- DL manuals
- NEC
- Voicemail
- Univerge SV9100
- Manual
NEC Univerge SV9100 Manual
Summary of Univerge SV9100
Page 1
Networking manual a50-035910-004 au issue 2.0
Page 2
Contents of this manual are subject to change without prior notice at the discretion of nec corporation. This document has been prepared for the use of employees and customers of nec corporation and may not be reproduced without prior written approval of nec corporation. Univerge is a registered tra...
Page 3: Introduction
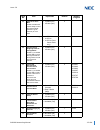
Sv9100 networking manual i table of contents introduction section 1 general overview .................................................................................... 1-1 section 2 manual organization ............................................................................... 1-1 section 3 co...
Page 4
Ii table of contents issue 2.0 2.3.1 installing coiu-ls1/lg1, gcd-4odta, gcd-4diopa, or gcd-2bria blades .............................................................................................. 2-4 section 3 installing the gcd-ccta (ccis trunk interface) ................................. 2-5 3...
Page 5
Sv9100 networking manual iii issue 2.0 section 5 k-ccis features ...................................................................................... 4-5 automatic recall – k-ccis ............................................................................4-6 brokerage hotline – k-ccis ..............
Page 6
Iv table of contents issue 2.0 section 1 system outline ........................................................................................ 5-1 1.1 ip k-ccis application using the gpz-iple ........................................ 5-1 1.1.1 ccis networking via ip (non peer-to-peer connections ba...
Page 7
Sv9100 networking manual v issue 2.0 2.6 ip k-ccis assignment ...................................................................... 5-26 2.7 ip k-ccis (peer-to-peer) assignment .............................................. 5-26 2.8 ccis over ip codec information setup ................................
Page 8: Chapter 2 Ip Networking
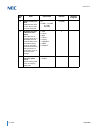
Vi table of contents issue 2.0 book 2 – sv9100 ip networking chapter 1 general information section 1 univerge sv9100 ip networking ........................................................ 1-1 section 2 voice over ip .......................................................................................
Page 9: Chapter 4 Programming
Sv9100 networking manual vii issue 2.0 chapter 3 general ip configuration section 1 introduction ............................................................................................. 3-1 section 2 network addressing overview .............................................................. 3-1 ...
Page 10: Chapter 6 Sip Trunking
Viii table of contents issue 2.0 section 3 internet based connections (xdsl, cable, etc.) ................................. 5-5 section 4 firewalls and nat .................................................................................. 5-6 4.1 understanding the infrastructure .......................
Page 11: Chapter 7 H.323 Trunking
Sv9100 networking manual ix issue 2.0 section 4 video support over sip trunks ............................................................. 6-6 section 5 guide to feature programming ............................................................. 6-7 chapter 7 h.323 trunking section 1 introduction ......
Page 12
X table of contents issue 2.0 3.1 connecting to an ip telephone ........................................................... 8-3 3.2 operation during power failure .......................................................... 8-5 section 4 lan connection ....................................................
Page 13
Sv9100 networking manual xi issue 2.0 14.2 checking the firmware version ......................................................... 8-24 14.3 upgrading automatically .................................................................... 8-24 section 15 ip station (sip multiline telephone) ................
Page 14: Chapter 10 Sv9100 Netlink
Xii table of contents issue 2.0 section 5 programming ......................................................................................... 9-13 5.1 configure voipdb networking information ....................................... 9-13 5.1.1 voipdb (dsp) basic setup ..................................
Page 15
Sv9100 networking manual xiii issue 2.0 3.2.4 general limitations .........................................................................10-9 3.3 dsp ................................................................................................. 10-13 3.4 e911 ......................................
Page 16: Chapter 11 Napt
Xiv table of contents issue 2.0 section 16 voip handling ...................................................................................... 10-45 section 17 netlink multi-sip carrier .................................................................... 10-50 section 18 how to enter programming mo...
Page 17: Chapter 13 Aspirenet
Sv9100 networking manual xv issue 2.0 chapter 13 aspirenet 1.1 what is aspirenet? ............................................................................ 13-1 1.2 sv9100 pcbs .................................................................................... 13-2 1.3 available features ..........
Page 18
Xvi table of contents issue 2.0 3.11 department calling .......................................................................... 13-29 3.12 department step call ...................................................................... 13-30 3.13 direct inward dialing (ddi) ..............................
Page 19
Sv9100 networking manual xvii issue 2.0 5.1 aspirenet - isdn bri .................................................................... 13-164 5.2 aspirenet - isdn pri .................................................................... 13-165 5.3 aspirenet - ip ..........................................
Page 20
Xviii table of contents issue 2.0
Page 21: Introduction
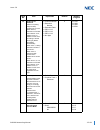
Sv9100 networking manual xix list of figures introduction book 1 – sv9100 k-ccis chapter 1 general information figure 1-1 k-ccis system outline .................................................................................................1-1 figure 1-2 clock supply route ............................
Page 22: Chapter 5 Sv9100 Ip K-Ccis
Xx list of figures issue 2.0 chapter 4 features and specifications figure 4-1 k-ccis call rerouting ................................................................................................ 4-18 figure 4-1 link reconnect for station calls .........................................................
Page 23: Chapter 4 Programming
Sv9100 networking manual xxi issue 2.0 figure 3-4 tcp/ip properties screen ..............................................................................................3-7 figure 3-5 testing the network connection ....................................................................................3...
Page 24
Xxii list of figures issue 2.0 figure 8-13 quick ‘n easy ftp server ........................................................................................... 8-19 figure 8-14 quick ‘n easy ftp server configuration .................................................................... 8-20 figure 8-1...
Page 25: Chapter 10 Sv9100 Netlink
Sv9100 networking manual xxiii issue 2.0 chapter 9 ip single line telephone (sip) chapter 10 sv9100 netlink figure 10-1 netlink fail-over example ..........................................................................................10-2 figure 10-2 two sv9100 systems connected via the wan .........
Page 26
Xxiv list of figures issue 2.0
Page 27: Introduction
Sv9100 networking manual xxv list of tables introduction table i-1 common terms and associated abbreviations .........................................................1-1 book 1 – sv9100 k-ccis chapter 1 general information table 1-1 12-multiframe bit assignment .........................................
Page 28: Chapter 5 Sv9100 Ip K-Ccis
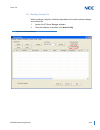
Xxvi list of tables issue 2.0 chapter 5 sv9100 ip k-ccis table 5-1 voipdb led indications ........................................................................................... 5-6 table 5-2 voipdb led cn1 transmit/receive data indications .............................................. 5-7 tabl...
Page 29: Chapter 6 Sip Trunking
Sv9100 networking manual xxvii issue 2.0 chapter 5 network design considerations table 5-1 type of service field (ip precedence - i ref. Rec 1349) .......................................5-23 table 5-2 diffserv parameters ..................................................................................
Page 30: Chapter 10 Sv9100 Netlink
Xxviii list of tables issue 2.0 table 8-3 ip phone relocation ................................................................................................ 8-74 chapter 9 ip single line telephone (sip) chapter 10 sv9100 netlink table 10-1 voip resource chart .........................................
Page 31: Introduction
Sv9100 networking manual i-1 univerge ® sv9100 introduction s ection 1 g eneral o verview this manuals provides information for networking for the univerge sv9100 systems. Networking can be accomplished using one of the following methods: sv9100 k-ccis (us only) sv9100 ip k-ccis sv9100 netlink s ect...
Page 32
Issue 2.0 i-2 gcd-2bria briu 2briu 2-port basic rate interface blade gpz-2bria 2briudb briudb 2-port basic rate daughter board, mounted on the gcd-2bria gcd-ccta cchu ccis cchu ccis trunk interface blade gcd-4cotc 4coiu 4-port loop/ground start trunk blade gpz-4cotg 4coiudb 4coiu daughter board 4-po...
Page 33: Book 1 – Sv9100 K-Ccis
Book 1 – sv9100 k-ccis.
Page 34: Chapter 1
Sv9100 networking manual 1-1 chapter 1 univerge ® sv9100 general information this chapter provides a system outline, the name and functions of the circuit cards required, system capacity, time slot assignments, system specifications and network structure considerations for univerge sv9100 k-ccis. S ...
Page 35
Issue 2.0 1-2 general information 1.1 common channel handler (gcd-ccta) the common channel handler (gcd-ccta) blade provides a common channel signal to a univerge sv9100 network. It is responsible for signaling between the key telephone system (kts) and the univerge sv9100 network under control of t...
Page 36
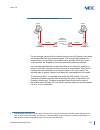
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 1-3 figure 1-3 k-ccis system configuration shows the system configuration of k-ccis provided using a digital network. S ection 2 dti s pecifications the following specifications apply to the gcd-ccta. 2.1 characteristics figure 1-3 k-ccis system configuration outpu...
Page 37
Issue 2.0 1-4 general information 2.2 frame configuration for 24 dti according to the at&t specifications for 24-channel transmission, there are two frame configurations: 12 multiframe (d4) and 24 multiframe (esf). 12 multi-frame (d4) this frame has 12 multiframes, and each multiframe has a 24-chann...
Page 38
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 1-5 table 1-1 12-multiframe bit assignment frame number s-bit terminal synchronization (ft) signal synchronization (fs) 1 1 2 0 3 0 4 0 5 1 6 1 7 0 8 1 9 1 10 1 11 0 12 0 the s-bit is the first bit in each frame. Frames are repeated in the order shown in this table...
Page 39
Issue 2.0 1-6 general information 24- multiframe (extended superframe – esf) this frame has 24 multiframes and each multiframe has a 24-channel pcm signal (8 bits/channel) and an s (superframe) bit. Figure 1-5 frame configuration of 24-dti (24 multiframe) s ch1 ch2 ch3 ch24 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 1 2 3 4 5...
Page 40
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 1-7 s ection 3 n etwork s tructure c onsiderations 3.1 determining system configurations the configuration of the network and the number of lines (channels) is determined by the traffic between each office. The topologies listed in this section are supported in the...
Page 41
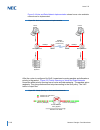
Issue 2.0 1-8 general information mesh topology is supported only when the kts is the end-point in a pbx-to-kts network. Refer to figure 1-8 mesh topology (pbx-to-kts) . Figure 1-6 star topology (kts-to-kts or pbx-to-kts) main hub a b c e d.
Page 42
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 1-9 figure 1-7 tree topology (kts-to-kts or pbx-to-kts) tree topology supports a total of 255 systems. Even though 255 systems are al- lowed, only five hops* are permitted. Software does not limit the number of hops. The limitation is due to the cch message delay t...
Page 43
Issue 2.0 1-10 general information 3.2 determining number of k-ccis routes when the system is a central office or tandem office, two or more routes to other offices are required. Each gcd-ccta can support one k-ccis link. Up to eight gcd-ccta blades can be installed in a univerge sv9100 system. The ...
Page 44
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 1-11 one gcd-ccta provides 24 channels. One common signaling channel port must be assigned on the digital trunk interface in case two systems are connected by one digital link. One common signaling channel can be assigned even if two digital links are connected bet...
Page 45
Issue 2.0 1-12 general information one gcd-ccta can be assigned to one common signaling channel. Tandem k-ccis connections require one gcd-ccta for every connection as shown in figure 1-11 one gcd-ccta assigned per common signaling channel . Common signaling channels cannot be connected to another g...
Page 46
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 1-13 3.4 determining which systems should be the central office if using a kts-to-kts only network and features such as voice mail integration – k-ccis are used, the key system that has the voice mail system installed, must be programmed as the central/originating ...
Page 47
Issue 2.0 1-14 general information data assignment for system b data assignment for system c 3.6 determining cch link to send messages the tandem office must be programmed with the proper information to indicate how the cch (in its own system) is connected to other offices in the network. Every offi...
Page 48
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 1-15 data assignment for system a data assignment for system b data assignment for system c data assignment for system d 3.7 determining circuit identification code (cic) the gcd-ccta trunk must distinguish between voice path and common signaling channel. The trunk...
Page 49
Issue 2.0 1-16 general information figure 1-15 circuit identification codes (cic).
Page 50
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 1-17 3.8 determining numbering plan the uniform numbering plan is the numbering plan in the k-ccis network. The f-route (flexible route selection) and the automatic route selection (ars) feature provide the open numbering plan. When an outgoing call is placed throu...
Page 51
Issue 2.0 1-18 general information figure 1-16 closed numbering plan example 28 00 office location (access code analyzed by program 44-02-01) station number when a call is originated from office a to office c, 2800 is dialed. When using a closed numbering plan, the station numbers can have two to ei...
Page 52
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 1-19 figure 1-17 open numbering plan example when using the open numbering plan, the following combination of digits can be used: when the access code is set for two digits, the office code can have only two digits. Access code = xx office code = xx station number ...
Page 53
Issue 2.0 1-20 general information.
Page 54: Chapter 2
Sv9100 networking manual 2-1 chapter 2 univerge ® sv9100 hardware installation s ection 1 i nstallation p recautions preinstallation planning is essential. Advanced planning minimizes installation time, cost, and disruption of the customer business activities. Never install telephone wiring during a...
Page 55
Issue 2.0 2-2 hardware installation 1.1 busying out extension/line blades the extension/trunk blades may "busy-out" idle circuits. Extensions/lines cannot make or receive calls during this condition. Calls in progress before the blade is "made-busy" are not affected. The blade can be pulled out with...
Page 56
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 2-3 2.2 order of installing extension blades the order in which the station blades (esiu and sliu) are physically inserted determines the numbering plan. For example, when a digital station blade (gcd-16dlca) is in slot #1 (ext. 301~316) and three additional digita...
Page 57
Issue 2.0 2-4 hardware installation the system automatically recognizes each blade installed in the system. If a blade was previously installed in a slot and another type of blade is to be installed in that same slot, the blade must be removed from the chassis and then the slot definition removed us...
Page 58
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 2-5 s ection 3 i nstalling the gcd-ccta (ccis trunk interface) 3.1 description the gcd-ccta blade is common to both univerge sv9100 and sv9300 systems. The common channel handler interface blade is a digital trunk blade that terminates ft1 trunks (up to 24 ds-0 cha...
Page 59
Issue 2.0 2-6 hardware installation 3.2 installation install the gcd-ccta in any universal slot. 3.3 led indications led indications for the gcd-ccta are listed in table 2-4 gcd-ccta led indications . Each led is listed with its associated function and led and operational status. Refer to figure 2-3...
Page 60
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 2-7 3.4 connectors table 2-5 gcd-ccta rj-45 cable connector pin-outs shows the pin-outs for the rj-45 connector. Refer to figure 2-2 gcd-ccta blade on page 2-5 for an illustration showing the location of the connectors on the gcd-ccta blade. Figure 2-3 gcd-ccta led...
Page 61
Issue 2.0 2-8 hardware installation.
Page 62: Chapter 3
Sv9100 networking manual 3-1 chapter 3 univerge ® sv9100 system data programming s ection 1 k-ccis p rogramming this chapter lists the programs that must be assigned to support k-ccis. The programming used depends on the k-ccis features that are used. The tables provided in this section provide a co...
Page 63
Issue 2.0 3-2 system data programming 10-03-06 blade setup – number of ports auto 4 ports 8 ports 12 ports 16 ports 20 ports 10-03-07 blade setup – wiring type auto cross straight 14-05-01 trunk group assign trunk to trunk groups/outbound priority trunk group = 1~100 default is 1 priority = 1 ~ 400 ...
Page 64
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 3-3 1.2 ccis assignment use these programming assignments to set the availability of ccis. Table 3-2 ccis programming assignments program/ item no. Description/ selection assigned data comments 50-01-01 ccis system setting – ccis availability 0=disable 1=enable def...
Page 65
Issue 2.0 3-4 system data programming 1.3 numbering plan assignment use these programming assignments to indicate to the system the number of digits that are assigned to stations, the number of digits assigned to access codes, and to assign stations to ports. 1.4 programming for closed numbering pla...
Page 66
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 3-5 1.5 programming for open numbering plan use these programs to assign the number of digits to access code and to make ars assignments. 44-02-03 dial analysis table for ars/f-route access – additional data 2 = 0 ~ 500 (0 = no setting) default is 0 when setting da...
Page 67
Issue 2.0 3-6 system data programming 44-05-02 ars/f-route table – delete digits 0 = no setting 1 ~ 255 = number of digits to delete (255 = delete all) default is 0 enter the number of digits to be deleted from the dialed number. 44-05-03 ars/f-route table – additional dial number table 0 = no setti...
Page 68
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 3-7 1.6 closed number programming example this section provides the steps needed to program a closed numbering plan. Step 1: t1 tie lines the following diagram is an example of programs that should be assigned for t1 tie lines. The example assumes that the sv9100 s...
Page 69
Issue 2.0 3-8 system data programming step 2: closed numbering plan the following diagram provides an example of programs that should be assigned for closed numbering. The example assumes that step 1: t1 tie lines was completed. Ac = access code blk = closed numbering block mb = memory block acg = a...
Page 70
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 3-9 step 3: k-ccis activation the following diagram provides an example of programs that should be assigned for k-ccis. The example assumes that step 1: t1 tie lines and step 2: closing number plan are completed. Dstcch = destination point code cch = control channe...
Page 71
Issue 2.0 3-10 system data programming prg 50-02-04 prg 50-02-04 prg 50-02-04 ccis route id1 = dest. Point code 2 ccis route id1 = dest. Point code 1 ccis route id1 = dest. Point code 2 ccis route id2 = dest. Point code 3 prg 50-02-06 ccis route id1 = cch1 ccis route id2 = cch2 prg 50-03-01 prg 50-0...
Page 72
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 3-11 1.7 open number programming example this sections provides the steps needed to program an open numbering plan. Step 1: t1 tie lines the following diagram provides an example of program and item numbers that should be assigned for t1 tie lines. The example assu...
Page 73
Issue 2.0 3-12 system data programming step 2: open numbering plan the following diagram provides an example of programs and item numbers that should be assigned for open numbering. The example assumes that step 1: t1 tie lines was completed. Abbreviations used in the diagram: ac = access code acg =...
Page 74
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 3-13 step 3: k-ccis activation the following diagram provides an example of programs and item numbers that are assigned for k-ccis. The example assumes that step 1: t1 tie lines and step 2: open number plan are completed. Prg 44-05-02 prg 44-05-02 prg 44-05-02 f-ro...
Page 75
Issue 2.0 3-14 system data programming prg 50-02-02 prg 50-02-02 prg 50-02-02 ccis route id1 = 56k ccis route id1 = 56k ccis route id1 = 56k ccis route id2 = 56k prg 50-02-03 prg 50-02-03 prg 50-02-03 ccis route id1 = org. Point code 1 ccis route id1 = org. Point code 2 ccis route id1 = org. Point c...
Page 76
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 3-15 1.8 dedicated tandem co trunk calls the following diagram provides an example of sv9100 programs that should be assigned when all local and long distance co calls, from the remote site, are routed through the main site using flexible routing (f-routes) and aut...
Page 77
Issue 2.0 3-16 system data programming prg 44-02-02 analysis tbl1 = f-route analysis tbl2 = f-route prg 44-02-03 analysis tbl1 = data f-route 2 analysis tbl2 = data f-route 3 prg 44-05-01 f-route tbl1 = tg 10 f-route tbl2 = tg 10 f-route tbl3 = tg 10 prg 44-05-08 f-route tbl1 = ars treatment tbl1 pr...
Page 78
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 3-17 1.9 shared tandem co trunk calls the following diagram provides an example of programs and item numbers that should be assigned when two sites share co lines for reducing long distance calls using automatic route selection (ars). The example assumes that the u...
Page 79
Issue 2.0 3-18 system data programming prg 26-02-03 prg 26-02-03 ars analysis tbl1 = f-route tbl1 ars analysis tbl1 = f-route tbl1 ars analysis tbl2 = f-route tbl1 ars analysis tbl2 = f-route tbl1 ars analysis tbl3 = add data tg 01 ars analysis tbl3 = add data tg 01 prg 44-05-01 prg 44-05-01 f-route...
Page 80: Chapter 4
Sv9100 networking manual 4-1 chapter 4 univerge ® sv9100 features and specifications s ection 1 g eneral i nformation key-common channel interoffice signaling (k-ccis) allows multiple systems to be connected together to provide additional feature compatibility, above what normal tie lines provide. T...
Page 81
Issue 2.0 4-2 features and specifications hot line – k-ccis on page 4-76 multiple call forwarding – all calls – k-ccis on page 4-82 multiple call forwarding – busy/no answer - k-ccis on page 4-87 paging access – k-ccis on page 4-92 quick transfer to voice mail – k-ccis on page 4-100 station-to-stati...
Page 82
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 4-3 s ection 3 s ervice c onditions general: each univerge sv9100 system can have up to eight k-ccis routes. One gcd-ccta is required to support each k-ccis link. A maximum of eight k-ccis links are supported. The k-ccis feature shares the co/pbx/tie/did trunks ava...
Page 83
Issue 2.0 4-4 features and specifications are passed through and supported. An univerge sv9100 k-ccis network should never have more than five hops (tandem connections) because of the message delay through each tandem system. A star topology network supports up to eight systems. A tree topology netw...
Page 84
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 4-5 internal calls, transferred calls, and k-ccis calls do not provide caller id to single line telephones. Caller id call return feature is not supported with k-ccis calls. S ection 4 r elated f eature l ist t1 connections universal slots s ection 5 k-ccis f eatur...
Page 85: Automatic Recall – K-Ccis
Issue 2.0 4-6 features and specifications automatic recall – k-ccis f eature d escription this feature allows a call to be release transferred to another station in another office in the k-ccis network and recall back to the originator of the transfer after a programmed time. S ystem a vailability a...
Page 86
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 4-7 6. Hang up. S ervice c onditions if prg 34-07-05 is left at default (30) the transferred call recalls to the station that performed the transfer when not answered. A univerge sv9100 station can receive a k-ccis transferred call as a camp-on call if allowed by c...
Page 87: Brokerage Hotline – K-Ccis
Issue 2.0 4-8 features and specifications brokerage hotline – k-ccis f eature d escription this feature provides a ringdown connection between two stations, each using a multiline terminal, in different offices in the ccis network. S ystem a vailability all terminals required components: gcd-ccta - ...
Page 88
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 4-9 r elated f eature l ist call transfer – all calls - k-ccis station-to-station calling – k-ccis uniform numbering plan – k-ccis g uide to f eature p rogramming program/ item no. Description/selection assigned data comments 15-07-01 programmable function keys 01 ...
Page 89: K-Ccis
Issue 2.0 4-10 features and specifications call forwarding – all calls – k-ccis f eature d escription this feature allows all calls destined for a particular station to be routed to another station or to an attendant, in another office in the k-ccis network, regardless of the status (busy or idle) o...
Page 90
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 4-11 to set call forward – all calls – k-ccis from a multiline telephone (open numbering plan): 1. Press the call forward – all on/off key. 2. Dial 1 to set. 3. Dial the trunk access code (normally 9). 4. Dial the office code number. 5. Dial the distant k-ccis stat...
Page 91
Issue 2.0 4-12 features and specifications number. Trunk-to-trunk transfer must be allowed in prg 14-01-13 (trunk-to-trunk transfer yes/no selection). A single line telephone user can transfer a trunk call to another internal station that is set for call forwarding – all calls – k-ccis, however, whe...
Page 92
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 4-13 20-13-06 class of service options (supplementary service) – automatic off hook signaling (automatic override) 0 = off 1 = on default is 1 must be off for call forward – busy to operate. 15-07-01 programmable function keys 10 = call forward – immediate 11 = cal...
Page 93
Issue 2.0 4-14 features and specifications call forwarding – busy/no answer – k-ccis f eature d escription this feature permits a call to a busy or unanswered station to be forwarded to another station or an attendant, in another office in the k-ccis network. The activation and cancellation of this ...
Page 94
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 4-15 to set call forward – busy/no answer - k-ccis from a multiline telephone (open numbering plan): 1. Press the call forward – busy/no answer on/off key. 2. Dial 1 to set. 3. Dial the trunk access code (normally 8). 4. Dial the office code number. 5. Dial the dis...
Page 95
Issue 2.0 4-16 features and specifications trunk-to-trunk transfer must be allowed in prg 14-01-13 for each trunk (trunk-to-trunk transfer yes/no selection). A single line telephone user can transfer a trunk call to another internal station that is set for call forwarding – all calls - k-ccis, howev...
Page 96
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 4-17 15-07-01 programmable function keys 10 = call forward – immediate 11 = call forward – busy 12 = call forward – no answer 13 = call forward – busy no answer service codes: 741 742 743 744 14-01-13 basic trunk data setup – trunk-to-trunk transfer loop supervisio...
Page 97: K-Ccis Call Rerouting
Issue 2.0 4-18 features and specifications k-ccis call rerouting f eature d escription the ccis call rerouting feature allows a system to use multiple call routing priorities when remote system trunks are all busy. The four priorities can be local or remote trunks. For example using ars and f-route ...
