- DL manuals
- ABB
- Protection Device
- REQ650
- Applications Manual
ABB REQ650 Applications Manual
Summary of REQ650
Page 1
Relion ® 650 series breaker protection req650 application manual.
Page 3
Document id: 1mrk 505 291-uen issued: october 2016 revision: a product version: 1.3 © copyright 2013 abb. All rights reserved.
Page 4
Copyright this document and parts thereof must not be reproduced or copied without written permission from abb, and the contents thereof must not be imparted to a third party, nor used for any unauthorized purpose. The software and hardware described in this document is furnished under a license and...
Page 5
Disclaimer the data, examples and diagrams in this manual are included solely for the concept or product description and are not to be deemed as a statement of guaranteed properties. All persons responsible for applying the equipment addressed in this manual must satisfy themselves that each intende...
Page 6
Conformity this product complies with the directive of the council of the european communities on the approximation of the laws of the member states relating to electromagnetic compatibility (emc directive 2004/108/ec) and concerning electrical equipment for use within specified voltage limits (low-...
Page 7
Table of contents section 1 introduction.....................................................................15 this manual...................................................................................... 15 intended audience.........................................................................
Page 8
Preprocessing blocks (smai)...................................................... 45 calculating settings for global base values for setting function gbsval...................................................................................... 46 calculating settings for instantaneous phase overcurre...
Page 9
Section 5 local human-machine interface..................................... 77 local hmi......................................................................................... 77 display.........................................................................................77 leds..................
Page 10
Setting guidelines...................................................................... 113 four step residual overcurrent protection, zero, negative sequence direction ef4ptoc .......................................................115 identification....................................................
Page 11
Setting guidelines................................................................. 145 directional underpower protection guppdup..........................149 identification......................................................................... 149 setting guidelines..................................
Page 12
Identification.............................................................................. 168 application.................................................................................168 setting guidelines...................................................................... 169 rate-of-change...
Page 13
Identification ............................................................................. 197 application.................................................................................197 auto-reclosing operation off and on.................................200 start auto-reclosing and conditions...
Page 14
Permanent fault and reclosing unsuccessful signal............. 219 lock-out initiation................................................................. 219 automatic continuation of the reclosing sequence............... 221 thermal overload protection holding the auto-reclosing function back...........
Page 15
Setting guidelines...................................................................... 243 automation bits autobits............................................................243 identification.............................................................................. 243 application..............
Page 16
Setting guidelines...................................................................... 256 integer to boolean 16 conversion with logic node representation ib16fcvb.......................................................................................256 identification.................................
Page 17
Binary input signals.............................................................. 274 analog input signals............................................................. 274 sub-function parameters...................................................... 275 consideration...................................
Page 18
Self supervision with internal event list ..........................................297 identification.............................................................................. 297 application.................................................................................297 time synchronizatio...
Page 19
Identification.............................................................................. 311 application.................................................................................311 authorization handling in the ied......................................... 312 authority status athstat.......
Page 20
14.
Page 21
Section 1 introduction 1.1 this manual the application manual contains application descriptions and setting guidelines sorted per function. The manual can be used to find out when and for what purpose a typical protection function can be used. The manual can also provides assistance for calculating ...
Page 22
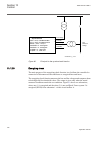
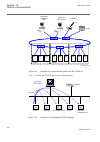
1.3 product documentation 1.3.1 product documentation set iec07000220-3-en.Vsd p la nn in g & p u rc h a se e n g in e e ri ng in st al lin g c om m is si o n in g o p e ra tio n m a in te na n ce d ec om m is si o n in g d ei n st a lli n g & d is po sa l application manual operation manual install...
Page 23
Chronological order in which the ied should be commissioned. The relevant procedures may be followed also during the service and maintenance activities. The operation manual contains instructions on how to operate the ied once it has been commissioned. The manual provides instructions for the monito...
Page 24
650 series manuals identity number cyber security deployment guidelines 1mrk 511 285-uen point list manual, dnp 3.0 1mrk 511 283-uen engineering manual 1mrk 511 284-uen operation manual 1mrk 500 096-uen installation manual 1mrk 514 016-uen accessories, 650 series 1mrk 513 023-ben mics 1mrg 010 656 p...
Page 25
1.4.2 document conventions • abbreviations and acronyms in this manual are spelled out in the glossary. The glossary also contains definitions of important terms. • push button navigation in the lhmi menu structure is presented by using the push button icons. For example, to navigate between the opt...
Page 26
20
Page 27
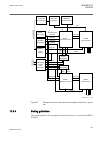
Section 2 application 2.1 req650 application the breaker protection ied provides a standalone solution for applications, where the functions related to the breaker is not preferred or suitable to be integrated into the main protection function that is, the line distance protection for a line. The ad...
Page 28
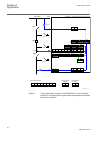
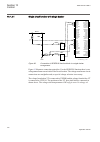
Req650-a01 – single busbar single breaker 10ai (4i+1i+5u) three phase variant smb rrec 79 0->1 smp ptrc 94 1->0 ses rsyn 25 sync tcs scbr cond spvn zbat cond other configured functions ov2 ptov 59 3u> ph pioc 50 3i>> cc rbrf 50bf v mmxu meter. C mmxu meter. Etp mmtr wh qa1 qb1 qb9 qc9 qc2 qc1 ef4 pt...
Page 29
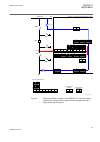
Req650-a11 – single busbar single breaker 10ai (4i+1i+5u) single phase variant stb rrec 79 0->1 spt ptrc 94 1->0 ses rsyn 25 sync tcs scbr cond spvn zbat cond other configured functions ov2 ptov 59 3u> spt pioc 50 i>> csp rbrf 50bf v mmxu meter. C mmxu meter. Etp mmtr wh qa1 qb1 qb9 qc9 qc2 qc1 ef4 ...
Page 30
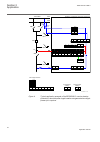
Qa1 qb1 qb2 qb9 qc9 qc2 qc1 wa1 wa2 132 kv bus 132kv/110v 132kv/ 110v 132kv/ 110v req650-b11 – double busbar single breaker 10ai (4i+1i+5u) single phase variant stb rrec 79 0->1 spt ptrc 94 1->0 ses rsyn 25 sync etp mmtr wh ef4 ptoc 51n/67n in> cv mmxn meter. Oc4s ptoc 51/67 3i> sde psde 67n in lc p...
Page 31
2.2 available functions 2.2.1 back-up protection functions iec 61850 or function name ansi function description breaker req650 req650 (a01) 3ph/1cb/1bb req650 (a11) 1ph/1cb/1bb req650 (b11) 1ph/1cb/2bb current protection phpioc 50 instantaneous phase overcurrent protection, 3– phase output 0–1 1 spt...
Page 32
Iec 61850 or function name ansi function description breaker req650 req650 (a01) 3ph/1cb/1bb req650 (a11) 1ph/1cb/1bb req650 (b11) 1ph/1cb/2bb saptuf 81 underfrequency function 0–2 2 2 2 saptof 81 overfrequency function 0–2 2 2 2 sapfrc 81 rate-of-change frequency protection 0–2 2 2 2 2.2.2 control ...
Page 33
Iec 61850 or function name ansi function description breaker req650 req650 (a01) 3ph/1cb/1bb req650 (a11) 1ph/1cb/1bb req650 (b11) 1ph/1cb/2bb cbc1 circuit breaker control for 1cb 1 1 1 1 secondary system supervision ccsrdif 87 current circuit supervision 0–1 1 1 1 sddrfuf fuse failure supervision 0...
Page 34
Iec 61850 or function name ansi function description breaker req650 req650 (a01) 3ph/1cb/1bb req650 (a11) 1ph/1cb/1bb req650 (b11) 1ph/1cb/2bb ib16fcvb integer to boolean 16 conversion with logic node representation 16 16 16 16 teiggio elapsed time integrator with limit transgression and overflow su...
Page 35
Iec 61850 or function name ansi function description breaker req650 req650 (a01) 3ph/1cb/1bb req650 (a11) 1ph/1cb/1bb req650 (b11) 1ph/1cb/2bb i103ar function status auto-recloser for iec60870-5-103 1 1 1 1 i103ef function status earth-fault for iec60870-5-103 1 1 1 1 i103fltprot function status fau...
Page 36
Iec 61850 or function name ansi function description breaker req650 req650 (a01) 3ph/1cb/1bb req650 (a11) 1ph/1cb/1bb req650 (b11) 1ph/1cb/2bb mst2tcp dnp3.0 for tcp/ip communication protocol 1 1 1 1 mst3tcp dnp3.0 for tcp/ip communication protocol 1 1 1 1 mst4tcp dnp3.0 for tcp/ip communication pro...
Page 37
2.2.4 basic ied functions iec 61850/function block name function description basic functions included in all products interrsig self supervision with internal event list 1 selfsupevlst self supervision with internal event list 1 timesynchgen time synchronization 1 sntp time synchronization 1 dtsbegi...
Page 38
• application 1: line bay in a solidly earthed network, connected to single busbar switchyard • application 2: line bay in a high impedance earthed network, connected to single busbar switchyard • application 3: line bay in a solidly earthed network, connected to double busbar switchyard • applicati...
Page 39
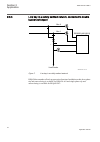
2.3.3 line bay in a high impedance earthed network, connected to single busbar switchyard iec10000135 v1 en figure 6: line bay in a high impedance earthed network req650 has a number of back-up protection functions. In addition to this, three-phase trip and autoreclosing is available for req650 a01 ...
Page 40
2.3.4 line bay in a solidly earthed network, connected to double busbar switchyard 3 3 1 req650 (a01)/(b11) 1 bus 1 bus 2 line/feeder iec10000136-1-en.Vsd iec10000136 v1 en figure 7: line bay in a solidly earthed network req650 has a number of back-up protection functions. In addition to this, three...
Page 41
2.3.5 line bay in a high impedance earthed network, connected to double busbar switchyard 3 3 1 req650 (a01)/(b11) 1 bus 1 bus 2 line/feeder iec10000137-1-en.Vsd iec10000137 v1 en figure 8: line bay in a high impedance earthed network req650 has a number of back-up protection functions. In addition ...
Page 42
Table 5: recommended functions in the different application examples function application 1 application 2 application 3 application 4 instantaneous phase overcurrent protection,3-phase output phpioc , three-phase trip (a01) on on on on instantaneous phase overcurrent protection, phase segregated out...
Page 43
Function application 1 application 2 application 3 application 4 overfrequency protection saptof (instance 2) application dependent application dependent application dependent application dependent rate of change of frequency sapfrc (instance 1) application dependent application dependent applicatio...
Page 44
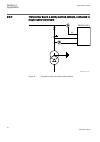
2.3.7 transformer bay in a solidly earthed network, connected to single busbar switchyard 3 3 3 req650 (a01) alt. Iec10000138-1-en.Vsd iec10000138 v1 en figure 9: transformer bay in a solidly earthed system section 2 1mrk 505 291-uen a application 38 application manual.
