- DL manuals
- Vacon
- Controller
- 100 flow
- Applications Manual
Vacon 100 flow Applications Manual
Summary of 100 flow
Page 1
Vacon 100 flow ac drives application manual ®.
Page 3: Preface
Preface document details document id: dpd01083g date: 12.6.2017 software version: fw0159v017 about this manual this manual is copyright of vacon ltd. All rights reserved. The manual is subject to change without prior notice. The language of the original instructions is english. In this manual, you c...
Page 4
• how to use the parameters. • digital and analogue input programming. • application-specific functions. Chapter 11, fault tracing • the faults and their causes. • resetting the faults. Chapter 12, appendix • data on the different default values of the applications. This manual includes a large quan...
Page 5
Functions of the vacon ® ac drive • you can select the necessary application for your process: standard, hvac, pid control, multi-pump (single drive) or multi-pump (multidrive). The drive automatically makes some of the necessary settings, which makes the commissioning easy. • wizards for the first ...
Page 6
Vacon · 6 local contacts: http://drives.Danfoss.Com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/.
Page 7: Table of Contents
Table of contents preface document details 3 about this manual 3 functions of the vacon ® ac drive 5 1 quick startup guide 12 1.1 control panel and keypad 12 1.2 the displays 12 1.3 first startup 13 1.4 description of the applications 14 1.4.1 standard and hvac applications 14 1.4.2 pid control appl...
Page 8
4 monitoring menu 113 4.1 monitor group 113 4.1.1 multimonitor 113 4.1.2 trend curve 114 4.1.3 basic 117 4.1.4 i/o 119 4.1.5 temperature inputs 119 4.1.6 extras and advanced 120 4.1.7 timer functions monitoring 121 4.1.8 pid controller monitoring 122 4.1.9 external pid controller monitoring 123 4.1....
Page 9
7 i/o and hardware menu 191 7.1 basic i/o 191 7.2 option board slots 193 7.3 real time clock 194 7.4 power unit settings 194 7.5 keypad 195 7.6 fieldbus 196 8 user settings, favourites and user level menus 197 8.1 user settings 197 8.1.1 user settings 197 8.1.2 parameter backup 198 8.2 favourites 19...
Page 10
10.5 ramps and brakes setup 247 10.5.1 ramp 1 247 10.5.2 ramp 2 248 10.5.3 start magnetising 249 10.5.4 dc brake 250 10.5.5 flux braking 250 10.6 i/o configuration 250 10.6.1 programming of digital and analogue inputs 250 10.6.2 default functions of programmable inputs 261 10.6.3 digital inputs 261 ...
Page 11
10.17 maintenance counters 342 10.18 fire mode 343 10.19 motor preheat function 346 10.20 drive customizer 347 10.21 pump control 348 10.21.1 auto-cleaning 348 10.21.2 jockey pump 350 10.21.3 priming pump 352 10.21.4 anti-blocking function 353 10.21.5 frost protection 353 10.21.6 flow switch 354 10....
Page 12: Quick Startup Guide
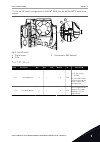
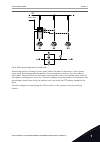
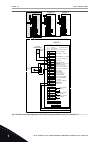
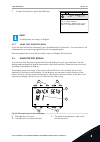
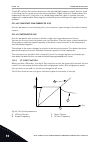
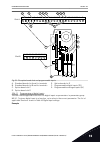
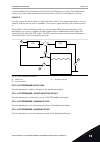
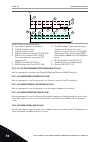
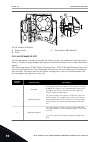
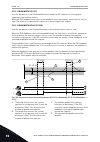
1 quick startup guide 1.1 control panel and keypad the control panel is the interface between the ac drive and the user. With the control panel, you can control the speed of a motor and monitor the status of the ac drive. You can also set the parameters of the ac drive. A b c i h d g f e fig. 1: the...
Page 13
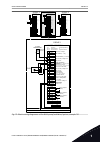
Stop ready i/o main menu a b c d e f h g quick setup ( 17 ) monitor ( 5 ) parameters ( 12 ) m1 id: fig. 2: the graphical display a. The first status field: stop/run b. The rotation direction of the motor c. The second status field: ready/not ready/fault d. The alarm field: alarm/- e. The control pla...
Page 14
1 language selection (p6.1) the selection is different in all the language packages 2 daylight saving* (p5.5.5) russia us eu off 3 time* (p5.5.2) hh:mm:ss 4 year* (p5.5.4) yyyy 5 date* (p5.5.3) dd.Mm. * if a battery is installed, you see these steps 6 run startup wizard? Yes no select yes and push t...
Page 15
When you control the drive with the i/o terminal, the frequency reference signal is connected to ai1 (0…10v) or ai2 (4…20ma). The connection is specified by the type of the signal. There are also 3 preset frequency references available. You can activate the preset frequency references with di4 and d...
Page 16
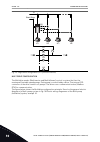
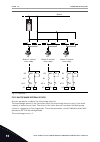
Di4 di5 **) *) modbus rtu, n2, bacnet 1 6 2 3 4 5 18 19 30 12 7 13 8 9 10 14 15 16 21 22 23 11 17 a b 24 25 26 32 33 28 29 ma fault run run ao1- +24 vin 24 v out gnd gnd di1 di2 di3 di4 di5 di6 r o1/1 nc r o1/2 cm r o1/3 no cm cm rs485 rs485 r o2/1 nc r o2/2 cm r o2/3 no r o3/2 cm r o3/3 no standard...
Page 17
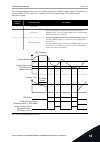
** = for the dip switch configurations in vacon ® 100 x, see the vacon 100 ® x installation manual. A b c fig. 5: the dip switch a. Digital inputs b. Float c. Connected to gnd (default) table 2: m1.1 wizards index parameter min max unit default id description 1.1.1 startup wizard 0 1 0 1170 0 = do n...
Page 18
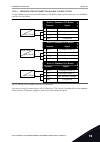
Table 3: m1 quick setup index parameter min max unit default id description 1.2 application 0 4 0 212 0 = standard 1 = hvac 2 = pid control 3 = multi-pump (single drive) 4 = multi-pump (multi- drive) 1.3 minimum frequency reference 0.00 p1.4 hz 0.0 101 the minimum fre- quency reference that is accep...
Page 19
Table 3: m1 quick setup index parameter min max unit default id description 1.10 motor nominal fre- quency 8.0 320.0 hz 50 / 60 111 find this value f n on the nameplate of the motor. 1.11 motor nominal speed 24 19200 rpm varies 112 find this value n n on the nameplate of the motor. 1.12 motor nomina...
Page 20
Table 3: m1 quick setup index parameter min max unit default id description 1.18 automatic reset 0 1 0 731 0 = disabled 1 = enabled 1.19 response to external fault 0 3 2 701 0 = no action 1 = alarm 2 = fault (stop accord- ing to stop mode) 3 = fault (stop by coasting) 1.20 response to ai low fault 0...
Page 21
Table 3: m1 quick setup index parameter min max unit default id description 1.22 i/o control refer- ence a selection 0 20 5 117 the selection of the frequency reference source when the con- trol place is i/o a. 0 = pc 1 = preset frequency 0 2 = keypad reference 3 = fieldbus 4 = ai1 5 = ai2 5 = ai1+a...
Page 22
Table 3: m1 quick setup index parameter min max unit default id description 1.29 ro3 function 0 74 1 11007 see p3.5.3.2.1 1.30 ao1 function 0 31 2 10050 see p3.5.4.1.1 table 4: m1.31 standard / m1.32 hvac index parameter min max unit default id description 1.31.1 preset frequency 1 p1.3 p1.4 hz 10.0...
Page 23
1 6 2 3 4 5 18 19 30 12 7 13 8 9 10 14 15 16 21 22 23 11 17 a b 24 25 26 28 29 32 33 modbus rtu + - *) **) ma fault run run ao1-/gnd +24 vin 24 v out gnd gnd di1 di2 di3 di4 di5 di6 cm cm rs485 rs485 standard i/o board terminal signal description +10vref ai1+ ai1- ai2+ ai2- 24vout reference output a...
Page 24
** = for the dip switch configurations in vacon ® 100 x, see the vacon ® 100 x installation manual. A b c fig. 7: the dip switch a. Digital inputs b. Float c. Connected to gnd (default) table 5: m1.1 wizards index parameter min max unit default id description 1.1.1 startup wizard 0 1 0 1170 0 = do n...
Page 25
Table 6: m1 quick setup index parameter min max unit default id description 1.2 application 0 4 2 212 0 = standard 1 = hvac 2 = pid control 3 = multi-pump (single drive) 4 = multi-pump (multi- drive) 1.3 minimum frequency reference 0.00 p1.4 hz 0.0 101 the minimum fre- quency reference that is accep...
Page 26
Table 6: m1 quick setup index parameter min max unit default id description 1.10 motor nominal fre- quency 8.0 320.0 hz 50.0 / 60.0 111 find this value f n on the nameplate of the motor. 1.11 motor nominal speed 24 19200 rpm varies 112 find this value n n on the nameplate of the motor. 1.12 motor no...
Page 27
Table 6: m1 quick setup index parameter min max unit default id description 1.18 automatic reset 0 1 0 731 0 = disabled 1 = enabled 1.19 response to external fault 0 3 2 701 0 = no action 1 = alarm 2 = fault (stop accord- ing to stop mode) 3 = fault (stop by coasting) 1.20 response to ai low fault 0...
Page 28
Table 6: m1 quick setup index parameter min max unit default id description 1.22 i/o control refer- ence a selection 1 20 6 117 the selection of the frequency reference source when the con- trol place is i/o a. 0 = pc 1 = preset frequency 0 2= keypad reference 3 = fieldbus 4 = ai1 5 = ai2 6 = ai1+ai...
Page 29
Table 7: m1.33 pid control index parameter min max unit default id description 1.33.1 pid gain 0.00 100.00 % 100.00 118 if the value of the parameter is set to 100%, a change of 10% in the error value cau- ses the controller out- put to change by 10%. 1.33.2 pid integration time 0.00 600.00 s 1.00 1...
Page 30
Table 7: m1.33 pid control index parameter min max unit default id description 1.33.11 sp1 sleep delay 0 3000 s 0 1017 the minimum quantity of time that the fre- quency stays below the sleep level before the drive stops. 0 = not used 1.33.12 sp1 wake up level varies varies varies varies 1018 the wak...
Page 31
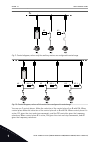
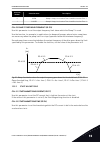
Pt start / stop fig. 8: multi-pump (single drive) configuration autochange function (change of start order) makes the wear of the motors in the system more equal. Autochange function monitors the running hours and sets the start order of each motor. The motor that has the lowest running hours starts...
Page 32
K2 k3 fig. 9: control diagram, where only the auxiliary motors are configured to autochange k1 k2 k2 k1.1 k2.1 k3.1 fig. 10: control diagram, where all the motors are configured to autochange you can use 2 control places. Make the selection of the control place a or b with di6. When control place ma...
Page 33
You can configure all the drive outputs freely in all the applications. There are 1 analogue output (output frequency) and 3 relay outputs (run, fault, ready) available on the basic i/o board. Quick startup guide vacon · 33 local contacts: http://drives.Danfoss.Com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/ 1.
Page 34
1 6 2 3 4 5 18 19 30 12 7 13 8 9 10 14 15 16 21 22 23 11 17 a b 24 25 26 28 29 modbus rtu *) 32 33 **) + - a1 a1 a1 a2 a2 a2 ma motor 1 control (multi-pump k2 contactor) motor 2 control (multi-pump k2 contactor) motor 3 control (multi-pump k2 contactor) ao1-/gnd +24v in gnd gnd di1 di2 di3 di4 di5 d...
Page 35
** = for the dip switch configurations in vacon ® 100 x, see the vacon ® 100 x installation manual. A b c fig. 12: the dip switch a. Digital inputs b. Float c. Connected to gnd (default) table 8: m1.1 wizards index parameter min max unit default id description 1.1.1 startup wizard 0 1 0 1170 0 = do ...
Page 36
Table 9: m1 quick setup index parameter min max unit default id description 1.2 application 0 4 2 212 0 = standard 1 = hvac 2 = pid control 3 = multi-pump (single drive) 4 = multi-pump (multi- drive) 1.3 minimum frequency reference 0.00 p1.4 hz 0.0 101 the minimum fre- quency reference that is accep...
Page 37
Table 9: m1 quick setup index parameter min max unit default id description 1.10 motor nominal fre- quency 8.0 320.0 hz 50.0 / 60.0 111 find this value f n on the nameplate of the motor. 1.11 motor nominal speed 24 19200 rpm varies 112 find this value n n on the nameplate of the motor. 1.12 motor no...
Page 38
Table 9: m1 quick setup index parameter min max unit default id description 1.18 automatic reset 0 1 0 731 0 = disabled 1 = enabled 1.19 response to external fault 0 3 2 701 0 = no action 1 = alarm 2 = fault (stop accord- ing to stop mode) 3 = fault (stop by coasting) 1.20 response to ai low fault 0...
Page 39
Table 9: m1 quick setup index parameter min max unit default id description 1.22 i/o control refer- ence a selection 1 20 6 117 the selection of the frequency reference source when the con- trol place is i/o a. 0 = pc 1 = preset frequency 0 2= keypad reference 3 = fieldbus 4 = ai1 5 = ai2 6 = ai1+ai...
Page 40
Table 10: m1.34 multi-pump (single drive) index parameter min max unit default id description 1.34.1 pid gain 0.00 100.00 % 100.00 118 if the value of the parameter is set to 100%, a change of 10% in the error value causes the controller output to change by 10%. 1.34.2 pid integration time 0.00 600....
Page 41
Table 10: m1.34 multi-pump (single drive) index parameter min max unit default id description 1.34.10 sp1 sleep fre- quency limit 0.0 320.0 hz 0.0 1016 the drive goes to the sleep mode when the output frequency stays below this limit for longer than is specified by parameter sleep delay. 0 = not use...
Page 42
Table 10: m1.34 multi-pump (single drive) index parameter min max unit default id description 1.34.16 autochange 0 2 1 1027 disable/enable the rotation of the start order and the pri- ority of the motors. 0 = disabled 1 = enabled (inter- val) 2 = enabled (week- days) 1.34.17 autochanged pump 0 1 1 1...
Page 43
Table 10: m1.34 multi-pump (single drive) index parameter min max unit default id description 1.34.23 bandwidth 0 100 % 10 1097 the percent of the setpoint. For exam- ple, setpoint = 5 bar bandwidth = 10% when the feedback value stays between 4.5 and 5.5 bar, the motor stays connected. 1.34.24 bandw...
Page 44
The checklist for the commissioning a multi-pump (multidrive) system is in 10.16.1 multi- pump (multidrive) commissioning checklist. Each motor has a drive controls that applicable motor. The drives of the system communicate with each other by modbus rtu communication. Pt fb start / stop fig. 13: mu...
Page 45
A p1 p2 p3 f max f min rpm t fig. 14: control in the multifollower mode the figure below shows an example of the multimaster mode, where the speed of the regulating motor locks to the constant production speed b, when next motor starts. Curves a show the regulating of the pumps. P1 p2 p3 a b f max f...