Page 98
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 4-19 k-ccisoip license (5012) s ervice c onditions general: the originating system must have a dial treatment of d019re where 9 is the ars trunk access code in the destination system for this feature to work. Ars must be enabled in all systems for this feature to w...
Page 99
Issue 2.0 4-20 features and specifications programming example the following example will use the first two priorities of system a to route 10 digit local calls out trunk group one of system b and if that fails the call is routed out trunk group one of system a. This example assumes the following: s...
Page 100
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 4-21 44-02-02 closed numbering setup – set to f- route table (2). 2 2 44-02-03 closed numbering setup – set to use f-route table 1 for intercom calls. 1 1 44-05-01 closed numbering setup – set table 1 first priority to use ccis trunk group 10. 10 10 44-05-09 closed...
Page 101
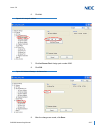
Issue 2.0 4-22 features and specifications g uide to f eature p rogramming this guide provides a list of associated programs that support this feature. . Program number program name/description input data default 10-12-01 gcd-cp10 network setup - ip address should be set to 0.0.0.0 when using prg 10...
Page 102
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 4-23 11-02-01 extension numbering assign extension numbers to extension ports. The telephone programming identity follows the port number – not the extension number. Maximum of eight digits. 1 101 2 102 ~ ~ 99 199 100 3101 ~ ~ 199 3200 200 3201 ~ ~ 960 3513 14-01-3...
Page 103
Issue 2.0 4-24 features and specifications 26-01-01 automatic route selection service – ars service ars must be enabled in all system for this feature to work. 0 = disabled (ars service is off) 1 = enabled (ars service is on) default = 0 26-01-06 automatic route selection service – class of service ...
Page 104
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 4-25 26-02-02 dial analysis table for ars – ars service type for each dial analysis table used (1~2000), select service type 2 – f-route selected to have the dialed number controlled by the f- route table. If service type 2 is selected and f-route operation is on, ...
Page 105
Issue 2.0 4-26 features and specifications 44-02-03 dial analysis table for ars/f-route access – additional data if a service type is set to f-route in program 44-02-02, set which f-route table to use. 1 = delete digit = 0 ~ 255 (255: delete all digits) 2 = 0 ~ 500 (0 = no setting) 3 = dial extensio...
Page 106
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 4-27 50-03-01 ccis destination system settings – destination point code assign the destination transfer point code for tandem kts. 0 ~ 16367 default = 0 50-03-03 ccis destination system settings – ip address (ip only) assign remote system ip network information xxx...
Page 107
Issue 2.0 4-28 features and specifications call park retrieve – k-ccis f eature d escription this feature allows a station user to retrieve parked calls at remote sites across k-ccis. Locally parked calls can be retrieved from a remote system, connected via k-ccis, by dialing the call park hold grou...
Page 108
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 4-29 a station connected to a pbx can retrieve a parked call in an univerge sv9100, but the station connected to the univerge sv9100 system cannot retrieve a parked call in a pbx. A park hold key cannot be used to retrieve a parked call from a distant system. F-rou...
Page 109
Issue 2.0 4-30 features and specifications g uide to f eature p rogramming this guide provides a list of associated programs that support this feature. Park originate system remote system (call park retrieve) program/ item no. Description/selection assigned data comments 11-12-32 answer for park *6 ...
Page 110
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 4-31 44-02-03 dial analysis table for ars/ f-route access – additional data 0 = no setting 1 = delete digits = 0~255 (255 = delete all digits) 2 = 0~500 3 = dial extension analyze table number = 0~4 default is 0 enter additional data required for the service type s...
Page 111
Issue 2.0 4-32 features and specifications programming example: for the following example, to retrieve a call which is parked, use the following access codes from any system: call parked at call park retrieve access codes notes system a 501+05 501 = system a call park retrieve access code 05 = park ...
Page 112
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 4-33 prg 44-02-01 table 2 = dial 502 (ars table #4) (park retrieve system b) prg 44-02-01 table 2 = dial 501 (park retrieve system a) prg 44-02-01 table 2 = dial 501 (park retrieve system a) prg 44-02-01 table 3 = dial 503 (park retrieve system c) prg 44-02-01 tabl...
Page 113
Issue 2.0 4-34 features and specifications call transfer – all calls – k-ccis f eature d escription this feature allows a station user to transfer incoming or outgoing central office, intraoffice, and interoffice calls to another station in the k-ccis network without attendant assistance. For more d...
Page 114
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 4-35 using a multiline terminal with a call in progress (open numbering plan): 1. Press transfer, and receive internal dial tone. The call is placed on non-exclusive hold. 2. Dial the trunk access code (normally 8). 3. Dial the office code number. 4. Dial the dista...
Page 115
Issue 2.0 4-36 features and specifications g uide to f eature p rogramming this guide provides a list of associated programs that support this feature. Program/ item no. Description/selection assigned data comments 20-09-07 class of service options (incoming call service) – call queuing 0 = off 1 = ...
Page 116
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 4-37 calling name display – k-ccis f eature d escription this feature permits the station name of a calling or called party at another switching office to be displayed on a multiline terminal, through the k-ccis network. For more details, refer to the univerge sv91...
Page 117
Issue 2.0 4-38 features and specifications r elated f eature l ist calling number display – k-ccis station-to-station calling – k-ccis uniform numbering plan – k-ccis g uide to f eature p rogramming this guide provides a list of associated programs that support this feature. Program/ item no. Descri...
Page 118
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 4-39 calling number display – k-ccis f eature d escription this feature permits the number of a calling or called party at another switching office, to be displayed on a multiline terminal through the k-ccis network. For more details, refer to the univerge sv9100 f...
Page 119
Issue 2.0 4-40 features and specifications r elated f eature l ist calling name display – k-ccis station-to-station calling – k-ccis uniform numbering plan – k-ccis g uide to f eature p rogramming this guide provides a list of associated programs that support this feature. Program/ item no. Descript...
Page 120: Station – K-Ccis
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 4-41 calling party number (cpn) presentation from station – k-ccis f eature d escription calling party number (cpn) presentation from station k-ccis feature allows each station of the remote systems a unique 10-digit number (the did number of the originating statio...
Page 121
Issue 2.0 4-42 features and specifications outbound call. The calling party number (cpn) is not sent to the network when the originating station of the remote system calls a station in the main system that is call forwarded off site. R elated f eature l ist isdn compatibility automatic route selecti...
Page 122
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 4-43 centralized billing – k-ccis f eature d escription this feature sends the billing information from local systems to a billing center office for central management of all billing information in the network. The univerge sv9100 can send billing information to a ...
Page 123
Issue 2.0 4-44 features and specifications restrictions: in a k-ccis network, the pbx must be the main system where billing information is sent. Centralized billing cannot be used in a kts-to-kts network. Station-to-station calls in their own system are not reported to the billing center office with...
Page 124
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 4-45 g uide to f eature p rogramming this guide provides a list of associated programs that support this feature. For centralized billing installation program/ item no. Description/ selection assigned data comments 14-01-24 basic trunk data setup – trunk-to-trunk o...
Page 125
Issue 2.0 4-46 features and specifications for station message detail recording (smdr) for centralized billing k-ccis program/ item no. Description/selection assigned data comments 21-01-03 system options for outgoing calls – trunk interdigit time (external) 0~64800 seconds default is 5 the system w...
Page 126: Centralized Blf (K-Ccis)
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 4-47 centralized blf (k-ccis) f eature d escription this feature provides a busy indication for another station across the k-ccis network on programmed direct station selection/busy lamp field (dss/blf) keys. The busy indication is a red led associated with a featu...
Page 127
Issue 2.0 4-48 features and specifications using a feature access or a one-touch key programmed for centralized dss/blf: 1. Press the programmed feature access or one-touch key. Hear ringback tone. 2. When the called party answers, lift the handset or talk using handsfree if allowed. S ervice c ondi...
Page 128
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 4-49 blf receiving service conditions: blf information can be received for up to 120 remote extensions per system. All multiline terminals in the system can assign centralized dss/blf keys for the supported remote extensions. The led indication of the dss/blf butto...
Page 129
Issue 2.0 4-50 features and specifications r elated f eature l ist do not disturb (dnd) feature access – user programmable voice mail message indication on line keys g uide to f eature p rogramming (f or m ain s ystem ) this guide provides a list of associated programs that support this feature. (fo...
Page 130
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 4-51 (for receiving system) 50-10-01 ccis centralized blf interval time assignment – type of interval time 0 = 4 seconds 1 = 8 seconds 2 = 12 seconds 3 = 16 seconds default is 0 assign blf sending interval to each sending system. Program/ item no. Description/selec...
Page 131
Issue 2.0 4-52 features and specifications centralized day/night mode change – k-ccis f eature d escription this feature switches the day/night mode of a remote office that is linked to a main office using k-ccis, in accordance with the day/night mode switching from an attendant position at the main...
Page 132
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 4-53 - or - 1. Press the night transfer key on the attendant add-on console. Remote office: no manual operation is required. S ervice c onditions general: a maximum of 16 remote offices can be controlled by one main office. If automatic day/night mode switching is ...
Page 133
Issue 2.0 4-54 features and specifications r elated f eature l ist assigned night answer (ana) authorization code automatic day/night mode switching centralized billing – k-ccis code restriction dial access to attendant – k-ccis direct inward termination (dit) flexible ringing assignment night call ...
Page 134
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 4-55 for night transfer feature 50-11-02 ccis centralized day/night switching sending group assignment – ccis route id send group (1~16) ccis route id (0~8) 0 = no setting default is 0 select the remote office to send day/night switching control message. 50-12-01 c...
Page 135
Issue 2.0 4-56 features and specifications 30-03-01 dss console key assignment key number (001~114) 00~99 = general functional level *00~*99 = appearance functional level default is extensions. 101~160 customize key assignments for dss consoles 1~32. 20-07-01 class of service options (administrator ...
Page 136: Centralized E911 – K-Ccis
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 4-57 centralized e911 – k-ccis f eature d escription this feature allows a remote system to transmit a calling party number to the 911 emergency system over a k-ccis direct or tandem connection. S ystem a vailability terminal type: all stations required components ...
Page 137
Issue 2.0 4-58 features and specifications dispatcher from hearing the caller. It is recommended that this option be kept at its default setting of 0 to prevent any problems with dialing 911. The attendant receives a notification each time a co-worker dials an emergency 911 call. This notification i...
Page 138
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 4-59 g uide to f eature p rogramming this guide provides a list of associated programs that support this feature. Program/ item no. Description/ selection assigned data comments 20-08-13 class of service options (outgoing call service) – isdn clip 0=off 1=on defaul...
Page 139
Issue 2.0 4-60 features and specifications dial access to attendant – k-ccis f eature d escription this feature allows a station user to call an attendant by dialing a call code through the k-ccis network. For more details, refer to the univerge sv9100 features and specifications manual. S ystem a v...
Page 140
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 4-61 this feature is also available when the attendant console is in a neax2000 ivs2 or neax2400 in the ccis network. When an univerge sv9100 station calls a neax desk console attendant position, operator is displayed on the lcd during the incoming ring. If using a...
Page 141
Issue 2.0 4-62 features and specifications for remote system 20-17-01 operator extension – operator extension number up to eight digits default is 101. Define extension numbers that are used as operators. Assign only in kts-to-kts network. Program/ item no. Description/selection assigned data commen...
Page 142
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 4-63 programming example (dest pc) 44-05-09 ars/f-route table – maximum digit 0~24 default is 0 assign max. Digits for call park retrieve access code. 44-05-10 ars/f-route table – ccis over ip destination point code 0~16367 default is 0 assign remote ip destination...
Page 143
Issue 2.0 4-64 features and specifications program 44-05-09 table 1 = max digit 1 program 44-05-09 table 1 = max digit 1 * program 44-05-10 f-route table 1 dpc = 1 *program 44-05-10 f-route table 1 dpc = 1 * for ccisoip programming only. System a (101s) system b (201s) system c (301s).
Page 144
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 4-65 direct inward dialing – k-ccis f eature d escription this feature allows an incoming did call (centralized did) to be routed directly across a k-ccis link to reach a station in the remote system without attendant assistance. For more details, refer to the univ...
Page 145
Issue 2.0 4-66 features and specifications restrictions: program 20-02-15 (caller id display mode) must be set to 0 to display the did name on incoming did calls. Refer to the key-common channel interoffice signaling (k-ccis) feature for more details related to single line telephone and ip (k-ccis) ...
Page 146: Dual Hold – K-Ccis
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 4-67 dual hold – k-ccis f eature d escription this feature allows two connected multiline telephones to be placed on hold simultaneously over the k-ccis link. This enables the held parties to answer or originate a call from a secondary line or intercom path. For mo...
Page 147
Issue 2.0 4-68 features and specifications g uide to f eature p rogramming this guide provides a list of associated programs that support this feature. Program/ item no. Description/selection assigned data comments 24-01-01 system options for hold – hold recall time 0~64800 seconds default is 90 a c...
Page 148
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 4-69 elapsed time display – k-ccis f eature d escription this feature provides an elapsed call time on the lcd which shows the duration of time that a multiline terminal is connected to any call through the k-ccis network. For more details, refer to the univerge sv...
Page 149
Issue 2.0 4-70 features and specifications r elated f eature l ist station-to-station calling – k-ccis g uide to f eature p rogramming this guide provides a list of associated programs that support this feature. Program/ item no. Description/selection assigned data comments 20-13-36 class of service...
Page 150
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 4-71 flexible numbering of stations – k-ccis f eature d escription this feature allows telephone numbers to be assigned to any stations in the k-ccis network, based solely upon numbering plan limitations. Station numbers can be assigned by the 10's group for 4-digi...
Page 151
Issue 2.0 4-72 features and specifications s ervice c onditions general: give careful consideration to the network numbering plan to avoid needless loss of access codes or duplication of telephone numbers. The first digit or first two digits of a telephone number distinguishes one system from anothe...
Page 152
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 4-73 11-20-01 dial extension analyze table – dial (up to eight digits) use tables 01~128 to assign the digits to be dialed using the dial extension analyze tables. These tables are used when program 11-01-01 is set to option 9 = dial extension analyze. (up to eight...
Page 153
Issue 2.0 4-74 features and specifications handsfree answerback – k-ccis f eature d escription this feature allows multiline telephone station users to respond to voice calls through a k-ccis network without lifting the handset. For more details, refer to the univerge sv9100 features and specificati...
Page 154
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 4-75 r elated f eature l ist voice calls – k-ccis g uide to f eature p rogramming this guide provides a list of associated programs that support this feature. Program/ item no. Description/selection assigned data comments 11-16-03 single digit service code setup – ...
Page 155: Hot Line – K-Ccis
Issue 2.0 4-76 features and specifications hot line – k-ccis f eature d escription this feature allows two stations at different nodes in the k-ccis network to be mutually associated on automatic ringdown through the k-ccis network. For more details, refer to the univerge sv9100 features and specifi...
Page 156
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 4-77 call transfer – all calls - k-ccis station-to-station calling – k-ccis uniform numbering plan – k-ccis g uide to f eature p rogramming this guide provides a list of associated programs that support this feature. Program/item no. Description/ selection assigned...
Page 157: Link Reconnect – K-Ccis
Issue 2.0 4-78 features and specifications link reconnect – k-ccis f eature d escription this feature provides the system that is connected to a k-ccis network with the ability to release the redundant k-ccis link connections and reconnect the link with the system for efficient usage of the k-ccis t...
Page 158
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 4-79 a trunk call (co/pbx/tie/did/k-ccis) over a k-ccis network is transferred or forwarded to another station or trunk within the same office as the original incoming trunk. (refer to figure 4-2 link reconnect for trunk tandem calls .) figure 4-1 link reconnect fo...
Page 159
Issue 2.0 4-80 features and specifications link reconnect occurs after answering a transferred or forwarded k-ccis call. Restrictions: answer supervision is required for link reconnect to occur. For outgoing calls on analog trunks, answer supervision is based on the elapsed call time - program 21-01...
Page 160
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 4-81 when connecting a sv9100 to a neax pbx, link reconnect needs to be turned off in the pbx to the sv9100. R elated f eature l ist call forwarding – all calls – k-ccis call forwarding – busy/no answer – k-ccis call transfer – all calls – k-ccis multiple call forw...
Page 161
Issue 2.0 4-82 features and specifications multiple call forwarding – all calls – k-ccis f eature d escription this feature allows a multiple call forwarding – all calls sequence to be forwarded over a k-ccis network to a station in another office. For more details, refer to the univerge sv9100 feat...
Page 162
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 4-83 to set call forward – all calls – k-ccis from a multiline telephone (open numbering plan): 1. Press the call forward – all call on/off key, and dial 1 to set. 2. Dial the trunk access code (normally 8). 3. Dial the office code number. 4. Dial the distant k-cci...
Page 163
Issue 2.0 4-84 features and specifications for multiple call forwarding – all calls/busy (immediate) calls, the display on the calling party multiline telephone displays the terminating station user name and the station number for the first station of a distant system in the multiple call forwarding...
Page 164
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 4-85 r elated f eature l ist call transfer – all calls – k-ccis call forwarding – all calls – k-ccis call forwarding – busy/no answer – k-ccis multiple call forwarding – busy/no answer – k-ccis link reconnect – k-ccis uniform numbering plan – k-ccis figure 4-3 mult...
Page 165
Issue 2.0 4-86 features and specifications g uide to f eature p rogramming this guide provides a list of associated programs that support this feature. Program/item no. Description/selection assigned data comments 20-06-01 class of service for extensions 0~15 default: ext.101 is in class 15. All oth...
Page 166
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 4-87 multiple call forwarding – busy/no answer - k-ccis f eature d escription this feature allows a multiple call forwarding – busy/no answer sequence to be forwarded over a k-ccis network to a station in another office. For more details, refer to the univerge sv91...
Page 167
Issue 2.0 4-88 features and specifications to set call forward – busy/no answer - k-ccis from a multiline telephone (open numbering plan): 1. Press the call forward – busy/no answer on/off key. 2. Dial 1 to set. 3. Dial the trunk access code (normally 8). 4. Dial the office code number. 5. Dial the ...
Page 168
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 4-89 to cancel for any station for attendant positions only: 1. Pick up the handset or press speaker. 2. Dial the call forward busy/no answer for any extension to destination service code (default: 793). 3. Dial 0(cancel). 4. Dial the station number, which is forwa...
Page 169
Issue 2.0 4-90 features and specifications in program 50-05-01 (k-ccis maximum call forwarding hop assignment). Multiple call forwarding – all calls – k-ccis can forward a call a maximum of seven times across k-ccis link (maximum of seven hops) depending on system data assignments. An example of mul...
Page 170
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 4-91 g uide to f eature p rogramming this guide provides a list of associated programs that support this feature. Program/item no. Description/selection assigned data comments 20-06-01 class of service for extensions 0~15 default: ext.101 is in class 15. All others...
Page 171: Paging Access – K-Ccis
Issue 2.0 4-92 features and specifications paging access – k-ccis f eature d escription this feature allows users to access internal or external paging from remote sites across the k-ccis network. Local stations where the external paging equipment is installed can use the meet-me answer feature to a...
Page 172
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 4-93 program 31-02-01 (internal paging group number) applies to paging access – (k-ccis). Program 31-02-02 (internal all call paging receiving) applies to paging access – (k-ccis). Restrictions: amplifiers and speakers must be locally provided. Combined paging is n...
Page 173
Issue 2.0 4-94 features and specifications 11-12-22 service code setup (service access) – meet me answer to external paging default is 765 the service code assigned in this program is used for meet me answer to external paging. 15-07-01 programmable function keys 19 = external. Group paging 1~8 20 =...
Page 174
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 4-95 for remote system 31-06-01 external speaker control – broadcast splash tone before paging (paging start tone) 0 = no tone 1 = splash tone 2 = chime tone default is 2 enable splash tone before paging. 31-06-02 external speaker control – broadcast splash tone af...
Page 175
Issue 2.0 4-96 features and specifications 44-05-01 ars/f-route table – trunk group number 0 = not set 1 ~ 100 = trunk group from 14-05 101 ~ 150 networking 255 = extension call default is 0 select trunk group number used for outgoing ars calls. Setting 255 = internal extension call. 44-05-02 ars/f-...
Page 176
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 4-97 programming example (external) paging access for system a = 511(0~9) paging access for system b = 512(0~9) system a (101s) system b (201s) prg 11-01-01 51 = 2 digits: f-route prg 11-01-01 51 = 2 digits: f-route prg 11-12-20 external paging = 703 (page system a...
Page 177
Issue 2.0 4-98 features and specifications programming example (internal) paging access for system a = 521 paging access for system b = 522 prg 44-05-03 table 1 = add dial 1 table 2 = add dial 0 prg 44-05-03 table 1 = add dial 1 table 2 = add dial 0 prg 44-05-09 table 1 = max digit 0 table 2 = max d...
Page 178
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 4-99 program 44-06-01 table 1 = dial 701 program 44-06-01 table 1 = dial 701 system a (101’s) system b (201’s).
Page 179
Issue 2.0 4-100 features and specifications quick transfer to voice mail – k-ccis f eature d escription a station user transferring a call can force the call to be transferred to the called party voice mail box after the transferred call recalls, after an internal station number is dialed while perf...
Page 180
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 4-101 s ervice c onditions general: the quick transfer to voice mail feature is allowed when: listening to the ring back tone (rbt) listening to the call waiting tone (cwt) in handsfree answerback mode in voice over mode this feature is allowed from a single line t...
Page 181
Issue 2.0 4-102 features and specifications programming example 45-01-14 voice mail integration options – ccis centralized voice mail number up to eight digits default not assigned. Default is no setting assign the ccis centralized voice mail pilot number for remote sites. Program/ item no. Descript...
Page 182
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 4-103 station-to-station calling – k-ccis f eature d escription this feature permits any multiline terminal user to dial another multiline terminal directly through a k-ccis network. For more details, refer to the univerge sv9100 features and specifications manual....
Page 183
Issue 2.0 4-104 features and specifications r elated f eature l ist call transfer – all calls - k-ccis calling name display – k-ccis calling number display – k-ccis dual hold – k-ccis elapsed time display – k-ccis flexible numbering of stations – k-ccis hands-free answerback – k-ccis key-common chan...
Page 184
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 4-105 uniform numbering plan – k-ccis f eature d escription in a k-ccis network, a uniform numbering plan enables a multiline terminal user to call any other multiline terminal in the network. Two types of numbering plans are provided. In the first plan, the statio...
Page 185
Issue 2.0 4-106 features and specifications s ervice c onditions general: in a closed numbering plan, the location of the office can be identified by the first digit or first two digits of the telephone number. In an open numbering plan, each office in the k-ccis network is assigned a one-, two- or ...
Page 186: Voice Call – K -Ccis
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 4-107 voice call – k -ccis f eature d escription this feature provides a voice path, through the k-ccis network, between a mlt in one office and a mlt in another office. This path is established from the calling party to the called party built-in speaker. If the ca...
Page 187
Issue 2.0 4-108 features and specifications during voice call, the icm key is flashing (red). Restrictions: the calling party must wait for at least one ring back before voice call is attempted. After the calling party changes ring back to voice call, it cannot be changed back to tone. Voice call ca...
Page 188
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 4-109 voice mail integration – k-ccis f eature d escription this feature allows any station user in the k-ccis network to use the voice mail system (vms) in another office in the k-ccis network. For more details, refer to the univerge sv9100 features and specificat...
Page 189
Issue 2.0 4-110 features and specifications 1. When finished hang up. To program a one-touch/feature access key for easy message access: 1. Press feature. 2. Dial 751. 3. Press one-touch/feature access key. 4. Dial 1, followed by voice mail extension number. 5. Press hold. S ervice c onditions gener...
Page 190
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 4-111 in a kts to kts network, centralized voice mail is supported only via closed numbering plan and only up to 7-digit station numbers. In a pbx to kts network, centralized voice mail is supported only via closed numbering plan. In a pbx to kts network, centraliz...
Page 191
Issue 2.0 4-112 features and specifications r elated f eature l ist key-common channel interoffice signaling (k-ccis) call forwarding – all calls - k-ccis call forwarding – busy/no answer - k-ccis multiple call forwarding – all calls - k-ccis multiple call forwarding – busy/no answer - k-ccis g uide...
Page 192
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 4-113 16-02-01 department group assignment for extensions groups 1~64 priority 1~999 default = 1-xxx assign the department groups. The initial priority value becomes the numerical port order assigned in prg 11-02 and 11-04 (ports 1~256). 11-11-01 service code setup...
Page 193
Issue 2.0 4-114 features and specifications 20-11-12 class of service options (hold/transfer service) – call forwarding off premise (external call forwarding) 0 = off 1 = on default is 0 enable call forward – off-premise at an extension. 20-11-13 class of service options (hold/transfer service) – op...
Page 194
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 4-115 30-03-01 dss console key assignment key numbers 001~114 00~99 = general functional level *00~*99 = appearance function level default is extensions. 101~160 customize key assignments for dss consoles 1~32. 45-01-01 voice mail integration options – voice mail d...
