- DL manuals
- H3C
- Switch
- S5120-EI Series
- Configuration Manual
H3C S5120-EI Series Configuration Manual
Summary of S5120-EI Series
Page 1
H3c s5120-ei switch series high availability configuration guide hangzhou h3c technologies co., ltd. Http://www.H3c.Com software version: release 2220 document version: 6w100-20130810
Page 2
Copyright © 2013, hangzhou h3c technologies co., ltd. And its licensors all rights reserved no part of this manual may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means without prior written consent of hangzhou h3c technologies co., ltd. Trademarks h3c, , h3cs, h3cie, h3cne, aolynk, , h 3 car...
Page 3
Preface the h3c s5120-ei documentation set includes 10 configuration guides, which describe the software features for the h3c s5120-ei switch series release 2220, and guide you through the software configuration procedures. These configuration guides also provide configuration examples to help you a...
Page 4
Conventions this section describes the conventions used in this documentation set. Command conventions convention description boldface bold text represents commands and keywords that you enter literally as shown. Italic italic text represents arguments that you replace with actual values. [ ] square...
Page 5
Convention description tip an alert that provides helpful information. Network topology icons represents a generic network device, such as a router, switch, or firewall. Represents a routing-capable device, such as a router or layer 3 switch. Represents a generic switch, such as a layer 2 or layer 3...
Page 6
Category documents purposes software configuration configuration guides describe software features and configuration procedures. Command references provide a quick reference to all available commands. Operations and maintenance release notes provide information about the product release, including t...
Page 7
I contents high availability overview ··········································································································································· 1 availability requirements ······························································································...
Page 8
Ii cfd configuration example ·········································································································································· 27 configuring dldp ················································································································...
Page 9
Iii how smart link works ·········································································································································· 98 smart link collaboration mechanisms ·································································································...
Page 10
1 high availability overview communication interruptions can seriously affect widely-deployed value-added services such as iptv and video conference. Therefore, the basic network infrastructures must be able to provide high availability. The following are the effective ways to improve availability: ...
Page 11
2 high availability technologies increasing mtbf or decreasing mttr can enhance the availability of a network. The high availability technologies described in this section meet the level 2 and level 3 high availability requirements by decreasing mttr. High availability technologies can be classified...
Page 12
3 technology introduction reference track the track module is used to implement collaboration between different modules. The collaboration here involves three parts: the application modules, the track module, and the detection modules. These modules collaborate with one another through collaboration...
Page 13
4 configuring ethernet oam ethernet oam overview ethernet operation, administration and maintenance (oam) is a tool that monitors layer 2 link status and addresses common link-related issues on the "last mile." you can use it to monitor the status of the point-to-point link between two directly conn...
Page 14
5 field description subtype the specific protocol being encapsulated in the ethernet oampdu the value is 0x03. Flags status information of an ethernet oam entity code type of the ethernet oampdu note: throughout this document, a port with ethernet oam enabled is an ethernet oam entity or an oam enti...
Page 15
6 item active ethernet oam mode passive ethernet oam mode transmitting event notification oampdus available available transmitting information oampdus without any tlv available available transmitting loopback control oampdus available unavailable responding to loopback control oampdus available—if b...
Page 16
7 a second in which errored frames appear is called an "errored frame second." remote fault detection information oampdus are exchanged periodically among ethernet oam entities across established oam connections. In a network where traffic is interrupted due to device failures or unavailability, the...
Page 17
8 task remarks configuring errored frame period event detection optional configuring errored frame seconds event detection optional configuring ethernet oam remote loopback enabling ethernet oam remote loopback optional rejecting the ethernet oam remote loopback request from a remote port optional c...
Page 18
9 step command remarks 1. Enter system view. System-view n/a 2. Configure the ethernet oam handshake packet transmission interval. Oam timer hello interval optional. 1000 millisecond by default. 3. Configure the ethernet oam connection timeout timer. Oam timer keepalive interval optional. 5000 milli...
Page 19
10 step command remarks 3. Configure the errored frame period event triggering threshold. Oam errored-frame-period threshold threshold-value optional. 1 by default. Configuring errored frame seconds event detection important: make sure the errored frame seconds triggering threshold is less than the ...
Page 20
11 loopback command to disable ethernet oam remote loopback; and ethernet oam connection timing out. • ethernet oam remote loopback is only applicable to individual links. It is not applicable to link aggregation member ports. In addition, do not assign ports where ethernet oam remote loopback is be...
Page 21
12 step command remarks 3. Reject the ethernet oam remote loopback request from a remote port. Oam loopback reject-request by default, a port does not reject the ethernet oam remote loopback request from a remote port. Displaying and maintaining ethernet oam configuration task command remarks displa...
Page 22
13 configuration procedure 1. Configure device a: # configure gigabitethernet 1/0/1 to operate in passive ethernet oam mode and enable ethernet oam for it. System-view [devicea] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1 [devicea-gigabitethernet1/0/1] oam mode passive [devicea-gigabitethernet1/0/1] oam enable ...
