- DL manuals
- H3C
- Switch
- S5120-EI Series
- Operation Manual
H3C S5120-EI Series Operation Manual
Summary of S5120-EI Series
Page 1
H3c s5120-ei series ethernet switches operation manual hangzhou h3c technologies co., ltd. Manual version: 6w100-20090630 product version: release 2202.
Page 2
Copyright © 2009, hangzhou h3c technologies co., ltd. And its licensors h3c technologies co., ltd., a subsidiary of 3com corporation. All rights reserved no part of this manual may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means without prior written consent of hangzhou h3c technologies co....
Page 3: About This Manual
About this manual organization h3c s5120-ei series ethernet switches operation manual is organized as follows: volume features 00-product overview product overview acronyms ethernet port link aggregation port isolation dldp lldp mstp smart link monitor link vlan gvrp qinq bpdu tunneling 01-access vo...
Page 5
Related documentation in addition to this manual, each h3c s5120-ei series ethernet switch documentation set includes the following: manual description h3c s5120-ei series ethernet switches installation manual it introduces the installation procedure, commissioning, maintenance and monitoring of the...
Page 6
Implementation services are offered to fill resource gaps and ensure the success of your networking projects. More information on 3com maintenance and professional services is available at http://www.H3cnetworks.Com. Contact your authorized reseller or 3com for a complete list of the value-added ser...
Page 7: Table of Contents
I table of contents 1 obtaining the documentation ··················································································································1-1 h3c website ························································································································...
Page 8: Obtaining The Documentation
1-1 1 obtaining the documentation h3c technologies co., ltd. Provides two ways for you to obtain documentation, through which you can obtain the product documentations and those concerning newly added new features. The documentations are available in one of the following ways: z h3c website z softwa...
Page 9: Product Features
2-1 2 product features introduction to product h3c s5120-ei series ethernet switches are gigabit ethernet switching products developed by hangzhou h3c technologies co., ltd. The s5120-ei series switches have abundant service features. They are designed as distribution and access devices for intranet...
Page 10
2-2 volume features login basic system configuration device management file system management http snmp rmon mac address table management system maintaining and debugging information center poe track nqa ntp hotfix cluster management 07-system volume irf stack automatic configuration.
Page 11: Features
3-1 3 features the following sections provide an overview of the main features of each module supported by the s5120-ei series. Access volume table 3-1 features in access volume features description ethernet port this document describes: z combo port configuration z basic ethernet interface configur...
Page 12
3-2 features description lldp lldp enables a device to maintain and manage its own and its immediate neighbor’s device information, based on which the network management system detects and determines the conditions of the communications links. This document describes: z introduction to lldp z perfor...
Page 13: Ip Services Volume
3-3 features description bpdu tunnel bpdu tunneling enables transparently transmission of customer network bpdu frames over the service provider network. This document describes: z introduction to bpdu tunneling z configuring bpdu transparent transmission z configuring destination multicast mac addr...
Page 14
3-4 features description arp address resolution protocol (arp) is used to resolve an ip address into a data link layer address. This document describes: z arp overview z configuring arp z configuring gratuitous arp z proxy arp and local proxy arp configuration z arp attack defense configuration dhcp...
Page 15: Ip Routing Volume
3-5 ip routing volume table 3-3 features in the ip routing volume features description ip routing overview this document describes: z introduction to ip routing and routing table z routing protocol overview static routing a static route is manually configured by the administrator. The proper configu...
Page 16: Qos Volume
3-6 qos volume table 3-5 features in the qos volume features description qos this document describes: z qos overview z qos policy configuration z priority mapping configuration z traffic policing configuration z traffic shaping configuration z line rate configuration z congestion management z traffi...
Page 17: System Volume
3-7 features description port security port security is a mac address-based security mechanism for network access controlling. It is an extension to the existing 802.1x authentication and mac authentication. This document describes: z enabling port security z setting the maximum number of secure mac...
Page 18
3-8 features description basic system configuration basic system configuration involves the configuration of device name, system clock, welcome message, user privilege levels and so on. This document describes: z configuration display z basic configurations z cli features device management through t...
Page 19
3-9 features description system maintenance and debugging for the majority of protocols and features supported, the system provides corresponding debugging information to help users diagnose errors. This document describes: z maintenance and debugging overview z maintenance and debugging configurati...
Page 20
3-10 features description ntp network time protocol (ntp) is the tcp/ip that advertises the accurate time throughout the network. This document describes: z ntp overview z configuring the operation modes of ntp z configuring optional parameters of ntp z configuring access-control rights z configurin...
Page 21: Appendix A Acronyms
A-1 appendix a acronyms # a b c d e f g h i k l m n o p q r s t u v w x z acronyms full spelling # return 10ge ten-gigabitethernet a return aaa authentication, authorization and accounting abc activity based costing abr area border router ac alternating current ack acknowledgement acl access control...
Page 22
A-2 acronyms full spelling bgp border gateway protocol bims branch intelligent management system bootp bootstrap protocol bpdu bridge protocol data unit bri basic rate interface bsr bootstrap router bt bittorrent bt burst tolerance c return ca call appearance ca certificate authority car committed a...
Page 23
A-3 acronyms full spelling cv connectivity verification d return dar deeper application recognition dce data circuit-terminal equipment dd database description ddn digital data network dhcp dynamic host configuration protocol dis designated is dlci data link connection identifier dldp device link de...
Page 24
A-4 acronyms full spelling fdi forward defect indication fec forwarding equivalence class ffd fast failure detection fg forwarding group fib forwarding information base fifo first in first out fqdn full qualified domain name fr frame relay frr fast reroute frtt fairness round trip time ft functional...
Page 25
A-5 acronyms full spelling ibm international business machines icmp internet control message protocol icmpv6 internet control message protocol for ipv6 id identification/identity ieee institute of electrical and electronics engineers ietf internet engineering task force igmp internet group managemen...
Page 26
A-6 acronyms full spelling lacp link aggregation control protocol lacpdu link aggregation control protocol data unit lan local area network lcp link control protocol ldap lightweight directory access protocol ldp label distribution protocol ler label edge router lfib label forwarding information bas...
Page 27
A-7 acronyms full spelling mld multicast listener discovery protocol mld-snooping multicast listener discovery snooping mmc meet-me conference modem modulator-demodulator mp multilink ppp mp-bgp multiprotocol extensions for bgp-4 mpe middle-level pe mp-group multilink point to point protocol group m...
Page 28
A-8 acronyms full spelling nms network management station npdu network protocol data unit npe network provider edge nqa network quality analyzer nsap network service access point nsc netstream collector n-sel nsap selector nssa not-so-stubby area ntdp neighbor topology discovery protocol ntp network...
Page 29
A-9 acronyms full spelling poe power over ethernet pop point of presence pos packet over sdh ppp point-to-point protocol pptp point to point tunneling protocol ppvpn provider-provisioned virtual private network pq priority queuing prc primary reference clock pri primary rate interface ps protection ...
Page 30
A-10 acronyms full spelling rpr resilient packet ring rpt rendezvous point tree rrpp rapid ring protection protocol rsb reservation state block rsoh regenerator section overhead rstp rapid spanning tree protocol rsvp resource reservation protocol rtcp real-time transport control protocol rte route t...
Page 31
A-11 acronyms full spelling spf shortest path first spt shortest path tree ssh secure shell ssm synchronization status marker ssm source-specific multicast st shared tree stm-1 sdh transport module -1 stm-16 sdh transport module -16 stm-16c sdh transport module -16c stm-4c sdh transport module -4c s...
Page 32
A-12 acronyms full spelling v return vbr variable bit rate vci virtual channel identifier ve virtual ethernet vfs virtual file system vlan virtual local area network vll virtual leased lines vod video on demand voip voice over ip vos virtual operate system vpdn virtual private dial-up network vpdn v...
Page 33: Access Volume Organization
Access volume organization manual version 6w100-20090630 product version release 2202 organization the access volume is organized as follows: features description ethernet port this document describes: z combo port configuration z basic ethernet interface configuration z configuring flow control on ...
Page 34
Features description dldp in the use of fibers, link errors, namely unidirectional links, are likely to occur. Dldp is designed to detect such errors. This document describes: z dldp introduction z enabling dldp z setting dldp mode z setting the interval for sending advertisement packets z setting t...
Page 35
Features description gvrp gvrp is a garp application. This document describes: z garp overview z gvrp configuration z garp timers configuration qinq as defined in ieee802.1q, 12 bits are used to identify a vlan id, so a device can support a maximum of 4094 vlans. The qinq feature extends the vlan sp...
Page 36
Features description port mirroring port mirroring copies packets passing through a port to another port connected with a monitoring device for packet analysis to help implement network monitoring and troubleshooting. This document describes: z port mirroring overview z local port mirroring configur...
Page 37: Table of Contents
I table of contents 1 ethernet interface configuration ·············································································································1-1 general ethernet interface configuration ···························································································...
Page 38
1-1 1 ethernet interface configuration general ethernet interface configuration ge and 10ge ports on the s5120-ei series ethernet switches are numbered in the following format: interface type a/b/c. Z a: number of a member device in an irf stack. If no irf stack is formed, this value is 1. Z b: slot...
Page 39
1-2 in case of a combo port, only one interface (either the optical port or the electrical port) is active at a time. That is, once the optical port is active, the electrical port will be inactive automatically, and vice versa. Basic ethernet interface configuration configuring an ethernet interface...
Page 40
1-3 z 10ge ports can be displayed only when 10ge interface module expansion cards are available on the device. Z 10ge ports do not support the duplex command or the speed command. Configuring flow control on an ethernet interface when flow control is enabled on both sides, if traffic congestion occu...
Page 41
1-4 configuring loopback testing on an ethernet interface you can enable loopback testing to check whether the ethernet interface functions properly. Note that no data packets can be forwarded during the testing. Loopback testing falls into the following two categories: z internal loopback testing, ...
Page 42
1-5 to do… use the command… remarks add ethernet interfaces to the manual port group group-member interface-list required configuring an auto-negotiation transmission rate usually, the transmission rate on an ethernet port is determined through negotiation with the peer end, which can be any rate wi...
Page 43
1-6 z this function is available for auto-negotiation-capable gigabit layer-2 ethernet electrical ports only.. Z if you repeatedly use the speed and the speed auto commands to configure the transmission rate on a port, only the latest configuration takes effect. Configuring storm suppression you can...
Page 45
1-8 to do… use the command… remarks interface interface-type interface-number frames in ethernet interface view jumboframe enable the length of 9,216 bytes to pass through all layer 2 ethernet interfaces. Enabling loopback detection on an ethernet interface if a port receives a packet that it sent o...
Page 46
1-9 z loopback detection on a given port is enabled only after the loopback-detection enable command has been configured in both system view and the interface view of the port. Z loopback detection on all ports will be disabled after the configuration of the undo loopback-detection enable command un...
Page 48
1-11 with the storm constrain function enabled on an ethernet interface, you can specify the system to act as follows when the traffic detected exceeds the threshold. Z blocking the interface. In this case, the interface is blocked and thus stops forwarding the traffic of this type till the traffic ...
Page 49
1-12 z for network stability sake, configure the interval for generating traffic statistics to a value that is not shorter than the default. Z the storm constrain function, after being enabled, requires a complete statistical period (specified by the storm-constrain interval command) to collect traf...
Page 50: Table of Contents
I table of contents 1 link aggregation configuration ··············································································································1-1 overview ····························································································································...
Page 51: Overview
1-1 1 link aggregation configuration when configuring link aggregation, go to these sections for information you are interested in: z overview z link aggregation configuration task list z configuring an aggregation group z configuring an aggregate interface z configuring a load sharing mode for load...
Page 52
1-2 z selected: a selected port can forward user traffic. Z unselected: an unselected port cannot forward user traffic. The rate of an aggregate interface is the sum of the selected member ports’ rates. The duplex mode of an aggregate interface is consistent with that of the selected member ports. N...
Page 53
1-3 class-two configurations class-two configurations are listed in table 1-1 . In an aggregation group, if the configurations of a member port are different from the class-two configurations, that member port cannot be a selected port. Table 1-1 class-two configurations type considerations port iso...
Page 54
1-4 z static aggregation limits the number of selected ports in an aggregation group. When the number of the candidate selected ports is under the limit, all the candidate selected ports become selected ports. When the limit is exceeded, set the candidate selected ports with smaller port numbers in ...
Page 55
1-5 for static and dynamic aggregation modes: z in an aggregation group, the port to be a selected port must be the same as the reference port in port attributes, and class-two configurations. To keep these configurations consistent, you should configure the port manually. Z because changing a port ...
Page 56
1-6 configuring an aggregation group z the following ports cannot be assigned to an aggregation group: stack ports, rrpp-enabled ports, mac address authentication-enabled ports, port security-enabled ports, ip source guard-enabled ports, and 802.1x-enabled ports. Z you are recommended not to assign ...
Page 57
1-7 configuring a dynamic aggregation group follow these steps to configure a layer 2 dynamic aggregation group: to do... Use the command... Remarks enter system view system-view — set the system lacp priority lacp system-priority system-priority optional by default, the system lacp priority is 3276...
Page 58
1-8 z enabling linkup/linkdown trap generation for an aggregate interface z shutting down an aggregate interface configuring the description of an aggregate interface follow these steps to configure the description of an aggregate interface: to do... Use the command... Remarks enter system view syst...
Page 59: Aggregation Groups
1-9 to do... Use the command... Remarks enter layer 2 aggregate interface view interface bridge-aggregation interface-number — shut down the aggregate interface shutdown required by default, aggregate interfaces are up. After shutting down an aggregate interface, you are recommended not to use the s...
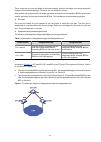
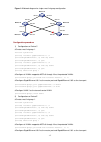
Page 61
1-11 aggregate the ports on each device to form a static link aggregation group, thus balancing outgoing traffic across the member ports. In addition, perform load sharing based on source and destination mac addresses. Figure 1-1 network diagram for layer 2 static aggregation configuration procedure...
Page 62
1-12 figure 1-2 network diagram for layer 2 dynamic aggregation configuration procedure 1) configure device a # configure the device to perform load sharing based on source and destination mac addresses for link aggregation groups. System-view [devicea] link-aggregation load-sharing mode source-mac ...
Page 63
1-13 figure 1-3 network diagram for layer 2 aggregation load sharing mode configuration ge1 /0/1 ge1 /0/2 ge1 /0/3 ge1 /0/4 ge1 /0/1 ge1/0/2 ge1/0/3 ge 1/0 /4 configuration procedure 1) configure device a # configure the global link aggregation load sharing mode as the source mac-based load sharing ...
Page 64: Table of Contents
I table of contents 1 port isolation configuration ·····················································································································1-1 introduction to port isolation ·································································································...
Page 65: Port Isolation Configuration
1-1 1 port isolation configuration when configuring port isolation, go to these sections for information you are interested in: z introduction to port isolation z configuring the isolation group for a single-isolation-group device z displaying and maintaining isolation groups z port isolation config...
Page 66
1-2 displaying and maintaining isolation groups to do… use the command… remarks display the isolation group information on a single-isolation-group device display port-isolate group available in any view port isolation configuration example network requirements z users host a, host b, and host c are...
Page 67
1-3 port-isolate group information: uplink port support: no group id: 1 group members: gigabitethernet1/0/1 gigabitethernet1/0/2 gigabitethernet1/0/3.
Page 68: Table of Contents
I table of contents 1 dldp configuration ··································································································································1-1 overview ····················································································································...
Page 69: Dldp Configuration
1-1 1 dldp configuration when performing dldp configuration, go to these sections for information you are interested in: z overview z dldp configuration task list z enabling dldp z setting dldp mode z setting the interval for sending advertisement packets z setting the delaydown timer z setting the ...
Page 70
1-2 figure 1-2 unidirectional fiber link: a fiber not connected or disconnected device a device b pc ge1/0/50 ge1/0/50 ge1/0/51 ge1/0/51 dldp introduction device link detection protocol (dldp) can detect the link status of a fiber cable or twisted pair. On detecting a unidirectional link, dldp can s...
Page 71
1-3 state indicates… disable a port enters this state when: z a unidirectional link is detected. Z the contact with the neighbor in enhanced mode gets lost. In this state, the port does not receive or send packets other than dldpdus. Delaydown a port in the active, advertisement, or probe dldp link ...
Page 72
1-4 dldp timer description delaydown timer a device in the active, advertisement, or probe dldp link state transits to delaydown state rather than removes the corresponding neighbor entry and transits to the inactive state when it detects a port-down event. When a device transits to this state, the ...
Page 73
1-5 figure 1-3 a case for enhanced dldp mode z in normal dldp mode, only fiber cross-connected unidirectional links (as shown in figure 1-1 ) can be detected. Z in enhanced dldp mode, two types of unidirectional links can be detected. One is fiber cross-connected links (as shown in figure 1-1 ). The...
Page 74
1-6 table 1-4 dldp packet types and dldp states dldp state type of dldp packets sent active advertisement packet with rsy tag advertisement normal advertisement packet probe probe packet disable disable packet and recoverprobe packet when a device transits from a dldp state other than inactive state...
Page 75
1-7 packet type processing procedure if the corresponding neighbor entry does not exist, creates the neighbor entry, triggers the entry timer, and transits to probe state. If the neighbor information it carries conflicts with the corresponding locally maintained neighbor entry, drops the packet. Ech...
Page 76: Dldp Configuration Task List
1-8 the dldp down port sends out a recoverprobe packet, which carries only information about the local port, every two seconds. Upon receiving the recoverprobe packet, the remote end returns a recoverecho packet. Upon receiving the recoverecho packet, the local port checks whether neighbor informati...
Page 77: Enabling Dldp
1-9 z to ensure unidirectional links can be detected, make sure these settings are the same on the both sides: dldp state (enabled/disabled), the interval for sending advertisement packets, authentication mode, and password. Z keep the interval for sending advertisement packets adequate to enable un...
Page 78: Setting The Delaydown Timer
1-10 setting the interval for sending advertisement packets you can set the interval for sending advertisement packets to enable unidirectional links to be detected in time. Follow these steps to set the interval for sending advertisement packets: to do… use the command… remarks enter system view sy...
Page 79: Resetting Dldp State
1-11 z manual mode. This mode applies to networks with low performance, where normal links may be treated as unidirectional links. It protects service packet transmission against false unidirectional links. In this mode, dldp only detects unidirectional links and generates log and traps. The operati...
Page 80
1-12 user-defined port shutdown mode. To enable the port to perform dldp detect again, you can reset the dldp state of the port in one of the following methods: z if the port is shut down with the shutdown command manually, use the undo shutdown command on the port. Z if the port is shut down by dld...
Page 81: Dldp Configuration Example
1-13 to do… use the command… remarks clear the statistics on dldp packets passing through a port reset dldp statistics [interface-type interface-number ] available in user view dldp configuration example dldp configuration example network requirements z device a and device b are connected through tw...
Page 82: Troubleshooting
1-14 [devicea] dldp work-mode enhance # set the port shutdown mode as auto mode. [devicea] dldp unidirectional-shutdown auto # enable dldp globally. [devicea] dldp enable # check the information about dldp. [devicea] display dldp dldp global status : enable dldp interval : 6s dldp work-mode : enhanc...
Page 83
1-15 analysis: the problem can be caused by the following. Z the intervals for sending advertisement packets on device a and device b are not the same. Z dldp authentication modes/passwords on device a and device b are not the same. Solution: make sure the interval for sending advertisement packets,...
Page 84: Table of Contents
I table of contents 1 lldp configuration···································································································································1-1 introduction to lldp ········································································································...
Page 85: Lldp Configuration
1-1 1 lldp configuration when configuring lldp, go to these sections for information you are interested in: z introduction to lldp z lldp configuration task list z performing basic lldp configuration z configuring the encapsulation format for lldpdus z configuring the encapsulation format of the man...
Page 86
1-2 to enable the neighboring devices to be informed of the existence of a device or an lldp operating mode change (from the disable mode to txrx mode, or from the rx mode to tx mode) timely, a device can invoke the fast sending mechanism. In this case, the interval to send lldpdus changes to one se...
Page 87
1-3 type description remarks port description tlv carries ethernet port description system name tlv carries device name system description tlv carries system description system capabilities tlv carries information about system capabilities management address tlv carries the management address, the c...
Page 88: Lldp Configuration Task List
1-4 z extended power-via-mdi tlv, which carries the information about the power supply capability of the current device. Z hardware revision tlv, which carries the hardware version of an med device. Z firmware revision tlv, which carries the firmware version of an med device. Z software revision tlv...
Page 89
1-5 to do… use the command… remarks enter system view system-view — enable lldp globally lldp enable required by default, lldp is enabled globally. Enter ethernet interface view interface interface-type interface-number enter ethernet interface view/port group view enter port group view port-group m...
Page 90
1-6 configuring lldpdu tlvs follow these steps to configure lldpdu tlvs: to do… use the command… remarks enter system view system-view — set the ttl multiplier lldp hold-multiplier value optional 4 by default. Enter ethernet interface view interface interface-type interface-number enter ethernet int...
Page 91
1-7 z to enable med related lldp tlv sending, you need to enable lldp-med capabilities tlv sending first. Conversely, to disable lldp-med capabilities tlv sending, you need to disable the sending of other med related lldp tlvs. Z to disable mac/phy configuration/status tlv sending, you need to disab...
Page 92
1-8 to do… use the command… remarks set the delay period to send lldpdus lldp timer tx-delay value optional 2 seconds by default to enable local device information to be updated on neighboring devices before being aged out, make sure the interval to send lldpdus is shorter than the ttl of the local ...
Page 93
1-9 the configuration does not apply to lldp-cdp packets, which use only snap encapsulation. Configuring the encapsulation format of the management address lldp encapsulates the management address in the form of numbers or strings in management address tlvs and then advertises it. By default, manage...
Page 94: Configuring Lldp Trapping
1-10 tlv for the ip phones to configure the voice vlan automatically. Thus, the voice traffic is confined in the configured voice vlan to be differentiated from other types of traffic. Cdp-compatible lldp operates in one of the follows two modes: z txrx where cdp packets can be transmitted and recei...
Page 95: Lldp Configuration Examples
1-11 follow these steps to configure lldp trap: to do… use the command… remarks enter system view system-view — enter ethernet interface view interface interface-type interface-number enter ethernet interface view/port group view enter port group view port-group manual port-group-name either of the ...
Page 96
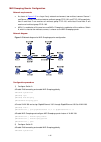
1-12 figure 1-1 network diagram for lldp configuration nms switch a switch b med设备 ge1/0/1 ge1/0/2 ge1/0/1 configuration procedure 1) configure switch a. # enable lldp globally. System-view [switcha] lldp enable # enable lldp on gigabitethernet 1/0/1 and gigabitethernet 1/0/2, setting the lldp opera...
Page 97
1-13 transmit interval : 30s hold multiplier : 4 reinit delay : 2s transmit delay : 2s trap interval : 5s fast start times : 3 port 1 [gigabitethernet1/0/1] : port status of lldp : enable admin status : rx_only trap flag : no roll time : 0s number of neighbors : 1 number of med neighbors : 1 number ...
Page 98
1-14 trap flag : no roll time : 0s number of neighbors : 1 number of med neighbors : 1 number of cdp neighbors : 0 number of sent optional tlv : 0 number of received unknown tlv : 5 port 2 [gigabitethernet1/0/2] : port status of lldp : enable admin status : rx_only trap flag : no roll time : 0s numb...
Page 99
1-15 # configure the link type of the ports to be trunk and enable the voice vlan feature on gigabitethernet 1/0/1 and gigabitethernet 1/0/2. [switcha] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1 [switcha-gigabitethernet1/0/1] port link-type trunk [switcha-gigabitethernet1/0/1] voice vlan 2 enable [switcha-giga...
Page 100: Table of Contents
I table of contents 1 mstp configuration ··································································································································1-1 mstp overview················································································································...
Page 101
Ii configuration prerequisites ···········································································································1-35 configuration procedure················································································································1-36 configuration exa...
Page 102: Mstp Configuration
1-1 1 mstp configuration when configuring mstp, go to these sections for information you are interested in: z mstp overview z configuration task list z configuring the root bridge z configuring leaf nodes z performing mcheck z configuring digest snooping z configuring no agreement check z configurin...
Page 103
1-2 there is one and only one root bridge in the entire network, and the root bridge can change along with changes of the network topology. Therefore, the root bridge is not fixed. After network convergence, the root bridge generates and sends out configuration bpdus at a certain interval, and other...
Page 104
1-3 all the ports on the root bridge are designated ports. Path cost path cost is a reference value used for link selection in stp. By calculating path costs, stp selects relatively robust links and blocks redundant links, and finally prunes the network into a loop-free tree. How stp works the devic...
Page 105
1-4 table 1-2 selection of the optimum configuration bpdu step actions 1 upon receiving a configuration bpdu on a port, the device performs the following: z if the received configuration bpdu has a lower priority than that of the configuration bpdu generated by the port, the device discards the rece...
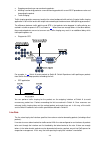
Page 106
1-5 step description 3 the device compares the calculated configuration bpdu with the configuration bpdu on the port of which the port role is to be defined, and acts depending on the comparison result: z if the calculated configuration bpdu is superior, the device considers this port as the designa...
Page 107
1-6 device port name bpdu of port cp1 {2, 0, 2, cp1} device c cp2 {2, 0, 2, cp2} z comparison process and result on each device the following table shows the comparison process and result on each device. Table 1-5 comparison process and result on each device device comparison process bpdu of port af...
Page 108
1-7 device comparison process bpdu of port after comparison z port cp1 receives the configuration bpdu of device a {0, 0, 0, ap2}. Device c finds that the received configuration bpdu is superior to the configuration bpdu of the local port {2, 0, 2, cp1}, and updates the configuration bpdu of cp1. Z ...
Page 109
1-8 figure 1-3 the final calculated spanning tree the spanning tree calculation process in this example is only simplified process. The bpdu forwarding mechanism in stp z upon network initiation, every switch regards itself as the root bridge, generates configuration bpdus with itself as the root, a...
Page 110
1-9 for this reason, as a mechanism for state transition in stp, the newly elected root ports or designated ports require twice the forward delay time before transiting to the forwarding state to ensure that the new configuration bpdu has propagated throughout the network. Z hello time is the time i...
Page 111
1-10 z mstp divides a switched network into multiple regions, each containing multiple spanning trees that are independent of one another. Z mstp prunes a loop network into a loop-free tree, thus avoiding proliferation and endless cycling of packets in a loop network. In addition, it provides multip...
Page 112
1-11 multiple mst regions can exist in a switched network. You can use an mstp command to assign multiple devices to the same mst region. 3) vlan-to-msti mapping table as an attribute of an mst region, the vlan-to-msti mapping table describes the mapping relationships between vlans and mstis. In fig...
Page 113
1-12 during mstp calculation, a boundary port’s role on an msti is consistent with its role on the cist. But that is not true with master ports. A master port on mstis is a root port on the cist. 11) roles of ports mstp calculation involves these port roles: root port, designated port, master port, ...
Page 114
1-13 in mstp, port states fall into the following three: z forwarding: the port learns mac addresses and forwards user traffic; z learning: the port learns mac addresses but does not forward user traffic; z discarding: the port neither learns mac addresses nor forwards user traffic. When in differen...
Page 115: Configuration Task List
1-14 implementation of mstp on devices mstp is compatible with stp and rstp. Stp and rstp protocol packets can be recognized by devices running mstp and used for spanning tree calculation. In addition to basic mstp functions, many special functions are provided for ease of management, as follows: z ...
Page 116
1-15 task remarks configuring an mst region required configuring the work mode of an mstp device optional configuring the timeout factor optional configuring the maximum port rate optional configuring ports as edge ports optional configuring path costs of ports optional configuring port priority opt...
Page 117: Configuring The Root Bridge
1-16 configuring the root bridge configuring an mst region configuration procedure follow these steps to configure an mst region: to do... Use the command... Remarks enter system view system-view — enter mst region view stp region-configuration — configure the mst region name region-name name option...
Page 118
1-17 configuration example # configure the mst region name to be “info”, the mstp revision level to be 1, and vlan 2 through vlan 10 to be mapped to msti 1 and vlan 20 through vlan 30 to msti 2. System-view [sysname] stp region-configuration [sysname-mst-region] region-name info [sysname-mst-region]...
Page 119
1-18 z there is one and only one root bridge in effect in a spanning tree instance. If two or more devices have been designated to be root bridges of the same spanning tree instance, mstp will select the device with the lowest mac address as the root bridge. Z you can specify multiple secondary root...
Page 120
1-19 [sysname] stp mode stp configuring the priority of the current device the priority of a device determines whether it can be elected as the root bridge of a spanning tree. A lower value indicates a higher priority. By setting the priority of a device to a low value, you can specify the device as...
Page 121
1-20 to do... Use the command... Remarks enter system view system-view — configure the maximum hops of the mst region stp max-hops hops optional 20 by default a larger maximum hops setting means a larger size of the mst region. Only the maximum hops configured on the regional root bridge can restric...
Page 122
1-21 configuring timers of mstp mstp involves three timers: forward delay, hello time and max age. You can configure these three parameters for mstp to calculate spanning trees. Configuration procedure follow these steps to configure the timers of mstp: to do... Use the command... Remarks enter syst...
Page 123
1-22 we recommend that you specify the network diameter with the stp root primary command and let mstp automatically calculate optimal settings of these three timers. Configuration example # set the forward delay to 1,600 centiseconds, hello time to 300 centiseconds, and max age to 2,100 centisecond...
Page 124
1-23 configuration procedure follow these steps to configure the maximum rate of a port or a group of ports: to do... Use the command... Remarks enter system view system-view — enter ethernet interface view or layer-2 aggregate interface view interface interface-type interface-number enter interface...
Page 125
1-24 configuration procedure follow these steps to specify a port or a group of ports as edge port(s): to do... Use the command... Remarks enter system view system-view — enter ethernet interface view or layer-2 aggregate interface view interface interface-type interface-number enter interface view ...
Page 126
1-25 configuration procedure follow these steps to set the type of a connected link to p2p: to do... Use the command... Remarks enter system view system-view — enter ethernet interface view or layer-2 aggregate interface view interface interface-type interface-number enter interface view or port gro...
Page 127
1-26 configuration procedure follow these steps to configure the mstp packet format to be supported by a port or a group of ports: to do... Use the command... Remarks enter system view system-view — enter ethernet interface view or layer-2 aggregate interface view interface interface-type interface-...
Page 129: Configuring Leaf Nodes
1-28 [sysname-gigabitethernet1/0/1] undo stp enable configuring leaf nodes configuring an mst region refer to configuring an mst region in the section about root bridge configuration. Configuring the work mode of mstp refer to configuring the work mode of an mstp device in the section about root bri...
Page 130
1-29 table 1-7 link speed vs. Path cost link speed duplex state 802.1d-1998 802.1t private standard 0 — 65535 200,000,000 200,000 10 mbps single port aggregate link 2 ports aggregate link 3 ports aggregate link 4 ports 100 100 100 100 2,000,000 1,000,000 666,666 500,000 2,000 1,800 1,600 1,400 100 m...
Page 131
1-30 z if you change the standard that the device uses in calculating the default path cost, the port path cost value set through the stp cost command will be invalid. Z when the path cost of a port is changed, mstp will re-calculate the role of the port and initiate a state transition. If you use 0...
Page 132: Performing McHeck
1-31 configuration example # set the priority of port gigabitethernet 1/0/1 to 16 in msti 1. System-view [sysname] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1 [sysname-gigabitethernet1/0/1] stp instance 1 port priority 16 setting the link type of a port to p2p refer to setting the link type of a port to p2p in ...
Page 133: Configuring Digest Snooping
1-32 performing mcheck in interface view follow these steps to perform mcheck in interface view: to do... Use the command... Remarks enter system view system-view — enter ethernet interface view or layer-2 aggregate interface view interface interface-type interface-number — perform mcheck stp mcheck...
Page 134
1-33 configuration procedure follow these steps to configure digest snooping: to do... Use the command... Remarks enter system view system-view — enter ethernet interface view or layer-2 aggregate interface view interface interface-type interface-number enter interface view or port group view enter ...
Page 135
1-34 figure 1-6 digest snooping configuration configuration procedure 1) enable digest snooping on device a. # enable digest snooping on gigabitethernet1/0/1. System-view [devicea] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1 [devicea-gigabitethernet1/0/1] stp config-digest-snooping [devicea-gigabitethernet1/0/1...
Page 136
1-35 figure 1-7 rapid state transition of an mstp designated port root port designated port root port blocks other non-edge ports root port changes to forwarding state and sends agreement downstream switch upstream switch agreement proposal for rapid transition designated port changes to forwarding ...
Page 137
1-36 configuration procedure follow these steps to configure no agreement check: to do... Use the command... Remarks enter system view system-view — enter ethernet interface view or layer-2 aggregate interface view interface interface-type interface-number enter interface or port group view enter po...
Page 138
1-37 z loop guard z tc-bpdu attack guard z bpdu dropping among loop guard, root guard and edge port settings, only one function can take effect on a port at the same time. Configuration prerequisites mstp has been correctly configured on the device. Enabling bpdu guard we recommend that you enable b...
Page 139
1-38 enabling root guard we recommend that you enable root guard on a designated port. The root bridge and secondary root bridge of a panning tree should be located in the same mst region. Especially for the cist, the root bridge and secondary root bridge are generally put in a high-bandwidth core r...
Page 140
1-39 by keeping receiving bpdus from the upstream device, a device can maintain the state of the root port and blocked ports. However, due to link congestion or unidirectional link failures, these ports may fail to receive bpdus from the upstream devices. In this case, the downstream device will res...
Page 141
1-40 we recommend that you keep this feature enabled. Enabling bpdu dropping in a stp-enabled network, some users may send bpdu packets to the switch continuously in order to destroy the network. When a switch receives the bpdu packets, it will forward them to other switches. As a result, stp calcul...
Page 143
1-42 system-view [devicea] stp region-configuration # configure the region name, vlan-to-msti mappings and revision level of the mst region. [devicea-mst-region] region-name example [devicea-mst-region] instance 1 vlan 10 [devicea-mst-region] instance 3 vlan 30 [devicea-mst-region] instance 4 vlan 4...
Page 144
1-43 [deviceb] stp enable # view the mst region configuration information that has taken effect. [deviceb] display stp region-configuration oper configuration format selector :0 region name :example revision level :0 instance vlans mapped 0 1 to 9, 11 to 29, 31 to 39, 41 to 4094 1 10 3 30 4 40 3) co...
Page 145
1-44 system-view [deviced] stp region-configuration [deviced-mst-region] region-name example # configure the region name, vlan-to-msti mappings and revision level of the mst region. [deviced-mst-region] instance 1 vlan 10 [deviced-mst-region] instance 3 vlan 30 [deviced-mst-region] instance 4 vlan 4...
Page 146: Table of Contents
I table of contents 1 smart link configuration ·························································································································1-1 smart link overview ············································································································...
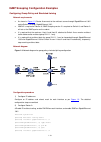
Page 147: Smart Link Configuration
1-1 1 smart link configuration when configuring smart link, go to these sections for information that you are interested in: z smart link overview z configuring a smart link device z configuring an associated device z displaying and maintaining smart link z smart link configuration examples smart li...