Page 45
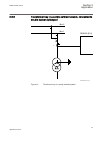
2.3.8 transformer bay in a solidly earthed network, connected to double busbar switchyard 3 req650 (b11) bus 1 bus 2 iec10000139-1-en.Vsd iec10000139 v1 en figure 10: transformer bay in a solidly earthed system 1mrk 505 291-uen a section 2 application 39 application manual.
Page 46
2.3.9 transformer bay in a high impedance earthed network, connected to single busbar switchyard iec10000140 v1 en figure 11: transformer bay in a high impedance earthed system 2.3.10 functionality table the proposal for functionality choice for the different application cases are shown in table 9 ....
Page 47
Table 9: recommended functions in the different application examples function application 5 application 6 application 7 instantaneous phase overcurrent protection phpioc , three-phase on on on four step phase overcurrent protection oc4ptoc , three-phase on on on instantaneous residual overcurrent pr...
Page 48
42.
Page 49
Section 3 req650 setting examples 3.1 setting example for a line bay with backup protection unit req650 a01 the application example has a 145 kv line bay with backup protection unit req650 a01. The main protection of the line is a distance protection unit, not covered in this setting example. 3 3 1 ...
Page 50
Item data low positive sequence source impedance j3.2 ohm (about 6000 mva) high zero sequence source impedance j8 ohm low zero sequence source impedance j5 ohm high positive sequence source impedance at the remote line end j10 ohm (about 1900 mva) low positive sequence source impedance at the remote...
Page 51
All fault clearance is done by means of three-phase tripping of the circuit breaker. 3.1.1 calculating settings for analogue trm inputs 4i 1i 5u the transformer module (trm) has the capability of 4 current inputs (tapped to 1 or 5 a), 1 current input (tapped 0.1 or 0.5 a) and 5 voltage inputs. The l...
Page 52
3.1.3 calculating settings for global base values for setting function gbsval each function uses primary base values for reference of settings. The base values are defined in global base values for settings function. It is possible to include six global base values for settings gbasval functions: gl...
Page 53
3.1.5 calculating settings for four step phase overcurrent protection 3-phase output i> oc4ptoc the purpose of the delayed phase overcurrent protection is: • backup protection for short circuits on the whole line length • backup protection for short circuits in the remote busbar • backup protection ...
Page 54
145 3 3 3 2.6 85 2 2 10 2.5 17.5 ph sc sc line u i ka z z j j = × = × = Ð ° + + + equation2342 v1 en 3 3 1 req650 (a01) z sc : high ph – ph short circuit iec10000147-1-en.Vsd iec10000147 v1 en figure 13: fault for step 1 setting in case of a three-phase short circuit in zone 1 reach in the shortest ...
Page 55
3 3 1 req650 (a01) z sc : low three-phase short circuit line protection zone 1 reach iec10000148-1-en.Vsd iec10000148 v1 en figure 14: fault for step 1 setting recommended current setting is therefore 2000 a. 1. Set dirmode1 to forward. 2. Set characterist1 to iec def. Time. For the time delay chara...
Page 56
3 3 1 req650 (a01) z sc : high ph – ph short circuit iec10000149-1-en.Vsd iec10000149 v1 en figure 15: fault for step 2 setting in case of a three-phase short circuit in zone 1 reach in the shortest line from the busbar as shown in figure 16 , the current to the protection is i = 1.8 ka. Section 3 1...
Page 57
3 3 1 req650 (a01) z sc : low three phase short circuit line protection zone 1 reach iec10000150-1-en.Vsd iec10000150 v1 en figure 16: fault for step 2 setting recommended current setting is therefore 2000 a. 1. Set dirmode2 to reverse. 2. Set characterist1 is set to iec def. Time. For the time dela...
Page 58
For the time delay characteristic, definite time is used in this network. 3. Set i3> to 80% of ibase (800 a primary current). 4. Set t3 to 1.2 s. The time delay is set longer than zone 3 (0.8 s) of the distance protection in the system. 3.1.6 calculating settings for instantaneous residual overcurre...
Page 59
3.1.7 calculating settings for four step residual overcurrent protection 3i0> ef4ptoc the purpose of the delayed residual overcurrent protection is: • backup protection for earth faults on the whole line length • backup protection for earth faults in the remote busbar • backup protection for earth f...
Page 60
3 3 1 req650 (a01) z sc : high iec10000151-2-en.Vsd phase – earth fault iec10000151 v2 en figure 17: fault for step 1 setting in case of a single phase earth-fault in zone 1 reach in the shortest line from the remote busbar, as shown in figure 18 , the current to the protection is i 0 = 1.1 ka. Sect...
Page 61
3 3 1 req650 (a01) z sc : low phase-earth fault line protection zone 1 reach iec10000152-1-en.Vsd iec10000152 v1 en figure 18: fault for step 1 setting proposed current setting is therefore 1200 a. 1. Set dirmode1 to forward. 2. Set characterist1 to iec def. Time. For the time delay characteristic, ...
Page 62
3 3 1 req650 (a01) z sc : high ph – ea fault iec10000153-1-en.Vsd iec10000153 v1 en figure 19: fault for step 2 setting in case of a single-phase earth-fault in zone 1 reach in the shortest line from the remote busbar, as shown in figure 20 , the current to the protection is i = 1.0 ka. Section 3 1m...
Page 63
3 3 1 req650 (a01) z sc : low earth fault line protection zone 1 reach iec10000154-1-en.Vsd iec10000154 v1 en figure 20: fault for step 2 setting proposed current setting is therefore 1200 a. 1. Set dirmode2 to reverse. 2. Set in2> to 120% of ibase (1200 a primary current). 3. Set t2 to 0.4 s. 3.1.7...
Page 64
3.1.8 calculating settings for breaker failure protection 3-phase activation and output ccrbrf breaker failure protection, 3-phase activation and output can use either contact function in the circuit breaker or current measurement to detect correct breaker function. Current measurement breaker check...
Page 65
Time the fault occurs protection operate time trip and start ccrbrf normal t cbopen margin retrip delay t1 t cbopen after re-trip t bfpreset minimum back-up trip delay t2 critical fault clearance time for stability iec05000479_2_en.Vsd iec05000479 v2 en figure 21: time sequences for breaker failure ...
Page 66
The current detected shall be active if all phase currents are higher than the setting. 7. Set currunsymlevel to 80%. Pole discordance is detected if the magnitude of the lowest phase current is lower than the fraction currunsymlevel (%) of the highest phase current. Section 3 1mrk 505 291-uen a req...
Page 67
Section 4 analog inputs 4.1 introduction analog input channels in the ied must be set properly in order to get correct measurement results and correct protection operations. For power measuring and all directional and differential functions the directions of the input currents must be defined in ord...
Page 68
Current flows. Although the phase angle difference between the different phases is firm, the whole system appears to be rotating when the measurement functions are observed. 4.2.2 relationships between setting parameter base current, ct rated primary current and minimum pickup of a protection ied no...
Page 69
A positive value of current, power, and so on (forward) means that the quantity has a direction towards the object. - a negative value of current, power, and so on (reverse) means a direction away from the object. See figure 22 . Protected object line, transformer, etc forward reverse definition of ...
Page 70
Transformer protection transformer line line setting of current input: set parameter ctstarpoint with transformer as reference object. Correct setting is "toobject" forward reverse definition of direction for directional functions line protection setting of current input: set parameter ctstarpoint w...
Page 71
Transformer protection setting of current input: set parameter ctstarpoint with transformer as reference object. Correct setting is "toobject" forward reverse definition of direction for directional functions line protection setting of current input: set parameter ctstarpoint with transformer as ref...
Page 72
I sec i p ri s1 (x1) p1 (h1) p2 (h2) s2 (x2) p2 (h2) p1 (h1) x x a) b) c) en06000641.Vsd s2 (x2) s1 (x1) iec06000641 v1 en figure 25: commonly used markings of ct terminals where: a) is symbol and terminal marking used in this document. Terminals marked with a dot indicates the primary and secondary...
Page 73
L1 il 1 il 2 il 3 l2 l3 protected object ct 600/5 star connected il1 il2 il3 ied iec13000002-4-en.Vsdx 1 2 3 4 smai2 block revrot ^grp2l1 ^grp2l2 ^grp2l3 ^grp2n ai3p ai1 ai2 ai3 ai4 ai n 5 in iec13000002 v4 en figure 26: star connected three-phase ct set with star point towards the protected object ...
Page 74
3) these three connections are the links between the three current inputs and the three input channels of the preprocessing function block 4). Depending on the type of functions, which need this current information, more than one preprocessing block might be connected in parallel to the same three p...
Page 75
L1 il 1 il 2 il 3 l2 l3 protected object ct 800/1 star connected il1 il2 il3 ied iec11000026-4-en.Vsdx 4 1 2 3 smai2 block revrot ^grp2l1 ^grp2l2 ^grp2l3 ^grp2n ai3p ai1 ai2 ai3 ai4 ai n 5 in iec11000026 v4 en figure 27: star connected three-phase ct set with its star point away from the protected o...
Page 76
Protected object l1 l2 l3 ied in p ins ins 2 iec11000029-4-en.Vsdx 4 3 c t 1000 /1 a) b) (+) (+) (-) (-) (+) (-) 1 smai2 block revrot ^grp2l1 ^grp2l2 ^grp2l3 ^grp2n ai3p ai1 ai2 ai3 ai4 ai n iec11000029 v4 en figure 28: connections for single-phase ct input where: 1) shows how to connect single-phas...
Page 77
4.2.4 setting of voltage channels as the ied uses primary system quantities the main vt ratios must be known to the ied. This is done by setting the two parameters vtsec and vtprim for each voltage channel. The phase-to-phase value can be used even if each channel is connected to a phase-to-earth vo...
Page 78
It shall be noted that depending on national standard and utility practices the rated secondary voltage of a vt has typically one of the following values: • 100 v • 110 v • 115 v • 120 v • 230 v the ied fully supports all of these values and most of them will be shown in the following examples. 4.2....
Page 79
L1 ied l2 l3 66 3 110 3 kv v 1 3 2 66 3 110 3 kv v 66 3 110 3 kv v . #not used 5 iec06000599-4-en.Vsdx 4 smai2 block revrot ^grp2l1 ^grp2l2 ^grp2l3 ^grp2n ai3p ai1 ai2 ai3 ai4 ai n iec06000599 v4 en figure 30: a three phase-to-earth connected vt where: 1) shows how to connect three secondary phase-t...
Page 80
3) are three connections made in signal matrix tool (smt), which connect these three voltage inputs to first three input channels of the preprocessing function block 5). Depending on the type of functions which need this voltage information, more then one preprocessing block might be connected in pa...
Page 81
L1 ied l2 l3 1 2 3 4 13.8 120 kv v iec11000032-1-en.Vsd smai_20 iec11000032 v1 en figure 31: a phase-to-phase connected vt where: 1) shows how to connect the secondary side of a phase-to-phase vt to the vt inputs on the ied 2) is the trm or aim where this voltage input is located. The following sett...
Page 82
76.
