- DL manuals
- 3Com
- Telephone System
- NBX 100
- Installation Manual
3Com NBX 100 Installation Manual
Summary of NBX 100
Page 1
Http://www.3com.Com/ nbx ® 100 installation guide release 2.8 part no. 900-0026-01 november 2000
Page 2
3com corporation 5400 bayfront plaza santa clara, california 95052-8145 copyright © 2000, 3com corporation. All rights reserved. No part of this documentation may be reproduced in any form or by any means or used to make any derivative work (such as translation, transformation, or adaptation) withou...
Page 3: Ontents
C ontents a bout t his g uide how to use this guide 13 conventions 14 international terminology 15 documentation 15 format 15 paper documents 15 software and documents on cd-rom 16 your comments 17 year 2000 compliance 17 1 i ntroduction overview of nbx 100 hardware components 19 chassis 19 network ...
Page 4
Language support 37 installation requirements 38 electrical requirements 38 environmental requirements 38 physical requirements 39 local telephone service 40 installation questions 40 who should install the nbx 100? 40 does the telephone company need to be involved? 40 can existing office telephone ...
Page 5
Managing the dial plan configuration file 61 nbx 100 database 61 nbx 100 dial plan 62 creating dial plan configuration files 63 gaining access to the dial plan 65 importing and exporting dial plan configuration files 66 importing a north american dial plan 67 importing an international dial plan 67 ...
Page 6: Nbx 100 H
3 i nstalling nbx 100 h ardware c omponents getting started 130 nbx 100 user terminology 130 required and recommended tools and equipment 130 important safety information 132 general safety precautions 132 lithium battery safety 134 consignes importantes de sécurité 134 batterie au lithium 136 wicht...
Page 7: Nbx 100 S
Using auto discovery for initial system configuration 164 initial system configuration 166 disabling auto discovery 167 configuring 4-port line cards 167 mapping line card ports to telephone lines 167 re-assigning extensions and setting line card port options 170 connecting telephone lines 172 4 c o...
Page 8
Creating and managing telephone groups 202 creating a new telephone group 202 using button mappings 204 creating button mappings for a telephone 204 creating dss/blf mappings 208 creating a delayed ringing pattern 209 installing an adjunct 210 auto discovering an adjunct 211 connecting an adjunct 21...
Page 9: (T1, E1,
7 c onfiguring d igital l ine c ards (t1, e1, and bri c ards ) preparation 240 inserting the t1 digital line card 241 configuring the t1 digital line card 241 configuring for e&m signaling 241 activating the span 242 checking the span status 243 modifying the span 243 configuring a group 244 checkin...
Page 10: , D
8 m aintenance , d iagnostics , and t roubleshooting troubleshooting 269 using the telephone local user interface (lui) utility 274 using h3pingip 278 technical support 278 a nbx 100 s ystem s pecifications 6-slot chassis 279 network call processor 280 4-port line card 281 t1 and e1 digital line car...
Page 11: 2000 S
D w indows 2000 s upport nbx connextions 295 windows 2000 environment specifications 296 installation sequence 296 finalize installation 297 nbx 100 call detail reports 298 windows 2000 environment specifications 298 installation sequence 298 nbx pcxset 299 windows 2000 environment specifications 29...
Page 13: Bout
A bout t his g uide this guide provides information and instructions for installing the nbx ® 100 communications system. It is intended for installation technicians and the system administrator. If the information in the release notes (readme.Pdf on the nbx 100 resource pack cd) differs from the inf...
Page 14
14 a bout t his g uide conventions table 2 and table 3 list conventions that are used throughout this guide. Table 2 notice icons icon notice type description information note information that describes important features or instructions caution information that alerts you to potential loss of data ...
Page 15
International terminology 15 international terminology this section lists terms used in the nbx 100 documentation and the international equivalents of these terms: documentation this section describes the documentation delivery formats and lists the titles of documents that pertain to the nbx 100. F...
Page 16
16 a bout t his g uide ■ nbx business telephone guide this guide provides an overview of the features in the nbx 100 communications system as they relate to the nbx business telephone. These guides are shipped with the network call processor. They can also be found in .Pdf files on the nbx 100 resou...
Page 17
Year 2000 compliance 17 your comments your suggestions are very important to us. They help us to make our documentation more useful to you. Please send e-mail comments about this guide or any of the documentation and help systems to: nbx_techpubs_comments@3com.Com please include the following inform...
Page 18
18 a bout t his g uide.
Page 19: Ntroduction
1 i ntroduction this chapter covers the following topics: ■ overview of nbx 100 hardware components ■ installation overview ■ installation requirements ■ installation questions see the nbx 100 administrator’s guide for information about maintaining the 3com nbx ® 100 communications system. Overview ...
Page 20
20 c hapter 1: i ntroduction figure 1 nbx 100 chassis up to six cards slide into the front of the chassis. The top slot has no access to the backplane. Always cover the top slot with a blank faceplate. An internal backplane connects the cards to each other. Network call processor the top active slot...
Page 21
Overview of nbx 100 hardware components 21 ■ vol - moh this mini-jack (mono or stereo) accepts music-on-hold audio from the line-output of a cd player, tape player, or the like. The adjusting screw next to the jack controls the moh volume. ■ paging this rj11 connector provides an audio output or a d...
Page 22
22 c hapter 1: i ntroduction ■ analog connectors (labeled 1 through 4) these connect a local analog line between an nbx 100 and a central office switch. See “testing the installed hardware” in chapter 3 for information about what the leds indicate during system startup and operation. T1 digital line...
Page 23
Overview of nbx 100 hardware components 23 the t1 digital line card has the following leds and connectors: ■ t1 this rj-48c connector makes a patch cord connection to a t1 interface (csu/dsu). ■ leds these lights indicate the status of the card’s signaling, synchronization, and loopback test. ■ 10bt...
Page 24
24 c hapter 1: i ntroduction ■ console this db-9 connector provides an rs-232 (dce) tty terminal connection for maintenance access. If you require an alternative (bare wire-end) cable to use with the isdn pri digital line card, contact a 3com customer support representative. Caution: this equipment ...
Page 25
Overview of nbx 100 hardware components 25 figure 7 single-port analog terminal adapter — front view figure 8 single-port analog terminal adapter — rear view the single-port analog terminal adapter contains the following leds and connectors: ■ analog port leds (s1,s2,s3) the s1 and s2 lights below t...
Page 26
26 c hapter 1: i ntroduction 8-port hub card the nbx 100 hub card provides eight 10base-t ports to connect telephones (or other 10base-t devices) to the lan. The card also has a 10base2 connection to allow you to connect to another hub or switch. (although cards within a single chassis have lan conn...
Page 27
Preparing for installation 27 caution: to avoid damage to the business telephone, do not connect a telephone directly to a standard telephone line. Although the rj11 connector for a traditional telephone fits into the business telephone’s rj45 jack, the electrical interfaces are not compatible and t...
Page 28
28 c hapter 1: i ntroduction see the nbx 100 isdn pri module quickstart guide on the nbx 100 resource pack cd for specific information required outside north america. Table 5 system planning information category information required for plan contact ■ company name ■ primary contact name and telephon...
Page 29
Preparing for installation 29 preliminary information ■ number of telephones installed on current telephone system: ■ number of telephones being installed on the nbx 100 system: ■ number of users anticipated in near future: ■ planned location of nbx 100 system: ■ number of chassis required: ■ how nb...
Page 30
30 c hapter 1: i ntroduction site survey - cable ■ plenum ___ pvc ___ ■ data cable: cat/level: singles dual quad ■ voice only cable: cat/level: singles dual quad ■ total number of locations/drops: single dual quad ■ riser cable: plenum ___ pvc ___ shielded ____ copper ____ number of pairs: length: f...
Page 31
Preparing for installation 31 site survey - lan/wan ■ do you have ip networking/internet access? Yes ____ no ____ ■ what is the fixed ip address to be assigned to the ncp: (default: 192.168.1.190) default gateway: (default: 0.0.0.0) subnet mask: (default: 255.255.255.0) host name: (default: nbx100) ...
Page 32
32 c hapter 1: i ntroduction site survey - telephone lines ■ number of co (pots) lines: ■ fax lines: ■ modem lines: ■ alarm lines: ■ other: ■ ami? Yes ____ no ____ ■ dnis? Yes ____ no ____ ■ did? Yes ____ no ____ ■ d4 channel bank? Yes ____ no ____ ■ t1? Yes ____ no ____ ■ pri? Yes ____ no _____ ■ e...
Page 33
Preparing for installation 33 class of service - attendant ■ intercom calls day ____ night ____ ■ external (local) day ____ night ____ ■ external (long distance) day ____ night ____ ■ external (international) day ____ night ____ ■ external (toll free) day ____ night ____ ■ external (900, 976) day __...
Page 34
34 c hapter 1: i ntroduction class of service - customer defined (1-3) ■ intercom calls day ____ night ____ ■ external (local) day ____ night ____ ■ external (long distance) day ____ night ____ ■ external (international) day ____ night ____ ■ external (toll free) day ____ night ____ ■ external (900,...
Page 35
Preparing for installation 35 peripheral devices - external paging/alerts ■ paging amplifier: yes ____ no ____ ■ make: model: ■ paging port _______ line port ________ ■ adapter required: peripheral devices - ringers/music on hold (moh) ■ door telephone? Yes ____ no ____ make: model: ■ will moh be im...
Page 36
36 c hapter 1: i ntroduction ordering telephone lines after you complete the system plan, have the client contact the local telephone service provider to order the necessary lines and services. If the client is ordering t1 lines, see appendix b for additional information. Developing a dial plan the ...
Page 37
International feature support 37 ■ configure system-wide settings ■ install and configure telephones ■ set up users and features ■ configure 4-port line cards ■ configure digital line cards ■ add external hardware, such as a music-on-hold (moh) device international feature support for international ...
