- DL manuals
- ABB
- Transformer
- Relion 670 series
- Commissioning Manual
ABB Relion 670 series Commissioning Manual
Summary of Relion 670 series
Page 1
Relion® 670 series — transformer protection ret670 version 2.2 ansi commissioning manual.
Page 3
Document id: 1mrk 504 165-uus issued: may 2017 revision: - product version: 2.2 © copyright 2017 abb. All rights reserved.
Page 4
Copyright this document and parts thereof must not be reproduced or copied without written permission from abb, and the contents thereof must not be imparted to a third party, nor used for any unauthorized purpose. The software and hardware described in this document is furnished under a license and...
Page 5
Disclaimer the data, examples and diagrams in this manual are included solely for the concept or product description and are not to be deemed as a statement of guaranteed properties. All persons responsible for applying the equipment addressed in this manual must satisfy themselves that each intende...
Page 6
Conformity this product complies with the directive of the council of the european communities on the approximation of the laws of the member states relating to electromagnetic compatibility (emc directive 2004/108/ec) and concerning electrical equipment for use within specified voltage limits (low-...
Page 7
Table of contents section 1 introduction..........................................................................13 this manual............................................................................................ 13 intended audience..............................................................
Page 8
Checking the binary input/output circuits................................................55 binary input circuits............................................................................55 binary output circuits......................................................................... 56 checking ...
Page 9
Verifying the ieee c37.118/1344 tcp communication.................... 79 verifying the ieee c37.118/1344 udp communication.................... 85 optical budget calculation for pmu - pdc communication.................... 86 section 10 testing ied operation...............................................
Page 10
Completing the test.....................................................................109 restricted earth fault protection, low impedance refpdif (87n).. 110 verifying the settings.................................................................. 110 completing the test..............................
Page 11
Verifying the settings.................................................................. 143 testing the power swing detection function zmrpsb (68)........ 144 testing the tr1 timer.................................................................. 144 testing the block input, interaction between fdp...
Page 12
Instantaneous residual overcurrent protection efpioc (50n)........ 180 measuring the trip limit of set values.......................................... 180 completing the test.....................................................................181 four step residual overcurrent protection, (zero seq...
Page 13
Completing the test.....................................................................201 capacitor bank protection cbpgapc............................................. 201 verifying the settings and operation of the function....................202 completing the test.................................
Page 14
Completing the test.....................................................................225 rate-of-change frequency protection sapfrc (81)....................... 225 verifying the settings.................................................................. 225 completing the test........................
Page 15
Check the overcurrent block function......................................... 251 single transformer...................................................................... 252 parallel voltage regulation.......................................................... 253 completing the test...................
Page 16
Completing the test.....................................................................273 monitoring.............................................................................................273 gas medium supervision ssimg.................................................... 273 testing the gas ...
Page 17
Load drop compensation function, ldc.......................................... 287 voltage control of parallel transformers......................................... 289 minimum circulating current (mcc) method...................................289 master follower (mf) method............................
Page 18
12.
Page 19
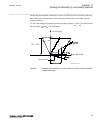
Section 1 introduction 1.1 this manual the commissioning manual contains instructions on how to commission the ied. The manual can also be used by system engineers and maintenance personnel for assistance during the testing phase. The manual provides procedures for the checking of external circuitry...
Page 20
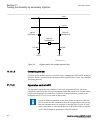
1.3 product documentation 1.3.1 product documentation set iec07000220-4-en.Vsd p la n n in g & p u rc h a se e n gi n e e rin g in st a lli n g c o m m is si o n in g o p e ra tio n m ai n te n a n ce d e co m m is si o n in g d e in st a lli n g & d is p o sa l application manual operation manual i...
Page 21
The commissioning manual contains instructions on how to commission the ied. The manual can also be used by system engineers and maintenance personnel for assistance during the testing phase. The manual provides procedures for the checking of external circuitry and energizing the ied, parameter sett...
Page 22
1.3.3 related documents documents related to ret670 document numbers application manual 1mrk 504 163-uus commissioning manual 1mrk 504 165-uus product guide 1mrk 504 166-ben technical manual 1mrk 504 164-uus type test certificate 1mrk 504 166-tus 670 series manuals document numbers operation manual ...
Page 23
Class 1 laser product. Take adequate measures to protect the eyes and do not view directly with optical instruments. The caution icon indicates important information or warning related to the concept discussed in the text. It might indicate the presence of a hazard which could result in corruption o...
Page 24
• the character ^ in front of an input/output signal name indicates that the signal name may be customized using the pcm600 software. • the character * after an input signal name indicates that the signal must be connected to another function block in the application configuration to achieve a valid...
Page 25
Function block name edition 1 logical nodes edition 2 logical nodes bdcgapc swsggio bbcswi bdcgapc bdzsgapc bbs6lln0 bdzsgapc lln0 bdzsgapc bfptrc_f01 bfptrc bfptrc bfptrc_f02 bfptrc bfptrc bfptrc_f03 bfptrc bfptrc bfptrc_f04 bfptrc bfptrc bfptrc_f05 bfptrc bfptrc bfptrc_f06 bfptrc bfptrc bfptrc_f07...
Page 26
Function block name edition 1 logical nodes edition 2 logical nodes busptrc_b1 busptrc bbsplln0 busptrc busptrc_b2 busptrc busptrc busptrc_b3 busptrc busptrc busptrc_b4 busptrc busptrc busptrc_b5 busptrc busptrc busptrc_b6 busptrc busptrc busptrc_b7 busptrc busptrc busptrc_b8 busptrc busptrc busptrc...
Page 27
Function block name edition 1 logical nodes edition 2 logical nodes bznpdif_z2 bznpdif bznpdif bznpdif_z3 bznpdif bznpdif bznpdif_z4 bznpdif bznpdif bznpdif_z5 bznpdif bznpdif bznpdif_z6 bznpdif bznpdif bznspdif_a bznspdif bzasgapc bzaspdif bznsgapc bznspdif bznspdif_b bznspdif bzbsgapc bzbspdif bzn...
Page 28
Function block name edition 1 logical nodes edition 2 logical nodes cvmmxn cvmmxn cvmmxn d2ptoc d2lln0 d2ptoc ph1ptrc d2ptoc ph1ptrc dpgapc dpggio dpgapc drprdre drprdre drprdre ecpsch ecpsch ecpsch ecrwpsch ecrwpsch ecrwpsch ef2ptoc ef2lln0 ef2ptrc ef2rdir gen2phar ph1ptoc ef2ptrc ef2rdir gen2phar ...
Page 29
Function block name edition 1 logical nodes edition 2 logical nodes l4cpdif l4clln0 l4cpdif l4cptrc lln0 l4cgapc l4cpdif l4cpsch l4cptrc l4ufcnt l4ufcnt l4ufcnt l6cpdif l6cpdif l6cgapc l6cpdif l6cphar l6cptrc lappgapc lapplln0 lapppdup lapppupf lapppdup lapppupf lccrptrc lccrptrc lccrptrc lcnsptoc l...
Page 30
Function block name edition 1 logical nodes edition 2 logical nodes ns2ptoc ns2lln0 ns2ptoc ns2ptrc ns2ptoc ns2ptrc ns4ptoc ef4lln0 ef4ptrc ef4rdir gen4phar ph1ptoc ef4ptrc ef4rdir ph1ptoc o2rwptov gen2lln0 o2rwptov ph1ptrc o2rwptov ph1ptrc oc4ptoc oc4lln0 gen4phar ph3ptoc ph3ptrc gen4phar ph3ptoc p...
Page 31
Function block name edition 1 logical nodes edition 2 logical nodes schlcch schlcch schlcch scilo scilo scilo scswi scswi scswi sdepsde sdepsde sdepsde sdeptoc sdeptov sdeptrc sesrsyn rsy1lln0 aut1rsyn man1rsyn synrsyn aut1rsyn man1rsyn synrsyn slgapc slggio slgapc smbrrec smbrrec smbrrec smpptrc sm...
Page 32
Function block name edition 1 logical nodes edition 2 logical nodes tr1atcc tr1atcc tr1atcc tr8atcc tr8atcc tr8atcc trpttr trpttr trpttr u2rwptuv gen2lln0 ph1ptrc u2rwptuv ph1ptrc u2rwptuv uv2ptuv gen2lln0 ph1ptrc uv2ptuv ph1ptrc uv2ptuv vdcptov vdcptov vdcptov vdspvc vdrfuf vdspvc vmmxu vmmxu vmmxu...
Page 33
Function block name edition 1 logical nodes edition 2 logical nodes zmmapdis zmmapdis zmmapdis zmmpdis zmmpdis zmmpdis zmqapdis zmqapdis zmqapdis zmqpdis zmqpdis zmqpdis zmrapdis zmrapdis zmrapdis zmrpdis zmrpdis zmrpdis zmrpsb zmrpsb zmrpsb zsmgapc zsmgapc zsmgapc 1mrk 504 165-uus - section 1 intro...
Page 34
28.
Page 35
Section 2 safety information 2.1 symbols on the product all warnings must be observed. Read the entire manual before doing installation or any maintenance work on the product. All warnings must be observed. Class 1 laser product. Take adequate measures to protect your eyes and do not view directly w...
Page 36
Do not touch circuitry during operation. Potentially lethal voltages and currents are present. Always use suitable isolated test pins when measuring signals in open circuitry. Potentially lethal voltages and currents are present. Never connect or disconnect a wire and/or a connector to or from a ied...
Page 37
The ied with accessories should be mounted in a cubicle in a restricted access area within a power station, substation or industrial or retail environment. 2.3 caution signs whenever changes are made in the ied, measures should be taken to avoid inadvertent tripping. The ied contains components whic...
Page 38
2.4 note signs observe the maximum allowed continuous current for the different current transformer inputs of the ied. See technical data. Section 2 1mrk 504 165-uus - safety information 32 transformer protection ret670 2.2 ansi commissioning manual.
Page 39
Section 3 available functions the following tables list all the functions available in the ied. Those functions that are not exposed to the user or do not need to be configured are not described in this manual. 3.1 main protection functions table 2: example of quantities 2 = number of basic instance...
Page 40
Iec 61850 or function name ansi function description transformer ret670 (customized) zmmpdis, zmmapdis 21 full-scheme distance protection, quadrilateral for ground faults 0-5 zdmrdir 21d directional impedance element for mho characteristic 0-2 zdardir additional distance protection directional funct...
Page 41
Iec 61850 or function name ansi function description ret670 (customized) sdepsde 67n sensitive directional residual overcurrent and power protection 0-3 lcpttr 26 thermal overload protection, one time constant, celsius 0-2 lfpttr 26 thermal overload protection, one time constant, fahrenheit 0-2 trpt...
Page 42
3.3 control and monitoring functions iec 61850 or function name ansi function description transformer ret670 (customized) control sesrsyn 25 synchrocheck, energizing check and synchronizing 0-6 apc30 3 control functionality for up to 6 bays, max 30 objects (6cbs), including interlocking (see table 4...
Page 43
Iec 61850 or function name ansi function description transformer ret670 (customized) smpptrc 94 tripping logic 12 tmagapc trip matrix logic 12 almcalh logic for group alarm 5 wrncalh logic for group warning 5 indcalh logic for group indication 5 and, gate, inv, lld, or, pulsetimer, rsmemory, srmemor...