Page 148
1-2 master port master port is a port role in a smart link group. When both ports in a smart link group are up, the master port preferentially transits to the forwarding state. Once the master port fails, the slave port takes over to forward traffic. During this period, if the smart link group is no...
Page 149
1-3 z uplink traffic-triggered mac address learning, where update is triggered by uplink traffic. This mechanism is applicable to environments with devices not supporting smart link, including devices of other vendors’. Z flush update where a smart link-enabled device updates its information by tran...
Page 150
1-4 to do… use the command… remarks configure protected vlans for the smart link group protected-vlan reference-instance instance-id-list required by default, no protected vlan is configured for a smart link group. In smart link group view port interface-type interface-number master specify the mast...
Page 151
1-5 z configure vlan 20 for flush update. Configuration procedure system-view [sysname] vlan 20 [sysname-vlan20] quit [sysname] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1 [sysname-gigabitethernet1/0/1] undo stp enable [sysname-gigabitethernet1/0/1] port link-type trunk [sysname-gigabitethernet1/0/1] port trunk...
Page 152
1-6 z configure all the control vlans to receive flush messages. Z if no control vlan is specified for processing flush messages, the device forwards the received flush messages directly without processing them. Z make sure that the receive control vlan is the same as the transmit control vlan confi...
Page 153
1-7 figure 1-2 network diagram for single smart link group configuration device a device b device c device e device d ge1/0/1 ge1/0/2 ge1/0/1 ge1/0/2 ge1/0/2 ge1/0/3 ge1/0/1 ge1/0/1 ge1/0/1 ge1/0/2 ge1/0/2 ge1/0/3 configuration procedure 1) configuration on device c # create smart link group 1. Syst...
Page 154
1-8 [devicee-smlk-group1] port gigabitethernet1/0/2 master [devicee-smlk-group1] port gigabitethernet1/0/1 slave # configure vlan 1 as the transmit control vlan. [devicee-smlk-group1] flush enable 3) configuration on device b # configure vlan 1 as the receive control vlan for gigabitethernet 1/0/1, ...
Page 155
1-9 z the traffic of vlan 1 through vlan 200 on device c are dually uplinked to device a by device b and device d. Implement load sharing to uplink the traffic of vlan 1 through vlan 100 and the traffic of vlan 101 through vlan 200 over different links to device a. Z implement dual link backup on de...
Page 156
1-10 # configure protected vlans for smart link group 1. [devicec-smlk-group1] protected-vlan reference-instance 0 # configure gigabitethernet 1/0/1 as the master port and gigabitethernet 1/0/2 as the slave port. [devicec-smlk-group1] port gigabitethernet1/0/1 master [devicec-smlk-group1] port gigab...
Page 157
1-11 [deviced-gigabitethernet1/0/1] smart-link flush enable control-vlan 10 101 [deviced-gigabitethernet1/0/1] quit [deviced] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/2 [deviced-gigabitethernet1/0/2] port link-type trunk [deviced-gigabitethernet1/0/2] port trunk permit vlan 1 to 200 [deviced-gigabitethernet1/0...
Page 158: Table of Contents
I table of contents 1 monitor link configuration ······················································································································1-1 overview ························································································································...
Page 159: Monitor Link Configuration
1-1 1 monitor link configuration when configuring monitor link, go to these sections for information you are interested in: z overview z configuring monitor link z displaying and maintaining monitor link z monitor link configuration example overview monitor link is a port collaboration function used...
Page 160: Configuring Monitor Link
1-2 do not manually shut down or bring up the downlink ports in a monitor link group. Configuring monitor link configuration prerequisites before assigning a port to a monitor link group, make sure the port is not the member port of any aggregation group. Configuration procedure follow these steps t...
Page 161
1-3 configuration procedure system-view [sysname] monitor-link group 1 [sysname-mtlk-group1] port gigabitethernet 1/0/1 uplink [sysname-mtlk-group1] port gigabitethernet 1/0/2 downlink displaying and maintaining monitor link to do… use the command… remarks display monitor link group information disp...
Page 162
1-4 [devicec] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1 [devicec-gigabitethernet1/0/1] undo stp enable [devicec-gigabitethernet1/0/1] quit [devicec] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/2 [devicec-gigabitethernet1/0/2] undo stp enable [devicec-gigabitethernet1/0/2] quit [devicec] smart-link group 1 # configure the s...
Page 163
1-5 [deviced-mtlk-group1] port gigabitethernet 1/0/1 uplink [deviced-mtlk-group1] port gigabitethernet 1/0/2 downlink # configure vlan 1 as the control vlan for receiving flush messages on gigabitethernet 1/0/1 and gigabitethernet 1/0/2. [deviced-mtlk-group1] quit [deviced] interface gigabitethernet...
Page 164: Table of Contents
I table of contents 1 vlan configuration ··································································································································1-1 introduction to vlan ········································································································...
Page 165: Vlan Configuration
1-1 1 vlan configuration when configuring vlan, go to these sections for information you are interested in: z introduction to vlan z configuring basic vlan settings z configuring basic settings of a vlan interface z port-based vlan configuration z mac-based vlan configuration z protocol-based vlan c...
Page 166
1-2 2) confining broadcast traffic within individual vlans. This reduces bandwidth waste and improves network performance. 3) improving lan security. By assigning user groups to different vlans, you can isolate them at layer 2. To enable communication between vlans, routers or layer 3 switches are r...
Page 167
1-3 z the ethernet ii encapsulation format is used here. Besides the ethernet ii encapsulation format, other encapsulation formats, including 802.2 llc, 802.2 snap, and 802.3 raw, are also supported by ethernet. The vlan tag fields are also added to frames encapsulated in these formats for vlan iden...
Page 168
1-4 z as the default vlan, vlan 1 cannot be created or removed. Z you cannot manually create or remove vlans reserved for special purposes. Z dynamic vlans cannot be removed with the undo vlan command. Z a vlan with a qos policy applied cannot be removed. Z for isolate-user-vlans or secondary vlans,...
Page 169
1-5 before creating a vlan interface for a vlan, create the vlan first. Port-based vlan configuration introduction to port-based vlan port-based vlans group vlan members by port. A port forwards traffic for a vlan only after it is assigned to the vlan. Port link type you can configure the link type ...
Page 170
1-6 z do not set the voice vlan as the default vlan of a port in automatic voice vlan assignment mode. Otherwise, the system prompts error information. For information about voice vlan, refer to voice vlan configuration . Z the local and remote ports must use the same default vlan id for the traffic...
Page 171
1-7 in vlan view, only assign the layer-2 ethernet interface to the current vlan. 2) in interface or port group view follow these steps to assign an access port (in interface view) or multiple access ports (in port group view) to a vlan: to do… use the command… remarks enter system view system-view ...
Page 172
1-8 follow these steps to assign a trunk port to one or multiple vlans: to do… use the command… remarks enter system view system-view — enter ethernet interface view interface interface-type interface-number enter layer-2 aggregate interface view interface bridge-aggregation interface-number enter i...
Page 173
1-9 to do… use the command… remarks enter system view system-view — enter ethernet interface view interface interface-type interface-number enter layer-2 aggregate interface view interface bridge-aggregation interface-number enter interface view or port group view enter port group view port-group ma...
Page 174: Mac-Based Vlan Configuration
1-10 mac-based vlan configuration introduction to mac-based vlan mac-based vlans group vlan members by mac address. They only apply to untagged frames. When receiving an untagged frame, the device looks up the list of mac-to-vlan mappings based on the mac address of the frame for a match. If a match...
Page 175
1-11 to do... Use the command... Remarks enter ethernet interface view interface interface-type interface-number enter ethernet interface view or port group view enter port group view port-group manual port-group-name use either command. In ethernet interface view, the subsequent configurations appl...
Page 176
1-12 configuring a protocol-based vlan follow these steps to configure a protocol-based vlan: to do… use the command… remarks enter system view system-view — enter vlan view vlan vlan-id required if the specified vlan does not exist, this command creates the vlan first. Create a protocol template fo...
Page 177
1-13 z do not configure both the dsap-id and ssap-id arguments in the protocol-vlan command as 0xe0 or 0xff when configuring the user-defined template for llc encapsulation. Otherwise, the encapsulation format of the matching packets will be the same as that of the ipx llc or ipx raw packets respect...
Page 178
1-14 to do… use the command… remarks associate an ip subnet with the current vlan ip-subnet-vlan [ ip-subnet-index ] ip ip-address [ mask ] required the ip network segment or ip address to be associated with a vlan cannot be a multicast network segment or a multicast address. Return to system view q...
Page 180
1-16 [devicea] vlan 2 [devicea-vlan2] quit [devicea] vlan 100 [devicea-vlan100] vlan 6 to 50 please wait... Done. # enter gigabitethernet 1/0/1 interface view. [devicea] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1 # configure gigabitethernet 1/0/1 as a trunk port and configure its default vlan id as 100. [devic...
Page 181
1-17 vlan permitted: 2, 6-50, 100 trunk port encapsulation: ieee 802.1q port priority: 0 peak value of input: 0 bytes/sec, at 2000-04-26 12:01:40 peak value of output: 0 bytes/sec, at 2000-04-26 12:01:40 last 300 seconds input: 0 packets/sec 0 bytes/sec -% last 300 seconds output: 0 packets/sec 0 by...
Page 182: Overview
2-1 2 isolate-user-vlan configuration when configuring an isolate-user vlan, go to these sections for information you are interested in: z overview z configuring isolate-user-vlan z displaying and maintaining isolate-user-vlan z isolate-user-vlan configuration example overview an isolate-user-vlan a...
Page 183
2-2 3) assign non-trunk ports to the isolate-user-vlan and ensure that at least one port takes the isolate-user-vlan as its default vlan; 4) assign non-trunk ports to each secondary vlan and ensure that at least one port in a secondary vlan takes the secondary vlan as its default vlan; 5) associate ...
Page 184
2-3 displaying and maintaining isolate-user-vlan to do... Use the command... Remarks display the mapping between an isolate-user-vlan and its secondary vlan(s) display isolate-user-vlan [ isolate-user-vlan-id ] available in any view isolate-user-vlan configuration example network requirements z conn...
Page 185
2-4 [deviceb] vlan 2 [deviceb-vlan2] port gigabitethernet 1/0/2 [deviceb-vlan2] quit # associate the isolate-user-vlan with the secondary vlans. [deviceb] isolate-user-vlan 5 secondary 2 to 3 2) configure device c # configure the isolate-user-vlan. System-view [devicec] vlan 6 [devicec-vlan6] isolat...
Page 186
2-5 gigabitethernet 1/0/2 gigabitethernet 1/0/5 vlan id: 3 vlan type: static isolate-user-vlan type : secondary route interface: not configured description: vlan 0003 name: vlan 0003 tagged ports: none untagged ports: gigabitethernet 1/0/1 gigabitethernet 1/0/5.
Page 187: Voice Vlan Configuration
3-1 3 voice vlan configuration when configuring a voice vlan, go to these sections for information you are interested in: z overview z configuring a voice vlan z displaying and maintaining voice vlan z voice vlan configuration overview a voice vlan is configured specially for voice traffic. After as...
Page 188
3-2 voice vlan assignment modes a port can be assigned to a voice vlan in one of the following two modes: z in automatic mode, the system matches the source mac addresses in the untagged packets sent when the ip phone is powered on against the oui addresses. If a match is found, the system automatic...
Page 189: Configuring A Voice Vlan
3-3 if an ip phone sends tagged voice traffic and its connecting port is configured with 802.1x authentication and guest vlan, you should assign different vlan ids for the voice vlan, the default vlan of the connecting port, and the 802.1x guest vlan. Z the default vlans for all ports are vlan 1. Yo...
Page 190
3-4 setting a port to operate in automatic voice vlan assignment mode follow these steps to set a port to operate in automatic voice vlan assignment mode: to do... Use the command... Remarks enter system view system-view — set the voice vlan aging time voice vlan aging minutes optional 1440 minutes ...
Page 191
3-5 to do... Use the command... Remarks add a recognizable oui address voice vlan mac-address oui mask oui-mask[ description text] optional by default, each voice vlan has default oui addresses configured. Refer to table 3-1 for the default oui addresses of different vendors. Enter interface view in...
Page 192
3-6 voice vlan configuration examples automatic voice vlan mode configuration example network requirements as shown in figure 3-1 , z the mac address of ip phone a is 0011-1100-0001. The phone connects to a downstream device named pc a whose mac address is 0022-1100-0002 and to gigabitethernet 1/0/1...
Page 193
3-7 [devicea] voice vlan mac-address 0011-1100-0001 mask ffff-ff00-0000 description ip phone a [devicea] voice vlan mac-address 0011-2200-0001 mask ffff-ff00-0000 description ip phone b # configure gigabitethernet 1/0/1 to operate in automatic voice vlan assignment mode. (optional. By default, a por...
Page 194
3-8 manual voice vlan assignment mode configuration example network requirements z create vlan 2 and configure it as a voice vlan permitting only voice traffic to pass through. Z the ip phones send untagged voice traffic. Configure gigabitethernet 1/0/1 as a hybrid port. Z configure gigabitethernet ...
Page 195
3-9 verification # display the oui addresses, oui address masks, and description strings supported currently. Display voice vlan oui oui address mask description 0001-e300-0000 ffff-ff00-0000 siemens phone 0003-6b00-0000 ffff-ff00-0000 cisco phone 0004-0d00-0000 ffff-ff00-0000 avaya phone 0011-2200-...
Page 196: Table of Contents
I table of contents 1 gvrp configuration ··································································································································1-1 introduction to gvrp ········································································································...
Page 197: Gvrp Configuration
1-1 1 gvrp configuration the garp vlan registration protocol (gvrp) is a garp application. It functions based on the operating mechanism of garp to maintain and propagate dynamic vlan registration information for the gvrp devices on the network. When configuring gvrp, go to these sections for inform...
Page 198
1-2 z hold timer –– when a garp application entity receives the first registration request, it starts a hold timer and collects succeeding requests. When the timer expires, the entity sends all these requests in one join message. This helps you save bandwidth. Z join timer –– a garp participant send...
Page 199
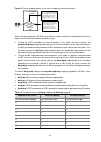
1-3 garp message format figure 1-1 garp message format figure 1-1 illustrates the garp message format. Table 1-1 describes the garp message fields. Table 1-1 description on the garp message fields field description value protocol id protocol identifier for garp 1 message one or multiple messages, ea...
Page 200: Gvrp Configuration Task List
1-4 about active vlan members and through which port they can be reached. It thus ensures that all gvrp participants on a bridged lan maintain the same vlan registration information. The vlan registration information propagated by gvrp includes both manually configured local static entries and dynam...
Page 201: Configuring Garp Timers
1-5 to do… use the command… remarks enter ethernet interface view or layer 2 aggregate interface view interface interface-type interface-number enter ethernet interface view, layer 2 aggregate interface view, or port-group view enter port-group view port-group manual port-group-name required perform...
Page 202
1-6 to do… use the command… remarks enter ethernet or layer 2 aggregate interface view interface interface-type interface-number enter ethernet interface view, layer 2 aggregate interface view, or port-group view enter port-group view port-group manual port-group-name required perform either of the ...
Page 203: Gvrp Configuration Examples
1-7 to do… use the command… remarks display the current gvrp state display gvrp state interface interface-type interface-number vlan vlan-id available in any view display statistics about gvrp display gvrp statistics [ interface interface-list ] available in any view display the global gvrp state di...
Page 204
1-8 [deviceb] gvrp # configure port gigabitethernet 1/0/1 as a trunk port, allowing all vlans to pass through. [deviceb] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1 [deviceb-gigabitethernet1/0/1] port link-type trunk [deviceb-gigabitethernet1/0/1] port trunk permit vlan all # enable gvrp on trunk port gigabitet...
Page 205
1-9 [devicea-gigabitethernet1/0/1] quit # create vlan 2 (a static vlan). [devicea] vlan 2 2) configure device b # enable gvrp globally. System-view [deviceb] gvrp # configure port gigabitethernet 1/0/1 as a trunk port, allowing all vlans to pass through. [deviceb] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1 [de...
Page 206
1-10 [devicea] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1 [devicea-gigabitethernet1/0/1] port link-type trunk [devicea-gigabitethernet1/0/1] port trunk permit vlan all # enable gvrp on gigabitethernet 1/0/1 and set the gvrp registration type to forbidden on the port. [devicea-gigabitethernet1/0/1] gvrp [device...
Page 207: Table of Contents
I table of contents 1 qinq configuration ···································································································································1-1 introduction to qinq ·······································································································...
Page 208: Qinq Configuration
1-1 1 qinq configuration when configuring qinq, go to these sections for information you are interested in: z introduction to qinq z qinq configuration task list z configuring basic qinq z configuring selective qinq z configuring the tpid value in vlan tags z qinq configuration examples throughout t...
Page 209
1-2 figure 1-1 schematic diagram of the qinq feature network service provider network vlan 1~10 vlan 1~10 vlan 1~20 vlan 1~20 vlan 3 vlan 3 vlan 4 vlan 4 customer network a customer network a customer network b customer network b as shown in figure 1-1 , customer network a has cvlans 1 through 10, w...
Page 210
1-3 figure 1-2 single-tagged frame structure vs. Double-tagged ethernet frame structure the default maximum transmission unit (mtu) of an interface is 1500 bytes. The size of an outer vlan tag is 4 bytes. Therefore, you are recommended to increase the mtu of each interface on the service provider ne...
Page 211
1-4 figure 1-3 vlan tag structure of an ethernet frame the device determines whether a received frame carries a svlan tag or a cvlan tag by checking the corresponding tpid value. Upon receiving a frame, the device compares the configured tpid value with the value of the tpid field in the frame. If t...
Page 212: Qinq Configuration Task List
1-5 qinq configuration task list table 1-2 qinq configuration task list configuration task remarks configuring basic qinq optional configuring selective qinq configuring an outer vlan tagging policy optional configuring the tpid value in vlan tags optional z qinq requires configurations only on the ...
Page 213: Qinq Configuration Examples
1-6 qinq condition are handled with selective qinq on this port first, and the left frames are handled with basic qinq. Follow these steps to configure an outer vlan tagging policy: to do... Use the command... Remarks enter system view system-view — enter ethernet or layer-2 aggregate interface view...
Page 214
1-7 z customer a1, customer a2, customer b1 and customer b2 are edge devices on the customer network. Z third-party devices with a tpid value of 0x8200 are deployed between provider a and provider b. Make configuration to achieve the following: z frames of vlan 200 through vlan 299 can be exchanged ...
Page 215
1-8 [providera] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/2 [providera-gigabitethernet1/0/2] port link-type hybrid [providera-gigabitethernet1/0/2] port hybrid pvid vlan 50 [providera-gigabitethernet1/0/2] port hybrid vlan 50 untagged # enable basic qinq on gigabitethernet 1/0/2. [providera-gigabitethernet1/0/2...
Page 216
1-9 configure the third-party devices between provider a and provider b as follows: configure the port connecting gigabitethernet 1/0/3 of provider a and that connecting gigabitethernet 1/0/3 of provider b to allow tagged frames of vlan 10 and 50 to pass through. Comprehensive selective qinq configu...
Page 217
1-10 [providera] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1 [providera-gigabitethernet1/0/1] port link-type hybrid [providera-gigabitethernet1/0/1] port hybrid vlan 1000 2000 untagged # tag cvlan 10 frames with svlan 1000. [providera-gigabitethernet1/0/1] qinq vid 1000 [providera-gigabitethernet1/0/1-vid-1000]...
Page 218
1-11 [providerb-gigabitethernet1/0/2] port link-type hybrid [providerb-gigabitethernet1/0/2] port hybrid vlan 2000 untagged # tag cvlan 20 frames with svlan 2000. [providerb-gigabitethernet1/0/2] qinq vid 2000 [providerb-gigabitethernet1/0/2-vid-2000] raw-vlan-id inbound 20 # set the tpid value in t...
Page 219: Table of Contents
I table of contents 1 bpdu tunneling configuration················································································································1-1 introduction to bpdu tunneling ·······································································································...
Page 220: Bpdu Tunneling Configuration
1-1 1 bpdu tunneling configuration when configuring bpdu tunneling, go to these sections for information you are interested in: z introduction to bpdu tunneling z configuring bpdu tunneling z bpdu tunneling configuration examples introduction to bpdu tunneling as a layer 2 tunneling technology, bpdu...
Page 221
1-2 3) the encapsulated layer 2 protocol packet (called bridge protocol data unit, bpdu) is forwarded to pe 2 at the other end of the service provider network, which decapsulates the packet, restores the original destination mac address of the packet, and then sends the packet to user a network 2. D...
Page 222
1-3 to allow each network to calculate an independent spanning tree with stp, bpdu tunneling was introduced. Bpdu tunneling delivers the following benefits: z bpdus can be transparently transmitted. Bpdus of the same customer network can be broadcast in a specific vlan across the service provider ne...
Page 223: Configuring Bpdu Tunneling
1-4 configuring bpdu tunneling configuration prerequisites z before configuring bpdu tunneling for a protocol, enable the protocol in the customer network first. Z assign the port on which you want to enable bpdu tunneling on the pe device and the connected port on the ce device to the same vlan. Z ...
Page 224
1-5 enabling bpdu tunneling for a protocol in layer 2 aggregate interface view follow these steps to enable bpdu tunneling for a protocol in layer 2 aggregate interface view: to do… use the command… remarks enter system view system-view — enter layer 2 aggregate interface view interface bridge-aggre...
Page 225
1-6 it is required that, after the configuration, ce 1 and ce 2 implement consistent spanning tree calculation across the service provider network, and that the destination multicast mac address carried in bpdus be 0x0100-0ccd-cdd0. Figure 1-3 network diagram for configuring bpdu tunneling for stp c...
Page 226
1-7 bpdu tunneling for pvst configuration example network requirements as shown in figure 1-4 : z ce 1 and ce 2 are edges devices on the geographically dispersed network of user a; pe 1 and pe 2 are edge devices on the service provider network. Z all ports used to connect devices in the service prov...
Page 227
1-8 [pe2] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/2 [pe2-gigabitethernet1/0/2] port link-type trunk [pe2-gigabitethernet1/0/2] port trunk permit vlan all # disable stp on gigabitethernet 1/0/2, and then enable bpdu tunneling for stp and pvst on it. [pe2-gigabitethernet1/0/2] undo stp enable [pe2-gigabitethern...
Page 228: Table of Contents
I table of contents 1 ethernet oam configuration ....................................................................................................................1-1 ethernet oam overview ................................................................................................................
Page 229: Ethernet Oam Configuration
1-1 1 ethernet oam configuration when configuring the ethernet oam function, go to these sections for information you are interested in: z ethernet oam overview z ethernet oam configuration task list z configuring basic ethernet oam functions z configuring link monitoring z enabling oam loopback tes...
Page 230
1-2 figure 1-1 formats of different types of ethernet oampdus the fields in an oampdu are described as follows: table 1-1 description of the fields in an oampdu field description dest addr destination mac address of the ethernet oampdu. It is a slow protocol multicast address 0180c2000002. Source ad...
Page 231
1-3 ethernet oam connection establishment ethernet oam connection is the base of all the other ethernet oam functions. Oam connection establishment is also known as the discovery phase, where an ethernet oam entity discovers remote oam entities and establishes sessions with them. In this phase, inte...
Page 232
1-4 the interval to send information oampdus is determined by a timer. Up to ten information oampdus can be sent in a second. Link monitoring error detection in an ethernet is difficult, especially when the physical connection in the network is not disconnected but network performance is degrading g...
Page 233
1-5 table 1-5 critical link error events ethernet oam link events description link fault peer link signal is lost. Dying gasp an unexpected fault, such as power failure, occurred. Critical event an undetermined critical event happened. As information oampdus are exchanged periodically across establi...
Page 235
1-7 follow these steps to configure errored frame event detection: to do… use the command… remarks enter system view system-view — configure the errored frame event detection interval oam errored-frame period period-value optional 1 second by default configure the errored frame event triggering thre...
Page 236
1-8 enabling oam loopback testing follow these steps to enable ethernet oam loopback testing: to do… use the command… remarks enter system view system-view — enter ethernet port view interface interface-type interface-number — enable ethernet oam loopback testing oam loopback required disabled by de...
Page 237
1-9 to do… use the command… remarks clear statistics on ethernet oam packets and ethernet oam link error events reset oam [ interface interface-type interface-number] available in user view only ethernet oam configuration example network requirements z enable ethernet oam on device a and device b to...
Page 238
1-10 -------------------------------------------------------------------------- errored-symbol event period(in seconds) : 1 errored-symbol event threshold : 1 errored-frame event period(in seconds) : 20 errored-frame event threshold : 10 errored-frame-period event period(in ms) : 1000 errored-frame-...
Page 239: Table of Contents
I table of contents 1 connectivity fault detection configuration ···························································································1-1 overview ···································································································································...
Page 240: Overview
1-1 1 connectivity fault detection configuration when configuring cfd, go to these sections for information you are interested in: z overview z cfd configuration task list z basic configuration tasks z configuring cc on meps z configuring lb on meps z configuring lt on meps z displaying and maintain...
Page 241
1-2 figure 1-1 two nested mds cfd exchanges messages and performs operations on a per-domain basis. By planning mds properly in a network, you can use cfd to locate failure points rapidly. Maintenance association a maintenance association (ma) is a set of maintenance points (mps) in a md. An ma is i...
Page 242
1-3 figure 1-2 outward-facing mep figure 1-3 inward-facing mep z mip a mip is internal to an md. It cannot send cfd packets actively; however, it can handle and respond to cfd packets. The ma and md that a mip belongs to define the vlan attribute and level of the packets received. By cooperating wit...
Page 243
1-4 figure 1-4 levels of mps basic functions of cfd cfd works effectively only in properly-configured networks. Its functions, which are implemented through the mps, include: z continuity check (cc); z loopback (lb) z linktrace (lt) continuity check continuity check is responsible for checking the c...
Page 244: Cfd Configuration Task List
1-5 source mep can identify the path to the destination mep. Note that ltms are multicast frames while ltrs are unicast frames. Protocols and standards the cfd function is implemented in accordance with ieee p802.1ag. Cfd configuration task list for cfd to work effectively, you should first design t...
Page 245
1-6 based on the network design, you should configure meps or the rules for generating mips on each device. However, before doing this you must first configure the service instance. Configuring service instance a service instance is indicated by an integer to represent an ma in an md. The md and ma ...
Page 246: Configuring Cc On Meps
1-7 to do... Use the command... Remarks configure a remote mep for a mep in the same service instance cfd remote-mep remote-mep-id service-instance instance-id mep mep-id required no remote mep is configured for a mep by default. Enable the mep cfd mep service-instance instance-id mep mep-id enable ...
Page 247: Configuring Lb On Meps
1-8 configuration prerequisites before configuring this function, you should first complete the mep configuration. Configuring procedure follow these steps to configure cc on a mep: to do... Use the command... Remarks enter system view system-view — configure the interval field value in the ccm mess...
Page 249: Cfd Configuration Examples
1-10 displaying and maintaining cfd to do... Use the command... Remarks display cfd status display cfd status available in any view display md configuration information display cfd md available in any view display ma configuration information display cfd ma [ [ma-name] md md-name ] available in any ...
Page 250
1-11 figure 1-5 network diagram for md configuration configuration procedure 1) configuration on device a (configuration on device e is the same as that on device a) system-view [devicea] cfd enable [devicea] cfd md md_a level 5 [devicea] cfd ma ma_md_a md md_a vlan 100 [devicea] cfd service-instanc...
Page 251
1-12 z decide the remote mep for each mep, and enable these meps. According to the network diagram as shown in figure 1-6 , perform the following configurations: z in md_a, there are three edge ports: gigabitethernet 1/0/1 on device a, gigabitethernet 1/0/3 on device d and gigabitethernet 1/0/4 on d...
Page 252
1-13 [deviced-gigabitethernet1/0/3] cfd remote-mep 1001 service-instance 1 mep 4002 [deviced-gigabitethernet1/0/3] cfd remote-mep 5001 service-instance 1 mep 4002 [deviced-gigabitethernet1/0/3] cfd mep service-instance 1 mep 4002 enable [deviced-gigabitethernet1/0/3] cfd cc service-instance 1 mep 40...
Page 253
1-14 configuration procedure 1) configure device b system-view [deviceb] cfd mip-rule explicit service-instance 1 2) configure device c system-view [devicec] cfd mip-rule default service-instance 2 after the above operation, you can use the display cfd mp command to verify your configuration. Config...
Page 254: Table of Contents
I table of contents 1 rrpp configuration ··································································································································1-1 rrpp overview ···············································································································...
Page 255: Rrpp Configuration
1-1 1 rrpp configuration when configuring rrpp, go to these sections for information you are interested in: z rrpp overview z rrpp configuration task list z configuring master node z configuring transit node z configuring edge node z configuring assistant edge node z configuring ring group z display...
Page 256
1-2 basic concepts in rrpp figure 1-1 rrpp networking diagram rrpp domain the interconnected devices with the same domain id and control vlans constitute an rrpp domain. An rrpp domain contains the following elements: primary ring, subring, control vlan, master node, transit node, primary port, seco...
Page 257
1-3 a data vlan is a vlan dedicated to transferring data packets. Both rrpp ports and non-rrpp ports can be assigned to a data vlan. Node each device on an rrpp ring is referred to as a node. The role of a node is configurable. There are the following node roles: z master node: each ring has one and...
Page 258
1-4 as shown in figure 1-1 , device b and device c lie on ring 1 and ring 2. Device b’s port 1 and port 2 and device c’s port 1 and port 2 access the primary ring, so they are common ports. Device b’s port 3 and device c’s port 3 access only the subring, so they are edge ports. Rrpp ring group to re...
Page 259
1-5 secondary port receives the hello packets sent by the local master node before the fail timer expires, the overall ring is in health state. Otherwise, the ring transits into disconnect state. Z in an rrpp domain, a transit node learns the hello timer value and the fail timer value on the master ...
Page 260
1-6 broadcast storm suppression mechanism in a multi-homed subring in case of srpt failure as shown in figure 1-5 , ring 1 is the primary ring, and ring 2 and ring 3 are subrings. When the two srpts between the edge node and the assistant-edge node are down, the master nodes of ring 2 and ring 3 wil...
Page 261
1-7 single ring figure 1-2 single ring there is only a single ring in the network topology. In this case, you only need to define an rrpp domain. Tangent rings figure 1-3 tangent rings there are two or more rings in the network topology and only one common node between rings. In this case, you need ...
Page 262
1-8 intersecting rings figure 1-4 intersecting rings there are two or more rings in the network topology and two common nodes between rings. In this case, you only need to define an rrpp domain, and set one ring as the primary ring and the other rings as subrings. Dual homed rings figure 1-5 dual ho...
Page 263
1-9 single-ring load balancing figure 1-6 network diagram for single-ring load balancing domain 1 ring 1 device a device b device d device c domain 2 in a single-ring network, you can achieve load balancing by configuring multiple domains. As shown in figure 1-6 , ring 1 is configured as the primary...
Page 264: Rrpp Configuration Task List
1-10 protocols and standards rfc 3619 extreme networks' ethernet automatic protection switching (eaps) version 1 is related to rrpp. Rrpp configuration task list z rrpp does not have an auto election mechanism, so you must configure each node in the ring network properly for rrpp to monitor and prot...
Page 265: Configuring Master Node
1-11 z the link type of these ports must be trunk. Z they must be layer 2 ge ports. Z they must not be member ports of any aggregation group or smart link group. Z stp is disabled on them. Z the 802.1p priority of trusted packets on the ports is configured, so that rrpp packets take higher precedenc...
Page 266: Configuring Transit Node
1-12 to do… use the command… remarks configure the timer for the rrpp domain timer hello-timer hello-value fail-timer fail-value optional by default, the hello timer value is 1 second and the fail timer value is 3 seconds. Enable the rrpp ring ring ring-id enable required by default, the rrpp ring i...
Page 267
1-13 to do… use the command… remarks specify protected vlans for the rrpp domain protected-vlan reference-instance instance-id-list required no protected vlan is specified for an rrpp domain by default. Specify the current device as the transit node of the ring, and specify the primary port and the ...
Page 268: Configuring Edge Node
1-14 configuring edge node follow these steps to configure edge node: to do… use the command… remarks enter system view system-view — create an rrpp domain and enter its view rrpp domain domain-id required specify a control vlan for the rrpp domain control-vlan vlan-id required specify protected vla...
Page 269
1-15 z before specifying rrpp rings for an rrpp domain, you must specify protected vlans for the domain. Z before specifying rings for an rrpp domain, you can delete or modify the protected vlans configured for the rrpp domain; after specifying rings for an rrpp domain, you can delete or modify the ...
Page 270: Configuring Ring Group
1-16 to do… use the command… remarks specify the current device as the assistant-edge node of the subring, and specify an edge port ring ring-id node-mode assistant-edge [ edge-port interface-type interface-number ] required enable the primary ring ring ring-id enable required by default, the rrpp r...
Page 271
1-17 you need to configure ring groups on both the edge node and the assistant-edge node at the same time. The two ring groups must be configured with the same subrings. Otherwise, the ring groups cannot operate properly. Configuration prerequisites z the rrpp domain, control vlans, protected vlans,...
Page 272
1-18 to do… use the command… remarks clear rrpp statistics reset rrpp statistics domain domain-id [ ring ring-id ] available in user view rrpp typical configuration examples configuring single ring topology networking requirements z device a, device b, device c, and device d constitute rrpp domain 1...
Page 273
1-19 configuration procedure 1) perform the following configuration on device a: # configure rrpp ports gigabitethernet1/0/1 and gigabitethernet1/0/2. System-view [devicea] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1 [devicea-gigabitethernet1/0/1] undo stp enable [devicea-gigabitethernet1/0/1] port link-type tr...
Page 274
1-20 # create rrpp domain 1, configure vlan 4092 as the primary control vlan of rrpp domain 1, and configure the vlans mapped to mstis 0 through 16 as the protected vlans of rrpp domain 1. [deviceb] rrpp domain 1 [deviceb-rrpp-domain1] control-vlan 4092 [deviceb-rrpp-domain1] protected-vlan referenc...
Page 275
1-21 z specify the control vlan for the rrpp domain. Z configure the protected vlans to reference all mstis. The msti id ranges from 0 to 16. Z specify the node mode of a device on an rrpp ring and the ports accessing the rrpp ring on the device. Z enable these two rrpp rings. Z enable rrpp figure 1...
Page 276
1-22 [devicea-rrpp-domain1] ring 1 enable [devicea-rrpp-domain1] quit # enable rrpp. [devicea] rrpp enable 2) configuration on device b # configure rrpp ports gigabitethernet1/0/1, gigabitethernet1/0/2 and gigabitethernet1/0/3. System-view [deviceb] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1 [deviceb-gigabitet...
Page 277
1-23 system-view [devicec] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1 [devicec-gigabitethernet1/0/1] undo stp enable [devicec-gigabitethernet1/0/1] port link-type trunk [devicec-gigabitethernet1/0/1] port trunk permit vlan all [devicec-gigabitethernet1/0/1] qos trust dot1p [devicec-gigabitethernet1/0/1] quit [...
