- DL manuals
- Anritsu
- Signal Processors
- MS2830A
- Operation manual
Anritsu MS2830A Operation manual
Document No.: M-W3335AE-18.0
ANRITSU CORPORATION
● For safety and warning information, please read this
manual before attempting to use the equipment.
● Additional safety and warning information is provided
within the MS2830A Signal Analyzer Operation Manual
(Mainframe Operation), MS2840A Signal Analyzer
Operation Manual (Mainframe Operation), or MS2850A
Signal Analyzer Operation Manual (Mainframe
Operation). Please also refer to this document before
using the equipment.
● Keep this manual with the equipment.
MS2830A/MS2840A/MS2850A
Signal Analyzer
Operation Manual
Signal Analyzer Function
Operation
18th Edition
Summary of MS2830A
Page 1
Document no.: m-w3335ae-18.0 anritsu corporation ● for safety and warning information, please read this manual before attempting to use the equipment. ● additional safety and warning information is provided within the ms2830a signal analyzer operation manual (mainframe operation), ms2840a signal ana...
Page 2: Danger
Ii safety symbols to prevent the risk of personal injury or loss related to equipment malfunction, anritsu corporation uses the following safety symbols to indicate safety-related information. Ensure that you clearly understand the meanings of the symbols before using the equipment. Some or all of t...
Page 3
Iii notes on export management this product and its manuals may require an export license/approval by the government of the product's country of origin for re-export from your country. Before re-exporting the product or manuals, please contact us to confirm whether they are export-controlled items o...
Page 4
Iv.
Page 5: About This Manual
I about this manual operation manual configuration the operation manual configuration of the ms2830a/ms2840a, and ms2850a signal analyzer is shown below. Ms2690a/ms2691a/ms2692a and ms2830a/ms2840a/ms2850a signal analyzer operation manual (phase noise measurement function operation) ms2690a/ms2691...
Page 6
Ii • signal analyzer operation manual (mainframe operation) • signal analyzer operation manual (mainframe remote control) description of basic operations, maintenance procedures, common functions and common remote functions of the mainframe • signal analyzer operation manual (signal analyzer functio...
Page 7: Table Of Contents
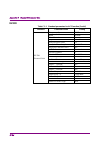
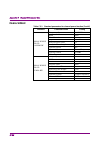
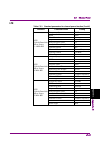
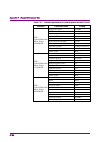
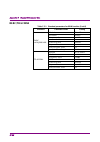
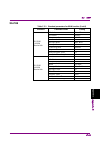
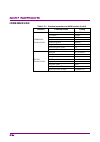
1 iii 2 3 4 5 6 7 a ppen di x index table of contents about this manual................................................. I overview ........................................... 1-1 chapter 1 1.1 overview of signal analyzer ......................................... 1-2 1.2 features of signal analyzer ...
Page 8: Chapter 6
Iv. System setting ................................. 6-1 chapter 6 6.1 setting system .............................................................. 6-2 6.2 erasing warm up message .......................................... 6-3 6.3 setting title .........................................................
Page 9
1-1 1 o ver view overview chapter 1 this chapter describes an overview of the signal analyzer function. 1.1 overview of signal analyzer ......................................... 1-2 1.2 features of signal analyzer .......................................... 1-3.
Page 10
Chapter 1 overview 1-2 1.1 overview of signal analyzer the ms2830a, ms2840a, and ms2850a signal analyzer is a spectrum analyzer to which options such as real-time signal analysis and vector modulation analysis can be added. The signal analyzer application (hereinafter “this application”) enables hig...
Page 11
1.2 features of signal analyzer 1-3 1 o ver view 1.2 features of signal analyzer a signal analyzer can perform analysis with both the frequency and time axes. It achieves high-speed spectrum analysis by using fast fourier transformation (fft) technology. Differences from a sweep type spectrum analyz...
Page 12
Chapter 1 overview 1-4 figure 1.2-2 principle of signal analyzer analyzing captured iq data in various domains the signal analyzer can analyze simultaneous input signals by capturing iq data for a certain time interval. Spectrum: performs spectrum analysis by the fft method. It performs noise measur...
Page 13
1.2 features of signal analyzer 1-5 1 o ver view figure 1.2-3 multiple analyses as shown in figure 1.2-3, once the iq data for a certain time interval is captured, 6 types of analysis methods can be selected for analysis in the time range. When no trace is selected, only iq data is captured without ...
Page 14
Chapter 1 overview 1-6..
Page 15
2-1 2 basic operat ion basic operation chapter 2 this chapter describes the basic operation for the signal analyzer function. 2.1 display description ....................................................... 2-2 2.2 setting frequency ......................................................... 2-3 2.2.1 ...
Page 16: 2.1 Display
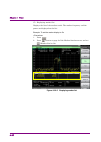
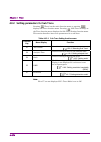
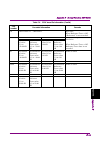
Chapter 2 basic operation 2-2 2.1 display description this section describes the display items on the main screen of the signal analyzer function. Figure 2.1-1 main screen of signal analyzer function the main function menu on the main screen is described below. Table 2.1-1 main function menu functio...
Page 17: 2.2 Setting
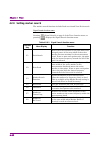
2.2 setting frequency 2-3 2 basic operation 2.2 setting frequency the signal analyzer function can set the following four measurement frequencies. center frequency frequency span start frequency stop frequency pressing (frequency) from page 1 of the main function menu, or pressing displays t...
Page 18
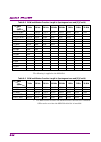
Chapter 2 basic operation 2-4 table 2.2-1 frequency function menu function key menu display function page 1 frequency press frequency to display this menu. F1 center sets the center frequency. 2.2.1 “setting center frequency” f2 start sets the start frequency. 2.2.3 “setting start frequency” f3 stop...
Page 19
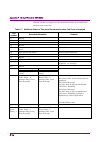
2.2 setting frequency 2-5 2 basic operation table 2.2-1 frequency function menu (cont’d) function key menu display function page 2 frequency press frequency, and then press to display this menu. F1 external mixer (on/off) turn on when using external mixer. This function is available with ms2830a-044...
Page 20
Chapter 2 basic operation 2-6 the display items related to the frequency parameters are described below. Figure 2.2-2 display items related to frequency parameters table 2.2-2 display items related to frequency parameters no. Display description [1] center freq. Or start freq. Displays the center fr...
Page 21
2.2 setting frequency 2-7 2 basic operation the relationships between the center frequency, frequency span, start frequency, and stop frequency are always as shown in figure 2.2-3. When any of the center frequency, start frequency, stop frequency, and frequency span are set, the remaining 2 frequenc...
Page 22
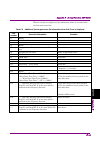
Chapter 2 basic operation 2-8 2.2.1 setting center frequency example: to set the center frequency to 1 mhz 1. Press , or press (center) from the frequency function menu. 2. After pressing , press (mhz) to set the center frequency. Setting range and resolution for center frequency setting range: ms28...
Page 23
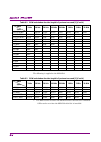
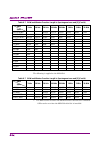
2.2 setting frequency 2-9 2 basic operation ms2840a-044: 300 mhz to 6 ghz ms2840a-046: 300 mhz to 6 ghz with ms2840a-077/177/078/178, with ms2840a-067/167, and frequency span > 31.25 mhz ms2840a-044: 300 mhz to 26.5 ghz ms2840a-046: 300 mhz to 44.5 ghz ms2850a frequency span ≤ 31.25 mhz ms2840a-047:...
Page 24
Chapter 2 basic operation 2-10 2.2.2 setting frequency span example: to set the frequency span to 1 khz 1. Press , or press (span) from the frequency function menu. 2. After pressing , press (khz) to set the frequency span. Setting range and resolution for frequency span setting range: 1 khz to 10 m...
Page 25
2.2 setting frequency 2-11 2 basic operation table 2.2.2-1 frequency span and sampling rate frequency span sampling rate ms2830a-006/106 ms2840a-006/106 ms2830a-005/105/007/009/109/077/078 ms2840a-005/105/009/109/077/177/078/178 ms2850a-032/033/133/034/134 1 khz 2 khz 2.5 khz 5 khz 5 khz 10 khz 10 k...
Page 26
Chapter 2 basic operation 2-12 2.2.3 setting start frequency example: to set the start frequency to 10 mhz 1. Press . 2. Press (start). 3. After pressing , press (mhz) to set the start frequency. Setting range and resolution for start frequency setting range: ms2830a without ms2830a-077/078, or freq...
Page 27
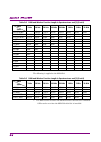
2.2 setting frequency 2-13 2 basic operation with ms2840a-077/177/078/178, and frequency span ≤ 31.25 mhz ms2840a-040: 300 mhz 2 x hz to 3.6 ghz 2 x hz ms2840a-041: 300 mhz 2 x hz to 6.0 ghz 2 x hz with ms2840a-077/177/078/178, without ms2840a-067/167, and frequency span > 31.25 mhz ms2840a-044: 300...
Page 28
Chapter 2 basic operation 2-14 2.2.4 setting stop frequency example: to set the stop frequency to 1 ghz 1. Press . 2. Press (stop). 3. After pressing , press (ghz) to set the stop frequency. Setting range and resolution for stop frequency setting range: ms2830a without ms2830a-077/078, or frequency ...
Page 29
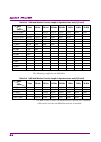
2.2 setting frequency 2-15 2 basic operation with ms2840a-077/177/078/178, and frequency span ≤ 31.25 mhz ms2840a-040: 300 mhz + 2 x hz to 3.6 ghz + 2 x hz ms2840a-041: 300 mhz + 2 x hz to 6.0 ghz + 2 x hz with ms2840a-077/177/078/178, without ms2840a-067/167, and frequency span > 31.25 mhz ms2840a-...
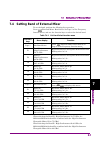
Page 30: 2.2.5 Setting
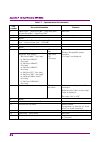
Chapter 2 basic operation 2-16 2.2.5 setting frequency band note: this function can be used when ms2830a-041/043/044/045 or ms2840a-041/044/046 is installed. The frequency band of the preselector can be changed by changing the frequency band mode. The setting procedure for the band mode is as follow...
Page 31: 2.2.6 Switching
2.2 setting frequency 2-17 2 basic operation 2.2.6 switching speed selects the normal or fast frequency switching speed. Table 2.2.6-1 switching speed switching speed descriptions fast tuning the operation is done so as to increase the frequency switching speed. (fast switching) normal the operation...
Page 32: 2.2.7 Setting Step Size
Chapter 2 basic operation 2-18 2.2.7 setting step size the step size of the center, start and stop frequency can be set. Example: to set the step size to 1 ghz. 1. Press . 2. Press (step size). 3. After pressing , press (ghz) to set the stop frequency. Setting range and resolution for step size sett...
Page 33
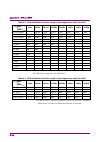
2.2 setting frequency 2-19 2 basic operation with ms2840a-077/177/078/178, without ms2840a-067/167, and frequency span > 31.25 mhz ms2840a-044: 1 hz to 6 ghz ms2840a-046: 1 hz to 6 ghz with ms2840a-077/177/078/178, with ms2840a-067/167, and frequency span > 31.25 mhz ms2840a-044: 1 hz to 26.5 ghz ms...
Page 34
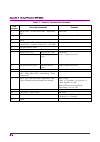
Chapter 2 basic operation 2-20 2.2.8 low phase noise display this function is available when ms2830a-062/066 or ms2840a-066/166 low phase noise is installed. Low phase noise is displayed when the low phase noise performance function is enabled at the conditions in table 2.2.8-1. Refer to section 3.4...
Page 35: 2.3 Setting
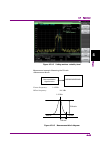
2.3 setting level 2-21 2 basic operation 2.3 setting level pressing (amplitude) from the main function menu, or pressing displays the amplitude function menu. Figure 2.3-1 amplitude key.
Page 36
Chapter 2 basic operation 2-22 table 2.3-1 amplitude function menu function key menu display function page 1 amplitude press amplitude to display this menu. F1 reference level sets the maximum level of the input signal. 2.3.1 “setting reference level” f2 attenuator (auto/manual) sets the input atten...
Page 37
2.3 setting level 2-23 2 basic operation the display items related to the level parameters are described below. Figure 2.3-2 display items related to level parameters table 2.3-2 display items related to level parameters no. Display description [1] ref. Level displays the reference level. [2] ref. L...
Page 38
Chapter 2 basic operation 2-24 table 2.3-3 and table 2.3-4 show the level display modes of the signal analyzer function and the reference level (top of the amplitude scale) setting range of each mode. Table 2.3-3 reference level setting range (when pre-amp is set to off) scale mode unit reference le...
Page 39
2.3 setting level 2-25 2 basic operation 2.3.1 setting reference level the reference level (upper end of amplitude scale) can be set. Example: to set the reference level to 10 dbm 1. Press . 2. Press (reference level). 3. After pressing , press (dbm) to set the reference level. Setting range and re...
Page 40
Chapter 2 basic operation 2-26 2.3.2 setting input attenuator this configures the input attenuator settings. (1) auto mode the input attenuator is automatically set according to the set reference level. Table 2.3.2-1 and table 2.3.2-2 show the settings in the auto mode. Table 2.3.2-1 input attenuato...
Page 41
2.3 setting level 2-27 2 basic operation table 2.3.2-2 input attenuators set in auto mode (when pre-amp is set to on) n=reference level (dbm) attenuator auto (db) resolution 2 db resolution 10 db –120 n ≤ –20 10 10 –20 n ≤ –18 12 20 –18 n ≤ –16 14 20 –16 n ≤ –14 16 20 –14 n ≤ –12 18 20 –12 n ≤ –10 2...
Page 42
Chapter 2 basic operation 2-28 (2) manual setting in the auto mode, the input attenuator is set so that the level can be measured with high accuracy, without any effect of gain compression, with a low noise level, when a signal at the same level as the reference level is input. However, to measure m...
Page 43
2.3 setting level 2-29 2 basic operation *: the input attenuator resolution of the ms2850a is fixed to 2 db regardless of option, att mode, or span. Table 2.3.2-4 input attenuator setting range (when pre-amp is set to off) attenuator manual lower limit upper limit logic* ( = 0, = 1, = 2) the ...
Page 44
Chapter 2 basic operation 2-30 setting the input attenuator example: to set the input attenuator to 30 db using the auto mode 1. Press . 2. Press (attenuator auto/manual) and select auto. 3. Press (reference level). 4. After pressing , press (dbm). The input attenuator is set to 30 db. Example: to s...
Page 45
2.3 setting level 2-31 2 basic operation displaying level over when the rf input signal level exceeds the specified value, distortion occurs and correct measurement values cannot be obtained. In this case, is displayed on the screen. When is displayed, lower the rf input signal level, or do the foll...
Page 46: 2.3.3 Setting
Chapter 2 basic operation 2-32 2.3.3 setting scale pressing (scale) from the amplitude function menu displays the scale function menu. Table 2.3.3-1 scale function menu function key menu display function f1 scale (log/lin) sets the scale mode (log/lin). This switches f2 and f3 display. Cannot be set...
Page 47
2.3 setting level 2-33 2 basic operation (1) setting the log scale example: to set log scale division to 20 db/div and the number of scale lines to 12 1. Press . 2. Press (scale). 3. Press (scale log/lin) and select log. 4. Press (log scale division). 5. After pressing , press (db/div) to set the lo...
Page 48
Chapter 2 basic operation 2-34 2.3.4 setting reference level unit note: this function can be set only when the scale mode is log. In the log scale, there are 7 types of units for the reference level: dbm, db v, dbmv, dbv (emf), v, w, and dbv/m. Example: to set the reference level to 10 dbmv 1. Pr...
Page 49
2.3 setting level 2-35 2 basic operation 2.3.5 setting reference level offset the reference level and waveform trace can be displayed with any offset value added. Figure 2.3.5-1 adding an offset value example: to set the reference level offset value to 10 db 1. Press . 2. Press (offset value). 3. Af...
Page 50: 2.3.6 Pre-Amp
Chapter 2 basic operation 2-36 2.3.6 pre-amp note: this function can be set when ms2830a-008/108/068/168 or ms2840a-008/108/068/168/069/169, ms2850a-068/168 preamplifier is installed. The level sensitivity can be increased by setting pre-amp to on. Example: to set pre-amp to on 1. Press . 2. Press (...