Page 83
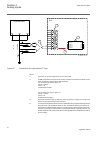
Section 5 local human-machine interface 5.1 local hmi iec12000175 v1 en figure 32: local human-machine interface the lhmi of the ied contains the following elements: • display (lcd) • buttons • led indicators • communication port for pcm600 the lhmi is used for setting, monitoring and controlling. 5...
Page 84
Iec13000063-1-en.Vsd iec13000063 v1 en figure 33: display layout 1 path 2 content 3 status 4 scroll bar (appears when needed) the function button panel shows on request what actions are possible with the function buttons. Each function button has a led indication that can be used as a feedback signa...
Page 85
The alarm led panel shows on request the alarm text labels for the alarm leds. Three alarm led pages are available. Guid-d20bb1f1-fdf7-49ad-9980-f91a38b2107d v1 en figure 35: alarm led panel the function button and alarm led panels are not visible at the same time. Each panel is shown by pressing on...
Page 86
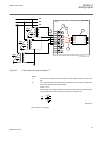
Iec11000247 v2 en figure 36: lhmi keypad with object control, navigation and command push- buttons and rj-45 communication port 1...5 function button 6 close 7 open 8 escape 9 left 10 down 11 up 12 right 13 user log on 14 enter 15 remote/local 16 uplink led 17 ethernet communication port (rj-45) 18 ...
Page 87
The start and trip leds are configured via the disturbance recorder. The yellow and red status leds are configured in the disturbance recorder function, drprdre, by connecting a start or trip signal from the actual function to a bxrbdr binary input function block using the pcm600 and configure the s...
Page 88
Table 14: alarm indications led state description off normal operation. All activation signals are off. On • follow-s sequence: the activation signal is on. • latchedcoll-s sequence: the activation signal is on, or it is off but the indication has not been acknowledged. • latchedack-f-s sequence: th...
Page 89
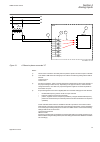
Guid-d71ba06d-3769-4acb-8a32-5d02ea473326 v1 en figure 37: rj-45 communication port and green indicator led 1 rj-45 connector 2 green indicator led when a computer is connected to the ied front port with a crossed-over cable, the ied's dhcp server for the front interface assigns an ip address to the...
Page 90
84.
Page 91
Section 6 current protection 6.1 instantaneous phase overcurrent protection 3-phase output phpioc 6.1.1 identification function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number instantaneous phase overcurrent protection 3-phase output phpioc 3i>> symbol-z v...
Page 92
6.1.3 setting guidelines the parameters for instantaneous phase overcurrent protection 3-phase output phpioc are set via the local hmi or pcm600. This protection function must operate only in a selective way. So check all system and transient conditions that could cause its unwanted operation. Only ...
Page 93
Then a fault in a has to be applied and the through fault current i fa has to be calculated, figure 39 . In order to get the maximum through fault current, the minimum value for z b and the maximum value for z a have to be considered. Iec09000023-1-en.Vsd ~ ~ z a z b z l a b ied i fa fault iec090000...
Page 94
Iec09000024-1-en.Vsd ~ ~ z a z b z l a b ied i f fault iec09000024 v1 en figure 40: fault current: i f 100 is ip ibase >>= × equation1147 v3 en (equation 5) 6.1.3.2 meshed network with parallel line in case of parallel lines, the influence of the induced current from the parallel line to the protect...
Page 95
Iec09000025-1-en.Vsd ~ ~ z a z b z l1 a b i m fault ied z l2 m c line 1 line 2 iec09000025 v1 en figure 41: two parallel lines. Influence from parallel line to the through fault current: i m the minimum theoretical current setting for the overcurrent protection function (imin) will be: imin max i fa...
Page 96
6.2 instantaneous phase overcurrent protection phase segregated output sptpioc 6.2.1 identification function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number instantaneous phase overcurrent protection, phase segregated output sptpioc 3i>> symbol-z v1 en 50 ...
Page 97
Detailed network studies can determine the operating conditions under which the highest possible fault current is expected on the line . In most cases, this current appears during three-phase fault conditions. But also examine single-phase-to-earth and two-phase-to-earth conditions. Also, study tran...
Page 98
Iec10000276-1-en.Vsd ~ ~ z a z b z l a b ied i fa fault iec10000276 v1 en figure 43: through fault current from b to a: i fa the ied must not trip for any of the two through fault currents. Hence the minimum theoretical current setting (imin) will be: fa fb imin max(i , i ) ³ eq1 v1 en (equation 9) ...
Page 99
The ied setting value ip>> is given in percentage of the primary base current value, ibase. The value for ip>> is given from this formula: 100 is ip ibase >>= × equation1147 v3 en (equation 11) 6.2.3.2 meshed network with parallel line in case of parallel lines, the influence of the induced current ...
Page 100
Where i fa and i fb have been described in the previous paragraph. Considering the safety margins mentioned previously, the minimum setting is as given in equation below: is ³1.3·imin equation83 v2 en (equation 13) the protection function can be used for the specific application only if this setting...
Page 101
If vt inputs are not available or not connected, setting parameter dirmodex (x = step 1, 2, 3 or 4) shall be left to default value non- directionalor set to off. In many applications several steps with different current pick up levels and time delays are needed. Oc4ptoc can have up to four different...
Page 102
Meastype: selection of discrete fourier filtered (dft) or true rms filtered (rms) signals. Rms is used when the harmonic contents are to be considered, for example in applications with shunt capacitors. Operation: the protection can be set to off or on 2ndharmstab: operate level of 2nd harmonic curr...
Page 103
6.3.3.1 settings for steps 1 to 4 n means step 1 and 4. X means step 1, 2, 3 and 4. Dirmodex: the directional mode of step x. Possible settings are off/non-directional/ forward/reverse. Characteristn: selection of time characteristic for step n. Definite time delay and different types of inverse tim...
Page 104
Tnmin: minimum operate time for all inverse time characteristics. At high currents the inverse time characteristic might give a very short operation time. By setting this parameter the operation time of the step can never be shorter than the setting. Setting range: 0.000 - 60.000s in steps of 0.001s...
Page 105
2ndharmstab: the rate of 2nd harmonic current content for activation of the 2nd harmonic restrain signal, to block chosen steps. The setting is given in % of the fundamental frequency residual current. The setting range is 5 - 100% in steps of 1%. The default setting is 20% and can be used if a deep...
Page 106
Im ax ipu 1.2 k ³ × equation1262 v2 en (equation 15) where: 1.2 is a safety factor k is the resetting ratio of the protection imax is the maximum load current the maximum load current on the line has to be estimated. There is also a demand that all faults, within the zone that the protection shall c...
Page 107
Max 1.2 t sc high i k i ³ × × equation1265 v1 en (equation 18) where: 1.2 is a safety factor k t is a factor that takes care of the transient overreach due to the dc component of the fault current and can be considered to be less than 1.1 iscmax is the largest fault current at a fault at the most re...
Page 108
To assure selectivity between different protections, in the radial network, there have to be a minimum time difference dt between the time delays of two protections. The minimum time difference can be determined for different cases. To determine the shortest possible time difference, the operation t...
Page 109
I> i> a1 b1 feeder time axis t=0 t=t 1 t=t 2 t=t 3 the fault occurs protection b1 trips breaker at b1 opens protection a1 resets en05000205.Vsd iec05000205 v1 en figure 50: sequence of events during fault where: t=0 is when the fault occurs t=t 1 is when the trip signal from the overcurrent protecti...
Page 110
6.4 four step phase overcurrent protection phase segregated output oc4sptoc 6.4.1 identification function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number four step phase overcurrent protection, phase segregated output oc4sptoc id-2147.Vsd v1 en 51/67 6.4.2...
Page 111
Current of the phase overcurrent protection. The inrush current has a large second harmonic content. This can be used to avoid the unwanted operation of the protection. Therefore, oc4sptoc (51/67) function has a possibility of a second harmonic restrain if the level of this harmonic current reaches ...
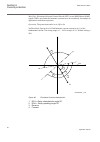
Page 112
U ref i dir iec09000636_1_vsd 1 2 2 3 4 iec09000636 v1 en figure 51: directional function characteristic 1. Rca = relay characteristic angle 55° 2. Roa = relay operating angle 80° 3. Reverse 4. Forward 6.4.3.1 settings for steps 1 to 4 n: means step 1 and 4. X means step 1, 2, 3 and 4. Dirmodex: the...
Page 113
Characteristn: selection of time characteristic for step n. Definite time delay and different types of inverse time characteristics are available according to table 16 . Step 2 and 3 are always definite time delayed. Table 16: inverse time characteristics curve name ansi extremely inverse ansi very ...
Page 114
Iec09000164-2 operate time current tx tnmin iminn iec09000164 v2 en figure 52: minimum operating current and operation time for inverse time characteristics in order to fully comply with curves definition setting parameter tnmin shall be set to the value which is equal to the operate time of the sel...
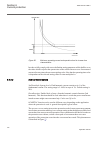
Page 115
Operating current current i the ied does not reset line phase current time t reset current iec10000274-1-en.Vsd iec10000274 v1 en figure 53: operating and reset current for an overcurrent protection the lowest setting value can be written according to equation 15 . Im ax ipu 1.2 k ³ × equation1262 v...
Page 116
Im ax 1.2 ipu 0.7 isc min k × £ £ × equation1264 v2 en (equation 22) the high current function of the overcurrent protection, which only has a short delay of the operation, must be given a current setting so that the protection is selective to other protection in the power system. It is desirable to...
Page 117
Iec10000273-1-en.Vsd iec10000273 v1 en figure 54: fault time with maintained selectivity to assure selectivity between different protections, in the radial network, there have to be a minimum time difference ∆t between the time delays of two protections. The minimum time difference can be determined...
Page 118
I> i> a1 b1 feeder time axis t=0 t=t 1 t=t 2 t=t 3 the fault occurs protection b1 trips breaker at b1 opens protection a1 resets iec10000279-1-en.Vsd iec10000279 v1 en figure 55: sequence of events during fault where: • t=0 is when the fault occurs. • t=t1 is when the trip signal from the overcurren...
Page 119
6.5 instantaneous residual overcurrent protection efpioc 6.5.1 identification function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number instantaneous residual overcurrent protection efpioc in>> ief v1 en 50n 6.5.2 application in many applications, when faul...
Page 120
~ ~ z a z b z l a b ied i fb fault iec09000022-1-en.Vsd iec09000022 v1 en figure 56: through fault current from a to b: i fb iec09000023-1-en.Vsd ~ ~ z a z b z l a b ied i fa fault iec09000023 v1 en figure 57: through fault current from b to a: i fa the function shall not operate for any of the calc...
Page 121
Iec09000025-1-en.Vsd ~ ~ z a z b z l1 a b i m fault ied z l2 m c line 1 line 2 iec09000025 v1 en figure 58: two parallel lines. Influence from parallel line to the through fault current: i m the minimum theoretical current setting (imin) will in this case be: i m in m a x i fa i fb i m , , ( ) ³ equ...
Page 122
6.6.1 identification function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number four step residual overcurrent protection, zero or negative sequence direction ef4ptoc 2 iec11000263 v1 en 51n/67n 6.6.2 application the four step residual overcurrent protection...