Page 44
Table 3: total number of instances for basic configurable logic blocks basic configurable logic block total number of instances and 280 gate 40 inv 420 lld 40 or 298 pulsetimer 40 rsmemory 40 srmemory 40 timerset 60 xor 40 table 4: number of function instances in apc30 function name function descrip...
Page 45
Function name function description total number of instances locrem handling of lr-switch positions 5 xlnproxy proxy for signals from switching device via goose 42 goosexlnrcv goose function block to receive a switching device 42 table 5: total number of instances for configurable logic blocks q/t c...
Page 46
Iec 61850 or function name ansi function description transformer ret670 (customized) monitoring cvmmxn power system measurement 6 cmmxu current measurement 10 vmmxu voltage measurement phase-phase 6 cmsqi current sequence measurement 6 vmsqi voltage sequence measurement 6 vnmmxu voltage measurement ...
Page 47
Iec 61850 or function name ansi function description transformer ret670 (customized) metering pcfcnt pulse-counter logic 16 etpmmtr function for energy calculation and demand handling 6 3.4 communication iec 61850 or function name ansi function description transformer ret670 (customized) station com...
Page 48
Iec 61850 or function name ansi function description transformer ret670 (customized) multicmdrcv, multicmdsnd multiple command and transmit 60/10 optical103 iec 60870-5-103 optical serial communication 1 rs485103 iec 60870-5-103 serial communication for rs485 1 agsal generic security application com...
Page 49
Iec 61850 or function name ansi function description transformer ret670 (customized) ldcmrecbins2_2m receive binary status from ldcm, 2mbit 3 ldcmrecbins3_2m receive binary status from remote ldcm, 2mbit 3 scheme communication zcpsch 85 scheme communication logic with delta based blocking scheme sig...
Page 50
Iec 61850 or function name description chnglck change lock function smbi signal matrix for binary inputs smbo signal matrix for binary outputs smmi signal matrix for ma inputs smai1 - smai12 signal matrix for analog inputs 3phsum summation block 3 phase athstat authority status athchck authority che...
Page 51
Section 4 starting up 4.1 factory and site acceptance testing testing the proper ied operation is carried out at different occasions, for example: • acceptance testing • commissioning testing • maintenance testing this manual describes the workflow and the steps to carry out the commissioning testin...
Page 52
• three-phase test kit or other test equipment depending on the complexity of the configuration and functions to be tested. • pc with pcm600 installed along with the connectivity packages corresponding to the ieds to be tested. • administration rights on the pc, to set up ip addresses • product docu...
Page 53
Set the ied time if no time synchronization source is configured. To ensure that the ied is according to the delivery and ordering specifications documents delivered together with each ied, the user should also after start-up use the built in hmi to check the ied's: • software version, main menu/dia...
Page 54
Each ied has an rj-45 ethernet interface connector on the front. The front ethernet connector is recommended to be used for communication with pcm600. When an ethernet-based station protocol is used, pcm600 communication can use the same ethernet port and ip address. To connect pcm600 to the ied, tw...
Page 55
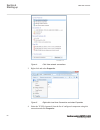
Iec13000057-1-en.Vsd iec13000057 v1 en figure 3: select: search programs and files 2. Type view network connections and click on the view network connections icon. 1mrk 504 165-uus - section 4 starting up transformer protection ret670 2.2 ansi 49 commissioning manual.
Page 56
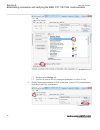
Iec13000058-1-en.Vsd iec13000058 v1 en figure 4: click view network connections 3. Right-click and select properties. Iec13000059-1-en.Vsd iec13000059 v1 en figure 5: right-click local area connection and select properties 4. Select the tcp/ipv4 protocol from the list of configured components using ...
Page 57
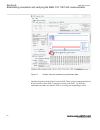
Iec13000060-1-en.Vsd iec13000060 v1 en figure 6: select the tcp/ipv4 protocol and open properties 5. Select use the following ip address and define ip address and subnet mask if the front port is used and if the ip address is not set to be obtained automatically by the ied, see figure 7 . The ip add...
Page 58
Iec13000062-1-en.Vsd iec13000062 v1 en figure 7: select: use the following ip address 6. Use the ping command to verify connectivity with the ied. 7. Close all open windows and start pcm600. The pc and ied must belong to the same subnetwork for this set-up to work. Setting up the pc to access the ie...
Page 59
The red led on the ied flashes, and the green led is lit while the ied is in the configuration mode. When the configuration is written and completed, the ied is automatically set into normal mode. For further instructions please refer to the users manuals for pcm600. 4.7 checking ct circuits check t...
Page 60
If the ct secondary circuit ground connection is removed without the current transformer primary being de-energized, dangerous voltages may result in the secondary ct circuits. 4.8 checking vt circuits check that the wiring is in strict accordance with the supplied connection diagram. Correct possib...
Page 61
Still isolated and the ied is in test mode. Before removing the test handle, check the measured values in the ied. Not until the test handle is completely removed, the trip and alarm circuits are restored for operation. Verify that the contact sockets have been crimped correctly and that they are fu...
Page 62
4.10.2 binary output circuits preferably, disconnect the binary output connector from the binary output cards. Check all connected signals so that both load and polarity are in accordance with ied specifications. 4.11 checking optical connections check that the tx and rx optical connections are corr...
Page 63
Section 5 configuring the ied and changing settings 5.1 overview the customer specific values for each setting parameter and a configuration file have to be available before the ied can be set and configured, if the ied is not delivered with a configuration. Use the configuration tools in pcm600 to ...
Page 64
5.2 configuring analog ct inputs the analog input channels must be configured to get correct measurement results as well as correct protection functionality. Because all protection algorithms in the ied utilize the primary system quantities, it is extremely important to make sure that connected curr...
Page 65
Each logical i/o module has an error flag that indicates signal or module failure. The error flag is also set when the physical i/o module of the correct type is not detected in the connected slot. 1mrk 504 165-uus - section 5 configuring the ied and changing settings transformer protection ret670 2...
Page 66
60
Page 67
Section 6 establishing connection and verifying the spa/iec communication 6.1 entering settings if the ied is connected to a monitoring or control system via the rear spa/iec103 port, the spa/iec103 port has to be set either for spa or iec103 use. 6.1.1 entering spa settings the spa/iec port is loca...
Page 68
Procedure: 1. Set the port for iec use on the local hmi under main menu /configuration / communication /station communication/port configuration/slm optical serial port/protocol:1. When the communication protocol is selected, the ied is automatically restarted, and the port then operates as an iec p...
Page 69
1. Check that the master system time-out for response from the ied, for example after a setting change, is > 40 seconds. 2. Use a protocol analyzer and record the communication between the ied and the iec master. Check in the protocol analyzer’s log that the ied answers the master messages. 3. Gener...
Page 70
Distance 1 km glass distance 25 m plastic losses in connection box, two contacts (1 db/contact) - 2 db margin for 2 repair splices (0.5 db/splice) 1 db - maximum total attenuation 11 db 7 db section 6 1mrk 504 165-uus - establishing connection and verifying the spa/iec communication 64 transformer p...
Page 71
Section 7 establishing connection and verifying the lon communication 7.1 communication via the rear ports 7.1.1 lon communication lon communication is normally used in substation automation systems. Optical fiber is used within the substation as the physical communication link. The test can only be...
Page 72
The control center and also from other ieds via bay-to-bay horizontal communication. For lon communication an slm card should be ordered for the ieds. The fibre optic lon bus is implemented using either glass core or plastic core fibre optic cables. Table 12: specification of the fibre optic connect...
Page 73
The hv control 670 software module and 670 series object type files are used with both 650 and 670 series ieds. Use the lon network tool (lnt) to set the lon communication. This is a software tool applied as one node on the lon bus. To communicate via lon, the ieds need to know • the node addresses ...
Page 74
Table 14: lon node information parameters parameter range default unit parameter description neuronid* 0 - 12 not loaded - neuron hardware identification number in hexadecimal code location 0 - 6 no value - location of the node *can be viewed on the local hmi ade settings are available on the local ...
Page 75
Distance 1 km glass distance10 m plastic losses in connection box, two contacts (1db/contact) - 2 db margin for repair splices (0.5 db/splice) 0.5 db - maximum total attenuation 11 db 7 db 1mrk 504 165-uus - section 7 establishing connection and verifying the lon communication transformer protection...
Page 76
70
Page 77
Section 8 establishing connection and verifying the iec 61850 communication 8.1 overview the rear optical ethernet ports are used for: • process bus (iec/uca 61850-9-2le) communication • ieee c37.118/1344 communication • substation bus (iec 61850-8-1) communication 8.2 setting the station communicat...
Page 78
8.3 verifying the communication to verify that the communication is working a test/analyzing tool, for example itt600, can be used. Verifying redundant iec 61850-8-1 communication ensure that the ied receives iec 61850-8-1 data on the selected ethernet ports. Browse in the local hmi to main menu/dia...
Page 79
Section 9 establishing connection and verifying the ieee c37.118/1344 communication 9.1 overview the ied can support synchrophasor data communication via ieee c37.118 and/or ieee1344 with maximum 8 tcp clients and 6 udp client groups, simultaneously. The rear oem ports are used for ieee c37.118/1344...
Page 80
9.3 setting the pmu station communication (pmu configuration) to enable ieee c37.118/1344 communication, the corresponding oem ports must be activated. The galvanic ethernet front port and the rear optical ports can be used for ieee c37.118/1344 communication. To enable ieee c37.118/1344 synchrophas...
Page 81
9.4 setting the tcp/udp client communication as an example of a tcp/udp client, the openpdc tool (pmu connection tester ver. 4.2.12) from grid protection alliance is used in this section. Install pmu connection tester tool on a pc with ethernet network adaptor available. The same pc used for pcm600 ...
Page 82
Iec140000134-1-en.Vsd iec140000134 v1 en 1.1. Navigate to the settings tab. 1.2. Force the ip stack to ipv4 by setting the parameter forceipv4 to true. 2. Set the connection parameters on pmu connection tester for tcp communication according to the pmu configuration. Iec140000135-1-en.Vsd iec1400001...
Page 83
2.1. Set host ip to the pmu ip address configured for the port in use. Here the lanab:1 ipaddress (192.168.1.10) is set. 2.2. Set port to the ied's tcp port set in the pmu under parameter c37.118tcpport (4712 is default). Alternatively, in order to make an ieee1344 communication, the 1344tcpport par...
Page 84
Iec140000137-1-en.Vsd iec140000137 v1 en 3.3. Set the host ip as the pmu ip address configured for the port in use. Here the lanab:1 ipaddress (192.168.1.10) is set. 3.4. Set the port as the tcp port defined in the pmu for control of data sent over udp client group 1 (default value: 4713). This can ...
Page 85
Set the pmu connection tester parameters in order to establish an ieee c37.118 connection with the pmu. 9.5.1 verifying the ieee c37.118/1344 tcp communication after setting both pmu configuration and the tcp client configuration (as explained in sections setting the pmu station communication (pmu r...
Page 86
Iec140000139-1-en.Vsd iec140000139 v1 en figure 11: graphic view over streaming synchrophasor data • open the drop-down menu in the command field. There is a list of commands that can be sent from the client (pmu connection tester) to the pmu. Try different commands and make sure that the pmu is rec...
Page 87
Iec140000140-1-en.Vsd iec140000140 v1 en figure 12: drop-down menu with commands for testing the pmu • switch to the protocol specific tab. Here, all the ieee c37.118 message types can be seen. If the headerframe is not included, ask the pmu to send the header frame via the send header frame command...
