- DL manuals
- H3C
- Switch
- S5120-EI Series
- Configuration Manual
H3C S5120-EI Series Configuration Manual
Summary of S5120-EI Series
Page 1
H3c s5120-ei switch series layer 2 - lan switching configuration guide hangzhou h3c technologies co., ltd. Http://www.H3c.Com software version: release 2210 document version: 6w100-20110915.
Page 2
Copyright © 2011, hangzhou h3c technologies co., ltd. And its licensors all rights reserved no part of this manual may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means without prior written consent of hangzhou h3c technologies co., ltd. Trademarks h3c, , aolynk, , h 3 care, , top g, , irf, n...
Page 3
Preface the h3c s5120-ei documentation set includes 10 configuration guides, which describe the software features for the h3c s5120-ei switch series release 2210, and guide you through the software configuration procedures. These configuration guides also provide configuration examples to help you a...
Page 4
Feature module new features changed features ethernet link aggregation • restoring the default setting of an aggregate interface • limiting the number of selected ports in an aggregation group • assigning aggregation priority to ports in a static aggregation group n/a port isolation n/a n/a spanning...
Page 6
About the s5120-ei documentation set the h3c s5120-ei documentation set includes: documents purposes product description and specifications marketing brochure describe product specifications and benefits. Technology white papers provide an in-depth description of software features and technologies. ...
Page 7
[technical support & documents > software download] – provides the documentation released with the software version. Technical support customer_service@h3c.Com http://www.H3c.Com documentation feedback you can e-mail your comments about product documentation to info@h3c.Com. We appreciate your comme...
Page 8
I contents ethernet interface configuration ·································································································································· 1 ethernet interface naming conventions ·····················································································...
Page 9
Ii mac information configuration ································································································································28 overview································································································································...
Page 10
Iii implementation of mstp on devices···················································································································· 66 protocols and standards ·······················································································································...
Page 11
Iv assigning an access port to a vlan ················································································································114 assigning a trunk port to a vlan··················································································································...
Page 12
V qinq configuration················································································································································· 163 introduction to qinq··············································································································...
Page 13
1 ethernet interface configuration ethernet interface naming conventions the ge and 10-ge interfaces on the s5120-ei switches are named in the format of interface-type a/b/c, where the following definitions apply: • a represents the id of the switch in an irf fabric. If the switch is not assigned to...
Page 14
2 to do… use the command… remarks activate the current interface undo shutdown optional by default, of the two ports that compose a combo interface, the one with a smaller port id is active. Configuring basic settings of an ethernet interface you can set an ethernet interface to operate in one of th...
Page 15
3 note: make sure that the fiber port speed matches the speed requirement of the inserted transceiver module. For example, after you insert a 1000-mbps transceiver module into a fiber port, configure the port speed with the speed 1000 or speed auto command. Shutting down an ethernet interface you mi...
Page 16
4 figure 1 speed auto negotiation application scenario ip network server 1 server 2 server 3 switch a ge1/0/1 ge1/0/2 ge1/0/3 ge1/0/4 as shown in figure 1 , all ports on switch a are operating in speed auto negotiation mode, with the highest speed of 1000 mbps. If the transmission rate of each serve...
Page 17
5 to handle unidirectional traffic congestion on a link, configure the flow-control receive enable command at one end, and the flow-control command at the other. To enable both ends of the link to handle traffic congestion, configure the flow-control command at both ends. Follow these steps to enabl...
Page 18
6 to do… use the command… remarks set a link-down event suppression interval link-delay delay-time required link-down event suppression is disabled by default. Configuring link-up event suppression follow these steps to configure link-up event suppression on an ethernet interface: to do… use the com...
Page 19
7 note: • on an interface that is physically down, you can only perform internal loopback testing. On an interface administratively shut down, you can perform neither internal nor external loopback testing. • the speed, duplex, mdi, and shutdown commands are not available during loopback testing. • ...
Page 20
8 to do… use the command… remarks enter system view system-view — create a manual port group and enter manual port group view port-group manual port-group-name required assign ethernet interfaces to the manual port group group-member interface-list required if you use the group-member interface-type...
Page 21
9 configuring storm suppression you can use the storm suppression function to limit the size of a particular type of traffic (broadcast, multicast, or unknown unicast traffic) as a whole globally in system view or on a per-interface basis in ethernet interface view or port group view. Note: the stor...
Page 22
10 to do… use the command… remarks enter ethernet interface view interface interface-type interface-number — set the statistics polling interval on the ethernet interface flow-interval interval optional the default interface statistics polling interval is 300 seconds. To display the interface statis...
Page 23
11 when a loop is detected, for example, to shut down the interface. Depending on whether a protective action is configured, the switch takes the actions in table 1 to alleviate the impact of the loop condition. Table 1 actions to take upon detection of a loop condition actions port type no protecti...
Page 25
13 • when a straight-through cable is used, set the interface to work in the mdi mode different than its peer. • when a crossover cable is used, set the interface to work in the same mdi mode as its peer, or set either end to work in auto mode. Follow these steps to set the mdi mode of an ethernet i...
Page 26
14 to do… use the command… remarks enter system view system-view — enter ethernet interface view interface interface-type interface-number — test the cable connected to the ethernet interface virtual-cable-test required configuring storm control on an ethernet interface storm control compares broadc...
Page 27
15 to do… use the command… remarks enable the interface to send storm control threshold event traps. Storm-constrain enable trap optional by default, the interface sends traps when monitored traffic exceeds the upper threshold or drops below the lower threshold from the upper threshold. Enable the i...
Page 29
17 loopback and null interface configuration configuring a loopback interface introduction to the loopback interface a loopback interface is a software-only virtual interface. It delivers the following benefits. • the physical layer state and link-layer protocols of a loopback interface are always u...
Page 30
18 note: you can configure settings such as ip addresses and ip routes on loopback interfaces. For more information, see layer 3—ip services configuration guide and layer 3—ip routing configuration guide . Configuring the null interface introduction to the null interface a null interface is a comple...
Page 32
20 mac address table configuration overview an ethernet device uses a mac address table for forwarding frames through unicast instead of broadcast. This table describes from which port a mac address (or host) can be reached. When forwarding a frame, the device first looks up the mac address of the f...
Page 33
21 • blackhole entries, which are manually configured and never age out. Blackhole entries are configured for filtering out frames with specific source or destination mac addresses. For example, to block all packets destined for a specific user for security concerns, you can configure the mac addres...
Page 35
23 to do… use the command… remarks enable global mac address learning undo mac-address mac-learning disable optional enabled by default. Enter interface view or port group view • enter layer 2 ethernet interface view or layer 2 aggregate interface view: interface interface-type interface-number • en...