Page 38
38 c hapter 1: i ntroduction installation requirements verify that you meet the prerequisites detailed in the following sections before you install the nbx 100. Electrical requirements verify that the site meets the following electrical requirements. ■ in north america, each nbx chassis requires a s...
Page 39
Installation requirements 39 ■ the area must be safe from physical interference. For example, do not put the chassis where it might be struck by a swinging door or where cables might be pinched by a door or snagged by people passing by. ■ do not install the nbx 100 in an area that is exposed to stro...
Page 40
40 c hapter 1: i ntroduction local telephone service before you install the nbx 100, be sure the client site meets the following local telephone service requirements: ■ the client’s local telephone company has installed local telephone lines and assigned telephone numbers. ■ if necessary, you have e...
Page 41
Installation questions 41 caution: to avoid damage to the business telephone, do not connect an telephone directly to a standard telephone line. Although the rj11 connector for a traditional telephone fits into the businesss telephone’s rj45 jack, the electrical interfaces are not compatible and the...
Page 42
42 c hapter 1: i ntroduction what external devices can connect to an nbx 100? The following devices can connect to an nbx 100: ■ music-on-hold device, such as a radio, tape player, disk player, or computer sound card, equipped with a line out (600 ohm) connection can be connected directly into the c...
Page 43
Installation questions 43 ■ each automated attendant example: ■ with 100 business telephones, the system can accommodate up to 100 additional devices, in any combination of card ports, dss/blf, t1 channels and so on. ■ with 124 telephones, the system can have no more than 76 additional devices. ■ wi...
Page 44
44 c hapter 1: i ntroduction nbx 100 quality of service quality of service (qos) is a way to allocate resources in data switches and routers so that data can be prioritized, with the most time-critical data receiving higher priority. At layer 2, the nbx 100 supports ethernet 802.1q, “standard for vi...
Page 45: Onfiguring
2 c onfiguring the d ial p lan this chapter provides information about the nbx ® 100 dial plan. It covers the following topics: ■ overview ■ extension settings ■ external settings ■ dial plan tables ■ managing the dial plan configuration file ■ managing external settings ■ managing dial plan tables ...
Page 46
46 c hapter 2: c onfiguring the d ial p lan translation performed before the nbx 100 interprets a sequence of incoming digits or transmits outgoing digits is pretranslation. Example 1: if, for an incoming telephone call, the telephone company passes you 4 digit numbers from 6000 through 6199, the nb...
Page 47
Extension settings 47 when you define call routing, you can also instruct the nbx 100 to perform translations (digit manipulations). Both destination routes and timed routes have digit manipulation commands (append, prepend, replace, striplead, or striptrail). The dial plan configuration file includ...
Page 48
48 c hapter 2: c onfiguring the d ial p lan some countries (for example, sweden) reserve numbers beginning with 11 for numbers of national importance. To accommodate this requirement, you can begin the telephone extension range at 120. Telephones the telephone extension range depends on the number o...
Page 49
External settings 49 through 5599. If you have several different menus, or if you expect many simultaneous sessions, you may use more numbers within this range; in rare cases, you may need to extend the range beyond 599 (beyond 5599 in a 4-digit system). Hunt groups the size of the hunt group extens...
Page 50
50 c hapter 2: c onfiguring the d ial p lan dial plan tables dial plan tables contain information that controls how the nbx 100 routes calls. Each dial plan configuration file consists of at least three dial plan tables: ■ internal (must be table id 1) ■ incoming (must be table id 2) ■ least cost ro...
Page 51
Dial plan tables 51 internal dial plan table the internal dial plan table defines the handling of calls placed from internal devices such as business telephones, to a destination; a destination can be another internal device, such as a local telephone, or an external telephone line (analog or digita...
Page 52
52 c hapter 2: c onfiguring the d ial p lan example 2: the min value for the 90 entry is 2, because often, 90 is the way an internal caller dials the external telephone company operator (9 to get an outside line, and then 0 to get the operator). The max value could be 64, because the caller can cont...
Page 53
Dial plan tables 53 do not delete or modify any predefined routes. You can create new routes. Each device can use a normal table and a least cost routing table. Telephones use the internal dial plan table (table id 1) as their normal dial plan table, and the least cost routing table (table id 3) as ...
Page 54
54 c hapter 2: c onfiguring the d ial p lan incoming dial plan table the incoming dial plan table (table id 2) defines how calls arriving from outside the nbx 100 are routed to extensions. Incoming calls can arrive on analog telephone lines or via digital line card ports. Each table entry contains: ...
Page 55
Dial plan tables 55 least cost routing dial plan table the least cost routing table (table id 3) defines how to route calls in order to minimize the cost of those calls. Example: you might use two different long distance carriers, one for a specific geographic region, and one for all other areas of ...
Page 56
56 c hapter 2: c onfiguring the d ial p lan see one possible way accomplish this using the dial plan configuration file. Outbound call processing the nbx 100 processes outbound calls using the internal dial plan table or the least cost routing table. If the least cost routing table exists, it takes ...
Page 57
Pretranslators 57 a typical pretranslator function involves mapping incoming ddi/did telephone calls to internal extension numbers. Example: the ddi/did telephone numbers range from 508-323-4200 to 508-323-4299. The telephone company sends you the last 4 digits of the total telephone number. Interna...
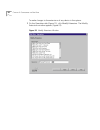
Page 58
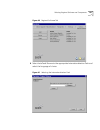
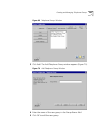
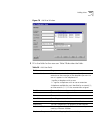
58 c hapter 2: c onfiguring the d ial p lan 3 click devices using. The devices using pretranslator screen appears (if you select “none,” you see a list of devices that have no associated pretranslator.) figure 12 devices using pretranslator window 4 the items in this screen are: 5 highlight a device...
Page 59
Pretranslators 59 6 click close. See “managing dial plan pretranslators” on page 94 for detailed information and examples on creating and managing dial plan pretranslators. Pretranslators for outgoing calls on outgoing calls, pretranslators are used to allow the external called party to identify the...
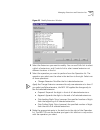
Page 60
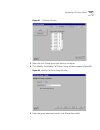
60 c hapter 2: c onfiguring the d ial p lan figure 13 devices using pretranslator for cli window 3 click devices using for cli. The devices using pretranslator for cli dialog box appears (if you select “none,” you see the devices that have no pretranslator for cli dialog box). This displays a list o...
Page 61
Managing the dial plan configuration file 61 caution: you cannot remove a pretranslator if any device is currently using it. If you want to remove the pretranslator, you must first remove all devices from the devices using pretranslator list. 1 from the dial plan window (figure 15), click the pretra...
Page 62
62 c hapter 2: c onfiguring the d ial p lan ■ button mappings for the business telephones. ■ call group definitions. ■ software license information. ■ user profiles. Nbx 100 dial plan an ascii text file known as the dial plan configuration file defines each nbx 100 dial plan. You import a dial plan ...
Page 63
Managing the dial plan configuration file 63 rebooting the nbx 100 disrupts service to the telephones. You should reboot at a time that does not inconvenience telephone users. The dial plan configuration file contains the following elements: ■ extension settings (page 75) ■ external settings (page 8...
Page 64
64 c hapter 2: c onfiguring the d ial p lan digits — specifies one or more of the leading digits in a sequence. The nbx 100 uses this field in conjunction with min and max to determine when to make the call routing decision. Example: if digits = 2, min = 4, and max = 4, the system knows that if the ...
Page 65
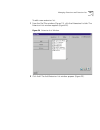
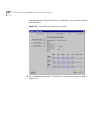
Managing the dial plan configuration file 65 figure 14 dial plan configuration file command format gaining access to the dial plan you can import a dial plan configuration file and modify it using the netset interface. To access a dial plan, click the dial plan icon on the netset main menu. The dial...
Page 66
66 c hapter 2: c onfiguring the d ial p lan figure 15 dial plan window importing and exporting dial plan configuration files this section tells you how to import and export dial plan configuration files. You import a configuration file either to implement changes you have made by editing the file, o...
Page 67
Importing and exporting dial plan configuration files 67 importing a north american dial plan the default dial plan for use with the nbx 100 is northamerica.Txt . Customized dial plans are also provided for use in other countries. See the release notes (called readme.Txt) for the most up-to-date inf...
Page 68
68 c hapter 2: c onfiguring the d ial p lan international dial plan issues if there is no customized dial plan for your country, you must modify the default dial plan. See “modifying a dial plan configuration file” on page 70 for details on how to modify the default dial plan. If you have made chang...
Page 69
Importing and exporting dial plan configuration files 69 exporting (saving) a dial plan configuration file when you export (save) the current configuration, the nbx 100 creates a new dial plan configuration file from the current database. You save the new text file using a name that you choose. 3com...
Page 70
70 c hapter 2: c onfiguring the d ial p lan this example refers to netscape 4.7. If you use internet explorer or another browser, you may need to use slightly different procedures. 5 click save to save the file. Modifying a dial plan configuration file this section tells you how to modify the curren...
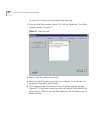
Page 71
Importing and exporting dial plan configuration files 71 4 click yes. The nbx 100 imports the modified dial plan. The dial plan consistency window appears, displaying the results of the error and consistency checks. 5 make a note of any errors, and correct them by editing the file. You do not need t...
Page 72
72 c hapter 2: c onfiguring the d ial p lan you can also use day and time settings to test whether the class of service settings operate as expected. Example: you can configure the dial plan to allow toll calls from an extension during open business hours, but to disallow such calls when the busines...
Page 73
Importing and exporting dial plan configuration files 73 for some tests, the day and time settings are unimportant. You can leave the settings at their default values (sunday, 00, and 00). 6 click test. The test runs and the results appear in the window (figure 18). 7 if the test results extend beyo...
Page 74
74 c hapter 2: c onfiguring the d ial p lan the report provides information on common errors. These errors include: ■ dial plan table entries that point to non-existent routes. ■ timed route entries that point to non-existent destination routes. ■ destination route entries that point to non-existent...