Page 88
Iec140000141-1-en.Vsd iec140000141 v1 en figure 13: all the ieee c37.118 message types • it is also possible to capture the ieee c37.118 synchrophasor data in an excel file. This is done by navigating to file/capture/start stream debug capture... The tool will ask to set stream debug capture file na...
Page 89
Iec140000142-1-en.Vsd iec140000142 v1 en figure 14: start capturing the ieee c37.118 synchrophasor data • the synchrophasor data capturing process can be stopped at any point of time by navigating to file/capture/stop stream debug capture... 1mrk 504 165-uus - section 9 establishing connection and v...
Page 90
Iec140000143-1-en.Vsd iec140000143 v1 en figure 15: stop capturing the ieee c37.118 synchrophasor data • open the capture file and observe the captured synchrophasor data. In order to get the phasor names on top of each column (see figure 16 ), the capture process should start before connecting the ...
Page 91
Iec140000144 v1 en figure 16: captured synchrophasor data 9.5.2 verifying the ieee c37.118/1344 udp communication after setting both pmu configuration and the udp client configuration (as explained in sections setting the pmu station communication (pmu report) , setting the pmu station communication...
Page 92
Iec140000145-1-en.Vsd iec140000145 v1 en figure 17: verifying the udp communication using pmu connection tester • now it should be possible to see the streaming synchrophasor data. • verify the communication by following the same steps as in section verifying the ieee c37.118/1344 tcp communication ...
Page 93
14 12 10 8 6 4 2 0 0 0.5 1.0 1.5 2.0 2.5 3.0 3.5 4.0 62.5/125 µm 50/125 µm o p b – o p t ic a l p o w e r b u d g e t - d b fiber optic cable length - km iec11000409_1_en.Vsd iec11000409 v1 en figure 18: optical power budget for fiber optic cable lengths as shown in the graph, if one uses a 62.5/125...
Page 94
88.
Page 95
Section 10 testing ied operation 10.1 preparing for test 10.1.1 requirements ied test requirements: • calculated settings • application configuration diagram • signal matrix (smt) configuration • terminal connection diagram • technical manual • three-phase test equipment • pcm600 the setting and con...
Page 96
Prepare the ied for test before testing a particular function. Consider the logic diagram of the tested protection function when performing the test. All included functions in the ied are tested according to the corresponding test instructions in this chapter. The functions can be tested in any orde...
Page 97
Included in the test mode and is not prevented to trip during the test operations. The test switch should then be connected to the ied. Verify that analog input signals from the analog input module are measured and recorded correctly by injecting currents and voltages required by the specific ied. T...
Page 98
1. Browse to the testmode menu and press e. The testmode menu is found on the local hmi under main menu/test/ied test mode/testmode 2. Use the up and down arrows to choose enabled and press e. 3. Press the left arrow to exit the menu. The dialog box save changes appears. 4. Choose yes, press e and e...
Page 99
Cause a massive potential build up that may damage the transformer and cause personal injury. 10.4 connecting the test equipment to the ied connect the test equipment according to the ied specific connection diagram and the needed input and output signals for the function under test. An example of a...
Page 100
10.5 releasing the function to be tested release or unblock the function to be tested. This is done to ensure that only the function or the chain of functions to be tested are in operation and that other functions are prevented from operating. Release the tested function(s) by setting the correspond...
Page 101
Apply input signals as needed according to the actual hardware and the application configuration. 1. Inject a symmetrical three-phase voltage and current at rated value. 2. Compare the injected value with the measured values. The voltage and current phasor menu in the local hmi is located under main...
Page 102
Iec10000032-1-en.Vsd iec10000032 v1 en figure 20: pcm600 report tool display after communication interruption 10.7 testing the protection functionality each protection function must be tested individually by secondary injection. • verify operating levels (trip) and timers. • verify alarm and blockin...
Page 103
10.8 forcing of binary input/output signals for testing 10.8.1 forcing concept forcing of binary inputs and outputs is a convenient way to test wiring in substations as well as testing configuration logic in the ieds. Basically it means that all binary inputs and outputs on the ied i/o modules (bom,...
Page 104
Iec15000029 v1 en 2. Exit back to the root menu. 3. Select yes in the save dialogue box. Once the ied is in test mode the yellow start led starts to blink. 10.8.2.2 enable forcing using testmode function block • use the testmode function block, appropriately configured in pcm600/act. It may be conve...
Page 105
Iec15000021 v1 en figure 21: value line of the desired signal 3. Use the up/down arrows on the lhmi to change the signal value or the appropriate menu in pcm600. The status of the signal changes automatically to forced (i.E. There is no need to set the status to forced manually). On the lhmi, these ...
Page 106
It is possible to power-cycle the ied in this state without losing the forcing states and values. This means that once a signal is forced, and the ied remains in ied test mode, the input or output will appear “frozen” at the value selected by the user, even if the ied is switched off and back on aga...
Page 107
1. Right click on the ied in the plant structure and select signal monitoring. 2. Click on the list view tab. 3. Click forcing session in the menu ied/start forcing. Iec15000023 v1 en 4. Click start editing signal value for forcing on the tool bar. Iec15000024 v1 en the signal monitoring menu change...
Page 108
Iec15000026 v1 en this commits the values to the ied and exits the editing session. 7. Click cancel to abort the changes and revert back to actual ied values. Iec15000032 v1 en regardless if the forcing changes are commited or canceled, the forcing is still active. To force more signals, click the b...
Page 109
1. Set iedtestmode to off in the lhmi menu. 2. Exit from the menu and click yes in the save dialogue box. This immediately undoes all forcing, regardless of how it was accomplished and disabled. 10.8.4.3 undo forcing by using pcm600 1. Uncheck forcing session under the menu ied. Iec15000031 v1 en 2....
Page 110
104.
Page 111
Section 11 testing functionality by secondary injection 11.1 testing disturbance report 11.1.1 introduction the following sub-functions are included in the disturbance report function: • disturbance recorder • event list • event recorder • trip value recorder • indications if the disturbance report ...
Page 112
A new recording begins. The view is updated if you leave the menu and return. 1.2. Navigate to general information or to trip values to obtain more detailed information. 2. Open the disturbance handling tool for the ied in the plant structure in pcm600. 2.1. Right-click and select execute manual tri...
Page 113
When the ied is brought into normal service it is recommended to delete all events resulting from commissioning tests to avoid confusion in future fault analysis. All events in the ied can be cleared in the local hmi under main menu//clear/clear internal event list or main menu/clear/clear process e...
Page 114
4. Check that the trip and alarm contacts operate according to the configuration logic. 5. Decrease the current slowly from operate value and note the reset value. Depending on the power transformer phase shift/vector group (yd (wye/delta) and so on), the single-phase injection current may appear as...
Page 115
11.3.2.1 verifying the settings 1. Connect single-phase or three-phase test set to inject the operating voltage. The injection is done across the measuring branch. The required trip and alarm voltage, as well as the used stabilizing resistance value must be set in the function. Note as well that use...
Page 116
11.3.3 restricted earth fault protection, low impedance refpdif (87n) prepare the ied for verification of settings outlined in section "preparing the ied to verify settings" . 11.3.3.1 verifying the settings 1. Connect the test set for single-phase current injection to the protection terminals conne...
Page 117
Prepare the ied for verification of settings outlined in section 1 “overview” and section 2 “preparing for test” in this chapter. Current variation local criteria procedure 1. Set operation to enabled. 2. Connect the test set for three phase current injection to the appropriate ied terminals. 3. Inj...
Page 118
1. Connect the test set for three phase voltage injection (a, b, c) or residual voltage injection (n) to the appropriate ied terminals. This is dependent on how the ied is fed from the ct . 2. Increase the injected zero sequence current and note the trip value (pickup value) of the studied step of t...
Page 119
Measure operating characteristics during constant current conditions. Keep the measured current as close as possible to its rated value or lower. But make sure it is higher than the set minimum operating current. Ensure that the maximum continuous current to the ied does not exceed four times its ra...
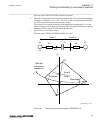
Page 120
X1 r x (o/phase) 50% 80% 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 80% of rldfwd 40% of rldfwd 0.5 x rfpp 12 ansi05000368-1-en.Vsd 13 b 120° 20° a c ansi05000368 v1 en figure 23: distance protection characteristic with test points for phase-to-phase measurements table 18: test points for phase-to-phase loops l1-l2 (o...
Page 121
Test point reach set value comments 9 x –0.4 x rldfw x tan(argdir=20°) r 0.4 x rldfw 10 x 0.5 x x1 set exact –0.5 x r1 set x tan(argnegres=30°) r –0.23 x x1 set 11 x 0.8 x x1 set exact –0.5 x r1 set x tan(argnegres=30°) r –0.37 x x1 set 12 x 0.5 x x1 set r 0.5 x r1 set 13 x 0 only used when rldfw > ...
Page 122
Table 19: test points for phase-to-earth l3-e (ohm/loop) test point reach value comments 1 x (2 x x1 set +x0 set )/3 r 0 2 x (2 x x1 set + x0 set )/3 r 2 x r1 set + r0 set )/3 3 x 0.8 x (2 x x1 set + x0 set )/3 r 0.8 x (2 x r1 set + r0 set )/3 +rfpe set 4 x 0.5 x (2 x x1 set + r0 set )/3 r 0.5 x (2 ...
Page 123
1. Subject the ied to healthy normal load conditions for at least two seconds. 2. Apply the fault condition and slowly decrease the measured impedance to find the operating value of the phase-to-phase fault for zone 1 according to test point 1 in figure 23 and table 18 . Compare the result of the me...
Page 124
11.4.2 phase selection, quad, fixed angle, load encroachment fdpspdis (21) prepare the ied for verification of settings outlined in section "preparing the ied to verify settings" . The phase selectors operate on the same measuring principles as the impedance measuring zones. So it is necessary to fo...
Page 125
Table 20: test points for phase-to-ground loop cg (ohm/loop) test point reach value comments 1 x [x1+xn] xn=(x 0 -x 1 )/3 r 0 2 x 0 r rldfwd when rldfwd r rfltfwpg when rldfwdpg > rfltfwpg 3 x 0.85·[x1+xn] r≈0.491·(x1+xn)+rfltfwdpg r 4 x 0.85·[x1+xn] can be limited by rfltfwpg r -0.85·[x1+xn]· tan (...
Page 126
Table 21: test points for phase-to-phase loops a-b (ohm/phase) test point reach value comments 1 x x1 r 0 2 x 0 r rldfwd when rldfwd r 0.5·rfldfwpp when rldfwd > 0,5·rfldfwpp 3 x 0.85·x1 r=0.491·x1+0.5 rfldfwdpp r 0.85·x1·1/tan(60°)+0.5 rfldfwdpp 4 x 0.85·x1 can be limited by rfldfwpp r -0.85·x1·tan...
Page 127
When the load encroachment characteristic is deliberately set very high in order not to have an influence, then the test points 2 and 5 can be replaced by test point 7. 4. Repeat steps 1 to 3 to find the operate value for the phase-to-phase fault in a - c according to figure 26 and table 21 . 11.4.2...
Page 128
11.4.3.1 phase-to-phase faults zangpp zpp 1 2 3 ohm/phase r x iec07000009-4-en.Vsd 50% iec07000009 v4 en figure 27: proposed test points for phase-to-phase fault table 22: test points for phase-to-phase (ohms / phase) test points reach value comments 1 x zpp · sin(zangpp) r zpp · sin(zangpp) 2 x 0,5...