Page 36
24 follow these steps to configure the mac learning limit on a layer 2 ethernet interface or all ports in a port group: to do… use the command… remarks enter system view system-view — enter interface view or port group view enter layer 2 ethernet interface view: interface interface-type interface-nu...
Page 37
25 figure 4 mac address tables of devices when client a associates with ap c irf device a device b client a ap d ap c port a1 port b1 mac address port mac a a1 mac address port mac a a1 if client a roams to ap d, device b learns the mac address of client a and advertises it to device a to ensure ser...
Page 39
27 # add a blackhole mac address entry. [sysname] mac-address blackhole 000f-e235-abcd vlan 1 # set the aging timer for dynamic mac address entries to 500 seconds. [sysname] mac-address timer aging 500 # display the mac address entry for port gigabitethernet 1/0/1. [sysname] display mac-address inte...
Page 40
28 mac information configuration overview introduction to mac information to monitor a network, you must monitor users who are joining and leaving the network. Because a mac address uniquely identifies a network user, you can monitor users who are joining and leaving a network by monitoring their ma...
Page 42
30 mac information configuration example network requirements as shown in figure 7 : • host a is connected to a remote server (server) through device. • enable mac information on gigabitethernet 1/0/1 on device. Device sends mac address changes in syslog messages to host b through gigabitethernet 1/...
Page 43
31 ethernet link aggregation configuration overview ethernet link aggregation, or simply link aggregation, combines multiple physical ethernet ports into one logical link, called an “aggregate link”. Link aggregation delivers the following benefits: • increases bandwidth beyond the limits of any sin...
Page 44
32 configuration classes every configuration setting on a port might affect its aggregation state. Port configurations fall into the following classes: • port attribute configurations, including port rate, duplex mode, and link status (up/down). These are the most basic port configurations. • class-...
Page 45
33 the ieee 802.3ad lacp offers basic lacp functions and extended lacp functions, as described in table 3 . Table 3 basic and extended lacp functions category description basic lacp functions implemented through the basic lacpdu fields, including the system lacp priority, system mac address, port ag...
Page 46
34 table 5 a comparison between static and dynamic aggregation modes aggregation mode lacp status on member ports pros cons static disabled aggregation is stable. Peers do not affect the aggregation state of the member ports. The member ports do not adjust the aggregation state according to that of ...
Page 47
35 figure 9 setting the aggregation state of a member port in a static aggregation group note: • to ensure stable aggregation state and service continuity, do not change port attributes or class-two configurations on any member port. • if a static aggregation group has reached the limit on selected ...
Page 48
36 2. The system with the smaller system id selects the port with the smallest port id as the reference port. A port id comprises a port aggregation priority and a port number. The port with the lower aggregation priority value wins. If two ports have the same aggregation priority, the system compar...
Page 49
37 note: • a dynamic link aggregation group preferably sets full-duplex ports as the selected ports, and will set one, and only one, half-duplex port as a selected port when none of the full-duplex ports can be selected or only half-duplex ports exist in the group. • to ensure stable aggregation sta...
Page 50
38 configuring an aggregation group configuration guidelines you cannot assign a port to an aggregation group if any of the features listed in table 6 is configured on the port. Table 6 features incompatible with aggregation groups feature reference rrpp rrppin high availability configuration guide ...
Page 51
39 to do... Use the command... Remarks enter ethernet interface view interface interface-type interface-number assign the ethernet interface to the aggregation group port link-aggregation group number required repeat these two steps to assign more ethernet interfaces to the aggregation group. Assign...
Page 52
40 to do... Use the command... Remarks assign the port an aggregation priority link-aggregation port-priority port-priority optional by default, the aggregation priority of a port is 32768. Changing the aggregation priority of a port might affect the aggregation state of the ports in the dynamic agg...
Page 54
42 • when an aggregate interface is shut down, all selected ports in the corresponding aggregation group become unselected and their link state becomes down. • when an aggregate interface is brought up, the aggregation state of ports in the corresponding aggregation group is recalculated and their l...
Page 56
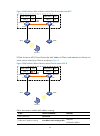
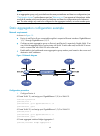
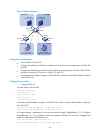
44 when you aggregate ports on different member switches in an irf fabric, you can use local-first load sharing to reduce traffic on irf links, as shown in figure 11 . For more information about irf, see irf configuration guide. Figure 11 local-first link-aggregation load sharing follow these steps ...
Page 57
45 caution: • link-aggregation traffic redirection applies only to dynamic link aggregation groups and only to known unicast packets. • to prevent traffic interruption, enable link-aggregation traffic redirection on devices at both ends of the aggregate link. • to prevent packet loss that might occu...
Page 58
46 note: in an aggregation group, only ports that have the same port attributes and class-two configurations (see “ configuration classes ”) as the reference port (see “ reference port ”) can operate as selected ports. Make sure that all member ports have the same port attributes and class-two confi...
Page 59
47 [devicea-bridge-aggregation1] quit # assign ports gigabitethernet 1/0/1 through gigabitethernet 1/0/3 to link aggregation group 1. [devicea] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1 [devicea-gigabitethernet1/0/1] port link-aggregation group 1 [devicea-gigabitethernet1/0/1] quit [devicea] interface gigabit...
Page 60
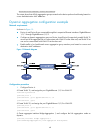
48 destination-mac address, source-mac address the output shows that all link aggregation groups created on the device perform load sharing based on source and destination mac addresses. Dynamic aggregation configuration example network requirements as shown in figure 13 : • device a and device b ar...
Page 61
49 # assign ports gigabitethernet 1/0/1 through gigabitethernet 1/0/3 to link aggregation group 1 one at a time. [devicea] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1 [devicea-gigabitethernet1/0/1] port link-aggregation group 1 [devicea-gigabitethernet1/0/1] quit [devicea] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/2 [devic...
Page 62
50 destination-mac address, source-mac address the output shows that all link aggregation groups created on the device perform load sharing based on source and destination mac addresses..
Page 63
51 port isolation configuration introduction to port isolation port isolation enables isolating layer 2 traffic for data privacy and security without using vlans. You can also use this feature to isolate the hosts in a vlan from one another. To use the feature, you assign ports to a port isolation g...
Page 64
52 port isolation configuration example network requirements as shown in figure 14 , host a, host b, and host c are connected to gigabitethernet 1/0/1, gigabitethernet 1/0/2, and gigabitethernet 1/0/3 of device, and device is connected to the internet through gigabitethernet 1/0/4. All these ports a...