Page 46
1 6 2 3 4 5 18 19 30 12 7 13 8 9 10 14 15 16 21 22 23 11 17 a b 24 25 26 28 29 32 33 *) **) + - ma fault run run ao1- +24 vin actual value gnd gnd di1 di2 di3 di4 di5 di6 ro1/1 nc ro1/2 cm ro1/3 no cm cm rs485 rs485 ro2/1 nc ro2/2 cm ro2/3 no ti1+ ti1- standard i/o board terminal signal description ...
Page 47
** = for the dip switch configurations in vacon vacon ® x, see the vacon ® 100 x installation manual. A b c fig. 17: the dip switch a. Digital inputs b. Float c. Connected to gnd (default) each drive has a pressure sensor. When the redundancy level is high, the drive and the pressure sensors are red...
Page 48
1 +10v ref 2 ai1 + 3 ai1 - 4 ai2 + 5 ai2 - 6 +24v out 7 gnd 8 din1 9 din2 10 din3 11 cm 12 +24v out 13 gnd 14 din4 15 din5 16 din6 17 cm 18 ao1 + 19 ao1 - 30 +24v in a rs485 b rs485 21 ro1 22 ro1 23 ro1 24 ro2 25 ro2 26 ro2 32 ro3 33 ro3 0 auto man 2-wire transmitter p i pressure sensor 1 1s1 2 4 1 ...
Page 49
1 +10v ref 2 ai1 + 3 ai1 - 4 ai2 + 5 ai2 - 6 +24v out 7 gnd 8 din1 9 din2 10 din3 11 cm 12 +24v out 13 gnd 14 din4 15 din5 16 din6 17 cm 18 ao1 + 19 ao1 - 30 +24v in a rs485 b rs485 21 ro1 22 ro1 23 ro1 24 ro2 25 ro2 26 ro2 32 ro3 33 ro3 0 auto man 2-wire transmitter p i pressure sensor 1 1s1 2 4 1 ...
Page 50
1 +10v ref 2 ai1 + 3 ai1 - 4 ai2 + 5 ai2 - 6 +24v out 7 gnd 8 din1 9 din2 10 din3 11 cm 12 +24v out 13 gnd 14 din4 15 din5 16 din6 17 cm 18 ao1 + 19 ao1 - 30 +24v in a rs485 b rs485 21 ro1 22 ro1 23 ro1 24 ro2 25 ro2 26 ro2 32 ro3 33 ro3 0 auto man 2-wire transmitter p i pressure sensor 1 1s1 2 4 1 ...
Page 51
1 sensor is connected to all the drives. The redundancy level of the system is low because only the drives are redundant. • if there is a drive failure, the next drive starts to operate as master. • if there is a sensor failure, the system stops. An individual switch that has an auto, off and man se...
Page 52
1 +10v ref 2 ai1 + 3 ai1 - 4 ai2 + 5 ai2 - 6 +24v out 7 gnd 8 din1 9 din2 10 din3 11 cm 12 +24v out 13 gnd 14 din4 15 din5 16 din6 17 cm 18 ao1 + 19 ao1 - 30 +24v in a rs485 b rs485 21 ro1 22 ro1 23 ro1 24 ro2 25 ro2 26 ro2 32 ro3 33 ro3 0 auto man 2-wire transmitter p i pressure sensor 1 1s1 2 4 1 ...
Page 53
1 +10v ref 2 ai1 + 3 ai1 - 4 ai2 + 5 ai2 - 6 +24v out 7 gnd 8 din1 9 din2 10 din3 11 cm 12 +24v out 13 gnd 14 din4 15 din5 16 din6 17 cm 18 ao1 + 19 ao1 - 30 +24v in a rs485 b rs485 21 ro1 22 ro1 23 ro1 24 ro2 25 ro2 26 ro2 32 ro3 33 ro3 0 auto man 2-wire transmitter p i pressure sensor 1 1s1 2 4 1 ...
Page 54
1 +10v ref 2 ai1 + 3 ai1 - 4 ai2 + 5 ai2 - 6 +24v out 7 gnd 8 din1 9 din2 10 din3 11 cm 12 +24v out 13 gnd 14 din4 15 din5 16 din6 17 cm 18 ao1 + 19 ao1 - 30 +24v in a rs485 b rs485 21 ro1 22 ro1 23 ro1 24 ro2 25 ro2 26 ro2 32 ro3 33 ro3 0 auto man 2-wire transmitter p i pressure sensor 1 1s1 2 4 1 ...
Page 55
2 drives have individual pressure sensors. The redundancy level of the system is medium because the drives and the pressure sensors are duplicated. • if there is a drive failure, the second drive starts to operate as master. • if there is a sensor failure, the second drive (that has a separate senso...
Page 56
1 +10v ref 2 ai1 + 3 ai1 - 4 ai2 + 5 ai2 - 6 +24v out 7 gnd 8 din1 9 din2 10 din3 11 cm 12 +24v out 13 gnd 14 din4 15 din5 16 din6 17 cm 18 ao1 + 19 ao1 - 30 +24v in a rs485 b rs485 21 ro1 22 ro1 23 ro1 24 ro2 25 ro2 26 ro2 32 ro3 33 ro3 0 auto man 2-wire transmitter p i pressure sensor 1 1s1 2 4 1 ...
Page 57
1 +10v ref 2 ai1 + 3 ai1 - 4 ai2 + 5 ai2 - 6 +24v out 7 gnd 8 din1 9 din2 10 din3 11 cm 12 +24v out 13 gnd 14 din4 15 din5 16 din6 17 cm 18 ao1 + 19 ao1 - 30 +24v in a rs485 b rs485 21 ro1 22 ro1 23 ro1 24 ro2 25 ro2 26 ro2 32 ro3 33 ro3 0 auto man 2-wire transmitter p i pressure sensor 1 1s1 2 4 1 ...
Page 58
1 +10v ref 2 ai1 + 3 ai1 - 4 ai2 + 5 ai2 - 6 +24v out 7 gnd 8 din1 9 din2 10 din3 11 cm 12 +24v out 13 gnd 14 din4 15 din5 16 din6 17 cm 18 ao1 + 19 ao1 - 30 +24v in a rs485 b rs485 21 ro1 22 ro1 23 ro1 24 ro2 25 ro2 26 ro2 32 ro3 33 ro3 0 auto man 2-wire transmitter p i pressure sensor 1 1s1 2 4 1 ...
Page 59
1 common pressure sensor is connected to 2 drives. The redundancy level of the system is low because only the drives are redundant. • if there is a drive failure, the second drive starts to operate as master. • if there is a sensor failure, the system stops. An individual switch that has an auto, of...
Page 60
+ - 0 p i 2 4 1 3 drive 1 vacon 100 flow p1.2 application = multipump(multidrive) p3.15.3 pump id number = 1 p3.15.4 start & feedback = signals connected 2-wire transmitter pressure sensor 1 reference voltage not used (0...10v) output frequency (0...20ma) pid feedback (4...20ma) 24v auxilary voltage...
Page 61
0 2 4 1 3 drive 2 vacon 100 flow p1.2 application = multipump(multidrive) p3.15.3 pump id number = 2 p3.15.4 start & feedback = signals connected reference voltage not used (0...10v) output frequency (0...20ma) pid feedback (4...20ma) 24v auxilary voltage out 24v auxilary voltage in i/o ground i/o g...
Page 62
0 2 4 1 3 drive 3 vacon 100 flow p1.2 application = multipump(multidrive) p3.15.3 pump id number = 3 p3.15.4 start & feedback = signals connected reference voltage not used (0...10v) output frequency (0...20ma) pid feedback (4...20ma) 24v auxilary voltage out 24v auxilary voltage in i/o ground i/o g...
Page 63
1 pressure sensor is connected to the first drive. The system is not redundant, because the system stops if there is a drive or sensor failure. Quick startup guide vacon · 63 local contacts: http://drives.Danfoss.Com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/ 1.
Page 64
+ - p i 2 1 drive 1 vacon 100 flow p1.2 application = multipump(multidrive) p3.15.3 pump id number = 1 p3.15.4 start & feedback = signals connected 2-wire transmitter pressure sensor 1 reference voltage not used (0...10v) output frequency (0...20ma) pid feedback (4...20ma) 24v auxilary voltage out 2...
Page 65
Drive 2 vacon 100 flow p1.2 application = multipump(multidrive) p3.15.3 pump id number = 2 p3.15.4 start & feedback = signals connected reference voltage not used (0...10v) output frequency (0...20ma) pid feedback (4...20ma) 24v auxilary voltage out 24v auxilary voltage in i/o ground i/o ground faul...
Page 66
Drive 3 vacon 100 flow p1.2 application = multipump(multidrive) p3.15.3 pump id number = 3 p3.15.4 start & feedback = signals connected reference voltage not used (0...10v) output frequency (0...20ma) pid feedback (4...20ma) 24v auxilary voltage out 24v auxilary voltage in i/o ground i/o ground faul...
Page 67
Table 11: m1.1 wizards index parameter min max unit default id description 1.1.1 startup wizard 0 1 0 1170 0 = do not activate 1 = activate the selection activate starts the startup wiz- ard (see chapter 1.3 first startup). 1.1.2 fire mode wizard 0 1 0 1672 the selection activate starts the fire mod...
Page 68
Table 12: m1 quick setup index parameter min max unit default id description 1.2 application 0 4 2 212 0 = standard 1 = hvac 2 = pid control 3 = multi-pump (sin- gle drive) 4 = multi-pump (multidrive) 1.3 minimum frequency reference 0.00 p1.4 hz 0.0 101 the minimum fre- quency reference that is acce...
Page 69
Table 12: m1 quick setup index parameter min max unit default id description 1.10 motor nom- inal fre- quency 8.0 320.0 hz 50.0 / 60.0 111 find this value f n on the nameplate of the motor. 1.11 motor nom- inal speed 24 19200 rpm varies 112 find this value n n on the nameplate of the motor. 1.12 mot...
Page 70
Table 12: m1 quick setup index parameter min max unit default id description 1.18 automatic reset 0 1 0 731 0 = disabled 1 = enabled 1.19 response to external fault 0 3 2 701 0 = no action 1 = alarm 2 = fault (stop according to stop mode) 3 = fault (stop by coasting) 1.20 response to ai low fault 0 ...
Page 71
Table 12: m1 quick setup index parameter min max unit default id description 1.22 i/o control reference a selection 1 20 6 117 the selection of the frequency reference source when the control place is i/o a. 0 = pc 1 = preset fre- quency 0 2= keypad reference 3 = fieldbus 4 = ai1 5 = ai2 6 = ai1+ai2...
Page 72
Table 12: m1 quick setup index parameter min max unit default id description 1.28 ro2 func- tion 0 74 3 11004 see p3.5.3.2.1 1.29 ro3 func- tion 0 74 1 11007 see p3.5.3.2.1 1.30 ao1 func- tion 0 31 2 10050 see p3.5.4.1.1 vacon · 72 quick startup guide 1 local contacts: http://drives.Danfoss.Com/danf...
Page 73
Table 13: m1.35 multi-pump (multidrive) index parameter min max unit default id description 1.35.1 pid gain 0.00 100.00 % 100.00 118 if the value of the parameter is set to 100%, a change of 10% in the error value causes the controller output to change by 10%. 1.35.2 pid integration time 0.00 600.00...
Page 74
Table 13: m1.35 multi-pump (multidrive) index parameter min max unit default id description 1.35.10 sp1 sleep fre- quency limit 0.0 320.0 hz 0.0 1016 the drive goes to the sleep mode when the output frequency stays below this limit for longer than is specified by parameter sleep delay. 0 = not used ...
Page 75
Table 13: m1.35 multi-pump (multidrive) index parameter min max unit default id description 1.35.16 start and feed- back signals 0 2 1 1782 use this parameter to select if the start signal and/or the pidfeedback sig- nals are connected to the drive. 0 = not connected 1 = only start sig- nal connecte...
Page 76
Table 13: m1.35 multi-pump (multidrive) index parameter min max unit default id description 1.35.21 autochange days 0 127 1786 range: monday to sunday 1.35.22 autochange time of day time 1787 range: 00:00:00 to 23:59:59 1.35.23 autochange: frequency limit 0.00 p3.3.1.2 hz 25:00 1031 these parameters...
Page 77: Wizards
2 wizards 2.1 standard application wizard the application wizard helps you to set the basic parameters that are related to the application. To start the standard application wizard, set the value standard to parameter p1.2 application (id 212) in the keypad. Note! If you start the standard applicati...
Page 78
2.2 hvac application wizard the application wizard helps you to set the basic parameters that are related to the application. To start the hvac application wizard, set the value hvac to parameter p1.2 application (id 212) in the keypad. 1 select the type or process (or application) that you control....
Page 79
11 set a value for p3.4.1.2 acceleration time 1 range: 0.1-3000.0 s 12 set a value for p3.4.1.3 deceleration time 1 range: 0.1-3000.0 s next the wizard goes to steps that are specified by the application. 13 select the control place (where you give the start and stop commands and the frequency refer...
Page 80
1 set a value for p3.1.2.2 motor type (so that it agrees with the nameplate of the motor) pm motor induction motor reluctance motor 2 set a value for p3.1.1.1 motor nominal voltage (so that it agrees with the nameplate of the motor) range: varies 3 set a value for p3.1.1.2 motor nominal frequency (s...
Page 81
17 set the signal range of the analogue input 0 = 0-10v / 0-20ma 1 = 2-10v / 4-20ma 18 set a value for p3.13.1.8 error inversion 0 = normal 1 = inverted 19 set a value for p3.13.2.6 setpoint source selection see table setpoints in table 76 feedback set- tings if you select an analogue input signal, ...
Page 82
1 set a value for p3.1.2.2 motor type (so that it agrees with the nameplate of the motor) pm motor induction motor reluctance motor 2 set a value for p3.1.1.1 motor nominal voltage (so that it agrees with the nameplate of the motor) range: varies 3 set a value for p3.1.1.2 motor nominal frequency (s...
Page 83
17 set the signal range of the analogue input 0 = 0-10v / 0-20ma 1 = 2-10v / 4-20ma 18 set a value for p3.13.1.8 error inversion 0 = normal 1 = inverted 19 set a value for p3.13.2.6 setpoint source selection see table setpoints in table 75 setpoint set- tings if you select an analogue input signal, ...
Page 84
29 set a value for p3.15.7 autochanged pumps 0 = auxiliary pumps 1 = all pumps step 30 shows only if you set the value enabled (interval) to parameter autochange in step 28. 30 set a value for p3.15.8 autochange interval range: 0-3000 h steps 31 and 32 show only if you set the value enabled (weekday...
Page 85
1 set a value for p3.1.2.2 motor type (so that it agrees with the nameplate of the motor) pm motor induction motor reluctance motor 2 set a value for p3.1.1.1 motor nominal voltage (so that it agrees with the nameplate of the motor) range: varies 3 set a value for p3.1.1.2 motor nominal frequency (s...
Page 86
17 set the signal range of the analogue input 0 = 0-10v / 0-20ma 1 = 2-10v / 4-20ma 18 set a value for p3.13.1.8 error inversion 0 = normal 1 = inverted 19 set a value for p3.13.2.6 setpoint source selection see table setpoints in chapter table 75 set- point settings if you select an analogue input ...
Page 87
23 set a value for p3.13.5.1 sp1 sleep frequency limit range: 0.00-320.00 hz 24 set a value for p3.13.5.2 sp1 sleep delay range: 0-3000 s 25 set a value for p3.13.5.3 sp1 wake up level the range is specified by the set process unit. 26 set a value for p3.15.1 multi-pump mode multifollower multimaste...
