- DL manuals
- Anritsu
- Remote Control
- MS2690A
- Operation Manual
Anritsu MS2690A Operation Manual
MS2690A/MS2691A/MS2692A
and MS2830A
Signal Analyzer
Operation Manual
Phase Noise Measurement Function
Remote Control
Third Edition
• For safety and warning information, please read this
manual before attempting to use the equipment.
• Additional safety and warning information is provided
within the “MS2690A/MS2691A/MS2692A and
MS2830A Signal Analyzer Operation Manual
(Mainframe Operation)”. Please also refer to this
document before using the equipment.
• Keep this manual with the equipment.
ANRITSU CORPORATION
Document No.: M-W3118AE-3.0
Summary of MS2690A
Page 1
Ms2690a/ms2691a/ms2692a and ms2830a signal analyzer operation manual phase noise measurement function remote control third edition • for safety and warning information, please read this manual before attempting to use the equipment. • additional safety and warning information is provided within the ...
Page 2: Danger
Safety symbols to prevent the risk of personal injury or loss related to equipment malfunction, anritsu corporation uses the following safety symbols to indicate safety-related information. Ensure that you clearly understand the meanings of the symbols before using the equipment. Some or all of the ...
Page 3
Notes on export management this product and its manuals may require an export license/approval by the government of the product's country of origin for re-export from your country. Before re-exporting the product or manuals, please contact us to confirm whether they are export-controlled items or no...
Page 4
Iv.
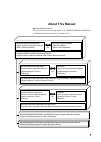
Page 5: About This Manual
About this manual associated documents the operation manual configuration of the ms2690a/ms2691a/ms2692a and ms2830a signal analyzer is shown below. Ms2690a/ms2691a/ms2692a signal analyzer operation manual (main frame operation) ms2690a/ms2691a/ms2692a and ms2830a signal analyzer operation manual (p...
Page 6
Ii • signal analyzer operation manual (mainframe operation) • signal analyzer operation manual (mainframe remote control) description of basic operations, maintenance procedures, common functions and common remote functions of the mainframe • signal analyzer operation manual (signal analyzer functio...
Page 7: Table of Contents
Iii 3 2 1 table of contents about this manual ........................................ I chapter 1 overview.................................... 1-1 1.1 overview ....................................................................... 1-2 1.2 native mode...................................................
Page 8
Iv..
Page 9
Chapter 1 overview 1-1 1 overvi ew this chapter provides an overview of the remote control of the phase noise measurement function (hereinafter, referred to as “this application”). 1.1 overview ....................................................................... 1-2 1.1.1 interface..................
Page 10: 1.1 Overview
Chapter 1 overview 1-2 1.1 overview this application can be controlled from an external controller (pc) by remote control commands using the ms2690/ms2691/ms2692a or ms2830a signal analyzer (hereinafter, referred to as “this instrument”). The remote control commands are defined by the scpi format. 1...
Page 11: 1.1.2 Controlled
1.1 overview 1-3 1 overvi ew 1.1.2 controlled application two types of the remote control commands can be used with this instrument: commands that are commonly applied to this instrument itself or all the applications (hereinafter, referred to as “common commands”), and the other commands unique to ...
Page 12: 1.2 Native Mode
Chapter 1 overview 1-4 1.2 native mode in this instrument, the syntax/format types of the remote control commands are defined as “language mode.” the language mode has two modes: scpi and native. (1) scpi mode the scpi mode processes commands conforming to the syntax/format defined in scpi (ver1999....
Page 14
Chapter 1 overview 1-6 [2] delete those layers which can be deleted. :display:window:trace:y[:scale]:rlevel ↓ :display:window:trace:y:rlevel [3] alter all long forms into short ones. :display:window:trace:y:rlevel ↓ :disp:wind:trac:y:rlev [4] delete the colon mark (“:”) at the head. : disp:wind:trac...
Page 15
1.3 setting numeric program data 1-7 1 overvi ew 1.3 setting numeric program data the following character programs can be used for setting numeric program data (numeric parameter). (1) default after default is set to numeric program data, the target parameter is set to the initial value. (2) minimum...
Page 16
Chapter 1 overview 1-8..
Page 17
Chapter 2 scpi device message details 2-1 2 scpi device message details this chapter describes the detailed specifications of scpi remote control commands for executing the functions of this application. The device messages are listed according to each function. Refer to the “ms2690a/ms2691a/ms2692a...