Page 65
53 spanning tree configuration as a layer 2 management protocol, the spanning tree protocol (stp) eliminates layer 2 loops by selectively blocking redundant links in a network, putting them in a standby state, which still also allows for link redundancy. The recent versions of stp include the rapid ...
Page 66
54 basic concepts in stp root bridge a tree network must have a root bridge. The entire network contains only one root bridge. The root bridge is not permanent, but can change with changes of the network topology. Upon initialization of a network, each device generates and periodically sends configu...
Page 67
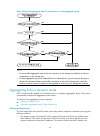
55 calculation process of the stp algorithm note: the spanning tree calculation process described in the following sections is a simplified process for example only. The stp algorithm uses the following calculation process: 1. Initial state upon initialization of a device, each port generates a bpdu...
Page 68
56 table 9 selection of the optimum configuration bpdu step actions 1 upon receiving a configuration bpdu on a port, the device compares the priority of the received configuration bpdu with that of the configuration bpdu generated by the port, and: • if the former priority is lower, the device disca...
Page 69
57 table 10 initial state of each device device port name configuration bpdu on the port port a1 {0, 0, 0, port a1} device a port a2 {0, 0, 0, port a2} port b1 {1, 0, 1, port b1} device b port b2 {1, 0, 1, port b2} port c1 {2, 0, 2, port c1} device c port c2 {2, 0, 2, port c2} note: in table 10 , ea...
Page 70
58 device comparison process configuration bpdu on ports after comparison • port b1 receives the configuration bpdu of port a1 {0, 0, 0, port a1}, finds that the received configuration bpdu is superior to its existing configuration bpdu {1, 0, 1, port b1}, and updates its configuration bpdu. • port ...
Page 71
59 device comparison process configuration bpdu on ports after comparison • device c finds that the root path cost of port c1 (10) (root path cost of the received configuration bpdu (0) plus path cost of port c1 (10)) is larger than that of port c2 (9) (root path cost of the received configuration b...
Page 72
60 • if the configuration bpdu received on a designated port has a lower priority than the configuration bpdu of the local port, the port immediately sends its own configuration bpdu in response. • if a path becomes faulty, the root port on this path no longer receives new configuration bpdus and th...
Page 73
61 pvst pvst was introduced to improve link bandwidth usage in network environments where multiple virtual lans (vlans) exist. Unlike stp and rstp whose bridges in a lan must forward their vlan packets in the same spanning tree, pvst allows each vlan to build a separate spanning tree. Pvst uses the ...
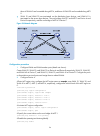
Page 74
62 figure 18 basic concepts in mstp mst region 1 mst region 2 mst region 3 mst region 4 vlan 1 msti 1 vlan 2 msti 2 other vlans msti 0 vlan 1 msti 1 vlan 2 msti 2 other vlans msti 0 vlan 1 msti 1 vlan 2 msti 2 other vlans msti 0 vlan 1 msti 1 vlan 2&3 msti 2 other vlans msti 0 cst figure 19 network ...
Page 75
63 • same vlan-to-instance mapping configuration • same mstp revision level • physically linked together multiple mst regions can exist in a switched network. You can assign multiple devices to the same mst region. In figure 18 , the switched network comprises four mst regions, mst region 1 through ...
Page 76
64 port roles a port can play different roles in different mstis. As shown in figure 20 , an mst region comprises device a, device b, device c, and device d. Port a1 and port a2 of device a connect to the common root bridge. Port b2 and port b3 of device b form a loop. Port c3 and port c4 of device ...
Page 77
65 • forwarding: the port receives and sends bpdus, obtains mac addresses, and forwards user traffic. • learning: the port receives and sends bpdus, obtains mac addresses, but does not forward user traffic. Learning is an intermediate port state. • discarding: the port receives and sends bpdus, but ...
Page 78
66 implementation of mstp on devices mstp is compatible with stp and rstp. Devices that are running mstp and that are used for spanning tree calculation can identify stp and rstp protocol packets. In addition to basic mstp functions, the following functions are provided for ease of management: • roo...
Page 79
67 task remarks setting the spanning tree mode required configure the device to work in stp-compatible mode. Configuring the device priority optional configuring the timeout factor optional configuring the maximum port rate optional configuring path costs of ports optional configuring the port prior...
Page 80
68 task remarks setting the spanning tree mode required configure the device to work in rstp mode. Configuring the device priority optional configuring the timeout factor optional configuring the maximum port rate optional configuring edge ports optional configuring path costs of ports optional conf...
Page 81
69 task remarks setting the spanning tree mode required configure the device to work in pvst mode. Configuring the device priority optional configuring the timeout factor optional configuring the maximum port rate optional configuring edge ports optional configuring path costs of ports optional conf...
Page 82
70 task remarks setting the spanning tree mode optional by default, the device works in mstp mode. Configuring an mst region required configuring the device priority optional configuring the timeout factor optional configuring the maximum port rate optional configuring edge ports optional configurin...
Page 83
71 configuring the spanning tree setting the spanning tree mode the spanning tree modes include: • stp-compatible mode: the device sends stp bpdus through all ports. • rstp mode: the device sends rstp bpdus through all ports, and ports that connect to stp devices automatically transitions to the stp...
Page 84
72 to do... Use the command... Remarks instance instance-id vlan vlan-list configure the vlan-to-instance mapping table vlan-mapping modulo modulo optional use either command. All vlans in an mst region are mapped to the cist (or msti 0) by default. Configure the mstp revision level of the mst regio...
Page 85
73 bridge. If you have specified multiple secondary root bridges for an instance, when the root bridge fails, the secondary root bridge with the lowest mac address is selected as the new root bridge. Configuring the current device as the root bridge of a specific spanning tree follow these steps to ...
Page 86
74 to do... Use the command... Remarks configure the priority of the current device (in mstp mode) stp [ instance instance-id ] priority priority caution: • you cannot change the priority of a device after it is configured as the root bridge or as a secondary root bridge. • during root bridge select...
Page 87
75 note: • based on the network diameter you configured, the system automatically sets an optimal hello time, forward delay, and max age for the device. • in stp/rstp/mstp mode, each mst region is considered as a device and the configured network diameter is effective only for the cist (or the commo...
Page 88
76 to do... Use the command... Remarks configure the hello timer (in stp/rstp/mstp mode) stp timer hello time configure the hello timer (in pvst mode) stp vlan vlan-list timer hello time optional use either command. 200 centiseconds by default. Configure the max age timer (in stp/rstp/mstp mode) stp...
