- DL manuals
- ABB
- Security Sensors
- ret650
- Technical manual
ABB ret650 Technical manual
Summary of ret650
Page 1
Relion ® 650 series transformer protection ret650 technical manual.
Page 3
Document id: 1mrk 504 135-uen issued: october 2016 revision: a product version: 1.3 © copyright 2013 abb. All rights reserved.
Page 4
Copyright this document and parts thereof must not be reproduced or copied without written permission from abb, and the contents thereof must not be imparted to a third party, nor used for any unauthorized purpose. The software and hardware described in this document is furnished under a license and...
Page 5
Disclaimer the data, examples and diagrams in this manual are included solely for the concept or product description and are not to be deemed as a statement of guaranteed properties. All persons responsible for applying the equipment addressed in this manual must satisfy themselves that each intende...
Page 6
Conformity this product complies with the directive of the council of the european communities on the approximation of the laws of the member states relating to electromagnetic compatibility (emc directive 2004/108/ec) and concerning electrical equipment for use within specified voltage limits (low-...
Page 7
Table of contents section 1 introduction.....................................................................29 this manual...................................................................................... 29 intended audience.........................................................................
Page 8
Basic part for led indication module............................................... 58 identification................................................................................ 58 function block............................................................................. 58 signals................
Page 9
Restrained and unrestrained limits of the differential protection................................................................................94 fundamental frequency negative sequence differential currents.................................................................................. 96 inter...
Page 10
Operation principle.................................................................... 125 resistive reach in forward direction..................................... 126 resistive reach in reverse direction..................................... 127 reactive reach in forward and reverse direction........
Page 11
Identification ............................................................................. 143 functionality.............................................................................. 143 function block........................................................................... 144 signals.........
Page 12
Operation principle.................................................................... 175 technical data........................................................................... 179 breaker failure protection 3-phase activation and output ccrbrf 179 identification...................................
Page 13
Signals.......................................................................................198 settings......................................................................................199 monitored data...........................................................................200 operation p...
Page 14
Design.................................................................................. 219 technical data........................................................................... 221 overexcitation protection oexpvph ............................................ 221 identification...................
Page 15
Technical data........................................................................... 238 rate-of-change frequency protection sapfrc .............................238 identification.............................................................................. 239 functionality.......................
Page 16
Settings................................................................................ 259 circuit breaker sxcbr..............................................................259 signals..................................................................................259 settings......................
Page 17
Interlocking for bus-section breaker a1a2_bs..........................275 identification......................................................................... 275 functionality......................................................................... 276 function block................................
Page 18
Identification......................................................................... 322 functionality......................................................................... 322 function block...................................................................... 323 logic diagram..................
Page 19
Operation principle.................................................................... 355 selector mini switch vsggio.........................................................355 identification.............................................................................. 355 functionality.............
Page 20
Signals.......................................................................................366 settings......................................................................................367 function commands generic for iec 60870-5-103 i103gencmd.367 functionality.................................
Page 21
Fixed signals fxdsign..................................................................391 identification.............................................................................. 391 functionality.............................................................................. 391 function block.....
Page 22
Signals.......................................................................................404 settings......................................................................................405 operation principle.................................................................... 405 operation ac...
Page 23
Settings................................................................................ 426 monitored data..................................................................... 427 operation principle.................................................................... 427 measurement supervision.......
Page 24
Settings................................................................................ 452 analog input signals a4radr...................................................455 identification......................................................................... 455 function block......................
Page 25
Input signals......................................................................... 477 operation principle.................................................................... 477 technical data........................................................................... 477 trip value recorder.......
Page 26
Identification.............................................................................. 487 functionality.............................................................................. 488 function block........................................................................... 488 signals.........
Page 27
Operation counter.................................................................505 accumulation of i y t................................................................506 remaining life of the circuit breaker..................................... 508 circuit breaker spring charged indication........
Page 28
Status for user defined signals for iec 60870-5-103 i103usrdef521 functionality.............................................................................. 521 function block........................................................................... 522 signals........................................
Page 29
Operation principle.................................................................... 540 goose vctr configuration for send and receive goosevctrconf...................................................................... 541 identification...............................................................
Page 30
Iec 60870-5-103 communication protocol..................................... 549 functionality.............................................................................. 549 settings......................................................................................550 iec 61850-8-1 redundant st...
Page 31
Time system, summer time ends dstend...............................566 identification......................................................................... 566 settings................................................................................ 566 time zone from utc timezone....................
Page 32
Product information ....................................................................... 579 identification.............................................................................. 579 functionality.............................................................................. 579 settings......
Page 33
Function block........................................................................... 596 signals.......................................................................................596 settings......................................................................................596 operation ...
Page 34
Signal outputs.................................................................................617 power outputs.................................................................................617 data communication interfaces...................................................... 618 enclosure class...
Page 35
Section 1 introduction 1.1 this manual the technical manual contains application and functionality descriptions and lists function blocks, logic diagrams, input and output signals, setting parameters and technical data, sorted per function. The manual can be used as a technical reference during the ...
Page 36
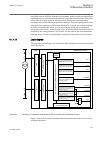
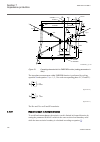
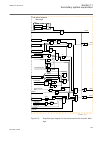
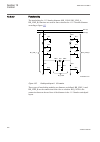
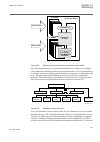
1.3 product documentation 1.3.1 product documentation set iec07000220-3-en.Vsd p la nn in g & p u rc h a se e n g in e e ri ng in st al lin g c om m is si o n in g o p e ra tio n m a in te na n ce d ec om m is si o n in g d ei n st a lli n g & d is po sa l application manual operation manual install...
Page 37
Chronological order in which the ied should be commissioned. The relevant procedures may be followed also during the service and maintenance activities. The operation manual contains instructions on how to operate the ied once it has been commissioned. The manual provides instructions for the monito...
Page 38
650 series manuals identity number cyber security deployment guidelines 1mrk 511 285-uen point list manual, dnp 3.0 1mrk 511 283-uen engineering manual 1mrk 511 284-uen operation manual 1mrk 500 096-uen installation manual 1mrk 514 016-uen accessories, 650 series 1mrk 513 023-ben mics 1mrg 010 656 p...
Page 39
1.4.2 document conventions • abbreviations and acronyms in this manual are spelled out in the glossary. The glossary also contains definitions of important terms. • push button navigation in the lhmi menu structure is presented by using the push button icons. For example, to navigate between the opt...
Page 40
34.
Page 41
Section 2 available functions 2.1 main protection functions iec 61850 or function name ansi function description transformer ret650 ret650 (a01 ) 2w/1cb ret650 (a05 ) 3w/1cb ret650 (a07 ) oltc differential protection t2wpdif 87t transformer differential protection, two winding 0–1 1 t3wpdif 87t tran...
Page 42
Iec 61850 or function name ansi function description transformer ret650 ret650 (a01) 2w/1cb ret650 (a05) 3w/1cb ret650 (a07) oltc ccrbrf 50bf breaker failure protection, 3–phase activation and output 0–3 2 3 ccrpld 52pd pole discordance protection 0–3 2 3 guppdup 37 directional underpower protection...
Page 43
Iec 61850 or function name ansi function description transformer ret650 ret650 (a01) 2w/1cb ret650 (a05) 3w/1cb ret650 (a07) oltc i103iedcmd ied commands for iec60870-5-103 1 1 1 1 i103usrcmd function commands user defined for iec60870-5-103 4 4 4 4 i103gencmd function commands generic for iec60870-...
Page 44
Iec 61850 or function name ansi function description transformer ret650 ret650 (a01) 2w/1cb ret650 (a05) 3w/1cb ret650 (a07) oltc inverter configurable logic blocks 140 140 140 140 pulsetimer configurable logic blocks 40 40 40 40 gate configurable logic blocks 40 40 40 40 xor configurable logic bloc...
Page 45
Iec 61850 or function name ansi function description transformer ret650 ret650 (a01) 2w/1cb ret650 (a05) 3w/1cb ret650 (a07) oltc aisvbas function block for service values presentation of the analog inputs 1 1 1 1 tm_p_p2 function block for service values presentation of primary analog inputs 600trm...
Page 46
Iec 61850 or function name ansi function description transformer ret650 ret650 (a01) 2w/1cb ret650 (a05) 3w/1cb ret650 (a07) oltc metering pcggio pulse counter 16 16 16 16 etpmmtr function for energy calculation and demand handling 3 3 3 3 2.4 station communication iec 61850 or function name ansi fu...
Page 47
Iec 61850 or function name ansi function description transformer ret650 ret650 (a01) 2w/1cb ret650 (a05) 3w/1cb ret650 (a07) oltc dnpfrec dnp3.0 fault records for tcp/ip communication protocol 1 1 1 1 optical103 iec60870-5-103 optical serial communication 1 1 1 1 rs485103 iec60870-5-103 serial commu...
Page 48
Iec 61850/function block name function description timesynchgen time synchronization 1 sntp time synchronization 1 dtsbegin, dtsend, timezone time synchronization, daylight saving 1 irig-b time synchronization 1 setgrps setting group handling 1 actvgrp parameter setting groups 1 testmode test mode f...
Page 49
Section 3 analog inputs 3.1 introduction analog input channels in the ied must be set properly in order to get correct measurement results and correct protection operations. For power measuring and all directional and differential functions the directions of the input currents must be defined in ord...
Page 50
Protected object line, transformer, etc forward reverse definition of direction for directional functions measured quantity is positive when flowing towards the object e.G. P, q, i reverse forward definition of direction for directional functions e.G. P, q, i measured quantity is positive when flowi...
Page 51
3.4 settings dependent on ordered ied type. Table 1: aisvbas non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description phaseangleref trm - channel 1 trm - channel 2 trm - channel 3 trm - channel 4 trm - channel 5 trm - channel 6 trm - channel 7 trm - channel 8 trm - channel 9 trm ...
Page 52
Name values (range) unit step default description ctstarpoint6 fromobject toobject - - toobject toobject= towards protected object, fromobject= the opposite ctsec6 0.1 - 10.0 a 0.1 1.0 rated ct secondary current ctprim6 1 - 99999 a 1 1000 rated ct primary current vtsec7 0.001 - 999.999 v 0.001 110.0...
Page 53
Name values (range) unit step default description ctprim7 1 - 99999 a 1 1000 rated ct primary current ctstarpoint8 fromobject toobject - - toobject toobject= towards protected object, fromobject= the opposite ctsec8 0.1 - 10.0 a 0.1 1.0 rated ct secondary current ctprim8 1 - 99999 a 1 1000 rated ct ...
Page 54
Table 5: trm_4i_6u non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description ctstarpoint1 fromobject toobject - - toobject toobject= towards protected object, fromobject= the opposite ctsec1 0.1 - 10.0 a 0.1 1 rated ct secondary current ctprim1 1 - 99999 a 1 1000 rated ct primary ...
Page 55
Name values (range) unit step default description ctstarpoint3 fromobject toobject - - toobject toobject= towards protected object, fromobject= the opposite ctsec3 0.1 - 10.0 a 0.1 1 rated ct secondary current ctprim3 1 - 99999 a 1 1000 rated ct primary current ctstarpoint4 fromobject toobject - - t...
Page 56
Name values (range) unit step default description ctprim4 1 - 99999 a 1 1000 rated ct primary current ctstarpoint5 fromobject toobject - - toobject toobject= towards protected object, fromobject= the opposite ctsec5 0.1 - 10.0 a 0.1 1.0 rated ct secondary current ctprim5 1 - 99999 a 1 1000 rated ct ...
Page 57
Section 4 binary input and output modules 4.1 binary input 4.1.1 binary input debounce filter the debounce filter eliminates bounces and short disturbances on a binary input. A time counter is used for filtering. The time counter is increased once in a millisecond when a binary input is high, or dec...
Page 58
Each binary input has an oscillation count parameter oscillationcountx and an oscillation time parameter oscillationtimex, where x is the number of the binary input of the module in question. 4.1.3 settings 4.1.3.1 setting parameters for binary input modules table 8: bio_9bi non group settings (basi...
Page 59
Name values (range) unit step default description oscillationtime6 0.000 - 600.000 s 0.001 0.000 oscillation time for input 6 threshold7 6 - 900 %ub 1 65 threshold in percentage of station battery voltage for input 7 debouncetime7 0.000 - 0.100 s 0.001 0.005 debounce time for input 7 oscillationcoun...
Page 60
Name values (range) unit step default description threshold4 6 - 900 %ub 1 65 threshold in percentage of station battery voltage for input 4 debouncetime4 0.000 - 0.100 s 0.001 0.005 debounce time for input 4 oscillationcount4 0 - 255 - 1 0 oscillation count for input 4 oscillationtime4 0.000 - 600....
Page 61
Name values (range) unit step default description debouncetime12 0.000 - 0.100 s 0.001 0.005 debounce time for input 12 oscillationcount12 0 - 255 - 1 0 oscillation count for input 12 oscillationtime12 0.000 - 600.000 s 0.001 0.000 oscillation time for input 12 1mrk 504 135-uen a section 4 binary in...
Page 62
56.
Page 63
Section 5 local human-machine-interface lhmi 5.1 local hmi screen behaviour 5.1.1 identification function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number local hmi screen behaviour screen - - 5.1.2 settings table 12: screen non group settings (basic) name ...
Page 64
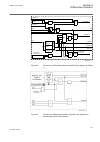
Lhmictrl clrleds hmi-on red-s yellow-s yellow-f clrpulse ledsclrd iec09000320-1-en.Vsd iec09000320 v1 en figure 3: lhmictrl function block 5.2.3 signals table 13: lhmictrl input signals name type default description clrleds boolean 0 input to clear the lcd-hmi leds table 14: lhmictrl output signals ...
Page 65
Ledgen block reset newind ack iec09000321-1-en.Vsd iec09000321 v1 en figure 4: ledgen function block grp1_led1 ^hm1l01r ^hm1l01y ^hm1l01g iec09000322 v1 en figure 5: grp1_led1 function block the grp1_led1 function block is an example, all 15 led in each of group 1 - 3 has a similar function block. 5...
Page 66
5.3.4 settings table 18: ledgen non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description operation off on - - off operation off/on trestart 0.0 - 100.0 s 0.1 0.0 defines the disturbance length tmax 0.0 - 100.0 s 0.1 0.0 maximum time for the definition of a disturbance table 19: g...
Page 67
5.4.3 signals table 20: fnkeymd1 input signals name type default description ledctl1 boolean 0 led control input for function key table 21: fnkeymd1 output signals name type description fkeyout1 boolean output controlled by function key 5.4.4 settings table 22: fnkeymd1 non group settings (basic) na...
Page 68
5.5 operation principle 5.5.1 local hmi iec12000175 v1 en figure 7: local human-machine interface the lhmi of the ied contains the following elements: • display (lcd) • buttons • led indicators • communication port for pcm600 the lhmi is used for setting, monitoring and controlling. 5.5.1.1 display ...
Page 69
Iec13000063-1-en.Vsd iec13000063 v1 en figure 8: display layout 1 path 2 content 3 status 4 scroll bar (appears when needed) • the path shows the current location in the menu structure. If the path is too long to be shown, it is truncated from the beginning, and the truncation is indicated with thre...
Page 70
Iec13000045-1-en.Vsd iec13000045 v1 en figure 9: truncated path the number before the function instance, for example ethfrnt:1, indicates the instance number. The function button panel shows on request what actions are possible with the function buttons. Each function button has a led indication tha...
Page 71
Guid-d20bb1f1-fdf7-49ad-9980-f91a38b2107d v1 en figure 11: alarm led panel the function button and alarm led panels are not visible at the same time. Each panel is shown by pressing one of the function buttons or the multipage button. Pressing the esc button clears the panel from the display. Both t...
Page 72
Iec11000247 v2 en figure 12: lhmi keypad with object control, navigation and command push- buttons and rj-45 communication port 1...5 function button 6 close 7 open 8 escape 9 left 10 down 11 up 12 right 13 user log on 14 enter 15 remote/local 16 uplink led 17 ethernet communication port (rj-45) 18 ...
Page 73
Each indication led on local hmi can be set individually to operate in 6 different sequences; two as follow type and four as latch type. Two of the latching sequence types are intended to be used as a protection indication system, either in collecting or restarting mode, with reset functionality. Th...
Page 74
• from function input • the active indications can also be acknowledged/reset from an input, ack_rst, to the function. This input can for example be configured to a binary input operated from an external push button. The function is positive edge triggered, not level triggered. This means that even ...
Page 75
Activating signal led iec01000228_2_en.Vsd iec01000228 v2 en figure 14: operating sequence 1 (follow-s) if inputs for two or more colors are active at the same time to one led the priority is as described above. An example of the operation when two colors are activated in parallel is shown in figure...
Page 76
Activating signal led acknow. En01000231.Vsd iec01000231 v1 en figure 16: operating sequence 3 latchedack-f-s when an acknowledgment is performed, all indications that appear before the indication with higher priority has been reset, will be acknowledged, independent of if the low priority indicatio...
Page 77
Activating signal red led acknow. Iec09000314-1-en.Vsd activating signal yellow g y r r y activating signal green iec09000314 v1 en figure 18: operating sequence 3, three colors involved, alternative 1 if an indication with higher priority appears after acknowledgment of a lower priority indication ...
Page 78
Iec01000235_2_en.Vsd activating signal led reset iec01000235 v2 en figure 20: operating sequence 5 latchedcoll-s that means if an indication with higher priority has reset while an indication with lower priority still is active at the time of reset, the led will change color according to figure 21 ....
Page 79
Iec01000239_2-en.Vsd activating signal 2 led 2 manual reset activating signal 1 automatic reset led 1 disturbance trestart iec01000239 v2 en figure 22: operating sequence 6 (latchedreset-s), two indications within same disturbance figure 23 shows the timing diagram for a new indication after trestar...
Page 80
Figure 24 shows the timing diagram when a new indication appears after the first one has reset but before trestart has elapsed. Iec01000241_2_en.Vsd activating signal 2 led 2 manual reset activating signal 1 automatic reset led 1 disturbance trestart iec01000241 v2 en figure 24: operating sequence 6...
Page 81
Iec01000242_2_en.Vsd activating signal 2 led 2 manual reset activating signal 1 automatic reset led 1 disturbance trestart iec01000242 v2 en figure 25: operating sequence 6 (latchedreset-s), manual reset 5.5.3 function keys 5.5.3.1 functionality local human-machine-interface (lhmi) has five function...
Page 82
Operating sequence the operation mode is set individually for each output, either off, toggle or pulsed. Setting off this mode always gives the output the value. A change of the input value does not affect the output value. Input value output value iec09000330-1-en.Vsd iec09000330 v1 en figure 26: s...
Page 83
Input value t pulse t pulse output value iec09000332_1_en.Vsd iec09000332 v1 en figure 28: sequence diagram for setting pulsed input function all inputs work the same way: when the lhmi is configured so that a certain function button is of type control, then the corresponding input on this function ...
Page 84
78.
Page 85
Section 6 differential protection 6.1 transformer differential protection 6.1.1 functionality the transformer differential protection, two-winding t2wpdif and transformer differential protection, three-winding t3wpdif are provided with internal ct ratio matching and vector group compensation and set...
Page 86
Stabilization is included for inrush and overexcitation currents respectively, cross- blocking is also available. Adaptive stabilization is also included for system recovery inrush and ct saturation during external faults. A high set unrestrained differential current protection element is included f...
Page 87
Table 25: t2wpdif output signals name type description trip boolean general trip signal tripres boolean start signal from restrained differential protection tripunre boolean start signal from unrestrained differential protection trnsunr boolean start signal from unrestrained negative sequence differ...
Page 88
Name values (range) unit step default description idunre 1.00 - 50.00 ib 0.01 10.00 unrestrained protection limit, multiple of w1 rated current i2/i1ratio 5.0 - 100.0 % 0.1 15.0 maximum ratio of 2nd harmonic to fundamental harmonic differential current i5/i1ratio 5.0 - 100.0 % 0.1 25.0 maximum ratio...
Page 89
6.1.2.5 monitored data table 28: t2wpdif monitored data name type values (range) unit description idl1mag real - a magnitude of fundamental frequency differential current, phase l1 idl2mag real - a magnitude of fundamental frequency differential current, phase l2 idl3mag real - a magnitude of fundam...
Page 90
6.1.3.3 signals table 29: t3wpdif input signals name type default description i3pw1ct1 group signal - three phase current connection winding 1 (w1) ct1 i3pw2ct1 group signal - three phase current connection winding 2 (w2) ct1 i3pw3ct1 group signal - three phase current connection winding 3 (w3) ct1 ...
Page 91
6.1.3.4 settings table 31: t3wpdif group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description operation off on - - off operation off / on idmin 0.10 - 0.60 ib 0.01 0.30 section 1 sensitivity current, usually w1 current endsection1 0.20 - 1.50 ib 0.01 1.25 end of section 1, multiple of ...
Page 92
Name values (range) unit step default description connecttypew3 wye (y) delta (d) - - delta (d) connection type of winding 3: y-wye or d- delta clocknumberw2 0 [0 deg] 1 [30 deg lag] 2 [60 deg lag] 3 [90 deg lag] 4 [120 deg lag] 5 [150 deg lag] 6 [180 deg] 7 [150 deg lead] 8 [120 deg lead] 9 [90 deg...
Page 93
6.1.4 operation principle the task of the power transformer differential protection is to determine whether a fault is within the protected zone, or outside of the protected zone. The protected zone is limited by the position of current transformers (see figure 32 ), and in principle can include mor...
Page 94
Proportional bias, which makes the protection operate for a certain percentage differential current related to the current through the transformer. This stabilizes the protection under through fault conditions while still permitting the system to have good basic sensitivity. The following chapters e...
Page 95
1 1_ 1 1_ 2 1_ 3 _ 2 _ 3 2 2 _ 1 2 _ 2 2 _ 3 _ 1 _ 1 3 3 _ 1 3_ 2 3 _ 3 idl il w il w il w un w un w idl a il w b il w c il w un w un w idl il w il w il w é ù é ù é ù é ù ê ú ê ú ê ú ê ú = × + × × + × × ê ú ê ú ê ú ê ú ê ú ê ú ê ú ê ú ë û ë û ë û ë û 1 2 3 4 equation1556 v2 en (equation 2) where: 1....
Page 96
When the end user enters all these parameters, transformer differential function automatically determines the matrix coefficients based on the following rules: for the phase reference, the highest voltage star (y) connected winding is used. For example, if the power transformer is a yd1 power transf...
Page 97
Matrix with zero sequence reduction set to on matrix with zero sequence reduction set to off matrix for winding with 120° lagging 1 1 2 1 2 1 1 3 1 2 1 - - × - - - - é ù ê ú ê ú ê ú ë û equation1233 v1 en (equation 9) 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 1 0 é ù ê ú ê ú ê ú ë û equation1234 v1 en (equation 10) matrix for ...
Page 98
1. Hv star (y) connected winding will be used as reference winding and zero sequence currents shall be subtracted on that side 2. The lv winding is lagging for 150° with the help of table 34 , the following matrix equation can be written for this power transformer: 1 2 1 1 1_ 1 1 0 1 1_ 2 1 _ 2 1 2 ...
Page 99
6.1.4.3 differential current alarm the fundamental frequency differential current level is monitored at all times within the differential function. As soon as all three fundamental frequency differential currents are set above the set alarm level (idiffalarm), the pickup timer is started. When the p...
Page 100
In false differential currents - consisting exclusively of the zero sequence currents. If high enough, these false differential currents can cause an unwanted disconnection of the healthy power transformer. They must therefore be subtracted from the fundamental frequency differential currents if an ...
