...
Page 756
21.3 ftp access with password ftpaccs 21.3.1 identification guid-c037d0b0-1aa0-4592-9293-92c7eded3261 v1 function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number ftp access with ssl ftpaccs - - 21.3.2 ftp access with tls, ftpaccs guid-9e64ea68-6fa9-4576-b5...
Page 757
21.4 authority status athstat 21.4.1 identification guid-79c63688-4d7d-4954-ac3c-b9484d084f6f v1 function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number authority status athstat - - 21.4.2 functionality semod158529-5 v6 authority status athstat function i...
Page 758
21.4.5 settings guid-ece18aa9-15cc-4522-aa31-78c4f0f052e4 v3 the function does not have any parameters available in local hmi or in protection and control ied manager (pcm600) 21.4.6 operation principle semod158543-4 v5 authority status (athstat) function informs about two events related to the ied ...
Page 759
21.5.3 signals ip9674-1 v2 pid-4077-outputsignals v6 table 581: interrsig output signals name type description fail boolean internal fail warning boolean internal warning tsyncerr boolean time synchronization error rtcerr boolean real time clock error disable boolean application disable 21.5.4 setti...
Page 760
Iec15000414-2-en.Vsdx iec15000414 v2 en-us figure 290: ied general status in local hm the self supervision records internal signal changes in an internal event list. A maximum of 40 internal events are stored in a first-in, first-out manner. Guid-b481701f-05b4-4b29-83d4-18f13886febe v1 en-us figure ...
Page 761
Individual error signals from i/o modules can be obtained from respective module in the signal matrix tool. Error signals from time synchronization can be obtained from the interrsig function block via two outputs tsyncerr and rtcerr . 21.5.5.1 internal signals m11401-173 v9 self supervision provide...
Page 762
Name of signal description displayed on local hmi as reasons for activation apperror runtime application error status runtime app error this signal will be active if one or more of the application threads are not in the state that runtime engine expects. The states can be created, initialized, runni...
Page 763
Card name of signal description displayed on local hmi as reasons for activation adm adm-error a/d module error status adm32 activated if the module has a hardware error. Oem oem-error optical ethernet module error status oem3nn activated if the module has a hardware error. N = slot number ldcm ldcm...
Page 764
21.6 changelock function chnglck guid-e8a1c33a-dd65-42b5-ba13-cfae40c2c9ad v2 21.6.1 functionality guid-00784fc0-b39d-462d-854b-aaf62626dd0a v3 change lock function chnglck is used to block further changes to the ied configuration and settings once the commissioning is complete. The purpose is to bl...
Page 765
The function, when activated, will still allow the following changes of the ied state that does not involve reconfiguring of the ied: • monitoring • reading events • resetting events • reading disturbance data • clear disturbances • reset leds • reset counters and other runtime component states • co...
Page 766
The denial of service functionality in fronstatus, schlcch and rchlcch measures the ied load from communication and, if necessary, limits it from jeopardizing the ied's control and protection functionality. The function has the following outputs: • rchlcch • linkaup and linkbup indicates the etherne...
Page 767
Section 22 basic ied functions 22.1 time synchronization timesynchgen ip1750-1 v2 22.1.1 functionality m11344-3 v10 the time synchronization source selector is used to select a common source of absolute time for the ied. For res670 as a phasor measurement unit (pmu) an accurate time synchronization ...
Page 768
Pid-6251-settings v1 table 587: timesynchgen non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description finesyncsource disabled gps irig-b gps+irig-b - - disabled fine time synchronization source syncmaster disabled sntp-server - - disabled activate iedas synchronization master app...
Page 769
Pid-3967-settings v7 table 590: dstbegin non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description monthinyear january february march april may june july august september october november december - - march month in year when daylight time starts dayinweek sunday monday tuesday we...
Page 770
Pid-3968-settings v7 table 591: dstend non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description monthinyear january february march april may june july august september october november december - - october month in year when daylight time ends dayinweek sunday monday tuesday wedn...
Page 771
Pid-4138-settings v5 table 592: timezone non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description timezone -12:00 -11:00 -10:00 -9:30 -9:00 -8:00 -7:00 -6:00 -5:00 -4:30 -4:00 -3:30 -3:00 -2:00 -1:00 0:00 1:00 2:00 3:00 3:30 4:00 4:30 5:00 5:30 5:45 6:00 6:30 7:00 8:00 8:45 9:00 ...
Page 772
Pid-5187-settings v5 table 593: irig-b non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description synchtype bnc opto - - opto type of synchronization timedomain localtime utc - - localtime time domain encoding irig-b 1344 1344tz - - irig-b type of encoding timezoneas1344 minustz pl...
Page 773
Sw time time regulator time tagging and general synchronization time regulator commu- nication events synchronization for differential protection (echo mode or gps) diff. Commu- nication *iec 61850-9-2 iec140000113-2-en.Vsdx external synchronization sources mergin units* gps irig-b off protection an...
Page 774
Been reached. The protection function is then enabled and the synchronization remains in fast mode or switches to slow mode depending on the setting. Synchronization principle m11346-83 v4 from a general point of view synchronization can be seen as a hierarchical structure. A function is synchronize...
Page 775
Power is off, the time in the ied may drift with maximum 0.5 second per day for two days, and after this the time will be lost. Real-time clock at startup m11346-63 v4 at ied startup, the internal time is free running. If the rtc is still alive since the last up time, the time in the ied will be acc...
Page 776
22.1.3.3 synchronization alternatives m11346-3 v7 three main alternatives of external synchronization sources are available. The ied also supports redundant time synchronization via both gps and irig-b. The synchronization message is applied: • via gps • via irig-b • via gps + irig-b synchronization...
Page 777
The tz offset supplied in the message equals utc at all times. For res670, optical irig-b 00x with ieee1344 support is recommended. Redundant time synchronization via both gps and irig-b guid-478abf9c-8315-49e5-bc91-8d93ce354a06 v1 in order to improve the time reliability of the pmu, time synchroniz...
Page 778
Predefined is meant that it is not mandatory to have a predefined synchronization tree, as the master (grand master) may shift. Consider instead ptp as a synchronization grouping, i.E. All devices connected to the ptp group will be synchronized to the same source or, if there is no external source t...
Page 779
To setup a ptp network with no obvious grand master, you simply connect the ieds to one network and configure ptp to be “on” on all ieds. On one ied, the one from which you want to set the time in the station, you set the priority2 to 127, instead of default 128. Now, this ied has higher priority th...
Page 780
22.2.2 function block ip9661-1 v1 m12010-3 v3 ansi05000433-2-en.Vsd activegroup actgrp1 actgrp2 actgrp3 actgrp4 actgrp5 actgrp6 grp1 grp2 grp3 grp4 grp5 grp6 grp_chgd ansi05000433 v2 en-us figure 295: activegroup function block 22.2.3 signals ip14073-1 v2 pid-6558-inputsignals v6 table 597: actvgrp ...
