- DL manuals
- KEB
- Recording Equipment
- COMBIVERT F5
- Instruction Manual
KEB COMBIVERT F5 Instruction Manual - General
11
General
1.4.10 High Frequency Shielding
Use of shielded cable is recommended when high frequency emissions or easily
disturbed signals are present. Examples are as follows:
- motor wires connected to inverters: connect shield to ground at both the
inverter and motor, NOTE the shield should never be used as the protective
ground conductor required by NEC. Always use a separate conductor for this.
- digital control wires: connect shield to ground at both ends.
- analog control wires: connect shield to ground only at the inverter.
The connection of meshed shields to the ground connection should not be done
through a single strand of the shield, but with metallic clamps to provide 360° contact
around the surface of the shield to the ground point. Connection with a single wire
bundle from the braided shield reduces the effectiveness of the shield 70%. Metal
conduit clamps work well for this. Be sure the fit is tight.
Ridged metal conduit can be used as the shield of the motor wires. Always observe
the following points :
- remove all paint from the control cabinet and motor housing where the conduit
is fastened
- securely fasten all conduit fittings
- run only the motor wires through the conduit, all other wires, high voltage AC
and low voltage signal, should be pulled through a separate conduit.
- connect the control panel to the Sub-panel with a heavy ground strap.
If EMI filters are used, they should be mounted to the inverter or as close as possible
to the inverter and on the same sub-panel as the inverter. Good metallic surface
contact to the sub-panel is required to provide adequate high frequency grounding of
the filter. Always use the shielding plate provided with the filter when connecting the
filter to the inverter.
Shielding of control wires:
If digital signal wires are terminated on a terminal block in the control panel, the
shields should be firmly connected to the sub-panel on both sides of the terminal
block.
The shields of digital signal wires originating outside the control cabinet which are
not terminated on a terminal block, must be connected to the sub-panel at the point
where the cable enters the control panel and at the inverter.
If the shield is terminated to the sub-panel within 8 inches (20cm) of the inverter,
then the shield no longer needs to be connected to the inverter.
When using un-shielded signal wires, they should always be installed as a twisted
pair (signal and common).
Low voltage signal wires should cross high voltage wires at right angles.
Summary of COMBIVERT F5
Page 1
Instruction manual 00.F5.Lub-k131 combivert f5 r elevator drive.
Page 3: Table of Contents
Table of contents 1. General ................................................ .....5 1.2 model number information ................................ .....6 1.3 mounting instructions ........................................ .....7 1.3.1 classification ......................................................
Page 4: Tabel of Contents
Tabel of contents carrier frequency ............................................................ .....75 set speed shl, high leveling speed .............................. .....76 set speed sint, intermediate speed ............................. .....76 starting jerk .....................................
Page 5: General
5 general 1. General 1.1 product description in selecting the combivert f5 series inverter, you have chosen a fre- quency inverter with the highest quality and dynamic performance. It is exclusively designed for smooth speed regulation of a three-phase motor. The operation of other electrical loads ...
Page 6: General
6 general 1.2 model number information part number 15.F5.M1g-rl00 unit identification 0 = software/function rev 0 1 = software/function rev 1 a = special hardware rev 0 feedback card 0 = none installed at the factory d = ttl input, ttl output j = htl input, ttl output m = sincos, ttl output f = hipe...
Page 7: General
7 general 1.3 mounting instructions 1.3.1 classification the elevator drive is classified as an "open type" inverter with an ip20 rating and is intended for use in a "pollution degree 2 environ- ment." the unit must be mounted inside of a control cabinet offering proper environmental protection. 1.3...
Page 8: General
8 1.4.1 safety first risk of electric shock! Always disconnect supply voltage before servicing the f5 elevator drive. After disconnecting the supply voltage, always wait 5 minutes before attempting to change the wiring. The internal dc bus capacitors must discharge. 1.4.2 voltage supply the f5 serie...
Page 9: General
9 1.4.3 disconnect switch a disconnect switch or contactor should be provided as a means of turning off the supply voltage when the unit is not in use or when it must be serviced. Repetitive cycling on and off of the input supply voltage more than once every two minutes can lead to damage of the inv...
Page 10: General
10 general 1.4.8 high voltage connections always note inverter voltage, select appropriate over current protection devices, select disconnect device, and select proper wire size before beginning the wiring process. Wire the inverter according to nec class 1 requirements. The correct wire gauge for e...