Page 101
Section 1 operate conditionally unrestrainedlimit section 2 section 3 restrain operate unconditionally 5 4 3 2 1 0 0 1 2 3 4 5 idmin endsection1 endsection2 restrain current [ times ibase ] operate current [ times ibase ] slopesection2 slopesection3 en05000187-2.Vsd iec05000187 v2 en figure 33: desc...
Page 102
Section 2: in section 2, a certain minor slope is introduced which is supposed to cope with false differential currents due to higher than normal currents through the current transformers, such as during a transformer overloading situation. Section 3: the more pronounced slope in section 3 is design...
Page 103
2 2 1 _ 2 1 1 _ 1 1 0 1 _ 2 1 _ 2 1 2 _ 1 2 1 _ 1 1 1 0 _ 2 3 _ 1 3 3 _ 1 1 2 _ 1 0 1 1 _ 2 idl ns ins w ins w ur w idl ns a ins w a ins w ur w idl ns a ins w a ins w - - - = - - × + - × - - - × × × × × × × é ù é ù é ù é ù é ù ê ú ê ú ê ú ê ú ê ú ê ú ê ú ê ú ê ú ê ú ê ú ê ú ê ú ê ú ê ú ë û ë û ë û ë...
Page 104
Current from the w2 side compensated for eventual power transformer phase shift and transferred to the power transformer w1 side. These negative sequence current contributions are phasors, which are further used in directional comparisons, to characterize a fault as internal or external. See section...
Page 105
1. Iminnegseq 2. Negseqroa 0 deg 180 deg 90 deg 270 deg 120 deg iminnegseq if one or the other of currents is too low, then no measurement is done, and 120 degrees is mapped external fault region internal fault region internal/external fault boundary negseqroa (relay operate angle) en05000188-3-en.V...
Page 106
• if the negative sequence current contributions from the w1 and the w2 sides are in phase, the fault is internal • if the negative sequence currents contributions from w1 and w2 sides are 180 degrees out of phase, the fault is external for example, for any unsymmetrical external fault, ideally the ...
Page 107
Zero value. However, during heavy faults, ct saturation might cause the measured phase angle to differ from 180 degrees for an external, and from 0 degrees for an internal fault. See figure 36 for an example of a heavy internal fault with transient ct saturation. En05000190.Vsd 0.5 ka 30 210 60 240 ...
Page 108
Because one or more of the fundamental frequency differential currents entered the operate region on the operate - restrain characteristic. So, this protection is not independent of the traditional restrained differential protection - it is activated after the first start signal has been placed. If ...
Page 109
6.1.4.10 instantaneous differential currents the instantaneous differential currents are calculated from the instantaneous values of the input currents in order to perform the harmonic analysis and waveform analysis upon each one of them (see section "harmonic and waveform block criteria" for more i...
Page 110
Iec05000343 v1 en figure 37: inrush currents to a transformer as seen by a protection ied. Typical is a high amount of the 2 nd harmonic, and intervals of low current, and low rate-of-change of current within each period. Cross-blocking between phases with the cross-blocking function, one of the thr...
Page 111
Sinusoidal currents will flow from the very beginning. In this case the waveform block algorithm removes all its three block signals in a very short interval of time. This quick reset of the waveblock criterion will temporarily disable the second harmonic blocking feature of the differential protect...
Page 112
The following currents are inputs to the power transformer differential protection function. They must all be expressed in power system (primary) a. 1. Instantaneous values of currents (samples) from the hv, and lv sides for two- winding power transformers, and from the hv, the first lv, and the sec...
Page 113
Idunre idl1mag 2nd harmonic 5th harmonic wave block idl1 and cross block from l2 or l3 opcrossblock=on or 1 ibias tripunrel1 stl1 tripresl1 blk2hl1 blkwavl1 en06000545.Vsd a b b>a or and cross block to l2 or l3 and and and blkunres block blkres blk5hl1 s w itc h o n to f au lt lo gi c iec06000545 v1...
Page 114
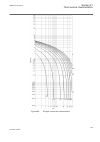
En05000278.Vsd tripresl1 tripresl2 tripresl3 or tripres tripunrel1 tripunrel2 tripunrel3 or tripunre or trip trnsunr trnssens iec05000278 v1 en figure 41: transformer differential protection internal grouping of tripping signals iec05000279-tiff v1 en figure 42: transformer differential protection i...
Page 115
All phases with set start signal are free of their respective block signals, a restrained trip tripres and common trip trip are issued 3. If a start signal is issued in a phase, and the fault has been classified as internal, then any eventual block signals are overridden and a unrestrained negative-...
Page 116
6.1.5 technical data table 35: t2wpdif, t3wpdif technical data function range or value accuracy operating characteristic adaptable ± 1.0% of ir for i ± 1.0% of i for i > ir reset ratio >94% - unrestrained differential current limit (1.00-50.00)x ibase on high voltage winding ± 1.0% of set value base...
Page 117
6.2.2 functionality restricted earth-fault protection, low-impedance function refpdif can be used on all directly or low-impedance earthed windings. The refpdif function provides high sensitivity and high speed tripping as it protects each winding separately and thus does not need inrush stabilizati...
Page 118
Signal description idiff magnitude of fundamental frequency differential current angle direction angle from zero sequence feature i2ratio second harmonic ratio 6.2.5 settings table 38: basic general settings for the function refpdif (ref1-) parameter range step default unit description globalbasesel...
Page 119
6.2.7 operation principle 6.2.7.1 fundamental principles of the restricted earth-fault protection restricted earth-fault protection, low impedance function (refpdif) detects earth faults on earthed power transformer windings, most often an earthed star winding. Refpdif is a winding protection of the...
Page 120
Iec09000108-3-en.Vsd return path via power system l1 l2 l3 i n = - 3izs1 uzs current in the neutral (measured as i n ) serves as a directional reference because it has the same direction for both internal and external faults. Zone of protection i zs1 i zs1 i zs1 return path through transformer i l1 ...
Page 121
Refpdif is a differential protection where the line zero sequence (residual) current is calculated from 3 line (terminal) currents, a bias quantity must give stability against false operations due to high through fault currents. To stabilize refpdif at external faults, a fixed bias characteristic is...
Page 122
Bias current in per unit zero- sequence diff. Current in per unit 0 1 2 3 4 5 idmin section 1 operate conditionally i operate slope = ----------------* 100 % i restrain sec. 2 section 3 the characteristic can be moved up and down (vertically) by changing the setting idmin end section 1 end section 2...
Page 123
If there are two feeders included in the zone of protection of refpdif, then the respective bias current is found as the relatively highest of the following currents, that is, those which are connected in an application: 1 current[1] = max (i3pw1ct1) ctfactorpri1 × equation1526 v1 en (equation 27) 1...
Page 124
(refpdif) must remain stable during an external fault, and immediately after the fault has been cleared by some other protection. For an external earth faults with no ct saturation, the residual current in the lines (3i o ) and the neutral current (i n in figure 45 ) are theoretically equal in magni...
Page 125
Calculated. If it is found to be above 60% the trip request counter is reset and trip remains zero. 9. Finally, a check is made if the trip request counter is equal to or higher than 2. If it is and that at the same instance of time t reftrip , the actual bias current at this instance of time t reft...
Page 126
6.3.2 introduction the 1ph high impedance differential protection hzpdif functions can be used when the involved ct cores have the same turns ratio and similar magnetizing characteristics. Each utilizes an external summation of the currents in the interconnected cts, a series resistor, and a voltage...
Page 127
6.3.5 settings table 46: hzpdif group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description operation off on - - off operation off / on u>alarm 2 - 500 v 1 10 alarm voltage level in volts on ct secondary side talarm 0.000 - 60.000 s 0.001 5.000 time delay to activate alarm u>trip 5 - 90...
Page 128
Iec05000301 v1 en figure 49: logic diagram for 1ph high impedance differential protection hzpdif 6.3.8 technical data table 48: hzpdif technical data function range or value accuracy operate voltage (20-400) v i=u/r ± 1.0% of i r reset ratio >95% - maximum continuous power u>trip 2 /seriesresistor ≤...
Page 129
Section 7 impedance protection 7.1 power swing detection zmrpsb 7.1.1 identification function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number power swing detection zmrpsb zpsb symbol-ee v1 en 68 7.1.2 functionality power swings may occur after disconnectio...
Page 130
7.1.4 signals table 49: zmrpsb input signals name type default description i3p group signal - three phase group signal for current inputs u3p group signal - three phase group signal for voltage inputs block boolean 0 block of function blki01 boolean 0 block inhibit of start output for slow swing con...
Page 131
Name values (range) unit step default description kldrfw 0.50 - 0.90 mult 0.01 0.75 multiplication factor for inner resistive load boundary, forward kldrrv 0.50 - 0.90 mult 0.01 0.75 multiplication factor for inner resistive load boundary, reverse iminoppe 5 - 30 %ib 1 10 minimum operate current in ...
Page 132
R jx argld argld rldoutfw rldinfw r1finfw r1finrv rldinrv rldoutrv x1infw x1outfw zl r1lin x1inrv x1outrv iec09000222_1_en.Vsd d rv d rv d rv d rv d rv d fw d fw d fw d fw d fw d fw j j j iec09000222 v1 en figure 51: operating characteristic for zmrpsb function (setting parameters in italic) the imp...
Page 133
Rldinfw = kldrfw·rldoutfw equation1185 v2 en (equation 32) where: kldrfw is a settable multiplication factor less than 1 the slope of the load encroachment inner and outer boundary is defined by setting the parameter argld. The load encroachment in the fourth quadrant uses the same settings as in th...
Page 134
Argument of the tilted lines outside the load encroachment is the same as the tilted lines in the first quadrant. The distance between the inner and outer boundary is the same as for the load encroachment in reverse direction, that is drv. 7.1.6.3 reactive reach in forward and reverse direction the ...
Page 135
Iec05000113-2-en.Vsd and zinl1 and det-l1 or and and zoutl1 -loop zoutl2 zoutl3 or detected or -loop 0-tp1 0 0-tp2 0 0 0-tw iec05000113 v2 en figure 52: detection of power swing in phase l1 iec09000223_2_en.Vsd i0check and blki02 t 10 ms and blki01 block inhibit zoutl3 zoutl2 zoutl1 external and sta...
Page 136
7.1.6.5 operating and inhibit conditions figure 53 presents a simplified logic diagram for the power swing detection function zmrpsb. The load encroachment characteristic can be switched off by setting the parameter operationldch = off, but notice that the dfw and drv will still be calculated from r...
Page 137
7.2.2 functionality the underimpedance protection for generators and transformers zgcpdis, has the offset mho characteristic as a three zone back-up protection for detection of phase-to- phase short circuits in transformers and generators. The full scheme three zones have independent measuring phase...
Page 138
7.2.4 signals table 55: zgcpdis input signals name type default description i3p group signal - three phase group signal for current u3p group signal - three phase group signal for voltage block boolean 0 block of function blkz boolean 0 block due to fuse fail ldcnd integer 56 load enchroachment bina...
Page 139
Name values (range) unit step default description opmodez3 disable-zone enable-zone - - disable-zone operation mode of zone 3 z3fwd 0.005 - 3000.000 ohm/p 0.001 30.000 forward reach setting for zone 3 z3rev 0.005 - 3000.000 ohm/p 0.001 30.000 reverse reach setting for zone 3 tz3 0.000 - 60.000 s 0.0...
Page 140
R jx mho, zone3 mho, zone2 mho, zone1 iec09000172_1_en.Vsd iec09000172 v1 en figure 56: mho, offset mho characteristic zone 3 can be equipped with a load encroachment function which cuts off a section of the characteristic when enabled. The function is activated by setting the parameter loadenchmodz...
Page 141
Impedanceang x r z1 fw d z1 re v iec10000176-2-en.Vsd iec10000176 v2 en figure 57: mho, offset mho characteristic for zone 1 with setting parameters z1fwd, z1rev and impedanceang the three impedance zones can be time delayed individually by setting the parameter tzx (where x is 1-3 depending on sele...
Page 142
The characteristic for offset mho is a circle where two points on the circle are the setting parameters zxfwd and zxrev. The vector zxfwd in the impedance plane has the settable angle impedanceang and the angle for zxrev is impedanceang+180°. The condition for operation at phase-to-phase fault is th...
Page 143
7.2.7 technical data table 60: zgcpdis technical data function range or value accuracy number of zones 3 - forward positive sequence impedance (0.005-3000.000) Ω/ phase ± 2.0% static accuracy conditions: • voltage range: (0.1-1.1) x u r • current range: (0.5-30) x i r • angle: at 85 degrees reverse ...
Page 144
7.3.3 function block lepdis i3p* u3p* block stcndle iec10000119-1-en.Vsd iec10000119 v1 en figure 59: lepdis function block 7.3.4 signals table 61: lepdis input signals name type default description i3p group signal - three phase group signal for current inputs u3p group signal - three phase group s...
Page 145
The difference compared to the distance zone measuring function is in the combination of measuring quantities (currents and voltages) for different types of faults. The current start condition stcndle is based on the following criteria: 1. Residual current criteria 2. Load encroachment characteristi...
Page 146
7.3.6.2 simplified logic diagrams figure 61 schematically presents the creation of the phase-to-phase operating conditions. Iec10000226-1-en.Vsd & & t 10 ms t 20 ms & bool to integer stcndle block & block 0 3 0.1 i 0 3 0.4 phmax i i × & or 0 3 0.05 i ³ 0 3 0.2 phmax i i ³ × r x l1 l1l2 & iec10000226...
Page 147
Section 8 current protection 8.1 instantaneous phase overcurrent protection 3-phase output phpioc 8.1.1 identification function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number instantaneous phase overcurrent protection 3-phase output phpioc 3i>> symbol-z v...
Page 148
8.1.5 settings table 68: phpioc group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description operation off on - - off operation off / on ip>> 5 - 2500 %ib 1 200 operate phase current level in % of ibase table 69: phpioc non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default des...
Page 149
Function range or value accuracy reset time 30 ms typically at 2 to 0 x i set - critical impulse time 10 ms typically at 0 to 2 x i set - operate time 10 ms typically at 0 to 5 x i set - reset time 40 ms typically at 5 to 0 x i set - critical impulse time 2 ms typically at 0 to 5 x i set - dynamic o...
Page 150
8.2.3 function block iec08000002-2-en.Vsd oc4ptoc i3p* u3p* block blkst1 blkst2 blkst3 blkst4 trip tr1 tr2 tr3 tr4 start st1 st2 st3 st4 stl1 stl2 stl3 2ndharm iec08000002 v2 en figure 63: oc4ptoc function block 8.2.4 signals table 72: oc4ptoc input signals name type default description i3p group si...
Page 151
Name type description stl1 boolean start signal from phase l1 stl2 boolean start signal from phase l2 stl3 boolean start signal from phase l3 st2ndhrm boolean second harmonic detected 8.2.5 settings table 74: oc4ptoc group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description operation ...
Page 152
Name values (range) unit step default description dirmode3 off non-directional forward reverse - - non-directional directional mode of step 3 off / non- directional / forward / reverse i3> 5 - 2500 %ib 1 250 phase current operate level for step3 in % of ibase t3 0.000 - 60.000 s 0.001 0.800 definite...
Page 153
Table 76: oc4ptoc non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description globalbasesel 1 - 6 - 1 1 selection of one of the global base value groups meastype dft rms - - dft selection between dft and rms measurement 8.2.6 monitored data table 77: oc4ptoc monitored data name type...
Page 154
En05000740-2-en.Vsd direction element 4 step over current element one element for each step harmonic restraint mode selection dirph1flt dirph2flt dirph3flt harmrestrblock enabledir enablestep1-4 directionalmode1-4 faultstate element faultstate i3p u3p start trip iec05000740 v2 en figure 64: function...
Page 155
Signal is common for all three phases and all steps. It shall be noted that the selection of measured value (dft or rms) do not influence the operation of directional part of oc4ptoc. Service value for individually measured phase currents are also available on the local hmi for oc4ptoc function, whi...
Page 156
U ref i dir iec09000636_1_vsd 1 2 2 3 4 iec09000636 v1 en figure 65: directional characteristic of the phase overcurrent protection 1 rca = relay characteristic angle 55° 2 roa = relay operating angle 80° 3 reverse 4 forward if no blockings are given the start signals will start the timers of the st...
Page 158
8.2.9 technical data table 78: oc4ptoc technical data function setting range accuracy operate current (5-2500)% of lbase ± 1.0% of i r at i ≤ i r ± 1.0% of i at i > i r reset ratio > 95% at (50–2500)% of lbase - min. Operating current (5-10000)% of lbase ± 1.0% of i r at i ≤ i r ± 1.0% of i at i > i...
Page 159
8.3.2 functionality the instantaneous residual overcurrent protection efpioc has a low transient overreach and short tripping times to allow use for instantaneous earth-fault protection, with the reach limited to less than typical eighty percent of the transformer impedance at minimum source impedan...
Page 160
8.3.6 monitored data table 83: efpioc monitored data name type values (range) unit description in real - a residual current 8.3.7 operation principle the sampled analog residual currents are pre-processed in a discrete fourier filter (dft) block. From the fundamental frequency components of the resi...
Page 161
8.4.1 identification function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number four step residual overcurrent protection, zero or negative sequence direction ef4ptoc 2 iec11000263 v1 en 51n/67n 8.4.2 functionality the four step residual overcurrent protecti...
Page 162
8.4.3 function block iec08000004-2-en.Vsd ef4ptoc i3p* u3p* i3ppol* i3pdir* block blkst1 blkst2 blkst3 blkst4 trip tr1 tr2 tr3 tr4 start st1 st2 st3 st4 stfw strv 2ndharmd iec08000004 v2 en figure 69: ef4ptoc function block 8.4.4 signals table 85: ef4ptoc input signals name type default description ...
Page 163
Name type description st2 boolean start signal step 2 st3 boolean start signal step 3 st4 boolean start signal step 4 stfw boolean forward directional start signal strv boolean reverse directional start signal 2ndharmd boolean 2nd harmonic block signal 8.4.5 settings table 87: ef4ptoc group settings...
Page 164
Name values (range) unit step default description characterist1 ansi ext. Inv. Ansi very inv. Ansi norm. Inv. Ansi mod. Inv. Ansi def. Time l.T.E. Inv. L.T.V. Inv. L.T. Inv. Iec norm. Inv. Iec very inv. Iec inv. Iec ext. Inv. Iec s.T. Inv. Iec l.T. Inv. Iec def. Time reserved ri type rd type - - ans...
Page 165
Name values (range) unit step default description dirmode4 off non-directional forward reverse - - non-directional directional mode of step 4 (off, non- directional, forward, reverse) characterist4 ansi ext. Inv. Ansi very inv. Ansi norm. Inv. Ansi mod. Inv. Ansi def. Time l.T.E. Inv. L.T.V. Inv. L....
Page 166
8.4.6 monitored data table 89: ef4ptoc monitored data name type values (range) unit description stdir integer 3=both 1=forward 2=reverse 0=no direction - fault direction coded as integer iop real - a operating current level upol real - kv polarizing voltage level ipol real - a polarizing current lev...
Page 167
• parallel connection of current instrument transformers in all three phases (holm-green connection). • one single core balance, current instrument transformer (cable ct). • one single current instrument transformer located between power system star point and earth (that is, current transformer loca...
Page 168
1. Directly measured (when a dedicated vt input of the ied is connected in pcm600 to the fourth analog input of the pre-processing block connected to ef4ptoc function input u3p). This dedicated ied vt input shall be then connected to open delta winding of a three phase main vt. 2. Calculated from th...
Page 169
Current polarizing when current polarizing is selected the function will use an external residual current (3i 0 ) or the calculated negative sequence current (i 2 ) as polarizing quantity ipol. The user can select the required current. The residual current can be: 1. Directly measured (when a dedica...
Page 170
Order to calculate equivalent polarizing voltage uipol in accordance with the following formula: 0s uipol z ipol (rnpol j xnpol) ipol = × = + × × equation1877 v2 en (equation 47) which will be then used, together with the phasor of the operating directional current, in order to determine the directi...
Page 171
1. Four residual overcurrent steps. 2. Directional supervision element for residual overcurrent steps with integrated directional comparison step for communication based earth-fault protection schemes (permissive or blocking). 3. Second harmonic blocking element with additional feature for sealed-in...
Page 173
Strv 0.6 * in>dir stfw -rca -85 deg 40% of in>dir in>dir rca 65° u = -3u pol 0 i = 3i op 0 rca +85 deg rca -85 deg characteristic for strv operating area operating area characteristic for stfw characteristic for reverse release of measuring steps characteristic for forward release of measuring steps...
Page 175
Strv 0.6 * i>dir stfw -rca -85 deg 40% of i>dir i>dir rca 65 deg u = -u pol 2 i = i op 2 rca +85 deg rca -85 deg characteristic for strv operating area operating area characteristic for stfw characteristic for reverse release of measuring steps characteristic for forward release of measuring steps -...
Page 176
These signals shall be used for communication based earth-fault teleprotection communication schemes (permissive or blocking). Simplified logic diagram for directional supervision element with integrated directional comparison step is shown in figure 74 : x a a>b b i>dir polmethod=voltage polmethod=...
Page 178
Function range or value accuracy minimum polarizing voltage, zero sequence (1–100)% of ubase ± 0.5% of u r minimum polarizing voltage, negative sequence (1–100)% of ubase ± 0.5% of u r minimum polarizing current, zero sequence (2–100)% of ibase ± 1.0% of i r minimum polarizing current, negative sequ...
Page 179
The thermal overload protection estimates the internal heat content of the transformer/ generator (temperature) continuously. This estimation is made by using a thermal model of the transformer/generator with two time constants, which is based on current measurement. Two warning levels are available...
Page 180
8.5.5 settings table 93: trpttr group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description operation off on - - off operation off / on iref 10.0 - 1000.0 %ib 1.0 100.0 reference current in % of ibase ibase1 30.0 - 250.0 %ib 1.0 100.0 base current ibase1 without cooling input in % of ib...
Page 181
8.5.6 monitored data table 95: trpttr monitored data name type values (range) unit description ttrip real - - estimated time to trip (in min) ttripcal integer - - calculated time status to trip: not active/long time/ active trescal integer - - calculated time status to reset: not active/long time/ac...
Page 182
If final n q > q equation1172 v1 en (equation 50) ( ) 1 1 1 t n n final n e t d - - - æ ö q = q + q - q × - ç ÷ è ø equation1173 v1 en (equation 51) if final n q equation1174 v1 en (equation 52) ( ) 1 t n final final n e t d - - q = q - q - q × equation1175 v1 en (equation 53) where: q n is the calc...
Page 183
The temperature of the object is above the set lockout release temperature setting reslo. The time to lockout release is calculated, that is, a calculation of the cooling time to a set value. _ _ ln final lockout release lockout release final n t t æ ö q - q = - × ç ÷ ç ÷ q - q è ø equation1177 v1 e...
Page 184
Calculation of final temperature i3p calculation of heat content final temp > triptemp actual heat comtent actual temp > alarm1,alarm2 temp actual temp > triptemp alarm1 trip actual temp temp start calculation of time to trip calculation of time to reset of lockout ttrip treslo management of setting...
Page 185
8.5.8 technical data table 96: trpttr technical data function range or value accuracy base current 1 and 2 (30–250)% of ibase ± 1.0% of i r operate time: 2 2 2 2 p ref i i t ln i i t æ ö - ç ÷ = × ç ÷ - è ø equation1356 v2 en (equation 56) i = actual measured current ip = load current before overloa...