Page 123
Choice of time characteristics: there are several types of time characteristics available such as definite time delay and different types of inverse time characteristics. The selectivity between different overcurrent protections is normally enabled by co-ordination between the operate time of the di...
Page 124
6.6.3 setting guidelines when inverse time overcurrent characteristic is selected, the operate time of the stage will be the sum of the inverse time delay and the set definite time delay. Thus, if only the inverse time delay is required, it is important to set the definite time delay for that stage ...
Page 125
Shortest possible time difference, the operation time of protections, breaker opening time and protection resetting time must be known. These time delays can vary significantly between different protective equipment. The following time delays can be estimated: protection operate time: 15-60 ms prote...
Page 126
In order to fully comply with curves definition the setting parameter txmin shall be set to the value which is equal to the operate time of the selected iec inverse curve for measured current of twenty times the set current pickup value. Note that the operate time value is dependent on the selected ...
Page 127
Current polarizing is useful when the local source is strong and a high sensitivity is required. In such cases the polarizing voltage (3u 0 ) can be below 1% and it is then necessary to use current polarizing or dual polarizing. Multiply the required set current (primary) with the minimum impedance ...
Page 128
6.7 sensitive directional residual overcurrent and power protection sdepsde 6.7.1 identification function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number sensitive directional residual over current and power protection sdepsde - 67n 6.7.2 application in ne...
Page 129
When should the sensitive directional residual overcurrent protection be used and when should the sensitive directional residual power protection be used? Consider the following facts: • sensitive directional residual overcurrent protection gives possibility for better sensitivity. The setting possi...
Page 130
Earth-fault current larger than what normal high impedance gives but smaller than the phase-to-phase short circuit current. In a high impedance system the fault current is assumed to be limited by the system zero sequence shunt impedance to earth and the fault resistance only. All the series impedan...
Page 131
C n 0 c n jx 3r z jx 3r - × = - + equation1946 v1 en (equation 32) where r n is the resistance of the neutral point resistor in many systems there is also a neutral point reactor (petersen coil) connected to one or more transformer neutral points. In such a system the impedance z 0 can be calculated...
Page 132
Substation a substation b z lineab,1 (pos. Seq) z lineab,0 (zero seq) z linebc,1 (pos. Seq) z linebc,0 (zero seq) u 0a u 0b 3i 0 phase to earth fault r n z t,1 (pos. Seq) z t,0 (zero seq) source impedance z sc (pos. Seq) en06000654.Vsd iec06000654 v1 en figure 62: equivalent of power system for calc...
Page 133
The residual power, measured by the sensitive earth-fault protections in a and b will be: 0 a 0 a 0 s 3u 3i = × equation1951 v1 en (equation 37) 0 b 0 b 0 s 3u 3i = × equation1952 v1 en (equation 38) the residual power is a complex quantity. The protection will have a maximum sensitivity in the char...
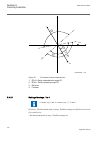
Page 134
= = 0 , 0 rcadir roadir 0 3i ϕ = − 0 ref ang(3i ) ang(3u ) − = 0 ref 3u u 0 3i cos ⋅ ϕ iec06000648-3-en.Vsd iec06000648 v3 en figure 63: characteristic for rcadir equal to 0° the characteristic is for rcadir equal to -90° is shown in figure 64 . Iec06000649_3_en.Vsd ref u = − = 90 , 90 rcadir roadir...
Page 135
-3u 0 operate area 3i 0 rcadir = 0º roadir = 80º iec06000652-3-en.Vsd iec06000652 v3 en figure 65: characteristic for rcadir = 0° and roadir = 80° dirmode is set forward or reverse to set the direction of the trip function from the directional residual current function. All the directional protectio...
Page 136
Sn> is the operate power level for the directional function when opmode is set 3i03u0cosfi. The setting is given in % of sbase. The setting should be based on calculation of the active or capacitive earth-fault residual power at required sensitivity of the protection. The input transformer for the s...
Page 137
Iec long time inverse iec definite time asea ri rxidg (logarithmic) the different characteristics are described in technical manual. Tinnondir is the definite time delay for the non directional earth-fault current protection, given in s. Opun> is set on to activate the trip function of the residual ...
Page 138
In stressed situations in the power system it can be required to overload lines and cables for a limited time. This should be done without risks. The thermal overload protection provides information that makes a temporary overloading of cables and lines possible. The thermal overload protection esti...
Page 139
Similar values are stated for overhead lines. A suitable setting can be about 15°c (59°f) below the trip value. Recltemp: temperature where lockout signal lockout from the protection is released. When the thermal overload protection trips a lock-out signal is activated. This signal is intended to bl...
Page 140
6.9.3 setting guidelines the parameters for breaker failure protection 3-phase activation and output ccrbrf are set via the local hmi or pcm600. The following settings can be done for the breaker failure protection. Globalbasesel: selects the global base value group used by the function to define (i...
Page 141
Failure. 1 out of 3 means that at least one current of the three-phase currents shall be high to indicate breaker failure. 1 out of 4 means that at least one current of the three- phase currents or the residual current shall be high to indicate breaker failure. In most applications 1 out of 3 is suf...
Page 142
It is often required that the total fault clearance time shall be less than a given critical time. This time is often dependent of the ability to maintain transient stability in case of a fault close to a power plant. Time the fault occurs protection operate time trip and start ccrbrf normal t cbope...
Page 143
It is from practical and economical reason not feasible to duplicate the circuit breaker for the protected component. Instead a breaker failure protection is used. The breaker failure protection, phase segregated activation and output (csprbrf ) issues a back-up trip command to adjacent circuit brea...
Page 144
Table 19: dependencies between parameters retripmode and functionmode retripmode functionmode description retrip off n/a the re-trip function is not activated cb pos chec k current a phase current must be larger than the operate level to allow re-trip contact re-trip is done when circuit breaker is ...
Page 145
T1: time delay of the re-trip. The setting can be given within the range 0 – 60 s in steps of 0.001 s. Typical setting is 0 – 50 ms. T2: time delay of the back-up trip. The choice of this setting is made as short as possible at the same time as unwanted operation must be avoided. Typical setting is ...
Page 146
6.11 stub protection stbptoc 6.11.1 identification function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number stub protection stbptoc 3i>stub symbol-t v1 en 50stb 6.11.2 application stub protection stbptoc is a simple phase overcurrent protection, fed from t...
Page 147
Globalbasesel: selects the global base value group used by the function to define (ibase), (ubase) and (sbase). Operation: off/on i>: current level for the stub protection, set in % of ibase. This parameter should be set so that all faults on the stub can be detected. The setting should thus be base...
Page 148
6.12.3 setting guidelines the parameters for the pole discordance protection ccrpld are set via the local hmi or pcm600. The following settings can be done for the pole discordance protection. Globalbasesel: selects the global base value group used by the function to define (ibase), (ubase) and (sba...
Page 149
6.13.3 setting guidelines globalbasesel: selects the global base value group used by the function to define (ibase), (ubase) and (sbase). Broken conductor check brcptoc must be set to detect open phase/s (series faults) with different loads on the line. Brcptoc must at the same time be set to not op...
Page 150
Reverse power protection. There are several contingencies that may cause reverse power: break of a main steam pipe, damage to one or more blades in the steam turbine or inadvertent closing of the main stop valves. In the last case, it is highly desirable to have a reliable reverse power protection. ...
Page 151
Than 5%. It is necessary to obtain information from the engine manufacturer and to measure the reverse power during commissioning. Gas turbines usually do not require reverse power protection. Figure 69 illustrates the reverse power protection with underpower protection and with overpower protection...
Page 152
Mode: the voltage and current used for the power measurement. The setting possibilities are shown in table 20 . For reverse power applications posseq or arone modes are strongly recommended. Table 20: complex power calculation set value mode formula used for complex power calculation l1, l2, l3 * * ...
Page 153
Operate angle1(2) power1(2) p q en06000440.Vsd iec06000440 v1 en figure 70: overpower mode the setting power1(2) gives the power component pick up value in the angle1(2) direction. The setting is given in p.U. Of the generator rated power, see equation 54 . Minimum recommended setting is 1.0% of s n...
Page 154
Operate angle1(2 ) = 180 o power1(2) p q iec06000557-2-en.Vsd iec06000557 v2 en figure 71: for reverse power the set angle should be 180° in the overpower function tripdelay1(2) is set in seconds to give the time delay for trip of the stage after pick up. The possibility to have low pass filtering o...
Page 155
6.14.3 directional underpower protection guppdup 6.14.3.1 identification function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number directional underpower protection guppdup p 2 symbol-ll v2 en 37 6.14.3.2 setting guidelines globalbasesel: selects the global...
Page 156
Set value mode formula used for complex power calculation l1 * 1 1 3 l l s u i = × × equation1703 v1 en (equation 62) l2 * 2 2 3 l l s u i = × × equation1704 v1 en (equation 63) l3 * 3 3 3 l l s u i = × × equation1705 v1 en (equation 64) the function has two stages that can be set independently. Wit...
Page 157
3 n s ubase ibase = × × equation1708 v1 en (equation 65) the setting angle1(2) gives the characteristic angle giving maximum sensitivity of the power protection function. The setting is given in degrees. For active power the set angle should be 0° or 180°. 0° should be used for generator low forward...
Page 158
The value of k=0.98 or even k=0.99 is recommended in generator low forward power applications as the trip delay is normally quite long. This filtering will improve accuracy of the power function. 6.15 negative sequence based overcurrent function dnsptoc 6.15.1 identification function description iec...
Page 159
• setting rcadir to value +65 degrees, that is, the negative sequence current typically lags the inverted negative sequence voltage for this angle during the fault • setting roadir to value 90 degrees • setting lowvolt_vm to value 2%, that is, the negative sequence voltage level above which the dire...
Page 160
154.
Page 161
Section 7 voltage protection 7.1 two step undervoltage protection uv2ptuv 7.1.1 identification function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number two step undervoltage protection uv2ptuv 3u symbol-r-2u-greater-than v2 en 27 7.1.2 application two-step...
Page 162
Uv2ptuv prevents sensitive equipment from running under conditions that could cause their overheating and thus shorten their life time expectancy. In many cases, it is a useful function in circuits for local or remote automation processes in the power system. 7.1.3 setting guidelines all the voltage...
Page 163
7.1.3.6 settings for two step undervoltage protection the following settings can be done for two step undervoltage protection (uv2ptuv). Globalbasesel: selects the global base value group used by the function to define (ibase), (ubase) and (sbase). Conntype: sets whether the measurement shall be pha...
Page 164
T1min longer than the operation time for other protections such unselective tripping can be avoided. K1: time multiplier for inverse time characteristic. This parameter is used for coordination between different inverse time delayed undervoltage protections. The function must be externally blocked w...
Page 165
Falling down to a crossing overhead line, transformer flash over fault from the high voltage winding to the low voltage winding and so on). 2. Malfunctioning of a voltage regulator or wrong settings under manual control (symmetrical voltage decrease). 3. Low load compared to the reactive power gener...
Page 166
High impedance earthed systems in high impedance earthed systems, earth-faults cause a voltage increase in the non- faulty phases. Ov2ptov can be used to detect such faults. The setting must be above the highest occurring "normal" voltage and below the lowest occurring voltage during faults. A metal...