Page 781
22.2.4 settings ip11026-1 v2 pid-3572-settings v5 table 599: setgrps non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description activesetgrp settinggroup1 settinggroup2 settinggroup3 settinggroup4 settinggroup5 settinggroup6 - - settinggroup1 active setting group maxnosetgrp 1 - 6 ...
Page 782
Logical high. The setting changes over iec 61850 is enabled with the setting enablesettings in the iec 61850-8-1 configuration under main menu/configuration/ communication/station communication/iec 61850-8-1/iec 61850-8-1. Please refer to documentation for iec 61850 for further details. Switching ca...
Page 783
When leaving testmode, all blockings are removed (except for functions that have their block input active), and the ied resumes normal operation. However, if during testmode operation, power is removed and later restored, the ied will remain in testmode with the same protection functions blocked or ...
Page 784
22.3.4 settings ip11343-1 v2 pid-6730-settings v1 table 602: testmode non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description iedtestmode disabled enabled - - disabled activate ied test mode eventdisable disabled enabled - - disabled event disable during test mode blockallfunc d...
Page 785
Each of the functions includes the blocking from the testmode function block. The functions can also be blocked from sending events over iec 61850 station bus to prevent filling station and scada databases with test events, for example during a commissioning or maintenance test. 22.4 ied identifiers...
Page 786
22.5 product information prodinf guid-f67243ca-2429-4118-bbff-3d62bf55e080 v2 22.5.1 functionality guid-d78786e6-c34a-4e63-9d1e-0582c8f1f7e1 v8 product information contains unchangeable data that uniquely identifies the ied. Product information data is visible on the local hmi under main menu/ diagn...
Page 787
• describes the firmware version. • the firmware version can be checked from main menu/diagnostics/ied status/product identifiers • firmware version numbers run independently from the release production numbers. For every release number there can be one or more firmware versions depending on the sma...
Page 788
22.6.2 function block m15306-3 v3 iec05000434-2-en.Vsd smbi ^vin1 ^vin2 ^vin3 ^vin4 ^vin5 ^vin6 ^vin7 ^vin8 ^vin9 ^vin10 ^bi1 ^bi2 ^bi3 ^bi4 ^bi5 ^bi6 ^bi7 ^bi8 ^bi9 ^bi10 iec05000434 v2 en-us figure 298: smbi function block 22.6.3 signals semod55814-1 v2 pid-3940-inputsignals v5 table 604: smbi inp...
Page 789
Name type description bi8 boolean binary input 8 bi9 boolean binary input 9 bi10 boolean binary input 10 22.6.4 operation principle m15305-3 v5 the signal matrix for binary inputs (smbi) function , see figure 298 , receives its inputs from the real (hardware) binary inputs via the signal matrix tool...
Page 790
22.7.3 signals semod55887-1 v2 pid-3831-inputsignals v5 table 606: smbo input signals name type default description bo1 boolean 0 signal name for bo1 in signal matrix tool bo2 boolean 0 signal name for bo2 in signal matrix tool bo3 boolean 0 signal name for bo3 in signal matrix tool bo4 boolean 0 si...
Page 791
22.8.2 function block semod54866-4 v3 smmi ^ai1 ^ai2 ^ai3 ^ai4 ^ai5 ^ai6 ^ai1 ^ai2 ^ai3 ^ai4 ^ai5 ^ai6 iec05000440.Vsd iec05000440 v3 en-us figure 300: smmi function block 22.8.3 signals semod55924-1 v2 pid-3832-inputsignals v5 table 607: smmi input signals name type default description ai1 real 0 s...
Page 792
The outputs on smmi can also be connected to the iec 61850 generic communication i/o functions (mvgapc) for further use of the ma signals elsewhere in a substation system. 22.9 signal matrix for analog inputs smai semod55751-1 v2 22.9.1 functionality semod55744-4 v10 signal matrix for analog inputs ...
Page 793
Semod54997-4 v10 smai2 block revrot ^grp2_a ^grp2_b ^grp2_c ^grp2_n g2ai3p g2ai1 g2ai2 g2ai3 g2ai4 g2n ansi14000028-1-en.Vsd ansi14000028 v1 en-us figure 302: smai2 function block figure 302 is an example of smai2:n to smai12:m in each of the four task time groups 1, 2, 3 or 4 where: • n=2 and m=12 ...
Page 794
Name type description g1ai2 group signal group 1 analog input 2 g1ai3 group signal group 1 analog input 3 g1ai4 group signal group 1 analog input 4 g1n group signal group parameter for residual sample pid-3406-inputsignals v6 table 611: smai2 input signals name type default description block boolean...
Page 795
Pid-3405-settings v5 table 613: smai1 non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description globalbasesel 1 - 12 - 1 1 selection of one of the global base value groups dftrefextout internaldftref dftrefgrp1 dftrefgrp2 dftrefgrp3 dftrefgrp4 dftrefgrp5 dftrefgrp6 dftrefgrp7 dftr...
Page 796
Pid-3406-settings v5 table 615: smai2 non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description globalbasesel 1 - 12 - 1 1 selection of one of the global base value groups dftreference internaldftref dftrefgrp1 dftrefgrp2 dftrefgrp3 dftrefgrp4 dftrefgrp5 dftrefgrp6 dftrefgrp7 dftr...
Page 797
The output signal ai1 to ai4 are direct output of the, in smt, connected input to grpx_a, grpxb, grpxc and grpx_n, x=1-12. Ain is always calculated residual sum from the first three inputs. A3p is grouped, three-phase information containing all relevant information about four connected inputs. Note ...
Page 798
The same type of connection can be used but the smai connectiontype setting must still be ph-ph and this has to be accounted for when setting minvalfreqmeas. If smai setting connectiontype is ph-n and the same voltage is connected to all three smai inputs, the positive sequence voltage will be zero ...
Page 799
22.10.3 signals semod55989-1 v2 pid-6428-inputsignals v3 table 617: 3phsum input signals name type default description block boolean 0 block blkgr1 boolean 0 block input for group 1 blkgr2 boolean 0 block input for group 2 revrot boolean 0 reverse rotation g1ai3p group signal - group 1 three phase a...
Page 800
Pid-6428-settings v3 table 619: 3phsum non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description globalbasesel 1 - 12 - 1 1 selection of one of the global base value groups summationtype group1+group2 group1-group2 group2-group1 -(group1+group2) - - group1+group2 summation type df...
Page 801
22.11.2 functionality guid-d58eca9a-9771-443d-bf84-8ef582a346bf v4 global base values function (gbasval) is used to provide global values, common for all applicable functions within the ied. One set of global values consists of values for current, voltage and apparent power and it is possible to hav...
Page 802
22.12.3 settings pid-1626-settings v17 table 622: primval non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description frequency 50.0 - 60.0 hz 10.0 50.0 rated system frequency phaserotation normal=abc inverse=acb - - normal=abc system phase rotation section 22 1mrk 511 408-uus a bas...