Page 23
14 [devicea] display oam critical-event port : gigabitethernet1/0/1 link status : up event statistic : ------------------------------------------------------------------------- link fault :0 dying gasp : 0 critical event : 0 the output shows that no critical link event occurred on the link between d...
Page 24
15 configuring cfd overview connectivity fault detection (cfd) is an end-to-end per-vlan link layer oam mechanism used for link connectivity detection, fault verification, and fault location. It conforms to ieee 802.1ag cfm and itu-t y.1731. Basic cfd concepts this section explains the concepts of c...
Page 25
16 an ma serves a vlan. Packets sent by the mps in an ma carry the relevant vlan tag. An mp can receive packets sent by other mps in the same ma. The level of an ma equals the level of the md that the ma belongs to. Mp an mp is configured on a port and belongs to an ma. Mps include maintenance assoc...
Page 26
17 configured on the ports of device a through device f. Port 1 of device b is configured with the following mps—a level 5 mip, a level 3 inward-facing mep, a level 2 inward-facing mep, and a level 0 outward-facing mep. Figure 5 cfd grading example mep list a mep list is a collection of configurable...
Page 27
18 is considered faulty and a log is generated. When multiple meps send ccms at the same time, the multipoint-to-multipoint link check is achieved. Ccm frames are multicast frames. Lb similar to ping at the ip layer, lb verifies the connectivity between a source device and a target device. To implem...
Page 28
19 the tst frame, the target mep determines the bit errors by calculating and comparing the content of the tst frame. Tst frames are unicast frames. Protocols and standards • ieee 802.1ag, virtual bridged local area networks amendment 5: connectivity fault management • itu-t y.1731, oam functions an...
Page 29
20 • the port is configured as a mip or an inward-facing mep that can still receive and send cfd messages except ccm messages. For more information about the spanning tree feature, see layer 2—lan switching configuration guide. Configuring basic cfd settings this section provides procedures for conf...
Page 30
21 • service instance without the md name, which takes effect in only cfd ieee 802.1ag. You can create either type of service instance as needed. Creating a service instance with the md name to create a service instance with the md name, create the md and ma for the service instance first. To config...
Page 32
23 table 9 relationship between the interval field value in the ccm message, the interval between ccm messages, and the timeout time of the remote mep the interval field value in the ccm message the interval between ccm messages the timeout time of the remote mep 4 1 second 3.5 seconds 5 10 second 3...
Page 33
24 ttl field in the ltm frames set to the maximum value 255. Based on the ltrs that the mips return, the fault source can be located. To configure lt on meps: step command remarks 1. Find the path between a source mep and a target mep. Cfd linktrace service-instance instance-id mep mep-id { target-m...
Page 35
26 configuring tst the tst function detects bit errors on a link, and monitors and manages the link transmission performance. The tst function takes effect only in cfd ieee 802.1ag. To configure tst: step command remarks 1. Enter system view. System-view n/a 2. Configure tst. Cfd tst service-instanc...
Page 37
28 • the mips of md_b are designed on device c, and are configured on all ports. You should configure the mip generation rule as default. • configure cc to monitor the connectivity among all the meps in md_a and md_b. Configure lb to locate link faults, and use the ais function to suppress the error...
Page 38
29 [deviceb] cfd md md_b level 3 [deviceb] cfd ma ma_b md md_b vlan 100 [deviceb] cfd service-instance 2 md md_b ma ma_b configure device d in the same way as device b. # create md_b (level 3) on device c, create ma_b that serves vlan 100, in md_b, and then create service instance 2 for md_b and ma_...
Page 39
30 [deviceb] cfd mip-rule explicit service-instance 1 # configure the mip generation rule in service instance 2 on device c as default. [devicec] cfd mip-rule default service-instance 2 6. Configure cc: # on device a, enable the sending of ccm frames for mep 1001 in service instance 1 on gigabitethe...
Page 40
31 send:5 received:5 lost:0 after the whole network status is obtained with the cc function, use the lt function to identify the paths between source and target meps and to locate faults. 2. Verify the lt function: # identify the path between mep 1001 and mep 5001 in service instance 1 on device a. ...
Page 41
32 # test the two-way frame delay from mep 1001 to mep 4002 in service instance 1 on device a. [devicea] cfd dm two-way service-instance 1 mep 1001 target-mep 4002 frame delay: reply from 0010-fc00-6514: 10ms reply from 0010-fc00-6514: 9ms reply from 0010-fc00-6514: 11ms reply from 0010-fc00-6514: 5...
Page 42
33 configuring dldp dldp overview background unidirectional links occur when one end of a link can receive packets from the other end, but the other end cannot receive packets sent by the first end. Unidirectional links result in problems such as loops in an stp-enabled network. For example, the lin...
Page 43
34 performs operations such as identifying peer devices, detecting unidirectional links, and shutting down unreachable ports. The auto-negotiation mechanism and dldp work together to make sure that physical/logical unidirectional links are detected and shut down, and to prevent failure of other prot...
