- DL manuals
- H3C
- Switch
- S5120-EI Series
- Configuration Manual
H3C S5120-EI Series Configuration Manual
Summary of S5120-EI Series
Page 1
H3c s5120-ei switch series irf configuration guide hangzhou h3c technologies co., ltd. Http://www.H3c.Com software version: release 2220 document version: 6w100-20130810
Page 2
Copyright © 2013, hangzhou h3c technologies co., ltd. And its licensors all rights reserved no part of this manual may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means without prior written consent of hangzhou h3c technologies co., ltd. Trademarks h3c, , h3cs, h3cie, h3cne, aolynk, , h 3 car...
Page 3
Preface the h3c s5120-ei documentation set includes 10 configuration guides, which describe the software features for the h3c s5120-ei switch series release 2220, and guide you through the software configuration procedures. These configuration guides also provide configuration examples to help you a...
Page 5
Port numbering in examples the port numbers in this document are for illustration only and might be unavailable on your device. About the s5120-ei documentation set the h3c s5120-ei documentation set includes: category documents purposes product description and specifications marketing brochure desc...
Page 6
Click the links on the top navigation bar to obtain different categories of product documentation: [technical support & documents > technical documents] – provides hardware installation, software upgrading, and software feature configuration and maintenance documentation. [products & solutions] – pr...
Page 7
I contents irf overview ································································································································································· 1 hardware compatibility ·························································································...
Page 8
Ii configuring lacp mad ········································································································································ 21 configuring arp mad ····················································································································...
Page 9
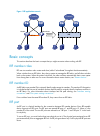
1 irf overview the h3c intelligent resilient framework (irf) technology creates a large irf fabric from multiple switches to provide data center class availability and scalability. Irf virtualization technology offers processing power, interaction, unified management, and uninterrupted maintenance o...
Page 10
2 figure 1 irf application scenario basic concepts this section describes the basic concepts that you might encounter when working with irf. Irf member roles irf uses two member roles: master and slave (called "subordinate" throughout the documentation). When switches form an irf fabric, they elect ...
Page 11
3 for two neighboring devices, their irf physical links must be bound to irf-port 1 on one device and to irf-port 2 on the other. Physical irf port physical irf ports connect irf member devices and must be bound to an irf port. They forward irf protocol packets between irf member devices and data pa...
Page 12
4 forwarding problems on the network. To quickly detect a multi-active collision, configure at least one mad mechanisms (see " irf multi-active detection "). Figure 3 irf split irf merge irf merge occurs when two split irf fabrics reunite or when you configure and connect two independent irf fabrics...
Page 13
5 [master] interface gigabitethernet 3/0/1 [master-gigabitethernet3/0/1] port link-type trunk file system naming conventions on a standalone switch, you can use the name of storage device to access its file system. For more information about storage device naming conventions, see fundamentals config...
Page 14
6 configuration synchronization mechanism irf uses a strict running-configuration synchronization mechanism so all chassis in an irf fabric can work as a single node, and after the master fails, other members can operate normally. In an irf fabric, all chassis get and run the running configuration o...
Page 15
7 detection the mad implementation of the switch detects active irf fabrics with the same layer 3 global configuration by extending the lacp or gratuitous arp protocol. These mad mechanisms identify each irf fabric with a domain id and an active id (the member id of the master). If multiple active i...
Page 16
8 figure 5 lacp mad application scenario arp mad arp mad detects multi-active collisions by using extended gratuitous arp packets that convey the irf domain id and the active id. You can set up arp mad links between neighbor irf member devices, or between each irf member device and an intermediate d...
Page 17
9 figure 6 arp mad application scenario each irf member compares the domain id and the active id in incoming extended gratuitous arp packets with its domain id and active id: • if the domain ids are different, the extended gratuitous arp packet is from a different irf fabric, and the device does not...
Page 18
10 configuring irf read the configuration restrictions and guidelines carefully when you connect and set up an irf fabric. General restrictions and configuration guidelines this section describes the restrictions and configuration guidelines you must follow. Software requirements all irf member swit...
Page 19
11 mad • configure at least one mad mechanism for prompt irf split detection and irf fabric recovery. • if lacp mad or arp mad runs between two irf fabrics, assign each fabric a unique irf domain id. • to exclude a port from the shutdown action that is executed when an irf fabric transits to the rec...
Page 20
12 h3c recommends the following irf fabric setup and configuration procedure: task remarks 1. Planning the irf fabric setup required. 2. Assigning a member id to each irf member switch required. Perform this task on each member switch. 3. Specifying a priority for each member switch required. Perfor...
Page 21
13 • hardware compatibility and restrictions • irf fabric size • master switch • irf physical ports • member id and priority assignment scheme • fabric topology and cabling scheme for more information about hardware and cabling, see the switch installation guide. Assigning a member id to each irf me...
