- DL manuals
- H3C
- Switch
- S5120-EI Series
- Configuration Manual
H3C S5120-EI Series Configuration Manual
Summary of S5120-EI Series
Page 1
H3c s5120-ei switch series acl and qos configuration guide hangzhou h3c technologies co., ltd. Http://www.H3c.Com software version: release 2220 document version: 6w100-20130810
Page 2
Copyright © 2013, hangzhou h3c technologies co., ltd. And its licensors all rights reserved no part of this manual may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means without prior written consent of hangzhou h3c technologies co., ltd. Trademarks h3c, , h3cs, h3cie, h3cne, aolynk, , h 3 car...
Page 3
Preface the h3c s5120-ei documentation set includes 10 configuration guides, which describe the software features for the h3c s5120-ei switch series release 2220, and guide you through the software configuration procedures. These configuration guides also provide configuration examples to help you a...
Page 5
Represents a generic switch, such as a layer 2 or layer 3 switch, or a router that supports layer 2 forwarding and other layer 2 features. Port numbering in examples the port numbers in this document are for illustration only and might be unavailable on your device. About the s5120-ei documentation ...
Page 6
Obtaining documentation you can access the most up-to-date h3c product documentation on the world wide web at http://www.H3c.Com . Click the links on the top navigation bar to obtain different categories of product documentation: [technical support & documents > technical documents] – provides hardw...
Page 7
I contents configuring acls ························································································································································· 1 overview ···········································································································...
Page 8
Ii configuration procedure ······································································································································ 20 defining a traffic behavior ···········································································································...
Page 9
Iii configuration procedure ······································································································································ 47 configuration example ················································································································...
Page 10
Iv appendix b packet precedences ······························································································································ 71 ip precedence and dscp values ···········································································································...
Page 11
1 configuring acls unless otherwise stated, acls refer to both ipv4 and ipv6 acls throughout this document. Overview an access control list (acl) is a set of rules (or permit or deny statements) for identifying traffic based on criteria such as source ip address, destination ip address, and port num...
Page 12
2 basic or advanced acl, its acl number and name must be unique among all ipv6 acls. You can assign an ipv4 acl and an ipv6 acl the same number and name. Match order the rules in an acl are sorted in a specific order. When a packet matches a rule, the device stops the match process and performs the ...
Page 13
3 you can also add a rule range remark to indicate the start or end of a range of rules created for the same purpose. A rule range remark always appears above the specified acl rule. If the specified rule has not been created yet, the position of the comment in the acl is as follows: • if the match ...
Page 14
4 task remarks configuring a basic acl required configure at least one task. Applicable to ipv4 and ipv6 except that simple acls are for ipv6. Configuring an advanced acl configuring an ethernet frame header acl copying an acl optional applicable to ipv4 and ipv6. Configuring packet filtering with a...
Page 21
11 step command remarks 5. Set the interval for generating and outputting ipv4 packet filtering logs. Acl logging frequence frequence by default, the interval is 0. No ipv4 packet filtering logs are generated. Applying an ipv6 acl for packet filtering step command remarks 1. Enter system view. Syste...
Page 22
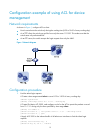
12 configuration example of using acl for device management network requirements as shown in figure 1 , configure acls so that: • host a can telnet to the switch only during the working time (8:30 to 18:00 of every working day). • as a tftp client, the switch can get files from only the server 11.1....
Page 23
13 2. Limit the access to the tftp server: # create ipv4 basic acl 2001, and configure a rule for the acl to permit only the packets sourced from 11.1.1.100. [switch] acl number 2001 [switch-acl-basic-2001] rule permit source 11.1.1.100 0 [switch-acl-basic-2001] quit # use acl 2001 to control the sw...
Page 24
14 [devicea-acl-basic-2009] rule permit source 192.168.1.2 0 time-range study logging [devicea-acl-basic-2009] rule deny source any time-range study [devicea-acl-basic-2009] quit # enable the device to generate and output ipv4 packet filtering logs at 10-minute intervals. [devicea] acl logging frequ...