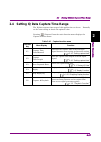
Page 51
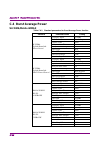
2.4 setting iq data capture time range 2-37 2 basic operation 2.4 setting iq data capture time range the iq data capture time range of this application can be set. Normally set the auto setting to obtain the optimal value. Pressing (capture) from the main function menu displays the capture function ...
Page 52
Chapter 2 basic operation 2-38 2.4.1 setting capture time the capture time length can be set. (1) auto the required time range for the shortest measurement time is automatically set based on the current setting. Upon parameter changes, no re-analysis of the captured iq data is performed, and capture...
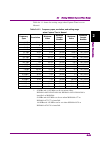
Page 53
2.4 setting iq data capture time range 2-39 2 basic operation table 2.4.1-1 shows the setting range when capture time is set to manual. Table 2.4.1-1 frequency span, resolution, and setting range when capture time is manual frequency span resolution minimum value minimum sample number maximum value ...
Page 54
Chapter 2 basic operation 2-40 the following table shows the setting range for the ms2850a when the frequency span is 50 mhz or higher. The resolution is displayed up to three decimal digits. (example: 0.769 ns) table 2.4.1-1 frequency span, resolution, and setting range when capture time is manual ...
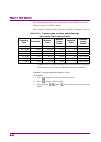
Page 55
2.4 setting iq data capture time range 2-41 2 basic operation 2.4.2 recapture and reanalysis the signal analyzer can capture and save iq data for a certain time interval to analyze the data many times. This can be used for analysis of the same iq data with different parameters. Reanalysis in capture...
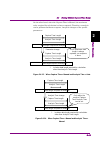
Page 56
Chapter 2 basic operation 2-42 figure 2.4.2-1 when capture time = auto and analysis time = auto also, when the analysis time is set manually, the capture time is automatically changed and the iq data is recaptured. Figure 2.4.2-2 when capture time = auto and analysis time = manual in addition, recap...
Page 57
2.4 setting iq data capture time range 2-43 2 basic operation on the other hand, when the capture time is manual, the maximum value required for calculation is always captured. Therefore, reanalysis can be performed without recapture, except for changes of the specific parameters. Figure 2.4.2-3 whe...
Page 58
Chapter 2 basic operation 2-44 2.4.3 parameters recaptured when capture time is set to manual some parameters may be recaptured and/or reanalyzed when they are changed. Tables 2.4.3-1 through 2.4.3-7 list the parameters that are recaptured upon a change. Table 2.4.3-1 common parameters recaptured up...
Page 59
2.4 setting iq data capture time range 2-45 2 basic operation table 2.4.3-2 common parameters recaptured upon a change in spectrum trace parameter marker to center freq. Marker to ref. Level standard load standard parameter noise cancel table 2.4.3-3 common parameters recaptured upon a change in pow...
Page 60
Chapter 2 basic operation 2-46..
Page 61
3-1 3 selecting w aveform captur e method selecting waveform capture method chapter 3 this chapter describes waveform capture methods and capture methods using triggers. 3.1 single/continuous measurement .................................. 3-2 3.1.1 continuous measurement mode ...................... ...
Page 62: 3.1 Single/continuous
Chapter 3 selecting waveform capture method 3-2 3.1 single/continuous measurement the capture mode of this application is determined by pressing . Figure 3.1-1 single key and continuous key 3.1.1 continuous measurement mode when the trigger function is off, measurement is executed continuously. When...
Page 63: 3.2 Trigger
3.2 trigger function 3-3 3 selecting w aveform captur e met h od 3.2 trigger function the trigger functions of the signal analyzer function include normal measurement and trigger measurement. For trigger measurement, video, wide if video, sg marker, frame and external can be selected as a trigger so...
Page 64
Chapter 3 selecting waveform capture method 3-4 table 3.2-1 trigger function menu function key menu display function f1 trigger switch (on/off) sets the capture start condition. 3.2.1 “normal measurement” f2 trigger source selects the trigger source. 3.2.2 “trigger measurement” f3 trigger slope (ris...
Page 65
3.2 trigger function 3-5 3 selecting w aveform captur e met h od the display items related to the trigger parameters are described below. Figure 3.2-2 display items related to trigger parameters table 3.2-2 display items related to trigger parameters no. Display description [1] trigger displays the ...
Page 66: 3.2.1 Normal
Chapter 3 selecting waveform capture method 3-6 3.2.1 normal measurement in the continuous measurement mode, waveforms are captured repeatedly and continuously. In the single measurement mode, a waveform is captured when is pressed. 1. Press . 2. Press (trigger switch on/off) and select off to set t...
Page 67: 3.2.2 Trigger
3.2 trigger function 3-7 3 selecting w aveform captur e met h od 3.2.2 trigger measurement measurement starts when the conditions for the selected trigger source are met. The following five types of triggers are available: video trigger wide if video trigger sg marker trigger (when any of the ...
Page 68
Chapter 3 selecting waveform capture method 3-8 1. Press . 2. Press (trigger source) and then press (video). 3. After pressing , press (dbm) to set the trigger level. 4. Press to return to the original menu. 5. Press (trigger delay). 6. After pressing , press (s) to set the trigger delay. 7. Press (...
Page 69
3.2 trigger function 3-9 3 selecting w aveform captur e met h od *: 25 mhz and 31.25 mhz can be set when ms2830a-005/105/007/009/109, ms2840a-005/105/009/109 is installed, or ms2850a. 50 mhz and 62.5 mhz can be set when ms2830a-077 or ms2840a-077/177 is installed. 100 mhz and 125 mhz can be set when...
Page 70
Chapter 3 selecting waveform capture method 3-10 (2) wide if video trigger an if signal with a wide passing band of about 50 mhz or greater is detected, and waveform capture starts in synchronization with the rise or fall of the detected signal. Operation example: setting the trigger level to 30 db...
Page 71
3.2 trigger function 3-11 3 selecting w aveform captur e met h od operation example: setting the external 2 trigger 1. Press . 2. Press (trigger source) and select external 2. 3. Press (trigger slope) to select either rise or fall. Setting range and resolution for trigger delay as shown in table 3.2...
Page 72
Chapter 3 selecting waveform capture method 3-12 pressing (frame sync setup) on the trigger source function menu displays the frame sync setup function menu. Table 3.2.2-3 frame sync setup function menu function key menu display function f1 off captures waveforms according to the equipment-internal ...
Page 73
3.2 trigger function 3-13 3 selecting w aveform captur e met h od operation example: setting the sg marker trigger 1. Press . 2. Press (trigger source) and then press (sg marker). Press to return to the original menu. 3. Press (trigger slope) to select either rise or fall. Setting range and resoluti...
Page 74
Chapter 3 selecting waveform capture method 3-14..
Page 75
4-1 4 tr ac e trace chapter 4 this chapter describes the parameters and measurements for each trace. 4.1 selecting trace ............................................................. 4-3 4.2 spectrum ....................................................................... 4-4 4.2.1 what is spectrum t...
Page 76
Chapter 4 trace 4-2 4.5.5 setting detection mode ................................. 4-147 4.5.6 setting markers ............................................ 4-148 4.5.7 setting methods ............................................ 4-154 4.6 ccdf ...........................................................
Page 77: 4.1 Selecting
4.1 selecting trace 4-3 4 tr ac e 4.1 selecting trace pressing (trace) on the main function menu, or pressing and then (trace mode) displays the trace mode function menu. The trace type can be selected from this menu. Figure 4.1-1 trace key table 4.1-1 trace mode function menu function key menu disp...
Page 78: 4.2 Spectrum
Chapter 4 trace 4-4 4.2 spectrum 4.2.1 what is spectrum trace? Spectrum trace is a screen that converts captured iq data from time domain data to frequency domain data by fast fourier transformation (fft) processing to display a spectrum. The display items for a spectrum trace are described below. F...
Page 79
4.2 spectrum 4-5 4 tr ac e table 4.2.1-1 display items for spectrum trace no. Display descriptions [1] analysis start time/ analysis time length displays the analysis start time and analysis time length. [2] rbw displays the resolution bandwidth (rbw). [3] det. Displays the detection mode. [4] trace...
Page 80
Chapter 4 trace 4-6 4.2.2 setting spectrum parameters after selecting spectrum for trace mode, pressing (trace) from the main function menu or pressing displays the trace function menu. The trace function menu consists of 2 pages that are toggled by pressing . 4.1 “selecting trace” table 4.2.2-1 tra...
Page 81
4.2 spectrum 4-7 4 tr ac e table 4.2.2-1 trace function menu (cont’d) function key menu display function f7 time detection used for setting related to detection. 4.2.7 “setting detection mode” f8 sub trace setting used for setting related to sub-trace. 4.9 “sub-trace” page2 trace press (trace), and ...
Page 82
Chapter 4 trace 4-8 4.2.3 setting analysis time pressing (analysis time) on the trace function menu, or pressing displays the analysis time function menu. Table 4.2.3-1 analysis time function menu function key menu display function f1 time (main trace) (auto/manual) switches between auto setting and...
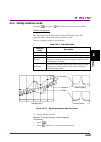
Page 83
4.2 spectrum 4-9 4 tr ac e setting analysis time analysis time is the target time range for spectrum trace analysis. The analysis time is specified with the analysis start position (analysis start time) and analysis time length (analysis time length). Figure 4.2.3-1 analysis time the auto mode and m...
Page 84
Chapter 4 trace 4-10 table 4.2.3-2 setting analysis time in auto mode capture time analysis start time [s] analysis time length [s] auto 0 0 manual 0 1 x 1 x : capture time length [s] 2.4 “setting iq data capture time range” (2) manual mode the analysis start time and analysis time length are set ma...
Page 85
4.2 spectrum 4-11 4 tr ac e analysis start time and analysis time length resolution table 4.2.3-5 frequency span and setting resolution frequency span setting resolution 1 khz 0.5 ms 2.5 khz 0.2 ms 5 khz 0.1 ms 10 khz 50 s 25 khz 20 s 50 khz 10 s 100 khz 5 s 250 khz 2 s 500 khz 1 s 1 mhz 0.5 ...
Page 86
Chapter 4 trace 4-12 the following table shows the setting range for the ms2850a when frequency span is 50 mhz or higher. The resolution is displayed up to three decimal digits. (example: 0.769 ns) table 4.2.3-5 frequency span and setting resolution (cont’d) frequency span setting resolution 50 mhz ...
Page 87: 4.2.4 Setting
4.2 spectrum 4-13 4 tr ac e 4.2.4 setting scale scale function menu pressing (trace) on the main function menu, or pressing and then (scale) displays the scale function menu. Table 4.2.4-1 scale function menu function key menu display function f1 vertical used for setting related to the vertical axi...
Page 88
Chapter 4 trace 4-14 horizontal function menu pressing (horizontal) on the scale function menu displays the horizontal function menu. Table 4.2.4-3 horizontal function menu function key menu display function f1 center sets the center frequency of the horizontal axis scale. F2 width sets the frequenc...
Page 89
4.2 spectrum 4-15 4 tr ac e (2) setting the horizontal axis scale in a spectrum trace, the display frequency range (horizontal axis scale) can be changed freely within the range of the center frequency and frequency span. To set the display frequency range, the setting for center (center of the disp...
Page 90
Chapter 4 trace 4-16 4.2.5 setting resolution bandwidth (rbw) pressing (rbw) on the trace function menu, or pressing displays the rbw function menu. Table 4.2.5-1 rbw function menu function key menu display function f1 rbw (auto/manual) selects auto setting or manual setting for the resolution bandw...
Page 91
4.2 spectrum 4-17 4 tr ac e resolution bandwidth setting range the setting range of the resolution bandwidth varies depending on the setting of marker result. Table 4.2.5-2 pattern of marker result integration density peak (fast) peak (accuracy) [1] [1] [2] [3] table 4.2.5-3 setting range of resolut...
Page 92
Chapter 4 trace 4-18 510 mhz can be set when the ms2850a-033/133/034/134 is installed. 1 ghz can be set when the ms2850a-034/134 is installed. Rbw is set with the 1-3 sequence. (3) setting the resolution bandwidth example: to set the resolution bandwidth to 100 khz 1. Press . 2. Press (rbw). 3. Pres...
Page 93
4.2 spectrum 4-19 4 tr ac e 4.2.6 setting storage mode pressing and then (storage) displays the storage function menu. Table 4.2.6-1 storage function menu function key menu display function f1 mode used for setting related to the updating and displaying of trace data. F2 count sets the storage count...
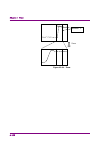
Page 94
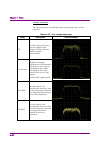
Chapter 4 trace 4-20 storage mode types in a spectrum trace, the following four storage mode types can be selected. Table 4.2.6-2 four storage mode types mode description display example off at each capture, the trace data are updated and displayed. These data are used for normal measurement. Lin av...
Page 95
4.2 spectrum 4-21 4 tr ac e (1) selecting the storage mode and storage count example: to set the storage mode to lin average and storage count to 100 1. Press . 2. Press (storage). 3. Press (mode) and select lin average. 4. Press (count). 5. Press , and then press (set) to set the storage count. Set...
Page 96
Chapter 4 trace 4-22 (2) averaging function the digital averaging function, which performs an averaging operation at a point on the horizontal axis each time trace data is captured and displays the trace, can be executed by selecting lin average in the storage mode. When the measurement mode is sing...
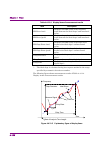
Page 97
4.2 spectrum 4-23 4 tr ac e figure 4.2.6-1 averaging function capture count s/n impro vemen t d egree.
Page 98
Chapter 4 trace 4-24 4.2.7 setting detection mode the detection mode can be selected by pressing and then (time detection). Detection mode types the detection mode in the analysis range is set. The detection mode can be selected from the three types: average, positive, and negative. Table 4.2.7-1 de...
Page 99
4.2 spectrum 4-25 4 tr ac e detection mode when analysis time is auto when capture time and analysis time are set to auto, in the spectrum trace, the analysis time range is minimized (to one fft) to make the measurement time fastest. Therefore, there is only one data for detection even when the dete...
Page 100
Chapter 4 trace 4-26 on the other hand, when capture time is set to manual mode and analysis time is set to auto, in the spectrum trace, the analysis time range is the time set in capture time length. Therefore, detection is performed for the fft spectrums of all the iq data captured. Figure 4.2.7-3...
Page 101: 4.2.8 Setting
4.2 spectrum 4-27 4 tr ac e 4.2.8 setting markers this section describes various marker functions provided by the zone marker, and the functions to improve measurement efficiency, such as marker search and parameter setting with marker values. Pressing (marker) on page 2 of the trace function menu, ...
Page 102
Chapter 4 trace 4-28 table 4.2.8-1 marker function menu function key menu function page1 marker press (marker) to display. F1 active marker sets the active marker. F2 normal sets the marker mode of the active marker to normal. The frequency (time) and the level are displayed on the screen. The norma...
Page 103
4.2 spectrum 4-29 4 tr ac e table 4.2.8-1 marker function menu (cont’d) function key menu function page2 marker press (marker), and then press to display. F1 marker list (on/off) sets the marker list display on/off. F2 marker result opens the marker result function menu. Set the display type of the ...
Page 104
Chapter 4 trace 4-30 zone width function menu on the marker function menu, press (zone width) to display the zone width function menu. Table 4.2.8-2 zone width function menu function key menu function f1 type (zone/spot) switches between the spot marker and the zone marker. F2 zone width sets the zo...
Page 105
4.2 spectrum 4-31 4 tr ac e figure 4.2.8-1 display items of marker result table 4.2.8-4 display items of marker result no. Display descriptions [1] frequency displays the frequency of each marker. [2] frequency difference the frequency difference between the active marker and the marker set by relat...
Page 106
Chapter 4 trace 4-32 changing position and width of zone marker the area enclosed by the dashed lines at the center of the screen in figure 4.2.8-2 is called a zone marker. The integral power, average power, or peak power is displayed as a marker value. Figure 4.2.8-2 zone width, zone center frequen...
Page 107
4.2 spectrum 4-33 4 tr ac e setting range and resolution for zone center and zone width setting range: refer to table 4.2.8-5. Zone center minimum resolution: 2 1 x x [hz] the resolution is 0.01 hz. Zone width minimum resolution: trace frequency resolution unit 1 x : sampling rate [hz] 2.2.2 “settin...
Page 108
Chapter 4 trace 4-34 (3) zoom in display setting example: to enlarge the zone range of the active zone marker 1. Press . 2. Press to display the page 2 of marker function menu. 3. Press (zoom) to enlarge the specified range. As shown in figure 4.2.8-3, when the zoom function is performed after setti...