Page 186
Contact check criteria can be used where the fault current through the breaker is small. Breaker failure protection, 3-phase activation and output (ccrbrf) current criteria can be fulfilled by one or two phase currents the residual current, or one phase current plus residual current. When those curr...
Page 187
8.6.5 settings table 99: ccrbrf group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description operation off on - - off operation off / on functionmode current contact current&contact - - current detection principle for back-up trip butripmode 2 out of 4 1 out of 3 1 out of 4 - - 1 out of ...
Page 188
8.6.7 operation principle breaker failure protection, 3-phase activation and output ccrbrf is initiated from protection trip command, either from protection functions within the ied or from external protection devices. The start signal is general for all three phases. A re-trip attempt can be made a...
Page 189
And and and and and or or or a b a>b and a b a>b i>blkcont and time out l1 bfp started l1 reset l1 cbcldl1 current high l1 contact closed l1 iec09000977-2-en.Vsd functionmode or or current contact current and contact 1 ip> cb closed l1 il1 iec09000977 v2 en figure 80: simplified logic scheme of the ...
Page 190
Iec16000503-1-en.Vsd bfp started l1 t t2 and bfp started l2 bfp started l3 from other phases or or and t 60 s and a b a>b in in> 1 out of 4 and or 1 out of 3 current high l2 current high l3 from other phases and current high l1 or contact closed l1 or backup trip l1 200 ms backup trip l2 or from oth...
Page 191
Function range or value accuracy timers (0.000-60.000) s ± 0.5% ±10 ms operate time for current detection 20 ms typically - reset time for current detection 10 ms maximum - 8.7 pole discordance protection ccrpld 8.7.1 identification function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identificat...
Page 192
8.7.4 signals table 104: ccrpld input signals name type default description i3p group signal - three phase group signal for current inputs block boolean 0 block of function closecmd boolean 0 close order to cb opencmd boolean 0 open order to cb extpdind boolean 0 pole discordance signal from cb logi...
Page 193
8.7.6 monitored data table 108: ccrpld monitored data name type values (range) unit description imin real - a lowest phase current imax real - a highest phase current 8.7.7 operation principle the detection of pole discordance can be made in two different ways. If the contact based function is used ...
Page 194
Block contsel and extpdind unsymmetrical current detection or closecmd opencmd ttrip+200 ms and or and trip t ttrip 150 ms currsel iec08000014-2-en.Vsd iec08000014 v2 en figure 85: simplified block diagram of pole discordance function - contact and current based the pole discrepancy protection is bl...
Page 195
• any phase current is lower than currunsymlevel of the highest current in the three phases. • the highest phase current is greater than currrellevel of ibase. If these conditions are true, an unsymmetrical condition is detected. This detection is enabled to generate a trip after a set time delay tt...
Page 196
8.8.2 directional overpower protection goppdop 8.8.2.1 identification function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number directional overpower protection goppdop p > 2 document172362-img158942 v2 en 32 8.8.2.2 function block iec08000506-2-en.Vsd gopp...
Page 197
Name type description start1 boolean start signal from stage 1 start2 boolean start signal from stage 2 p real active power ppercent real active power in % of calculated power base value q real reactive power qpercent real reactive power in % of calculated power base value 8.8.2.4 settings table 112...
Page 198
8.8.2.5 monitored data table 115: goppdop monitored data name type values (range) unit description p real - mw active power ppercent real - % active power in % of calculated power base value q real - mvar reactive power qpercent real - % reactive power in % of calculated power base value 8.8.3 direc...
Page 199
8.8.3.3 signals table 116: guppdup input signals name type default description i3p group signal - three phase group signal for current inputs u3p group signal - three phase group signal for voltage inputs block boolean 0 block of function blkst1 boolean 0 block of step 1 blkst2 boolean 0 block of st...
Page 200
Table 119: guppdup group settings (advanced) name values (range) unit step default description k 0.00 - 0.99 - 0.01 0.00 low pass filter coefficient for power measurement, u and i table 120: guppdup non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description globalbasesel 1 - 6 - 1 ...
Page 201
Iec09000018-2-en.Vsd chosen current phasors chosen voltage phasors complex power calculation p derivation of s(composant) in char angle s(angle) s(angle) power1 t trip1 start1 q p = powre q = powim s(angle) power2 t trip2 start2 iec09000018 v2 en figure 88: simplified logic diagram of the power prot...
Page 202
Set value: mode formula used for complex power calculation l1 * 1 1 3 l l s u i = × × equation1703 v1 en (equation 63) l2 * 2 2 3 l l s u i = × × equation1704 v1 en (equation 64) l3 * 3 3 3 l l s u i = × × equation1705 v1 en (equation 65) the active and reactive power is available from the function ...
Page 203
( ) old calculated s k s 1 k s = × + - × equation1959 v1 en (equation 66) where s is a new measured value to be used for the protection function s old is the measured value given from the function in previous execution cycle s calculated is the new calculated value in the present execution cycle k t...
Page 204
8.9.2 functionality negative sequence based overcurrent function dnsptoc is typically used as sensitive earth-fault protection of power lines, where incorrect zero sequence polarization may result from mutual induction between two or more parallel lines. Additionally, it is applied in applications o...
Page 205
Table 125: dnsptoc output signals name type description trip boolean general trip signal troc1 boolean trip signal from step 1 (oc1) troc2 boolean trip signal from step 2 (oc2) start boolean general start signal stoc1 boolean start signal from step 1 (oc1) stoc2 boolean start signal from step 2 (oc2...
Page 206
Name values (range) unit step default description currmult_oc2 1.0 - 10.0 - 0.1 2.0 multiplier for current operate level for step 2 (oc2) tdef_oc2 0.00 - 6000.00 s 0.01 0.50 independent (definite) time delay for step 2 (oc2) dirmode_oc2 non-directional forward reverse - - non-directional directional...
Page 207
8.9.8 technical data table 129: dnsptoc technical data function range or value accuracy operate current (2.0 - 200.0) % of ibase ± 1.0% of i r at i r ± 1.0% of i at i > i r reset ratio > 95 % - low polarizing voltage level (0.0 - 5.0) % of ubase r relay characteristic angle (-180 - 180) degrees ± 2....
Page 208
202.
Page 209
Section 9 voltage protection 9.1 two step undervoltage protection uv2ptuv 9.1.1 identification function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number two step undervoltage protection uv2ptuv 3u symbol-r-2u-greater-than v2 en 27 9.1.2 functionality underv...
Page 210
9.1.4 signals table 130: uv2ptuv input signals name type default description u3p group signal - three phase group signal for voltage inputs block boolean 0 block of function blkst1 boolean 0 block of step 1 blkst2 boolean 0 block of step 2 table 131: uv2ptuv output signals name type description trip...
Page 211
Name values (range) unit step default description operationstep2 off on - - on enable execution of step 2 opmode2 1 out of 3 2 out of 3 3 out of 3 - - 1 out of 3 number of phases required to operate (1 of 3, 2 of 3, 3 of 3) from step 2 u2 1 - 100 %ub 1 50 voltage start value (dt & idmt) in % of ubas...
Page 212
U ubase kv ⋅ (%) ( ) 3 equation1429 v2 en (equation 67) and operation for phase-to-phase voltage under: u (%) ubase(kv) × equation1990 v1 en (equation 68) when phase-to-earth voltage measurement is selected the function automatically introduces division of the base value by the square root of three....
Page 213
The lowest voltage is always used for the inverse time delay integration. The details of the different inverse time characteristics are shown in section 21.3 "inverse time characteristics" . Voltage idmt voltage time ul1 ul2 ul3 iec12000186-1-en.Vsd iec12000186 v1 en figure 91: voltage used for the ...
Page 214
Start st1l1 st1l2 st1l3 tr1 start st2 tr2 trip minvoltselect start & trip output logic step 1 start & trip output logic step 2 phase 3 phase 2 phase 1 phase 3 phase 2 phase 1 timer t2 voltage phase selector opmode2 time integrator or timer t1 voltage phase selector opmode1 1 out of 3 2 out of 3 3 ou...
Page 215
Function range or value accuracy definite time delay, step 1 (0.00 - 6000.00) s ± 0.5% ± 25 ms definite time delays, step 2 (0.000-60.000) s ± 0.5% ±25 ms minimum operate time, inverse characteristics (0.000–60.000) s ± 0.5% ± 25 ms operate time, start function 30 ms typically at 1.2 to 0.5u set - r...
Page 216
9.2.3 function block iec09000278-2-en.Vsd ov2ptov u3p* block blkst1 blkst2 trip tr1 tr2 start st1 st1l1 st1l2 st1l3 st2 iec09000278 v2 en figure 93: ov2ptov function block 9.2.4 signals table 136: ov2ptov input signals name type default description u3p group signal - three phase group signal for vol...
Page 217
9.2.5 settings table 138: ov2ptov group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description operation off on - - off operation off / on operationstep1 off on - - on enable execution of step 1 characterist1 definite time inverse curve a inverse curve b inverse curve c - - definite time...
Page 218
9.2.7 operation principle two step overvoltage protection ov2ptov is used to detect high power system voltage. Ov2ptov has two steps with separate time delays. If one-, two- or three- phase voltages increase above the set value, a corresponding start signal is issued. Ov2ptov can be set to start/tri...
Page 219
9.2.7.2 time delay the time delay for step 1 can be either definite time delay (dt) or inverse time delay (idmt). Step 2 is always definite time delay (dt). For the inverse time delay three different modes are available: • inverse curve a • inverse curve b • inverse curve c the type a curve is descr...
Page 220
Iec05000016-2-en.Vsd voltage idmt voltage time ul1 ul2 ul3 iec05000016 v2 en figure 94: voltage used for the inverse time characteristic integration a trip requires that the overvoltage condition continues for at least the user set time delay. This time delay is set by the parameter t1 and t2 for de...
Page 221
Start st1l1 st1l2 st1l3 st1 tr1 start st2 tr2 start trip iec08000012-3-en.Vsd comparator u > u1> comparator u > u1> comparator u> u1> maxvoltselect comparator u> u2> comparator u> u2> comparator u > u2> start & trip output logic step 1 start & trip output logic step 2 phase 3 phase 2 phase 1 phase 3...
Page 222
9.2.8 technical data table 141: ov2ptov technical data function range or value accuracy operate voltage, step 1 and 2 (1-200)% of ubase ± 0.5% of u r at u r ± 0.5% of u at u > u r reset ratio >98% - inverse time characteristics for steps 1 and 2, see table 562 - see table 562 definite time delay, st...
Page 223
Rov2ptov has two voltage steps, where step 1 can be set as inverse or definite time delayed. Step 2 is always definite time delayed. 9.3.3 function block rov2ptov u3p* block blkst1 blkst2 trip tr1 tr2 start st1 st2 iec09000273_1_en.Vsd iec09000273 v1 en figure 96: rov2ptov function block 9.3.4 signa...
Page 224
Name values (range) unit step default description u1> 1 - 200 %ub 1 30 voltage start value (dt & idmt) in % of ubase for step 1 t1 0.00 - 6000.00 s 0.01 5.00 definite time delay of step 1 t1min 0.000 - 60.000 s 0.001 5.000 minimum operate time for inverse curves for step 1 k1 0.05 - 1.10 - 0.01 0.05...
Page 225
9.3.7.1 measurement principle the residual voltage is measured continuously, and compared with the set values, u1> and u2>. To avoid oscillations of the output start signal, a hysteresis has been included. 9.3.7.2 time delay 9.3.7.3 blocking it is possible to block two step residual overvoltage prot...
Page 226
Iec08000013-3-en.Vsd un st1 tr1 st2 tr2 start trip comparator un > u1> start & trip output logic step 2 phase 1 phase 1 timer t2 start start & trip output logic step 1 time integrator or timer t1 comparator un > u2> start trip trip or or iec08000013 v3 en figure 97: schematic design of two step resi...
Page 227
9.3.8 technical data table 147: rov2ptov technical data function range or value accuracy operate voltage, step 1 (1-200)% of ubase ± 0.5% of u r at u r ± 0.5% of u at u > u r operate voltage, step 2 (1–100)% of ubase ± 0.5% of u r at u r ± 0.5% of u at u > u r reset ratio > 98% - inverse time charac...
Page 228
Adjacent parts in a relatively short time. The function has settable inverse operating curves and independent alarm stages. 9.4.3 function block oexpvph u3p* block reset trip start alarm iec09000008-2-en.Vsd iec09000008 v2 en figure 98: oexpvph function block 9.4.4 signals table 148: oexpvph input s...
Page 229
Table 151: oexpvph non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description globalbasesel 1 - 6 - 1 1 selection of one of the global base value groups voltconn pos seq ul1 ul2 ul3 ul1l2 ul2l3 ul3l1 - - pos seq selection of measured voltage only posseq or ul1l2 should be selected ...
Page 230
E . F n bmax a 4 44 = × × × × equation898 v2 en (equation 76) the relative excitation m is therefore according to equation 77 . ( ) ( ) ( ) e f m p.U. = ur fr iecequation2296 v1 en (equation 77) disproportional variations in quantities e and f may give rise to core overfluxing. If the core flux dens...
Page 231
E f fr v hz > £ iecequation2297 v2 en (equation 79) where: v/hz> is the maximum continuously allowed voltage at no load, and rated frequency. V/hz> is a setting parameter. The setting range is 100% to 180%. If the user does not know exactly what to set, then the default value for v/hz> = 110 % given...
Page 232
9.4.7.2 operate time of the overexcitation protection the operate time of oexpvph is a function of the relative overexcitation. The so called ieee law approximates an inverse-square law and has been chosen based on analysis of the various transformer overexcitation capability characteristics. They m...
Page 233
0 m max - v/hz> m max tmin v/hz> e max e (only if f = fr = const) 1800 inverse delay law overexcitation under - excitation delay in s iec09000114-1-en.Vsd overexcitation m-v/hz> excitation m m=v/hz> iec09000114 v1 en figure 99: restrictions imposed on inverse delays by a definite maximum time of 180...
Page 234
1 10 1 10 100 1000 2 40 3 4 5 20 30 kforieee = 2 kforieee = 3 kforieee = 4 kforieee = 5 kforieee = 6 kforieee = 7 kforieee = 8 kforieee = 9 kforieee = 10 kforieee = 20 kforieee = 60 kforieee = 1 overexcitation in % time (s) ieee overexcitation curves iec09000115-1-en.Vsd (m-emaxcont)*100) iec0900011...
Page 235
Applied, with a time constant of 20 minutes. This means that if the voltage and frequency return to normal values (no more overexcitation), the normal temperature is assumed to be reached after approximately 5 times the time constant of 20 minutes. If an overexcitation condition would return before ...
Page 236
9.4.7.6 logic diagram iec09000161_3_en.Vsd t t t 1 & & ei m= (ei / f) (ur / fr) m = relative v/hz as service value v/hz>> m>v/hz>> v/hz> m>v/hz> talarm tmin kforieee calc ulation of inte rnal induced voltage ei k m m t>talarm t>tmin alarm alarml evel 1800 s u3p block 100 ms trip iec09000161 v3 en fi...
Page 237
Section 10 frequency protection 10.1 underfrequency protection saptuf 10.1.1 identification function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number underfrequency protection saptuf f symbol-p v1 en 81 10.1.2 functionality underfrequency occurs as a result...
Page 238
10.1.4 signals table 154: saptuf input signals name type default description u3p group signal - three phase group signal for voltage inputs block boolean 0 block of function table 155: saptuf output signals name type description trip boolean general trip signal start boolean general start signal res...
Page 239
Voltage is lower than the set blocking voltage in the preprocessing function, the function is blocked and no start or trip signal is issued. 10.1.7.1 measurement principle the frequency measuring element continuously measures the frequency of the positive sequence voltage and compares it to the sett...
Page 240
When the measured frequency returns to the level corresponding to the setting restorefreq, a 100ms pulse is given on the output restore after a settable time delay (trestore). 10.1.7.3 blocking it is possible to block underfrequency protection saptuf completely, by binary input signal: block: blocks...
Page 241
10.2.1 identification function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number overfrequency protection saptof f > symbol-o v1 en 81 10.2.2 functionality overfrequency protection function saptof is applicable in all situations, where reliable detection of ...
Page 242
Table 160: saptof output signals name type description trip boolean general trip signal start boolean general start signal blkdmagn boolean measurement blocked due to low amplitude 10.2.5 settings table 161: saptof group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description operation of...
Page 243
Percent of the global parameter ubase. To avoid oscillations of the output start signal, a hysteresis has been included. Start start trip start & trip output logic definite time delay timedlyoperate block iec09000033-1.Vsd frequency comparator f > startfrequency trip blkdmagn block or freqnotvalid i...
Page 244
Voltage start start trip start & trip output logic time integrator definite time delay timedlyoperate timedlyreset comparator u block en05000735.Vsd frequency comparator f > startfrequency trip blkdmagn block or blktrip iec05000735 v1 en figure 107: schematic design of overfrequency protection sapto...
Page 245
10.3.1 identification function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number rate-of-change frequency protection sapfrc df/dt > symbol-n v1 en 81 10.3.2 functionality the rate-of-change frequency protection function sapfrc gives an early indication of a ...
Page 246
10.3.5 settings table 166: sapfrc group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description operation off on - - off operation off / on startfreqgrad -10.00 - 10.00 hz/s 0.01 0.50 frequency gradient start value, the sign defines direction ttrip 0.000 - 60.000 s 0.001 0.200 operate tim...
Page 247
Fulfilled again within a defined reset time, the start output is reset after the reset time has elapsed. After an issue of the trip output signal, the restore output of sapfrc is set after a time delay (trestore), when the measured frequency has returned to the level corresponding to restorefreq. If...
Page 248
10.3.7 technical data table 167: sapfrc technical data function range or value accuracy operate value, start function (-10.00-10.00) hz/s ± 10.0 mhz/s operate value, restore enable frequency (45.00 - 65.00) hz ± 2.0 mhz timers (0.000 - 60.000) s operate time, start function at 50 hz: 100 ms typicall...
Page 249
Section 11 secondary system supervision 11.1 fuse failure supervision sddrfuf 11.1.1 identification function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number fuse failure supervision sddrfuf - - 11.1.2 functionality the aim of the fuse failure supervision f...
Page 250
11.1.3 function block sddrfuf i3p* u3p* block cbclosed mcbop discpos blkz blku 3ph dld1ph dld3ph iec08000220 v1 en figure 110: sddrfuf function block 11.1.4 signals table 168: sddrfuf input signals name type default description i3p group signal - three phase group signal for current inputs u3p group...
Page 251
11.1.5 settings table 170: sddrfuf group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description operation off on - - on operation off / on opmode off unsins uzsizs uzsizs or unsins uzsizs and unsins optimzsns - - uzsizs operating mode selection 3u0> 1 - 100 %ub 1 30 operate level of resi...
Page 252
11.1.6 monitored data table 172: sddrfuf monitored data name type values (range) unit description 3i0 real - a magnitude of zero sequence current 3i2 real - a magnitude of negative sequence current 3u0 real - kv magnitude of zero sequence voltage 3u2 real - kv magnitude of negative sequence voltage ...
Page 253
Il1 il2 il3 zero sequence filter negative sequence filter ul1 ul2 ul3 zero sequence filter negative sequence filter currzeroseq currnegseq a b a>b a b a>b a b a>b a b a>b 3i2 t 100 ms t 100 ms voltzeroseq voltnegseq and and fusefaildetzeroseq fusefaildetnegseq sequence detection 3u0> 3u2> 3i0 3i2 3u...
Page 254
• the magnitude of the phase current in the same phase is higher than the setting iph> • the circuit breaker is closed (cbclosed = true) the first criterion means that detection of failure in one phase together with a current in the same phase greater than 50p will set the output. The measured phase...
Page 256
11.1.7.3 dead line detection a simplified diagram for the functionality is found in figure 113 . A dead phase condition is indicated if both the voltage and the current in one phase is below their respective setting values udld and idld. If at least one phase is considered to be dead the output dld1...
Page 257
• uzsizs or unsins. Both negative and zero sequence is activated and working in parallel (or-condition for operation). • uzsizs and unsins. Both negative and zero sequence is activated and working in series (and-condition for operation). • optimzsns. Optimum of negative and zero sequence current (th...
Page 258
The input signal discpos is supposed to be connected via a terminal binary input to the n.C. Auxiliary contact of the line disconnector. The discpos signal sets the output signal blku in order to block the voltage related functions when the line disconnector is open. The impedance protection functio...
Page 259
Sealin = on all ul usealin any ul usealin t 5 s and 3ph mcbop all ul > usealin t 60 sec cbclosed block and test test active and blocfuse = yes opmode and t 200 ms and or discpos blku blkz and and fusefaildetzeroseq uzsizs or unsins uzsizs and unsins uzsizs unsins optimzsns and fusefaildetnegseq or a...
Page 260
11.1.8 technical data table 173: sddrfuf technical data function range or value accuracy operate voltage, zero sequence (1-100)% of ubase ± 1.0% of u r operate current, zero sequence (1–100)% of ibase ± 1.0% of i r operate voltage, negative sequence (1–100)% of ubase ± 0.5% of u r operate current, n...
Page 261
11.2.4 signals table 174: tcsscbr input signals name type default description tcs_state boolean 0 trip circuit fail indication from i/o-card block boolean 0 block of function table 175: tcsscbr output signals name type description alarm boolean trip circuit fault indication 11.2.5 settings table 176...
Page 262
To protect the trip circuit supervision circuits in the ied, the output contacts are provided with parallel transient voltage suppressors. The breakdown voltage of these suppressors is 400 +/– 20 v dc. Timer once activated, the timer runs until the set value tdelay is elapsed. The time characteristi...
Page 263
Section 12 control 12.1 apparatus control 12.1.1 functionality the apparatus control function apc8 for up to 8 apparatuses is used for control and supervision of circuit breakers, disconnectors and earthing switches within a bay. Permission to operate is given after evaluation of conditions from oth...
Page 264
12.1.2.3 function block scswi block psto l_sel l_open l_close au_open au_close bl_cmd res_ext sy_inpro sync_ok en_open en_close xpos* exe_op exe_cl selected start_sy position openpos closepos cmd_blk l_cause pos_intr xout iec09000087_1_en.Vsd iec09000087 v1 en figure 117: scswi function block 12.1.2...
Page 265
Name type description closepos boolean closed position indication cmd_blk boolean commands are blocked l_cause integer latest value of the error indication during command pos_intr boolean stopped in intermediate position xout boolean execution information to xcbr/xswi 12.1.2.5 settings table 180: sc...
Page 266
Table 182: sxcbr output signals name type description xpos group signal group connection to cswi exe_op boolean executes the command for open direction exe_cl boolean executes the command for close direction op_blkd boolean indication that the function is blocked for open commands cl_blkd boolean in...
Page 267
Name type default description bl_close boolean 0 signal to block the close command bl_upd boolean 0 steady signal for block of the position updating posopen boolean 0 signal for open position of apparatus from i/o posclose boolean 0 signal for close position of apparatus from i/o tr_open boolean 0 s...
Page 268
12.1.5 bay control qcbay 12.1.5.1 identification function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number bay control qcbay - - 12.1.5.2 functionality the bay control qcbay function is used together with local remote and local remote control functions to h...
Page 269
12.1.5.5 settings table 189: qcbay non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description allpstovalid priority no priority - - priority priority of originators 12.1.6 local remote locrem 12.1.6.1 identification function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identifica...
Page 270
Table 191: locrem output signals name type description off boolean control is disabled local boolean local control is activated remote boolean remote control is activated valid boolean outputs are valid 12.1.6.5 settings table 192: locrem non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step defa...