Page 89
77 configuring the maximum port rate the maximum rate of a port refers to the maximum number of bpdus the port can send within each hello time. The maximum rate of a port is related to the physical status of the port and the network structure. Follow these steps to configure the maximum rate of a po...
Page 90
78 note: • if bpdu guard is disabled, a port set as an edge port will become a non-edge port again if it receives a bpdu from another port. To restore the edge port, re-enable it. • if a port directly connects to a user terminal, configure it as an edge port and enable bpdu guard for it. This enable...
Page 91
79 path cost link speed port type ieee 802.1d-1998 ieee 802.1t private standard aggregate interface containing 2 selected ports 1,000,000 1800 aggregate interface containing 3 selected ports 666,666 1600 aggregate interface containing 4 selected ports 500,000 1400 single port 200,000 200 aggregate i...
Page 92
80 to do... Use the command... Remarks configure the path cost of the ports (in stp/rstp mode) stp cost cost configure the path cost of the ports (in pvst mode) stp vlan vlan-list cost cost configure the path cost of the ports (in mstp mode) stp [ instance instance-id ] cost cost required use any co...
Page 93
81 to do... Use the command... Remarks configure the port priority (in stp/rstp mode) stp port priority priority configure the port priority (in pvst mode) stp vlan vlan-list port priority priority configure the port priority (in mstp mode) stp [ instance instance-id ] port priority priority require...
Page 94
82 by default, the packet format recognition mode of a port is auto. The port automatically distinguishes the two mstp packet formats, and determines the format of packets that it will send based on the recognized format. You can configure the mstp packet format on a port. When working in mstp mode ...
Page 95
83 enabling the spanning tree feature (in stp/rstp/mstp mode) in stp/rstp/mstp mode, make sure that the spanning tree feature is enabled globally and on the desired ports. Follow these steps to enable the spanning tree feature in stp/rstp/mstp mode: to do... Use the command... Remarks enter system v...
Page 96
84 note: • to globally enable or disable the spanning tree feature (not for vlans), use the stp enable command or undo stp enable command in system view. To enable or disable the spanning tree feature for specific vlans, use the stp vlan enable command or undo stp vlan enable command. • you can disa...
Page 97
85 spanning tree implementations vary with vendors, and the configuration digests calculated using private keys is different, so devices of different vendors in the same mst region cannot communicate with each other. To enable communication between an h3c device and a third-party device, enable the ...
Page 98
86 digest snooping configuration example 1. Network requirements as shown in figure 21 : • device a and device b connect to device c, which is a third-party device. All these devices are in the same region. • enable digest snooping on the ports of device a and device b that connect to device c, so t...
Page 99
87 both rstp and mstp devices can perform rapid transition on a designated port only when the port receives an agreement packet from the downstream device. Rstp and mstp devices have the following differences: • for mstp, the root port of the downstream device sends an agreement packet only after it...
Page 100
88 • configure the same region name, revision level and vlan-to-instance mappings on the two devices, assigning them to the same region. Configuring the no agreement check function to make the no agreement check feature take effect, enable it on the root port. Follow these steps to configure no agre...
Page 101
89 figure 25 tc snooping application scenario in the network, the irf fabric transparently transmits the received bpdus and does not participate in spanning tree calculations. When a topology change occurs to the irf fabric or user network networks, the irf fabric may need a long time to learn the c...
Page 102
90 configuring protection functions a spanning tree device supports the following protection functions: • bpdu guard • root guard • loop guard • tc-bpdu guard • bpdu drop configuration prerequisites the spanning tree feature has been correctly configured on the device. Enabling bpdu guard for access...
Page 103
91 in the msti, without forwarding the packet. This is equivalent to disconnecting the link connected with this port in the msti. If the port receives no bpdus with a higher priority within twice the forwarding delay, it reverts to its original state. Configure root guard on a designated port. Follo...
Page 104
92 note: • do not enable loop guard on a port that connects user terminals. Otherwise, the port will stay in the discarding state in all mstis because it cannot receive bpdus. • you cannot configure edge port settings and loop guard, or configure root guard and loop guard on a port at the same time....
Page 105
93 note: because a port with bpdu drop enabled also drops the received 802.1x packets, do not enable bpdu drop and 802.1x on a port at the same time. For more information about 802.1x, see security configuration guide . Displaying and maintaining the spanning tree to do... Use the command... Remarks...
Page 106
94 those of vlan 40 are forwarded along msti 4, and those of vlan 20 are forwarded along msti 0. • vlan 10 and vlan 30 are terminated on the distribution layer devices, and vlan 40 is terminated on the access layer devices. The root bridges of msti 1 and msti 3 are device a and device b respectively...
Page 107
95 3. Configure device b. # enter mst region view, configure the mst region name as example, map vlan 10, vlan 30, and vlan 40 to msti 1, msti 3, and msti 4 respectively, and configure the revision level of the mst region as 0. System-view [deviceb] stp region-configuration [deviceb-mst-region] regi...
Page 108
96 [deviced-mst-region] instance 4 vlan 40 [deviced-mst-region] revision-level 0 # activate mst region configuration. [deviced-mst-region] active region-configuration [deviced-mst-region] quit # enable the spanning tree feature globally. [deviced] stp enable 6. Verify the configurations you can use ...
Page 109
97 3 gigabitethernet1/0/2 alte discarding none 4 gigabitethernet1/0/3 root forwarding none based on the output, you can draw the msti mapped to each vlan, as shown in figure 27 . Figure 27 mstis mapped to different vlans pvst configuration example network requirements as shown in figure 28 : • devic...
Page 110
98 figure 28 network diagram configuration procedure 1. Configure vlans and vlan member ports. (details not shown) create vlan 10, vlan 20, and vlan 30 on device a and device b respectively, vlan 10, vlan 20, and vlan 40 on device c, and vlan 20, vlan 30, and vlan 40 on device d. Configure the ports...
Page 111
99 # enable the spanning tree feature globally and for vlans 10, 20, and 40. [devicec] stp enable [devicec] stp vlan 10 20 40 enable 5. Configure device d. # set the spanning tree mode to pvst. System-view [deviced] stp mode pvst # enable the spanning tree feature globally and for vlans 20, 30, and ...
Page 112
100 20 gigabitethernet1/0/1 alte forwarding none 20 gigabitethernet1/0/2 root discarding none 20 gigabitethernet1/0/3 alte discarding none 30 gigabitethernet1/0/1 root forwarding none 30 gigabitethernet1/0/2 alte discarding none 40 gigabitethernet1/0/3 root forwarding none based on the output, you c...