Page 109
4.2 spectrum 4-35 4 tr ac e (4) zoom out display setting example: to reduce the current screen display data into the zone of the active zone marker 1. Press . Press to display the page 2 of marker function menu. Press (zoom out) to downsize the entire screen to fit in the active zone of the zone mar...
Page 110
Chapter 4 trace 4-36 (5) displaying marker list displays the list of the marker result. The marker frequency and the power are displayed on the list. Example: to set the marker display to on 1. Press . 2. Press to move to page 2 of the marker function menu, and set (marker list) to on. Figure 4.2.8-...
Page 111
4.2 spectrum 4-37 4 tr ac e table 4.2.8-6 marker list display items item descriptions mkr displays the marker number. When a number is displayed, it indicates a marker number. When is displayed, it indicates the level or frequency difference between the active marker and the marker set by relative...
Page 112: 4.2.9 Setting
Chapter 4 trace 4-38 4.2.9 setting marker search the marker search functions include peak search and next peak search. Signal search function menu pressing (signal search) on page 2 of the trace function menu, or pressing displays the signal search function menu. Table 4.2.9-1 signal search function...
Page 113
4.2 spectrum 4-39 4 tr ac e threshold function menu pressing (threshold) from the signal search function menu displays the threshold function menu. Table 4.2.9-2 threshold function menu function key menu display function f1 threshold (on/off) selects on/off for the detection threshold function for i...
Page 114
Chapter 4 trace 4-40 (1) executing peak search the zone of the active marker is moved to the position where the marker value becomes the maximum in the measurement band. If two or more marker values exist, it is moved to the point with the lower marker frequency. When marker result is integration or...
Page 115
4.2 spectrum 4-41 4 tr ac e setting range and resolution for search resolution setting range: 0.01 to 50.00 db minimum resolution: 0.01 db rotary knob resolution: 0.1 db step key resolution: 1 db (4) setting the search threshold the threshold to restrict marker values to be searched is set. A search...
Page 116
Chapter 4 trace 4-42 figure 4.2.9-1 marker to center freq. / marker to ref. Level (7) setting marker search function sorts the markers set in search peaks number by frequency (time) or level. Note marker search function can be executed when marker result is set to peak (fast) or peak (accuracy). Exa...
Page 117
4.2 spectrum 4-43 4 tr ac e figure 4.2.9-2 setting markers sorted by level measurement example: measuring the cn ratio center frequency: 1.9 ghz offset frequency: 100 khz figure 4.2.9-3 measurement block diagram c/n ratio 1.9 ghz 100 khz non-modulation signal source ms2830a/ms2840a.
Page 118
Chapter 4 trace 4-44 1. Press and then press (preset). 2. Press . 3. Press and then press (khz) to set the frequency span. 4. Press . 5. Press and then press (ghz) to set the center frequency. 6. Press and then press (delta) to set the marker mode to delta. 7. Press to display page 2 of the marker f...
Page 119
4.2 spectrum 4-45 4 tr ac e figure 4.2.9-4 measurement results the measurement values can be converted to values in dbc/hz units by the following formula: ) log( 10 rbw m cn where: cn c/n measurement value [dbc/hz] m difference marker value [db] rbw rbw setting value [hz] change the rbw value to sel...
Page 120: 4.2.10 Measure Measurement
Chapter 4 trace 4-46 4.2.10 measure measurement measure function menu pressing (measure) on page 2 of the trace function menu, or pressing displays the measure function menu. Table 4.2.10-1 measure function menu function key menu display function f1 acp performs adjacent channel leakage power measur...
Page 121
4.2 spectrum 4-47 4 tr ac e acp function menu pressing (acp) on the measure function menu displays the acp function menu. Table 4.2.10-2 acp function menu function key menu display function f1 acp (on/off) when it is set to on, other measure functions of the same trace are set to off. F2 acp referen...
Page 122
Chapter 4 trace 4-48 in band setup function menu press (in band setup) on the acp function menu to display the in band setup menu. Table 4.2.10-3 in band setup function menu function key menu display function f1 carrier number sets the number of carriers. F2 in-band center sets the center frequency ...
Page 123
4.2 spectrum 4-49 4 tr ac e offset setup function menu pressing (offset setup) on the acp function menu displays the offset setup function menu. The offset setup function menu consists of two pages. Press to change the page. Table 4.2.10-4 offset setup function menu function key menu display functio...
Page 124
Chapter 4 trace 4-50 (1) measuring the adjacent channel leakage power the leakage power of the adjacent channel is measured. The display items for the measurement results when power result type is set to offset are described below. Figure 4.2.10-1 display items for measurement results table 4.2.10-5...
Page 125
4.2 spectrum 4-51 4 tr ac e the display items for the measurement results when power result type is set to carrier are described below. Figure 4.2.10-2 display items for measurement results table 4.2.10-6 display items for measurement results no. Display descriptions [1] span total displays the inte...
Page 126
Chapter 4 trace 4-52 channel power function menu pressing (channel power) on the measure function menu displays the channel power function menu. Table 4.2.10-7 channel power function menu function key menu display function f1 channel power (on/off) when it is set to on, other measure functions of th...
Page 127
4.2 spectrum 4-53 4 tr ac e (2) measuring the channel power the channel power is measured. The display items for the measurement results are described below. Figure 4.2.10-3 display items for measurement results table 4.2.10-8 display items for measurement results no. Display descriptions [1] channe...
Page 128
Chapter 4 trace 4-54 obw function menu pressing (obw) on the measure function menu displays the obw function menu. Table 4.2.10-9 obw function menu function key menu display function f1 obw (on/off) when this is set to on, other measure functions of the same trace are set to off. F2 method (n%/xdb) ...
Page 129
4.2 spectrum 4-55 4 tr ac e (3) measuring the occupied bandwidth the occupied bandwidth is measured. The display items for the measurement results are described below. Figure 4.2.10-4 display items for measurement results table 4.2.10-10 display items for measurement results no. Display description ...
Page 130
Chapter 4 trace 4-56 (4) example of adjacent channel leakage power measurement for measurement of the adjacent channel leakage power of the w-cdma modulation method signal, the detection mode is set to average. Center frequency: 1.92 ghz frequency span: 25 mhz rbw: 30 khz figure 4.2.10-5 measurement...
Page 131
4.2 spectrum 4-57 4 tr ac e 19. Press , and then press (set) to set a roll-off factor. 20. Press to switch the function menu to page 2. 21. Press (offset-1). 22. Press , and then press (mhz) to set offset frequency-1. 23. Press (offset-2). 24. Press , and then press (mhz) to set offset frequency-2. ...
Page 132
Chapter 4 trace 4-58 figure 4.2.10-6 results of measurement example.
Page 133
4.2 spectrum 4-59 4 tr ac e (5) example of channel power measurement center frequency: 1.92 ghz frequency span: 10 mhz rbw: 100 khz figure 4.2.10-7 measurement block diagram 1. Press , and then press (preset). 2. Press . 3. Press , and then press (mhz) to set the frequency span. 4. Press . 5. Press ...
Page 134
Chapter 4 trace 4-60 note: weighting can be done with the filter. Rect: rectangular filter nyquist: nyquist filter root nyquist: root nyquist filter for the nyquist filter and root nyquist filter, set the roll-off factor. Figure 4.2.10-8 measurement results (6) example of occupied frequency bandwidt...
Page 135
4.2 spectrum 4-61 4 tr ac e figure 4.2.10-10 occupied bandwidth 1. Press , and then press (preset). 2. Press . 3. Press , and then press (mhz) to set the frequency span. 4. Press . 5. Press , and then press (ghz) to set the center frequency. 6. Press . 7. Press , and then press (khz) to set the reso...
Page 136
Chapter 4 trace 4-62 figure 4.2.10-11 measurement results.
Page 137
4.2 spectrum 4-63 4 tr ac e 4.2.11 executing return to spectrogram after analyze with spectrum trace has been executed on the spectrogram trace, move on to the spectrum trace, and press and, (return to spectrogram). Then you can return to the spectrogram trace. If you move on to spectrogram trace by...
Page 138
Chapter 4 trace 4-64 table 4.2.11-2 analysis length parameter analysis length parameter the setting of capture time auto/manual was changed. Center frequency was changed. The setting of capture time length was changed when capture time = manual. The setting of span was changed. The setting of termin...
Page 139: 4.3 Power
4.3 power vs time 4-65 4 tr ac e 4.3 power vs time 4.3.1 what is power vs time trace? Power vs time trace is a screen to observe the time fluctuations of power of the obtained measured signal. Figure 4.3.1-1 display items for power vs time trace table 4.3.1-1 display items for power vs time trace no...
Page 140
Chapter 4 trace 4-66 4.3.2 setting power vs time parameters after selecting “power vs time” for trace mode, pressing (trace) from the main function menu or pressing displays the trace function menu. The trace function menu consists of two pages, which can be toggled by pressing . 4.1 “selecting trac...
Page 141
4.3 power vs time 4-67 4 tr ac e 4.3.3 setting analysis time pressing (analysis time) from the trace function menu, or pressing displays the analysis time function menu. Setting analysis time on the power vs time trace normalizes a set time that exceeds five valid digits in addition to rounding up b...
Page 142
Chapter 4 trace 4-68 setting the analysis time analysis time is the time to be analyzed. The analysis time can be specified with the analysis start position (analysis start time) and analysis time length (analysis time length). Figure 4.3.3-1 analysis time (1) auto mode when capture time is set to a...
Page 143
4.3 power vs time 4-69 4 tr ac e (2) manual mode the analysis start time and analysis time length are set manually. This is an effective method to perform measurement of discontinuous signals such as burst. Analysis start time setting range table 4.3.3-3 analysis start time setting range in manual m...
Page 144
Chapter 4 trace 4-70 analysis start time resolution table 4.3.3-5 frequency span and setting resolution frequency span setting resolution 1 khz 0.5 ms 2.5 khz 0.2 ms 5 khz 0.1 ms 10 khz 50 s 25 khz 20 s 50 khz 10 s 100 khz 5 s 250 khz 2 s 500 khz 1 s 1 mhz 0.5 s 2.5 mhz 0.2 s 5 mhz 0.1 s 10...
Page 145
4.3 power vs time 4-71 4 tr ac e the following table shows the setting range for the ms2850a when frequency span is 50 mhz or higher. The resolution is displayed up to three decimal digits. (example: 0.769 ns) table 4.3.3-5 frequency span and setting resolution (cont’d) frequency span setting resolu...
Page 146: 4.3.4 Setting
Chapter 4 trace 4-72 4.3.4 setting scale scale function menu pressing and then (scale) displays the scale function menu. Table 4.3.4-1 scale function menu function key menu display function f1 vertical used for setting related to the vertical axis (level axis) scale. Vertical function menu pressing ...
Page 147
4.3 power vs time 4-73 4 tr ac e (1) vertical axis scale the scale range log scale and lin scale of the level axis are set. Example: to set the vertical axis scale range (log scale) to 0.1 db/div 1. Press . 2. Press (scale). 3. Press (vertical), and then press (log scale division). 4. Press , and th...
Page 148: 4.3.5 Setting
Chapter 4 trace 4-74 4.3.5 setting filter pressing (filter) on the trace function menu, or pressing displays the filter function menu. Table 4.3.5-1 filter function menu function key menu display function f1 type selects the filter type. F2 roll-off factor sets the roll-off factor. F3 band width set...
Page 149
4.3 power vs time 4-75 4 tr ac e table 4.3.5-2 filter band setting range (rect) frequency span minimum value maximum value 1 khz n/a 2.5 khz 1 khz 2 khz 5 khz 1 khz 4 khz 10 khz 1 khz 9 khz 25 khz 1 khz 23 khz 50 khz 2 khz 47 khz 100 khz 4 khz 95 khz 250 khz 8 khz 238 khz 500 khz 16 khz 476 khz 1 mh...
Page 150
Chapter 4 trace 4-76 table 4.3.5-3 filter band setting range (gauss, nyquist, root nyquist) frequency span minimum value maximum value 1 khz n/a 2.5 khz 1 khz 1 hz (gauss only) 1 khz 5 khz 1 khz 2 khz 10 khz 1 khz 4 khz 25 khz 1 khz 10 khz 50 khz 2 khz 20 khz 100 khz 4 khz 40 khz 250 khz 8 khz 100 k...
Page 151
4.3 power vs time 4-77 4 tr ac e (1) gauss filter example: to set the filter shape to gaussian, filter bandwidth to 3.84 mhz, and filter frequency offset to 1 mhz 1. Press . 2. Press (type) and select gaussian. 3. Press (band width). 4. Press , and then press (mhz) to set the filter band. 5. Press (...
Page 152
Chapter 4 trace 4-78 (3) nyquist filter example: to set the filter shape to nyquist, filter bandwidth to 3.84 mhz, filter frequency offset to 1 mhz, and roll-off factor to 0.22 1. Press . 2. Press (type) and select nyquist. 3. Press (band width). 4. Press , and then press (mhz) to set the filter ban...
Page 153: 4.3.6 Setting
4.3 power vs time 4-79 4 tr ac e 4.3.6 setting smoothing pressing and then (view) displays the view function menu. Table 4.3.6-1 view function menu function key menu display function f1 smoothing (on/off) sets smoothing to on/off. F2 smoothing time length sets the smoothing time length. (1) setting ...
Page 154
Chapter 4 trace 4-80 4.3.7 setting storage mode pressing and then (storage) displays the storage function menu. Table 4.3.7-1 storage function menu function key menu display function f1 mode used for setting related to update and display of trace data. F2 count sets the storage count. F3 stop stops ...
Page 155
4.3 power vs time 4-81 4 tr ac e storage mode types in a power vs time trace, the following four storage mode types can be selected. Table 4.3.7-2 four storage mode types mode description display example off at each capture, the trace data are updated and displayed. These data are used for normal me...
Page 156
Chapter 4 trace 4-82 (1) selecting the storage mode and storage count example: to set the storage mode to average and storage count to 100 1. Press . 2. Press (storage). 3. Press (mode) and select lin average. 4. Press (count). 5. Press , and then press (set). Setting range and minimum resolution fo...
Page 157
4.3 power vs time 4-83 4 tr ac e table 4.3.7-3 averaging capture count n measurement value m(n) displayed value y(n) 1 m (1) y (1) = m (1) 2 m (2) y (2) = 2 2 m 1 y ) ( ) ( 3 m (3) y (3) = 3 3 m 2 y 2 ) ( ) ( … ... … n 1 m (n 1) y (n 1) = 1 n 1 n m 2 n y 2 n ) ( ) ( ) ( n m (n) y (n) = n n m 1 n...
Page 158
Chapter 4 trace 4-84 4.3.8 setting detection mode the detection mode can be selected by pressing and then (detection). Detection mode types the detection mode in the analysis range (detection) is set. The detection mode can be selected from the 4 types: average, positive, negative, and pos & neg. Ta...
Page 159
4.3 power vs time 4-85 4 tr ac e (1) setting the detection mode example: to set the detection mode to positive 1. Press . 2. Press (detection), select positive, and then press ..
Page 160: 4.3.9 Setting
Chapter 4 trace 4-86 4.3.9 setting markers this section describes various functions as well as the functions to improve measurement efficiency, such as marker search and parameter setting with marker values. For the marker’s setting range and resolution, refer to the setting ranges and resolutions i...
Page 161
4.3 power vs time 4-87 4 tr ac e figure 4.3.9-1 display items for marker results table 4.3.9-2 display items for marker results no. Display description [1] mkr1/mkr2 displays the power at each marker time position. [2] (2 1) displays the ratio of the power at the marker time positions (marker 1 m...
Page 162
Chapter 4 trace 4-88 (1) changing the marker position note: the marker position of power vs time, frequency vs time, phase vs time synchronizes one another. The power in the specified time can be measured by using the marker displayed in figure 4.3.9-2. Figure 4.3.9-2 marker example: to set 1.5 s f...
Page 163
4.3 power vs time 4-89 4 tr ac e 3. Press (marker 2 on/off) and select on. 4. Press (active marker 1/2/1&2) and select the active marker. (3) setting zooming in the range from marker 1 to marker 2 can be zoomed in. Example: to zoom in on marker 1 1. Press . 2. Press (zoom) to zoom in on the range en...
Page 164
Chapter 4 trace 4-90 (4) setting zooming out the analysis range can be zoomed out to the range from marker 1 to marker 2. 1. Press . 2. Press (zoom out) to zoom out the displayed waveform data to the range enclosed with markers 1 and 2. As shown in figure 4.3.9-4, when zoom out is performed after se...