Page 18
Chapter 2 scpi device message details 2-2 :display:window[1]:trace:y[:scale]:rlevel:offset:state?......................... 2-22 2.2.9 pre amp .................................................................................................................... 2-23 [:sense]:power[:rf]:gain[:state] off...
Page 20: 2.1 Selecting Application
Chapter 2 scpi device message details 2-4 2.1 selecting application table 2.1-1 lists the device messages for setup operations such as starting/selecting/initializing an application. Table 2.1-1 selecting application parameter device message load application :system:application:load pnoise unload ap...
Page 21: 2.1.1 Load
2.1 selecting application 2-5 2 scpi device message details 2.1.1 load application :system:application:load pnoise load application function activates this application. Command :system:application:load pnoise details this function activates an installed application and registers it to the applicatio...
Page 23
2.1 selecting application 2-7 2 scpi device message details :instrument[:select]? Application switch query function reads out the control-targeted application. Query :instrument[:select]? Response parameter application name pnoise phase noise sigana signal analyzer spect spectrum analyzer config con...
Page 25
2.1 selecting application 2-9 2 scpi device message details :instrument:system? Pnoise application status query function reads out the application status. Query :instrument:system? Pnoise response , parameter application status curr executed and targeted for control run executed but not targeted for...
Page 26: 2.1.3 Initialization
Chapter 2 scpi device message details 2-10 2.1.3 initialization :instrument:default initialization function initializes the setting and the status of the selected application. Command :instrument:default example of use to initialize the setting and the status of the selected application. Inst:def :s...
Page 27
2.2 setting basic parameter 2-11 2 scpi device message details 2.2 setting basic parameter this section describes parameters commonly applied to this application, such as frequency and level. Table 2.2-1 basic parameter settings parameter device message [:sense]:frequency:center carrier frequency [:...
Page 28: 2.2.1 Carrier
Chapter 2 scpi device message details 2-12 2.2.1 carrier frequency [:sense]:frequency:center carrier frequency function sets the carrier frequency. Command [:sense]:frequency:center parameter carrier frequency range 10 mhz to the upper limit, depending on the main unit resolution 1 hz suffix code hz...
Page 29
2.2 setting basic parameter 2-13 2 scpi device message details [:sense]:frequency:center? Carrier frequency query function reads out the set carrier frequency. Query [:sense]:frequency:center? Response parameter carrier frequency range 10 mhz to the upper limit, depending on the main unit resolution...
Page 30: 2.2.2 Start
Chapter 2 scpi device message details 2-14 2.2.2 start offset [:sense]:frequency:offset:start frequency start offset function this command sets the start of offset frequency. Command [:sense]:frequency:offset:start parameter start of offset frequency. Range 10 hz, 100 hz, 1 khz suffix code hz ,khz h...
Page 31: 2.2.3 Stop
2.2 setting basic parameter 2-15 2 scpi device message details 2.2.3 stop offset [:sense]:frequency:offset:stop frequency stop offset function this command sets the stop of offset frequency. Command [:sense]:frequency:offset:stop parameter stop of offset frequency range 100 khz, 1 mhz, 10 mhz suffix...
Page 32: 2.2.4 Reference
Chapter 2 scpi device message details 2-16 2.2.4 reference level :display:window[1]:trace:y[:scale]:rlevel reference level function sets the reference level. Command :display:window[1]:trace:y[:scale]:rlevel parameter reference level range −120.00 + offset to 50.00 + offset (pre-amp off) −120.00 + o...
Page 33
2.2 setting basic parameter 2-17 2 scpi device message details :display:window[1]:trace:y[:scale]:rlevel? Reference level query function reads out the reference level. Query :display:window[1]:trace:y[:scale]:rlevel? Response parameter reference level range −120.00 + offset to 50.00 + offset (pre-am...
Page 34: 2.2.5 Rf
Chapter 2 scpi device message details 2-18 2.2.5 rf attenuator [:sense]:power[:rf]:attenuation rf attenuator function sets the attenuator. Command [:sense]:power[:rf]:attenuation parameter attenuator value range 0 to 60 db resolution 2 db step suffix code db db is used when omitted. Initial value 10...
Page 35
2.2 setting basic parameter 2-19 2 scpi device message details [:sense]:power[:rf]:attenuation? Rf attenuator query function reads out the attenuation. Query [:sense]:power[:rf]:attenuation? Response parameter attenuator value range 0 to 60 db resolution 2 db value is returned in db units. Example o...