Page 88
34 set a value for p3.15.9 autochange days range: monday to sunday 35 set a value for p3.15.10 autochange time of day range: 00:00:00 to 23:59:59 36 set a value for p3.15.13 bandwidth range: 0-100% 37 set a value for p3.15.14 bandwidth delay range: 0-3600 s the multi-pump (multidrive) application wi...
Page 89
4 set a value for parameters p3.17.4 fire mode acti- vation on open / p3.17.5 fire mode activation on close make a selection of a digital input to activate fire mode. See also chapter 10.6.1 program- ming of digital and analogue inputs. 5 set a value for parameter p3.17.6 fire mode reverse make a se...
Page 90: User Interfaces
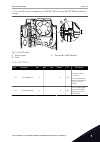
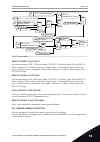
3 user interfaces 3.1 navigation on the keypad the data of the ac drive is in menus and submenus. To move between the menus, use the arrow buttons up and down in the keypad. To go into a group or an item, push the ok button. To go back to the level where you were before, push the back/reset button. ...
Page 91
Main menu submenus submenus submenus main menu main menu m2 monitor m1 quick setup m1.1 wizards (content depends on p1.2, app select.) m2.1 multimonitor m3.1 motor settings m3.2 start/stop setup m 3.3 r eferences m3.4 r amps and br ak es m3.5 i/ o configur ation m3.6 fb data mapping m3.10 a utoma ti...
Page 92
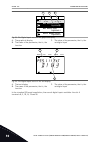
3.2 using the graphical display stop ready i/o main menu a b c d e f h g quick setup ( 17 ) monitor ( 5 ) parameters ( 12 ) m1 id: fig. 33: the main menu of the graphical display a. The first status field: stop/run b. The rotation direction c. The second status field: ready/not ready/fault d. The al...
Page 93
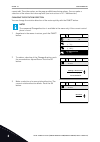
2 to go to the edit mode, push the ok button 2 times or push the arrow button right. Stop ready i/o rem control place m3.2.1 id: edit help add to favourites 3 to set a new value, push the arrow buttons up and down. Stop ready i/o rem control place m3.2.1 id: fieldbusctrl i/o control 4 to accept the ...
Page 94
3 if the value is numerical, move from digit to digit with the arrow buttons left and right. Change the digits with the arrow buttons up and down. Stop ready i/o minfreqreference p3.3.1.1 id:101 00.00 hz min: 0.00hz max: 50.00hz 4 to accept the change, push the ok button. To ignore the change, go ba...
Page 95
2 to move in the list of values, use the arrow buttons up and down. Stop ready i/o m 3.12.1.3.1 id: days monday tuesday wednesday thursday friday sunday 3 to add a value into your selection, select the box that is next to it with the arrow button right. Stop ready i/o m 3.12.1.3.1 id: days monday tu...
Page 96
Changing the control place 1 anywhere in the menu structure, push the funct button. Stop ready keypad id: m1 main menu monitor ( 12 ) ( 21 ) ( 6 ) parameters diagnostics 2 to make a selection of the local/remote, use the arrow buttons up and down. Push the ok button. Stop ready keypad id:1805 choose...
Page 97
Going into the control page it is easy to monitor the most important values in the control page. 1 anywhere in the menu structure, push the funct button. Stop ready i/o main menu ( 21 ) ( 6 ) parameters ( 12 ) monitor diagnostics m1 id: 2 to make a selection of the control page, push the arrow butto...
Page 98
Cannot edit. The other values on the page are multimonitoring values. You can make a selection of the values that show up here (see instructions in 4.1.1 multimonitor). Changing the rotation direction you can change the rotation direction of the motor quickly with the funct button. Note! The command...
Page 99
4 the rotation direction changes immediately. You can see that the arrow indication in the status field of the display changes. Stop ready i/o id: m1 main menu monitor ( 7 ) parameters ( 15 ) diagnostics ( 6 ) the quick edit function with the quick edit function, you can have a quick access to a par...
Page 100
Saving the parameters to the control panel 1 go into the user settings menu. Stop ready keypad id: m6 main menu i/o and hardware ( 9 ) user settings ( 4 ) favourites ( 0 ) 2 go into the parameter backup submenu. Stop ready keypad id: m6.5 user settings language selection english parameter backup ( 7...
Page 101
Note! If you have not saved the parameter set with which you want to compare the current set, the display shows the text comparing failed. Using the function parameter compare 1 go into parameter compare in the user settings menu. Stop ready i/o id: m6.6 user settings language selection parameter ba...
Page 102
4 examine the comparing between the current values and the values of the other set. Stop ready i/o id:113 active set-set 1 motor nom currnt motor cos phi 0.56a 1.90a 0.68 1.74 a b c d a. The current value b. The value of the other set c. The current value d. The value of the other set 3.2.6 help tex...
Page 103
3 to open the help text, push the ok button. Stop ready i/o id:403 m3.5.1.1 ctrl signal 1 a start signal 1 for control place i/o a. Start signal 1 functionality chosen with i/o a logic in start/stop setup menu. Note! The help texts are always in english. 3.2.7 using the favourites menu if you use th...
Page 104
D. The current location in the menu e. The indicators of the control place f. The indicators of the rotation direction 3.3.1 editing the values changing the text value of a parameter set the value of a parameter with this procedure. 1 find the parameter with the arrow buttons. Ready fault alarm stop...
Page 105
3 move from digit to digit with the arrow buttons left and right. Change the digits with the arrow buttons up and down. 4 accept the change with the ok button. To ignore the change, go back to the level where you were before with the back/reset button. 3.3.2 resetting a fault to reset a fault, you c...
Page 106
2 to make a selection of the local/remote, use the arrow buttons up and down. Push the ok button. Ready fault alarm stop run keypad i/o rev fwd bus 3 to make a selection of local or remote, use the arrow buttons up and down again. To accept the selection, push the ok button. Ready fault alarm stop r...
Page 107
2 to make a selection of the control page, push the arrow buttons up and down. Go in with the ok button. The control page opens. Ready fault alarm stop run keypad i/o rev fwd bus 3 if you use the local control place and the keypad reference, you can set p3.3.1.8 keypad reference with the ok button. ...
Page 108
1 anywhere in the menu structure, push the funct button. 2 push the arrow buttons up and down to make a selection of quick edit and accept with the ok button. 3 write the id number of a parameter or monitoring value. Push ok. The display shows the parameter value in the edit mode and the monitoring ...
Page 109
3.4 menu structure menu function quick setup see 1.4 description of the applications. Monitor multimonitor* trend curve* basic i/o extras/advanced timer functions pid controller external pid controller multi-pump maintenance counters fiedbus data parameters see 5 parameters menu. Diagnostics active ...
Page 110
Menu function i/o and hardware user settings slot c slot d slot e real time clock power unit settings keypad rs-485 ethernet user settings language selections parameter backup* parameter compare drive name favourites * see 8.2 favourites. User levels see 5 parameters menu. * = the function is not av...
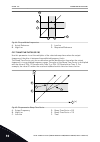
Page 111
Note! The multimonitor menu is not available in the text display. Trend curve the trend curve function is a graphical presentation of 2 monitor values at the same time. See 4.1.2 trend curve. Basic the basic monitoring values can include statuses, measurements, and the actual values of parameters an...
Page 112
Fieldbus commissioning. See 4.1.12 fieldbus process data monitoring. 3.5 vacon ® live vacon ® live is a pc tool for commissioning and maintenance of the vacon ® 10, vacon ® 20, and vacon ® 100 family ac drives. You can download vacon ® live from http:// drives.Danfoss.Com. The vacon ® live pc tool i...
Page 113: Monitoring Menu
4 monitoring menu 4.1 monitor group you can monitor the actual values of the parameters and signals. You can also monitor the statuses and measurements. You can customise some of the values that you can monitor. 4.1.1 multimonitor on the multimonitor page, you can collect 4 to 9 items to monitor. Ma...
Page 114
4 to make a selection of a new item in the list, push ok. Stop ready i/o id:1 m2.1.1.1 freqreference 0.00 % motor power output frequency freqreference motor speed motor current motor torque 0.00 hz 10.00 hz 0.00 rpm 0.00 a 0.00 % 4.1.2 trend curve the trend curve is a graphical presentation of 2 mon...
Page 115
3 you can monitor only 2 values as trend curves at the same time. The current selections, freqreference and motor speed, are at the bottom of the display. To make a selection of the current value that you wish to change, use the arrow buttons up and down. Push ok. Stop ready i/o freqreference motor ...
Page 116
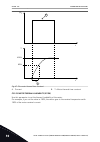
1 in trend curve view, make a curve active with the arrow button up. The frame of the display turns bold. Run ready alarm i/o motor current motor speed 0.02a -317rpm 2 push ok at the target point of the curve. Run ready alarm i/o motor current motor speed 0.02a -327rpm 3 a vertical line comes into v...
Page 117
4 to move the line to see the values of some other location, use the arrow buttons left and right. Run ready alarm i/o motor current motor speed 0.01a -254rpm table 15: the trend curve parameters index parameter min max unit default id description m2.2.1 view trend curve go into this menu to monitor...
Page 118
Table 16: items in the monitoring menu index monitoring value unit scale id description v2.3.1 output frequency hz 0.01 1 v2.3.2 frequency refer- ence hz 0.01 25 v2.3.3 motor speed rpm 1 2 v2.3.4 motor current a varies 3 v2.3.5 motor torque % 0.1 4 v2.3.7 motor shaft power % 0.1 5 v2.3.8 motor shaft...
Page 119
4.1.4 i/o table 17: i/o signal monitoring index monitoring value unit scale id description v2.4.1 slot a din 1, 2, 3 1 15 v2.4.2 slot a din 4, 5, 6 1 16 v2.4.3 slot b ro 1, 2, 3 1 17 v2.4.4 analogue input 1 % 0.01 59 slot a.1 as default. V2.4.5 analogue input 2 % 0.01 60 slot a.2 as default. V2.4.6 ...
Page 120
4.1.6 extras and advanced table 19: monitoring of the advanced values index monitoring value unit scale id description v2.6.1 drive status word 1 43 b1 = ready b2 = run b3 = fault b6 = runenable b7 = alarmactive b10 = dc current in stop b11 = dc brake active b12 = runrequest b13 = motorregulatoracti...
Page 121
Table 19: monitoring of the advanced values index monitoring value unit scale id description v2.6.7 motor current 1 decimal 0.1 45 v2.6.8 frequency refer- ence source 1 1495 0 = pc 1 = preset freqs 2 = keypad reference 3 = fieldbus 4 = ai1 5 = ai2 6 = ai1+ai2 7 = pid controller 8 = motor potentiom. ...
Page 122
Table 20: monitoring of the timer functions index monitoring value unit scale id description v2.7.1 tc 1, tc 2, tc 3 1 1441 v2.7.2 interval 1 1 1442 v2.7.3 interval 2 1 1443 v2.7.4 interval 3 1 1444 v2.7.5 interval 4 1 1445 v2.7.6 interval 5 1 1446 v2.7.7 timer 1 s 1 1447 v2.7.8 timer 2 s 1 1448 v2....
Page 123
4.1.9 external pid controller monitoring table 22: monitoring of the values of the external pid controller index monitoring value unit scale id description v2.9.1 extpid setpoint varies as set in p3.14.1.1 0 (see 5.14 group 3.14: external pid con- troller) 83 v2.9.2 extpid feedback varies as set in ...
Page 124
Table 23: multi-pump monitoring index monitoring value unit scale id description v2.10.1 motors running 1 30 v2.10.2 autochange 1 1114 v2.10.3 next autochange h 0.1 1503 v2.10.4 operate mode 1 1505 0 = slave 1 = master v2.10.5 multi-pump status 1 1628 0 = not used 10 = stopped 20 = sleep 30 = anti-b...
Page 125
4.1.11 maintenance counters table 24: maintenance counter monitoring index monitoring value unit scale id description v2.11.1 maintenance counter 1 h/ krev varies 1101 4.1.12 fieldbus process data monitoring table 25: fieldbus process data monitoring index monitoring value unit scale id description ...
Page 126
4.1.13 drive customizer monitoring table 26: drive customizer monitoring index monitoring value unit scale id description v2.13.2 block out.1 15020 v2.13.3 block out.2 15040 v2.13.4 block out.3 15060 v2.13.5 block out.4 15080 v2.13.6 block out.5 15100 v2.13.7 block out.6 15120 v2.13.8 block out.7 15...
Page 127: Parameters Menu
5 parameters menu you can change and edit the parameters in the parameters menu (m3) at all times. 5.1 group 3.1: motor settings table 27: motor nameplate parameters index parameter min max unit default id description p3.1.1.1 motor nominal volt- age varies varies v varies 110 p3.1.1.2 motor nominal...
Page 128
Table 28: motor control settings index parameter min max unit default id description p3.1.2.2 motor type 0 1 0 650 0 = induction motor 1 = pm motor 2 = reluctance motor p3.1.2.3 switching frequency 1.5 varies khz varies 601 p3.1.2.4 identification 0 2 0 631 0 = no action 1 = at standstill 2 = with r...
Page 129
Table 30: open loop settings index parameter min max unit default id description p3.1.4.1 u/f ratio 0 2 0 108 0=linear 1=squared 2=programmable p3.1.4.2 field weakening point frequency 8.00 p3.3.1.2 hz varies 602 p3.1.4.3 voltage at field weakening point 10.00 200.00 % 100.00 603 p3.1.4.4 u/f midpoi...
Page 130
Table 32: torque stabilator parameters index parameter min max unit default id description p3.1.4.13.1 torque stabilator gain 0.0 500.0 % 50.0 1412 p3.1.4.13.2 torque stabilator gain at field weak- ening point 0.0 500.0 % 50.0 1414 p3.1.4.13.3 torque stabilator damping time con- stant 0.0005 1.0000 ...
Page 131
5.2 group 3.2: start/stop setup table 33: start/stop setup menu index parameter min max unit default id description p3.2.1 remote control place 0 1 0 * 172 0 = i/o control 1 = fieldbus control p3.2.2 local/remote 0 1 0 * 211 0 = remote 1 = local p3.2.3 keypad stop button 0 1 0 114 0 = yes 1 = no p3....
Page 132
Table 33: start/stop setup menu index parameter min max unit default id description p3.2.8 fieldbus start logic 0 1 0 889 0 = a rising edge is necessary 1 = state p3.2.9 start delay 0.000 60.000 s 0.000 524 p3.2.10 remote to local function 0 2 2 181 0 = keep run 1 = keep run & refer- ence 2 = stop p...
Page 133
5.3 group 3.3: references table 34: frequency reference parameters index parameter min max unit default id description p3.3.1.1 minimum frequency reference 0.00 p3.3.1.2 hz 0.00 101 p3.3.1.2 maximum frequency reference p3.3.1.1 320.00 hz 50.00 / 60.00 102 p3.3.1.3 positive frequency reference limit ...
Page 134
Table 34: frequency reference parameters index parameter min max unit default id description p3.3.1.7 keypad control ref- erence selection 0 20 1 * 121 0 = pc 1 = preset frequency 0 2 = keypad reference 3 = fieldbus 4 = ai1 5 = ai2 6 = ai1+ai2 7 = pid 8 = motor potentiome- ter 11 = block out.1 12 = ...