Page 195
Issue 2.0 4-116 features and specifications.
Page 196: Chapter 5
Sv9100 networking manual 5-1 chapter 5 univerge ® sv9100 sv9100 ip k-ccis this chapter describes the system outline, hardware installation, and programming procedures for providing ip k-ccis using the gpz-iple on the univerge sv9100 system. S ection 1 s ystem o utline 1.1 ip k-ccis application using...
Page 197
Issue 2.0 5-2 sv9100 ip k-ccis the gpz-iple is required for connections between ip terminals and ip trunks. A maximum of one gpz-iple can be accommodated per system with a maximum of 256 dsp resources per system. 1.2 description the gpz-iple board is an optional interface package for converting the ...
Page 198
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 5-3 calling from a tdm phone and out a ip trunk uses one dsp. Calling from a tdm phone across ip k-ccis to another tdm phone uses one dsp. Calling from an ip phone across ip k-ccis to another ip phone uses two dsp resources at each location. 1.3 systems requirement...
Page 199
Issue 2.0 5-4 sv9100 ip k-ccis 1.4.1 hot swap the gpz-iple is not hot swappable and cannot be removed from the gcd-cp10 without first powering down the chassis and removing the gcd-cp10. 1.4.2 connectors the gpz-iple has the following connectors: cn1 - rj-45 gigabit ethernet lan interface cn3 - conn...
Page 200
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 5-5 1.4.7 led indications refer to figure 5-3 gcd-cp10 blade with daughter board installed . Figure 5-3 gcd-cp10 blade with daughter board installed gpz-iple blade battery.
Page 201
Issue 2.0 5-6 sv9100 ip k-ccis see figure 5-4 gcd-cp10 led locations for the location of the leds on the blade. Led indications for the gpz-iple daughter board are shown in table 5-1 voipdb led indications . Each led is listed with its associated function, led status and operation status. Figure 5-4...
Page 202
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 5-7 the following table shows the led indication when transmitting or receiving data on cn1. Table 5-2 voipdb led cn1 transmit/receive data indications led link up auto negotiation mode force mode 1000m bps 100mbps 10mbps 1000m bps 100mbps 10mbps half full half ful...
Page 203
Issue 2.0 5-8 sv9100 ip k-ccis 1.4.8 connectors figure 5-5 voip connections shows a typical connection layout. Figure 5-6 connecting a voipdb to a network/pc on page 5-9 illustrates how to connect a voip daughter board to a network or pc. Figure 5-5 voip connections gcd-cp10 gpd-8/16dlcb.
Page 204
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 5-9 1.5 ip addressing figure 5-6 connecting a voipdb to a network/pc shows how the voipdb is connected to a network or pc. One valid ip address must be assigned for all the dsp's that are used in iple. Figure 5-6 connecting a voipdb to a network/pc (.
Page 205
Issue 2.0 5-10 sv9100 ip k-ccis the gpz-iple needs only one ip address. 1.5.1 general ip configuration the voice quality of voip depends on variables such as available bandwidth, network latency, and quality of service initiatives (qos), all of which are controlled by the network and internet servic...
Page 206
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 5-11 ip precedence ip precedence uses the first three bits of the tos field to give eight possible precedence values (0~7). Under normal circumstances, the higher the number, the higher the priority. However, the administrator can assign these precedence values wit...
Page 207
Issue 2.0 5-12 sv9100 ip k-ccis dscp dscp stands for differential services code point (or diffserv for short). It uses the first 6 bits of the tos field, therefore, giving 64 possible values. The following table lists the most common dscp code points, the binary value, and the associated name. Table...
Page 208
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 5-13 the following table shows the 8 bit tos field and the associated diffserv bits. Assignments for the ip precedence/diffserv values in the system are submitted in command 84-10. Rtp/rtcp = voice packets ccis= signaling packets table 5-6 tos field with diffserv s...
Page 209
Issue 2.0 5-14 sv9100 ip k-ccis 1.5.3 bandwidth the bandwidth required for voip calls depends on several factors. Layer 2 media codec packet size rtp header compression voice activity detection (vad) number of simultaneous calls possibly add encryption after research. Layer 2 media is concerned with...
Page 210
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 5-15 voip packet with rtp header compression voice activity detection (vad) is suppression of silence packets from being sent across the network. In a voip network all conversations are packetized and sent, including silence. On an average a typical conversation co...
Page 211
Issue 2.0 5-16 sv9100 ip k-ccis bandwidth calculation ( [ layer 2 overhead + ip/udp/rtp header + voice payload ] / voice payload ) * default codec speed = total bandwidth example of a g.711 call over ethernet using a 20 ms packet size and not using rtp header compression (.020 * 64000) / 8 = 160 byt...
Page 212
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 5-17 1.5.6 some network considerations before adding the univerge sv9100 to a customer network, a detailed network diagram of the existing network must be obtained from the customer. This diagram provides information about any network condition that can prevent or ...
Page 213
Issue 2.0 5-18 sv9100 ip k-ccis firewall another regular device in customer networks that can hinder voip performance is a firewall. Most corporate lans connect to the public internet through a firewall. A firewall is filtering software built into a router or a stand alone server unit. It is used to...
Page 214
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 5-19 vpn another common feature is the use of the internet as the wan between customer locations. When this is done vpns are typically used between the locations. A vpn (virtual private network) is a private data network that maintains privacy through the use of tu...
Page 215
Issue 2.0 5-20 sv9100 ip k-ccis s ection 2 univerge sv9100 c hassis p rogramming the following data programs are used when installing the gpz-iple daughter board for univerge sv9100 ip (k-ccis). If any address or nic setting is changed, the system must be reset for the changes to take affect. 2.1 di...
Page 216
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 5-21 10-19-01 voip dsp resource selection – voip dsp resource selection slot number 1: dsp resource number: 01 ~ 256 0 = common use for both ip extensions and trunks 1 = ip extension 2 = sip trunk 3 = networking/ccis 4 = netlink 5 = blocked 6 = common without unica...
Page 217
Issue 2.0 5-22 sv9100 ip k-ccis 2.2 voip ip address assignments for this feature, the gpz-iple, daughter board is installed on the gcd-cp10 blade. The gpz-iple daughter board reduces the maximum capacity of trunks in the system. 22-02-01 incoming call trunk setup – trunk type 001 ~ 400 0 = normal 1 ...
Page 218
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 5-23 2.3 local numbering plan assignment use these programs to assign system, extension and virtual extension numbering for the local numbering plan. 2.4 closed numbering plan – using closed number blocks use these programs to assign system numbering and ars/f-rout...
Page 219
Issue 2.0 5-24 sv9100 ip k-ccis 2.5 open numbering plan – using ars table 1, 2, or 3 use these programs to assign system numbering, ars/f-route dialed digits and trunk groups as well as other ars/f-route table information for an open numbering plan. 44-02-03 dial analysis table for ars/f-route acces...
Page 220
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 5-25 44-05-01 ars/f-route table – trunk group number 0-100,101-150,255 0 = not set 1~100 = trunk group from prg 14-05 101~150 = networking 255 = extension call default is 0 select the trunk group to be used for the outgoing k-ccis call. 44-05-02 ars/f-route table –...
Page 221
Issue 2.0 5-26 sv9100 ip k-ccis 2.6 ip k-ccis assignment use these programs to assign ccis availability, origination and destination point codes for ip k-ccis. 2.7 ip k-ccis (peer-to-peer) assignment use these programs to assign the ccips over ip connection method and the tcp server port number. Tab...
Page 222
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 5-27 2.8 ccis over ip codec information setup use these programs to assign ccis over ip codec information, including the number of g.711/g.723/g.729 type, number of audio frames, voice activity detection mode, jitter buffers and other codec related information. Tab...
Page 223
Issue 2.0 5-28 sv9100 ip k-ccis 84-21-08 ccis over ip codec information basic setup – g.729 voice activity detection mode 0 = disable 1 = enable default is 0 84-21-09 ccis over ip codec information basic setup – g.729 jitter buffer min 0 ~ 300 ms default is 30 84-21-10 ccis over ip codec information...
Page 224
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 5-29 84-21-27 ccis over ip codec information basic setup – g.722 audio frame number 1 ~ 4 1 = 10 ms 2 = 20 ms 3 = 30 ms 4 = 40 ms default is 3 84-21-29 ccis over ip codec information basic setup – g.722 jitter buffer (min) 0 ~ 300 ms default is 30 84-21-30 ccis ove...
Page 225
Issue 2.0 5-30 sv9100 ip k-ccis 2.9 sip-mlt codec information fixed mode setup use these programs to assign the fixed mode audio capacity and number of audio frames for the sip mlt.. 84-21-36 ccis over ip codec information basic setup – g.726 jitter buffer (max) 0 ~ 300 ms default is 120 84-21-37 --...
Page 226
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 5-31 84-29-02 sip-mlt codec information fixed mode setup – number of audio frames type: 1 ~ 6 1 = multicast 2 = reserved 3 = reserved 4 = reserved 5 = reserved size 1 = 10ms 2 = 20ms 3 = 30ms 4 = 40ms 5 = 50ms 6 = 60ms default is 2 program/ item no. Description/sel...
Page 227
Issue 2.0 5-32 sv9100 ip k-ccis s ection 3 p rogramming e xample 3.1 sv9100 ip k-ccis programming example 1 this is an example of univerge sv9100 program data assignments for a 4-digit closed numbering plan using closed number blocks. The following system configurations are used for all four systems...
Page 228
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 5-33 3.1.1 card interface slot assignment (prg 10-03) the following slot assignments were set using program 10-03. 3.1.2 digital trunk assignments this example shows digital trunk assignments made for systems a and b. Slot card type during 1st power on card type an...
Page 229
Issue 2.0 5-34 sv9100 ip k-ccis 3.1.3 voip address assignments this example shows voip address assignments made for systems a and b. 3.1.4 ip k-ccis availability this example shows ip k-ccis availability assignments made for systems a and b. 3.1.5 ip k-ccis assignment this example shows ip k-ccis as...
Page 230
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 5-35 3.1.6 ip k-ccis (peer-to-peer) assignment this example shows ip k-ccis peer-to-peer assignments made for systems a and b. 3.1.7 local numbering plan assignment this example shows local numbering plan assignments made for systems a and b. System a system b prog...
Page 231
Issue 2.0 5-36 sv9100 ip k-ccis 3.1.8 closed numbering plan – using closed number blocks this example shows closed numbering plan assignments made for systems a and b. System a system b program 11-01-01 dial 10 = 4 digit; extension dial 11 = 4 digit; f-route program 11-01-01 dial 10 = 4 digit; f-rou...
Page 232
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 5-37 3.1.9 tandem connections this example shows tandem connections assignments made for systems a and b. Figure 5-12 tel 302 (sip mlt) makes call to tel 202 (sip mlt) via ip k-ccis illustrates calls between two sip multiline terminals over ip-ccis. System a system...
Page 233
Issue 2.0 5-38 sv9100 ip k-ccis 3.2 univerge sv9100 ip k-ccis and electra elite ipk ii programming example 2 the following example provides programming details for three systems connected by the ip cch for neax application and one system connected by legacy (t1) k-ccis. 3.2.1 chassis programming ass...
Page 234
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 5-39 each system has 16 multiline terminals. Each system has eight analog trunks. Assume that the systems were defaulted (first power on) with the following cards installed as described below. Card interface slot assignment (prg 10-03) system a slot card type durin...
Page 235
Issue 2.0 5-40 sv9100 ip k-ccis 3.2.2 digital trunk assignments this example shows digital trunk assignments for systems a, b and c. System c slot card type during 1st power on card type and ports card type ports 1 gcd-cp10 with gpz-iple blade/daughter board gcd-cp10 with gpz-iple blade/daughter boa...
Page 236
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 5-41 3.2.3 cch assignment this example shows cch assignments for systems a, b and c. Program 22-02-01 trunks 9 ~ 32 assign lk 6 (tie line) program 10-40-04 assign number of ports for ccis for slot 1 = 24 program 22-02-01 trunks 5 ~ 28 assign lk 6 (tie line) program...
Page 237
Issue 2.0 5-42 sv9100 ip k-ccis s ection 4 p ort d esignations this section provides port number designations for ip applications. Program 50-02-02 1. Select ccis route id 1 2. Assign data speed lk 2 (56k) program 50-02-01 1. Select ccis route id 1 2. Assign channel port 28 program 50-02-02 1. Selec...
Page 238
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 5-43 s ection 5 ccis n etworking via ip (p eer - to -p eer c onnections b asis ) description ip-kccis supports peer-to-peer calls between ip terminals residing in different offices, without using dsp resources. Two dsp resources in each office/system are consumed f...
Page 239
Issue 2.0 5-44 sv9100 ip k-ccis s ection 6 s ervice c onditions for inmail remote ccis extensions are not supported in a centralized directory. Dt800/dt700 terminals are supported for peer-to-peer connections via a p2p ccis call. Standard sip terminals are not supported for peer-to-peer connection. ...
Page 240
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 5-45 sv9100 to sv9100 or neax pbx (sv9300, sv9500, etc.), ip terminal to ip terminal via peer-to-peer, the ip terminals' codec must match and the packet size is auto negotiated. Sv9100 to neax pbx (sv9300, sv9500, etc.), ip terminal to tdm via peer-to- peer, the ip...
Page 241
Issue 2.0 5-46 sv9100 ip k-ccis ■ ip k-ccis – ccis networking ■ common – common usage for ccis networking, 3rd party sip station, sip mlt stations, sip trunks. ■ pressing feature + 4 from any mlt terminal shows the following: what type of gpz-iple daughter board is installed on the gcd-cp10. How man...
Page 242
Book 2 – sv9100 ip networking.
Page 243: Chapter 1
Sv9100 networking manual 1-1 chapter 1 univerge ® sv9100 general information s ection 1 univerge sv9100 ip n etworking univerge sv9100 is an enterprise ip telephony solution that allows businesses and organizations to converge their voice and data network to secure the many advantages of ip telephon...
Page 244
Issue 2.0 1-2 general information table 1-1 voip specifications category feature notes ip address dhcp server gcd-cp10 dhcp client ip phone qos 802.1p/1q gcd-cp10 l3 qos (tos) diffserv/ip precedence maintenance http server gcd-cp10 vlan tag and port-based vlan vocoder g.711 µ-law/a-law g.729a jitter...
Page 245: Chapter 2
Sv9100 networking manual 2-1 chapter 2 univerge ® sv9100 ip networking s ection 1 i ntroduction1 ip networking uses voip technology to connect two or more telephone systems together. This allows calls to be made between sites without using the public telephone network. This saves considerable money,...
Page 246
Issue 2.0 2-2 ip networking s ection 3 ip t runks the sip trunks method of networking allows connection to sip devices. This could be a pbx system or a third-party product. When using sip, the feature set is limited and the advanced networking features cannot be used. If these features are required,...
Page 247
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 2-3 s ection 4 e xample c onfigurations 4.1 network configurations figure 2-1 example ip network configuration shows four sites networked via ip trunks. Each site has a point code and an ip address. The programing for office a and c is shown below. This would be su...
Page 248
Issue 2.0 2-4 ip networking 4.2 univerge sv9100 ip k-ccis programming example 1 this is an example of univerge sv9100 program data assignments for a 4-digit closed numbering plan using closed number blocks. The following system configurations are used for all four systems: each system is a single ca...
Page 249
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 2-5 4.2.1 card interface slot assignment (prg 10-03 etu setup) the following table provides information for assigning the blade interface slots. 4.2.2 digital trunk assignments use the table below to make the appropriate assignments for digital trunks. Note it is a...
Page 250
Issue 2.0 2-6 ip networking 4.2.3 voip address assignments use the table below to make the appropriate assignments for voipdb (gpz-iple) addresses. 4.2.4 ccis availability use the table below to make the appropriate assignments for ccis availability. 4.2.5 ip ccisoip assignment use the table below t...
Page 251
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 2-7 4.2.6 ccis assignment use the table below to make the appropriate system-wide ccis assignments. System a system b program 50-03-01 1. System id 1~255 – enter destination point code 2. System id 1 = dpc 02 program 50-03-01 1. System id 1~255 – enter destination ...
Page 252
Issue 2.0 2-8 ip networking 4.2.7 centralized day night switching assignments use the table below to make the appropriate assignments for centralized day and night switching. System a system b prg 50-06-02 ccis feature availability - centralized day/night switching 0 = disable (default) 1 = enable p...
Page 253
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 2-9 4.2.8 centralized blf assignments use the table below to make the appropriate assignments for centralized blf. System a system b prg 50-08-01 ccis centralized blf sending group assignment – destination point code select group id (1~8) + destination point code. ...
Page 254
Issue 2.0 2-10 ip networking 4.2.9 local numbering plan assignment use the table below to make local numbering plan assignments. 4.2.10 closed numbering plan - using closed number blocks use the table below to make closed numbering plan assignments. Program/ item no. Description/ selection assigned ...
Page 255
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 2-11 4.2.11 tandem connections use the table below to make assignments for tandem connections. S ection 5 dtmf r elay when sending dtmf over an sv9100 ccisoip network it may be necessary to configure the item below. This allows the sending univerge sv9100 to detect...
Page 256
Issue 2.0 2-12 ip networking.
Page 257: Chapter 3
Sv9100 networking manual 3-1 chapter 3 univerge ® sv9100 general ip configuration s ection 1 i ntroduction the univerge sv9100 system uses ip for various applications, including: system programming voice over ip switching this section describes the procedure for connecting the univerge sv9100 system...
Page 258
Issue 2.0 3-2 general ip configuration a public address is normally only used when a device is directly connected to the internet. This is unlikely in the case of the equipment. If public addressing is used, the numbers are normally allocated by an isp. 2.2 subnet mask as the ip address includes inf...
Page 259
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 3-3 s ection 3 c onfiguration e xamples the following configuration examples illustrate a typical network configuration for an existing network that uses a static address and a typical configuration for a new network that uses a dynamic address. 3.1 example configu...
Page 260
Issue 2.0 3-4 general ip configuration assume that a univerge sv9100 is added to the existing data network. The network administrator (or it manager) should provide the following: ip address (for the gcd-cp10 blade) ip addresses (for the gpz-iple daughter board) subnet mask default gateway a spare s...
Page 261
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 3-5 3.2 example configuration 2 - new network with dynamic addressing figure 3-3 example configuration 2 - new network with dynamic addressing on page 3-6 shows a typical network configuration using dynamic ip addressing, and the univerge sv9100 internal dhcp serve...
Page 262
Issue 2.0 3-6 general ip configuration the network administrator (or it manager) should provide the following: ip address (for the gcd-cp10 blade) ip addresses (for the gpz-iple) subnet mask default gateway range(s) of ip addresses to assign list of permanent ip addresses, with corresponding mac add...
Page 263
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 3-7 if the client pcs are now connected to the network (and restarted), they should be assigned an ip address in the range 192.168.1.50 to 192.168.1.150, a subnet mask of 255.255.255.0 and a default gateway of 192.168.1.254. When the server tries to obtain an ip ad...
Page 264
Issue 2.0 3-8 general ip configuration s ection 4 t esting the univerge sv9100 n etwork c onnection to test the univerge sv9100 network connection, it is possible to use the icmp (internet control message protocol) ping command. This basically sends a small amount of data from one device to another ...
Page 265: Chapter 4
Sv9100 networking manual 4-1 chapter 4 univerge ® sv9100 programming s ection 1 b efore y ou s tart p rogramming this chapter provides you with detailed information about the univerge sv9100 program blocks that may be required to connect the sv9100 to a data network and to configure the voip functio...
Page 266
Issue 2.0 4-2 programming the second row of the display ky01 = *01 indicates that key 01 is being programmed with the entry of *01. The third row allows you to move the cursor to the left or right, depending on which arrow is pressed. To learn how to enter the programming mode, refer to section 2 ho...
Page 267
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 4-3 s ection 3 h ow to e xit p rogramming m ode to exit the programming mode: to exit programming mode, first exit the programming options mode. 1. Press answer to exit program options, if needed. 2. Press speaker. If changes were made to the system programming, sa...
Page 268
Issue 2.0 4-4 programming s ection 5 p rogramming n ames and t ext m essages several programs (e.G., program 20-16: selectable display messages) require you to enter text. Use the following chart when entering and editing text. When using the keypad digits, press the key once for the first character...
Page 269
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 4-5 s ection 6 u sing s oftkeys f or p rogramming each univerge sv9100 display telephone provides interactive softkeys for intuitive feature access. The options for these keys will automatically change depending on where you are in the system programming. Simply pr...
Page 270
Issue 2.0 4-6 programming s ection 7 w hat the s oftkey d isplay p rompts m ean when using a display telephone in programming mode, various softkey options are displayed. These keys will allow you to easily select, scan, or move through the programs. S ection 8 p rograms this sections describes the ...
Page 271: 10-03 : Etu Setup
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 4-7 description use program 10-03 : etusetup to setup and confirm the basic configuration data for each blade. When changing a defined terminal type, first set the type to 0 and then plug the new device in to have the system automatically define it or you may have ...
Page 272
Issue 2.0 4-8 programming 02 logical port number (b1) 0 = not set 1 = multiline terminal (1~960) 6 = pgd(2)-u13 (paging) (1~8) 7 = pgd(2)-u13 (for tone ringer) (1~8) 8 = pgd(2)-u13 (for door box) (1~8) 9 = pgd(2)-u13 (for aci) (1~96) 10 = dss (1~32) 11 = --- not used --- 0 03 --- not used --- b-chan...
Page 273
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 4-9 for lca pkg setup for cotc unit setup 11 handset option information 0 = no option 1 = psa/psd 2 = bluetooth cordless handset 0 physical port number 01~16 item no. Item input data default 01 logical port number 0~960 0 03 transmit gain level (s-level) 1~57 (-15....
Page 274
Issue 2.0 4-10 programming for odtb pkg setup for diop pkg setup physical port number 01~04 item no. Item input data default 01 logical port number 0~400 0 02 2/4 wire 0 = 2 wire 1 = 4 wire 1 03 e&m line control method 0 = type i 1 = type v 0 physical port number 01~04 item no. Item input data defau...
Page 275
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 4-11 for bria pkg setup isdn line number 01~04 item no item input data default 01 isdn line mode 0 = not used 1 = t-point:1~400 2 = s-point:1~960 3 = nw mode (leased line): 1~256 4 = nw mode (interconnected line): 1~256 5 = nw mode (interconnected line, fixed layer...
Page 276
Issue 2.0 4-12 programming 14 s-point service protocol 0 = keypad facility 1 = specified protocol 0 15 s-point call busy mode 0 = alerting message 1 = disconnect message 0 17 isdn line ringback tone if telco does not provide ringback tone, sv9100 can if set to 1:enable. 0 = disable 1 = enable 0 18 t...
Page 277
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 4-13 for prta pkg setup isdn line number 01~24 item no. Item input data default 01 --- not used --- 02 logical port number the start port number of a pri line is displayed. 1 = for t-bus 1~400 1 03 --- not used --- 04 layer 3 timer type each timer value of layer 3 ...
Page 278
Issue 2.0 4-14 programming 13 loss-of-signal detection limit if the transmit/receive voltage is less than the setting in 10-03-13, the system considers this as loss-of-signal and the prta does not come up. Note that there are different values based on the setting in 10-03-12 for the pri. 0 = level 0...
Page 279
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 4-15 for dti (t1) pkg setup 23 straight/cross wiring 0 = auto 1 = manual (cross) 2 = manual (straight) 0 physical port number 01~24 item no. Item input data default 01 logical port number the start port number of a t1 line is displayed, and 24 logic ports are autom...
Page 280
Issue 2.0 4-16 programming for iple pkg setup for vm00 pkg setup for ccta pkg setup physical port number 001~256 item no. Item input data default 01 voip type 0 = not used 1 = not used 2 = not used 3 = iple none (will be determined when installed) 02 number of channels 0 ~ 256 (read only) 0 03 numbe...
Page 281
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 4-17 conditions when changing a defined terminal type, first set the type to 0 and then plug the new device in to have the system automatically define it, or redefine the type manually. The system must have a blade installed to view/change the options for that type...
Page 282: 10-04 : Music On Hold Setup
Issue 2.0 4-18 programming description use program 10-04 : music on hold setup to set the music on hold (moh) source. For internal music on hold, the system can provide a service tone callers on hold or one of eleven synthesized selections. Conditions none program 10 : system configuration setup 10-...
Page 283
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 4-19 feature cross reference analog communications interface (aci) background music music on hold.
Page 284
Issue 2.0 4-20 programming description use program 10-12 : gcd-cp10 network setup to setup the ip address, subnet-mask, and default gateway addresses. Program 10 : system configuration setup 10-12 : gcd-cp10 network setup level: sa input data item no. Item input data default description 01 ip addres...
Page 285
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 4-21 04 time zone 0~24 (0 = -12 hours and 24 = +12 hours) +7 (-5 hours) determine the offset from greenwich mean time (gmt) time. Then enter its respective value. For example, eastern time (us and canada) has a gmt offset of -5. The program data would then be 7 (0=...