Page 167
To prevent damages to the protected object. The speed might be important for example in case of protection of transformer that might be overexcited. The time delay must be co-ordinated with other automated actions in the system. T1min: minimum operating time for inverse time characteristic for step ...
Page 168
7.3.3 setting guidelines all the voltage conditions in the system where rov2ptov performs its functions should be considered. The same also applies to the associated equipment, its voltage and time characteristic. There is a very wide application area where general single input or residual overvolta...
Page 169
Iec07000190 v1 en figure 74: earth fault in non-effectively earthed systems 7.3.3.3 direct earthed system in direct earthed systems, an earth fault on one phase indicates a voltage collapse in that phase. The two healthy phases will have normal phase-to-earth voltages. The residual sum will have the...
Page 170
Iec07000189 v1 en figure 75: earth fault in direct earthed system 7.3.3.4 settings for two step residual overvoltage protection globalbasesel: selects the global base value group used by the function to define (ibase), (ubase) and (sbase). Operation: off or on ubase is used as voltage reference for ...
Page 171
Characteristic1: this parameter gives the type of time delay to be used. The setting can be, definite time or inverse curve a or inverse curve b or inverse curve c. The choice is highly dependent of the protection application. Un>: set overvoltage operate value for step n (n=step 1 and 2), given as ...
Page 172
To the circuit breaker is not required, lovptuv is used for signallization only through an output contact or through the event recording function. 7.4.3 setting guidelines loss of voltage check (lovptuv) is in principle independent of the protection functions. It requires to be set to open the circu...
Page 173
Section 8 frequency protection 8.1 underfrequency protection saptuf 8.1.1 identification function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number underfrequency protection saptuf f symbol-p v1 en 81 8.1.2 application underfrequency protection saptuf is app...
Page 174
1. To protect equipment against damage due to low frequency, such as generators, transformers, and motors. Overexcitation is also related to low frequency 2. To protect a power system, or a part of a power system, against breakdown, by shedding load, in generation deficit situations. The under frequ...
Page 175
Between the actual generation and the load demand. High fundamental frequency in a power system indicates that the available generation is too large compared to the power demanded by the load connected to the power grid. Saptof detects such situations and provides an output signal, suitable for gene...
Page 176
8.3.1 identification function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number rate-of-change frequency protection sapfrc df/dt > symbol-n v1 en 81 8.3.2 application rate-of-change frequency protection (sapfrc), is applicable in all situations, where reliab...
Page 177
Sapfrcstart value is set in hz/s. All voltage magnitude related settings are made as a percentage of a settable base voltage, which normally is set to the primary nominal voltage level (phase-phase) of the power system or the high voltage equipment under consideration. Sapfrc is not instantaneous, s...
Page 178
172.
Page 179
Section 9 secondary system supervision 9.1 current circuit supervision ccsrdif 9.1.1 identification function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number current circuit supervision ccsrdif - 87 9.1.2 application open or short circuited current transfor...
Page 180
Current circuit supervision ccsrdif compares the residual current from a three- phase set of current transformer cores with the neutral point current on a separate input taken from another set of cores on the same current transformer. The minimum operate current, iminop, must be set as a minimum to ...
Page 181
The negative sequence detection algorithm, based on the negative-sequence measuring quantities, a high value of voltage 3u 2 without the presence of the negative-sequence current 3i 2 , is recommended for use in isolated or high-impedance earthed networks. The zero sequence detection algorithm, base...
Page 182
When closing the local breaker when the line is already energized from the other end. When the remote breaker closes the voltage will return except in the phase that has a persistent fuse fail. Since the local breaker is open there is no current and the dead phase indication will persist in the phas...
Page 183
3 2 3 2 100 = × i i ibase equation1520 v3 en (equation 73) where: 3i2 is the maximal negative sequence current during normal operating conditions, plus a margin of 10...20% ibase is the setting of base current for the function 9.2.3.4 zero sequence based the relay setting value 3u0> is given in perc...
Page 184
Normal switching conditions in the network. The delta current and delta voltage function shall always be used together with either the negative or zero sequence algorithm. If usetprim is the primary voltage for operation of du/dt and isetprim the primary current for operation of di/dt, the setting o...
Page 185
9.3.2 application tcsscbr detects faults in the electrical control circuit of the circuit breaker. The function can supervise both open and closed coil circuits. This kind of supervision is necessary to find out the vitality of the control circuits continuously. Trip circuit supervision generates a ...
Page 186
1 psm 2 rs (+) (-) hw s w po1 tcs1 is v is: constant current generator. Current level ~ 1,0 ma (i c ) v: transient voltage suppressor breakdown voltage 380 to 400 vdc i c cbpos_open tcsscbr tcs_state block alarm iec13000026-2-en.Vsd guid-6b09f9c7-86d0-4a7a-8e08-8e37cae53249 v3 en figure 77: operatin...
Page 187
Several trip-circuit supervision functions parallel in circuit not only the trip circuit often have parallel trip contacts, it is also possible that the circuit has multiple tcs circuits in parallel. Each tcs circuit causes its own supervising current to flow through the monitored coil and the actua...
Page 188
Table 22: values recommended for the external resistor r ext operating voltage u c shunt resistor r ext 48 v dc 10 kΩ, 5 w 60 v dc 22 kΩ, 5 w 110 v dc 33 kΩ, 5 w 220 v dc 68 kΩ, 5 w due to the requirement that the voltage over the tcsscbr contact must be 20v or higher, the correct operation is not g...
Page 189
Section 10 control 10.1 synchrocheck, energizing check, and synchronizing sesrsyn 10.1.1 identification function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number synchrocheck, energizing check, and synchronizing sesrsyn sc/vc symbol-m v1 en 25 10.1.2 applic...
Page 190
Frequencies must also be within a range of +/- 5 hz from the rated frequency. When the synchronizing option is included also for autoreclose there is no reason to have different frequency setting for the manual and automatic reclosing and the frequency difference values for synchronism check should ...
Page 191
The need for a check of synchronization increases if the meshed system decreases since the risk of the two networks being out of synchronization at manual or automatic closing is greater. The synchrocheck function measures the conditions across the circuit breaker and compares them to set limits. Ou...
Page 192
Synchrocheck fuse fail fuse fail line voltage line reference voltage bus voltage . U-bus > 80 % of gblbaseselbus u-line > 80 % of gblbaseselline udiffsc phasediffm phasediffa freqdiffm freqdiffa iec08000021_2_en.Vsd iec08000021 v2 en figure 80: principle for the synchrocheck function 10.1.2.3 energi...
Page 193
~ 1 2 a b energizingcheck bus voltage . U-bus (live) > 80% of gblbaseselbus u-line (live) > 80% of gblbaseselline u-bus (dead) u-line (dead) u-bus and u-line and/or gblbaseselline line voltage iec08000022-3-en.Vsd iec08000022 v3 en figure 81: principle for the energizing check function the energizin...
Page 194
Auxiliary contacts, the right voltages for the synchronizing, synchrocheck and energizing check functions can be selected. Available voltage selection types are for single circuit breaker with double busbars and the 1½ circuit breaker arrangement. A double circuit breaker arrangement and single circ...
Page 195
Slggio block psto up down ^p01 ^p02 ^p03 ^p04 ^p05 ^p06 ^p07 ^p08 ^p09 ^p10 ^p11 ^p12 ^p13 ^p14 ^p15 ^p16 ^p17 ^p18 ^p19 ^p20 ^p21 ^p22 ^p23 ^p24 ^p25 ^p26 ^p27 ^p28 ^p29 ^p30 ^p31 ^p32 swposn intone iec08000023-2-en.Vsd sesrsyn u3pbb1* u3pbb2* u3pln1* u3pln2* block blksynch blksc blkenerg b1qopen b...
Page 196
10.1.3.1 single circuit breaker with single busbar line bus 1 qb1 qa1 fuse vt iec08000024_2_en.Vsd ubus uline fuse vt smai smai grp_off sesrsyn u3pbb1* u3pbb2* u3pln1* u3pln2* block blksynch blksc blkenerg b1qopen b1qcld b2qopen b2qcld ln1qopen ln1qcld ln2qopen ln2qcld ub1ok ub1ff ub2ok ub2ff uln1ok...
Page 197
10.1.3.2 single circuit breaker with double busbar, external voltage selection bus 1 bus 2 qb1 qb2 line qa1 fuse vt fuse vt fuse vt iec08000025_2_en.Vsd ubus sesrsyn u3pbb1* u3pbb2* u3pln1* u3pln2* block blksynch blksc blkenerg b1qopen b1qcld b2qopen b2qcld ln1qopen ln1qcld ln2qopen ln2qcld ub1ok ub...
Page 198
10.1.3.3 single circuit breaker with double busbar, internal voltage selection bus 1 bus 2 qb1 qb2 line qa1 fuse vt fuse vt iec09000738-2-en.Vsd smai grp_off smai smai ubus1 ubus2 uline fuse vt sesrsyn u3pbb1* u3pbb2* u3pln1* u3pln2* block blksynch blksc blkenerg b1qopen b1qcld b2qopen b2qcld ln1qop...
Page 199
X:sesrsyn has been divided into four different setting groups: general, synchronizing, synchrocheck and energizing check. General settings operation: the operation mode can be set on or off. The setting off disables the whole function. Gblbaseselbus and gblbaseselline these configuration settings ar...
Page 200
• a. Different phase-neutral voltages are selected (for example ul1 for bus and ul2 for line); • b. One available voltage is phase-phase and the other one is phase-neutral (for example ul1l2 for bus and ul1 for line). The set value is added to the measured line phase angle. The bus voltage is refere...
Page 201
Note! The freqdiffmin shall be set to the same value as freqdiffm respective freqdiffa for sesrsyn irrespective of whether the functions are used for manual operation, autoreclosing or both. Freqdiffmax the setting freqdiffmax is the maximum slip frequency at which synchronizing is accepted. 1/freqd...
Page 202
With the setting on, the function is in service and the output signal depends on the input conditions. Udiffsc setting for voltage difference between line and bus in p.U. This setting in p.U is defined as (measured u-bus/ubase for bus according to gblbaseselbus) - (measured u-line/ ubase for line ac...
Page 203
Group, and the bus voltage is above 80% of the bus base voltage ubase, according to the setting gblbaseselbus. • dbll, dead bus live line, the bus voltage is below 40% of the bus base voltage ubase, according to the setting gblbaseselbus about the global base value group, and the line voltage is abo...
Page 204
Of the line breakers. The dead time selected should be long enough to ensure a high probability of arc de-ionization and successful reclosing. For individual line breakers, auto-reclosing equipment or functions, the auto- reclosing open time is used to determine line “dead time”. When simultaneous t...
Page 205
End. If auto-reclosing functions are included in duplicated line protection, which means two auto-reclosing functions per cb, one should take measures to avoid uncoordinated reclosing commands. In 1 1/2 breaker, double-breaker and ring bus arrangements, two cbs per line end are operated. One auto-re...
Page 206
A permanent fault will cause the line protection to trip again when it recloses in an attempt to clear the fault. The auto-reclosing function allows a number of parameters to be adjusted. Examples: • number of auto-reclosing shots • auto-reclosing open times (dead time) for each shot 10.2.2.1 auto-r...