Page 135
Table 35: preset frequency parameters index parameter min max unit default id description p3.3.3.1 preset frequency mode 0 1 0 * 182 0 = binary coded 1 = number of inputs p3.3.3.2 preset frequency 0 p3.3.1.1 p3.3.1.2 hz 5.00 180 p3.3.3.3 preset frequency 1 p3.3.1.1 p3.3.1.2 hz 10.00 * 105 p3.3.3.4 p...
Page 136
Table 37: flushing parameters index parameter min max unit default id description p3.3.6.1 flushing reference activation digin slot0.1 * 530 p3.3.6.2 flushing reference -maxref maxref hz 0.00 * 1239 * the default value of the parameter is specified by the application that you select with parameter p...
Page 137
Table 40: start magnetisation parameters index parameter min max unit default id description p3.4.3.1 start magnetising current 0.00 il a ih 517 0 = disabled p3.4.3.2 start magnetising time 0.00 600.00 s 0.00 516 table 41: dc brake parameters index parameter min max unit default id description p3.4....
Page 138
5.5 group 3.5: i/o configuration table 43: digital input settings index parameter default id description p3.5.1.1 control signal 1 a digin slota.1 * 403 p3.5.1.2 control signal 2 a digin slota.2 * 404 p3.5.1.3 control signal 3 a digin slot0.1 434 p3.5.1.4 control signal 1 b digin slot0.1 * 423 p3.5....
Page 139
Table 43: digital input settings index parameter default id description p3.5.1.23 preset frequency selection 2 digin slot0.1 * 421 p3.5.1.24 motor potentiometer up digin slot0.1 418 open = not active closed = active p3.5.1.25 motor potentiometer down digin slot0.1 417 open = not active closed = acti...
Page 140
Table 43: digital input settings index parameter default id description p3.5.1.46 pump 5 interlock digin slot0.1 430 open = not active closed = active p3.5.1.47 pump 6 interlock digin slot0.1 486 open = not active closed = active p3.5.1.48 pump 7 interlock digin slot0.1 487 open = not active closed ...
Page 141
Table 44: analogue input 1 settings index parameter min max unit default id description p3.5.2.1.1 ai1 signal selection anin slota.1 * 377 p3.5.2.1.2 ai1 signal filter time 0.00 300.00 s 0.1 * 378 p3.5.2.1.3 ai1 signal range 0 1 0 * 379 0 = 0…10v / 0…20ma 1 = 2…10v / 4…20ma p3.5.2.1.4 ai1 custom. Mi...
Page 142
Table 46: analogue input 3 settings index parameter min max unit default id description p3.5.2.3.1 ai3 signal selection anin slotd.1 141 see p3.5.2.1.1. P3.5.2.3.2 ai3 signal filter time 0.00 300.00 s 0.1 142 see p3.5.2.1.2. P3.5.2.3.3 ai3 signal range 0 1 0 143 see p3.5.2.1.3. P3.5.2.3.4 ai3 custom...
Page 143
Table 49: analogue input 6 settings index parameter min max unit default id description p3.5.2.6.1 ai6 signal selection anin slote.2 199 see p3.5.2.1.1. P3.5.2.6.2 ai6 signal filter time 0.00 300.00 s 0.1 200 see p3.5.2.1.2. P3.5.2.6.3 ai6 signal range 0 1 0 201 see p3.5.2.1.3. P3.5.2.6.4 ai6 custom...
Page 144
Table 50: digital output settings on standard i/o board, slot b index parameter min max unit default id description p3.5.3.2.1 ro1 function 0 74 varies 11001 the function selection for r01: 0 = none 1 = ready 2 = run 3 = general fault 4 = general fault inver- ted 5 = general alarm 6 = reversed 7 = a...
Page 145
Table 50: digital output settings on standard i/o board, slot b index parameter min max unit default id description p3.5.3.2.1 ro1 function 0 74 varies 11001 26 = time channel 2 27 = time channel 3 28 = fb controlword b13 29 = fb controlword b14 30 = fb controlword b15 31 = fb process- data1.B0 32 =...
Page 146
Table 50: digital output settings on standard i/o board, slot b index parameter min max unit default id description p3.5.3.2.1 ro1 function 0 74 varies 11001 55 = multi-pump k7 control 56 = multi-pump k8 control 69 = selected parame- ter set 72 = ahf cap discon- nect 73 = ahf cap discon- nect inv 74...
Page 147
Table 51: standard i/o board analogue output settings, slot a index parameter min max unit default id description p3.5.4.1.1 ao1 function 0 31 2 * 10050 0 = test 0% (not used) 1 = test 100% 2 = output freq (0 - fmax) 3 = freq reference (0 - fmax) 4 = motor speed (0 - motor nominal speed) 5 = output ...
Page 148
Table 51: standard i/o board analogue output settings, slot a index parameter min max unit default id description p3.5.4.1.1 ao1 function 0 31 2 * 10050 17 = processdatain4 (0-100%) 18 = processdatain5 (0-100%) 19 = processdatain6 (0-100%) 20 = processdatain7 (0-100%) 21 = processdatain8 (0-100%) 22...
Page 149
5.6 group 3.6: fieldbus data mapping table 52: fieldbus data mapping index parameter min max unit default id description p3.6.1 fieldbus data out 1 selection 0 35000 1 852 p3.6.2 fieldbus data out 2 selection 0 35000 2 853 p3.6.3 fieldbus data out 3 selection 0 35000 3 854 p3.6.4 fieldbus data out 4...
Page 150
5.7 group 3.7: prohibit frequencies table 54: prohibit frequencies index parameter min max unit default id description p3.7.1 prohibit frequency range 1 low limit -1.00 320.00 hz 0.00 509 0 = not used p3.7.2 prohibit frequency range 1 high limit 0.00 320.00 hz 0.00 510 0 = not used p3.7.3 prohibit f...
Page 151
5.8 group 3.8: supervisions table 55: supervision settings index parameter min max unit default id description p3.8.1 supervision #1 item selection 0 17 0 1431 0 = output frequency 1 = frequency reference 2 = motor current 3 = motor torque 4 = motor power 5 = dc-link voltage 6 = analogue input 1 7 =...
Page 152
5.9 group 3.9: protections table 56: general protections settings index parameter min max unit default id description p3.9.1.2 response to external fault 0 3 2 701 0 = no action 1 = alarm 2 = fault (stop accord- ing to stop function) 3 = fault (stop by coasting) p3.9.1.3 input phase fault 0 1 0 730 ...
Page 153
Table 57: motor thermal protection settings index parameter min max unit default id description p3.9.2.1 motor thermal pro- tection 0 3 2 704 0 = no action 1 = alarm 2 = fault (stop by stop mode) 3 = fault (stop by coasting) p3.9.2.2 ambient tempera- ture -20.0 100.0 °c 40.0 705 p3.9.2.3 zero speed ...
Page 154
Table 59: motor underload protection settings index parameter min max unit default id description p3.9.4.1 underload fault 0 3 0 713 0 = no action 1 = alarm 2 = fault (stop accord- ing to stop mode) 3 = fault (stop by coasting) p3.9.4.2 underload protec- tion: field weaken- ing area load 10.0 150.0 ...
Page 155
Table 61: temperature input fault 1 settings index parameter min max unit default id description p3.9.6.1 temperature signal 1 0 63 0 739 b0 = temperature sig- nal 1 b1 = temperature sig- nal 2 b2 = temperature sig- nal 3 b3 = temperature sig- nal 4 b4 = temperature sig- nal 5 b5 = temperature sig- ...
Page 156
Table 62: temperature input fault 2 settings index parameter min max unit default id description p3.9.6.5 temperature signal 2 0 63 0 763 b0 = temperature sig- nal 1 b1 = temperature sig- nal 2 b2 = temperature sig- nal 3 b3 = temperature sig- nal 4 b4 = temperature sig- nal 5 b5 = temperature sig- ...
Page 157
Table 63: ai low protection settings index parameter min max unit default id description p3.9.8.1 analogue input low protection 0 2 767 0 = no protection 1 = protection enabled in run state 2 = protection enabled in run and stop state p3.9.8.2 analogue input low fault 0 5 0 700 0 = no action 1 = ala...
Page 158
5.10 group 3.10: automatic reset table 64: autoreset settings index parameter min max unit default id description p3.10.1 automatic reset 0 1 0 * 731 0 = disabled 1 = enabled p3.10.2 restart function 0 1 1 719 0 = flying start 1 = according to p3.2.4. P3.10.3 wait time 0.10 10000.0 0 s 0.50 717 p3.1...
Page 159
5.11 group 3.11: application settings table 65: application settings index parameter min max unit default id description p3.11.1 password 0 9999 0 1806 p3.11.2 c/f selection 0 1 0 * 1197 0 = celsius 1 = fahrenheit p3.11.3 kw/hp selection 0 1 0 1198 0 = kw 1 = hp p3.11.4 multimonitor view 0 2 1 1196 ...
Page 160
Table 68: interval 3 index parameter min max unit default id description p3.12.3.1 on time 00:00:00 23:59:59 hh:mm: ss 00:00:00 1474 see interval 1. P3.12.3.2 off time 00:00:00 23:59:59 hh:mm: ss 00:00:00 1475 see interval 1. P3.12.3.3 days 1476 see interval 1. P3.12.3.4 assign to channel 1478 see i...
Page 161
Table 71: timer 1 index parameter min max unit default id description p3.12.6.1 duration 0 72000 s 0 1489 p3.12.6.2 timer 1 diginslot 0.1 447 p3.12.6.3 assign to channel 1490 b0 = time channel 1 b1 = time channel 2 b2 = time channel 3 table 72: timer 2 index parameter min max unit default id descrip...
Page 162
5.13 group 3.13: pid controller table 74: pid controller 1 basic settings index parameter min max unit default id description p3.13.1.1 pid gain 0.00 1000.00 % 100.00 118 p3.13.1.2 pid integration time 0.00 600.00 s 1.00 119 p3.13.1.3 pid derivation time 0.00 100.00 s 0.00 132 p3.13.1.4 process unit...
Page 163
Table 74: pid controller 1 basic settings index parameter min max unit default id description p3.13.1.5 process unit min varies varies varies 0 1033 p3.13.1.6 process unit max varies varies varies 100 1034 p3.13.1.7 process unit deci- mals 0 4 2 1035 p3.13.1.8 error inversion 0 1 0 340 0 = normal (f...
Page 164
Table 75: setpoint settings index parameter min max unit default id description p3.13.2.1 keypad setpoint 1 p3.13.1. 5 p3.13.1. 6 p3.13.1 .4 0 167 p3.13.2.2 keypad setpoint 2 p3.13.1. 5 p3.13.1. 6 p3.13.1 .4 0 168 p3.13.2.3 setpoint ramp time 0.00 300.0 s 0.00 1068 p3.13.2.4 pid setpoint boost activ...
Page 165
Table 75: setpoint settings index parameter min max unit default id description p3.13.2.7 setpoint 1 minimum -200.00 200.00 % 0.00 1069 p3.13.2.8 setpoint 1 maximum -200.00 200.00 % 100.00 1070 p3.13.2.9 setpoint 1 boost -2.0 2.0 x 1.0 1071 p3.13.2.10 setpoint source 2 selection 0 varies 2 * 431 see...
Page 166
Table 76: feedback settings index parameter min max unit default id description p3.13.3.1 feedback function 1 9 1 * 333 1 = only source1 in use 2 = sqrt(source1); (flow=constant x sqrt(pressure)) 3 = sqrt(source1- source 2) 4 = sqrt(source 1) + sqrt (source 2) 5 = source 1 + source 2 6 = source 1 - ...
Page 167
Table 76: feedback settings index parameter min max unit default id description p3.13.3.5 feedback 1 maxi- mum -200.00 200.00 % 100.00 337 p3.13.3.6 feedback 2 source selection 0 30 0 335 see p3.13.3.3. P3.13.3.7 feedback 2 minimum -200.00 200.00 % 0.00 338 see p3.13.3.4. M3.13.3.8 feedback 2 maxi- ...
Page 168
Table 78: sleep function settings index parameter min max unit default id description p3.13.5.1 sp1 sleep fre- quency limit 0.00 320.00 hz 0.00 1016 0 = not used p3.13.5.2 sp1 sleep delay 0 3000 s 0 1017 0 = not used p3.13.5.3 sp1 wake up level -214748. 36 214748. 36 varies 0.0000 1018 0 = not used ...
Page 169
Table 79: feedback supervision parameters index parameter min max unit default id description p3.13.6.1 enable feedback supervision 0 1 0 735 0 = disabled 1 = enabled p3.13.6.2 upper limit -99999.9 9 99999.9 9 varies varies 736 p3.13.6.3 lower limit -99999.9 9 99999.9 9 varies varies 758 p3.13.6.4 d...
Page 170
Table 81: soft fill settings index parameter min max unit default id description p3.13.8.1 soft fill function 0 2 0 1094 0 = disabled 1 = enabled, level 2 = enabled, timeout p3.13.8.2 soft fill frequency 0.00 p3.3.1.2 hz 20.00 1055 p3.13.8.3 soft fill level -99999.9 9 99999.9 9 varies 0.0000 1095 p3...
Page 171
Table 82: input pressure supervision parameters index parameter min max unit default id description p3.13.9.1 enable super- vision 0 1 0 1685 0 = disabled 1 = enabled p3.13.9.2 supervision signal 0 23 0 1686 0 = analogue input 1 1 = analogue input 2 2 = analogue input 3 3 = analogue input 4 4 = anal...
Page 172
Table 82: input pressure supervision parameters index parameter min max unit default id description p3.13.9.6 supervision unit maximum value -99999.99 99999.99 p3.13.9.3 10.00 1690 p3.13.9.7 supervision alarm level p3.13.9.5 p3.13.9.6 p3.13.9.3 varies 1691 p3.13.9.8 supervision fault level p3.13.9.5...
Page 173
Table 84: multi-setpoint parameters index parameter min max unit default id description p3.13.12.1 multi-setpoint 0 p3.13.1.5 p3.13.1.6 p3.13.1.4 0.0 15560 p3.13.12.2 multi-setpoint 1 p3.13.1.5 p3.13.1.6 p3.13.1.4 0.0 15561 p3.13.12.3 multi-setpoint 2 p3.13.1.5 p3.13.1.6 p3.13.1.4 0.0 15562 p3.13.12...
Page 174
Table 84: multi-setpoint parameters index parameter min max unit default id description p3.13.12.19 multi-setpoint selection 2 digin slot0.1 15578 p3.13.12.20 multi-setpoint selection 3 digin slot0.1 15579 5.14 group 3.14: external pid controller table 85: basic settings for the external pid control...
Page 175
Table 86: setpoints of the external pid controller index parameter min max unit default id description p3.14.2.1 keypad setpoint 1 p3.14.1. 8 p3.14.1. 9 varies 0.00 1640 p3.14.2.2 keypad setpoint 2 p3.14.1. 8 p3.14.1. 9 varies 0.00 1641 p3.14.2.3 setpoint ramp time 0.00 300.00 s 0.00 1642 p3.14.2.4 ...
Page 176
Table 86: setpoints of the external pid controller index parameter min max unit default id description p3.14.2.8 setpoint source 2 selection 0 32 2 1646 see p3.14.2.5. P3.14.2.9 setpoint 2 minimum -200.00 200.00 % 0.00 1647 p3.14.2.10 setpoint 2 maximum -200.00 200.00 % 100.00 1648 table 87: feedbac...