Page 11: General
11 general 1.4.10 high frequency shielding use of shielded cable is recommended when high frequency emissions or easily disturbed signals are present. Examples are as follows: - motor wires connected to inverters: connect shield to ground at both the inverter and motor, note the shield should never ...
Page 12: 2. Technical Data
12 the recommended motor rating is for 4/6 pole standard motors. When using motors with different numbers of poles, the inverter must be dimensioned based on the motor rated current. Contact the manufacturer for special frequency motors. The power rating of the inverter must be derated for operation...
Page 13: Technical Data
13 technical data 1) this is the maximum carrier frequency the power stage can support. The actual operating carrier frequency is adjusted and limited by the control card. 2) this data pertains only to units with the braking circuit installed. All inverters in the g,h,r housing are supplied with the...
Page 14: Technical Data
14 technical data the recommended motor rating is for 4/6 pole standard motors. When using motors with different numbers of poles, the inverter must be dimensioned based on the motor rated current. Contact the manufacturer for special frequency motors. The power rating of the inverter must be derate...
Page 15: Technical Data
15 technical data 1) this is the maximum carrier frequency the power stage can support. The actual operating carrier frequency is adjusted and limited by the control card. 2) this data pertains only to units with the braking circuit installed. All inverters in the g,h,r housing are supplied with the...
Page 16: Technical Data
16 inverter size 20 21 22 23 24 26 recommended motor power [hp] 50 60 75 100 125 175 housing size h r r r u u u input ratings supply voltage [v] 305...500 ±0 (460 v nominal voltage ) supply voltage frequency [hz] 50 / 60 +/- 2 input phases 3 3 3 3 3 3 rated input current [a] 72 85 106 136 172 231 re...
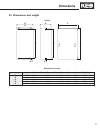
Page 17: Dimensions
17 dimensions 2.3 dimensions and weight inverter dimensions in inches housing a b b2 c c2 f g h weight [lb] e 5.12 11.4 - 8.75 - 0.28 - 10.8 11 g 6.7 13.4 - 10.0 - 0.28 5.9 13.0 22 h 11.7 13.4 - 10.0 - 0.28 9.8 13.0 31 r 13.5 20.5 - 14.0 - 0.394 11.8 19.5 55-64 u 13.5 31.5 - 14.0 - 0.394 11.8 30.5 1...
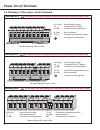
Page 18: Power Circuit Terminals
18 power circuit terminals n/l2 l3 pb u v w t1 t2 -- ++ l1 l1 l2 l3 -- ++ pb t1 t2 u v w l1 l2 pe l3 pe ++ pb -- t1 t2 pe u w v l1, l2, l3 3 phase supply voltage + +, - - dc supply connection + +, pb connection for braking resistor housing size h note always verify input voltage with name plate for ...
Page 19: Power Circuit Terminals
19 power circuit terminals +pa - t1 t2 u v w pb l1 l2 l3 housing size r and u t1, t2 connection for temperature sensor u, v, w motor connection connection for earth ground note always verify input voltage with name plate for proper connection l1, l2, l3 3 phase supply voltage + +, - - dc supply conn...
Page 20
20 t1 t2 t1 t2 t1 t2 pa pb ++ pb connection of braking resistor (braking circuit installed as standard in housing sizes e,g,h, r and u.) external motor temperature sensor (for all units) thermal switch (nc-contact) no jumper required, when a sensor is not connected temperature sensor (ptc ) 1650 Ω.....
Page 21: Overload Characteristic
21 30 60 90 120 150 180 210 240 270 300 0 105 110 115 120 125 130 135 140 145 150 160 170 180 190 200 2.6 time dependent overload curve n n n n n less than size 24 time [s] load [%] o o o o o size 24 and greater time [s] load [%] overload characteristic if the load current exceeds the rated current ...
Page 22: Overload Characteristic
22 overload characteristic 0 3 hz 150% 105% e. Ol e. Ol2 f [hz] load [%] 2.7 low speed overload permanent current (0 hz) at low speeds (below 3 hz) the rms current flowing through the power transistors is higher, reaching 1.4 times the rated 60hz rms value. This is caused by the low frequency sine w...
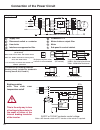
Page 23
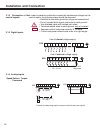
23 3.1.1 terminal strip connections 3.1 control circuit: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 x2a pin function name description 1 analog input 1 + an1+ pattern speed input or resolution: 12 bit 2 analog input 1 - an1- torque command input 3 analog input 2 + a...