Page 129
Zangpg 50% ohm/loop r x ansi07000010-1-en.Vsd ansi07000010 v1 en figure 28: proposed test points for phase-to-ground faults table 23: test points for phase-to-ground loops a-b (ohm/loop) test points reach value comments 1 x zpg · sin(zangpg) r zpg · cos(zangpg) 2 x 0,5·zpg · sin(zangpg) r 0,5·zpg + ...
Page 130
11.4.5 distance protection zones, quadrilateral characteristic, separate settings zmrpdis (21) prepare the ied for verification of settings as outlined in section "preparing for test" in this chapter. Consider releasing zone 1 with the phase selection with load encroachment, quadrilateral characteri...
Page 131
X1 r x (o/phase) 50% 80% 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 80% of rldfwd 40% of rldfwd 0.5 x rfpp 12 ansi05000368-1-en.Vsd 13 b 120° 20° a c ansi05000368 v1 en figure 29: distance protection characteristic with test points for phase-to-phase measurements table 24 is used in conjunction with figure 29 . 50% 80...
Page 132
Table 24: test points for phase-to-phase loops l1-l2 (ohm/loop) test point reach set value comments 1 x x1 set r 0 2 x x1 set r r1 set 3 x 0.8 x x1 set r 0.8 x r1 set + rfpp/2 4 x 0.5 x x1 set r 0.5 x r1 set + rfpp/2 5 x 0.85 x rfpp x tan (ldangle) ldangle = angle for the maximal load transfer r 0.8...
Page 133
Test point reach value comments 3 x 0.8 x (2 x x1 set + x0 set )/3 r 0.8 x (2 x r1 set + r0 set )/3 +rfpg set 4 x 0.5 x (2 x x1 set + r0 set )/3 r 0.5 x (2 x r1 set +r0 set )/3 + rfpg set 5 x 0.85 x rfpg set x tan(ldangleset) ldangle = angle for the maximal load transfer. R 0.85 x rfpg 6 x rldfwdset...
Page 134
Observe that the zones that are not tested have to be blocked and the zone that is tested has to be released. 4. Repeat steps 1 to 3 above to find the operating value for the phase-to-ground fault l3-g according to figure 30 and table 25 . Test points 8, 9, 10 and 11 are intended to test the directi...
Page 135
Ensure that the maximum continuous current of an ied does not exceed four times its rated value, if the measurement of the operating characteristics runs under constant voltage conditions. To verify the settings the operating points according to figures 31 and 32 should be tested. See also tables 26...
Page 136
X1 r x 85% 1 3 5 2 6 4 50% rldfwd argnegres 0.5·rfltfwdpp ldangle ansi09000735-1-en.Vsd argdir 60° ) / ( phase w ) / ( phase w 7 ansi09000735 v1 en figure 32: operating characteristic for phase selection function, forward direction phase-to-phase faults table 26: test points for phase-to-ground loop...
Page 137
Table 27: test points for phase-to-phase loops a-b test point value comments 1 x x1 r 0 2 x 0 r rldfwd 3 x 0.85·x1 r=0.491·x1+0.5 rfldfwdpp r 0.85·x1·1/tan(60°)+0.5 rfldfwdpp 4 x 0.85·x1 r -0.85·x1·tan (angnegres-90°) 5 x 0.5·rfldfwdpp·tan (argld) r 0.5·rfldfwdpp 6 x -0.5·rldfwd·tan (argdir) r 0.5·r...
Page 138
11.4.6.2 completing the test continue to test another function or end the test by changing the testmode setting to disabled. Restore connections and settings to their original values, if they were changed for testing purposes. 11.4.7 high speed distance protection zones, quadrilateral and mho charac...
Page 139
X1 r x (o/phase) 50% 80% 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 80% of rldfwd 40% of rldfwd 0.5 x rfpp 12 ansi05000368-1-en.Vsd 13 b 120° 20° a c ansi05000368 v1 en figure 33: distance protection characteristic with test points for phase-to-phase measurements table 28: test points for phase-to-phase loops a-b (ohm...
Page 140
Test point reach set value comments 9 x –0.4 x rldfwd x tan(argdir=20°) r 0.4 x rldfwd 10 x 0.5 x x1 set exact –0.5 x r1 set x tan(argnegres=30°) r –0.23 x x1 set 11 x 0.8 x x1 set exact –0.5 x r1 set x tan(argnegres=30°) r –0.37 x x1 set 12 x 0.5 x x1 set r 0.5 x r1 set 13 x 0 r 0.5 x rfppzx table ...
Page 141
Table 29: test points for phase-to-ground c-g (ohm/loop) test point reach value comments 1 x (2 x x1 set +x0 set )/3 r 0 2 x (2 x x1 set + x0 set )/3 r 2 x r1 set + r0 set )/3 3 x 0.8 x (2 x x1 set + x0 set )/3 r 0.8 x (2 x r1 set + r0 set )/3 +rfpg set 4 x 0.5 x (2 x x1 set + r0 set )/3 r 0.5 x (2 ...
Page 142
1. Subject the ied to healthy normal load conditions for at least two seconds. 2. Apply the fault condition and slowly decrease the measured impedance to find the operating value of the phase-to-phase fault for zone 1 according to test point 1 in figure 33 and table 28 . Compare the result of the me...
Page 143
11.4.8 high speed distance for series compensated line zones, quadrilateral and mho characteristic zmfcpdis (21) prepare the ied for verification of settings outlined in section "preparing the ied to verify settings" . Measure operating characteristics during constant current conditions. Keep the me...
Page 144
X1 r x (o/phase) 50% 80% 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 80% of rldfwd 40% of rldfwd 0.5 x rfpp 12 ansi05000368-1-en.Vsd 13 b 120° 20° a c ansi05000368 v1 en figure 35: distance protection characteristic with test points for phase-to-phase measurements table 30: test points for phase-to-phase loops a-b (ohm...
Page 145
Test point reach set value comments 9 x –0.4 x rldfwd x tan(argdir=20°) r 0.4 x rldfwd 10 x 0.5 x x1 set exact –0.5 x r1 set x tan(argnegres=30°) r –0.23 x x1 set 11 x 0.8 x x1 set exact –0.5 x r1 set x tan(argnegres=30°) r –0.37 x x1 set 12 x 0.5 x x1 set r 0.5 x r1 set 13 x 0 r 0.5 x rfppzx table ...
Page 146
Table 31: test points for phase-to-ground c-g (ohm/loop) test point reach value comments 1 x (2 x x1 set +x0 set )/3 r 0 2 x (2 x x1 set + x0 set )/3 r 2 x r1 set + r0 set )/3 3 x 0.8 x (2 x x1 set + x0 set )/3 r 0.8 x (2 x r1 set + r0 set )/3 +rfpgzx set 4 x 0.5 x (2 x x1 set + r0 set )/3 r 0.5 x (...
Page 147
1. Subject the ied to healthy normal load conditions for at least two seconds. 2. Apply the fault condition and slowly decrease the measured impedance to find the operating value of the phase-to-phase fault for zone 1 according to test point 1 in figure 35 and table 30 . Compare the result of the me...
Page 148
11.4.9 power swing detection zmrpsb (68) the aim is to verify that the settings of the power swing detection function zmrpsb (68) is according to the setting table and to verify that zmrpsb (68) operates as expected. Prepare the ied for verification of settings outlined in section "preparing the ied...
Page 149
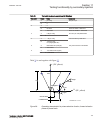
X1outrv zl j j r x x1outfw x1infw 1 rldoutfw rldinfw rldoutrv rldinrv 2 3 4 x1inrv iec09000226_1_en.Vsd iec09000226 v1 en figure 37: operating principle and characteristic of the power swing detection function (settings parameters in italic) where: rldinfw = rldoutfw · kldrfw rldinrv = rldoutrv · kl...
Page 150
1. Keep the measured current as close as possible to its rated value or lower. Keep it constant during the test, but ensure that it is higher than the set minimum operating current. 2. Ensure that the maximum continuous current to the ied does not exceed four times its rated value, if the measuremen...
Page 151
1. Program the test equipment for a single-phase to ground fault and energize fdpspdis (21) or frpsdis (21) and check that the input block on the power swing detection function zmrpsb (68) is activated. 2. Make a test sequence so that a single-phase to ground fault occurs after that the trajectory o...
Page 152
Impedance. For this reason it is necessary to enable the logic by connecting the pupsd input signal to some other functional signal, which is used for testing purposes. Make sure that the existing configuration permits monitoring of the cs, trip signals on the binary outputs of the ied. If not, conf...
Page 153
1. Initiate a single phase-to-ground fault within both power-swing zones. Make sure that none of cs or trip output signals appear after the time delays tcs and ttrip. Blkzmur must appear together with the fault and must remain active until the fault has been switched off plus the time delay, as set ...
Page 154
11.4.10.4 completing the test continue to test another function or end the test by changing the testmode setting to disabled. Restore connections and settings to their original values, if they were changed for testing purposes. 11.4.11 pole slip protection pspppam (78) prepare the ied for verificati...
Page 155
Now the signals trip1 and trip should be activated. 6. With reduced amplitude of the injected voltage to 0.8 vbase the current amplitude and angle is changed via zc + (za – zc)/2 to a value corresponding to half ibase and 180° between the injected current and voltage. This is done with a speed so th...
Page 156
0.2 £ f(ucos) £ 8hz and and pickup z cross line za - zc z cross line zc - zb and and zone1 zone2 counter n1limit a b a ³ b and trip1 counter n2limit a b a ³ b and trip2 or trip ansi07000100_2_en.Vsd imin > 0.10 ibase vmax vbase d ³ pickupangle d £ tripangle ansi07000100 v2 en figure 39: logic diagra...
Page 157
Slip is usually allowed before the generator-transformer unit is disconnected. A parameter setting is available to take into account the circuit breaker opening time. If there are several out-of-step relays in the power system, then the one which finds the center of oscillation in its zone 1 should ...
Page 158
I = i(50 hz) + i(49.5 hz) iec10000141 v2 en figure 40: trajectory of the impedance z(r, x) for the injected current with two components: a 50 hz component and a 49.5 hz current component the test of the out-of-step protection function requires the injection of the analog quantities for a quite long ...
Page 159
The parameter reachz1 defines the boundary between zone 1 and zone 2; it is expressed in percent of the parameter forwardx. If the setting of reachz1 = 12%, then corresponding primary value of the reactance is x reachz forwardx zbase rz 1 1 100 100 12 100 59 33 100 0 9522 0 = × × = × × = . . .0068Ω ...
Page 160
And the voltages that are related to them: v z i r x i t fwdz fwdz t fwdr fwdx t , . . . = × = + × = + × = 2 2 2 2 0 078 0 565 20918 0 5700 20918 11931 × = v equation14052 v1 en (equation 12) v z i r x i t rvsz rvsz t rvsr rvsx t , . . . = × = + × = + × = 2 2 2 2 0 003 0 282 20918 0 2822 20918 5899 ...
Page 161
• the point re (r fwdr , x fwdx ) • a point which is related to the parameter reachz1 (boundary between zone 1 and zone 2) • the point se (r rvsr , x rvsx ) the phase angle of the test voltages is equal to: • arctan (forwardx/forwardr) for tests in the quadrant 1 and 2 of the r-x plane • arctan (rev...