Page 177
5.15 group 3.15: multi-pump table 89: multi-pump parameters index parameter min max unit default id description p3.15.1 multi-pump mode 0 2 0 * 1785 0 = single drive 1 = multifollower 2 = multimaster p3.15.2 number of pumps 1 8 1 * 1001 p3.15.3 pump id number 1 8 0 1500 p3.15.4 start and feedback si...
Page 178
Table 89: multi-pump parameters index parameter min max unit default id description p3.15.16 running pumps limit 1 p3.15.2 3 * 1187 m3.15.17 interlock signals see the interlock signal parameters below. M3.15.18 overpressure super- vision see the overpressure supervision parameters below. M3.15.19 pu...
Page 179
Table 92: pump running time counter parameters index parameter min max unit default id description p3.15.19.1 set runtime counter 0 1 0 1673 0 = no action 1 = set the value that is specified by p3.15.19.2 to the runtime counter of the selected pump. P3.15.19.2 set runtime coun- ter: value 0 300 000 ...
Page 180
5.16 group 3.16: maintenance counters table 94: maintenance counters index parameter min max unit default id description p3.16.1 counter 1 mode 0 2 0 1104 0 = not used 1 = hours 2 = revolutions * 1000 p3.16.2 counter 1 alarm limit 0 2147483 647 h/krev 0 1105 0 = not used p3.16.3 counter 1 fault limi...
Page 181
5.17 group 3.17: fire mode table 95: fire mode parameters index parameter min max unit default id description p3.17.1 fire mode password 0 9999 0 1599 1002 = enabled 1234 = test mode p3.17.2 fire mode frequency source 0 18 0 1617 0 = fire mode fre- quency 1 = preset speeds 2 = keypad 3 = fieldbus 4 ...
Page 182
Table 95: fire mode parameters index parameter min max unit default id description p3.17.9 fire mode run indi- cation current 0 100 % 10 15580 5.18 group 3.18: motor preheat parameters table 96: motor preheat parameters index parameter min max unit default id description p3.18.1 motor preheat func- ...
Page 183
5.20 group 3.21: pump control table 98: auto-cleaning parameters index parameter min max unit default id description p3.21.1.1 cleaning function 0 3 0 1714 0 = disabled 1 = enabled (din) 2 = enabled (current) 3 = enabled (weekdays) p3.21.1.2 cleaning activation digin slot0.1 1715 p3.21.1.3 cleaning ...
Page 184
Table 99: jockey pump parameters index parameter min max unit default id description p3.21.2.1 jockey function 0 2 0 1674 0 = not used 1 = pid sleep 2 = pid sleep (level) p3.21.2.2 jockey start level varies varies varies 0.00 1675 p3.21.2.3 jockey stop level varies varies varies 0.00 1676 table 100:...
Page 185
Table 102: frost protection parameters index parameter min max unit default id description p3.21.5.1 frost protection 0 1 0 1704 0 = disabled 1 = enabled p3.21.5.2 temperature signal 0 29 6 1705 0 = temperature input 1 (-50-200 c) 1 = temperature input 2 (-50-200 c) 2 = temperature input 3 (-50-200 ...
Page 186
Table 102: frost protection parameters index parameter min max unit default id description p3.21.5.5 frost protection temperature limit p3.21.5. 3 p3.21.5.4 °c/°f 5.00 (°c) 1708 p3.21.5.6 frost protection fre- quency 0.0 p3.3.1.2 hz 10.0 1710 v3.21.5.7 frost temperature monitoring varies varies °c/°...
Page 187: Diagnostics Menu
6 diagnostics menu 6.1 active faults when there is a fault or many faults, the display shows the name of the fault and blinks. Push ok to go back to the diagnostics menu. The submenu active faults shows the number of faults. To see the fault-time data, make a selection of a fault and push ok. The fa...
Page 188
Table 105: the total counter parameters in the diagnostics menu index parameter min max unit default id description v4.4.1 energy counter varies 2291 the quantity of energy from the mains. You cannot reset the coun- ter. In the text display: the highest energy unit that the display shows is mw. If t...
Page 189
Table 105: the total counter parameters in the diagnostics menu index parameter min max unit default id description v4.4.14 power on time (text keypad) hh:min: ss the power on time in hours, minutes and seconds. V4.4.15 start command counter 2295 the number of times that the power unit is started. 6...
Page 190
6.6 software info table 107: the software info parameters in the diagnostics menu index parameter min max unit default id description v4.6.1 software package (graphical keypad) the code for the soft- ware identification v4.6.2 software package id (text keypad) v4.6.3 software package version (text k...
Page 191: I/o and Hardware Menu
7 i/o and hardware menu in the i/o and hardware menu, there are different settings that are related to the options. The values in this menu are raw values, that is, they are not scaled by the application. 7.1 basic i/o in the basic i/o menu, you can monitor the statuses of the inputs and the outputs...
Page 192
Table 108: the basic i/o parameters in the i/o and hardware menu index parameter min max unit default id description v5.1.1 digital input 1 0 1 0 2502 status of the digital input signal v5.1.2 digital input 2 0 1 0 2503 status of the digital input signal v5.1.3 digital input 3 0 1 0 2504 status of t...
Page 193
Table 108: the basic i/o parameters in the i/o and hardware menu index parameter min max unit default id description v5.1.11 analogue output 1 mode 1 3 1 2512 shows the mode that is set for the analogue input signal. The selec- tion is made with a dip switch on the control board. 1 = 0...20ma 3 = 0....
Page 194
7.3 real time clock table 110: the real time clock parameters in the i/o and hardware menu index parameter min max unit default id description v5.5.1 battery state 1 3 2205 status of the battery. 1 = not installed 2 = installed 3 = replace the battery p5.5.2 time hh:mm: ss 2201 the current time of t...
Page 195
Table 111: power unit settings index parameter min max unit default id description p5.6.1.1 fan control mode 0 1 1 2377 0 = always on 1 = optimised p5.6.4.1 sine filter 0 1 0 2527 0 = not used 1 = in use p5.6.5.1 harmonic filter 0 1 0 2497 0 = not used 1 = in use 7.5 keypad table 112: the keypad par...
Page 196
* = the selection of the application with parameter p1.2 application gives the default value. See the default values in 12.1 the default values of parameters in the different applications. ** only available with the graphical keypad. 7.6 fieldbus in the i/o and hardware menu, there are the parameter...
Page 197: Menus
8 user settings, favourites and user level menus 8.1 user settings 8.1.1 user settings table 113: general settings in the user settings menu index parameter min max unit default id description p6.1 language selections varies varies varies 802 the selection is differ- ent in all the language packages...
Page 198
8.1.2 parameter backup table 114: the parameter backup parameters in the user settings menu index parameter min max unit default id description p6.5.1 restore factory defaults 831 restores the default parameter values and starts the startup wiz- ard. P6.5.2 save to keypad * 0 1 0 saves the parameter...
Page 199
If you use the same items frequently, you can add them into favourites. You can collect a set of parameters or monitoring signals from all the keypad menus. It is not necessary to find them in the menu structure one by one. As an alternative, add them into the favourites folder where it is easy to f...
Page 200
2 find the item that you want to remove. Push the ok button. Stop ready i/o favourites motor nom freq 50.00 hz 3 make a selection of rem from favourites. Stop ready i/o motor nom freq rem from favourites help monitor 4 to remove the item, push the ok button again. 8.3 user levels use the user level ...
Page 201
Table 115: the user level parameters index parameter min max unit default id description p8.1 user level 1 3 1 1194 1 = normal. All the menus are visible in the main menu. 2 = monitoring. Only the monitoring and user level menus are visible in the main menu. 3 = favourites. Only the favourites and u...
Page 202
2 go to the item access code and push the arrow button right. Stop ready alarm keypad main menu normal user level 00000 access code p8.2 id:2362 3 to change the digits of the access code, use all the arrow buttons. Stop ready alarm i/o id:2362 p8.2 access code min:0 max:9 00000 4 accept the change w...
Page 203
9 monitoring value descriptions this chapter gives you the basic descriptions of all monitoring values. 9.1 basic v2.3.1 output frequency (id 1) this monitoring value shows the actual output frequency to the motor. V2.3.2 frequency reference (id 25) this monitoring value shows the actual frequency r...
Page 204
V2.3.11 unit temperature (id 8) this monitoring value shows the measured heatsink temperature of the drive. The unit of the monitoring value is celsius degrees or fahrenheit degrees, depending on the 'c/f selection' parameter value. V2.3.12 motor temperature (id 9) this monitoring value shows the ca...
Page 205
V2.4.6 analog input 3 (id 61) this monitoring value shows the value of the analogue input signal as a percentage of the used range. V2.4.7 analog input 4 (id 62) this monitoring value shows the value of the analogue input signal as a percentage of the used range. V2.4.8 analog input 5 (id 75) this m...
Page 206
The unit of the monitoring value is celsius degrees or fahrenheit degrees, depending on the 'c/f selection' parameter value. V2.5.4 temperature input 4 (id 69) this monitoring value shows the measured value of the temperature. The unit of the monitoring value is celsius degrees or fahrenheit degrees...
Page 207
Note! The values are visible as checkboxes on the graphical display. If a box is selected, the value is active. V2.6.5 din status word 1 (id 56) this monitoring value shows the bit-coded status of the digital input signals. The monitoring value is a 16 bit word, where each bit shows the status of 1 ...
Page 208
Note! The values are visible as checkboxes on the graphical display. If a box is selected, the limit controller is active. V2.6.14 motor shaft power 1 decimal (id 98) this monitoring value shows the actual shaft power of the motor (calculated value with one decimal). The unit of measurement is kw or...
Page 209
9.6 pid controller v2.8.1 pid setpoint (id 20) this monitoring value shows the value of the pid setpoint signal in process units. You can use the parameter p3.13.1.7 to select the process unit (see 10.14.1 basic settings). V2.8.2 pid feedback (id 21) this monitoring value shows the value of the pid ...
Page 210
V2.9.4 extpid output (id 86) this monitoring value shows the output of the pid controller as a percentage (0-100%). You can give this value to, for example, the analogue output. V2.9.5 extpid status (id 87) this monitoring value shows the state of the pid controller. 9.8 multi-pump v2.10.1 motors ru...
Page 211
V2.10.11 pump 5 running time (id 1624) this monitoring value shows the operating hours of the pump in multi-pump system. V2.10.12 pump 6 running time (id 1625) this monitoring value shows the operating hours of the pump in multi-pump system. V2.10.13 pump 7 running time (id 1626) this monitoring val...
Page 212
Table 116: fieldbus control word bit descriptions value = 0 (false) value = 1 (true) bit 0 stop request from fieldbus start request from fieldbus bit 1 forward direction request reverse direction request bit 2 no action reset active faults and alarms (on rising edge 0=>1) bit 3 no action force stop ...
Page 213
V2.12.3 fb data in 1 (id 876) this monitoring value shows the raw value of process data in a 32-bit signed format. V2.12.4 fb data in 2 (id 877) this monitoring value shows the raw value of process data in a 32-bit signed format. V2.12.5 fb data in 3 (id 878) this monitoring value shows the raw valu...
Page 214
Table 117: fieldbus status word bit descriptions value = 0 (false) value = 1 (true) bit 0 not ready to operate ready to operate bit 1 not running running bit 2 running in the forward direction running in the reverse direction bit 3 no fault fault is active bit 4 no alarm alarm is active bit 5 reques...
Page 215
V2.12.15 fb data out 3 (id 868) this monitoring value shows the raw value of process data in a 32-bit signed format. V2.12.16 fb data out 4 (id 869) this monitoring value shows the raw value of process data in a 32-bit signed format. V2.12.17 fb data out 5 (id 870) this monitoring value shows the ra...
Page 216
V2.13.7 block out.6 (id 15120) this monitoring value shows the value of the function block output in the drive customizer function. V2.13.8 block out.7 (id 15140) this monitoring value shows the value of the function block output in the drive customizer function. V2.13.9 block out.8 (id 15160) this ...
Page 217: Parameter Descriptions
10 parameter descriptions in this chapter, you can find information on all the parameters of your vacon ® 100 application. If other information is necessary, see chapter 5 parameters menu or contact your nearest distributor. P1.2 application (id212) use this parameter to select the application confi...
Page 218
P2.2.5 channel 2 min (id 2371) this parameter is used in scaling by default. Adjustments can be necessary. P2.2.6 channel 2 max (id 2372) this parameter is used in scaling by default. Adjustments can be necessary. P2.2.7 autoscale (id 2373) use this parameter to set autoscaling on or off. If autosca...
Page 219
10.2.2 motor control parameters p3.1.2.2 motor type (id 650) use this parameter to set the type of motor in your process. Selection number selection name description 0 induction motor (im) make this selection if you use an induction motor. 1 permanent magnet motor (pm) make this selection if you use...
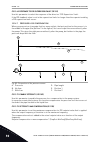
Page 220
Selection number selection name description 0 no action no identification requested. 1 identification at standstill the drive operates without speed when you do the identifica- tion run for the motor parameters. The motor receives cur- rent and voltage, but the frequency is zero. The u/f ratio and s...
Page 221
0 1 b a fig. 36: the motor switch between the drive and the motor a. The motor switch b. Mains p3.1.2.10 overvoltage control (id 607) use this parameter to set the overvoltage controller out of operation. The function is necessary when • the supply voltage changes, for example, between -15% and +10%...
Page 222
• to get energy from the motor to keep the dc link voltage at a minimum level when the voltage is near the lowest permitted limit, and • to make sure that the drive does not trip because of an undervoltage fault. Note! The drive can trip when the overvoltage and undervoltage controllers are disabled...
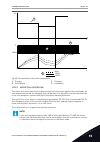
Page 223
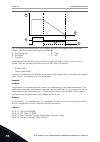
Field weakening point field weakening point voltage motor nominal voltage motor nominal frequency stator voltage adjust back -emf zero frequency voltage (50..200%) 200% 100% 50% f [hz] u [v] fig. 37: the stator voltage adjustment p3.1.2.15 stator resistance voltage drop (id 662) use this parameter t...
Page 224
P3.1.2.17 motor bem voltage (id 674) use this parameter to set the back electromotive force (back-emf) voltage of a permanent magnet motor. The value of this parameter is the motor terminal voltage when the motor current is zero. The value is given as line-to-line rms voltage at nominal operating fr...
Page 225
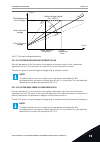
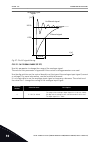
Selection number selection name description 0 linear the voltage of the motor changes linearly as a function of the output frequency. The voltage changes from the value of p3.1.4.6 (zero frequency voltage) to the value of p3.1.4.3 (voltage at field weakening point) at a frequency set in p3.1.4.2 (fi...
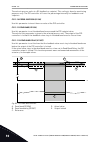
Page 226
C b a p1 p2 p3 id604 id605 id606 un id603 id602 u[v] f[hz] fig. 39: the programmable u/f curve a. Default: nominal voltage of the motor b. Field weakening point c. Default: nominal frequency of the motor when the parameter motor type has the value pm motor (permanent magnet motor), this parameter is...
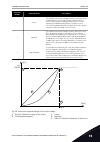
Page 227
P3.1.4.4 u/f midpoint frequency (id 604) use this parameter to set the middle point frequency of the u/f curve. Note! This parameter gives the middle point frequency of the curve if the value of p3.1.4.1 is programmable. P3.1.4.5 u/f midpoint voltage (id 605) use this parameter to set the middle poi...