Page 286
Issue 2.0 4-22 programming conditions none feature cross reference voice over internet protocol (voip) 11 nic setup 0 = auto detect 1 = 100mbps, full-duplex 3 = 10mbps, full-duplex 5 = 1 gbps, full-duplex 0 set for iple. 13 dns primary address 0.0.0.0 ~ 126.255.255.254 128.0.0.1 ~ 191.255.255.254 19...
Page 287: 10-13 : In-Dhcp Server Setup
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 4-23 description use program 10-13 : in-dhcp server setup to setup the dhcp server built into the gcd-cp10 blade. Conditions the system must be reset in order for these changes to take affect. Feature cross reference voice over internet protocol (voip) program 10 :...
Page 288
Issue 2.0 4-24 programming description use program 10-14 : managed network setup to set up the range of the ip address which the dhcp server leases to a client. Conditions none feature cross reference voice over internet protocol (voip) program 10 : system configuration setup 10-14 : managed network...
Page 289
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 4-25 description use program 10-15 : client information setup to set up the client information when the dhcp server needs to assign a fixed ip address to clients. Conditions none feature cross reference voice over internet protocol (voip) program 10 : system config...
Page 290
Issue 2.0 4-26 programming description use program 10-16 : option information setup to set up the option given from the dhcp server to each client. Program 10 : system configuration setup 10-16 : option information setup level: sa input data item no. Item input data default 01 router set the router ...
Page 291
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 4-27 09 encryption information set an encryption information used for autoconfig (for dt800/dt700 series). Code number 0~255 43 (fixed) sub code number 164 maximum 128 character strings no setting 10 ftp server address set a ftp server address used for autoconfig. ...
Page 292
Issue 2.0 4-28 programming 18 ftp server code number 0~255 141 (fixed) ip address 0.0.0.0 ~ 126.255.255.254 128.0.0.1 ~ 191.255.255.254 192.0.0.1 ~ 223.255.255.254 0.0.0.0 19 config file name code number 0~255 151 (fixed) maximum 15 character strings no setting 20 lds server 1 code number 0~255 162 ...
Page 293
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 4-29 conditions none feature cross reference voice over internet protocol (voip).
Page 294
Issue 2.0 4-30 programming description use program 10-19 : voip dsp resource selection to define the criteria for each dsp resource on the voip blade. Conditions none feature cross reference none program 10 : system configuration setup 10-19 : voip dsp resource selection level: sa input data slot nu...
Page 295
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 4-31 description use program 10-54 : license configuration for each package to set the license information for each unit. Conditions if applying more than 255 licenses to a slot the licenses must be applied across multiple indexes. For example assigning 256 voip re...
Page 296
Issue 2.0 4-32 programming description use program 15-05 : ip telephone terminal basic data setup to set up the basic settings for an ip telephone. Program 20 : system option setup 15-05 : ip telephone terminal basic data setup level: in input data extension number maximum eight digits item no. Item...
Page 297
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 4-33 18 ip duplication allowed group 0 = disable 1 = enable 0 when this program is 1 = enable, the duplication of an ip address is allowed at the time of sip/dt700 terminal registration. 10-03-09 15-05-22 19 side option information 0 = no option 1 = 8lk unit 2 = 16...
Page 298
Issue 2.0 4-34 programming 26 d800/dt700 terminal type 0 = not set 1 = itl-**e-1d/ip-*e-1 2 = itl-**d-1d/itl- 12bt1d/itl- 12pa-1d [without 8lki(lcd)-l] 3 = itl-**d-1d/itl-12bt- 1d/itl-12pa-1d [with 8lki(lcd)-l] 4 = itl-320c-1 5 = softphone 6 = cti 7 = agw 8 = ip3at-8wv 9 = not used 10 = itl-**dg-3 1...
Page 299
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 4-35 31 alarm tone during conversation (rtp packet loss alarm) 0 = not ringing 1 = ringing 1 32 key calling 0 = not used 1 = used 0 33 lan side ip address of terminal 0.0.0.0~255.255.255.255 0.0.0.0. Read-only 34 terminal touch panel on/off 0 = off 1 = on 1 set whe...
Page 300
Issue 2.0 4-36 programming 43 video mode 0 = disable 1 = enable 0 this program is used to select the video function with the standard sip terminal. If the standard sip terminal supports the video function, the sv9100 transfers the video codec in sdp information. 44 using standard sip display for cpn...
Page 301
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 4-37 conditions 15-05-04 – nickname must be unique in the system. The system programming must be exited before these program options take affect. Feature cross reference voice over internet protocol (voip) 49 receiving sip info 0 = disable 1 = allowed any time 2 = ...
Page 302: 84-09 : Vlan Setup
Issue 2.0 4-38 programming description use program 84-09 : vlan setup to set up the vlan data. Conditions system programming must be exited before these program options take affect. Feature cross reference voice over internet protocol (voip) program 84 : hardware setup for voip 84-09 : vlan setup le...
Page 303: 84-10 : Tos Setup
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 4-39 description use program 84-10 : tos setup to set up the type of service data. Program 84 : hardware setup for voip 84-10 : tos setup level: in input data protocol type 1 = not used 2 = not used 3 = voice control 4 = h.323 5 = rtp/rtcp 6 = sip 7 = ccisoip 8 = s...
Page 304
Issue 2.0 4-40 programming conditions the system must be reset for these program options to take affect. Feature cross reference voice over internet protocol (voip).
Page 305
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 4-41 description use program 84-21 : ccis over ip codec information basic setup to set the codec parameters of the gpz-iple. Program 84 : hardware setup for voip 84-21 : ccis over ip codec information basic setup level: in input data item no. Item input data defaul...
Page 306
Issue 2.0 4-42 programming 19 1st priority of audio capability 0 = g.711 pt 2 = g.729 pt 3 = g.722 4 = g.726 0 20 2nd priority of audio capability 0 = g.711 pt 2 = g.729 pt 3 = g.722 pt 4 = g.726 pt 2 22 jitter buffer mode 1 = static 3 = self adjusting 3 23 voice activity detection threshold 0 ~ 30 ...
Page 307
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 4-43 conditions none feature cross reference voice over internet protocol (voip).
Page 308: 84-33: Fax Over Ip Setup
Issue 2.0 4-44 programming description use program 84-33 : fax over ip setup to set up the parameters of the fax over ip function. Program 84 : hardware setup for voip 84-33: fax over ip setup level: in index 1 type 1 = h.323 trunk 2 = networking 3 = sip trunk 4 = sip extension 5 = ccis over ip 6 = ...
Page 309
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 4-45 conditions none feature cross reference voice over internet protocol (voip) 10 t.38 tcf method 1 = voipdb 2 = g3fe 1 11 t.38 ecm (error correction mode) 0 = disable 1 = enable 1 12 fax codec 1 = g.711 a-law 2 = g.711 u-law 3 = g.726 1 13 payload size 1 ~ 4 (10...
Page 310
Issue 2.0 4-46 programming description use program 90-23 : deleting registration of ip telephones to delete the registered ip telephone from the system. Conditions none feature cross reference voice over internet protocol (voip) program 90 : maintenance program 90-23 : deleting registration of ip te...
Page 311: 90-34 : Firmware Information
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 4-47 description use program 90-34 : firmware information to list the package type and firmware blades installed in the system. Conditions these programs are ‘read only.’ feature cross reference none program 90 : maintenance program 90-34 : firmware information lev...
Page 312
Issue 2.0 4-48 programming.
Page 313: Chapter 5
Sv9100 networking manual 5-1 chapter 5 univerge ® sv9100 network design considerations s ection 1 i ntroduction this chapter explains some issues that should be considered when planning a univerge sv9100 voip installation. This is a generalized explanation and therefore does not discuss vendor-speci...
Page 314
Issue 2.0 5-2 network design considerations of all the delays at the different network devices and across the network links through which voice traffic passes. Many factors contribute to end-to-end delay, which are covered next. The buffering, queuing, and switching or routing delay of ip routers pr...
Page 315
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 5-3 users. If packet drops become epidemic, the quality of all transmissions degrades. Packet loss rate must be less than five percent for minimum quality and less than one percent for toll quality. 2.2 voice quality improvements this section describes various tech...
Page 316
Issue 2.0 5-4 network design considerations used at certain times of the day for data connectivity. This data connectivity is very light, only 20kbps or so during most of the day, but does spike to 50kbps during certain points of the day. This data is not time sensitive like the voice data, so if ne...
Page 317
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 5-5 ip precedence - layer 3 qos: allows you to specify the class of service for a packet. You use the three precedence bits in the ipv4 header type of service (tos) field for this purpose. Using the tos bits, you can define up to six classes of service. Other devic...
Page 318
Issue 2.0 5-6 network design considerations network address translation (nat) usually, the equipment that your isp provides (cable modem, adsl router, etc.) uses network address translation. This allows several devices to share one public ip address. The issues relating to the use of nat are outline...
Page 319
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 5-7 it is necessary to create some kind of intranet environment (across the internet), with fixed network characteristics, where voip solutions can tolerate some minor variations. It personnel have been tasked with implementing different mechanisms in the network t...
Page 320
Issue 2.0 5-8 network design considerations 4.3 virtual private network (vpn) tunnelling a virtual private network is a private data network that maintains privacy through using a tunneling protocol and security procedures. Allowing for remote networks (including voip devices), which reside behind n...
Page 321
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 5-9 vpns can be implemented in hardware or software. Single users, such as traveling sales personnel, may have a software based vpn client on their laptop computer. This connects back to the head office vpn server. For larger sites, the vpn is typically implemented...
Page 322
Issue 2.0 5-10 network design considerations the common scenario for remote ip deployment is: implementation of an ip phone with a public ip address talking with an univerge sv9100 behind nat. An example would be a telecommuter. Implementation of an ip phone behind a nat, which connects to the inter...
Page 323
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 5-11 g.726 g.726 is an itu-t adpcm speech codec standard covering voice transmission at rates of 16, 24, 32, and 40kbit/s. It was introduced to supersede both g.721, which covered adpcm at 32kbit/s, and g.723, which described adpcm for 24 and 40kbit/s. G.726 also i...
Page 324
Issue 2.0 5-12 network design considerations 5.2 bandwidth the bandwidth required for voip calls depends on several factors, including: number of simultaneous calls codec used frame size data networking protocol used univerge sv9100 ccis network parameters the more frames encapsulated into each pack...
Page 325
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 5-13 s ection 6 dsp r esource c alculation voice over ip (neci sip, sip stations, sip trunks) requires dsp resources to be able to convert from tdm 3 to ip technologies. Dsps (digital signal processors) take a tdm signal and convert to realtime transport protocol (...
Page 326
Issue 2.0 5-14 network design considerations to calculate the maximum dsps required: the manual calculations listed below are used in the univerge sv9100. Non-peer-to-peer mode (program15-05-50=0): it is easy to calculate the maximum number of dsps for a system that is not peer-to-peer. This is a si...
Page 327
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 5-15 for this example, each end of the network has only.One host typically, many hosts are sending data over the narrow bandwidth. The routers buffer packets and transmit them over the wan lines as efficiently as possible. When this occurs, certain packets are drop...
Page 328
Issue 2.0 5-16 network design considerations figure 5-4 voice and data network implementation shows how a voice and data network can be implemented. After the router is configured for qos, it examines incoming packets and allocates a priority to the packet. Figure 5-5 priority queuing on voice and d...
Page 329
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 5-17 to enable this type of queuing it is necessary to: a configure the voip equipment to mark its packets with a specific value so that the switches/routers can identify that it is voice – called marking. B configure the network equipment to recognize the differen...
Page 330
Issue 2.0 5-18 network design considerations protocol structure - ieee 802.1p: lan layer 2 qos figure 5-6 protocol structure for layer 2 qos illustrates the format of an ethernet frame and the user priority field that is used for layer 2 qos. The following define the fields used for the protocol str...
Page 331
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 5-19 user priority - defines user priority, giving eight priority levels. Ieee 802.1p defines the operation for these three user priority bits. Cfi - canonical format indicator is always set to zero for ethernet switches. Cfi is used for compatibility reason betwee...
Page 332
Issue 2.0 5-20 network design considerations figure 5-7 ethernet frame example - layer 2 qos enabled (continued) 802.1q virtual lan 101. .... .... .... = priority: 5 (layer 2 priority = 5) ...0 .... .... .... = cfi: 0 .... 0000 0110 0011 = id: 99 type: ip (0x0800) internet protocol, src addr: 172.16...
Page 333
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 5-21 7.3 layer 3 qos qos is most commonly implemented at layer 3. This allows the voip packets to be prioritized by routers, before they are forwarded to their next hop. Layer 3 qos uses the type of service (tos) field of the ip packet. This is an 8-bit field in th...
Page 334
Issue 2.0 5-22 network design considerations listed below are the fields used in figure 5-8 layer 3 qos example . Version – the version of ip currently used. Ip header length (ihl) – datagram header length. Points to the beginning of the data. The minimum value for a correct header is 5. Type-of-ser...
Page 335
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 5-23 7.4 ip precedence ip precedence is a qos method that combines a priority value with different on/off parameters; delay, throughput, reliability and cost. The mbz (must be zero) bit is not used. Using the tos bits, you can define up to eight classes of service....
Page 336
Issue 2.0 5-24 network design considerations 7.5 diffserv (differentiated service) differentiated services (diffserv) uses the tos field in an ip header. Diffserv is now commonly used instead of ip precedence (refer to 7.4 ip precedence on page 5-23 ) as it provides greater flexibility. This method ...
Page 337
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 5-25 7.6 comparison of ip precedence and diffserv values as stated earlier, ip precedence and diffserv use the same 8-bit tos field in the ip header to mark packets. It is possible to have the same tos value for either method which means that the two methods can wo...
Page 338
Issue 2.0 5-26 network design considerations table 5-3 ip precedence and diffserv values comparison dscp decimal dscp binary ip precedence description 0 000000 0 class selector 0 1 000001 2 000010 3 000011 4 000100 5 000101 6 000110 7 000111 8 001000 1 class selector 1 9 001001 10 001010 af11 (assur...
Page 339
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 5-27 29 011101 30 011110 af33 (assured forwarding) 31 011111 32 100000 4 class selector 4 33 100001 34 100010 af41 (assured forwarding) 35 100011 36 100100 af42 (assured forwarding) 37 100101 38 100110 af43 (assured forwarding) 39 100111 40 101000 5 class selector ...
Page 340
Issue 2.0 5-28 network design considerations 7.7 programming qos in the univerge sv9100 system 7.7.1 marking voice traffic - program 84-10-xx before programming the univerge sv9100 system, discuss the requirements with the network engineering staff or the managed network provider. If the tos marking...
Page 341
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 5-29 7.7.3 configuring diffserv use program 84-10-10 to select the logic for marking the tos field (refer to program 84-10 : tos setup on page 5-32 ). The choices are: table 5-5 diffserv configuration number tos mode programs enabled 0 none none – tos bits are: 000...
Page 342
Issue 2.0 5-30 network design considerations 7.7.4 configuration examples for classification and queuing figure 5-10 common network with cisco router shows a typical network scenario and an example of a cisco router configuration. This document provides a general description of voip technology, but ...
Page 343
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 5-31 configuration example explanation: 1. Defines a class map called voipclass. 2. Matches any packets that have the tos field set to ip precedence 5 / dscp 40 and assigns them to voipclass. 3. Defines a policy map called voippolicy. 4. Creates a class called voip...
Page 344: 84-10 : Tos Setup
Issue 2.0 5-32 network design considerations description use program 84-10 : tos setup to set up the type of service data. Program 84 : hardware setup for voip 84-10 : tos setup level: in input data protocol type 1 = not used 2 = not used 3 = voice control 4 = h.323 5 = rtp/rtcp 6 = sip 7 = ccisoip ...
Page 345
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 5-33 conditions the system must be reset for these program options to take affect. Feature cross reference voice over internet protocol (voip) s ection 8 p ort d esignations the following lists the port numbers for supported ip applications. 07 priority (d.S.C.P. -...
Page 346
Issue 2.0 5-34 network design considerations ip trunk voice with gpz-iple 10020~10531 udp sv9100 netlink primary system signaling 58000/58001 tcp secondary system signaling 58002 tcp ip dsp resource with gpz-iple 10020~10531 udp nec proprietary sip (sip mlt) sip mlt signaling 5080 udp sip trunk voic...
Page 347: Chapter 6
Sv9100 networking manual 6-1 chapter 6 univerge ® sv9100 sip trunking s ection 1 d escription the univerge sv9100 ip trunk sip package sends the real time voice over the corporate lan or wan. The voice from the telephone is digitized and then put into frames to be sent over a network using internet ...
Page 348
Issue 2.0 6-2 sip trunking conditions the option to set the sip trunk codec to g711 or g729 fixed is supported in program 84-13-28. A maximum of 400 ip trunks are supported in the sv9100. The sv9100 supports g.711 or t.38 for fax. The sv9100 does not support fallback to g.711 from g.729/g.726 for da...
Page 349
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 6-3 voipdb cancels the vad and echo canceller automatically when changed into the vbd codec. Rtp forwarding (program 10-26-02) is not running if vad is enabled. When using vad on sdp (version 7000 or higher) the setting is effective for g.711 and g.729 codec types....
Page 350
Issue 2.0 6-4 sip trunking s ection 2 sip t runk e.164 s upport description with sip trunk e.164 support enabled, the pbx is able to support sip configurations where the number presentation within the sip messages is formatted using the e.164 international numbering scheme. Specifically the system i...
Page 351
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 6-5 terminals all multiline terminals trunks ip sip required component(s) gcd-cp10 gpz-iple r2 enhancement license (0412) system port license (0300) voip resource license (5103) ip trunk license (5001) s ection 3 sip t runk e.164 clip e nhancement description with ...
Page 352
Issue 2.0 6-6 sip trunking default settings disabled system availability terminals all multiline terminals trunks ip sip required component(s) gcd-cp10 gpz-iple r2 enhancement license (0412) system port license (0300) voip resource license (5103) ip trunk license (5001) s ection 4 v ideo s upport ov...
Page 353
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 6-7 changed to a video call. A video caller cannot use cti/oai at the same time as the cti/oai feature needs p2p to be set to off. When the video interconnection using a sip trunk is configured, other sip connections, such as a sip carrier connection is not support...
Page 354
Issue 2.0 6-8 sip trunking feature. Level 3 – these programs are not often assigned and require an expert level working knowledge of the system to be properly assigned. Ip trunk – (sip) session initiation protocol: program number program name/description input data default level 1 2 3 10-12-03 gcd-c...
Page 355
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 6-9 10-12-11 gcd-cp10 network setup – nic setup define the lan interface speed and mode of the voip application supported. iple daughter board does not support half duplex connection. 0 = auto detect 1 = 100mbps, full duplex 3 = 10mbps, full duplex 5 = 1gbps, ful...
Page 356
Issue 2.0 6-10 sip trunking 10-28-05 sip system information setup – domain assignment define the domain assignment. This entry is determined by what information the sip carrier provides. If the sip carrier provides a server name: sipconnect-sca@l0.Cbeyond.Net, then the domain is: l0.Cbeyond.Net and ...
Page 357
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 6-11 10-29-06 sip server information setup – registrar ip address define the registrar ip address. The carrier may provide an ip address. In most cases, a domain name is used so this entry is left at the default. 0.0.0.0 ~ 126.255.255.254 128.0.0.1 ~ 191.255.255.25...
Page 358
Issue 2.0 6-12 sip trunking 10-29-15 sip server information setup – registration expiry (expire) time this program defines the sip trunk registration timer. This timer is negotiated between the carrier and the sv9100 during the registration process. The carrier will make the final decision on the va...
Page 359
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 6-13 10-37-02 upnp setup – retry time define the retry time for upnp. 0, 60 ~ 3600 (1 ~ 59 cannot be input) 60 10-54-01 license configuration for each package – license code assign voip resource licenses (5103) to gcd-cp10 slot (1). 1 ~ 255 resource licenses 0 10-6...
Page 360
Issue 2.0 6-14 sip trunking 14-05-01 trunk group – trunk group number assign trunks to trunk groups. Trunk port 1 ~ 400 = priority 1 ~ 400 default = trunks 1 ~ 400 assigned to trunk group 1 with priorities equal to the trunk number. Trunk 1 = priority 1 trunk 400 = priority 400. 14-18-05 ip trunk da...
Page 361
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 6-15 22-02-01 incoming call trunk setup assign the incoming trunk type for each trunk. Trunks 1 ~ 400 0 = normal 1 = vrs (second dial tone if no vrs installed) 2 = disa 3 = did 4 = dil 5 = e&m tie line 6 = delayed vrs 7 = ani/dnis 8 = did(ddi) mode switching 0 44-0...
Page 362
Issue 2.0 6-16 sip trunking 84-10-02 tos setup – priority, ip precedence 1 = router queuing priority. 0 ~ 7 0 = low 7 = high 0 84-10-03 tos setup – low delay 1 = optimize for low delay routing. 0 ~ 1 0 = normal delay, low delay 0 84-10-04 tos setup – wideband (throughout) 1 = optimize for high bandw...
Page 363
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 6-17 84-13-07 sip trunk codec information basic setup – number of g.729 audio frames set the g.729 audio frame number. 1 = 10ms 2 = 20ms 3 = 30ms 4 = 40ms 5 = 50ms 6 = 60ms (profile 1 ~ profile 2) 2 84-13-08 sip trunk codec information basic setup – g.729 voice act...
Page 364
Issue 2.0 6-18 sip trunking 84-13-33 sip trunk codec information basic setup – number of g.722 audio frames define the number of g.722 audio frames. 1 ~ 4 1 = 10ms 2 = 20ms 3 = 30ms 4 = 40ms (profile 1 ~ profile 2) 3 84-13-35 sip trunk codec information basic setup – g.722 jitter buffer (min) define...
Page 365
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 6-19 84-13-65 sip trunk codec information basic setup – vad negotiation on sdp used to determine the vad method for setting vad information on sdp. This is effective when vad is enabled on each codec. supports g.711 and g.729. 0 = disable 1 = enable (default = 0)...
Page 366
Issue 2.0 6-20 sip trunking 84-14-10 sip trunk basic information setup – url type define the url type for sip trunks. 0 = sip-url 1 = tel-url 0 84-14-11 sip trunk basic information setup – url/to headersetting information when set to a 0 (proxy server domain), the sv9100 will use the proxy settings ...
Page 367
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 6-21 sip trunk e.164 support sip trunk e.164 clip enhancement program number program name/description input data default level 1 2 3 10-02-01 location setup – country code enter the country code. Dial (maximum of four digits) 0 ~ 9, , # 1 10-02-02 location setup – ...
Page 368
Issue 2.0 6-22 sip trunking video support over sip trunks 84-14-13 sip trunk basic information setup – incoming/ outgoing sip trunk for e.164 when this data is set to 1, then for any outbound sip calls a + is added as a prefix to the request-uri, to and from header fields of the sip message. When it...
Page 369
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 6-23 10-12-09 gcd-cp10 network setup – ip address set ip address for iple. the ip address assigned in program 10-12-01 cannot start with the same leading digits as the ip address assigned here. 0.0.0.0 ~ 126.255.255.254 128.0.0.1 ~ 191.255.255.254 192.0.0.1 ~ 223...
Page 370
Issue 2.0 6-24 sip trunking 10-36-02 sip trunk registration information setup – user id assign the sip user id provided by your sip carrier. In most cases this is your 10 digit main billing number. This field is also used to send outbound caller id information when not programmed on a per station or...
Page 371
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 6-25 15-05-50 ip telephone terminal basic data setup – peer to peer mode on a per station basis enable or disable peer to peer mode. for video call to function set to 1 (enable). 0 = disable 1 = enable 1 20-08-13 class of service options (outgoing call service) –...
Page 372
Issue 2.0 6-26 sip trunking operation sip trunk e.164 support to make a call using e.164 number format: 1. Lift the handset or press speaker. 2. Dial 00441202223344 # . ¸ the system automatically modifies the required header fields of the sip invite message using the configuration settings in the ta...
Page 373
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 6-27 sip trunk e.164 clip enhancement delete the + only from an incoming sip invite using e.164 numbering scheme: incoming call from: +4902131795770 displayed in terminal incoming caller history as: table 6-1 sip invite header fields program 84-14-13 program 10-02-...
Page 374
Issue 2.0 6-28 sip trunking delete and replace the + and matched country code from an incoming sip invite using e.164 numbering scheme: incoming call from: +4902131795770 program 10-02-02 = 00 displayed in terminal incoming caller history as: delete and replace the + and matched country code from an...
Page 375
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 6-29 incoming call from: +4902131795770 program 10-02-02 = 00 program 10-02-03 = 9 displayed in terminal incoming caller history as: making an outgoing call from history of incoming calls: 1. From an idle multiline terminal. 2. Press soft key list. 3. Press soft ke...
Page 376
Issue 2.0 6-30 sip trunking.