Page 803
Section 23 ied hardware 23.1 overview ip14270-1 v1 23.1.1 variants of case size with local hmi display m15024-3 v5 ansi04000458-2-en.Psd ansi04000458 v2 en-us figure 305: 1/2 19” case with local hmi display. 1mrk 511 408-uus a section 23 ied hardware phasor measurement unit res670 2.2 ansi 797 techn...
Page 804
Ansi05000762-2-en.Psd ansi05000762 v2 en-us figure 306: 3/4 19” case with local hmi display. Ansi04000460 -2-en.Psd ansi04000460 v2 en-us figure 307: 1/1 19” case with local hmi display. Section 23 1mrk 511 408-uus a ied hardware 798 phasor measurement unit res670 2.2 ansi technical manual.
Page 805
23.1.2 case from the rear side ip16286-1 v1 m16105-3 v8 table 623: designations for 1/2 x 19” casing with 1 trm slot 1mrk002801-ac-2-670-1.2-pg v.3 en 1mrk002801-ac-2-670-1.2-pg v4 en-us rear position module x11 psm x31 and x32 etc. To x51 and x52 bim, bom, som, iom or mim x301, x302, x303, x304 sfp...
Page 806
Semod111882-4 v7 table 624: designations for 3/4 x 19” casing with 1 trm slot 1mrk002801-ac-3-670-1.2-pg v4 en-us rear position module x11 psm x31 and x32 etc. To x101 and x102 bim, bom, som, iom or mim x301, x302, x303, x304 sfp x305 ldcm x306 ldcm or oem x3061, x3062 sfp if oem is selected x311: a...
Page 807
Semod111884-4 v6 table 625: designations for 3/4 x 19” casing with 2 trm slot 1mrk002801-ac-4-670-1.2-pg v.3 en 1mrk002801-ac-4-670-1.2-pg v4 en-us rear position module x11 psm x31 and x32 etc. To x71 and x72 bim, bom, som, iom or mim x301. X302, x303, x304 sfp x305 ldcm x306 ldcm or oem x3061, x306...
Page 808
M16106-3 v8 table 626: designations for 1/1 x 19” casing with 1 trm slot 1mrk002801-ac-5-670-1.2-pg v.3 en 1mrk002801-ac-5-670-1.2-pg v4 en-us rear position module x11 psm x31 and x32 etc. To x161 and x162 bim, bom, som, iom or mim x301, x302, x303, x304 sfp x305 ldcm x306 ldcm or oem x3061, x3062 s...
Page 809
M16108-3 v9 table 627: designations for 1/1 x 19” casing with 2 trm slots 1mrk002801-ac-6-670-1.2-pg v.3 en 1mrk002801-ac-6-670-1.2-pg v4 en-us rear position module x11 psm x31 and x32 etc. To x131 and x132 bim, bom, som, iom or mim x301, x302, x303, x304 sfp x305 ldcm x306 ldcm or oem x3061, x3062 ...
Page 810
23.2 hardware modules ip14529-1 v1 23.2.1 overview m11562-3 v9 table 628: basic modules module description power supply module (psm) including a regulated dc/dc converter that supplies auxiliary voltage to all static circuits. • an internal fail alarm output is available. Numerical module (num) modu...
Page 811
Module description ma input module (mim) analog input module with 6 independent, galvanically separated channels gps time synchronization module (gtm) used to provide the ied with gps time synchronization and pulse per second (pps) output static output module (som) module with 6 fast static outputs ...
Page 812
The num is equipped with a real time clock. It uses a capacitor to keep track of the time when the ied is not energized. The num is passively cooled, which is possible due to its low power dissipation. 23.2.2.3 technical data semod55319-1 v1 semod55310-2 v11 table 630: sfp - optical ethernet port qu...
Page 813
23.2.3 power supply module (psm) ip15594-1 v1 23.2.3.1 introduction m11595-3 v6 the power supply module is used to provide the correct internal voltages and full isolation between the ied and the battery system. An internal fail alarm output is available. Alternative connectors of ring lug or compre...
Page 814
23.2.4 local human-machine interface (local hmi) semod56218-5 v4 refer to section local hmi for information. 23.2.5 transformer input module (trm) ip15581-1 v1 23.2.5.1 introduction m14875-3 v9 the transformer input module is used to galvanically separate and adapt the secondary currents and voltage...
Page 815
Ansi08000479 v1 en-us figure 309: trm connection diagram 23.2.5.3 technical data semod55412-1 v1 m16988-1 v11 table 634: trm - energizing quantities, rated values and limits for protection transformer description value frequency rated frequency f r 50/60 hz operating range f r ± 10% current inputs r...
Page 816
Description value dynamic withstand 250 × i r one half wave burden r = 1 a r = 5 a *) max. 350 a for 1 s when combitest test switch is included. Voltage inputs **) rated voltage u r 110 or 220 v operating range 0 - 340 v thermal withstand 450 v for 10 s 420 v continuously burden **) all values for i...
Page 817
23.2.6 analog digital conversion module (adm) ip14285-1 v2 23.2.6.1 introduction m13664-3 v5 the analog digital conversion module (adm) has 12 analog inputs, two pc-mip slots and one pmc slot. Pc-mip slots are used for pc-mip cards, and pmc slot is used for pmc cards as described in table 636 . The ...
Page 818
Pmc pci to pci pc-mip pc-mip ad3 ad1 ad2 ad4 channel 1 channel 2 channel 3 channel 4 channel 5 channel 6 channel 7 channel 8 channel 9 channel 10 channel 11 channel 12 1.2v 2.5v level shift en05000474.Vsd iec05000474 v1 en-us figure 310: the adm layout section 23 1mrk 511 408-uus a ied hardware 812 ...
Page 819
23.2.7 binary input module (bim) ip14535-1 v1 23.2.7.1 introduction m1769-3 v4 the binary input module has 16 optically isolated inputs and is available in two versions, one standard and one with enhanced pulse counting capabilities on the inputs to be used with the pulse counter function. The binar...
Page 820
300 176 144 88 72 38 32 19 17 24/30v 48/60v 110/125v 220/250v [v] xx99000517-2_ansi.Vsd ansi99000517 v2 en-us figure 311: voltage dependence for the binary inputs iec99000517-abc v1 en-us operation operation uncertain no operation this binary input module communicates with the numerical module (num)...
Page 821
En07000104-3.Vsd 50 55 [ms] [ma] iec07000104 v3 en-us figure 312: approximate binary input inrush current for the standard version of bim. En07000105-1.Vsd 50 5.5 [ms] [ma] iec07000105 v2 en-us figure 313: approximate binary input inrush current for the bim version with enhanced pulse counting capab...
Page 822
Iec99000503 v3 en-us figure 314: connection diagram 23.2.7.3 signals pid-6435-outputsignals v5 table 637: bim output signals name type description status boolean binary input module status bi1 boolean binary input 1 value bi2 boolean binary input 2 value bi3 boolean binary input 3 value table contin...