Page 113
101 bpdu tunneling configuration introduction to bpdu tunneling as a layer 2 tunneling technology, bpdu tunneling enables layer 2 protocol packets from geographically dispersed customer networks to be transparently transmitted over specific tunnels across a service provider network. Background dedic...
Page 114
102 • ethernet operation, administration and maintenance (eoam) • garp vlan registration protocol (gvrp) • hw group management protocol (hgmp) • link aggregation control protocol (lacp) • link layer discovery protocol (lldp) • port aggregation protocol (pagp) • per vlan spanning tree (pvst) • spanni...
Page 115
103 figure 31 bpdu tunneling implementation the upper section of figure 31 represents the service provider network (isp network). The lower section, including user a network 1 and user a network 2, represents the customer networks. Enabling bpdu tunneling on edge devices (pe 1 and pe 2) in the servi...
Page 116
104 enabling bpdu tunneling you can enable bpdu tunneling for different protocols in different views. Note: • settings made in layer 2 ethernet interface view or layer 2 aggregate interface view take effect only on the current port. Settings made in port group view take effect on all ports in the po...
Page 117
105 follow these steps to configure destination multicast mac address for bpdus: to do… use the command… remarks enter system view system-view — configure the destination multicast mac address for bpdus bpdu-tunnel tunnel-dmac mac-address optional 0x010f-e200-0003 by default note: for bpdus to be re...
Page 118
106 [pe1] vlan 2 [pe1-vlan2] quit [pe1] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1 [pe1-gigabitethernet1/0/1] port access vlan 2 # disable stp on gigabitethernet 1/0/1, and then enable bpdu tunneling for stp on it. [pe1-gigabitethernet1/0/1] undo stp enable [pe1-gigabitethernet1/0/1] bpdu-tunnel dot1q stp 2. C...
Page 119
107 configuration procedure 1. Configure pe 1. # configure the destination multicast mac address for bpdus as 0x0100-0ccd-cdd0. System-view [pe1] bpdu-tunnel tunnel-dmac 0100-0ccd-cdd0 # configure gigabitethernet 1/0/1 as a trunk port and assign it to all vlans. [pe1] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1...
Page 120
108 vlan configuration overview vlan ethernet is a network technology based on the carrier sense multiple access/collision detect (csma/cd) mechanism. Because the medium is shared, collisions and excessive broadcasts are common on ethernet networks. To address the issue, virtual lan (vlan) was intro...
Page 121
109 the format of vlan-tagged frames is defined in ieee 802.1q issued by the institute of electrical and electronics engineers (ieee) in 1999. In the header of a traditional ethernet data frame, the field after the destination mac address and the source mac address is the type field, which indicates...
Page 122
110 • other criteria this chapter covers port-based vlan, mac-based vlan, protocol-based vlan, and ip-based vlan. The port-based vlan implementation is the basis of all other vlan implementations. To use any other vlan implementations, you must configure port-based vlan settings. You can configure a...
Page 123
111 configuring basic settings of a vlan interface vlan interface overview for hosts of different vlans to communicate, you must use a router or layer 3 switch to perform layer 3 forwarding. You use vlan interfaces to achieve this. Vlan interfaces are virtual interfaces used for layer 3 communicatio...
Page 124
112 vlan interface configuration example network requirements as shown in figure 37 , pc a is assigned to vlan 5. Pc b is assigned to vlan 10. The pcs belong to different ip subnets and cannot communicate with each other. Configure vlan interfaces on switch a and configure the pcs to enable layer 3 ...
Page 125
113 verifying the configurations 1. The pcs can ping each other. 2. Display brief information about layer 3 interfaces on switch a to verify the configuration. Display ip interface brief *down: administratively down (s): spoofing interface physical protocol ip address description vlan-interface5 up ...
Page 126
114 note: • do not set the voice vlan as the pvid of a port in automatic voice vlan assignment mode. For information about voice vlan, see the chapter “voice vlan configuration.” • h3c recommends that you set the same pvid id for local and remote ports. • make sure that a port is assigned to its pvi...
Page 127
115 follow these steps to assign an access port (in interface view) or multiple access ports (in port group view) to a vlan: to do… use the command… remarks enter system view system-view — enter interface view or port group view enter layer 2 ethernet interface view: interface interface-type interfa...
Page 128
116 follow these steps to assign a trunk port to one or multiple vlans: to do… use the command… remarks enter system view system-view — enter interface view or port group view enter layer 2 ethernet interface view: interface interface-type interface-number enter layer 2 aggregate interface view: int...
Page 129
117 to do… use the command… remarks enter interface view or port group view enter layer 2 ethernet interface view: interface interface-type interface-number enter layer 2 aggregate interface view: interface bridge-aggregation interface-number enter port group view: port-group manual port-group-name ...
Page 130
118 figure 38 network diagram configuration procedure 1. Configure device a. # create vlan 100, and assign port gigabitethernet 1/0/1 to vlan 100. System-view [devicea] vlan 100 [devicea-vlan100] port gigabitethernet 1/0/1 [devicea-vlan100] quit # create vlan 200, and assign port gigabitethernet 1/0...
Page 131
119 [devicea-gigabitethernet1/0/3] display vlan 200 vlan id: 200 vlan type: static route interface: not configured description: vlan 0200 name: vlan 0200 tagged ports: gigabitethernet1/0/3 untagged ports: gigabitethernet1/0/2 mac-based vlan configuration introduction to mac-based vlan the mac-based ...
Page 132
120 • if not, the port selects a vlan for the frame by tagging the untagged frame with the pvid tag and obtaining the tag, and then reports the source mac address of the frame. 2. After reporting the source mac address of the frame, the port looks up the source mac address in the mac-to-vlan map, an...
Page 133
121 dynamic mac-based vlan you can use dynamic mac-based vlan with access authentication (such as 802.1x authentication based on mac addresses) to implement secure, flexible terminal access. After configuring dynamic mac-based vlan on the device, you must configure the username-to-vlan entries on th...
Page 134
122 to do... Use the command... Remarks enter interface view or port group view enter layer 2 ethernet interface view: interface interface-type interface-number enter port group view: port-group manual port-group-name use either command. • the configuration made in ethernet interface view applies on...
Page 135
123 follow these steps to configure dynamic mac-based vlan: to do... Use the command... Remarks enter system view system-view — enter ethernet interface view interface interface-type interface-number enter interface view or port group view enter port group view port-group manual port-group-name use ...