Page 75
Managing extensions and extension lists 75 figure 20 dial plan report (partial) managing extensions and extension lists this section tells you how to: ■ view and change various dial plan settings for extensions, such as extension length and extension ranges. ■ make changes to the extensions of all d...
Page 76
76 c hapter 2: c onfiguring the d ial p lan within an extension list, you can assign a priority to each extension. When the nbx 100 accesses an extension list, it attempts to use the highest priority extension first. The nbx 100 uses 1 as the highest priority and 99 as the lowest. Example: if the ex...
Page 77
Managing extensions and extension lists 77 appears at the top of the list, because 1 is the highest priority (99 is the maximum); extensions with lower priorities appear in priority order farther down the list. You can assign the same priority number to multiple extensions. The nbx 100 processes ext...
Page 78
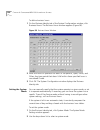
78 c hapter 2: c onfiguring the d ial p lan table 10 extension ranges range (3-digit) range (4 digit) description 100–449 1000–4949 telephones 500–599 500, 501, plus 5500–5599 auto attendant 450–499 4950–4999 hunt groups 601–609 6001–6009 call park extensions 600–619 n/a (6010–6019 included in the r...
Page 79
Managing extensions and extension lists 79 settings this section tells you how to view and change dial plan settings for extensions, such as extension length and extension ranges. If you are changing from a 3-digit to a 4-digit plan, make sure that you import the 4-digit dial plan configuration file...
Page 80
80 c hapter 2: c onfiguring the d ial p lan table 11 dial plan extension settings field purpose telephone extensions the range of extensions for telephones. The default range for a 3-digit system is 100–449, and for a 4-digit system is 1000–4949. Length: this field specifies the number of digits for...
Page 81
Managing extensions and extension lists 81 3 click ok. Changing extensions you can use this process to change the extension number of devices you select. Normally, you use this procedure only after you have changed the extension ranges for the nbx 100, in order to align the extensions with the new r...
Page 82
82 c hapter 2: c onfiguring the d ial p lan to make changes to the extensions of any device in the system: 1 on the operations tab (figure 15), click modify extensions. The modify extensions window appears (figure 22). Figure 22 modify extensions window.
Page 83
Managing extensions and extension lists 83 figure 23 modify extensions window 2 select the extensions you want to modify. You can use shift-click to select a block of extensions, and control-click to select several extensions at different locations in the list. 3 select the operation you want to per...
Page 84
84 c hapter 2: c onfiguring the d ial p lan example 1: if you select change extension from the operation list, the nbx 100 replaces the selected extension with the number you type in the text box. Example 2: if you select strip leading digits from the list, and type the number 2 in the text box, the...
Page 85
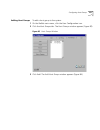
Managing extensions and extension lists 85 to add a new extension list: 1 from the dial plan window (figure 15), click the extensions list tab. The extension lists window appears (figure 24). Figure 24 extension lists window 2 click add. The add extension list window appears (figure 25)..
Page 86
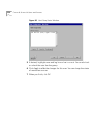
86 c hapter 2: c onfiguring the d ial p lan figure 25 add extension lists window 3 type the number you want to assign to the new extension list in the list extension text box. The nbx 100 supplies a default number, but you can change it if you want. You must not choose a number currently being used ...
Page 87
Managing extensions and extension lists 87 6 move as many extensions as you want to the left scroll list. If you move an extension to the left scroll list by mistake, you can highlight it and click >> to move the extension back to the extensions not in list scroll list. The priority function applies...
Page 88
88 c hapter 2: c onfiguring the d ial p lan figure 26 modify extension list window 3 to modify the name of the extension list, edit the contents of the name text box. Changing the name of an extension list invalidates any aspect of the dial plan that refers to the name. Example: if any destination r...
Page 89
Managing external settings 89 6 when you are finished making changes, click ok. The changes take effect. Removing an extension list this section tells you how to remove an extension list from the dial plan. To remove an extension list: 1 in the extension list window (figure 24), highlight the extens...
Page 90
90 c hapter 2: c onfiguring the d ial p lan extension for each analog line and each digital line card channel, if you want. In the current product release, you must use the default value (500) in the dial plan configuration file. Managing dial plan tables a dial plan table consists of a series of en...
Page 91
Managing dial plan tables 91 you can route incoming calls to the auto attendant port, and you can instruct the auto attendant to route these calls to any internal or external number. Caution: if you configure the auto attendant so that it can access external numbers, you risk the possibility of toll...
Page 92
92 c hapter 2: c onfiguring the d ial p lan to view lists of devices and any tables they are using: 1 from the dial plan window (figure 15), click the tables tab. The tables window appears (figure 27.) figure 27 tables window 2 select a dial plan table from the list. 3 select the table for which you...
Page 93
Managing dial plan tables 93 figure 28 devices using a dial plan window 5 click normal to see which devices are using the normal table. 6 click least cost to see which devices are using the least cost table. Each device can use only one normal and one least cost table. 7 to add an extension to the d...
Page 94
94 c hapter 2: c onfiguring the d ial p lan 8 to remove an extension from the scroll list, highlight it the devices using table scroll list and click >>. The extension moves to the devices not using table scroll list. 9 click close when you are finished. Removing a dial plan table this section tells...
Page 95
Managing dial plan pretranslators 95 commands” on page 119 to see one way to accomplish this pretranslation using the dial plan configuration file. To enable this pretranslator, you must first update the dial plan. 1 in the netset icon menu, click the dial plan icon. 2 in the dial plan window, click...
Page 96
96 c hapter 2: c onfiguring the d ial p lan each device can specify only one ddi/did pretranslator and one clip pretranslator. To create or modify a pretranslator, you can either edit a dial plan configuration file and import it, or use netset and modify an existing dial plan configuration file. The...
Page 97
Managing dial plan pretranslators 97 figure 29 pretranslator window 3 select a pretranslator from the scroll list. 4 you can view either the devices using the pretranslator or the devices using the pretranslator to create calling line id (cli). A for a list of devices using the selected pretranslato...
Page 98
98 c hapter 2: c onfiguring the d ial p lan figure 30 devices using pretranslator window 5 to move a device to the devices using pretranslator list, highlight it in the devices not using pretranslator list and click 6 to move a device to the devices not using pretranslator list, highlight it in the ...
Page 99
Managing dial plan pretranslators 99 figure 31 devices using pretranslator for cli window table 14 fields in the devices using pretranslator for cli window field purpose pretranslator id the id of the pretranslator as specified in the dial plan. Pretranslator name the name of the pretranslator as sp...
Page 100
100 c hapter 2: c onfiguring the d ial p lan removing a pretranslator this section tells you how to remove a pretranslator from the dial plan. Caution: you cannot remove a pretranslator if any device is currently using it. If you want to remove the pretranslator, you must first remove all devices fr...
Page 101
Dial plan configuration file commands 101 example: when e-mail arrives the nbx 100 dials the telephone number of the user’s pager. Typically, you use a system-wide prefix to designate which device or devices you want to use for outdialing purposes, including offsite notification calls. Example: if t...
Page 102
102 c hapter 2: c onfiguring the d ial p lan those lines containing one or more syntax errors. The nbx 100 treats any line beginning with / (forward slash) as a comment and ignores it. Caution: do not place comments at the end of a command line. Table create description: this command creates a dial ...
Page 103
Dial plan configuration file commands 103 tableentry create description: creates an entry in a dial plan table that specifies a string of digits to compare to dialed digits. If the dial plan table entry already exists, this command overwrites it with the new information. Dial plan table entries cont...
Page 104
104 c hapter 2: c onfiguring the d ial p lan npriority — an integer, not presently used. Always set to zero (0). Nrouteid — an integer specifying the id of the route to use when this dial plan entry is matched. A route id of zero (0) indicates that this entry has no defined route (example: telephone...
Page 105
Dial plan configuration file commands 105 destinationrouteentry create description: this command creates a destination route entry that identifies a single destination device or device list. If the specified destination route entry already exists, this command overwrites it with the new information....
Page 106
106 c hapter 2: c onfiguring the d ial p lan destinationrouteoperation create description: creates a digit manipulation operation for a destination route entry. If the specified digit manipulation operation already exists, this command overwrites it with the new information. During routing the nbx 1...
Page 107
Dial plan configuration file commands 107 timedroute create description: creates a timed route (a route that the nbx 100 uses based on defined criteria for time of day and day of week). If the timed route already exists, this command removes all of its entries and overwrites its description and defa...
Page 108
108 c hapter 2: c onfiguring the d ial p lan timedrouteentry create description: creates a timed route entry specifying either a time of day or system mode, day of the week criteria, and the destination route to use if that criteria are met. If the specified timed route entry already exists, this co...
Page 109
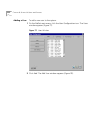
Dial plan configuration file commands 109 example: if you define business hours from 8:00 to 17:00 on mondays, wednesdays and fridays, and from 9:00 to 18:00 tuesdays and thursdays, then a timed route entry both szstarttime and szendtime set to “open” applies differently on monday, wednesday, and fr...
Page 110
110 c hapter 2: c onfiguring the d ial p lan the number 6 designates destination route 6, defined in the nbx 100 routes table. Because this entry applies to the “open for business” hours, route 6 could define a least cost route for outgoing long distance calls. The second entry is timed route 7, tim...
Page 111
Dial plan configuration file commands 111 timedrouteoperation create description: creates a digit manipulation operation for a timed route entry. If the specified digit manipulation operation already exists, this command overwrites it with the new information. During routing, the nbx 100 processes t...
Page 112
112 c hapter 2: c onfiguring the d ial p lan pretranslator create description: creates a pretranslator. If the pretranslator already exists, this command removes all of its entries and operations, and overwrites its description with the new information. Syntax: pretranslator create npretranslatorid ...
Page 113
Dial plan configuration file commands 113 pretranslatorentry create description: creates a pretranslator entry and specifies a string of digits to be compared to the incoming digits. If the pretranslator entry already exists, this command overwrites it with the new information. Syntax: pretranslator...