Page 823
Name type description bi4 boolean binary input 4 value bi5 boolean binary input 5 value bi6 boolean binary input 6 value bi7 boolean binary input 7 value bi8 boolean binary input 8 value bi9 boolean binary input 9 value bi10 boolean binary input 10 value bi11 boolean binary input 11 value bi12 boole...
Page 824
23.2.7.6 technical data semod55338-1 v1 m12576-1 v9 table 640: bim - binary input module quantity rated value nominal range binary inputs 16 - dc voltage, rl 24/30 v 48/60 v 125 v 220/250 v rl ±20% rl ±20% rl ±20% rl ±20% power consumption 24/30 v, 50 ma 48/60 v, 50 ma 125 v, 50 ma 220/250 v, 50 ma ...
Page 825
Maximum 176 binary input channels may be activated simultaneously with influencing factors within nominal range. 23.2.8 binary output modules (bom) ip14536-1 v1 23.2.8.1 introduction m6938-3 v4 the binary output module has 24 independent output relays and is used for trip output or any signaling pur...
Page 826
Ansi_xx00000299.Vsd 2 1 3 output module ansi00000299 v1 en-us figure 315: relay pair example 1 output connection from relay 1 2 output signal power source connection 3 output connection from relay 2 section 23 1mrk 511 408-uus a ied hardware 820 phasor measurement unit res670 2.2 ansi technical manu...
Page 827
Iec99000505 v3 en-us figure 316: connection diagram 23.2.8.3 signals pid-3439-inputsignals v2 table 642: bom input signals name type default description block boolean 0 block binary outputs bo1 boolean 0 binary output 1 bo2 boolean 0 binary output 2 bo3 boolean 0 binary output 3 bo4 boolean 0 binary...
Page 828
Name type default description bo9 boolean 0 binary output 9 bo10 boolean 0 binary output 10 bo11 boolean 0 binary output 11 bo12 boolean 0 binary output 12 bo13 boolean 0 binary output 13 bo14 boolean 0 binary output 14 bo15 boolean 0 binary output 15 bo16 boolean 0 binary output 16 bo17 boolean 0 b...
Page 829
23.2.8.5 monitored data pid-3439-monitoreddata v2 table 645: bom monitored data name type values (range) unit description status boolean 0=ok 1=error - binary output part of iom module status bo1value boolean 1=1 0=0 - binary output 1 value bo1force boolean 0=normal 1=forced - binary output 1 force ...
Page 830
Name type values (range) unit description bo6 boolean 0=normal 1=forced 2=blocked - binary output 6 status bo7value boolean 1=1 0=0 - binary output 7 value bo7force boolean 0=normal 1=forced - binary output 7 force bo7 boolean 0=normal 1=forced 2=blocked - binary output 7 status bo8value boolean 1=1...
Page 831
Name type values (range) unit description bo13force boolean 0=normal 1=forced - binary output 13 force bo13 boolean 0=normal 1=forced 2=blocked - binary output 13 status bo14value boolean 1=1 0=0 - binary output 14 value bo14force boolean 0=normal 1=forced - binary output 14 force bo14 boolean 0=nor...
Page 832
Name type values (range) unit description bo20value boolean 1=1 0=0 - binary output 20 value bo20force boolean 0=normal 1=forced - binary output 20 force bo20 boolean 0=normal 1=forced 2=blocked - binary output 20 status bo21value boolean 1=1 0=0 - binary output 21 value bo21force boolean 0=normal 1...
Page 833
Function or quantity trip and signal relays current carrying capacity per relay, continuous per relay, 1 s per process connector pin, continuous 8 a 10 a 12 a making capacity at inductive load with l/r > 10 ms 0.2 s 1.0 s 30 a 10 a breaking capacity for ac, cos j > 0.4 250 v/8.0 a breaking capacity ...
Page 834
• can-bus to backplane cbm • io-connectors to binary outputs (2 pcs.) the following parts are supervised: • interruption in relay coil • short circuit of relay coil • driver failure z iec09000974-1-en.Vsd iec09000974 v1 en-us figure 317: som static output principle 1mrk002802-ab-13-670-1.2-pg-ansi v...
Page 835
Name type default description bo4 boolean 0 binary output 4 bo5 boolean 0 binary output 5 bo6 boolean 0 binary output 6 bo7 boolean 0 static binary output 7 bo8 boolean 0 static binary output 8 bo9 boolean 0 static binary output 9 bo10 boolean 0 static binary output 10 bo11 boolean 0 static binary o...
Page 836
Name type values (range) unit description bo2force boolean 0=normal 1=forced - binary output 2 force bo2 boolean 0=normal 1=forced 2=blocked - binary output 2 status bo3value boolean 1=1 0=0 - binary output 3 value bo3force boolean 0=normal 1=forced - binary output 3 force bo3 boolean 0=normal 1=for...
Page 837
Name type values (range) unit description bo9value boolean 1=1 0=0 - binary output 9 value bo9force boolean 0=normal 1=forced - binary output 9 force bo9 boolean 0=normal 1=forced 2=blocked - binary output 9 status bo10value boolean 1=1 0=0 - binary output 10 value bo10force boolean 0=normal 1=force...
Page 838
Function of quantity static binary output trip making capacity at capacitive load with the maximum capacitance of 0.2 μf : 0.2 s 30 a 30 a 1.0 s 10 a 10 a breaking capacity for dc with l/r ≤ 40 ms 48 v/1 a 110 v/0.4 a 60 v/0.75 a 125 v/0.35 a 220 v/0.2 a 250 v/0.15 a operating time table 652: som - ...
Page 839
Relays per bom/iom/som should be activated continuously due to power dissipation. 23.2.10 binary input/output module (iom) ip15582-1 v1 23.2.10.1 introduction m6939-3 v6 the binary input/output module is used when only a few input and output channels are needed. The ten standard output channels are ...
Page 840
Xx04000069.Vsd iec04000069 v1 en-us figure 319: iom with mov protection, relay example 23.2.10.3 signals pid-6434-outputsignals v4 table 653: iomin output signals name type description status boolean binary input part of iom module status bi1 boolean binary input 1 value bi2 boolean binary input 2 v...
Page 841
Name type default description bo9 boolean 0 binary output 9 bo10 boolean 0 binary output 10 bo11 boolean 0 binary output 11 bo12 boolean 0 binary output 12 23.2.10.4 settings pid-4050-settings v2 table 655: iomin non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description operation ...
Page 842
Name type values (range) unit description bo2 boolean 0=normal 1=forced 2=blocked - binary output 2 status bo3value boolean 1=1 0=0 - binary output 3 value bo3force boolean 0=normal 1=forced - binary output 3 force bo3 boolean 0=normal 1=forced 2=blocked - binary output 3 status bo4value boolean 1=1...