Page 162
Verifying the settings by secondary injection it is advised to connect the analog output channels of the function block oosppam to the internal disturbance recorder (and in particular to the function block a4radr) in order to perform a better analysis of the tests. If the device is in test mode, the...
Page 163
I i i i a s cts ctp 50 50 10459 1 9000 1 162 = × = × = . Equation14059 v1 en (equation 19) ∠i 50s =0° frequency of i 50s = 50 hz it i i i a fs cts ctp tf = × = × = 10459 1 9000 1 162 . Equation14062 v1 en (equation 20) ∠i tfs =0° frequency of i tfs = 50 hz • check that the service values (voltage, c...
Page 164
I tfs =0 a • state 2: main test step. Define the following three-phase symmetrical quantities (the phase angle is related to phase l1): v v v v v ts t fwdz vt s vt p = × × = × × = 1 1 1 1 11931 0 1 13 8 95 1 . . . . . , , , equation14057 v1 en (equation 23) ∠ = = = v forwardx forwardr ts arctan ...
Page 165
∠ = = = v forwardx forwardr ts arctan arctan . . 59 33 8 19 82..14° equation14058 v1 en (equation 28) frequency of v ts = 50 hz i i i i a s cts ctp 50 50 10459 1 9000 1 162 = × = × = . Equation14059 v1 en (equation 29) ∠i 50s = 0º frequency of i 50s = 50 hz it i i i a fs cts ctp tf = × = × = 104...
Page 166
∠ = = = v forwardx forwardr ts arctan arctan . . 59 33 8 19 82..14° equation14058 v1 en (equation 32) frequency of v ts = 50 hz i 50s = 0 a i tfs = 0 a • state 2: main test step. Define the following three-phase symmetrical quantities (the phase angle is related to phase l1): v v v v v ts t fwdz...
Page 167
11.4.12.3 test of the boundary between zone 1 and zone 2, which is defined by the parameter reachz1 the trajectory of the impedance traverses the lens characteristic in zone 2 preliminary steady state test at 50 hz • go to main menu/test/function status/impedance protection/ outofstep(78,ucos)/oospp...
Page 168
Note that these values identify a point inside the lens characteristic, in the zone 2, that is close to the boundary between zone 1 and zone 2. The start is issued, but no trip is performed. Execution of the dynamic test the test may be performed by using two states of a sequence tool that is a basi...
Page 169
It i i i a fs cts ctp tf = × = × = 10459 1 9000 1 162 . Equation14062 v1 en (equation 46) ∠i tfs = 180º frequency of i tfs = 49.5 hz expected result: start of the protection function and trip in zone 2 when trip conditions are fulfilled. The trajectory of the impedance traverses the lens characteris...
Page 170
• voltage = 1.29 kv • current = 20918 a • r = 0.89% • x=6.42% • rotorang = -3.04 rad note that these values identify a point inside the lens characteristic in zone 1, that is close to the boundary between zone 1 and zone 2. The start is issued, but no trip is performed. Execution of the dynamic test...
Page 171
I i i i a s cts ctp 50 50 10459 1 9000 1 162 = × = × = . Equation14059 v1 en (equation 55) ∠i 50s = 0º frequency of i 50s = 50 hz it i i i a fs cts ctp tf = × = × = 10459 1 9000 1 162 . Equation14062 v1 en (equation 56) ∠i tfs = 180º frequency of i tfs = 49.5 hz expected result: start of the protect...
Page 172
It i i i a fs cts ctp tf = × = × = 10459 1 9000 1 162 . Equation14062 v1 en (equation 60) ∠i tfs = 0º frequency of i tf = 50 hz • check that the service values (voltage, current, r(%), x(%)) are according to the injected quantities and that rotorang is close to 3.14 rad. For this particular injectio...
Page 173
V v v v v ts t rvsz vt s vt p = × × = × × = 0 9 0 9 5899 0 1 13 8 38 47 . . . . . , , , equation14067 v1 en (equation 63) 29.60 arctan 180 arctan 180 90.56 0.29 ts reversex v reverser Ð = - ° = - ° = - ° æ ö æ ö ç ÷ ç ÷ è ø è ø equation14068 v1 en (equation 64) frequency of v ts = 50 hz i i i i a s ...
Page 174
I i i i a s cts ctp 50 50 10459 1 9000 1 162 = × = × = . Equation14059 v1 en (equation 69) ∠i 50s = 0º frequency of i 50s = 50 hz it i i i a fs cts ctp tf = × = × = 10459 1 9000 1 162 . Equation14062 v1 en (equation 70) ∠i tfs = 0º frequency of i tf = 50 hz • check that the service values (voltage, ...
Page 175
I tfs = 0 a • state 2: main test step. Define the following three-phase symmetrical quantities (the phase angle is related to phase l1): v v v v v ts t rvsz vt s vt p = × × = × × = 1 1 1 1 5899 0 1 13 8 47 02 . . . . . , , , equation14069 v1 en (equation 73) 29.60 arctan 180 arctan 180 90.56 0.29 ts...
Page 176
Iec10000142-1-en.Vsd 0 1 2 common trip command (trip) -1 0 1 tripz1 (tripzone1) 0 1 2 tripz2 (tripzone2) 0 1 2 start (start) 0 1 2 genmode (generatormode) 0 0.5 1 1.5 2 2.5 3 3.5 4 4.5 5 -1 0 1 time in seconds → motmode (motormode) iec10000142 v1 en figure 41: boolean output signals for the injected...
Page 177
1. Set autoinitmode to dld disabled and mode to impedance. 2. Activate the switch onto fault bc input. During normal operating conditions, the bc input is de-energized. 3. Apply a three-phase fault condition corresponding to a fault at approximately 45% of the line or with impedance at 50% of the us...
Page 178
11.4.14 phase preference logic pplphiz prepare the ied for verification of settings outlined in section "preparing the ied to verify settings" . The phase preference logic function pplphiz is tested with a three-phase testing equipment for distance protections. Pplphiz is tested in co-operation with...
Page 179
11.4.14.1 completing the test continue to test another function or end the test by changing the testmode setting to disabled. Restore connections and settings to their original values, if they were changed for testing purposes. 11.4.15 under impedance protection for generator zgvpdis prepare the ied...
Page 180
P1 p3 p4 x r lineangle z1fwd z1rev p2 iec11000312-2-en.Vsd iec11000312 v2 en figure 42: proposed four test points for phase-to-phase fault where, z1fwd is the forward positive sequence impedance setting for zone 1 z1rev is the reverse positive sequence impedance setting for zone 1 lineangle is the i...
Page 181
To verify zone 2 and zone 3 mho characteristic, at least two points must be tested. The default measuring loop selected is maximum current phase to current loop. Hence the below characteristics are tested with phase–to-ground fault conditions. P1 p3 p4 x r lineangle zxfwd zxrev p2 iec11000313-1-en.V...
Page 182
Change the magnitude and angle of phase-to-phase voltage to achieve impedances at test points p1, p2, p3 and p4. For each test point, observe that the output signals, pickup and pu_zx are activated (where x is 2 or 3 depending on selected zone). After the trip time delay of the respective zone has e...
Page 183
Is tested, then set the parameter blocked to no under main menu/tests/function test modes/impedance/zgvpdis/1: zgvpdis for the function, or for each individual function in a chain, to be tested next. Remember to set the parameter blocked to yes, for each individual function that has been tested. 11....
Page 184
Observe: do not exceed the maximum permitted overloading of the current circuits in the ied. 5. Compare the measured operating current with the set value. 6. Set the operation mode to 2 out of 3 and inject current into one of the phases and then check that no trln signal appears. 11.5.1.2 completing...
Page 185
If 3 out of 3 currents are chosen for operation: connect the symmetrical three-phase injection current into phases a, b and c. 2. Connect the test set for the appropriate three-phase voltage injection to the ied phases a, b and c. The protection shall be fed with a symmetrical three-phase voltage. 3...
Page 186
11.5.2.2 completing the test continue to test another function or end the test by changing the testmode setting to disabled. Restore connections and settings to their original values, if they were changed for testing purposes. 11.5.3 instantaneous residual overcurrent protection efpioc (50n) prepare...
Page 187
11.5.3.2 completing the test continue to test another function or end the test by changing the testmode setting to disabled. Restore connections and settings to their original values, if they were changed for testing purposes. 11.5.4 four step residual overcurrent protection, (zero sequence or negat...
Page 188
For inverse time curves, check the trip time at a current equal to 110% of the trip current for txmin. 9. Check that all trip and pickup contacts trip according to the configuration (signal matrixes) 10. Reverse the direction of the injected current and check that the step does not trip. 11. Check t...
Page 189
Be activated. Check under ns4ptoc function service values that correct i2 magnitude is measured by the function. 3. Set the injected negative sequence polarizing voltage slightly larger than the set minimum polarizing voltage (default 5 % of vn) and set the injection current to lag the voltage by an...
Page 190
Ansi09000021-1-en.Vsd ied test set ni ied ni v_a v_b v_c v_n v1 v2 v3 v_n trip ansi09000021 v1 en figure 44: principle connection of the test set values of the logical signals belonging to the sensitive directional residual overcurrent and power protection are available on the local hmi under main m...
Page 191
4. Compare the result with the set value and make sure that the new injected 3i 0 · cos φ is equal to the setting incosphipu.. Take the set characteristic into consideration, see figure 45 and figure 46 . 5. Measure the trip time of the timer by injecting a current two times the set incosphipu value...
Page 192
Trip area roadir ansi06000650-3-en.Vsd 0 rcadir 0 3i 0 3 i cos 0 3 ref v v ansi06000650 v3 en figure 45: characteristic with roadir restriction section 11 1mrk 504 165-uus - testing functionality by secondary injection 186 transformer protection ret670 2.2 ansi commissioning manual.
Page 193
-3v 0 =v ref trip area instrument transformer angle error 3i 0 (prim) 3i 0 (to prot) characteristic after angle compensation rcacomp ansi06000651-2-en.Vsd rcadir = 0º ansi06000651 v2 en figure 46: explanation of rcacomp operation mode 3i 0 · 3v 0 · cos φ 1. Set the polarizing voltage to 1.2 · vnrelp...
Page 194
The function activates the pickup and pudirin outputs. 3. Assume that φ´ is the phase angle between injected voltage (3v 0 ) and current (3i 0 ) i.E. φ´ = rcadir-φ. Change φ´ to for example 45 degrees. Increase the injected current until the function trips. 4. Compare the result with the set value a...
Page 195
V ref =-3v 0 operate area 3i 0 rca = 0º roa = 80º ansi06000652-2-en.Vsd ansi06000652 v2 en figure 47: example characteristic non-directional ground fault current protection procedure 1. Measure that the trip current is equal to the innondirpu setting. The function activates the pickup and pudirin ou...
Page 196
4. Inject a voltage 0.8 · vnrelpu and a current high enough to trip the directional function at the chosen angle. 5. Increase the voltage until the directional function is released. 6. Compare the measured value with the set vnrelpu trip value. 11.5.6.2 completing the test continue to test another f...
Page 197
11. Switch on the injection current and check that alarm1 and alarm2 contacts trip at the set percentage level and that the trip time for tripping is in accordance with the set time constant 1 (tau1). With setting itr = 101%ibase1 and injection current 1.50 · ibase1, the trip time from zero content ...