Page 278
1-24 [deviced] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/2 [deviced-gigabitethernet1/0/2] undo stp enable [deviced-gigabitethernet1/0/2] port link-type trunk [deviced-gigabitethernet1/0/2] port trunk permit vlan all [deviced-gigabitethernet1/0/2] qos trust dot1p [deviced-gigabitethernet1/0/2] quit # create rrpp...
Page 279
1-25 # enable rrpp. [devicee] rrpp enable 6) verification after the configuration, you can use the display command to view rrpp configuration result on each device. Configuring intersecting-ring load balancing networking requirements z device a, device b, device c, device d, and device f constitute ...
Page 280
1-26 figure 1-10 network diagram for intersecting-ring load balancing configuration configuration procedure 1) configure device a as the master node of the primary ring # create vlans 10 and 20, and map vlan 10 to msti 1 and vlan 20 to msti 2. System-view [devicea] vlan 10 [devicea-vlan10] quit [dev...
Page 281
1-27 [devicea-gigabitethernet1/0/2] quit # create rrpp domain 1, configure vlan 100 as the primary control vlan of rrpp domain 1, and configure the vlan mapped to msti 1 as the protected vlan of rrpp domain 1. [devicea] rrpp domain 1 [devicea-rrpp-domain1] control-vlan 100 [devicea-rrpp-domain1] pro...
Page 282
1-28 [deviceb-gigabitethernet1/0/1] qos trust dot1p [deviceb-gigabitethernet1/0/1] quit [deviceb] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/2 [deviceb-gigabitethernet1/0/2] undo stp enable [deviceb-gigabitethernet1/0/2] port link-type trunk [deviceb-gigabitethernet1/0/2] undo port trunk permit vlan 1 [deviceb-g...
Page 283
1-29 [deviceb-rrpp-domain2] ring 1 node-mode transit primary-port gigabitethernet 1/0/1 secondary-port gigabitethernet 1/0/2 level 0 [deviceb-rrpp-domain2] ring 1 enable # configure device b as the assistant-edge node of subring 2 in rrpp domain 2, with gigabitethernet1/0/3 as the edge port, and ena...
Page 284
1-30 [devicec-gigabitethernet1/0/4] undo stp enable [devicec-gigabitethernet1/0/4] port link-type trunk [devicec-gigabitethernet1/0/4] undo port trunk permit vlan 1 [devicec-gigabitethernet1/0/4] port trunk permit vlan 10 [devicec-gigabitethernet1/0/4] qos trust dot1p [devicec-gigabitethernet1/0/4] ...
Page 285
1-31 [deviced-vlan20] quit [deviced] stp region-configuration [deviced-mst-region] instance 1 vlan 10 [deviced-mst-region] instance 2 vlan 20 [deviced-mst-region] active region-configuration [deviced-mst-region] quit # configure rrpp ports gigabitethernet1/0/1 and gigabitethernet1/0/2. [deviced] int...
Page 286
1-32 5) configure device e as the master node of subring ring 2 in domain 2 # create vlan 20, and map vlan 20 to msti 2. System-view [devicee] vlan 20 [devicee-vlan20] quit [devicee] stp region-configuration [devicee-mst-region] instance 2 vlan 20 [devicee-mst-region] active region-configuration [de...
Page 287: Troubleshooting
1-33 [devicef-mst-region] quit # configure rrpp ports gigabitethernet1/0/1 and gigabitethernet1/0/2. [devicef] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1 [devicef-gigabitethernet1/0/1] undo stp enable [devicef-gigabitethernet1/0/1] port link-type trunk [devicef-gigabitethernet1/0/1] undo port trunk permit vlan...
Page 288
1-34 when the link state is normal, the master node cannot receive hello packets, and the master node unblocks the secondary port. Analysis: the reasons may be: z rrpp is not enabled on some nodes in the rrpp ring. Z the domain id or primary control vlan id is not the same for the nodes in the same ...
Page 289: Table of Contents
I table of contents 1 port mirroring configuration ····················································································································1-1 introduction to port mirroring ··································································································...
Page 290: Port Mirroring Configuration
1-1 1 port mirroring configuration when configuring port mirroring, go to these sections for information you are interested in: z introduction to port mirroring z configuring local port mirroring z configuring remote port mirroring z displaying and maintaining port mirroring z port mirroring configu...
Page 291
1-2 figure 1-1 local port mirroring implementation pc mirroring port monitor port data monitoring device mirroring port how the device processes packets monitor port traffic mirrored to remote port mirroring remote port mirroring can mirror all packets but protocol packets. Remote port mirroring is ...
Page 292
1-3 z destination device the destination device is the device where the monitor port is located. On it, you must create the remote destination mirroring group. When receiving a packet, the destination device compares the vlan id carried in the packet with the id of the probe vlan configured in the r...
Page 293
1-4 z a local port mirroring group takes effect only after its mirroring and monitor ports are configured. Z to ensure operation of your device, do not enable stp, mstp, or rstp on the monitor port. Z a port mirroring group can have multiple mirroring ports, but only one monitor port. Z a mirroring ...
Page 295
1-6 z to remove the vlan configured as a remote probe vlan, you must remove the remote probe vlan with undo mirroring-group remote-probe vlan command first. Removing the probe vlan can invalidate the remote source mirroring group. Z you are recommended to use a remote probe vlan exclusively for the ...
Page 296
1-7 when configuring the monitor port, use the following guidelines: z the port can belong to only the current mirroring group. Z disable these functions on the port: stp, mstp, and rstp. Z you are recommended to use a monitor port only for port mirroring. This is to ensure that the data monitoring ...
Page 297
1-8 figure 1-3 network diagram for local port mirroring configuration switch c data monitoring device r&d department switch a switch b ge1/0/2 ge1/0/1 ge1/0/3 marketing department configuration procedure configure switch c. # create a local port mirroring group. System-view [switchc] mirroring-group...
Page 298
1-9 as shown in figure 1-4 , the administrator wants to monitor the packets sent from department 1 and 2 through the data monitoring device. Use the remote port mirroring function to meet the requirement. Perform the following configurations: z use switch a as the source device, switch b as the inte...
Page 299
1-10 [switcha-gigabitethernet1/0/3] port link-type trunk [switcha-gigabitethernet1/0/3] port trunk permit vlan 2 2) configure switch b (the intermediate device). # configure port gigabitethernet 1/0/1 as a trunk port and configure the port to permit the packets of vlan 2. System-view [switchb] inter...
Page 300: Manual Version
Ip services volume organization manual version 6w100-20090630 product version release 2202 organization the ip services volume is organized as follows: features description ip address an ip address is a 32-bit address allocated to a network interface on a device that is attached to the internet. Thi...
Page 301
Features description udp helper udp helper functions as a relay agent that converts udp broadcast packets into unicast packets and forwards them to a specified server. This document describes: z udp helper overview z udp helper configuration ipv6 basics internet protocol version 6 (ipv6), also calle...
Page 302: Table of Contents
I table of contents 1 ip addressing configuration····················································································································1-1 ip addressing overview·············································································································...
Page 303: Ip Addressing Configuration
1-1 1 ip addressing configuration when assigning ip addresses to interfaces on your device, go to these sections for information you are interested in: z ip addressing overview z configuring ip addresses z displaying and maintaining ip addressing ip addressing overview this section covers these topi...
Page 304
1-2 table 1-1 ip address classes and ranges class address range remarks a 0.0.0.0 to 127.255.255.255 the ip address 0.0.0.0 is used by a host at bootstrap for temporary communication. This address is never a valid destination address. Addresses starting with 127 are reserved for loopback test. Packe...
Page 305: Configuring Ip Addresses
1-3 in the absence of subnetting, some special addresses such as the addresses with the net id of all zeros and the addresses with the host id of all ones, are not assignable to hosts. The same is true for subnetting. When designing your network, you should note that subnetting is somewhat a tradeof...
Page 306
1-4 z the primary ip address you assigned to the interface can overwrite the old one if there is any. Z you cannot assign secondary ip addresses to an interface that has bootp or dhcp configured. Z the primary and secondary ip addresses you assign to the interface can be located on the same network ...
Page 307
1-5 ping 172.16.1.2 ping 172.16.1.2: 56 data bytes, press ctrl_c to break reply from 172.16.1.2: bytes=56 sequence=1 ttl=255 time=25 ms reply from 172.16.1.2: bytes=56 sequence=2 ttl=255 time=27 ms reply from 172.16.1.2: bytes=56 sequence=3 ttl=255 time=26 ms reply from 172.16.1.2: bytes=56 sequence...
Page 308: Table of Contents
I table of contents 1 arp configuration·····································································································································1-1 arp overview················································································································...
Page 309
Ii introduction······································································································································3-4 configuring arp packet source mac address consistency check ··············································3-5 configuring arp packet rate limit ···...
Page 310: Arp Configuration
1-1 this document is organized as follows: z arp configuration z proxy arp configuration z arp attack defense configuration 1 arp configuration when configuring arp, go to these sections for information you are interested in: z arp overview z configuring arp z configuring gratuitous arp z displaying...
Page 311
1-2 hardware address length field is "6”. For an ip(v4) address, the value of the protocol address length field is “4”. Z op: operation code. This field specifies the type of arp message. The value “1” represents an arp request and “2” represents an arp reply. Z sender hardware address: this field s...
Page 312: Configuring Arp
1-3 which the target ip address is the ip address of host b. After obtaining the mac address of host b, the gateway sends the packet to host b. Arp table after obtaining the mac address for the destination host, the device puts the ip-to-mac mapping into its own arp table. This mapping is used for f...
Page 313
1-4 to do… use the command… remarks enter system view system-view — configure a permanent static arp entry arp static ip-address mac-address vlan-id interface-type interface-number required no permanent static arp entry is configured by default. Configure a non-permanent static arp entry arp static ...
Page 314: Configuring Gratuitous Arp
1-5 enabling the arp entry check the arp entry check function disables the device from learning multicast mac addresses. With the arp entry check enabled, the device cannot learn any arp entry with a multicast mac address, and configuring such a static arp entry is not allowed; otherwise, the system...
Page 315
1-6 z determining whether its ip address is already used by another device. Z informing other devices of its mac address change so that they can update their arp entries. A device receiving a gratuitous arp packet adds the information carried in the packet to its own dynamic arp table if it finds no...
Page 316: Proxy Arp Configuration
2-1 2 proxy arp configuration when configuring proxy arp, go to these sections for information you are interested in: z proxy arp overview z enabling proxy arp z displaying and maintaining proxy arp proxy arp overview if a host sends an arp request for the mac address of another host that actually r...
Page 317: Enabling Proxy Arp
2-2 you can solve the problem by enabling proxy arp on switch. After that, switch can reply to the arp request from host a with the mac address of vlan-interface 1, and forward packets sent from host a to host b. In this case, switch seems to be a proxy of host b. A main advantage of proxy arp is th...
Page 318
2-3 to do… use the command… remarks enable local proxy arp local-proxy-arp enable required disabled by default. Displaying and maintaining proxy arp to do… use the command… remarks display whether proxy arp is enabled display proxy-arp [ interface vlan-interface vlan-id ] available in any view displ...
Page 319
2-4 [switch-vlan-interface1] quit [switch] interface vlan-interface 2 [switch-vlan-interface2] ip address 192.168.20.99 255.255.255.0 [switch-vlan-interface2] proxy-arp enable [switch-vlan-interface2] quit local proxy arp configuration example in case of port isolation network requirements z host a ...
Page 320
2-5 # configure an ip address of vlan-interface 2. System-view [switcha] vlan 2 [switcha-vlan2] port gigabitethernet 1/0/2 [switcha-vlan2] quit [switcha] interface vlan-interface 2 [switcha-vlan-interface2] ip address 192.168.10.100 255.255.0.0 the ping operation from host a to host b is unsuccessfu...
Page 321
2-6 [switchb-vlan2] port gigabitethernet 1/0/2 [switchb-vlan2] quit [switchb] vlan 3 [switchb-vlan3] port gigabitethernet 1/0/3 [switchb-vlan3] quit [switchb] vlan 5 [switchb-vlan5] port gigabitethernet 1/0/1 [switchb-vlan5] isolate-user-vlan enable [switchb-vlan5] quit [switchb] isolate-user-vlan 5...
Page 322
3-1 3 arp attack defense configuration when configuring arp attack defense, go to these sections for information you are interested in: z configuring arp source suppression z configuring arp defense against ip packet attacks z configuring arp active acknowledgement z configuring source mac address b...
Page 323
3-2 displaying and maintaining arp source suppression to do… use the command… remarks display the arp source suppression configuration information display arp source-suppression available in any view configuring arp defense against ip packet attacks introduction to arp defense against ip packet atta...
Page 324
3-3 z if an arp reply is received within five seconds, the gateway updates the arp entry; z if not, the arp entry is not updated. Configuring the arp active acknowledgement function follow these steps to configure arp active acknowledgement: to do… use the command… remarks enter system view system-v...
Page 325
3-4 follow these steps to configure protected mac addresses: to do… use the command… remarks enter system view system-view — configure protected mac addresses arp anti-attack source-mac exclude-mac mac-address& optional not configured by default. Configuring the aging timer for protected mac address...
Page 326: Configuring Arp Detection
3-5 arp detection also checks source mac address consistency of arp packets, but it is enabled on an access device to detect only arp packets sent to it. Configuring arp packet source mac address consistency check follow these steps to enable arp packet source mac address consistency check: to do… u...
Page 327
3-6 enabling arp detection based on dhcp snooping entries/802.1x security entries/static ip-to-mac bindings with this feature enabled, the device compares the source ip and mac addresses of an arp packet received from the vlan against the dhcp snooping entries, 802.1x security entries, or static ip-...
Page 328
3-7 to do… use the command… remarks enter system view system-view — enter vlan view vlan vlan-id — enable arp detection for the vlan arp detection enable required disabled by default. That is, arp detection based on dhcp snooping entries/802.1x security entries/static ip-to-mac bindings is not enabl...
Page 329
3-8 during the dhcp assignment process, when the client receives the dhcp-ack message from the dhcp server, it broadcasts a gratuitous arp packet to detect address conflicts. If no response is received in a pre-defined time period, the client uses the assigned ip address. If the client is enabled wi...
Page 330
3-9 z if both the arp detection based on specified objects and the arp detection based on snooping entries/802.1x security entries/static ip-to-mac bindings are enabled, the former one applies first, and then the latter applies. Z before enabling arp detection based on dhcp snooping entries, make su...
Page 331
3-10 configuration procedure 1) add all the ports on switch b into vlan 10, and configure the ip address of vlan-interface 10 on switch a (the configuration procedure is omitted). 2) configure a dhcp server (the configuration procedure is omitted). 3) configure host a and host b as dhcp clients (the...
Page 332
3-11 figure 3-2 network diagram for arp detection configuration configuration procedure 1) add all the ports on switch b into vlan 10, and configure the ip address of vlan-interface 10 on switch a (the configuration procedure is omitted). 2) configure a dhcp server (the configuration procedure is om...
Page 333: Table of Contents
I table of contents 1 dhcp overview··········································································································································1-1 introduction to dhcp ······································································································...
Page 334
Ii prerequisites····································································································································4-5 configuring dhcp snooping to support option 82 ········································································4-5 displaying and maintainin...
Page 335: Dhcp Overview
1-1 this document is organized as follows: z dhcp overview z dhcp relay agent configuration z dhcp client configuration z dhcp snooping configuration z bootp client configuration 1 dhcp overview introduction to dhcp the fast expansion and growing complexity of networks result in scarce ip addresses ...
Page 336: Dhcp Address Allocation
1-2 dhcp address allocation allocation mechanisms dhcp supports three mechanisms for ip address allocation. Z manual allocation: the network administrator assigns an ip address to a client like a www server, and dhcp conveys the assigned address to the client. Z automatic allocation: dhcp assigns a ...
Page 337: Dhcp Message Format
1-3 z after receiving the dhcp-ack message, the client probes whether the ip address assigned by the server is in use by broadcasting a gratuitous arp packet. If the client receives no response within a specified time, the client can use this ip address. Otherwise, the client sends a dhcp-decline me...
Page 338: Dhcp Options
1-4 z secs: filled in by the client, the number of seconds elapsed since the client began address acquisition or renewal process. Currently this field is reserved and set to 0. Z flags: the leftmost bit is defined as the broadcast (b) flag. If this flag is set to 0, the dhcp server sent a reply back...
Page 339
1-5 z option 121: classless route option. It specifies a list of classless static routes (the destination addresses in these static routes are classless) that the requesting client should add to its routing table. Z option 33: static route option. It specifies a list of classful static routes (the d...
Page 340
1-6 figure 1-6 format of the value field of the acs parameter sub-option z the value field of the service provider identifier sub-option contains the service provider identifier. Z figure 1-7 shows the format of the value field of the pxe server address sub-option. Currently, the value of the pxe se...
Page 341
1-7 figure 1-8 sub-option 1 in normal padding format z sub-option 2: padded with the mac address of the dhcp relay agent interface or the mac address of the dhcp snooping device that received the client’s request. The following figure gives its format. The value of the sub-option type is 2, and that...
Page 342: Protocols and Standards
1-8 z sub-option 1: ip address of the primary network calling processor, which is a server serving as the network calling control source and providing program downloads. Z sub-option 2: ip address of the backup network calling processor that dhcp clients will contact when the primary one is unreacha...
Page 343
2-1 2 dhcp relay agent configuration when configuring the dhcp relay agent, go to these sections for information you are interested in: z introduction to dhcp relay agent z dhcp relay agent configuration task list z configuring the dhcp relay agent z displaying and maintaining dhcp relay agent confi...
Page 344
2-2 figure 2-1 dhcp relay agent application ip network dhcp server dhcp relay agent dhcp client dhcp client dhcp client dhcp client no matter whether a relay agent exists or not, the dhcp server and client interact with each other in a similar way (see section dynamic ip address allocation process )...
Page 345
2-3 if a client’s requesting message has… handling strategy padding format the dhcp relay agent will… drop random drop the message. Keep random forward the message without changing option 82. Normal forward the message after replacing the original option 82 with the option 82 padded in normal format...
Page 346
2-4 follow these steps to enable dhcp: to do… use the command… remarks enter system view system-view — enable dhcp dhcp enable required disabled by default. Enabling the dhcp relay agent on an interface with this task completed, upon receiving a dhcp request from the enabled interface, the relay age...
Page 347
2-5 to do… use the command… remarks correlate the dhcp server group with the current interface dhcp relay server-select group-id required by default, no interface is correlated with any dhcp server group. Z you can specify up to twenty dhcp server groups on the relay agent and eight dhcp server addr...
Page 348
2-6 z the dhcp relay address-check enable command is independent of other commands of the dhcp relay agent. That is, the invalid address check takes effect when this command is executed, regardless of whether other commands are used. Z the dhcp relay address-check enable command only checks ip and m...
Page 349
2-7 follow these steps to enable unauthorized dhcp server detection: to do… use the command… remarks enter system view system-view — enable unauthorized dhcp server detection dhcp relay server-detect required disabled by default. With the unauthorized dhcp server detection enabled, the device puts a...
Page 350
2-8 configuring the dhcp relay agent to support option 82 follow these steps to configure the dhcp relay agent to support option 82: to do… use the command… remarks enter system view system-view — enter interface view interface interface-type interface-number — enable the relay agent to support opti...
Page 352
2-10 configuration procedure # specify ip addresses for the interfaces (omitted). # enable dhcp. System-view [switcha] dhcp enable # add dhcp server 10.1.1.1 into dhcp server group 1. [switcha] dhcp relay server-group 1 ip 10.1.1.1 # enable the dhcp relay agent on vlan-interface 1. [switcha] interfa...
Page 353
2-11 # enable the dhcp relay agent to support option 82, and perform option 82-related configurations. [switcha-vlan-interface1] dhcp relay information enable [switcha-vlan-interface1] dhcp relay information strategy replace [switcha-vlan-interface1] dhcp relay information circuit-id string company0...
Page 354: Dhcp Client Configuration
3-1 3 dhcp client configuration when configuring the dhcp client, go to these sections for information you are interested in: z introduction to dhcp client z enabling the dhcp client on an interface z displaying and maintaining the dhcp client z dhcp client configuration example z the dhcp client co...
Page 355
3-2 z an interface can be configured to acquire an ip address in multiple ways, but these ways are mutually exclusive. The latest configuration will overwrite the previous one. Z after the dhcp client is enabled on an interface, no secondary ip address is configurable for the interface. Z if the ip ...
Page 356
3-3 system-view [switchb] interface vlan-interface 1 [switchb-vlan-interface1] ip address dhcp-alloc.
Page 357: Dhcp Snooping Configuration
4-1 4 dhcp snooping configuration when configuring dhcp snooping, go to these sections for information you are interested in: z dhcp snooping overview z configuring dhcp snooping basic functions z configuring dhcp snooping to support option 82 z displaying and maintaining dhcp snooping z dhcp snoopi...
Page 358
4-2 recording ip-to-mac mappings of dhcp clients dhcp snooping reads dhcp-request messages and dhcp-ack messages from trusted ports to record dhcp snooping entries, including mac addresses of clients, ip addresses obtained by the clients, ports that connect to dhcp clients, and vlans to which the po...
Page 359
4-3 figure 4-2 configure trusted ports in a cascaded network table 4-1 describes roles of the ports shown in figure 4-2 . Table 4-1 roles of ports device untrusted port trusted port disabled from recording binding entries trusted port enabled to record binding entries switch a ge1/0/1 ge1/0/3 ge1/0/...
Page 360
4-4 if a client’s requesting message has… handling strategy padding format the dhcp snooping device will… drop random drop the message. Keep random forward the message without changing option 82. Normal forward the message after replacing the original option 82 with the option 82 padded in normal fo...
Page 361
4-5 z you need to specify the ports connected to the valid dhcp servers as trusted to ensure that dhcp clients can obtain valid ip addresses. The trusted port and the port connected to the dhcp client must be in the same vlan. Z you can specify layer 2 ethernet interfaces and layer 2 aggregate inter...
Page 364
4-8 [switchb-gigabitethernet1/0/1] dhcp-snooping trust [switchb-gigabitethernet1/0/1] quit dhcp snooping option 82 support configuration example network requirements z as shown in figure 4-3 , enable dhcp snooping and option 82 support on switch b. Z configure the handling strategy for dhcp requests...
Page 365: Bootp Client Configuration
5-1 5 bootp client configuration while configuring a bootp client, go to these sections for information you are interested in: z introduction to bootp client z configuring an interface to dynamically obtain an ip address through bootp z displaying and maintaining bootp client configuration z bootp c...
Page 366: Through Bootp
5-2 because a dhcp server can interact with a bootp client, you can use the dhcp server to configure an ip address for the bootp client, without any bootp server. Obtaining an ip address dynamically a dhcp server can take the place of the bootp server in the following dynamic ip address acquisition....
Page 367
5-3 displaying and maintaining bootp client configuration to do… use the command… remarks display related information on a bootp client display bootp client [ interface interface-type interface-number ] available in any view bootp client configuration example network requirement as shown in figure 5...
Page 368: Table of Contents
I table of contents 1 dns configuration·····································································································································1-1 dns overview················································································································...
Page 369: Dns Configuration
1-1 1 dns configuration when configuring dns, go to these sections for information you are interested in: z dns overview z configuring the dns client z configuring the dns proxy z displaying and maintaining dns z dns configuration examples z troubleshooting dns configuration this document only cover...
Page 370
1-2 3) the dns server looks up the corresponding ip address of the domain name in its dns database. If no match is found, it sends a query to a higher level dns server. This process continues until a result, whether successful or not, is returned. 4) the dns client returns the resolution result to t...
Page 371
1-3 if an alias is configured for a domain name on the dns server, the device can resolve the alias into the ip address of the host. Dns proxy introduction to dns proxy a dns proxy forwards dns requests and replies between dns clients and a dns server. As shown in figure 1-2 , a dns client sends a d...
Page 372: Configuring The Dns Client
1-4 configuring the dns client configuring static domain name resolution follow these steps to configure static domain name resolution: to do… use the command… remarks enter system view system-view –– configure a mapping between a host name and ip address in the static name resolution table ip host ...
Page 373: Configuring The Dns Proxy
1-5 configuring the dns proxy follow these steps to configure the dns proxy: to do… use the command… remarks enter system view system-view — enable dns proxy dns proxy enable required disabled by default. Displaying and maintaining dns to do… use the command… remarks display the static domain name r...
Page 374
1-6 56 data bytes, press ctrl_c to break reply from 10.1.1.2: bytes=56 sequence=1 ttl=128 time=1 ms reply from 10.1.1.2: bytes=56 sequence=2 ttl=128 time=4 ms reply from 10.1.1.2: bytes=56 sequence=3 ttl=128 time=3 ms reply from 10.1.1.2: bytes=56 sequence=4 ttl=128 time=2 ms reply from 10.1.1.2: by...
Page 375
1-7 in figure 1-5 , right click forward lookup zones, select new zone, and then follow the instructions to create a new zone named com. Figure 1-5 create a zone # create a mapping between the host name and ip address. Figure 1-6 add a host in figure 1-6 , right click zone com, and then select new ho...
Page 376
1-8 figure 1-7 add a mapping between domain name and ip address 2) configure the dns client # enable dynamic domain name resolution. System-view [sysname] dns resolve # specify the dns server 2.1.1.2. [sysname] dns server 2.1.1.2 # configure com as the name suffix. [sysname] dns domain com 3) config...
Page 377
1-9 dns proxy configuration example network requirements z specify switch a as the dns server of switch b (the dns client). Z switch a acts as a dns proxy. The ip address of the real dns server is 4.1.1.1. Z switch b implements domain name resolution through switch a. Figure 1-8 network diagram for ...
Page 378
1-10 # specify the dns server 2.1.1.2. [switchb] dns server 2.1.1.2 4) configuration verification # execute the ping host.Com command on switch b to verify that the communication between the switch and the host is normal and that the corresponding destination ip address is 3.1.1.1. [switchb] ping ho...
Page 379: Table of Contents
I table of contents 1 ip performance optimization configuration···························································································1-1 ip performance overview ······················································································································...
Page 380: Ip Performance Overview
1-1 1 ip performance optimization configuration when optimizing ip performance, go to these sections for information you are interested in: z ip performance overview z enabling reception and forwarding of directed broadcasts to a directly connected network z configuring tcp optional parameters z con...
Page 381
1-2 enabling forwarding of directed broadcasts to a directly connected network follow these steps to enable the device to forward directed broadcasts: to do… use the command… remarks enter system view system-view — enter interface view interface interface-type interface-number — enable the interface...
Page 382
1-3 [switcha-vlan-interface3] ip address 1.1.1.2 24 [switcha-vlan-interface3] quit [switcha] interface vlan-interface 2 [switcha-vlan-interface2] ip address 2.2.2.2 24 # enable vlan-interface 2 to forward directed broadcasts. [switcha-vlan-interface2] ip forward-broadcast z configure switch b # enab...
Page 383
1-4 the actual length of the finwait timer is determined by the following formula: actual length of the finwait timer = (configured length of the finwait timer – 75) + configured length of the synwait timer configuring icmp to send error packets sending error packets is a major function of icmp. In ...
Page 384
1-5 z when receiving a packet with the destination being local and transport layer protocol being udp, if the packet’s port number does not match the running process, the device will send the source a “port unreachable” icmp error packet. Z if the source uses “strict source routing" to send packets,...
Page 385
1-6 displaying and maintaining ip performance optimization to do… use the command… remarks display current tcp connection state display tcp status display tcp connection statistics display tcp statistics display udp statistics display udp statistics display statistics of ip packets display ip statis...
Page 386: Table of Contents
I table of contents 1 udp helper configuration ························································································································1-1 introduction to udp helper ······································································································...
Page 387: Udp Helper Configuration
1-1 1 udp helper configuration when configuring udp helper, go to these sections for information you are interested in: z introduction to udp helper z configuring udp helper z displaying and maintaining udp helper z udp helper configuration examples udp helper can be currently configured on vlan int...
Page 388
1-2 to do… use the command… remarks enter interface view interface interface-type interface-number — specify the destination server to which udp packets are to be forwarded udp-helper server ip-address required no destination server is specified by default. Z the udp helper enabled device cannot for...
Page 389
1-3 figure 1-1 network diagram for udp helper configuration configuration procedure the following configuration assumes that a route from switch a to the network segment 10.2.0.0/16 is available. # enable udp helper. System-view [switcha] udp-helper enable # enable the forwarding broadcast packets w...
Page 390: Table of Contents
I table of contents 1 ipv6 basics configuration ························································································································1-1 ipv6 overview ··················································································································...
Page 391: Ipv6 Basics Configuration
1-1 1 ipv6 basics configuration when configuring ipv6 basics, go to these sections for information you are interested in: z ipv6 overview z ipv6 basics configuration task list z configuring basic ipv6 functions z configuring ipv6 ndp z configuring pmtu discovery z configuring ipv6 tcp properties z c...
Page 392
1-2 the ipv4 address size, the basic ipv6 header size is 40 bytes and is only twice the ipv4 header size (excluding the options field). Figure 1-1 comparison between ipv4 packet header format and basic ipv6 packet header format adequate address space the source and destination ipv6 addresses are bot...
Page 393
1-3 enhanced neighbor discovery mechanism the ipv6 neighbor discovery protocol is implemented through a group of internet control message protocol version 6 (icmpv6) messages that manage the information exchange between neighbor nodes on the same link. The group of icmpv6 messages takes the place of...
Page 394
1-4 z multicast address: an identifier for a set of interfaces (typically belonging to different nodes), similar to an ipv4 multicast address. A packet sent to a multicast address is delivered to all interfaces identified by that address. Z anycast address: an identifier for a set of interfaces (typ...
Page 395
1-5 z unassigned address: the unicast address "::” is called the unassigned address and may not be assigned to any node. Before acquiring a valid ipv6 address, a node may fill this address in the source address field of an ipv6 packet. It cannot be used as a destination ipv6 address. Multicast addre...
Page 396
1-6 introduction to ipv6 neighbor discovery protocol the ipv6 neighbor discovery protocol (ndp) uses five types of icmpv6 messages to implement the following functions: z address resolution z neighbor reachability detection z duplicate address detection z router/prefix discovery and address autoconf...
Page 397
1-7 figure 1-3 address resolution the address resolution procedure is as follows: 1) node a multicasts an ns message. The source address of the ns message is the ipv6 address of the sending interface of node a and the destination address is the solicited-node multicast address of node b. The ns mess...
Page 398
1-8 2) if node b uses this ipv6 address, node b returns an na message. The na message contains the ipv6 address of node b. 3) node a learns that the ipv6 address is being used by node b after receiving the na message from node b. Otherwise, node b is not using the ipv6 address and node a can use it....
Page 399
1-9 the path mtu (pmtu) discovery mechanism is to find the minimum mtu of all links in the path from the source to the destination. Figure 1-5 shows the working procedure of pmtu discovery. Figure 1-5 working procedure of pmtu discovery the working procedure of the pmtu discovery is as follows: 1) t...
Page 400
1-10 z rfc 2463: internet control message protocol (icmpv6) for the internet protocol version 6 (ipv6) specification z rfc 2464: transmission of ipv6 packets over ethernet networks z rfc 2526: reserved ipv6 subnet anycast addresses z rfc 3307: allocation guidelines for ipv6 multicast addresses z rfc...
Page 401
1-11 z manual assignment: ipv6 link-local addresses can be assigned manually. Follow these steps to configure an ipv6 unicast address: to do... Use the command... Remarks enter system view system-view — enter interface view interface interface-type interface-number — manually assign an ipv6 address ...
Page 402: Configuring Ipv6 Ndp
1-12 configuring ipv6 ndp configuring a static neighbor entry the ipv6 address of a neighbor node can be resolved into a link-layer address dynamically through ns and na messages or through a manually configured static neighbor entry. The device uniquely identifies a static neighbor entry according ...
Page 403
1-13 configuring parameters related to ra messages you can enable an interface to send ra messages, and configure the interval for sending ra messages and parameters in ra messages. After receiving an ra message, a host can use these parameters to perform corresponding operations. Table 1-4 lists th...
Page 404
1-14 to do… use the command… remarks configure the hop limit ipv6 nd hop-limit value optional 64 by default. Enter interface view interface interface-type interface-number — disable the ra message suppression undo ipv6 nd ra halt required by default, ra messages are suppressed. Configure the maximum...
Page 405: Configuring Pmtu Discovery
1-15 the maximum interval for sending ra messages should be less than or equal to the router lifetime in ra messages. Configuring the maximum number of attempts to send an ns message for dad an interface sends a neighbor solicitation (ns) message for duplicate address detection after acquiring an ip...
Page 406
1-16 mtu. After the aging time expires, the dynamic pmtu is removed and the source host re-determines a dynamic path mtu through the pmtu mechanism. The aging time is invalid for a static pmtu. Follow these steps to configure the aging time for dynamic pmtus: to do… use the command… remarks enter sy...
Page 407
1-17 successively sent exceeds the capacity of the token bucket, the additional icmpv6 error packets cannot be sent out until the capacity of the token bucket is restored. Follow these steps to configure the capacity and update interval of the token bucket: to do… use the command… remarks enter syst...
Page 408: Configuring Ipv6 Dns Client
1-18 configuring ipv6 dns client configuring static ipv6 domain name resolution configuring static ipv6 domain name resolution is to establish the mapping between a host name and an ipv6 address. When using such applications as telnet, you can directly input a host name and the system will resolve t...
Page 409
1-19 displaying and maintaining ipv6 basics configuration to do… use the command… remarks display dns suffix information display dns domain [ dynamic ] display ipv6 dynamic domain name cache information display dns ipv6 dynamic-host display ipv6 dns server information display dns ipv6 server [ dynam...
Page 410: Ipv6 Configuration Example
1-20 the display dns domain command is the same as the one of ipv4 dns. For details about the commands, refer to dns commands in the ip services volume. Ipv6 configuration example network requirements z host, switch a and switch b are directly connected through ethernet ports. Add the ethernet ports...
Page 411
1-21 [switcha-vlan-interface1] ipv6 address 2001::1/64 [switcha-vlan-interface1] undo ipv6 nd ra halt z configure switch b # enable ipv6. System-view [switchb] ipv6 # configure an aggregatable global unicast address for vlan-interface 2. [switchb] interface vlan-interface 2 [switchb-vlan-interface2]...
Page 412
1-22 inbadheaders: 0 inbadoptions: 0 reasmreqds: 0 reasmoks: 0 infragdrops: 0 infragtimeouts: 0 outfragfails: 0 inunknownprotos: 0 indelivers: 47 outrequests: 89 outforwdatagrams: 48 innoroutes: 0 intoobigerrors: 0 outfragoks: 0 outfragcreates: 0 inmcastpkts: 6 inmcastnotmembers: 25747 outmcastpkts:...
Page 413
1-23 inbadheaders: 0 inbadoptions: 0 reasmreqds: 0 reasmoks: 0 infragdrops: 0 infragtimeouts: 0 outfragfails: 0 inunknownprotos: 0 indelivers: 159 outrequests: 1012 outforwdatagrams: 35 innoroutes: 0 intoobigerrors: 0 outfragoks: 0 outfragcreates: 0 inmcastpkts: 79 inmcastnotmembers: 65 outmcastpkts...