Page 44
35 dldp timer description echo timer this timer is set to 10 seconds. It is triggered when a device transits to the probe state or when an enhanced detect is launched. When the echo timer expires and no echo packet has been received from a neighbor device, the state of the link is set to unidirectio...
Page 45
36 table 12 dldp mode and neighbor entry aging dldp mode detecting a neighbor after the corresponding neighbor entry ages out removing the neighbor entry immediately after the entry timer expires triggering the enhanced timer after an entry timer expires normal dldp mode no yes no enhanced dldp mode...
Page 46
37 • non-authentication: { the sending side sets the authentication field and the authentication type field of dldp packets to 0. { the receiving side checks the values of the two fields of received dldp packets and drops the packets where the two fields conflict with the corresponding local configu...
Page 47
38 packet type processing procedure if the corresponding neighbor entry already exists, resets the entry timer and transits to probe state. Normal advertisement packet retrieves the neighbor information if the corresponding neighbor entry does not exist, creates the neighbor entry, triggers the entr...
Page 48
39 packet type processing procedure local port operates in enhanced mode if yes and the local port is not in disable state, sets the state of the corresponding neighbor to unidirectional, and then checks the state of other neighbors. If all the neighbors are unidirectional, transitions the local por...
Page 49
40 table 17 description on dldp neighbor states dldp neighbor state description unknown a neighbor is in this state when it is just detected and is being probed. A neighbor is in this state only when it is being probed. It transits to two way state or unidirectional state after the probe operation f...
Page 50
41 enabling dldp to properly configure dldp on the device, first enable dldp globally, and then enable it on each port. To enable dldp: step command remarks 1. Enter system view. System-view n/a 2. Enable dldp globally. Dldp enable globally disabled by default. 3. Enter layer 2 ethernet interface vi...
Page 51
42 to set the interval to send advertisement packets: step command remarks 1. Enter system view. System-view n/a 2. Set the interval to send advertisement packets. Dldp interval time optional. 5 seconds by default. Note: • the interval for sending advertisement packets applies to all dldp-enabled po...
Page 52
43 if the device is busy, or the cpu usage is high, normal links may be treated as unidirectional links. In this case, you can set the port shutdown mode to manual mode to alleviate the impact caused by false unidirectional link report. To set port shutdown mode: step command remarks 1. Enter system...
Page 53
44 step command 1. Enter system view. System-view 2. Reset dldp state. Dldp reset resetting dldp state in interface view/port group view resetting dldp state in interface view or port group view applies to the current port or all ports in the port group. To reset dldp state in interface view/port gr...
Page 54
45 figure 9 network diagram configuration procedure 1. Configure device a: # enable dldp globally. System-view [devicea] dldp enable # configure gigabitethernet 1/0/49 to operate in full duplex mode and at 1000 mbps, and enable dldp on the port. [devicea] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/49 [devicea-gi...
Page 55
46 # enable dldp globally. System-view [deviceb] dldp enable # configure gigabitethernet 1/0/49 to operate in full duplex mode and at 1000 mbps, and enable dldp on it. [deviceb] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/49 [deviceb-gigabitethernet1/0/49] duplex full [deviceb-gigabitethernet1/0/49] speed 1000 [d...
Page 56
47 neighbor mac address : 0023-8956-3600 neighbor port index : 60 neighbor state : two way neighbor aged time : 12 the output shows that both gigabitethernet 1/0/49 and gigabitethernet 1/0/50 are in advertisement state, which means both links are bidirectional. # enable system information monitoring...
Page 57
48 %jan 18 17:47:35:894 2013 devicea ifnet/3/link_updown: gigabitethernet1/0/50 link status is up. The output shows that the link status of both gigabitethernet 1/0/49 and gigabitethernet 1/0/50 is now up. Manually shutting down unidirectional links network requirements • as shown in figure 10 , dev...
Page 58
49 # configure gigabitethernet 1/0/50 to operate in full duplex mode and at 1000 mbps, and enable dldp on the port. [devicea] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/50 [devicea-gigabitethernet1/0/50] duplex full [devicea-gigabitethernet1/0/50] speed 1000 [devicea-gigabitethernet1/0/50] dldp enable [devicea-g...
Page 59
50 interface gigabitethernet1/0/49 dldp port state : advertisement dldp link state : up the neighbor number of the port is 1. Neighbor mac address : 0023-8956-3600 neighbor port index : 59 neighbor state : two way neighbor aged time : 11 interface gigabitethernet1/0/50 dldp port state : advertisemen...
Page 60
51 system-view [devicea] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/49 [devicea-gigabitethernet1/0/49] shutdown %jan 18 18:16:12:044 2013 devicea ifnet/3/link_updown: gigabitethernet1/0/49 link status is down. [devicea-gigabitethernet1/0/49] quit [devicea] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/50 [devicea-gigabitetherne...
Page 61
52 configuring rrpp rrpp overview the rapid ring protection protocol (rrpp) is a link layer protocol designed for ethernet rings. Rrpp can prevent broadcast storms caused by data loops when an ethernet ring is healthy, and rapidly restore the communication paths between the nodes in the event that a...