Page 207
Auto-reclosing start pulse is generated and latched in the function, subject to the usual checks. Then the reclosing sequence continues as usual. One needs to connect signals from manual tripping and other functions, which shall prevent reclosing, to the input inhibit. 10.2.2.4 blocking of the autor...
Page 208
When issuing a cb closing command a “reclaim” timer treclaim is started. If no tripping takes place during that time the auto-reclosing function resets to the “ready” state and the signal active resets. If the first reclosing shot fails, 2nd to 5th reclosing shots will follow, if selected. 10.2.2.9 ...
Page 209
Hardwired, or carried out by means of communication. There are also different alternatives regarding what shall generate lock-out. Examples of questions are: • shall back-up time delayed trip give lock-out (normally yes) • shall lock-out be generated when closing onto a fault (mostly) • shall lock-o...
Page 210
Close command or smbrrec or ccrbrf bu-trip zcvpsof-trip inhibit unsuccl trbu iec08000246-2-en.Vsd smpptrc and reset lock-out or or sesrsyn software or io reset auto stop man enok man close smbrrec close cllout rstlout iec08000246 v2 en figure 88: lock-out arranged with internal logic with manual clo...
Page 211
Recommendations for input signals please see examples in figure 89 . On and off these inputs can be connected to binary inputs or to a communication interface block for external control. Start it should be connected to the trip output protection function, which starts the autorecloser for 3-phase op...
Page 212
Trsotf this is the signal “trip by switch onto fault”. It is usually connected to the “switch onto fault” output of line protection if multi-shot auto-reclose attempts are used. The input will start the shots 2-5. For single shot applications the input is set to false. Tholhold signal “thermal overl...
Page 213
Active indicates that smbrrec is active, from start until end of reclaim time. Inprogr indicates that a sequence is in progress, from start until reclosing command. Unsuccl indicates unsuccessful reclosing. Closecb connect to a binary output for circuit-breaker closing command. Ready indicates that ...
Page 214
On off blkon blockoff inhibit blocked seton inprogr active unsuccl succl closecb cbready cbpos wfmaster reset start tholhold ready trsotf sync input xx xx xx xx xx xx xx xx xx >1 >1 output xx xx xx xx xx xx xx xx xx xx protection xxxx-trip zcvpsof-trip zqmpdis--trip sesrsyn-autook bio bio smbrrec ie...
Page 215
Pollution etc. Can influence the required dead time. Some users apply delayed auto- reclosing (dar) with delays of 10s or more. The delay of reclosing shot 2 and possible later shots are usually set at 30s or more. A check that the cb duty cycle can manage the selected setting must be done. The sett...
Page 216
Tcbclosedmin a typical setting is 5.0 s. If the cb has not been closed for at least this minimum time, a reclosing start will not be accepted. Cbauxconttype , cb auxiliary contact type it shall be set to correspond to the cb auxiliary contact used. A normopen contact is recommended in order to gener...
Page 217
Autocont and tautocontwait , automatic continuation to the next shot if the cb is not closed within the set time the normal setting is autocont = off. The tautocontwait is the length of time smbrrec waits to see if the breaker is closed when autocont is set to on. Normally, the setting can be tautoc...
Page 218
In st an t o f f au lt s tb r r e c re se t open closed operate time line protection circuit breaker break time t rip c om m an d c on ta ct s se pa ra te d a re e xt in gu is he rs fault duration stbrrec open time for breaker fault duration r es et s o pe ra te s break time closing time operate tim...
Page 219
Residual current protections (earth fault protection) with the single pole tripping and the auto-reclosing function. Attention shall also be paid to “pole discrepancy” (pole discordance) that arises when circuit breakers are provided with single pole operating devices. These breakers need pole discr...
Page 220
Automatic-reclosing should not be attempted when closing a cb and energizing a line onto a fault (sotf), except when multiple-shots are used where shots 2 etc. Will be started at sotf. Likewise a cb in a multi-breaker bus bar arrangement which was not closed when a fault occurred should not be close...
Page 221
• number of auto-reclosing shots • auto-reclosing program • auto-reclosing open times (dead time) for each shot. 10.3.2.1 auto-reclosing operation off and on operation of the automatic reclosing can be set off and on by a setting parameter and by external control. Parameter operation = off, or on se...
Page 222
10.3.2.4 blocking of the autorecloser auto-reclose attempts are expected to take place only in the event of transient faults on the own line. The auto-recloser must be blocked for the following conditions: • tripping from delayed distance protection zones • tripping from back-up protection functions...
Page 223
The decision is also made in the tripping function block (tr) where the setting 3ph, 1/3ph is selected. 10.3.2.8 firstshot=3ph (normal setting for a single 3 phase shot) 3-phase reclosing, one to five shots according to setting noofshots. The output three- phase trip prep3p is always set (high). A t...
Page 224
Noofshots parameter). During 3-phase trip (tr2p low and tr3p high) the auto- reclosing will be blocked and no reclosing takes place. 10.3.2.11 firstshot=1ph + 1*3ph 1-phase or 3-phase reclosing in the first shot at 1-phase trip, the operation is as described above. If the first reclosing shot fails,...
Page 225
10.3.2.14 reclosing reclaim timer the reclaim timer treclaim defines the time it takes from issue of the reclosing command, until the reclosing function resets. Should a new trip occur during this time, it is treated as a continuation of the first fault. The reclaim timer is started when the cb clos...
Page 226
• shall back-up time delayed trip give lock-out (normally yes) • shall lock-out be generated when closing onto a fault (mostly) • shall lock-out generated when the auto-recloser was off at the fault • shall lock-out be generated if the breaker did not have sufficient operating power for an auto-recl...
Page 227
10.3.2.18 automatic continuation of the reclosing sequence the auto-reclosing function can be programmed to proceed to the following reclosing shots (if selected) even if the start signals are not received from the protection functions, but the breaker is still not closed. This is done by setting pa...
Page 228
On off blkon blockoff inhibit blocked seton inprogr active unsuccl succl closecb cbready cbpos wfmaster reset start tholhold ready trsotf sync input xx xx xx xx xx xx xx xx xx >1 >1 output xx xx xx xx xx xx xx xx xx xx protection xxxx-trip zcvpsof-trip zqdpdis or zmopdis--trip sesrsyn-autook bio bio...
Page 229
Is often a combination of signals from external ieds via the io and internal functions. An or gate is then used for the combination. Cbpos and cbready these should be connected to binary inputs to pick-up information from the cb. The cbpos input is interpreted as cb closed, if parameter cbauxconttyp...
Page 230
Blockoff used to unblock the auto-reclosing function when it has gone to block due to activating input blkon or by an unsuccessful auto-reclose attempt if the setting blockbyunsuccl is set to on. Input is normally set to false. Reset used to reset the auto-recloser to start condition. Possible therm...
Page 231
Prep3p prepare three-phase trip is usually connected to the trip block to force a coming trip to be a three-phase one. If the function cannot make a single- or two-phase reclosing, the tripping should be three-phase. Wfmaster wait from master is used in high priority units to hold back reclosing of ...
Page 232
By national regulations. For multiple shots the setting of shots 2-5 must be longer than the circuit breaker duty cycle time. Extended t1 and textended t1 extended auto-reclosing open time for shot 1. The communication link in a permissive (not strict) line protection scheme, for instance a power li...
Page 233
Tcbclosedmin a typical setting is 5.0 s. If the cb has not been closed for at least this minimum time, a reclosing start will not be accepted. Cbauxconttype , cb auxiliary contact type it shall be set to correspond to the cb auxiliary contact used. A normopen contact is recommended in order to gener...
Page 234
Autocont and tautocontwait , automatic continuation to the next shot if the cb is not closed within the set time the normal setting is autocont = off. The tautocontwait is the length of time stbrrec waits to see if the breaker is closed when autocont is set to on. Normally the setting can be tautoco...
Page 235
Station hmi gw cc station bus breakers disconnectors earthing switches iec08000227.Vsd apparatus control ied i/o local hmi apparatus control ied i/o apparatus control ied i/o local hmi local hmi iec08000227 v1 en figure 94: overview of the apparatus control functions features in the apparatus contro...
Page 236
• bay control qcbay • local remote locrem • local remote control locremctrl scswi, sxcbr, qcbay and sxswi are logical nodes according to iec 61850. The signal flow between these function blocks appears in figure 95 . The function logical node interlocking (scilo) in the figure 95 is the logical node...
Page 237
Accepted originator categories for psto if the requested command is accepted due to the authority allocation control, the respective value will change. Otherwise the attribute blocked-by-switcing-hierarky is set in the cause signal. If the psto value is changed under a command, then the command is r...
Page 238
• a request initiates to reserve other bays to prevent simultaneous operation. • actual position inputs for interlocking information are read and evaluated if the operation is permitted. • the synchrocheck/synchronizing conditions are read and checked, and performs operation upon positive response. ...
Page 239
Iec13000016-1-en.Vsd iec13000016 v1 en figure 96: apc - local remote function block 10.4.3 interaction between modules a typical bay with apparatus control function consists of a combination of logical nodes or functions that are described here: • the switch controller (scswi) initializes all operat...
Page 240
• the autorecloser (smbrrec) consists of the facilities to automatically close a tripped breaker with respect to a number of configurable conditions. • the logical node interlocking (scilo) provides the information to scswi whether it is permitted to operate due to the switchyard topology. The inter...
Page 241
Iec09000207_1_en.Vsd oc4ptoc (overcurrent) sxcbr (circuit breaker) interlocking function block (not a ln) scswi (switching control) qcbay (bay control) smbrrec (auto- recloser) i/o trip close rel. Selected s ta rt s m b r r e c close cb position reserved operator place selection scswi (switching con...
Page 242
10.4.4.1 switch controller (scswi) the parameter ctlmodel specifies the type of control model according to iec 61850. For normal control of circuit breakers, disconnectors and earthing switches the control model is set to sbo enh (select-before-operate) with enhanced security. When the operation sha...
Page 243
10.5 interlocking 10.5.1 identification function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number logical node for interlocking scilo - 3 interlocking for busbar earthing switch bb_es - 3 interlocking for bus-section breaker a1a2_bs - 3 interlocking for bus...
Page 244
Earthing switches are allowed to connect and disconnect earthing of isolated points. Due to capacitive or inductive coupling there may be some voltage (for example 40% of rated voltage) before earthing and some current (for example earthing of a line. Circuit breakers are usually not interlocked. Cl...
Page 245
10.5.5 interlocking for bus-section breaker a1a2_bs 10.5.6 interlocking for bus-section disconnector a1a2_dc 10.5.7 interlocking for bus-coupler bay abc_bc 10.5.8 interlocking for 1 1/2 cb bh 10.5.9 interlocking for double cb bay db 10.5.10 interlocking for line bay abc_line 10.5.11 interlocking for...
Page 246
Slggio can be activated both from the local hmi and from external sources (switches), via the ied binary inputs. It also allows the operation from remote (like the station computer). Swposn is an integer value output, giving the actual output number. Since the number of positions of the switch can b...