Page 228
The bit b7 controls the rotation direction of the injected high frequency signal, which is used in the flying start of synchronous reluctance machines. Signal injection is used to detect the frequency of the rotor. If the rotor is in a blind angle when the signal is injected, the rotor frequency is ...
Page 229
P3.1.4.12.1 i/f start (id 534) use this parameter to enable the i/f start function. When you activate the i/f start function, the drive starts to operate in the current control mode. A constant current is led to the motor until the output frequency increases above the level that is set in p3.1.4.12....
Page 230
P3.1.4.13.3 torque stabilator damping time constant (id 1413) use this parameter to set the damping time constant of the torque stabiliser. P3.1.4.13.4 torque stabilator damping time constant for pm motors (id 1735) use this parameter to set the damping time constant of the torque stabiliser for per...
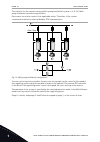
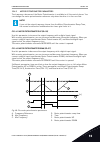
Page 231
I/o sel g in 0 in 1 sel g in 0 in 1 sel g in 0 in 1 sel g in 0 in 1 sel g in 0 in 1 sel g in 0 in 1 mux k in 0 in 1 p3.5.1.7 i/o b ctrl force i/o i/o a p v fieldbus v keypad v keypad v pc c i/o b v p3.2.1 remote control place p p3.2.2 local/remote fb cw.Bit8 for ce to fb control i/o p3.5.1.9 fieldbu...
Page 232
P3.2.2 local/remote (id 211) use this parameter to switch between the local and remote control places. Local control place is always keypad control. The remote control place can be i/o or fieldbus, depending on the 'remote control place' parameter value. P3.2.3 keypad stop button (id 114) use this p...
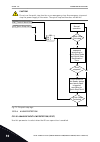
Page 233
P3.2.6 i/o a start/stop logic (id 300) use this parameter to control the start and stop of the drive with the digital signals. The selections can include the word 'edge' to help you prevent an accidental start. An accidental start can occur, for example, in these conditions • when you connect the po...
Page 234
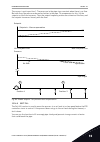
3. Cs1 becomes inactive and causes the direction to start to change (fwd to rev), because cs2 is still active. 4. Cs2 becomes inactive and the frequency that is fed to the motor goes to 0. 5. Cs2 activates again and causes the motor to accelerate (rev) to the set frequency. 6. Cs2 becomes inactive a...
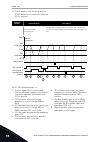
Page 235
Set frequency 0 hz keypad stop button ctrl signal 3 t output frequency fwd rev ctrl signal 2 ctrl signal 1 run enable set frequency 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 9 8 10 fig. 44: i/o a start/stop logic = 1 1. Control signal (cs) 1 activates and causes the output frequency to increase. The motor operates forward. 2. ...
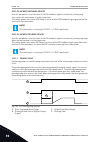
Page 236
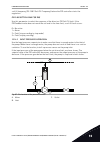
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 t output frequency fwd rev ctrl signal 2 ctrl signal 1 run enable set frequency set frequency 0 hz keypad stop button fig. 45: i/o a start/stop logic = 2 1. Control signal (cs) 1 activates and causes the output frequency to increase. The motor operates forward. 2. Cs2 acti...
Page 237
Selection number selection name description 3 cs1 = start cs2 = reverse 1 2 3 4 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 5 t output frequency fwd rev ctrl signal 2 ctrl signal 1 run enable set frequency set frequency 0 hz keypad stop button keypad start button fig. 46: i/o a start/stop logic = 3 1. Control signal (cs) 1 ac...
Page 238
12. The attempt to start the drive with the start button is not successful, because cs1 is inactive. Selection number selection name description 4 cs1 = start (edge) cs2 = reverse use this function to prevent an accidental start. Before you can start the motor again, you must open the start/stop con...
Page 239
9. The stop button on the keypad is pushed and the frequency that is fed to the motor goes to 0. (this signal only works if the value of p3.2.3 keypad stop button is yes.) 10. Before the drive can start, you must open and close cs1 again. 11. Cs1 becomes inactive and the frequency goes to 0. P3.2.7 ...
Page 240
Selection number selection name description 0 restart delay not used 10.4 references 10.4.1 frequency reference it is possible to program the source of the frequency reference in all the control places, except the pc tool. If you use your pc, it always takes the frequency reference from the pc tool....
Page 241
P3.3.1.6 i/o control reference b selection (id 131) use this parameter to select the reference source when the control place is i/o b. See p3.3.1.5 for more information. You can force the i/o b control place to be active only with a digital input (p3.5.1.7). P3.3.1.7 keypad control reference selecti...
Page 242
P3.3.3.3 preset frequency 1 (id 105) use this parameter to set the preset frequency reference when the preset frequencies function is used. Select the preset frequencies with the digital input signals. P3.3.3.4 preset frequency 2 (id 106) use this parameter to set the preset frequency reference when...
Page 243
Necessary step activated frequency make a selection of the value 0 for parameter p3.3.1.5. Preset frequency 0 table 118: the selection of preset frequencies when p3.3.3.1 = binary coded activated digital input signal activated frequency reference preset freq sel2 (p3.3.3.12) preset freq sel1 (p3.3.3...
Page 244
Table 119: the selection of preset frequencies when p3.3.3.1 = number of inputs activated digital input signal activated frequency reference preset freq sel2 (p3.3.3.12) preset freq sel1 (p3.3.3.11) preset freq sel0 (p3.3.3.10) preset frequency 0 only if preset freq 0 is set as frequency reference s...
Page 245
10.4.3 motor potentiometer parameters the frequency reference of the motor potentiometer is available in all the control places. You can change the motor potentiometer reference only when the drive is in the run state. Note! If you set the output frequency slower than the motor potentiometer ramp ti...
Page 246
P3.3.4.3 motor potentiometer ramp time (id 331) use this parameter to set the rate of change in the motor potentiometer reference when it is increased or decreased. The parameter value is entered as hz/second. P3.3.4.4 motor potentiometer reset (id 367) use this parameter to set the logic for the re...
Page 247
10.5 ramps and brakes setup 10.5.1 ramp 1 p3.4.1.1 ramp 1 shape (id 500) use this parameter to make the start and the end of the acceleration and deceleration ramps smoother. With the parameters ramp 1 shape and ramp 2 shape, you can make smoother the start and the end of the acceleration and decele...
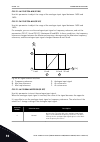
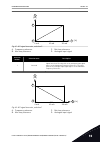
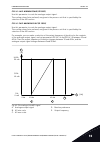
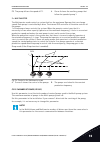
Page 248
10.5.2 ramp 2 p3.4.2.1 ramp 2 shape (id 501) use this parameter to make the start and the end of the acceleration and deceleration ramps smoother. With the parameters ramp 1 shape and ramp 2 shape, you can make smoother the start and the end of the acceleration and deceleration ramps. If you set the...
Page 249
Selection number selection name description 0 open ramp 1 shape, acceleration time 1 and deceleration time 1 1 closed ramp 2 shape, acceleration time 2 and deceleration time 2 p3.4.2.5 ramp 2 threshold frequency (id 533) use this parameter to set the output frequency limit above which the ramp 2 is ...
Page 250
10.5.4 dc brake p3.4.4.1 dc brake current (id 507) use this parameter to set the current that is fed into the motor during dc braking. If the value of this parameter is set to 0, the dc brake function is disabled. P3.4.4.2 dc braking time at stop (id 508) use this parameter to set the braking is on ...
Page 251
2 1 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 30 a b 21 22 23 24 25 26 33 34 slot a slot b c a b d e a.1 g f a.2 a.1 a.2 a.3 a.4 a.5 a.6 fig. 52: the option board slots and programmable inputs a. Standard board slot a and its terminals b. Standard board slot b and its terminals c. Option board slo...
Page 252
Stop ready i/o id:405 p3.5.1.11 digital inputs b a c diginslota.3 diginslot0.2 diginslota.6 fault reset close ext fault open ext fault close fig. 53: the digital inputs menu in the graphical display a. The graphical display b. The name of the parameter, that is, the function c. The value of the para...
Page 253
Input type (graphi- cal display) input type (text dis- play) slot input # explanation digin di a 1 digital input #1 (terminal 8) on a board in slot a (standard i/o board). Digin di a 2 digital input #2 (terminal 9) on a board in slot a (standard i/o board). Digin di a 3 digital input #3 (terminal 10...
Page 254
2 in the edit mode, the slot value digin slota is underlined and blinks. If you have more digital inputs available in your i/o, for example, because of option boards in slots c, d or e, make a selection of them. Stop ready i/o ext fault close p3.5.1.11 id:405 min: max: digin slota.3 3 to activate th...
Page 255
Programming in the text display 1 make a selection of a parameter. To go into the edit mode, push the ok button. Ready fault alarm stop run keypad 1/o rev fwd bus 2 in the edit mode, the letter d blinks. If you have more digital inputs available in your i/o, for example, because of option boards in ...
Page 256
5 if the digital input di6 was already used for some other function, a message scrolls on the display. Change one of these selections. Ready fault alarm stop run keypad 1/o rev fwd bus after the steps, a digital signal to the digital input di6 controls the function external fault close. The value of...
Page 257
Ready fault alarm stop run keypad 1/o rev fwd bus a b c fig. 56: the analogue inputs menu in the text display a. The text display b. The name of the parameter c. The value of the parameter, that is, the set analogue input in the standard i/o board compilation, there are 2 analogue inputs available: ...
Page 258
Programming of analogue inputs in the graphical display 1 to make a selection of the parameter, push the arrow button right. Stop ready i/o analogue input 1 ai1 filter time ai1 signal range anin slota.1 0.10s 0-10v/0-20ma ai1 signal sel p3.5.2.1.1 id:377 2 in the edit mode, the value anin slota is u...
Page 259
2 in the edit mode, the letter a blinks. Ready fault alarm stop run keypad 1/o rev fwd bus 3 to change the value to c, push the arrow button up. Accept the change with the ok button. Ready fault alarm stop run keypad 1/o rev fwd bus parameter descriptions vacon · 259 local contacts: http://drives.Da...
Page 260
10.6.1.3 descriptions of signal sources source function slot0.# digital inputs: you can use this function to set a digital signal to be in a constant open or closed state. The manufacturer set some signals so that they are always in the closed state, for example parameter p3.5.1.15 (run ena- ble). T...
Page 261
10.6.2 default functions of programmable inputs table 120: default functions of the programmable digital and analogue inputs input terminal(s) reference function parameter index di1 8 a.1 control signal 1 a p3.5.1.1 di2 9 a.2 control signal 2 a p3.5.1.2 di3 10 a.3 external fault close p3.5.1.11 di4 ...
Page 262
P3.5.1.5 control signal 2 b (id 424) use this parameter to select the digital input signal (control signal 2) that starts and stops the drive when the control place is i/o b. P3.5.1.6 control signal 3 b (id 435) use this parameter to select the digital input signal (control signal 3) that starts and...
Page 263
When the contact is open, the start of the motor is disabled. When the contact is closed, the start of the motor is enabled. To stop, the drive obeys the value of p3.2.5 stop function. P3.5.1.16 run interlock 1 (id 1041) use this parameter to select the digital input signal that prevents to start th...
Page 264
P3.5.1.25 motor potentiometer down (id 417) use this parameter to decrease the output frequency with a digital input signal. The motor potentiometer reference decreases until the contact is open. P3.5.1.26 quick stop activation (id 1213) use this parameter to select the digital input signal that act...
Page 265
P3.5.1.33 external pid setpoint selection (id 1048) use this parameter to set the digital input signal that selects the pid setpoint value to be used. P3.5.1.34 reset maintenance counter 1 (id 490) use this parameter to select the digital input that reset the value of the maintenance counter. P3.5.1...
Page 266
The selection of the application with parameter p1.2 application gives the default value. P3.5.1.44 pump 3 interlock (id 428) use this parameter to select the digital input signal that is used as interlock signal for the multi-pump system. The selection of the application with parameter p1.2 applica...
Page 267
P3.5.1.54 multi-setpoint selection 0 (id 15576) use this parameter to select the digital input signal that is used as a selector for the pid multi-setpoint function. P3.5.1.55 multi-setpoint selection 1 (id 15577) use this parameter to select the digital input signal that is used as a selector for t...
Page 268
[%] 100% 63% id378 t [s] filtered signal unfiltered signal analogue input signal fig. 57: the ai1 signal filtering p3.5.2.1.3 ai1 signal range (id 379) use this parameter to change the range of the analogue signal. The value of this parameter is bypassed if the custom scaling parameters are used. Us...
Page 269
0% 100% 50% c b a d 0 ma 20 ma 10 ma [hz] [%] fig. 58: the analogue input signal range, selection 0 a. Frequency reference b. Max freq reference c. Min freq reference d. Analogue input signal selection number selection name description 1 2...10v / 4...20ma the range of the analogue input signal is 2...
Page 270
P3.5.2.1.4 ai1 custom. Min (id 380) use this parameter to adjust the range of the analogue input signal between -160% and 160%. P3.5.2.1.5 ai1 custom. Max (id 381) use this parameter to adjust the range of the analogue input signal between -160% and 160%. For example, you can use the analogue input ...
Page 271
0% 100% 50% c b a d [hz] [%] 0 ma 20 ma 10 ma fig. 61: ai1 signal inversion, selection 0 a. Frequency reference b. Max freq reference c. Min freq reference d. Analogue input signal selection number selection name description 1 inverted signal inversion. The value 0% of the analogue input signal agre...
Page 272
10.6.5 digital outputs p3.5.3.2.1 ro1 function (id 11001) use this parameter to select a function or a signal that is connected to the relay output. Vacon · 272 parameter descriptions 10 local contacts: http://drives.Danfoss.Com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/.
Page 273
Table 121: the output signals through ro1 selection number selection name description 0 not used the output is not used. 1 ready the ac drive is ready to operate. 2 run the ac drive operates (the motor runs). 3 general fault a fault trip occurred. 4 general fault inverted a fault trip did not occur....
Page 274
Table 121: the output signals through ro1 selection number selection name description 23 input pressure alarm the input pressure of the pump is below the value that was set with parameter p3.13.9.7. 24 frost protection alarm the measured temperature of the pump is below the level that was set with p...
Page 275
Table 121: the output signals through ro1 selection number selection name description 42 block out.7 the output of the programmable block 7.See parameter menu m3.19 block programming. 43 block out.8 the output of the programmable block 8. See parameter menu m3.19 block programming. 44 block out.9 th...
Page 276
P3.5.3.2.3 ro1 off delay (id 11003) use this parameter to set the off delay for the relay output. 10.6.6 analogue outputs p3.5.4.1.1 ao1 function (id 10050) use this parameter to select a function or a signal that is connected to the analogue output. The contents of the analogue output signal 1 are ...
Page 277
Selection number selection name description 0 test 0% (not used) the analogue output is set to 0% or 20% so that it agrees with parameter p3.5.4.1.3. 1 test 100% the analogue output is set to 100% of the signal (10v / 20ma). 2 output frequency the actual output frequency from 0 to maximum frequency ...