Page 22
14 a member priority change affects the election result at the next master election, but does not cause immediate master re-election. To specify a priority for the switch: step command remarks 1. Enter system view. System-view n/a 2. Specify a priority for the switch. Irf member member-id priority p...
Page 23
15 binding physical ports to irf ports to establish an irf connection between two devices, you must bind at least one physical port to irf-port 1 on one device and to irf-port 2 on the other. For link redundancy and load sharing, bind multiple physical ports to one irf port. When you bind physical p...
Page 24
16 step command remarks 8. Enter ethernet interface view or interface range view. • enter interface range view: { method 1: interface range { interface-type interface-number [ to interface-type interface-number ] } & { method 2: interface range name name [ interface { interface-type interface-number...
Page 25
17 • remote login—remotely log in at a layer 3 interface on any member switch by using a methods including telnet, web, and snmp. For more information, see the chapter on login in fundamentals configuration guide. Accessing the cli of a subordinate switch you can log in to the cli of a subordinate s...
Page 26
18 step command remarks 1. Enter system view. System-view n/a 2. Configure the description of a member. Irf member member-id description text by default, no member switch description is configured. Configuring irf link load sharing mode on an irf port that has multiple links, traffic is balanced acr...
Page 27
19 configuring irf bridge mac persistence an irf fabric by default uses the bridge mac address of the master switch as its bridge mac address. This bridge mac address is used by layer 2 protocols, for example, lacp, to identify the irf fabric, and must be unique on a switched lan for proper communic...
Page 28
20 the software auto-update function automatically propagates the system software image of the master to all members in the irf fabric. If software auto-update is disabled, you must manually update the switch with the system software image of the master. When you add a switch to the irf fabric, the ...
Page 29
21 step command remarks 1. Enter system view. System-view n/a 2. Set the irf link down report delay. Irf link-delay interval the default irf link down report delay is 4 seconds. If your irf fabric requires a quick master/subordinate or irf link switchover or has deployed the bfd or gr feature, h3c r...
Page 30
22 • use dynamic link aggregation mode. Mad is lacp dependent. Even though lacp mad can be configured on both static and dynamic aggregate interfaces, it takes effect only on dynamic aggregate interfaces. • configure link aggregation settings also on the intermediate device. To configure lacp mad: s...
Page 31
23 to configure arp mad: step command remarks 1. Enter system view. System-view n/a 2. Assign a domain id to the irf fabric. Irf domain domain-id the default irf domain id is 0. 3. Create a vlan dedicated to arp mad. Vlan vlan-id the default vlan on the device is vlan 1. 4. Return to system view. Qu...
Page 32
24 caution: excluding a vlan interface and its layer 2 ports from the shutdown action introduces ip collision risks because the vlan interface might be active on both the irf fabric in active state and the irf fabric in recovery state. By default, all ports except the console and physical irf ports ...
Page 33
25 figure 11 active-state irf fabric fails before the irf link is recovered to manually recover an irf fabric in recovery state: step command 1. Enter system view. System-view 2. Change the state of the irf fabric from recovery to active. Mad restore after the irf fabric is recovered, all ports that...
Page 35
27 # change the member id of device b to 2. System-view [deviceb] irf member 1 renumber 2 warning: renumbering the switch number may result in configuration change or loss. Continue? [y/n]:y [deviceb] 2. Power off the devices, connect irf links as shown in figure 12 , and power on the two devices. 3...
Page 36
28 [current domain is: 0]: the assigned domain id is: 0 info: mad lacp only enable on dynamic aggregation interface. # assign ports gigabitethernet 1/0/1 and gigabitethernet 2/0/1 to the aggregate interface. [devicea] interface range gigabitethernet 1/0/1 gigabitethernet 2/0/1 [devicea-if-range] por...
Page 37
29 configuration procedure this example assumes that the system names of device a, device b and device c are devicea, deviceb, and devicec, respectively, before the irf fabric is formed. 1. Assign member ids: # keep the default member id of device a unchanged. # change the member id of device b to 2...
Page 38
30 # enable the spanning tree feature globally on the irf fabric to prevent loops. System-view [devicea] stp enable # connect the arp mad links as shown in figure 13 . # configure the irf fabric to change its bridge mac address as soon as the master leaves. [devicea] undo irf mac-address persistent ...
Page 39
31 index a b c d e f g h i m p s a accessing the irf fabric, 16 application scenario, 1 assigning a member id to each irf member switch, 13 assigning an irf domain id to the irf fabric, 17 b basic concepts, 2 binding physical ports to irf ports, 15 c configuration examples, 26 configuration synchron...