Page 114
114 c hapter 2: c onfiguring the d ial p lan pretranslatorentry delete description: deletes a pretranslator entry or all entries for a particular pretranslator. Syntax: pretranslatorentry delete npretranslatorid nentryid arguments: npretranslatorid — an integer in the range 1 through 32768. Nentryid...
Page 115
Dial plan configuration file commands 115 pretranslatoroperation create description: creates a digit manipulation operation for a pretranslator entry. If the specified digit manipulation operation already exists, this command overwrites it with the new information. During pretranslation, the nbx 100...
Page 116
116 c hapter 2: c onfiguring the d ial p lan extensionlength description: specifies the length of extension numbers for system devices. The default is 3. Syntax: extensionlength nextensionlength arguments: nextensionlength — an integer in the range 3 to 4..
Page 117
Dial plan configuration file commands 117 extensionrange description: specifies a range of extensions for each type of device. When the nbx 100 automatically generates extensions it assigns them from within this range. When you manually generate an extension number, be sure that it is within the val...
Page 118
118 c hapter 2: c onfiguring the d ial p lan external settings description: specifies settings for several aspects of external devices. Syntax: externalsettings szexternalkeysetprefix szfirstautodiscoverextension szdefaultautoextension arguments: szexternalkeysetprefix — the digits to be prepended f...
Page 119
Sample solutions using dial plan configuration file commands 119 sample solutions using dial plan configuration file commands this section describes several requirements that a customer might have, and for each one, provides a sample solution. An explanation follows each step in the solution. Custom...
Page 120
120 c hapter 2: c onfiguring the d ial p lan pretranslatoroperation create 1 1 2 prepend 3 explanation: creates the second operation associated with pretranslator 1, pretranslatorentry 2. Defines a prepend operation that adds the digit 3 at the beginning of the 3-digit string (created by the previou...
Page 121
Sample solutions using dial plan configuration file commands 121 tableentry create 1 47 91 12 12 longdistance 0 2 explanation: creates, in table id 1 (the internal table), entry 47, which directs the nbx 100 to look for the digits 91 at the beginning of any 12-digit sequence (min and max are both 12...
Page 122
122 c hapter 2: c onfiguring the d ial p lan tableentry create 1 51 91978 7 7 longdistance 0 1 explanation: creates, in table id 1 (the internal table), entry 48, which directs the nbx 100 to look for the digits 91978 at the beginning of any 12-digit sequence (min and max are both 12). If the nbx 10...
Page 123
Sample solutions using dial plan configuration file commands 123 these entries in a dial plan configuration file would accomplish the pretranslation: pretranslator create 1 4-to-3-digit t1 did/ddi pretranslator explanation: create pretranslator table 1, called “4-to-3-digit t1 did/ddi pretranslator....
Page 124
124 c hapter 2: c onfiguring the d ial p lan this example assumes that all numbers begin with the same 7 digits (4567-89-3) and differ only in the last 3 digits. If this assumption is incorrect, you can add pretranslatorentry create lines to describe all of the possible variations. Pretranslatoroper...
Page 125
Sample solutions using dial plan configuration file commands 125 customer requirement 6 requirement: you want to use two different long distance carriers at different times of the day, to obtain a cost saving. To select one long distance carrier between the time the client’s business opens (7:30 a.M...
Page 126
126 c hapter 2: c onfiguring the d ial p lan explanation: for destinationroute 29, create entry 1, which uses extension list *0002, the extension list that contains all extensions associated with digital line cards. Destinationrouteoperation create 29 1 1 striplead 2 explanation: for destinationrout...
Page 127
Sample solutions using dial plan configuration file commands 127 ■ selects timed route 29. ■ prepends 1010321 to the outgoing call to select the first long distance carrier. Example 2: if you make a long distance call at any time on any saturday, the nbx 100 uses these timed route definitions, and: ...
Page 128
128 c hapter 2: c onfiguring the d ial p lan.
Page 129: Nstalling
3 i nstalling nbx 100 h ardware c omponents this chapter provides information and instructions for installing both standard and optional nbx ® 100 hardware components. It covers the following topics: ■ getting started ■ important safety information ■ unpacking and examining the components ■ recordin...
Page 130
130 c hapter 3: i nstalling nbx 100 h ardware c omponents getting started perform these tasks before installing the nbx 100 hardware: ■ complete the system plan (see the nbx 100 communications system planning guide and “preparing for installation” in chapter 1 for more information.) ■ prepare the di...
Page 131
Getting started 131 for wall-mounting the chassis: ■ screws for mounting the nbx 100 chassis to a prepared wall surface. The screws must support a fully configured chassis. ■ plywood, 1.25 cm (½ inch) or greater, mounted to the wall with toggle bolts or screwed into the wall studs. ■ drill and drill...
Page 132
132 c hapter 3: i nstalling nbx 100 h ardware c omponents important safety information before you install or remove any components or perform any maintenance procedures on the system, you must read the following safety information. Warning: warnings contain directions that you must follow for your p...
Page 133
Important safety information 133 ■ never use a telephone that is near the source of a gas leak to report the leak. ■ the nbx 100 chassis is equipped with a three-prong grounding plug. Do not defeat the protection offered by the plug by clipping the grounding prong or using an adapter to connect the ...
Page 134
134 c hapter 3: i nstalling nbx 100 h ardware c omponents ■ this unit operates under selv (safety extra low voltage) conditions according to iec 60950. These conditions are maintained only if the equipment to which the unit is connected also operates under selv conditions. ■ france only: this unit c...
Page 135
Consignes importantes de sécurité 135 ■ l’unité ne devrait pas etre branchée à une prise de courant alternatif (c.A.) sous aucun prétexte sans un branchement mise à la terre protectrice (mise à la masse). ■ vous devez raccorder cette unité à une sortie mise à la terre protectrice (mise à la masse) a...
Page 136
136 c hapter 3: i nstalling nbx 100 h ardware c omponents ■ l’appareil fonctionne à une tension extrêmement basse de sécurité qui est conforme à la norme iec 60950. Ces conditions ne sont maintenues que si l'équipement auquel il est raccordé fonctionne dans les mêmes conditions. ■ uniquement pour la...
Page 137
Wichtige sicherheitsinformationen 137 wichtige sicher- heitsinformationen sie müssen die folgenden sicherheitsinformationen sorgfältig durchlesen, bevor sie das gerät installieren oder ausbauen. Warnhinweis : warnhinweise enthalten anweisungen, die sie zu ihrer eigenen sicherheit befolgen müssen. Al...
Page 138
138 c hapter 3: i nstalling nbx 100 h ardware c omponents ■ der gerätestecker (der anschluß an das gerät, nicht der wandsteckdosenstecker) muß eine passende konfiguration für einen geräteeingang gemäß en60320/iec320 haben. ■ die netzsteckdose muß in der nähe des geräts und leicht zugänglich sein. Di...
Page 139
Unpacking and examining the components 139 unpacking and examining the components unpack the nbx 100 and examine the components. Depending on the size and configuration of the system, there might multiple chassis, hub cards, and line cards. There should be only one network call processor (ncp) per s...
Page 140
140 c hapter 3: i nstalling nbx 100 h ardware c omponents recording 4-port line card and 4-port ata card macs write down the mac address printed on the label attached to each 4-port line card and each 4-port ata card. When you install these cards into a chassis, write down the location of each port/...
Page 141
Recording mac addresses 141 recording digital line card macs each digital line card has a white label that contains one master mac address that identifies the board and span. There are also 12 additional mac addresses, based on the master mac address, which identify the 24 channels. Each mac address...
Page 142
142 c hapter 3: i nstalling nbx 100 h ardware c omponents installing the nbx 100 chassis 3com recommends that you install the disk drive in the chassis, then mount the chassis. Installing the disk drive the disk drive holds the nbx 100 call processor software, the configuration database, and apx voi...
Page 143
Installing the nbx 100 chassis 143 figure 32 installing the disk drive and data cable 2 attach the disk drive data cable (ide ribbon cable) to the ide connector on the disk drive. The cable connectors and the connector on the disk drive are keyed to ensure proper alignment. Use only the ide cable su...
Page 144
144 c hapter 3: i nstalling nbx 100 h ardware c omponents mounting the chassis in a rack you can rack-mount or wall-mount a chassis. If you are installing three or more chassis, put the lowest serial number on top and the highest serial number on the bottom. (the serial number appears on the label l...
Page 145
Installing the nbx 100 chassis 145 3 lift the chassis and slip the keyed slots of the mounting brackets onto the two screws you installed in step 1. The chassis should have the disk drive installed, the top cover installed, but no cards installed. 4 hold the chassis in place, install a mounting scre...
Page 146
146 c hapter 3: i nstalling nbx 100 h ardware c omponents caution: if you wall-mount the system, you must attach the nbx 100 chassis securely to a plywood mounting board which is firmly attached to the wall. A fully configured 6-slot chassis can weigh up to 13.5 kg (30 pounds). 2 drill pilot holes a...
Page 147
Installing the nbx 100 chassis 147 ■ every system must have one, and only one, nbx 100 ncp and disk drive. The call processor must reside in the first slot of the chassis, just below the space reserved for future expansion of the call processor card. The disk drive resides in the same chassis as the...
Page 148
148 c hapter 3: i nstalling nbx 100 h ardware c omponents installing nbx 100 ncp and other cards although the chassis has seven blank faceplate covers, it holds six cards. The space behind the top faceplate cover is for future expansion of the ncp. You cannot install a card in this top space — it do...
Page 149
Installing nbx 100 ncp and other cards 149 installing cable guides each nbx 100 chassis comes with a package of plastic cable guides which clip into the chassis beside each card slot. These guides can help you keep the lan and co line wires organized. Snap the guides into the holes to the right of t...
Page 150
150 c hapter 3: i nstalling nbx 100 h ardware c omponents if you use 100m cable that is not within the 10base-t specification, and the device does not work, the problem is typically not related to the power supply. For international users, the adapter (3c10125-xx) on the power line kit is provided w...