Page 843
Name type values (range) unit description bo9force boolean 0=normal 1=forced - binary output 9 force bo9 boolean 0=normal 1=forced 2=blocked - binary output 9 status bo10value boolean 1=1 0=0 - binary output 10 value bo10force boolean 0=normal 1=forced - binary output 10 force bo10 boolean 0=normal ...
Page 844
Maximum 176 binary input channels may be activated simultaneously with influencing factors within nominal range. M12318-1 v8 table 659: iom - binary input/output module contact data (reference standard: iec 61810-2) function or quantity trip and signal relays fast signal relays (parallel reed relay)...
Page 845
M12584-1 v7 table 660: iom with mov and iom 220/250 v, 110ma - contact data (reference standard: iec 61810-2) function or quantity trip and signal relays fast signal relays (parallel reed relay) binary outputs iom: 10 iom: 2 max system voltage 250 v ac, dc 250 v dc test voltage across open contact, ...
Page 846
23.2.11 ma input module (mim) ip14537-1 v1 23.2.11.1 introduction m15020-3 v4 the milli-ampere input module is used to interface transducer signals in the –20 to +20 ma range from for example oltc position, temperature or pressure transducers. The module has six independent, galvanically separated c...
Page 847
M6380-35 v3 iec99000504 v2 en-us figure 320: mim connection diagram 1mrk 511 408-uus a section 23 ied hardware phasor measurement unit res670 2.2 ansi 841 technical manual.
Page 848
23.2.11.3 signals pid-4110-outputsignals v5 table 661: mim output signals name type description status boolean milliampere input module status ch1 real analog input 1 ch2 real analog input 2 ch3 real analog input 3 ch4 real analog input 4 ch5 real analog input 5 ch6 real analog input 6 23.2.11.4 set...
Page 849
Name values (range) unit step default description valuemaxch2 -10000000000.000 - 10000000000.000 - 0.001 20.000 max primary value corr. To imaxch2 endeadbandch3 disabled enabled - - disabled enable amplitude deadband reporting for channel 3 deadbandch3 0.00 - 20.00 ma 0.01 1.00 deadband amplitude fo...
Page 850
Name values (range) unit step default description imaxch6 -25.00 - 25.00 ma 0.01 20.00 max current of transducer for channel 6 valueminch6 -10000000000.000 - 10000000000.000 - 0.001 4.000 min primary value corr. To iminch6 valuemaxch6 -10000000000.000 - 10000000000.000 - 0.001 20.000 max primary val...
Page 851
23.2.12 galvanic rs485 communication module semod174899-1 v1 23.2.12.1 introduction semod158664-5 v3 the galvanic rs485 communication module (rs485) is used for dnp3.0 and iec 60870-5-103 communication. The module has one rs485 communication port. The rs485 is a balanced serial communication that ca...
Page 852
Screw terminal x3 1 2 1 2 3 4 5 6 screw terminal x1 backplane angle bracket rs485 pwb iec06000517 v1 en-us figure 321: rs485 connector • 2-wire: connect pin 1 to pin 6 and pin 2 to pin 5 • termination (2-wire): connect pin 1 to pin 3 • termination (4-wire): connect pin 1 to pin 3 and pin 4 to pin 6 ...
Page 853
23.2.13 optical ethernet module 23.2.13.1 introduction m16073-3 v7 the optical ethernet module (oem) provides two additional optical ethernet ports. The port connectors are of lc type. 23.2.13.2 functionality m14948-3 v5 the functionality of the sfp cages on the optical ethernet module (oem) is the ...
Page 854
23.2.14 gps time synchronization module (gtm) ip15586-1 v2 23.2.14.1 introduction m14851-3 v4 this module includes a gps receiver used for time synchronization. The gps has one sma contact for connection to an antenna. It also includes an optical pps st- connector output. 23.2.14.2 design m14856-3 v...
Page 855
23.2.15 gps antenna semod55676-1 v1 23.2.15.1 introduction semod55674-5 v4 in order to receive gps signals from the satellites orbiting the earth a gps antenna with applicable cable must be used. 23.2.15.2 design semod55680-1 v1 semod55682-4 v4 the antenna with a console for mounting on a horizontal...
Page 856
Antenna cable semod55682-28 v4 use a 50 ohm coaxial cable with a male tnc connector in the antenna end and a male sma connector in the receiver end to connect the antenna to gtm. Choose cable type and length so that the total attenuation is max. 26 db at 1.6 ghz. Make sure that the antenna cable is ...
Page 857
Optical pulse-width modulated signal (irig-b 00x). The irig-b module is mounted as a mezzanine card on the analog digital conversion module (adm). St y2 t a1 iec06000304=1=en=original.Ai iec06000304 v2 en-us figure 324: irig-b pc-mip board with top left st connector for optical irig-b 00x 820 nm mul...
Page 858
23.2.16.4 technical data semod141132-1 v1 semod141136-2 v8 table 672: irig-b quantity rated value number of channels irig-b 1 number of optical channels 1 electrical connector: electrical connector irig-b bnc pulse-width modulated 5 vpp amplitude modulated – low level – high level 1-3 vpp 3 x low le...
Page 859
23.3 dimensions ip11490-1 v3 23.3.1 case with rear cover semod53199-1 v1 m11985-110 v4 c b d e a iec08000163-2-en.Vsd iec08000163 v2 en-us figure 325: case with rear cover 1mrk 511 408-uus a section 23 ied hardware phasor measurement unit res670 2.2 ansi 853 technical manual.
Page 860
Iec08000165-2-en.Vsdx j g f k h iec08000165 v2 en-us figure 326: case with rear cover and 19” rack mounting kit iec05000503-2-en.Vsd iec05000503 v2 en-us figure 327: rear cover case with details m11985-120 v4 case size (inches) a b c d e f g h j k 6u, 1/2 x 19” 10.47 8.81 9.53 10.07 8.10 7.50 8.02 1...
Page 861
23.3.2 case without rear cover semod53195-1 v1 m2152-3 v5 c b d e a iec08000164-3-en.Vsdx iec08000164 v3 en-us figure 328: case without rear cover 1mrk 511 408-uus a section 23 ied hardware phasor measurement unit res670 2.2 ansi 855 technical manual.
Page 862
Iec08000166-2-en.Vsdx j g f k h iec08000166 v2 en-us figure 329: case without rear cover with 19” rack mounting kit m2152-11 v4 case size (inches) a b c d e f g h j k 6u, 1/2 x 19” 10.5 8.81 8.03 9.83 8.10 7.50 8.03 9.53 7.43 10.20 6u, 3/4 x 19” 10.5 13.23 8.03 9.83 12.51 7.50 12.44 13.95 7.43 14.61...
Page 863
23.3.3 flush mounting dimensions m11571-3 v6 c a iec04000465-3-en.Vsd b e d iec04000465 v3 en-us figure 330: flush mounting case size tolerance cut-out dimensions (inches) a +/0.04 b +/0.04 c d 6u, 1/2 x 19” 8.27 10.01 0.16–0.39 0.53 6u, 3/4 x 19” 12.69 10.01 0.16–0.39 0.53 6u, 1/1 x 19” 17.11 10.01...