Page 165
4.3 power vs time 4-91 4 tr ac e (5) peak to peak measurement the am modulation degree of the measured signal is measured based on the displayed trace data in the marker range. The measurement start and stop points are the trace points of the marker position. When the marker is off, the entire analy...
Page 166
Chapter 4 trace 4-92 table 4.3.9-3 display items for measurement results no. Display item [1] +peak displays the positive peak am modulation degree calculated from the following formula: 100 * ave ave max plus v v v p where p plus : +peak [%] v max : maximum voltage [v] v ave : average voltage [v] [...
Page 167
4.3 power vs time 4-93 4 tr ac e 4.3.10 setting marker search the marker search functions include peak search and next peak search. Signal search function menu pressing (signal search) on page 2 of the trace function menu, or pressing displays the signal search function menu. Table 4.3.10-1 signal s...
Page 168
Chapter 4 trace 4-94 (1) executing peak search the active marker is moved to the position where the marker value becomes maximal in the measurement band. If two or more marker values exist, the point with the lower marker time is selected. Example: to execute a peak search 1. Press . 2. Press (peak ...
Page 169
4.3 power vs time 4-95 4 tr ac e (4) setting the search threshold the threshold to restrict marker values to be searched is set. A search is performed for marker values above or below the threshold. Example: to set threshold limitation to on and marker values below 10 dbm as search targets 1. Press...
Page 170: 4.3.11 Measure Measurement
Chapter 4 trace 4-96 4.3.11 measure measurement measure function menu pressing (measure) on page 2 of the trace function menu, or pressing displays the measure function menu. Table 4.3.11-1 measure function menu function key menu display function f1 burst average power measures the average power of ...
Page 171
4.3 power vs time 4-97 4 tr ac e burst average power function menu press (burst average power) on the measure function menu to display the burst average power function menu. Table 4.3.11-2 burst average power function menu function key menu display function f1 burst average power (on/off) the other ...
Page 172
Chapter 4 trace 4-98 (1) measuring the burst average power the average power of the burst signal displayed on the screen is measured. The measurement start and stop points are marker positions. When either of the markers is set to off, the entire analysis range will be measured. The display items fo...
Page 173
4.3 power vs time 4-99 4 tr ac e example: to obtain the effective average power within the range set by the marker center frequency: 1.9 ghz figure 4.3.11-2 measurement block and interval measurement interval power level start point stop point digital modulation (phs) signal source ms2830a/ms2840a 0...
Page 174
Chapter 4 trace 4-100 1. Press , and then select (preset). 2. Press . 3. Press , and then press (ghz) to set the center frequency. 4. Press . 5. Press (trace mode), and then press (power vs time) to set the trace type. 6. Set the ref. Level 3 db above the peak. 7. Press , and then press (trigger sou...
Page 175
4.3 power vs time 4-101 4 tr ac e figure 4.3.11-3 trigger level to obtain the average power between the burst frame, the measurement interval is set to the burst frame time for measurement. Figure 4.3.11-4 measurement interval figure 4.3.11-5 measurement results (burst frame) start point stop point ...
Page 176
Chapter 4 trace 4-102 (2) am depth measurement measures the am modulation degree of the measured signal, based on the trace data within the marker range. The measurement range is between marker 1 and 2 points on the trace. When either of the markers is set to off, the measurement is performed throug...
Page 177
4.3 power vs time 4-103 4 tr ac e table 4.3.11-4 description of displayed measurement result items no. Display item [1] +peak displays the positive peak am modulation degree. Calculated from the following formula: 100 * ave ave max plus v v v p however, p plus :+peak[%] v max :maximum voltage [v] v ...
Page 178: 4.4 Frequency Vs Time
Chapter 4 trace 4-104 4.4 frequency vs time 4.4.1 what is frequency vs time trace? Frequency vs time trace is a screen that displays time fluctuations of the frequency from the obtained iq digital data. The display items for a frequency vs time trace are described below. Figure 4.4.1-1 display items...
Page 179
4.4 frequency vs time 4-105 4 tr ac e 4.4.2 setting frequency vs time parameters after selecting frequency vs time for trace mode, pressing (trace) from the main function menu or pressing displays the trace function menu. The trace function menu consists of two pages, which can be toggled by pressin...
Page 180
Chapter 4 trace 4-106 4.4.3 setting analysis time pressing (analysis time) from the trace function menu, or pressing displays the analysis time function menu. Setting analysis time on the frequency vs time trace normalizes a set time that exceeds five valid digits in addition to rounding up by time ...
Page 181
4.4 frequency vs time 4-107 4 tr ac e setting the analysis time analysis time is the time to be analyzed. The analysis time can be specified with the analysis start position (analysis start time) and analysis time length (analysis time length). Figure 4.4.3-1 analysis time (1) auto mode when capture...
Page 182
Chapter 4 trace 4-108 (2) manual mode the analysis start time and analysis time length are set manually. This is an effective method for measuring discontinuous signals such as burst. Analysis start time setting range table 4.4.3-3 analysis start time setting range in manual mode capture time minimu...
Page 183
4.4 frequency vs time 4-109 4 tr ac e analysis start time resolution table 4.4.3-5 frequency span and setting resolution frequency span setting resolution 1 khz 0.5 ms 2.5 khz 0.2 ms 5 khz 0.1 ms 10 khz 50 s 25 khz 20 s 50 khz 10 s 100 khz 5 s 250 khz 2 s 500 khz 1 s 1 mhz 0.5 s 2.5 mhz 0.2 ...
Page 184
Chapter 4 trace 4-110 the following table shows the setting range for the ms2850a when frequency span is 50 mhz or higher. The resolution is displayed up to three decimal digits. (example: 0.769 ns) table 4.4.3-5 frequency span and setting resolution (cont’d) frequency span setting resolution 50 mhz...
Page 185: 4.4.4 Setting
4.4 frequency vs time 4-111 4 tr ac e 4.4.4 setting scale scale function menu pressing and then (scale) displays the scale function menu. Table 4.4.4-1 scale function menu function key menu display function f1 vertical used for setting related to the vertical axis (frequency axis) scale. Vertical fu...
Page 186
Chapter 4 trace 4-112 (1) setting the vertical axis scale unit in a frequency vs time trace, there are the following two types of units (frequency scale units) for the vertical axis scale. Hz: measurement frequency data is displayed. hz: difference from the center frequency is displayed. Example: t...
Page 187: 4.4.5 Setting
4.4 frequency vs time 4-113 4 tr ac e 4.4.5 setting filter pressing (filter) on the trace function menu, or pressing displays the filter function menu. Table 4.4.5-1 filter function menu function key menu display function f1 filter auto/manual sets the filter band auto setting function. When it is s...
Page 188
Chapter 4 trace 4-114 table 4.4.5-2 filter band setting range frequency span minimum value maximum value 1 khz 30 hz 300 hz 2.5 khz 100 hz 1 khz 5 khz 100 hz 1 khz 10 khz 300 hz 3 khz 25 khz 1 khz 10 khz 50 khz 1 khz 10 khz 100 khz 3 khz 30 khz 250 khz 10 khz 100 khz 500 khz 10 khz 100 khz 1 mhz 30 ...
Page 189: 4.4.6 Setting
4.4 frequency vs time 4-115 4 tr ac e 4.4.6 setting smoothing pressing and then (view) displays the view function menu. Table 4.4.6-1 view function menu function key menu display function f1 smoothing (on/off) sets the smoothing to on/off. F2 smoothing time length sets the smoothing time length. (1)...
Page 190
Chapter 4 trace 4-116 4.4.7 setting storage mode pressing and then (storage) displays the storage function menu. Table 4.4.7-1 storage function menu function key menu display function f1 mode used for setting related to update and display of trace data. F2 count sets the storage count. F3 stop stops...
Page 191
4.4 frequency vs time 4-117 4 tr ac e (1) selecting the storage mode and storage count the setting procedure for the storage mode and storage count is as follows. Example: to set the storage mode to max hold and storage count to 100 1. Press . 2. Press (storage). 3. Press (mode) and select max hold....
Page 192
Chapter 4 trace 4-118 4.4.8 setting detection mode the detection mode can be selected by pressing and then (detection). Detection mode types the detection mode in the analysis range (detection) is set. The detection mode can be selected from four types: average, positive, negative, and pos&neg. Tabl...
Page 193
4.4 frequency vs time 4-119 4 tr ac e (1) setting the detection mode example: to set the detection mode to negative 1. Press . 2. Press (detection) and select negative..
Page 194: 4.4.9 Setting
Chapter 4 trace 4-120 4.4.9 setting markers this section describes various marker functions as well as the functions to improve measurement efficiency, such as marker search and parameter setting with marker values. For the marker’s setting range and resolution, refer to the setting ranges and resol...
Page 195
4.4 frequency vs time 4-121 4 tr ac e figure 4.4.9-1 display items for marker results table 4.4.9-2 display items for marker results no. Display description [1] mrk1 / mrk2 displays the frequency at each marker time position. [2] (2 1) displays the frequency difference (marker 2 marker 1) at th...
Page 196
Chapter 4 trace 4-122 (1) changing the marker position note: the marker position of power vs time, frequency vs time, phase vs time synchronizes one another. The frequency in the specified time can be measured by using the marker displayed in figure 4.4.9-2. Figure 4.4.9-2 marker example: to set mar...
Page 197
4.4 frequency vs time 4-123 4 tr ac e (2) selecting the active marker note: this setting is enabled when both markers 1 and 2 are on. The active marker is selected. The marker position of the active marker can be set with the rotary knob or step key. Example: to set the active marker 1. Press . 2. P...
Page 198
Chapter 4 trace 4-124 (4) setting zooming out note: this setting is enabled when both markers 1 and 2 are on. Example: to reduce the analysis range to the range of markers 1 and 2 1. Press . 2. Press (zoom out). The displayed waveform data is zoomed out to the range enclosed with markers 1 and 2. As...
Page 199
4.4 frequency vs time 4-125 4 tr ac e (5) peak to peak measurement the maximum/minimum frequency is measured based on the displayed trace data in the marker range. The measurement start and stop points are the trace points of the marker position. When any of the markers is off, the entire analysis r...
Page 200
Chapter 4 trace 4-126 4.4.10 setting marker search the marker search functions include peak search, next peak search, dip search, and next dip search. Signal search function menu pressing (signal search) on page 2 of the trace function menu, or pressing displays the signal search function menu. Tabl...
Page 201
4.4 frequency vs time 4-127 4 tr ac e threshold function menu pressing (threshold) on the signal search function menu displays the threshold function menu. Table 4.4.10-2 threshold function menu function key menu display function f1 threshold (on/off) sets the detection threshold function for peak p...
Page 202
Chapter 4 trace 4-128 (1) executing peak search the active marker is moved to the position where the marker value becomes maximal in the analysis time range. If two or more marker values exist, the point with the lower marker frequency is selected. When the detection mode is pos&neg, a search is exe...
Page 203
4.4 frequency vs time 4-129 4 tr ac e (4) executing next dip search the second lowest local maximum point (dip) next to the marker value of the current active marker is detected and the active marker is moved to that position. If two or more marker values exist, the point with the lower marker frequ...
Page 204: 4.4.11 Measure Measurement
Chapter 4 trace 4-130 4.4.11 measure measurement measure function menu press (measure) on page 2 of trace menu or press to display measure function menu. Table 4.4.11-1 measure function menu function key menu display function f1 fm deviation (on/off) executes fm deviation measurement. F2 fm cw execu...
Page 205
4.4 frequency vs time 4-131 4 tr ac e (1) fm deviation measurement measures the maximum and minimum frequency, based on the trace data within the marker range. The measurement range is between marker 1 and 2 points on the trace. When either of marker 1 and 2 is set to off, the measurement is perform...
Page 206
Chapter 4 trace 4-132 (2) fm cw measurement measures the linearity of the time versus frequency slope of a signal in which the frequency increases or decreases with time (chirp signal) among the fm cw signals. In the fm cw measurement, the measurement range can be set by automatic detection or marke...
Page 207
4.4 frequency vs time 4-133 4 tr ac e if either of start or end of a slope is outside the analysis time length as the following figure, the slope is not detected automatically. Figure 4.4.11-3 cases where a slope is not detected automatically slope end is missing slope start is missing.
Page 208
Chapter 4 trace 4-134 fm cw function menu press (fm cw) on measure function menu to display fm cw function menu. Table 4.4.11-3 fm cw function menu. Function key menu display function f1 fm cw (on/off) sets the fm cw measurement function to on/off. When it is set to on, other measure functions of th...
Page 209
4.4 frequency vs time 4-135 4 tr ac e when detecting slopes automatically with meas interval set to auto, the target slope is shown on a blue background as the following figure. Except the target, downslopes are shown on a green background and upslopes on a purple one. Figure 4.4.11-4 slopes on colo...
Page 210
Chapter 4 trace 4-136 table 4.4.11-4 display items of measurement results item description fm error (rms) displays the rms value of the frequency error between the ideal slope* and measured value. Fm error (peak) displays the peak value of the frequency error between the ideal slope* and measured va...
Page 211: 4.5 Phase Vs Time
4.5 phase vs time 4-137 4 tr ac e 4.5 phase vs time 4.5.1 what is phase vs time trace? Phase vs time trace is the display system to display the time fluctuation of phase from the acquired iq digital data. Display items of phase vs time trace are as follows: figure 4.5.1-1 display items for phase vs ...
Page 212
Chapter 4 trace 4-138 4.5.2 setting phase vs time parameters after selecting phase vs time for trace mode, pressing (trace) from the main function key or pressing displays the trace function menu. The trace function menu consists of two pages, which can be toggled by pressing . 4.1 “selecting trace”...
Page 213
4.5 phase vs time 4-139 4 tr ac e table 4.5.2-1 trace function menu function key menu display function page1 trace press (trace) to display this page. F1 trace mode sets the trace type. 4.1 “selecting trace” f2 analysis time used for setting related to the analysis time. 4.5.3 “setting analysis time...
Page 214
Chapter 4 trace 4-140 4.5.3 setting analysis time pressing (analysis time) from the trace function menu or pressing displays the analysis time function menu. Figure 4.5.3-1 analysis time function menu setting analysis time on the power vs time trace normalizes a set time that exceeds five valid digi...
Page 215
4.5 phase vs time 4-141 4 tr ac e setting the analysis time analysis time is the time to be analyzed. The analysis time can be specified with the analysis start position (analysis start time) and analysis time length (analysis time length). Figure 4.5.3-2 analysis time (1) auto mode when capture tim...
Page 216
Chapter 4 trace 4-142 (2) manual mode the analysis start time and analysis time length are set manually. This is an effective method to perform measurement of discontinuous signals such as burst. Analysis start time setting range table 4.5.3-3 analysis start time setting range in manual mode capture...
Page 217
4.5 phase vs time 4-143 4 tr ac e analysis start time resolution table 4.5.3-5 frequency span and setting resolution frequency span setting resolution 1 khz 0.5 ms 2.5 khz 0.2 ms 5 khz 0.1 ms 10 khz 50 s 25 khz 20 s 50 khz 10 s 100 khz 5 s 250 khz 2 s 500 khz 1 s 1 mhz 0.5 s 2.5 mhz 0.2 s 5 ...
Page 218
Chapter 4 trace 4-144 the following table shows the setting range for the ms2850a when frequency span is 50 mhz or higher. The resolution is displayed up to three decimal digits. (example: 0.769 ns) table 4.5.3-5 frequency span and setting resolution (cont’d) frequency span setting resolution 50 mhz...
Page 219: 4.5.4 Setting
4.5 phase vs time 4-145 4 tr ac e 4.5.4 setting scale scale function menu pressing and then (scale) displays the scale function menu. Figure 4.5.4-1 scale function menu table 4.5.4-1 scale function menu menu display function vertical used for setting related to the vertical axis (phase axis) scale. ...
Page 220
Chapter 4 trace 4-146 vertical function menu pressing (vertical) on the scale function menu displays the vertical function menu. Figure 4.5.4-2 vertical function menu table 4.5.4-2 vertical function menu menu display function scale division sets the range of the vertical axis. (1) setting the numeri...
Page 221
4.5 phase vs time 4-147 4 tr ac e 4.5.5 setting detection mode pressing , and then (detection) selects the detection mode. Detection mode types the detection mode within analysis range (detection) is set. The detection mode can be selected from the four types: average, sample, positive, and negative...
Page 222: 4.5.6 Setting
Chapter 4 trace 4-148 4.5.6 setting markers this section describes various marker functions and the functions to improve measurement efficiency, such as marker search and parameter setting with marker values. For the marker’s setting range and resolution, refer to the setting ranges and resolutions ...