Page 37: 2.2.7 Level
2.2 setting basic parameter 2-21 2 scpi device message details 2.2.7 level offset :display:window[1]:trace:y[:scale]:rlevel:offset level offset value function sets the offset value of the reference level. Command :display:window[1]:trace:y[:scale]:rlevel:offset parameter offset value range −99.99 to...
Page 40: 2.2.10 Log Scale Line
Chapter 2 scpi device message details 2-24 2.2.10 log scale line :display:window[1]:trace:y[:scale]:line scale lines function this command sets the log scale line of level axis. Command :display:window[1]:trace:y[:scale]:line parameter line value range 10, 16 default 10 example of use to set the log...
Page 41: 2.2.11 Reference Value
2.2 setting basic parameter 2-25 2 scpi device message details 2.2.11 reference value :display:window[1]:trace:y[:scale]:rvalue reference value function this command sets the upper limit of level axis. Command :display:window[1]:trace:y[:scale]:rvalue parameter upper limit range –140 to –50 (log sca...
Page 43: 2.3.2 Display
2.3 utility function 2-27 2 scpi device message details 2.3.1 erase warm up message :display:annotation:wup:erase erase warm up message function erases the warm-up messages displayed right after activation. Command :display:annotation:wup:erase example of use to erase warm-up messages. Disp:ann:wup:...
Page 44: 2.3.3 Title
Chapter 2 scpi device message details 2-28 :display:annotation:title[:state]? Display title query function reads out on/off of the title display. Query :display:annotation:title[:state]? Response parameter title display on/off 1 on 0 off example of use to read out the title display setting. Disp:ann...
Page 45
2.3 utility function 2-29 2 scpi device message details :display:annotation:title:data? Title entry query function reads out the title character string. Query :display:annotation:title:data? Response parameter character string within 32 characters enclosed by double quotation marks (“ ”) or single q...
Page 48
Chapter 2 scpi device message details 2-32 :initiate:mode:continuous continuous measurement function starts continuous measurement. Command :initiate:mode:continuous example of use to perform continuous measurement. Init:mode:cont :initiate:mode:single single measurement function starts single measu...
Page 49
2.4 common measurement function 2-33 2 scpi device message details :initiate[:immediate] initiate function starts measurement in the selected measurement mode. Command :initiate[:immediate] details this command is an asynchronous command. Note that it does not support synchronized control in the con...
Page 50: 2.4.2 Save Result Data
Chapter 2 scpi device message details 2-34 2.4.2 save result data :mmemory:store:trace [[,]] save result data function saves the measurement result into a csv file. Command :mmemory:store:trace [[,]] parameter file name character string within 32 characters (not including an extension) enclosed by d...
Page 51: 2.5 Log Plot Measurement
2.5 log plot measurement 2-35 2 scpi device message details 2.5 log plot measurement this section describes the device messages related to log plot measurement. Table 2.5-1 lists the commands to perform log plot measurement and the queries to read out the results. Table 2.5-1 device messages for log...
Page 52
Chapter 2 scpi device message details 2-36 table 2.5-3 lists the commands to set a parameter for log plot measurement. Table 2.5-3 device messages for setting for log plot measurement parameter parameter device message [:sense]:lplot:average:count average count [:sense]:lplot:average:count? Table 2....
Page 53: 2.5.1 Measure
2.5 log plot measurement 2-37 2 scpi device message details 2.5.1 measure :configure:lplot configure function selects the log plot measurement function. No measurement is performed. Command :configure:lplot example of use to select the log plot measurement. Conf:lpl :initiate:lplot initiate function...
Page 54
Chapter 2 scpi device message details 2-38 :fetch:lplot[n]? Fetch function reads out the result of the log plot measurement. Query :fetch:lplot[n]? Response ,, -999.0,-999.0,-999.0, , (n = 1 or when omitted) (n = 2) ,,, ...... (n = 3) parameter carrier level carrier frequency phase noise level at th...
Page 55
2.5 log plot measurement 2-39 2 scpi device message details :read:lplot[n]? Read function reads out the result after the single measurement of the log plot is performed in the current setting value. Query :read:lplot[n]? Response refer to :fetch:lplot[n]? Example of use to perform the log plot measu...
Page 56: 2.5.2 Average
Chapter 2 scpi device message details 2-40 2.5.2 average count [:sense]:lplot:average:count average count function sets the average count. Command [:sense]:lplot:average:count parameter average count range 1 to 999 resolution 1 initial value 1 example of use to set average count to 10. Lpl:aver:coun...
