- DL manuals
- Intermec
- Printer
- EasyCoder 501XP
- Reference Manual
Intermec EasyCoder 501XP Reference Manual
Summary of EasyCoder 501XP
Page 1
Programmer’s reference manual intermec direct protocol v7.80
Page 2
Intermec technologies corporation corporate headquarters 6001 36th ave. W. Everett, wa 98203 u.S.A. Www.Intermec.Com the information contained herein is proprietary and is provided solely for the purpose of allowing customers to operate and service intermec- manufactured equipment and is not to be r...
Page 3: Contents
Intermec direct protocol v7.80 programmer’s reference manual iii contents contents 1 introduction 1.1 introduction ......................................................................... 2 2 getting started 2.1 computer connection ......................................................... 4 2.2 med...
Page 4: Setting Up The Printer
Iv intermec direct protocol v7.80 programmer’s reference manual contents 4.5 image field ......................................................................... 37 4.6 box field ............................................................................ 39 4.7 line field ............................
Page 5: File Handling
Intermec direct protocol v7.80 programmer’s reference manual v contents 7 reading the printer’s status 7.1 introduction ....................................................................... 78 7.2 returning information to host .......................................... 78 7.3 reading date and time...
Page 6
Vi intermec direct protocol v7.80 programmer’s reference manual contents.
Page 7: Introduction
Intermec direct protocol v7.80 programmer’s reference manual 1 1 introduction this chapter gives a quick introduction to the intermec direct protocol..
Page 8: 1.1 Introduction
2 intermec direct protocol v7.80 programmer’s reference manual chapter 1 — introduction 1.1 introduction intermec direct protocol v7.80 is an easy-to-use printer protocol that has been developed for use with the easycoder 501 xp/601 xp and easycoder f2/f4 direct thermal and/or thermal transfer print...
Page 9: Getting Started
Intermec direct protocol v7.80 programmer’s reference manual 3 2 getting started this chapter how to connect the printer to a computer using the serial interface, switch on the printer, use intermec shell to select the direct protocol, and how to check that the communication between printer and the ...
Page 10: 2.1 Computer Connection
4 intermec direct protocol v7.80 programmer’s reference manual chapter 2 — getting started 2.1 computer connection the intermec direct protocol is included in the intermec fingerprint fi rmware, which is stored in the flash simm package fi tted on the printer’s cpu board at delivery. No operative sy...
Page 11: 2.3 Switch On The Printer
Intermec direct protocol v7.80 programmer’s reference manual 5 chapter 2 — getting started 2.3 switch on the printer check that the printhead is lowered. Switch on the power using the on/off switch, which is fi tted on the printer’s rear plate, and check that the “power” control lamp comes on. Then ...
Page 12: 2.5 No Startup Program
6 intermec direct protocol v7.80 programmer’s reference manual chapter 2 — getting started 2.5 no startup program if the printer starts up in the immediate mode of intermec finger- print (because you have already selected the fingerprint application in intermec shell, or because the printer for some...
Page 13: Abcdefghijklm
Intermec direct protocol v7.80 programmer’s reference manual 7 chapter 2 — getting started each line will be acknowledged by an “ ok ” on the screen, provided it has been entered correctly. When you press the “carriage return” key the third time, the printer will feed out a label, ticket, tag, or pi...
Page 14
8 intermec direct protocol v7.80 programmer’s reference manual chapter 2 — getting started.
Page 15: Principles of Operation
Intermec direct protocol v7.80 programmer’s reference manual 9 3 principles of operation this chapter explains how to enter the direct protocol from intermec shell and from the immediate mode. It also describes the special features of the direct protocol and shows how to send instructions to the pri...
Page 16: Direct Protocol
10 intermec direct protocol v7.80 programmer’s reference manual chapter 3 — principles of operation 3.1 entering from intermec shell in intermec shell, select the “intermec direct protocol” option under the “select application” headline. After a few seconds, the display will show the message: direct...
Page 18: Continuous String
12 intermec direct protocol v7.80 programmer’s reference manual chapter 3 — principles of operation layout and printable data in one sequence continuous string enter the instructions as a continuous string, where the instructions are separated by colons (:). Bf on:bf "swiss 721 bt",6:pp 10,10: px 43...
Page 19: Creating The Layout
Intermec direct protocol v7.80 programmer’s reference manual 13 chapter 3 — principles of operation layout and variable input data in separate sequences all necessary commands for setting up the printer (see chapter 6) should be issued before the layout input ... Layout end sequence. The only except...