Page 136
124 figure 40 network diagram device a device c device b server1 ip: 1.1.1.1/24 server2 ip: 1.1.2.1/24 ge1/0/1 ge1/0/1 laptop1 ip: 1.1.1.2/24 mac: 000d-88f8-4e71 laptop2 ip: 1.1.2.2/24 mac: 0014-222c-aa69 vlan 100 vlan 200 ge1/0/2 ge1/0/2 ge1/0/3 ge1/0/4 ge1/0/14 ge1/0/13 vlan 100 vlan 200 configura...
Page 137
125 [devicea-gigabitethernet1/0/1] port hybrid vlan 100 200 untagged please wait... Done. [devicea-gigabitethernet1/0/1] mac-vlan enable [devicea-gigabitethernet1/0/1] quit # to enable the laptops to access server 1 and server 2, configure the uplink port gigabitethernet 1/0/2 as a trunk port, and a...
Page 138
126 configuration guidelines 1. Mac-based vlan can be configured only on hybrid ports. 2. Mac-based vlan is usually configured on the downlink ports of access layer devices, and cannot be configured together with the link aggregation function. Protocol-based vlan configuration introduction to protoc...
Page 139
127 to do… use the command… remarks enter interface view or port group view enter layer 2 ethernet interface view: interface interface-type interface-number enter layer 2 aggregate interface view: interface bridge-aggregation interface-number enter port group view: port-group manual port-group-name ...
Page 140
128 figure 41 network diagram ge1/0/2 ge1/0/1 ge1/0/11 ge1/0/12 ipv4 host a ipv4 host b ipv6 host a ipv6 host b ipv4 server ipv6 server device l2 switch a l2 switch b vlan 100 vlan 100 vlan 100 vlan 200 vlan 200 vlan 200 configuration consideration create vlans 100 and 200. Associate vlan 100 with i...
Page 141
129 [device-gigabitethernet1/0/1] port link-type hybrid [device-gigabitethernet1/0/1] port hybrid vlan 100 200 untagged please wait... Done. # associate port gigabitethernet 1/0/1 with the ipv4 protocol template of vlan 100 and the ipv6 protocol template of vlan 200. [device-gigabitethernet1/0/1] po...
Page 142
130 ====================================================== 100 1 ipv4 200 1 ipv6 configuration guidelines protocol-based vlan configuration applies only to hybrid ports. Ip subnet-based vlan configuration introduction in this approach, packets are assigned to vlans based on their source ip addresses...
Page 143
131 to do… use the command… remarks enter interface view or port group view enter layer 2 ethernet interface view: interface interface-type interface-number enter layer 2 aggregate interface view: interface bridge-aggregation interface-number enter port group view: port-group manual port-group-name ...
Page 144
132 configuration consideration • create vlans 100 and 200. • associate ip subnets with the vlans. • assign ports to the vlans. Configuration procedure # associate ip subnet 192.168.5.0/24 with vlan 100. System-view [devicec] vlan 100 [devicec-vlan100] ip-subnet-vlan ip 192.168.5.0 255.255.255.0 [de...
Page 145
133 [devicec-gigabitethernet1/0/12] quit # associate interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1 with ip subnet-based vlans 100 and 200. [devicec] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1 [devicec-gigabitethernet1/0/1] port link-type hybrid [devicec-gigabitethernet1/0/1] port hybrid vlan 100 200 untagged please wait... ...
Page 147
135 isolate-user-vlan configuration overview an isolate-user-vlan uses a two-tier vlan structure. In this approach, the following types of vlans, isolate-user-vlan and secondary vlan, are configured on the same device. The following are the characteristics of the isolate-user-vlan implementation: • ...
Page 148
136 downstream ports can be added to the isolate-user-vlan associated with the secondary vlan synchronously. 3. Associate the isolate-user-vlan with the specified secondary vlans. 4. To enable users in the isolate-user-vlan to communicate with other networks at layer 3, follow these steps: • configu...
Page 151
139 # configure the uplink port gigabitethernet 1/0/5 to operate in promiscuous mode in vlan 5. [deviceb] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/5 [deviceb-gigabitethernet1/0/5] port isolate-user-vlan 5 promiscuous [deviceb-gigabitethernet1/0/5] quit # assign downlink ports gigabitethernet 1/0/1 to vlan 3 an...
Page 152
140 vlan id: 5 vlan type: static isolate-user-vlan type : isolate-user-vlan route interface: not configured description: vlan 0005 name: vlan 0005 tagged ports: none untagged ports: gigabitethernet1/0/1 gigabitethernet1/0/2 gigabitethernet1/0/5 vlan id: 2 vlan type: static isolate-user-vlan type : s...
Page 153
141 voice vlan configuration overview a voice vlan is configured for voice traffic. After assigning the ports that connect to voice devices to a voice vlan, the system automatically configures quality of service (qos) parameters for voice traffic, to improve the transmission priority of voice traffi...
Page 154
142 • in automatic mode, the system matches the source mac address carried in the untagged packets sent when an ip phone is powered on against the device’s oui addresses. If the system finds a match, it automatically assigns the receiving port to the voice vlan, issues acl rules, and configures the ...
Page 155
143 table 15 required configurations on ports of different link types for them to support tagged voice traffic port link type voice vlan assignment mode support for tagged voice traffic configuration requirements automatic access manual no — automatic the pvid of the port cannot be the voice vlan. T...
Page 156
144 security mode and normal mode of voice vlans depending on their inbound packet filtering mechanisms, voice vlan-enabled ports operate in the following modes: • normal mode: voice vlan-enabled ports receive packets that carry the voice vlan tag, and forward packets in the voice vlan without compa...
Page 157
145 if the configuration order is reversed, your priority configuration will fail. For more information, see “ configuring qos priority settings for voice traffic on an interface .” • configure the voice vlan assignment mode. For more information, see “ configuring a port to operate in automatic voi...
Page 158
146 to do... Use the command... Remarks enable the voice vlan security mode voice vlan security enable optional by default, the voice vlan security mode is enabled. Add a recognizable oui address voice vlan mac-address oui mask oui-mask [ description text ] optional by default, each voice vlan has d...
Page 159
147 to do... Use the command... Remarks assign the access, trunk, or hybrid port in manual voice vlan assignment mode to the voice vlan for the configuration procedure, see the chapter “vlan configuration.” required after you assign an access port to the voice vlan, the voice vlan becomes the pvid o...
Page 160
148 • configure gigabitethernet 1/0/1 and gigabitethernet 1/0/2 to work in automatic voice vlan assignment mode. In addition, if one of them has not received any voice packet in 30 minutes, the port is removed from the corresponding voice vlan automatically. Figure 47 network diagram configuration p...