Page 414
1-24 reasmoks: 0 infragdrops: 0 infragtimeouts: 0 outfragfails: 0 inunknownprotos: 0 indelivers: 117 outrequests: 83 outforwdatagrams: 0 innoroutes: 0 intoobigerrors: 0 outfragoks: 0 outfragcreates: 0 inmcastpkts: 28 inmcastnotmembers: 0 outmcastpkts: 7 inaddrerrors: 0 indiscards: 0 outdiscards: 0 #...
Page 415
1-25 round-trip min/avg/max = 3/3/3 ms as shown in the output information, host can ping switch b and switch a. Troubleshooting ipv6 basics configuration symptom the peer ipv6 address cannot be pinged. Solution z use the display current-configuration command in any view or the display this command i...
Page 416: Table of Contents
I table of contents 1 dual stack configuration··························································································································1-1 dual stack overview·············································································································...
Page 417: Dual Stack Configuration
1-1 1 dual stack configuration when configuring dual stack, go to these sections for information you are interested in: z dual stack overview z configuring dual stack dual stack overview dual stack is the most direct approach to making ipv6 nodes compatible with ipv4 nodes. The best way for an ipv6 ...
Page 419: Table of Contents
I table of contents 1 sflow configuration ··································································································································1-1 sflow overview··············································································································...
Page 420: Sflow Configuration
1-1 1 sflow configuration when configuring sflow, go to these sections for information you are interested in: z sflowoverview z configuring sflow z displaying and maintaining sflow z sflow configuration example z troubleshooting sflow configuration sflow overview introduction to sflow sampled flow (...
Page 421: Configuring Sflow
1-2 3) when the sflow packet buffer overflows or the one-second timer expires, the sflow agent sends sflow packets to the specified sflow collector. Configuring sflow the sflow feature enables the remote sflow collector to monitor the network and analyze sflow packet statistics. Follow these steps t...
Page 422
1-3 sflow configuration example network requirements z host a and server are connected to switch through gigabitethernet 1/0/1 and gigabitethernet 1/0/2 respectively. Z host b works as an sflow collector with ip address 3.3.3.2 and port number 6343, and is connected to switch through gigabitethernet...
Page 423
1-4 collector ip:3.3.3.2 port:6343 interval(s): 30 sflow port information: interface direction rate mode status ge1/0/1 in/out 100000 random active troubleshooting sflow configuration the remote sflow collector cannot receive sflow packets symptom the remote sflow collector cannot receive sflow pack...
Page 424: Manual Version
Ip routing volume organization manual version 6w100-20090630 product version release 2202 organization the ip routing volume is organized as follows: features description ip routing overview this document describes: z introduction to ip routing and routing table z routing protocol overview static ro...
Page 425: Table of Contents
I table of contents 1 ip routing overview··································································································································1-1 ip routing and routing table·································································································...
Page 426: Ip Routing Overview
1-1 1 ip routing overview go to these sections for information you are interested in: z ip routing and routing table z routing protocol overview z displaying and maintaining a routing table the term “router” in this document refers to a router in a generic sense or a layer 3 switch. Ip routing and r...
Page 427
1-2 z network mask: specifies, in company with the destination address, the address of the destination network. A logical and operation between the destination address and the network mask yields the address of the destination network. For example, if the destination address is 129.102.8.10 and the ...
Page 428: Routing Protocol Overview
1-3 figure 1-1 a sample routing table router a router b router h router e 16.0.0.2 17.0.0.3 15.0.0.0 12.0.0.0 17.0.0.0 11.0.0.0 16.0.0.0 13.0.0.0 14.0.0.0 router c router d router f router g 11.0.0.1 12.0.0.1 12.0.0.2 15.0.0.1 15.0.0.2 17.0.0.1 16.0.0.1 13.0.0.1 13.0.0.2 14.0.0.1 14.0.0.2 14.0.0.3 1...
Page 429
1-4 routing approach priority direct 0 static 60 unknown 256 z the smaller the priority value, the higher the priority. Z the priority for a direct route is always 0, which you cannot change. Any other type of routes can have their priorities manually configured. Z each static route can be configure...
Page 430
1-5 to do… use the command… remarks display ipv6 routing information for an ipv6 address range display ipv6 routing-table ipv6-address1 prefix-length1 ipv6-address2 prefix-length2 [ verbose ] available in any view clear specified ipv6 routing table statistics reset ipv6 routing-table statistics prot...
Page 431: Table of Contents
I table of contents 1 static routing configuration····················································································································1-1 introduction ·····················································································································...
Page 432: Static Routing Configuration
1-1 1 static routing configuration when configuring a static route, go to these sections for information you are interested in: z introduction z configuring a static route z detecting reachability of the static route’s nexthop z displaying and maintaining static routes z static route configuration e...
Page 433: Configuring A Static Route
1-2 application environment of static routing before configuring a static route, you need to know the following concepts: 1) destination address and mask in the ip route-static command, an ipv4 address is in dotted decimal format and a mask can be either in dotted decimal format or in the form of ma...
Page 434
1-3 z when configuring a static route, the static route does not take effect if you specify the next hop address first and then configure it as the ip address of a local interface. Z if you do not specify the preference when configuring a static route, the default preference will be used. Reconfigur...
Page 435
1-4 z to configure this feature for an existing static route, simply associate the static route with a track entry. For a non-existent static route, configure it and associate it with a track entry. Z if a static route needs route recursion, the associated track entry must monitor the nexthop of the...
Page 436
1-5 configuration procedure 1) configuring ip addresses for interfaces (omitted) 2) configuring static routes # configure a default route on switch a. System-view [switcha] ip route-static 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 1.1.4.2 # configure two static routes on switch b. System-view [switchb] ip route-static 1.1.2....
Page 437
1-6 127.0.0.0/8 direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 inloop0 127.0.0.1/32 direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 inloop0 1.1.6.0/24 direct 0 0 192.168.1.47 vlan100 1.1.6.1/32 direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 inloop0 # use the ping command on host b to check reachability to host a, assuming windows xp runs on the two hosts. C:\documents and sett...
Page 438: Table of Contents
I table of contents 1 ipv6 static routing configuration ···········································································································1-1 introduction to ipv6 static routing··································································································...
Page 439
1-1 1 ipv6 static routing configuration when configuring ipv6 static routing, go to these sections for information you are interested in: z introduction to ipv6 static routing z configuring an ipv6 static route z displaying and maintaining ipv6 static routes z ipv6 static routing configuration examp...
Page 440
1-2 z enabling ipv6 packet forwarding z ensuring that the neighboring nodes are ipv6 reachable configuring an ipv6 static route follow these steps to configure an ipv6 static route: to do… use the commands… remarks enter system view system-view — configure an ipv6 static route ipv6 route-static ipv6...
Page 441
1-3 configuration procedure 1) configure the ipv6 addresses of all vlan interfaces (omitted) 2) configure ipv6 static routes. # configure the default ipv6 static route on switcha. System-view [switcha] ipv6 route-static :: 0 4::2 # configure two ipv6 static routes on switchb. System-view [switchb] i...
Page 442
1-4 reply from 3::1 bytes=56 sequence=1 hop limit=254 time = 63 ms reply from 3::1 bytes=56 sequence=2 hop limit=254 time = 62 ms reply from 3::1 bytes=56 sequence=3 hop limit=254 time = 62 ms reply from 3::1 bytes=56 sequence=4 hop limit=254 time = 63 ms reply from 3::1 bytes=56 sequence=5 hop limi...
Page 443: Manual Version
Ip multicast volume organization manual version 6w100-20090630 product version release 2202 organization the ip multicast volume is organized as follows: features description multicast overview this document describes the main concepts in multicast: z introduction to multicast z multicast models z m...
Page 444: Table of Contents
I table of contents 1 multicast overview ····································································································································1-1 introduction to multicast ·································································································...
Page 445: Multicast Overview
1-1 1 multicast overview this manual chiefly focuses on the ip multicast technology and device operations. Unless otherwise stated, the term “multicast” in this document refers to ip multicast. Introduction to multicast as a technique coexisting with unicast and broadcast, the multicast technique ef...
Page 446
1-2 figure 1-1 unicast transmission source receiver receiver receiver host a host b host c host d host e packets for host b packets for host d packets for host e ip network assume that host b, host d and host e need the information. A separate transmission channel needs to be established from the in...
Page 447
1-3 figure 1-2 broadcast transmission assume that only host b, host d, and host e need the information. If the information is broadcast to the subnet, host a and host c also receive it. In addition to information security issues, this also causes traffic flooding on the same subnet. Therefore, broad...
Page 448
1-4 figure 1-3 multicast transmission the multicast source (source in the figure) sends only one copy of the information to a multicast group. Host b, host d and host e, which are receivers of the information, need to join the multicast group. The routers on the network duplicate and forward the inf...
Page 449: Multicast Models
1-5 for a better understanding of the multicast concept, you can assimilate multicast transmission to the transmission of tv programs, as shown in table 1-1 . Table 1-1 an analogy between tv transmission and multicast transmission tv transmission multicast transmission a tv station transmits a tv pr...
Page 450: Multicast Architecture
1-6 asm model in the asm model, any sender can send information to a multicast group as a multicast source, and numbers of receivers can join a multicast group identified by a group address and obtain multicast information addressed to that multicast group. In this model, receivers are not aware of ...
Page 451
1-7 multicast addresses to allow communication between multicast sources and multicast group members, network-layer multicast addresses, namely, multicast ip addresses must be provided. In addition, a technique must be available to map multicast ip addresses to link-layer multicast mac addresses. Ip...
Page 452
1-8 address description 224.0.0.7 shared tree (st) routers 224.0.0.8 st hosts 224.0.0.9 routing information protocol version 2 (ripv2) routers 224.0.0.11 mobile agents 224.0.0.12 dynamic host configuration protocol (dhcp) server/relay agent 224.0.0.13 all protocol independent multicast (pim) routers...
Page 453
1-9 bit description t z when set to 0, it indicates that this address is an ipv6 multicast address permanently-assigned by iana z when set to 1, it indicates that this address is a transient, or dynamically assigned ipv6 multicast address z scope: 4 bits, indicating the scope of the ipv6 internetwor...
Page 454
1-10 the high-order four bits of a multicast ipv4 address are 1110, indicating that this address is a multicast address, and only 23 bits of the remaining 28 bits are mapped to a mac address, so five bits of the multicast ipv4 address are lost. As a result, 32 multicast ipv4 addresses map to the sam...
Page 455
1-11 figure 1-8 positions of layer 3 multicast protocols 1) multicast management protocols typically, the internet group management protocol (igmp) or multicast listener discovery protocol (mld) is used between hosts and layer 3 multicast devices directly connected with the hosts. These protocols de...
Page 456
1-12 figure 1-9 position of layer 2 multicast protocols source receiver receiver ipv4/ipv6 multicast packets igmp snooping /mld snooping multicast vlan /ipv6 multicast vlan 1) igmp snooping/mld snooping running on layer 2 devices, internet group management protocol snooping (igmp snooping) and multi...
Page 457: Table of Contents
I table of contents 1 igmp snooping configuration ·················································································································1-1 igmp snooping overview···············································································································...
Page 458: Igmp Snooping Configuration
1-1 1 igmp snooping configuration when configuring igmp snooping, go to the following sections for information you are interested in: z igmp snooping overview z igmp snooping configuration task list z displaying and maintaining igmp snooping z igmp snooping configuration examples z troubleshooting i...
Page 459
1-2 z reducing layer 2 broadcast packets, thus saving network bandwidth. Z enhancing the security of multicast traffic. Z facilitating the implementation of per-host accounting. Basic concepts in igmp snooping igmp snooping related ports as shown in figure 1-2 , router a connects to the multicast so...
Page 460
1-3 aging timers for dynamic ports in igmp snooping and related messages and actions table 1-1 aging timers for dynamic ports in igmp snooping and related messages and actions timer description message before expiry action after expiry dynamic router port aging timer for each dynamic router port, th...
Page 461
1-4 when receiving a membership report a host sends an igmp report to the igmp querier in the following circumstances: z upon receiving an igmp query, a multicast group member host responds with an igmp report. Z when intended to join a multicast group, a host sends an igmp report to the igmp querie...
Page 462
1-5 upon receiving the igmp leave message from a host, the igmp querier resolves the multicast group address in the message and sends an igmp group-specific query to that multicast group through the port that received the leave message. Upon receiving the igmp group-specific query, the switch forwar...
Page 463
1-6 z configurations made in igmp snooping view are effective for all vlans, while configurations made in vlan view are effective only for ports belonging to the current vlan. For a given vlan, a configuration made in igmp snooping view is effective only if the same configuration is not made in vlan...
Page 464
1-7 z igmp snooping must be enabled globally before it can be enabled in a vlan. Z when you enable igmp snooping in a specified vlan, this function takes effect for the ports in this vlan only. Configuring the version of igmp snooping by configuring an igmp snooping version, you actually configure t...
Page 465
1-8 configuring aging timers for dynamic ports if the switch receives no igmp general queries or pim hello messages on a dynamic router port, the switch removes the port from the router port list when the aging timer of the port expires. If the switch receives no igmp reports for a multicast group o...
Page 466
1-9 follow these steps to configure static ports: to do... Use the command... Remarks enter system view system-view — interface interface-type interface-number enter ethernet port/layer 2 aggregate port view or port group view port-group manual port-group-name required use either approach configure ...
Page 467
1-10 follow these steps to configure simulated joining: to do... Use the command... Remarks enter system view system-view — interface interface-type interface-number enter ethernet port/layer 2 aggregate port view or port group view port-group manual port-group-name required use either approach conf...
Page 468
1-11 configuring fast leave processing on a port or a group of ports follow these steps to configure fast leave processing on a port or a group of ports: to do... Use the command... Remarks enter system view system-view — interface interface-typeinterface-number enter ethernet port/layer 2 aggregate...
Page 469
1-12 follow these steps to enable igmp snooping querier: to do... Use the command... Remarks enter system view system-view — enter vlan view vlan vlan-id — enable igmp snooping querier igmp-snooping querier required disabled by default it is meaningless to configure an igmp snooping querier in a mul...
Page 470
1-13 configuring igmp queries and responses in a vlan follow these steps to configure igmp queries and responses in a vlan: to do... Use the command... Remarks enter system view system-view — enter vlan view vlan vlan-id — configure igmp general query interval igmp-snooping query-interval interval o...
Page 471
1-14 configuring an igmp snooping policy configuration prerequisites before configuring an igmp snooping policy, complete the following task: z enable igmp snooping in the vlan or enable igmp on the desired vlan interface before configuring an igmp snooping policy, prepare the following data: z acl ...
Page 472
1-15 configuring multicast source port filtering with the multicast source port filtering feature enabled on a port, the port can be connected with multicast receivers only rather than with multicast sources, because the port will block all multicast data packets while it permits multicast protocol ...
Page 473
1-16 to do... Use the command... Remarks enter system view system-view — enter vlan view vlan vlan-id — enable the function of dropping unknown multicast data igmp-snooping drop-unknown required disabled by default configuring igmp report suppression when a layer 2 device receives an igmp report fro...
Page 474
1-17 z when the number of multicast groups a port has joined reaches the maximum number configured, the system deletes all the forwarding entries persistent to that port from the igmp snooping forwarding table, and the hosts on this port need to join the multicast groups again. Z if you have configu...
Page 475
1-18 configuring multicast group replacement on a port or a group of ports follow these steps to configure multicast group replacement on a port or a group of ports: to do... Use the command... Remarks enter system view system-view — interface interface-type interface-number enter ethernet port/laye...
Page 476
1-19 igmp snooping configuration examples configuring group policy and simulated joining network requirements z as shown in figure 1-3 , router a connects to the multicast source through gigabitethernet 1/0/2 and to switch a through gigabitethernet 1/0/1. Z igmpv2 is required on router a, igmp snoop...
Page 477
1-20 [routera-gigabitethernet1/0/2] pim dm [routera-gigabitethernet1/0/2] quit 3) configure switch a # enable igmp snooping globally. System-view [switcha] igmp-snooping [switcha-igmp-snooping] quit # create vlan 100, assign gigabitethernet 1/0/1 through gigabitethernet 1/0/4 to this vlan, and enabl...
Page 478
1-21 ip group(s):the following ip group(s) match to one mac group. Ip group address:224.1.1.1 (0.0.0.0, 224.1.1.1): attribute: host port host port(s):total 2 port. Ge1/0/3 (d) ( 00:03:23 ) ge1/0/4 (d) ( 00:04:10 ) mac group(s): mac group address:0100-5e01-0101 host port(s):total 2 port. Ge1/0/3 ge1/...
Page 479
1-22 network diagram figure 1-4 network diagram for static port configuration source 1.1.1.1/24 router a igmp querier ge1/0/1 10.1.1.1/24 ge1/0/2 1.1.1.2/24 switch a switch c switch b ge1/0/1 g e 1 /0 /2 g e 1 /0 /3 g e 1 /0 /1 ge1/0/2 g e 1 /0 /1 ge1/0/2 host c host b host a receiver receiver g e 1...
Page 480
1-23 [switcha-vlan100] quit # configure gigabitethernet 1/0/3 to be a static router port. [switcha] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/3 [switcha-gigabitethernet1/0/3] igmp-snooping static-router-port vlan 100 [switcha-gigabitethernet1/0/3] quit 4) configure switch b # enable igmp snooping globally. Syst...
Page 481
1-24 vlan(id):100. Total 1 ip group(s). Total 1 ip source(s). Total 1 mac group(s). Router port(s):total 2 port. Ge1/0/1 (d) ( 00:01:30 ) ge1/0/3 (s) ip group(s):the following ip group(s) match to one mac group. Ip group address:224.1.1.1 (0.0.0.0, 224.1.1.1): attribute: host port host port(s):total...
Page 482
1-25 igmp snooping querier configuration network requirements z as shown in figure 1-5 , in a layer 2–only network environment, two multicast sources source 1 and source 2 send multicast data to multicast groups 224.1.1.1 and 225.1.1.1 respectively, host a and host c are receivers of multicast group...
Page 483
1-26 # enable the igmp-snooping querier function in vlan 100 [switcha-vlan100] igmp-snooping querier # set the source ip address of igmp general queries and group-specific queries to 192.168.1.1 in vlan 100. [switcha-vlan100] igmp-snooping general-query source-ip 192.168.1.1 [switcha-vlan100] igmp-s...
Page 484
1-27 troubleshooting igmp snooping configuration switch fails in layer 2 multicast forwarding symptom a switch fails to implement layer 2 multicast forwarding. Analysis igmp snooping is not enabled. Solution 1) enter the display current-configuration command to view the running status of igmp snoopi...
Page 485: Table of Contents
I table of contents 1 multicast vlan configuration··················································································································1-1 introduction to multicast vlan······································································································...
Page 486: Multicast Vlan Configuration
1-1 1 multicast vlan configuration when configuring multicast vlan, go to these sections for information you are interested in: z introduction to multicast vlan z multicast vlan configuration task list z configuring sub-vlan-based multicast vlan z configuring port-based multicast vlan z displaying a...
Page 487
1-2 figure 1-2 sub-vlan-based multicast vlan source router a igmp querier vlan 2 vlan 3 vlan 4 switch a receiver host a receiver host b receiver host c multicast packets vlan 2 vlan 3 vlan 4 vlan 10 (multicast vlan) after the configuration, igmp snooping manages router ports in the multicast vlan an...
Page 488
1-3 z for information about igmp snooping, router ports, and member ports, refer to igmp snooping configuration in the ip multicast volume. Z for information about vlan tags, refer to vlan configuration in the access volume. Multicast vlan configuration task list complete the following tasks to conf...
Page 489
1-4 z the vlan to be configured as a multicast vlan must exist. Z the vlans to be configured as sub-vlans of the multicast vlan must exist and must not be sub-vlans of another multicast vlan. Z the total number of sub-vlans of a multicast vlan must not exceed 63. Configuring port-based multicast vla...
Page 491
1-6 configuring multicast vlan ports in port view or port group view follow these steps to configure multicast vlan ports in port view or port group view: to do… use this command… remarks enter system view system-view — configure the specified vlan as a multicast vlan and enter multicast vlan view m...
Page 492
1-7 z configure the sub-vlan-based multicast vlan feature so that router a just sends multicast data to switch a through the multicast vlan and switch a forwards the traffic to the receivers that belong to different user vlans. Network diagram figure 1-4 network diagram for sub-vlan-based multicast ...
Page 493
1-8 [switcha-vlan2] port gigabitethernet 1/0/2 [switcha-vlan2] quit the configuration for vlan 3 and vlan 4 is similar to the configuration for vlan 2. # create vlan 10, assign gigabitethernet 1/0/1 to this vlan and enable igmp snooping in the vlan. [switcha] vlan 10 [switcha-vlan10] port gigabiteth...
Page 494
1-9 total 1 ip group(s). Total 1 ip source(s). Total 1 mac group(s). Router port(s):total 0 port. Ip group(s):the following ip group(s) match to one mac group. Ip group address:224.1.1.1 (0.0.0.0, 224.1.1.1): host port(s):total 1 port. Ge1/0/3 (d) mac group(s): mac group address:0100-5e01-0101 host ...
Page 495
1-10 port-based multicast vlan configuration network requirements z as shown in figure 1-5 , router a connects to a multicast source (source) through gigabitethernet 1/0/1, and to switch a through gigabitethernet 1/0/2. Z igmpv2 is required on router a. Igmpv2 snooping is required on switch a. Route...
Page 496
1-11 [routera-gigabitethernet1/0/1] quit [routera] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/2 [routera-gigabitethernet1/0/2] pim dm [routera-gigabitethernet1/0/2] igmp enable 3) configure switch a # enable igmp snooping globally. System-view [switcha] igmp-snooping [switcha-igmp-snooping] quit # create vlan 10...
Page 497
1-12 total 1 multicast-vlan(s) multicast vlan 10 subvlan list: no subvlan port list: ge1/0/2 ge1/0/3 ge1/0/4 # view the igmp snooping multicast group information on switch a. [switcha] display igmp-snooping group total 1 ip group(s). Total 1 ip source(s). Total 1 mac group(s). Port flags: d-dynamic ...
Page 498: Table of Contents
I table of contents 1 mld snooping configuration···················································································································1-1 mld snooping overview ···············································································································...
Page 499: Mld Snooping Configuration
1-1 1 mld snooping configuration when configuring mld snooping, go to these sections for information you are interested in: z mld snooping overview z mld snooping configuration task list z displaying and maintaining mld snooping z mld snooping configuration examples z troubleshooting mld snooping ml...
Page 500
1-2 z reducing layer 2 broadcast packets, thus saving network bandwidth. Z enhancing the security of multicast traffic. Z facilitating the implementation of per-host accounting. Basic concepts in mld snooping mld snooping related ports as shown in figure 1-2 , router a connects to the multicast sour...
Page 501
1-3 z whenever mentioned in this document, a router port is a router-connecting port on the switch, rather than a port on a router. Z unless otherwise specified, router/member ports mentioned in this document include static and dynamic ports. Z on an mld snooping-enabled switch, the ports that recei...
Page 502
1-4 general queries the mld querier periodically sends mld general queries to all hosts and routers (ff02::1) on the local subnet to find out whether ipv6 multicast group members exist on the subnet. Upon receiving an mld general query, the switch forwards it through all ports in the vlan except the...
Page 503
1-5 z if the forwarding table entry does not exist or if the outgoing port list does not contain the port, the switch discards the mld done message instead of forwarding it to any port. Z if the forwarding table entry exists and the outgoing port list contains the port, the switch forwards the mld d...
Page 504
1-6 task remarks configuring an ipv6 multicast group filter optional configuring ipv6 multicast source port filtering optional configuring mld report suppression optional configuring maximum multicast groups that can be joined on a port optional configuring an mld snooping policy configuring ipv6 mu...
Page 505
1-7 to do... Use the command... Remarks enter vlan view vlan vlan-id — enable mld snooping in the vlan mld-snooping enable required disabled by default z mld snooping must be enabled globally before it can be enabled in a vlan. Z when you enable mld snooping in a specified vlan, this function takes ...
Page 506
1-8 z configure the corresponding port groups before configuring mld snooping port functions, prepare the following data: z aging time of dynamic router ports, z aging timer of dynamic member ports, and z ipv6 multicast group and ipv6 multicast source addresses configuring aging timers for dynamic p...
Page 507
1-9 follow these steps to configure static ports: to do... Use the command... Remarks enter system view system-view — interface interface-type interface-number enter ethernet port/layer 2 aggregate port view or port group view port-group manual port-group-name required use either approach configure ...
Page 508
1-10 follow these steps to configure simulated joining: to do... Use the command... Remarks enter system view system-view — interface interface-type interface-number enter ethernet port/layer 2 aggregate port view or port group view port-group manual port-group-name required use either approach conf...
Page 509
1-11 configuring fast leave processing on a port or a group of ports follow these steps to configure fast leave processing on a port or a group of ports: to do... Use the command... Remarks enter system view system-view — interface interface-type interface-number enter ethernet port/layer 2 aggregat...
Page 510
1-12 to do... Use the command... Remarks enter system view system-view — enter vlan view vlan vlan-id — enable the mld snooping querier mld-snooping querier required disabled by default it is meaningless to configure an mld snooping querier in an ipv6 multicast network running mld. Although an mld s...
Page 511
1-13 configuring mld queries and responses in a vlan follow these steps to configure mld queries and responses in a vlan to do... Use the command... Remarks enter system view system-view — enter vlan view vlan vlan-id — configure mld query interval mld-snooping query-interval interval optional 125 s...
Page 512
1-14 configuring an mld snooping policy configuration prerequisites before configuring an mld snooping policy, complete the following tasks: z enable mld snooping in the vlan or enable mld on the desired vlan interface before configuring an mld snooping policy, prepare the following data: z ipv6 acl...
Page 513
1-15 configuring ipv6 multicast source port filtering with the ipv6 multicast source port filtering feature enabled on a port, the port can be connected with ipv6 multicast receivers only rather than with multicast sources, because the port will block all ipv6 multicast data packets while it permits...
Page 514
1-16 mld reports from the same multicast group to the layer 3 device. This helps reduce the number of packets being transmitted over the network. Follow these steps to configure mld report suppression: to do... Use the command... Remarks enter system view system-view — enter mld snooping view mld-sn...
Page 515
1-17 z when the number of ipv6 multicast groups that can be joined on a port reaches the maximum number configured, the system deletes all the forwarding entries persistent to that port from the mld snooping forwarding table, and the hosts on this port need to join ipv6 multicast groups again. Z if ...
Page 516
1-18 configuring ipv6 multicast group replacement on a port or a group of ports follow these steps to configure ipv6 multicast group replacement on a port or a group of ports: to do... Use the command... Remarks enter system view system-view — interface interface-type interface-number enter ethernet...
Page 517
1-19 mld snooping configuration examples configuring ipv6 group policy and simulated joining network requirements z as shown in figure 1-3 , router a connects to the ipv6 multicast source through gigabitethernet 1/0/2 and to switch a through gigabitethernet 1/0/1. Router a is the mld querier on the ...
Page 518
1-20 [routera-gigabitethernet1/0/2] pim ipv6 dm [routera-gigabitethernet1/0/2] quit 3) configure switch a # enable mld snooping globally. System-view [switcha] mld-snooping [switcha-mld-snooping] quit # create vlan 100, assign gigabitethernet 1/0/1 through gigabitethernet 1/0/4 to this vlan, and ena...
Page 519
1-21 ip group address:ff1e::101 (::, ff1e::101): attribute: host port host port(s):total 2 port. Ge1/0/3 (d) ( 00:03:23 ) ge1/0/4 (d) ( 00:04:10 ) mac group(s): mac group address:3333-0000-1001 host port(s):total 2 port. Ge1/0/3 ge1/0/4 as shown above, gigabitethernet 1/0/3 and gigabitethernet 1/0/4...
Page 520
1-22 network diagram figure 1-4 network diagram for static port configuration source 1::1/64 router a mld querier ge1/0/1 2001::1/64 ge1/0/2 1::2/64 switch a switch c switch b ge1/0/1 g e 1 /0 /2 g e 1 /0 /3 g e 1 /0 /1 ge1/0/2 g e 1 /0 /1 ge1/0/2 host c host b host a receiver receiver g e 1 /0 /3 g...
Page 521
1-23 [switcha-vlan100] quit # configure gigabitethernet 1/0/3 to be a static router port. [switcha] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/3 [switcha-gigabitethernet1/0/3] mld-snooping static-router-port vlan 100 [switcha-gigabitethernet1/0/3] quit 4) configure switch b # enable mld snooping globally. System...
Page 522
1-24 vlan(id):100. Total 1 ip group(s). Total 1 ip source(s). Total 1 mac group(s). Router port(s):total 2 port. Ge1/0/1 (d) ( 00:01:30 ) ge1/0/3 (s) ip group(s):the following ip group(s) match to one mac group. Ip group address:ff1e::101 (::, ff1e::101): attribute: host port host port(s):total 1 po...
Page 523
1-25 mld snooping querier configuration network requirements z as shown in figure 1-5 , in a layer-2-only network environment, two multicast sources source 1 and source 2 send ipv6 multicast data to multicast groups ff1e::101 and ff1e::102 respectively, host a and host c are receivers of multicast g...
Page 524: Troubleshooting Mld Snooping
1-26 [switchb] ipv6 [switchb] mld-snooping [switchb-mld-snooping] quit # create vlan 100, add gigabitethernet 1/0/1 through gigabitethernet 1/0/4 into vlan 100. [switchb] vlan 100 [switchb-vlan100] port gigabitethernet 1/0/1 to gigabitethernet 1/0/4 # enable the mld snooping feature in vlan 100. [sw...
Page 525
1-27 configured ipv6 multicast group policy fails to take effect symptom although an ipv6 multicast group policy has been configured to allow hosts to join specific ipv6 multicast groups, the hosts can still receive ipv6 multicast data addressed to other groups. Analysis z the ipv6 acl rule is incor...
Page 526: Table of Contents
I table of contents 1 ipv6 multicast vlan configuration ·········································································································1-1 introduction to ipv6 multicast vlan ···································································································...
Page 527
1-1 1 ipv6 multicast vlan configuration when configuring ipv6 multicast vlan, go to these sections for information you are interested in: z introduction to ipv6 multicast vlan z ipv6 multicast vlan configuration task list z configuring ipv6 sub-vlan-based ipv6 multicast vlan z configuring port-based...
Page 528
1-2 figure 1-2 sub-vlan-based ipv6 multicast vlan source router a mld querier vlan 2 vlan 3 vlan 4 switch a receiver host a receiver host b receiver host c ipv6 multicast packets vlan 2 vlan 3 vlan 4 vlan 10 (ipv6 multicast vlan) after the configuration, mld snooping manages router ports in the ipv6...
Page 529
1-3 z for information about mld snooping, router ports, and member ports, refer to mld snooping configuration in the ip multicast volume. Z for information about vlan tags, refer to vlan configuration in the access volume. Ipv6 multicast vlan configuration task list complete the following tasks to c...
Page 530
1-4 to do… use the command… remarks configure the specified vlan(s) as sub-vlan(s) of the ipv6 multicast vlan subvlan vlan-list required by default, an ipv6 multicast vlan has no sub-vlans. Z the vlan to be configured as an ipv6 multicast vlan must exist. Z the vlans to be configured as the sub-vlan...
Page 531
1-5 to do... Use the command... Remarks enter system view system-view — interface interface-type interface-number enter port view or port group view port-group manual port-group-name required use either approach. Configue the user port link type as hybrid port link-type hybrid required access by def...
Page 532
1-6 configure ipv6 multicast vlan ports in terface view or port group view follow these steps to configure ipv6 multicast vlan ports in port view or port group view: to do… use this command… remarks enter system view system-view — configure the specified vlan as an ipv6 multicast vlan and enter ipv6...
Page 533
1-7 z configure the sub-vlan-based ipv6 multicast vlan feature so that router a just sends ipv6 multicast data to switch a through the ipv6 multicast vlan and switch a forwards the traffic to the receivers that belong to different user vlans. Figure 1-4 network diagram for sub-vlan-based ipv6 multic...
Page 534
1-8 the configuration for vlan 3 and vlan 4 is similar to the configuration for vlan 2. # create vlan 10, assign gigabitethernet 1/0/1 to this vlan and enable mld snooping in the vlan. [switcha] vlan 10 [switcha-vlan10] port gigabitethernet 1/0/1 [switcha-vlan10] mld-snooping enable [switcha-vlan10]...
Page 535
1-9 ip group(s):the following ip group(s) match to one mac group. Ip group address:ff1e::101 (::, ff1e::101): host port(s):total 1 port. Ge1/0/3 (d) mac group(s): mac group address:3333-0000-0101 host port(s):total 1 port. Ge1/0/3 vlan(id):4. Total 1 ip group(s). Total 1 ip source(s). Total 1 mac gr...
Page 536
1-10 z switch a’s gigabitethernet 1/0/1 belongs to vlan 10, gigabitethernet 1/0/2 through gigabitethernet 1/0/4 belong to vlan 2 through vlan 4 respectively, and host a through host c are attached to gigabitethernet 1/0/2 through gigabitethernet 1/0/4 of switch a. Z the ipv6 multicast source sends i...
Page 537
1-11 # create vlan 10, assign gigabitethernet 1/0/1 to vlan 10, and enable mld snooping in this vlan. [switcha] vlan 10 [switcha-vlan10] port gigabitethernet 1/0/1 [switcha-vlan10] mld-snooping enable [switcha-vlan10] quit # create vlan 2 and enable mld snooping in the vlan. [switcha] vlan 2 [switch...
Page 538
1-12 total 1 mac group(s). Port flags: d-dynamic port, s-static port, c-copy port subvlan flags: r-real vlan, c-copy vlan vlan(id):10. Total 1 ip group(s). Total 1 ip source(s). Total 1 mac group(s). Router port(s):total 1 port. Ge1/0/1 (d) ip group(s):the following ip group(s) match to one mac grou...
Page 539: Qos Volume Organization
Qos volume organization manual version 6w100-20090630 product version release 2202 organization the qos volume is organized as follows: features description qos this document describes: z qos overview z qos policy configuration z priority mapping configuration z traffic policing configuration z traf...
Page 540: Table of Contents
I table of contents 1 qos overview ············································································································································1-1 introduction ············································································································...
Page 541
Ii 5 congestion management ··························································································································5-1 overview ··········································································································································...
Page 542: Qos Overview
1-1 1 qos overview this chapter covers these topics: z introduction z traditional packet forwarding service z new requirements from emerging services z congestion: causes, impacts, and countermeasures z major traffic management techniques introduction quality of service (qos) is a concept concerning...
Page 543
1-2 the emerging applications demand higher service performance of ip networks. Better network services during packets forwarding are required, such as providing dedicated bandwidth, reducing packet loss ratio, managing and avoiding congestion, regulating network traffic, and setting the precedence ...
Page 544
1-3 a more effective solution is to provide differentiated services for different applications through traffic control and resource allocation. In this way, resources can be used more properly. During resources allocation and traffic control, the direct or indirect factors that might cause network c...
Page 545
1-4 this section is focused on traffic classification, and the subsequent sections will introduce the other technologies in details. Traffic classification traffic classification organizes packets with different characteristics into different classes using match criteria. It is the basis for providi...
Page 546: Qos Policy Configuration
2-1 2 qos policy configuration when configuring qos policy, go to these sections for information that you are interested in: z overview z configuring a qos policy z displaying and maintaining qos policies overview qos policy includes the following three elements: class, traffic behavior and policy. ...