Page 66
Chapter 2 scpi device message details 2-50..
Page 67
Chapter 3 scpi status register 3-1 3 s c pi status register this chapter describes the scpi commands and the status register for querying application statuses. 3.1 querying measurement status ...............................................................................................................
Page 68
Chapter 3 scpi status register 3-2 3.1 querying measurement status :status:error? Measurement status query function queries the measurement status. Query :status:error? Response parameter measurement status value = bit0 + bit1 + bit2 + bit3 + bit4 + bit5 + bit6 + bit7 + bit8 + bit9 + bit10 + bit11 +...
Page 69
3.2 status:questionable register 3.2 status:questionable register fig. 3.2-1, table 3.2-1, fig. 3.2-2, and table 3.2-2 show the layer structure of the questionable status register. 3-3 voltage (not used) db0 current (not used) db1 time (not used) db2 power (not used) db3 temperature (not used) db4 f...
Page 70
Chapter 3 scpi status register 3-4 table 3.2-3 lists the device messages for the questionable status register. Table 3.2-3 device messages for questionable status register function device message questionable status register event :status:questionable[:event]? Questionable status register condition ...
Page 71
3.2 status:questionable register 3-5 3 s c pi status register :status:questionable[:event]? Questionable status register event function queries the event register of the questionable status register. Query :status:questionable[:event]? Response parameter byte summation of event register resolution 1...
Page 72
Chapter 3 scpi status register 3-6 :status:questionable:enable questionable status register enable function sets the event enable register of the questionable status register. Command :status:questionable:enable parameter byte summation of event enable register resolution 1 range 0 to 65535 example ...
Page 73
3.2 status:questionable register 3-7 3 s c pi status register :status:questionable:ntransition questionable status register negative transition function sets the transition filter (negative transition) of the questionable status register. Command :status:questionable:ntransition parameter byte summa...
Page 74
Chapter 3 scpi status register 3-8 :status:questionable:ptransition questionable status register positive transition function sets the transition filter (negative transition) of the questionable status register. Command :status:questionable:ptransition parameter byte summation of transition filter (...
Page 75
3.2 status:questionable register 3-9 3 s c pi status register :status:questionable:measure[:event]? Questionable measure register event function queries the event register of the questionable measure register. Query :status:questionable[:event]? Response parameter byte summation of event register re...
Page 76
Chapter 3 scpi status register 3-10 :status:questionable:measure:enable questionable measure register enable function sets the event enable register of the questionable measure register. Command :status:questionable:enable parameter byte summation of event enable register resolution 1 range 0 to 655...
Page 77
3.2 status:questionable register 3-11 3 s c pi status register :status:questionable:measure:ntransition questionable measure register negative transition function sets the transition filter (negative transition) of the questionable measure register. Command :status:questionable:ntransition parameter...
Page 78
Chapter 3 scpi status register 3-12 :status:questionable:measure:ptransition questionable measure register positive transition function sets the transition filter (positive transition) of the questionable measure register. Command :status:questionable:ptransition parameter byte summation of transiti...
Page 79
3.3 status:operation register 3.3 status:operation register fig. 3.3-1 and table 3.3-1 show the layer structure of the operation status register. 3-13 calibrating db0 settling db1 ranging (not used) db2 sweeping db3 measuring db4 wainting for trig db5 waiting for arm (not used) db6 correcting (not u...
Page 80
Chapter 3 scpi status register 3-14 :status:operation[:event]? Operation status register event function queries the event register of the operation status register. Query :status:operation[:event]? Response parameter byte summation of event register resolution 1 range 0 to 65535 example of use to qu...
Page 81
3.3 status:operation register 3-15 3 s c pi status register :status:operation:enable operation status register enable function sets the event enable register of the operation status register. Command :status:operation:enable parameter byte summation of event enable register resolution 1 range 0 to 6...
Page 82
Chapter 3 scpi status register 3-16 :status:operation:ntransition operation status register negative transition function sets the transition filter (negative transition) of the operation status register. Command :status:operation:ntransition parameter byte summation of transition filter (negative tr...
Page 83
3.3 status:operation register 3-17 3 s c pi status register :status:operation:ptransition operation status register positive transition function sets the transition filter (positive transition) of the operation status register. Command :status:operation:ptransition parameter byte summation of transi...
Page 84
Chapter 3 scpi status register 3-18..