Page 24: Installation and Connection
24 gb installation and connection 3.1.2 connection of the control signals in order to prevent a malfunction caused by interference voltages on the control inputs, the following steps should be observed: • establish a true earth ground for all ground connections! • do not connect drive signal commons...
Page 25: Installation and Connection
25 10 11 17 18 19 20 gnd x2a 21 22 23 + 3.1.7 relay outputs 3.1.8 analog outputs x2a 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 gnd 0...±10 vdc 5 ma 3.1.6 digital outputs 10 18 19 20 gnd x2a 21 22 23 a total of max. 50 ma dc for both outputs 3.1.9 voltage output 3.1.5 voltage input / external power supply the voltage output...
Page 26: Installation and Connection
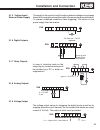
26 gb 3.2 encoder connections 3.2.1 x3a rs422/ttl incremental encoder input connect the incremental encoder mounted on the motor to the 15-pin sub-d connector at x3a on the combivert f5m. This connection provides speed feedback and is imperative to the proper operation of the f5m. Input wiring a + b...
Page 27: Installation and Connection
27 for maximum noise immunity, the encoder cable shall consist of individu- ally shielded twisted pairs with one overall shield. The individual shields should be connected to 0v (com) pin 13 on the sub d connector and be kept separate from the outer shield. The outer shield should be con- nected to ...
Page 28: Installation and Connection
28 gb 3.2.2 x3a ttl inc. Enc. In screw terminals connect the incremental encoder mounted on the motor to the 8 position terminal connector at x3a. This connection provides speed feedback and is imperative to the proper operation of the f5m. Input equivalent circuit a + b + a - b - approx. 120 Ω only...
Page 29: Installation and Connection
29 selection of the supply voltage the maximum load capacity is dependant on the selected voltage supply. Max. Load capacity with 15v internal supply: 300 ma max. Load capacity with 24 v internal supply:170 ma max. Load capacity with an external 24v supply 1 a (dependent on the external voltage sour...
Page 30: Installation and Connection
30 gb 3.2.3 x3a hiperface encoder installation and connection the hiperface encoder provides two differential analog channels for incremental position and one serial data channel for comunication with the encoder. This serial data channel can provide the drive with the absolute position of the motor...
Page 31: Installation and Connection
31 5 4 3 2 1 10 9 8 7 6 15 14 13 12 11 max. Load capacity depending on voltage supply max. Load capacity at +7.5 v:300 ma. The specified current is reduced by the current taken from the second encoder interface x3b interface (see section 3.2.4). Pre-manufactured hiperface cables offer the best solut...
Page 32: Installation and Connection
32 gb installation and connection technical data input resistance: 120 ohm process data channel: 1vpp parameter channel: eia rs485 half duplex maximum input frequency: 200 khz encoder line number: 1...16383 inc (recommended: 1024 inc.At speeds maximum cable length: 100 m (based on signal levels) the...
Page 33: Installation and Connection
33 3.2.4 x3a endat encoder the endat encoder provides two differential analog channels for incre- mental position and one serial data channel with clock for comunication with the encoder. This serial data channel can provide the drive with the absolute position of the motor as well as other operatin...
Page 34: Installation and Connection
34 gb 5 4 3 2 1 10 9 8 7 6 15 14 13 12 11 max. Load capacity depending on voltage supply max. Load capacity at +5.0 v:300 ma. The specified current is reduced by the current taken from the second encoder interface x3b interface (see section 3.2.4). Pre-manufactured endat cables offer the best soluti...
Page 35: Installation and Connection
35 technical data input resistance: 120 ohm process data channel: 1vpp parameter channel: eia rs485 half duplex clock signal output: eia rs485 maximum input frequency: 200 khz encoder line number: 1...16383 inc (recommended: 2048 inc.At speeds 4500 rpm) maximum cable length: 100 m (based on signal l...
Page 36: Installation and Connection
36 gb the second incremental encoder connection serves as a buffered output of the motor encoder. This can be used by other control systems for speed or position control. The output signals are according to the rs422 line driver signal standard. 5 4 3 2 1 9 8 7 6 3.2.5 x3b incremental encoder output...
Page 37
37 gb signal channels a and b com +b com +a t 2...5v 2...5v 0...0,5v 0...0,5v com -a 2...5v 0...0,5v com -b 2...5v 0...0,5v.