Page 151
Setting up ip connectivity for netset 151 setting up ip connectivity for netset you need ip connectivity to configure and manage the nbx 100 using the netset administration program. You do not need to install any special software to run netset, and you do not need a connection to the internet, but y...
Page 152
152 c hapter 3: i nstalling nbx 100 h ardware c omponents the system to the lan. The ip configuration required to enable access to netset depends on the current ip environment. Table 22 describes possible network environments and the configuration needed to enable ip connectivity to the nbx 100. Tab...
Page 153
Setting up ip connectivity for netset 153 to establish ip connectivity: 1 connect the computer’s 10base-t card directly to a port on the nbx 100 hub or a hub connected to the nbx 100. Make sure the hub is not yet connected to the lan. Isolating the nbx 100 eliminates the influence of routers and pro...
Page 154
154 c hapter 3: i nstalling nbx 100 h ardware c omponents installing lan connections after completing ip connectivity, install the lan connections. These connections may be a single chassis to external hubs or a multi-chassis configuration. Connecting lan cables — single chassis to external hubs you...
Page 155
Installing lan connections 155 use the following procedure to connect nbx 100 chassis using 10base2 connections. 1 using 10base2-compliant thin coax cable with bnc connectors and bnc “t” connectors, connect the 10base2 connector on the ncp to an nbx 100 hub card, and then to the external ethernet hu...
Page 156
156 c hapter 3: i nstalling nbx 100 h ardware c omponents figure 38 multiple chassis with isolated backplane testing the installed hardware to test the installed hardware: 1 make sure that all cards are fully seated into the backplane. 2 apply power to the chassis by connecting the power cord. 3 mak...
Page 157
Testing the installed hardware 157 nbx 100 system status lights as shown in figure 39, each card in the nbx 100 chassis contains status lights (leds) that indicate the card’s status during system power-up. Figure 39 nbx 100 status lights the following tables briefly describe the status lights..
Page 158
158 c hapter 3: i nstalling nbx 100 h ardware c omponents table 23 network control processor status lights condition status s1, s2, steady flash (approximately two flashes per second) hardware initializing. S1 on, s2 off operating software has booted successfully. S1 on; s2 on operating software has...
Page 159
Selecting regional software and components 159 selecting regional software and components after completing the hardware installation test, you can download your preferred regional language software and components. A “region” consists of a country and language pairing, such as, “france (french)” or “...
Page 160
160 c hapter 3: i nstalling nbx 100 h ardware c omponents ■ static voice messages heard by callers, telephone users, and administrators. These are messages that users or administrators are not able to change by re-recording a new message. Some examples are: help prompts used for setting up automated...
Page 161
Selecting regional software and components 161 figure 40 regional software tab 4 select install and browse to the appropriate internationalization pack and select the language of choice. Figure 41 selecting the internationalization pack.
Page 162
162 c hapter 3: i nstalling nbx 100 h ardware c omponents 5 after selecting the internationalization pack, click upgrade. This action installs nbx 100 software, including the appropriate regional components. After installing the regional software and components, you still must enable the language. T...
Page 163
Selecting regional software and components 163 cannot be removed). If you accept this option and remove all components, that region will be unavailable for all versions of the nbx 100 software. Click ok to remove the region. Iwhen you remove a region, all versions of that region are removed. For exa...
Page 164
164 c hapter 3: i nstalling nbx 100 h ardware c omponents figure 43 regional setting details this is a partial display of regional software details. You can scroll the message bar to see the complete report. Using auto discovery for initial system configuration after completing the hardware installa...
Page 165
Using auto discovery for initial system configuration 165 table 29 summarizes the auto discovery actions for nbx 100 components. . Table 29 auto discovery actions on nbx 100 components component auto discovery action 4-port line card gathers configuration information from each port on the card, assi...
Page 166
166 c hapter 3: i nstalling nbx 100 h ardware c omponents initial system configuration perform the following steps to use auto discovery for initial system configuration. 1 open netset using the administrator username and password. 2 on the main menu, click the system configuration icon. 3 on the sy...
Page 167
Configuring 4-port line cards 167 or, if you choose, you can now connect telephones to the lan one at a time and note the extension that appears on the telephone’s display panel. See chapter 3 “installing telephones and telephone lines” for more information. A fully initialized telephone displays it...
Page 168
168 c hapter 3: i nstalling nbx 100 h ardware c omponents when you connect the telephone lines, the order in which the telephone lines deliver calls matches the order of line card port extensions. For example, connect the line that rings first to the port with extension 701, connect the next telepho...
Page 169
Configuring 4-port line cards 169 the most common organization is left to right, top to bottom — the first port in the top-most line card receives the first line card port extension and the incoming telephone line that will ring first. You can configure the nbx 100 to behave in any one of the three ...
Page 170
170 c hapter 3: i nstalling nbx 100 h ardware c omponents re-assigning extensions and setting line card port options to re-assign extensions and set line card port options: 1 log on to netset using the administrator username and password. 2 click the device configuration icon, and then click the lin...
Page 171
Configuring 4-port line cards 171 6 repeat this procedure for each line card port. Table 30 modify line card port properties property description card type identifies the type of communications through this port. Auto discovery provides the correct setting for card type. You cannot modify this prope...
Page 172
172 c hapter 3: i nstalling nbx 100 h ardware c omponents connecting telephone lines after you have installed and configured the system for initial startup, connect the telephone company lines to the line card ports so you can start receiving outside calls..
Page 173: Onfiguring
4 c onfiguring nbx 100 s ystem -l evel s ettings this chapter provides information about using the system configuration function of netset to configure system level settings. It covers the following topics: ■ configuring system-level settings ■ configuring speed dial numbers ■ configuring business i...
Page 174
174 c hapter 4: c onfiguring nbx 100 s ystem -l evel s ettings perform the following steps to set system information. 1 click the system configuration icon. The system configuration window appears with the system settings tab displayed (figure 47). Figure 47 system configuration window 2 view the cu...
Page 175
Configuring system-level settings 175 3 to make changes to system-wide settings, click system-wide on the system settings tab. The system settingswindowappears (figure 48). Figure 48 system settings window subnet mask an ip setting that identifies the network and host portions of an ip address on th...
Page 176
176 c hapter 4: c onfiguring nbx 100 s ystem -l evel s ettings 4 to change information, select the value in the field you want to change and type over it or delete the value and enter new information. Table 32 describes each setting. Table 32 system settings window fields field purpose host name an ...
Page 177
Configuring system-level settings 177 5 when you finish, click apply. The new settings take effect. 6 click ok. The system configuration window reappears with the system settings tab displayed. Extensions start at the starting extension number used by auto discover telephones. You may select any unu...
Page 178
178 c hapter 4: c onfiguring nbx 100 s ystem -l evel s ettings enabling regional settings after you have installed regional software and components, you can enable these settings. Installing the regional internationalization packs makes the regional components available on you nbx 100, but to enable...
Page 179
Configuring system-level settings 179 advanced regional settings from the regional settings window, you can control several advanced regional settings. From the regional settings window (figure 49), follow these steps: 1 click the advanced button to see this window: figure 50 advanced regional setti...
Page 180
180 c hapter 4: c onfiguring nbx 100 s ystem -l evel s ettings setting the system date and time if necessary, you can set the nbx 100 date and time. It is important that the date and time are accurate because the system date and time: ■ appear on an idle nbx 100 telephone display ■ affect business h...
Page 181
Configuring system-level settings 181 setting timers system timers enable you to set time-out periods for various nbx 100 features. To set system timers: 1 on the system settingstab (figure 48), click timers. The timerswindow appears (figure 52). Figure 52 timers window 2 enter the settings you want...
Page 182
182 c hapter 4: c onfiguring nbx 100 s ystem -l evel s ettings setting ringing patterns you can set system-wide ringing patterns to distinguish between internal and external calls. You can choose one, two, or three rings to distinguish between internal and external calls. Do not confuse ringing patt...
Page 183
Configuring system-level settings 183 2 select the ringing patterns you want for internal and external calls. 3 click ok. The system configuration window displays the system settings tab. Configuring multicast addresses the nbx 100 uses ip multicast addressing to distribute information for certain s...
Page 184
184 c hapter 4: c onfiguring nbx 100 s ystem -l evel s ettings figure 54 multicast address list window there are two methods for selecting multicast addresses: ■ change ip, which lets you select a starting address for all entries. ■ change bins, which lets you change a single entry by selecting from...
Page 185
Configuring speed dial numbers 185 to change an ip address: 1 highlight the entry in the multicast address list for which you want to change the ip address. 1 click change ip. The ip addresses window appears. 2 make the change you want to the ip starting address. The nbx 100 selects a set of address...
Page 186
186 c hapter 4: c onfiguring nbx 100 s ystem -l evel s ettings you can use a system speed dial number to hide the actual number being called. For example, you can program an nbx 100 administrator's home telephone number into the speed dial list. Users never see the telephone number, just the code as...
Page 187
Configuring business identity information 187 4 in the comment field, type a brief description for this speed dial. 5 click apply. The new speed dial takes effect. To print system speed dials 1 click the print icon. A new browser window opens, displaying a list of all system speed dials. 2 in the ne...
Page 188
188 c hapter 4: c onfiguring nbx 100 s ystem -l evel s ettings window appears (figure 56). (during installation, this window contains only defaults.) figure 56 current business information window 2 click business information. The business information window appears (figure 57)..
Page 189
Configuring business identity information 189 figure 57 business information window 3 enter the information you want, then click ok. The system configuration window appears, displaying the business identity tab with the information you entered. Setting business hours the business hour tables allow y...
Page 190
190 c hapter 4: c onfiguring nbx 100 s ystem -l evel s ettings to define business hours: 1 on the business identity tab of the system configuration window, click business hours. The business hours window appears (figure 58). Figure 58 business hours window 2 enter the hours of operation for each of ...