Page 25
15 [devicea] info-center source default channel 0 log level informational # apply ipv6 acl 2009 to filter incoming packets on gigabitethernet 1/0/1. [devicea] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1 [devicea-gigabitethernet1/0/1] packet-filter ipv6 2009 inbound [devicea-gigabitethernet1/0/1] quit.
Page 26
16 qos overview in data communications, quality of service (qos) is a network’s ability to provide differentiated service guarantees for diversified traffic in terms of bandwidth, delay, jitter, and drop rate. Network resources are scarce. The contention for resources requires that qos prioritize im...
Page 27
17 qos techniques the qos techniques include traffic classification, traffic policing, traffic shaping, rate limit, congestion management, and congestion avoidance. They address problems that arise at different positions of a network. Figure 4 placement of the qos techniques in a network as shown in...
Page 28
18 qos configuration approaches you can configure qos in these approaches: • mqc approach • non-mqc approach some features support both approaches, but some support only one. Mqc approach in modular qos configuration (mqc) approach, you configure qos service parameters by using qos policies (see " c...
Page 29
19 configuring a qos policy overview a qos policy is a set of class-behavior associations and defines the shaping, policing, or other qos actions to take on different classes of traffic. A class is a set of match criteria for identifying traffic and it uses the and or or operator: • and—a packet mus...
Page 30
20 configuration restrictions and guidelines • if a class that uses the and operator has multiple if-match acl, if-match acl ipv6, if-match customer-vlan-id or if-match service-vlan-id clauses, a packet that matches any of the clauses matches the class. • to successfully execute the traffic behavior...
Page 31
21 option description dscp dscp-list matches dscp values. The dscp-list argument is a list of up to eight dscp values. A dscp value can be a number from 0 to 63 or any keyword in table 10 . Destination-mac mac-address matches a destination mac address. Customer-dot1p 8021p-list matches the 802.1p pr...
Page 32
22 defining a policy you associate a behavior with a class in a qos policy to perform the actions defined in the behavior for the class of packets. Configuration restrictions and guidelines • if an acl is referenced by a qos policy for defining traffic match criteria, packets matching the acl are or...
Page 33
23 applying the qos policy to an interface a policy can be applied to multiple interfaces, but only one policy can be applied in inbound direction of an interface. To apply the qos policy to an interface: step command remarks 1. Enter system view. System-view n/a 2. Enter interface view or port grou...
Page 34
24 applying the qos policy to a vlan you can apply a qos policy to a vlan to regulate traffic of the vlan. Qos policies cannot be applied to dynamic vlans, such as vlans created by gvrp. To apply the qos policy to a vlan: step command remarks 1. Enter system view. System-view n/a 2. Apply the qos po...
Page 35
25 • in a qos policy for control planes, if a system index classifier is configured, the associated traffic behavior can contain only the car action or the combination of car and accounting packet actions. In addition, if the car action is configured, only its cir setting can be applied. • in the qo...
Page 36
26 clear the statistics for the qos policy applied to a control plane. Reset qos policy control-plane slot slot-number [ inbound ] available in user view.
Page 37
27 configuring priority mapping overview when a packet enters a device, depending on your configuration, the device assigns a set of qos priority parameters to the packet based on either a certain priority field carried in the packet or the port priority of the incoming port. This process is called ...
Page 38
28 priority trust mode on a port the priority trust mode on a port decides which priority is used for priority mapping table lookup. Port priority was introduced to use for priority mapping in addition to priority fields carried in packets. The switch series provides the following priority trust mod...
Page 39
29 table 5 priority mapping results of not trusting packet priority (when the default dot1p-lp priority mapping table is used) port priority local precedence queue id 0 (default) 2 2 1 0 0 2 1 1 3 3 3 4 4 4 5 5 5 6 6 6 7 7 7 the priority mapping procedure varies with the priority modes. For more inf...