Page 20: 3.5 Fields
14 intermec direct protocol v7.80 programmer’s reference manual chapter 3 — principles of operation note: if a label has been printed using a predefi ned layout and you want to return to the method of printing labels using layout and printable data in one sequence, the predefi ned layout must fi rst...
Page 21
Intermec direct protocol v7.80 programmer’s reference manual 15 chapter 3 — principles of operation 3.7 field-related formatting instructions depending on type of fi eld, additional formatting instructions can be used before you enter the input data: type of field formatting instructions single-line...
Page 22: 3.8 Layout Instructions
16 intermec direct protocol v7.80 programmer’s reference manual chapter 3 — principles of operation 3.8 layout instructions the layout should contain formatting parameters for all fi elds and input data to such fi elds that will always contain the same information. When the variable input data are a...
Page 23: 3.11 Setting Up The Printer
Intermec direct protocol v7.80 programmer’s reference manual 17 chapter 3 — principles of operation • rotating the platen roller during cleaning • feeding out an empty label, ticket, tag, or piece of strip • adjusting the label stop/black mark sensor 3.11 setting up the printer you can control how t...
Page 24
18 intermec direct protocol v7.80 programmer’s reference manual chapter 3 — principles of operation 3.12 reading printer’s status provided you have a two-way serial communication between printer and host, you can read the printer’s status regarding a number of functions back to the screen of the hos...
Page 25: 3.14 Syntax Descriptions
Intermec direct protocol v7.80 programmer’s reference manual 19 chapter 3 — principles of operation 3.14 syntax descriptions many commonly used instructions have a shorthand version to mini- mize the transfer of data. In the explanations of the various instruction that follow, both the full name and...
Page 26
20 intermec direct protocol v7.80 programmer’s reference manual chapter 3 — principles of operation.
Page 27: Label Design
Intermec direct protocol v7.80 programmer’s reference manual 21 4 label design this chapter describes how a label layout is made up of various types of fi elds and explains the instructions used for creating each type of fi eld..
Page 28: 4.1 Field Types
This is a multi- line text field with line-wrap and hyphen- ation multi-line text field single-line text field line field image field box field bar code field (w. Interpretation) 22 intermec direct protocol v7.80 programmer’s reference manual chapter 4 — label design 4.1 field types a label layout i...
Page 29: Origin
Intermec direct protocol v7.80 programmer’s reference manual 23 chapter 4 — label design 4.2 general formatting instructions origin the positioning of all printable objects on the label, that is text fi elds, bar code fi elds, images, boxes, and lines, uses a common system. The starting point is cal...
Page 30: Insertion Point
24 intermec direct protocol v7.80 programmer’s reference manual chapter 4 — label design insertion point the insertion point of any printable object is specifi ed within the coordi- nate system by means of prpos (pp). The coordinates must be selected so the fi eld fi ts completely inside the printab...
Page 31
Intermec direct protocol v7.80 programmer’s reference manual 25 chapter 4 — label design.
Page 32: Align 7
This is line number 1 and this is line 2 and now comes line 3 followed by no. 4. Align 7 this is line number 1 and this is line 2 and now comes line 3 followed by no. 4. Align 5 this is line number 1 and this is line 2 and now comes line 3 followed by no. 4. Align 1 align 3 this is line number 1 and...
Page 33: Directions
Dot-line on printhead x-coordinate x-start x -c oor dina te dot 0 insertion point = anchor point origin dir 1 dir 2 dir 3 dir 4 feed direction intermec direct protocol v7.80 programmer’s reference manual 27 chapter 4 — label design directions intermec direct protocol allows printing in four differen...
Page 34: Xor Mode
28 intermec direct protocol v7.80 programmer’s reference manual chapter 4 — label design enabling/disabling partial fields normally, any fi eld that extends outside the print window, as specifi ed by the printer’s setup in regard of media size (x-start, width, and length), will cause error 1003 “fie...
Page 35: 4.3 Text Fields
Intermec direct protocol v7.80 programmer’s reference manual 29 chapter 4 — label design 4.3 text fields a single-line text fi eld consists of one or several alphanumeric characters on the same line. There is no practical limit other than the size of the printable area on the media. Text is not wrap...
Page 36: Norimage
Norimage invimage 30 intermec direct protocol v7.80 programmer’s reference manual chapter 4 — label design select magnifi cation fonts can be magnifi ed 1-4 times independently in regard of height and width by means of a mag instruction. However, for outline fonts the printout quality will be better ...
Page 37: Summary
Intermec direct protocol v7.80 programmer’s reference manual 31 chapter 4 — label design summary to create a text fi eld, the following formatting instructions must be given (in most cases default values may substitute missing parameters). Input data to the fi eld and printing instructions are expla...