Page 38: 4. Operation of The Unit
38 the elevator drive uses a special operator which provides a user inter- face and functionality specific to elevator applications. The operator must be plugged into the drive in order for the drive to function correctly. Unplugging the operator while the drive is in operation will result in immedi...
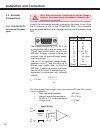
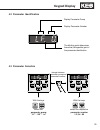
Page 39: Keypad Display
39 enter f/r start stop func. Speed enter f/r start stop func. Speed enter f/r keypad display 4.2 parameter identification the blinking point determines the active (changeable) part of the parameter identification display parameter group display parameter number 4.3 parameter selection change betwee...
Page 40: Keypad Display
40 start stop func. Speed start stop func. Speed enter f/r start stop func. Speed enter f/r keypad display 4.4 changing parameter values display parameter identification display parameter value increase/decrease parameter value changing parameter values all parameter changes are accepted for operati...
Page 41
41 f/r enter enter f/r 4.6 saving parameter values 4.7 error messages only the error message is cleared by pressing enter. To reset the error remove the cause and reset terminal x2.2 or do a power on reset. Some errors are automatically reset according to the adjustment of parameter lf.5. So it is p...
Page 42: 5. Initial Start-Up
42 5. Initial start-up 5.1 selecting the configuration initial start up before trying to operate the drive it is necessary to establish the correct mode of operation. The torqmax f5 drive is capable of driving different types of motors both open and closed loop. Therefore prior to operation, the typ...
Page 43: Initial Start Up
43 5.3 setting the control type the torqmax drive supports three different control modes, digital speed selection and control, analog speed control, analog torque control. The drive’s i/o will need to be set up according to the desired scheme. From the table below select the desired control scheme a...
Page 44: Initial Start Up
44 initial start up as the synchronous speed less 2.9%, so 1200 rpm - 35 rpm = 1165 rpm. Enter the rated fla of the motor in parameter lf.12. Enter the rated nameplate frequency in parameter lf.13. In some cases manufacturers of induction motors derate the motor by changing the frequency to somethin...
Page 45: Initial Start Up
45 5.5.3 measuring the motor resistance for best performance the resistance of the induction motor should be measured by the drive. Use the following steps to complete the measurement for induction motors. 1) remove one brake wire from the controller, preventing it from picking 2) verify lf.3 is set...
Page 46: Initial Start Up
46 5.7 machine data it is necessary to enter the machine data such that the drive can establish the relationship between linear travel, ft/min and rotary speed in rpm at the motor. Enter the job contract speed in parameter lf.20. Then enter the sheave diameter in lf.21. If this value is not known, i...
Page 47: Initial Start Up
47 enter in lf.27 the pulses per revolution of the encoder, i.E. 1024, 2048, 4096 etc. Lf.28 can be used to swap the encoder channels such that the encoder is incrementally counting in the same direction as the motor. Initially leave this parameter set to 0 or no reversal. Whether or not reversal is...
Page 48: Initial Start Up
48 5.11 running the motor 5.11.1 absolute encoder setup (no ropes) initial start up the following will outline the proceedure for aligning an absolute encoder for use with a permanent magnet motor and the following encoders: hiperface, endat, sin/cos. The motor must be mounted in place and be electr...
Page 49: Initial Start Up
49 initial start up alignment process 1) adjust lf.3 = conf 2) set lf.77 = 2206 3) press and hold the inspection up switch. Motor current will begin to flow in one phase and the current will ramp up to the motor’s rated value. The motor sheave should turn slowly and then stop when the motor rotor ha...
Page 50: Initial Start Up
50 5.11.2 absolute encoder setup (with ropes) initial start up the following will outline the procedure for aligning an absolute encoder for use with a permanent magnet motor and the following encoders: hiperface, endat, sin/cos. The motor must be mounted in place and be electrically connected to th...
Page 51: Initial Start Up
51 initial start up driving the car to a floor if possible let the car coast up to a floor where the weights can be loaded into the car to balance it. If this is not possible then it is possible to drive the car down under power. Note: the motor current will be high and therefore operation with this...
Page 52: Initial Start Up
52 initial start up verification of the encoder position. Due to friction and the inertial load or the cab and counter weights can lead to a small error in the actual position value. The following proceedure will verify whether the position is correct or not. 1) set lf.36 = to two times lf.17. 2) pi...