Page 247
10.7.2 application selector mini switch (vsggio) function is a multipurpose function used in the configuration tool in pcm600 for a variety of applications, as a general purpose switch. Vsggio can be used for both acquiring an external switch position (through the ipos1 and the ipos2 inputs) and rep...
Page 248
10.8 iec61850 generic communication i/o functions dpggio 10.8.1 identification function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number iec 61850 generic communication i/o functions dpggio - - 10.8.2 application the iec61850 generic communication i/o funct...
Page 249
Positions, the only functional position usable with the spc8ggio function block is remote. 10.9.3 setting guidelines the parameters for the single point generic control 8 signals (spc8ggio) function are set via the local hmi or pcm600. Operation: turning the function operation on/off. There are two ...
Page 250
10.10.3 setting guidelines autobits function block has one setting, (operation: on/off) enabling or disabling the function. These names will be seen in the dnp communication configuration tool in pcm600. Section 10 1mrk 505 291-uen a control 244 application manual.
Page 251
Section 11 logic 11.1 tripping logic common 3-phase output smpptrc 11.1.1 identification function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number tripping logic common 3-phase output smpptrc i->o symbol-k v1 en 94 11.1.2 application all trip signals from t...
Page 252
Iec11000054-1-en.Vsd iec11000054 v1 en figure 99: tripping logic common 3-phase output smpptrc is used for a simple three-phase tripping application 11.1.2.2 lock-out this function block is provided with possibilities to initiate lock-out. The lock-out can be set to only activate the block closing o...
Page 253
Operation: sets the mode of operation. Off switches the function off. The normal selection is on. Triplockout: sets the scheme for lock-out. Off only activates the lock-out output. On activates the lock-out output and latches the output trip. The normal selection is off. Autolock: sets the scheme fo...
Page 254
Transferred on the line during the dead time that arises before reclosing. Single phase tripping during single phase faults must be combined with single pole reclosing. 11.2.2.1 single- and/or three-phase tripping the single-/three-phase tripping will give single-phase tripping for single-phase faul...
Page 255
Iec11000055-1-en.Vsd iec11000055 v1 en figure 100: the tripping logic phase segregated output sptptrc used for single-phase tripping application 11.2.2.2 lock out this function block is provided with possibilities to initiate lock-out. The lock-out can be set to only activate the block closing outpu...
Page 256
Sets the mode of operation. Off switches the tripping off. The normal selection is on. Triplockout sets the scheme for lock-out. Off only activates lock-out output. On activates the lock- out output and latching output contacts. The normal selection is off. Autolock sets the scheme for lock-out. Off...
Page 257
Ondelay: used to prevent output signals to be given for spurious inputs. Normally set to 0 or a low value. Used only for modeoutputx: steady. Offdelay: defines a minimum on time for the outputs. When used for direct tripping of circuit breaker(s) the off delay time shall be set to approximately 0.15...
Page 258
Function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number timer function block timerset - - function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number and function block and - - function description iec 61850 identi...
Page 259
Iec09000695_2_en.Vsd iec09000695 v2 en figure 101: example designation, serial execution number and cycle time for logic function the execution of different function blocks within the same cycle is determined by the order of their serial execution numbers. Always remember this when connecting two or...
Page 260
Example for use of grp_off signal in fxdsign the restricted earth fault function refpdif can be used both for auto-transformers and normal transformers. When used for auto-transformers, information from both windings parts, together with the neutral point current, needs to be available to the functi...
Page 261
11.6.2 application boolean 16 to integer conversion function b16i is used to transform a set of 16 binary (logical) signals into an integer. It can be used – for example, to connect logical output signals from a function (like distance protection) to integer inputs from another function (like line d...
Page 262
11.8.2 application integer to boolean 16 conversion function (ib16a) is used to transform an integer into a set of 16 binary (logical) signals. It can be used – for example, to connect integer output signals from one function to binary (logical) inputs to another function. Ib16a function does not ha...
Page 263
11.10 elapsed time integrator with limit transgression and overflow supervision teiggio 11.10.1 identification function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number elapsed time integrator teiggio - - 11.10.2 application the function teiggio is used for...
Page 264
258.
Page 265
Section 12 monitoring 12.1 iec61850 generic communication i/o functions spggio 12.1.1 identification function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number iec 61850 generic communication i/o functions spggio - - 12.1.2 application iec 61850–8–1 generic ...
Page 266
12.2.3 setting guidelines the function does not have any parameters available in local hmi or protection and control ied manager (pcm600). 12.3 iec61850 generic communication i/o functions mvggio 12.3.1 identification function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c...
Page 267
12.4 measurements 12.4.1 identification function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number measurements cvmmxn p, q, s, i, u, f symbol-rr v1 en - phase current measurement cmmxu i symbol-ss v1 en - phase-phase voltage measurement vmmxu u symbol-uu v1...
Page 268
Proper direction orientation for distance or directional overcurrent protection function. The available measured values of an ied are depending on the actual hardware (trm) and the logic configuration made in pcm600. All measured values can be supervised with four settable limits that is, low-low li...
Page 269
The measuring functions cmsqi and vmsqi provide sequence component quantities: • i: sequence currents (positive, zero, negative sequence, amplitude and angle) • u: sequence voltages (positive, zero and negative sequence, amplitude and angle). The cvmmxn function calculates three-phase power quantiti...
Page 270
Parameters ibase, ubase and sbase have been implemented as a settings instead of a parameters, which means that if the values of the parameters are changed there will be no restart of the application. As restart is required to activate new parameters values, the ied must be restarted in some way. Ei...
Page 271
Limits are directly set in applicable measuring unit, v, a , and so on, for all measureing functions, except cvmmxn where limits are set in % of the base quantity. Xhihilim: high-high limit. Xhilim: high limit. Xlowlim: low limit. Xlowlowlim: low-low limit. Xlimhyst: hysteresis value in % of range a...
Page 272
Iec05000652 v2 en figure 104: calibration curves 12.4.4 setting examples three setting examples, in connection to measurement function (cvmmxn), are provided: • measurement function (cvmmxn) application for a 110kv ohl • measurement function (cvmmxn) application on the secondary side of a transforme...
Page 273
110kv busbar 110kv ohl p q 600/1 a 110 0,1 / 3 3 kv iec09000039-2-en.Vsd ied iec09000039-1-en v2 en figure 105: single line diagram for 110kv ohl application in order to monitor, supervise and calibrate the active and reactive power as indicated in figure 105 it is necessary to do the following: 1. ...
Page 274
Table 27: settings parameters for level supervision setting short description selected value comments pmin minimum value -100 minimum expected load pmax minimum value 100 maximum expected load pzerodb zero point clamping in 0.001% of range 3000 set zero point clamping to 45 mw that is, 3% of 200 mw ...
Page 275
12.5 event counter cntggio 12.5.1 identification function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number event counter cntggio s00946 v1 en - 12.5.2 application event counter (cntggio) has six counters which are used for storing the number of times each c...
Page 276
If applicable, the counter can be set to stop or rollover to zero and continue counting after reaching the maximum count value. The steady overflow output flag indicates the next count after reaching the maximum count value. It is also possible to set the counter to rollover and indicate the overflo...
Page 277
Disturbance report drprdre, always included in the ied, acquires sampled data of all selected analog and binary signals connected to the function blocks that is, • maximum 30 external analog signals, • 10 internal derived analog signals, and • 96 binary signals. Disturbance report function is a comm...
Page 278
Trip value rec event list event recorder indications disturbance recorder a1-4radr b1-6rbdr disturbance report binary signals analog signals a4radr b6rbdr drprdre iec09000337-2-en.Vsd iec09000337 v2 en figure 106: disturbance report functions and related function blocks for disturbance report functi...
Page 279
• disturbance reports are not stored. • led information (yellow - start, red - trip) is not stored or changed. Operation = on: • disturbance reports are stored, disturbance data can be read from the local hmi and from a pc using pcm600. • led information (yellow - start, red - trip) is stored. Every...
Page 280
Post retrigger (postretrig) can be set to on or off. Makes it possible to choose performance of disturbance report function if a new trig signal appears in the post- fault window. Postretrig = off the function is insensitive for new trig signals during post fault time. Postretrig = on the function c...
Page 281
If operationm = on, waveform (samples) will also be recorded and reported in graph. Nomvaluem: nominal value for input m. Overtrigopm, undertrigopm: over or under trig operation, disturbance report may trig for high/low level of analog input m (on) or not (off). Overtriglem, undertriglem: over or un...
Page 282
Handled if the recording functions do not have proper settings. The goal is to optimize the settings in each ied to be able to capture just valuable disturbances and to maximize the number that is possible to save in the ied. The recording time should not be longer than necessary (postfaultrect and ...
Page 283
12.8.3 setting guidelines the function does not have any parameters available in local hmi or protection and control ied manager (pcm600). Globalbasesel: selects the global base value group used by the function to define (ibase), (ubase) and (sbase). 12.9 station battery supervision spvnzbat 12.9.1 ...
Page 284
12.10 insulation gas monitoring function ssimg 12.10.1 identification function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number insulation gas monitoring function ssimg - 63 12.10.2 application insulation gas monitoring function (ssimg) is used for monitori...
Page 285
Function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number circuit breaker condition monitoring sscbr - - 12.12.2 application sscbr includes different metering and monitoring subfunctions. Circuit breaker status circuit breaker status monitors the position o...
Page 286
Remaining life of the breaker every time the breaker operates, the life of the circuit breaker reduces due to wearing. The wearing in the breaker depends on the tripping current, and the remaining life of the breaker is estimated from the circuit breaker trip curve provided by the manufacturer. Exam...
Page 287
The directional coefficient is calculated according to the formula: directional coef b a i i f r = = − log log . 2 2609 a070794 v2 en (equation 79) i r rated operating current = 630 a i f rated fault current = 16 ka a op number rated = 30000 b op number fault = 20 calculation for estimating the rema...
Page 288
282.
Page 289
Section 13 metering 13.1 pulse counter pcggio 13.1.1 identification function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number pulse counter pcggio s00947 v1 en - 13.1.2 application pulse counter (pcggio) function counts externally generated binary pulses, f...
Page 290
Input channels on the binary input output module (bio) have individual settings for debounce time, oscillation count and oscillation time. The values can be changed in the local hmi and pcm600 under main menu/configuration/i/o modules the debunce time should be set to the same value for all channels...
Page 291
The energy values can be read through communication in mwh and mvarh in monitoring tool of pcm600 and/or alternatively the values can be presented on the local hmi. The local hmi graphical display is configured with pcm600 graphical display editor tool (gde) with a measuring value which is selected ...
Page 292
Erfaccplsqty and erraccplsqty: gives the mvarh value in each pulse. It should be selected together with the setting of the pulse counter (pcggio) settings to give the correct total pulse value. For the advanced user there are a number of settings for direction, zero clamping, max limit, and so on. N...
Page 293
Section 14 station communication 14.1 iec61850-8-1 communication protocol 14.1.1 identification function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number iec 61850-8-1 communication protocol iec 61850-8-1 - - 14.1.2 application iec 61850-8-1 communication p...