Page 38: 4.4 Bar Code Field
32 intermec direct protocol v7.80 programmer’s reference manual chapter 4 — label design 4.4 bar code field the intermec direct protocol supports 53 of the most common bar code symbologies. 38 of these bar code symbologies are standard, whereas 15 are available as a dynamic module (see intermec fing...
Page 39
Intermec direct protocol v7.80 programmer’s reference manual 33 chapter 4 — label design ean-13 composite with cc-a or cc-b (dynamic module only) ean13_cc" ean 128 "ean128" ean 128 subset a "ean128a" ean 128 subset b "ean128b" ean 128 subset c "ean128c" ean 128 composite with cc-a or cc-b (dynamic m...
Page 40: Specify Bar Code Height
34 intermec direct protocol v7.80 programmer’s reference manual chapter 4 — label design upc-a composite with cc-a or cc-b (dynamic module only) "upca_cc" upc-d1 "upcd1" upc-d2 "upcd2" upc-d3 "upcd3" upc-d4 "upcd4" upc-d5 "upcd5" upc-e "upce" upc-e composite with cc-a or cc-b (dynamic module only) "...
Page 41: Bar Code Interpretation
Intermec direct protocol v7.80 programmer’s reference manual 35 chapter 4 — label design specify bar codes (combined instruction) the barset instruction is primarily intended for complex bar codes (see chapter 8.1), but can also be used to specify simple one-dimensional bar codes with a single instr...
Page 42: Summary
36 intermec direct protocol v7.80 programmer’s reference manual chapter 4 — label design summary to create a bar code fi eld, the following formatting instructions must be given (in most cases default values may substitute missing parameters). Input data and printing instructions are explained in ch...
Page 43: 4.5 Image Field
Intermec direct protocol v7.80 programmer’s reference manual 37 chapter 4 — label design 4.5 image field an image fi eld is a fi eld containing some kind of picture or logotype in .Pcx format. The image can either be stored in the permanent memory or in a memory card, or be downloaded as a fi le by ...
Page 44: Summary
38 intermec direct protocol v7.80 programmer’s reference manual chapter 4 — label design select normal/inverse printing normally, an image is printed in black on a transparent background, just as it was created. Using i nvimage , the black and transparent parts can be switched. The size of the backg...
Page 45: 4.6 Box Field
Intermec direct protocol v7.80 programmer’s reference manual 39 chapter 4 — label design 4.6 box field a box is a hollow square or rectangle that can be rotated with an incre- ment of 90° according to the print direction. If the line thickness is suffi ciently large, the box will appear to be fi lle...
Page 46: 4.7 Line Field
40 intermec direct protocol v7.80 programmer’s reference manual chapter 4 — label design 4.7 line field a line can be printed in right angles along or across the media path according to the print direction. In addition to the general formatting instructions prpos , align , and dir , a line fi eld is...
Page 47: 4.8 Layout Instructions
Intermec direct protocol v7.80 programmer’s reference manual 41 chapter 4 — label design 4.8 layout instructions start layout recorder the layout input instruction clears the printer’s working memory, starts the layout recorder, and allows you to assign a name and a device to the layout. The layout ...
Page 48: Save The Layout
42 intermec direct protocol v7.80 programmer’s reference manual chapter 4 — label design save the layout after having completed the layout, save it in the printer’s temporary memory ("tmp:"), turn off the layout recorder, and clear the printer’s working memory by means of a layout end instruction. T...
Page 49: Select A Layout
Intermec direct protocol v7.80 programmer’s reference manual 43 chapter 4 — label design 4.9 printable data instructions select a layout before any variable data can be transmitted to a preprogrammed layout, the layout must be selected by means of a layout run instruction. If the layout has been sav...
Page 50
44 intermec direct protocol v7.80 programmer’s reference manual chapter 4 — label design ..... Input data must not be enclosed by quotation marks. Example: abcdefg 123456789 note: if a label has been printed using a predefi ned layout and you want to return to the method of printing labels using lay...
Page 52: Input Data to Image Fields
46 intermec direct protocol v7.80 programmer’s reference manual chapter 4 — label design input data to bar code fields the input data to a bar code fi eld is given by means of a prbar instruc- tion. You can add the same types of data to a bar code fi eld as to a text fi eld, provided the type of dat...
Page 53
Intermec direct protocol v7.80 programmer’s reference manual 47 chapter 4 — label design input data from the printer’s clock/calendar the printer’s clock/calendar can be used to provide input data to text and bar code fi elds by including any of the following instructions in the prtxt , prbox , or p...