Page 53: Initial Start Up
53 it is necessary to determine whether or not the motor encoder is in phase with the rotation of the motor. As an example the motor is turning clockwise and the encoder is indicating clockwise rotation. The problem comes when the encoder indicates rotation opposite to the actual rotation of the mot...
Page 54: 6. Parameter Description
54 6. Parameter description 6.1 us-parameters password with different passwords different parameter groups can be accessed for advanced programming. By entering a value of 1, all the lf parameters are returned to the factory default values. Note the display will automatically change to show the valu...
Page 55
55 these us parameters are special parameter which are not needed in every applciation. They are turned off by default at the manufacturer. The following serves only as a list of these parameters. For further adjustment refer to section 8.0. Parameter description - basic set up other us parameters u...
Page 56
56 parameter description - basic set up 6.2 lf-elevator parameters this value determines the type of speed selection and rotation setting. Value range: d spd = digital speed selection a tor = analog torque control a spd = analog speed control sersp = serial com. Speed control factory setting: d spd ...
Page 57
57 digital speed setting uses preset digital values in the drive as command speeds. The drive creates the driving profile between selected speeds. Symbol: 1 = input is active 0 = input is not active x = setting has no effect or don’t care a) input coded set speed selection lf.02 = d spd d spd d spd ...
Page 58
58 a differential analog signal is connected to the terminals x2a.1(+) and x2a.2 (-). Terminals x2a.3 and x2a.4 can be used for pre-torque input. 0 ... ±10v = 0 ... ±max. System speed (lf.20) terminals x2a.14 and x2a.15 are used to activate the start and stop routine. The directions below must be fo...
Page 59
59 with lf.3 you disable the direction input to prevent the drive from responding. This allows the drive the measure the motor resistance or the alignment of the encoder on a pm motor by running the car on inspection. Value range: run run run run run ... Conf conf conf conf conf...Econf econf econf ...
Page 60
60 parameter description - basic set up electronic motor overload protection this parameter is used to activate and select the type of motor overload function. Depending on the setting of this parameter, the torqmax elevator drive will trigger a drive fault e.Oh2 causing the motor to stop. The trigg...
Page 61
61 parameter description - motor data electronic overload current this parameter sets the current threshold in amps above which the elevator drive activates the motor overload function. Unit: ampere value range: 1.0...1.1 x drive rated current factory setting: 8.0a adjustment value: in accordance wi...
Page 62
62 unit: rpm value range : 10.0....6000.0 or 500.0 (based on config mode) factory setting: 1165.0 or 150.0 (based on config mode) adjustment value: in accordance with the motor name plate you may not enter the motor-synchronous speed (e.G. 1800 rpm for a 4 pole motor, 1200 rpm for a 6 pole motor, an...
Page 63
63 parameter description - motor data lf.11 rated motor speed continued. Once all the other parameter adjustments are made it may necessary to come back to parameter lf.11 in order to fine tune the operation of the elevator drive with the motor. The parameter lf.11 will determine how much torque the...
Page 64
64 enter the exact rated frequency of the motor. Unit: hertz value range: 4.0...100.0 hz factory setting : 60.0 hz adjustment value: in accordance with the motor name plate enter the name plate rated voltage. Unit: volt value range: 120...500 v factory setting: 230 or 460 v based on drive voltage ad...
Page 65
65 this parameter is not the efficiency of the motor but the ratio of the magnetizing current to the total phase current of the motor. Lower power factor values will increase the magnetizing current to the motor and thus increase the field strength resulting in tighter control of the motor. Higher v...
Page 66
66 rated motor torque for im the torque value is calculated from the rated speed (lf.11) and rated power (lf.10). Therefore this value is read only. Unit: lb ft value range: 1...10000 lb ft factory setting: calculated for pm motors the torque value must be entered and is used to establish the torque...
Page 67
67 motor leakage inductance this information is not used for induction motors and therefore the parameter is not visible in induction motor mode. This is the total phase to phase reflected leakage inductance of the motor winding. The inductance listed on the manufacturer’s data sheet will most likel...
Page 68
68 unit: 1 value range: 1.00 ... 99.99 factory setting: 30.00 adjustment value: in accordance with the gear name plate, the ratio can be determined by counting the revolutions of the motor during one rev of the traction sheave. Once the car is running on high speed, if the measured speed is slightly...