Page 62
53 rrpp ring a ring-shaped ethernet topology is called an "rrpp ring". Rrpp rings fall into two types: primary ring and subring. You can configure a ring as either the primary ring or a subring by specifying its ring level. The primary ring is of level 0, and a subring is of level 1. An rrpp domain ...
Page 63
54 primary port and secondary port each master node or transit node has two ports connected to an rrpp ring, one serving as the primary port and the other serving as the secondary port. You can determine the port’s role. 1. In terms of functionality, the primary port and the secondary port of a mast...
Page 64
55 type description common-flush-fdb the master node initiates common-flush-fdb packets to instruct the transit nodes to update their own mac entries and arp/nd entries when an rrpp ring transits to disconnect state. Fdb stands for forwarding database. Complete-flush-fdb the master node initiates co...
Page 65
56 vlans and sending common-flush-fdb packets to instruct all transit nodes to update their own mac entries and arp/nd entries. Link down alarm mechanism the transit node, the edge node or the assistant-edge node sends link-down packets to the master node immediately when they find any of its own po...
Page 66
57 packets frequently. If more subrings are configured or if load balancing is configured for multiple domains, device b and device c will send or receive a mass of edge-hello packets. To reduce edge-hello traffic, you can assign ring 2 and ring 3 to an rrpp ring group configured on the edge node de...
Page 67
58 figure 13 schematic diagram for a tangent-ring network intersecting rings as shown in figure 14 , two or more rings are in the network topology and two common nodes exist between rings. You only need to define an rrpp domain and configure one ring as the primary ring and the other rings as subrin...
Page 68
59 figure 15 schematic diagram for a dual-homed-ring network single-ring load balancing in a single-ring network, you can achieve load balancing by configuring multiple domains. As shown in figure 16 , ring 1 is configured as the primary ring of both domain 1 and domain 2. Domain 1 and domain 2 are ...
Page 69
60 figure 17 schematic diagram for an intersecting-ring load balancing network protocols and standards rfc 3619 extreme networks' ethernet automatic protection switching (eaps) version 1 is related to rrpp. Rrpp configuration task list you can create rrpp domains based on service planning, specify c...
Page 70
61 task remarks configuring an rrpp ring group optional. Perform this task on the edge node and assistant-edge node in the rrpp domain. Note: • rrpp does not have an auto election mechanism, so you must configure each node in the ring network properly for rrpp to monitor and protect the ring network...
Page 71
62 configuration procedure to configure control vlans: step command 1. Enter system view. System-view 2. Enter rrpp domain view. Rrpp domain domain-id 3. Configure the primary control vlan for the rrpp domain. Control-vlan vlan-id configuring protected vlans before configuring rrpp rings in an rrpp ...
Page 73
64 configuration procedure to configure rrpp ports: step command remarks 1. Enter system view. System-view n/a 2. Enter layer 2 ethernet interface view or layer 2 aggregation interface view. Interface interface-type interface-number n/a 3. Configure the link type of the interface as trunk. Port link...
Page 74
65 step command 3. Specify the current device as a transit node of the ring, and specify the primary port and the secondary port. Ring ring-id node-mode transit [ primary-port interface-type interface-number ] [ secondary-port interface-type interface-number ] level level-value specifying an edge no...
Page 75
66 to prevent hello packets of subrings from being looped on the primary ring, enable the primary ring on its master node before enabling the subrings on their separate master nodes. On an edge node or assistant-edge node, enable/disable the primary ring and subrings separately: • enable the primary...
Page 76
67 configuration restrictions and guidelines • you can assign a subring to only one rrpp ring group. Make sure the rrpp ring group configured on the edge node and the rrpp ring group configured on the assistant-edge node contain the same subrings. Otherwise, the rrpp ring group cannot operate proper...
Page 77
68 rrpp configuration examples single ring configuration example networking requirements as shown in figure 18 , • device a, device b, device c, and device d form rrpp domain 1. Specify the primary control vlan of rrpp domain 1 as vlan 4092. Rrpp domain 1 protects vlans 1 through 30. • device a, dev...
Page 78
69 [devicea-gigabitethernet1/0/1] qos trust dot1p [devicea-gigabitethernet1/0/1] port link-type trunk [devicea-gigabitethernet1/0/1] port trunk permit vlan 1 to 30 [devicea-gigabitethernet1/0/1] quit [devicea] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/2 [devicea-gigabitethernet1/0/2] undo link-delay [devicea-gi...
Page 79
70 [deviceb-gigabitethernet1/0/2] port link-type trunk [deviceb-gigabitethernet1/0/2] port trunk permit vlan 1 to 30 [deviceb-gigabitethernet1/0/2] quit # create rrpp domain 1. Configure vlan 4092 as the primary control vlan of rrpp domain 1, and configure the vlans mapped to msti 1 as the protected...