Page 223
4.5 phase vs time 4-149 4 tr ac e figure 4.5.6-2 display items for marker results table 4.5.6-2 display items for marker results no. Display description [1] mrk1 / mrk2 displays the phase at each marker time position. [2] Δ( 2 – 1 ) displays the phase difference (marker 2 – marker 1) at marker time ...
Page 224
Chapter 4 trace 4-150 (1) changing the marker position note: the marker position of power vs time, frequency vs time, phase vs time synchronizes one another. The phase in the specified time can be measured by using the marker displayed in figure 4.5.6-3. Figure 4.5.6-3 marker example: to set marker ...
Page 225
4.5 phase vs time 4-151 4 tr ac e (2) selecting the active marker note: this setting is enabled when both marker 1 and 2 are on. The active marker is selected. The marker position of the active marker can be set with the rotary knob or step key. Example: to set the active marker 1. Press . 2. Press ...
Page 226
Chapter 4 trace 4-152 figure 4.5.6-4 zoom zoom markers1,2.
Page 227
4.5 phase vs time 4-153 4 tr ac e (4) setting zooming out note: this setting is enabled when both marker 1 and 2 are on. Example: to reduce the analysis range to the range of marker 1 and 2 1. Press . 2. Press (zoom out). The displayed waveform data is zoomed out to the range enclosed with marker 1 ...
Page 228: 4.5.7 Setting
Chapter 4 trace 4-154 4.5.7 setting methods method function menu pressing (method) on page 1 of trace function menu displays method function menu. Figure 4.5.7-1 method function menu table 4.5.7-1 method function menu menu display function phase mode sets wrap or unwrap. Phase offset sets the offset...
Page 229
4.5 phase vs time 4-155 4 tr ac e (1) setting the vertical axis offset vertical axis offset is set. The setting range is as follows: setting range of phase offset: –100 to +100 m example: to set the vertical axis offset to 10 1. Press . 2. Press (method). 3. Press (phase offset). 4. Press , and then...
Page 230: 4.6 Ccdf
Chapter 4 trace 4-156 4.6 ccdf 4.6.1 what is ccdf trace? Ccdf trace is a screen that performs a ccdf (complementary cumulative distribution function) analysis of the obtained iq digital data to display. The display items for a ccdf trace are as described below. Figure 4.6.1-1 display items for ccdf ...
Page 231
4.6 ccdf 4-157 4 tr ac e table 4.6.1-1 display items for ccdf trace no. Display descriptions [1] analysis start time/ analysis time length displays the analysis start time and analysis time length. [2] filter bw displays the filter bandwidth. “not filtered” is displayed when the filter is off. [3] m...
Page 232
Chapter 4 trace 4-158 4.6.2 setting ccdf parameters after selecting ccdf for trace mode, pressing (trace) on the main function menu or pressing displays the trace function menu. 4.1 “selecting trace” trace function menu consists of two pages, which can be toggled by pressing . Table 4.6.2-1 trace fu...
Page 233
4.6 ccdf 4-159 4 tr ac e 4.6.3 selecting measurement method pressing and then (method) displays the method function menu. Table 4.6.3-1 method function menu function key menu display function f1 measure method (ccdf/apd) selects the measurement method. F2 threshold (on/off) enables/disables the mini...
Page 234
Chapter 4 trace 4-160 (2) setting the minimum level the minimum level (threshold) of data used for measurement is set. When threshold is set to on, any sampling points under the level specified here are not included in the data. Example: to set the minimum level to 170 dbm 1. Press . 2. Press (meth...
Page 235
4.6 ccdf 4-161 4 tr ac e 4.6.4 setting analysis time pressing (analysis time) on the trace function menu, or pressing displays the analysis time function menu. Trace function menu consists of two pages, which can be toggled by pressing . Table 4.6.4-1 analysis time function menu function key menu di...
Page 236
Chapter 4 trace 4-162 setting the analysis time analysis time is the target time for analysis. The analysis time can be specified with the analysis start position (analysis start time) and analysis time length (analysis time length). Figure 4.6.4-1 analysis time (1) auto mode when capture time is se...
Page 237
4.6 ccdf 4-163 4 tr ac e (2) manual mode the analysis start time and analysis time length are set manually. This is an effective method for measuring discontinuous signals such as burst. Analysis start time setting range table 4.6.4-3 analysis start time setting range in manual mode capture time min...
Page 238
Chapter 4 trace 4-164 analysis start time and analysis time length resolution table 4.6.4-5 frequency span and setting resolution frequency span setting resolution 1 khz 0.5 ms 2.5 khz 0.2 ms 5 khz 0.1 ms 10 khz 50 s 25 khz 20 s 50 khz 10 s 100 khz 5 s 250 khz 2 s 500 khz 1 s 1 mhz 0.5 s 2.5 ...
Page 239
4.6 ccdf 4-165 4 tr ac e the following table shows the setting range for the ms2850a when frequency span is 50 mhz or higher. The resolution is displayed up to three decimal digits. (example: 0.769 ns) table 4.6.4-5 frequency span and setting resolution (cont’d) frequency span setting resolution 50 ...
Page 240
Chapter 4 trace 4-166 figure 4.6.4-2 setting gate mode setting procedure for gate mode example: to set the period to 6 ms 1. Open the second page of the analysis time function menu, and press (gate mode) to set the gate mode to on. 2. Press (period). 3. The period is set when pressing and (ms). Rang...
Page 241: 4.6.5 Setting
4.6 ccdf 4-167 4 tr ac e 4.6.5 setting range when pressing (analysis time), (range setup) and after pressing , the range setup function menu is displayed. Table 4.6.5-1 explanation of range function menu function key menu display function f1 edit range number edits the range number to be measured. F...
Page 242
Chapter 4 trace 4-168 4.6.6 setting display format pressing and then (scale) displays the scale function menu. Table 4.6.6-1 scale function menu function key menu display function f2 horizontal changes the scale of the power axis. (1) setting the horizontal scale the power axis scale is set. Example...
Page 243
4.6 ccdf 4-169 4 tr ac e 4.6.7 setting cumulative data reset pressing and then (storage) displays the storage function menu. Table 4.6.7-1 storage function menu function key menu display function f1 reset every capture (on/off) sets whether to reset the results for each measurement. F2 restart clear...
Page 244
Chapter 4 trace 4-170 4.6.8 setting up trace display this allows you to configure settings related to trace display for ccdf. Pressing (view) on the trace function menu displays the view function menu. Table 4.6.8-1 view function menu function key menu display function f1 store to ref trace temporar...
Page 245: 4.6.9 Setting
4.6 ccdf 4-171 4 tr ac e 4.6.9 setting filter the setting related to the filter is performed. Pressing (filter) from the trace function menu, or pressing displays the filter function menu. Table 4.6.9-1 filter function menu function key menu display function f1 type selects the filter type. F3 band ...
Page 246: 4.6.10 Setting Markers
Chapter 4 trace 4-172 4.6.10 setting markers this section describes various marker functions. Pressing (marker) on page 2 of the trace function menu, or pressing displays the marker function menu. Table 4.6.10-1 marker function menu function key menu display function f1 marker (on/off) sets the mark...
Page 247
4.6 ccdf 4-173 4 tr ac e figure 4.6.10-1 display items for marker results table 4.6.10-2 display items for marker results no. Display descriptions [1] mkr/meas. Displays the power deviation for the probability specified by the marker, or probability for the power deviation specified by the marker. [...
Page 248
Chapter 4 trace 4-174 changing the marker position the power deviation with the specified probability or the probability of the specified power deviation can be measured depending on the displayed marker. (1) setting the marker axis the marker axis can be selected from the following two types. Distr...
Page 249
4.6 ccdf 4-175 4 tr ac e example: setting the probability position value to 10% 1. Press . 2. Press (probability position). 3. Press , and then press (%) to set the marker position on the probability distribution axis. Setting range and resolution for probability position setting range: 0.0001 to 10...
Page 250: 4.7 Spectrogram
Chapter 4 trace 4-176 4.7 spectrogram 4.7.1 what is spectrogram trace? Spectrogram trace analyzes the captured iq data by using fft (fast fourier transform) and diagrams the changes in a spectrum over time. The display items of spectrogram trace are described below: figure 4.7.1-1 spectrogram trace ...
Page 251
4.7 spectrogram 4-177 4 tr ac e 4.7.2 setting spectrogram parameter press (trace) or press on the main function menu of the spectrogram trace to display trace function menu. Trace function menu has 2 pages. Press to switch the pages. 4.1 “selecting trace” table 4.7.2-1 trace function menu function k...
Page 252: 4.7.3 Setting
Chapter 4 trace 4-178 4.7.3 setting analysis time press (analysis time) on the trace function menu or press to display the analysis time function menu. Setting analysis time on the spectrogram trace normalizes a set time that exceeds five valid digits in addition to rounding up by time resolution. T...
Page 253
4.7 spectrogram 4-179 4 tr ac e setting the analysis time analysis time is the time during which the analysis is performed. It is set by the analysis start time (analysis start time) and the analysis time length (analysis time length). Figure 4.7.3-1 analysis time (1) auto mode when capture time is ...
Page 254
Chapter 4 trace 4-180 (2) manual mode manual mode allows you to set the analysis start time and the analysis time length manually. It is useful to measure a discontinuous signal such as burst. Setting range for analysis start time table 4.7.3-3 setting range in manual mode capture time minimum[s] ma...
Page 255
4.7 spectrogram 4-181 4 tr ac e setting resolution of analysis start time table 4.7.3-5 frequency span and setting resolution frequency span setting resolution 1 khz 0.5 ms 2.5 khz 0.2 ms 5 khz 0.1 ms 10 khz 50 s 25 khz 20 s 50 khz 10 s 100 khz 5 s 250 khz 2 s 500 khz 1 s 1 mhz 0.5 s 2.5 mhz ...
Page 256
Chapter 4 trace 4-182 the following table shows the setting range for the ms2850a when frequency span is 50 mhz or higher. The resolution is displayed up to three decimal digits. (example: 0.769 ns) table 4.7.3-5 frequency span and setting resolution (cont’d) frequency span setting resolution 50 mhz...
Page 257: 4.7.4 Setting
4.7 spectrogram 4-183 4 tr ac e 4.7.4 setting scale scale function menu on the main function menu, press (trace) or press , and then press (scale) to display the scale function menu. Table 4.7.4-1 scale function menu function key menu item function f3 level full scale sets the scale range of the lev...
Page 258
Chapter 4 trace 4-184 4.7.5 setting resolution bandwidth (rbw) on the trace function menu, press (rbw) or press to display the rbw function menu. Table 4.7.5-1 rbw function menu function key menu item function f1 rbw (auto/manual) sets auto/manual for the resolution bandwidth (rbw). F2 rbw sets the ...
Page 259
4.7 spectrogram 4-185 4 tr ac e 4.7.6 setting storage mode press and then press (storage) to display the storage function menu. Table 4.7.6-1 storage function menu function key menu item function f1 mode sets the mode to update and display the trace data. F2 count sets the storage count. F3 stop sto...
Page 260
Chapter 4 trace 4-186 setting the storage mode and the storage count example: to set the storage mode to lin average and set the storage count to 100 1. Press . 2. Press (storage). 3. Press (mode) and select lin average. 4. Press (count). 5. Press and then press (set) to set the storage count. Setti...
Page 261: 4.7.7 Setting
4.7 spectrogram 4-187 4 tr ac e 4.7.7 setting detection mode press and then press (detection) to select the detection mode. Type of detection mode the detection mode can be selected from three options: average, positive, and negative. Table 4.7.7-1 detection mode within analysis range mode descripti...
Page 262: 4.7.8 Setting
Chapter 4 trace 4-188 4.7.8 setting marker this section describes the functions to improve the measurement efficiency of the functions, such as parameter settings by a marker value. Press (marker) on page 2 of the trace function menu or press to display the marker function menu. The marker function ...
Page 263
4.7 spectrogram 4-189 4 tr ac e marker result function menu press (marker result) on page 2 of the marker function menu to display the marker result function menu. Table 4.7.8-2 marker result function menu function key menu function f1 integration displays the total power in the zone band. F2 densit...
Page 264
Chapter 4 trace 4-190 figure 4.7.8-1 display items of marker result table 4.7.8-3 display item of marker result no. Display descriptions [1] mrk 1/mkr 2/mkr1 □/mkr 2 □ displays the frequency and time of the active marker. When marker result is set to peak, the peak point is displayed as □ on the tra...
Page 265
4.7 spectrogram 4-191 4 tr ac e setting of marker result the settings of marker result are shown below: integration: displays the total power within the zone maker band. Density: displays the power per 1 hz within the zone marker width. Peak (fast): displays the peak power within the zone marker wid...
Page 266
Chapter 4 trace 4-192 changing the marker position and width on figure 4.7.8-2 below, the frequency markers are displayed as f on the vertical (frequency) axis, and the time markers are displayed as t on the horizontal (time) axis. When marker type is set to zone, the time markers (t1 and t2) are di...
Page 267
4.7 spectrogram 4-193 4 tr ac e (2) changing the position of the time marker example: to set the position of the time marker 1 to 0.6 ms 1. Press . 2. Press (time 1) on the marker main function menu. 3. Press and then press (ms) to set the position of the time marker. (3) selecting the active marker...
Page 268
Chapter 4 trace 4-194 (6) executing marker to center freq. Sets the marker frequency to the center frequency (center frequency). Example: to detect the peak power within the measurement bandwidth and set it to the center frequency 1. Press . 2. Press (marker to center freq.) on page 2 of the marker ...
Page 269
4.7 spectrogram 4-195 4 tr ac e after executed, the parameters on spectrum trace are set to the setting values, as table 4.7.8-4 shows: table 4.7.8-4 parameter values set after executing analyze with spectrum trace parameter on spectrum trace setting value rbw auto/manual rbw auto/manual on spectrog...
Page 270: 4.8 No
Chapter 4 trace 4-196 4.8 no trace 4.8.1 what is no trace? No trace mode does not execute signal analysis. Therefore, “iq data output” and “iq data readout using remote commands” can be executed quickly without the need to wait for completion of analysis. As analysis is not executed, save waveform f...
Page 271
4.8 no trace 4-197 4 tr ac e 4.8.2 setting no trace parameters press (trace) or press on the main function menu of the no trace to display trace function menu. 4.1 “selecting trace” table 4.8.2-1 trace function menu function key menu function f1 trace mode sets the trace mode. 4.1 “selecting trace” ...
Page 272: 4.8.3 Setting
Chapter 4 trace 4-198 4.8.3 setting analysis time press (analysis time) on the trace function menu or press to display the analysis time function menu. Table 4.8.3-1 analysis time function menu function key menu function f1 time (main trace) (auto/manual) sets auto/manual for the analysis start time...
Page 273
4.8 no trace 4-199 4 tr ac e setting the analysis time analysis time is the time during which the analysis is performed. If no trace is selected as the trace mode, then analysis is not executed. Analysis time setting may, however, be required in outputting iq data. It is set by the analysis start ti...
Page 274
Chapter 4 trace 4-200 (2) manual mode manual mode allows you to set the analysis start time and the analysis time length manually. Setting range for analysis start time table 4.8.3-3 setting range in manual mode capture time minimum[s] maximum[s] auto 0 1 2 x x manual 0 1 3 x x 1 x : analysis time l...
Page 275
4.8 no trace 4-201 4 tr ac e setting resolution of analysis start time table 4.8.3-5 frequency span and setting resolution frequency span setting resolution 1 khz 0.5 ms 2.5 khz 0.2 ms 5 khz 0.1 ms 10 khz 50 s 25 khz 20 s 50 khz 10 s 100 khz 5 s 250 khz 2 s 500 khz 1 s 1 mhz 0.5 s 2.5 mhz 0.2...
Page 276
Chapter 4 trace 4-202 the following table shows the setting range for the ms2850a when frequency span is 50 mhz or higher. The resolution is displayed up to three decimal digits. (example: 0.769 ns) table 4.8.3-5 frequency span and setting resolution (cont’d) frequency span setting resolution 50 mhz...
Page 277: 4.9 Sub-Trace
4.9 sub-trace 4-203 4 tr ac e 4.9 sub-trace 4.9.1 what is sub trace? A sub-trace can be displayed as an aid to the normal trace (main trace). Select either power vs time or spectrogram as the sub-trace to display the trace data for any time range. Displaying the sub-trace allows the analysis range o...
Page 278
Chapter 4 trace 4-204 4.9.2 setting parameters for sub trace pressing (trace) on the main function menu or pressing displays the trace function menu. Pressing (sub trace setting) on the trace function menu displays the sub trace setting function menu. This section describes how to set parameters for...