Page 40
30 figure 6 priority mapping procedure for an ethernet packet note: if 802.1p priority marking is performed for packets, the device performs priority mapping for the packets based on the marked 802.1p priority values according to the flow shown in figure 6 . The dscp marking action does not affect p...
Page 42
32 step command remarks 2. Enter interface view or port group view. • enter interface view: interface interface-type interface-number • enter port group view: port-group manual port-group-name use either command. Settings in interface view take effect on the current interface. Settings in port group...
Page 43
33 configuration procedure # assign port priority to gigabitethernet 1/0/1 and gigabitethernet 1/0/2. Make sure that the priority of gigabitethernet 1/0/1 is higher than that of gigabitethernet 1/0/2, and no trusted packet priority type is configured on gigabitethernet 1/0/1 or gigabitethernet 1/0/2...
Page 44
34 figure 8 network diagram configuration procedure 1. Configure trusting port priority: # set the port priority of gigabitethernet 1/0/1 to 3. System-view [device] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1 [device-gigabitethernet1/0/1] qos priority 3 [device-gigabitethernet1/0/1] quit # set the port priority...
Page 45
35 [device-maptbl-dot1p-lp] import 5 export 4 [device-maptbl-dot1p-lp] quit 3. Configure priority marking: # mark the http traffic of the management department, marketing department, and r&d department to the internet with 802.1p priorities 4, 5, and 3, respectively. Use the priority mapping table y...
Page 46
36 configuring traffic policing, traffic shaping, and rate limit overview traffic policing, traffic shaping, and rate limit are qos technologies that help assign network resources, such as assign bandwidth. They increase network performance and user satisfaction. For example, you can configure a flo...
Page 47
37 • peak information rate (pir)—rate at which tokens are put into bucket e, which specifies the average packet transmission or forwarding rate allowed by bucket e. • excess burst size (ebs)—size of bucket e, which specifies the transient burst of traffic that bucket e can forward. Cbs is implemente...
Page 48
38 traffic shaping important: traffic shaping shapes the outbound traffic. Traffic shaping limits the outbound traffic rate by buffering exceeding traffic. You can use traffic shaping to adapt the traffic output rate on a device to the input traffic rate of its connected device to avoid packet loss....
Page 49
39 the rate limit of a physical interface specifies the maximum rate for forwarding packets (including critical packets). Rate limit also uses token buckets for traffic control. With rate limit configured on an interface, all packets to be sent through the interface are handled by the token bucket a...
Page 50
40 step command remarks 4. Return to system view. Quit n/a 5. Create a behavior and enter behavior view. Traffic behavior behavior-name n/a 6. Configure a traffic policing action. Car cir committed-information-rate [ cbs committed-burst-size [ ebs excess-burst-size ] ] [ pir peak-information-rate ] ...
Page 51
41 to configure the rate limit: step command remarks 1. Enter system view. System-view n/a 2. Enter interface view or port group view. • enter interface view: interface interface-type interface-number • enter port group view: port-group manual port-group-name use either command. Settings in interfac...
Page 52
42 figure 13 network diagram configuration procedures 1. Configure device a: # configure acl 2001 and acl 2002 to match traffic from server and host a, respectively. System-view [devicea] acl number 2001 [devicea-acl-basic-2001] rule permit source 1.1.1.1 0 [devicea-acl-basic-2001] quit [devicea] ac...
Page 53
43 [devicea-qospolicy-car] quit # apply qos policy car to the incoming traffic of port gigabitethernet 1/0/1. [devicea] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1 [devicea-gigabitethernet1/0/1] qos apply policy car inbound 2. Configure device b: # configure advanced acl 3001 to match http traffic. System-view ...
Page 54
44 configuring congestion management overview network congestion degrades service quality on a traditional network. Congestion is a situation where the forwarding rate decreases due to insufficient resources, resulting in extra delay. Congestion is more likely to occur in complex packet switching ci...