Page 80
71 figure 19 network diagram configuration procedure 1. Configure device a: # create vlans 1 through 30, map these vlans to msti 1, and activate the mst region configuration. System-view [devicea] vlan 1 to 30 [devicea] stp region-configuration [devicea-mst-region] instance 1 vlan 1 to 30 [devicea-m...
Page 81
72 [devicea-rrpp-domain1] protected-vlan reference-instance 1 # configure device a as the master node of primary ring 1, with gigabitethernet 1/0/1 as the primary port and gigabitethernet 1/0/2 as the secondary port, and enable ring 1. [devicea-rrpp-domain1] ring 1 node-mode master primary-port giga...
Page 82
73 # configure device b as a transit node of primary ring 1, with gigabitethernet 1/0/1 as the primary port and gigabitethernet 1/0/2 as the secondary port, and enable ring 1. [deviceb-rrpp-domain1] ring 1 node-mode transit primary-port gigabitethernet 1/0/1 secondary-port gigabitethernet 1/0/2 leve...
Page 83
74 [devicec] rrpp domain 1 [devicec-rrpp-domain1] control-vlan 4092 [devicec-rrpp-domain1] protected-vlan reference-instance 1 # configure device c as a transit node of primary ring 1, with gigabitethernet 1/0/1 as the primary port and gigabitethernet 1/0/2 as the secondary port, and enable ring 1. ...
Page 84
75 # configure device d as the transit node of primary ring 1, with gigabitethernet 1/0/1 as the primary port and gigabitethernet 1/0/2 as the secondary port, and enable ring 1. [deviced-rrpp-domain1] ring 1 node-mode transit primary-port gigabitethernet 1/0/1 secondary-port gigabitethernet 1/0/2 le...
Page 85
76 [devicee] rrpp enable 6. Verify the configuration: use the display command to view rrpp configuration and operational information on each device. Dual homed rings configuration example networking requirements as shown in figure 20 , • device a through device h form rrpp domain 1. Specify the prim...
Page 86
77 figure 20 network diagram configuration procedure 1. Configure device a: # create vlans 1 through 30, map these vlans to msti 1, and activate the mst region configuration. System-view [devicea] vlan 1 to 30 [devicea] stp region-configuration [devicea-mst-region] instance 1 vlan 1 to 30 [devicea-m...
Page 87
78 [devicea] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/3 [devicea-gigabitethernet1/0/3] undo link-delay [devicea-gigabitethernet1/0/3] undo stp enable [devicea-gigabitethernet1/0/3] qos trust dot1p [devicea-gigabitethernet1/0/3] port link-type trunk [devicea-gigabitethernet1/0/3] port trunk permit vlan 1 to 30 ...
Page 88
79 to 802.1p priority. Configure the four ports as trunk ports, and assign them to vlans 1 through 30. [deviceb] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1 [deviceb-gigabitethernet1/0/1] undo link-delay [deviceb-gigabitethernet1/0/1] undo stp enable [deviceb-gigabitethernet1/0/1] qos trust dot1p [deviceb-gigab...
Page 89
80 [deviceb-rrpp-domain1] ring 3 node-mode assistant-edge edge-port gigabitethernet 1/0/3 [deviceb-rrpp-domain1] ring 3 enable [deviceb-rrpp-domain1] quit # enable rrpp. [deviceb] rrpp enable 3. Configure device c: # create vlans 1 through 30, map these vlans to msti 1, and activate the mst region c...
Page 90
81 # create rrpp domain 1. Configure vlan 4092 as the primary control vlan of rrpp domain 1, and configure the vlans mapped to msti 1 as the protected vlans of rrpp domain 1. [devicec] rrpp domain 1 [devicec-rrpp-domain1] control-vlan 4092 [devicec-rrpp-domain1] protected-vlan reference-instance 1 #...
Page 91
82 [deviced-gigabitethernet1/0/2] port trunk permit vlan 1 to 30 [deviced-gigabitethernet1/0/2] quit [deviced] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/3 [deviced-gigabitethernet1/0/3] undo link-delay [deviced-gigabitethernet1/0/3] undo stp enable [deviced-gigabitethernet1/0/3] qos trust dot1p [deviced-gigabit...
Page 92
83 # cancel the physical state change suppression interval setting on gigabitethernet 1/0/1 and gigabitethernet 1/0/2, disable the spanning tree feature, and set the trusted packet priority type to 802.1p priority. Configure the two ports as trunk ports, and assign them to vlans 1 through 30. [devic...
Page 93
84 [devicef-gigabitethernet1/0/1] port link-type trunk [devicef-gigabitethernet1/0/1] port trunk permit vlan 1 to 30 [devicef-gigabitethernet1/0/1] quit [devicef] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/2 [devicef-gigabitethernet1/0/2] undo link-delay [devicef-gigabitethernet1/0/2] undo stp enable [devicef-gi...
Page 94
85 [deviceg-gigabitethernet1/0/2] port trunk permit vlan 1 to 30 [deviceg-gigabitethernet1/0/2] quit # create rrpp domain 1. Configure vlan 4092 as the primary control vlan of rrpp domain 1, and configure the vlans mapped to msti 1 as the protected vlans of rrpp domain 1. [deviceg] rrpp domain 1 [de...