Page 54
48 intermec direct protocol v7.80 programmer’s reference manual chapter 4 — label design weeknumber (""[,]) returns the weeknumber from a given date or the current date. Can be specifi ed in the standard format “yymmdd” or by a date$ instruction. By default, the week number is calculated according to...
Page 55: Feeding & Printing
Intermec direct protocol v7.80 programmer’s reference manual 49 5 feeding & printing instructions this chapter describes the various instructions used for controlling the media feed and the printing of labels..
Page 56: 5.1 Media Feed
50 intermec direct protocol v7.80 programmer’s reference manual chapter 5 — feeding & printing instructions 5.1 media feed in order to provide maximum fl exibility, there are several instructions for controlling the media feed and an optional paper cutter: cleanfeed runs the printer’s media feed mec...
Page 57: • Fixed Length Strip
Intermec direct protocol v7.80 programmer’s reference manual 51 chapter 5 — feeding & printing instructions black marks. At the same time, the sensitivity of the sensor is adjusted according to the characteristics of the media, for example the transpar- ency of the liner. In case of continuous stock...
Page 58
52 intermec direct protocol v7.80 programmer’s reference manual chapter 5 — feeding & printing instructions the relation between media and printhead at the moment when the actual printing starts decides all positioning along the y-axis, that is along the media path. Likewise, the relation between th...
Page 59: 5.2 Label Printing
Intermec direct protocol v7.80 programmer’s reference manual 53 chapter 5 — feeding & printing instructions 5.2 label printing when a printfeed instruction is issued, the fi rmware processes all previously entered text fi elds, bar code fi elds, image fi elds, box fi elds, and line fi elds into a bi...
Page 60: 5.3 Batch Printing
54 intermec direct protocol v7.80 programmer’s reference manual chapter 5 — feeding & printing instructions 5.3 batch printing introduction the term “batch printing” means the process of printing several labels without stopping the media feed motor between labels. The labels may be exact copies or d...
Page 61
Intermec direct protocol v7.80 programmer’s reference manual 55 chapter 5 — feeding & printing instructions % = fieldno is the same alphanumeric designator as in the corresponding cll instruction followed by a mandatory % sign. Example: in this example, the text “month” is kept in the image buffer, ...
Page 62: Reprinting A Lost Label
56 intermec direct protocol v7.80 programmer’s reference manual chapter 5 — feeding & printing instructions reprinting a lost label an out-of-paper, an out-of-ribbon condition, or a media jam may cause serious trouble when printing batches of labels, especially with consecu- tive numbering. If the p...
Page 63: Setting Up The Printer
Intermec direct protocol v7.80 programmer’s reference manual 57 6 setting up the printer this chapter describes how to use various instructions to set up the printer..
Page 64
58 intermec direct protocol v7.80 programmer’s reference manual chapter 6 — setting up the printer 6.1 enabling/disabling intermec direct protocol unless you use intermec shell to select the intermec direct protocol, you must issue this instruction to switch from the intermec fingerprint immediate m...
Page 65: 6.3 Setting Time and Date
Intermec direct protocol v7.80 programmer’s reference manual 59 chapter 6 — setting up the printer 6.3 setting time and date the printer is, or can be, provided with an internal real-time clock/calen- dar (rtc) which retains its setting even when the printer is switched off. Note: if no rtc is insta...
Page 66
60 intermec direct protocol v7.80 programmer’s reference manual chapter 6 — setting up the printer 6.4 selecting format for date and time the formats for printing dates and time in connection with date$("f") , dateadd$("f") , time$("f") , and timeadd$("f") , see chapter 4.9, can be specifi ed by the...
Page 67
Intermec direct protocol v7.80 programmer’s reference manual 61 chapter 6 — setting up the printer in many cases, it is desired to have the names of months and weekdays printed in plain text rather than as a number. There are two instructions that allow you to assign names in any language to months ...
Page 68: 6.5 Changing Separators
62 intermec direct protocol v7.80 programmer’s reference manual chapter 6 — setting up the printer 6.5 changing separators when transmitting variable input data to a predefi ned layout, the string must contain certain separating characters. By default, you should use as start-of-text separator, as f...
Page 69: 6.6 Creating Counters
Intermec direct protocol v7.80 programmer’s reference manual 63 chapter 6 — setting up the printer 6.6 creating counters you can create a number of counters for use in text and bar code fi elds, where each counter is specifi ed by a cnt no.>$ instruction, see chapter 4.9. The counters are global, wh...
Page 71
Intermec direct protocol v7.80 programmer’s reference manual 65 chapter 6 — setting up the printer 6.8 enabling/disabling automatic cutting some printers can, as an option, be fi tted with a paper cutter that can cut non-adhesive continuous stock or the liner between labels. As an alternative to iss...