Page 55
45 figure 15 sp queuing in figure 15 , sp queuing classifies eight queues on a port into eight classes, numbered 7 to 0 in descending priority order. In figure 15 , sp queuing classifies four queues on a port into four classes, numbered 3 to 0 in descending priority order. Sp queuing schedules the e...
Page 56
46 figure 16 wrr queuing assume a port provides eight output queues. Wrr assigns each queue a weight value (represented by w7, w6, w5, w4, w3, w2, w1, or w0) to decide the proportion of resources assigned to the queue. On a 1000 mbps port, you can configure the weight values of wrr queuing to 5, 5, ...
Page 57
47 • by setting the minimum guaranteed bandwidth, you can make sure that each wfq queue is assured of certain bandwidth. • the assignable bandwidth is allocated based on the weight of each queue (assignable bandwidth = total bandwidth – the sum of minimum guaranteed bandwidth of each queue). For exa...
Page 59
49 configuration example network requirements • enable byte-count wrr on port gigabitethernet 1/0/1. • assign queues 0 through 7 to the wrr group, with their weights being 1, 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, and 14, respectively. Configuration procedure # enter system view. System-view # configure wrr queuing on...
Page 61
51 step command remarks 2. Enter interface view or port group view. • enter interface view: interface interface-type interface-number • enter port group view: port-group manual port-group-name use either command. Settings in interface view take effect on the current interface. Settings in port group...
Page 62
52 configuring sp+wfq queuing configuration procedure to configure sp + wfq queuing: step command remarks 1. Enter system view. System-view n/a 2. Enter interface view or port group view. • enter interface view: interface interface-type interface-number • enter port group view: port-group manual por...
Page 63
53 [sysname] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1 [sysname-gigabitethernet1/0/1] qos wfq weight [sysname-gigabitethernet1/0/1] qos wfq 0 group sp [sysname-gigabitethernet1/0/1] qos wfq 1 group sp [sysname-gigabitethernet1/0/1] qos wfq 2 group sp [sysname-gigabitethernet1/0/1] qos wfq 3 group sp [sysname-...
Page 64
54 configuring traffic filtering traffic filtering filters traffic matching certain criteria. For example, you can filter packets sourced from a specific ip address according to network status. Configuration procedure to configure traffic filtering: step command remarks 1. Enter system view. System-...
Page 65
55 traffic filtering configuration example network requirements as shown in figure 18 , host is connected to gigabitethernet 1/0/1 of device. Configure traffic filtering to filter the packets with source port being 21, and received on gigabitethernet 1/0/1. Figure 18 network diagram configuration pr...
Page 66
56 configuring priority marking priority marking sets the priority fields or flag bits of packets to modify the priority of traffic. For example, you can use priority marking to set ip precedence or dscp for a class of ip traffic to change its transmission priority in the network. Priority marking c...
Page 67
57 important: do not use the remark command together with the car command in a traffic behavior to perform color-based marking. Configuration procedure to configure priority marking: step command remarks 1. Enter system view. System-view n/a 2. Create a class and enter class view. Traffic classifier...
Page 68
58 local precedence re-marking configuration example network requirements as shown in figure 19 , the company’s enterprise network interconnects hosts with servers through device. The network is described as follows: • host a and host b are connected to gigabitethernet 1/0/1 of device. • the data se...
Page 69
59 # create advanced acl 3002, and configure a rule to match packets with destination ip address 192.168.0.3. [device] acl number 3002 [device-acl-adv-3002] rule permit ip destination 192.168.0.3 0 [device-acl-adv-3002] quit # create a class named classifier_dbserver, and use acl 3000 as the match c...
Page 70
60 configuring traffic redirecting traffic redirecting is the action of redirecting the packets matching the specific match criteria to a certain location for processing. The following redirect actions are supported: • redirecting traffic to the cpu—redirects packets that require processing by the c...