Page 69
69 estimated gear ratio this parameter is read only and will change when adjustments are made to lf.11, lf.20, lf.21 or lf.23. This parameter can be used to estimate the gear ratio if it is not known. After correctly entering values into lf.11, lf.20, lf.21, and lf.23, read this value and then enter...
Page 70
70 encoder feedback this parameter displays the type of encoder feedback installed in the drive. It is also used to confirm a change in the encoder feedback card when a different card is installed or a change of motor encoder when an absolute encoder is used. Normally it is not necessary to make any...
Page 71
71 parameter description - control settings encoder sample time this parameter is used to adjust the sample time of the encoder feedback for calculation of the actual motor speed value. With certain motors or encoders it may be beneficial to use a time other than the factory setting. Lower values le...
Page 72
72 control method used in conjunction with lf.2 to adjust the control method. Unit: 1 value range: 0...4 factory setting: 0 adjustment values 0 or 1 open loop induction motor operation for construction, inspection and test purposes only. 2 closed loop speed control. Valid when lf.2 = 2 or 4. 3 close...
Page 73
73 kp speed proportional gain of the speed controller. The default values are a good staring point and will work for most applications. How- ever if the motor does not track the speed command tight enough, then the value should be increased. If the motor makes audible noise or vibration in the car, ...
Page 74
74 kp current proportional gain of the current controller. The correct value is calculated from the motor data. Unit: 1 value range: 1...32767 factory setting: calculated! Adjustment value: do not change. This peak torque limit prevents the motor from exceeding its breakdown torque limit. If the tor...
Page 75
75 us unit: feet per minute value range: 0... 66% of lf.20 factory setting: 0 ft/min adjusted value: approx. 100 ft/min set speed s i , inspection speed selected by x2a.13. Carrier frequency using parameter lf.38 the switching frequency of the inverter can be set. The switching frequency can be cons...
Page 76
76 unit: feet per second 3 value range: off, 0.30...32.00 ft/s 3 factory setting: 2.00 ft/s 3 adjusted value: dependent on the mechanical system (values which are too high can lead to oscillations in the cabin) note: 32.0 = no start ramp and should be used for analog speed or torque control. General...
Page 77
77 us parameter description - driving profile unit: feet per second 2 value range: 0.30...12.0 ft/s 2 factory setting: 3.00 ft/s 2 adjustment value: according to comfort, note: 12.0 = no accel ramp and should be used for analog speed or torque control. Acceleration deceleration jerk unit: feet per s...
Page 78
78 speed following error triggers a drive fault if the actual motor speed deviates from the commanded speed by more than the window defined in parameter lf.58 and for the length of time defined in lf. 59. This function only works in close loop speed control mode, ie. Lf30=2 or 3. Settings: 0 = off (...
Page 79: Parameter Description
79 us brake set speed in open loop it is not possible to produce holding torque at zero speed. Therefore, it is necessary to drop the brake just before the motor reached zero speed. This is parameter is only used when operating in open loop mode lf.4 = 0, and will cause the dro output x2a.27...29 to...
Page 80: Parameter Description
80 parameter description pre-torque direction this parameter can be used to invert the direction of the pretorque being applied to the motor. Unit: 1 value range: 0 => +10v = positive torque 1 => -10v = positive torque factory setting: 0 adjusted value: depends on the required torque direction speed...
Page 81: Parameter Description
81 us parameter description ki decel current control gain unit: - value range: 1...500 factory setting: 30 unit: - value range: 0.00...2.55 factory setting: 2.00 this parameter is only visible in open loop mode (lf.4 = iopen). This parameter is used to prevent spotting and or overshoot during the de...
Page 82: Parameter Description
82 this parameter is only visible in closed loop pm motor mode (lf.4 = pclsd or p9lss). Lf.77 displays the position of the encoder in relation to one of the motor poles. Unit: 1 value range: 0 … 65535h factory setting: 0 adjusted value: according to encoder position if the position value is already ...
Page 83: Parameter Description
83 us brake drop delay parameter description this parameter determines how long the drive will maintain full current and control of the motor after the direction inputs, x2a.14 and x2a.15 have been turned off. After the adjusted time, motor current will continue to flow, however the analog input wil...
Page 84: Diagnostic Parameters
84 display of the software version of the elevator operator. Software version software date display of the software date. Format ddmm.Y diagnostic parameters note: the lead character of the date may be blanked if it is a zero. Example: data code 0208.1 display reads as 208.1.