Page 72
66 intermec direct protocol v7.80 programmer’s reference manual chapter 6 — setting up the printer 6.11 formatting the printer’s memory by formatting the printer’s memory, you will either erase all fi les stored in the permanent memory or all fi les except system fi les (that is, fi les with names s...
Page 73
Intermec direct protocol v7.80 programmer’s reference manual 67 chapter 6 — setting up the printer 6.12 preprocessing input data all input data to the printer come in binary form via the standard in channel (by default "uart1:"). Characters are transmitted in ascii format, which upon reception will ...
Page 74: 6.13 Selecting Character Set
68 intermec direct protocol v7.80 programmer’s reference manual chapter 6 — setting up the printer 6.13 selecting character set the nasc instruction is used to select a character set that decides how the various characters will be printed. This instruction makes it possible to adapt the printer to v...
Page 75: 6.14 Rebooting The Printer
Intermec direct protocol v7.80 programmer’s reference manual 69 chapter 6 — setting up the printer 6.14 rebooting the printer as an alternative to cycling the power to the printer using the on/off switch, you can issue a reboot instruction. Any data or layout in the temporary memory, that has not be...
Page 76: 6.17 Error Handling
70 intermec direct protocol v7.80 programmer’s reference manual chapter 6 — setting up the printer 6.17 error handling when an input on instruction is executed, the error-handler of the intermec direct protocol starts. By default, it handles fi ve error condi- tions (see below). All other errors are...
Page 77
Intermec direct protocol v7.80 programmer’s reference manual 71 chapter 6 — setting up the printer head lifted: a message is shown in the display and a beep is emitted. The printer waits for the printhead to be lowered, then a formfeed is performed. If the error stopped a print operation, the operat...
Page 78
72 intermec direct protocol v7.80 programmer’s reference manual chapter 6 — setting up the printer 6.18 setting break for batch printing when printing large batches of labels, it is useful to be able to break the printing, if for example an error should be detected. You can break the printing either...
Page 80: Important!
74 intermec direct protocol v7.80 programmer’s reference manual chapter 6 — setting up the printer important! In the syntax description below, bold characters separated by vertical bars indicate alternatives, n-nnnnn indicate variable numeric input. Double- headed arrows ( ↔) indicate compulsory spa...
Page 81: 6.22 Minimum Gap Length
Intermec direct protocol v7.80 programmer’s reference manual 75 chapter 6 — setting up the printer 6.20 selecting centronics type sysvar(25) = = 0 standard type: 500 ns ack, busy inactivated after ack fi nishes (default). = 1 ibm/epson type: 2500 ns ack, busy inactivated as soon as ack pulse starts. ...
Page 82
76 intermec direct protocol v7.80 programmer’s reference manual chapter 6 — setting up the printer 6.24 overriding media feed setup the lblcond instruction allows you to override the media feed setup, switch off the label stop/black mark sensor (lss), or to select mode for controlling the printing o...
Page 83: Reading The Printer’S
Intermec direct protocol v7.80 programmer’s reference manual 77 7 reading the printer’s status this chapter describes the various methods and instruction that enables the programmer to read how the printer is set up..
Page 84: 7.1 Introduction
78 intermec direct protocol v7.80 programmer’s reference manual chapter 7 — reading the printer’s status 7.1 introduction provided there is a working two-way serial communication between the printer and the host computer, the printer’s status in regard of various functions can be read back to the ho...
Page 85: 7.5 Testing The Printhead
Intermec direct protocol v7.80 programmer’s reference manual 79 chapter 7 — reading the printer’s status 7.5 testing the printhead the thermal printhead can be tested in three ways: ? Functest$ ("head") the printhead is tested for number of dots and possible faults. There are 3 possible responses: “...
Page 86
80 intermec direct protocol v7.80 programmer’s reference manual chapter 7 — reading the printer’s status 7.7 reading sensors and straps there are a number of sensors, hardware strap, and setup parameters in the printer that can be read and their status or value be returned to the host: ? Sysvar () =...
Page 87
Intermec direct protocol v7.80 programmer’s reference manual 81 chapter 7 — reading the printer’s status the instruction immediate allows you see the status of various printer modes and the setting of the standard in and out channels: ? Immediate mode prints a line to the standard out port with info...
Page 88
82 intermec direct protocol v7.80 programmer’s reference manual chapter 7 — reading the printer’s status.
Page 89: File Handling
Intermec direct protocol v7.80 programmer’s reference manual 83 8 file handling this chapter explains how to read the contents in the various parts of the printer’s memory and how to remove, copy, and download fi les..