Page 71
61 step command remarks 11. Apply the qos policy. • applying the qos policy to an interface • applying the qos policy to a vlan • applying the qos policy globally • applying the qos policy to the control plane choose one application destination as needed..
Page 72
62 configuring class-based accounting class-based accounting collects statistics (in packets) on a per-traffic class basis. For example, you can define the action to collect statistics for traffic sourced from a certain ip address. By analyzing the statistics, you can determine whether anomalies hav...
Page 73
63 class-based accounting configuration example network requirements as shown in figure 20 , host is connected to gigabitethernet 1/0/1 of device a. Configure class-based accounting to collect statistics for traffic sourced from 1.1.1.1/24 and received on gigabitethernet 1/0/1. Figure 20 network dia...
Page 74
64 operator: and rule(s) : if-match acl 2000 behavior: behavior_1 accounting enable: 28529 (packets).
Page 75
65 configuring the data buffer overview data buffer the switch series provides the data buffer to buffer packets to be sent out ports to avoid packet loss when bursty traffic causes congestion. The switch controls how a port uses the data buffer by allocating the cell resource and packet resource (c...
Page 76
66 • on a per-port basis—as illustrated by the vertical lines in figure 21 , the switch automatically divides the dedicated resource among all ports evenly. • on a per-queue basis—as illustrated by the horizontal lines in figure 21 , the dedicated resource of each port is proportionately allocated a...
Page 77
67 using the burst function to configure the data buffer setup the burst function allows the switch to automatically determine the shared resource size, the minimum guaranteed resource size for each queue, the maximum shared resource size for each queue, and the maximum shared resource size per port...
Page 78
68 step command remarks 2. Configure the shared resource area of the cell resource in percentage. Buffer egress [ slot slot-number ] cell total-shared ratio ratio optional. By default, the shared resource area of the cell resource is 60%. Configuring the minimum guaranteed resource size for a queue ...
Page 79
69 allocate the remaining dedicated resource space among all queues that are not manually assigned a minimum guaranteed resource space. For example, if you set the minimum guaranteed resource size to 30% for a queue, the remaining seven queues will each share 10% of the dedicated resource of the por...
Page 80
70 appendix a default priority mapping tables priority mapping tables for the default dscp-dscp mapping table, an input value yields a target value equal to it. Table 7 default dot1p-lp and dot1p-dp priority mapping tables input priority value dot1p-lp mapping dot1p-dp mapping 802.1p priority (dot1p...
Page 81
71 appendix b packet precedences ip precedence and dscp values figure 23 tos and ds fields as shown in figure 23 , the tos field in the ipv4 header contains eight bits, where the first three bits (0 to 2) represent ip precedence from 0 to 7; the traffic classes field in the ipv6 header contains eigh...
Page 82
72 dscp value (decimal) dscp value (binary) description 20 010100 af22 22 010110 af23 26 011010 af31 28 011100 af32 30 011110 af33 34 100010 af41 36 100100 af42 38 100110 af43 8 001000 cs1 16 010000 cs2 24 011000 cs3 32 100000 cs4 40 101000 cs5 48 110000 cs6 56 111000 cs7 0 000000 be (default) 802.1...
Page 83
73 figure 25 802.1q tag header table 11 description on 802.1p priority 802.1p priority (decimal) 802.1p priority (binary) description 0 000 best-effort 1 001 background 2 010 spare 3 011 excellent-effort 4 100 controlled-load 5 101 video 6 110 voice 7 111 network-management.
Page 84
74 index a c d i l m n o p q t u a acl configuration task list, 3 applying the qos policy, 22 c changing the port priority of an interface, 31 class-based accounting configuration example, 63 color-based priority marking, 56 configuration example of using acl for device management, 12 configuration ...
Page 85
75 qos techniques, 17 t traffic filtering configuration example, 55 traffic policing configuration example, 41 u using the burst function to configure the data buffer setup, 67.