Page 271
12.1.7.3 function block iec09000074_1_en.Vsd locremctrl ^psto1 ^psto2 ^psto3 ^psto4 ^psto5 ^psto6 ^psto7 ^psto8 ^psto9 ^psto10 ^psto11 ^psto12 ^hmictr1 ^hmictr2 ^hmictr3 ^hmictr4 ^hmictr5 ^hmictr6 ^hmictr7 ^hmictr8 ^hmictr9 ^hmictr10 ^hmictr11 ^hmictr12 iec09000074 v1 en figure 120: locremctrl funct...
Page 272
Name type description hmictr6 integer bitmask output 6 to local remote lhmi input hmictr7 integer bitmask output 7 to local remote lhmi input hmictr8 integer bitmask output 8 to local remote lhmi input hmictr9 integer bitmask output 9 to local remote lhmi input hmictr10 integer bitmask output 10 to ...
Page 273
Name type default description select4 boolean 0 select signal of control 4 select5 boolean 0 select signal of control 5 select6 boolean 0 select signal of control 6 select7 boolean 0 select signal of control 7 select8 boolean 0 select signal of control 8 select9 boolean 0 select signal of control 9 ...
Page 274
In three steps, the selection, command evaluation and the supervision of position. Each step ends up with a pulsed signal to indicate that the respective step in the command sequence is finished. If an error occurs in one of the steps in the command sequence, the sequence is terminated and the error...
Page 275
Interaction with synchrocheck and synchronizing functions the switch controller (scswi) works in conjunction with the synchrocheck and the synchronizing function (sesrsyn). It is assumed that the synchrocheck function is continuously in operation and gives the result to scswi. The result from the sy...
Page 276
Select tselect timer execute command t1 t1>tselect, then long- operation-time in 'cause' is set en05000092.Vsd iec05000092 v1 en figure 123: tselect the timer texecutionfb supervises the time between the execute command and the command termination, see figure 124 . Execute command position l1 t1>tex...
Page 277
Execute command sy_inpro sync_ok t2>tsynchronizing, then blocked-by-synchrocheck in 'cause' is set tsynchrocheck t1 start_sy tsynchronizing t2 en05000095.Vsd iec05000095 v1 en figure 125: tsynchrocheck and tsynchronizing error handling depending on the error that occurs during the command sequence, ...
Page 278
Local panel switch the local panel switch is a switch that defines the operator place selection. The switch connected to this function can have three positions remote/local/off. The positions are here defined so that remote means that operation is allowed from station/remote level and local from the...
Page 279
• blocking of position indications, bl_upd. This input will block all inputs related to apparatus positions for all configured functions within the bay. • blocking of commands, bl_cmd. This input will block all commands for all configured functions within the bay. • blocking of function, block, sign...
Page 280
Defined in the ied. Otherwise the default authority level, superuser, can handle the control without logon. The users and passwords are defined in pcm600. 12.2 interlocking 12.2.1 interlocking for busbar earthing switch bb_es 12.2.1.1 identification function description iec 61850 identification iec ...
Page 281
12.2.1.4 logic diagram exdu_bb en04000546.Vsd vp_bb_dc bb_dc_op 1 qcrel qcitl & bbesoptr bbescltr qc_op qc_cl bb_es iec04000546 v1 en 12.2.1.5 signals table 199: bb_es input signals name type default description qc_op boolean 0 busbar earthing switch qc is in open position qc_cl boolean 0 busbar ear...
Page 282
12.2.2.2 functionality the interlocking for bus-section breaker (a1a2_bs) function is used for one bus- section circuit breaker between section 1 and 2 according to figure 129 . The function can be used for different busbars, which includes a bus-section circuit breaker. Qa1 wa1 (a1) qb2 qc4 qb1 qc3...
Page 283
12.2.2.4 logic diagram qa1_op qb1_op qa1_cl qb1_cl qb2_cl qb2_op qc3_op qc4_cl s2qc2_cl qc4_op s2qc2_op s1qc1_cl s1qc1_op 1 qa1opitl qa1oprel en04000542.Vsd =1 =1 =1 =1 =1 =1 =1 qc3_cl vps2qc2 vps1qc1 vpqc4 vpqc3 vpqb2 vpqb1 vpqa1 a1a2_bs & >1 & & vpqb1 qb1_op qa1o_ex1 vpqb2 qb2_op qa1o_ex2 vp_bbtr ...
Page 284
Vpqa1 vpqc4 vpqc3 vps2qc2 qc3_op qa1_op qc4_op exdu_es vps2qc2 s2qc2_op qb2_ex1 vpqc4 s2qc2_cl qc4_cl qb1_op qb2_op qb1_op qa1_op qb2_cl vpqb2 qb2_op vpqb1 qb1_cl qb1_op vpqb2 vpqb1 vpqa1 1 qb2itl qb2rel en04000543.Vsd exdu_es qb2_ex2 vpqb1 vpqb2 1 qc3rel qc3itl qb2_op >1 1 s1s2cltr qb2optr & & 1 qc...
Page 285
Name type default description exdu_12 boolean 0 no transmission error from any bay connected to busbar 1 and 2 exdu_es boolean 0 no transmission error from bays containing earthing switches qc1 or qc2 qa1o_ex1 boolean 0 external open condition for apparatus qa1 qa1o_ex2 boolean 0 external open condi...
Page 286
12.2.2.6 settings the function does not have any settings available in local hmi or protection and control ied manager (pcm600). 12.2.3 interlocking for bus-section disconnector a1a2_dc 12.2.3.1 identification function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 dev...
Page 287
12.2.3.3 function block a1a2_dc qb_op qb_cl s1qc1_op s1qc1_cl s2qc2_op s2qc2_cl s1dc_op s2dc_op vps1_dc vps2_dc exdu_es exdu_bb qbcl_ex1 qbcl_ex2 qbop_ex1 qbop_ex2 qbop_ex3 qboprel qbopitl qbclrel qbclitl dcoptr dccltr vpdctr iec09000067_1_en.Vsd iec09000067 v1 en figure 132: a1a2_dc function block ...
Page 288
Name type default description s1qc1_cl boolean 0 qc1 on bus section 1 is in closed position s2qc2_op boolean 0 qc2 on bus section 2 is in open position s2qc2_cl boolean 0 qc2 on bus section 2 is in closed position s1dc_op boolean 0 all disconnectors on bus section 1 are in open position s2dc_op bool...
Page 289
12.2.4.1 identification function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number interlocking for bus-coupler bay abc_bc - 3 12.2.4.2 functionality the interlocking for bus-coupler bay (abc_bc) function is used for a bus-coupler bay connected to a double b...
Page 290
12.2.4.3 function block abc_bc qa1_op qa1_cl qb1_op qb1_cl qb2_op qb2_cl qb7_op qb7_cl qb20_op qb20_cl qc1_op qc1_cl qc2_op qc2_cl qc11_op qc11_cl qc21_op qc21_cl qc71_op qc71_cl bbtr_op bc_12_cl vp_bbtr vp_bc_12 exdu_es exdu_12 exdu_bc qa1o_ex1 qa1o_ex2 qa1o_ex3 qb1_ex1 qb1_ex2 qb1_ex3 qb2_ex1 qb2_...
Page 291
Vpqa1 vpqc1 vpqb2 vpqc2 qa1_op vpqc11 qb2_op qc2_op vpqb2 qb1_ex1 qc1_op exdu_es qc11_op vp_bc_12 exdu_bc vpqc1 qb1_ex2 vpqc11 bc_12_cl qb2_cl qc1_cl qb1_ex3 exdu_es qc11_cl 1 qb1itl en04000534.Vsd & & >1 & qb1rel iec04000534 v1 en vpqa1 vpqc1 vpqb1 vpqc2 qa1_op vpqc21 qb1_op qc2_op vpqb1 qb2_ex1 qc...
Page 292
Vpqa1 vpqc1 vpqb20 vpqc2 qa1_op vpqc71 qb20_op qc2_op vpqc2 qb7_ex1 qc1_op exdu_es qc71_op vpqc71 exdu_es vpqa1 qb7_ex2 vpqb7 qc71_cl qc2_cl vpqc1 qb20_ex1 exdu_es qc21_op qc2_op qc1_op qb7_op qa1_op vpqc21 vpqc2 vpqc2 vpqc21 exdu_es qc21_cl qc2_cl qb20_ex2 qb20rel 1 qb20itl en04000536.Vsd & & >1 & ...
Page 293
12.2.4.5 signals table 205: abc_bc input signals name type default description qa1_op boolean 0 qa1 is in open position qa1_cl boolean 0 qa1 is in closed position qb1_op boolean 0 qb1 is in open position qb1_cl boolean 0 qb1 is in closed position qb2_op boolean 0 qb2 is in open position qb2_cl boole...
Page 294
Name type default description qa1o_ex3 boolean 0 external open condition for apparatus qa1 qb1_ex1 boolean 0 external condition for apparatus qb1 qb1_ex2 boolean 0 external condition for apparatus qb1 qb1_ex3 boolean 0 external condition for apparatus qb1 qb2_ex1 boolean 0 external condition for app...
Page 295
Name type description bc12optr boolean no connection via the own bus coupler between wa1 and wa2 bc12cltr boolean connection exists via the own bus coupler between wa1 and wa2 bc17optr boolean no connection via the own bus coupler between wa1 and wa7 bc17cltr boolean connection exists via the own bu...
Page 296
12.2.5.2 functionality the interlocking for 1 1/2 breaker diameter (bh_conn, bh_line_a, bh_line_b) functions are used for lines connected to a 1 1/2 breaker diameter according to figure 135 . Wa1 (a) wa2 (b) qb1 qc1 qa1 qc2 qc9 qb6 qb9 qb2 qc1 qa1 qc2 qc3 qb6 qc3 qb62 qb61 qa1 qc1 qc2 qc9 qb9 bh_lin...
Page 297
12.2.5.3 function block bh_conn qa1_op qa1_cl qb61_op qb61_cl qb62_op qb62_cl qc1_op qc1_cl qc2_op qc2_cl 1qc3_op 1qc3_cl 2qc3_op 2qc3_cl qb61_ex1 qb61_ex2 qb62_ex1 qb62_ex2 qa1clrel qa1clitl qb61rel qb61itl qb62rel qb62itl qc1rel qc1itl qc2rel qc2itl iec09000072_1_en.Vsd iec09000072 v1 en figure 13...
Page 298
Bh_line_b qa1_op qa1_cl qb6_op qb6_cl qb2_op qb2_cl qc1_op qc1_cl qc2_op qc2_cl qc3_op qc3_cl qb9_op qb9_cl qc9_op qc9_cl cqa1_op cqa1_cl cqb62_op cqb62_cl cqc1_op cqc1_cl cqc2_op cqc2_cl qc21_op qc21_cl volt_off volt_on exdu_es qb6_ex1 qb6_ex2 qb2_ex1 qb2_ex2 qb9_ex1 qb9_ex2 qb9_ex3 qb9_ex4 qb9_ex5...
Page 299
12.2.5.4 logic diagrams qa1_op qb61_op qa1_cl qb61_cl qb62_cl qb62_op qc1_op qc2_cl 2qc3_cl qc2_op 2qc3_op 1qc3_cl 1qc3_op en04000560.Vsd =1 =1 =1 =1 =1 =1 =1 qc1_cl vp2qc3 vp1qc3 vpqc2 vpqc1 vpqb62 vpqb61 vpqa1 bh_conn vpqb61 1 qa1clitl & 1 qb62itl qb62rel vpqa1 vpqc1 vpqc2 vp2qc3 qa1_op qc1_op qc2...
Page 300
Qa1_op qb1_op qa1_cl qb1_cl qb6_cl qb6_op qc9_op qb9_cl qc3_op qc2_cl qb9_op qc2_op qc1_cl qc1_op qc3_cl cqc1_op cqc1_cl cqa1_cl cqa1_op 1 qb6itl qb6rel en04000554.Vsd =1 =1 =1 =1 =1 =1 =1 =1 =1 =1 qc9_cl vpcqc1 vpcqa1 vpqc3 vpqc2 vpqc1 vpqb9 vpqc9 vpqb6 vpqb1 vpqa1 bh_line_a =1 =1 cqc2_op cqc2_cl c...
Page 301
Vpqa1 vpqb6 vpqc9 qb9_ex2 qb6_op qb9_ex1 vpcqc2 vpcqc1 vpcqb61 vpqc3 vpqc2 vpqc1 qa1_op 1 qb9itl qb9rel en04000555.Vsd & vpcqa1 >1 & & >1 & 1 qb1itl qb1rel 1 qc1itl qc1rel & 1 qc2itl qc2rel & 1 qc3itl qc3rel >1 qc1_op qc2_op qb9_ex3 vpqa1 vpqc1 vpqc2 vpqc11 qa1_op qc1_op qc2_op qc11_op exdu_es qb1_e...
Page 302
Qa1_op qb2_op qa1_cl qb2_cl qb6_cl qb6_op qc9_op qb9_cl qc3_op qc2_cl qb9_op qc2_op qc1_cl qc1_op qc3_cl cqc1_op cqc1_cl cqa1_cl cqa1_op 1 qb6itl qb6rel en04000557.Vsd =1 =1 =1 =1 =1 =1 =1 =1 =1 =1 qc9_cl vpcqc1 vpcqa1 vpqc3 vpqc2 vpqc1 vpqb9 vpqc9 vpqb6 vpqb2 vpqa1 bh_line_b =1 =1 cqc2_op cqc2_cl c...
Page 303
Vpqa1 vpqb6 vpqc9 qb9_ex2 qb6_op qb9_ex1 vpcqc2 vpcqc1 vpcqb62 vpqc3 vpqc2 vpqc1 qa1_op 1 qb9itl qb9rel en04000558.Vsd & vpcqa1 >1 & & >1 & 1 qb2itl qb2rel 1 qc1itl qc1rel & 1 qc2itl qc2rel & 1 qc3itl qc3rel >1 qc1_op qc2_op qb9_ex3 vpqa1 vpqc1 vpqc2 vpqc21 qa1_op qc1_op qc2_op qc21_op exdu_es qb2_e...
Page 304
12.2.5.5 signals table 207: bh_conn input signals name type default description qa1_op boolean 0 qa1 is in open position qa1_cl boolean 0 qa1 is in closed position qb61_op boolean 0 qb61 is in open position qb61_cl boolean 0 qb61 is in closed position qb62_op boolean 0 qb62 is in open position qb62_...
Page 305
Name type default description qc9_cl boolean 0 qc9 is in closed position cqa1_op boolean 0 qa1 in module bh_conn is in open position cqa1_cl boolean 0 qa1 in module bh_conn is in closed position cqb61_op boolean 0 qb61 in module bh_conn is in open position cqb61_cl boolean 0 qb61 in module bh_conn i...
Page 306
Name type default description qc2_op boolean 0 qc2 is in open position qc2_cl boolean 0 qc2 is in closed position qc3_op boolean 0 qc3 is in open position qc3_cl boolean 0 qc3 is in closed position qb9_op boolean 0 qb9 is in open position qb9_cl boolean 0 qb9 is in closed position qc9_op boolean 0 q...
Page 307
Table 210: bh_conn output signals name type description qa1clrel boolean closing of qa1 is allowed qa1clitl boolean closing of qa1 is forbidden qb61rel boolean switching of qb61 is allowed qb61itl boolean switching of qb61 is forbidden qb62rel boolean switching of qb62 is allowed qb62itl boolean swi...
Page 308
Table 212: bh_line_b output signals name type description qa1clrel boolean closing of qa1 is allowed qa1clitl boolean closing of qa1 is forbidden qb6rel boolean switching of qb6 is allowed qb6itl boolean switching of qb6 is forbidden qb2rel boolean switching of qb2 is allowed qb2itl boolean switchin...
Page 309
12.2.6.2 functionality the interlocking for a double busbar double circuit breaker bay including db_bus_a, db_bus_b and db_line functions are used for a line connected to a double busbar arrangement according to figure 139 . Wa1 (a) wa2 (b) qb1 qc1 qa1 qc2 qc9 qb61 qb9 qb2 qc4 qa2 qc5 qc3 qb62 db_bu...
Page 310
12.2.6.3 function block db_bus_a qa1_op qa1_cl qb1_op qb1_cl qb61_op qb61_cl qc1_op qc1_cl qc2_op qc2_cl qc3_op qc3_cl qc11_op qc11_cl exdu_es qb61_ex1 qb61_ex2 qb1_ex1 qb1_ex2 qa1clrel qa1clitl qb61rel qb61itl qb1rel qb1itl qc1rel qc1itl qc2rel qc2itl qb1optr qb1cltr vpqb1tr iec09000077_1_en.Vsd ie...
Page 311
12.2.6.4 logic diagrams qa1_op qb61_op qa1_cl qb61_cl qb1_cl qb1_op qc1_op qc2_cl qc11_cl qc2_op qc11_op qc3_cl qc3_op en04000547.Vsd =1 =1 =1 =1 =1 =1 =1 qc1_cl vpqc11 vpqc3 vpqc2 vpqc1 vpqb1 vpqb61 vpqa1 db_bus_a vpqb61 1 qa1clitl & & >1 & 1 qb1itl qb1rel vpqa1 vpqc1 vpqc2 vpqc11 qa1_op qc1_op qc2...
Page 312
Qa2_op qb62_op qa2_cl qb62_cl qb2_cl qb2_op qc4_op qc5_cl qc21_cl qc5_op qc21_op qc3_cl qc3_op en04000552.Vsd =1 =1 =1 =1 =1 =1 =1 qc4_cl vpqc21 vpqc3 vpqc5 vpqc4 vpqb2 vpqb62 vpqa2 db_bus_b vpqb62 1 qa2clitl & & >1 & 1 qb2itl qb2rel vpqa2 vpqc4 vpqc5 vpqc21 qa2_op qc4_op qc5_op qc21_op vpqc4 vpqc21...
Page 313
Qa1_op qa2_op qa1_cl qa2_cl qb61_cl qb61_op qc1_op qc2_cl qc5_op qc4_cl qc2_op qc4_op qb62_cl qb62_op qc5_cl qc3_op qc3_cl qb9_cl qb9_op 1 qb9itl qb9rel en04000549.Vsd =1 =1 =1 =1 =1 =1 =1 =1 =1 =1 qc1_cl vpqc3 vpqb9 vpqc5 vpqc4 vpqb62 vpqc2 vpqc1 vpqb61 vpqa2 vpqa1 db_line =1 =1 qc9_op qc9_cl volt_...
Page 314
1 qc3itl qc3rel en04000551.Vsd vpqb62 vpqb9 qb61_op qb62_op qb9_op vpqb9 vpvolt qb9_op volt_off & & vpqb61 1 qc9itl qc9rel iec04000551 v1 en 12.2.6.5 signals table 213: db_bus_a input signals name type default description qa1_op boolean 0 qa1 is in open position qa1_cl boolean 0 qa1 is in closed pos...
Page 315
Name type default description qb62_op boolean 0 qb62 is in open position qb62_cl boolean 0 qb62 is in closed position qc4_op boolean 0 qc4 is in open position qc4_cl boolean 0 qc4 is in closed position qc5_op boolean 0 qc5 is in open position qc5_cl boolean 0 qc5 is in closed position qc3_op boolean...
Page 316
Name type default description qc3_cl boolean 0 qc3 is in closed position qc9_op boolean 0 qc9 is in open position qc9_cl boolean 0 qc9 is in closed position volt_off boolean 0 there is no voltage on the line and not vt (fuse) failure volt_on boolean 0 there is voltage on the line or there is a vt (f...
Page 317
Name type description qc5rel boolean switching of qc5 is allowed qc5itl boolean switching of qc5 is forbidden qb2optr boolean qb2 is in open position qb2cltr boolean qb2 is in closed position vpqb2tr boolean switch status of qb2 is valid (open or closed) table 218: db_line output signals name type d...
Page 318
Qb1 qb2 qc1 qa1 qc2 qb9 qc9 wa1 (a) wa2 (b) wa7 (c) qb7 en04000478.Vsd iec04000478 v1 en figure 143: switchyard layout abc_line the interlocking functionality in 650 series can not handle the transfer bus (wa7)c. Section 12 1mrk 504 135-uen a control 312 technical manual.
Page 319
12.2.7.3 function block abc_line qa1_op qa1_cl qb9_op qb9_cl qb1_op qb1_cl qb2_op qb2_cl qb7_op qb7_cl qc1_op qc1_cl qc2_op qc2_cl qc9_op qc9_cl qc11_op qc11_cl qc21_op qc21_cl qc71_op qc71_cl bb7_d_op bc_12_cl bc_17_op bc_17_cl bc_27_op bc_27_cl volt_off volt_on vp_bb7_d vp_bc_12 vp_bc_17 vp_bc_27 ...
Page 320
12.2.7.4 logic diagram qa1_op qb9_op qa1_cl qb9_cl qb1_cl qb1_op qb2_op qb7_cl qc9_op qc2_cl qb7_op qc2_op qc1_cl qc1_op qc9_cl qc21_op qc21_cl qc11_cl qc11_op 1 qb9itl qb9rel en04000527.Vsd =1 =1 =1 =1 =1 =1 =1 =1 =1 =1 qb2_cl vpqc21 vpqc11 vpqc9 vpqc2 vpqc1 vpqb7 vpqb2 vpqb1 vpqb9 vpqa1 abc_line =...
Page 321
& & & ³1 qb1rel qb1itl vpqa1 vpqb2 vpqc1 vpqc2 vpqc11 qa1_op qb2_op qc1_op qc2_op qc11_op exdu_es qb1_ex1 vpqb2 vp_bc_12 qb2_cl bc_12_cl exdu_bc qb1_ex2 vpqc1 vpqc11 qc1_cl qc11_cl exdu_es qb1ex3 en04000528.Vsd 1 iec04000528 v1 en 1mrk 504 135-uen a section 12 control 315 technical manual.
Page 322
& & & ³1 1 qb2rel qb2itl vpqa1 vpqb1 vpqc1 vpqc2 vpqc21 qa1_op qb1_op qc1_op qc2_op qc21_op exdu_es qb2_ex1 vpqb1 vp_bc_12 qb1_cl bc_12_cl exdu_bc qb2_ex2 vpqc1 vpqc21 qc1_cl qc21_cl exdu_es qb2_ex3 en04000529.Vsd iec04000529 v1 en section 12 1mrk 504 135-uen a control 316 technical manual.
Page 323
& & >1 1 vpqc9 vpqc71 vp_bb7_d vp_bc_17 vp_bc_27 qc9_op qc71_op exdu_es bb7_d_op exdu_bpb bc_17_op bc_27_op exdu_bc qb7_ex1 vpqa1 vpqb1 vpqc9 vpqb9 vpqc71 vp_bb7_d vp_bc_17 qa1_cl qb1_cl qc9_op qb9_cl qc71_op exdu_es bb7_d_op exdu_bpb bc_17_cl exdu_bc qb7_ex2 qb7rel qb7itl iec04000530 v1 en 1mrk 504...
Page 324
Vpqa1 vpqc9 vpqb2 vpqb9 vp_bb7_d vpqc71 vp_bc_27 qb2_cl exdu_es qa1_cl qc71_op qb9_cl qc9_op bb7_d_op bc_27_cl qb7_ex3 exdu_bc vpqc9 exdu_bpb vpqc71 qb2_op qb1_op vpqb9 vpqb2 vpqb1 qb7_ex4 exdu_es qc71_cl qc9_cl qb9_op vpqb7 qb9_op qb7_op vpvolt vpqb9 volt_off & & & & >1 1 1 qc1itl qc1rel qc2rel qc2...