Page 90
84 intermec direct protocol v7.80 programmer’s reference manual chapter 8 — file handling 8.1 reading the printer’s memory there are a number of instructions for returning the content in the printer’s memory to the host. This requires a working two-way serial communication (see setstdio in chapter 6...
Page 91: 8.3 Copying Files
Intermec direct protocol v7.80 programmer’s reference manual 85 chapter 8 — file handling 8.3 copying files you can copy a fi le from any part of the printer’s memory to another part, provided it is not read-only. You can also use the copy instruction to give the copy a new name. Copy "[]"[,"[]"] th...
Page 92
86 intermec direct protocol v7.80 programmer’s reference manual chapter 8 — file handling.
Page 93: Advanced Features
Intermec direct protocol v7.80 programmer’s reference manual 87 9 advanced features this chapter gives short descriptions on how to use complex two-dimensional bar code symbologies and international character sets including double-byte fonts. Please refer to the intermec fingerprint v.7.80, programm...
Page 94
88 intermec direct protocol v7.80 programmer’s reference manual chapter 9 — advanced features 9.1 specifying complex bar codes complex two-dimensional bar codes or dot codes, for example pdf417, maxicode, or leb, require many specifying parameters. Therefore, there is a complex instruction that allo...
Page 95: Unicode Fonts
Intermec direct protocol v7.80 programmer’s reference manual 89 chapter 9 — advanced features 9.2 using international character sets the data input to text fi elds and bar codes takes the form of an ascii string. Even compound data, such as... Prtxt "label no.";cnt1$;" date ";date$("f") ...Is expand...
Page 96: Nasc and Nascd Tables
90 intermec direct protocol v7.80 programmer’s reference manual chapter 9 — advanced features nasc and nascd tables there are many national and international standards for mapping ascii strings to strings of unicode. The intermec direct protocol v7.80 pro- vides support for virtually all of these. T...
Page 97: Double-Byte Fonts
Intermec direct protocol v7.80 programmer’s reference manual 91 chapter 9 — advanced features double-byte fonts as discussed above, the ascii data input to text fi elds and human readable parts of bar codes can contain a mixture of single-byte and double-byte codes, which are mapped to unicodes by t...
Page 98
92 intermec direct protocol v7.80 programmer’s reference manual chapter 9 — advanced features.
Page 99: Character Sets and
Intermec direct protocol v7.80 programmer’s reference manual 93 10 character sets and fonts this chapter lists the various single-byte character sets used in intermec direct protocol v7.80 and provides printout samples of the resident fonts..
Page 100: 10.1 Character Sets
94 intermec direct protocol v7.80 programmer’s reference manual chapter 10 — character sets and fonts 10.1 character sets this chapter contains the various single-byte character sets, that can be selected using the nasc instruction. They are illustrated using the font ”swiss 721 bt”. Other fonts may...
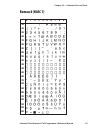
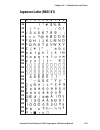
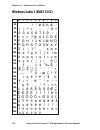
Page 101: Roman 8 (Nasc 1)
0 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 110 120 130 140 150 160 170 180 190 200 210 220 230 240 250 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 intermec direct protocol v7.80 programmer’s reference manual 95 chapter 10 — character sets and fonts roman 8 (nasc 1).
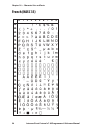
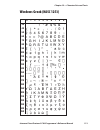
Page 102: French (Nasc 33)
0 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 110 120 130 140 150 160 170 180 190 200 210 220 230 240 250 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 96 intermec direct protocol v7.80 programmer’s reference manual chapter 10 — character sets and fonts french (nasc 33).
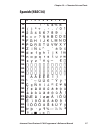
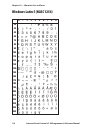
Page 103: Spanish (Nasc 34)
0 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 110 120 130 140 150 160 170 180 190 200 210 220 230 240 250 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 intermec direct protocol v7.80 programmer’s reference manual 97 chapter 10 — character sets and fonts spanish (nasc 34).
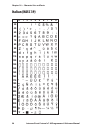
Page 104: Italian (Nasc 39)
0 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 110 120 130 140 150 160 170 180 190 200 210 220 230 240 250 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 98 intermec direct protocol v7.80 programmer’s reference manual chapter 10 — character sets and fonts italian (nasc 39).
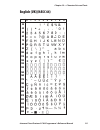
Page 105: English (Uk) (Nasc 44)
0 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 110 120 130 140 150 160 170 180 190 200 210 220 230 240 250 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 intermec direct protocol v7.80 programmer’s reference manual 99 chapter 10 — character sets and fonts english (uk) (nasc 44).