Page 377
Table 6-5 sip packet sequence 1,180 ringing -> local rbt 2,180 ringing + sdp -> far side in-band rbt 3,183 session progress + sdp -> far side in-band rbt bye ack ack 200 ok prack invite + auth invite register + auth register 401 200 ok 200 ok 200 ok 401 or 407 100 trying 180 ringing if authenticatio...
Page 378: Chapter 7
Sv9100 networking manual 7-1 chapter 7 univerge ® sv9100 h.323 trunking s ection 1 i ntroduction h.323 is an international telecommunication union (itu) standard for packet based multimedia communication systems. The univerge sv9100 can use h.323 to connect to another univerge sv9100 system or a thi...
Page 379
Issue 2.0 7-2 h.323 trunking s ection 2 h.323 t runk i mplementation the univerge sv9100 implementation and programming for sip and h.323 are very similar. The call routing, call features and speech handling (rtp) are the same – only the signaling protocol is different. For this reason, the descript...
Page 380
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 7-3 2.2 configure voipdb trunk ports after installing iple (voip daughter board) in univerge sv9100 system, voipdb trunk ports need to be defined in 10-68-01. By default the voipdb trunk ports are defined as none. When using h.323, you need to change the trunk port...
Page 381
Issue 2.0 7-4 h.323 trunking 2.2.2 configure voipdb networking information use the following programs to assign voipdb network configuration information. 2.2.3 voipdb (dsp) basic setup use the following programs to assign voipdb (dsp) basic setup information. Table 7-2 voipdb network configuration a...
Page 382
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 7-5 2.3 configure signaling information (h.323) h.323 requires a gatekeeper to be configured to manage registration of h.323 endpoints. The univerge sv9100 has a built-in h.323 gatekeeper and also supports connection to an external gatekeeper. In most cases, the sv...
Page 383
Issue 2.0 7-6 h.323 trunking 2.3.2 h.323 alias address setup use the following programs to assign h.323 alias address setup information. 10-17-04 h.323 gatekeeper setup – preferred gatekeeper maximum 124 characters default not assigned if program 10-17-01 is set to 1, enter the gatekeeper id. When r...
Page 384
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 7-7 2.4 configure call routing for h.323 enter the remote destination information in program 10-23. This allows up to 1000 sip or h.323 destinations (remote systems) to be entered. If more than 1000 destinations are required, it is necessary to use an external h.32...
Page 385
Issue 2.0 7-8 h.323 trunking 2.4.2 caller id (h.323) use the following programs to assign h.323 caller id. Table 7-7 h.323 caller id assignments program/ item no. Description/ selection assigned data comments 21-17-01 ip trunk (sip) calling party number setup for trunk up to 16 digits (1~0, *, #) de...
Page 386
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 7-9 the clip that is actually sent is based on the following priority: 2.5 codec selection for ip networking ip networking can use various codecs. A codec is a standard for converting an analog signal to digital. This conversion process is handled by the dsp (digit...
Page 387
Issue 2.0 7-10 h.323 trunking 2.5.1 codec selection for ip networking (h.323) use the following programs to assign codec selections for h.323. Table 7-8 ip networking (h.323) codec assignments program/ item no. Description/ selection assigned data comments 84-01-02 h.323 trunk basic information setu...
Page 388
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 7-11 84-01-17 h.323 trunk basic information setup – g.711 jitter buffer (average) 0~300ms default is 60 84-01-18 h.323 trunk basic information setup – g.711 jitter buffer (max) 0~300ms default is 120 84-01-22 voice activity detection threshold 0~30 (-19db~ +10db an...
Page 389
Issue 2.0 7-12 h.323 trunking 2.6 h.323 tie line programming example figure 7-1 h.323 tie line programming example illustrates how to program a tie line for h.323. The following programs are assigned in this example. 84-01-67 h.323 trunk basic information setup – g.722 jitter buffer (max) 0~300ms de...
Page 390
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 7-13 prg 22-02-01 set all ip trunks to tie prg 44-02-01 (table 1) 4 1 prg 44-02-02 (table 1) f-route f-route prg 44-02-03 (table 1) 1 1 prg 44-05-01 (f-route 1) trunk group 10 trunk group 10 prg 44-05-09 (max digits) 3 3 prg 84-26-01 (dsp) 192.168.1.11 192.168.2.11...
Page 391
Issue 2.0 7-14 h.323 trunking.
Page 392: Chapter 8
Sv9100 networking manual 8-1 chapter 8 univerge ® sv9100 ip multiline station (sip) s ection 1 i ntroduction1 the univerge sv9100 system supports ip extensions using a variety of multiline terminals. These telephones have the same look and functionality as typical multiline telephones, but they are ...
Page 393
Issue 2.0 8-2 ip multiline station (sip) s ection 2 ip to tdm c onversion when an ip telephone calls a dt300/dt400 multiline telephone, single line telephone or trunk, the speech must be converted from ip to tdm (time division multiplexing) technology. The gpz-iple daughter board provides this funct...
Page 394
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 8-3 2.2 conditions when using dt800/dt700 ip phones, it is not recommended to assign the following features to a large number of phones (100 or more): the same trunk line assignment (squared key system) the same virtual extension assignment paging key with led on a...
Page 395
Issue 2.0 8-4 ip multiline station (sip) figure 8-2 power fail adapter connection gcd-cp10 voip switch ip telephone ip telephone (with power fail adapter) pstn an al og t ru nk public switched telephone network univerge sv9100
Page 396
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 8-5 3.2 operation during power failure if the telephone becomes disconnected from the power supply (e.G., power loss) the telephone display is blank. To make a call, lift the handset to receive dial tone from the analog line. Dial as normal. If a call is received o...
Page 397
Issue 2.0 8-6 ip multiline station (sip) if a call is received on the analog line, the power fail adapter rings. Lift the handset to answer. Handsfree (speaker) mode is not supported on calls made to or from the power fail adapter. The handset must always be used. A special dial pad option is suppli...
Page 398
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 8-7 s ection 5 p roviding p ower ip telephones require power to function. This can be provided in various ways. 5.1 local power the ip telephone has a connector for external power. This is supplied by an ac adapter that outputs 27v dc. This means that a power outle...
Page 399
Issue 2.0 8-8 ip multiline station (sip) s ection 7 m iscellaneous 7.1 system tones and ring tones ip phones do not use program 80-01: service tone setup entries. The tones are generated locally by the ip telephone. When a door box chime rings an ip telephone, the system activates the chimes using a...
Page 400
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 8-9 : the following examples show typical scenarios and basic programming required. These examples assume that the programming steps are performed on a default system (i.E., no existing configuration). 8.2 example configuration 1 - static ip addressing, one lan thi...
Page 401
Issue 2.0 8-10 ip multiline station (sip) 8.3 example configuration 2 - dynamic ip addressing, one lan this example shows system ip phones connected to a single lan (no routers) with dynamic ip addresses. The dhcp server could be: customer supplied (e.G., windows server) indhcp internal dhcp server ...
Page 402
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 8-11 programming - gcd-cp10: 10-12-01 : gcd-cp10 network setup - ip address (for gcd-cp10) 10-12-10 : gcd-cp10 network setup - subnet mask 10-12-03 : gcd-cp10 network setup - default gateway 10-12-09 : gcd-cp10 network setup - ip address (this assignment is for gcd...
Page 403
Issue 2.0 8-12 ip multiline station (sip) 8.4 example configuration 3 - static ip addressing, routed wan this example shows ip phones connected to an univerge sv9100 system over a wide area network (wan), with static ip addressing. This is a typical scenario - a small branch office connecting to the...
Page 404
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 8-13 s ection 9 ip p hone p rogramming i nterface this section describes how to access the programming interface for ip phones. To access the user menu follow the steps listed below. 1. Using a dt800/dt700 telephone, press the menu button to enter program mode. The...
Page 405
Issue 2.0 8-14 ip multiline station (sip) s ection 10 dhcp s erver c onfiguration it is possible to use either an external dhcp server (e.G., windows server) or the univerge sv9100 internal dhcp server. With ip phones, either of these options requires the dhcp server to be configured to supply the i...
Page 406
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 8-15 11.2 building config file when building a config file, follow the steps below to launch the phone manager and create a file. 1. Launch the ip phone manager software. 2. Once the software is launched, click auto config. Figure 8-8 ip phone manager.
Page 407
Issue 2.0 8-16 ip multiline station (sip) 3. Click terminal. 4. Click 1st server address. 5. Assign the 1st server address using the ip address programmed in command 10-12-09. Figure 8-9 config setup apl.
Page 408
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 8-17 6. Click ok . 7. Click 1st server port. Assign port number 5080. 8. Click ok. 9. After the changes are made, click save. Figure 8-10 assign ip address figure 8-11 network settings - 1st server port.
Page 409
Issue 2.0 8-18 ip multiline station (sip) 10. When the save window opens, click save as... 11. In the save as window, name the file xxx.Gz. Example: to name the file test, enter test.Gz 12. Place this file in the ftp server. Figure 8-12 save as/name file window.
Page 410
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 8-19 11.3 configuring an ftp server the file generated in the ip phone manager must be placed in an anonymous login folder. The ftp server must be configured with an anonymous login account. The following procedure is an example using quick and easy ftp server. 1. ...
Page 411
Issue 2.0 8-20 ip multiline station (sip) 2. Click on the advanced tab to specify the directory to store files. 3. Place the file (for example: test.Gz) in the default home directory. 4. After the file is loaded to the proper directory, click start to start the ftp server. 5. At this point the ftp s...
Page 412
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 8-21 11.4 dhcp server setup windows server this section provides instructions for defining vendor classes and setting defining vendor classes 1. In the dhcp server highlight the server machine on the left side. Right click on the server and select define vendor cla...
Page 413
Issue 2.0 8-22 ip multiline station (sip) configuring options 1. Highlight scope options on the left side. Then right click and choose configure options. 2. Click advanced and change the vendor class to necdt800/dt700. 3. Place a check mark next to 141 ftp address. Down below assign the ip address o...
Page 414
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 8-23 s ection 13 s ystem ip p hones and a nalog t runks due to the nature of analog-to-digital conversion, considerable echo may be encountered when using analog trunks with ip phones. Due to all analog trunks being different, padding of the analog trunks in prg 81...
Page 415
Issue 2.0 8-24 ip multiline station (sip) 8. To select download by file, press option 1 (download file). 9. To boot the program, press 3 (boot program). 10. Press the softkey. The ip phone downloads the firmware from the ftp/tftp server and reboots when the download is complete. 14.2 checking the fi...
Page 416
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 8-25 important below is an example of this setup. This is just an example, you must enter your own local information. Enter the ip address of the tftp server that the ip phone firmware is stored on. If using ftp, change the server mode to ftp and enter the proper i...
Page 417
Issue 2.0 8-26 ip multiline station (sip) s ection 15 ip s tation (sip m ultiline t elephone ) 15.1 ip phone registration modes the sip mlt supports three different registration modes. Plug and play automatic login manual login plug and play registration plug and play registration mode allows for no...
Page 418
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 8-27 manual login when set to manual login, no user name, password, or extension number is entered into the configuration of the telephone. The user is prompted to enter this user name and password into the ip phone. This information is cross referenced in the phon...
Page 419
Issue 2.0 8-28 ip multiline station (sip) conditions encryption is not supported on dt800/dt700 series phones that are connected via napt. Encryption is not supported on dt800/dt700 series phones that are registered to a secondary netlink system. Dt800/dt700 series phones that are registered to a pr...
Page 420
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 8-29 to ensure a network meets the specific requirements for voip implementation, an ip ready check and a site survey must be completed at each site before voip implementation. One way delay must not exceed 100ms. Round trip delay must not exceed 200ms. Packet loss...
Page 421
Issue 2.0 8-30 ip multiline station (sip) the following procedures describe two methods for tagging the voice packets and the data packets separately, using the pc, or using the phone keypad. 15.3.1 logging in on the pc follow these steps to log into a pc. 1. Web browse to the ip address of phone. 2...
Page 422
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 8-31 15.3.2 tagging voice packets using ip phone follow these steps to program for voice packet tagging using an ip telephone. 1. Log in. Refer to section 15.3.1 logging in on the pc on page 8-30 . 2. To apply a tag to the voice packets only, go to network settings...
Page 423
Issue 2.0 8-32 ip multiline station (sip) 5. Select either enable or disable (default) and click ok. 6. Vlan id allows an entry of 1~4094 for the vlan id. Vlan mode must be enabled for this entry to be valid. Enter the vlan id and click ok. 7. Vlan priority allows an entry of 0~7 for the vlan priori...
Page 424
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 8-33 15.3.3 tagging data packets using ip phone follow these steps program for data packet tagging using an ip telephone. 1. While logged in to the ip address of the phone on the pc, go to network settings>advanced settings>pc port settings. Refer to section 15.3.1...
Page 425
Issue 2.0 8-34 ip multiline station (sip) 4. Select either enable or disable (default) and click ok . The remaining data packets settings for vlan on the pc port are the same as those for the voice packets. 5. Vlan id allows an entry of 1~4094 for the vlan id. Vlan mode must be enabled for this entr...
Page 426
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 8-35 7. Click save. 8. After saving settings, click ok to confirm. The telephone reboots and applies the vlan settings. Figure 8-25 save network settings figure 8-26 save confirmation window.
Page 427
Issue 2.0 8-36 ip multiline station (sip) 15.3.4 entering vlan settings by phone (voice packets only) follow these steps to enter vlan settings using a telephone. 1. Log in. Refer to section 15.3.1 logging in on the pc on page 8-30 . 2. Press and hold the phone menu button until the screen changes. ...
Page 428
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 8-37 8. Enter a valid vlan id of 1~4094. Press the ok soft key after the setting is changed. 9. Press 4 on the dial pad for port vlan priority. 10. Enter the vlan priority of 0~7. Press the ok soft key after the setting is changed. 11. If no more changes are made, ...
Page 429
Issue 2.0 8-38 ip multiline station (sip) working in conjunction with ip precedence, the next 4 bits in the tos field are designed to influence the delivery of data based on delay, throughput, reliability, and cost. However these fields are typically not used. The following table shows the 8-bit tos...
Page 430
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 8-39 the following table shows the 8 bit tos field and the associated diffserv bits. Ip precedence/diffserv values submitted in command 84-10 assignments for the ip precedence/diffserv values in the system are submitted in command 84-10. This setting data affects o...
Page 431
Issue 2.0 8-40 ip multiline station (sip) individual. If different ip phones require different tos assignments, due to the network configuration, these assignments must be set at each individual station command 84-23 requires a hexadecimal representation of the 8 bit tos field. For example, to assig...
Page 432
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 8-41 the following table shows the common ip precedence/diffserv values and their hexadecimal equivalent. Table 8-2 common ip precedence/diffserv values and hexadecimal equivalent ip precedence name hex value ip precedence 1 20 ip precedence 2 40 ip precedence 3 60...
Page 433
Issue 2.0 8-42 ip multiline station (sip) enter values on a per phone basis by the web browser by configuration mode through the dial pad to enter the values per phone, browse to the individual phone or enter the configuration mode through dial pad. The following example describes assigning these fi...
Page 434
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 8-43 access the following menus to select options: rtp - voice packets sip - signalling packets 4. After selecting save, the following message appears. 5. Select ok and the phone reboots. Once online, the phone tags all packets with the applied settings. Assign val...
Page 435
Issue 2.0 8-44 ip multiline station (sip) 9. Press 2 on the dial pad for sip (signaling packets), enter the hexadecimal value, and then press the ok soft key. 10. If no more changes are to be made, press the exit soft key three times, and then press the save soft key. The phone reboots. 15.5 bandwid...
Page 436
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 8-45 voip packet with rtp header compression voice activity detection (vad) is suppression of silence packets from being sent across the network. In a voip network all conversations are packetized and sent, including silence. On an average a typical conversation co...
Page 437
Issue 2.0 8-46 ip multiline station (sip) bandwidth calculation ( [ layer 2 overhead + ip/udp/rtp header + voice payload ] / voice payload ) * default codec speed = total bandwidth example of a g.711 call over ethernet using a 20ms packet size and not using rtp header compression (.020 * 64000) / 8 ...
Page 438
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 8-47 when using video (h.263) soft phone, add the bandwidth for the video portion to the call. The estimated bandwidth per video stream is as follows: approximately 40k ~ 120k approximately 40k ~ 120k 15.6 some network considerations when adding the sv9100 to a cus...
Page 439
Issue 2.0 8-48 ip multiline station (sip) the green arrow in the diagram above represents the data packets leaving the ip phone destined for the sv91000 on the headquarters lan. The firewall on the headquarters network is not configured to recognize the udp ports used by the nec equipment thus block...
Page 440
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 8-49 the following diagram shows three sites connected together via vpn. This network is not fully meshed due to the lack of a vpn tunnel between sites b and c. With peer-to-peer enabled, the ip phones on site a can communicate with ip phones on sites b and c. Ip p...
Page 441
Issue 2.0 8-50 ip multiline station (sip) to correct this issue another vpn connection between sites b and c is required. If an additional vpn cannot be implemented, due to network limitations, the peer- to-peer feature can be disabled in the sv8100. With peer-to-peer disabled, all packets (signalin...
Page 442
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 8-51 15.7 guide to feature programming program number program name description/comments assigned data 1 2 3 10-12-03 gcd-cp10 network setup – default gateway iple uses the default gateway that is assigned here. 0.0.0.0~ 126.255.255.254 128.0.0.1~ 191.254.255.254 19...
Page 443
Issue 2.0 8-52 ip multiline station (sip) 10-46-01 dt800/dt700 server information setup – register mode define which of the three registration modes you wish the sip mlts to use. Normal when the phone boots up it will report the ext assigned in the phone or choose the next available extension in the...
Page 444
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 8-53 10-46-08 dt800/dt700 server information setup – encryption type assign the encryption type. 0 = mode 1 default is 0 x 10-46-09 dt800/dt700 server information setup – one-time password password used when program 10-46-07 is set to all. Assign a character string...
Page 445
Issue 2.0 8-54 ip multiline station (sip) 15-05-21 ip telephone terminal basic data setup –handset option information read only cm showing type of handset installed on the telephone. 0 = normal handset 1 = handset for power failure (psa/psd) 2 = bch default is 0 read only x 15-05-22 ip telephone ter...
Page 446
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 8-55 15-05-27 ip telephone terminal basic data setup –personal id index for sip multiline phone using manual/auto registration. Assign each phone a unique personal index. When complete go to command 84-22 and set the user name and password. 0 = not set 1-960 = set ...
Page 447
Issue 2.0 8-56 ip multiline station (sip) 84-10-xx tos setup assignments deal with setting of the layer 3 ip header tos field as it leaves the voipdb unit. Specify the protocol to assign the tos field for, and select the populated field to conform to either ip precedence or differentiated services. ...
Page 448
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 8-57 84-23-03 dt800/dt700 multiline basic information setup – session expire timer at half the value of this timer the ip terminal sends a re-invite message. Range: 60~65535 sec. Default is 180 x 84-23-04 dt800/dt700 multiline basic information setup – minimum sess...
Page 449
Issue 2.0 8-58 ip multiline station (sip) 84-23-11 dt800/dt700 multiline basic information setup – password lock time time to leave the terminal locked out after entering the wrong security code. Range; 0 ~ 120 default: 0 default is 0 x 84-23-12 dt800/dt700 multiline basic information setup – refere...
Page 450
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 8-59 84-24-05 dt800/dt700 multiline codec basic information setup – g.711 jitter buffer average average value of the dynamic jitter buffer. Range: 0 ~ 300ms default is 40 x 84-24-06 dt800/dt700 multiline codec basic information setup – g.711 jitter buffer maximum m...
Page 451
Issue 2.0 8-60 ip multiline station (sip) 84-24-17 dt800/dt700 multiline codec basic information setup – jitter buffer mode 1 = static 2 = self adjusting 3 = adaptive immediate default is 2 x 84-24-18 dt800/dt700 multiline codec basic information setup - voice activity detection threshold 0 ~ 30 def...
Page 452
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 8-61 15.8 sip mlt quick startup guide the following guides describe the setup for a sip mlt from a default state for these modes: plug and play automatic registration manual registration 15.8.1 plug and play 1. Program 10-12 assign the iple registration/signaling i...
Page 453
Issue 2.0 8-62 ip multiline station (sip) leave gateway ip address at 0.0.0.0. Figure 8-34 system data 10-12: gcd-cp10 network setup.
Page 454
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 8-63 2. Program 84-26 assign ip addresses to the dsps that are to be used. The ip addresses assigned must be in the same subnet as the address in program 10-12-09. After these commands are uploaded to the cpu, a system reset must be applied. Assign an ip address to...
Page 455
Issue 2.0 8-64 ip multiline station (sip) after one port in a block of two is used by a voip station, the remaining port can be used only for another voip extension. 4. This step is optional. To enable key data and other station feature programming (before ip phone is brought online) the extensions ...
Page 456
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 8-65 programs. 5. The sip mlt station requires assignments to be made in the phone itself. Enter the program mode in the station using the following steps. Figure 8-37 pcpro programming unregistered phones figure 8-38 ip phone list.
Page 457
Issue 2.0 8-66 ip multiline station (sip) network settings dhcp mode – dhcp disable. Click ok. Ip address – enter the ip address for the station, and click ok. Default gateway – enter the default gateway address, and click ok. If you are testing without a router/gateway, this must be left at the def...
Page 458
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 8-67 2. Same as plug and play mode. 3. Same as plug and play mode. 4. To enable key data and other station feature programming before ip phone is brought online, the extensions must be identified as ip phones. Once checked in the ip phone list in pc-pro (see images...
Page 459
Issue 2.0 8-68 ip multiline station (sip) 5. Program 10-46 change program 10-46-01 to automatic. 6. Program 15-05-27 each ip phone requires a unique personal id index. Valid settings are 1 ~ 960. 7. Program 84-22-01 assign the user id and password to be associated with the personal id index assigned...
Page 460
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 8-69 8. The sip mlt station requires assignments to be made in the phone itself. Enter the program mode in the station using the following steps. Figure 8-44 automatic registration user name and password assignment.
Page 461
Issue 2.0 8-70 ip multiline station (sip) network settings dhcp mode - dhcp disable. Click ok. Ip address - enter the ip address for the station, and click ok. Default gateway - enter the default gateway address, and click ok. If you are testing without a router/gateway, this must be left at the def...
Page 462
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 8-71 follow these steps for manual registration. Steps 1~4 are the same as for section 15.8.2 automatic registration on page 8-66 . 1. Same as for automatic registration mode. 2. Same as for automatic registration mode. 3. Same as for automatic registration mode. 4...
Page 463
Issue 2.0 8-72 ip multiline station (sip) network settings dhcp mode - dhcp disable. Click ok. Ip address - enter the ip address for the station, and click ok. Default gateway - enter the default gateway address, and click ok. If you are testing without a router/gateway, this must be left at the def...
Page 464
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 8-73 15.9 ip phone relocation the ip phone relocation feature gives users access to their ip telephone from any location by using the override login function. Users have the flexibility of logging into their ip station in the office as well as remotely at the home ...
Page 465
Issue 2.0 8-74 ip multiline station (sip) override is not supported in a sv9100 system that had a 3rd party cti connection to the cpu (i.E., uc suites apps shared services, ucb), or to a terminal with a 1st party cti connection (i.E., pc assistant/attendant and softphone or 1st party tapi driver), a...
Page 466
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 8-75 ip phone relocation flow chart the following flow chart can be used to enable the ip phone relocation feature. Every user must enter both login id and password. Figure 8-46 ip phone relocation flow chart.
Page 467
Issue 2.0 8-76 ip multiline station (sip).
Page 468: Chapter 9
Sv9100 networking manual 9-1 chapter 9 univerge ® sv9100 ip single line telephone (sip) s ection 1 i ntroduction session initiation protocol (sip) station feature provides voice over internet protocol (voip) for ip stations. This feature is defined by the internet engineering task force (ietf) rfc32...
Page 469
Issue 2.0 9-2 ip single line telephone (sip) voice at rates of 16-, 24-, 32-, and 40kbps. The sip station feature set supports the hold and trf features based on rfc draft. Draft-ietf-sipping-service-examples-09.Txt. Draft-ietf-sipping-service-examples- (transfer - attended) 15.Txt ietf rfc is defin...
Page 470
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 9-3 s ection 2 std sip c onference description with sv9100 software 2.00 or higher standard sip terminals can initiate a conference call. Conditions prg 20-13-08 must be enabled for the class of service the standard sip terminal is in. A dsp resource is needed for ...
Page 471
Issue 2.0 9-4 ip single line telephone (sip) video calls are not supported. The following conference features are not supported with standard sip: meet me conference barge in to conference split between the parties in conference transfer a call into a conference default setting none system availabil...
Page 472
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 9-5 programming operation polycom vvx 500 to establish a conference: 1. Establish an intercom or trunk call. 2. Press the “hold” softkey to hold the first call. 3. Establish a second call (intercom or trunk), which is to be added in the conference. 4. When called p...