Page 279: 4.9.3 Selecting
4.9 sub-trace 4-205 4 tr ac e 4.9.3 selecting sub trace pressing (trace mode) on the sub trace setting function menu displays the trace mode (sub trace) function menu. This section describes how to set sub-trace types. Table 4.9.3-1 trace mode (sub trace) function menu function key menu display func...
Page 280
Chapter 4 trace 4-206 4.9.4 setting analysis time pressing (analysis time) on the sub trace setting function menu displays the analysis time (sub trace) function menu. This section describes how to set the analysis time for a sub-trace. When the sub-trace is set to power vs time or spectrogram, you ...
Page 281
4.9 sub-trace 4-207 4 tr ac e setting analysis time the analysis start time and analysis time length of the main trace are highlighted within the sub-trace for easier viewing. Figure 4.9.4-1 analysis time display in sub-trace table 4.9.4-2 display items for sub-trace no. Descriptions [1] displays th...
Page 282: 4.9.5 Setting
Chapter 4 trace 4-208 4.9.5 setting scale pressing (scale) on the sub trace setting function menu displays the scale (sub trace) function menu. This section describes how to set the scale range for a sub-trace. Table 4.9.5-1 scale function menu function key menu display function f3 level full scale ...
Page 283
4.9 sub-trace 4-209 4 tr ac e 4.9.6 setting resolution bandwidth (rbw) pressing (rbw) on the sub trace setting function menu displays the rbw (sub trace) function menu. This setting is enabled only when the sub-trace is set to spectrogram. Table 4.9.6-1 rbw (sub trace) function menu function key men...
Page 284
Chapter 4 trace 4-210. 4.9.7 setting detection mode pressing (detection) on the sub trace setting function menu displays the detection function menu. Select with the cursor key, and set with (set) or enter. This section describes the detection mode of a sub-trace. Table 4.9.7-1 detection modes in de...
Page 285
5-1 5 d ig it iz e f un ctio n digitize function chapter 5 this chapter describes how to save iq data to external memory and data file formats and how to replay the saved iq data. 5.1 saving iq data.............................................................. 5-2 5.1.1 format of data information fi...
Page 286: 5.1 Saving Iq Data
Chapter 5 digitize function 5-2 5.1 saving iq data pressing (capture) from the main function menu and then pressing (save captured data) displays the save captured data function menu. Note: iq data should be saved or digitized after a single sweeping has been executed and ended, even when trigger fu...
Page 287
5.1 saving iq data 5-3 5 d ig it iz e f un ctio n the iq data stored in the internal memory at the time of execution of this function is saved to the external memory. Example: to save iq data 1. Press (capture) from the main function menu. 2. Press (save captured data). 3. Press (device) from the sa...
Page 288
Chapter 5 digitize function 5-4 the rate of the output data when capture time is set to manual can be changed. The setting range of the output data rate and the resolution change according to the frequency span are as shown in table 5.1-2. Table 5.1-2 frequency span and setting resolution/setting ra...
Page 289
5.1 saving iq data 5-5 5 d ig it iz e f un ctio n the following table shows the setting range for the ms2850a when frequency span is 50 mhz or higher. Table 5.1-2 frequency span and setting resolution/setting range (cont’d) frequency span setting resolution minimum value maximum value 50 mhz 1 khz 5...
Page 290
Chapter 5 digitize function 5-6 5.1.1 format of data information file the information on the saved iq data is recorded in the data information file. Table 5.1.1-1 shows the details of the recorded parameters. Table 5.1.1-1 format of data information file item description capturedate year/month/day o...
Page 291
5.1 saving iq data 5-7 5 d ig it iz e f un ctio n table 5.1.1-1 format of data information file (cont’d) item description triggersource trigger source “video”: video trigger “wideif”: wide if video trigger “external”: external trigger 1 “external 2”: external trigger 2 “sgmarker”: sg marker trigger ...
Page 292: 5.1.2 Format of Data File
Chapter 5 digitize function 5-8 5.1.2 format of data file the data file is created in binary format. From the beginning of the file, i-phase data and q-phase data are recorded by 4 bytes. The i-phase data and q-phase data are recorded as a float type (ieee real*4). I-phase data 1 (4 bytes) q-phase d...
Page 293: 5.2 Replay Function
5.2 replay function 5-9 5 d ig it iz e f un ctio n 5.2 replay function the replay function allows you to replay the saved iq data. Pressing (capture) on the main function menu and then (replay) displays the replay function menu. Table 5.2-1 description of replay function menu function key menu displ...
Page 294
Chapter 5 digitize function 5-10 5.2.1 starting replay function start the replay function using the following procedure. Example: to start the replay function 1. Press (capture) on the main function menu. 2. Press (replay) on the capture function menu. 3. Press (device) on the replay function menu t...
Page 295
5.2 replay function 5-11 5 d ig it iz e f un ctio n reanalysis of digitized file when the target iq data is saved with save captured data of this application, it can be analyzed in the same range as the analysis range when the data was saved, by setting the capture time to manual. Note: iq data file...
Page 296
Chapter 5 digitize function 5-12 5.2.2 display during replay function execution appears if the iq data file meets the following conditions: • frequency reference is unlocked when iq data is saved • level over occurs when iq data is saved.
Page 297
5.2 replay function 5-13 5 d ig it iz e f un ctio n 5.2.3 restrictions during replay function execution since the signals to be analyzed are fixed during replay, the following functions are restricted. Table 5.2.3-1 functions restricted during replay function center frequency start frequency stop fr...
Page 298
Chapter 5 digitize function 5-14 also, during replay, the reference level setting range is as follows, regardless of the attenuator and preamplifier. Table 5.2.3-2 reference level range with replay function on. Scale mode unit reference level range log scale dbm –120 to +50 dbm dbµv –13.01 to +156.9...
Page 299
5.2 replay function 5-15 5 d ig it iz e f un cti on 5.2.4 condition of iq data file for replay the condition of iq data files for which replay analysis is possible is as follows. Format of waveform data file: i, q (binary format) table 5.2.4-1 lists the combinations of frequency span and sampling ra...
Page 300
Chapter 5 digitize function 5-16 the following table shows the setting range for the ms2850a when frequency span is 50 mhz or higher. Table 5.2.4-1 frequency span and sampling rate (cont’d) frequency span sampling rate 50 mhz 81.25 mhz 62.5 mhz 81.25 mhz 100 mhz 162.5 mhz 125 mhz 162.5 mhz 255 mhz 3...
Page 301: 5.3 Playback Function
5.3 playback function 5-17 5 d ig it iz e f un ctio n 5.3 playback function the playback function converts the captured data into waveform patterns and outputs them by loading into the vector signal generator option. Press (capture) in the main function menu, and then press (capture & playback) in t...
Page 302
Chapter 5 digitize function 5-18 package default playback available characters alphanumeric characters and the following symbols ! % & ( ) + = ‘ { } _ - ^ @ [ ] character number 31 characters at maximum pattern name default same as saving files in 5.1 “saving iq data”. Available characters alphanume...
Page 303
5.3 playback function 5-19 5 d ig it iz e f un ctio n 5.3.1 starting playback function start the playback function using the following procedure : 1. Press (capture) on the main function menu. 2. Press (capture & playback) on the capture function menu. Note: an error message appears and playback is ...
Page 304
Chapter 5 digitize function 5-20 5.3.2 display during playback function execution while executing playback function, the capture & playback function menu and the capture & playback dialog box are displayed. Table 5.3.2-1 description of capture & playback function menu function key menu display funct...
Page 305
5.3 playback function 5-21 5 d ig it iz e f un ctio n figure 5.3.2-2 capture & playback icon transition output waveform patterns (select loaded waveform patterns) execute capture & playback capture & playback completed displays progress 100% playback icon lighting saving captured data converting int...
Page 306
Chapter 5 digitize function 5-22. 5.3.3 aborting playback function while executing playback function, pressing (cancel) in the capture & playback function menu can abort the operation. The processing of generated data files differs depending on the aborted timing of playback function. Saving capture...
Page 307
6-1 6 sy ste m s etti ng system setting chapter 6 this chapter describes how to save iq data to external memory and data file formats and how to replay the saved iq data. 6.1 setting system .............................................................. 6-2 6.2 erasing warm up message ..................
Page 308: 6.1 Setting System
Chapter 6 system setting 6-2 6.1 setting system pressing (accessory) from the main function menu displays the accessory function menu. Table 6.1-1 accessory function menu function key menu display function f1 title specifies the title. F2 title (on/off) sets whether to display the title. F4 erase wa...
Page 309
6.2 erasing warm up message 6-3 6 sy ste m s etti ng 6.2 erasing warm up message if the warm up message ( ) indicating that the level and frequency are not stable is displayed upon power on, the message can be forcefully erased. Setting example: erasing the warm up message 1. Press (accessory) from ...
Page 310: 6.3 Setting Title
Chapter 6 system setting 6-4 6.3 setting title settings related to the title displayed on the screen can be configured. For the signal analyzer function, a title of up to 32 characters can be displayed on the screen. (character strings of up to 17 characters can be displayed on a function menu.) exa...
Page 311
6.4 adjusting internal reference clock signal 6-5 6 sy ste m s etti ng 6.4 adjusting internal reference clock signal pressing (reference clock) from the accessory function menu displays the reference clock function menu. Table 6.4-1 reference clock function menu function key menu display function f1...
Page 312
Chapter 6 system setting 6-6 6.5 input source for reference clock signal the reference clock signal used is displayed on the screen. Ref.Int: the internal reference clock signal is used. Ref.Int unlock: the internal reference clock signal is unlocked. The internal hardware may be faulty. Ref.Ext: th...
Page 313
6.6 pre-amp on/off display 6-7 6 sy ste m s etti ng 6.6 pre-amp on/off display if the ms2830a-008/108/068/168, ms2840a-008/108/068/168/069/169, or ms2850a-068/168 pre-amp is installed, whether the pre-amp is on or off is displayed at the lower left of the screen. Figure 6.6-1 pre-amp display.
Page 314
Chapter 6 system setting 6-8. 6.7 selecting preselector this function is available for ms2830a-044/045, ms2840a-044/046, ms2850a-047/046. Pressing (preselector) from the accessory function menu displays the preselector function menu. You can also execute the preselector auto tune function by pressin...
Page 315
7-1 7 e xter na l m ix er external mixer chapter 7 this section describes the operation of the external mixer and measurement procedure using examples. 7.1 external mixer overview ............................................... 7-2 7.2 external mixer ....................................................
Page 316
Chapter 7 external mixer 7-2 7.1 external mixer overview external mixer function is ms2830a-044/045 or ms2840a-044/046 dedicated function. The frequency range of ms2830a-044/045 or ms2840a-044/046 extends up to 325 ghz by using optional external mixer. Ma2806a, ma2808a and ma2743c to 51c are product...
Page 317: 7.2 External Mixer
7.2 external mixer 7-3 7 e xter na l m ix er 7.2 external mixer press (frequency) in page 1 of the main function menu, or press to display the frequency function menu. Then press (more) to show the second page of the frequency function menu for external mixer settings. Table 7.2-1 frequency function...
Page 318
Chapter 7 external mixer 7-4 table 7.2-1 frequency function menu (cont’d) function keys menu display function page 2 frequency press frequency, and then press to display this menu. F1 external mixer* (on/off) turn on when using external mixer. This function is available with ms2830a-044/045 or ms284...
Page 319
7.2 external mixer 7-5 7 e xter na l m ix er *: the following restrictions apply when external mixer is on: ● spurious emission measurement cannot be set to on. Conversely, in spurious emission measurement mode, external mixer cannot be set to on. ● sweep type rule is fixed to swept only. ● att cann...
Page 320
Chapter 7 external mixer 7-6 7.3 connecting external mixer 1. Fix the external mixer to the device under test. 2. Using the coaxial cable (commercially available), connect the external mixer to the 1st local output on the front panel. Figure 7.3-1 external mixer connection notes: ● to connect an ext...
Page 321
7.4 setting band of external mixer 7-7 7 e xter na l m ix er 7.4 setting band of external mixer to set the band, perform the following key operation: press (external mixer band select) on page 2 of the frequency function menu, and use the function keys to select the desired band. Table 7.4-1 ext ban...
Page 322
Chapter 7 external mixer 7-8 the below equation shows the measurable side band phase noise on the selected band. Sideband phase noise = –95 + 20 log (n) dbc, typical value measurement of band f+ to j+ is made possible in conjunction with other manufacture’s external mixer. When using high performanc...
Page 323
7.5 setting external mixer bias 7-9 7 e xter na l m ix er 7.5 setting external mixer bias sets the external mixer bias. Press (external mixer bias) on page 2 of the frequency function menu, and use the numeric keypad or rotary knob to input so that the received signal level becomes maximum. The disp...
Page 324
Chapter 7 external mixer 7-10. 7.6 setting conversion loss of external mixer to set the conversion loss of the external mixer, perform the following operations: press (external mixer loss) on page 2 of the frequency function menu, and use rotary knob to input. If correct level measurement is necessa...
Page 325
A-1 a p p e n d ix a ppe ndi x a appendix a error message table a-1 error messages message description out of range the settable range is exceeded. Not available if not vector signal generator option. This operation is invalid when the vector signal generator option is not installed. Not available i...
Page 326
Appendix a error message a-2 table a-1 error messages (cont’d) message description not available if main trace is spectrum. This operation is invalid when the main trace is spectrum. Not available if main trace is ccdf or no trace. This operation is invalid when the main trace is ccdf or no trace. N...
Page 327
Appendix a error message a-3 a p p e n d ix a ppe ndi x a table a-1 error messages (cont’d) message description not available if not pre-selector lower frequency expansion option. This operation is invalid when the preselector lower frequency extension option is not installed. Can not set under 4 db...
Page 328
Appendix a error message a-4 table a-1 error messages (cont’d) message description not available when acp reference is set to span total. It is not available when acp reference is set to span total. Not available when freq. Span is 50 mhz or more. The setting is impossible when freq. Span is 50 mhz ...
Page 329
Appendix a error message a-5 a p p e n d ix a ppe ndi x a table a-1 error messages (cont’d) message description unable to set this standard parameter while replaying. This standard parameter cannot be set while the replay function is being executed. Unable to set this standard parameter since captur...
Page 330
Appendix a error message a-6. Table a-1 error messages (cont’d) message description not available in external mixer on. The following restrictions will apply when external mixer is set to on. • spurious emission measurement cannot be set to on. • sweep type rule is fixed to swept only. • att cannot ...
Page 331
B-1 a p p e n d ix a ppe ndi x b appendix b default value list frequency center frequency 3.6 ghz frequency span 31.25 mhz (ms2830a-005/105/007/009/109/ 077/078, ms2840a-005/105/009/109/ 077/177/078/178, ms2850a-032/033/133/034/134) 10 mhz (ms2830a-006/106, ms2840a-006/106) start frequency 3.584375 ...
Page 332
Appendix b default value list b-2 amplitude reference level 0 dbm attenuator auto, 10 db log scale unit dbm scale log log scale division 10db/div log scale line 10 reference level offset off offset value 0 db pre-amp off trigger trigger switch off trigger source video trigger slope rise trigger leve...
Page 333
Appendix b default value list b-3 a p p e n d ix a ppe ndi x b minimum burst off length time length×10 ramp off ramp length time length×10 accessory title on, “signal analyzer” reference clock factory-adjusted value.
Page 334
Appendix b default value list b-4 analysis time auto/manual auto start time 0 s time length 0 s scale vertical log scale division 10 db/div lin scale division 10%/div log scale line 10 horizontal center 3.6 ghz width 31.25 mhz (ms2830a-005/105/007/009/109/ 077/078, ms2840a-005/105/009/109/ 077/177/0...
Page 335
Appendix b default value list b-5 a p p e n d ix a ppe ndi x b channel power on/off off channel center 3.6 ghz channel width 3.84 mhz filter type root nyquist roll-off factor 0.22 obw on/off off method n% n% of ratio 99% xdb value 25 db marker active marker marker1 zone center 3.6 ghz zone width 3.1...
Page 336
Appendix b default value list b-6 signal search resolution 1 db threshold on/off off above/below above level − 50 dbm search peaks number 10
Page 337
Appendix b default value list b-7 a p p e n d ix a ppe ndi x b analysis time auto/manual auto start 0 s length 100 ms scale vertical log scale division 10 db/div lin scale division 10%/div log scale line 10 storage mode off count 10 filter type off roll-off factor 0.22 band width 5 mhz freq. Offset ...