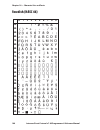
Page 106: Swedish (Nasc 46)
0 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 110 120 130 140 150 160 170 180 190 200 210 220 230 240 250 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 100 intermec direct protocol v7.80 programmer’s reference manual chapter 10 — character sets and fonts swedish (nasc 46).
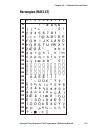
Page 107: Norwegian (Nasc 47)
0 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 110 120 130 140 150 160 170 180 190 200 210 220 230 240 250 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 intermec direct protocol v7.80 programmer’s reference manual 101 chapter 10 — character sets and fonts norwegian (nasc 47).
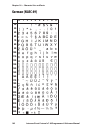
Page 108: German (Nasc 49)
0 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 110 120 130 140 150 160 170 180 190 200 210 220 230 240 250 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 102 intermec direct protocol v7.80 programmer’s reference manual chapter 10 — character sets and fonts german (nasc 49).
Page 109: Japanese Latin (Nasc 81)
0 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 110 120 130 140 150 160 170 180 190 200 210 220 230 240 250 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 intermec direct protocol v7.80 programmer’s reference manual 103 chapter 10 — character sets and fonts japanese latin (nasc 81).
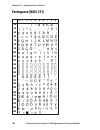
Page 110: Portuguese (Nasc 351)
0 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 110 120 130 140 150 160 170 180 190 200 210 220 230 240 250 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 104 intermec direct protocol v7.80 programmer’s reference manual chapter 10 — character sets and fonts portuguese (nasc 351).
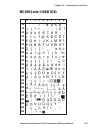
Page 111: Ms-Dos Latin 1 (Nasc 850)
0 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 110 120 130 140 150 160 170 180 190 200 210 220 230 240 250 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 intermec direct protocol v7.80 programmer’s reference manual 105 chapter 10 — character sets and fonts ms-dos latin 1 (nasc 850).
Page 112: Ms-Dos Greek 1 (Nasc 851)
0 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 110 120 130 140 150 160 170 180 190 200 210 220 230 240 250 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 106 intermec direct protocol v7.80 programmer’s reference manual chapter 10 — character sets and fonts ms-dos greek 1 (nasc 851).
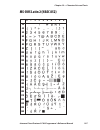
Page 113: Ms-Dos Latin 2 (Nasc 852)
0 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 110 120 130 140 150 160 170 180 190 200 210 220 230 240 250 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 intermec direct protocol v7.80 programmer’s reference manual 107 chapter 10 — character sets and fonts ms-dos latin 2 (nasc 852).
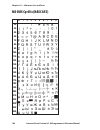
Page 114: Ms-Dos Cyrillic (Nasc 855)
0 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 110 120 130 140 150 160 170 180 190 200 210 220 230 240 250 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 108 intermec direct protocol v7.80 programmer’s reference manual chapter 10 — character sets and fonts ms-dos cyrillic (nasc 855).
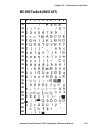
Page 115: Ms-Dos Turkish (Nasc 857)
0 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 110 120 130 140 150 160 170 180 190 200 210 220 230 240 250 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 intermec direct protocol v7.80 programmer’s reference manual 109 chapter 10 — character sets and fonts ms-dos turkish (nasc 857).
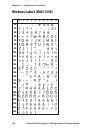
Page 116: Windows Latin 2 (Nasc 1250)
0 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 110 120 130 140 150 160 170 180 190 200 210 220 230 240 250 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 110 intermec direct protocol v7.80 programmer’s reference manual chapter 10 — character sets and fonts windows latin 2 (nasc 1250).
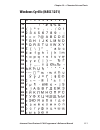
Page 117: Windows Cyrillic (Nasc 1251)
0 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 110 120 130 140 150 160 170 180 190 200 210 220 230 240 250 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 intermec direct protocol v7.80 programmer’s reference manual 111 chapter 10 — character sets and fonts windows cyrillic (nasc 1251).
Page 118: Windows Latin 1 (Nasc 1252)
0 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 110 120 130 140 150 160 170 180 190 200 210 220 230 240 250 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 112 intermec direct protocol v7.80 programmer’s reference manual chapter 10 — character sets and fonts windows latin 1 (nasc 1252).
Page 119: Windows Greek (Nasc 1253)
0 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 110 120 130 140 150 160 170 180 190 200 210 220 230 240 250 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 intermec direct protocol v7.80 programmer’s reference manual 113 chapter 10 — character sets and fonts windows greek (nasc 1253).