Page 198
1. Apply the fault condition, including bfi_3p of ccrbrf (50bf), with a current below set pickup_ph. 2. Repeat the fault condition and increase the current in steps until a trip occurs. 3. Compare the result with the set pickup_ph. 4. Disconnect ac and bfi_3p input signals. If no cbpos check or retr...
Page 199
Checking the case without re-trip, retripmode = retrip off 1. Set retripmode = retrip off. 2. Apply the fault condition, including initiation of ccrbrf (50bf), well above the set current value. 3. Verify that no re-trip, but back-up trip is achieved after set time. 4. Disconnect ac and bfi_3p input ...
Page 200
The normal mode butripmode = 1 out of 3 should have been verified in the tests above. In applicable cases the modes 1 out of 4 and 2 out of 4 can be checked. Choose the mode below, which corresponds to the actual case. Checking the case butripmode = 1 out of 4 it is assumed that the ground-fault cur...
Page 201
1. Repeat the check of back-up trip time. Disconnect current and input signals. 2. Activate the input 52fail. The output cbalarm (cb faulty alarm) should appear after set time tcbalarm. Keep the input activated. 3. Apply the fault condition, including initiation of ccrbrf (50bf), with current above ...
Page 202
Checking the case with fault current below set value pickup_blkcont it simulates a case where the fault current is very low and operation will depend on cb position signal from cb auxiliary contact. It is suggested that re-trip without current check is used, setting retripmode = no cbpos check. 1. S...
Page 203
No trip signal should appear. 6. Reset both blkdbyar and extpdind binary inputs. 7. Activate the block binary input. 8. Activate extpdind binary input. No trip signal should appear. 9. Reset both block and extpdind binary inputs. 10. If internal detection logic contact function selection = contactse...
Page 204
The test is made by means of injection of voltage and current where the amplitude of both current and voltage and the phase angle between the voltage and current can be controlled. During the test, the analog outputs of active and reactive power shall be monitored. 1. Connect the test set for inject...
Page 205
Set value: mode formula used for complex power calculation a * 3 a a s v i = × × equation2061-ansi v1 en (equation 86) b * 3 b b s v i = × × equation2062-ansi v1 en (equation 87) c * 3 c c s v i = × × equation2063-ansi v1 en (equation 88) 2. Adjust the injected current and voltage to the set values ...
Page 206
Current and voltage and the phase angle between the voltage and current can be controlled. During the test the analog outputs of active and reactive power shall be monitored. 1. Connect the test set for injection of voltage and current corresponding to the mode to be used in the application. If a th...
Page 207
Observe to not exceed the maximum permitted overloading of the current circuits in the terminal. 3. Switch on the fault current and measure the operating time of brcptoc (46). Trip is controlled by gate 13 in the configuration. Use the trip signal from the configured binary output to stop the timer....
Page 208
Connect the secondary test set to the ct inputs on the ied dedicated for the scb currents. Single- or three-phase test equipment can be used but it may be required to have facility to vary the frequency of the injected current signal(s). 11.5.13.1 verifying the settings and operation of the function...
Page 209
Note that the operation of this feature is based on current peak value. That means that this overcurrent function is also able to trip for the same current magnitude but for different injected frequencies. If required repeat this injection procedure for example for the 3rd harmonic by just simply in...
Page 210
4. If any of these signals are used for tripping, signaling and/or local/remote indication check that all relevant contacts and leds have operated and that all relevant goose messages have been sent. 5. Check that service value from the function for current in phase a, on the local hmi under main me...
Page 211
Note that operation of this feature is based on internally calculated voltage peak rms value. That means that this feature is also able to trip for current signals with varying frequency. Here will be shown how to test the fourth point from the above table. Other points can be tested in the similar ...
Page 212
Note that it is recommended to test idmt operating times by injected current with the rated frequency. Above procedure can also be used to test definite time step. Pay attention that idmt step can also trip during such injection. Therefore make sure that appropriate settings are entered in order to ...
Page 213
Used. A two phase short-circuit gives a negative sequence current of a magnitude: magnitude = (1/√3) · fault current. 5. Increase the injected current and note the value at which the step 1 of the function operates. Pickup signal pu_st1 must be activated when amplitude of the negative sequence curre...
Page 214
The service value output nscurr indicating amplitude of negative sequence current in primary amperes should be 962a approximative. 11.5.14.2 completing the test continue to test another functions or end the test by changing the test mode setting to off. Restore connections and settings to their orig...
Page 215
Pickup curr ibase ct ctprim vdepfact _ sec 100 1 100 × × × − v vhighlimit vbase vt vtprim strainvoltage − ( ) × × × − 25 100 25 10 sec re 0 0 100 × × + × vbase vt vtprim pickup curr ib sec _ a ase ct ctprim vdepfact × × sec 100 ansiequation2433 v2 en (equation 92) third part of the characteristic ...
Page 216
• va: ampl = 105/ √3; angle = 0° • vb: ampl = 105/ √3; angle = 240° • vc: ampl = 105 / √3; angle = 120° 4. Inject the voltages that are related to the first part of the characteristic, and then slowly increase the phase current ia from 0.0 a up to the value the function trips. The pickup and stoc si...
Page 217
If tdef_oc is set to a value different from 0 s, then this time delay is added to the one that is defined by the idmt characteristic. 10. Check the pickup and trip information that are stored in the event menu. 11. The previous step 8 or 9 may be repeated also for the first and second section of the...
Page 218
11.5.15.2 completing the test continue to test another function or end the test by changing the testmode setting to disabled. Restore connections and settings to their original values, if they were changed for testing purposes. 11.6 voltage protection 11.6.1 two step undervoltage protection uv2ptuv ...
Page 219
9. Check the inverse time delay by injecting a voltage corresponding to 0.8 × vpickup for example, if the inverse time curve a is selected, the trip signals trst1 and trip trip after a time corresponding to the equation: ( ) 1 1 td t s v vpickup = æ ö - ç ÷ è ø ansiequation2428 v1 en (equation 98) w...
Page 220
Verification of single-phase voltage and time delay to trip for step 1 1. Apply single-phase voltage below the set value pickup1. 2. Slowly increase the voltage until the pu_st1 signal appears. 3. Note the trip value and compare it with the set value pickup1. The trip value in secondary volts is cal...
Page 221
11.6.3 two step residual overvoltage protection rov2ptov (59n) prepare the ied for verification of settings outlined in section "preparing the ied to verify settings" . 11.6.3.1 verifying the settings 1. Apply a single-phase voltage either to a single-phase voltage input or to a residual voltage inp...
Page 222
11.6.3.2 completing the test continue to test another function or end the test by changing the testmode setting to disabled. Restore connections and settings to their original values, if they were changed for testing purposes. 11.6.4 overexcitation protection oexpvph (24) prepare the ied for verific...
Page 223
11.6.4.2 completing the test continue to test another function or end the test by changing the testmode setting to disabled. Restore connections and settings to their original values, if they were changed for testing purposes. 11.6.5 voltage differential protection vdcptov (60) prepare the ied for v...
Page 224
Va vb vc vn va va vb vc ie d t e s t s e t ie d ansi07000106-1-en.Vsd vb vc vn 1 2 ansi07000106 v2 en figure 48: connection of the test set to the ied for test of v1 block level where: 1 is three-phase voltage group1 (v1) 2 is three-phase voltage group2 (v2) 3. Decrease slowly the voltage in phase v...
Page 225
Va vb vc vn va va vb vc ie d t e s t s e t ie d ansi07000107-1-en.Vsd vb vc vn 1 2 ansi07000107 v2 en figure 49: connection of the test set to the ied for test of v2 block level where: 1 is three-phase voltage group1 (v1) 2 is three-phase voltage group2 (v2) 2. Apply voltage higher than the highest ...
Page 226
Va vb vc vn va va vb vc ie d t e s t s e t ie d ansi07000108-1-en.Vsd vb vc vn 1 2 ansi07000108 v2 en figure 50: connection of the test set to the ied for test of alarm levels, trip levels and trip timer where: 1 is three-phase voltage group1 (v1) 2 is three-phase voltage group2 (v2) 2. Apply 1.2 · ...
Page 227
11.6.5.3 check of trip and trip reset timers procdure 1. Connect voltages to the ied according to valid connection diagram and figure 50 . 2. Set vn (rated voltage) to the v1 inputs and increase v2 voltage until differential voltage is 1.5 · operating level (vdtrip). 3. Switch on the test set. Measu...
Page 228
11.6.6 loss of voltage check lovptuv (27) prepare the ied for verification of settings outlined in section "preparing the ied to verify settings" . 11.6.6.1 measuring the trip limit of set values 1. Check that the input logical signals block, cbopen and blku are logical zero. 2. Supply a three-phase...
Page 229
11.7 frequency protection 11.7.1 underfrequency protection saptuf (81) prepare the ied for verification of settings outlined in section "preparing the ied to verify settings" . 11.7.1.1 verifying the settings verification of pickup value and time delay to trip 1. Check that the ied settings are appr...
Page 230
1. Check that the ied settings are appropriate, for example the pufrequency, vmin, and the tdelay. 2. Supply the ied with three-phase voltages at rated values. 3. Slowly decrease the magnitude of the applied voltage, until the blkdmagn signal appears. 4. Note the voltage magnitude value and compare ...
Page 231
Extended testing 1. The test above can be repeated to check the time to reset. Verification of the low voltage magnitude blocking 1. Check that the settings in the ied are appropriate, for example the pufrequency and the tdelay. 2. Supply the ied with three-phase voltages at their rated values. 3. S...
Page 232
6. Check that the pickup signal resets. 7. Instantaneously decrease the frequency of the applied voltage to a value about 20% lower than the nominal value. 8. Measure the time delay for the trip signal, and compare it with the set value. Extended testing 1. The test above can be repeated to check a ...
Page 233
11.8.1.1 built-in overcurrent feature (non-directional) procedure 1. Go to main menu/test/function test modes/multipurpose protection/ generalcurrentvoltage(gapc)/cvgapc:x and make sure that cvgapc to be tested is unblocked and other functions that might disturb the evaluation of the test are blocke...
Page 234
11.8.1.3 overcurrent feature with voltage restraint procedure 1. Connect the test set for injection of three-phase currents and three-phase voltages to the appropriate current and voltage terminals of the ied. 2. Inject current(s) and voltage(s) in a way that relevant measured (according to setting ...
Page 235
4. Overall check in principal as above (non-directional overcurrent feature) 5. Reverse the direction of the injection current and check that the protection does not trip. 6. Check with low polarization voltage that the feature becomes non-directional, blocked or with memory according to the setting...
Page 236
The signal monitoring in pcm600 shows the same signals that are available on the local hmi. The condition for this procedure is that the set value of iminop is lower than the set value of pickup_block. 11.9.1.1 verifying the settings 1. Check the input circuits and the trip value of the iminop curre...
Page 237
• the signal blkv should appear with almost no time delay. • the signals blkz and 3ph should not appear on the ied. • only the distance protection function can trip. • undervoltage-dependent functions must not trip. 3. Disconnect the dc voltage from the 89b binary input terminal. 4. Connect the nomi...
Page 238
2 2 3 a b c v v a v a v × = + × + × equation1818-ansi v1 en (equation 104) where: a b c and v v v equation1820-ansi v1 en are the measured phase voltages 2 3 3 1 0, 5 2 j a e j p × = × = - + . Iecequation00022 v2 en 4. Compare the result with the set value of the negative-sequence operating voltage ...