Page 473
Issue 2.0 9-6 ip single line telephone (sip) s ection 3 std sip t ransfer –u nattended description any standard sip terminal can perform an unattended (blind/unsupervised) transfer. Conditions program 10-05-50 (peer-to-peer mode) must be disabled for the unattended transfer to be performed. A sip te...
Page 474
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 9-7 required components gcd-cp10 gpz-iple related features ip single line telephone (sip) transfer s ection 4 nat m ode for s tandard sip t elephone description the sv9100 supports nat for standard sip terminals. Conditions when prg 10-33-05 nat mode for sip phone ...
Page 475
Issue 2.0 9-8 ip single line telephone (sip) system availability terminals standard sip terminal required components gcd-cp10 gpz-iple related features ip single line telephone (sip) transfer programming program number program name description/comments assigned data 1 2 3 10-12-03 gcd-cp10 network s...
Page 476
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 9-9 10-12-10 gcd-cp10 network setup – subnet mask define the media gateway subnet mask address. 128.0.0.0 192.0.0.0 224.0.0.0 240.0.0.0 248.0.0.0 252.0.0.0 254.0.0.0 255.0.0.0 255.128.0.0 255.192.0.0 255.224.0.0 255.240.0.0 255.248.0.0 255.252.0.0 255.254.0.0 255.2...
Page 477
Issue 2.0 9-10 ip single line telephone (sip) 10-33-02 sip registar/proxy information basic setup - authentication mode when connecting a standard sip terminal via nat, this opion must be enabled to prohibit illegal sip phone registration. 0 = disable 1 = enable (default = 0) x 10-33-05 sip registar...
Page 478
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 9-11 10-58-02 network address – subnet mask this program sets the netmask for the ip addresses assigned in program 10-58- 01. 128.0.0.0 / 192.0.0.0 224.0.0.0 / 240.0.0.0 248.0.0.0 / 252.0.0.0 254.0.0.0 / 255.0.0.0 255.128.0.0 255.192.0.0 255.224.0.0 255.240.0.0 255...
Page 479
Issue 2.0 9-12 ip single line telephone (sip) 15-05-45 ip telephone terminal basic data setup – nat plug and play this program is valid when program 10-46-14 is on (nat feature activated). Select sending rtp port number to remote router, use from negotiation result (0) or received rtp packet (1). Sv...
Page 480
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 9-13 s ection 5 p rogramming 5.1 configure voipdb networking information the voipdb should be connected to the same ip subnet as the gcd-cp10. It also requires a valid ip address. Use these programs to assign voipdb network related information. If any ip address or...
Page 481
Issue 2.0 9-14 ip single line telephone (sip) 5.1.1 voipdb (dsp) basic setup use these programs to make basic voipdb assignments. 5.1.2 voip tos setup use this programs to define tos. 5.1.3 sip peer-to-peer use these programs to make sip peer-to-peer assignments. Program number program name descript...
Page 482
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 9-15 5.1.4 ip extension numbering use these programs to assign ip extension numbering. 5.1.5 sip extension codec information use these programs assign sip extension codec information. Program number program name description/ comments assigned data 1 2 3 11-01-01 sy...
Page 483
Issue 2.0 9-16 ip single line telephone (sip) 84-19-06 sip extension codec information basic setup – g.711 jitter buffer (max) define g.711 jitter buffer maximum accepted value. 0~300ms default is 80 84-19-07 sip extension codec information basic setup – number of g.729 audio frames define the g.729...
Page 484
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 9-17 84-19-33 sip extension codec information basic setup – number of g.722 audio frames 1~4 1 = 10ms 2 = 20ms 3 = 30ms 4 = 40ms default is 3 84-19-35 sip extension codec information basic setup – g.722 jitter buffer (min) 0~300ms default is 30 84-19-36 sip extensi...
Page 485
Issue 2.0 9-18 ip single line telephone (sip) 5.1.6 sip extension basic information setup use these programs to assign basic sip extension information. 5.1.7 ip phone configuration use these programs assign ip phone configuration information. Program number program name description/ comments assigne...
Page 486
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 9-19 15-05-02 ip telephone terminal basic data setup – ip phone fixed port assignment mac address of registered mlt sip phone is stored and/or can input the mac address of an mlt sip phone so when it comes online it is provided with the extension in which the mac a...
Page 487
Issue 2.0 9-20 ip single line telephone (sip) 5.2 sip phone example the following example show a sip phone attached to an sv9100 system. 15-05-49 ip telephone terminal basic setup - receiving sip info determines whether sip info messages are received by the system. 0 = disable 1 = allowed any time 2...
Page 488: Chapter 10
Sv9100 networking manual 10-1 chapter 10 univerge ® sv9100 sv9100 netlink introduction s ection 1 i ntroduction netlink networking provides a seamless connection, using an ip network, to join multiple sv9100 communication servers into what would appear to be a single communications server. With a un...
Page 489
Issue 2.0 10-2 sv9100 netlink an added feature of netlink is the fail-over feature. If the primary system is turned off or disconnected, without the fail-over feature, all communication servers would stop working. With fail-over, the server locates one of the secondary systems as based on the sv9100...
Page 490
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 10-3 s ection 2 sv9100 r equirements 2.1 hardware each sv9100 communications server needs the following items: gcd-cp10 gpz-iple install the station/trunk blades as required for your configuration. When installing a secondary system in a netlink network, and the se...
Page 491
Issue 2.0 10-4 sv9100 netlink 2.6 determining primary system to determine the primary system which should be controlling the netlink network, the primary system is selected based on system id. The lowest id number becomes primary system. If you add a new communication server to netlink once the prim...
Page 492
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 10-5 general ip configuration the voice quality of voip depends on variables such as available bandwidth, network latency, and quality of service initiatives (qos), all of which are controlled by the network and internet service providers. Because these variables a...
Page 493
Issue 2.0 10-6 sv9100 netlink figure 10-2 two sv9100 systems connected via the wan shows two sv9100 systems. One on the corporate local lan and one on a remote network connected via the wan. The remote site cannot call the main site, therefore, it is not working. The green arrow in figure 10-2 two s...
Page 494
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 10-7 the following diagram shows three sites connected together via vpn. This network is not fully meshed due to the lack of a vpn tunnel between sites b and c. Site a can communicate with phones on sites b and c. Phones on sites b and c cannot communicate with eac...
Page 495
Issue 2.0 10-8 sv9100 netlink netlink with ip phones connected via napt 3.2 limitations 3.2.1 features synchronous ringing via netlink is not supported. 3.2.2 ip terminal all dt800/dt700 terminals and softphones must register to the primary system. All dt800/dt700 terminals can register to either th...
Page 496
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 10-9 the sv9100 encryption feature is only supported in the primary system. 3.2.3 ip trunks when configuring sip trunks on netlink secondary system, only sip profile one is supported. 3.2.4 general limitations sv8100 cpu is not supported in a netlink environment wi...
Page 497
Issue 2.0 10-10 sv9100 netlink after seven days or 28 days the license expires. To renew the license, a connection to the original primary site must be re-established. (once the connection to the primary is recovered, if fail-over occurs again, the license is once again enabled for the specified dur...
Page 498
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 10-11 with the t-1 ccta blade is supported in the primary system and/or secondary systems. When using mobile extension in a netlink network, the isdn/pri must be used in the primary system. Inmail is supported in a netlink network; however, replication should be sc...
Page 499
Issue 2.0 10-12 sv9100 netlink data switches must be manageable routers must provide qos adequate bandwidth for estimated voip traffic depending on how qos policies are built in the network, assignments may be needed in the cpu. Table 10-1 voip resource chart the number of conference blocks in a net...
Page 500
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 10-13 in-mail and vrs use the vmdb of the primary (main) site. Apsu can be installed in the secondary (remote) system, however the netlink time zone follows the primary (main) system. When installing a secondary system in a netlink network and the secondary system ...
Page 501
Issue 2.0 10-14 sv9100 netlink a dsp is used on the system gcd-cp10 which has the call. For instance, when a trunk on system id 2 uses a receiver, a dsp on system id 2 is used. The primary system must control dsp resources on the secondary systems but it cannot control all of them. There are five zo...
Page 502
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 10-15 primary moh moh secondary hold when a terminal is placed on hold, moh comes from the communications server in which the terminal resides. Primary moh moh secondary hold trunk when a terminal is placed on hold, moh comes from the communications server in which...
Page 503
Issue 2.0 10-16 sv9100 netlink external paging uses an output on the gcd-cp10 of the primary system. A pgd(2)-u10 adp must be used if external paging is required in the secondary systems. 3.6 bandwidth the following example shows the approximate bandwidth used for the netlink signaling: bandwidth si...
Page 504
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 10-17 for inmail remote ccis extensions are not supported in a centralized directory. 3.9 foip foip (fax over ip) is supported in a netlink network. S ection 4 l ist of s upported f eatures in s econdary s ystem the following table lists supported features. Table 1...
Page 505
Issue 2.0 10-18 sv9100 netlink background music conditions if using background music, each site must provide its own music source. Primary and secondary systems cannot share a source. If the primary system is set to music off of the gcd-cp10, then all secondary systems also must get their music off ...
Page 506
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 10-19 code restriction, dial block yes conference yes conference, voice call/privacy release yes continued dialing yes cordless dect terminals yes cordless telephone connection yes data line security yes delayed ringing yes department calling yes department step ca...
Page 507
Issue 2.0 10-20 sv9100 netlink flexible system numbering yes flexible timeouts yes forced trunk disconnect no group call pickup yes group listen yes handset mute yes handsfree and monitor yes handsfree answerback/forced intercom ringing yes headset operation yes hold yes hot key-pad yes hotel/motel ...
Page 508
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 10-21 maintenance conditions web pro and pc pro can be used to view the individual card configuration screens of all systems in a netlink network, however the system data is for all systems combined. Meet me conference yes meet me paging yes meet me paging transfer...
Page 509
Issue 2.0 10-22 sv9100 netlink programming from a multiline terminal yes pulse to tone conversion yes redial function yes remote (system) upgrade yes repeat redial yes resident system program yes reverse voice over yes ring groups yes ringdown extension, internal/ external yes room monitor yes save ...
Page 510
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 10-23 sv9100 uc suite applications conditions the sv9100 uc suite must connect to the primary system. Sv9100 internal router yes sv9100 poe gigabit switch yes sv9100/sv9300 terminals yes synchronous ringing no tandem ringing yes tandem trunking (unsupervised confer...
Page 511
Issue 2.0 10-24 sv9100 netlink volume controls yes warning tone for long conversation yes wireless dect (sip) conditions all ip terminals connect to the primary system. Table 10-3 supported features in secondary system (continued) feature name supported in secondary system comments.
Page 512
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 10-25 s ection 5 n et l ink f unctions 5.1 programming the following programs require a gcd-cp10 reset after making a change via pcpro, web pro and handset programming. Minimum required programming 10-12-09 : gcd-cp10 network setup – voip daughter board ip address ...
Page 513
Issue 2.0 10-26 sv9100 netlink enter ip addresses for any communications server which is included in the network (especially the primary sv9100). Once the communications server connects to the primary sv9100, this setting is updated by the primary sv9100 when program 51-13-01 is enabled. This allows...
Page 514
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 10-27 51-06-02 : netlink primary system automatic integration setting – blade reset timing option when the primary automatic integration reestablishes the netlink network, the blades in the secondary sv9100s are reset. This option determines if the secondary sv9100...
Page 515
Issue 2.0 10-28 sv9100 netlink 51-07-02 : netlink forced change of primary system settings – blade reset timing option when the forced change of primary settings is performed, the blades in the secondary communication servers are reset. This option determines if the secondary sv9100 blades are reset...
Page 516
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 10-29 51-09-07 : netlink tcp port settings – database replication primary system detection port define the port used for communication so that the primary sv9100 may synchronize the secondary sv9100 with the program data (0~65535). If 0 is entered, the port is sele...
Page 517
Issue 2.0 10-30 sv9100 netlink if program 51-16-01 is set to 1, set the time to replicate the program data (0000~2359). 51-16-03 : netlink system data replication mode setting – system data replication interval setting if program 51-16-01 is set to 2, set the interval time between replicating the pr...
Page 518
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 10-31 the primary system is selected based on the primary candidate order and system id. The decision for the new primary system is based first on the value of the primary candidate order. The lower the number, the higher the priority. If the value is the same numb...
Page 519
Issue 2.0 10-32 sv9100 netlink if communication server database is set up as follows, system id 4 becomes the new primary system. Required programs: 51-01-01 : netlink system settings - netlink system id this is the id number (0 = disabled, 1-50) that identifies each sv9100 in the netlink network. E...
Page 520
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 10-33 51-04-01 : ip address for top priority primary system – internet protocol address for top priority primary system enter the ip address of the primary sv9100. This setting is needed to use the primary sv9100 automatic integration feature (program 51-06-01). If...
Page 521
Issue 2.0 10-34 sv9100 netlink when the attendant's telephone exists on a secondary system, alarm information cannot be displayed on the attendant's telephone. Only the voice mail connected with the primary system can be used. Since the recording data of the voice mail is not synchronized, the conte...
Page 522
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 10-35 s ection 7 t op p riority p rimary s ystem (p rimary s ystem a utomatic i ntegration ) when the primary system is temporarily disconnected/powered down, another communications server can become the new primary system. To have the original primary system resto...
Page 523
Issue 2.0 10-36 sv9100 netlink 51-06-02 : netlink primary system automatic integration setting – blade reset timing option when the primary automatic integration reestablishes the netlink network, the blades in the secondary sv9100s are reset. This option determines if the secondary sv9100 blades ar...
Page 524
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 10-37 51-08-02 : new primary system setting - system id of new primary if you already have an ip address registered in program 51-11-03, you can execute a forced change primary sv9100 by entering the system id. If this id is set to 0, the top priority sv9100 is sel...
Page 525
Issue 2.0 10-38 sv9100 netlink be careful when changing the communication server database. If the primary system is changed before synchronization, the edited data is lost. 8.1 asynchronous settings the following program settings are not updated by the primary system: 10-01, 10-02, 10-12, 10-13, 10-...
Page 526
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 10-39 51-16-06 : netlink system data replication mode setting – system data replication interval set the time to start replication to the next node after replication has completed to one node (1~86400 seconds). S ection 9 c reate r ecovery d atabase before assignin...
Page 527
Issue 2.0 10-40 sv9100 netlink however, the license of secondary system is temporary – lasting 28 days. After the specified duration, the communication server is reset and the licenses are removed. If the link is recovered and original primary system is back in service, the licenses are returned to ...
Page 528
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 10-41 s ection 12 m aintenance f eatures confirming netlink basic information from a multiline terminal, press feature + 5. The lcd display shows the system id, primary/secondary, ip address of the voipdb (not gcd-cp10), and the primary system id. Confirming commun...
Page 529
Issue 2.0 10-42 sv9100 netlink primary system secondary system 1 connected first secondary system 2 connected second as described above, port assignment is performed in the order which the communication server connects. With this condition, if a gcd-4cot is installed to the communication server 1 – ...
Page 530
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 10-43 this function allows the primary system to control 240 slots and, users can check what kind of blade is installed in each communication server and how many blades are available in the link. Virtual slot image related programming: 51-10-01 : remaining virtual ...
Page 531
Issue 2.0 10-44 sv9100 netlink communication server no longer appears in program 51-11. S ection 15 t ime z one s etup if a communication server in the network is in a different location, the time zone may be different. To adjust the clock display on multiline terminals, the user can define the offs...
Page 532
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 10-45 s ection 16 v o ip h andling using voip equipment is permitted with netlink. A maximum of voip 256 channels can be controlled. When an analog/digital terminal talks via netlink, a voip resource in the communications server to which the terminal is connecting ...
Page 533
Issue 2.0 10-46 sv9100 netlink the number in each box indicates how many voip resources are required to talk. About voip dsp settings program 84-26 determines the voipdb ip address and port number. The settings are programmed by the primary system. If you assign a voipdb ip address in the secondary ...
Page 534
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 10-47 sample configurations netlink netlink netlink system id = 1 system id = 2 system id = 3 lan lan secondary primary secondary system id = 1 system id = 2 system id = 3.
Page 535
Issue 2.0 10-48 sv9100 netlink configuration flow (case 1) – primary based on system id 1. Create a recovery database – recommended . Because each communication server database and communication server configuration are updated by the primary system, creating a recovery database is recommended. This...
Page 536
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 10-49 for centralized voice mail the voice mail must be installed in the primary system (site a). Assigning top priority primary system and primary system automatic integration are recommended. Specify the communication server in site-a for the top priority primary...
Page 537
Issue 2.0 10-50 sv9100 netlink 5. When the communication servers come up, the primary system and secondary systems are connected and start working. 6. For database synchronization, wait three minutes (or more). S ection 17 n et l ink m ulti -sip c arrier when the secondary netlink system calls out u...
Page 538
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 10-51 default setting no sip trunks are defined programming this section lists each program in numerical order. For example, program 10-01 is at the beginning of the section and program 92-01 is at the end. The information on each program is subdivided into the fol...
Page 539
Issue 2.0 10-52 sv9100 netlink s ection 18 h ow to e nter p rogramming m ode to enter programming mode: 1. Go to any working display telephone. In a newly installed system, use extension (port 1). 2. Do not lift the handset. 3. Press speaker. 4. # # . 5. Dial the system password + transfer. Refer to...
Page 540
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 10-53 s ection 19 h ow to e xit p rogramming m ode to exit the programming mode: when you are done programming, you must be out of a program option to exit (press answer to exit the program option). 1. Press answer to exit the program options, if needed. 2. Press s...
Page 541
Issue 2.0 10-54 sv9100 netlink mic press mic to switch between the different input data fields. The cursor moves up to the top row of the display. Press mic again to move the cursor back to the middle row. Line keys use programmed settings to help with the program entry. These settings vary between ...
Page 542
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 10-55 s ection 21 p rogramming n ames and t ext m essages several programs (e.G., program 20-16 : selectable display messages) require you to enter text. Use the following chart when entering and editing text. When using the keypad digits, press the key once for th...
Page 543
Issue 2.0 10-56 sv9100 netlink s ection 22 u sing s oftkeys f or p rogramming each univerge sv9100 display telephone provides interactive softkeys for intuitive feature access. The options for these keys automatically change depending on where you are in the system programming. Press the softkey loc...
Page 544
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 10-57 description use program 10-12 : gcd-cp10 network setup to setup the ip address, subnet-mask, and default gateway addresses. Caution! If any ip address or nic settings are changed, the system must be reset for the changes to take affect. Program 10 : system co...
Page 545
Issue 2.0 10-58 sv9100 netlink 04 time zone 0~24 (0 = -12 hours and 24 = +12 hours) +7 (-5 hours) determine the offset from greenwich mean time (gmt) time. Then enter its respective value. For example, eastern time (us and canada) has a gmt offset of -5. The program data would then be 7 (0= -12, 1= ...
Page 546
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 10-59 conditions the system must be reset for these changes to take affect. Feature cross reference voice over internet protocol (voip) 11 nic setup 0 = auto detect 1 = 100mbps, full-duplex 3 = 10mbps, full-duplex 5 = 1 gbps, full-duplex 0 set for iple. Input data ...
Page 547
Issue 2.0 10-60 sv9100 netlink description use program 10-54 : license configuration for each package to set the license information for each unit. Conditions if applying more than 255 licenses to a slot the licenses must be applied across multiple indexes. For example assigning 256 voip resource li...
Page 548: Program 51 : Netlink Service
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 10-61 description use program 51-01 : netlink system property setting to define the parameters of the netlink feature. Program 51 : netlink service 51-01 : netlink system property setting level: in note ❍ each system must be set with its own information. ❍ when the...
Page 549
Issue 2.0 10-62 sv9100 netlink conditions none feature cross reference none 04 signal transmit method 0 = immediate this is the default setting which does not use nagle algorithm. When this is enabled data packets are immediately sent across the network with no buffering delay. 1 = buffering nagle a...
Page 550: Program 51 : Netlink Service
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 10-63 description use program 51-02 : netlink system individual setting to set system data for each netlink system. Program 51 : netlink service 51-02 : netlink system individual setting level: in note program 51-02-03 is not used in us, but is used in other countr...
Page 551
Issue 2.0 10-64 sv9100 netlink conditions none feature cross reference none.
Page 552: Program 51 : Netlink Service
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 10-65 description use program 51-03 : netlink internet protocol address list setting to set the ip address of the netlink system. Conditions the system seeks primary system based on this list. When there is no primary system yet, or fail-over occurs, node list is r...
Page 553: Program 51 : Netlink Service
Issue 2.0 10-66 sv9100 netlink description use program 51-04 : ip address setting of top priority primary system of netlink to set the ip address of the new primary system. Conditions none feature cross reference none program 51 : netlink service 51-04 : ip address setting of top priority primary sy...
Page 554: Program 51 : Netlink Service
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 10-67 description use program 51-05 : netlink timer settings to set the various timers within the netlink system. Conditions none feature cross reference none program 51 : netlink service 51-05 : netlink timer settings level: in item no. Item input data default 01 ...
Page 555: Program 51 : Netlink Service
Issue 2.0 10-68 sv9100 netlink description use program 51-06 : netlink primary automatic integration settings to set the automatic integration of the primary system. Conditions none feature cross reference none program 51 : netlink service 51-06 : netlink primary automatic integration setting level:...
Page 556: Program 51 : Netlink Service
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 10-69 description use program 51-07 : netlink primary compulsion specification setting to set compulsion specification of the primary system. Conditions none feature cross reference none program 51 : netlink service 51-07 : netlink primary compulsion specification ...
Page 557: Program 51 : Netlink Service
Issue 2.0 10-70 sv9100 netlink description use program 51-08 : primary netlink setting to set the ip address and system id of the compulsory specification of the primary system. (this program is available only via telephone programming and not through pc programming). Conditions none feature cross r...
Page 558: Program 51 : Netlink Service
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 10-71 description use program 51-09 : netlink communication port settings to set the various communication ports used on the system. Program 51 : netlink service 51-09 : netlink communication port settings level: in input data item no. Item input data default 01 pr...
Page 559
Issue 2.0 10-72 sv9100 netlink conditions none feature cross reference none 07 database replication primary detection port replicate database. If 0 is specified, temporary port is selected dynamically. 0~65535 0 input data (continued) item no. Item input data default.
Page 560: Program 51 : Netlink Service
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 10-73 description use program 51-10: virtual slot setting to view the number of virtual slots that are remaining in a netlink network. There can be up to 240 virtual slots available in netlink. Conditions this program is read only. Feature cross reference none prog...
Page 561: Program 51 : Netlink Service
Issue 2.0 10-74 sv9100 netlink description use program 51-11: netlink system information to reference information about other systems in the netlink network. Conditions this program is read only. Feature cross reference none program 51 : netlink service 51-11 : netlink system information level: in i...
Page 562: Program 51 : Netlink Service
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 10-75 description use program 51-12: primary system information to reference information about the primary system in the netlink network. Conditions this program is read only. Feature cross reference none program 51 : netlink service 51-12 : primary system informat...
Page 563: Program 51 : Netlink Service
Issue 2.0 10-76 sv9100 netlink description use program 51-13: netlink options to enable automatic ip address list operation updates, time zone information, and mac address authorization. Conditions none feature cross reference none program 51 : netlink service 51-13 : netlink options level: in data ...
Page 564: Program 51 : Netlink Service
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 10-77 description use program 51-14: netlink system control to delete system and slot information. Conditions none feature cross reference none program 51 : netlink service 51-14 : netlink system control level: in note this program is available only via telephone p...
Page 565: Program 51 : Netlink Service
Issue 2.0 10-78 sv9100 netlink description use program 51-15: demonstration setting to automatically set the minimum setting values in netlink. A system reset occurs after this command is executed.. . Conditions none feature cross reference none program 51 : netlink service 51-15 : demonstration set...
Page 566: Program 51 : Netlink Service
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 10-79 description use program 51-16: netlink system data replication mode setting to set the system data replication between the primary and secondary systems. . Program 51 : netlink service 51-16 : netlink system data replication mode setting level: in input data ...
Page 567
Issue 2.0 10-80 sv9100 netlink conditions none feature cross reference none.
Page 568: Program 51 : Netlink Service
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 10-81 description use program 51-17: netlink dt800/dt700 server individual information setup to set the netlink port information. Conditions none feature cross reference none program 51 : netlink service 51-17 : netlink dt800/dt700 server individual information set...
Page 569: Program 51 : Netlink Service
Issue 2.0 10-82 sv9100 netlink description use program 51-18: netlink configuration options to set the netlink fail-over limits. Conditions none feature cross reference none program 51 : netlink service 51-18 : netlink configuration options level: in input data item no. Item input data default 01 ne...
Page 570: Program 51 : Netlink Service
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 10-83 description use program 51-19: netlink ip trunk (sip) calling party number setup for extension to set cpn transmission for each secondary system. Conditions none feature cross reference none program 51 : netlink service 51-19 : netlink ip trunk (sip) calling ...