Page 864
23.3.4 side-by-side flush mounting dimensions m11984-3 v6 iec06000182-2-en.Vsd iec06000182 v2 en-us figure 331: a 1/2 x 19” size ied side-by-side with rhgs6 xx05000505.Vsd b a c g d e f iec05000505 v1 en-us figure 332: panel-cut out dimensions for side-by-side flush mounting section 23 1mrk 511 408-...
Page 865
Case size (inches) tolerance a ±0.04 b ±0.04 c ±0.04 d ±0.04 e ±0.04 f ±0.04 g ±0.04 6u, 1/2 x 19” 8.42 10.21 9.46 7.50 1.35 0.52 0.25 diam 6u, 3/4 x 19” 12.85 10.21 13.89 7.50 1.35 0.52 0.25 diam 6u, 1/1 x 19” 17.27 10.21 18.31 7.50 1.35 0.52 0.25 diam 23.3.5 wall mounting dimensions m11569-3 v4 ie...
Page 866
23.4 mounting alternatives ip11721-1 v1 23.4.1 flush mounting ip10303-1 v1 23.4.1.1 overview m11967-3 v5 the flush mounting kit can be used for case sizes: • 1/2 x 19” • 3/4 x 19” • 1/1 x 19” • 1/4 x 19” (rhgs6 6u) only a single case can be mounted in each cut-out on the cubicle panel, for class ip5...
Page 867
23.4.1.2 mounting procedure for flush mounting m11942-2 v5 1 5 6 3 iec16000080=1=en.Vsd 2 4 iec16000080 v1 en-us figure 334: flush mounting details. Posno description quantity type 1 sealing strip, used to obtain ip54 class. The sealing strip is factory mounted between the case and front plate. - - ...
Page 868
A separately ordered rack mounting kit for side-by-side mounted ieds or ieds together with rhgs cases should be selected so that the total size equals 19”. Use only the screws included in the mounting kit when mounting the plates and the angles on the ied. Screws with wrong dimension may damage the ...
Page 869
23.4.2.2 mounting procedure for 19” panel rack mounting m11948-2 v6 1a iec08000160-3-en.Vsdx 1a 2 3 iec08000160 v3 en-us figure 335: 19” panel rack mounting details the required torque for the screws is 3.5 nm. 1mrk 511 408-uus a section 23 ied hardware phasor measurement unit res670 2.2 ansi 863 te...
Page 870
Posno description quantity type 1a, 1b mounting angles, can be mounted either to the left or the right side of the case 2 - 2 screw 8 m4x6 3 washer 8 m4x6 23.4.3 wall mounting ip10316-1 v1 23.4.3.1 overview m11973-3 v6 all case sizes, 1/2 x 19”, 3/4 x 19”,1/1 x 19”, can be wall mounted. It is also p...
Page 871
23.4.3.2 mounting procedure for wall mounting m11949-2 v2 iec130 00266-1-en.Vsd 1 2 3 4 5 6 iec13000266 v1 en-us figure 336: wall mounting details. Posno description quantity type 1 bushing 4 - 2 screw 8 m4x10 3 screw 4 m6x12 or corresponding 4 mounting bar 2 - 5 screw 6 m5x8 6 side plate 2 - 23.4.3...
Page 872
To reach the rear side of the ied, a free space of 3.2 inches is required on the unhinged side. 3.2" view from above 1 ansi_en06000135.Vsd 3 2 (80 mm) ansi06000135 v1 en-us figure 337: how to reach the connectors on the rear side of the ied. Posno description type 1 screw m4x10 2 screw m5x8 3 rear p...
Page 873
23.4.4.2 mounting procedure for side-by-side rack mounting m11955-2 v3 iec040004563enoriginal.Vsdx 1 2 3 4 3 iec04000456 v3 en-us figure 338: side-by-side rack mounting details. The required torque for the screws is 3.5 nm. Posno description quantity type 1 mounting plate 2 - 2, 3 screw 16 m4x6 4 mo...
Page 874
8 8 8 7 5 6 3 4 2 7 5 6 7 5 6 3 4 2 3 4 2 1 1 2 1 1 1 8 7 5 6 3 4 2 2 1 iec06000180-2-en.Vsd iec06000180 v2 en-us figure 339: ied (1/2 x 19”) mounted with a rhgs6 case containing a test switch module equipped with only a test switch and a rx2 terminal base 23.4.5 side-by-side flush mounting ip10329-...
Page 875
Please contact factory for special add on plates for mounting ft switches on the side (for 1/2 19" case) or bottom of the relay. 23.4.5.2 mounting procedure for side-by-side flush mounting m12730-6 v4 1 2 3 4 iec06000181-2-en.Vsd iec06000181 v2 en-us figure 340: side-by-side flush mounting details (...
Page 876
23.5 technical data ip16276-1 v1 23.5.1 enclosure ip16278-1 v1 m11778-1 v6 table 673: case material steel sheet front plate stainless steel with cut-out for hmi surface treatment aluzink preplated steel finish light grey (ral 7035) m12327-1 v4 table 674: water and dust protection level according to ...
Page 877
23.5.3 connection system semod53371-1 v1 semod53376-2 v6 table 677: ct and vt circuit connectors connector type rated voltage and current maximum conductor area screw compression type 250 v ac, 20 a 4 mm 2 (awg12) 2 x 2.5 mm 2 (2 x awg14) terminal blocks suitable for ring lug terminals 250 v ac, 20 ...
Page 878
Table 680: auxiliary dc supply voltage influence on functionality during operation dependence on reference value within nominal range influence ripple, in dc auxiliary voltage operative range max. 2% full wave rectified 15% of el 0.01%/% auxiliary voltage dependence, operate value ±20% of el 0.01%/%...
Page 879
Test type test values reference standards surge immunity test 2-4 kv, 1.2/50 ms high energy iec 60255-26, zone a power frequency immunity test 150-300 v iec 60255-26, zone a conducted common mode immunity test 15 hz-150 khz iec 61000-4-16, class iv power frequency magnetic field test 1000 a/m, 3 s 1...
Page 880
Table 685: ce compliance test according to immunity en 60255–26 emissivity en 60255–26 low voltage directive en 60255–27 table 686: mechanical tests test type test values reference standards vibration response test class ii iec 60255-21-1 vibration endurance test class i iec 60255-21-1 shock respons...
Page 881
Section 24 labels 24.1 labels on ied semod168249-4 v4 front view of ied 10 9 8 7 7 6 6 5 1 2 3 4 11 =iec15000506=2=en=original.Vsdx iec15000506 v2 en-us figure 341: example of ied label 1 qr-code containing the complete ordering code 2 power supply module (psm) 3 ma input module (mim) 4 ordering and...