Page 161
149 # configure gigabitethernet 1/0/2. [devicea] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/2 [devicea-gigabitethernet1/0/2] port link-type hybrid [devicea-gigabitethernet1/0/2] voice vlan mode auto [devicea-gigabitethernet1/0/2] voice vlan 3 enable verifying the configurations # display the oui addresses, oui a...
Page 162
150 figure 48 network diagram device a device b ge1/0/1 ge1/0/1 vlan 2 010-1001 oui: 0011-2200-0000 mask: ffff-ff00-0000 0755-2002 internet configuration procedure # configure the voice vlan to operate in security mode. A voice vlan operates in security mode by default. (optional) system-view [devic...
Page 163
151 # display the states of voice vlans. Display voice vlan state maximum of voice vlans: 8 current voice vlans: 1 voice vlan security mode: security voice vlan aging time: 1440 minutes voice vlan enabled port and its mode: port vlan mode cos dscp ----------------------------------------------------...
Page 164
152 gvrp configuration the generic attribute registration protocol (garp) provides a generic framework for devices in a switched lan, such as end stations and switches, to register and deregister attribute values. The garp vlan registration protocol (gvrp) is a garp application that registers and de...
Page 165
153 a garp participant sends join messages when it wishes to declare its attribute values or receives join messages from other garp participants. Join messages fall into joinempty and joinin. A garp participant sends joinempty messages to declare attribute values that it has not registered. It sends...
Page 166
154 a garp participant starts a leave timer when it receives a leave message for an attribute value. If the garp participant receives no join message for the attribute value before the timer expires, it deregisters the attribute value. 4. Leaveall timer when a garp application is enabled, a leaveall...
Page 167
155 field description value attribute consists of an attribute length, an attribute event, and an attribute value –– attribute length length of an attribute, inclusive of the attribute length field 2 to 255 (in bytes) attribute event event that the attribute describes • 0x00: leaveall event • 0x01: ...
Page 168
156 gvrp configuration task list complete these tasks to configure gvrp: task remarks configuring gvrp functions required configuring the garp timers optional note: • gvrp configuration made in ethernet interface view or layer 2 aggregate interface view takes effect on the current interface only; gv...
Page 169
157 note: • for more information about the port link-type trunk and port trunk permit vlan all commands, see layer 2—lan switching command reference . • gvrp can work with stp, rstp, or mstp cist but not pvst. When gvrp runs on the cist, blocked ports on the cist cannot receive or send gvrp packets....
Page 170
158 table 19 dependencies of the garp timers timer lower limit upper limit hold 10 centiseconds no greater than half of the join timer join no less than twice the hold timer less than half of the leave timer leave greater than twice the join timer less than the leaveall timer leaveall greater than t...
Page 171
159 • enable gvrp and configure the normal registration mode on ports to enable the registration and deregistration of dynamic and static vlan information between the two devices. Figure 51 network diagram configuration procedure 1. Configure device a. # enable gvrp globally. System-view [devicea] g...
Page 172
160 according to the output, information about vlan 1, static vlan information of vlan 2 on the local device, and dynamic vlan information of vlan 3 on device b are all registered through gvrp. # display the local vlan information that gvrp maintains on port gigabitethernet 1/0/1 of device b. [devic...
Page 173
161 [deviceb-gigabitethernet1/0/1] port link-type trunk [deviceb-gigabitethernet1/0/1] port trunk permit vlan all # enable gvrp on gigabitethernet 1/0/1, and set the gvrp registration mode to fixed on the port. [deviceb-gigabitethernet1/0/1] gvrp [deviceb-gigabitethernet1/0/1] gvrp registration fixe...
Page 174
162 [devicea] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1 [devicea-gigabitethernet1/0/1] port link-type trunk [devicea-gigabitethernet1/0/1] port trunk permit vlan all # enable gvrp on gigabitethernet 1/0/1, and set the gvrp registration mode to forbidden on the port. [devicea-gigabitethernet1/0/1] gvrp [device...
Page 175
163 qinq configuration note: throughout this document, customer network vlans (cvlans), also called inner vlans, refer to the vlans that a customer uses on the private network; and service provider network vlans (svlans), also called outer vlans, refer to the vlans that a service provider uses to ca...
Page 176
164 figure 54 typical qinq application scenario ce 1 customer network a pe 1 public network pe 2 ce 2 vlans 1 to 10 vlans 1 to 20 ce 3 vlans 1 to 20 vlans 1 to 10 ce 4 customer network a customer network b customer network b ip network vlan 4 vlan 4 vlan 3 vlan 3 as shown in figure 54 , customer net...
Page 177
165 figure 55 single-tagged ethernet frame header and double-tagged ethernet frame header note: the default maximum transmission unit (mtu) of an interface is 1500 bytes. The size of an outer vlan tag is 4 bytes. H3c recommends you to increase the mtu of each interface on the service provider networ...
Page 178
166 figure 56 vlan tag structure of an ethernet frame the switch determines whether a received frame carries a vlan tag by checking the tpid value. For example, if a frame carries a vlan tag with tpid value 0x8100, but the configured tpid value is 0x9100, the switch considers that the frame does not...
Page 179
167 qinq configuration task list complete the follows tasks to configure qinq: task remarks enabling basic qinq required configuring basic qinq configuring vlan transparent transmission optional configuring an outer vlan tagging policy configuring selective qinq configuring an inner-outer vlan 802.1...
Page 180
168 the port not to add its pvid tag to packets carrying specific inner vlan tags when they pass through it, so that these packets are transmitted in the service provider network with single tags. Follow these steps to configure vlan transparent transmission: to do... Use the command... Remarks ente...
Page 181
169 follow these steps to configure an outer vlan tagging policy in the port-based approach: to do... Use the command... Remarks enter system view system-view — enter interface view or port group view • enter layer 2 ethernet interface view or layer 2 aggregate interface view: interface interface-ty...
Page 182
170 to do... Use the command... Remarks create a traffic behavior and enter traffic behavior view traffic behavior behavior-name required configure a marking action or an inner-to-outer tag priority copying action mark the 802.1p priorities in outer vlan tags: remark dot1p 8021p copy the inner 802.1...
Page 183
171 • the two branches of company a, site 1 and site 2, are connected through the service provider network and use cvlans 10 through 70. The two branches of company b, site 3 and site 4, are connected through the service provider network and use cvlans 30 through 90. • pe 1 and pe 2 are edge devices...