Page 548
2-3 form description dscp dscp-list specifies to match packets by dscp precedence. The dscp-list argument is a list of dscp values in the range of 0 to 63. Even though you can provide up to eight space-separated dscp values for this argument, the s5120-ei switch supports only one dscp value in a rul...
Page 549
2-4 configuration example 1) network requirements configure a class named test to match the packets with their ip precedence being 6. 2) configuration procedure # enter system view. System-view # create the class. (this operation leads you to class view.) [sysname] traffic classifier test # define t...
Page 550
2-5 to do… use the command… remarks configure accounting action accounting configure traffic policing action car cir committed-information-rate [ cbs committed-burst-size [ ebs excess-burst-size ] ] [ pir peak-information-rate ] [ green action ] [ red action ] [ yellow action ] configure traffic fil...
Page 551
2-6 to do… use the command… remarks enter system view system-view — create a policy (this operation leads you to policy view) qos policy policy-name — specify the traffic behavior for a class classifier classifier-name behavior behavior-name required applying a policy you can apply a qos policy in d...
Page 552
2-7 to do… use the command… remarks apply an associated policy qos apply policy policy-name inbound required applying a qos policy to online users you can apply a qos policy to traffic of multiple online users. You can apply only one policy in one direction (inbound or outbound) of the traffic of on...
Page 553
2-8 z qos policies cannot be applied to dynamic vlans, for example, vlans created by gvrp. Z do not apply a qos policy to a vlan and the ports in the vlan at the same time. Configuration example 1) configuration example 1 configure a qos policy test_policy. Associate the traffic behavior test_behavi...
Page 554
2-9 to do… use the command… remarks display information about the policies applied on a port display qos policy interface [ interface-type interface-number ] [ inbound ] available in any view display information about a traffic behavior display traffic behavior user-defined [ behavior-name ] availab...
Page 555: Priority Mapping
3-1 3 priority mapping when configuring priority mapping, go to these sections for information you are interested in: z priority overview z priority mapping overview z configuring a priority mapping table z configuring the port priority z configuring port priority trust mode z displaying and maintai...
Page 556
3-2 ip precedence (decimal) ip precedence (binary) description 6 110 internet 7 111 network in a network providing differentiated services, traffics are grouped into the following four classes, and packets are processed according to their dscp values. Z expedited forwarding (ef) class: in this class...
Page 557
3-3 dscp value (decimal) dscp value (binary) description 56 111000 cs7 0 000000 be (default) 2) 802.1p priority 802.1p priority lies in layer 2 packet headers and is applicable to occasions where the layer 3 packet header does not need analysis but qos must be assured at layer 2. Figure 3-2 an ether...
Page 558: Priority Mapping Overview
3-4 the precedence is called 802.1p priority because the related applications of this precedence are defined in detail in the 802.1p specifications. Priority mapping overview when a packet reaches a switch, the switch assigns the packet parameters according to it configuration, such as 802.1p preced...
Page 559
3-5 figure 3-4 priority mapping process in the case of supporting trusting port priority y n search for the set of precedence values corresponding to the trusted type of priority of the packet in the corresponding priority mapping tables and assigns the set of matching precedence values to the packe...
Page 560
3-6 table 3-5 the default values of dscp-dp mapping, dscp-dot1p mapping, and dscp-dscp mapping imported priority value dscp-dp mapping dscp-dot1p mapping dscp-dscp mapping dscp precedence (dscp) drop precedence (dp) 802.1p precedence (dot1p) dscp precedence (dscp) 0 to 7 0 0 0 to 7 8 to 15 0 1 8 to ...
Page 561
3-7 you cannot configure to map any dscp value to drop precedence 1. Configuration example network requirements modify the dot1p-lp mapping table as those listed in table 3-6 . Table 3-6 the specified dot1p-lp mapping 802.1p precedence local precedence 0 0 1 0 2 1 3 1 4 2 5 2 6 3 7 3 configuration p...
Page 562
3-8 configuration prerequisites the port priority of the port is determined. Configuration procedure follow these steps to configure port priority: to do… use the command… remarks enter system view system-view — enter port view interface interface-type interface-number enter port view or port group ...
Page 563
3-9 configuration procedure follow these steps to configure the port priority trust mode: to do… use the command… remarks enter system view system-view — enter port view interface interface-type interface-number enter port view or port group view enter port group view port-group manual port-group-na...
Page 564: Configuration
4-1 4 traffic policing, traffic shaping,and line rate configuration when configuring traffic classification, traffic policing, traffic shaping, and line rate, go to these section for information you are interested in: z traffic policing, traffic shaping, and line rate overview z traffic evaluation a...
Page 565
4-2 packet forwarding authority must be taken out; otherwise, this means too many tokens have been used — the traffic is in excess of the specification. Complicated evaluation you can set two token buckets (referred to as the c bucket and e bucket respectively) in order to evaluate more complicated ...
Page 566
4-3 z dropping conforming or non-conforming packets. Z marking a conforming packet or a non-conforming packet with a new dscp precedence value and forwarding the packet. Z traffic shaping traffic shaping provides measures to adjust the rate of outbound traffic actively. A typical traffic shaping app...
Page 567
4-4 figure 4-2 line rate implementation in the token bucket approach to traffic control, burst traffic can be transmitted so long as enough tokens are available in the token bucket; if tokens are inadequate, packets cannot be transmitted until the required number of tokens are generated in the token...
Page 568
4-5 to do… use the command… remarks port group view enter port group view port-group manual port-group-name settings in port group view take effect on all ports in the port group. Configure gts for a queue qos gts queue queue-number cir committed-information-rate[ cbs committed-burst-size] required ...
Page 569: Displaying Line Rate
4-6 displaying line rate to do… use the command… remarks display the line rate configuration of interfaces display qos lr interface [ interface-type interface-number ] available in any view.
Page 570: Congestion Management
5-1 5 congestion management when configuring congestion management, go to these section for information that you are interested in: z overview z congestion management policy z configuring an sp queue z configuring a wrr queue z configuring a wfq queue z configuring sp+wrr queues z displaying and mai...
Page 571
5-2 figure 5-1 diagram for sp queuing sp queue-scheduling algorithm is specially designed for critical service applications. An important feature of critical services is that they demand preferential service in congestion in order to reduce the response delay. Assume that there are eight output queu...
Page 572
5-3 a port of the switch supports eight outbound queues. The wrr queue-scheduling algorithm schedules all the queues in turn to ensure that every queue can be assigned a certain service time. Assume there are eight output queues on the port. The eight weight values (namely, w 7, w 6, w 5, w 4, w 3, ...
Page 573: Configuring An Sp Queue
5-4 z the allocable bandwidth (allocable bandwidth = the total bandwidth – the sum of the minimum guaranteed bandwidth for each queue) is divided and allocated to each queue based on queue precedence. For example, assume that the total bandwidth of an interface is 10 mbps and there are five flows on...
Page 574: Configuring A Wrr Queue
5-5 configuration example network requirements configure gigabitethernet1/0/1 to adopt sp queue scheduling algorithm. Configuration procedure # enter system view. System-view # configure an sp queue for gigabitethernet1/0/1 port. [sysname] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1 [sysname-gigabitethernet1/0/...
Page 575: Configuring A Wfq Queue
5-6 [sysname-gigabitethernet1/0/1] qos wrr 1 group 1 weight 2 [sysname-gigabitethernet1/0/1] qos wrr 2 group 1 weight 4 [sysname-gigabitethernet1/0/1] qos wrr 3 group 1 weight 6 [sysname-gigabitethernet1/0/1] qos wrr 4 group 1 weight 8 [sysname-gigabitethernet1/0/1] qos wrr 5 group 1 weight 10 [sysn...
Page 576: Configuring Sp+Wrr Queues
5-7 [sysname-gigabitethernet1/0/1] qos wfq [sysname-gigabitethernet1/0/1] qos wfq 0 weight 1 [sysname-gigabitethernet1/0/1] qos wfq 1 weight 2 [sysname-gigabitethernet1/0/1] qos wfq 2 weight 4 [sysname-gigabitethernet1/0/1] qos wfq 3 weight 6 [sysname-gigabitethernet1/0/1] qos wfq 4 weight 8 [sysnam...
Page 577
5-8 configuration procedure # enter system view. System-view # enable the sp+wrr queue scheduling algorithm on gigabitethernet1/0/1. [sysname] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1 [sysname-gigabitethernet1/0/1] qos wrr [sysname-gigabitethernet1/0/1] qos wrr 0 group sp [sysname-gigabitethernet1/0/1] qos w...
Page 578: Overview
6-1 6 traffic mirroring configuration when configuring traffic mirroring, go to these sections for information that you are interested in: z overview z configuring traffic mirroring z displaying and maintaining traffic mirroring z traffic mirroring configuration example overview traffic mirroring is...
Page 579
6-2 displaying and maintaining traffic mirroring to do… use the command… remarks display the configuration information about the user-defined traffic behavior display traffic behavior user-defined behavior-name display the configuration information about the user-defined policy display qos policy us...
Page 580
6-3 [sysname-behavior-1] quit # configure a qos policy and associate traffic behavior 1 with classification rule 1. [sysname] qos policy 1 [sysname-policy-1] classifier 1 behavior 1 [sysname-policy-1] quit # apply the policyin the inbound direction of gigabitethernet1/0/1. [sysname] interface gigabi...
Page 581: Table of Contents
I table of contents 1 user profile configuration ························································································································1-1 user profile overview ·········································································································...
Page 582: User Profile Configuration
1-1 1 user profile configuration when configuring user profile, go to these sections for information you are interested in: z user profile overview z user profile configuration z displaying and maintaining user profile user profile overview user profile provides a configuration template to save pred...
Page 583
1-2 creating a user profile configuration prerequisites before creating a user profile, you need to configure authentication parameters. User profile supports 802.1x authentications. You need to perform the related configurations (for example, username, password, authentication scheme, domain and bi...
Page 584
1-3 z when a user profile is active, you cannot configure or remove the qos policy applied to it. Z the qos policies applied in user profile view support only the remark, car, and filter actions. Z do not apply an empty qos policy in user profile view, because even if you can do that, the user profi...
Page 585: Security Volume Organization
Security volume organization manual version 6w100-20090630 product version release 2202 organization the security volume is organized as follows: features description aaa authentication, authorization and accounting (aaa) provide a uniform framework used for configuring these three security function...
Page 586
Features description port security port security is a mac address-based security mechanism for network access controlling. It is an extension to the existing 802.1x authentication and mac authentication. This document describes: z enabling port security z setting the maximum number of secure mac add...
Page 587: Table of Contents
I table of contents 1 aaa configuration ····································································································································1-1 introduction to aaa ········································································································...
Page 588
Ii specifying the hwtacacs authorization servers·······································································1-31 specifying the hwtacacs accounting servers ··········································································1-32 setting the shared key for hwtacacs packets···········...
Page 589: Aaa Configuration
1-1 1 aaa configuration when configuring aaa, go to these sections for information you are interested in: z introduction to aaa z introduction to radius z introduction to hwtacacs z protocols and standards z aaa configuration task list z configuring aaa z configuring radius z configuring hwtacacs z ...
Page 590: Introduction to Radius
1-2 requirements. For example, you can use the hwtacacs server for authentication and authorization, and the radius server for accounting. The three security functions are described as follows: z authentication: identifies remote users and judges whether a user is legal. Z authorization: grants diff...
Page 591
1-3 figure 1-2 radius server components z users: stores user information such as the usernames, passwords, applied protocols, and ip addresses. Z clients: stores information about radius clients, such as the shared keys and ip addresses. Z dictionary: stores information about the meanings of radius ...
Page 592
1-4 1) the host initiates a connection request carrying the username and password to the radius client. 2) having received the username and password, the radius client sends an authentication request (access-request) to the radius server, with the user password encrypted by using the message-digest ...
Page 593
1-5 code packet type description 3 access-reject from the server to the client. If any attribute value carried in the access-request is unacceptable, the server rejects the user and sends an access-reject response. 4 accounting-request from the client to the server. A packet of this type carries use...
Page 594
1-6 no. Attribute no. Attribute 11 filter-id 55 event-timestamp 12 framed-mtu 56-59 (unassigned) 13 framed-compression 60 chap-challenge 14 login-ip-host 61 nas-port-type 15 login-service 62 port-limit 16 login-tcp-port 63 login-lat-port 17 (unassigned) 64 tunnel-type 18 reply_message 65 tunnel-medi...
Page 595: Introduction to Hwtacacs
1-7 the attribute types listed in table 1-2 are defined by rfc 2865, rfc 2866, rfc 2867, and rfc 2568. Extended radius attributes the radius protocol features excellent extensibility. Attribute 26 (vender-specific) defined by rfc 2865 allows a vender to define extended attributes to implement functi...
Page 596
1-8 table 1-3 primary differences between hwtacacs and radius hwtacacs radius uses tcp, providing more reliable network transmission. Uses udp, providing higher transport efficiency. Encrypts the entire packet except for the hwtacacs header. Encrypts only the user password field in an authentication...
Page 597
1-9 figure 1-6 basic message exchange process of hwtacacs for a telnet user host hwtacacs client hwtacacs server 1) the user logs in 2) start-authentication packet 3) authentication response requesting the username 4) request for username 5) the user inputs the username 6) authentication continuance...
Page 598: Protocols and Standards
1-10 12) the hwtacacs client sends the user authorization request packet to the hwtacacs server. 13) the hwtacacs server sends back the authorization response, indicating that the user is authorized now. 14) knowing that the user is now authorized, the hwtacacs client pushes the configuration interf...
Page 599
1-11 aaa configuration task list task remarks creating an isp domain required configuring isp domain attributes optional configuring aaa authentication methods for an isp domain required for local authentication, refer to configuring local user attributes . For radius authentication, refer to config...
Page 600: Configuring Aaa
1-12 hwtacacs configuration task list task remarks creating a hwtacacs scheme required specifying the hwtacacs authentication servers required specifying the hwtacacs authorization servers optional specifying the hwtacacs accounting servers optional setting the shared key for hwtacacs packets requir...
Page 601
1-13 follow these steps to create an isp domain: to do… use the command… remarks enter system view system-view — create an isp domain and enter isp domain view domain isp-name required return to system view quit — specify the default isp domain domain default enable isp-name optional by default, the...
Page 602
1-14 a self-service radius server, for example, comprehensive access management system (cams/imc), is required for the self-service server localization function to work. With the self-service function, a user can manage and control his or her accounting information or card number. A server with self...
Page 604
1-16 authorization can work only after radius authentication is successful, and the authorization information is carried in the access-accept message. Hwtacacs authorization is separate from hwtacacs authentication, and the authorization information is carried in the authorization response after suc...
Page 605
1-17 z the authorization method specified with the authorization default command is for all types of users and has a priority lower than that for a specific access mode. Z radius authorization is special in that it takes effect only when the radius authorization scheme is the same as the radius auth...
Page 606
1-18 to do… use the command… remarks enter system view system-view — create an isp domain and enter isp domain view domain isp-name required enable the accounting optional feature accounting optional optional disabled by default specify the default accounting method for all types of users accounting...
Page 607
1-19 configuring local user attributes for local authentication, you need to create local users and configure user attributes on the device as needed. A local user represents a set of user attributes configured on a device, and such a user set is uniquely identified by the username. For a user reque...
Page 609
1-21 attributes for the local users in the group. Currently, you can configure password control attributes and authorization attributes for a user group. By default, every newly added local user belongs to the user group of system and bears all attributes of the group. User group system is automatic...
Page 610: Configuring Radius
1-22 configuring radius the radius protocol is configured on a per scheme basis. After creating a radius scheme, you need to configure the ip addresses and udp ports of the radius servers for the scheme. The servers include authentication/authorization servers and accounting servers, or primary serv...
Page 611
1-23 to do… use the command… remarks specify the primary radius authentication/authorization server primary authentication ip-address [ port-number ] specify the secondary radius authentication/authorization server secondary authentication ip-address [ port-number ] required configure at least one o...
Page 612
1-24 z it is recommended to specify only the primary radius accounting server if backup is not required. Z if both the primary and secondary accounting servers are specified, the secondary one is used when the primary one is not reachable. Z in practice, you can specify two radius servers as the pri...
Page 613
1-25 to retransmit the radius request. If the number of transmission attempts exceeds the specified limit but it still receives no response, it considers that the authentication has failed. Follow these steps to set the upper limit of radius request retransmission attempts: to do… use the command… r...
Page 614
1-26 when both the primary and secondary servers are available, the device sends request packets to the primary server. Once the primary server fails, the primary server turns into the state of block, and the device turns to the secondary server. In this case: z if the secondary server is available,...
Page 616
1-28 z primary server quiet timer (timer quiet): if the primary server is not reachable, its state changes to blocked, and the device will turn to the specified secondary server. If the secondary server is reachable, the device starts this timer and communicates with the secondary server. After this...
Page 617
1-29 follow these steps to specify a security policy server: to do… use the command… remarks enter system view system-view — create a radius scheme and enter its view radius scheme radius-scheme-name required by default, no radius scheme is present. Specify a security policy server security-policy-s...
Page 619
1-31 to do… use the command… remarks specify the primary hwtacacs authentication server primary authentication ip-address [ port-number ] specify the secondary hwtacacs authentication server secondary authentication ip-address [ port-number ] required configure at least one of the commands no authen...
Page 620
1-32 z it is recommended to specify only the primary hwtacacs authorization server if backup is not required. Z if both the primary and secondary authorization servers are specified, the secondary one is used when the primary one is not reachable. Z the ip addresses of the primary and secondary auth...
Page 621
1-33 setting the shared key for hwtacacs packets when using a hwtacacs server as an aaa server, you can set a key to secure the communications between the device and the hwtacacs server. The hwtacacs client and hwtacacs server use the md5 algorithm to encrypt packets exchanged between them and a sha...
Page 622
1-34 z if a hwtacacs server does not support a username with the domain name, you can configure the device to remove the domain name before sending the username to the server. Z the nas-ip command in hwtacacs scheme view is only for the current hwtacacs scheme, while the hwtacacs nas-ip command in s...
Page 624
1-36 [switch-ui-vty0-4] quit # configure the hwtacacs scheme. [switch] hwtacacs scheme hwtac [switch-hwtacacs-hwtac] primary authentication 10.1.1.1 49 [switch-hwtacacs-hwtac] primary authorization 10.1.1.1 49 [switch-hwtacacs-hwtac] primary accounting 10.1.1.1 49 [switch-hwtacacs-hwtac] key authent...
Page 625
1-37 figure 1-8 configure aaa by separate servers for telnet users configuration procedure # configure the ip addresses of various interfaces (omitted). # enable the telnet server on the switch. System-view [switch] telnet server enable # configure the switch to use aaa for telnet users. [switch] us...
Page 626
1-38 [switch-isp-bbb] quit # configure the default aaa methods for all types of users. [switch] domain bbb [switch-isp-bbb] authentication default local [switch-isp-bbb] authorization default hwtacacs-scheme hwtac [switch-isp-bbb] accounting default radius-scheme cams when telneting into the switch,...
Page 627
1-39 z specify the ip address of the switch as 192.168.1.70 z set both the shared keys for authentication and accounting packets to expert z select lan access service as the service type z specify the ports for authentication and accounting as 1812 and 1813 respectively z select extensible protocol ...
Page 628: Troubleshooting Aaa
1-40 system-view [switch] interface vlan-interface 2 [switch-vlan-interface2] ip address 192.168.1.70 255.255.255.0 [switch-vlan-interface2] quit # generate rsa and dsa key pairs and enable the ssh server. [switch] public-key local create rsa [switch] public-key local create dsa [switch] ssh server ...
Page 629
1-41 4) the password of the user is incorrect. 5) the radius server and the nas are configured with different shared key. Solution: check that: 1) the nas and the radius server can ping each other. 2) the username is in the userid@isp-name format and a default isp domain is specified on the nas. 3) ...
Page 630: Table of Contents
I table of contents 1 802.1x configuration·································································································································1-1 802.1x overview··············································································································...
Page 631: 802.1X Configuration
1-1 1 802.1x configuration when configuring 802.1x, go to these sections for information you are interested in: z 802.1x overview z configuring 802.1x z configuring a guest vlan z configuring an auth-fail vlan configuration prerequisites z create the vlan to be specified as the auth-fail vlan. Z to ...
Page 632: 802.1X Overview
1-2 z different ports can be configured with different auth-fail vlans, but a port can be configured with only one auth-fail vlan. Z the auth-fail vlan function and the free ip function in ead fast deployment are mutually exclusive on a port. Z if you configure both an mafv for 802.1x authentication...
Page 633
1-3 z eap over lans z eap over radius z 802.1x authentication triggering z authentication process of 802.1x z 802.1x timers z features working together with 802.1x architecture of 802.1x 802.1x operates in the typical client/server model and defines three entities: client, device, and server, as sho...
Page 634
1-4 z the uncontrolled port is always open in both the inbound and outbound directions to allow eapol protocol frames to pass, guaranteeing that the client can always send and receive authentication frames. Z the controlled port is open to allow data traffic to pass only when it is in the authorized...
Page 635
1-5 eap over lans eapol frame format eapol, defined in 802.1x, is intended to carry eap protocol packets between clients and devices over lans. Figure 1-3 shows the eapol frame format. Figure 1-3 eapol frame format z pae ethernet type: protocol type. It takes the value 0x888e. Z protocol version: ve...
Page 636
1-6 an eap packet of the type of success or failure has no data field, and has a length of 4. An eap packet of the type of request or response has a data field in the format shown in figure 1-5 . The type field indicates the eap authentication type. A value of 1 represents identity, indicating that ...
Page 637
1-7 802.1x authentication triggering 802.1x authentication can be initiated by either a client or the device. Unsolicited triggering of a client a client initiates authentication by sending an eapol-start frame to the device. The destination address of the frame is 01-80-c2-00-00-03, the multicast a...
Page 638
1-8 figure 1-8 message exchange in eap relay mode eapol eapor eapol-start eap-request / identity eap-response / identity eap-request / md5 challenge eap-success eap-response / md5 challenge radius access-request (eap-response / identity) radius access-challenge (eap-request / md5 challenge) radius a...
Page 639
1-9 9) when receiving the radius access-request packet, the radius server compares the password information encapsulated in the packet with that generated by itself. If the two are identical, the authentication server considers the user valid and sends to the device a radius access-accept packet. 10...
Page 640
1-10 figure 1-9 message exchange in eap termination mode eapol eapor eapol-start eap-request / identity eap-response / identity eap-request / md5 challenge eap-success eap-response / md5 challenge handshake request [ eap-request / identity ] handshake response [ eap-response / identity ] eapol-logof...
Page 641
1-11 z handshake timer (handshake-period): after a client passes authentication, the device sends to the client handshake requests at this interval to check whether the client is online. If the device receives no response after sending the allowed maximum number of handshake requests, it considers t...
Page 642
1-12 the assigned vlan neither changes nor affects the configuration of a port. However, as the assigned vlan has higher priority than the initial vlan of the port, it is the assigned vlan that takes effect after a user passes authentication. After the user goes offline, the port returns to the init...
Page 643
1-13 if a user of a port in the guest vlan initiates authentication process but fails the authentication, the device will add the user to the auth-fail vlan of the port configured for the port, if any. If no auth-fail vlan is configured, the device will keep the user in the guest vlan. If a user of ...
Page 644: Configuring 802.1X
1-14 authentication domain for authentication, authorization, and accounting of all 802.1x users on the port. In this way, users accessing the port cannot use any account in other domains. Meanwhile, for eap relay mode 802.1x authentication that uses certificates, the certificate of a user determine...
Page 646
1-16 configuring 802.1x parameters for a port follow these steps to configure 802.1x parameters for a port: to do… use the command… remarks enter system view system-view — enter ethernet interface view interface interface-type interface-number — set the port access control mode for the port dot1x po...
Page 647: Configuring A Guest Vlan
1-17 configuring a guest vlan configuration prerequisites z enable 802.1x. Z create the vlan to be specified as the guest vlan. Z to configure a port-based guest vlan, make sure that the port access control method is portbased, and the 802.1x multicast trigger function is enabled. Z to configure a m...
Page 648
1-18 configuration prerequisites z create the vlan to be specified as the auth-fail vlan. Z to configure a port-based auth-fail vlan, make sure that the port access control method is portbased, and the 802.1x multicast trigger function is enabled. Z to configure a mac-based auth-fail vlan, make sure...
Page 649: 802.1X Configuration Example
1-19 to do… use the command… remarks clear 802.1x statistics reset dot1x statistics [ interface interface-list ] available in user view 802.1x configuration example network requirements z the access control method of macbased is required on the port gigabitethernet 1/0/1 to control clients. Z all cl...
Page 650
1-20 the following configuration procedure covers most aaa/radius configuration commands for the device, while configuration on the 802.1x client and radius server are omitted. For information about aaa/radius configuration commands, refer to aaa configuration in the security volume. # configure the...
Page 651
1-21 [device-isp-aabbcc.Net] authentication default radius-scheme radius1 local [device-isp-aabbcc.Net] authorization default radius-scheme radius1 local [device-isp-aabbcc.Net] accounting default radius-scheme radius1 local # set the maximum number of users for the domain as 30. [device-isp-aabbcc....
Page 652
1-22 figure 1-11 network diagram for guest vlan configuration internet update server authenticator server supplicant vlan 10 ge1/0/1 vlan 1 ge1/0/2 vlan 5 ge1/0/3 vlan 2 ge1/0/4 switch figure 1-12 network diagram with the port in the guest vlan.
Page 653
1-23 figure 1-13 network diagram when the client passes authentication configuration procedure z the following configuration procedure uses many aaa/radius commands. For detailed configuration of these commands, refer to aaa configuration in the security volume. Z configurations on the 802.1x client...
Page 654
1-24 [device] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/2 [device-gigabitethernet1/0/2] dot1x # set the port access control method to portbased. [device-gigabitethernet1/0/2] dot1x port-method portbased # set the port access control mode to auto. [device-gigabitethernet1/0/2] dot1x port-control auto [device-gig...
Page 655
1-25 configuration procedure # configure the ip addresses of the interfaces. (omitted) # configure the radius scheme. System-view [device] radius scheme 2000 [device-radius-2000] primary authentication 10.1.1.1 1812 [device-radius-2000] primary accounting 10.1.1.2 1813 [device-radius-2000] key authe...
Page 656: Ead Fast Deployment Overview
2-1 2 ead fast deployment configuration when configuring ead fast deployment, go to these sections for information you are interested in: z ead fast deployment overview z configuring ead fast deployment z displaying and maintaining ead fast deployment z ead fast deployment configuration example z tr...
Page 657
2-2 configuring ead fast deployment currently, mac authentication and port security cannot work together with ead fast deployment. Once mac authentication or port security is enabled globally, the ead fast deployment is disabled automatically. Configuration prerequisites z enable 802.1x globally. Z ...
Page 658
2-3 configuring the ie redirect url follow these steps to configure the ie redirect url: to do… use the command… remarks enter system view system-view — configure the ie redirect url dot1x url url-string required no redirect url is configured by default. The redirect url and the freely accessible ne...
Page 659
2-4 ead fast deployment configuration example network requirements as shown in figure 2-1 , the host is connected to the device, and the device is connected to the freely accessible network segment and outside network. It is required that: z before successful 802.1 authentication, the host using ie ...
Page 660
2-5 c:\>ping 192.168.2.3 pinging 192.168.2.3 with 32 bytes of data: reply from 192.168.2.3: bytes=32 time reply from 192.168.2.3: bytes=32 time reply from 192.168.2.3: bytes=32 time reply from 192.168.2.3: bytes=32 time ping statistics for 192.168.2.3: packets: sent = 4, received = 4, lost = 0 (0% l...
Page 661: Table of Contents
I table of contents 1 habp configuration ··································································································································1-1 introduction to habp·········································································································...
Page 662: Habp Configuration
1-1 1 habp configuration when configuring habp, go to these sections for the information you are interested in: z introduction to habp z configuring habp z displaying and maintaining habp z habp configuration example introduction to habp the hw authentication bypass protocol (habp) is used to enable...
Page 663: Configuring Habp
1-2 figure 1-1 network diagram for habp application internet switch b switch c authenticator supplicant switch a supplicant supplicant switch d switch e authentication server habp is a link layer protocol that works above the mac layer. It is built on the client-server model. Generally, the habp ser...
Page 664: Habp Configuration Example
1-3 to do… use the command… remarks configure habp to work in server mode habp server vlan vlan-id required habp works in client mode by default. Set the interval to send habp requests habp timer interval optional 20 seconds by default configuring an habp client configure the habp client function on...
Page 665
1-4 figure 1-2 network diagram for habp configuration configuration procedure 1) configure switch a # enable habp. System-view [switcha] habp enable # configure habp to work in server mode, allowing habp packets to be transmitted in vlan 2. [switcha] habp server vlan 2 # set the interval to send hab...
Page 666: Table of Contents
I table of contents 1 mac authentication configuration··········································································································1-1 mac authentication overview ············································································································...
Page 667: Mac Authentication Overview
1-1 1 mac authentication configuration when configuring mac authentication, go to these sections for information you are interested in: z mac authentication overview z related concepts z configuring mac authentication z configuring a guest vlan z displaying and maintaining mac authentication z mac a...
Page 668: Related Concepts
1-2 related concepts mac authentication timers the following timers function in the process of mac authentication: z offline detect timer: at this interval, the device checks to see whether there is traffic from a user. Once detecting that there is no traffic from a user within this interval, the de...
Page 669
1-3 mac authentication supports mac-based guest vlan (mgv). With mgv configured on a port, users failing the authentication on the port are authorized to access the resources in the guest vlan. If a user in the guest vlan initiates another authentication process but fails the authentication, the dev...
Page 671
1-5 z different ports can be configured with different guest vlans, but a port can be configured with only one guest vlan. Z if you configure both the 802.1x authentication mgv and the mac authentication mgv on a port, only the 802.1x authentication mgv will take effect. For description on 802.1x au...
Page 672
1-6 configuration procedure 1) configure mac authentication on the device # add a local user, setting the username and password as 00-e0-fc-12-34-56, the mac address of the user. System-view [device] local-user 00-e0-fc-12-34-56 [device-luser-00-e0-fc-12-34-56] password simple 00-e0-fc-12-34-56 [dev...
Page 673
1-7 current online user number is 1 mac addr authenticate state authindex 00e0-fc12-3456 mac_authenticator_success 29 radius-based mac authentication configuration example network requirements as illustrated in figure 1-2 , a host is connected to the device through port gigabitethernet 1/0/1. The de...
Page 674
1-8 [device] domain 2000 [device-isp-2000] authentication default radius-scheme 2000 [device-isp-2000] authorization default radius-scheme 2000 [device-isp-2000] accounting default radius-scheme 2000 [device-isp-2000] quit # enable mac authentication globally. [device] mac-authentication # enable ma...
Page 675
1-9 z configure the radius server to assign acl 3000. Z on port gigabitethernet 1/0/1 of the switch, enable mac authentication and configure acl 3000. After the host passes mac authentication, the radius server assigns acl 3000 to port gigabitethernet 1/0/1 of the switch. As a result, the host can a...
Page 676
1-10 [sysname] acl number 3000 [sysname-acl-adv-3000] rule 0 deny ip destination 10.0.0.1 0 [sysname-acl-adv-3000] quit # enable mac authentication globally. [sysname] mac-authentication # specify the isp domain for mac authentication users. [sysname] mac-authentication domain 2000 # specify the mac...
Page 677: Table of Contents
I table of contents 1 portal configuration ··································································································································1-1 portal overview············································································································...
Page 678: Portal Configuration
1-1 1 portal configuration when configuring portal, go to these sections for information you are interested in: z portal overview z portal configuration task list z displaying and maintaining portal z portal configuration examples z troubleshooting portal portal overview this section covers these to...
Page 679
1-2 z resource access limit: a user passing identity authentication can access only network resources like the anti-virus server or os patch server, which are called the restricted resources. Only users passing security authentication can access more network resources, which are called the unrestric...
Page 680
1-3 security policy server server that interacts with portal clients and access devices for security authentication and resource authorization. The above five components interact in the following procedure: 1) when an unauthenticated user enters a website address in the address bar of the ie to acce...
Page 681
1-4 authentication. This solves the problem about ip address planning and allocation and proves to be useful. For example, a service provider can allocate public ip addresses to broadband users only when they access networks beyond the residential community network. Layer 3 authentication layer 3 po...
Page 682
1-5 direct authentication/layer 3 authentication process figure 1-2 direct authentication/layer 3 authentication process the direct authentication/layer 3 authentication process is as follows: 2) a portal user initiates an authentication request through http. When the http packet arrives at the acce...
Page 683
1-6 re-dhcp authentication process figure 1-3 re-dhcp authentication process authentication/ accounting server authentication client portal server access device 6) authentication succeeds security policy server 12) security authentication 13) authorization 7) the user obtains a new ip address 8) dis...
Page 684: Basic Portal Configuration
1-7 task remarks basic portal configuration required configuring a portal-free rule optional configuring an authentication subnet optional logging out users optional specifying a mandatory authentication domain optional basic portal configuration configuration prerequisites the portal feature provid...
Page 686: Logging Out Users
1-9 z if you specify both a vlan and an interface in a portal-free rule, the interface must belong to the vlan. Z you cannot configure two or more portal-free rules with the same filtering conditions. Otherwise, the system prompts that the rule already exists. Z no matter whether portal authenticati...
Page 687
1-10 specifying a mandatory authentication domain after you specify a mandatory authentication domain for an interface, the device will use the mandatory authentication domain for authentication, authorization, and accounting (aaa) of the portal users on the interface, ignoring the domain names carr...
Page 689
1-12 # set the server type to extended. [switch-radius-rs1] server-type extended # specify the primary authentication server and primary accounting server, and configure the keys for communication with the servers. [switch-radius-rs1] primary authentication 192.168.0.112 [switch-radius-rs1] primary ...
Page 690
1-13 configuring re-dhcp portal authentication network requirements z the host is directly connected to the switch and the switch is configured for re-dhcp authentication. The host is assigned with an ip address through the dhcp server. Before portal authentication, the host uses an assigned private...
Page 691
1-14 # set the server type to extended. [switch-radius-rs1] server-type extended # specify the primary authentication server and primary accounting server, and configure the keys for communication with the servers. [switch-radius-rs1] primary authentication 192.168.0.113 [switch-radius-rs1] primary ...
Page 692
1-15 # configure the ip address of the interface connected with the portal server. [switch] interface vlan-interface 2 [switch–vlan-interface2] ip address 192.168.0.100 255.255.255.0 [switch–vlan-interface2] quit configuring layer 3 portal authentication network requirements z switch a is configured...
Page 693
1-16 [switcha-radius-rs1] primary accounting 192.168.0.112 [switcha-radius-rs1] key authentication radius [switcha-radius-rs1] key accounting radius # specify that the isp domain name should not be included in the username sent to the radius server. [switcha-radius-rs1] user-name-format without-doma...
Page 694
1-17 passed security authentication, they can access only subnet 192.168.0.0/24. After passing security authentication, they can access unrestricted internet resources. Z a radius server serves as the authentication/accounting server. Figure 1-7 configure direct portal authentication with extended f...