Page 239
1. Simulate normal operating conditions with the three-phase currents in phase with their corresponding phase voltages and with all of them equal to their rated values. 2. Slowly decrease the measured voltage in one phase until the blkv signal appears. 3. Record the measured voltage and calculate th...
Page 240
4. Apply three-phase currents with their rated value and zero voltages. 5. Decrease the measured current in one phase until the dld1ph signal appears. 6. This is the point at which the dead line condition is detected. Check the value of the decreased current with the set value idldpu (idldpu is in p...
Page 241
11.9.2.6 completing the test continue to test another function or end the test by changing the testmode setting to disabled. Restore connections and settings to their original values, if they were changed for testing purposes. 11.9.3 fuse failure supervision prepare the ied for verification of setti...
Page 242
11.9.3.1 completing the test continue to test another function or end the test by changing the testmode setting to disabled. Restore connections and settings to their original values, if they were changed for testing purposes. 11.10 control 11.10.1 synchrocheck, energizing check, and synchronizing s...
Page 243
Figure 52 shows the general test connection for a breaker-and-a-half diameter with one- phase voltage connected to the line side. Test equipment vmeasure ph/n ph/ph ansi05000480-3-en.Vsd v-bus v-line n ied v-bus n va vb vc vn input phase a,b,c ab,bc,ca vmeasure ph/n ph/ph input phase a,b,c ab,bc,ca ...
Page 244
Ansi05000481-4-en.Vsd ansi05000481 v4 en figure 52: general test connection for a breaker-and-a-half diameter with one- phase voltage connected to the line side 11.10.1.1 testing the synchronizing function the voltage inputs used are: v3pl1 va, vb or vc line 1 voltage inputs on the ied v3pbb1 bus1 v...
Page 246
1. Apply voltages v-line (for example) = 80% gblbaseselline and v-bus = 80% gblbaseselbusgblbaseselbus with the same phase-angle and frequency. 2. Check that the autosyok and mansyok outputs are activated. 3. The test can be repeated with different voltage values to verify that the function trips wi...
Page 247
+d j -d j v-bus v-line operation v-bus no operation en05000551_ansi.Vsd ansi05000551 v1 en figure 53: test of phase difference 3. Change the phase angle between +dφ and -dφ and verify that the two outputs are activated for phase differences between these values but not for phase differences outside,...
Page 248
The voltage difference between the voltage connected to v-bus and v-line should be 0%, so that the autosyok and mansyok outputs are activated first. 2. Change the v-line voltage connection to v-line2 without changing the setting on the local hmi. Check that the two outputs are not activated. 11.10.1...
Page 249
1. Verify the settings autoenerg or manenerg to be dbll. 2. Apply a single-phase voltage of 30% gblbaseselbus to the v-bus and a single- phase voltage of 100% gblbaseselline to the v-line. 3. Check that the autoenok and manenok outputs are activated after set tautoenerg respectively tmanenerg. 4. De...
Page 250
100% gblbaseselline to the v-line and a single-phase voltage of 100% gblbaseselbus to the v-bus. If the vb1/2ok inputs for the fuse failure are used, they must be activated, during tests below. Also verify that deactivation prevents operation and gives an alarm. 1. Connect the signals above to binar...
Page 251
Table 34: voltage selection logic sesrsyn cbconfig setting section to be synchroniz ed activated b1qcld input on ied from activated b2qcld input on ied from activated ln1qcld input on ied from activated ln2qcld input on ied from indication from sesrsyn on ied sesrsyn 1 (operates on cb1 52) breaker- ...
Page 252
Bus 1 bus 2 cb1 52 (sesrsyn 1) cb3 352 (sesrsyn 3) cb2 252 (sesrsyn 2) line 1 line 2 ln1 989 ln2 989 ansi11000274.En.V1 ansi11000274 v1 en figure 54: objects used in the voltage selection logic 11.10.1.5 completing the test continue to test another function or end the test by changing the testmode s...
Page 253
11.10.3 voltage control tr1atcc, tr8atcc, tcmyltc, tclyltc prepare the ied for verification of settings outlined in section "preparing the ied to verify settings" . The automatic voltage control for tap changer, single control tr1atcc (90) is based on a transformer configuration that consists of one...
Page 254
• short circuit impedance, available on the local hmi under main menu/ settings/general settings/control/transformervoltagecontrol(atcc, 90)/tr1atcc:x/tr8atcc:x/xr2. • confirm that the setting for tcmyltc (84) or tclyltc (84) is in accordance with transformer data: • tap change timeout duration - ef...
Page 255
Also note that for simplicity, the parameter setting menu structures included in the following procedure are referred to universally as vcp1, for example, main menu/settings/setting group n/control/ transformervoltagecontrol(atcc,90)/tr1atcc:x/ tr8atcc:x/time/t1 and t2l. For cases where single-mode ...
Page 256
• automatic transformer voltage control main menu/settings/setting group n/control/ transformervoltagecontrol(atcc,90)/tr1atcc:x/tr8atcc:x/general/ operation • enable tap command main menu/settings/general settings/control/ transformertapchanger(yltc,84)/tcmyltc:x/tclyltc:x/ enabtapcmd while the tes...
Page 257
Binary output for a low pulse command in the signal matrix in pcm600 and monitoring a positive from this output. 6. Return the applied voltage to vset. 11.10.3.4 check the undervoltage block function 1. Confirm the setting for vblock, nominally at 80% of rated voltage. 2. Confirm the voltage control...
Page 258
1. Confirm the setting for iblock in the local hmi under main menu/settings/setting group n/control/transformervoltagecontrol(atcc,91)/tr1atcc:x/ tr8atcc:x/tcctrl/iblock 2. Confirm the voltage control function response to an applied current above iblock, by reviewing the settings in the local hmi un...
Page 259
, , , , vl im vb im xline il re rline il im = - × - × equation2085-ansi v1 en (equation 110) where: vb is the complex value of the busbar voltage il is the complex value of the line current (secondary side) rline is the value of the line resistance xline is the value of the line reactance for compar...
Page 260
Settings/setting group n/control/transformervoltagecontrol(atcc,90)/ tr8atcc:x/parctrl the general parallel arrangement of transformers are defined by setting tnrxop to enabled or disabled. The following rules are applicable on the settings t1rxop – t4rxop. If ied t1 and t2 are connected, • t1rxop s...
Page 261
Values and respective compensating factors, and is therefore more complex for greater than two transformers. 1. Confirm that operationpar is set to cc for the transformers in the parallel group. 2. For parallel operation, it is also recommended that settings be confirmed for parallel group membershi...
Page 262
_ vdi ci icc i xi = × × equation2089-ansi v1 en (equation 112) the voltage regulation algorithm then increases (for transformer t2) or decreases (for transformer t1) the measured voltage by vdi and compares vi against the voltage deadband limits v1 and v2 for the purposes of voltage regulation. Vi v...
Page 263
Transformer can be observed as service values on the local hmi and raise/lower commands detected from the binary output mapped in the signal matrix. The voltage injection equal to vset is required for both transformers during this test. 12. Confirm that a tap change command is issued from the voltag...
Page 264
11.10.3.9 completing the test continue to test another function or end the test by changing the testmode setting to disabled. Restore connections and settings to their original values, if they were changed for testing purposes. 11.10.4 single command, 16 signals singlecmd for the single command func...
Page 265
Activation of the different zones verifies that the cs signal is issued from the intended zones. The cs signal from the independent tripping zone must have a tsendmin minimum time. Check the tripping function by activating the cr and cr_guard inputs with the overreaching zone used to achieve the plt...
Page 266
1. Deactivate the receive (cr) signal of the ied. 2. Apply healthy normal load conditions to the ied for at least two seconds. 3. Apply a fault condition within the forward directed zone used for scheme communication tripping. 4. Check that correct trip outputs and external signals are obtained for ...
Page 267
11.11.1.5 checking of unblocking logic check the unblocking function (if the function is required) when checking the communication scheme. Command function with continuous unblocking ( unblock = 1 ) procedure 1. Activate the guard input signal (cr_guard) of the ied. 2. Using the scheme selected, che...
Page 268
5. Check that other zones operate according to their zone timers and that the send (cs_x) signal is obtained only for the zone and phase configured to generate the actual signal. 6. Deactivate the receive (crlx) signal in the ied. 7. Check that the trip time complies with the zone timers and that co...
Page 269
7. Apply a fault condition in the forward directed zone used for scheme communication tripping. 8. Check that the no trip from scheme communication occurs. 9. Check that the trip time from the forward directed zone used for scheme communication tripping complies with the zone timer and that correct ...
Page 270
The forward zone timer must be set longer than the tdelayrev set value. 1. Set the healthy condition to an impedance at 50% of the reach of the reverse zone connected to irv. 2. Activate the receive (crl) signal. 3. After the pickup condition is obtained for reverse zone, apply a fault at 50% of the...
Page 271
The setting parameter wei is set to echo & trip. 1. Apply input signals according table 35 . 2. Activate the receive (cr) signal. 3. After the ied has operated, turn off the input signals. 4. Check that trip, send signal, and indication are obtained. The echo output gives only a 200 ms pulse. 11.11....
Page 272
1. Inject the polarizing voltage 3v0 at 5% of vbase (ef4ptoc, 51n67n) where the current is lagging the voltage by 65°. 2. Inject current (65° lagging the voltage) in one phase at about 110% of the set operating current, and switch the current off with the switch. 3. Switch the fault current on and m...
Page 273
6. Switch the fault current on (110% of the set operating current) and measure the operating time of the ecpsch (85) logic. Use the trip signal from the configured binary output to stop the timer. 7. Compare the measured time with the setting for tcoord. 8. Activate the block digital input. 9. Switc...
Page 274
1. Inject the polarizing voltage 3v0 to 5% of vbase and the phase angle between voltage and current to 155°, the current leads the voltage. 2. Inject current (180° — anglerca) in one phase to about 110% of the set operating current of the four step residual overcurrent protection (indir). 3. Check t...
Page 275
No echo and cs should appear. 9. Switch off the polarizing voltage and reset the block and crl binary input. If setting wei = echo & trip 1. Inject the polarizing voltage 3v0 to about 90% of the setting (3v0pu) operating voltage. 2. Activate the crl binary input. No echo, cs and trwei outputs should...
Page 276
No echo and trwei should appear. 14. Switch the current off and check that the echo, cs and trwei appear on the corresponding binary output during 200ms after resetting the directional element. If ef4ptoc also trips in forward direction, cs should be obtained. 15. Switch the polarizing voltage off a...
Page 277
11.12.1.2 1p/3p operating mode in addition to various other tests, the following tests should be performed. They depend on the complete configuration of an ied: procedure 1. Make sure that triplockout and autolock are both set to disabled. 2. Initiate different single-phase-to-ground faults one at a...
Page 278
Single-pole trip should occur for each separate fault and only one of the trip outputs (tr_a, tr_b, tr_c) should be activated at a time. Functional outputs trip and tr1p should be active at each fault. No other outputs should be active. 3. Initiate different phase-to-phase faults one at a time. Take...
Page 279
9. Activate the trip signal lockout function, set triplockout = enabled and repeat. All trip outputs (tr_a, tr_b, tr_c) and functional outputs trip and tr3p must be active and stay active after each fault, cllkout should be set. 10. Reset the lockout. All functional outputs should reset. 11. Deactiv...