Page 95
86 # configure device h as the master node of subring 5, with gigabitethernet 1/0/1 as the primary port and gigabitethernet 1/0/2 as the secondary port, and enable subring 5. [deviceh-rrpp-domain1] ring 5 node-mode master primary-port gigabitethernet 1/0/1 secondary-port gigabitethernet 1/0/2 level ...
Page 96
87 figure 21 network diagram configuration procedure 1. Configure device a: # create vlans 1 and 2, map vlan 1 to msti 1 and vlan 2 to msti 2, and activate mst region configuration. System-view [devicea] vlan 1 to 2 [devicea] stp region-configuration [devicea-mst-region] instance 1 vlan 1 [devicea-m...
Page 97
88 [devicea-gigabitethernet1/0/2] quit # create rrpp domain 1. Configure vlan 100 as the primary control vlan of rrpp domain 1, and configure the vlan mapped to msti 1 as the protected vlan of rrpp domain 1. [devicea] rrpp domain 1 [devicea-rrpp-domain1] control-vlan 100 [devicea-rrpp-domain1] prote...
Page 98
89 [deviceb-gigabitethernet1/0/2] undo link-delay [deviceb-gigabitethernet1/0/2] undo stp enable [deviceb-gigabitethernet1/0/2] qos trust dot1p [deviceb-gigabitethernet1/0/2] port link-type trunk [deviceb-gigabitethernet1/0/2] port trunk permit vlan 1 2 [deviceb-gigabitethernet1/0/2] quit # cancel t...
Page 99
90 # configure device b as the transit node of primary ring 1, with gigabitethernet 1/0/1 as the primary port and gigabitethernet 1/0/2 as the secondary port, and enable ring 1. [deviceb-rrpp-domain2] ring 1 node-mode transit primary-port gigabitethernet 1/0/1 secondary-port gigabitethernet 1/0/2 le...
Page 100
91 [devicec-gigabitethernet1/0/3] qos trust dot1p [devicec-gigabitethernet1/0/3] port link-type trunk [devicec-gigabitethernet1/0/3] undo port trunk permit vlan 1 [devicec-gigabitethernet1/0/3] port trunk permit vlan 2 [devicec-gigabitethernet1/0/3] port trunk pvid vlan 2 [devicec-gigabitethernet1/0...
Page 101
92 [devicec] rrpp enable 4. Configure device d: # create vlans 1 and 2, map vlan 1 to msti 1 and vlan 2 to msti 2, and activate mst region configuration. System-view [deviced] vlan 1 to 2 [deviced] stp region-configuration [deviced-mst-region] instance 1 vlan 1 [deviced-mst-region] instance 2 vlan 2...
Page 102
93 [deviced-rrpp-domain2] ring 1 node-mode transit primary-port gigabitethernet 1/0/1 secondary-port gigabitethernet 1/0/2 level 0 [deviced-rrpp-domain2] ring 1 enable [deviced-rrpp-domain2] quit # enable rrpp. [deviced] rrpp enable 5. Configure device e: # create vlan 2, map vlan 2 to msti 2, and a...
Page 103
94 # enable rrpp. [devicee] rrpp enable 6. Configure device f: # create vlan 1, map vlan 1 to msti 1, and activate mst region configuration. System-view [devicef] vlan 1 [devicef-vlan1] quit [devicef] stp region-configuration [devicef-mst-region] instance 1 vlan 1 [devicef-mst-region] active region-...
Page 104
95 # create rrpp ring group 1 on device c, and add subrings 2 and 3 to the rrpp ring group. [devicec] rrpp ring-group 1 [devicec-rrpp-ring-group1] domain 2 ring 2 [devicec-rrpp-ring-group1] domain 1 ring 3 8. Verify the configuration: use the display command to view rrpp configuration and operationa...
Page 105
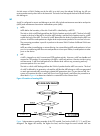
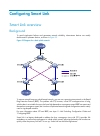
96 configuring smart link smart link overview background to avoid single-point failures and guarantee network reliability, downstream devices are usually dual-homed to upstream devices, as shown in figure 22 . Figure 22 diagram for a dual uplink network to remove network loops on a dual-homed networ...
Page 106
97 • dedicated to dual uplink networks • subsecond convergence • easy to configure terminology smart link group a smart link group consists of only two member ports: the master and the slave ports. At a time, only one port is active for forwarding, and the other port is blocked and in standby state....
Page 107
98 how smart link works link backup mechanism as shown in figure 22 , the link on port1 of device c is the master link, and the link on port2 of device c is the slave link. Typically, port1 is in forwarding state, and port2 is in standby state. When the master link fails, port2 takes over to forward...
Page 108
99 function to monitor the uplink ports of the upstream devices. Monitor link adapts the up/down state of downlink ports to the up/down state of uplink ports, triggering smart link to perform link switchover on the downstream device. For more information about monitor link, see " configuring monitor...