Page 338
Appendix b default value list b-8 analysis time auto/manual auto start 0 s length 100 ms scale vertical scale unit hz width span/5 storage mode off count 10 filter auto/manual auto filter bandwidth 10 mhz (ms2830a-005/105/007/009/109/ 077/078, ms2840a-005/105/009/109/ 077/177/078/178, ms2850a-032/03...
Page 339
Appendix b default value list b-9 a p p e n d ix a ppe ndi x b measurement interval auto meas slope auto analysis time auto/manual auto start 0 s length 100 ms scale vertical scale division 36.00 deg/div time detection sample marker marker 1 on, 0 s marker 2 on, 100 ms active marker 1 method phase o...
Page 340
Appendix b default value list b-10 analysis time auto/manual auto start 0 s length 100 ms gate mode off period 100 ms range setup edit range number 1 range on start time 0 s stop time 100 ms edit range number 2 range off start time 0 s stop time 100 ms edit range number 3 range off start time 0 s st...
Page 341
Appendix b default value list b-11 a p p e n d ix a ppe ndi x b analysis time auto/manual auto start 0 s length 100 ms scale level full scale 100 db storage mode off count 10 rbw auto, 100 khz time detection positive marker active marker 1 marker on/off on zone center 3.6 ghz zone width 3.125 mhz 1....
Page 342
Appendix b default value list b-12. Trace mode off analysis time auto/manual auto start 0 s length 100 ms scale level full scale 100 db time detection average analysis time auto/manual auto start 0 s length 100 ms scale level full scale 100 db rbw auto, 100 khz time detection positive.
Page 343
C-1 a p p e n d ix a ppe ndi x c appendix c standard parameter list the parameters set by the standard functions are listed below. The standard functions can only be selected if ms2830a-005/105/007/009/109, ms2840a-005/105/009/109 is installed, or ms2850a. C.1 acp ......................................
Page 344: C.1 Acp
Appendix c standard parameter list c-2 c.1 acp 5g pre-standard table c.1-1 standard parameters for acp function standard parameter name setting 5g pre-standard (99 mhz 1 carrier) frequency span 510 mhz rbw 300 khz time detection average capture time auto analysis start time 0 s analysis time length ...
Page 345
C.1 acp c-3 a p p e n d ix a ppe ndi x c table c.1-1 standard parameters for acp function (cont’d) standard parameter name setting 5g pre-standard (100 mhz 1 carrier) frequency span 510 mhz rbw 300 khz time detection average capture time auto analysis start time 0 s analysis time length 1 ms adjacen...
Page 346
Appendix c standard parameter list c-4 table c.1-1 standard parameters for acp function (cont’d) standard parameter name setting 5g pre-standard (99 mhz 2 carrier) frequency span 1 ghz rbw 300 khz time detection average capture time auto analysis start time 0 s analysis time length 10 ms adjacent ch...
Page 347
C.1 acp c-5 a p p e n d ix a ppe ndi x c table c.1-1 standard parameters for acp function (cont’d) standard parameter name setting 5g pre-standard (100 mhz 2 carrier) frequency span 1 ghz rbw 300 khz time detection average capture time auto analysis start time 0 s analysis time length 10 ms adjacent...
Page 348
Appendix c standard parameter list c-6 table c.1-1 standard parameters for acp function (cont’d) standard parameter name setting 5g pre-standard (99 mhz 4 carrier) frequency span 1 ghz rbw 300 khz time detection average capture time auto analysis start time 0 s analysis time length 1 ms adjacent cha...
Page 349
C.1 acp c-7 a p p e n d ix a ppe ndi x c table c.1-1 standard parameters for acp function (cont’d) standard parameter name setting 5g pre-standard (100 mhz 4 carrier) frequency span 1 ghz rbw 300 khz time detection average capture time auto analysis start time 0 s analysis time length 1 ms adjacent ...
Page 350: W-Cdma
Appendix c standard parameter list c-8 w-cdma table c.1-1 standard parameters for acp function (cont’d) standard parameter name setting w-cdma uplink frequency span 25 mhz rbw 30 khz time detection average capture time auto analysis start time 0 s analysis time length 10 ms adjacent channel power on...
Page 351
C.1 acp c-9 a p p e n d ix a ppe ndi x c table c.1-1 standard parameters for acp function (cont’d) standard parameter name setting w-cdma downlink (single carrier) frequency span 25 mhz rbw 30 khz time detection average capture time auto analysis start time 0 s analysis time length 10 ms adjacent ch...
Page 352
Appendix c standard parameter list c-10 table c.1-1 standard parameters for acp function (cont’d) standard parameter name setting w-cdma downlink (2 carriers) frequency span 31.25 mhz rbw 30 khz time detection average capture time auto analysis start time 0 s analysis time length 10 ms adjacent chan...
Page 353: Mobile Wimax
C.1 acp c-11 a p p e n d ix a ppe ndi x c mobile wimax table c.1-1 standard parameters for acp function (cont’d) standard parameter name setting mobile wimax dl/ul 10 mhz bw frequency span 31.25 mhz rbw 30 khz time detection average capture time auto analysis start time 0 s analysis time length 5 ms...
Page 354
Appendix c standard parameter list c-12 table c.1-1 standard parameters for acp function (cont’d) standard parameter name setting mobile wimax dl/ul 5 mhz bw frequency span 25 mhz rbw 30 khz time detection average capture time auto analysis start time 0 s analysis time length 5 ms adjacent channel p...
Page 355: Lte
C.1 acp c-13 a p p e n d ix a ppe ndi x c lte table c.1-1 standard parameters for acp function (cont’d) standard parameter name setting lte uplink/downlink 1.4 mhz bw (utra 5 mhz) frequency span 25 mhz rbw 10 khz time detection average capture time auto analysis start time 0 s analysis time length 1...
Page 356
Appendix c standard parameter list c-14 table c.1-1 standard parameters for acp function (cont’d) standard parameter name setting lte tdd uplink/downlink 1.4 mhz bw (utra 1.6 mhz) frequency span 10 mhz rbw 10 khz time detection average capture time auto analysis start time 0 s analysis time length 1...
Page 357
C.1 acp c-15 a p p e n d ix a ppe ndi x c table c.1-1 standard parameters for acp function (cont’d) standard parameter name setting lte uplink/downlink 1.4 mhz bw (e-utra 1.4 mhz) frequency span 10 mhz rbw 10 khz time detection average capture time auto analysis start time 0 s analysis time length 1...
Page 358
Appendix c standard parameter list c-16 table c.1-1 standard parameters for acp function (cont’d) standard parameter name setting lte tdd uplink/downlink 1.4 mhz bw (e-utra 1.4 mhz) frequency span 10 mhz rbw 10 khz time detection average capture time auto analysis start time 0 s analysis time length...
Page 359
C.1 acp c-17 a p p e n d ix a ppe ndi x c table c.1-1 standard parameters for acp function (cont’d) standard parameter name setting lte uplink/downlink 3 mhz bw (utra 5 mhz) frequency span 25 mhz rbw 30 khz time detection average capture time auto analysis start time 0 s analysis time length 10 ms a...
Page 360
Appendix c standard parameter list c-18 table c.1-1 standard parameters for acp function (cont’d) standard parameter name setting lte tdd uplink/downlink 3 mhz bw (utra 1.6mhz) frequency span 10 mhz rbw 30 khz time detection average capture time auto analysis start time 0 s analysis time length 1 ms...
Page 361
C.1 acp c-19 a p p e n d ix a ppe ndi x c table c.1-1 standard parameters for acp function (cont’d) standard parameter name setting lte uplink/downlink 3 mhz bw (e-utra 3 mhz) frequency span 25 mhz rbw 30 khz time detection average capture time auto analysis start time 0 s analysis time length 10 ms...
Page 362
Appendix c standard parameter list c-20 table c.1-1 standard parameters for acp function (cont’d) standard parameter name setting lte tdd uplink/downlink 3 mhz bw (e-utra 3 mhz) frequency span 25 mhz rbw 30 khz time detection average capture time auto analysis start time 0 s analysis time length 1 m...
Page 363
C.1 acp c-21 a p p e n d ix a ppe ndi x c table c.1-1 standard parameters for acp function (cont’d) standard parameter name setting lte uplink/ downlink 5 mhz bw (utra 5 mhz) frequency span 25 mhz rbw 30 khz time detection average capture time auto analysis start time 0 s analysis time length 10 ms ...
Page 364
Appendix c standard parameter list c-22 table c.1-1 standard parameters for acp function (cont’d) standard parameter name setting lte tdd uplink/downlink 5 mhz bw (utra 1.6 mhz) frequency span 25 mhz rbw 30 khz time detection average capture time auto analysis start time 0 s analysis time length 1 m...
Page 365
C.1 acp c-23 a p p e n d ix a ppe ndi x c table c.1-1 standard parameters for acp function (cont’d) standard parameter name setting lte tdd downlink 5 mhz bw (utra 5 mhz) frequency span 25 mhz rbw 30 khz time detection average capture time auto analysis start time 0 s analysis time length 1 ms adjac...
Page 366
Appendix c standard parameter list c-24 table c.1-1 standard parameters for acp function (cont’d) standard parameter name setting lte uplink/downlink 5 mhz bw (e-utra 5 mhz) frequency span 25 mhz rbw 30 khz time detection average capture time auto analysis start time 0 s analysis time length 10 ms a...
Page 367
C.1 acp c-25 a p p e n d ix a ppe ndi x c table c.1-1 standard parameters for acp function (cont’d) standard parameter name setting lte tdd uplink/downlink 5 mhz bw (e-utra 5 mhz) frequency span 25 mhz rbw 30 khz time detection average capture time auto analysis start time 0 s analysis time length 1...
Page 368: Dsrc
Appendix c standard parameter list c-26 dsrc table c.1-1 standard parameters for acp function (cont’d) standard parameter name setting dsrc π /4dqpsk/ask frequency span 25 mhz rbw 30 khz time detection positive capture time auto analysis start time 0 s analysis time length 7.032 ms adjacent channel ...
Page 369: Td-Scdma
C.1 acp c-27 a p p e n d ix a ppe ndi x c td-scdma table c.1-1 standard parameters for acp function (cont’d) standard parameter name setting td-scdma 1 carrier frequency span 10 mhz rbw 30 khz time detection average capture time auto analysis start time 0 s adjacent channel power on acp reference ca...
Page 370
Appendix c standard parameter list c-28 table c.1-1 standard parameters for acp function (cont’d) standard parameter name setting td-scdma 2 carrier frequency span 10 mhz rbw 30 khz time detection average capture time auto analysis start time 0 s adjacent channel power on acp reference carrier selec...
Page 371
C.1 acp c-29 a p p e n d ix a ppe ndi x c table c.1-1 standard parameters for acp function (cont’d) standard parameter name setting td-scdma 3 carrier frequency span 25 mhz rbw 30 khz time detection average capture time auto analysis start time 0 s adjacent channel power on acp reference carrier sel...
Page 372
Appendix c standard parameter list c-30 table c.1-1 standard parameters for acp function (cont’d) standard parameter name setting td-scdma 4 carrier frequency span 25 mhz rbw 30 khz time detection average capture time auto analysis start time 0 s adjacent channel power on acp reference carrier selec...
Page 373
C.1 acp c-31 a p p e n d ix a ppe ndi x c table c.1-1 standard parameters for acp function (cont’d) standard parameter name setting td-scdma 5 carrier frequency span 25 mhz rbw 30 khz time detection average capture time auto analysis start time 0 s adjacent channel power on acp reference carrier sel...
Page 374
Appendix c standard parameter list c-32 table c.1-1 standard parameters for acp function (cont’d) standard parameter name setting td-scdma 6 carrier frequency span 25 mhz rbw 30 khz time detection average capture time auto analysis start time 0 s adjacent channel power on acp reference carrier selec...
Page 375: Cdma2000
C.1 acp c-33 a p p e n d ix a ppe ndi x c cdma2000 table c.1-1 standard parameters for acp function (cont’d) standard parameter name setting cdma2000 forward link frequency span 5 mhz rbw 30 khz time detection average capture time auto analysis start time 0 s analysis time length 1.25 ms adjacent ch...
Page 376: Ev-Do
Appendix c standard parameter list c-34 ev-do table c.1-1 standard parameters for acp function (cont’d) standard parameter name setting ev-do forward link frequency span 5 mhz rbw 30 khz time detection average capture time auto analysis start time 0 s analysis time length 1.666667 ms adjacent channe...
Page 377: C.2 Channel Power
C.2 channel power c-35 a p p e n d ix a ppe ndi x c c.2 channel power w-cdma table c.2-1 standard parameters for channel power function standard parameter name setting w-cdma uplink/downlink (mean power) frequency span 10 mhz rbw auto time detection average capture time auto analysis start time 0 s ...
Page 378: Mobile Wimax
Appendix c standard parameter list c-36 mobile wimax table c.2-1 standard parameters for channel power function (cont’d) standard parameter name setting mobile wimax dl/ul 10 mhz bw frequency span 31.25 mhz rbw auto time detection average capture time auto analysis start time 0 s analysis time lengt...
Page 379: Lte
C.2 channel power c-37 a p p e n d ix a ppe ndi x c lte table c.2-1 standard parameters for channel power function (cont’d) standard parameter name setting lte uplink/downlink mean power 1.4 mhz bw frequency span 5 mhz rbw auto time detection average capture time auto analysis start time 0 s analysi...
Page 380
Appendix c standard parameter list c-38 table c.2-1 standard parameters for channel power function (cont’d) standard parameter name setting lte uplink/downlink mean power 10 mhz bw frequency span 25 mhz rbw auto time detection average capture time auto analysis start time 0 s analysis time length 10...
Page 381
C.2 channel power c-39 a p p e n d ix a ppe ndi x c table c.2-1 standard parameters for channel power function (cont’d) standard parameter name setting lte uplink/ downlink filtered power 1.4 mhz bw frequency span 5 mhz rbw auto time detection average capture time auto analysis start time 0 s analys...
Page 382
Appendix c standard parameter list c-40 table c.2-1 standard parameters for channel power function (cont’d) standard parameter name setting lte uplink/downlink filtered power 10 mhz bw frequency span 25 mhz rbw auto time detection average capture time auto analysis start time 0 s analysis time lengt...
Page 383: Lte Tdd
C.2 channel power c-41 a p p e n d ix a ppe ndi x c lte tdd table c.2-1 standard parameters for channel power function (cont’d) standard parameter name setting lte tdd uplink/downlink mean power 1.4 mhz bw frequency span 5 mhz rbw auto time detection average capture time auto analysis start time 0 s...
Page 384
Appendix c standard parameter list c-42 table c.2-1 standard parameters for channel power function (cont’d) standard parameter name setting lte tdd uplink/downlink mean power 10 mhz bw frequency span 25 mhz rbw auto time detection average capture time auto analysis start time 0 s analysis time lengt...
Page 385
C.2 channel power c-43 a p p e n d ix a ppe ndi x c table c.2-1 standard parameters for channel power function (cont’d) standard parameter name setting lte tdd uplink/downlink filtered power 1.4 mhz bw frequency span 5 mhz rbw auto time detection average capture time auto analysis start time 0 s ana...
Page 386
Appendix c standard parameter list c-44 table c.2-1 standard parameters for channel power function (cont’d) standard parameter name setting lte tdd uplink/downlink filtered power 10 mhz bw frequency span 25 mhz rbw auto time detection average capture time auto analysis start time 0 s analysis time l...
Page 387: Dsrc/td-Scdma
C.2 channel power c-45 a p p e n d ix a ppe ndi x c dsrc/td-scdma table c.2-1 standard parameters for channel power function (cont’d) standard parameter name setting dsrc π /4dqpsk frequency span 10 mhz rbw auto time detection average capture time auto analysis start time 0 s analysis time length 7....
Page 388: Xg-Phs
Appendix c standard parameter list c-46 xg-phs table c.2-1 standard parameters for channel power function (cont’d) standard parameter name setting xg-phs mean power 10 mhz bw frequency span 25 mhz rbw auto time detection average capture time auto analysis start time 0 s analysis time length 500 ms c...
Page 389: Cdma2000/ev-Do
C.2 channel power c-47 a p p e n d ix a ppe ndi x c cdma2000/ev-do table c.2-1 standard parameters for channel power function (cont’d) standard parameter name setting cdma2000 forward link frequency span 5 mhz rbw auto time detection average capture time auto analysis start time 0 s analysis time le...
Page 390: Isdb-Tmm
Appendix c standard parameter list c-48 isdb-tmm table c.2-1 standard parameters for channel power function (cont’d) standard parameter name setting isdb-tmm 14.2 mhz bw (mean power) frequency span 25 mhz rbw 10 khz time detection average capture time auto analysis start time 0 analysis time length ...