Page 571: 90-57 : Backup Recovery Data
Issue 2.0 10-84 sv9100 netlink description use program 90-57 : backup recovery data to backup the system data in the flash memory on the gcd-cp10 and to make the recovery data. Conditions none feature cross reference none program 90 : maintenance program 90-57 : backup recovery data level: in input ...
Page 572
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 10-85 description use program 90-58 : restore recovery data to select the recovery data stored in the flash memory of the gcd-cp10. After this command is executed, the system restarts automatically. Conditions none feature cross reference none program 90 : maintena...
Page 573: 90-59 : Delete Recovery Data
Issue 2.0 10-86 sv9100 netlink description use program 90-59 : delete recovery data to select and delete the recovery data stored in the flash memory of the gcd-cp10. Conditions none feature cross reference none program 90 : maintenance program 90-59 : delete recovery data level: sa input data data ...
Page 574: Chapter 11
Sv9100 networking manual 11-1 chapter 11 univerge ® sv9100 napt s ection 1 napt 1.1 introduction napt, or network address port translation, is a method by which a private address, or addresses, and their tcp/udp ports are translated into a single public address and its tcp/udp ports. In the case of ...
Page 575
Issue 2.0 11-2 napt the example below is with 256 dsp resources licensed to the gcd-cp10. Your port forwarding range could change depending on number of dsp resource licenses. 1.2 requirements the following information provides requirements for napt. 1.2.1 main software napt is supported with the v1...
Page 576
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 11-3 1.2.4 license the system must be licensed for this feature (license 0031). The system must be licensed for dt800/dt700 itl terminals. Ip terminal license (5111) system port license (0300) version 1 license (0411) 1.3 installation the following settings have be...
Page 577
Issue 2.0 11-4 napt wan settings: 0. Config/ 2. Sip settings/ 8. Nat traversal/ 3. Wan settings [eco, value, sophisticated] self port settings: 0. Config/ 1. Network settings/ 6. Advanced settings/ 5. Self port settings [eco, value, sophisticated] number and name of setting setting value default val...
Page 578
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 11-5 1.4 programming example napt, or network address port translation, is a method by which a private address or addresses and their tcp/udp ports are translated into a single public address and its tcp/udp ports. In the case of ip phones with the sv9100 it allows...
Page 579
Issue 2.0 11-6 napt.
Page 580
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 11-7.
Page 581
Issue 2.0 11-8 napt.
Page 582
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 11-9.
Page 583
Issue 2.0 11-10 napt.
Page 584
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 11-11.
Page 585
Issue 2.0 11-12 napt s ection 2 c onditions napt is supported for dt800/dt700, and standard sip terminals. “license exceeded” will display on the dt800/dt700 terminal when trying to register a nat phone, if the feature is not licensed. Terminals using napt must be at firmware v3.0.0.0 or higher. Ip ...
Page 586
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 11-13 each napt terminal can have a separate register and subscribe expire timer. The load of the cpu will increase with each napt terminal using a short timer. The following chart shows the minimum timer settings based on the number of napt terminals using prg 15-...
Page 587
Issue 2.0 11-14 napt it is assumed that port numbers are not changed by the nat router on the terminal side. If a port number is changed by nat router, nec does not guarantee proper operation. If installing multiple terminals in the domain of the nat router on the terminal side, the sip port number ...
Page 588
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 11-15 10-12-09 gcd-cp10 network setup – ip address set for iple the ip address assigned in program 10-12-01 cannot start with the same leading digits as the ip address assigned here. 0.0.0.0 ~ 126.255.255.254 128.0.0.1 ~ 191.255.255.254 192.0.0.1 ~ 223.255.255.254 ...
Page 589
Issue 2.0 11-16 napt 10-46-01 dt800/dt700 server information setup - register mode normal mode: when the phone boots up, it reports the ext. Assigned in the phone or chooses the next available extension in the system. No password is required. Auto mode: if set to auto, the sip user name and password...
Page 590
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 11-17 10-58-02 network address - subnet mask this program sets the local area network of the dt800/dt700 terminal when the system has a nat router and a local router. 248.0.0.0 / 252.0.0.0 / 254.0.0.0 / 255.0.0.0 255.128.0.0 / 255.192.0.0 / 255.224.0.0 255.240.0.0 ...
Page 591
Issue 2.0 11-18 napt 15-05-47 registration expire timer for napt on a per station basis, this setting defines the sip registration expiry timer. This setting only applies to dt800/dt700 stations connected via napt. If this value is set to 0, for a napt terminal, the value in prg 84-23-01 is applied....
Page 592: Chapter 12
Sv9100 networking manual 12-1 chapter 12 univerge ® sv9100 all dsp busy indication s ection 1 i ntroduction the all dsp busy feature is used to alert users via telephone displays and/or alarm reports when all dsp resources in the system are being used. This can be used to trouble shoot issues or to ...
Page 593
Issue 2.0 12-2 all dsp busy indication alarm report example: the report example below shows an alarm for all busy station and trunk dsps. Lcd display s ection 2 s ervice c onditions when using ip phones, the alarm is shown on both terminals involved in that call if they are both on the same system, ...
Page 594
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 12-3 s ection 3 r elated f eatures ip multiline station (sip) ip trunk – (sip) session initiation protocol k-ccis – ip sv9100 netlink s ection 4 g uide to f eature p rogramming program number program name description/comments assigned data level 1 2 3 20-13-52 voip...
Page 595
Issue 2.0 12-4 all dsp busy indication.
Page 596: Chapter 13
Sv9100 networking manual 13-1 chapter 13 univerge ® sv9100 aspirenet introduction s ection 1 i ntroduction 1.1 what is aspirenet? The aspirenet package provides a seamless connection of multiple systems into a single “virtual” communications system using isdn (pri/bri) and voip lines with a unified ...
Page 597
Issue 2.0 13-2 aspirenet paging aspirenet allows a user to place paging call to a networked system. If you need to get through to a co- worker who is not at their desk then place a paging call to their system. Call forwarding you can forward your calls to an extension at another networked extension....
Page 598
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 13-3 sv9100 system requirements aspirenet is supported on the gcd-cp10 blade 1.3 available features feature name ars/f-route barge in blf indication (at hotline / dss console key) call forwarding override caller id display call forwarding: immediately busy no answe...
Page 599
Issue 2.0 13-4 aspirenet 1.4 using this manual this chapter is in four sections: section 1: introduction this section provides an introduction for the aspirenet. Section 2: setting up aspirenet this section guides you step by step in setting up a basic aspirenet system. Section 3: aspirenet features...
Page 600
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 13-5 when reading an instruction using programmable keys, you will see a notation similar to (pgm 15-07 or sc 751: 06). This means that the key requires function code 06, and you can program this code through program 15-07 or by dialing service code 751. Refer to t...
Page 601
Issue 2.0 13-6 aspirenet the installation of each mode is shown in the following diagrams. Mode 3 bri/pri network mode (leased line) mode 4 bri/pri network mode (interconnected line). Mode 5 bri/pri interconnection mode (interconnected line, layer 1 = nt). ° 10-03-03: pcb setup - connection type the...
Page 602
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 13-7 example: ° 10-03-10 : pcb setup - master/slave system determine which system will be the master system and which one(s) will be the slave system(s). If one end of the line is set as the master, the other end of the line must be set as the slave. The choice of ...
Page 603
Issue 2.0 13-8 aspirenet 2.3.1 system ip address ° 10-12-09 : gcd-cp10 network setup - ipl ip address (iple) select the ip address of the iple blade (default: 172.16.0.10). A static ip address is required. Each sv9100 system within the network must have a unique ip address. The system must be reset ...
Page 604
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 13-9 2.3.3 ip address of other systems within the network ° 10-27 : ip system id - ip address the ip addresses of all other systems within the network must be defined in this program. Each system is identified by a 'system number' (1 to 50), this is used within the...
Page 605
Issue 2.0 13-10 aspirenet example: 2.3.5 networking tcp port ° 84-02-35 : h.225, h.245 information basic setup - fast start mode if ipla is used for networking, the fast start option must be enabled. Type of external equipment 1- cti server 2- acd mis 3- - reserve - 4- network system 5- - reserve - ...
Page 606
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 13-11 2.4 aspirenet multi site aspirenet multi site is a network of three or more systems connected by either aspirenet isdn or aspirenet ip. The configuration for three or more sites is the same as for two sites, refer to aspirenet isdn or aspirenet ip for details...
Page 607
Issue 2.0 13-12 aspirenet the same also applies for aspirenet isdn, an isdn channel will be used from site a to b and also from site b to c. 2.5 numbering plan ° 11-01-01 : system numbering set the system’s internal (intercom) numbering plan and system id to route to networked systems. The numbering...
Page 608
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 13-13 step 3: assign a function to the code selected after entering a code and specifying its length, you must assign its function. This is the dial type column in the table. The choices are: --changing the dial type for a range of codes can have a dramatic affect ...
Page 609
Issue 2.0 13-14 aspirenet example: this example shows two separate extension numbers assigned for the networked systems. System a dials 4xx to reach system b, while system b dials 3xx to reach system a. The following example shows a unified extension number assignment. All users dial a 4-digit exten...
Page 610
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 13-15 ° program 11-02-01 : extension numbering assign the extension numbers to the ports. The extension number can be up to eight digits long. The first/ second digit(s) of the number should be assigned in program 11-01. This lets an employee move to a new location...
Page 611
Issue 2.0 13-16 aspirenet ° 44-05-03 : ars/f-route table - additional dial number table enter the table number (defined in program 44-06) for additional digits to be dialed (0-1000). Using the 4-digit extension number example in program 11-01-01, the entry would be: ars/f-route table number 1: prior...
Page 612
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 13-17 s ection 3 a spire n et f eatures refer to the sv9100 feature & specifications manual for complete description and programming information for the following features. The information detailed here applies only to the feature when used in a networked system 3....
Page 613
Issue 2.0 13-18 aspirenet set call forward to an f-route number. The full digit length must be set in program 11-01 to allow the user to enter the full f-route destination number. For example if 11-01 was set to 1 digit number length in the example above a user who sets call forward can only enter 1...
Page 614
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 13-19 3.2 barge in barge in is available in the networking feature with the following options: • barge into a conversation between an extension’s own system and a networked system • barge into a conversation between callers in a networked system • barge into a call...
Page 615
Issue 2.0 13-20 aspirenet 3.3 call forwarding call forwarding immediate / busy / no answer / busy-no answer / both ring options are available with the networking feature. With a networked system, when call forwarding enabled, there is a slight difference in the telephone’s dis- play. With a single s...
Page 616
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 13-21 related programs 3.4 call forwarding/ do not disturb override the extension user may be able to call an extension which has call forwarding or do not disturb set. Operation to override an extension’s call forwarding or do not disturb: 1. Call the forwarded or...
Page 617
Issue 2.0 13-22 aspirenet ture works the same in a networked system as it does in a single system. A call to an extension at a remote system will forward to the abbreviated dial bin using a trunk at the remote system. Operation to activate call forwarding off-premise 1. At system phone, press spk ke...
Page 618
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 13-23 phone’s display. With a single system, the destination extension displays the extension name for the phone with follow-me enabled. With a networked system, the extension number is displayed. Operation to activate call forward follow me: 1. At a system phone o...
Page 619
Issue 2.0 13-24 aspirenet 3.7 camp on with camp on, an extension user may call a busy extension and wait in line (camp-on) without hanging up. The call goes through when the busy extension becomes free. Camp on helps extension users to get through as soon as a busy extension becomes free. It also le...
Page 620
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 13-25 3.8 caller id display caller id information can be sent to the target extension in a networked system and show the caller id on the phone’s display. The abb name is also shown on lcd by searching abb table at the target system. Operation a ddi call routed dir...
Page 621
Issue 2.0 13-26 aspirenet 3.9 central office calls, placing: seizing a trunk in a networked system the system allows a user to seize a trunk in a networked system using the following methods: operation the operation is automatic, the user dials the trunk access code in the normal way. Abbreviated di...
Page 622
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 13-27 ference 3.10 conference the user can create a conference call to include a user in a networked system. Operation to establish a conference: keyset 1. Establish intercom or trunk call. 2. Press conf or conference key (pgm 15-07 or sc 751: 07) or press hold and...
Page 623
Issue 2.0 13-28 aspirenet related programs program number title 15-02-24 conf key operation mode (for system phones) 15-07-01 programming function keys - conference (code 07) 20-06-01 calls of service for extensions 20-13-08 class of service options (supplementary service) - conference.
Page 624
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 13-29 epartment calling 3.11 department calling department group access is available via networking. When the extension at system a tries to make a department call to system b, system a should have a numbering plan which defines the department access code at system...
Page 625
Issue 2.0 13-30 aspirenet department step call 3.12 department step call after calling a busy department calling group member in a networked system, an extension user can have department step calling quickly call another member in the group. Operation to make a step call: you step through extension ...
Page 626
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 13-31 direct inward dialling (ddi) 3.13 direct inward dialing (ddi) an incoming ddi call can be routed to an extension in a networked system. Operation for incoming ddi calls, the system refers to program 22-11: ddi translation number conversion to deter- mine how ...
Page 627
Issue 2.0 13-32 aspirenet direct inward line (dil) 3.14 direct inward line (dil) a direct inward line (dil) is a trunk that rings an extension, virtual extension or department group directly. Since dils only ring one extension or group (i.E., the dil destination), employees always know which calls a...
Page 628
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 13-33 direct inward system access (disa) 3.15 direct inward system access (disa) networking allows disa callers to place a call to an extension in a networked system. Some system fea- tures can also be accessed from the networked system. The class of service is det...
Page 629
Issue 2.0 13-34 aspirenet related programs 3.16 hold this feature is available with no changes in programming or operation. The moh tone is sourced at the local system where the caller is hearing the hold tone. For example a user at system a places a call to system b and puts the call on hold, the m...
Page 630
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 13-35 holdhotline / direct station selection (dss) 3.17 hotline / direct station selection (dss) an extension user can have a hotline key to a networked extension. The hotline or dss console keys can display the status lamp indication of an extension in a networked...
Page 631
Issue 2.0 13-36 aspirenet related programs 3.18 intercom an extension user can make an intercom call to a networked system if the networked extensions are defined with the network access code (program 11-01, dial type = 8) a user can change the signaling type for the intercom call they place to eith...
Page 632
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 13-37 keep alive operation 3.19 keep alive operation the keep alive operation will check that the distant end is available. A dummy message is sent that the distant end must respond to, if no response is received the line will be taken out of service. Keep alive op...
Page 633
Issue 2.0 13-38 aspirenet last number redial 3.20 last number redial last number redial allows an extension user to quickly redial the last number dialed. When used with a networked system, the system can use the same trunk route on which the call was originally placed, even if the trunk is a trunk ...
Page 634
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 13-39 message waiting 3.21 message waiting this feature can be used when placing an intercom call to a networked extension and receives either no answer or hears a busy tone. With a networked system, when a message waiting has been left, there is a slight differenc...
Page 635
Issue 2.0 13-40 aspirenet operator, centralised 3.22 operator, centralized it is possible to have a centralized network operator extension that can be dialed with the operator access code (0). Calls to the operator will be queued and answered in order. Up to 32 calls can be queued at the operator ex...
Page 636
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 13-41 3.23 paging an extension user can make internal or external pages to a networked system. Paging to a networked sys- tem can only be activated by dialing a service code and the target network’s system id. Operation to make an internal page 1. Dial 701. 2. Dial...
Page 637
Issue 2.0 13-42 aspirenet related programs program number title 11-12-19 service code setup (for service access) - internal group paging 11-12-20 service code setup (for service access) - external paging 11-12-24 service code setup (for service access) - combined paging 31-01 system options for inte...
Page 638
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 13-43 park 3.24 park park places a call in a waiting state (called a park orbit) so that an extension user may pick it up. Any extension user who is in the same park group as the extension which placed the call in park can answer the call. This includes extension u...
Page 639
Issue 2.0 13-44 aspirenet related programs 3.25 ringdown extension, internal/external a networked system can have a phone defined as a ringdown extension to dial either an internal or exter- nal number. Operation to place a call if your extension has ringdown programmed: 1. Lift handset. If you want...
Page 640
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 13-45 selectable display messaging 3.26 selectable display messaging an extension user can select a preprogrammed selectable display message for their extension. This mes- sage will be displayed on an incoming intercom caller’s lcd when they call the extension in a...
Page 641
Issue 2.0 13-46 aspirenet toll restriction 3.27 toll restriction toll restriction limits the numbers an extension user may dial. When accessing a trunk at a remote system the toll restriction class of service is defined by the calling extension’s system, but the toll restriction tables will be used ...
Page 642
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 13-47 transfer 3.28 transfer the following types of transfer are available with networking: • screened transfer • unscreened transfer • transfer to busy extension operation transferring trunk calls to transfer a trunk call to a co-worker’s extension: 1. At system p...
Page 643
Issue 2.0 13-48 aspirenet transferring intercom calls to transfer your intercom call: 1. At system phone, press hold. Or at single line telephone, hookflash. 2. Dial extension to receive your call. If the extension is busy, doesn’t answer or does not want the call, you can dial another extension num...
Page 644
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 13-49 voice mail, centralised 3.29 voice mail, centralized networking will support the use of a single voice mail for the entire network. A user may call into the voice mail from anywhere in the network and perform most functions as if the voice mail were located o...
Page 645
Issue 2.0 13-50 aspirenet if 102 (in-skin/external voice mail) is selected for the ring group instead of 103, the voice mail within the extension’s own system will be called. Ddi, disa: mis-dial calls if the centralized voice mail is set in program 25-03:103 as the transferred destination for ddi/di...
Page 646
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 13-51 only local voice mail l • the inbound and outbound calls in systems a and b can access the centralized voice mail (600). • program 11-07-01 must be set to none (for the vm group) in system-a otherwise the operation of cen- tralized voice mail will be disabled...
Page 647
Issue 2.0 13-52 aspirenet local voice mail at each sv9100 system • the inbound and outbound calls in system-a can access the local voice mail (600), • the inbound and outbound calls in system-b can access the local voice mail (500). • access to the voice mail of the remote system is available only w...
Page 648
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 13-53 local and centralized voice mail this configuration is not supported, the local voice mail should be removed and only the centralized voice mail used. Related programs program number title 11-01 system numbering plan 11-07 icm pilot calling number 11-12-51 se...
Page 649
Issue 2.0 13-54 aspirenet s ection 4 p rogramming 4.1 before reading this section this section provides you with detailed information about the system programs. By changing a program, you change the way the feature associated with that program works. In this section, you find out about each program,...
Page 650
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 13-55 sion . The second row of the display “ky01 = *01” indicates that key 01 is being programmed with the entry of *01. The third row allows you to move the cursor to the left or right, depending on which arrow is pressed. To learn how to enter the programming mod...
Page 651
Issue 2.0 13-56 aspirenet 4.4 how to exit programming mode to exit the programming mode: when you are done programming, you must be out of a program option to exit (pressing the answer key will exit the program option). 1. Press answer key to exit the program options, if needed. 2. Press speaker. If...
Page 652
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 13-57 4.6 programming names and text messages several programs (e.G., program 20-16 : selectable display messages) require you to enter text. Use the following chart when entering and editing text. When using the keypad digits, press the key once for the first char...
Page 653
Issue 2.0 13-58 aspirenet 4.7 using softkeys for programming each univerge sv9100 display telephone provides interactive softkeys for intuitive feature access. The options for these keys will automatically change depending on where you are in the system programming. Simply press the softkey located ...
Page 654
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 13-59 4.8 what the softkey display prompts mean when using a display telephone in programming mode, various softkey options are displayed. These keys will allow you to easily select, scan, or move through the programs. Table 13-4 softkey display prompts softkey dis...
Page 655: 10-03 : Etu Setup
Issue 2.0 13-60 aspirenet description use program 10-03 : etusetup to setup and confirm the basic configuration data for each blade. When changing a defined terminal type, first set the type to 0 and then plug the new device in to have the system automatically define it or you may have to reset the ...
Page 656
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 13-61 02 logical port number (b1) 0 = not set 1 = multiline terminal (1~960) 2 = slt adapter (1~960) 3 = bluetooth cordless handset (bch) (1~960) 6 = pgd(2)-u13 (paging) (1~8) 7 = pgd(2)-u13 (for tone ringer) (1~8) 8 = pgd(2)-u13 (for door box) (1~8) 9 = pgd(2)-u13...
Page 657
Issue 2.0 13-62 aspirenet for lca pkg setup for cotc unit setup 10 bottom option information (only applies to dtl–style telephones) 0 =no option 1 =apr 2 =ada 3 =bha 4 =no used 5 =bca 0 11 handset option information 0 =no option 1 =psa/psd 2 =bluetooth cordless handset 0 physical port number 01~16 i...
Page 658
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 13-63 for odtb pkg setup for diop pkg setup physical port number 01~04 item no. Item input data default 01 logical port number 0~400 0 02 2/4 wire 0 = 2 wire 1 = 4 wire 1 03 e&m line control method 0 = type i 1 = type v 1 physical port number 01~04 item no. Item in...
Page 659
Issue 2.0 13-64 aspirenet for bria pkg setup isdn line number 01~04 item no item input data default 01 isdn line mode 0 =no setting 1 =t-point 2 =s-point 3 =nw mode (leased line) 4 =nw mode (interconnected line) 5 =nw mode (interconnected line, fixed layer1=nt) 6 =s-point (leased line) 1 02 logical ...
Page 660
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 13-65 10 master/slave system if set to 0, system is synchronized to network clock. If set to 1, system is not synchronized to the network clock. 0 =slave system 1 =master system 0 11 networking system no. 0 - 50 0 14 service protocol for s-point 0 =keypad facility ...
Page 661
Issue 2.0 13-66 aspirenet for prta pkg setup isdn line number 01~24 item no. Item input data default 01 isdn line mode 0 =no setting 1 =t-point 2 =s-point 3 =nw mode (leased line) 4 =nw mode (interconnected line) 5 =nw mode (interconnected line, fixed layer1=nt) 6 =s-point (leased line) 1 02 logical...
Page 662
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 13-67 11 networking system number (network mode only) 0 - 50 0 12 --- not used --- 13 loss-of-signal detection limit if the transmit/receive voltage is less than the setting in 10-03-13, the system considers this as loss-of-signal and the prta does not come up. Not...
Page 663
Issue 2.0 13-68 aspirenet for dti (t1) pkg setup 21 number of ports 0 =auto 1 =4 ports 2 =8 ports 3 =12 ports 4 =16 ports 5 =20 ports 6 =24 ports 7 =28 ports 0 22 qsig operation mode 0 =disable 1 =enable 0 23 straight/cross wiring 0 = auto 1 = manual (cross) 2 = manual (straight) 0 physical port num...
Page 664
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 13-69 for iple pkg setup for vm00 pkg setup for ccta pkg setup 07 straight/cross wiring 0 = auto 1 = manual (cross) 2 = manual (straight) 0 item no. Item input data 01 voip type iple 02 number of channel 256 03 number of voice channels 256 physical port number 01~1...
Page 665
Issue 2.0 13-70 aspirenet conditions when changing a defined terminal type, first set the type to 0 and then plug the new device in to have the system automatically define it, or redefine the type manually. The system must have a blade installed to view/change the options for that type of blade. Fea...
Page 666
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 13-71 description use program 10-12 : gcd-cp10 network setup to setup the ip address, subnet-mask, and default gateway addresses. Program 10 : system configuration setup 10-12 : gcd-cp10 network setup level: sa caution if any ip address or nic setting is changed, t...
Page 667
Issue 2.0 13-72 aspirenet 04 time zone 0~24 (0 = -12 hours and 24 = +12 hours) 12 determine the offset from greenwich mean time (gmt) time. Then enter its respective value. For example, eastern time (us and canada) has a gmt offset of -5. The program data would then be 7 (0= -12, 1= -11, 2= -10, 3= ...
Page 668
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 13-73 conditions the system must be reset for these changes to take affect. Feature cross reference voice over internet protocol (voip) 10 subnet mask 128.0.0.0 192.0.0.0 224.0.0.0 240.0.0.0 248.0.0.0 252.0.0.0 254.0.0.0 255.0.0.0 255.128.0.0 255.192.0.0 255.224.0....
Page 669
Issue 2.0 13-74 aspirenet description use program 10-19 : voip dsp resource selection to define the criteria for each dsp resource on the voip blade. Conditions none feature cross reference none program 10 : system configuration setup 10-19 : voip dsp resource selection level: sa input data slot num...
Page 670
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 13-75 description use program 10-20 : lan setup for external equipment to define the tcp port/address/etc. For communicating to external equipment. Program 10 : system configuration setup 10-20 : lan setup for external equipment level: in input data type of externa...
Page 671
Issue 2.0 13-76 aspirenet conditions none feature cross reference none.
Page 672
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 13-77 description use program 10-27 : h.323 interconnection with application setup to set the ip address of the networked ip systems. Conditions none feature cross reference none program 10 : system configuration setup 10-27 : h.323 system interconnection with appl...