Page 120: Windows Latin 5 (Nasc 1254)
0 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 110 120 130 140 150 160 170 180 190 200 210 220 230 240 250 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 114 intermec direct protocol v7.80 programmer’s reference manual chapter 10 — character sets and fonts windows latin 5 (nasc 1254).
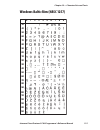
Page 121
0 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 110 120 130 140 150 160 170 180 190 200 210 220 230 240 250 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 intermec direct protocol v7.80 programmer’s reference manual 115 chapter 10 — character sets and fonts windows baltic rim (nasc 1257).
Page 122: Pcmap (Nasc -1)
0 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 110 120 130 140 150 160 170 180 190 200 210 220 230 240 250 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 116 intermec direct protocol v7.80 programmer’s reference manual chapter 10 — character sets and fonts pcmap (nasc -1).
Page 123: Ansi (Nasc -2)
0 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 110 120 130 140 150 160 170 180 190 200 210 220 230 240 250 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 intermec direct protocol v7.80 programmer’s reference manual 117 chapter 10 — character sets and fonts ansi (nasc -2).
Page 124: 10.2 Resident Fonts
118 intermec direct protocol v7.80 programmer’s reference manual chapter 10 — character sets and fonts 10.2 resident fonts all fonts in this list contains the euro currency sign (€) with the excep- tion of ocr-a bt, ocr-b 10 pitch bt, and dingdings swa..
Page 125: Error Messages
Intermec direct protocol v7.80 programmer’s reference manual 119 11 error messages this chapter lists the number and messages for the various errors conditions..
Page 126
120 intermec direct protocol v7.80 programmer’s reference manual chapter 11 — error messages code message/explanation 0 no error. 1 syntax error. 2 unbalanced parenthesis. 3 feature not implemented. 4 evaluation syntax error. 5 unrecognized token. 6 tokenized line too long. 7 evaluation stack overfl ...
Page 127
Intermec direct protocol v7.80 programmer’s reference manual 121 chapter 11 — error messages code message/explanation 1008 lss too low. 1009 invalid parameter. 1010 hardware error. 1011 i/o error. 1012 too many fi les opened. 1013 device not found. 1014 file not found. 1015 file is read-only. 1016 il...
Page 128
122 intermec direct protocol v7.80 programmer’s reference manual chapter 11 — error messages code message/explanation 1223 single byte map table is missing. 1224 character map function is missing. 1225 double byte font is not selected. 1301 index outside collection bounds. 1302 collection could not ...
Page 129: Reference Lists
Intermec direct protocol v7.80 programmer’s reference manual 123 12 reference lists this chapter lists the instructions in alphabetic order with short explanations and references to the related chapters. It also provides a shortlist of instruction syntaxes..
Page 130
124 intermec direct protocol v7.80 programmer’s reference manual chapter 12 — reference lists 12.1 instructions in alphabetical order instruction chapter purpose align (an) 4.2 specifying which part (anchor point) of a text, bar code field, image field, line, or box will be positioned at the inserti...
Page 131
Intermec direct protocol v7.80 programmer’s reference manual 125 chapter 12 — reference lists instruction chapter purpose date$ 4.9, 6.3, 7.3 setting or returning the current date. Dateadd$ 4.9 returning a new date after a number of days have been added to, or subtracted from, the current date or op...
Page 132
126 intermec direct protocol v7.80 programmer’s reference manual chapter 12 — reference lists instruction chapter purpose formfeed (ff) 5.1 activating the paper feed mechanism in order to feed out or pull back a certain length of the paper web. Fre 8.1 returning the number of free bytes in a part of...
Page 133
Intermec direct protocol v7.80 programmer’s reference manual 127 chapter 12 — reference lists instruction chapter purpose map 6.12 changing the ascii value of a character when received on the standard in channel, or optionally on another specified communica- tion channel. Name date$ 6.4 formatting t...
Page 134
128 intermec direct protocol v7.80 programmer’s reference manual chapter 12 — reference lists instruction chapter purpose remove image/font 8.2 removing a specified image or bitmap font from the printer’s memory. Reprint on/off 5.3 enabling/disabling reprinting. Setstdio 6.2 selecting standard in an...
Page 138
132 intermec direct protocol v7.80 programmer’s reference manual chapter 12 — reference lists.
Page 140
Intermec technologies corporation corporate headquarters 6001 36th avenue west everett, wa 98203 u.S.A. Tel 425.348.2600 fax 425.355.9551 www.Intermec.Com *1-960633-00* intermec direct protocol v7.80 programmer’s reference manual *1-960633-00*.