Page 184
172 • configure gigabitethernet 1/0/2. # configure gigabitethernet 1/0/2 as a trunk port and assign it to vlan 100 and vlan 200. [pe1] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/2 [pe1-gigabitethernet1/0/2] port link-type trunk [pe1-gigabitethernet1/0/2] port trunk permit vlan 100 200 # set the tpid value in the...
Page 185
173 [pe2] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/3 [pe2-gigabitethernet1/0/3] port link-type trunk [pe2-gigabitethernet1/0/3] port trunk permit vlan 100 10 to 70 # configure vlan 100 as the pvid for the port. [pe2-gigabitethernet1/0/3] port trunk pvid vlan 100 # enable basic qinq on the port. [pe2-gigabiteth...
Page 186
174 note: make sure that you have configured the devices in the service provider network to allow qinq packets to pass through. 1. Configure pe 1. • configure gigabitethernet 1/0/1. # configure gigabitethernet 1/0/1 as a hybrid port to permit frames of vlan 10 and vlan 20 to pass through tagged, and...
Page 187
175 [pe2-gigabitethernet1/0/1-vid-100] raw-vlan-id inbound 10 [pe2-gigabitethernet1/0/1-vid-100] quit # configure the port to tag vlan 20 frames with outer vlan id 200. [pe2-gigabitethernet1/0/1] qinq vid 200 [pe2-gigabitethernet1/0/1-vid-200] raw-vlan-id inbound 20 [pe2-gigabitethernet1/0/1-vid-200...
Page 188
176 lldp configuration overview background in a heterogeneous network, a standard configuration exchange platform ensures that different types of network devices from different vendors can discover one another and exchange configuration for the sake of interoperability and management. The ietf draft...
Page 189
177 table 21 fields in an ethernet ii-encapsulated lldpdu field description destination mac address the mac address to which the lldpdu is advertised. It is fixed to 0x0180-c200-000e, a multicast mac address. Source mac address the mac address of the sending port. If the port does not have a mac add...
Page 190
178 an lldpdu can carry up to 28 types of tlvs. Mandatory tlvs include chassis id tlv, port id tlv, time to live tlv, and end of lldpdu tlv. Other tlvs are optional. Tlvs tlvs are type, length, and value sequences that carry information elements. The type field identifies the type of information, th...
Page 191
179 type description port and protocol vlan id indicates whether the device supports protocol vlans and, if so, what vlan ids these protocols will be associated with. An lldpdu can carry multiple different tlvs of this type. Vlan name specifies the textual name of any vlan to which the port belongs....
Page 192
180 type description network policy allows a network device or terminal device to advertise the vlan id of the specific port, the vlan type, and the priorities for specific applications. Extended power-via-mdi allows a network device or terminal device to advertise power supply capability. This tlv ...
Page 193
181 • a new neighbor is discovered. A new lldpdu is received and carries device information new to the local device. • the lldp operating mode of the port changes from disable or rx to txrx or tx. This is the fast sending mechanism of lldp. With this mechanism, a specific number of lldpdus are sent ...
Page 194
182 to do… use the command… remarks enter system view system-view — enable lldp globally lldp enable required by default, lldp is globally enabled. Enter layer 2 ethernet interface view interface interface-type interface-number enter ethernet interface view or port group view enter port group view p...
Page 195
183 enabling lldp polling with lldp polling enabled, a device periodically searches for local configuration changes. On detecting a configuration change, the device sends lldpdus to inform neighboring devices of the change. Follow these steps to enable lldp polling: to do… use the command… remarks e...
Page 196
184 follow these steps to configure a management address to be advertised and its encoding format on a port or group of ports: to do… use the command… remarks enter system view system-view — enter layer 2 ethernet interface view interface interface-type interface-number enter ethernet interface view...
Page 197
185 to do… use the command… remarks set the number of lldpdus sent each time fast lldpdu transmission is triggered lldp fast-count count optional 3 by default. Note: • to make sure that lldp neighbors can receive lldpdus to update information about the current device before it ages out, configure bo...
Page 198
186 to make your device work with cisco ip phones, you must enable cdp compatibility. If your lldp-enabled device cannot recognize cdp packets, it does not respond to the requests of cisco ip phones for the voice vlan id configured on the device. As a result, a requesting cisco ip phone sends voice ...
Page 199
187 configuring lldp trapping lldp trapping notifies the network management system (nms) of events such as newly-detected neighboring devices and link malfunctions. Lldp traps are sent periodically, and the interval is configurable. To prevent excessive lldp traps from being sent when the topology i...
Page 200
188 lldp configuration examples basic lldp configuration example network requirements as shown in figure 62 , the nms and switch a are located in the same ethernet. An med device and switch b are connected to gigabitethernet 1/0/1 and gigabitethernet 1/0/2 of switch a. Enable lldp on the ports of sw...
Page 201
189 [switchb-gigabitethernet1/0/1] quit 3. Verify the configuration # display the global lldp status and port lldp status on switch a. [switcha] display lldp status global status of lldp: enable the current number of lldp neighbors: 2 the current number of cdp neighbors: 0 lldp neighbor information ...
Page 202
190 lldp neighbor information last changed time: 0 days,0 hours,5 minutes,20 seconds transmit interval : 30s hold multiplier : 4 reinit delay : 2s transmit delay : 2s trap interval : 5s fast start times : 3 port 1 [gigabitethernet1/0/1]: port status of lldp : enable admin status : rx_only trap flag ...
Page 203
191 figure 63 network diagram configuration procedure 1. Configure a voice vlan on switch a. # create vlan 2. System-view [switcha] vlan 2 [switcha-vlan2] quit # set the link type of gigabitethernet 1/0/1 and gigabitethernet 1/0/2 to trunk and enable voice vlan on them. [switcha] interface gigabitet...
Page 204
192 port id : port 1 sofrware version : p0030301mfg2 platform : cisco ip phone 7960 duplex : full cdp neighbor-information of port 2[gigabitethernet1/0/2]: cdp neighbor index : 2 chassis id : sep00141cbcdbff port id : port 1 sofrware version : p0030301mfg2 platform : cisco ip phone 7960 duplex : ful...
Page 205
193 index a b c d e g i l m o p q r s t v a assigning a port to the isolation group, 51 b bpdu tunneling configuration examples, 105 c configuring a combo interface, 1 configuring a loopback interface, 17 configuring a port group, 7 configuring a voice vlan, 144 configuring an aggregate interface, 4...
Page 206
194 lldp configuration task list, 181 m mac address table configuration example, 26 mac information configuration example, 30 mac-based vlan configuration, 119 mstp, 61 o overview(mac address table), 20 overview(mac information), 28 overview(ethernet link aggregation), 31 overview(isolate-user-vlan)...