Page 278
Selection number selection name description 21 fieldbus process data in 8 fieldbus process data in 8: 0…10000 (this agrees with 0… 100.00%). 22 block out.1 the output of the programmable block 1: 0…10000 (this agrees with 0…100.00%). See parameter menu m3.19 drive customizer. 23 block out.2 the outp...
Page 279
P3.5.4.1.4 ao1 minimum scale (id 10053) use this parameter to scale the analogue output signal. The scaling values (min and max) are given in the process unit that is specified by the selection of the ao function. P3.5.4.1.5 ao1 maximum scale (id 10054) use this parameter to scale the analogue outpu...
Page 280
10.7 fieldbus data map p3.6.1 fb dataout 1 selection (id 852) use this parameter to select the data that is sent to the fieldbus with the id number of the parameter or monitor value. The data is scaled to an unsigned 16-bit format according to the format on the control panel. For example, value 25.5...
Page 281
P3.6.8 fb dataout 8 selection (id 859) use this parameter to select the data that is sent to the fieldbus with the id number of the parameter or monitor value. The data is scaled to an unsigned 16-bit format according to the format on the control panel. For example, value 25.5 on the display equals ...
Page 282
D a b c c b fig. 64: the prohibited frequencies a. Actual reference b. High lim c. Low lim d. Requested reference p3.7.7 ramp time factor (id 518) use this parameter to set the multiplier of the selected ramp times when the output frequency of the drive is between the prohibited frequency limits. Th...
Page 283
10.9 supervisions p3.8.1 supervision #1 item selection (id 1431) use this parameter to select the supervision item. The output of the supervision function can be selected to the relay output. P3.8.2 supervision #1 mode (id 1432) use this parameter to set the supervision mode. When the 'low limit' mo...
Page 284
If a fault occurs, the drive can show a notification of it on the display of the drive. An external fault is activated with a digital input signal. The default digital input is di3. You can also program the response data into a relay output. P3.9.1.3 input phase fault (id 730) use this parameter to ...
Page 285
If the pid feedback value is not within the supervision limits for longer than the supervision delay, a pid supervision fault occurs. See p3.9.1.2. P3.9.1.11 response to external pid supervision fault (id 757) use this parameter to select the response of the drive to a 'pid supervision' fault. If th...
Page 286
P3.9.2.1 motor thermal protection (id 704) use this parameter to select the response of the drive to a 'motor overtemperature' fault. If the motor thermal protection function detects that the temperature of the motor is too high, a motor overtemperature fault occurs. Note! If you have a motor thermi...
Page 287
P3.9.2.4 motor thermal time constant (id 707) use this parameter to set the motor thermal time constant. The time constant is the time within which the calculated thermal stage has reached 63% of its final value. The final thermal stage equals to running the motor continuously with nominal load at n...
Page 288
I/it 100% 63% t t t a b fig. 67: the motor thermal time constant a. Current b. T = motor thermal time constant p3.9.2.5 motor thermal loadability (id 708) use this parameter to set the thermal loadability of the motor. For example, if you set the value to 130%, the motor goes to the nominal temperat...
Page 289
T t i/i t 105% a c b d 80% 100% 130% fig. 68: the calculation of the motor temperature a. Current b. Fault/alarm c. Trip area d. Loadability 10.10.3 motor stall protection the motor stall protection function gives protection to the motor against short overloads. An overload can be caused, for exampl...
Page 290
P3.9.3.1 motor stall fault (id 709) use this parameter to select the response of the drive to a 'motor stall' fault. If the stall protection detects that the shaft of the motor is stalled, a motor stall fault occurs. P3.9.3.2 stall current (id 710) use this parameter to set the limit above which the...
Page 291
Note! For a stall state to occur, the output frequency must be below this limit for a certain time. 10.10.4 underload (dry pump) protection the motor underload protection makes sure that there is a load on the motor when the drive operates. If the motor loses the load, a problem can occur in the pro...
Page 292
Id714 id715 f 5 hz underload area torque field weakening point fig. 70: setting of the minimum load p3.9.4.3 underload protection: zero frequency load (id 715) use this parameter to set the minimum torque that the motor needs when the output frequency of the drive is 0. If you change the value of pa...
Page 293
Id716 a b c d e f fig. 71: the underload time counter function a. Underload time counter b. Trip area c. Trip/warning id713 d. Time e. Underload f. No underload 10.10.5 quick stop p3.9.5.1 quick stop mode (id 1276) use this parameter to select how the drive stops when the quick stop command is given...
Page 294
Caution! Do not use the quick stop function as an emergency stop. An emergency stop must stop the power supply to the motor. The quick stop function does not do this. Or in 1 in 2 fb i/o yes control word b12 quick stop activ. Normal operation start stop sequence according to quick stop mode and quic...
Page 295
Use the ai low protection to find failures in the analogue input signals. This function gives protection only to the analogue inputs that are used as frequency reference or in the pid/ extpid controllers. You can have the protection on when the drive is in the run status, or in the run and stop stat...
Page 296
10.11 automatic reset p3.10.1 automatic reset (id 731) use this parameter to enable the automatic reset function. To select the faults that are reset automatically, enter the value 0 or 1 to parameters from p3.10.6 to p3.10.13. Note! The automatic reset function is available only for some fault type...
Page 297
Fault trigger autoreset trial time wait time wait time wait time id717 reset 1 reset 2 trial time id718 fault active alarm number of trials: (id759 = 2) id717 id717 fig. 73: the automatic reset function p3.10.6 autoreset: undervoltage (id 720) use this parameter to enable the automatic reset after a...
Page 298
P3.10.12 autoreset: external fault (id 726) use this parameter to enable the automatic reset after an external fault. P3.10.13 autoreset: underload fault (id 738) use this parameter to enable the automatic reset after an underload fault. P3.10.14 autoreset: pid supervision fault (id 776) use this pa...
Page 299
Note! We do not recommend that you use the timer functions without an auxiliary battery. The time and date settings of the drive are reset at each power down, if there is no battery for the rtc. Time channels you can assign the output of the interval and/or timer functions to time channels 1-3. You ...
Page 300
A b d c e fig. 75: the activation signal comes from a digital input or a virtual digital input, like a time channel. The timer counts down from the falling edge. A. Remaining time b. Activation c. Duration d. Time e. Out the parameters below will set the timer active when the digital input 1 on the ...
Page 301
17:00:00 07:00:00 m3.12.1.3 id:1466 stop ready i/o interval 1 days off time on time 0 fig. 76: using timer functions to make an interval m3.12.1.3 id: stop ready i/o edit help add to favourites days fig. 77: going into the edit mode stop ready i/o days m3.12.1.3.1 id: monday tuesday wednesday thursd...
Page 302
Interval 1 days = monday to friday on = 07:00:00 hrs off = 17:00:00 hrs interval 2 days = saturday and sunday on = 09:00:00 hrs off = 13:00:00 hrs p ctrl signal 1a digital input 1 on slot a timer 1 duration = 1800 s time channel 1 start/stop fig. 79: time channel 1 is used as the control signal for ...
Page 303
You can use the time channels to control the on/off type functions, for example relay outputs or any functions that can be controlled by a di signal. 10.14 pid controller 10.14.1 basic settings p3.13.1.1 pid gain (id 118) use this parameter to adjust the gain of the pid controller. If this parameter...
Page 304
The value in process units at a 0% feedback or setpoint. This scaling is done for monitoring purposes only. The pid controller still uses the percentage internally for feedbacks and setpoints. P3.13.1.8 error inversion (id 340) use this parameter to invert the error value of the pid controller. P3.1...
Page 305
10.14.2 setpoints p3.13.2.1 keypad setpoint 1 (id 167) use this parameter to set the setpoint value of the pid controller when the setpoint source is 'keypad sp'. The value of this parameter is given in the selected process unit. P3.13.2.2 keypad setpoint 2 (id 168) use this parameter to set the set...
Page 306
P3.13.2.9 setpoint 1 boost (id 1071) use this parameter to set the multiplier for the setpoint boost function. When the setpoint boost command is given, the setpoint value is multiplied with the factor that is set with this parameter. 10.14.3 feedback p3.13.3.1 feedback function (id 333) use this pa...
Page 307
Use the feedback measurements of the actual controlled process value. The feedforward control uses other measurements that have an effect on the controlled process value. Example 1: you can control the water level of a tank with flow control. The target water level is set as a setpoint, and the actu...
Page 308
10.14.5 sleep function p3.13.5.1 sp1 sleep frequency (id 1016) use this parameter to set the limit below which the output frequency of the drive must stay for a set time before the drive goes to the sleep state. The value of this parameter is used when the signal of the pid controller setpoint is ta...
Page 309
Pid setpoint setpoint t wake up level fig. 82: wake-up mode: absolute level pid setpoint setpoint t wake up level fig. 83: wake-up mode: relative setpoint p3.13.5.5 sp1 sleep boost (id 1793) use this parameter to set the value that is added to the actual setpoint value when the sleep boost function ...
Page 310
P3.13.5.9 sp2 wake up level (id 1077) use this parameter to set the level at which the drive wakes up from the sleep state. P3.13.5.10 sp2 wake up mode (id 1020) use this parameter to select the operation for the wake up level parameter. P3.13.5.11 sp2 sleep boost (id 1794) use this parameter to set...
Page 311
A b c d e f g fig. 84: the feedback supervision function a. Upper limit (id736) b. Lower limit (id758) c. Actual value d. Reference e. Delay (id737) f. Regulating mode g. Alarm or fault p3.13.6.2 upper limit (id 736) use this parameter to set the high limit for the pid feedback signal. If the value ...
Page 312
P3.13.6.5 response to pid supervision fault (id 749) use this parameter to select the response of the drive to a 'pid supervision' fault. If the pid feedback value is not in the supervision limits for longer than the supervision delay, a pid supervision fault occurs. 10.14.7 pressure loss compensati...
Page 313
The sensor is put in position 1. The pressure in the pipe stays constant when there is no flow. But with flow, the pressure decreases farther in the pipe. To compensate for this, lift the setpoint as the flow increases. Then the output frequency makes an estimate of the flow, and the setpoint increa...
Page 314
We recommend that you always use the soft fill function when you use the multi-pump function. P3.13.8.1 soft fill function (id 1094) use this parameter to enable the soft fill function. You can use the function to fill an empty pipe slowly and prevent strong currents of fluid that could break the pi...
Page 315
Soft fill frequency (p3.13.8.2 soft fill frequency) before the pid controller starts the regulation. P3.13.8.5 soft fill fault (id 748) use this parameter to select the response of the drive to a pid soft fill fault. If the pidfeedback value does not reach the set level in the time limit, a soft fil...
Page 316
Input pressure supervision fault level input pressure alarm (digital output signal) supervision alarm level input pressure monitor pid setpoint pid setpoint supervision fault delay supervision fault delay motor running yes no pid setpoint reduction fig. 88: the input pressure supervision function p3...
Page 317
P3.13.9.7 supervision alarm level (id 1691) use this parameter to set the limit for the input pressure alarm. If the measured input pressure goes below this limit, an input pressure alarm occurs. P3.13.9.8 supervision fault level (id 1692) use this parameter to set the limit for the input pressure f...
Page 318
A b e f g i j d h a b c g h k c d e t t hz fig. 89: sleep, no demand detected a. The output frequency of the drive b. The pid feedback value c. The pid setpoint value d. Sndd frequency hysteresis (p3.13.10.3) e. Sndd error hysteresis (p3.13.10.2) the hysteresis area around the pid setpoint value. F....
Page 319
10.14.11 multi-setpoint p3.13.12.1 multi-setpoint 0 (id 15560) use this parameter to set the preset pid setpoint value when the multi-setpoint function is used. Make the selection of the multi-setpoint with the digital input signals. P3.13.12.2 multi-setpoint 1 (id 15561) use this parameter to set t...
Page 320
P3.13.12.11 multi-setpoint 10 (id 15570) use this parameter to set the preset pid setpoint value when the multi-setpoint function is used. Make the selection of the multi-setpoint with the digital input signals. P3.13.12.12 multi-setpoint 11 (id 15571) use this parameter to set the preset pid setpoi...
Page 321
10.15 external pid controller p3.14.1.1 enable external pid (id 1630) use this parameter to enable the pid controller. Note! This controller is for external use only. It can be used with an analoque output. P3.14.1.2 start signal (id 1049) use this parameter to set the signal for starting and stoppi...
Page 322
Step action 1 examine the wiring. • see the correct power cabling (mains cable, motor cable) of the drive in installation man- ual. • see the correct control cabling (i/o, pid feedback sensor, communication) in fig. 18 electric wiring diagramme of the multi-pump (multidrive) system, example 1a and i...
Page 323
Step action 7 set the id number of the pump. • go to parameter p1.35.15 (quick setup parameter menu). • the same parameter is in the menu parameters -> group 3.15 -> p3.15.3. • each drive in the multi-pump system must have an id number that no other drive has for the correct communication between dr...
Page 324
3 ~ pt m1 m2 m3 m8 m1 m2 m3 m8 start/stop ro2 ro3 ro8 fig. 90: single drive configuration (pt = pressure sensor) multidrive configuration the multidrive modes (multimaster and multifollower) control a system that has the maximum 8 variable speed pumps. Each pump is controlled by a drive. The interna...
Page 325
3 ~ pt m1 m2 m3 m8 m1 m2 m3 m8 start/stop fig. 91: multidrive configuration (pt = pressure sensor) p3.15.1 multi-pump mode (id 1785) use this parameter to select the configuration and the control mode of the multi-pump system. The multi-pump function lets you control a maximum of 8 motors (that is, ...
Page 326
P1 p2 p3 b rpm f min f max t fig. 92: control in the single drive mode p1 the pump that controls the system b the auxiliary pumps connected to the mains (direct on-line) 1 = multifollower the multifollower mode controls a system that has the maximum 8 pumps that can change speed. Each pump is contro...
Page 327
P3 the pump follows the speed of p1. A curve a shows the auxiliary pumps that follow the speed of pump 1. 2 = multimaster the multimaster mode controls a system that has the maximum 8 pumps that can change speed. Each pump is controlled by a drive. The internal pid controller of the drive controls a...
Page 328
P3.15.3 pump id number (id 1500) use this parameter to set the id number of the drive. This parameter is used only in the multifollower and multimaster modes. Each drive in the multi-pump system must have a unique sequence (id) number, always start from 1. Pump number 1 is always the primary master ...
Page 329
10.16.4 feedback sensor connection in a multi-pump system you get the best precision and redundancy in the multi-pump system when you use feedback sensors for each drive. 4 5 6 7 4 5 6 7 4 5 6 7 - + - + - + actual value (0)4..20ma actual value (0)4..20ma actual value (0)4..20ma drive 1: standard i/o...
Page 330
4 5 12 13 17 4 5 12 13 17 4 5 12 13 17 - + actual value (0)4..20ma drive 1: standard i/o board terminal signal a12+ a12- 24v out gnd analogue input 2+ analogue input 2- 24v auxiliary voltage i/o ground cm common for di1-di6 drive 2: standard i/o board terminal signal a12+ a12- 24v out gnd analogue i...
Page 331
4 5 6 7 4 5 6 7 4 5 6 7 - + - + actual value external 24v supply (0)4..20ma drive 1: standard i/o board drive 2: standard i/o board drive 3: standard i/o board terminal signal terminal signal signal a12+ a12- 24v out gnd analogue input 2+ analogue input 2- 24v auxiliary voltage i/o ground a12+ a12- ...