Page 85: Diagnostic Parameters
85 us diagnostic parameters terminal x2a this parameter displays the status of the digital inputs on terminal x2a. Each input has a specific value. See the table below for decoding. X2a input state displayed terminal value number(s) description 0 all x2 no signals are active on terminal x2a.10 to x2...
Page 86: Diagnostic Parameters
86 x2a output state terminal x2a this parameter displays the status of the digital outputs on terminal x2a. Each output has a specific value. If more than one output is active, the sum of the value is displayed. Value table: value output function terminal 1 x2a.18 +24vdc solidstate out - as, at spee...
Page 87: Diagnostic Parameters
87 us displays the actual motor speed in rpm measured from the motor encoder . Actual motor speed actual elevator speed display of the car speed in ft/min; only when the encoder is con- nected. Display of the actual inverter load in %. 100% equals rated load of the inverter. Inverter load displays t...
Page 88: Diagnostic Parameters
88 last error displays the last 8 drive faults which occurred. The fault list can be viewed by changing the number to the left of the lf on the display. This number is the parameter offset number. Zero is the newest fault and 7 is the oldest. See the adjustment steps below to view the fault mes- sag...
Page 89: Diagnostic Parameters
89 us start stop func. Speed enter f/r enter f/r start stop func. Speed enter f/r start stop func. Speed enter f/r start stop start stop func. Speed enter f/r enter f/r enter f/r diagnostic parameters change between parameter group and parameter number with the up, down keys select the respective pa...
Page 90: Error Messages
90 under voltage the dc bus voltage drops below the permissible value, the input is single phasing, or there is a phase imbalance of greater than 2%. The dc bus voltage rises above the permissible value either during motor regenerative operation or as a result of line side voltage spikes. Occurs whe...
Page 91: Error Messages
91 us the heat sink temperature rises above the permissible limit (see technical data) the external motor temperature sensor tripped over temperature reset possible error over speed this occurs for a short time during the power up of the drive, but will clear automatically if everything is ok error ...
Page 92: Error Messages
92 power unit code this indicates that there is a problem either with the serial communication between the drive and the encoder or the value of the data being transferred. The full meaning of this error must be decoded through parameter us.26. Error power unit code. During the initialization phase ...
Page 93: Diagnostic Parameters
93 us normal operating messages inverter status diagnostic parameters display significance nop no operation, terminal x2.1 (drive enable) is not set ls low speed, inverter is enabled but no direction of rotation is set, motor current still off facc forward acceleration fcon forward constant running ...
Page 94: Diagnostic Parameters
94 7.0 run parameters diagnostic parameters the run parameters display operational values within the elevator drive. They can be used for trouble shooting or calibration purposes. Each parameter is listed below along with a description of what it displays. Some parameters may display information onl...
Page 95: Diagnostic Parameters
95 us diagnostic parameters ru.11 commanded torque this is the internal torque command value which is fed into the current controller. Units: nm this is the actual torque value which is calculated from the motor current. Units: nm this is the load level of the inverter. 100% equals rated load. Units...
Page 96: Diagnostic Parameters
96 ru.20 output voltage this is the actual phase to phase output voltage to the motor. Units: volts the raw status of the input terminals. Each input is binary weighted according to the table below. If an input is activated the value corresponding to the input is displayed. If multiple inputs are ac...
Page 97: Diagnostic Parameters
97 us ru.24 output flag state this is the state of the internal output flags. Multiple active flags result in the sum of the values. Flag value 0 1 1 2 2 4 3 8 4 16 5 32 6 64 7 128 this is the state of the actual outputs. Multiple active outputs result in the sum of the values. Output function value...
Page 98: Diagnostic Parameters
98 ru.29 analog pre- torque raw ru.30 analog pre- torque processed this parameter displays the value of the actual pre-torque signal applied between terminal x2a.3 and x2a.4. The value is in percent +/- 100.0% = +/- 10.00v. This value is unfiltered and unprocessed. Units: % this parameter displays t...
Page 99: Diagnostic Parameters
99 us ru.37 motor pot value value of the internal function. Units:% this is the temperature of the output transistors. Units: °c overload counter display. Once the load of the drive goes above 100% this counter begins to increment. If the load drops below it decrements. If the counter reaches 100 th...
Page 100: Advanced Parameters
100 8.0 advanced adjustments there are additional us parameters which can provide further functional adjustments of the drive. This us parameters are all those greater than us.10. They are turned on or off through parameter us.8. Once turned on, the higher us parameters are unlocked and can be adjus...