Page 325
Vpqb2 vpqb1 qb2_op qb1_op 1 qb12cltr qb12optr en04000532.Vsd >1 & vpqb12tr qb7optr qb7cltr vpqb7tr qb7_op qb7_cl vpqb7 vpqb2 qb2_cl qb2_op qb2optr qb2cltr vpqb2tr qb1optr qb1cltr vpqb1tr qb1_op qb1_cl vpqb1 iec04000532 v1 en 12.2.7.5 signals table 219: abc_line input signals name type default descri...
Page 326
Name type default description qc21_cl boolean 0 earthing switch qc21 on busbar wa2 is in closed position qc71_op boolean 0 earthing switch qc71 on busbar wa7 is in open position qc71_cl boolean 0 earthing switch qc71 on busbar wa7 is in closed position bb7_d_op boolean 0 disconnectors on busbar wa7 ...
Page 327
Table 220: abc_line output signals name type description qa1clrel boolean closing of qa1 is allowed qa1clitl boolean closing of qa1 is forbidden qb9rel boolean switching of qb9 is allowed qb9itl boolean switching of qb9 is forbidden qb1rel boolean switching of qb1 is allowed qb1itl boolean switching...
Page 328
12.2.8.1 identification function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number interlocking for transformer bay ab_trafo - 3 12.2.8.2 functionality the interlocking for transformer bay (ab_trafo) function is used for a transformer bay connected to a doub...
Page 329
12.2.8.3 function block ab_trafo qa1_op qa1_cl qb1_op qb1_cl qb2_op qb2_cl qc1_op qc1_cl qc2_op qc2_cl qb3_op qb3_cl qb4_op qb4_cl qc3_op qc3_cl qc11_op qc11_cl qc21_op qc21_cl bc_12_cl vp_bc_12 exdu_es exdu_bc qa1_ex1 qa1_ex2 qa1_ex3 qb1_ex1 qb1_ex2 qb1_ex3 qb2_ex1 qb2_ex2 qb2_ex3 qa1clrel qa1clitl...
Page 330
Vpqa1 vpqc1 vpqb2 vpqc2 vpqc11 vpqc3 qa1_op qc1_op exdu_es qb2_op qc11_op qc3_op qc2_op qb1_ex1 vp_bc_12 bc_12_cl qc3_op qb2_cl exdu_bc vpqc3 vpqb2 vpqc3 vpqc2 vpqc1 qb1_ex2 1 qb1itl en04000539.Vsd & & >1 & qb1rel vpqc11 qc1_cl qc2_cl qc3_cl qc11_cl exdu_es qb1_ex3 iec04000539 v1 en vpqa1 vpqc1 vpqb...
Page 331
Vpqb1 vpqb3 vpqb2 vpqb4 qb2_op qb1_op qb3_op qb1_op qb4_op vpqb1 qb1_cl qb2_op vpqb1 1 1 qc1itl qc1rel qc2rel qc2itl en04000541.Vsd & qb1optr qb1cltr vpqb1tr >1 qb1_op qb2_op 1 qb12optr qb12cltr & vpqb2 vpqb12tr qb2_cl vpqb2 qb2optr qb2cltr vpqb2tr iec04000541 v1 en 12.2.8.5 signals table 221: ab_tr...
Page 332
Name type default description qa1_ex1 boolean 0 external condition for apparatus qa1 qa1_ex2 boolean 0 external condition for apparatus qa1 qa1_ex3 boolean 0 external condition for apparatus qa1 qb1_ex1 boolean 0 external condition for apparatus qb1 qb1_ex2 boolean 0 external condition for apparatus...
Page 333
12.2.9 position evaluation pos_eval 12.2.9.1 identification function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number position evaluation pos_eval - - 12.2.9.2 functionality position evaluation (pos_eval) function converts the input position data signal pos...
Page 334
12.2.9.5 signals table 223: pos_eval input signals name type default description position integer 0 position status including quality table 224: pos_eval output signals name type description openpos boolean open position closepos boolean close position 12.2.9.6 settings the function does not have an...
Page 335
The interlocking module is connected to the surrounding functions within a bay as shown in figure 148 . Interlocking modules in other bays interlocking module scilo scswi apparatus control modules sxcbr scilo scswi sxswi apparatus control modules scilo scswi sxswi apparatus control modules en0400052...
Page 336
When invalid data such as intermediate position, loss of a control ied, or input board error are used as conditions for the interlocking condition in a bay, a release for execution of the function will not be given. On the local hmi an override function exists, which can be used to bypass the interl...
Page 337
Tool pcm600. The inputs qx_exy on the interlocking modules are used to add these specific conditions. The input signals exdu_xx shall be set to true if there is no transmission error at the transfer of information from other bays. Required signals with designations ending in tr are intended for tran...
Page 338
12.3.2.1 identification function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number automatic voltage control for tap changer tr8atcc u iec10000166 v1 en 90 12.3.2.2 function block tr8atcc i3p1* i3p2* u3p2* horiz1* horiz2* horiz3* horiz4* atccin* block manctr...
Page 339
Name type default description lowerv boolean 0 binary "down" command eautoblk boolean 0 block voltage control in automatic control mode deblkaut boolean 0 binary "deblock auto" command lva1 boolean 0 activation of load voltage adjustment factor 1 lva2 boolean 0 activation of load voltage adjustment ...
Page 340
Name type description ulow boolean busbar voltage below the set limit voltbusbminlimit ublk boolean busbar voltage below the set limit voltbusbblocklimit hourhunt boolean number of commands within the latest hour exceeded maximum level dayhunt boolean number of commands within the last 24 hours exce...
Page 341
12.3.2.4 settings table 227: tr8atcc group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description operation off on - - off operation off / on measmode l1 l2 l3 l1l2 l2l3 l3l1 posseq - - posseq selection of measured voltage and current totalblock off on - - off total block of the voltage ...
Page 342
Name values (range) unit step default description lvaconst1 -20.0 - 20.0 %ub2 0.1 0.0 constant 1 for lva, % of regulated voltage lvaconst2 -20.0 - 20.0 %ub2 0.1 0.0 constant 2 for lva, % of regulated voltage lvaconst3 -20.0 - 20.0 %ub2 0.1 0.0 constant 3 for lva, % of regulated voltage lvaconst4 -20...
Page 343
Name values (range) unit step default description t2rxop off on - - off receive block operation from parallel transformer 2 t3rxop off on - - off receive block operation from parallel transformer 3 t4rxop off on - - off receive block operation from parallel transformer 4 tapposoffs -5 - 5 - 1 0 tap ...
Page 344
Name values (range) unit step default description tapposbk alarm auto block auto&man block - - auto block alarm, auto or auto&man block for position supervision uvbk alarm auto block auto&man block - - auto block alarm, auto block or auto&man block for undervoltage uvpartbk alarm auto&man block - - ...
Page 345
12.3.3.1 identification function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number tap changer control and supervision, 6 binary inputs tcmyltc iec10000167 v1 en 84 12.3.3.2 function block tcmyltc yltcin* tcinprog inerr reseterr outerr rs_clcnt rs_opcnt pari...
Page 346
Name type default description bierr boolean 0 error bit from tap changer for the tap position b1 boolean 0 bit 1 from tap changer for the tap position b2 boolean 0 bit 2 from tap changer for the tap position b3 boolean 0 bit 3 from tap changer for the tap position b4 boolean 0 bit 4 from tap changer...
Page 347
Table 233: tcmyltc non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description globalbasesel 1 - 6 - 1 1 selection of one of the global base value groups lowvolttap 1 - 63 - 1 1 tap position for the lowest voltage highvolttap 1 - 63 - 1 33 tap position for the highest voltage malow ...
Page 348
Tr8atccis designed to automatically maintain the voltage at the lv-side side of a power transformer within given limits around a set target voltage. A raise or lower command is generated whenever the measured voltage, for a given period of time, deviates from the set target value by more than the pr...
Page 349
• master-follower method • reverse reactance method • circulating current method. Parallel control with the master-follower method in the master-follower method, one of the transformers is selected to be master, and will regulate the voltage in accordance with the principles automatic voltage contro...
Page 350
The main objectives of the circulating current method for parallel voltage control are: 1. Regulate the busbar or load voltage to the preset target value. 2. Minimize the circulating current in order to achieve optimal sharing of the reactive load between parallel transformers. The busbar voltage ub...
Page 351
Because the transformer impedance is dominantly inductive, it is possible to use just the transformer reactances in the above formula. At the same time this means that t1 circulating current lags the busbar voltage by almost 90°, while t2 circulating current leads the busbar voltage by almost 90°. 1...
Page 352
Table 235: binary, bcd and gray conversion iec06000522 v1 en the gray code conversion above is not complete and therefore the conversion from decimal numbers to gray code is given below. Section 12 1mrk 504 135-uen a control 346 technical manual.
Page 353
Table 236: gray code conversion iec06000523 v1 en 1mrk 504 135-uen a section 12 control 347 technical manual.
Page 354
Via a ma input signal 12.3.4.3 connection between tr8atcc and tcmyltc the two function blocks automatic voltage control for tap changer, tr8atcc and tap changer control and supervision, 6 binary inputs tcmyltc are connected to each other according to figure 153 below. (rmk. In case of parallel contr...
Page 355
Table 238: binary signals contained in word “enableblocksignals”: atccout / yltcin signal description circcurrbl alarm/block tap changer operation because of high circulating current cmderrbl alarm/block tap changer operation because of command error ocbl alarm/block tap changer operation because of...
Page 356
Table 241: analog signals: atccout / horizx signal description voltagebusbar measured busbar voltage for this transformer ownload currim measured load current imaginary part for this transformer ownloadcurrre measured load current real part for this transformer reacsec transformer reactance in prima...
Page 357
12.3.5 technical data table 244: tr8atcc, tcmyltc technical data function range or value accuracy transformer reactance on atcc side (0.1–200.0)Ω, primary - time delay for lower command when fast step down mode is activated (1.0–100.0) s - voltage control set voltage (85.0–120.0)% of ub2 ±0.5% of u ...
Page 358
Function range or value accuracy time after position change before the value is accepted (1–60) s ± 0.5% ± 110 ms tap changer constant time- out (1–120) s ± 0.5% ± 110 ms raise/lower command output pulse duration (0.5–10.0) s ± 0.5% ± 110 ms 12.4 logic rotating switch for function selection and lhmi...
Page 359
12.4.3 function block iec09000091_1_en.Vsd slggio block psto up down ^p01 ^p02 ^p03 ^p04 ^p05 ^p06 ^p07 ^p08 ^p09 ^p10 ^p11 ^p12 ^p13 ^p14 ^p15 ^p16 ^p17 ^p18 ^p19 ^p20 ^p21 ^p22 ^p23 ^p24 ^p25 ^p26 ^p27 ^p28 ^p29 ^p30 ^p31 ^p32 swposn iec09000091 v1 en figure 154: slggio function block 12.4.4 signa...
Page 360
Name type description p11 boolean selector switch position 11 p12 boolean selector switch position 12 p13 boolean selector switch position 13 p14 boolean selector switch position 14 p15 boolean selector switch position 15 p16 boolean selector switch position 16 p17 boolean selector switch position 1...
Page 361
12.4.6 monitored data table 248: slggio monitored data name type values (range) unit description swposn integer - - switch position as integer value 12.4.7 operation principle the logic rotating switch for function selection and lhmi presentation (slggio) function has two operating inputs – up and d...
Page 362
12.5.2 functionality the selector mini switch vsggio function block is a multipurpose function used for a variety of applications, as a general purpose switch. Vsggio can be controlled from the menu or from a symbol on the single line diagram (sld) on the local hmi. 12.5.3 function block vsggio bloc...
Page 363
12.5.5 settings table 251: vsggio non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description operation off on - - off operation off / on ctlmodel dir norm sbo enh - - dir norm specifies the type for control model according to iec 61850 mode steady pulsed - - pulsed operation mode t...
Page 364
Ipos1 ipos2 name of displayed string default string value 0 0 posundefined p00 1 0 position1 p01 0 1 position2 p10 1 1 posbadstate p11 12.6 iec 61850 generic communication i/o functions dpggio 12.6.1 identification function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37....
Page 365
12.6.5 settings the function does not have any parameters available in local hmi or protection and control ied manager (pcm600). 12.6.6 operation principle upon receiving the input signals, the iec 61850 generic communication i/o functions (dpggio) function block will send the signals over iec 61850...
Page 366
12.7.4 signals table 254: spc8ggio input signals name type default description block boolean 0 block of function psto integer 2 operator place selection table 255: spc8ggio output signals name type description out1 boolean output 1 out2 boolean output 2 out3 boolean output 3 out4 boolean output 4 ou...
Page 367
Name values (range) unit step default description latched7 pulsed latched - - pulsed setting for pulsed/latched mode for output 7 tpulse7 0.01 - 6000.00 s 0.01 0.10 output 7 pulse time latched8 pulsed latched - - pulsed setting for pulsed/latched mode for output 8 tpulse8 0.01 - 6000.00 s 0.01 0.10 ...
Page 368
12.8.3 function block iec09000030-1-en.Vsd autobits block psto ^cmdbit1 ^cmdbit2 ^cmdbit3 ^cmdbit4 ^cmdbit5 ^cmdbit6 ^cmdbit7 ^cmdbit8 ^cmdbit9 ^cmdbit10 ^cmdbit11 ^cmdbit12 ^cmdbit13 ^cmdbit14 ^cmdbit15 ^cmdbit16 ^cmdbit17 ^cmdbit18 ^cmdbit19 ^cmdbit20 ^cmdbit21 ^cmdbit22 ^cmdbit23 ^cmdbit24 ^cmdbi...
Page 369
Name type description cmdbit8 boolean command out bit 8 cmdbit9 boolean command out bit 9 cmdbit10 boolean command out bit 10 cmdbit11 boolean command out bit 11 cmdbit12 boolean command out bit 12 cmdbit13 boolean command out bit 13 cmdbit14 boolean command out bit 14 cmdbit15 boolean command out b...
Page 370
Appropriate. Ex: pulse-on, on-time=100, off-time=300, count=5 would give 5 positive 100 ms pulses, 300 ms apart. There is a block input signal, which will disable the operation of the function, in the same way the setting operation: on/off does. That means that, upon activation of the block input, a...
Page 371
12.9.4 settings table 262: i103cmd non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description functiontype 1 - 255 - 1 1 function type (1-255) 12.10 ied commands for iec 60870-5-103 i103iedcmd 12.10.1 functionality i103iedcmd is a command block in control direction with defined ied...
Page 372
12.10.4 settings table 265: i103iedcmd non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description functiontype 1 - 255 - 1 255 function type (1-255) 12.11 function commands user defined for iec 60870-5-103 i103usrcmd 12.11.1 functionality i103usrcmd is a command block in control di...
Page 373
Name type description output6 boolean command output 6 output7 boolean command output 7 output8 boolean command output 8 12.11.4 settings table 268: i103usrcmd non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description functiontype 1 - 255 - 1 1 function type (1-255) pulsemode stea...
Page 374
12.12.2 function block iec10000285-1-en.Vsd i103gencmd block ^cmd_off ^cmd_on iec10000285 v1 en figure 161: i103gencmd function block 12.12.3 signals table 269: i103gencmd input signals name type default description block boolean 0 block of command table 270: i103gencmd output signals name type desc...
Page 375
The block input will block only the signals in monitoring direction (the position information), not the commands via iec 60870-5-103. The select input is used to indicate that the monitored apparatus has been selected (in a select-before-operate type of control) 12.13.2 function block iec10000286-1-...
Page 376
370
Page 377
Section 13 logic 13.1 tripping logic common 3-phase output smpptrc 13.1.1 identification function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number tripping logic common 3-phase output smpptrc i->o symbol-k v1 en 94 13.1.2 functionality a function block for ...
Page 378
13.1.4 signals table 274: smpptrc input signals name type default description block boolean 0 block of function trin boolean 0 trip all phases setlkout boolean 0 input for setting the circuit breaker lockout function rstlkout boolean 0 input for resetting the circuit breaker lockout function table 2...
Page 379
And block trin operation mode = on or t ttripmin trip en05000789.Vsd program = 3ph iec05000789 v1 en figure 164: simplified logic diagram for three phase trip lockout can be activated either by activating the input (setlkout) or automatically from trip input by setting autolock to on. A lockout cond...
Page 380
Tmaggio 3 output signals and the physical outputs allows the user to adapt the signals to the physical tripping outputs according to the specific application needs for settable pulse or steady output. 13.2.3 function block tmaggio input1 input2 input3 input4 input5 input6 input7 input8 input9 input1...
Page 381
Name type default description input10 boolean 0 binary input 10 input11 boolean 0 binary input 11 input12 boolean 0 binary input 12 input13 boolean 0 binary input 13 input14 boolean 0 binary input 14 input15 boolean 0 binary input 15 input16 boolean 0 binary input 16 input17 boolean 0 binary input 1...
Page 382
Name values (range) unit step default description modeoutput1 steady pulsed - - steady mode for output 1, steady or pulsed modeoutput2 steady pulsed - - steady mode for output 2, steady or pulsed modeoutput3 steady pulsed - - steady mode for output 3, steady or pulsed 13.2.6 operation principle the ...
Page 383
Pulsetime ondelay output 1 pulsetime ondelay output 2 pulsetime ondelay output 3 input 17 input 32 input 1 input 16 iec09000612_2_en.Vsd ³1 ³1 ³1 ³1 & & & & & & modeoutput1=pulsed ³1 modeoutput2=pulsed ³1 modeoutput3=pulsed t t t offdelay t t t t offdelay t offdelay t iec09000612 v2 en figure 166: t...
Page 384
• pulsetimer function block can be used, for example, for pulse extensions or limiting of operation of outputs, settable pulse time. • gate function block is used for whether or not a signal should be able to pass from the input to the output. • xor function block. Each block has two outputs where o...
Page 385
• xorqt xor function block. The function also propagates timestamp and quality of input signals. Each block has two outputs where one is inverted. • timersetqt function has pick-up and drop-out delayed outputs related to the input signal. The timer has a settable time delay. The function also propag...
Page 386
Functionality the or function is used to form general combinatory expressions with boolean variables. The or function block has six inputs and two outputs. One of the outputs is inverted. Function block or input1 input2 input3 input4 input5 input6 out nout iec09000288-1-en.Vsd iec09000288 v1 en figu...
Page 387
Function block inverter input out iec09000287-1-en.Vsd iec09000287 v1 en figure 168: inverter function block signals table 284: inverter input signals name type default description input boolean 0 input signal table 285: inverter output signals name type description out boolean output signal setting...
Page 388
Signals table 286: pulsetimer input signals name type default description input boolean 0 input signal table 287: pulsetimer output signals name type description out boolean output signal settings table 288: pulsetimer non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description t 0....
Page 389
Table 290: gate output signals name type description out boolean output signal settings table 291: gate group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description operation off on - - off operation off/on 13.3.1.6 exclusive or function block xor identification function description iec ...
Page 390
Table 293: xor output signals name type description out boolean output signal nout boolean inverted output signal settings the function does not have any parameters available in local hmi or protection and control ied manager (pcm600). 13.3.1.7 loop delay function block loopdelay function descriptio...
Page 391
13.3.1.8 timer function block timerset identification function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number timer function block timerset - - functionality the function block timerset has pick-up and drop-out delayed outputs related to the input signal....
Page 392
Table 297: timerset output signals name type description on boolean output signal, pick-up delayed off boolean output signal, drop-out delayed settings table 298: timerset group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description operation off on - - off operation off/on t 0.000 - 900...
Page 393
Signals table 299: and input signals name type default description input1 boolean 1 input signal 1 input2 boolean 1 input signal 2 input3 boolean 1 input signal 3 input4 boolean 1 input signal 4 table 300: and output signals name type description out boolean output signal nout boolean inverted outpu...
Page 394
Function block srmemory set reset out nout iec09000293-1-en.Vsd iec09000293 v1 en figure 176: srmemory function block signals table 302: srmemory input signals name type default description set boolean 0 input signal to set reset boolean 0 input signal to reset table 303: srmemory output signals nam...
Page 395
Table 305: truth table for rsmemory function block reset set out nout 0 0 last value inverted last value 0 1 0 1 1 0 1 0 1 1 0 1 function block rsmemory set reset out nout iec09000294-1-en.Vsd iec09000294 v1 en figure 177: rsmemory function block signals table 306: rsmemory input signals name type d...
Page 396
13.3.2 technical data table 309: configurable logic blocks logic block quantity with cycle time range or value accuracy 5 ms 20 ms 100 ms and 60 60 160 - - or 60 60 160 - - xor 10 10 20 - - inverter 30 30 80 - - srmemory 10 10 20 - - rsmemory 10 10 20 - - gate 10 10 20 - - pulsetimer 10 10 20 (0.000...
Page 397
13.4 fixed signals fxdsign 13.4.1 identification function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number fixed signals fxdsign - - 13.4.2 functionality the fixed signals function fxdsign generates nine pre-set (fixed) signals that can be used in the confi...
Page 398
13.4.5 settings the function does not have any settings available in local hmi or protection and control ied manager (pcm600). 13.4.6 operation principle there are nine outputs from fxdsign function block: • off is a boolean signal, fixed to off (boolean 0) value • on is a boolean signal, fixed to o...
Page 399
13.5.3 function block b16i block in1 in2 in3 in4 in5 in6 in7 in8 in9 in10 in11 in12 in13 in14 in15 in16 out iec09000035-1-en.Vsd iec09000035 v1 en figure 179: b16i function block 13.5.4 signals table 312: b16i input signals name type default description block boolean 0 block of function in1 boolean ...
Page 400
13.5.5 settings the function does not have any parameters available in local hmi or protection and control ied manager (pcm600) 13.5.6 monitored data table 314: b16i monitored data name type values (range) unit description out integer - - output value 13.5.7 operation principle the boolean 16 to int...
Page 401
Name of input type default description value when activated value when deactivated in14 boolean 0 input 14 8192 0 in15 boolean 0 input 15 16384 0 in16 boolean 0 input 16 32768 0 the sum of the numbers in column “value when activated” when all inx (where 1≤x≤16) are active that is=1; is 65535. 65535 ...
Page 402
13.6.3 function block b16ifcvi block in1 in2 in3 in4 in5 in6 in7 in8 in9 in10 in11 in12 in13 in14 in15 in16 out iec09000624-1-en.Vsd iec09000624 v1 en figure 180: b16ifcvi function block 13.6.4 signals table 315: b16ifcvi input signals name type default description block boolean 0 block of function ...
Page 403
Table 316: b16ifcvi output signals name type description out integer output value 13.6.5 settings the function does not have any parameters available in local hmi or protection and control ied manager (pcm600) 13.6.6 monitored data table 317: b16ifcvi monitored data name type values (range) unit des...
Page 404
Name of input type default description value when activated value when deactivated in10 boolean 0 input 10 512 0 in11 boolean 0 input 11 1024 0 in12 boolean 0 input 12 2048 0 in13 boolean 0 input 13 4096 0 in14 boolean 0 input 14 8192 0 in15 boolean 0 input 15 16384 0 in16 boolean 0 input 16 32768 0...
Page 405
13.7.4 signals table 318: ib16a input signals name type default description block boolean 0 block of function inp integer 0 integer input table 319: ib16a output signals name type description out1 boolean output 1 out2 boolean output 2 out3 boolean output 3 out4 boolean output 4 out5 boolean output ...
Page 406
This follows the general formulae: the sum of the values of all outx = 2 x-1 where 1≤x≤16 will be equal to the integer value on the input inp. The integer to boolean 16 conversion function (ib16a) will transfer an integer with a value between 0 to 65535 connected to the input inp to a combination of...