Page 882
11 product type rear view of ied iec06000573=2=en=original.Wsdx 1 2 2 3 iec06000573 v2 en-us 1 warning label 2 caution label 3 class 1 laser product label it is used when an optical sfp or an mr/lr ldcm is configured in the product. Iec06000575 v1 en-us section 24 1mrk 511 408-uus a labels 876 phaso...
Page 883
Section 25 connection diagrams guid-cf4effa5-3081-4fc7-9a14-ed127c3c0fde v6 the connection diagrams are delivered in the ied connectivity package as part of the product delivery. The latest versions of the connection diagrams can be downloaded from http://www.Abb.Com/protection-control . Connection ...
Page 884
878.
Page 885
Section 26 inverse time characteristics 26.1 application m16686-3 v5 in order to assure time selectivity between different overcurrent protections at different points in the network different time delays for the different protections are normally used. The simplest way to do this is to use definite ...
Page 886
En05000131.Vsd time fault point position iec05000131 v1 en-us figure 344: inverse time overcurrent characteristics with inst. Function the inverse time characteristic makes it possible to minimize the fault clearance time and still assure the selectivity between protections. To assure selectivity be...
Page 887
En05000132_ansi.Vsd 51 51 a1 b1 feeder time axis t=0 t=t 1 t=t 2 t=t 3 ansi05000132 v1 en-us figure 345: selectivity steps for a fault on feeder b1 where: t=0 is the fault occurs t=t 1 is protection b1 trips t=t 2 is breaker at b1 opens t=t 3 is protection a1 resets in the case protection b1 shall t...
Page 888
• if there is a risk of intermittent faults. If the current ied, close to the faults, picks up and resets there is a risk of unselective trip from other protections in the system. • delayed resetting could give accelerated fault clearance in case of automatic reclosing to a permanent fault. • overcu...
Page 889
[ ] = × - + æ ö ç ÷ ç ÷ ç ÷ æ ö ç ÷ ç ÷ ç ÷ è ø è ø p a t td i c pickupn s b equation1640 v1 en-us (equation 87) where: p, a, b, c are constants defined for each curve type, pickupn is the set pickup current for step n, td is set time multiplier for step n and i is the measured current. For inverse ...
Page 890
( ) = d × - ³ × æ ö æ ö ç ÷ ç ÷ ç ÷ è ø è ø å 1 p n j i j t c a td pickupn equation1644 v1 en-us (equation 90) where: j = 1 is the first protection execution cycle when a fault has been detected, that is, when > 1 i pickupn equation1646 v1 en-us d t is the time interval between two consecutive execu...
Page 891
Iec05000133-3-en.Vsd tmin current operate time imin iec05000133 v2 en-us figure 346: minimum time-lag operation for the iec curves in order to fully comply with iec curves definition setting parameter tmin shall be set to the value which is equal to the operating time of the selected iec inverse tim...
Page 892
The rd inverse curve gives a logarithmic delay, as used in the combiflex protection rxidg. The curve enables a high degree of selectivity required for sensitive residual ground-fault current protection, with ability to detect high-resistive ground faults. The curve is described by equation 92 : [ ] ...
Page 893
[ ] 2 1 r t t s td i pickupn = × - æ ö ç ÷ ç ÷ ç ÷ æ ö ç ç ÷ ÷ è è ø ø ansiequation1197 v1 en-us (equation 94) where: the set value t r is the reset time in case of zero current after fault clearance. The possibility of choice of reset characteristics is to some extent dependent of the choice of tim...
Page 894
Definite time delay. Thus, if only the inverse time delay is required, it is important to set the definite time delay for that stage to zero. 26.3 inverse characteristics ip15797-1 v2 m12388-1 v21 table 687: ansi inverse time characteristics function range or value accuracy operating characteristic:...
Page 895
Table 688: iec inverse time characteristics function range or value accuracy operating characteristic: ( ) = × - æ ö ç ÷ ç ÷ è ø 1 p a t td i equation1653 v1 en-us i = i measured /i set 0.10 ≤ td ≤ 3.00 1.5 x i set ≤ i ≤ 20 x i set iec 60255-151, ±2.0% or ±40 ms whichever is greater iec normal inver...
Page 896
Guid-19f8e187-4ed0-48c3-92f6-0d9eaa2b39bb v3 table 690: ansi inverse time characteristics for sensitive directional residual overcurrent and power protection function range or value accuracy operating characteristic: ( ) = + × - æ ö ç ÷ ç ÷ è ø 1 p a t b td i equation1651 v1 en-us reset characterist...
Page 897
Table 691: iec inverse time characteristics for sensitive directional residual overcurrent and power protection function range or value accuracy operating characteristic: ( ) = × - æ ö ç ÷ ç ÷ è ø 1 p a t td i equation1653 v1 en-us i = i measured /i set 0.10 ≤ k ≤ 2.00 1.5 x i set ≤ i ≤ 20 x i set i...
Page 898
Table 692: ri and rd type inverse time characteristics for sensitive directional residual overcurrent and power protection function range or value accuracy ri type inverse characteristic = × - 1 0.236 0.339 t td i equation1656 v1 en-us i = i measured /i set 0.10 ≤ k ≤ 2.00 1.5 x i set ≤ i ≤ 20 x i s...
Page 899
Table 694: iec inverse time characteristics for voltage restrained time overcurrent protection function range or value accuracy operating characteristic: ( ) = × - æ ö ç ÷ ç ÷ è ø 1 p a t td i equation1653 v1 en-us i = i measured /i set td = (0.05-2.00) in steps of 0.01 iec 60255-151, ±5.0% or ±40 m...
Page 900
Semod116978-2 v10 table 695: inverse time characteristics for overvoltage protection function range or value accuracy type a curve: = - æ ö ç ÷ è ø t td v vpickup vpickup equation1661 v1 en-us v = v measured td = (0.05-1.10) in steps of 0.01 ±5.0% or ±45 ms whichever is greater type b curve: 32 0.5 ...
Page 901
Table 696: inverse time characteristics for undervoltage protection function range or value accuracy type a curve: = - æ ö ç ÷ è ø td t vpickup v vpickup equation1658 v1 en-us v = v measured td = (0.05-1.10) in steps of 0.01 ±5.0% or ±45 ms whichever is greater type b curve: × = + - × - æ ö ç ÷ è ø ...
Page 902
Table 697: inverse time characteristics for residual overvoltage protection function range or value accuracy type a curve: = - æ ö ç ÷ è ø t td v vpickup vpickup equation1661 v1 en-us v = v measured td = (0.05-1.10) in steps of 0.01 ±5.0% or ±45 ms whichever is greater type b curve: 32 0.5 = ⋅ − ⋅ −...
Page 903
Semod118114-4 v4 a070750 v2 en-us figure 347: ansi extremely inverse time characteristics 1mrk 511 408-uus a section 26 inverse time characteristics phasor measurement unit res670 2.2 ansi 897 technical manual.