Page 673
Issue 2.0 13-78 aspirenet description use program 10-31 : networking keep alive setup to set the interval and retry count of the aspirenet networking keep alive message. The keep alive is used for isdn and ip networking. The keep alive message is automatically responded to by the destination sv9100,...
Page 674
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 13-79 conditions the keep alive message must be sent and a response not received for the retry count, for the link to be taken out of service and the calls in progress and park hold orbits to be released. For example: if an isdn net link connection is disconnected ...
Page 675
Issue 2.0 13-80 aspirenet description use program 10-32 : pri networking maximum pri channel setup to assign the number of b- channels to be used for each isdn blade. This allows for fractional pris when used with multiple site networking. If this program is limited to less than "30" on one side of ...
Page 676: 11-01 : System Numbering
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 13-81 description use program 11-01 : system numbering to set the system numbering plan. The numbering plan assigns the first and second digits dialed and affects the digits an extension user must dial to access other extensions and features, such as service codes ...
Page 677
Issue 2.0 13-82 aspirenet entering two digits lets you define codes based on the first two digits a user dials. For example, entering 60 allows you to define the function of all codes beginning with 60. In the default program, only and # use 2-digit codes. All the other codes are single digit. If yo...
Page 678
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 13-83 default see the following tables for default settings. 9 dial extension analyze 11-20 : dial extension analyze table changing the dial type for a range of codes can have a dramatic affect on how your system operates. Assume, for example, the site is a hotel t...
Page 679
Issue 2.0 13-84 aspirenet 27 0 0 28 0 0 29 0 0 20 0 0 2 0 0 2 # 0 0 3x 4 2 31 0 0 32 0 0 33 0 0 34 0 0 35 0 0 36 0 0 37 0 0 38 0 0 39 0 0 30 0 0 3 0 0 3 # 0 0 4x 3 1 41 0 0 42 0 0 43 0 0 44 0 0 45 0 0 46 0 0 47 0 0 48 0 0 49 0 0 table 13-5 system numbering default settings (continued) dial types: 1=...
Page 680
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 13-85 40 0 0 4 0 0 4 # 0 0 5x 3 1 51 0 0 52 0 0 53 0 0 54 0 0 55 0 0 56 0 0 57 0 0 58 0 0 59 0 0 50 0 0 5 0 0 5 # 0 0 6x 3 1 61 0 0 62 0 0 63 0 0 64 0 0 65 0 0 66 0 0 67 0 0 68 0 0 69 0 0 60 0 0 6 0 0 6 # 0 0 table 13-5 system numbering default settings (continued)...
Page 681
Issue 2.0 13-86 aspirenet 7x 3 1 71 0 0 72 0 0 73 0 0 74 0 0 75 0 0 76 0 0 77 0 0 78 0 0 79 0 0 70 0 0 7 0 0 7 # 0 0 8x 1 1 81 0 0 82 0 0 83 0 0 84 0 0 85 0 0 86 0 0 87 0 0 88 0 0 89 0 0 80 0 0 8 0 0 8 # 0 0 9x 1 5 91 0 0 92 0 0 table 13-5 system numbering default settings (continued) dial types: 1=...
Page 682
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 13-87 93 0 0 94 0 0 95 0 0 96 0 0 97 0 0 98 0 0 99 0 0 90 0 0 9 0 0 9 # 0 0 0x 1 3 01 0 0 02 0 0 03 0 0 04 0 0 05 0 0 06 0 0 07 0 0 08 0 0 09 0 0 00 0 0 0 0 0 0 # 0 0 x 42 1 1 0 0 2 0 0 3 0 0 4 0 0 5 0 0 table 13-5 system numbering default settings (continued) dial...
Page 683
Issue 2.0 13-88 aspirenet conditions none feature cross reference flexible system numbering 6 0 0 7 0 0 8 0 0 9 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 # 0 0 # x 0 0 # 1 2 1 # 2 2 1 # 3 2 1 # 4 2 1 # 5 2 1 # 6 2 1 # 7 2 1 # 8 2 1 # 9 2 1 # 0 2 1 # 4 1 ## 2 1 table 13-5 system numbering default settings (continued) dial type...
Page 684: 11-02 : Extension Numbering
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 13-89 description use program 11-02 : extension numbering to set the extension number. The extension number can have up to eight digits. The first/second digit(s) of the number should be assigned in program 11-01 or program 11-20. This allows an employee to move to...
Page 685
Issue 2.0 13-90 aspirenet department calling flexible system numbering intercom.
Page 686
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 13-91 description use program 11-07 : department group pilot numbers to assign pilot numbers to each department group set up in program 16-02. The pilot number is the number users dial for department calling and department step calling. The pilot number can have up...
Page 687
Issue 2.0 13-92 aspirenet description use program 11-10 : service code setup (for system administrator) to customize the service codes for the system administrator. You can customize additional service codes in programs 11-11~11-16. The following chart shows: the number of each code (01~42). The fun...
Page 688
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 13-93 13 --- not used --- 14 --- not used --- 15 --- not used --- 16 leaving message waiting (requires cpu to be licensed for hotel/motel) mlt 626 11-11-09 17 dial block by supervisor mlt 601 90-19 18 off-premise call forward by door box mlt 722 13-05 19 --- not us...
Page 689
Issue 2.0 13-94 aspirenet conditions none feature cross reference refer to input data chart on the previous pages. 39 --- not used --- 40 --- not used --- 41 date setting mlt not set 20-07-30 42 maintenance service mlt not set 43 --- not used --- 44 --- not used --- 45 --- not used --- 46 watch mess...
Page 690
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 13-95 description use program 11-11 : service code setup (for setup/entry operation) to customize the service codes which are used for registration and setup. You can customize additional service codes in programs 11-10, and 11-12 ~ 11-16. The following chart shows...
Page 691
Issue 2.0 13-96 aspirenet 14 text message setting mlt no setting 15 enable handsfree incoming intercom calls mlt 721 20-09-05 20-02-12 16 force ringing of incoming intercom calls mlt 723 20-09-05 20-02-12 17 programmable function key programming (2-digit service codes) mlt 751 15-07 11-11-38 18 bgm ...
Page 692
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 13-97 37 ring volume set mlt 729 38 programmable function key programming (3-digit service codes) mlt 752 15-07 11-11-17 39 station speed dial number entry mlt, slt 755 40 --- not used --- 41 tandem ringing mlt, slt no setting 15-07 30-03 42 --- not used --- 43 hea...
Page 693
Issue 2.0 13-98 aspirenet conditions none feature cross reference refer to the input data chart above. 58 call forward with personal greeting mlt, slt 713 59 call forward to attendant except busy mlt, slt no setting 15-01-08 60 call forward to attendant/no answer mlt, slt no setting 15-01-09 62 head...
Page 694
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 13-99 description use program 11-12 : service code setup (for service access) to customize the service codes which are used for service access. You can customize additional service codes in programs 11-10, 11- 11, and 11-13 through 11-16. The following chart shows:...
Page 695
Issue 2.0 13-100 aspirenet 12 last number dial mlt, slt # 5 13 saved number dial mlt, slt 715 14 trunk group access mlt, slt 704 15 specified trunk access mlt, slt # 9 16 trunk access via networking mlt, slt no setting 17 clear last number dialing data mlt, slt 776 18 clear saved number dialing data...
Page 696
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 13-101 40 station speed dialing mlt, slt # 7 41 voice over mlt, slt 690 11-16-08 42 flash on trunk lines slt # 3 43 answer no-ring line (universal answer) mlt, slt # 0 14-05 14-06 44 callback test for slt slt 799 45 enabled on hook when holding (slt) slt 749 15-03-...
Page 697
Issue 2.0 13-102 aspirenet conditions none feature cross reference refer to the input data chart on the previous pages. 63 watch mode start mlt, slt 717 64 security sensor mode start mlt, slt 719 mlt = multiline terminal slt = single line telephone input data (continued) item no. Item terminals defa...
Page 698
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 13-103 description use program 11-16 : single digit service code setup to customize the one-digit service codes used when a busy or ring back signal is heard. You can customize additional service codes in programs 11- 10 ~ 11-15. The following chart shows: the numb...
Page 699
Issue 2.0 13-104 aspirenet conditions none feature cross reference refer to the input data chart on previous pages..
Page 700
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 13-105 description use program 14-01 : basic trunk data setup to set the basic options for each trunk port. Refer to the chart below for a description of each option, its range and default setting. Program 14 : trunk, basic setup 14-01 : basic trunk data setup leve...
Page 701
Issue 2.0 13-106 aspirenet 04 transmit gain level for conference and transfer calls use this option to select the codec gain type used by the trunk when it is part of an unsupervised conference. 1~63 (-15.5db ~ +15.5db in 0.5db intervals) 32 (0db) 05 receive gain level for conference and transfer ca...
Page 702
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 13-107 10 dtmf tones for outgoing calls use this option to enable (1) or disable (0) dtmf tones for outgoing trunk calls. 0 =disable (no) 1 =enable (yes) 0 11 account code required 0 =disable (no) 1 =enable (yes) 1 12 --- not used --- 13 trunk-to-trunk transfer use...
Page 703
Issue 2.0 13-108 aspirenet 17 trunk to trunk warning tone for long conversation alarm use this option to enable or disable the warning tone for long conversation feature for disa callers. 0 =disable (no) 1 =enable (yes) 0 18 warning beep tone signaling 0 =disable (no) 1 =enable (yes) 0 19 privacy mo...
Page 704
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 13-109 22 caller id to voice mail enable or disable the system ability to send the caller id digits (remote log-on protocol) to voice mail. 0 =disable (no) 1 =enable (yes) 0 23 least cost routing 0 =lcr off 1 =lcr on 2 =lcr on (cost center code only) 0 24 trunk-to-...
Page 705
Issue 2.0 13-110 aspirenet 33 apsu trunk receive gain additional pad when a trunk call connects to apsu voice mail. 1~57 (-15.5db ~ +12.5db in 0.5db intervals) 32 (0db) 35 dt800/dt700 large led illumination setup sets led color for incoming trunk call. In dt800/dt700 local terminal setting menu, ill...
Page 706
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 13-111 38 outgoing cli selection select cli (calling party number) sending way to trunk. When set to 0, extension cli number set in prg21-13-01, prg21-18-01, or prg21-19-01is sent according to seized trunk type (isdn/ h.323/sip) automatically. When set to 1, callin...
Page 707
Issue 2.0 13-112 aspirenet default trunk port number name 1 line 001 2 line 002 : : 400 line 400
Page 708
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 13-113 conditions none feature cross reference refer to features in the input data table..
Page 709: 14-06 : Trunk Group Routing
Issue 2.0 13-114 aspirenet description use program 14-06 : trunk group routing to set up an outbound routing table for the trunk groups you assigned in program 14-05. When users dial 9, the system routes their calls in the order (priority) specified. For example, if a user dials 9 and all calls in t...
Page 710
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 13-115 default - route 1, order number 1 = 1 (trunk group 1). - order numbers 2, 3, 4 = 0 (not specified). - all other routes (2~100) and order numbers (1~4) = 0 (not specified). Conditions none feature cross reference none input data route table number 001~100 ite...
Page 711
Issue 2.0 13-116 aspirenet description use program 16-01 : department group basic data setup to set the function mode for each department group. There are 64 available department groups. Program 16 : department group setup 16-01 : department group basic data setup level: in input data department gro...
Page 712
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 13-117 conditions none feature cross reference 05 extension group all ring mode operation determine whether calls ringing a department group should ring all extensions in the group simultaneously automatically or manually when using the service code defined in prog...
Page 713
Issue 2.0 13-118 aspirenet department calling.
Page 714
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 13-119 description use program 16-02 : department group assignment for extensions to set the department groups. The system uses these groups (64 department groups) for department calling. Assign pilot numbers to department groups you set up in program 11-07. This l...
Page 715: 20-01 : System Options
Issue 2.0 13-120 aspirenet description use program 20-01 : system options to set various system options. Program 20 : system option setup 20-01 : system options level: in input data ite m no. Item input data defaul t description related program 01 operator access mode 0 =step call 1 =circular 0 use ...
Page 716
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 13-121 conditions none feature cross reference refer to the input data table at the beginning of this section..
Page 717
Issue 2.0 13-122 aspirenet description use program 21-16 : trunk group routing for networks to assign program 14-06 routes for a networked system. This is required to seize the trunk in a networked system (extension in system a tries to make an external call using a trunk in system b). The route num...
Page 718
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 13-123 description use program 22-05 : incoming trunk ring group assignment to assign trunks to incoming ring groups.There are 100 available ring groups. Conditions none feature cross reference ring groups program 22 : incoming call setup 22-05 : incoming trunk rin...
Page 719
Issue 2.0 13-124 aspirenet description uor dil delayed ringing, use program 22-08 : dil/irg no answer destination to assign the dil no answer ring group. An unanswered dil rings this group after the dil no answer time expires (program 22-01-04). Dil delayed ringing can also reroute outside calls rin...
Page 720
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 13-125 description use program 22-10 : did translation table setup to specify the size of the did translation tables. There are 4000 translation table entries that you can allocate among 20 translation tables. Program 22 : incoming call setup 22-10 : did translatio...
Page 721
Issue 2.0 13-126 aspirenet default table conditions none feature cross reference direct inward dialing (did) conversion table area 1st 2nd start table end table start table end table 1 1 200 0 0 2 201 400 0 0 3 401 600 0 0 4 601 800 0 0 5 801 1000 0 0 6 1001 1200 0 0 7 1201 1400 0 0 8 1401 1600 0 0 ...
Page 722
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 13-127 description use program 22-11 : did translation table number conversion to specify for each translation table entry (2000). The digits received by the system (eight maximum) the extension the system dials after translation (24 digits maximum) the name that s...
Page 723
Issue 2.0 13-128 aspirenet * enter characters: + , - . / : ; ? B e s ¢ £ # # = accepts an entry (only required if two letters on the same key are needed - ex: tom). Pressing # again = space. (in system programming mode, use the right arrow soft key instead to accept and/or add a space.) recall clear...
Page 724
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 13-129 05 transfer destination number 1 0 = no setting 1~100 = incoming group 102 = in-skin/external voice mail or inmail 103 = centralized vm 201~264 = extension group 400 = valid extension number 401 = disa 501~599 = disa/vrs message 1000~1999 = speed dial number...
Page 725
Issue 2.0 13-130 aspirenet default the default value of prg22-11-01/prg22-11-02 is shown as below. Conversion table received number target number 1 01 101 : : : 99 99 199 100 00 100 101 no setting no setting : : : 200 no setting no setting 201 01 101 : : : 299 99 199 300 00 100 301 no setting no set...
Page 726
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 13-131 conditions - when the trunk type is set to 3 (did) in 22-02-01, the did transfer destination for each did feature is not supported. This feature is supported only for did trunks when assigned as vrs. Feature cross reference direct inward dialing (did).
Page 727
Issue 2.0 13-132 aspirenet description for each did translation table, use program 22-12 : did intercept ring group to define the first destination group for did calls. Depending on the entry in program 22-09-02 and 22-11-04, the incoming calls route to the first destination group by the following: ...
Page 728
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 13-133 conditions none feature cross reference direct inward dialing (did).
Page 729: Program 25 : Vrs/disa Setup
Issue 2.0 13-134 aspirenet description use program 25-03 : vrs/disa transfer ring group with incorrect dialing to set what happens to a call when the disa or automated attendant caller dials incorrectly or waits too long to dial. The call can either disconnect (0) or transfer to an alternate destina...
Page 730: Program 25 : Vrs/disa Setup
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 13-135 description use program 25-04 : vrs/disa transfer ring group with no answer/busy to set the operating mode of each disa trunk. This sets what happens to the call when the disa or automated attendant caller calls a busy or unanswered extension. The call can e...
Page 731: Program 25 : Vrs/disa Setup
Issue 2.0 13-136 aspirenet description use program 25-08 : disa user id setup to set the 6-digit disa password for each user. There are 15 users each with one 6-digit password. Conditions none feature cross reference direct inward system access (disa) program 25 : vrs/disa setup 25-08 : disa user id...
Page 732
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 13-137 description use program 44-01 : system options for ars/f-route to define the system options for the ars/f-route feature. Conditions none feature cross reference automatic route selection (ars) uniform numbering network program 44 : ars/f-route setup 44-01 : ...
Page 733
Issue 2.0 13-138 aspirenet description use program 44-02 : dial analysis table for ars/f-route access to set the pre-transaction table for selecting ars/f-route. Program 44 : ars/f-route setup 44-02 : dial analysis table for ars/f-route access level: in input data dial analysis table number 1~120 it...
Page 734
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 13-139 conditions none feature cross reference automatic route selection (ars) 03 additional data for the service type selected in 44-02-02, enter the additional data required. 1: delete digit = 0~255 (255 = delete all digits) 2: [program 44-01 : 0] ars/f-route tab...
Page 735
Issue 2.0 13-140 aspirenet description when program 44-02-02 is set to type 3, use program 44-03 : dial analysis extension table to set the dial extension analysis table. These tables are used when the analyzed digits must be more than eight digits. If the received digits do not match the digits set...
Page 736
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 13-141 conditions none feature cross reference automatic route selection (ars) dial analysis table number : 251 item no. Item input data default 03 ars/f-route select table number 0~500 (ars/f-route table number) with program 44-01 set to 0, program 44-05 is checke...
Page 737
Issue 2.0 13-142 aspirenet description use program 44-04 : ars/f-route selection for time schedule to assign each ars/f-route selection number to an ars/f-route table number for each ars/f-route time mode. There are eight time modes for ars/f-route access. Conditions none feature cross reference aut...
Page 738: 44-05 : Ars/f-Route Table
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 13-143 description use program 44-05 : ars/f-route table to set the ars/f-route table. There are four kinds of order. If the higher priority trunk groups are busy, the next order group is used. If a lower priority route is selected, the caller may be notified with ...
Page 739
Issue 2.0 13-144 aspirenet conditions none feature cross reference automatic route selection (ars) 08 dial treatment select the dial treatment to be used for the table. If a dial treatment is selected, programs 44-05-02 and 44-05-03 are ignored and the dial treatment defined in program 26-03-01 is u...
Page 740
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 13-145 description use program 44-06 : additional dial table to set the additional dial table to add prior to the dialed ars/f- route number. The additional dial table used is determined in program 44-05-03. Conditions none feature cross reference automatic route s...
Page 741
Issue 2.0 13-146 aspirenet description use program 44-07 : gain table for ars/f-route access to set the gain/pad table. If an extension dials ars/f-route number: the extension dial gain table, assigned in program 44-05, is activated. The extension dial gain table follows outgoing transmit and outgoi...
Page 742
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 13-147 conditions none feature cross reference automatic route selection (ars).
Page 743
Issue 2.0 13-148 aspirenet description use program 44-08 : time schedule for ars/f-route to define the daily pattern of the ars/f-route feature. Ars/f-route has 10 time patterns. These patterns are used in program 44-09 and 44-10. The daily pattern consists of 20 time settings. Default all schedule ...
Page 744
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 13-149 conditions none feature cross reference automatic route selection (ars).
Page 745
Issue 2.0 13-150 aspirenet description use program 44-09 : weekly schedule for ars/f-route to define a weekly schedule for using ars/f- route. The pattern number is defined in program 44-08-01. Conditions none feature cross reference automatic route selection (ars) program 44 : ars/f-route setup 44-...
Page 746
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 13-151 description use program 44-10 : holiday schedule for ars/f-route to define a yearly schedule for ars/f-route. This schedule is used for setting special days such as national holidays. The pattern number is defined in program 44-08-01. Conditions none feature...
Page 747
Issue 2.0 13-152 aspirenet description use program 45-01 : voice mail integration options to customize certain voice mail integration options. Program 45 : voice mail integration 45-01 : voice mail integration options level: in input data ite m no. Item input data default 01 voice mail department gr...
Page 748
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 13-153 conditions none feature cross reference voice mail integration (analog) 09 centralized voice mail master name assigns the centralized voice mail master name. Up to 12 characters “c.V.M.” 10 new nsl protocol support 0 = off 1 = on 0 11 prefix for call screeni...
Page 749
Issue 2.0 13-154 aspirenet description use program 84-01 : h.323 trunk basic information setup to set the basic information of the h.323 trunk. Program 84 : hardware setup for voip 84-01 : h.323 trunk basic information setup level: in input data item no. Item input data default 02 number of g.711 au...
Page 750
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 13-155 conditions none feature cross reference voice over internet protocol (voip) 22 vad threshold 0~30 (-19db~ +10db and self adjustment) 0 = self adjustment 1 = -19db (-49dbm) : 20 = 0db (-30dbm) : 29 = 9db (-21dbm) 30 = 10db (-20dbm) 20 33 priority codec settin...
Page 751
Issue 2.0 13-156 aspirenet description use program 84-02 : h.225 and h.245 information basic setup to define the basic setup information of h.225 and h.245. Program 84 : hardware setup for voip 84-02 : h.225 and h.245 information basic setup level: in input data ite m no. Item input data default 01 ...
Page 752
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 13-157 conditions none feature cross reference voice over internet protocol (voip) 22 arq retry count 0~255 2 23 ras brq timer 0~255sec 5 24 brq retry count 0~255 2 25 ras irr timer 0~255sec 5 26 irr retry count 0~255 2 27 ras drq timer 0~255sec 8 28 drq retry coun...
Page 753
Issue 2.0 13-158 aspirenet description use program 84-12: networking codec information basic setup to define the codec information for networking. Program 84 : hardware setup for voip 84-12 : networking codec information basic setup level: in input data ite m no. Item input data default 01 number of...
Page 754
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 13-159 08 g.729 silence compression (vad) mode select whether to compress silence with g.729. When there is silence, the rtp packet is not sent. 0 =disable 1 =enable 0 09 g.729 jitter buffer - minimum set the minimum value of the jitter buffer of g.729 is set. Jitt...
Page 755
Issue 2.0 13-160 aspirenet 18 silence compression (vad) threshold set the voice level judged to be silence. Change value based .30 this entry is ignored if silence compression is disabled in 84-01- 03 with g.711, or 84-01-06 with g.729. 0-30 (self-adjustment and -19db ~ +10db) 0 = self-adjustment 1:...
Page 756
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 13-161 26 tx (transmit) gain define the setting to amplify and to attenuate the size of the transmission voice. The gain given when the voice packet is sent from the voipdb is set. 0-40 (-20 ~ +20) 0 = -20 dbm 1 = -19 dbm : 20 = 0 dbm : 39 = 19 dbm 40 = 20 dbm 20 (...
Page 757
Issue 2.0 13-162 aspirenet conditions none feature cross reference voice over internet protocol (voip) 34 g.722 silence compression mode select whether to compress silence with g.722. When there is silence, the rtp packet is not sent. 0 =disable 1 =enable 0 35 g.722 jitter buffer - minimum set the m...
Page 758: 84-26 : Ipl Basic Setup
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 13-163 description use program 84-26 : ipl basic setup to set the ip address of ipl and the port. Conditions none feature cross reference voice over internet protocol (voip) program 84 : hardware setup for voip 84-26 : ipl basic setup level: in input data slot numb...
Page 759
Issue 2.0 13-164 aspirenet s ection 5 a spire n et e xample the examples in this section are only a guide to the configuration required on the sv9100 to install aspirenet operation. 5.1 aspirenet - isdn bri aspirenet basic rate isdn is supported on all bri pcb’s (2, 4 or 8 briu). Each circuit of the...
Page 760
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 13-165 aspirenet - isdn pri 5.2 aspirenet - isdn pri aspirenet primary rate isdn is supported on the standard prta blade’s. Each prta blade can be set independently to trunk / s0 / aspirenet mode. When set to aspirenet a prta blade will require 30 of the aspirenet ...
Page 761
Issue 2.0 13-166 aspirenet aspirenet - ip 5.3 aspirenet - ip 5.3.1 voip networking example aspirenet ip requires the voipdb blade and sv9100 networking license. The voipdb blade provides the speech resources. The example below shows two sv9100 systems, each has a voipdb blade installed. The voipdb b...
Page 762
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 13-167 explanation of routing for ip aspirenet . When a user places a call to a remote extension number the dialed digits are checked against the number- ing scheme in program 11-01. This will provide the node id number of the route to the remote system. The sv9100...
Page 763
Issue 2.0 13-168 aspirenet 5.3.2multi-site networking example multi-site networking is a network of three or more sv9100 systems. The network can consist of either isdn or ip network connections. The example below shows three sv9100 systems, each has a voipdb blade installed. The voipdb blades are c...
Page 764
Issue 2.0 sv9100 networking manual 13-169 after programming, each system must be reset in order for the ip address changes to take affect. Program 84-12-31 dtmf relay mode 1 = rfc2833 (default: voipdb) program 84-12-31 dtmf relay mode 1 = rfc2833 (default: voipdb) program 84-12-31 dtmf relay mode 1 ...
Page 765
Issue 2.0 13-170 aspirenet.
Page 766: Networking Manual
Networking manual nec corporation issue 2.0