Page 109
100 • disable the spanning tree feature and rrpp on the ports that you want to add to the smart link group, and make sure the ports are not member ports of any aggregation group. Note: a loop may occur on the network during the time when the spanning tree feature is disabled but smart link has not y...
Page 110
101 step command remarks 8. Configure protected vlans for the smart link group. Protected-vlan reference-instance instance-id-list by default, no protected vlan is configured for a smart link group. Configuring member ports for a smart link group you can configure member ports for a smart link group...
Page 111
102 enabling the sending of flush messages the control vlan configured for a smart link group must be different from that configured for any other smart link group. Make sure the configured control vlan already exists, and assign the smart link group member ports to the control vlan. The control vla...
Page 112
103 configuring an associated device configuration prerequisites disable the spanning tree feature on the associated device’s ports that connect to the member ports of the smart link group; otherwise, the ports will discard flush messages when they are not in the forwarding state in case of a topolo...
Page 113
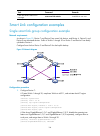
104 task command remarks clear the statistics about flush messages. Reset smart-link statistics available in user view smart link configuration examples single smart link group configuration example network requirements as shown in figure 23 , device c and device d are smart link devices, and device...
Page 114
105 [devicec-gigabitethernet1/0/1] undo stp enable [devicec-gigabitethernet1/0/1] port link-type trunk [devicec-gigabitethernet1/0/1] port trunk permit vlan 1 to 30 [devicec-gigabitethernet1/0/1] quit [devicec] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/2 [devicec-gigabitethernet1/0/2] shutdown [devicec-gigabite...
Page 115
106 [deviced-gigabitethernet1/0/2] shutdown [deviced-gigabitethernet1/0/2] undo stp enable [deviced-gigabitethernet1/0/2] port link-type trunk [deviced-gigabitethernet1/0/2] port trunk permit vlan 1 to 30 [deviced-gigabitethernet1/0/2] quit # create smart link group 1, and configure all vlans mapped...
Page 116
107 [deviceb] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/3 [deviceb-gigabitethernet1/0/3] port link-type trunk [deviceb-gigabitethernet1/0/3] port trunk permit vlan 1 to 30 [deviceb-gigabitethernet1/0/3] undo stp enable [deviceb-gigabitethernet1/0/3] smart-link flush enable control-vlan 10 [deviceb-gigabitethern...
Page 117
108 [devicea] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/2 [devicea-gigabitethernet1/0/2] port link-type trunk [devicea-gigabitethernet1/0/2] port trunk permit vlan 1 to 30 [devicea-gigabitethernet1/0/2] smart-link flush enable control-vlan 10 20 [devicea-gigabitethernet1/0/2] quit 6. Verify the configuration: y...
Page 118
109 figure 24 network diagram configuration procedure 1. Configure device c: # create vlan 1 through vlan 200. Map vlans 1 through 100 to msti 1. Map vlans 101 through 200 to msti 2, and activate mst region configuration. System-view [devicec] vlan 1 to 200 [devicec] stp region-configuration [device...
Page 119
110 # enable role preemption in smart link group 1, enable flush message sending, and configure vlan 10 as the transmit control vlan. [devicec-smlk-group1] preemption mode role [devicec-smlk-group-1] flush enable control-vlan 10 [devicec-smlk-group-1] quit # create smart link group 2, and configure ...
Page 120
111 # create vlan 1 through vlan 200. System-view [deviced] vlan 1 to 200 # configure gigabitethernet 1/0/1 as a trunk port and assign it to vlans 1 through 200. Enable flush message receiving and configure vlan 10 and vlan 110 as the receive control vlans on gigabitethernet 1/0/1. [deviced] interfa...
Page 121
112 protected vlan: reference instance 1 member role state flush-count last-flush-time ----------------------------------------------------------------------------- gigabitethernet1/0/1 master actvie 5 16:37:20 2013/02/21 gigabitethernet1/0/2 slave standby 1 17:45:20 2013/02/21 smart link group 2 in...
Page 122
113 figure 25 network diagram configuration procedure 1. Configure device a: # create vlan 1 through vlan 200. System-view [devicea] vlan 1 to 200 # configure gigabitethernet 1/0/1 and gigabitethernet 1/0/2 as trunk ports and assign them to vlans 1 through 200. Enable flush message receiving and con...
Page 123
114 [devicea-gigabitethernet1/0/1] cfd mep 1002 service-instance 1 outbound [devicea-gigabitethernet1/0/1] cfd mep service-instance 1 mep 1002 enable [devicea-gigabitethernet1/0/1] cfd cc service-instance 1 mep 1002 enable [devicea-gigabitethernet1/0/1] quit # create ma ma_b for the md and configure...
Page 124
115 # shut down gigabitethernet 1/0/1 and gigabitethernet 1/0/2, disable the spanning tree feature on gigabitethernet 1/0/1 and gigabitethernet 1/0/2 separately, configure the ports as trunk ports, and assign them to vlan 1 through vlan 200. [devicec] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1 [devicec-gigabit...