Page 695
1-18 # create an isp domain named dm1 and enter its view. [switch] domain dm1 # configure the isp domain to use radius scheme rs1. [switch-isp-dm1] authentication portal radius-scheme rs1 [switch-isp-dm1] authorization portal radius-scheme rs1 [switch-isp-dm1] accounting portal radius-scheme rs1 [sw...
Page 696
1-19 configuring re-dhcp portal authentication with extended functions network requirements z the host is directly connected to the switch and the switch is configured for re-dhcp authentication. The host is assigned with an ip address through the dhcp server. Before portal authentication, the host ...
Page 697
1-20 system-view [switch] radius scheme rs1 # set the server type to extended. [switch-radius-rs1] server-type extended # specify the primary authentication server and primary accounting server, and configure the keys for communication with the servers. [switch-radius-rs1] primary authentication 192...
Page 698
1-21 z ip address: 192.168.0.111 z key: portal z port number: 50100 z url: http://192.168.0.111/portal. [switch] portal server newpt ip 192.168.0.111 key portal port 50100 url http://192.168.0.111/portal # configure the switch as a dhcp relay agent, and enable the invalid address check function. [sw...
Page 699
1-22 configuration procedure you need to configure ip addresses for the devices as shown in figure 1-9 and ensure that routes are available between devices. Configure switch a: 1) configure a radius scheme # create a radius scheme named rs1 and enter its view. System-view [switcha] radius scheme rs1...
Page 700: Troubleshooting Portal
1-23 on the security policy server, you need to specify acl 3000 as the isolation acl and acl 3001 as the security acl. [switcha] acl number 3000 [switcha-acl-adv-3000] rule permit ip destination 192.168.0.0 0.0.0.255 [switcha-acl-adv-3000] quit [switcha] acl number 3001 [switcha-acl-adv-3001] rule ...
Page 701
1-24 solution z use the display portal server command to display the key for the portal server on the access device and view the key for the access device on the portal server. Z use the portal server command to modify the key on the access device or modify the key for the access device on the porta...
Page 702: Table of Contents
I table of contents 1 port security configuration······················································································································1-1 introduction to port security····································································································...
Page 703: Port Security Configuration
1-1 1 port security configuration when configuring port security, go to these sections for information you are interested in: z introduction to port security z port security configuration task list z displaying and maintaining port security z port security configuration examples z troubleshooting po...
Page 704
1-2 port security features ntk the need to know (ntk) feature checks the destination mac addresses in outbound frames and allows frames to be sent to only devices passing authentication, thus preventing illegal devices from intercepting network traffic. Intrusion protection the intrusion protection ...
Page 705
1-3 security mode description features userloginsecure in this mode, a port performs 802.1x authentication of users in portbased mode and services only one user passing 802.1x authentication. Userloginwithoui similar to the userloginsecure mode, a port in this mode performs 802.1x authentication of ...
Page 706
1-4 z currently, port security supports two authentication methods: 802.1x and mac authentication. Different port security modes employ different authentication methods or different combinations of authentication methods. Z the maximum number of users a port supports is the lesser of the maximum num...
Page 707: Enabling Port Security
1-5 enabling port security configuration prerequisites before enabling port security, you need to disable 802.1x and mac authentication globally. Configuration procedure follow these steps to enable port security: to do… use the command… remarks enter system view system-view — enable port security p...
Page 708
1-6 follow these steps to set the maximum number of secure mac addresses allowed on a port: to do… use the command… remarks enter system view system-view — enter ethernet port view interface interface-type interface-number — set the maximum number of secure mac addresses allowed on a port port-secur...
Page 709
1-7 configuring procedure follow these steps to enable any other port security mode: to do… use the command… remarks enter system view system-view — set an oui value for user authentication port-security oui oui-value index index-value optional not configured by default. The command is required for ...
Page 710
1-8 by default, ntk is disabled on a port and the port forwards all frames. With ntk configured, a port will discard any unicast packet with an unknown mac address no matter in which mode it operates. Follow these steps to configure the ntk feature: to do… use the command… remarks enter system view ...
Page 711
1-9 on a port operating in either the macaddresselseuserloginsecure mode or the macaddresselseuserloginsecureext mode, intrusion protection is triggered only after both mac authentication and 802.1x authentication for the same frame fail. Configuring trapping the trapping feature enables a device to...
Page 712
1-10 to do… use the command… remarks enter system view system-view — in system view port-security mac-address security mac-address interface interface-type interface-number vlan vlan-id interface interface-type interface-number configure a secure mac address in interface view port-security mac-addre...
Page 713
1-11 to do… use the command… remarks display information about blocked mac addresses display port-security mac-address block [ interface interface-type interface-number ] [ vlan vlan-id ] [ count ] available in any view port security configuration examples configuring the autolearn mode network requ...
Page 714
1-12 equipment port-security is enabled intrusion trap is enabled disableport timeout: 30s oui value: gigabitethernet1/0/1 is link-up port mode is autolearn needtoknow mode is disabled intrusion protection mode is disableporttemporarily max mac address number is 64 stored mac address number is 0 aut...
Page 715
1-13 gigabitethernet1/0/1 current state: port security disabled ip packet frame type: pktfmt_ethnt_2, hardware address: 000f-cb00-5558 description: gigabitethernet1/0/1 interface ...... The port should be re-enabled 30 seconds later. [switch-gigabitethernet1/0/1] display interface gigabitethernet 1/...
Page 716
1-14 configuration procedure z the following configuration steps cover some aaa/radius configuration commands. For details about the commands, refer to aaa configuration in the security volume. Z configurations on the host and radius servers are omitted. 1) configure the radius protocol # configure ...
Page 717
1-15 after completing the above configurations, you can use the following command to view the configuration information of the radius scheme named radsun: display radius scheme radsun schemename : radsun index : 1 type : standard primary auth ip : 192.168.1.2 port : 1812 state : active primary acct ...
Page 718
1-16 needtoknow mode is disabled intrusion protection mode is noaction max mac address number is not configured stored mac address number is 0 authorization is permitted after an 802.1x user gets online, you can see that the number of secure mac addresses stored is 1. You can also use the following ...
Page 719
1-17 1234-0300-0011 1 learned gigabitethernet1/0/1 aging --- 1 mac address(es) found --- configuring the macaddresselseuserloginsecure mode network requirements the client is connected to the switch through gigabitethernet 1/0/1. The switch authenticates the client by the radius server. If the authe...
Page 720
1-18 after completing the above configurations, you can use the following command to view the port security configuration information: display port-security interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1 equipment port-security is enabled trap is disabled disableport timeout: 20s oui value: gigabitethernet1/0/1 is...
Page 721
1-19 authentication mode is auto port control type is mac-based guest vlan: 0 max number of on-line users is 256 eapol packet: tx 16331, rx 102 sent eap request/identity packets : 16316 eap request/challenge packets: 6 eap success packets: 4, fail packets: 5 received eapol start packets : 6 eapol lo...
Page 722
1-20 analysis no secure mac address can be configured on a port operating in a port security mode other than autolearn. Solution set the port security modeto autolearn. [switch-gigabitethernet1/0/1] undo port-security port-mode [switch-gigabitethernet1/0/1] port-security max-mac-count 64 [switch-gig...
Page 723: Table of Contents
I table of contents 1 ip source guard configuration················································································································1-1 ip source guard overview ············································································································...
Page 724: Ip Source Guard Overview
1-1 1 ip source guard configuration when configuring ip source guard, go to these sections for information you are interested in: z ip source guard overview z configuring a static binding entry z configuring dynamic binding function z displaying and maintaining ip source guard z ip source guard conf...
Page 727
1-4 [switcha-gigabitethernet1/0/2] user-bind ip-address 192.168.0.3 mac-address 0001-0203-0405 [switcha-gigabitethernet1/0/2] quit # configure port gigabitethernet 1/0/1 of switch a to allow only ip packets with the source mac address of 00-01-02-03-04-06 and the source ip address of 192.168.0.1 to ...
Page 728
1-5 for detailed configuration of a dhcp server, refer to dhcp configuration in the ip service volume. Network diagram figure 1-2 network diagram for configuring dynamic binding function configuration procedure 1) configure switch a # configure dynamic binding function on port gigabitethernet 1/0/1....
Page 729
1-6 [switcha-gigabitethernet1/0/1] display dhcp-snooping dhcp snooping is enabled. The client binding table for all untrusted ports. Type : d--dynamic , s--static type ip address mac address lease vlan interface ==== =============== ============== ============ ==== ================= d 192.168.0.1 00...
Page 730: Table of Contents
I table of contents 1 ssh2.0 configuration································································································································1-1 ssh2.0 overview···············································································································...
Page 731: Ssh2.0 Configuration
1-1 1 ssh2.0 configuration when configuring ssh2.0, go to these sections for information you are interested in: z ssh2.0 overview z configuring the device as an ssh server z configuring the device as an ssh client z displaying and maintaining ssh z ssh server configuration examples z ssh client conf...
Page 732
1-2 stages description session request after passing authentication, the client sends a session request to the server. Interaction after the server grants the request, the client and server start to communicate with each other. Version negotiation 1) the server opens port 22 to listen to connection ...
Page 733
1-3 before the negotiation, the server must have already generated a dsa or rsa key pair, which is not only used for generating the session key, but also used by the client to authenticate the identity of the server. For details about dsa and rsa key pairs, refer to public key configuration in the s...
Page 734
1-4 session request after passing authentication, the client sends a session request to the server, while the server listens to and processes the request from the client. After successfully processing the request, the server sends back to the client an ssh_smsg_success packet and goes on to the inte...
Page 736
1-6 to do… use the command… remarks enter system view system-view — enter user interface view of one or more user interfaces user-interface vty number [ ending-number ] — set the login authentication mode to scheme authentication-mode scheme [ command-authorization ] required by default, the authent...
Page 737
1-7 z you are recommended to configure a client public key by importing it from a public key file. Z you can configure at most 20 client pubic keys on an ssh server. Configuring a client public key manually follow these steps to configure the client public key manually: to do… use the command… remar...
Page 739
1-9 z enabling the ssh server to be compatible with ssh1 client z setting the server key pair update interval, applicable to users using ssh1 client z setting the ssh user authentication timeout period z setting the maximum number of ssh authentication attempts setting the above parameters can help ...
Page 741
1-11 to do... Use the command… remarks configure the server public key refer to configuring a client public key required the method of configuring server public key on the client is similar to that of configuring client public key on the server. Specify the host public key name of the server ssh cli...
Page 743
1-13 [switch-ui-vty0-4] protocol inbound ssh [switch-ui-vty0-4] quit # create local user client001, and set the user command privilege level to 3 [switch] local-user client001 [switch-luser-client001] password simple aabbcc [switch-luser-client001] service-type ssh [router-luser-client001] authoriza...
Page 744
1-14 figure 1-2 ssh client configuration interface in the window shown in figure 1-2 , click open. If the connection is normal, you will be prompted to enter the username and password. After entering the correct username (client001) and password (aabbcc), you can enter the configuration interface. W...
Page 745
1-15 [switch] public-key local create dsa [switch] ssh server enable # configure an ip address for vlan interface 1. This address will serve as the destination of the ssh connection. [switch] interface vlan-interface 1 [switch-vlan-interface1] ip address 192.168.1.40 255.255.255.0 [switch-vlan-inter...
Page 746
1-16 figure 1-4 generate a client key pair 1) while generating the key pair, you must move the mouse continuously and keep the mouse off the green process bar shown in figure 1-5 . Otherwise, the process bar stops moving and the key pair generating process will be stopped..
Page 747
1-17 figure 1-5 generate a client key pair 2) after the key pair is generated, click save public key and specify the file name as key.Pub to save the public key. Figure 1-6 generate a client key pair 3).
Page 748
1-18 likewise, to save the private key, click save private key. A warning window pops up to prompt you whether to save the private key without any protection. Click yes and enter the name of the file for saving the key (private in this case). Figure 1-7 generate a client key pair 4) after generating...
Page 749
1-19 select connection/ssh/auth from the navigation tree.The following window appears. Click browse… to bring up the file selection window, navigate to the private key file and click ok. Figure 1-9 ssh client configuration interface 2) in the window shown in figure 1-9 , click open. If the connectio...
Page 750
1-20 # create rsa and dsa key pairs and enable the ssh server. System-view [switchb] public-key local create rsa [switchb] public-key local create dsa [switchb] ssh server enable # create an ip address for vlan interface 1, which the ssh client will use as the destination for ssh connection. [switch...
Page 751
1-21 after you enter the correct username, you can log into switch b successfully. Z if the client does not support first-time authentication, you need to perform the following configurations. # disable first-time authentication. [switcha] undo ssh client first-time # configure the host public key o...
Page 752
1-22 when switch acts as client for publickey authentication network requirements z as shown in figure 1-11 , switch a (the ssh client) needs to log into switch b (the ssh server) through the ssh protocol. Z publickey authentication is used, and the public key algorithm is dsa. Figure 1-11 switch ac...
Page 753
1-23 # specify the authentication type for user client002 as publickey, and assign the public key switch001 to the user. [switchb] ssh user client002 service-type stelnet authentication-type publickey assign publickey switch001 2) configure the ssh client # configure an ip address for vlan interface...
Page 754: Sftp Service
2-1 2 sftp service when configuring sftp, go to these sections for information you are interested in: z sftp overview z configuring an sftp server z configuring an sftp client z sftp client configuration example z sftp server configuration example sftp overview the secure file transfer protocol (sft...
Page 755: Configuring An Sftp Client
2-2 when the device functions as the sftp server, only one client can access the sftp server at a time. If the sftp client uses winscp, a file on the server cannot be modified directly; it can only be downloaded to a local place, modified, and then uploaded to the server. Configuring the sftp connec...
Page 757
2-4 to do… use the command… remarks create a new directory on the remote sftp server mkdir remote-path optional delete a directory from the sftp server rmdir remote-path& optional working with sftp files sftp file operations include: z changing the name of a file z downloading a file z uploading a f...
Page 759
2-6 # generate rsa and dsa key pairs and enable the ssh server. System-view [switchb] public-key local create rsa [switchb] public-key local create dsa [switchb] ssh server enable # enable the sftp server. [switchb] sftp server enable # configure an ip address for vlan interface 1, which the ssh cli...
Page 760
2-7 [switcha] quit after generating key pairs on a client, you need to transmit the saved public key file to the server through ftp or tftp and have the configuration on the server done before continuing configuration of the client. # establish a connection to the remote sftp server and enter sftp c...
Page 761
2-8 sftp-client> dir -rwxrwxrwx 1 noone nogroup 1759 aug 23 06:52 config.Cfg -rwxrwxrwx 1 noone nogroup 225 aug 24 08:01 pubkey2 -rwxrwxrwx 1 noone nogroup 283 aug 24 07:39 pubkey drwxrwxrwx 1 noone nogroup 0 sep 01 06:22 new -rwxrwxrwx 1 noone nogroup 225 sep 01 06:55 pub drwxrwxrwx 1 noone nogroup...
Page 762
2-9 authentication with the username being client002 and the password being aabbcc. The username and password are saved on the switch. Figure 2-2 network diagram for sftp server configuration configuration procedure 1) configure the sftp server # generate rsa and dsa key pairs and enable the ssh ser...
Page 763
2-10 z there are many kinds of ssh client software. The following takes the psftp of putty version 0.58 as an example. Z the psftp supports only password authentication. # establish a connection with the remote sftp server. Run the psftp.Exe to launch the client interface as shown in figure 2-3 , an...
Page 764: Table of Contents
I table of contents 1 pki configuration ······································································································································1-1 introduction to pki·······································································································...
Page 765: Pki Configuration
1-1 1 pki configuration when configuring pki, go to these sections for information you are interested in: z introduction to pki z pki configuration task list z displaying and maintaining pki z pki configuration examples z troubleshooting pki introduction to pki this section covers these topics: z pk...
Page 766
1-2 level. The root ca has a ca certificate signed by itself while each lower level ca has a ca certificate signed by the ca at the next higher level. Crl an existing certificate may need to be revoked when, for example, the user name changes, the private key leaks, or the user stops the business. R...
Page 767
1-3 ca a ca is a trusted authority responsible for issuing and managing digital certificates. A ca issues certificates, specifies the validity periods of certificates, and revokes certificates as needed by publishing crls. Ra a registration authority (ra) is an extended part of a ca or an independen...
Page 768: Pki Configuration Task List
1-4 2) the ra reviews the identity of the entity and then sends the identity information and the public key with a digital signature to the ca. 3) the ca verifies the digital signature, approves the application, and issues a certificate. 4) the ra receives the certificate from the ca, sends it to th...
Page 769
1-5 the configuration of an entity dn must comply with the ca certificate issue policy. You need to determine, for example, which entity dn parameters are mandatory and which are optional. Otherwise, certificate request may be rejected. Follow these steps to configure an entity dn: to do… use the co...
Page 770: Configuring A Pki Domain
1-6 configuring a pki domain before requesting a pki certificate, an entity needs to be configured with some enrollment information, which is referred to as a pki domain. A pki domain is intended only for convenience of reference by other applications like ike and ssl, and has only local significanc...
Page 773
1-9 z if a pki domain already has a local certificate, creating an rsa key pair will result in inconsistency between the key pair and the certificate. To generate a new rsa key pair, delete the local certificate and then issue the public-key local create command. For information about the public-key...
Page 774
1-10 z if a pki domain already has a ca certificate, you cannot retrieve another ca certificate for it. This is in order to avoid inconsistency between the certificate and registration information due to related configuration changes. To retrieve a new ca certificate, use the pki delete-certificate ...
Page 775: Deleting A Certificate
1-11 to do… use the command… remarks enter system view system-view — enter pki domain view pki domain domain-name — disable crl checking crl check disable required enabled by default return to system view quit — retrieve the ca certificate refer to retrieving a certificate manually required verify t...
Page 778
1-14 z subject dn: dn information of the ca, including the common name (cn), organization unit (ou), organization (o), and country (c). The other attributes may be left using the default values. # configure extended attributes. After configuring the basic attributes, you need to perform configuratio...
Page 779
1-15 generating keys... ++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++ ++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++ +++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++ +++++++++++++++++++++++ z apply for certificates # retrieve the ca certificate and save it locally. [switch] pki retrieval-certifi...
Page 780
1-16 not after : jan 8 09:26:53 2008 gmt subject: cn=switch subject public key info: public key algorithm: rsaencryption rsa public key: (1024 bit) modulus (1024 bit): 00d67d50 41046f6a 43610335 ca6c4b11 f8f89138 e4e905bd 43953ba2 623a54c0 ea3cb6e0 b04649ce c9cddd38 34015970 981e96d9 ff4f7b73 a51556...
Page 781
1-17 figure 1-3 request a certificate from a ca running windows 2003 server configuration procedure 1) configure the ca server z install the certificate server suites from the start menu, select control panel > add or remove programs, and then select add/remove windows components > certificate servi...
Page 782
1-18 # configure the url of the registration server in the format of http://host:port/ certsrv/mscep/mscep.Dll, where host:port indicates the ip address and port number of the ca server. [switch-pki-domain-torsa] certificate request url http://4.4.4.1:8080/certsrv/mscep/mscep.Dll # set the registrat...
Page 783
1-19 data: version: 3 (0x2) serial number: 48fa0fd9 00000000 000c signature algorithm: sha1withrsaencryption issuer: cn=ca server validity not before: nov 21 12:32:16 2007 gmt not after : nov 21 12:42:16 2008 gmt subject: cn=switch subject public key info: public key algorithm: rsaencryption rsa pub...
Page 784
1-20 configuring a certificate attribute-based access control policy network requirements z the client accesses the remote http security (https) server through the https protocol. Z ssl is configured to ensure that only legal clients log into the https server. Z create a certificate attribute-based ...
Page 785: Troubleshooting Pki
1-21 # create certificate attribute group mygroup2 and add two attribute rules. The first rule defines that the fqdn of the alternative subject name does not include the string of apple, and the second rule defines that the dn of the certificate issuer name includes the string aabbcc. [switch] pki c...
Page 786
1-22 failed to request a local certificate symptom failed to request a local certificate. Analysis possible reasons include these: z the network connection is not proper. For example, the network cable may be damaged or loose. Z no ca certificate has been retrieved. Z the current key pair has been b...
Page 787: Table of Contents
I table of contents 1 ssl configuration ·····································································································································1-1 ssl overview ··············································································································...
Page 788: Ssl Configuration
1-1 1 ssl configuration when configuring ssl, go to these sections for information you are interested in: z ssl overview z ssl configuration task list z displaying and maintaining ssl z troubleshooting ssl ssl overview secure sockets layer (ssl) is a security protocol providing secure connection ser...
Page 789: Ssl Configuration Task List
1-2 z for details about symmetric key algorithms, asymmetric key algorithm rsa and digital signature, refer to public key configuration in the security volume. Z for details about pki, certificate, and ca, refer to pki configuration in the security volume. Ssl protocol stack as shown in figure 1-2 ,...
Page 790
1-3 configuring an ssl server policy an ssl server policy is a set of ssl parameters for a server to use when booting up. An ssl server policy takes effect only after it is associated with an application layer protocol, http protocol, for example. Configuration prerequisites when configuring an ssl ...
Page 791
1-4 z if you enable client authentication here, you must request a local certificate for the client. Z currently, ssl mainly comes in these versions: ssl 2.0, ssl 3.0, and tls 1.0, where tls 1.0 corresponds to ssl 3.1. When the device acts as an ssl server, it can communicate with clients running ss...
Page 792
1-5 [device] pki domain 1 [device-pki-domain-1] ca identifier ca1 [device-pki-domain-1] certificate request url http://10.1.2.2/certsrv/mscep/mscep.Dll [device-pki-domain-1] certificate request from ra [device-pki-domain-1] certificate request entity en [device-pki-domain-1] quit # create the local ...
Page 793: Troubleshooting Ssl
1-6 configuration prerequisites if the ssl server is configured to authenticate the ssl client, when configuring the ssl client policy, you need to specify the pki domain to be used for obtaining the certificate of the client. Therefore, before configuring an ssl client policy, you must configure a ...
Page 794
1-7 analysis ssl handshake failure may result from the following causes: z no ssl server certificate exists, or the certificate is not trusted. Z the server is expected to authenticate the client, but the ssl client has no certificate or the certificate is not trusted. Z the cipher suites used by th...
Page 795: Table of Contents
I table of contents 1 public key configuration··························································································································1-1 public key algorithm overview···································································································...
Page 796: Public Key Configuration
1-1 1 public key configuration when configuring public keys, go to these sections for information you are interested in: z public key algorithm overview z configuring the local asymmetric key pair z configuring the public key of a peer z displaying and maintaining public keys z public key configurat...
Page 797
1-2 z encryption: the information encrypted with a receiver's public key can be decrypted by the receiver possessing the corresponding private key. This is used to ensure confidentiality. Z digital signature: the information encrypted with a sender's private key can be decrypted by anyone who has ac...
Page 798
1-3 z configuration of the public-key local create command can survive a reboot. Z the public-key local create rsa command generates two key pairs: one server key pair and one host key pair. Each key pair consists of a public key and a private key. Z the length of an rsa key modulus is in the range ...
Page 799
1-4 z configure it manually: you can input on or copy the public key of the peer to the local host. The copied public key must have not been converted and be in the distinguished encoding rules (der) encoding format. Z import it from the public key file: the system automatically converts the public ...
Page 800
1-5 public key configuration examples configuring the public key of a peer manually network requirements device a is authenticated by device b when accessing device b, so the public key of device a should be configured on device b in advance. In this example: z rsa is used. Z the host public key of ...
Page 801
1-6 ===================================================== time of key pair created: 09:50:07 2007/08/07 key name: server_key key type: rsa encryption key ===================================================== key code: 307c300d06092a864886f70d0101010500036b003068026100999089e7aee9802002d9eb2d0433b87b...
Page 802
1-7 figure 1-3 network diagram for importing the public key of a peer from a public key file configurtion procedure 1) create key pairs on device a and export the host public key # create rsa key pairs on device a. System-view [devicea] public-key local create rsa the range of public key size is (51...
Page 803
1-8 [devicea] quit 2) enable the ftp server function on device b # enable the ftp server function, create an ftp user with the username ftp and password 123. System-view [deviceb] ftp server enable [deviceb] local-user ftp [deviceb-luser-ftp] password simple 123 [deviceb-luser-ftp] service-type ftp ...
Page 804: Table of Contents
I table of contents 1 acl overview ············································································································································1-1 introduction to acl ·····································································································...
Page 805
Ii configuring a basic ipv6 acl·················································································································3-1 configuration prerequisites ·············································································································3-1 configurati...
Page 806: Acl Overview
1-1 1 acl overview in order to filter traffic, network devices use sets of rules, called access control lists (acls), to identify and handle packets. When configuring acls, go to these chapters for information you are interested in: z acl overview z ipv4 acl configuration z ipv6 acl configuration z ...
Page 807: Introduction to Ipv4 Acl
1-2 z when an acl is assigned to a piece of hardware and referenced by a qos policy for traffic classification, the switch does not take action according to the traffic behavior definition on a packet that does not match the acl. Z when an acl is referenced by a piece of software to control telnet, ...
Page 808
1-3 the name of an ipv4 acl must be unique among ipv4 acls. However, an ipv4 acl and an ipv6 acl can share the same name. Ipv4 acl match order an acl may consist of multiple rules, which specify different matching criteria. These criteria may have overlapping or conflicting parts. The match order is...
Page 809
1-4 1) sort rules by source mac address mask first and compare packets against the rule configured with more ones in the source mac address mask. 2) if two rules are present with the same number of ones in their source mac address masks, look at the destination mac address masks. Then, compare packe...
Page 810: Introduction to Ipv6 Acl
1-5 introduction to ipv6 acl this section covers these topics: z ipv6 acl classification z ipv6 acl naming z ipv6 acl match order z ipv6 acl step z effective period of an ipv6 acl ipv6 acl classification ipv6 acls, identified by acl numbers, fall into three categories, as shown in table 1-2 . Table ...
Page 811: Acl Application
1-6 1) sort rules by source ipv6 address prefix first and compare packets against the rule configured with a longer prefix for the source ipv6 address. 2) in case of a tie, compare packets against the rule configured first. Depth-first match for an advanced ipv6 acl the following shows how your devi...
Page 812: Ipv4 Acl Configuration
2-1 2 ipv4 acl configuration when configuring an ipv4 acl, go to these sections for information you are interested in: z creating a time range z configuring a basic ipv4 acl z configuring an advanced ipv4 acl z configuring an ethernet frame header acl z copying an ipv4 acl z displaying and maintaini...
Page 813: Configuring A Basic Ipv4 Acl
2-2 on the day or days of the week only within the specified period. For example, to create a time range that is active from 12:00 to 14:00 on wednesdays between january 1, 2004 00:00 and december 31, 2004 23:59, you may use the time-range test 12:00 to 14:00 wednesday from 00:00 01/01/2004 to 23:59...
Page 815
2-4 system-view [sysname] acl number 2000 [sysname-acl-basic-2000] rule deny source 1.1.1.1 0 # verify the configuration. [sysname-acl-basic-2000] display acl 2000 basic acl 2000, named -none-, 1 rule, acl's step is 5 rule 0 deny source 1.1.1.1 0 (5 times matched) configuring an advanced ipv4 acl ad...
Page 817
2-6 system-view [sysname] acl number 3000 [sysname-acl-adv-3000] rule permit tcp source 129.9.0.0 0.0.255.255 destination 202.38.160.0 0.0.0.255 destination-port eq 80 # verify the configuration. [sysname-acl-adv-3000] display acl 3000 advanced acl 3000, named -none-, 1 rule, acl's step is 5 rule 0 ...
Page 818: Copying An Ipv4 Acl
2-7 note that: z you can only modify the existing rules of an acl that uses the match order of config. When modifying a rule of such an acl, you may choose to change just some of the settings, in which case the other settings remain the same. Z you cannot create a rule with, or modify a rule to have...
Page 820
2-9 configuration procedure 1) create a time range for office hours # create a periodic time range spanning 8:00 to 18:00 in working days. System-view [switch] time-range trname 8:00 to 18:00 working-day 2) define an acl to control access to the salary query server # configure a rule to control acce...
Page 821
2-10 [switch] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/2 [switch-gigabitethernet1/0/2] qos apply policy p_rd inbound [switch-gigabitethernet1/0/2] quit # apply qos policy p_market to interface gigabitethernet 1/0/3. [switch] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/3 [switch-gigabitethernet1/0/3] qos apply policy p_marke...
Page 822: Ipv6 Acl Configuration
3-1 3 ipv6 acl configuration when configuring ipv6 acls, go to these sections for information you are interested in: z creating a time range z configuring a basic ipv6 acl z configuring an advanced ipv6 acl z copying an ipv6 acl z displaying and maintaining ipv6 acls z ipv6 acl configuration example...
Page 823
3-2 to do… use the command… remarks configure a description for the basic ipv6 acl description text optional by default, a basic ipv6 acl has no acl description. Configure a rule description rule rule-id comment text optional by default, an ipv6 acl rule has no rule description. Note that: z you can...
Page 824
3-3 advanced ipv6 acls are numbered in the range 3000 to 3999. Compared with basic ipv6 acls, they allow of more flexible and accurate filtering. Configuration prerequisites if you want to reference a time range in a rule, define it with the time-range command first. Configuration procedure follow t...
Page 825: Copying An Ipv6 Acl
3-4 z when the acl match order is auto, a newly created rule will be inserted among the existing rules in the depth-first match order. Note that the ids of the rules still remain the same. Z you can modify the match order of an ipv6 acl with the acl ipv6 number acl6-number [ name acl6-name ] match-o...
Page 827
3-6 [switch] traffic classifier c_rd [switch-classifier-c_rd] if-match acl ipv6 2000 [switch-classifier-c_rd] quit # configure traffic behavior b_rd to deny matching packets. [switch] traffic behavior b_rd [switch-behavior-b_rd] filter deny [switch-behavior-b_rd] quit # configure qos policy p_rd to ...
Page 828: Filtering Ethernet Frames
4-1 4 acl application for packet filtering when applying an acl for packet filtering, go to these sections for information you are interested in: z filtering ethernet frames z filtering ipv4 packets z filtering ipv6 packets z configuring packet filtering statistics function z acl application example...
Page 829: Filtering Ipv6 Packets
4-2 filtering ipv6 packets follow these steps to apply an ipv6 acl to an interface to filter ipv6 packets: to do… use the command… remarks enter system view system-view — enter ethernet interface view interface interface-type interface-number enter interface view enter vlan interface view interface ...
Page 830: Acl Application Examples
4-3 to do… use the command… remarks set the interval for ipv6 packet filtering statistics acl ipv6 logging frequence frequence 0 by default, which means no packet filtering statistics is collected. If you execute the display acl command to display the information about the acls, the device outputs p...
Page 831
4-4 [devicea] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1 [devicea-gigabitethernet1/0/1] packet-filter 2009 inbound [devicea-gigabitethernet1/0/1] quit # set the interval for packet filtering statistics to 10 minutes. [devicea] acl logging frequence 10 # configure a system information output rule to output log ...
Page 832: System Volume Organization
System volume organization manual version 6w100-20090630 product version release 2202 organization the system volume is organized as follows: features description login upon logging into a device, you can configure user interface properties and manage the system conveniently. This document describes...
Page 833
Features description file system management a major function of the file system is to manage storage devices, mainly including creating the file system, creating, deleting, modifying and renaming a file or a directory and opening a file. This document describes: z file system management z configurat...
Page 834
Features description poe the power over ethernet (poe) feature enables the power sourcing equipment (pse) to feed powered devices (pds) from ethernet ports through twisted pair cables. This document describes: z poe overview z configuring the poe interface z configuring poe power management z config...
Page 835
Features description cluster management a cluster is a group of network devices. Cluster management is to implement management of large numbers of distributed network devices. This document describes: z cluster management overview z configuring the management device z configuring the member devices ...
Page 836: Table of Contents
I table of contents 1 logging in to an ethernet switch ············································································································1-1 logging in to an ethernet switch ····································································································...
Page 837
Ii configuration procedure ··················································································································4-3 command accounting configuration example ·······················································································4-4 network diagram ·······...
Page 838
1-1 1 logging in to an ethernet switch when logging in to an ethernet switch, go to these sections for information you are interested in: z logging in to an ethernet switch z introduction to user interface z specifying source for telnet packets z controlling login users logging in to an ethernet swi...
Page 839
1-2 users and user interfaces a device can support one aux ports and multiple ethernet interfaces, and thus multiple user interfaces are supported. These user interfaces do not associate with specific users. Z when the user initiates a connection request, based on the login type the system automatic...
Page 841: Introduction
2-1 2 logging in through the console port when logging in through the console port, go to these sections for information you are interested in: z introduction z setting up the connection to the console port z console port login configuration z console port login configuration with authentication mod...
Page 842
2-2 z if you use a pc to connect to the console port, launch a terminal emulation utility (such as hyperterminal in windows 9x/windows 2000/windows xp) and perform the configuration shown in figure 2-2 through figure 2-4 for the connection to be created. Normally, the parameters of a terminal are co...
Page 843
2-3 figure 2-4 set port parameters terminal window z turn on the switch. The user will be prompted to press the enter key if the switch successfully completes post (power-on self test). The prompt (such as ) appears after the user presses the enter key. Z you can then configure the switch or check t...
Page 845: None
2-5 authentication mode console port login configuration description perform common configuration perform common configuration for console port login optional refer to common configuration for details. Specify to perform local authentication or radius authentication aaa configuration specifies wheth...
Page 846
2-6 configuration example network requirements assume the switch is configured to allow you to login through telnet, and your user level is set to the administrator level (level 3). After you telnet to the switch, you need to limit the console user at the following aspects. Z the user is not authent...
Page 847: Password
2-7 [sysname-ui-aux0] idle-timeout 6 after the above configuration, to ensure a successful login, the console user needs to change the corresponding configuration of the terminal emulation program running on the pc, to make the configuration consistent with that on the switch. Refer to setting up th...
Page 848
2-8 network diagram figure 2-6 network diagram for aux user interface configuration (with the authentication mode being password) configuration procedure # enter system view. System-view # enter aux user interface view. [sysname] user-interface aux 0 # specify to authenticate the user logging in thr...
Page 849: Scheme
2-9 console port login configuration with authentication mode being scheme configuration procedure follow these steps to perform console port login configuration (with authentication mode being scheme): to do… use the command… remarks enter system view system-view — enter aux user interface view use...
Page 850
2-10 note that, when you log in to an ethernet switch using the scheme authentication mode, your access rights depend on your user level defined in the aaa scheme. When the local authentication mode is used, the user levels are specified using the authorization-attribute level level command. When th...
Page 851
2-11 # create a local user named guest and enter local user view. [sysname] local-user guest # set the authentication password to 123456 (in plain text). [sysname-luser-guest] password simple 123456 # set the service type to terminal. [sysname-luser-guest] service-type terminal [sysname-luser-guest]...
Page 852
2-12 to do… use the command… remarks enter aux user interface view user-interface aux 0 — enable command authorization command authorization required disabled by default, that is, users can execute commands without authorization. Configuring command accounting command accounting allows the hwtacacs ...