Page 904
A070751 v2 en-us figure 348: ansi very inverse time characteristics section 26 1mrk 511 408-uus a inverse time characteristics 898 phasor measurement unit res670 2.2 ansi technical manual.
Page 905
A070752 v2 en-us figure 349: ansi normal inverse time characteristics 1mrk 511 408-uus a section 26 inverse time characteristics phasor measurement unit res670 2.2 ansi 899 technical manual.
Page 906
A070753 v2 en-us figure 350: ansi moderately inverse time characteristics section 26 1mrk 511 408-uus a inverse time characteristics 900 phasor measurement unit res670 2.2 ansi technical manual.
Page 907
A070817 v2 en-us figure 351: ansi long time extremely inverse time characteristics 1mrk 511 408-uus a section 26 inverse time characteristics phasor measurement unit res670 2.2 ansi 901 technical manual.
Page 908
A070818 v2 en-us figure 352: ansi long time very inverse time characteristics section 26 1mrk 511 408-uus a inverse time characteristics 902 phasor measurement unit res670 2.2 ansi technical manual.
Page 909
A070819 v2 en-us figure 353: ansi long time inverse time characteristics 1mrk 511 408-uus a section 26 inverse time characteristics phasor measurement unit res670 2.2 ansi 903 technical manual.
Page 910
A070820 v2 en-us figure 354: iec normal inverse time characteristics section 26 1mrk 511 408-uus a inverse time characteristics 904 phasor measurement unit res670 2.2 ansi technical manual.
Page 911
A070821 v2 en-us figure 355: iec very inverse time characteristics 1mrk 511 408-uus a section 26 inverse time characteristics phasor measurement unit res670 2.2 ansi 905 technical manual.
Page 912
A070822 v2 en-us figure 356: iec inverse time characteristics section 26 1mrk 511 408-uus a inverse time characteristics 906 phasor measurement unit res670 2.2 ansi technical manual.
Page 913
A070823 v2 en-us figure 357: iec extremely inverse time characteristics 1mrk 511 408-uus a section 26 inverse time characteristics phasor measurement unit res670 2.2 ansi 907 technical manual.
Page 914
A070824 v2 en-us figure 358: iec short time inverse time characteristics section 26 1mrk 511 408-uus a inverse time characteristics 908 phasor measurement unit res670 2.2 ansi technical manual.
Page 915
A070825 v2 en-us figure 359: iec long time inverse time characteristics 1mrk 511 408-uus a section 26 inverse time characteristics phasor measurement unit res670 2.2 ansi 909 technical manual.
Page 916
A070826 v2 en-us figure 360: ri-type inverse time characteristics section 26 1mrk 511 408-uus a inverse time characteristics 910 phasor measurement unit res670 2.2 ansi technical manual.
Page 917
A070827 v2 en-us figure 361: rd-type inverse time characteristics 1mrk 511 408-uus a section 26 inverse time characteristics phasor measurement unit res670 2.2 ansi 911 technical manual.
Page 918
Guid-acf4044c-052e-4cbd-8247-c6abe3796fa6 v1 en-us figure 362: inverse curve a characteristic of overvoltage protection section 26 1mrk 511 408-uus a inverse time characteristics 912 phasor measurement unit res670 2.2 ansi technical manual.
Page 919
Guid-f5e0e1c2-48c8-4dc7-a84b-174544c09142 v1 en-us figure 363: inverse curve b characteristic of overvoltage protection 1mrk 511 408-uus a section 26 inverse time characteristics phasor measurement unit res670 2.2 ansi 913 technical manual.
Page 920
Guid-a9898db7-90a3-47f2-aef9-45ff148cb679 v1 en-us figure 364: inverse curve c characteristic of overvoltage protection section 26 1mrk 511 408-uus a inverse time characteristics 914 phasor measurement unit res670 2.2 ansi technical manual.
Page 921
Guid-35f40c3b-b483-40e6-9767-69c1536e3cbc v1 en-us figure 365: inverse curve a characteristic of undervoltage protection 1mrk 511 408-uus a section 26 inverse time characteristics phasor measurement unit res670 2.2 ansi 915 technical manual.
Page 922
Guid-b55d0f5f-9265-4d9a-a7c0-e274aa3a6bb1 v1 en-us figure 366: inverse curve b characteristic of undervoltage protection section 26 1mrk 511 408-uus a inverse time characteristics 916 phasor measurement unit res670 2.2 ansi technical manual.
Page 923
Section 27 glossary m14893-1 v16 ac alternating current acc actual channel act application configuration tool within pcm600 a/d converter analog-to-digital converter adbs amplitude deadband supervision adm analog digital conversion module, with time synchronization ai analog input ansi american nati...
Page 924
Cb circuit breaker cbm combined backplane module ccitt consultative committee for international telegraph and telephony. A united nations-sponsored standards body within the international telecommunications union. Ccm can carrier module ccvt capacitive coupled voltage transformer class c protection ...
Page 925
Dbll dead bus live line dc direct current dfc data flow control dft discrete fourier transform dhcp dynamic host configuration protocol dip-switch small switch mounted on a printed circuit board di digital input dllb dead line live bus dnp distributed network protocol as per ieee std 1815-2012 dr di...
Page 926
Ftp file transfer protocol fun function type g.703 electrical and functional description for digital lines used by local telephone companies. Can be transported over balanced and unbalanced lines gcm communication interface module with carrier of gps receiver module gde graphical display editor with...
Page 927
Ieee p1386.1 pci mezzanine card (pmc) standard for local bus modules. References the cmc (ieee p1386, also known as common mezzanine card) standard for the mechanics and the pci specifications from the pci sig (special interest group) for the electrical emf (electromotive force). Ieee 1686 standard ...
Page 928
Lib 520 high-voltage software module lcd liquid crystal display ldcm line data communication module ldd local detection device led light-emitting diode lnt lon network tool lon local operating network mcb miniature circuit breaker mcm mezzanine carrier module mim milli-ampere module mpm main process...
Page 929
Pmc pci mezzanine card por permissive overreach pott permissive overreach transfer trip process bus bus or lan used at the process level, that is, in near proximity to the measured and/or controlled components prp parallel redundancy protocol psm power supply module pst parameter setting tool within...
Page 930
Sma connector subminiature version a, a threaded connector with constant impedance. Smt signal matrix tool within pcm600 sms station monitoring system sntp simple network time protocol – is used to synchronize computer clocks on local area networks. This reduces the requirement to have accurate hard...
Page 931
Trm transformer module. This module transforms currents and voltages taken from the process into levels suitable for further signal processing. Typ type identification umt user management tool underreach a term used to describe how the relay behaves during a fault condition. For example, a distance ...
Page 932
926.
Page 933
927.
Page 934
— abb ab grid automation products 721 59 västerås, sweden phone: +46 (0) 21 32 50 00 abb.Com/protection-control © copyright 2017 abb. All rights reserved. Specifications subject to change without notice. 1mrk 511 408-uus.