Page 191
Configuring system security 191 3 click apply. The system mode resets. 4 click ok. The system configuration window displays the business identity tab. Configuring system security the security function enables you to set system passwords, including the administrator password, the auto attendant passw...
Page 192
192 c hapter 4: c onfiguring nbx 100 s ystem -l evel s ettings 3 click apply to save the password. Setting the auto attendant password change the default auto attendant password to prevent access to system settings and functions. To set the auto attendant password: 1 on the security tab (figure 59),...
Page 193
Configuring system security 193 setting the system backup password the system backup password enables automated backups from an external system. To set the system backup password: 1 on the security tab (figure 59), click system backup password. The change system backup password window opens (figure ...
Page 194
194 c hapter 4: c onfiguring nbx 100 s ystem -l evel s ettings setting the reporting password you use the reporting password in conjunction with nbx 100. Call reports, an optional component of the nbx 100. See the 3com nbx 100 administrator’s guide for information about call reports. To change the r...
Page 195
Configuring tapi settings 195 to configure tapi settings: 1 on the netset main menu, click the system configuration icon. The system configuration window appears. 2 click the tapi settings tab. The tapi settings window appears (figure 63). Figure 63 tapi settings window 3 make changes as necessary t...
Page 196
196 c hapter 4: c onfiguring nbx 100 s ystem -l evel s ettings.
Page 197: Nstalling
5 i nstalling t elephones and t elephone l ines this chapter provides information and instructions for installing nbx ® business telephones, telephone lines, and external hardware. It covers the following topics: ■ connecting telephones to the lan ■ creating and managing telephone groups ■ using but...
Page 198
198 c hapter 5: i nstalling t elephones and t elephone l ines connecting power to the telephone connect the ac power converter provided with the telephone to the power connection on the bottom of the telephone and a suitable wall outlet. Connecting the telephone to connect the telephone, follow thes...
Page 199
Connecting telephones to the lan 199 figure 65 attachment positions for the telephone support bracket wall mounting a telephone wall mounting a telephone requires the following tools and materials: ■ two #10 round head wood screws, at least 1-inch (2.5 cm) ■ screwdriver ■ drill and drill bit make su...
Page 200
200 c hapter 5: i nstalling t elephones and t elephone l ines figure 66 marking the pilot holes for wall-mounting a telephone you can use a standard wall-mount telephone bracket, available through commercial electronics supply outlets, or drill holes and install two screws. (if you use a standard br...
Page 201
Connecting telephones to the lan 201 5 install the telephone support bracket in the wall mount position as shown in figure 65. 6 connect the ac power cord to the back of the telephone. 7 hang the telephone on the mounting screws. Be sure that the telephone slides down about ½-inch after you slip it ...
Page 202
202 c hapter 5: i nstalling t elephones and t elephone l ines creating and managing telephone groups telephone groups let you create a template for common button mappings. Button mappings let you assign specific actions to the buttons on an business telephone. When you place a telephone in a group, ...
Page 203
Creating and managing telephone groups 203 figure 69 telephone groups window 3 click add. The add telephone group window appears (figure 70). Figure 70 add telephone group window 4 enter the name of the new group in the group name: field. 5 click ok to add the new group..
Page 204
204 c hapter 5: i nstalling t elephones and t elephone l ines using button mappings the button mappings feature lets you assign specific actions to the access buttons on an business telephone. The business telephone includes 18 access buttons. You can assign co telephone lines or line pool access to...
Page 205
Using button mappings 205 figure 71 telephone groups window 3 select the group to which you want to apply mappings, and then click button mappings . The group button mappings window appears. Figure 72 group button mappings window.
Page 206
206 c hapter 5: i nstalling t elephones and t elephone l ines using this window, you can assign button mappings for telephone groups. For access buttons without lights, you can assign a function by choosing a button type . For the access buttons with lights, you must choose a type , and, depending o...
Page 207
Using button mappings 207 system intercom calls and outside calls from lines not mapped to specific buttons ring on a system button. To call an outside number from a system line, you must access a line pool by dialing either 9 or 8, depending on the line pool configuration. You do not need to enter ...
Page 208
208 c hapter 5: i nstalling t elephones and t elephone l ines notes on button mappings ■ telephone button mappings are part of a device. You assign a set of mappings to an individual by associating a particular device or group with a user. ■ users can see the button mappings in effect for their tele...
Page 209
Using button mappings 209 to create a dss/blf button mapping: 1 open netset using the administrator username and password. 2 on the main menu , click the device configuration icon. The device configuration window (figure 68) appears. 3 on the telephones tab, click a telephone in the list, and then c...
Page 210
210 c hapter 5: i nstalling t elephones and t elephone l ines 4 on the telephones tab, choose the second telephone in the progression of telephones where you want to create the delayed ringing pattern, and then click button mappings . 5 for the shared line appearance button, set the ring field to th...
Page 211
Installing an adjunct 211 one common use for an adjunct is to provide station appearances for every existing extension at the receptionist’s telephone (the attendant console). The receptionist can see at a glance the status of each extension — in use or available, and then quickly transfer incoming ...
Page 212
212 c hapter 5: i nstalling t elephones and t elephone l ines if you are installing more than one adjunct and using auto discovery to configure them, you should install the devices one at a time. This method makes it easier to keep track of which device you are configuring. Also, you should ensure t...
Page 213
Installing an adjunct 213 configuring the adjunct using auto discovery to configure the adjunct using auto discovery: 1 make sure that the adjunct is connected to the lan, and that all telephone extensions that will map to the adjunct have already been configured. If you add extensions to the system...
Page 214
214 c hapter 5: i nstalling t elephones and t elephone l ines changing the extension associated with an adjunct to change the extension associated with an adjunct: 1 on the netset main menu, click the device configuration icon. 2 on the device configuration window, click the adjunct tab. The adjunct...
Page 215
Installing an adjunct 215 figure 76 add dss/blf adjunct window 4 type the mac address of the adjunct you want to add. (the adjunct’s mac address appears on the label located on the bottom of the device.) 5 in the device name field, type a name that can help you identify this device when it appears i...
Page 216
216 c hapter 5: i nstalling t elephones and t elephone l ines setting adjunct access button mappings typically adjunct buttons provide an appearance for each extension in the system and are mapped during the auto discovery process. However, you can map an adjunct access button to any of the function...
Page 217
Installing an adjunct 217 table 35 adjunct button types button type description default indicates that this dss/blf button has no mapping. You do not need to specify a number or a prty. Other lets you assign speed dial numbers to access buttons. The type list lets you choose ssd (system speed dial) ...
Page 218
218 c hapter 5: i nstalling t elephones and t elephone l ines adding external hardware external devices connect to the front of the network call processor. For a list of external hardware that can connect to the call processor, see “what external devices can connect to an nbx 100?” on page 42. Conne...
Page 219
Configuring routing devices 219 connecting a paging amplifier connect the paging device to the paging connector on front of the nbx 100 network call processor. See the paging amplifier instructions for more information. The paging connector on the network call processor is an rj11 connector. It is a...
Page 220
220 c hapter 5: i nstalling t elephones and t elephone l ines 01:e0:bb:00:00:2d 01:e0:bb:00:00:29 01:e0:bb:00:00:21 01:e0:bb:00:00:17 01:e0:bb:00:00:13 01:e0:bb:00:00:1d slave command nbx 100 debug slave status download me request download service system state 01:e0:bb:00:00:11 01:e0:bb:00:00:0e 01:...
Page 221: Etting
6 s etting u p u sers and f eatures this chapter provides information about configuring user settings on the nbx ® 100 system. It covers the following topics: ■ adding users ■ configuring call pickup groups ■ configuring hunt groups ■ configuring class of service (cos) adding users this section tell...
Page 222
222 c hapter 6: s etting u p u sers and f eatures adding a user to add a new user to the system: 1 on the netset main menu, click the user configuration icon. The users window appears (figure 77). Figure 77 users window 2 click add. The add user window appears (figure 78)..
Page 223
Adding users 223 figure 78 add user window 3 fill in the fields for the new user. Table 38 describes the fields. Table 38 add user fields field purpose extension number enter the extension for this telephone. Specify an unused extension or the extension of the telephone you want to use as it appears...
Page 224
224 c hapter 6: s etting u p u sers and f eatures 4 click apply to add the new user. 5 repeat steps 3 and 4 to add additional users. 6 click ok when you are done adding users. Users must initialize their telephones by entering voice mail, entering the telephone extension as a password, then entering...
Page 225
Adding users 225 to configure a telephone as the attendant console: 1 on the netset main menu, click the user configuration icon. The users window appears (figure 77). The list box shows the telephone extension, the device name, and the user’s first and last names for each user. If you are adding a ...
Page 226
226 c hapter 6: s etting u p u sers and f eatures configuring the auto attendant line card port after you configure the telephone for the auto attendant, you must configure a line card port. 1 click the tab to it button, and then click the line card ports tab under device configuration . 2 click the...
Page 227
Adding users 227 ■ the priority number establishes the order for extensions when users make outgoing calls. When users pick up the handset to make a call, the system activates the line designated as priority 1. If priority 1 is busy, the system activates the priority 2 line. You can map all of the l...
Page 228
228 c hapter 6: s etting u p u sers and f eatures figure 80 ringer tones window 4 select the ringer tone you want from the ringer tone setting drop-down list. You can listen to sample ringer tones by selecting them from the sample ringer tones group of buttons. 5 click apply to effect the change. Co...
Page 229
Configuring call pickup groups 229 figure 81 call pickup window 3 select the call pickup group you want to configure. 4 click modify. The modify call pickup groupwindow appears (figure 82). Figure 82 modify call pickup group window 5 enter the group name you want in the group name field..
Page 230
230 c hapter 6: s etting u p u sers and f eatures 6 to allow users who are not members of the group to pick up calls directed to the group, enable the allow non-member pickup check box. 7 click apply to modify the group. 8 click ok. Configuring the membership of a call pickup group you can configure...