Page 101: Advanced Parameters
101 us advanced parameters us. 17 pre-torque timer ramp up us. 18 pre-torque timer ramp down this timer controls the build time for the pre-torque function. Once the direction input is activated this timer begins counting. In the mean time the current check takes place and then finally the motor is ...
Page 102: Advanced Parameters
102 us. 19 field weakening corner this parameter provides a better adjustment of the field weakening torque curve. Under certain situations, if the input voltage is sagging too low or the motor has very high slip, it is possible that the voltage limit might be reached. This can be confirmed by monit...
Page 103: Advanced Parameters
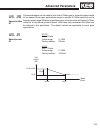
103 us total integral gain lf.32 lf.32+lf.33 lf.33 us.20 us.21 speed (ft/min) us. 20 speed for max ki these parameters can be used to tailor the ki offset gain to a specific speed range at low speed. Worm gear applications require a smaller ki offset value but over a broader speed range. Whereas a g...
Page 104: Advanced Parameters
104 us. 22 speed dependent kp gain these parameters allow the kp gain to be scaled dependent on the command speed of the elevator. In some cases it is beneficial to reduce the gain at high speed to minimize system response to hoistway vibrations or disturbances. Parameter us.22 turns the variable ga...
Page 105: Advanced Parameters
105 us this parameter can be used to select what type of current check is performed. Additionally it determines whether or not the brake on/off message is displayed. In the event there is a problem getting a consistently positive phase check, it is possible to switch to only a magnetizing current ch...
Page 106: Advanced Parameters
106 us. 27 power stage id code us. 28 hsp5 watchdog time us. 29 analog input noise clamp advanced parameters each voltage and size power stage has its own unique id code. This parameter displays the id number of the power stage. In the event the control card is replaced, when the new control card is...
Page 107
107 us 9.1 digital input parameters 9.0 input/output configuration the digital input parameters can be used to configure the digital inputs for operation. Normally these parameters only need to be adjusted by the elevator control builder. Di. 0 input type determines whether the inputs are pnp (sourc...
Page 108: Input/output Configuration
108 input/output configuration 9.2 digital output parameters the digital output parameters can be used to configure the digital outputs for operation. Normally these parameters only need to be adjusted by the elevator control builder. Do. 42 output inversion can be used to invert the function of the...
Page 109: Input/output Configuration
109 us input/output configuration designator function flt fault, output activates when there is a drive fault, e.Xxx rdy ready, output activates when the drive and ready for operation and there are no active faults e.Xxx dro drive on, output activates after the following conditions are met: enable i...
Page 110: Input/output Configuration
110 input/output configuration this page left blank..
Page 111
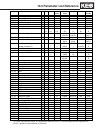
Para. Name e r res. Lower limit upper limit default unit visable in modes lf.02 steering/operating mode e 1 2 4 2 text g,m,s lf.03 drive configuration e 1 0 2 1 text g,m,s lf.04 drive mode e r 1 0 4 - text g,m,s lf.05 auto reset e 1 0 10 3 - g,m,s lf.08 electronic mtr protection e 1 0 1 0 text g,m,s...
Page 112: Parameter List Reference
G = open loop induction motor, m = closed loop induction motor, s= closed loop permanent magnet motor m,s1) = gearless mode induction or pm motor para. Name e r res. Lower limit upper limit default unit visable in modes lf.57 speed following error e 1 0 1 1 text m,s lf.58 speed difference e 1 0 30 1...
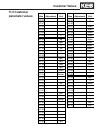
Page 113: 11.0 Customer
Size customer adjustment unit size customer adjustment unit lf.02 - lf.37 % lf.03 - lf.38 - lf.04 - lf.41 ft/min lf.05 - lf.42 ft/min lf.08 - lf.43 ft/min lf.09 a lf.44 ft/min lf.10 hp lf.45 ft/min lf.11 rpm lf.50 ft/sec 3 lf.12 a lf.51 ft/sec 2 lf.13 hz lf.52 ft/sec 3 lf.14 v lf.53 ft/sec 2 lf.15 -...
Page 115: Notes
Notes.
Page 116: Keb America Inc.
© keb 00.F5.Lub-k1 31 06/2005 keb america inc. 5100 valley industrial blvd. Shakopee, mn 55379 phone: 952-224-1400 www.Kebamerica.Com.