Page 407
13.8 integer to boolean 16 conversion with logic node representation ib16fcvb 13.8.1 identification function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number integer to boolean 16 conversion with logic node representation ib16fcvb - - 13.8.2 functionality i...
Page 408
Table 321: ib16fcvb output signals name type description out1 boolean output 1 out2 boolean output 2 out3 boolean output 3 out4 boolean output 4 out5 boolean output 5 out6 boolean output 6 out7 boolean output 7 out8 boolean output 8 out9 boolean output 9 out10 boolean output 10 out11 boolean output ...
Page 409
Activated outputs outx where 1≤x≤16. The values represented by the different outx are according to table 322 . When an outx is not activated, its value is 0. The ib16fcvb function is designed for receiving the integer input from a station computer - for example, over iec 61850. If the block input is...
Page 410
13.9.2 functionality elapsed time integrator (teiggio) function is a function that accumulates the elapsed time when a given binary signal has been high. The main features of teiggio are • applicable to long time integration (≤999 999.9 seconds). • supervision of limit transgression conditions and o...
Page 411
13.9.5 settings table 325: teiggio group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description operation 0 - 1 - 1 1 operation off / on twarning 1.00 - 999999.99 s 0.01 600.00 time limit for warning supervision talarm 1.00 - 999999.99 s 0.01 1200.00 time limit for alarm supervision 13.9...
Page 412
• applicable to long time integration (≤999 999.9 seconds) • output acctime presents integrated value in seconds to all tools • integrated value is retained in non-volatile memory, if any warning, alarm or overflow occurs • any retained value with a warning/alarm/overflow shall be available as the i...
Page 413
13.9.7 technical data table 326: teiggio technical data function cycle time (ms) range or value accuracy elapsed time integration 5 0 ~ 999999.9 s ±0.05% or ±0.01 s 20 0 ~ 999999.9 s ±0.05% or ±0.04 s 100 0 ~ 999999.9 s ±0.05% or ±0.2 s 1mrk 504 135-uen a section 13 logic 407 technical manual.
Page 414
408.
Page 415
Section 14 monitoring 14.1 measurements 14.1.1 functionality measurement functions is used for power system measurement, supervision and reporting to the local hmi, monitoring tool within pcm600 or to station level for example, via iec 61850. The possibility to continuously monitor measured values o...
Page 416
• p, q and s: three phase active, reactive and apparent power • pf: power factor • u: phase-to-phase voltage amplitude • i: phase current amplitude • f: power system frequency the output values are displayed in the local hmi under main menu/tests/function status/monitoring/cvmmxn/outputs the measuri...
Page 417
14.1.2.2 function block the available function blocks of an ied are depending on the actual hardware (trm) and the logic configuration made in pcm600. Cvmmxn i3p* u3p* s s_range p_inst p p_range q_inst q q_range pf pf_range ilag ilead u u_range i i_range f f_range iec08000222.Vsd iec08000222 v1 en f...
Page 418
Name type description i_range integer calculated current range f real system frequency magnitude of deadband value f_range integer system frequency range 14.1.2.4 settings table 329: cvmmxn non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description operation off on - - off operatio...
Page 419
Name values (range) unit step default description pfreptyp cyclic dead band int deadband - - cyclic reporting type umin 0.0 - 200.0 %ub 0.1 50.0 minimum value in % of ubase umax 0.0 - 200.0 %ub 0.1 200.0 maximum value in % of ubase ureptyp cyclic dead band int deadband - - cyclic reporting type imin...
Page 420
Name values (range) unit step default description qlimhyst 0.000 - 100.000 % 0.001 5.000 hysteresis value in % of range (common for all limits) ugenzerodb 1 - 100 %ub 1 5 zero point clamping in % of ubase pfdbrepint 1 - 300 type 1 10 cycl: report interval (s), db: in % of range, int db: in %s pfzero...
Page 421
Name values (range) unit step default description uampcomp100 -10.000 - 10.000 % 0.001 0.000 amplitude factor to calibrate voltage at 100% of ur iampcomp5 -10.000 - 10.000 % 0.001 0.000 amplitude factor to calibrate current at 5% of ir iampcomp30 -10.000 - 10.000 % 0.001 0.000 amplitude factor to ca...
Page 422
14.1.3.2 function block the available function blocks of an ied are depending on the actual hardware (trm) and the logic configuration made in pcm600. Cmmxu i3p il1 il1rang il1angl il2 il2rang il2angl il3 il3rang il3angl iec08000225 v1 en figure 186: cmmxu function block 14.1.3.3 signals table 332: ...
Page 423
Name values (range) unit step default description ilmax 0 - 500000 a 1 1300 maximum value ilreptyp cyclic dead band int deadband - - dead band reporting type ilangdbrepint 1 - 300 type 1 10 cycl: report interval (s), db: in % of range, int db: in %s table 335: cmmxu non group settings (advanced) nam...
Page 424
14.1.4 phase-phase voltage measurement vmmxu 14.1.4.1 identification function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number phase-phase voltage measurement vmmxu u symbol-uu v1 en - 14.1.4.2 function block the available function blocks of an ied are depe...
Page 425
Name type description ul31 real ul31 amplitude ul31rang integer ul31amplitude range ul31angl real ul31 angle 14.1.4.4 settings table 339: vmmxu non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description operation off on - - off operation off / on globalbasesel 1 - 6 - 1 1 selection...
Page 426
14.1.5 current sequence component measurement cmsqi 14.1.5.1 identification function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number current sequence component measurement cmsqi i1, i2, i0 symbol-vv v1 en - 14.1.5.2 function block the available function bl...
Page 427
Name type description i2 real i2 amplitude i2rang integer i2 amplitude range i2angl real i2angle 14.1.5.4 settings table 344: cmsqi non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description operation off on - - off operation off / on 3i0dbrepint 1 - 300 type 1 10 cycl: report inte...
Page 428
Table 345: cmsqi non group settings (advanced) name values (range) unit step default description 3i0zerodb 0 - 100000 m% 1 500 zero point clamping 3i0hihilim 0 - 500000 a 1 3600 high high limit (physical value) 3i0hilim 0 - 500000 a 1 3300 high limit (physical value) 3i0lowlim 0 - 500000 a 1 0 low l...
Page 429
14.1.6.2 function block the available function blocks of an ied are depending on the actual hardware (trm) and the logic configuration made in pcm600. Iec08000224-2-en.Vsd vmsqi u3p* 3u0 3u0rang 3u0angl u1 u1rang u1angl u2 u2rang u2angl iec08000224 v2 en figure 189: vmsqi function block 14.1.6.3 sig...
Page 430
14.1.6.4 settings table 349: vmsqi non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description operation off on - - off operation off / on 3u0dbrepint 1 - 300 type 1 10 cycl: report interval (s), db: in % of range, int db: in %s 3u0min 0 - 2000000 v 1 0 minimum value 3u0max 0 - 2000...
Page 431
Name values (range) unit step default description u1hihilim 0 - 2000000 v 1 96000 high high limit (physical value) u1hilim 0 - 2000000 v 1 86000 high limit (physical value) u1lowlim 0 - 2000000 v 1 71000 low limit (physical value) u1lowlowlim 0 - 2000000 v 1 66000 low low limit (physical value) u1li...
Page 432
Iec08000226-2-en.Vsd vnmmxu u3p* ul1 ul1rang ul1angl ul2 ul2rang ul2angl ul3 ul3rang ul3angl iec08000226 v2 en figure 190: vnmmxu function block 14.1.7.3 signals table 352: vnmmxu input signals name type default description u3p group signal - three phase group signal for voltage inputs table 353: vn...
Page 433
Name values (range) unit step default description ureptyp cyclic dead band int deadband - - dead band reporting type ulimhys 0.000 - 100.000 v 0.001 5.000 hysteresis value in % of range and is common for all limits uangdbrepint 1 - 300 type 1 10 cycl: report interval (s), db: in % of range, int db: ...
Page 434
Processing blocks. The number of processed alternate measuring quantities depends on the type of ied and built-in options. The information on measured quantities is available for the user at different locations: • locally by means of the local hmi • remotely using the monitoring tool within pcm600 o...
Page 435
En05000657.Vsd x_range= 1 x_range = 3 x_range=0 hysteresis high-high limit high limit low limit low-low limit x_range=2 x_range=4 y t x_range=0 iec05000657 v1 en figure 191: presentation of operating limits each analogue output has one corresponding supervision level output (x_range). The output sig...
Page 436
En05000500.Vsd v a lu e 1 y t v a lu e 2 v a lu e 3 v a lu e 4 value reported (1st) value reported v a lu e 5 value reported y1 y2 y5 value reported value reported y3 y4 (*)set value for t: xdbrepint t (*) t (*) t (*) t (*) iec05000500 v1 en figure 192: periodic reporting amplitude dead-band supervi...
Page 437
99000529.Vsd y t value reported (1st) value reported value reported y1 y2 y3 dy dy dy dy dy dy value reported iec99000529 v1 en figure 193: amplitude dead-band supervision reporting after the new value is reported, the ±Δy limits for dead-band are automatically set around it. The new value is report...
Page 438
99000530.Vsd y t value reported (1st) y1 value reported a1 y2 value reported y3 y4 a value reported a2 y5 a3 a4 a5 a7 a6 value reported a2 >= pre-set value a1 >= pre-set value a >= pre-set value a3 + a4 + a5 + a6 + a7 >= pre-set value iec99000530 v1 en figure 194: reporting with integral dead-band s...
Page 439
Set value for parameter “mode” formula used for complex, three- phase power calculation formula used for voltage and current magnitude calculation comment 4 l1l2 * * 1 2 1 2 ( ) = × - l l l l s u i i equation1391 v1 en (equation 91) 1 2 1 2 ( ) / 2 = = + l l l l u u i i i equation1392 v1 en (equatio...
Page 440
2 2 = = + s s p q equation1405 v1 en (equation 105) cos p pf s j = = equation1406 v1 en (equation 106) additionally to the power factor value the two binary output signals from the function are provided which indicates the angular relationship between current and voltage phasors. Binary output signa...
Page 441
Iec05000652 v2 en figure 195: calibration curves the first current and voltage phase in the group signals will be used as reference and the amplitude and angle compensation will be used for related input signals. Low pass filtering in order to minimize the influence of the noise signal on the measur...
Page 442
Default value for parameter k is 0.00. With this value the new calculated value is immediately given out without any filtering (that is, without any additional delay). When k is set to value bigger than 0, the filtering is enabled. Appropriate value of k shall be determined separately for every appl...
Page 443
Busbar protected object p q iec09000038-1-en.Vsd ied iec09000038-1-en v1 en figure 196: internal ied directionality convention for p & q measurements practically, it means that active and reactive power will have positive values when they flow from the busbar towards the protected object and they wi...
Page 444
Compensation at 5, 30 and 100% of rated current. The compensation below 5% and above 100% is constant and linear in between, see figure 195 . Phase currents (amplitude and angle) are available on the outputs and each amplitude output has a corresponding supervision level output (ilx_rang). The super...
Page 445
Function range or value accuracy apparent power, s 0.1 x u r r 0.2 x i r r ± 1.0% of s r at s ≤ s r ± 1.0% of s at s > s r apparent power, s three phase settings cos phi = 1 ± 0.5% of s at s > s r ± 0.5% of s r at s ≤ s r power factor, cos (φ) 0.1 x u r r 0.2 x i r r 14.2 event counter cntggio 14.2....
Page 446
Name type default description counter5 boolean 0 input for counter 5 counter6 boolean 0 input for counter 6 reset boolean 0 reset of function table 359: cntggio output signals name type description value1 integer output of counter 1 value2 integer output of counter 2 value3 integer output of counter...
Page 447
However gives as a result that it can take long time, up to several minutes, before a new value is stored in the flash memory. And if a new cntggio value is not stored before auxiliary power interruption, it will be lost. Cntggio stored values in flash memory will however not be lost at an auxiliary...
Page 448
14.3.3 principle of operation limit counter (l4ufcnt) counts the number of positive and/or negative flanks on the binary input signal depending on the function settings. L4ufcnt also checks if the accumulated value is equal or greater than any of its four settable limits. The four limit outputs will...
Page 449
Iec12000626_1_en.Vsd max value +3 ® max value -1 ® max value ® max value +1 ® max value +2 ® max value -1 ® max value ® 0 ® 1 2 ... ... ... ... Overflow indication actual value counted value iec12000626 v1 en figure 199: overflow indication when onmaxvalue is set to rollover pulsed the error output ...
Page 450
14.3.5 signals table 363: l4ufcnt input signals name type default description block boolean 0 block of function input boolean 0 input for counter reset boolean 0 reset of function table 364: l4ufcnt output signals name type description error boolean error indication on counter limit and/or initial v...
Page 451
14.3.7 monitored data table 366: l4ufcnt monitored data name type values (range) unit description value integer - - counted value 14.3.8 technical data table 367: l4ufcnttechnical data function range or value accuracy counter value 0-65535 - max. Count up speed 5-160 pulses/s - 14.4 disturbance repo...
Page 452
Used to get information about the recordings. The disturbance report files may be uploaded to pcm600 for further analysis using the disturbance handling tool. 14.4.2 disturbance report drprdre 14.4.2.1 identification function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c3...
Page 453
Name values (range) unit step default description maxnostorerec 10 - 100 - 1 100 maximum number of stored disturbances zeroangleref 1 - 30 ch 1 1 trip value recorder, phasor reference channel opmodetest off on - - off operation mode during test mode 14.4.2.5 monitored data table 370: drprdre monitor...
Page 454
Name type values (range) unit description untrigstatch10 boolean - - under level trig for analog channel 10 activated ovtrigstatch10 boolean - - over level trig for analog channel 10 activated untrigstatch11 boolean - - under level trig for analog channel 11 activated ovtrigstatch11 boolean - - over...
Page 455
Name type values (range) unit description untrigstatch22 boolean - - under level trig for analog channel 22 activated ovtrigstatch22 boolean - - over level trig for analog channel 22 activated untrigstatch23 boolean - - under level trig for analog channel 23 activated ovtrigstatch23 boolean - - over...
Page 456
Name type values (range) unit description untrigstatch34 boolean - - under level trig for analog channel 34 activated ovtrigstatch34 boolean - - over level trig for analog channel 34 activated untrigstatch35 boolean - - under level trig for analog channel 35 activated ovtrigstatch35 boolean - - over...
Page 457
14.4.3.2 function block a1radr ^grpinput1 ^grpinput2 ^grpinput3 ^grpinput4 ^grpinput5 ^grpinput6 ^grpinput7 ^grpinput8 ^grpinput9 ^grpinput10 iec09000348-1-en.Vsd iec09000348 v1 en figure 201: a1radr function block, analog inputs, example for a1radr, a2radr and a3radr 14.4.3.3 signals a1radr - a3rad...
Page 458
14.4.3.4 settings a1radr - a3radr settings setting tables for a1radr, a2radr and a3radr are similar except for channel numbers. • a1radr, channel01 - channel10 • a2radr, channel11 - channel20 • a3radr, channel21 - channel30 table 372: a1radr non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step d...
Page 459
Name values (range) unit step default description funtype5 0 - 255 - 1 0 function type for analog channel 5 (iec-60870-5-103) infno5 0 - 255 - 1 0 information number for analog channel 5 (iec-60870-5-103) funtype6 0 - 255 - 1 0 function type for analog channel 6 (iec-60870-5-103) infno6 0 - 255 - 1 ...
Page 460
Name values (range) unit step default description undertrigop03 off on - - off use under level trigger for analog channel 3 (on) or not (off) undertrigle03 0 - 200 % 1 50 under trigger level for analog channel 3 in % of signal overtrigop03 off on - - off use over level trigger for analog channel 3 (...
Page 461
Name values (range) unit step default description undertrigle08 0 - 200 % 1 50 under trigger level for analog channel 8 in % of signal overtrigop08 off on - - off use over level trigger for analog channel 8 (on) or not (off) overtrigle08 0 - 5000 % 1 200 over trigger level for analog channel 8 in % ...
Page 462
Channels 31-40 are not shown in lhmi. They are used for internally calculated analog signals. 14.4.4.3 signals table 374: a4radr input signals name type default description input31 real 0 analog channel 31 input32 real 0 analog channel 32 input33 real 0 analog channel 33 input34 real 0 analog channe...
Page 463
Name values (range) unit step default description infno31 0 - 255 - 1 0 information number for analog channel 31 (iec-60870-5-103) funtype32 0 - 255 - 1 0 function type for analog channel 32 (iec-60870-5-103) infno32 0 - 255 - 1 0 information number for analog channel 32 (iec-60870-5-103) funtype33 ...
Page 464
Name values (range) unit step default description overtrigop31 off on - - off use over level trigger for analog channel 31 (on) or not (off) overtrigle31 0 - 5000 % 1 200 over trigger level for analog channel 31 in % of signal nomvalue32 0.0 - 999999.9 - 0.1 0.0 nominal value for analog channel 32 u...
Page 465
Name values (range) unit step default description overtrigle36 0 - 5000 % 1 200 over trigger level for analog channel 36 in % of signal nomvalue37 0.0 - 999999.9 - 0.1 0.0 nominal value for analog channel 37 undertrigop37 off on - - off use under level trigger for analog channel 37 (on) or not (off)...
Page 466
14.4.5 binary input signals bxrbdr 14.4.5.1 identification function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number binary input signals b1rbdr - - binary input signals b2rbdr - - binary input signals b3rbdr - - binary input signals b4rbdr - - binary input...
Page 467
Table 377: b1rbdr input signals name type default description input1 boolean 0 binary channel 1 input2 boolean 0 binary channel 2 input3 boolean 0 binary channel 3 input4 boolean 0 binary channel 4 input5 boolean 0 binary channel 5 input6 boolean 0 binary channel 6 input7 boolean 0 binary channel 7 ...
Page 468
Name values (range) unit step default description setled02 off start trip start and trip - - off set led on hmi for binary channel 2 trigdr03 off on - - off trigger operation on/off setled03 off start trip start and trip - - off set led on hmi for binary channel 3 trigdr04 off on - - off trigger ope...
Page 469
Name values (range) unit step default description trigdr11 off on - - off trigger operation on/off setled11 off start trip start and trip - - off set led on hmi for binary channel 11 trigdr12 off on - - off trigger operation on/off setled12 off start trip start and trip - - off set led on hmi for bi...
Page 470
Name values (range) unit step default description funtype5 0 - 255 - 1 0 function type for binary channel 5 (iec -60870-5-103) infno5 0 - 255 - 1 0 information number for binary channel 5 (iec -60870-5-103) funtype6 0 - 255 - 1 0 function type for binary channel 6 (iec -60870-5-103) infno6 0 - 255 -...
Page 471
Table 379: b1rbdr non group settings (advanced) name values (range) unit step default description triglevel01 trig on 0 trig on 1 - - trig on 1 trigger on positive (1) or negative (0) slope for binary input 1 indicationma01 hide show - - hide indication mask for binary channel 1 triglevel02 trig on ...
Page 472
Name values (range) unit step default description triglevel13 trig on 0 trig on 1 - - trig on 1 trigger on positive (1) or negative (0) slope for binary input 13 indicationma13 hide show - - hide indication mask for binary channel 13 triglevel14 trig on 0 trig on 1 - - trig on 1 trigger on positive ...
Page 473
Trip value rec event list event recorder indications disturbance recorder a1-4radr b1-6rbdr disturbance report binary signals analog signals a4radr b6rbdr drprdre iec09000337-2-en.Vsd iec09000337 v2 en figure 204: disturbance report functions and related function blocks the whole disturbance report ...
Page 474
The memory limit does not affect the rest of the disturbance report (event list, event recorder, indications and trip value recorder). The maximum number of recordings depend on each recordings total recording time. Long recording time will reduce the number of recordings to less than 100. The ied f...
Page 475
14.4.6.6 disturbance recorder disturbance recorder records analog and binary signal data before, during and after the fault, see disturbance recorder section for detailed information. 14.4.6.7 time tagging the ied has a built-in real-time calendar and clock. This function is used for all time taggin...
Page 476
14.4.6.9 analog signals up to 40 analog signals can be selected for recording by the disturbance recorder and triggering of the disturbance report function. Out of these 40, 30 are reserved for external analog signals from analog input modules via preprocessing function blocks (smai) and summation b...
Page 477
Corresponding information is available on the non-calculated output (ai4) on the smai function block. Connect the signals to the axradr accordingly. For each of the analog signals, operation = on means that it is recorded by the disturbance recorder. The trigger is independent of the setting of oper...
Page 478
Manual trigger a disturbance report can be manually triggered from the local hmi, pcm600 or via station bus (iec 61850). When the trigger is activated, the manual trigger signal is generated. This feature is especially useful for testing. Binary-signal trigger any binary signal state (logic one or a...
Page 479
14.4.7 technical data table 380: drprdre technical data function range or value accuracy current recording - ± 1,0% of i r at i ≤ i r ± 1,0% of i at i > ir voltage recording - ± 1,0% of u r at u ≤ u r ± 1,0% of u at u > u r pre-fault time (0.05–3.00) s - post-fault time (0.1–10.0) s - limit time (0....
Page 480
14.5.2 function block the indications function has no function block of it’s own. 14.5.3 signals 14.5.3.1 input signals the indications function logs the same binary input signals as the disturbance report function. 14.5.4 operation principle the led indications display this information: green led: ...
Page 481
The name of the binary signal that appears in the indication function is the user- defined name assigned at configuration of the ied. The same name is used in disturbance recorder function, indications and event recorder function. 14.5.5 technical data table 381: drprdre technical data function valu...
Page 482
Generated by both internal logical signals and binary input channels. The internal signals are time-tagged in the main processor module, while the binary input channels are time-tagged directly in each i/o module. The events are collected during the total recording time (pre-, post-fault and limit t...
Page 483
14.7.3 signals 14.7.3.1 input signals the event list logs the same binary input signals as configured for the disturbance report function. 14.7.4 operation principle when a binary signal, connected to the disturbance report function, changes status, the event list function stores input name, status ...
Page 484
The trip value recorder calculates the values of all selected analog input signals connected to the disturbance recorder function. The result is magnitude and phase angle before and during the fault for each analog input signal. The trip value recorder information is available for the disturbances l...
Page 485
The trip value record is stored as a part of the disturbance report information and managed in pcm600 or via the local hmi. 14.8.5 technical data table 384: drprdre technical data function value buffer capacity maximum number of analog inputs 30 maximum number of disturbance reports 100 14.9 disturb...
Page 486
14.9.5 operation principle disturbance recording is based on the acquisition of binary and analog signals. The binary signals can be either true binary input signals or internal logical signals generated by the functions in the ied. The analog signals to be recorded are input channels from the trans...
Page 487
The recorded disturbance is now ready for retrieval and evaluation. The recording files comply with the comtrade standard iec 60255-24 and are divided into three files; a header file (hdr), a configuration file (cfg) and a data file (dat). The header file (optional in the standard) contains basic in...
Page 488
14.9.6 technical data table 385: drprdre technical data function value buffer capacity maximum number of analog inputs 40 maximum number of binary inputs 96 maximum number of disturbance reports 100 maximum total recording time (3.4 s recording time and maximum number of channels, typical value) 340...
Page 489
14.10.5 settings the function does not have any parameters available in local hmi or protection and control ied manager (pcm600). 14.10.6 operation principle upon receiving a signal at its input, iec61850 generic communication i/o functions (spggio) function sends the signal over iec 61850-8-1 to th...