Page 853: Logging In Through Telnet
3-1 3 logging in through telnet/ssh logging in through telnet when logging in through telnet, go to these sections for information you are interested in: z introduction z telnet connection establishment z telnet login configuration with authentication mode being none z telnet login configuration wit...
Page 854
3-2 # enable the telnet server function and configure the ip address of the management vlan interface as 202.38.160.92, and .The subnet mask as 255.255.255.0. System-view [sysname] telnet server enable [sysname] interface vlan-interface 1 [sysname-vlan-interface1] ip address 202.38.160.92 255.255.25...
Page 855
3-3 step 6: after successfully telnetting to a switch, you can configure the switch or display the information about the switch by executing corresponding commands. You can also type ? At any time for help. Refer to the following chapters for the information about the commands. Z a telnet connection...
Page 856
3-4 common configuration table 3-2 lists the common telnet configuration. Table 3-2 common telnet configuration configuration remarks enter system view system-view — make the switch to operate as a telnet server telnet server enable by default, a switch does not operate as a telnet server enter one ...
Page 857
3-5 table 3-3 telnet login configuration tasks when different authentication modes are adopted task description telnet login configuration with authentication mode being none configure not to authenticate users logging in user interfaces telnet login configuration with authentication mode being pass...
Page 858
3-6 figure 3-4 network diagram for telnet configuration (with the authentication mode being none) 3) configuration procedure # enter system view, and enable the telnet service. System-view [sysname] telnet server enable # enter vty 0 user interface view. [sysname] user-interface vty 0 # configure no...
Page 859
3-7 configuration example 1) network requirements assume that you are a level 3 aux user and want to perform the following configuration for telnet users logging in to vty 0: z authenticate users logging in to vty 0 using the local password. Z set the local password to 123456 (in plain text). Z comm...
Page 860
3-8 telnet login configuration with authentication mode being scheme configuration procedure follow these steps to perform telnet configuration (with authentication mode being scheme): to do… use the command… remarks enter system view system-view — enter one or more vty user interface views user-int...
Page 861
3-9 when the radius or hwtacacs authentication mode is used, the user levels are set on the corresponding radius or hwtacacs servers. For more information about aaa, radius, and hwtacacs, see aaa configuration in the security volume. Configuration example 1) network requirements assume that you are ...
Page 862: Logging In Through Ssh
3-10 # configure to authenticate users logging in to vty 0 in the scheme mode. [sysname-ui-vty0] authentication-mode scheme # configure telnet protocol is supported. [sysname-ui-vty0] protocol inbound telnet # set the maximum number of lines the screen can contain to 30. [sysname-ui-vty0] screen-len...
Page 863
3-11 configuring command accounting command accounting allows the hwtacacs server to record all commands executed on the device regardless of the command execution result. This helps control and monitor the user operations on the device. If command accounting is enabled and command authorization is ...
Page 864
4-1 4 user interface configuration examples user authentication configuration example network diagram as shown in figure 4-1 , command levels should be configured for different users to secure device: z the device administrator accesses device through the console port on host a. When the administrat...
Page 865
4-2 [device-ui-vty0-4] quit # create a radius scheme and configure the ip address and udp port for the primary authentication server for the scheme. Ensure that the port number be consistent with that on the radius server. Set the shared key for authentication packets to expert for the scheme and th...
Page 866
4-3 configuration procedure # assign an ip address to device to make device be reachable from host a and hwtacacs server respectively. The configuration is omitted. # enable the telnet service on device. System-view [device] telnet server enable # set to use username and password authentication when...
Page 867
4-4 command accounting configuration example network diagram as shown in figure 4-3 , configure the commands that the login users execute to be recorded on the hwtacacs server to control and monitor user operations. Figure 4-3 network diagram for configuring command accounting internet console conne...
Page 868
4-5 [device-radius-rad] quit # create isp domain system, and configure the isp domain system to use hwtacacs scheme tac for accounting of command line users [device] domain system [device-isp-system] accounting command hwtacacs-scheme tac [device-isp-system] quit.
Page 869: Management System
5-1 5 logging in through web-based network management system introduction an s5120-ei series switch has a built-in web server. You can log in to an s5120-ei series switch through a web browser and manage and maintain the switch intuitively by interacting with the built-in web server. To log in to an...
Page 870: Displaying Web Users
5-2 to do… use the command… remarks specify the service types for the local user service-type telnet optional by default, no service is authorized to a user. Start the web server ip http enable required execute this command in system view. Displaying web users after the above configurations, execute...
Page 871
5-3 step 4: log in to the switch through ie. Launch ie on the web-based network management terminal (your pc) and enter the ip address of the management vlan interface of the switch (here it is http://10.153.17.82). (make sure the route between the web-based network management terminal and the switc...
Page 872: Logging In Through Nms
6-1 6 logging in through nms when logging in through nms, go to these sections for information you are interested in: z introduction z connection establishment using nms introduction you can also log in to a switch through an nms (network management station), and then configure and manage the switch...
Page 873: Introduction
7-1 7 specifying source for telnet packets when specifying source ip address/interface for telnet packets, go to these sections for information you are interested in: z introduction z specifying source ip address/interface for telnet packets z displaying the source ip address/interface specified for...
Page 875: Controlling Login Users
8-1 8 controlling login users when controlling login users, go to these sections for information you are interested in: z introduction z controlling telnet users z controlling network management users by source ip addresses introduction multiple ways are available for controlling different types of ...
Page 877
8-3 controlling telnet users by source mac addresses this configuration needs to be implemented by layer 2 acl; a layer 2 acl ranges from 4000 to 4999. For the definition of acl, refer to acl configuration in the security volume. Follow these steps to control telnet users by source mac addresses: to...
Page 878
8-4 configuration procedure # define a basic acl. System-view [sysname] acl number 2000 match-order config [sysname-acl-basic-2000] rule 1 permit source 10.110.100.52 0 [sysname-acl-basic-2000] rule 2 permit source 10.110.100.46 0 [sysname-acl-basic-2000] rule 3 deny source any [sysname-acl-basic-20...
Page 880
8-6 controlling web users by source ip addresses the s5120-ei series ethernet switches support web-based remote management, which allows web users to access the switches using the http protocol. By referencing access control lists (acls), you can control the access of web users to the switches. Prer...
Page 881
8-7 figure 8-3 configure an acl to control the access of http users to the switch switch 10.110.100.46 host a ip network host b 10.110.100.52 configuration procedure # create a basic acl. System-view [sysname] acl number 2030 match-order config [sysname-acl-basic-2030] rule 1 permit source 10.110.10...
Page 882: Table of Contents
I table of contents 1 basic configurations·································································································································1-1 configuration display ·······································································································...
Page 883: Basic Configurations
1-1 1 basic configurations while performing basic configurations of the system, go to these sections for information you are interested in: z configuration display z basic configurations z cli features configuration display to avoid duplicate configuration, you can use the display commands to view t...
Page 884
1-2 z configuring the device name z configuring the system clock z enabling/disabling the display of copyright information z configuring a banner z configuring cli hotkeys z configuring user privilege levels and command levels z displaying and maintaining basic configurations entering/exiting system...
Page 886
1-4 configuration system clock displayed by the display clock command example if date-time is not in the daylight saving time range, date-time is displayed. Configure: clock datetime 1:00 2007/1/1 and clock summer-time ss one-off 1:00 2006/1/1 1:00 2006/8/8 2 display: 01:00:00 utc mon 01/01/2007 1 a...
Page 887
1-5 configuration system clock displayed by the display clock command example if date-time is not in the daylight saving time range, date-time is displayed. Configure: clock timezone zone-time add 1, clock summer-time ss one-off 1:00 2008/1/1 1:00 2008/8/8 2 and clock datetime 1:30 2008/1/1 display:...
Page 888
1-6 configuring a banner introduction to banners banners are prompt information displayed by the system when users are connected to the device, perform login authentication, and start interactive configuration. The administrator can set corresponding banners as needed. At present, the system support...
Page 889
1-7 to do… use the command… remarks configure the banner to be displayed when a user enters user view (non modem login users) header shell text optional configure the banner to be displayed before login header motd text optional configuring cli hotkeys follow these steps to configure cli hotkeys: to...
Page 890
1-8 hotkey function ctrl+x deletes all the characters to the left of the cursor. Ctrl+y deletes all the characters to the right of the cursor. Ctrl+z exits to user view. Ctrl+] terminates an incoming connection or a redirect connection. Esc+b moves the cursor to the leading character of the continuo...
Page 891
1-9 to do… use the command… remarks enter system view system-view — enable the command alias function command-alias enable required disabled by default, that is, you cannot configure command aliases. Configure command aliases command-alias mapping cmdkey alias required not configured by default. Con...
Page 892
1-10 follow these steps to configure user privilege level by using aaa authentication parameters: to do… use the command… remarks enter system view system-view — enter user interface view user-interface [ type ] first-number [ last-number ] — configure the authentication mode for logging in to the u...
Page 893
1-11 [sysname-luser-test] password cipher 123 [sysname-luser-test] service-type telnet after the above configuration, when users telnet to the device through vty 1, they need to input username test and password 123. After passing the authentication, users can only use the commands of level 0. If the...
Page 894
1-12 to do… use the command… remarks configure the privilege level of the user logging in from the current user interface user privilege level level optional by default, the user privilege level for users logging in from the console user interface is 3, and that for users logging from the other user...
Page 895
1-13 undo cancel current setting z authenticate the usesr logging in to the device through telnet, verify their passwords, and specify the user privilege levels as 2. System-view [sysname] user-interface vty 0 4 [sysname-ui-vty1] authentication-mode password [sysname-ui-vty0-4] set authentication pa...
Page 896
1-14 z when you configure the password for switching user privilege level with the super password command, the user privilege level is 3 if no user privilege level is specified. Z the password for switching user privilege level can be displayed in both cipher text and simple text. You are recommende...
Page 897: Cli Features
1-15 during daily maintenance or when the system is operating abnormally, you need to view each module’s running status to find the problem. Therefore, you are required to execute the corresponding display commands one by one. To collect more information one time, you can execute the display diagnos...
Page 898
1-16 file for next startup, you need to input st s at least; to enter system view, you need to input sy at least. You can press tab to complement the command, or you can input the complete command. Online help with command lines the following are the types of online help available with the cli: z fu...
Page 899
1-17 5) enter a command followed by a character string and a ?. All the keywords starting with this string are listed. Display ver? Version 6) press tab after entering the first several letters of a keyword to display the complete keyword, provided these letters can uniquely identify the keyword in ...
Page 900
1-18 key function tab pressing tab after entering part of a keyword enables the fuzzy help function. If finding a unique match, the system substitutes the complete keyword for the incomplete one and displays it in the next line; when there are several matches, if you repeatedly press tab, all the ke...
Page 901
1-19 character meaning remarks string$ ending sign, string appears only at the end of a line. For example, regular expression "user$” only matches a string ending with “user”, not “usera”. . Full stop, a wildcard used in place of any character, including single character, special character and blank...
Page 902
1-20 character meaning remarks \string used to match a character string starting with string. For example, “\ “domain” or string “doa”. String\> used to match a character string ending with string. For example, “do\>” can match word “undo” or string “abcdo”. \bcharacter2 used to match character1char...
Page 903
1-21 table 1-6 display functions action function press space when information display pauses continues to display information of the next screen page. Press enter when information display pauses continues to display information of the next line. Press ctrl+c when information display pauses stops the...
Page 904
1-22 command line error information the commands are executed only if they have no syntax error. Otherwise, error information is reported. Table 1-7 lists some common errors. Table 1-7 common command line errors error information cause the command was not found. The keyword was not found. Parameter ...
Page 905: Table of Contents
I table of contents 1 device management ··································································································································1-1 device management overview ···································································································...
Page 906: Device Management
1-1 1 device management when configuring device management, go to these sections for information you are interested in: z device management overview z device management configuration task list z configuring the exception handling method z rebooting a device z configuring the scheduled automatic exec...
Page 907: Rebooting A Device
1-2 z reboot: the system recovers itself through automatic reboot. Z maintain: the system maintains the current situation, and does not take any measure to recover itself. Therefore, you need to recover the system manually, such as reboot the system. Sometimes, it is difficult for the system to reco...
Page 908
1-3 z use the save command to save the current configuration before you reboot the device to avoid configuration lost. (for details of the save command, refer to file system management configuration in the system volume.) z use the display startup command and the display boot-loader command to verif...
Page 909: Disabling Boot Rom Access
1-4 z after the specified automatic execution time is reached, the system executes the specified command in the background without displaying any information except system information such as log, trap and debug. Z the system does not require any interactive information when it is executing the spec...
Page 910: Upgrading Boot Rom
1-5 in addition, you need to set the boot rom access password when you enter the boot rom menu for the first time to protect the boot rom against operations of illegal users. You can use the display startup command to view the status of the boot rom access function. For the detailed description of t...
Page 911
1-6 to do… use the command… remarks enter system view system-view — configure a detection interval shutdown-interval time optional the detection interval is 30 seconds by default. Clearing the 16-bit interface indexes not used in the current system in practical networks, the network management softw...
Page 912
1-7 table 1-1 commonly used pluggable transceivers transceiver type application environment whether can be an optical transceiver whether can be an electrical transceiver sfp (small form-factor pluggable) generally used for 100m/1000m ethernet interfaces or pos 155m/622m/2.5g interfaces yes yes sfp+...
Page 913
1-8 diagnosing pluggable transceivers the system outputs alarm information for you to diagnose and troubleshoot faults of pluggable transceivers. Optical transceivers customized by h3c also support the digital diagnosis function, which monitors the key parameters of a transceiver, such as temperatur...
Page 914
1-9 to do… use the command… remarks display detailed configurations of the scheduled automatic execution function display schedule job available in any view display the exception handling methods display system-failure available in any view device management configuration examples remote scheduled a...
Page 915
1-10 z use text editor on the ftp server to edit batch file auto-update.Txt. The following is the content of the batch file: return startup saved-configuration new-config.Cfg boot-loader file soft-version2.Bin main reboot 2) configuration on device # log in to the ftp server (note that the prompt ma...
Page 916
1-11 z the newest application soft-version2.Bin and the newest configuration file new-config.Cfg are both saved under the tftp server. Z the ip address of the irf stack system is 1.1.1.1/24, the ip address of the tftp server is 2.2.2.2/24, and the tftp server is reachable. Figure 1-2 network diagram...
Page 917
1-12 please wait ... Setting the master board ... ... Done! Setting the slave board ... Slot 2: set next configuration file successfully # specify file soft-version2.Bin as the boot file for the next boot for all members. Boot-loader file soft-version2.Bin slot all main this command will set the boo...
Page 918: Table of Contents
I table of contents 1 file system management configuration ·································································································1-1 file system management ·····················································································································...
Page 919
Ii single device upgrade····················································································································3-4 stacking system upgrade ···············································································································3-5.
Page 920: File System Management
1-1 1 file system management configuration when configuring file system management, go to these sections for information you are interested in: z file system management z configuration file management z displaying and maintaining device configuration file system management this section covers these ...
Page 921
1-2 format description length example path/file-name specifies a file in the specified folder under the current working directory. Path represents the folder name. You can specify multiple folders, indicating a file under a multi-level folder. 1 to 135 characters test/a.Txt: indicates that a file na...
Page 923
1-4 displaying file information to do… use the command… remarks display file or directory information dir [ /all ] [ file-url ] required available in user view displaying the contents of a file to do… use the command… remarks display the contents of a file more file-url required currently only a .Tx...
Page 924
1-5 z the files in the recycle bin still occupy storage space. To delete a file in the recycle bin, you need to execute the reset recycle-bin command in the directory that the file originally belongs. It is recommended to empty the recycle bin timely with the reset recycle-bin command to save storag...
Page 925
1-6 execution of a batch file does not guarantee the successful execution of every command in the batch file. If a command has error settings or the conditions for executing the command are not satisfied, the system will skip the command to the next one. Storage medium operations managing space of t...
Page 927
1-8 z saving the current configuration z setting configuration rollback z specifying a startup configuration file for the next system startup z backing up the startup configuration file z deleting the startup configuration file for the next startup z restoring the startup configuration file z displa...
Page 928
1-9 at a moment, there are at most one main startup configuration file and one backup startup configuration file. You can specify neither of the two files (displayed as null), or specify the two files as the same configuration file. You can specify the main and backup startup configuration files for...
Page 929
1-10 to do… use the command… remarks enter system view system-view — enable configuration file auto-save slave auto-update config optional enabled by default. Modes in saving the configuration z fast saving mode. This is the mode when you use the save command without the safely keyword. The mode sav...
Page 930
1-11 setting configuration rollback configuration rollback allows you to revert to a previous configuration state based on a specified configuration file. The specified configuration file must be a valid .Cfg file, namely, it can be generated by using either the backup function (manually or automati...
Page 931
1-12 configuration task list complete these tasks to configure the configuration rollback: task remarks configuring parameters for saving the current running configuration required saving the current running configuration automatically saving the current running configuration manually required use a...
Page 932
1-13 z the saving and rollback operations are executed only on the master. To make the configuration rollback take effect on the new master after an active/standby switchover, execute the archive configuration location command to specify the path and filename prefix of the saved configuration file o...
Page 933
1-14 saving the current running configuration manually automatic saving of the current running configuration occupies system resources, and frequent saving greatly affects system performance. Therefore, if the system configuration does not change frequently, you are recommended to disable the automa...
Page 934
1-15 specifying a startup configuration file for the next system startup a startup configuration file is the configuration file to be used at the next system startup. You can specify a configuration file as the startup configuration file to be used at the next system startup in the following two way...
Page 935
1-16 before the backup operation, you should: z ensure that the server is reachable, the server is enabled with tftp service, and the client has permission to read and write. Z use the display startup command (in user view) to see whether you have set the startup configuration file, and use the dir ...
Page 936
1-17 to do… use the command… remarks restore the startup configuration file to be used at the next system startup restore startup-configuration from src-addr src-filename required available in user view z the restore operation restores the main startup configuration file. Z before restoring a config...
Page 937: Ftp Configuration
2-1 2 ftp configuration when configuring ftp, go to these sections for information you are interested in: z ftp overview z configuring the ftp client z configuring the ftp server z displaying and maintaining ftp ftp overview introduction to ftp the file transfer protocol (ftp) is an application laye...
Page 938
2-2 table 2-1 configuration when the device serves as the ftp client device configuration remarks device (ftp client) use the ftp command to establish the connection to the remote ftp server if the remote ftp server supports anonymous ftp, the device can log in to it directly; if not, the device mus...
Page 939: Configuring The Ftp Client
2-3 configuring the ftp client establishing an ftp connection to access an ftp server, an ftp client must establish a connection with the ftp server. Two ways are available to establish a connection: using the ftp command to establish the connection directly; using the open command in ftp client vie...
Page 940
2-4 z if no primary ip address is configured on the specified source interface, no ftp connection can be established. Z if you use the ftp client source command to first configure the source interface and then the source ip address of the transmitted packets, the newly configured source ip address w...
Page 941
2-5 to do… use the command… remarks view the detailed information of the files/directories on the ftp server dir [ remotefile [ localfile ] ] optional view the names of the files/directories on the ftp server ls [ remotefile [ localfile ] ] optional download a file from the ftp server get remotefile...
Page 942
2-6 ftp client configuration example single device upgrade network requirements z as shown in figure 2-2 , use device as an ftp client and pc as the ftp server. Their ip addresses are 10.2.1.1/16 and 10.1.1.1/16 respectively. An available route exists between device and pc. Z device downloads a star...
Page 943
2-7 [ftp] put config.Cfg back-config.Cfg 227 entering passive mode (10,1,1,1,4,2). 125 ascii mode data connection already open, transfer starting for /config.Cfg. 226 transfer complete. Ftp: 3494 byte(s) sent in 5.646 second(s), 618.00 byte(s)/sec. [ftp] bye # specify newest.Bin as the main startup ...
Page 944
2-8 configuration procedure if the available memory space of the device is not enough, use the fixdisk command to clear the memory or use the delete /unreserved file-url command to delete the files not in use and then perform the following operations. # log in to the server through ftp. Ftp 10.1.1.1...
Page 945: Configuring The Ftp Server
2-9 reboot the startup file used for the next startup must be saved under the root directory of the storage medium. You can copy or move a file to the root directory of the storage medium. For the details of the boot-loader command, refer to device management commands in the system volume. Configuri...
Page 946
2-10 to do… use the command… remarks manually release the ftp connection established with the specified username free ftp user username optional available in user view configuring authentication and authorization on the ftp server to allow an ftp user to access certain directories on the ftp server,...
Page 947
2-11 ftp server configuration example single device upgrade network requirements z as shown in figure 2-4 , use device as an ftp server, and the pc as the ftp client. Their ip addresses are 1.2.1.1/16 and 1.1.1.1/16 respectively. An available route exists between device and pc. Z pc keeps the update...
Page 948
2-12 6 -rw- 478164 apr 26 2000 14:52:35 s5120ei_505.Btm 7 -rw- 368 apr 26 2000 12:04:04 patch_xxx.Bin 8 -rw- 2337 apr 26 2000 14:16:48 sfp.Cfg 9 -rw- 2195 apr 26 2000 14:10:41 5120ei.Cfg 31496 kb total (11004 kb free) delete /unreserved flash:/sfp.Cfg 2) configure the pc (ftp client) # log in to the...
Page 949
2-13 the startup file used for the next startup must be saved under the root directory of the storage medium. You can copy or move a file to the root directory of the storage medium. For the details of the boot-loader command, refer to device management commands in the system volume. Stacking system...
Page 950
2-14 [sysname] quit # check files on your device. Remove those redundant to ensure adequate space for the startup file to be uploaded. Dir directory of flash:/ 0 -rw- 10471471 sep 18 2008 02:45:15 s5120eih3c-d501.Bin 1 -rw- 9989823 jul 14 2008 19:30:46 s5120eih3cd_b57.Bin 2 -rw- 6 apr 26 2000 12:04:...
Page 951
2-15 copy newest.Bin slot2#flash:/ # specify newest.Bin as the main startup file to be used at the next startup for all the member devices. Boot-loader file newest.Bin slot all main this command will set the boot file of the specified board. Continue? [y/n]:y the specified file will be used as the m...
Page 952: Tftp Configuration
3-1 3 tftp configuration when configuring tftp, go to these sections for information you are interested in: z tftp overview z configuring the tftp client z displaying and maintaining the tftp client z tftp client configuration example tftp overview introduction to tftp the trivial file transfer prot...
Page 953: Configuring The Tftp Client
3-2 when the device serves as the tftp client, you need to perform the following configuration: table 3-1 configuration when the device serves as the tftp client device configuration remarks device (tftp client) z configure the ip address and routing function, and ensure that the route between the d...
Page 954
3-3 follow these steps to configure the tftp client: to do… use the command… remarks enter system view system-view — control the access to the tftp servers from the device through acl tftp-server [ ipv6] acl acl-number optional by default, the access to the tftp servers from the device is not contro...
Page 955
3-4 tftp client configuration example single device upgrade network requirements z as shown in figure 3-2 , use a pc as the tftp server and device as the tftp client. Their ip addresses are 1.2.1.1/16 and 1.1.1.1/16 respectively. An available route exists between device and pc. Z device downloads a ...
Page 956
3-5 the startup file used for the next startup must be saved under the root directory of the storage medium. You can copy or move a file to the root directory of the storage medium. For the details of the boot-loader command, refer to device management commands in the system volume. Stacking system ...
Page 957
3-6 z download application file newest.Bin from pc to the root directory of the storage medium on the master. Tftp 1.2.1.1 get newest.Bin z download application file newest.Bin from pc to the root directory of the storage medium on a slave (with the member id 2). Tftp 1.2.1.1 get newest.Bin slot2#fl...
Page 958: Table of Contents
I table of contents 1 http configuration···································································································································1-1 http overview················································································································...
Page 959: Http Configuration
1-1 1 http configuration when configuring http, go to these sections for information you are interested in: z http overview z enabling the http service z http configuration z associating the http service with an acl z displaying and maintaining http http overview the hypertext transfer protocol (htt...
Page 960
1-2 follow these steps to enable the http service: to do… use the command… remarks enter system view system-view — enable the http service ip http enable required configuring the port number of the http service configuration of the port number of the http service can reduce the attacks from illegal ...
Page 961: Https Configuration
2-1 2 https configuration when configuring https, go to these sections for information you are interested in: z https overview z https configuration task list z associating the https service with an ssl server policy z enabling the https service z associating the https service with a certificate att...
Page 962: Enabling The Https Service
2-2 configuration task remarks configuring the port number of the https service optional associating the https service with an acl optional associating the https service with an ssl server policy you need to associate the https service with a created ssl server policy before enabling the https servi...
Page 963: Control Policy
2-3 z after the https service is enabled, you can use the display ip https command to view the state of the https service and verify the configuration. Z enabling of the https service will trigger an ssl handshake negotiation process. During the process, if the local certificate of the device alread...
Page 964: Https Configuration Example
2-4 to do… use the command… remarks enter system view system-view — configure the port number of the https service ip https port port-number optional by default, the port number of the https service is 443. If you execute the ip https port command for multiple times, the last configured port number ...
Page 965
2-5 figure 2-1 network diagram for https configuration configuration procedure perform the following configurations on device: 1) apply for a certificate for device # configure a pki entity. System-view [device] pki entity en [device-pki-entity-en] common-name http-server1 [device-pki-entity-en] fqd...
Page 966
2-6 # configure certificate access control policy myacp and create a control rule. [device] pki certificate access-control-policy myacp [device-pki-cert-acp-myacp] rule 1 permit mygroup1 [device-pki-cert-acp-myacp] quit 4) reference an ssl server policy # associate the https service with the ssl ser...
Page 967: Table of Contents
I table of contents 1 snmp configuration··································································································································1-1 snmp overview·················································································································...
Page 968: Snmp Configuration
1-1 1 snmp configuration when configuring snmp, go to these sections for information you are interested in: z snmp overview z snmp configuration z configuring snmp logging z snmp trap configuration z displaying and maintaining snmp z snmp configuration example z snmp logging configuration example sn...
Page 969
1-2 snmp protocol version currently, snmp agents support snmpv3 and are compatible with snmpv1 and snmpv2c. Z snmpv1 uses community name for authentication, which defines the relationship between an snmp nms and an snmp agent. Snmp packets with community names that did not pass the authentication on...
Page 970: Snmp Configuration
1-3 figure 1-2 mib tree a 2 6 1 5 2 1 1 2 1 b snmp configuration as configurations for snmpv3 differ substantially from those of snmpv1 and snmpv2c, their snmp functionalities is introduced separately below. Follow these steps to configure snmpv3: to do… use the command… remarks enter system view sy...
Page 971
1-4 to do… use the command… remarks configure the maximum size of an snmp packet that can be received or sent by an snmp agent snmp-agent packet max-size byte-count optional 1,500 bytes by default configure the engine id for a local snmp agent snmp-agent local-engineid engineid optional company id a...
Page 973: Snmp Trap Configuration
1-6 z logs occupy storage space of the device, thus affecting the performance of the device. Therefore, it is recommended to disable snmp logging. Z the size of snmp logs cannot exceed that allowed by the information center, and the total length of the node field and value field of each log record c...
Page 974
1-7 to enable an interface to send linkup/linkdown traps when its state changes, you need to enable the trap function of interface state changes on an interface and globally. Use the enable snmp trap updown command to enable the trap function on an interface, and use the snmp-agent trap enable [ sta...
Page 975
1-8 to do… use the command… remarks configure the holding time of the traps in the queue snmp-agent trap life seconds optional 120 seconds by default z an extended linkup/linkdown trap is the standard linkup/linkdown trap (defined in rfc) appended with interface description and interface type inform...
Page 976: Snmp Configuration Example
1-9 snmp configuration example network requirements z the nms connects to the agent, a switch, through an ethernet. Z the ip address of the nms is 1.1.1.2/24. Z the ip address of the vlan interface on the switch is 1.1.1.1/24. Z the nms monitors and manages the agent using snmpv2c. The agent reports...
Page 977
1-10 with snmpv2c, the user needs to specify the read only community, the read and write community, the timeout time, and number of retries. The user can inquire and configure the device through the nms. The configurations on the agent and the nms must match. Snmp logging configuration example netwo...
Page 978
1-11 # enable snmp logging on the agent to log the get and set operations of the nms. [sysname] snmp-agent log get-operation [sysname] snmp-agent log set-operation z the following log information is displayed on the terminal when the nms performs the get operation to the agent. %jan 1 02:49:40:566 2...
Page 979: Mib Style Configuration
2-1 2 mib style configuration h3c private mib involves two styles, h3c compatible mib and h3c new mib. In the h3c compatible mib style, the device sysoid is under the h3c’s enterprise id 25506, and the private mib is under the enterprise id 2011. In the h3c new mib style, both the device sysoid and ...
Page 980: Table of Contents
I table of contents 1 rmon configuration ·································································································································1-1 rmon overview ················································································································...
Page 981: Rmon Configuration
1-1 1 rmon configuration when configuring rmon, go to these sections for information you are interested in: z rmon overview z configuring rmon z displaying and maintaining rmon z rmon configuration example rmon overview this section covers these topics: z introduction z rmon groups introduction remo...
Page 982
1-2 rmon groups among the ten rmon groups defined by rmon specifications (rfc 1757), the device supports the event group, alarm group, history group and statistics group. Besides, h3c also defines and implements the private alarm group, which enhances the functions of the alarm group. This section d...
Page 983: Configuring Rmon
1-3 if the count result overpasses the same threshold multiple times, only the first one can cause an alarm event. That is, the rising alarm and falling alarm are alternate. History group the history group periodically collects statistics on data at interfaces and saves the statistics in the history...
Page 985: Rmon Configuration Example
1-5 displaying and maintaining rmon to do… use the command… remarks display rmon statistics display rmon statistics [ interface-type interface-number ] available in any view display the rmon history control entry and history sampling information display rmon history [ interface-type interface-number...
Page 986
1-6 etherstatsbroadcastpkts : 56 , etherstatsmulticastpkts : 34 etherstatsundersizepkts : 0 , etherstatsoversizepkts : 0 etherstatsfragments : 0 , etherstatsjabbers : 0 etherstatscrcalignerrors : 0 , etherstatscollisions : 0 etherstatsdropevents (insufficient resources): 0 packets received according...
Page 987: Table of Contents
I table of contents 1 mac address table management configuration···················································································1-1 introduction to mac address table ········································································································1-1 how a m...
Page 988
1-1 1 mac address table management configuration when configuring mac address table management, go to these sections for information you are interested in: z configuring mac address table management z mac address table management configuration example z mac information configuration z mac informatio...
Page 989
1-2 when receiving a frame destined for mac-source, the device then looks up the mac address table and forwards it from port 1. To adapt to network changes, mac address table entries need to be constantly updated. Each dynamically learned mac address table entry has a life period, that is, an aging ...
Page 990
1-3 figure 1-1 forward frames using the mac address table configuring mac address table management the mac address table management configuration tasks include: z configuring mac address table entries z configuring the aging timer for dynamic mac address entries z configuring the mac learning limit ...
Page 991
1-4 configuring the aging timer for dynamic mac address entries the mac address table on your device is available with an aging mechanism for dynamic entries to prevent its resources from being exhausted. Set the aging timer appropriately: a long aging interval may cause the mac address table to ret...
Page 993: Overview
2-1 2 mac information configuration when configuring mac information, go to these sections for information you are interested in: z overview z configuring mac information z mac information configuration example overview introduction to mac information to monitor a network, you need to monitor users ...
Page 994
2-2 enabling mac information on an interface follow these steps to enable mac information on an interface: to do… use the command… remarks enter system view system-view — enter interface view interface interface-type interface-number — enable mac information on the interface mac-address information ...
Page 995
2-3 to do… use the command… remarks enter system view system-view — configure the mac information queue length mac-address information queue-length value optional 50 by default setting the mac information queue length to 0 indicates that the device sends a syslog or trap message to the network manag...
Page 996
2-4 [device] mac-address information mode syslog # enable mac information on gigabitethernet 1/0/1 [device] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1 [device-gigabitethernet1/0/1] mac-address information enable added [device-gigabitethernet1/0/1] mac-address information enable deleted [device-gigabitethernet1...
Page 997: Table of Contents
1-1 table of contents 1 system maintaining and debugging········································································································1-1 system maintaining and debugging overview ·······················································································1-1 int...
Page 998
1-1 1 system maintaining and debugging when maintaining and debugging the system, go to these sections for information you are interested in: z system maintaining and debugging overview z system maintaining and debugging z system maintaining example system maintaining and debugging overview introduc...
Page 999
1-2 2) the first hop (the layer 3 device that first receives the packet) responds by sending a ttl-expired icmp message to the source, with its ip address encapsulated. In this way, the source device can get the address of the first layer 3 device. 3) the source device sends a packet with a ttl valu...
Page 1002: Table of Contents
I table of contents 1 information center configuration············································································································1-1 information center overview ··········································································································...
Page 1003: Information Center Overview
1-1 1 information center configuration when configuring information center, go to these sections for information you are interested in: z information center configuration z configuring information center z displaying and maintaining information center z information center configuration examples info...
Page 1004
1-2 eight levels of system information the information is classified into eight levels by severity. The severity levels in the descending order are emergency, alert, critical, error, warning, notice, informational and debug. When the system information is output by level, the information with severi...
Page 1005
1-3 information channel number default channel name default output destination note 4 logbuffer log buffer receives log and debugging information, a buffer inside the router for recording information. 5 snmpagent snmp module receives trap information 6 channel6 not specified receives log, trap, and ...
Page 1006
1-4 table 1-3 default output rules for different output destinations log trap debug output destinati on modules allowed enabled/ disabled severity enabled/ disabled severity enabled/ disabled severity console default (all modules) enabled warning enabled debug enabled debug monitor terminal default ...
Page 1007
1-5 what follows is a detailed explanation of the fields involved: int_16 (priority) the priority is calculated using the following formula: facility*8+severity, in which facility represents the logging facility name and can be configured when you set the log host parameters. The facility ranges fro...
Page 1008
1-6 z if the timestamp starts with a %, the information is log information z if the timestamp starts with a #, the information is trap information z if the timestamp starts with a *, the information is debugging information source this field indicates the source of the information, such as the sourc...
Page 1013
1-11 outputting system information to the snmp module the snmp module receives the trap information only, and discards the log and debugging information even if you have configured to output them to the snmp module. To monitor the device running status, trap information is usually sent to the snmp n...
Page 1014
1-12 follow these steps to enable synchronous information output: to do… use the command… remarks enter system view system-view — enable synchronous information output info-center synchronous required disabled by default z if system information, such as log information, is output before you input an...
Page 1016
1-14 # specify the host with ip address 1.2.0.1/16 as the log host, use channel loghost to output log information (optional, loghost by default), and use local4 as the logging facility. [sysname] info-center loghost 1.2.0.1 channel loghost facility local4 # disable the output of log, trap, and debug...
Page 1017
1-15 be aware of the following issues while editing file /etc/syslog.Conf: z comments must be on a separate line and begin with the # sign. Z no redundant spaces are allowed after the file name. Z the logging facility name and the information level specified in the /etc/syslog.Conf file must be iden...
Page 1018
1-16 # disable the output of log, trap, and debugging information of all modules on channel loghost. [sysname] info-center source default channel loghost debug state off log state off trap state off as the default system configurations for different channels are different, you need to disable the ou...