Page 231
Configuring hunt groups 231 adding hunt groups to add a hunt group to the system: 1 on the netset main menu, click the user configuration icon. 2 click the hunt groups tab. The hunt groups window appears (figure 83). Figure 83 hunt groups window 3 click add. The add hunt group window appears (figure...
Page 232
232 c hapter 6: s etting u p u sers and f eatures figure 84 add hunt group window 4 complete the fields on this window to add a hunt group. Table 39 describes the fields. Table 39 hunt group window fields field purpose name a descriptive name for the hunt group. It will be used as the caller id. Ext...
Page 233
Configuring hunt groups 233 5 click apply to add the group. 6 add more new groups if you want, then click ok when you finish. Configuring hunt group status you can configure the status of the members of a particular hunt group. Each member of the group is listed, along with each member’s current sta...
Page 234
234 c hapter 6: s etting u p u sers and f eatures figure 85 hunt group status window 5 if desired, highlight a user and log him or her in or out. You can also lock or unlock the user from the group. 6 click apply to effect the changes for this user. You can change the status of more than one user. 7...
Page 235
Configuring hunt groups 235 configuring hunt group feature mappings feature mappings show the association of the hunt group login and logout feature codes and the currently configured hunt groups. To modify hunt group feature mappings: 1 on the netset main menu, click the user configuration icon. 2 ...
Page 236
236 c hapter 6: s etting u p u sers and f eatures configuring class of service (cos) class of service is a collection of calling permissions you assign to individual users. Most permissions are subject to the business hours parameters. For example, you could create a class where toll calls are allow...
Page 237
Configuring class of service (cos) 237 figure 87 class of service window 3 click add. The add cos window appears (figure 88). Figure 88 add cos window 4 enter the name of the new cos in the name field. 5 enable each cos category as business hours: open, closed, lunch, or other..
Page 238
238 c hapter 6: s etting u p u sers and f eatures 6 click apply to effect the changes. 7 click ok..
Page 239: Onfiguring
7 c onfiguring d igital l ine c ards (t1, e1, and bri c ards ) this chapter describes how to add and configure either a t1, e1, or bri digital line card to handle a t1 or e1 line (with one span each) or a bri line (4 bri spans for each bri card added). The nbx ® 100 can accommodate up to three t1/e1...
Page 240
240 c hapter 7: c onfiguring d igital l ine c ards (t1, e1, and bri c ards ) there are three different digital line cards, each of which supports different protocols: adding a t1 digital line card adding a t1 digital line card to an nbx 100 chassis requires: ■ preparation (ordering the t1 line and p...
Page 241
Configuring the t1 digital line card 241 inserting the t1 digital line card to insert the t1 digital line card into the nbx 100 chassis, do not remove power from the nbx 100. Perform these steps: 1 write down the mac address of the t1 card. You can find the mac address on a label on the board. The a...
Page 242
242 c hapter 7: c onfiguring d igital l ine c ards (t1, e1, and bri c ards ) 3 use the mac address of the t1 card (which you recorded before inserting the card into the chassis) to identify the card in the t1/isdn board list. 4 select the t1 card from the list and click modify. Figure 89 digital lin...
Page 243
Configuring the t1 digital line card 243 checking the span status to check that the span status changes from offline to ready, perform these steps. 1 return to the digital line cards tab. 2 select t1 span list from the select device type list. 3 click apply. 4 check that the word ready appears in th...
Page 244
244 c hapter 7: c onfiguring d igital l ine c ards (t1, e1, and bri c ards ) point (the point at which the telephone carrier’s wiring ends) and your nbx 100. 5 if the you are connecting to a t1 line supplied by the telephone carrier, choose loop as the timing mode. If you are connecting to a local d...
Page 245
Configuring the t1 digital line card 245 the nbx 100 presets the parameter values (channel protocol through trunk to trunk, excluding called party digits and calling party digits). 6 click the on line check box. 7 enter 500 in each of the four autoext text boxes. 8 click ok..
Page 246
246 c hapter 7: c onfiguring d igital l ine c ards (t1, e1, and bri c ards ) checking group membership to check that all channels are in the member list perform these steps. 1 return to the digital line cards tab. 2 from the select device type list, select t1 group list. 3 click apply. 4 select the ...
Page 247
Configuring the t1 digital line card 247 configuring for isdn pri signaling this section describes how to configure a t1 digital line card for isdn pri (primary rate interface) signaling. Caution: before you begin to configure the t1 card, you must wait 3 minutes after inserting the t1 card into the...
Page 248
248 c hapter 7: c onfiguring d igital l ine c ards (t1, e1, and bri c ards ) 6 to change the name of the t1 board, edit the contents of the board name field. To connect the t1 line and activate the span perform these steps. 1 plug the t1 line into the nbx 100 t1 board. 2 the card type field should a...
Page 249
Configuring the t1 digital line card 249 1 to change the name of the span, edit the span name field. You can use alphanumeric characters, dashes, and underscores. The maximum name length is 30 characters. 2 from the interface type pull-down list, select t1. 3 choose an entry from the co switch proto...
Page 250
250 c hapter 7: c onfiguring d igital l ine c ards (t1, e1, and bri c ards ) ■ b8zs (bipolar 8 zero substitution) the most common combinations of framing type and line code type are esf with b8zs, and d4 with ami. The combination of esf with b8zs is becoming more common. 6 select a line length from ...
Page 251
Configuring the t1 digital line card 251 6 select restricted from the trunk to trunk pull-down list. 7 click the on line check box. 8 enter 500 in each of the four autoext text boxes. 9 click ok. Checking group membership to check that all channels are in the member list, perform these steps. 1 retu...
Page 252
252 c hapter 7: c onfiguring d igital l ine c ards (t1, e1, and bri c ards ) 4 wait (approximately 30 seconds) for the status of each channel to change from ready to idle. While you are waiting, you can click apply to refresh the list of channels and see the updated status..
Page 253
Adding an e1 digital line card 253 adding an e1 digital line card adding an e1 digital line card to an nbx 100 chassis, requires: ■ preparation (ordering the e1 line and preparing the nbx 100) ■ inserting the e1 digital line card in the nbx 100 chassis ■ configuring the e1 digital line card paramete...
Page 254
254 c hapter 7: c onfiguring d igital l ine c ards (t1, e1, and bri c ards ) caution: when you insert the e1 digital line card, it begins an initialization sequence. Also, because you enabled the auto discover digital line cards check box, the system recognizes the addition of the e1 card and begins...
Page 255
Configuring the e1 digital line card 255 figure 97 digital line cards, modify board window 5 scroll through the channel list to check that the nbx 100 lists all 30 channels. Figure 97 shows the first few channels; the channel numbers appear after the mac address, separated by a dash. Example: in the...
Page 256
256 c hapter 7: c onfiguring d igital l ine c ards (t1, e1, and bri c ards ) 4 check that the word ready appears in the isdn pri span list line item that corresponds to this span. 5 to modify the span, highlight it in the span list and click the modify button immediately below the span list. Figure ...
Page 257
Configuring the e1 digital line card 257 9 choose one of the six entries in the framing type pull-down list. Check with your telephone carrier to determine which one is used on the e1 line they supplied. ■ multiframe with crc4 ■ double frame (multiframe without crc4) multiframe with crc4 is more com...
Page 258
258 c hapter 7: c onfiguring d igital l ine c ards (t1, e1, and bri c ards ) 4 from the isdn pri group list, select pri group 1. 5 click modify. Figure 99 digital line cards, modify group window 6 select restricted from the trunk to trunk pull-down list. 7 click the on line check box. 8 enter 500 in...
Page 259
Configuring the e1 digital line card 259 figure 100 digital line cards, manage group membership window 5 scroll through the list to make sure that all 30 channels are present. Completing the e1 installation to complete the e1 installation, perform these steps. 1 return to the digital line cards tab....
Page 260
260 c hapter 7: c onfiguring d igital l ine c ards (t1, e1, and bri c ards ) adding an isdn bri digital line card adding an isdn bri digital line card to an nbx 100 chassis, requires: ■ preparation (ordering the bri line and preparing the nbx 100) ■ inserting the bri digital line card in the nbx 100...
Page 261
Configuring the isdn bri digital line card 261 caution: when you insert the bri digital line card, it begins an initialization sequence. Also, because you enabled the auto discover digital line cards check box, the system recognizes the addition of the bri card and begins to update its database. All...
Page 262
262 c hapter 7: c onfiguring d igital l ine c ards (t1, e1, and bri c ards ) figure 101 isdn bri digital line card, modify board window 5 scroll through the channel list to check that the nbx 100 lists all eight channels. Figure 97 shows the first few channels; the channel numbers appear after the m...
Page 263
Configuring the isdn bri digital line card 263 3 click apply. 4 check that the word ready appears in the isdn bri span list line item that corresponds to this span. 5 to modify the span, highlight it in the span list and click the modify button immediately below the span list. Figure 102 digital lin...
Page 264
264 c hapter 7: c onfiguring d igital l ine c ards (t1, e1, and bri c ards ) configuring bri groups to configure the bri groups, perform these steps. 1 return to the digital line cards tab. 2 from the select device type list, select isdn bri group list. 3 click apply. 4 from the isdn bri group list,...
Page 265
Configuring the isdn bri digital line card 265 figure 104 digital line cards, manage group membership window 5 scroll through the list to make sure that all eight channels are present. Completing the bri installation to complete the bri installation, perform these steps. 1 return to the digital line...
Page 266
266 c hapter 7: c onfiguring d igital l ine c ards (t1, e1, and bri c ards ) example: carriers commonly pass either the last 3 digits or last 4 digits of the number for each incoming call. Sometimes the last digits of the telephone numbers the carrier assigns to you do not match the telephone extens...
Page 267
Configuring the isdn bri digital line card 267 t1 and e1 card leds the t1 card contains these leds: ■ cf: carrier fail (red alarm) ■ ra: remote alarm (yellow alarm) ■ lb: loopback ■ nominal: t1 or e1 board is framed bri card leds each of the four channels on a bri card has these leds: ■ d: ■ off ind...