Page 391: C.3 Obw
C.3 obw c-49 a p p e n d ix a ppe ndi x c c.3 obw w-cdma/mobile wimax table c.3-1 standard parameters for obw function standard parameter name setting w-cdma uplink/downlink method n% of power n% ratio 99.00% frequency span 10 mhz rbw 30 khz time detection average capture time auto analysis start ti...
Page 392: Lte
Appendix c standard parameter list c-50 lte table c.3-1 standard parameters for obw function (cont’d) standard parameter name setting lte uplink/downlink 1.4 mhz bandwidth lte tdd uplink/downlink 1.4 mhz bandwidth method n% of power n% ratio 99.00% frequency span 5 mhz rbw 10 khz time detection aver...
Page 393
C.3 obw c-51 a p p e n d ix a ppe ndi x c table c.3-1 standard parameters for obw function (cont’d) standard parameter name setting lte uplink/downlink 10 mhz bandwidth lte tdd uplink/downlink 10 mhz bandwidth method n% of power n% ratio 99.00% frequency span 25 mhz rbw 100 khz time detection averag...
Page 394: Dsrc/td-Scdma
Appendix c standard parameter list c-52 dsrc/td-scdma table c.3-1 standard parameters for obw function (cont’d) standard parameter name setting dsrc π /4dqpsk/ask method n% of power n% ratio 99.00% frequency span 10 mhz rbw 30 khz time detection positive capture time auto analysis start time 0 s ana...
Page 395: Xg-Phs
C.3 obw c-53 a p p e n d ix a ppe ndi x c xg-phs table c.3-1 standard parameters for obw function (cont’d) standard parameter name setting xg-phs 10 mhz bandwidth method n% of power n% ratio 99.00% frequency span 25 mhz rbw 100 khz storage mode max hold storage count 10 time detection positive captu...
Page 396: Cdma2000/ev-Do
Appendix c standard parameter list c-54 cdma2000/ev-do table c.3-1 standard parameters for obw function (cont’d) standard parameter name setting cdma2000 forward link method n% of power n% ratio 99.00% frequency span 5 mhz rbw 30 khz time detection positive capture time auto analysis start time 0 s ...
Page 397: Isdb-Tmm
C.3 obw c-55 a p p e n d ix a ppe ndi x c isdb-tmm table c.3-1 standard parameters for obw function (cont’d) standard parameter name setting isdb-tmm 14.2 mhz bw method n% of power n% ratio 99.00% frequency span 25 mhz rbw 10 khz time detection average capture time auto analysis start time 0 s analy...
Page 398: C.4 Burst Average Power
Appendix c standard parameter list c-56 c.4 burst average power w-cdma/mobile wimax table c.4-1 standard parameters for burst average power function standard parameter name setting w-cdma uplink/downlink (mean power) frequency span 10 mhz time detection pos & neg capture time auto analysis start tim...
Page 399: Lte
C.4 burst average power c-57 a p p e n d ix a ppe ndi x c lte table c.4-1 standard parameters for burst average power function (cont’d) standard parameter name setting lte uplink/downlink mean power 1.4 mhz bw lte tdd uplink/downlink mean power 1.4 mhz bw frequency span 5 mhz time detection average ...
Page 400
Appendix c standard parameter list c-58 table c.4-1 standard parameters for burst average power function (cont’d) standard parameter name setting lte uplink/downlink mean power 10 mhz bw lte tdd uplink/downlink mean power 10 mhz bw frequency span 25 mhz time detection average capture time auto analy...
Page 401
C.4 burst average power c-59 a p p e n d ix a ppe ndi x c table c.4-1 standard parameters for burst average power function (cont’d) standard parameter name setting lte uplink/downlink filtered power 1.4 mhz bw lte tdd uplink/downlink filtered power 1.4 mhz bw frequency span 5 mhz time detection aver...
Page 402
Appendix c standard parameter list c-60 table c.4-1 standard parameters for burst average power function (cont’d) standard parameter name setting lte uplink/downlink filtered power 10 mhz bw lte tdd uplink/downlink filtered power 10 mhz bw frequency span 25 mhz time detection average capture time au...
Page 403: Dsrc/td-Scdma
C.4 burst average power c-61 a p p e n d ix a ppe ndi x c dsrc/td-scdma table c.4-1 standard parameters for burst average power function (cont’d) standard parameter name setting dsrc frequency span 10 mhz time detection average capture time auto analysis start time 0 s analysis time length 782.00 µs...
Page 404: Cdma2000/ev-Do
Appendix c standard parameter list c-62. Cdma2000/ev-do table c.4-1 standard parameters for burst average power function (cont’d) standard parameter name setting cdma2000 forward link frequency span 5 mhz time detection average capture time auto analysis start time 0 s analysis time length 1.25 ms f...
Page 405
D-1 app e ndix a ppendix d appendix d fft and rbw the spectrum, spectrogram trace of the signal analyzer performs spectrum analysis via fft processing. Figure d-1 generating a spectrum waveform figure d-1 shows an overview of spectrum waveform generation. In fft processing, part of a long signal is ...
Page 406
Appendix d fft and rbw d-2 figure d-2 capture data length and window function length a value varies depending on the marker result settings. Table d-1 marker result settings integration density peak(fast) peak(accuracy) [1] [1] [2] [3] fft fft fft time window function length capture data fft fft fft...
Page 407
Appendix d fft and rbw d-3 app e ndix a ppendix d table d-2 rbw and window function length in spectrum trace and [1] rbw span 1 hz 3 hz 10 hz 30 hz 100 hz 300 hz 1 khz 100/125 mhz* 50/62.5 mhz* 25/31.25 mhz* 524288 262144 10 mhz 262144 131072 5 mhz 524288 131072 65536 2.5 mhz 262144 65536 32768 1 mh...
Page 408
Appendix d fft and rbw d-4 table d-2 rbw and window function length in spectrum trace and [1] (cont’d) rbw span 3 khz 10 khz 30 khz 100 khz 300 khz 1 mhz 3 mhz 10 mhz 100/125 mhz* 262144 65536 32768 8192 2048 2048 2048 50/62.5 mhz* 262144 65536 32768 8192 2048 2048 2048 25/31.25 mhz* 65536 32768 819...
Page 409
Appendix d fft and rbw d-5 app e ndix a ppendix d table d-3 rbw and window function length in spectrum trace and [2] rbw span 1 hz 3 hz 10 hz 30 hz 100 hz 300 hz 1 khz 100/125 mhz* 50/62.5 mhz* 25/31.25 mhz* 524288 10 mhz 524288 262144 5 mhz 262144 131072 2.5 mhz 524288 131072 65536 1 mhz 262144 655...
Page 410
Appendix d fft and rbw d-6 table d-3 rbw and window function length in spectrum trace and [2] (cont’d) rbw span 3 khz 10 khz 30 khz 100 khz 300 khz 1 mhz 3 mhz 10 mhz 100/125 mhz* 524288 131072 65536 16384 4096 2048 2048 50/62.5 mhz* 524288 131072 65536 16384 4096 2048 2048 25/31.25 mhz* 131072 6553...
Page 411
Appendix d fft and rbw d-7 app e ndix a ppendix d table d-4 rbw and window function length in spectrum trace and [3] rbw span 1 hz 3 hz 10 hz 30 hz 100 hz 300 hz 1 khz 100/125 mhz* 50/62.5 mhz* 25/31.25 mhz* 10 mhz 524288 5 mhz 524288 262144 2.5 mhz 262144 131072 1 mhz 524288 131072 32768 500 khz 26...
Page 412
Appendix d fft and rbw d-8 table d-4 rbw and window function length in spectrum trace and [3] (cont’d) rbw span 3 khz 10 khz 30 khz 100 khz 300 khz 1 mhz 3 mhz 10 mhz 100/125 mhz* 262144 131072 32768 8192 4096 2048 50/62.5 mhz* 262144 131072 32768 8192 4096 2048 25/31.25 mhz* 262144 131072 32768 819...
Page 413
Appendix d fft and rbw d-9 app e ndix a ppendix d table d-5 rbw and window function length in spectrogram trace and [1] rbw span 1 hz 3 hz 10 hz 30 hz 100 hz 300 hz 1 khz 100/125 mhz* 50/62.5 mhz* 25/31.25 mhz* 524288 262144 10 mhz 262144 131072 5 mhz 524288 131072 65536 2.5 mhz 262144 65536 32768 1...
Page 414
Appendix d fft and rbw d-10 table d-5 rbw and window function length in spectrogram trace and [1] (cont’d) rbw span 3 khz 10 khz 30 khz 100 khz 300 khz 1 mhz 3 mhz 10 mhz 100/125 mhz* 262144 65536 32768 8192 2048 1024 1024 50/62.5 mhz* 262144 65536 32768 8192 2048 1024 1024 25/31.25 mhz* 65536 32768...
Page 415
Appendix d fft and rbw d-11 app e ndix a ppendix d table d-6 rbw and window function length in spectrogram trace and [2] rbw span 1 hz 3 hz 10 hz 30 hz 100 hz 300 hz 1 khz 100/125 mhz* 50/62.5 mhz* 25/31.25 mhz* 524288 10 mhz 524288 262144 5 mhz 262144 131072 2.5 mhz 524288 131072 65536 1 mhz 262144...
Page 416
Appendix d fft and rbw d-12 table d-6 rbw and window function length in spectrogram trace and [2] (cont’d) rbw span 3 khz 10 khz 30 khz 100 khz 300 khz 1 mhz 3 mhz 10 mhz 100/125 mhz* 524288 131072 65536 16384 4096 2048 1024 50/62.5 mhz* 524288 131072 65536 16384 4096 2048 1024 25/31.25 mhz* 131072 ...
Page 417
Appendix d fft and rbw d-13 app e ndix a ppendix d table d-7 rbw and window function length in spectrogram trace and [3] rbw span 1 hz 3 hz 10 hz 30 hz 100 hz 300 hz 1 khz 100/125 mhz* 50/62.5 mhz* 25/31.25 mhz* 10 mhz 524288 5 mhz 524288 262144 2.5 mhz 262144 131072 1 mhz 524288 131072 32768 500 kh...
Page 418
Appendix d fft and rbw d-14. Table d-7 rbw and window function length in spectrogram trace and [3] (cont’d) rbw span 3 khz 10 khz 30 khz 100 khz 300 khz 1 mhz 3 mhz 10 mhz 100/125 mhz* 262144 131072 32768 8192 4096 1024 50/62.5 mhz* 262144 131072 32768 8192 4096 1024 25/31.25 mhz* 262144 131072 3276...
Page 419
E-1 a p p e n d ix a ppe ndi x e appendix e iq data time actually required iq data time actually required in fft and filtering processing, additional iq data time is required for calculation in addition to the specified capture time. The signal analyzer function automatically calculates the data len...
Page 420
Appendix e iq data time actually required e-2 the minimum capture time for the frequency vs time trace is as shown below. Figure e-3 iq data time for the frequency vs time trace the frequency vs time trace performs band limiting processing, so the data required for the calculation is captured, which...
Page 421
Appendix e iq data time actually required e-3 a p p e n d ix a ppe ndi x e the minimum capture time for the spectrogram trace is as shown below. Figure e-5 iq data time for the spectrogram trace the spectrogram trace uses the fft method for calculation, so data with window function length is capture...
Page 422
Appendix e iq data time actually required e-4. Auto mode and manual mode for capture time when capture time is set to the auto mode, the data length required for calculation is automatically set to the minimum data length. This makes the iq data time actually captured the shortest, allowing the user...
Page 423
F-1 a p p e n d ix a ppe nd ix f appendix f saving waveform csv data this appendix describes the trace-data file used when a signal analyzer application is used to save trace data (data displayed on the screen) to a file. Trace data to be saved trace mode trace data (trace data displayed on the scre...
Page 424
Appendix f saving waveform csv data f-2 table f-1 spectrum trace file information line number recorded information remarks 1 “main-trace”, “start freq (hz)”, “stop freq (hz)”, “center freq (hz)”, “span freq (hz)” data title 2 the data for the above main-trace: “spectrum” 3 blank 4 “analysis start ti...
Page 425
Appendix f saving waveform csv data f-3 a p p e n d ix a ppe ndi x f table f-1 spectrum trace file information (cont’d) line number recorded information remarks 15 blank 16 “storage mode” data title 17 the data for the above storage mode: “lin average” or “max hold” or “min hold” or “off” 18 blank 1...
Page 426
Appendix f saving waveform csv data f-4 table f-2 power vs time trace file information line number recorded information remarks 1 “main-trace”, “center freq (hz)”, “span freq (hz)” data title 2 the data for the above main-trace: “power vs time” 3 blank 4 “analysis start time (ms)”, “analysis time le...
Page 427
Appendix f saving waveform csv data f-5 a p p e n d ix a ppe ndi x f table f-2 power vs time trace file information (con’d) line number recorded information remarks 16 “storage mode” data title 17 the data for the above storage mode: “lin average” or “max hold” or “min hold” or “off” 18 blank 19 whe...
Page 428
Appendix f saving waveform csv data f-6 table f-3 freq vs time trace file information line number recorded information remarks 1 “main-trace”, “center freq (hz)”, “span freq (hz)” data title 2 the data for the above main-trace: “frequency vs time” 3 blank 4 “analysis start time (ms)”, “analysis time...
Page 429
Appendix f saving waveform csv data f-7 a p p e n d ix a ppe ndi x f table f-3 freq vs time trace file information (con’d) line number recorded information remarks 19 when scale unit = hz when scale unit = Δ hz data title “wave data (hz)”, “(neg)” “wave data (delta hz)”, “(neg)” 20 trace data at the...
Page 430
Appendix f saving waveform csv data f-8 table f-4 phase vs time trace file information line number recorded information remarks 1 “main-trace”, “center freq (hz)”, “span freq (hz)” data title 2 the data for the above main-trace: “phase vs time” 3 blank 4 “analysis start time (ms)”, “analysis time le...
Page 431
Appendix f saving waveform csv data f-9 a p p e n d ix a ppe ndi x f table f-4 phase vs time trace file information (cont’d) line number recorded information remarks 19 “phase offset” data title 20 the data for the above 21 blank 22 “wave data (degree)” data title 23 trace data at the trace point – ...
Page 432
Appendix f saving waveform csv data f-10 table f-5 spectrogram trace file information line number recorded information remarks 1 “main-trace”, “start freq (hz)”, “stop freq (hz)”,”center freq (hz)”, “span freq (hz)” data title 2 the data for the above main-trace: “spectrogram” 3 blank 4 “analysis st...
Page 433
Appendix f saving waveform csv data f-11 a p p e n d ix a ppe ndi x f table f-5 spectrogram trace file information (cont’d) line number recorded information remarks 19 “wave data time trace 0 (dbm)”, “wave data time trace 1 (dbm)”, ……“wave data time trace 0 (dbm)”, “wave data time trace” + nt-1 + “(...
Page 434
Appendix f saving waveform csv data f-12 table f-6 ccdf trace file information line number recorded information remarks 1 “main-trace”, “center freq (hz)”, “span freq (hz)” data title 2 the data for the above main-trace: “ccdf” 3 blank 4 “analysis start time (ms)”, “analysis time (ms)”, “capture tim...
Page 435
Appendix f saving waveform csv data f-13 a p p e n d ix a ppe ndi x f table f-6 ccdf trace file information (cont’d) line number recorded information remarks 19 “wave data (%)”, “(reference)” data title when reference trace = off, “(reference)” is not recorded. 20 when method = apd when method = ccd...
Page 436
Appendix f saving waveform csv data f-14 when a sub-trace is displayed, the information below is recorded after the last main trace line. Table f-7 additional power vs time trace file information when sub-trace is displayed line number recorded information remarks +1 blank +2 “sub-trace” data title ...
Page 437
Appendix f saving waveform csv data f-15 a p p e n d ix a ppe ndi x f when a sub-trace is displayed, the information below is recorded after the last main trace line. Table f-8 additional spectrogram trace file information when sub-trace is displayed line number recorded information remarks +1 blank...
Page 438
Appendix f saving waveform csv data f-16..
Page 439: Symbol And Numbers
Index index-1 inde x references are to page numbers. Symbol and numbers a accessory ....................................................... 2-2 amplitude ............................................ 2-2, 2-22 analysis start time ..................................... 4-9 analysis time ..................
Page 440
Index index-2. Offset ........................................................... 2-22 p positive ........................................................ 4-24 power vs time .............................................. 1-4 pre-amp ...................................................... 2-22 presele...