Page 294
Kiosk 2 kiosk 3 station hsi base system engineering workstation sms gateway printer cc iec09000135_en.V sd kiosk 1 ied 1 ied 2 ied 3 ied 1 ied 2 ied 3 ied 1 ied 2 ied 3 iec09000135 v1 en figure 109: example of a communication system with iec 61850–8–1 figure 110 shows the goose peer-to-peer communic...
Page 295
14.1.2.1 horizontal communication via goose goose messages are sent in horizontal communication between the ieds. The information, which is exchanged, is used for station wide interlocking, breaker failure protection, busbar voltage selection and so on. The simplified principle is shown in figure 11...
Page 296
Iec08000174.Vsd iec08000174 v1 en figure 112: smt: goose marshalling with smt goose receive function blocks extract process information, received by the data set, into single attribute information that can be used within the application configuration. Crosses in the smt matrix connect received value...
Page 297
Iec11000056-1-en.Vsd iec11000056 v1 en figure 113: smt: goose receive function block with converted signals 14.1.3 setting guidelines there are two settings related to the iec 61850–8–1 protocol: operation user can set iec 61850 communication to on or off. Goose has to be set to the ethernet link wh...
Page 298
14.3 iec 60870-5-103 communication protocol iec 60870-5-103 is an unbalanced (master-slave) protocol for coded-bit serial communication exchanging information with a control system, and with a data transfer rate up to 19200 bit/s. In iec terminology, a primary station is a master and a secondary sta...
Page 299
Switch a switch b 1 2 data data data data iec13000003-1-en.Vsd ied prpstatus 1 2 com03 a b duo redundancy supervision station control system iec13000003 v1 en figure 114: redundant station bus 14.6 setting guidelines the redundant station bus communication is configured using the local hmi, main men...
Page 300
The ethlan1_ab in the parameter setting tool is relevant only when the com03 module is present. Iec13000009-1-en.Vsd iec13000009 v1 en figure 115: prp1 configured in the parameter setting tool iec13000010-1-en.Vsd iec13000010 v1 en figure 116: lock/unlock parameter section 14 1mrk 505 291-uen a stat...
Page 301
Iec13000008-1-en.Vsd iec13000008 v1 en figure 117: pst screen: operationmode is set to prp(a+b) 1mrk 505 291-uen a section 14 station communication 295 application manual.
Page 302
296.
Page 303
Section 15 basic ied functions 15.1 self supervision with internal event list 15.1.1 identification function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number internal error signal interrsig - - internal event list selfsupevlst - - 15.1.2 application the pro...
Page 304
The internal events are time tagged with a resolution of 1 ms and stored in a list. The list can store up to 40 events. The list is based on the fifo principle, that is, when it is full, the oldest event is overwritten. The list can be cleared via the local hmi . The list of internal events provides...
Page 305
Time base for the ieds in a protection and control system. This makes comparison and analysis of events and disturbance data between all ieds in the power system possible. Time-tagging of internal events and disturbances are an excellent help when evaluating faults. Without time synchronization, onl...
Page 306
• off • sntp • irig-b the parameter syncmaster defines if the ied is a master, or not a master for time synchronization in a system of ieds connected in a communication network (iec61850-8-1). The syncmaster can have the following values: • off • sntp -server the time synchronization fine tunes the ...
Page 307
Iedtimeskew. But in linmastime it applies the time changes occurred between two synchronised messages. • iedtimeskew: the ied measures the offset in between its own time and the master time and applies the same offset for the messages sent. • evaltimeaccuracy evaluates time accuracy for invalid time...
Page 308
15.3.3 setting guidelines the setting activesetgrp, is used to select which parameter group to be active. The active group can also be selected with configured input to the function block actvgrp. The parameter maxnosetgrp defines the maximum number of setting groups in use to switch between. Only t...
Page 309
15.5 change lock chnglck 15.5.1 identification function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number change lock function chnglck - - 15.5.2 application change lock function chnglck is used to block further changes to the ied configuration once the comm...
Page 310
Permanently issue a logical one to the chnglck input. If such a situation would occur in spite of these precautions, then please contact the local abb representative for remedial action. 15.5.3 setting guidelines the change lock function chnglck does not have any parameters available in the local hm...
Page 311
15.7.2 application 15.7.2.1 factory defined settings the factory defined settings are very useful for identifying a specific version and very helpful in the case of maintenance, repair, interchanging ieds between different substation automation systems and upgrading. The factory made settings can no...
Page 312
15.8 primary system values primval 15.8.1 identification function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number primary system values primval - - 15.8.2 application the rated system frequency and phasor rotation are set under main menu/ configuration/ po...
Page 313
15.9.3 setting guidelines the parameters for the signal matrix for analog inputs (smai) functions are set via the local hmi or via the pcm600. Every smai function block can receive four analog signals (three phases and one neutral value), either voltage or current. Smai outputs give information abou...
Page 314
Settings dftrefextout and dftreference shall be set to default value internaldftref if no vt inputs are available. Even if the user sets the analoginputtype of a smai block to “current”, the minvalfreqmeas is still visible. However, using the current channel values as base for frequency measurement ...
Page 315
Example 1 smai_20_7:1 block dftspfc revrot ^grp1l1 ^grp1l2 ^grp1l3 ^grp1n spfcout ai3p ai1 ai2 ai3 ai4 ain smai_20_1-12:2 block dftspfc revrot ^grp1l1 ^grp1l2 ^grp1l3 ^grp1n spfcout ai3p ai1 ai2 ai3 ai4 ain iec09000028-2-en.Vsd iec09000028 v2 en figure 120: configuration for using an instance in tas...
Page 316
15.10.2 application summation block 3 phase function 3phsum is used to get the sum of two sets of three-phase analog signals (of the same type) for those ied functions that might need it. 15.10.3 setting guidelines the summation block receives the three-phase signals from smai blocks. The summation ...
Page 317
15.11.3 setting guidelines ubase: phase-to-phase voltage value to be used as a base value for applicable functions throughout the ied. Ibase: phase current value to be used as a base value for applicable functions throughout the ied. Sbase: standard apparent power value to be used as a base value fo...
Page 318
Iec12000202-1-en.Vsd iec12000202 v1 en figure 121: pcm600 user management tool 15.12.2.1 authorization handling in the ied at delivery the default user is the superuser. No log on is required to operate the ied until a user has been created with the ied user management.. Once a user is created and w...
Page 319
The cursor is focused on the user identity field, so upon pressing the key, one can change the user name, by browsing the list of users, with the “up” and “down” arrows. After choosing the right user name, the user must press the key again. When it comes to password, upon pressing the key, the follo...
Page 320
15.14 denial of service 15.14.1 identification function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number denial of service, frame rate control for front port dosfrnt - - function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 ...
Page 321
Section 16 requirements 16.1 current transformer requirements the performance of a protection function will depend on the quality of the measured current signal. Saturation of the current transformer (ct) will cause distortion of the current signal and can result in a failure to operate or cause unw...
Page 322
In the non-saturated region of operation. Class tpz according to iec is a non remanence type ct. Different standards and classes specify the saturation e.M.F. In different ways but it is possible to approximately compare values from different classes. The rated equivalent limiting secondary e.M.F. E...
Page 323
The current transformer requirements are based on the maximum fault current for faults in different positions. Maximum fault current will occur for three-phase faults or single phase-to-earth faults. The current for a single phase-to-earth fault will exceed the current for a three-phase fault when t...
Page 324
It is advisable to check the actual unwanted residual current during the commissioning. 16.1.6 rated equivalent secondary e.M.F. Requirements with regard to saturation of the current transformer all current transformers of high remanence and low remanence type that fulfill the requirements on the ra...
Page 325
Sn r al alreq op ct l 2 pn r i s e e 1,5 i r r i i æ ö ³ = × × × + + ç ÷ è ø equation1381 v1 en (equation 81) where: i op the primary operate value (a) i pn the rated primary ct current (a) i sn the rated secondary ct current (a) i r the rated current of the protection ied (a) r ct the secondary res...
Page 326
Independent of the value of i op the maximum required e al is specified according to the following: sn r al alreq max k max ct l 2 pn r i s e e i r r i i æ ö ³ = × × + + ç ÷ è ø equation1077 v1 en (equation 83) where i kmax maximum primary fundamental frequency current for close-in faults (a) 16.1.6...
Page 327
Comparing this with the required rated equivalent limiting secondary e.M.F. E alreq it is possible to judge if the ct fulfills the requirements. The requirements according to some other standards are specified below. 16.1.7.1 current transformers according to iec 61869-2, class p, pr a ct according ...
Page 328
E a lansi 20 i s n r c t u a nsi + × × 20 i s n r c t × × 20 i s n z b ansi × × + = = equation971 v1 en (equation 87) where: z bansi the impedance (that is, with a complex quantity) of the standard ansi burden for the specific c class (w) u ansi the secondary terminal voltage for the specific c clas...
Page 329
16.3 sntp server requirements 16.3.1 sntp server requirements the sntp server to be used is connected to the local network, that is not more than 4-5 switches or routers away from the ied. The sntp server is dedicated for its task, or at least equipped with a real-time operating system, that is not ...
Page 330
324.
Page 331
Section 17 glossary ac alternating current acc actual channel act application configuration tool within pcm600 a/d converter analog-to-digital converter adbs amplitude deadband supervision ai analog input ansi american national standards institute ar autoreclosing asct auxiliary summation current tr...
Page 332
Cr carrier receive crc cyclic redundancy check crob control relay output block cs carrier send ct current transformer cu communication unit cvt capacitive voltage transformer dar delayed autoreclosing darpa defense advanced research projects agency (the us developer of the tcp/ip protocol etc.) dbdl...
Page 333
Fox 20 modular 20 channel telecommunication system for speech, data and protection signals fox 512/515 access multiplexer fox 6plus compact time-division multiplexer for the transmission of up to seven duplex channels of digital data over optical fibers ftp file transfer protocal fun function type g...
Page 334
Specifications from the pci sig (special interest group) for the electrical emf (electromotive force). Ieee 1686 standard for substation intelligent electronic devices (ieds) cyber security capabilities ied intelligent electronic device i-gis intelligent gas-insulated switchgear instance when severa...
Page 335
Oltc on-load tap changer otev disturbance data recording initiated by other event than start/pick-up ov over-voltage overreach a term used to describe how the relay behaves during a fault condition. For example, a distance relay is overreaching when the impedance presented to it is smaller than the ...
Page 336
Sma connector subminiature version a, a threaded connector with constant impedance. Smt signal matrix tool within pcm600 sms station monitoring system sntp simple network time protocol – is used to synchronize computer clocks on local area networks. This reduces the requirement to have accurate hard...
Page 337
Umt user management tool underreach a term used to describe how the relay behaves during a fault condition. For example, a distance relay is underreaching when the impedance presented to it is greater than the apparent impedance to the fault applied to the balance point, that is, the set reach. The ...
Page 338
332.
Page 339
333.
Page 340
Contact us for more information please contact: abb ab grid automation products se-721 59 västerås, sweden phone +46 (0) 21 32 50 00 www.Abb.Com/protection-control note: we reserve the right to make technical changes or modify the contents of this document without prior notice. Abb ab does not accep...