Page 268
268 c hapter 7: c onfiguring d igital l ine c ards (t1, e1, and bri c ards ).
Page 269: Aintenance
8 m aintenance , d iagnostics , and t roubleshooting this chapter contains maintenance and troubleshooting information that can help you resolve simple problems. It contains the following topics: ■ troubleshooting ■ using the telephone local user interface (lui) utility troubleshooting the suggested...
Page 270
270 c hapter 8: m aintenance , d iagnostics , and t roubleshooting nbx 100 power cord is the nbx 100 power cord firmly attached at both the outlet and the chassis? No cards in the chassis you must have at least one card in the chassis and seated in the chassis backplane. Nbx 100 power supply if none...
Page 271
Troubleshooting 271 date/time display on telephones is wrong, either jan 1, 1997 or just random characters a power surge has corrupted the system time. If the display shows jan 1, 1997, use netset to reset the system time. If the display shows random characters, for example 00; 0 #, you must: 1 disc...
Page 272
272 c hapter 8: m aintenance , d iagnostics , and t roubleshooting routing problems if the local ip environment includes a proxy server, you might need to reconfigure the browser parameters to ignore the proxy server. See the browser’s online help. Invalid ip configuration on the nbx 100 the nbx 100...
Page 273
Troubleshooting 273 no more extensions available if the system has already allocated all available extensions, the auto discovery process will not complete. Use netset to set a new starting number, or manually configure the telephone. You are installing a telephone on a different subnet from the net...
Page 274
274 c hapter 8: m aintenance , d iagnostics , and t roubleshooting using the telephone local user interface (lui) utility the firmware within each business telephone includes a telephone diagnostic/configuration utility called local user interface (lui). To run the telephone diagnostic/configuration...
Page 275
Using the telephone local user interface (lui) utility 275 you use the access buttons to select certain menu items or to enter hexadecimal digits. Lui controls on the business telephone are shown in figure 91. Figure 105 lui controls on the business telephone nbx test menu scroll--options display pa...
Page 276
276 c hapter 8: m aintenance , d iagnostics , and t roubleshooting table 42 lui menu items test description 1 view settings use the scroll buttons to view the following: ■ telephone mac address ■ ncp mac address all fs indicates that the telephone responds to any network control processor, the defau...
Page 277
Using the telephone local user interface (lui) utility 277 7 audio x-conn cross connects the audio channels—handset mouthpiece to speaker, microphone to handset earpiece. The connection times out after ten seconds. (the telephone’s microphone is located in the lower right corner of the telephone.) 8...
Page 278
278 c hapter 8: m aintenance , d iagnostics , and t roubleshooting using h3pingip you can use the h3pingip menu item, ab14, to ping another device on the network to test the telephone’s connectivity. You can also use this test to check the packet delay. When using h3pingip to test for connectivity, ...
Page 279: Nbx 100 S
A nbx 100 s ystem s pecifications this appendix contains physical, environmental, electrical, and configuration specifications for: ■ 6-slot chassis ■ network call processor ■ 4-port line card ■ tapi service provider ■ 8-port hub card ■ 4-port ata ■ single-port ata ■ tapi service provider 6-slot cha...
Page 280
280 a ppendix a: nbx 100 s ystem s pecifications network call processor the call processor must reside in the top slot in the chassis. You need only one call processor per system, even when they system has than one chassis (table 44). Table 44 nbx 100 network call processor specifications weight 1 l...
Page 281
4-port line card 281 4-port line card a 4-port line card is the system’s interface to the telephone company’s co lines (table 45). T1 and e1 digital line card the t1/e1 digital line card is an optional card that enables you to connect a t1 or e1 line to the nbx 100. Table 45 nbx 100 4-port line card...
Page 282
282 a ppendix a: nbx 100 s ystem s pecifications bri line card the basic rate interface (bri) line card is an optional card that allows transmission of voice traffic over the integrated services digital network (isdn). The bri card is available in 2-port and 4-port options, which is controlled by so...
Page 283
8-port hub card 283 8-port hub card the nbx 100 8-port hub card is an optional component. You can connect any 10base-t hub or switch to the network call processor to provide lan connectivity to the system (table 46). 4-port ata the 4-port ata is an optional card that provides support for connecting ...
Page 284
284 a ppendix a: nbx 100 s ystem s pecifications tapi service provider the nbx 100 tapi service provider (nbxtsp) supports the basic telephony services as described in the microsoft tapi 2.1 specification. In addition, the nbxtsp supports selected functions of the supplementary telephony services of...
Page 285
Tapi service provider 285 linedial linesetagentstate lineanswer lineproxymessage linesetnumrings lineproxyresponse linegetnumrings linesetcallqualityofservice linesetcallprivilege linedrop linedeallocatecall linehandoff linegetnewcalls linegetconfrelatedcalls linetranslatedialog linegetcountry liner...
Page 286
286 a ppendix a: nbx 100 s ystem s pecifications.
Page 287: and
B t1 and isdn pri s ervices c ircuit p rovisioning this appendix describes the circuit provisioning requirements for t1 lines and for isdn pri services on t1 lines. It contains the following topics: ■ requirements for t1 configuration ■ isdn pri prerequisites ■ recommendations requirements for t1 co...
Page 288
288 a ppendix b: t1 and isdn pri s ervices c ircuit p rovisioning circuit type 4-wire is required. Did applications when using did or dnis, 3com recommends ordering telephone numbers that easily fit into the nbx 100 numbering plan. Although the numbering plan is extremely flexible, it is far easier ...
Page 289
Recommendations 289 recommendations 3com recommends the following for isdn pri services. Framing type recommended (also the default) configuration: extended super frame (esf) the multi-frame formats f4, f12 (d4 or sf), and f72 are also supported. Zero code suppression recommended (also the default) ...
Page 290
290 a ppendix b: t1 and isdn pri s ervices c ircuit p rovisioning.
Page 291: Uidelines
C g uidelines for r emote a udio d evice c onnections this appendix provides guidelines for connecting a remote audio device to the nbx ® 100 system. The remote audio device can be an business telephone, analog line card, single-port analog terminal adapter (ata), digital line card, or other product...
Page 292
292 a ppendix c: g uidelines for r emote a udio d evice c onnections large packet latency the round-trip latency on large packets, 300 bytes to full mtu, must be less than 450ms. The system will support an occasional packet delay of 450 to 900ms, but each such delay will cause retries and thus affec...
Page 293
Installing fax devices with atas 293 layer 3 adpcm audio (reduced bandwidth setting) the overhead for running a device as a layer 3 device results in a maximum bandwidth requirement of 54.7 kbps per party in the conversation. Thus, a point-to-point call requires this peak bandwidth in each direction...
Page 294
294 a ppendix c: g uidelines for r emote a udio d evice c onnections.
Page 295: Indows
D w indows 2000 s upport this appendix covers the support for windows 2000 in the following nbx 100 applications: ■ nbx connextions ■ nbx 100 call detail reports ■ nbx pcxset it also lists the windows environment specifications and the installation procedure for each of the applications. For informa...
Page 296
296 a ppendix d: w indows 2000 s upport windows 2000 environment specifications ■ operating system: windows nt 4.0 sp4 or higher, windows 2000. ■ os sw license: windows nt server or workstation or windows 2000 professional. ■ processor: minimum is a pentium 166 mhz. Pentium iii 800 mhz or equivalent...
Page 297
Nbx connextions 297 5 specify the number of configured h.323 ports. Do not exceed the number of licenses or the installation will have to be restarted. 6 specify a caller id label. Enter an outgoing caller id notification label of up to 33 digits. For example, 9787490000 (the caller id shows the cal...
Page 298
298 a ppendix d: w indows 2000 s upport nbx 100 call detail reports 3com nbx 100 communications systems can capture information about all outgoing and incoming calls made through the system. To view this call information in detail, you must install nbx 100 call detail reports on a networked computer...
Page 299
Nbx pcxset 299 nbx pcxset the pcxset pc telephone is a software application that enables a user’s multimedia computer to become a telephone with the same features, functionality, tapi, and imap4 client capabilities of the business telephone. Windows 2000 environment specifications the nbx pcxset spe...
Page 300
300 a ppendix d: w indows 2000 s upport 6 select a destination folder. The default is c:\program files\3combx 100bx pcxset 7 click next. 8 select a program folder for the windows start menu or accept the default by clicking next. 9 click next again. 10 click finish. You must restart the computer...
Page 301: Ndex
I ndex numerics 10base2 coax, terminating 155 port 155 4-port analog terminal adapter card 24 status indicators 24 4-port ata 284 4-port hub card installing 148 50-ohm terminating resistance 155 8-port hub card installing 148 911 and class of service 236 a access buttons 26 access permissions 236 ad...
Page 302
302 i ndex change ip 184 change system backup password 193 changing bins 185 chassis brackets 145 installing 144 multi-chassis configuration 144 multi-chassis installation 155 rack mounting 144 removing the cover 142 wall-mount 145 wall-mount dimensions 145 chassis cover, removing 142 chassis, numbe...
Page 303
I ndex 303 telephones 80 voice mail ports 78 , 79 extensions adding 76 , 77 auto attendant 48 call park 48 for attendant console 225 hunt group 49 telephones 48 external devices connecting to 42 external hub or switch connecting 154 external keyset prefix 81 external paging amplifier connector speci...
Page 304
304 i ndex l lan connections two-chassis installation 155 lcd testing 276 least cost dial plan table 55 led network call processor 20 telephone diagnostics 276 lights status 157 testing telephone leds 276 lines supported by the nbx system 42 local telephone service 40 local user interface 274 loop f...
Page 305
I ndex 305 s s1, s2, s3 157 safety information german 137 safety precautions 132 serial cable 150 serial number telephone 276 serial port access to the call processor 150 set system mode 190 silence suppression 43 single port analog terminal adapter 24 single port ata 283 single-port analog terminal...
Page 306
306 i ndex.