Page 490
14.11.4 signals table 387: sp16ggio input signals name type default description block boolean 0 block of function in1 boolean 0 input 1 status in2 boolean 0 input 2 status in3 boolean 0 input 3 status in4 boolean 0 input 4 status in5 boolean 0 input 5 status in6 boolean 0 input 6 status in7 boolean ...
Page 491
Name type values (range) unit description out7 group signal - - output 7 status out8 group signal - - output 8 status out9 group signal - - output 9 status out10 group signal - - output 10 status out11 group signal - - output 11 status out12 group signal - - output 12 status out13 group signal - - o...
Page 492
14.12.2 functionality iec61850 generic communication i/o functions (mvggio) function is used to send the instantaneous value of an analog signal to other systems or equipment in the substation. It can also be used inside the same ied, to attach a range aspect to an analog value and to permit measure...
Page 493
Name values (range) unit step default description mv llim -5000.00 - 5000.00 xbase 0.01 -800.00 low limit multiplied with the base prefix (multiplication factor) mv lllim -5000.00 - 5000.00 xbase 0.01 -900.00 low low limit multiplied with the base prefix (multiplication factor) mv min -5000.00 - 500...
Page 494
14.13.2 functionality the current and voltage measurements functions (cvmmxn, cmmxu, vmmxu and vnmmxu), current and voltage sequence measurement functions (cmsqi and vmsqi) and iec 61850 generic communication i/o functions (mvggio) are provided with measurement supervision functionality. All measure...
Page 495
Globalbasesel: selects the global base value group used by the function to define (ibase), (ubase) and (sbase). 14.13.6 operation principle the input signal must be connected to a range output of a measuring function block (cvmmxn, cmmxu, vmmxu, vnmmxu, cmsqi, vmsq or mvggio). The function block con...
Page 496
Spvnzbat activates the start and alarm outputs when the battery terminal voltage exceeds the set upper limit or drops below the set lower limit. A time delay for the overvoltage and undervoltage alarms can be set according to definite time characteristics. Spvnzbat operates after a settable operate ...
Page 497
14.14.6 measured values table 399: spvnzbat measured values name type default description u_batt real 0.00 battery terminal voltage that has to be supervised block boolean 0 blocks all the output signals of the function 14.14.7 monitored data table 400: spvnzbat monitored data name type values (rang...
Page 498
Low level detector the level detector compares the battery voltage u_batt with the set value of the battvoltlowlim setting. If the value of the u_batt input drops below the set value of the battvoltlowlim setting, the start signal st_ulow is activated. The measured voltage between the battery termin...
Page 499
14.15.2 functionality insulation gas monitoring function ssimg is used for monitoring the circuit breaker condition. Binary information based on the gas pressure in the circuit breaker is used as input signals to the function. In addition, the function generates alarms based on received information....
Page 500
Table 403: ssimg output signals name type description pressure real pressure service value pres_alm boolean pressure below alarm level pres_lo boolean pressure below lockout level temp real temperature of the insulation medium temp_alm boolean temperature above alarm level temp_lo boolean temperatur...
Page 501
Below the levels for more than the set time delays the corresponding signals, pres_alm, pressure below alarm level and pres_lo, pressure below lockout level alarm will be obtained. The input signal blk_alm is used to block the two alarms levels. The input signal block is used to block both the alarm...
Page 502
14.16.4 signals inputs level and temp together with settings levelalmlimit, levellolimit, tempalarmlimit and templolimit are not supported in this release of 650 series. Table 406: ssiml input signals name type default description block boolean 0 block of function blk_alm boolean 0 block all the ala...
Page 503
Name values (range) unit step default description ttempalarm 0.000 - 60.000 s 0.001 0.000 time delay for temperature alarm ttemplockout 0.000 - 60.000 s 0.001 0.000 time delay for temperture lockout tresetlevelalm 0.000 - 60.000 s 0.001 0.000 reset time delay for level alarm tresetlevello 0.000 - 60...
Page 504
14.17.2 functionality the circuit breaker condition monitoring function sscbr is used to monitor different parameters of the circuit breaker. The breaker requires maintenance when the number of operations has reached a predefined value. The energy is calculated from the measured input currents as a ...
Page 505
Name type default description lopres boolean 0 binary pressure input for lockout indication sprchrgn boolean 0 cb spring charging started input sprchrgd boolean 0 cb spring charged input cbcntrst boolean 0 reset input for cb remaining life and operation counter iaccrst boolean 0 reset accumulated cu...
Page 506
Name values (range) unit step default description acccurralmlvl 0.00 - 20000.00 - 0.01 2500.00 setting of alarm level for accumulated currents power acccurrlo 0.00 - 20000.00 - 0.01 2500.00 lockout limit setting for accumulated currents power dircoef -3.00 - -0.50 - 0.01 -1.50 directional coefficien...
Page 507
Name type values (range) unit description nooprday integer - - the number of days cb has been inactive cblifel1 integer - - cb remaining life phase l1 cblifel2 integer - - cb remaining life phase l2 cblifel3 integer - - cb remaining life phase l3 iaccl1 real - - accumulated currents power (iyt), pha...
Page 508
Guid-fe21bbdc-57a6-425c-b22b-8e646c1bd932 v1 en figure 216: functional module diagram 14.17.7.1 circuit breaker status the circuit breaker status subfunction monitors the position of the circuit breaker, that is, whether the breaker is in an open, closed or intermediate position. The operation of th...
Page 509
Guid-60adc120-4b5a-40d8-b1c5-475e4634214b v1 en figure 217: functional module diagram for monitoring circuit breaker status block and blk_alm inputs phase current check this module compares the three phase currents with the setting accdislevel. If the current in a phase exceeds the set level, inform...
Page 510
Inactivity timer the module calculates the number of days the circuit breaker has remained inactive, that is, has stayed in the same open or closed state. The calculation is done by monitoring the states of the posopen and posclose auxiliary contacts. The inactive days nooprday is available through ...
Page 511
Guid-3ad25f5a-639a-4941-aa61-e69fa2357afe v1 en there is a time difference t 1 between the start of the main contact opening and the opening of the posclose auxiliary contact. Similarly, there is a time gap t 2 between the time when the posopen auxiliary contact opens and the main contact is complet...
Page 512
Guid-ff1221a4-6160-4f92-9e7f-a412875b69e1 v1 en figure 220: functional module diagram for counting circuit breaker operations operation counter the operation counter counts the number of operations based on the state change of the binary auxiliary contacts inputs posclose and posopen. The number of ...
Page 513
Guid-dac3746f-dfbf-4186-a99d-1d972578d32a v1 en figure 221: functional module diagram for calculating accumulative energy and alarm accumulated energy calculator this module calculates the accumulated energy i y t [(ka) y s]. The factor y is set with the currexp setting. The calculation is initiated...
Page 514
Alarm limit check the iaccalm alarm is activated when the accumulated energy exceeds the value set with the acccurralmlvl threshold setting. However, when the energy exceeds the limit value set with the acccurrlo threshold setting, the iaccloal output is activated. The iaccalm and iaccloal outputs c...
Page 515
The remaining life is calculated separately for all three phases and it is available as a monitored data value cblifel1 (l2, l3). The values can be cleared by setting the parameter cb wear values in the clear menu from lhmi. Clearing cb wear values also resets the operation counter. Alarm limit chec...
Page 516
Alarm limit check if the time taken by the spring to charge is more than the value set with the tsprngchrgalm setting, the subfunction generates the sprchral alarm. It is possible to block the sprchral alarm signal by activating the block binary input. 14.17.7.8 gas pressure supervision the gas pres...
Page 517
14.17.8 technical data table 414: sscbr technical data function range or value accuracy alarm levels for open and close travel time (0-200) ms ± 0.5% ± 25 ms alarm levels for number of operations (0 - 9999) - setting of alarm for spring charging time (0.00-60.00) s ± 0.5% ± 25 ms time delay for gas ...
Page 518
Guid-b8a3a04c-430d-4488-9f72-8529fab0b17d v1 en figure 226: settings for cmmxu: 1 all input signals to iec 60870-5-103 i103meas must be connected in application configuration. Connect an input signals on iec 60870-5-103 i103meas that is not connected to the corresponding output on mmxu function, to ...
Page 519
14.18.3 signals table 415: i103meas input signals name type default description block boolean 0 block of service value reporting il1 real 0.0 service value for current phase l1 il2 real 0.0 service value for current phase l2 il3 real 0.0 service value for current phase l3 in real 0.0 service value f...
Page 520
14.19 measurands user defined signals for iec 60870-5-103 i103measusr 14.19.1 functionality i103measusr is a function block with user defined input measurands in monitor direction. These function blocks include the functiontype parameter for each block in the private range, and the information numbe...
Page 521
14.19.4 settings table 418: i103measusr non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description functiontype 1 - 255 - 1 25 function type (1-255) infno 1 - 255 - 1 1 information number for measurands (1-255) maxmeasur1 0.05 - 10000000000.00 - 0.05 1000.00 maximum value for measu...
Page 522
14.20.3 signals table 419: i103ar input signals name type default description block boolean 0 block of status reporting 16_aract boolean 0 information number 16, auto-recloser active 128_cbon boolean 0 information number 128, circuit breaker on by auto- recloser 130_blkd boolean 0 information number...
Page 523
14.21.4 settings table 422: i103ef non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description functiontype 1 - 255 - 1 160 function type (1-255) 14.22 function status fault protection for iec 60870-5-103 i103fltprot 14.22.1 functionality i103fltprot is used for fault indications in...
Page 524
14.22.2 function block iec10000291-1-en.Vsd i103fltprot block 64_stl1 65_stl2 66_stl3 67_stin 68_trgen 69_trl1 70_trl2 71_trl3 72_trbkup 73_scl 74_fw 75_rev 76_trans 77_recev 78_zone1 79_zone2 80_zone3 81_zone4 82_zone5 84_stgen 85_bfp 86_mtrl1 87_mtrl2 88_mtrl3 89_mtrn 90_ioc 91_ioc 92_ief 93_ief a...
Page 525
Name type default description 76_trans boolean 0 information number 76, signal transmitted 77_recev boolean 0 information number 77, signal received 78_zone1 boolean 0 information number 78, zone 1 79_zone2 boolean 0 information number 79, zone 2 80_zone3 boolean 0 information number 80, zone 3 81_z...
Page 526
14.23.2 function block i103ied block 19_ledrs 21_testm 22_setch 23_grp1 24_grp2 25_grp3 26_grp4 iec10000292-2-en.Vsd iec10000292 v2 en figure 232: i103ied function block 14.23.3 signals table 425: i103ied input signals name type default description block boolean 0 block of status reporting 19_ledrs ...
Page 527
14.24.2 function block iec10000293-1-en.Vsd i103superv block 32_measi 33_measu 37_ibkup 38_vtff 46_grwa 47_gral iec10000293 v1 en figure 233: i103superv function block 14.24.3 signals table 427: i103superv input signals name type default description block boolean 0 block of status reporting 32_measi...
Page 528
I103usrdef can be used, for example in mapping the inf numbers not supported directly by specific function blocks, like: inf17, inf18, inf20 or inf35. After connecting the appropriate signals to the i103usrdef inputs, the user must also set the infno_x values in the settings. Guid-391d4145-b7e6-4174...
Page 529
14.25.4 settings table 430: i103usrdef non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description functiontype 1 - 255 - 1 5 function type (1-255) infno_1 1 - 255 - 1 1 information number for binary input 1 (1-255) infno_2 1 - 255 - 1 2 information number for binary input 2 (1-255)...
Page 530
524.
Page 531
Section 15 metering 15.1 pulse counter pcggio 15.1.1 identification function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number pulse counter pcggio s00947 v1 en - 15.1.2 functionality pulse counter (pcggio) function counts externally generated binary pulses,...
Page 532
Table 432: pcggio output signals name type description invalid boolean the pulse counter value is invalid restart boolean the reported value does not comprise a complete integration cycle blocked boolean the pulse counter function is blocked new_val boolean a new pulse counter value is generated sca...
Page 533
The reporting time period can be set in the range from 1 second to 60 minutes and is synchronized with absolute system time. Interrogation of additional pulse counter values can be done with a command (intermediate reading) for a single counter. All active counters can also be read by iec 61850. Pul...
Page 534
The blocked signal is a steady signal and is set when the counter is blocked. There are two reasons why the counter is blocked: • the block input is set, or • the binary input module, where the counter input is situated, is inoperative. The new_val signal is a pulse signal. The signal is set if the ...
Page 535
15.2.3 function block etpmmtr p q stacc rstacc rstdmd accst eafpulse earpulse erfpulse errpulse eafalm earalm erfalm erralm eafacc earacc erfacc erracc maxpafd maxpard maxprfd maxprrd iec09000104 v1 en figure 237: etpmmtr function block 15.2.4 signals table 436: etpmmtr input signals name type defau...
Page 536
Name type description earacc real accumulated reverse active energy value erfacc real accumulated forward reactive energy value erracc real accumulated reverse reactive energy value maxpafd real maximum forward active power demand value for set interval maxpard real maximum reverse active power dema...
Page 537
Name values (range) unit step default description levzeroclampp 0.001 - 10000.000 mw 0.001 10.000 zero point clamping level at active power levzeroclampq 0.001 - 10000.000 mvar 0.001 10.000 zero point clamping level at reactive power direnergyact forward reverse - - forward direction of active energ...
Page 538
Outputs are available for forward as well as reverse direction. The accumulated energy values can be reset from the local hmi reset menu or with input signal rstacc. The maximum demand values for active and reactive power are calculated for the set time interval tenergy. The maximum values are updat...
Page 539
Section 16 station communication 16.1 dnp3 protocol dnp3 (distributed network protocol) is a set of communications protocols used to communicate data between components in process automation systems. For a detailed description of the dnp3 protocol, see the dnp3 communication protocol manual. 16.2 ie...
Page 540
The denial of service functions doslan1 and dosfrnt are included to limit the inbound network traffic. The communication can thus never compromise the primary functionality of the ied. The event system has a rate limiter to reduce cpu load. The event channel has a quota of 10 events/second after the...
Page 541
16.2.5 technical data table 444: communication protocol function value protocol tcp/ip ethernet communication speed for the ieds 100 mbit/s protocol iec 61850–8–1 communication speed for the ieds 100base-fx protocol dnp3.0/tcp communication speed for the ieds 100base-fx protocol, serial iec 60870–5–...
Page 542
16.3.2 function block gooseintlkrcv block ^resreq ^resgrant ^app1_op ^app1_cl app1val ^app2_op ^app2_cl app2val ^app3_op ^app3_cl app3val ^app4_op ^app4_cl app4val ^app5_op ^app5_cl app5val ^app6_op ^app6_cl app6val ^app7_op ^app7_cl app7val ^app8_op ^app8_cl app8val ^app9_op ^app9_cl app9val ^app10...
Page 543
Table 446: gooseintlkrcv output signals name type description resreq boolean reservation request resgrant boolean reservation granted app1_op boolean apparatus 1 position is open app1_cl boolean apparatus 1 position is closed app1val boolean apparatus 1 position is valid app2_op boolean apparatus 2 ...
Page 544
Name type description app13_op boolean apparatus 13 position is open app13_cl boolean apparatus 13 position is closed app13val boolean apparatus 13 position is valid app14_op boolean apparatus 14 position is open app14_cl boolean apparatus 14 position is closed app14val boolean apparatus 14 position...
Page 545
16.4.2 function block goosebinrcv block ^out1 out1val ^out2 out2val ^out3 out3val ^out4 out4val ^out5 out5val ^out6 out6val ^out7 out7val ^out8 out8val ^out9 out9val ^out10 out10val ^out11 out11val ^out12 out12val ^out13 out13val ^out14 out14val ^out15 out15val ^out16 out16val iec09000236_en.Vsd iec...
Page 546
Name type description out4val boolean valid data on binary output 4 out5 boolean binary output 5 out5val boolean valid data on binary output 5 out6 boolean binary output 6 out6val boolean valid data on binary output 6 out7 boolean binary output 7 out7val boolean valid data on binary output 7 out8 bo...
Page 547
The input of this goose block must be linked in smt by means of a cross to receive the binary values. The implementation for iec61850 quality data handling is restricted to a simple level. If quality data validity is good then the outxval output will be high. If quality data validity is invalid, que...
Page 548
16.5.3 settings table 451: goosevctrconf non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description sendoperation off on - - on send operation sendinterval 0.1 - 5.0 s 0.1 0.3 send interval receiveoperation off on - - on receive operation receiveinterval 0.1 - 10.0 s 0.1 0.8 receiv...
Page 549
16.6.4 signals table 452: goosevctrrcv input signals name type default description block boolean 0 block function table 453: goosevctrrcv output signals name type description vctr_rcv group signal output group connection to voltage control datavalid boolean data valid for output signals commvalid bo...
Page 550
16.7.2 functionality goosedprcv is used to receive a double point value using iec61850 protocol via goose. 16.7.3 function block iec10000249-1-en.Vsd goosedprcv block ^dpout datavalid commvalid test iec10000249 v1 en figure 242: goosedprcv function block 16.7.4 signals table 454: goosedprcv input si...
Page 551
The input of this goose block must be linked in smt by means of a cross to receive the double point values. The implementation for iec61850 quality data handling is restricted to a simple level. If quality data validity is good then the datavalid output will be high. If quality data validity is inva...
Page 552
Table 458: gooseintrcv output signals name type description intout integer integer output datavalid boolean data valid for integer output commvalid boolean communication valid for integer output test boolean test output 16.8.5 settings table 459: gooseintrcv non group settings (basic) name values (r...
Page 553
16.9.2 functionality goosemvrcv is used to receive measured value using iec61850 protocol via goose. 16.9.3 function block iec10000251-1-en.Vsd goosemvrcv block ^mvout datavalid commvalid test iec10000251 v1 en figure 244: goosemvrcv function block 16.9.4 signals table 460: goosemvrcv input signals ...
Page 554
The input of this goose block must be linked in smt by means of a cross to receive the float values. The implementation for iec61850 quality data handling is restricted to a simple level. If quality data validity is good then the datavalid output will be high. If quality data validity is invalid, qu...
Page 555
Table 464: goosesprcv output signals name type description spout boolean single point output datavalid boolean data valid for single point output commvalid boolean communication valid for single point output test boolean test output 16.10.5 settings table 465: goosesprcv non group settings (basic) n...
Page 556
Principle. The master must have software that can interpret iec 60870-5-103 communication messages. Function blocks available for the iec 60870–5–103 protocol are described in sections control and monitoring.The communication protocol manual for iec 60870-5-103 includes the 650 series vendor specifi...
Page 557
Table 467: rs485103 non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description slaveaddress 1 - 255 - 1 1 slave address baudrate 9600 bd 19200 bd - - 9600 bd baudrate on serial line cycmeasreptime 1.0 - 1800.0 s 0.1 5.0 cyclic reporting time of measurments mastertimedomain utc loca...
Page 558
The communication is performed in parallel, that is the same data package is transmitted on both channels simultaneously. The received package identity from one channel is compared with the data package identity from the other channel. If the identity is the same, the last package is discarded. Prps...
Page 559
16.12.3 function block prpstatus lan1-a lan1-b iec13000011-1-en.Vsd iec13000011 v1 en figure 247: prpstatus function block table 468: prpstatus output signals name type description lan1-a boolean lan1 channel a status lan1-b boolean lan1 channel b status 16.12.4 setting parameters the prpstatus func...
Page 560
Name values (range) unit step default description extlogsrv2type off syslog udp/ip syslog tcp/ip cef tcp/ip - - off external log server 2 type extlogsrv2port 1 - 65535 - 1 514 external log server 2 port number extlogsrv2ip 0 - 18 ip address 1 127.0.0.1 external log server 2 ip-address extlogsrv3type...
Page 561
16.15 security events on protocols secalarm 16.15.1 security alarm secalarm 16.15.2 signals table 470: secalarm output signals name type description eventid integer eventid of the generated security event seqnumber integer sequence number of the generated security event 16.15.3 settings table 471: s...
Page 562
556.
Page 563
Section 17 basic ied functions 17.1 self supervision with internal event list 17.1.1 functionality the self supervision with internal event list interrsig and selfsupevlst function reacts to internal system events generated by the different built-in self- supervision elements. The internal events ar...
Page 564
17.1.2.4 settings the function does not have any settings available in local hmi or protection and control ied manager (pcm600). 17.1.3 internal event list selfsupevlst 17.1.3.1 identification function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number intern...
Page 565
Iec09000390-1-en.Vsd power supply fault watchdog tx overflow master resp. Supply fault reboot i/o internal fail (cpu) power supply module i/o nodes cem and fault fault fault internal fail i/o nodes = bio xxxx = inverted signal iec09000390 v1 en figure 249: hardware self-supervision, potential-free c...
Page 566
Time synch error internal warning gents sync error gents sync ok s r gents rtc error s r >1 internal fail liodev stopped s r real time clock error e.G. Bio1- error settings changed settings changed rte fatal error wdog starved sw watchdog error gents rtc ok gents time reset >1 liodev started >1 liod...
Page 567
They are also called internal signals. The internal signals can be divided into two groups. • standard signals are always presented in the ied, see table 473 . • hardware dependent internal signals are collected depending on the hardware configuration, see table 474 . Explanations of internal signal...
Page 568
Name of signal reasons for activation time synch error this signal will be active when the source of the time synchronization is lost, or when the time system has to make a time reset. Runtime exec error this signal will be active if the runtime engine failed to do some actions with the application ...
Page 569
U 1 x 2 x 1 u 1 x 2 x 1 adx controller adx_high adx_low adx iec05000296-3-en.Vsd iec05000296 v3 en figure 251: simplified drawing of a/d converter for the ied. The technique to split the analog input signal into two a/d converter(s) with different amplification makes it possible to supervise the a/d...
Page 570
17.2 time synchronization 17.2.1 functionality the time synchronization source selector is used to select a common source of absolute time for the ied when it is a part of a protection system. This makes it possible to compare event and disturbance data between all ieds in a station automation syste...
Page 571
17.2.3.2 settings table 478: sntp non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description serverip-add 0 - 255 ip address 1 0.0.0.0 server ip-address redservip-add 0 - 255 ip address 1 0.0.0.0 redundant server ip-address 17.2.4 time system, summer time begin dstbegin 17.2.4.1 id...
Page 572
17.2.5 time system, summer time ends dstend 17.2.5.1 identification function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number time system, summer time ends dstend - - 17.2.5.2 settings table 480: dstend non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit st...
Page 573
17.2.6.2 settings table 481: timezone non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description nohalfhourutc -24 - 24 - 1 0 number of half-hours from utc 17.2.7 time synchronization via irig-b 17.2.7.1 identification function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identif...
Page 574
Sw-time protection and control functions time tagging and general synchronization commu - nication events iec09000210-2-en.Vsd external synchronization sources off sntp dnp irig-b time- regulator iec60870-5-103 iec09000210 v2 en figure 252: design of time system (clock synchronization) all time tagg...
Page 575
• the maximum error of the last used synchronization message • the time since the last used synchronization message • the rate accuracy of the internal clock in the function. 17.2.8.2 real-time clock (rtc) operation the ied has a built-in real-time clock (rtc) with a resolution of one second. The cl...
Page 576
17.2.8.3 synchronization alternatives two main alternatives of external time synchronization are available. The synchronization message is applied either via any of the communication ports of the ied as a telegram message including date and time or via irig-b. Synchronization via sntp sntp provides ...
Page 577
Synchronization via dnp the dnp3 communication can be the source for the coarse time synchronization, while the fine time synchronization needs a source with higher accuracy. See the communication protocol manual for a detailed description of the dnp3 protocol. Synchronization via iec60870-5-103 the...