Page 1019
1-17 # syslogd -r & ensure that the syslogd process is started with the -r option on a linux log host. After the above configurations, the system will be able to record log information into the log file. Outputting log information to the console network requirements z log information with a severity...
Page 1020
1-18 # enable the display of log information on a terminal. (optional, this function is enabled by default.) terminal monitor % current terminal monitor is on terminal logging % current terminal logging is on after the above configuration takes effect, if the specified module generates log informati...
Page 1021: Table of Contents
I table of contents 1 poe configuration ·····································································································································1-1 poe overview ··············································································································...
Page 1022: Poe Configuration
1-1 1 poe configuration when configuring poe, go to these sections for information you are interested in: z poe overview z poe configuration task list z configuring the poe interface z configuring poe power management z configuring the poe monitoring function z upgrading pse processing software onli...
Page 1023: Poe Configuration Task List
1-2 a pd is a device accepting power from the pse. There are standard pds and nonstandard pds. A standard pd refers to the one that complies with ieee 802.3af. The pd that is being powered by the pse can be connected to other power supply units for redundancy backup. Protocol specification the proto...
Page 1024
1-3 z signal cables modes: for a device with only signal cables, power is supplied over signal cables. Z spare cables modes: for a device with spare cables and signal cables, power can be supplied over spare cables or signal cables. S5120-ei series switches only support for signal mode. Configuring ...
Page 1025
1-4 to do… use the command… remarks enable poe for the poe interface poe enable required disabled by default. Configure the maximum power for the poe interface poe max-power max-power optional 15,400 milliwatts by default. Configure the poe mode for the poe interface poe mode signal optional signal ...
Page 1026
1-5 all pses implement the same pd power management policies. When the pse supplies power to a pd, z by default, no power will be supplied to a new pd if the pse power is overloaded. Z under the control of a priority policy, the pd with a lower priority is first powered off to guarantee the power su...
Page 1027
1-6 to do… use the command… remarks configure a pd power management priority policy poe pd-policy priority optional by default, no pd power management priority policy is configured. Configuring the poe monitoring function the poe monitoring function involves monitoring of poe power, pse and pd. Z mo...
Page 1029: Poe Configuration Example
1-8 displaying and maintaining poe to do… use the command… remarks display the mapping between id, module, and member id of all pses. Display poe device display the power state and information of the specified poe interface display poe interface [ interface-type interface-number ] display the power ...
Page 1030: Troubleshooting Poe
1-9 figure 1-1 network diagram for poe configuration procedure # enable poe on gigabitethernet 1/0/1, gigabitethernet 1/0/2, gigabitethernet 1/0/11, and gigabitethernet 1/0/12. System-view [sysname] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1 [sysname-gigabitethernet1/0/1] poe enable [sysname-gigabitethernet1/0...
Page 1031
1-10 z the priority of the poe interface is already set. Solution: z in the first case, you can solve the problem by increasing the maximum pse power, or by reducing the maximum power of the poe interface when the guaranteed remaining power of the pse cannot be modified. Z in the second case, you sh...
Page 1032: Table of Contents
I table of contents 1 track configuration···································································································································1-1 track overview ·············································································································...
Page 1033: Track Configuration
1-1 1 track configuration when configuring track, go to these sections for information you are interested in: z track overview z track configuration task list z configuring collaboration between the track module and the detection modules z configuring collaboration between the track module and the a...
Page 1034: Detection Modules
1-2 z if the probe succeeds, the status of the corresponding track object is positive; z if the probe fails, the status of the corresponding track object is negative. At present, the detection modules that can collaborate with the track module is the network quality analyzer (nqa). Refer to nqa conf...
Page 1035: Application Modules
1-3 when you configure a track object, the specified nqa test group and reaction entry can be nonexistent. In this case, the status of the configured track object is invalid. Configuring collaboration between the track module and the application modules configuring track-static routing collaboration...
Page 1036: Track Configuration Examples
1-4 z for the configuration of track-static routing collaboration, the specified static route can be an existent or nonexistent one. For an existent static route, the static route and the specified track object are associated directly; for a nonexistent static route, the system creates the static ro...
Page 1037
1-5 configuration procedure 1) configure the ip address of each interface as shown in figure 1-2 . 2) configure a static route on switch a and associate it with the track object. # configure the address of the next hop of the static route to switch c as 10.2.1.1, and configure the static route to as...
Page 1038
1-6 destination/mask proto pre cost nexthop interface 10.1.1.0/24 static 60 0 10.2.1.1 vlan3 10.2.1.0/24 direct 0 0 10.2.1.2 vlan3 10.2.1.2/32 direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 inloop0 127.0.0.0/8 direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 inloop0 127.0.0.1/32 direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 inloop0 the output information above indicates the nq...
Page 1039: Table of Contents
I table of contents 1 nqa configuration ····································································································································1-1 nqa overview ···············································································································...
Page 1040: Nqa Configuration
1-1 1 nqa configuration when configuring nqa, go to these sections for information you are interested in: z nqa overview z nqa configuration task list z configuring the nqa server z enabling the nqa client z creating an nqa test group z configuring an nqa test group z configuring the collaboration f...
Page 1041
1-2 collaboration with other modules is triggered. The implementation of collaboration is shown in figure 1-1 . Figure 1-1 implementation of collaboration track module policy routing static routing backup center vrrp detection modules nqa track module application modules policy routing static routin...
Page 1042
1-3 basic concepts of nqa test group before performing an nqa test, you need to create an nqa test group, and configure nqa test parameters such as test type, destination address and destination port. Each test group has an administrator name and operation tag, which can uniquely define a test group...
Page 1043: Nqa Configuration Task List
1-4 nqa test operation an nqa test operation is as follows: 1) the nqa client constructs packets with the specified type, and sends them to the peer device; 2) upon receiving the packet, the peer device replies with a response with a timestamp. 3) the nqa client computes the packet loss rate and rtt...
Page 1044: Configuring The Nqa Server
1-5 task remarks configuring optional parameters common to an nqa test group optional scheduling an nqa test group required configuring the nqa server before performing tcp, udp echo, udp jitter or voice tests, you need to configure the nqa server on the peer device. The nqa server makes a response ...
Page 1045
1-6 if you execute the nqa entry command to enter the test group view with test type configured, you will enter the test type view of the test group directly. Configuring an nqa test group configuring an icmp echo test an icmp echo test is used to test reachability of the destination host according ...
Page 1046
1-7 to do… use the command… remarks configure the source ip address of a probe request source ip ip-address optional by default, no source ip address is specified. If no source ip address is specified, but the source interface is specified, the ip address of the source interface is taken as the sour...
Page 1047
1-8 to do… use the command… remarks configure common optional parameters see configuring optional parameters common to an nqa test group optional z as dhcp test is a process to simulate address allocation in dhcp, the ip address of the interface performing the dhcp test will not be changed. Z after ...
Page 1049
1-10 to do… use the command… remarks configure the test type as http and enter test type view type http required configure the destination address for a test operation destination ip ip-address required by default, no destination ip address is configured for a test operation. The destination ip addr...
Page 1050
1-11 delay jitter refers to the difference between the interval of receiving two packets consecutively and the interval of sending these two packets. The procedure of a udp jitter test is as follows: z the source sends packets at regular intervals to the destination port. Z the destination affixes a...
Page 1051
1-12 to do… use the command… remarks configure the number of packets sent in a udp jitter probe probe packet-number packet-number optional 10 by default. Configure the interval for sending packets in a udp jitter probe probe packet-interval packet-interval optional 20 milliseconds by default. Config...
Page 1052
1-13 to do… use the command… remarks configure the destination address for a test operation destination ip ip-address required by default, no destination ip address is configured for a test operation. Specify the source port number for a probe request in a test operation source port port-number opti...
Page 1053
1-14 to do… use the command… remarks configure the destination port destination port port-number required by default, no destination port number is configured for a test operation. The destination port number must be consistent with port number of the listening service configured on the nqa server. ...
Page 1054
1-15 to do… use the command… remarks configure the destination port destination port port-number required by default, no destination port number is configured for a test operation. The destination port number must be the port number of the listening service configured on the nqa server. Configure th...
Page 1055
1-16 interval for the source to send these two successive packets, and thus the network status can be analyzed. The voice parameter values that indicate voip network status can also be calculated in a voice test, including: z calculated planning impairment factor (icpif): measures attenuation of voi...
Page 1056
1-17 to do… use the command… remarks configure the advantage factor for calculating mos and icpif values advantage-factor factor optional by default, the advantage factor is 0. Specify the source ip address for the requests in a test operation source ip ip-address optional by default, no source ip a...
Page 1057
1-18 configuration prerequisites enable the dlsw function on the peer device before dlsw test. Configuring a dlsw test follow these steps to configure a dlsw test: to do… use the command… remarks enter system view system-view — enter nqa test group view nqaentry admin-name operation-tag — configure ...
Page 1058: Configuring Trap Delivery
1-19 to do… use the command… remarks create a track object and associate it with the specified collaboration object of the nqa test group track entry-number nqa entry admin-name operation-tag reaction item-num required not created by default. Z you cannot modify the content of a reaction entry using...
Page 1059
1-20 configuring the nqa statistics function nqa puts the nqa tests completed in a specified interval into one group, and calculates the statistics of the test results of the group. These statistics form a statistics group. You can use the display nqa statistics command to view information of the st...
Page 1061: Scheduling An Nqa Test Group
1-22 scheduling an nqa test group with this configuration, you can set the start time and test duration for a test group to perform nqa tests. The start time can take a specific value or can be now, which indicates that a test is started immediately; the test duration can take a specific value or ca...
Page 1062: Nqa Configuration Examples
1-23 displaying and maintaining nqa to do… use the command… remarks display history records of nqa test operation information display nqa history [ admin-name operation-tag ] display the results of the last nqa test display nqa result [ admin-name operation-tag ] display the statistics of a type of ...
Page 1063
1-24 nqa entry(admin admin, tag test) test results: destination ip address: 10.2.2.2 send operation times: 10 receive response times: 10 min/max/average round trip time: 2/5/3 square-sum of round trip time: 96 last succeeded probe time: 2007-08-23 15:00:01.2 extended results: packet lost in test: 0%...
Page 1064
1-25 [switcha-nqa-admin-test] type dhcp [switcha-nqa-admin-test-dhcp] operation interface vlan-interface 2 [switcha-nqa-admin-test-dhcp] quit # enable dhcp test. [switcha] nqa schedule admin test start-time now lifetime forever # disable dhcp test after the test begins for a period of time. [switcha...
Page 1065
1-26 [devicea] nqa entry admin test [devicea-nqa-admin-test] type ftp [devicea-nqa-admin-test-ftp] destination ip 10.2.2.2 [devicea-nqa-admin-test-ftp] source ip 10.1.1.1 [devicea-nqa-admin-test-ftp] operation put [devicea-nqa-admin-test-ftp] username admin [devicea-nqa-admin-test-ftp] password syst...
Page 1066
1-27 figure 1-6 network diagram for the http tests configuration procedure # create an http test group and configure related test parameters. System-view [devicea] nqa entry admin test [devicea-nqa-admin-test] type http [devicea-nqa-admin-test-http] destination ip 10.2.2.2 [devicea-nqa-admin-test-ht...
Page 1067
1-28 udp jitter test configuration example network requirements use the nqa udp jitter function to test the delay jitter of packet transmission between device a and device b. Figure 1-7 network diagram for udp jitter tests configuration procedure 1) configure device b. # enable the nqa server and co...
Page 1068
1-29 failures due to sequence error: 0 failures due to internal error: 0 failures due to other errors: 0 packet(s) arrived late: 0 udp-jitter results: rtt number: 10 min positive sd: 4 min positive ds: 1 max positive sd: 21 max positive ds: 28 positive sd number: 5 positive ds number: 4 positive sd ...
Page 1069
1-30 min positive sd: 3 min positive ds: 1 max positive sd: 30 max positive ds: 79 positive sd number: 186 positive ds number: 158 positive sd sum: 2602 positive ds sum: 1928 positive sd average: 13 positive ds average: 12 positive sd square sum: 45304 positive ds square sum: 31682 min negative sd: ...
Page 1070
1-31 system-view [deviceb] snmp-agent sys-info version all [deviceb] snmp-agent community read public [deviceb] snmp-agent community write private 2) configurations on device a. # create an snmp query test group and configure related test parameters. System-view [devicea] nqa entry admin test [devic...
Page 1071
1-32 figure 1-9 network diagram for tcp tests configuration procedure 1) configure device b. # enable the nqa server and configure the listening ip address as 10.2.2.2 and port number as 9000. System-view [deviceb] nqa server enable [deviceb] nqa server tcp-connect 10.2.2.2 9000 2) configure device ...
Page 1072
1-33 nqa entry(admin admin, tag test) history record(s): index response status time 1 13 succeeded 2007-11-22 10:27:25.1 udp echo test configuration example network requirements use the nqa udp echo function to test the round trip time between device a and device b. The port number is 8000. Figure 1...
Page 1073
1-34 failures due to disconnect: 0 failures due to no connection: 0 failures due to sequence error: 0 failures due to internal error: 0 failures due to other errors: 0 packet(s) arrived late: 0 # display the history of udp echo tests. [devicea] display nqa history admin test nqa entry(admin admin, t...
Page 1074
1-35 nqa entry(admin admin, tag test) test results: destination ip address: 10.2.2.2 send operation times: 1000 receive response times: 1000 min/max/average round trip time: 31/1328/33 square-sum of round trip time: 2844813 last succeeded probe time: 2008-06-13 09:49:31.1 extended results: packet lo...
Page 1075
1-36 min/max/average round trip time: 15/1328/32 square-sum of round trip time: 7160528 extended results: packet lost in test: 0% failures due to timeout: 0 failures due to disconnect: 0 failures due to no connection: 0 failures due to sequence error: 0 failures due to internal error: 0 failures due...
Page 1076
1-37 dlsw test configuration example network requirements use the nqa dlsw function to test the response time of the dlsw device. Figure 1-12 network diagram for the dlsw tests configuration procedure # create a dlsw test group and configure related test parameters. System-view [devicea] nqa entry a...
Page 1077: Table of Contents
I table of contents 1 ntp configuration ·····································································································································1-1 ntp overview ··············································································································...
Page 1078: Ntp Configuration
1-1 1 ntp configuration when configuring ntp, go to these sections for information you are interested in: z ntp overview z ntp configuration task list z configuring the operation modes of ntp z configuring optional parameters of ntp z configuring access-control rights z configuring ntp authenticatio...
Page 1079
1-2 z ntp can unicast, multicast or broadcast protocol messages. How ntp works figure 1-1 shows the basic workflow of ntp. Device a and device b are interconnected over a network. They have their own independent system clocks, which need to be automatically synchronized through ntp. For an easy unde...
Page 1080
1-3 this is only a rough description of the work mechanism of ntp. For details, refer to rfc 1305. Ntp message format ntp uses two types of messages, clock synchronization message and ntp control message. An ntp control message is used in environments where network management is needed. As it is not...
Page 1081
1-4 z poll: 8-bit signed integer indicating the poll interval, namely the maximum interval between successive messages. Z precision: an 8-bit signed integer indicating the precision of the local clock. Z root delay: roundtrip delay to the primary reference source. Z root dispersion: the maximum erro...
Page 1082
1-5 symmetric peers mode figure 1-4 symmetric peers mode a device working in the symmetric active mode periodically sends clock synchronization messages, with the mode field in the message set to 1 (symmetric active); the device that receives this message automatically enters the symmetric passive m...
Page 1083: Ntp Configuration Task List
1-6 multicast mode figure 1-6 multicast mode network client server after receiving the first multicast message, the client sends a request clock synchronization message exchange (mode 3 and mode 4) periodically multicasts clock synchronization messages (mode 5) calculates the network delay between c...
Page 1084
1-7 configuring the operation modes of ntp devices can implement clock synchronization in one of the following modes: z client/server mode z symmetric mode z broadcast mode z multicast mode for the client/server mode or symmetric mode, you need to configure only clients or symmetric-active peers; fo...
Page 1085
1-8 z in the ntp-service unicast-server command, ip-address must be a unicast address, rather than a broadcast address, a multicast address or the ip address of the local clock. Z when the source interface for ntp messages is specified by the source-interface argument, the source ip address of the n...
Page 1086
1-9 configuring ntp broadcast mode the broadcast server periodically sends ntp broadcast messages to the broadcast address 255.255.255.255. After receiving the messages, the device working in ntp broadcast client mode sends a reply and synchronizes its local clock. For devices working in the broadca...
Page 1087
1-10 configuring a multicast client to do… use the command… remarks enter system view system-view — enter interface view interface interface-type interface-number enter the interface used to receive ntp multicast messages. Configure the device to work in the ntp multicast client mode ntp-service mul...
Page 1088
1-11 following these steps to specify the source interface for ntp messages: to do… use the command… remarks enter system view system-view — specify the source interface for ntp messages ntp-service source-interface interface-type interface-number required by default, no source interface is specifie...
Page 1089
1-12 configuring access-control rights with the following command, you can configure the ntp service access-control right to the local device. There are four access-control rights, as follows: z query: control query permitted. This level of right permits the peer devices to perform control query to ...
Page 1090
1-13 configuring ntp authentication the ntp authentication feature should be enabled for a system running ntp in a network where there is a high security demand. This feature enhances the network security by means of client-server key authentication, which prohibits a client from synchronizing with ...
Page 1092: Ntp Configuration Examples
1-15 the procedure of configuring ntp authentication on a server is the same as that on a client, and the same authentication key must be configured on both the server and client sides. Displaying and maintaining ntp to do… use the command… remarks view the information of ntp service status display ...
Page 1093
1-16 reference time: 00:00:00.000 utc jan 1 1900 (00000000.00000000) # specify switch a as the ntp server of switch b so that switch b is synchronized to switch a. System-view [switchb] ntp-service unicast-server 1.0.1.11 # view the ntp status of switch b after clock synchronization. [switchb] displ...
Page 1094
1-17 figure 1-8 network diagram for ntp symmetric peers mode configuration switch a switch b switch c 3.0.1.31/24 3.0.1.32/24 3.0.1.33/24 configuration procedure 1) configuration on device b: # specify device a as the ntp server of device b. System-view [deviceb] ntp-service unicast-server 3.0.1.31 ...
Page 1095
1-18 nominal frequency: 100.0000 hz actual frequency: 100.0000 hz clock precision: 2^18 clock offset: -21.1982 ms root delay: 15.00 ms root dispersion: 775.15 ms peer dispersion: 34.29 ms reference time: 15:22:47.083 utc sep 19 2005 (c6d95647.153f7ced) as shown above, device c has been synchronized ...
Page 1096
1-19 vlan-interface 2. System-view [switchc] interface vlan-interface 2 [switchc-vlan-interface2] ntp-service broadcast-server 2) configuration on switch d: # configure switch d to work in the broadcast client mode and receive broadcast messages on vlan-interface 2. System-view [switchd] interface v...
Page 1097
1-20 network requirements z the local clock of switch c is to be used as the master clock, with a stratum level of 2. Z switch c works in the multicast server mode and sends out multicast messages from vlan-interface 2. Z switch a and switch d work in the multicast client mode and receive multicast ...
Page 1098
1-21 figure 1-10 network diagram for ntp multicast mode configuration configuration procedure 1) configuration on switch c: # configure switch c to work in the multicast server mode and send multicast messages through vlan-interface 2. System-view [switchc] interface vlan-interface 2 [switchc-vlan-i...
Page 1099
1-22 # view the ntp session information of switch d, which shows that an association has been set up between switch d and switch c. [switchd-vlan-interface2] display ntp-service sessions source reference stra reach poll now offset delay disper ********************************************************...
Page 1100
1-23 as shown above, switch a has been synchronized to switch c, and the clock stratum level of switch a is 3, while that of switch c is 2. # view the ntp session information of switch a, which shows that an association has been set up between switch a and switch c. [switcha-vlan-interface3] display...
Page 1101
1-24 [switcha] ntp-service authentication-keyid 42 authentication-mode md5 anicekey # specify the key as a trusted key. [switcha] ntp-service reliable authentication-keyid 42 # view the ntp status of switch b after clock synchronization. [switchb] display ntp-service status clock status: synchronize...
Page 1102
1-25 figure 1-12 network diagram for configuration of ntp broadcast mode with authentication configuration procedure 1) configuration on switch c: # configure ntp authentication. System-view [switchc] ntp-service authentication enable [switchc] ntp-service authentication-keyid 88 authentication-mode...
Page 1103
1-26 clock precision: 2^7 clock offset: 0.0000 ms root delay: 31.00 ms root dispersion: 8.31 ms peer dispersion: 34.30 ms reference time: 16:01:51.713 utc sep 19 2005 (c6d95f6f.B6872b02) as shown above, switch d has been synchronized to switch c, and the clock stratum level of switch d is 4, while t...
Page 1104: Table of Contents
I table of contents 1 hotfix configuration ··································································································································1-1 hotfix overview ···········································································································...
Page 1105: Hotfix Configuration
1-1 1 hotfix configuration when configuring hotfix, go to these sections for information you are interested in: z hotfix overview z hotfix configuration task list z displaying and maintaining hotfix z hotfix configuration examples hotfix overview hotfix is a fast and cost-effective method to repair ...
Page 1106
1-2 install, and uninstall represent operations, corresponding to commands of patch load, patch active, patch run, patch deactive, patch delete, patch install, and undo patch install. For example, if you execute the patch active command for the patches in the deactive state, the patches turn to the ...
Page 1107
1-3 figure 1-2 patches are not loaded to the memory patch area currently, the system patch area supports up to 200 patches. Deactive state patches in the deactive state have been loaded to the memory patch area but have not run in the system yet. Suppose that there are seven patches in the patch fil...
Page 1108
1-4 figure 1-4 patches are activated running state after you confirm the running of the active patches, the state of the patches will become running and will be in the running state after system reboot. For the five patches in figure 1-4 , if you confirm the running the first three patches, their st...
Page 1109: Configuration Prerequisites
1-5 configuration prerequisites patches are released per device model type. Before patching the system, you need to save the appropriate patch files to the storage media of the device using ftp or tftp. When saving the patch files, note that: z the patch files match the device model and software ver...
Page 1110
1-6 z the patch matches the device type and software version. Z the patch install command changes the patch file location specified with the patch location command to the directory specified by the patch-location argument of the patch install command. Step-by-step patch installation step-by-step pat...
Page 1111
1-7 set the file transfer mode to binary mode before using ftp or tftp to upload/download patch files to/from the flash of the device. Otherwise, patch file cannot be parsed properly. Follow the steps below to load a patch file: to do… use the command… remarks enter system view system-view — load th...
Page 1112
1-8 one-step patch uninstallation you can use the undo patch install command to uninstall patches from all the member devices. The patches then turn to the idle state. This equals the execution of the commands patch deactive and patch delete on each member device. Follow these steps to uninstall the...
Page 1113
1-9 displaying and maintaining hotfix to do… use the command… remarks display the patch information display patch information available in any view hotfix configuration examples hotfix configuration example (single device) network requirements z the software running on device is of some problem, and...
Page 1114
1-10 do you want to continue running patches after reboot? [y/n]:y installing patches........ Installation completed, and patches will continue to run after reboot. Hotfix configuration example (irf stack device) network requirements z irf refers to an irf stack in this example and it consists of tw...
Page 1115
1-11 [device] patch install flash: patches will be installed. Continue? [y/n]:y do you want to continue running patches after reboot? [y/n]:y installing patches........ Installation completed, and patches will continue to run after reboot..
Page 1116: Table of Contents
I table of contents 1 cluster management configuration·········································································································1-1 cluster management overview··············································································································...
Page 1117: Cluster Management Overview
1-1 1 cluster management configuration when configuring cluster management, go to these sections for information you are interested in: z cluster management overview z cluster configuration task list z configuring the management device z configuring the member devices z configuring access between th...
Page 1118
1-2 figure 1-1 network diagram for a cluster as shown in figure 1-1 , the device configured with a public ip address and performs the management function is the management device, the other managed devices are member devices, and the device that does not belong to any cluster but can be added to a c...
Page 1119
1-3 introduction to ndp ndp is used to discover the information about directly connected neighbors, including the device name, software version, and connecting port of the adjacent devices. Ndp works in the following ways: z a device running ndp periodically sends ndp packets to its neighbors. An nd...
Page 1120
1-4 then forwards the ntdp topology collection request after its prior port forwards the ntdp topology collection request. Cluster management maintenance 1) adding a candidate device to a cluster you should specify the management device before creating a cluster. The management device discovers and ...
Page 1121
1-5 member device which is in disconnect state will be added to the cluster. After that, the state of the member device locally and on the management device will be changed to active. Besides, a member device informs the management device using handshake packets when there is a neighbor topology cha...
Page 1122
1-6 complete these tasks to configure a cluster: task remarks enabling ndp globally and for specific ports optional configuring ndp parameters optional enabling ntdp globally and for specific ports optional configuring ntdp parameters optional manually collecting topology information optional enabli...
Page 1123
1-7 z disabling the ndp and ntdp functions on the management device and member devices after a cluster is created will not cause the cluster to be dismissed, but will influence the normal operation of the cluster. Z when both the cluster function and the 802.1x function (or the mac address authentic...
Page 1124
1-8 configuring ndp parameters a port enabled with ndp periodically sends ndp packets to its neighbors. If no ndp information from the neighbor is received when the holdtime times out, the corresponding entry is removed from the ndp table. Follow these steps to configure ndp parameters: to do… use t...
Page 1125
1-9 of the devices in a specified range, thus avoiding unlimited topology collection. After the interval for collecting topology information is configured, the device collects the topology information at this interval. To avoid network congestion caused by large amounts of topology responses receive...
Page 1126
1-10 enabling the cluster function to do… use the command… remarks enter system view system-view — enable the cluster function globally cluster enable optional enabled by default. Establishing a cluster before establishing a cluster, you need to specify the management vlan, and you cannot modify the...
Page 1127
1-11 enabling management vlan auto-negotiation the management vlan limits the cluster management range. If the device discovered by the management device does not belong to the management vlan, meaning the cascade ports and the ports connecting with the management device do not allow the packets fro...
Page 1128
1-12 0180-c200-000a, cluster management packets cannot traverse these devices. For a cluster to work normally in this case, you can modify the destination mac address of a cluster management protocol packet without changing the current networking. The management device periodically sends mac address...
Page 1129: Member Devices
1-13 removing a member device to do… use the command… remarks enter system view system-view — enter cluster view cluster — remove a member device from the cluster delete-member member-number [ to-black-list ] required rebooting a member device to do… use the command… remarks enter system view system...
Page 1130
1-14 the member devices through the management device. You can manage member devices in a cluster through switching from the operation interface of the management device to that of a member device or configure the management device by switching from the operation interface of a member device to that...
Page 1131
1-15 to do… use the command… remarks add a candidate device to the cluster administrator-address mac-address name name required configuring advanced cluster functions this section covers these topics: z configuring topology management z configuring interaction for a cluster z snmp configuration sync...
Page 1133
1-17 to do… use the command… remarks configure the nm interface of the management device nm-interface vlan-interface vlan-interface-id optional to isolate management protocol packets of a cluster from packets outside the cluster, you are recommended to configure to prohibit packets from the manageme...
Page 1134
1-18 z the snmp-related configurations are retained when a cluster is dismissed or the member devices are removed from the whitelist. Z for information about snmp, refer to snmp configuration in the system volume. Configuring web user accounts in batches configuring web user accounts in batches enab...
Page 1135
1-19 displaying and maintaining cluster management to do… use the command… remarks display ndp configuration information display ndp [ interface interface-list ] display the global ntdp information display ntdp display the device information collected through ntdp display ntdp device-list [ verbose ...
Page 1136
1-20 figure 1-4 network diagram for cluster management configuration configuration procedure 1) configure the member device switch a # enable ndp globally and for port gigabitethernet 1/0/1. System-view [switcha] ndp enable [switcha] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1 [switcha-gigabitethernet1/0/1] ndp...
Page 1137
1-21 [switchb-gigabitethernet1/0/3] quit # configure the period for the receiving device to keep ndp packets as 200 seconds. [switchb] ndp timer aging 200 # configure the interval to send ndp packets as 70 seconds. [switchb] ndp timer hello 70 # enable ntdp globally and for ports gigabitethernet 1/0...
Page 1138
1-22 restore topology from local flash file,for there is no base topology. (please confirm in 30 seconds, default no). (y/n) n # enable management vlan auto-negotiation. [abc_0.Switchb-cluster] management-vlan synchronization enable # configure the holdtime of the member device information as 100 se...
Page 1139: Table of Contents
I table of contents 1 irf stack configuration····························································································································1-1 irf stack overview ············································································································...
Page 1140: Irf Stack Configuration
1-1 1 irf stack configuration when configuring irf stack, go to these sections for information you are interested in: z irf stack overview z irf stack working process z irf stack configuration task list z configuring irf stack z logging in to an irf stack z displaying and maintaining irf stack z irf...
Page 1141
1-2 z for the details of the interface modules, refer to h3c s5120-ei series ethernet switches installation manual. Z among s5120-ei series switches, s5120-28c-ei, s5120-52c-ei, s5120-28c-pwr-ei, and s5120-52c-pwr-ei switches support irf stack. You can connect physical stack ports of the s5120-ei se...
Page 1142
1-3 z ring connection: given a device, its logical stack port 1 is connected to logical stack port 2 of another device, and its logical stack port 2 is connected to logical stack port 1 of a third one, as shown in figure 1-2 . Figure 1-2 physical connections of irf stack bus connection irf ring conn...
Page 1143
1-4 figure 1-3 stack port correspondence based on the type and number of the interface module inserted on switch a, you can adopt one of the following typical correspondences to establish a stack connection. Z the dual-port 10 ge cx4 interface module is used in the following examples to introduce co...
Page 1144
1-5 figure 1-5 correspondence in non-aggregate mode for two interface modules when two dual-port interface modules are installed, if the correspondence is not in the aggregate mode, you can bind a logical stack port to any physical stack port ( figure 1-5 only shows one possibility). However, you mu...
Page 1145
1-6 addition, you can only bind irf-port 1 to physical stack ports 1 and 2, and irf-port 2 to physical ports 3 and 4. If one dual-port interface module and one single-port interface module are installed, you can bind two physical stack ports on the dual-port interface module to the logical stack por...
Page 1146: Irf Stack Working Process
1-7 not only the physical stack ports of members can be aggregated, but also the physical links between the stack system and the upper or lower layer devices can be aggregated, and thus the reliability of the stack system is increased through the link backup. The stack system comprises multiple memb...
Page 1147
1-8 z stack merge: the process of connecting two existing irf stacks with stack cables. After the mergence, stack election is held, and members of the loser side reboot and join the winner side as slaves. Z stack split: in an irf stack, the failure of stack cables or power-off of a member causes phy...
Page 1148
1-9 the front panel is numbered 0, and subslots of the two expansion slots on the rear panel are numbered 1 and 2 from left to right. Z interface serial number is dependent on the number of interfaces supported by the device. View the silkscreen on the lpu for the number of supported interfaces. For...
Page 1149
1-10 configuration related to its own port, it will apply the configuration; if not, no matter what configuration has been made to the port before the slave joins the stack, the slave will function using null-configuration. File system name you can use the name of the storage device to access the fi...
Page 1150
1-11 or: cd slot3#flash:/ mkdir test %created dir slot3#flash:/test. 3) to copy the test.App file on the master to the root directory of the flash on stack member slave 3, perform the following steps: pwd slot3#flash: //the above information indicates that the current working path is the root direct...
Page 1151: Configuring Irf Stack
1-12 complete the following tasks to configure irf stack: task remarks configuring stack ports required setting a member id for a device optional specifying a priority for a stack member required specifying the preservation time of stack bridge mac address optional enabling auto upgrade of boot file...
Page 1152
1-13 z the above configuration takes effect after the reboot of the device. Z a logical stack port that is bound with multiple physical stack ports is an aggregation stack port, which increases the bandwidth and reliability on the stack port. If you specify multiple physical stack ports with the por...
Page 1153
1-14 z the above setting takes effect after the reboot of the device. Z you can use the display irf configuration command to view the current member id of the device and the member id will be used after the device reboot. Z in an irf stack, member ids are not only used to identify devices, but also ...
Page 1154
1-15 address, which is called the stack bridge mac address. Typically, a stack uses the bridge mac address of the master device as the stack bridge mac address. You are recommended to configure the preservation time of stack bridge mac address properly, otherwise, network problems will occur: z if a...
Page 1155
1-16 from the master automatically, reboots with the new boot file, and joins the stack again. If the downloaded boot file and the local file have duplicate file names, the local file is overwritten. Follow these steps to enable auto upgrade of boot files in an irf stack: to do… use the command… rem...
Page 1156: Logging In to An Irf Stack
1-17 logging in to an irf stack logging in to the master after an irf stack is formed, you can access the console of the stack system through the aux or console port of any member device. Configure an ip address for the vlan interface of a member device and make sure that the route is reachable, and...
Page 1157
1-18 displaying and maintaining irf stack to do… use the command… remarks display related information of the stack display irf available in any view display topology information of the stack display irf topology available in any view display the pre-configurations of all members of the stack (the pr...
Page 1158
1-19 [switch2] irf member 1 irf-port 2 port 3 # configure switch 3. System-view [switch3] irf member 1 renumber 3 warning: renumbering the switch number may result in configuration change or loss. Continue?[y/n]:y [switch3] irf member 1 irf-port 2 port 3 2) power off the three devices. Connect them ...
Page 1159: Table of Contents
I table of contents 1 automatic configuration ··························································································································1-1 introduction to automatic configuration·························································································...
Page 1160: Automatic Configuration
1-1 1 automatic configuration when configuring automatic configuration, go to these sections for information you are interested in: z introduction to automatic configuration z typical networking of automatic configuration z how automatic configuration works introduction to automatic configuration au...
Page 1161
1-2 name of the tftp server from a dhcp response, the device can also resolve the domain name of the tftp server to the ip address of the tftp server through the dns server. If the dhcp server, tftp server, dns server, and the device that performs automatic configuration are not in the same segment,...
Page 1162
1-3 figure 1-2 work flow of automatic configuration start the device without loading the configuration file the interface obtains parameters through dhcp is the tftp server address contained in the parameters? Yes no yes no unicast a tftp request to obtain the configuration file yes yes broadcast a ...
Page 1163
1-4 z the configuration file name is saved in the option 67 or file field of the dhcp response. The device first resolves the option 67 field; if this field contains the configuration file name, the device does not resolve the file field; otherwise, it resolves the file field. Z temporary configurat...
Page 1164
1-5 you need to configure a client id (when a device works as the dhcp client, it uses the client id as its id) of the static binding when you configure manual address allocation. Therefore, you need to obtain the client id in this way: start the device that performs automatic configuration, enable ...
Page 1165
1-6 obtaining the configuration file figure 1-3 obtain the configuration file is the configuration file contained in the dhcp response? Obtain the network intermediate file search the domain name corresponding to the ip address in the network intermediate file yes obtain the specified configuration ...
Page 1166
1-7 z if the ip address and the domain name of the tftp server are not contained in the dhcp response or they are illegitimate, the device broadcasts a tftp request to the tftp server. Z when broadcasting a tftp request, the device obtains the configuration file from the tftp server who responds the...