Page 332
A b c fig. 98: isolation dip switch a. Digital inputs b. Float c. Connected to gnd (default) p3.15.6 autochange (id 1027) use this parameter to enable or disable the rotation of the start sequence and the priority of motors. The autochange changes the sequence in which the motors start to wear the m...
Page 333
Example after an autochange, the first motor is put last. The other motors move up 1 position. The start sequence of the motors: 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 --> autochange --> the start sequence of the motors: 2, 3, 4, 5, 1 --> autochange --> the start sequence of the motors: 3, 4, 5, 1, 2 p3.15.7 autochanged pum...
Page 334
K1 k1.1 k2 k2.1 k3 k3.1 k1 k1.1 k2 k2.1 k3 k3.1 k1.1 k1 k2 k3 k2 k3 k3 k1 k3 k1 k2 k1 k2.1 k2 k1 k3.1 k3 k2 mains m1 m2 m3 from relay motor 2 control motor 1 control from relay motor 3 control from relay fig. 99: selection 1 p3.15.8 autochange interval (id 1029) use this parameter to adjust the auto...
Page 335
• the multi-pump system operates (the start command is active), • the autochange interval time goes, • the pump that controls the system operates below the frequency specified by parameter p3.15.11 autochange frequency limit, • the number of pumps that operate is less or equal to the limit specified...
Page 336
P3.15.13 bandwidth (id 1097) use this parameter to set the bandwith area around the pid setpoint for starting and stopping of the auxiliary motors. When the pid feedback value stays in the bandwith area, the auxiliary motors do not start or stop. The value of this parameter is given as a percentage ...
Page 337
P3.15.15 constant production speed (id 1513) use this parameter to set the constant speed at which the motor locks when the next motor starts in the multimaster system. The value of this parameter is given as a percentage of the minimum frequency to the maximum frequency. P3.15.16 running pumps limi...
Page 338
P3.15.17.4 pump 4 interlock (id 429) use this parameter to select the digital input signal that is used as interlock signal for the multi-pump system. P3.15.17.5 pump 5 interlock (id 430) use this parameter to select the digital input signal that is used as interlock signal for the multi-pump system...
Page 339
Pressure m2 superv. Alarm level pid feedback pid setpoint m3 on off on off id1699 id167 (id21) fig. 101: the overpressure supervision function p3.15.18.2 supervision alarm level (id 1699) use this parameter to set the overpressure limit for the overpressure supervision. If the pid feedback becomes h...
Page 340
Note! In the multimaster and multifollower modes, it is possible to reset or set the necessary value only to the counter pump (1) running time. In the multimaster and multifollower modes, the monitoring value pump (1) running time shows the hours of the pump that is connected to this drive, the id n...
Page 341
1. Select pump 4 with parameter p3.15.19.3. 2. Set parameter p3.15.19.2 value to 0 h. 3. Push the button-type parameter p3.15.19.1. 4. Pump 4 running time is reset. P3.15.19.4 pump runtime alarm limit (id 1109) use this parameter to set the alarm limit for the runtime counter of the pump. When the v...
Page 342
P3.15.22.2 de-staging frequency (id 15546) use this parameter to adjust the output frequency level at which the auxiliary motor stops in the multi-pump system. Note! The parameter has no effect, if its value is set below min frequency reference (p3.3.1.1). By default, an auxiliary pump stops (is de-...
Page 343
P3.16.1 counter 1 mode (id 1104) use this parameter to enable the maintenance counter. A maintenance counter tells you that the maintenance must be done when the counter value goes above the set limit. P3.16.2 counter 1 alarm limit (id 1105) use this parameter to set the alarm limit for the maintena...
Page 344
Note! All other fire mode parameters will be locked when the fire mode is enabled and correct password is set in this parameter. Selection number selection name description 1002 enabled mode the drive resets all the faults and continues to operate at the same speed until it is not possible 1234 test...
Page 345
Normal start run enable run interlock 2 fire mode activation (close contact) motor speed stopped normal speed fire mode speed run interlock 1 fig. 104: the fire mode function p3.17.5 fire mode activation on close (id 1619) use this parameter to select the digital input signal that activates the fire...
Page 346
Note! You can not reset the counter. P3.17.9 fire mode run indication current (id 15580) use this parameter to set the current limit for the run indication signal of the relay output. This parameter only has effect if the value "run indication" is selected for a relay output and the fire mode is act...
Page 347
Selection number selection name description 0 not used the motor preheat function is disabled. 1 always in stop state the motor preheat function is activated always when the drive is in the stop state. 2 controlled by digital input the motor preheat function is activated by a digital input sig- nal,...
Page 348
Selection number selection name description 0 execute program the drive customizer is running. Configuration is not allowed for the drive customizer. 1 programming the drive customizer is not running. Configuration is allowed for the drive customizer. 10.21 pump control 10.21.1 auto-cleaning use the...
Page 349
Note! If the input is activated, the drive starts. P3.21.1.3 cleaning current limit (id 1712) use this parameter to set the current limit at which the auto-cleaning starts. If the current of the motor stays above this limit for longer than the set time, an auto- cleaning sequence starts. P3.21.1.4 c...
Page 350
P3.21.1.10 clean reverse frequency (id 1719) use this parameter to set the frequency reference of the drive for the reverse direction in the auto-cleaning cycle. See parameter p3.21.1.8 clean forward frequency. P3.21.1.11 clean reverse time (id 1720) use this parameter to set the operation time for ...
Page 351
The jockey pump function controls a jockey pump with a digital output signal. You can use a jockey pump if a pid controller is used to control the main pump. The function has 3 operation modes. Selection number selection name description 0 not used 1 pid sleep the jockey pump starts when the pid sle...
Page 352
P3.21.2.2 jockey start level (id 1675) use this parameter to set the level of the pid feedback signal at which the jockey pump starts when the main pump is in the sleep state. The jockey pump starts when pid sleep is active and the pid feedback signal goes below the level set in this parameter. Note...
Page 353
P3.21.3.1 priming function (id 1677) use this parameter to enable the priming pump function. A priming pump is a smaller pump that primes the inlet of the main pump to prevent the suction of air. The priming pump function controls a priming pump with a relay output signal. P3.21.3.2 priming time (id...
Page 354
P3.21.5.2 temperature signal (id 1705) use this parameter to select the source of the temperature signal that is used for the frost protection function. P3.21.5.3 temperature signal minimum (id 1706) use this parameter to set the minimum value of the temperature signal. For example, a temperature si...
Page 355
P3.21.6.4 flow switch minimum frequency (id 15587) use this parameter to set the output frequency level below which the flow switch supervision is disabled. 10.22 counters the vacon ® ac drive has different counters based on the operation time of the drive and the energy consumption. Some of the cou...
Page 356
• id1766: 1 (years) • id1767: 143 (days) • id1768: 2 (hours) • id1769: 21 (minutes) • id1770: 0 (seconds) id 2311 operating time trip counter reset you can reset the operating time trip counter with the pc, the control panel, or the fieldbus. If you use the pc or the control panel, reset the counter...
Page 357
• id1777: 1 (years) • id1778: 240 (days) • id1779: 2 (hours) • id1780: 18 (minutes) • id1781: 0 (seconds) 10.22.5 energy counter the energy counter counts the total quantity of energy that the drive gets from the supply network. The counter cannot be reset. To read the value of the counter through f...
Page 358
• 0 = kwh • 1 = mwh • 2 = gwh • 3 = twh • 4 = pwh example: if you receive the value 4500 from id2291, the value 42 from id2303, and the value 0 from id2305, the result is 45.00 kwh. 10.22.6 energy trip counter the energy trip counter counts the quantity of energy that the drive gets from the supply ...
Page 359
Id2309 energy trip counter unit the energy trip counter unit gives the unit for the value of the energy trip counter. • 0 = kwh • 1 = mwh • 2 = gwh • 3 = twh • 4 = pwh id2312 energy trip counter reset to reset the energy trip counter, use the pc, the control panel, or the fieldbus. If you use the pc...
Page 360: Fault Tracing
11 fault tracing when the control diagnostics of the ac drive find an unusual condition in the operation of the drive, the drive shows a notification about it. You can see the notification on the display of the control panel. The display shows the code, the name and a short description of the fault ...
Page 361
2 go to the submenu reset faults. Stop ready i/o id: m4.1 diagnostics ( 39 ) reset faults ( 0 ) active faults fault history 3 make a selection of the parameter reset faults. Stop ready i/o id: m4.2 reset faults help reset faults resetting with a parameter in the text display 1 go to the diagnostics ...
Page 362
3 make a selection of the value yes and push ok. Ready fault alarm stop run keypad i/o rev fwd bus 11.2 fault history in the fault history, you can find more data on the faults. There is a maximum number of 40 faults in the fault history. Examining the fault history in the graphical display 1 to see...
Page 363
3 you see the data in a list. Stop ready i/o code 39 source 3 source 1 id 380 state info old date 7.12.2009 time 04:46:33 operating time 862537s source 2 fault history m4.3.3.2 id: examining the fault history in the text display 1 push ok to go to fault history. Ready fault alarm stop run keypad 1/o...
Page 364
3 use the arrow button down to examine all the data. Ready fault alarm stop run keypad 1/o rev fwd bus ready fault alarm stop run keypad 1/o rev fwd bus ready fault alarm stop run keypad 1/o rev fwd bus vacon · 364 fault tracing 11 local contacts: http://drives.Danfoss.Com/danfoss-drives/local-conta...
Page 365
11.3 fault codes fault code fault id fault name possible cause how to correct the fault 1 1 overcurrent (hard- ware fault) there is too high a current (>4*i h) in the motor cable. Its cause can be 1 of these. • a sudden heavy load increase • a short circuit in the motor cables • the motor is not the...
Page 366
Fault code fault id fault name possible cause how to correct the fault 8 600 system fault there is no communication between the control board and the power. Reset the fault and restart the drive. Download the newest software from the danfoss drives website. Update the drive with it. If the fault occ...
Page 367
Fault code fault id fault name possible cause how to correct the fault 8 610 system fault defective component. Operation malfunction. Reset the fault and restart. Download the newest software from the danfoss drives website. Update the drive with it. If the fault occurs again, ask instructions from ...
Page 368
Fault code fault id fault name possible cause how to correct the fault 8 667 system fault ethernet phy is not recog- nised or it is in the wrong state. Reset the fault and restart the ac drive. Download the newest software from the danfoss drives website. Update the drive with it. If the fault occur...
Page 369
Fault code fault id fault name possible cause how to correct the fault 9 80 undervoltage (fault) the dc link voltage is lower than the limits. • the supply voltage is too low • a defective component • a defective input fuse • the external charge switch is not closed note! This fault becomes active o...
Page 370
Fault code fault id fault name possible cause how to correct the fault 14 130 ac drive overtemper- ature (fault, heatsink) the temperature is too low in the heatsink of the power unit or in the power board. The temperature limits of the heatsink are different in all the frames. Do a check of the act...
Page 371
Fault code fault id fault name possible cause how to correct the fault 26 250 startup prevented it is not possible to do a startup of the drive. When the run request is on, a new software (a firmware or an application), a parameter setting or other file that effects the operation of the drive, is lo...
Page 372
Fault code fault id fault name possible cause how to correct the fault 30 520 safety diagnostics the sto inputs have a dif- ferent status. Do a check of the external safety switch. Do a check of the input connection and cable of the safety switch. Reset the drive and restart. If the fault occurs aga...
Page 373
Fault code fault id fault name possible cause how to correct the fault 37 361 device changed (same type) the power unit was replaced by a new one that has the same size. The device is ready to be used. The parameters are availa- ble in the drive. Reset the fault. The drive reboots after you reset th...
Page 374
Fault code fault id fault name possible cause how to correct the fault 41 400 igbt temperature the calculated igbt tem- perature is too high. • the motor load is too high • the ambient tempera- ture is too high • hardware malfunction do a check of the parameter set- tings. Examine the actual quantit...
Page 375
Fault code fault id fault name possible cause how to correct the fault 47 663 software updated the software of the drive was updated, the full soft- ware package or an applica- tion. No steps are necessary. 50 1050 ai low fault 1 or more of the available analogue input signals is below 50% of the mi...
Page 376
Fault code fault id fault name possible cause how to correct the fault 57 1057 identification there was a failure in the identification run. Make sure that the motor is con- nected to the drive. Make sure that there is no load on the motor shaft. Make sure that the start command is not removed befor...
Page 377
Fault code fault id fault name possible cause how to correct the fault 68 1301 maintenance counter 1 alarm the value of the mainte- nance counter is higher than the alarm limit. Do the necessary maintenance. Reset the counter. See parameter b3.16.4 or p3.5.1.40. 1302 maintenance counter 1 fault the ...
Page 378
Fault code fault id fault name possible cause how to correct the fault 101 1101 feedback supervision fault (pid1) the pid controller: the feed- back value is not in the supervision limits (p3.13.6.2 and p3.13.6.3) and the delay (p3.13.6.4), if you set the delay. Do a check of the process. Do a check...
Page 379
Fault code fault id fault name possible cause how to correct the fault 118 1118 ahf over temp the advanced harmonic fil- ter function has caused an overtemperature fault through a digital input. Do a check of the advanced har- monic filter function. 300 700 unsupported the application is not com- pa...
Page 380: Appendix 1
12 appendix 1 12.1 the default values of parameters in the different applications the explanation of symbols in the table a = standard application b = hvac application c = pid control application d = multi-pump (single drive) application e = multi-pump (multidrive) application vacon · 380 appendix 1...
Page 381
Table 123: the default values of parameters in the different applications index parameter default unit id description a b c d e p3.2.1 remote control place 0 0 0 0 0 172 0 = i/o control p3.2.2 local/remote 0 0 0 0 0 211 0 = remote p3.2.6 i/o a logic 2 2 2 0 0 300 0 = forw-back 2 = forw-back (edge) p...
Page 382
Table 123: the default values of parameters in the different applications index parameter default unit id description a b c d e p3.5.1.2 ctrl signal 2 a 101 101 0 0 0 404 0 = digin slot0.1 101 = digin slota. 2 p3.5.1.4 ctrl signal 1 b 0 0 103 101 0 423 0 = digin slot0.1 101 = digin slota. 2 103 = di...
Page 383
Table 123: the default values of parameters in the different applications index parameter default unit id description a b c d e p3.5.1.23 preset freq selection 2 0 0 0 0 0 421 p3.5.1.31 pid setpoint selection 0 0 0 0 102 1047 0 = digin slot0.1 102 = digin slota. 3 p3.5.1.36 flushing refer- ence acti...
Page 384
Table 123: the default values of parameters in the different applications index parameter default unit id description a b c d e p3.5.2.2.6 ai2 signal inver- sion 0 0 0 0 0 398 p3.5.3.2.1 ro1 function 2 2 2 49 2 11001 2 = run p3.5.3.2.4 ro2 function 3 3 3 50 3 11004 3 = fault p3.5.3.2.7 ro3 function ...
Page 385
Table 123: the default values of parameters in the different applications index parameter default unit id description a b c d e p3.15.5 pump interlock- ing - - - 1 1 1032 0 = disabled 1 = enabled p3.15.6 autochange - - - 1 1 1027 0 = disabled 1 = enabled (interval) 2 = enabled (weekdays) p3.15.7 aut...
Page 386
Document id: dpd01083g rev. G sales code: doc-app100flow+dluk vacon ltd member of the danfoss group runsorintie 7 65380 vaasa finland www.Danfoss.Com.