Page 578
17.3.2.2 settings table 484: setgrps non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description activesetgrp settinggroup1 settinggroup2 settinggroup3 settinggroup4 - - settinggroup1 activesettinggroup maxnosetgrp 1 - 4 - 1 1 max number of setting groups 1-4 17.3.3 parameter settin...
Page 579
Table 486: actvgrp output signals name type description grp1 boolean setting group 1 is active grp2 boolean setting group 2 is active grp3 boolean setting group 3 is active grp4 boolean setting group 4 is active setchgd boolean pulse when setting changed 17.3.3.4 settings the function does not have ...
Page 580
Iox-bly1 iox-bly2 iox-bly3 iox-bly4 Æ Æ Æ Æ activate group 4 activate group 3 activate group 2 activate group 1 actgrp1 actgrp2 actgrp3 actgrp4 grp1 grp2 grp3 grp4 actvgrp setchgd iec09000063_en_1.Vsd iec09000063 v1 en figure 255: connection of the function to external circuits the above example als...
Page 581
Actually set and configured values within the ied. No settings will be changed, thus mistakes are avoided. Forcing of binary output signals is only possible when the ied is in test mode. 17.4.3 function block testmode input active output setting noevent iec09000219-1.Vsd iec09000219 v1 en figure 256...
Page 582
17.4.6 operation principle put the ied into test mode to test functions in the ied. Set the ied in test mode by • configuration, activating the input signal on the function block testmode. • setting testmode to on in the local hmi, under main menu/tests/ied test mode/1:testmode. While the ied is in ...
Page 583
The functions can also be blocked from sending events over iec 61850 station bus to prevent filling station and scada databases with test events, for example during a commissioning or maintenance test. 17.5 change lock function chnglck 17.5.1 identification function description iec 61850 identificat...
Page 584
Table 491: chnglck output signals name type description active boolean change lock active override boolean change lock override 17.5.5 settings the function does not have any parameters available in local hmi or protection and control ied manager (pcm600) 17.5.6 operation principle the change lock f...
Page 585
17.6.2 functionality ied identifiers (terminalid) function allows the user to identify the individual ied in the system, not only in the substation, but in a whole region or a country. Use only characters a-z, a-z and 0-9 in station, object and unit names. 17.6.3 settings table 492: terminalid non g...
Page 586
The settings are visible on the local hmi , under main menu/diagnostics/ied status/product identifiers they are very helpful in case of support process (such as repair or maintenance). 17.7.3 settings the function does not have any parameters available in the local hmi or pcm600. 17.8 primary system...
Page 587
The smai function is used within pcm600 in direct relation with the signal matrix tool or the application configuration tool. The smai function blocks for the 650 series of products are possible to set for two cycle times either 5 or 20ms. The function blocks connected to a smai function block shall...
Page 588
17.9.4 signals table 494: smai_20_1 input signals name type default description block boolean 0 block group 1 dftspfc real 20.0 number of samples per fundamental cycle used for dft calculation revrot boolean 0 reverse rotation group 1 grp1l1 string - first analog input used for phase l1 or l1-l2 qua...
Page 589
Table 497: smai_20_12 output signals name type description ai3p group signal grouped three phase signal containing data from inputs 1-4 ai1 group signal quantity connected to the first analog input ai2 group signal quantity connected to the second analog input ai3 group signal quantity connected to ...
Page 590
Table 499: smai_20_1 non group settings (advanced) name values (range) unit step default description negation off negaten negate3ph negate3ph+n - - off negation minvalfreqmeas 5 - 200 % 1 10 limit for frequency calculation in % of ubase even if the analoginputtype setting of a smai block is set to c...
Page 591
Even if the analoginputtype setting of a smai block is set to current, the minvalfreqmeas setting is still visible. This means that the minimum level for current amplitude is based on ubase. For example, if ubase is 20000, the minimum amplitude for current is 20000 * 10% = 2000. This has practical a...
Page 592
• it is not mandatory to connect all the inputs of smai function. However, it is very important that same set of three phase analog signals should be connected to one smai function. • the sequence of input connected to smai function inputs grpxl1, grpxl2, grpxl3 and grpxn should normally represent p...
Page 593
Reference will be used based on the calculated signal frequency from own group. Dftreference set to external dft ref will use reference based on input signal dftspfc. Settings dftrefextout and dftreference shall be set to default value internaldftref if no vt inputs are available. However, if it is ...
Page 594
Spfcout ai3p dftspfc smai_20_1:1 revrot grp1l2 grp1l1 grp1l3 ai1 ai2 block grp1n ai3 ai4 ain task time group 1 (5ms) task time group 2 (20ms) spfcout ai3p dftspfc smai_20_1:2 revrot grp1l2 grp1l1 grp1l3 ai1 ai2 block grp1n ai3 ai4 ain task time group 1 (5ms) smai instance 3 phase group smai_20_1:1 1...
Page 595
17.10 summation block 3 phase 3phsum 17.10.1 identification function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number summation block 3 phase 3phsum - - 17.10.2 functionality summation block 3 phase function 3phsum is used to get the sum of two sets of thre...
Page 596
Table 503: 3phsum output signals name type description ai3p group signal linear combination of two connected three phase inputs ai1 group signal linear combination of input 1 signals from both smai blocks ai2 group signal linear combination of input 2 signals from both smai blocks ai3 group signal l...
Page 597
17.11.1 identification function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number global base values gbasval - - 17.11.2 functionality global base values function (gbasval) is used to provide global values, common for all applicable functions within the ied....
Page 598
• local, through the local hmi • remote, through the communication ports the ied users can be created, deleted and edited only with pcm600 ied user management tool. Iec12000202-1-en.Vsd iec12000202 v1 en figure 262: pcm600 user management tool 17.12.3 settings the function does not have any paramete...
Page 599
Table 507: pre-defined user types user type access rights systemoperator control from local hmi, no bypass protectionengineer all settings designengineer application configuration (including smt, gde and cmt) useradministrator user and password administration for the ied the ied users can be created...
Page 600
Comes to password, upon pressing the key, the following characters will show up: “ ✳✳✳✳✳✳✳✳”. The user must scroll for every letter in the password. After all the letters are introduced (passwords are case sensitive) choose ok and press the key again. At successful log on, the local hmi shows the ne...
Page 601
17.14 ftp access with password ftpaccs 17.14.1 identification function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number ftp access with ssl ftpaccs - - 17.14.2 ftp access with ssl ftpaccs the ftp client defaults to the best possible security mode when tryin...
Page 602
17.15 authority status athstat 17.15.1 identification function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number authority status athstat - - 17.15.2 functionality authority status athstat function is an indication function block for user log-on activity. Us...
Page 603
• the fact that at least one user has tried to log on wrongly into the ied and it was blocked (the output usrblked) • the fact that at least one user is logged on (the output loggedon) whenever one of the two events occurs, the corresponding output (usrblked or loggedon) is activated. 17.16 denial o...
Page 604
17.16.2.4 settings the function does not have any parameters available in the local hmi or pcm600. 17.16.2.5 monitored data table 512: dosfrnt monitored data name type values (range) unit description state integer 0=off 1=normal 2=throttle 3=discardlow 4=discardall 5=stoppoll - frame rate control st...
Page 605
17.16.3.2 function block doslan1 linkup warning alarm iec09000134-1-en.Vsd iec09000134 v1 en figure 265: doslan1 function block 17.16.3.3 signals table 513: doslan1 output signals name type description linkup boolean ethernet link status warning boolean frame rate is higher than normal state alarm b...
Page 606
17.16.4 operation principle the denial of service functions (doslan1 and dosfrnt) measures the ied load from communication and, if necessary, limit it for not jeopardizing the ieds control and protection functionality due to high cpu load. The function has the following outputs: • linkup indicates t...
Page 607
Section 18 ied physical connections 18.1 protective earth connections the ied shall be earthed with a 16.0 mm 2 flat copper cable. The earth lead should be as short as possible, less than 1500 mm. Additional length is required for door mounting. Iec11000286 v1 en figure 266: the protective earth pin...
Page 608
Table 515: analog input modules trm terminal trm 6i + 4u trm 8i + 2u trm 4i + 1i + 5u trm 4i + 6u x101-1, 2 1/5a 1/5a 1/5a 1/5a x101-3, 4 1/5a 1/5a 1/5a 1/5a x101-5, 6 1/5a 1/5a 1/5a 1/5a x101-7, 8 1/5a 1/5a 1/5a 1/5a x101-9, 10 1/5a 1/5a 0.1/0.5a 100/220v x102-1, 2 1/5a 1/5a 100/220v 100/220v x102-...
Page 609
Table 517: auxiliary voltage supply of 110...250 v dc or 100...240 v ac case terminal description 3u full 19” x420-1 - input x420-3 + input table 518: auxiliary voltage supply of 48-125 v dc case terminal description 3u full 19” x420-1 - input x420-2 + input table 519: auxiliary voltage supply of 24...
Page 610
Terminal description pcm600 info hardware module instance hardware channel x304-13 common - for inputs 10-12 x304-14 binary input 10 + com_101 bi10 x304-15 binary input 11 + com_101 bi11 x304-16 binary input 12 + com_101 bi12 table 521: terminal description pcm600 info hardware module instance hardw...
Page 611
Terminal description pcm600 info hardware module instance hardware channel x329-6 binary input 3 + bio_4 bi3 x329-7 - x329-8 common - for inputs 4-5 x329-9 binary input 4 + bio_4 bi4 x329-10 binary input 5 + bio_4 bi5 x329-11 - x329-12 common - for inputs 6-7 x329-13 binary input 6 + bio_4 bi6 x329-...
Page 612
Table 524: binary inputs x339, 3u full 19” terminal description pcm600 info hardware module instance hardware channel x339-1 - for input 1 bio_6 bi1 x339-2 binary input 1 + bio_6 bi1 x339-3 - x339-4 common - for inputs 2-3 x339-5 binary input 2 + bio_6 bi2 x339-6 binary input 3 + bio_6 bi3 x339-7 - ...
Page 613
Table 525: output contacts x317, 3u full 19” terminal description pcm600 info hardware module instance hardware channel power output 1, normally open (tcs) x317-1 - psm_102 bo1_po_tcs x317-2 + power output 2, normally open (tcs) x317-3 - psm_102 bo2_po_tcs x317-4 + power output 3, normally open (tcs...
Page 614
Terminal description pcm600 info hardware module instance hardware channel x326-4 x326-5 power output 3, normally open bio_4 bo3_po x326-6 table 528: output contacts x331, 3u full 19” terminal description pcm600 info hardware module instance hardware channel x331-1 power output 1, normally open bio_...
Page 615
Table 530: output contacts x317, 3u full 19” terminal description pcm600 info hardware module instance hardware channel x317-13 signal output 1, normally open psm_102 bo7_so x317-14 x317-15 signal output 2, normally open psm_102 bo8_so x317-16 x317-17 signal output 3, normally open psm_102 bo9_so x3...
Page 616
Terminal description pcm600 info hardware module instance hardware channel x326-16 signal output 6, normally closed bio_4 bo9_so x326-17 signal output 6, normally open x326-18 signal output 6, common table 533: output contacts x331, 3u full 19” terminal description pcm600 info hardware module instan...
Page 617
18.3.3 irf the irf contact functions as a change-over output contact for the self-supervision system of the ied. Under normal operating conditions, the ied is energized and one of the two contacts is closed. When a fault is detected by the self-supervision system or the auxiliary voltage is disconne...
Page 618
The default ip address of the ied through this port is 10.1.150.3. The front port supports tcp/ip protocol. A standard ethernet cat 5 crossover cable is used with the front port. 18.4.2 station communication rear connection the default ip address of the ied through the ethernet connection is 192.168...
Page 619
Termination of the rs485 bus is always recommended regardless of the cable length. 18.4.5 communication interfaces and protocols table 536: supported station communication interfaces and protocols protocol ethernet serial 100base-fx lc glass fibre (st connector) eia-485 iec 61850–8–1 ● - - dnp3 ● ● ...
Page 620
614.
Page 621
Section 19 technical data 19.1 dimensions table 537: dimensions of the ied - 3u full 19" rack description value width 444 mm (17.48 inches) height 132 mm (5.20 inches), 3u depth 249.5 mm (9.82 inches) weight box 10 kg ( 19.2 power supply table 538: power supply description psm01 psm02 psm03 u aux no...
Page 622
19.3 energizing inputs table 539: trm — energizing quantities, rated values and limits for transformer inputs description value frequency rated frequency f r 50 or 60 hz operating range f r ± 10% current inputs rated current i r 0.1 or 0.5 a 1) 1 or 5 a 2) operating range 0 – 50 a 0 – 500 a thermal ...
Page 623
19.5 signal outputs table 541: signal output and irf output description value rated voltage 250 v ac/dc continuous contact carry 5 a make and carry for 3.0 s 10 a make and carry 0.5 s 30 a breaking capacity when the control-circuit time constant l/r ≤0.5 a/≤0.1 a/≤0.04 a 19.6 power outputs table 542...
Page 624
19.7 data communication interfaces table 544: ethernet interfaces ethernet interface protocol cable data transfer rate 100base-tx - cat 6 s/ftp or better 100 mbits/s 100base-fx tcp/ip protocol fibre-optic cable with lc connector 100 mbits/s table 545: fibre-optic communication link wave length fibre...
Page 625
Type value conditions supported bit rates 300, 600, 1200, 2400, 4800, 9600, 19200, 38400, 57600, 115200 - maximum number of 650 ieds supported on the same bus 32 - max. Cable length 925 m (3000 ft) cable: awg24 or better, stub lines shall be avoided table 549: serial rear interface type counter conn...
Page 626
19.10 environmental conditions and tests table 552: environmental conditions description value operating temperature range -25...+55ºc (continuous) short-time service temperature range -40...+70ºc ( note: degradation in mtbf and hmi performance outside the temperature range of -25...+55ºc relative h...
Page 627
Section 20 ied and functionality tests 20.1 electromagnetic compatibility tests table 554: electromagnetic compatibility tests description type test value reference 100 khz and 1 mhz burst disturbance test iec 61000-4-18, level 3 iec 60255-22-1 ansi c37.90.1-2012 • common mode 2.5 kv • differential ...
Page 628
Description type test value reference • continuous 100 a/m pulse magnetic field immunity test 1000a/m iec 61000–4–9, level 5 damped oscillatory magnetic field 100a/m, 100 khz and 1mhz iec 6100–4–10, level 5 power frequency immunity test iec 60255-22-7, class a iec 61000-4-16 • common mode 300 v rms ...
Page 629
20.2 insulation tests table 555: insulation tests description type test value reference dielectric tests: iec 60255-5 ansi c37.90-2005 • test voltage 2 kv, 50 hz, 1 min 1 kv, 50 hz, 1 min, communication impulse voltage test: iec 60255-5 ansi c37.90-2005 • test voltage 5 kv, unipolar impulses, wavefo...
Page 630
20.5 emc compliance table 558: emc compliance description reference emc directive 2004/108/ec standard en 50263 (2000) en 60255-26 (2007) section 20 1mrk 504 135-uen a ied and functionality tests 624 technical manual.
Page 631
Section 21 time inverse characteristics 21.1 application in order to assure time selectivity between different overcurrent protections in different points in the network different time delays for the different relays are normally used. The simplest way to do this is to use definite time delay. In mo...
Page 632
En05000131.Vsd time fault point position iec05000131 v1 en figure 269: inverse time overcurrent characteristics with inst. Function the inverse time characteristic makes it possible to minimize the fault clearance time and still assure the selectivity between protections. To assure selectivity betwe...
Page 633
En05000132.Vsd i> i> a1 b1 feeder time axis t=0 t=t 1 t=t 2 t=t 3 iec05000132 v1 en figure 270: selectivity steps for a fault on feeder b1 where: t=0 is the fault occurs t=t 1 is protection b1 trips t=t 2 is breaker at b1 opens t=t 3 is protection a1 resets in the case protection b1 shall operate wi...
Page 634
• if there is a risk of intermittent faults. If the current relay, close to the faults, starts and resets there is a risk of unselective trip from other protections in the system. • delayed resetting could give accelerated fault clearance in case of automatic reclosing to a permanent fault. • overcu...
Page 635
( ) - × × - = × > æ ö æ ö ç ÷ ç ÷ è ø è ø p op i t b k c a k in equation1190 v1 en (equation 109) where: t op is the operating time of the protection the time elapsed to the moment of trip is reached when the integral fulfils according to equation 110 , in addition to the constant time delay: 0 - × ...
Page 636
Iec05000133-3-en.Vsd tmin current operate time imin iec05000133 v2 en figure 271: minimum time-lag operation for the iec curves in order to fully comply with iec curves definition setting parameter tmin shall be set to the value which is equal to the operating time of the selected iec inverse time c...
Page 637
The rd inverse curve gives a logarithmic delay, as used in the combiflex protection rxidg. The curve enables a high degree of selectivity required for sensitive residual earth-fault current protection, with ability to detect high-resistive earth faults. The curve is described by equation 114 : [ ] 5...
Page 638
Table 560: iec inverse time characteristics function range or value accuracy operating characteristic: ( ) 1 = × - æ ö ç ÷ ç ÷ è ø p a t k i equation1251-small v1 en i = i measured /i set k = (0.05-999) in steps of 0.01 - iec normal inverse a=0.14, p=0.02 iec very inverse a=13.5, p=1.0 iec inverse a...
Page 639
Table 562: inverse time characteristics for overvoltage protection function range or value accuracy type a curve: = - > > æ ö ç ÷ è ø t k u u u equation1436-small v1 en u> = u set u = u measured k = (0.05-1.10) in steps of 0.01 ±5% +60 ms type b curve: 2.0 480 32 0.5 0.035 = × - > × - - > æ ö ç ÷ è ...
Page 640
Table 564: inverse time characteristics for residual overvoltage protection function range or value accuracy type a curve: = - > > æ ö ç ÷ è ø t k u u u equation1436-small v1 en u> = u set u = u measured k = (0.05-1.10) in steps of 0.01 ±5% +70 ms type b curve: 2.0 480 32 0.5 0.035 = × - > × - - > æ...
Page 641
A070750 v2 en figure 272: ansi extremely inverse time characteristics 1mrk 504 135-uen a section 21 time inverse characteristics 635 technical manual.
Page 642
A070751 v2 en figure 273: ansi very inverse time characteristics section 21 1mrk 504 135-uen a time inverse characteristics 636 technical manual.
Page 643
A070752 v2 en figure 274: ansi normal inverse time characteristics 1mrk 504 135-uen a section 21 time inverse characteristics 637 technical manual.
Page 644
A070753 v2 en figure 275: ansi moderately inverse time characteristics section 21 1mrk 504 135-uen a time inverse characteristics 638 technical manual.
Page 645
A070817 v2 en figure 276: ansi long time extremely inverse time characteristics 1mrk 504 135-uen a section 21 time inverse characteristics 639 technical manual.
Page 646
A070818 v2 en figure 277: ansi long time very inverse time characteristics section 21 1mrk 504 135-uen a time inverse characteristics 640 technical manual.
Page 647
A070819 v2 en figure 278: ansi long time inverse time characteristics 1mrk 504 135-uen a section 21 time inverse characteristics 641 technical manual.
Page 648
A070820 v2 en figure 279: iec normal inverse time characteristics section 21 1mrk 504 135-uen a time inverse characteristics 642 technical manual.
Page 649
A070821 v2 en figure 280: iec very inverse time characteristics 1mrk 504 135-uen a section 21 time inverse characteristics 643 technical manual.
Page 650
A070822 v2 en figure 281: iec inverse time characteristics section 21 1mrk 504 135-uen a time inverse characteristics 644 technical manual.
Page 651
A070823 v2 en figure 282: iec extremely inverse time characteristics 1mrk 504 135-uen a section 21 time inverse characteristics 645 technical manual.
Page 652
A070824 v2 en figure 283: iec short time inverse time characteristics section 21 1mrk 504 135-uen a time inverse characteristics 646 technical manual.
Page 653
A070825 v2 en figure 284: iec long time inverse time characteristics 1mrk 504 135-uen a section 21 time inverse characteristics 647 technical manual.
Page 654
A070826 v2 en figure 285: ri-type inverse time characteristics section 21 1mrk 504 135-uen a time inverse characteristics 648 technical manual.
Page 655
A070827 v2 en figure 286: rd-type inverse time characteristics 1mrk 504 135-uen a section 21 time inverse characteristics 649 technical manual.
Page 656
Guid-acf4044c-052e-4cbd-8247-c6abe3796fa6 v1 en figure 287: inverse curve a characteristic of overvoltage protection section 21 1mrk 504 135-uen a time inverse characteristics 650 technical manual.
Page 657
Guid-f5e0e1c2-48c8-4dc7-a84b-174544c09142 v1 en figure 288: inverse curve b characteristic of overvoltage protection 1mrk 504 135-uen a section 21 time inverse characteristics 651 technical manual.
Page 658
Guid-a9898db7-90a3-47f2-aef9-45ff148cb679 v1 en figure 289: inverse curve c characteristic of overvoltage protection section 21 1mrk 504 135-uen a time inverse characteristics 652 technical manual.
Page 659
Guid-35f40c3b-b483-40e6-9767-69c1536e3cbc v1 en figure 290: inverse curve a characteristic of undervoltage protection 1mrk 504 135-uen a section 21 time inverse characteristics 653 technical manual.
Page 660
Guid-b55d0f5f-9265-4d9a-a7c0-e274aa3a6bb1 v1 en figure 291: inverse curve b characteristic of undervoltage protection section 21 1mrk 504 135-uen a time inverse characteristics 654 technical manual.
Page 661
Section 22 glossary ac alternating current acc actual channel act application configuration tool within pcm600 a/d converter analog-to-digital converter adbs amplitude deadband supervision ai analog input ansi american national standards institute ar autoreclosing asct auxiliary summation current tr...
Page 662
Cr carrier receive crc cyclic redundancy check crob control relay output block cs carrier send ct current transformer cu communication unit cvt capacitive voltage transformer dar delayed autoreclosing darpa defense advanced research projects agency (the us developer of the tcp/ip protocol etc.) dbdl...
Page 663
Fox 20 modular 20 channel telecommunication system for speech, data and protection signals fox 512/515 access multiplexer fox 6plus compact time-division multiplexer for the transmission of up to seven duplex channels of digital data over optical fibers ftp file transfer protocal fun function type g...
Page 664
Specifications from the pci sig (special interest group) for the electrical emf (electromotive force). Ieee 1686 standard for substation intelligent electronic devices (ieds) cyber security capabilities ied intelligent electronic device i-gis intelligent gas-insulated switchgear instance when severa...
Page 665
Oltc on-load tap changer otev disturbance data recording initiated by other event than start/pick-up ov over-voltage overreach a term used to describe how the relay behaves during a fault condition. For example, a distance relay is overreaching when the impedance presented to it is smaller than the ...
Page 666
Sma connector subminiature version a, a threaded connector with constant impedance. Smt signal matrix tool within pcm600 sms station monitoring system sntp simple network time protocol – is used to synchronize computer clocks on local area networks. This reduces the requirement to have accurate hard...
Page 667
Umt user management tool underreach a term used to describe how the relay behaves during a fault condition. For example, a distance relay is underreaching when the impedance presented to it is greater than the apparent impedance to the fault applied to the balance point, that is, the set reach. The ...
Page 668
662.
Page 669
663.
Page 670
Contact us for more information please contact: abb ab grid automation products se-721 59 västerås, sweden phone +46 (0) 21 32 50 00 www.Abb.Com/protection-control note: we reserve the right to make technical changes or modify the contents of this document without prior notice. Abb ab does not accep...