Page 280
4. Also, reduce further the pressure level input below preslolimit or activate the binary input signal senpreslo, check that preslo signal appears after a set time delay of tpressurelo. 5. Activate block binary input and check that the outputs presalm, preslo, alarm and lockout disappear. 6. Reset t...
Page 281
11.13.2.1 testing the liquid medium supervision for level alarm and level lockout conditions 1. Connect the binary inputs to consider liquid level to initiate the alarms. 2. Consider the analogue level input senlevel and set senlevel to a value lower than levelalmlimit or activate binary input signa...
Page 282
11.13.3 breaker monitoring sscbr prepare the ied for verification of settings outlined in section “testing the ied operation”. The signal monitoring tool in pcm600 shows the service values that are available on the local hmi as well. Values of the logical signals belong to the breaker monitoring are...
Page 283
6.1. Test the set timing defined byratedopercurr, ratedfltcurr, opernorated, opernofault, dircoef, cblifealmlevel. 6.2. Vary the phase current in the selected phase from below rated operated current, ratedopercurr to above rated fault current, ratedfltcurr of a breaker. 6.3. The remaining life of cb...
Page 284
10.1. Test the actual set value defined bytdgaspresalm and tdgaspreslo. 10.2. The output gpresalm is activated after a time greater than set time of tdgaspresalm value if the input presalm is enabled. 10.3. The output gpreslo is activated after a set time of tdgaspreslo value if the input preslo is ...
Page 285
11.13.6 estimation of transformer insulation life lolsptr (26/49hs) prepare the ied for verification of settings outlined in section "preparing the ied to verify settings" . 11.13.6.1 verifying the signals and settings time measurement and the injection of current and voltage can be done using commo...
Page 286
10. Wait for a time corresponding to tdelaytoalarm1 from the appearance of warning1 signal. Make sure that the alarm1 signal appears. 11. Note the time taken for the appearance of alarm1 signal from the appearance of warning1 signal, and compare it with set value (tdelaytoalarm1). 12. Wait for a tim...
Page 287
11.14 metering 11.14.1 pulse-counter logic pcfcnt the test of the pulse-counter logic function pcfcnt requires the parameter setting tool in pcm600 or an appropriate connection to the local hmi with the necessary functionality. A known number of pulses with different frequencies are connected to the...
Page 288
10. Activate stopacc input after some time and supply the ied with same current and voltage. 11. Check that the accinprg signal disappears immediately and eafacc and erfacc outputs also stop updating. 12. Similarly the testing can be done for eafacc and erfacc outputs by changing the power inputs di...
Page 289
11.15 station communication 11.15.1 multiple command and transmit multicmdrcv / multicmdsnd the multiple command and transmit function (multicmdrcv / multicmdsnd) is only applicable for horizontal communication. Test of the multiple command function block and multiple transmit is recommended to be p...
Page 290
Test the correct functionality by simulating different kind of faults. Also check that sent and received data is correctly transmitted and read. A test connection is shown in figure 55 . A binary input signal (bi) at end1 is configured to be transferred through the communication link to end2. At end...
Page 291
11.17.1.1 verifying the settings 1. Check the configuration of binary inputs that control the selection of the active setting group. 2. Browse to the activegroup menu to achieve information about the active setting group. The activegroup menu is located on the local hmi undermain menu/test/ function...
Page 292
286.
Page 293
Section 12 primary injection testing whenever it becomes necessary to work on primary equipment, it is essential that all the necessary switching, locking, grounding and safety procedures are observed and obeyed in a rigid and formalized manner. Operating and testing procedures should be strictly fo...
Page 294
If the function ldc is set to zero, this test is omitted. 2. Open the voltage control display on the lhmi in main menu/control/ commands/transformervoltagecontrol (atcc, 90). Iec13000251-1-en.Vsd 3. In this view, check the following settings: 3.1. Check that control mode is set to manual. 3.2. Opera...
Page 295
Physical wiring or the current direction convention selected for the ct analogue input as part of the setting in the pst setting. 12.1.2 voltage control of parallel transformers in parallel operation, each transformer protection ied must be connected to the station communication bus for data exchang...
Page 296
Settings/general settings/control/transformervoltagecontrol(atcc,90)/ tr8atcc:x/parctrl/circcurrlimit. Iec13000252-1-en.Vsd 3. Connect all transformers in the parallel group to the same busbar on the secondary side. 4. Open the test display for transformer voltage control on the lhmi in main menu/ t...
Page 297
Vdeadband, the tap changer of t1 will try to decrease the controlled voltage. In the opposite case, that is, the voltage is close to the lower limit of vdeadband, the tap changer at t1 will not try to decrease the controlled voltage. The tap changer for t2 and t3 will not operate due to the fact tha...
Page 298
Iec13000252-1-en.Vsd 7. Manually execute raise commands to step up the tap changer one step for all transformers in the parallel group 8. Check that the value of busvolt is below overvoltage blocking level ovpartbk and above the undervoltage blocking level uvpartbk. 9. Set the control mode to auto f...
Page 299
Section 13 checking the directionality 13.1 overview before starting this process, all individual devices that are involved in the fault clearance process of the protected object must have been individually tested and must be set in operation. The circuit breaker must be ready for an open-close-open...
Page 300
The primary load impedance must have an angle (phi) between the setting angles for the directional lines. In case of default settings this means: • for forward (exported) load: -15 deg • for reverse (imported) load: 165 deg the settings for forward load: - argdir argnegres and the settings for rever...
Page 301
Impedance has an angle which is outside the above given valid angles for determining forward or reverse direction. If the directional function shows “no direction” for only some of the three phases, this probably means a wrong cts/vts connection. 4. The measured impedance information is available un...
Page 302
296.
Page 303
Section 14 commissioning and maintenance of the fault clearing system 14.1 commissioning tests during commissioning all protection functions shall be verified with the setting values used at each plant. The commissioning tests must include verification of all circuits by highlighting the circuit dia...
Page 304
• visual inspection of all equipment. • removal of dust on ventilation louvres and ieds if necessary. • periodic maintenance test for protection ieds of object where no redundant protections are provided. Every four to six years • periodic maintenance test for protection ieds of objects with redunda...
Page 305
Important components of ft test system are ft1, ftx, ft19, ft19rs, fr19rx switches and assemblies as well as ft-1 test plug. 14.2.2.1 preparation before starting maintenance testing, the test engineers should scrutinize applicable circuit diagrams and have the following documentation available: • te...
Page 306
14.2.2.5 self supervision check once secondary testing has been completed, it should be checked that no self-supervision signals are activated continuously or sporadically. Especially check the time synchronization system, gps or other, and communication signals, both station communication and remot...
Page 307
For transformer differential protection, the achieved differential current value is dependent on the tap changer position and can vary between less than 1% up to perhaps 10% of rated current. For line differential functions, the capacitive charging currents can normally be recorded as a differential...
Page 308
302.
Page 309
Section 15 troubleshooting 15.1 checking the self supervision signals 15.1.1 checking the self supervision function 15.1.1.1 determine the cause of an internal failure this procedure describes how to navigate the menus in order to find the cause of an internal failure when indicated by the flashing ...
Page 310
Indicated result possible reason proposed action real time clock ready no problem detected. None. Real time clock fail the real time clock has been reset. Set the clock. Adc-module ok no problem detected. None. Adc-module fail the ad conversion module has failed. Contact your abb representative for ...
Page 311
Hmi signal name: status description bomn ready / fail bom error. Binary output module error status. Iomn ready / fail iom-error. Input/output module error status. Mimn ready / fail ma input module mim1 failed. Signal activation will reset the ied rtc ready / fail this signal will be active when ther...
Page 312
Trm-stat termstatus - internal events the list of internal events provides valuable information, which can be used during commissioning and fault tracing. The internal events are time tagged with a resolution of 1ms and stored in a list. The list can store up to 40 events. The list is based on the f...
Page 313
• module that should be changed. • sequence of faults, if more than one unit is faulty. • exact time when the fault occurred. 15.2.3 diagnosing the ied status via the lhmi hint menu in order to help the user, there is an lhmi page labeled ‘hints’. This page is located under main menu/diagnostics/ied...
Page 314
Headline explanation frequency diff: ied vs sampled value identifier> where the hardware module identifier is the same as given in pcm600, e.G. Ap1: mu1_9201 svid: wrong cycle time for pmu report wrong cycle time on smai or 3phsum block connected to phasor report block. The smai or 3phsum block shou...
Page 315
15.3 repair instruction never disconnect the secondary connection of a current transformer circuit without short-circuiting the transformer’s secondary winding. Operating a current transformer with the secondary winding open will cause a massive potential build up that may damage the transformer and...
Page 316
8. Check that the new module has a correct identity number. 9. Check that the springs on the card rail are connected to the corresponding metallic area on the circuit board when the new module is inserted. 10. Reassemble the ied. If the ied has been calibrated with the system inputs, the calibration...
Page 317
Section 16 glossary ac alternating current acc actual channel act application configuration tool within pcm600 a/d converter analog-to-digital converter adbs amplitude deadband supervision adm analog digital conversion module, with time synchronization ai analog input ansi american national standard...
Page 318
Cb circuit breaker cbm combined backplane module ccitt consultative committee for international telegraph and telephony. A united nations-sponsored standards body within the international telecommunications union. Ccm can carrier module ccvt capacitive coupled voltage transformer class c protection ...
Page 319
Dbll dead bus live line dc direct current dfc data flow control dft discrete fourier transform dhcp dynamic host configuration protocol dip-switch small switch mounted on a printed circuit board di digital input dllb dead line live bus dnp distributed network protocol as per ieee std 1815-2012 dr di...
Page 320
Ftp file transfer protocol fun function type g.703 electrical and functional description for digital lines used by local telephone companies. Can be transported over balanced and unbalanced lines gcm communication interface module with carrier of gps receiver module gde graphical display editor with...
Page 321
Ieee p1386.1 pci mezzanine card (pmc) standard for local bus modules. References the cmc (ieee p1386, also known as common mezzanine card) standard for the mechanics and the pci specifications from the pci sig (special interest group) for the electrical emf (electromotive force). Ieee 1686 standard ...
Page 322
Lcd liquid crystal display ldcm line data communication module ldd local detection device led light-emitting diode lnt lon network tool lon local operating network mcb miniature circuit breaker mcm mezzanine carrier module mim milli-ampere module mpm main processing module mval value of measurement ...
Page 323
Por permissive overreach pott permissive overreach transfer trip process bus bus or lan used at the process level, that is, in near proximity to the measured and/or controlled components prp parallel redundancy protocol psm power supply module pst parameter setting tool within pcm600 ptp precision t...
Page 324
Smt signal matrix tool within pcm600 sms station monitoring system sntp simple network time protocol – is used to synchronize computer clocks on local area networks. This reduces the requirement to have accurate hardware clocks in every embedded system in a network. Each embedded node can instead sy...
Page 325
Typ type identification umt user management tool underreach a term used to describe how the relay behaves during a fault condition. For example, a distance relay is underreaching when the impedance presented to it is greater than the apparent impedance to the fault applied to the balance point, that...
Page 326
320
Page 327
321.
Page 328
— abb ab grid automation products 721 59 västerås, sweden phone: +46 (0) 21 32 50 00 abb.Com/protection-control © copyright 2017 abb. All rights reserved. Specifications subject to change without notice. 1mrk 504 1 65-uus.