Page 125
116 [devicec] cfd service-instance 1 md md ma ma_a # create a mep list in service instance 1, create and enable outward-facing mep 1001, and enable ccm sending in service instance 1 on gigabitethernet 1/0/1. [devicec] cfd meplist 1001 1002 service-instance 1 [devicec] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1...
Page 126
117 # configure gigabitethernet 1/0/2 as a trunk port and assign it to vlans 1 through 200. Disable the spanning tree feature and enable flush message receiving on it, and configure vlan 10 and vlan 110 as the receive control vlans. [deviced] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/2 [deviced-gigabitethernet1...
Page 127
118 configuring monitor link monitor link overview monitor link is a port collaboration function. Monitor link usually works together with layer 2 topology protocols. The idea is to monitor the states of uplink ports and adapt the up/down state of downlink ports to the up/down state of uplink ports,...
Page 128
119 • downlink ports are the monitoring ports. The state of the downlink ports in a monitor link group adapts to that of the monitor link group. When the state of a monitor link group changes, the state of its member downlink ports change accordingly. The state of the downlink ports in a monitor lin...
Page 130
121 figure 27 network diagram configuration procedure 1. Configure device c: # create vlans 1 through 30, map these vlans to msti 1, and activate mst region configuration. System-view [devicec] vlan 1 to 30 [devicec] stp region-configuration [devicec-mst-region] instance 1 vlan 1 to 30 [devicec-mst-...
Page 131
122 2. Configure device a: # create vlans 1 through 30. System-view [devicea] vlan 1 to 30 # configure gigabitethernet 1/0/1 and gigabitethernet 1/0/2 as trunk ports, assign them to vlans 1 through 30, and enable flush message receiving on them. [devicea] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1 [devicea-gig...
Page 132
123 # configure gigabitethernet 1/0/1 as a trunk port, assign it to vlans 1 through 30, and enable flush message receiving on it. [deviced] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1 [deviced-gigabitethernet1/0/1] port link-type trunk [deviced-gigabitethernet1/0/1] port trunk permit vlan 1 to 30 [deviced-gigab...
Page 133
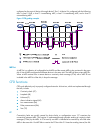
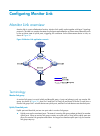
124 configuring track track overview introduction to collaboration the track module works between application and detection modules, as shown in figure 28 . It shields the differences between various detection modules from application modules. Collaboration is enabled after you associate the track m...
Page 134
125 • nqa • interface management module collaboration between the track module and an application module after being associated with an application module, when the status of the track entry changes, the track module notifies the application module, which then takes proper actions. Only static routi...
Page 135
126 • if the consecutive failures reach the specified threshold, the nqa module tells the track module that the tracked object malfunctions. Then the track module sets the track entry to the negative state. • if the specified threshold is not reached, the nqa module tells the track module that the t...
Page 136
127 step command remarks 2. Associate track with interface management. Create a track entry, associate it with the interface management module to monitor the physical status of an interface, and specify the delay time for the track module to notify the associated application module when the track en...
Page 137
128 • the invalid state of the track entry shows that the accessibility of the next hop of the static route is unknown and that the static route is valid. If a static route needs route recursion, the associated track entry must monitor the next hop of the recursive route instead of that of the stati...
Page 138
129 similarly, switch d is the default gateway of the hosts in segment 30.1.1.0/24. Two static routes to 20.1.1.0/24 exist on switch d, with the next hop being switch b and switch c, respectively. These two static routes back up each other as follows: • the static route with switch b as the next hop...
Page 139
130 [switcha-nqa-admin-test-icmp-echo] destination ip 10.2.1.4 [switcha-nqa-admin-test-icmp-echo] next-hop 10.1.1.2 # configure the test frequency as 100 ms. [switcha-nqa-admin-test-icmp-echo] frequency 100 # configure reaction entry 1, specifying that five consecutive probe failures trigger the tra...
Page 140
131 [switchd-nqa-admin-test-icmp-echo] frequency 100 # configure reaction entry 1, specifying that five consecutive probe failures trigger the track module. [switchd-nqa-admin-test-icmp-echo] reaction 1 checked-element probe-fail threshold-type consecutive 5 action-type trigger-only [switchd-nqa-adm...
Page 141
132 notification delay: positive 0, negative 0 (in seconds) reference object: nqa entry: admin test reaction: 1 # display the routing table of switch a. [switcha] display ip routing-table routing tables: public destinations : 10 routes : 10 destination/mask proto pre cost nexthop interface 10.1.1.0/...
Page 142
133 5 packet(s) transmitted 5 packet(s) received 0.00% packet loss round-trip min/avg/max = 1/1/2 ms.
Page 143
134 index a c d e h m o r s t a activating an rrpp domain, 65 associating the track module with a detection module, 125 associating the track module with an application module, 127 availability evaluation, 1 availability requirements, 1 c cfd configuration example, 27 cfd configuration task list, 19...
Page 144
135 troubleshooting dldp, 51.